Page 1

PAMS Technical Documentation
THF-12 Series Transceivers
Chapter 6
Tuning and Flashing
Instructions
Issue 3 02/2000
Page 2
THF-12
PAMS
Tuning and Flashing Instructions
Technical Documentation
AMENDMENT RECORD SHEET
Amendment
Number
Date Inserted By Comments
01/99 OJuntune Original
Issue 2 05/99 OJuntune Flashing added, pp.14 to 23
Flashing setup fig. p.15 updated
TOC and ARS updated
Issue 3 02/2000 OJuntune Tuning updated p.5–14
TOC and ARS updated
Page 2
Issue 3 02/2000
Page 3

PAMS
THF-12
Technical Documentation
Tuning and Flashing Instructions
CONTENTS
Tuning Instructions 4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
General 4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Minimum Required Servicing Equipment 4. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Equipment Setup 4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Equipment Setup For Tuning A Phone
Without Removing Covers 6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Equipment Setup For Tuning A Phone
With Covers Removed 7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Manual Tuning Steps 8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
General 8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1 – AFC Middle Frequency Tuning 9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2 – AFC Frequency Limits Tuning 9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3 – RSSI and AGC Tuning 10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4 – Deviation Tuning 10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
FFSK Deviation Tuning 11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Nominal Deviation Tuning 11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Maximum Deviation Tuning 11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Rx Tri Tuning 11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Phi Signal Deviation Tuning 11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5 – TX Output Power Tuning 12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6 – Battery Calibrations 12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
7 – Charger Calibrations 12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
8 – Show Tuning Values 13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Page No
Introduction to Flashing 14. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Equipment Setup For THF-12 Flashing 15. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Software for THF-12 flashing 16. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 16. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Prommer use interface 17. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
After sales version screen menu map 17. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Menu action descriptions 18. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
How to start Prommer software 18. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Troubleshooting 20. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Prommed does not run 20. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Corrupted phone flash ID 20. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Appendix A 22. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Appendix B: FPS–4 Front plate 23. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Appendix C, Vocabulary 24. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Issue 3 02/2000
Page 3
Page 4

THF-12
PAMS
Tuning and Flashing Instructions
Tuning Instructions
General
The tuning operations of the THF-12 are carried out using the Service
Software. The Service Software program turns the phone into Locals
Mode, in which the phone can be outwardly controlled via the M2BUS in-
terface.
Tuning is based on the Service Software communicating with the D/A and
A/D converters of the phone.
The calibration data of the phone resides on the EEPROM. The contents
of the EEPROM can be read by the Service Software. The program also
enables writing of the factory preset calibration data to the EEPROM, af-
ter which the whole tuning process should be carried out again.
If a repair has been carried out on the RF section of a system module
then the appropriate tunings should be performed as described in the fol-
lowing section and using th on–screen help menus as a guide. Spare sys-
tem modules will be delivered pre–tuned from the factory and will not re-
quire retuning.
Technical Documentation
During tuning, proceed as follows:
– Take care not to damage sensitive measuring instruments with exces-
sive RF power.
– Carry out all tuning steps in the shortest possible time to avoid exces-
sive heating of RF units.
– Perform all tuning steps in the order presented.
– Never try to mask a fault by tuning it out!
Minimum Required Servicing Equipment
–PC/AT Computer with Service Software installed: See Service Software
instructions.
–M2BUS cable DAU–9P and other service software accessories; see
equipment set–up pictures.
–Audio analyzer.
–RF power meter, power measurement sensitivity –10 dBm.
–RF generator.
–Device to provide specified test modulation to modulate RF generator.
–Multimeter or DVM.
–Attenuator and branching unit.
–Power supply, nom. voltage 3.6 V (with service battery BBD–3 voltage
is 8.2 V).
Equipment Setup
Turn off the computer before connecting the cable to avoid possible damage to the serial port.
Page 4
Issue 3 02/2000
Page 5

PAMS
THF-12
Technical Documentation
Caution:Do not connect the PKD–1 to the serial port. This could damage
the PKD–1 !
Connect the MBUS cable SCH–5 to the phone. Connect 9–pin male
D–connector in your PC serial port.
For transmit, audio measuring and adjustment connect ADS–1 EAR/MIC
breakout cables as follows:
– EAR line to test equipment AF INPUT
– MIC line to test equipment AF GEN OUTPUT
Connect BBD–3 service battery connectors to the power supply. Supplyvoltage should be set to 8.2 V.
Tuning and Flashing Instructions
Issue 3 02/2000
Page 5
Page 6
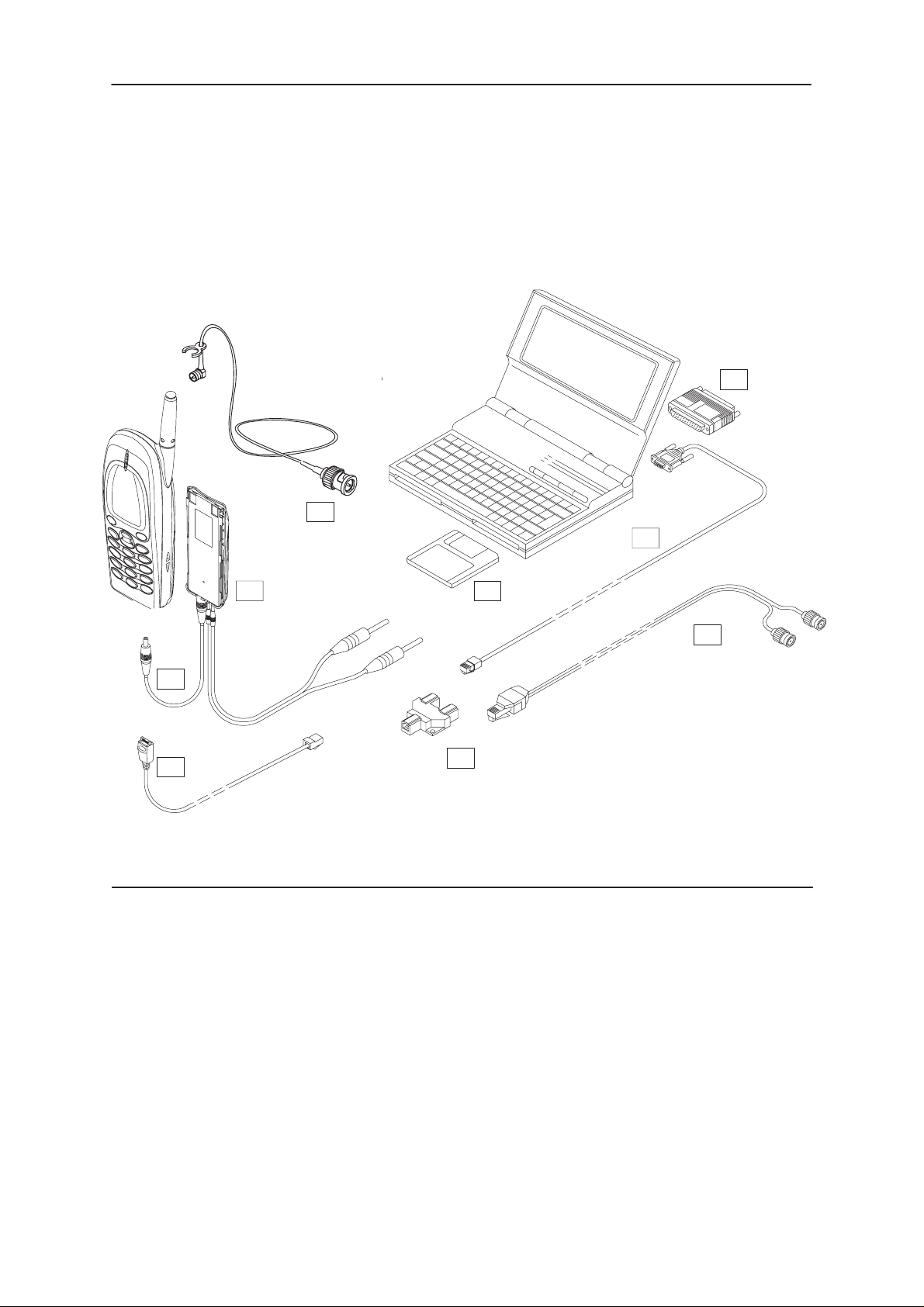
THF-12
PAMS
Tuning and Flashing Instructions
Technical Documentation
Equipment Setup For Tuning A Phone Without Removing Covers
4.
8.
7.
1.
+8.2 V
2.
3.
Item Service Accessory Type Code
1 Service Battery BBD–3 0775071
2 DC cable SCB–3 0730114
3 Service Cable SCH-5 0730098
4 Software protection key PKD-1 0750018
5 Service Software diskette 3.5” 0774112
6 Audio Cable ADS-1 0730011
7 Service MBUS Cable DAU–9S 0730108
8 Antenna Cable XRC–1B 0730128
9 Modular T-Connector 4626134
10 WinTesla Diskette 3,5” 0774071
alt Dongle Drivers for Win 3.1x, 95 and NT
(combined 16bit, 32bit) 0770137
5.
6.
9.
Page 6
Issue 3 02/2000
Page 7
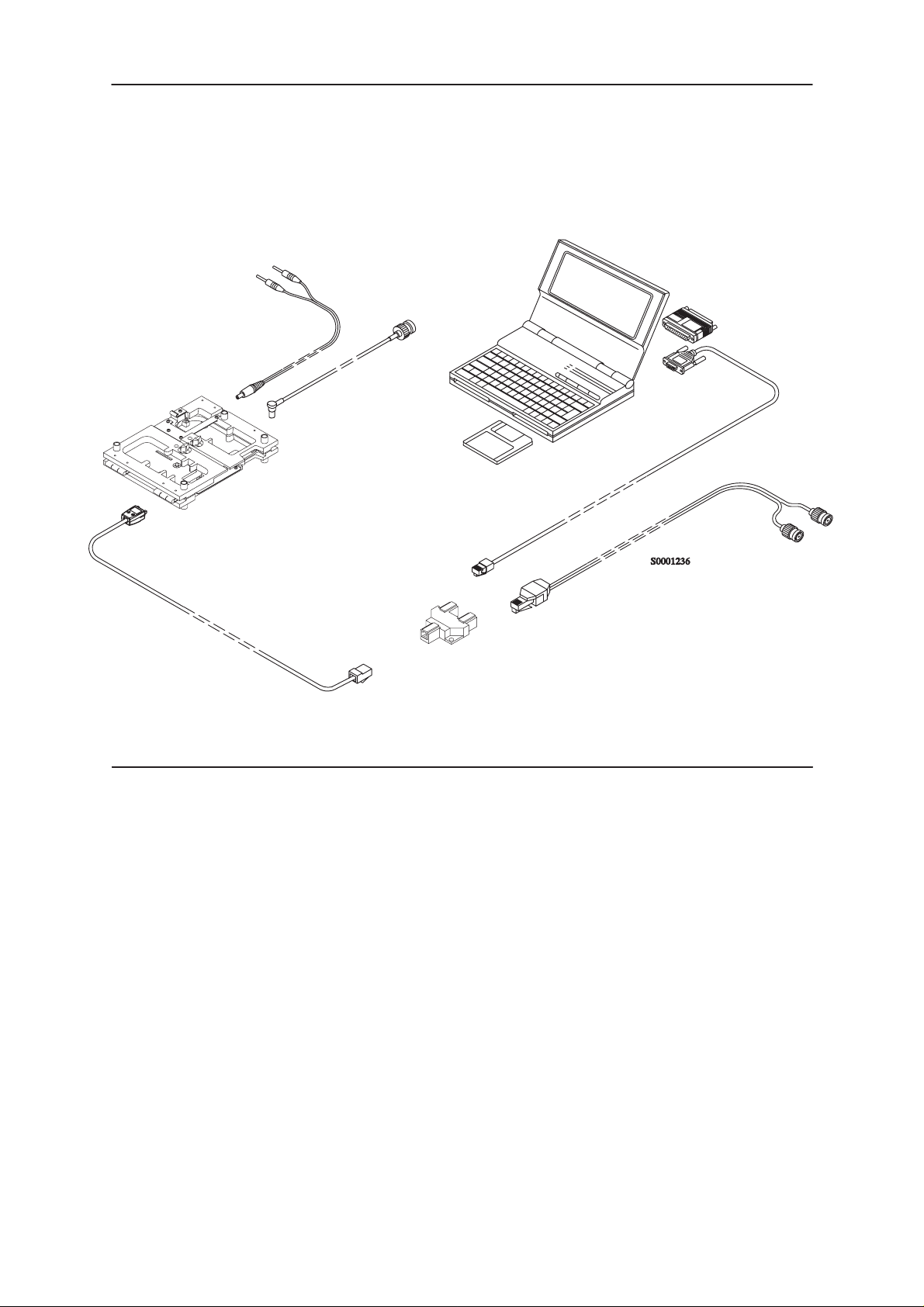
PAMS
THF-12
Technical Documentation
Tuning and Flashing Instructions
Equipment Setup For Tuning A Phone With Covers Removed
+3.6V
8.
3.
4.
9.
1.
6.
3.6V
5.
2.
Item: Service accessory: Type Code:
1 Test frame * JBS–24 0770167
2 Modular T-Connector 4626134
3 DC Cable PCS–1 0730012
4 Antenna Cable XRC–1B 0730128
5 Service Cable SCH-5 0730098
6 Service MBUS Cable DAU–9S 0730108
7 Audio Cable ADS-1 0730011
8 Software protection key PKD-1 0750018
9 WinTesla Diskette 3,5” 0774071
alt Dongle Drivers for Win 3.1x, 95 and NT
(combined 16bit, 32bit) 0770137
7.
*) The nominal operating voltage for the JBS is 3.6 V.
Issue 3 02/2000
Page 7
Page 8

THF-12
PAMS
Tuning and Flashing Instructions
Manual Tuning Steps
General
If any repairs or replacements have not been made, manual tuning is not
necessary on the phone. Spare modules have been tuned at the factory.
If some repair or replacements have been made, manual tuning is nessessary.
If you do not want to use phone country version dependent tuning channels, proceed as follows:
1. Choose RF controls from the Configure menu.
2. Change channel values.
3. Choose Write File –button in order to save channel values in ” TESLA.ini ” –file.
Technical Documentation
The program saves the channel settings and uses them every time when
Tunings or Testing menu is chosen. The program uses ordinary channels
depending on the phone country version, if you don’t change channels.
Default channels in RF–controls
dialog
Using
Channel low for 1 band phones Afc and afc–limits tuning, basic settings
Channel mid for 1 band phones Afc and afc–limits tuning, basic settings
Channel high for 1 band phones Afc and afc–limits tuning, basic settings
Channel low for 2 band phones Afc and afc–limits tuning, basic settings
Channel mid for 2 band phones Afc and afc–limits tuning, basic settings
Channel high for 2 band phones Afc and afc–limits tuning, basic settings
Rssi channel low band 1 Rssi ch compensation
Rssi channel mid band 1 Rssi ch compensation
Rssi levels and agc (1 band phones)
Rssi channel high band 1 Rssi ch compensation
Rssi channel low band 2 Rssi ch compensation
Page 8
Rssi channel mid band 2 Rssi ch compensation
Rssi channel high band 2 Rssi ch compensation
Rssi mid ch for 2 band phones Rssi levels and agc (2 band phones)
Issue 3 02/2000
Page 9

PAMS
THF-12
Technical Documentation
1 – AFC Middle Frequency Tuning
This dialog is used for adjusting the TX frequency for the phone’s middle
channel.
The phone is turned to the default middle channel (RX and TX) and transmitter is activated.
Note: Temperature during tuning should be approx. +25 °C.
AFC middle frequency tuning procedure:
– Select Tunings/AFC middle frequency tuning
– Connect devices and set values to measuring equipment according to
information texts.
– Measurement device shows the AFC frequency D/A converter reading.
Tuning and Flashing Instructions
– Tune until the value is the middle TX frequency.
– Use the arrow keys or mouse to change the value and ALT–S to write
the value to EEPROM.
2 – AFC Frequency Limits Tuning
This dialog is used for adjusting the TX frequency limits for the phone’s
middle channel.
The phone is turned to the default middle channel (RX and TX) and transmitter is activated.
AFC frequency limits tuning procedure:
– Select Tunings/AFC frequency limits tuning
– Set the RF–generator frequency and signal level according to the information given in dialog box..
– Measurement device shows the AFC frequency D/A converter reading.
– Tune until the value is the TX frequency ± 2.5 kHz.
– Use the arrow keys or mouse to change the value and ALT–S to write
the value to EEPROM.
Issue 3 02/2000
Page 9
Page 10

THF-12
PAMS
Tuning and Flashing Instructions
3 – RSSI and AGC Tuning
This dialog is used for adjusting the RSSI and AGC levels.
RSSI tuning procedure:
– Select Tunings/RSSI and AGC Tuning
– Set RF–generator frequencies and signal levels according to the in-
formation given by the Service Software.
– The Service Software reads values given by A/D converter for received
signal.
– The Service Software tunes three tuning points for channel compensa-
tion (Low, high and middle channel).
– The program also executes six tuning points for RSSI levels.
Technical Documentation
Tuning RF signal Level no
point level
1 –58 dBm 6
2 –68 dBm 5
3 –83 dBm 4
4 –93 dBm 3
5 –103 dBm 2
6 –115 dBm 1
AGC tuning procedure:
– Set the RF signal levels according to the information given by the Ser-
vice Software.
– The program shows the AGC ON and the AGC OFF levels.
4 – Deviation Tuning
Deviation tuning procedure:
– Select Tunings/Deviation tuning
Page 10
– Connect devices and set measurement equipment values according to
information texts.
– Use the arrow keys or mouse to change tuning values and ALT–S to
write them to the phone. Use TAB key to change field.
– Compare measurement device values to the program information text
values.
– Tune until the measured value is within range given by dialogs information texts.
Issue 3 02/2000
Page 11

PAMS
THF-12
Technical Documentation
FFSK Deviation Tuning
This adjustment is used to set outgoing FFSK data deviation.
The command turns the phone to default middle channel (RX and TX),
activates the transmitter, opens the data path, and sets up the modem to
send a continuous 1800 Hz, ”0” signal.
To adjust, enter values (0–15) for the D/A converter, and compare results
to the reading given by the deviation meter.
Nominal Deviation Tuning
The purpose of this tuning operation is to adjust the nominal deviation of
voice and DTMF signaling.
The command turns the phone to the default middle channel, and activates the transmitter.
To adjust, enter values from the range 0–7 into the D/A converter and
compare results with deviation meter readings.
Tuning and Flashing Instructions
Maximum Deviation Tuning
This adjustment has an effect on voice and DTMF signal maximum deviation.
The command turns the phone on the default middle channel, and activates the transmitter.
Enter various values from the range 0–7 into the D/A converter, and
compare results with the reading in the deviation meter.
Note: Deviation will increase when D/A reading is decreased.
Rx Tri Tuning
The purpose of this adjustment is to adjust Rx Trimmer.
The transmitter is turned off.
To adjust, enter values from the range 0–15 into the D/A converter.
Use ALT+1 and ALT+2 keys to enable/disable expander. Tune until the
level in EXTEAR–pin is the same with and without expander.
Phi Signal Deviation Tuning
The purpose of this adjustment is to adjust phi signal (SAT) deviation.
The command turns the phone on the default middle channel (RX and
TX), activates transmitter, and enables the φ loop.
To adjust, enter values (0–15) to the D/A converter and compare changes
to deviation meter readings.
Issue 3 02/2000
Page 11
Page 12

THF-12
PAMS
Tuning and Flashing Instructions
5 – TX Output Power Tuning
This adjustment writes the power levels of the phone transmitter into the
EEPROM. When doing this, a power meter must be used. THF–12 has
three power levels to tune. Power levels low and middle are adjusted
only at band 3. Power level high is tuned at all four bands.
Tuning can be interrupted when necessary by pressing Esc key.
Power levels tuning procedure:
– Connect power meter to the antenna connector of the phone.
– Adjust the phone supply voltage to +3.6 V !
– If service battery is used, the supply voltage is 8.2V.
– Select Tunings/TX output power
– Use the arrow keys, or mouse to change the tuning value.
– Change tuning value until the power meter value is at the target power
value given in dialog’s information texts..
Technical Documentation
– Use TAB key to change field and ALT–S to write values to EEPROM.
IMPORTANT: TX output power shall not be adjusted over 750mW in any
case.
6 – Battery Calibrations
Battery calibration procedure:
– Connect service battery to phone and set supply voltage to 8.2 V.
– Select Tunings/Battery Calibrations
– The program reads the Battery Voltage, Battery Size and Battery Tem-
perature values from phone and shows them to the user.
– Press Run–button. After that calibration is done by the service software
and the new values are written to the EEPROM. New values are also
shown to the user..
7 – Charger Calibrations
Charger calibration procedure:
– Connect service battery to phone and set supply voltage to 10.5 V.
Page 12
– Connect also dc cable between the phone and the service battery.
– Select Tunings/Battery Calibrations
– The program reads the Charger Voltage, Charger current offset and
reference values from phone and shows them to the user.
– Press Run–button. After that calibration is done by the service software
and the new values are written to the EEPROM. New values are also
shown to the user.
Issue 3 02/2000
Page 13

PAMS
THF-12
Technical Documentation
8 – Show Tuning Values
This dialog box enables reading of the phone tuning parameters, and
writing of the default values.
Note: Spare modules received from the factory are factory–tuned.
Tuning and Flashing Instructions
Issue 3 02/2000
Page 13
Page 14

THF-12
PAMS
Tuning and Flashing Instructions
Introduction to Flashing
The Flash Programming procedure can be divided into six main steps.
1. Prommer synchronous clock pin is set to low.
2. Phone power is switched on. The ASIC boot software is now ready to
receive the secondary boot code.
3. The secondary boot is loaded into the internal phone MCU RAM at a
low communication speed.
4. As response to a successful secondary boot down loading and execution the phone returns its current HW configuration and MCU SW version.
5. The prommer selects one of the target specific download codes and
sends it to the phone. The code selection is executed automatically based
on the phone configuration data. The transmission speed used is as
fast as the target HW allows. Down load code is loaded and executed in
the RAM.
Technical Documentation
6. MCU SW is programmed into the phone FLASH using the flashing algorithm provided in down load code. The data is transmitted in data
frames, frame size varies from one to several kilobytes. The download
code includes flash erase and flashblank check routines for the MCU SW
update purposes.
Page 14
Issue 3 02/2000
Page 15

PAMS
THF-12
Technical Documentation
Tuning and Flashing Instructions
Equipment Setup For THF-12 Flashing
9
3.
7.
8.
5. 6.
4.
1.
2.
Item: Service accessory: Product code:
1 Flash Loading Adapter FLA–5 0080178
2 Prommer FPS–4S 0085095
3 Service Battery BBD–3 0775071
4 Service Cable SCH–5 0730098
5 D15 – D15 Cable AXS–5 0730091
(Included in FLA–5 sales pack)
6 Printer Cable (Included in FPS–4 sales pack) 0730029
7 Software protection key PKD–1 0750018
8 SW flash program diskette 3.5” (see next page)
9 AC Charger ACL–3E 0680015
(Included in FPS–4 sales pack)
Issue 3 02/2000
Page 15
Page 16

THF-12
PAMS
Tuning and Flashing Instructions
Software for THF-12 flashing
SW THF–12 Flash Program diskette 3.5” THF–12 0774127
SW THF-12K Flash Program diskette 3.5” THF-12K 0774130
HW requirements: IBM compatible PC, CPU 80486 or later.
One Serial and one Parallel port.
Parallel port can be LPT1 to LPT3.
Serial port can be any of COM1 to COM4.
If selected port is non default (LPT1 or COM1) port you must run prom-
mer setup.
SW requirements: MSDOS 3.x (5.x) or later.
The installation program ’SETUP.BAT’ needs later DOSversion. It uses
DOS command ’choice.com’ which ismissing old (< 5.x) DOS versions.
Technical Documentation
Prommer software does not run under WINDOWS properly.
PC MCU speed have no affects to phone programming times!
MCUSW downloading speed depends directly on PC speed !
Installation
1. Connect parallel cable from PC LPT port to FPS–4 Parallel Input.
2. Connect serial cable from PC COM port to FPS–4 Serial Input.
3. Connect the Flash Loading Adapter to the FPS–4 Phone Connector.
4. Connect Power Plug to FPS–4 PWR connector.
5. Run setup utility program ’SETUP’ on your diskette drive.
Give the target directory in parameter ( e.g. A:> SETUP C:\FPS4 ).
Check that parallel and serial port numbers and your Flash loading
adapter type are selected correctly.
NOTE! You can change FPS–4 prommer i/o–port numbers later from
prommer setup menu when you run prommer with ’–S’ option ( e.g.
C:\FPS4> FPS4 –S ). The Flash adapter type can be changed any time
in setup menu.
Page 16
All prommer settings are saved to ’SETUP.FPS’ file in prommer default
directory.
Issue 3 02/2000
Page 17

PAMS
THF-12
Technical Documentation
Prommer use interface
After sales version screen menu map
Main Menu
Help on Help
Program Phone by Type
Program Phone by File Name
Advanced Options Menu...
Read Phone SW & HW ID
Download MCUSW to Prommer Box
Program Phone with Code in Box
Tuning and Flashing Instructions
Move MCUSW Prommer SRAM–>Flash
Delete MCUSW from Prommer
Setup (PC_HW & FPS4 SW)...
Prommer SW Version Info
Prommer SW Update...
Download FPGA
Download Application 1
Download Application 2 (Dummy)
PC Settings...
Serial Port: COM1
Parallel Port: LPT1
Parallel XMIT Speed: Fast
Sound at ’Error’
Screen Saver after 10 min
Hard Disk Suspender: Off
Prommer Maintance...
Check Code CSUM...
Secondary codes
Algorithm codes
Application 1 code
Application 2 code
FPGA codes
Issue 3 02/2000
Page 17
Page 18

THF-12
PAMS
Tuning and Flashing Instructions
MCUSW codes
Flashing Vpp Check
Prommer SRAM Clean Up
Prommer EEPROM...
Flashing Adapter: FLA–1 or 3
Exit to DOS
Menu action descriptions
Program Phone by Type
Action updates MCUSW code to target HW almost automatically; only
thing that user must do is to select correct target HW type from menu.
This action uses data file ’RELEASES.FPS’, which links each target HW
to MCUSW code file. This file must be update manually in DOS ASCII text
editor.
Technical Documentation
Program Phone by File Name
Action loads selected MCUSW file to prommer SRAM and flashes it immediately to target.
Read Phone SW & HW ID
Action displays detailed list of target HW & SW configuration.
Download MCUSW to Prommer Box
Action loads selected MCUSW file to prommer SRAM.
Program Phone with Code in Box
Action flashes selected MCUSW code in prommer memory to target.
Old MCUSW code is deleted automatically from target Flash before pro-
gramming.
Move MCUSW Prommer SRAM–>Flash
Action moves MCUSW code to prommer SRAM to Flash.
Delete MCUSW from Prommer
Action deletes MCUSW from prommer memory.
Prommer SW Version Info
Action displays all code versions (execpt MCUSW codes) in prommer
box.
How to start Prommer software
Preparations:
Install prommer software with ‘SETUP.BAT’ batch program.
1.Run flash prommer software called ‘FPS4’ in directory where FPS4 was
installed.
Page 18
Issue 3 02/2000
Page 19

PAMS
THF-12
Technical Documentation
NOTE! Prommer software do not run properly under WINDOWS.
Tuning and Flashing Instructions
Issue 3 02/2000
Page 19
Page 20

THF-12
PAMS
Tuning and Flashing Instructions
Technical Documentation
This page intentionally left blank.
Page 20
Issue 3 02/2000
Page 21

PAMS
THF-12
Technical Documentation
Tuning and Flashing Instructions
Troubleshooting
Prommed does not run
Failure: Prommer power LED does not light up.
Check internal fuse in the prommer box (size 5x20 mm, 500 mA).
Failure: Prommer internal RAM test is failed if both of Mode LEDs are blinking simultaneously.
Reboot prommer. If RAM test fails again, send prommer to service.
Failure: Prommer programs do not reach MAIN MENU.
1. If prommer is still in IDLE state:
Check Parallel cable and used PC port number.
Run setup to change LPT setup settings or restart FPS4 with ’–s’ option
and change LPT number.
2. If prommer is still in WAIT BOOT COMMAND state:
Check Serial cable and used PC port number.
Run setup to change COM setup settings or restart FPS4 with ’–s’ option
and change COM number.
3. If both of prommer MODE LEDs are off, prommer application does not
start properly:
Run setup or restart FPS4 with ’–s’ option and download FPGA and Application 1 in second setup menu.
4. If prommer is stuck on any reason and it does not give boot response,
you must disconnect ALL cables from prommer box.
Prommer power consumption is so low that it get power from communication cables and do not exit fail loop where it was stuck.
Prommer is in IDLE state when MODE 1 / MODE 2 LEDs are toggled
slowly (once /sec).
Prommer is in WAIT BOOT COMMAND state when Mode LEDs are
toggled very fast. This state has 20 second time–out. After time–out
prommer returns to the IDLE state.
Corrupted phone flash ID
If the target Flash ID bytes is set wrong way or they are corrupted, you
can not reprogram phone normally or even erase it without corrected
Flash ID bytes. There is two ways to change Flash ID bytes:
1. ’RELEASES.FPS’ file includes Flash ID description field which is
used when phone is programmed from ’Program Phone by Type’ menu.
Issue 3 02/2000
Page 21
Page 22

THF-12
PAMS
Tuning and Flashing Instructions
The Flash ID in target system is replaced always with Flash ID in
’RELEASES.FPS’ file.
2. ’Modify flash id bytes’ command (only in R&D version) in prommer
menu for FLASH ID byte modifying.
TIP! You can force prommer to use Flash id bytes in MCUSW file simply
by setting Flash id bytes to FF FF FF FF (Prommer act like Flash is
empty)
Wrong value of FLASH ID bytes may fail target erasing and programming
in many ways:
– The number of Flash devices is wrong
– Flash size is wrong
– Flash type is set to OTP
– Memory access too fast for Flash or SRAM memory
In the start of MCU code are four Flash ID bytes which defines the target
base band hardware. Do not confuse these bytes to two Flash manufacture and device identifier bytes, which are read directly from Flash device
HW and are descripted in ’DEV_LIST.FSP’ file.
Technical Documentation
Where prommer gets the Flash ID bytes?
1. Empty Flash (All Flash ID bytes are FFHs)
–> Prommer uses Flash ID in MCUSW file
2. Programmed Flash
– OTP device (First target Flash id byte bits xxx000xx are zeros)
–> NMP Flash id = OTP device
–> Prommer do not want to reprogram target
– Non OPT devices
–> Prommer uses Flash ID read from target device
3. FLASH ID bytes are modified
– New Flash ID bytes are entered by user. (MCUSW file Flash ID
byte are discard)
4. ’Program Phone by Type’ selection uses always Flash ID bytes in
’RELEASES.FPS’ file when available.
WARNING! Do not try to program phone with real OTP device!
Page 22
Issue 3 02/2000
Page 23

PAMS
THF-12
Technical Documentation
Appendix A
FPS–4 Flash prommer files
FPS4.EXE FPS–4 prommer user interface, executed in PC
FPGA0100.MCS Code for FPS–4 internal FPGA chip (update from setup
utility or FPS4 menus.
FPS4 may need to run with ’–S’ setup parameter) BBSW1x.xxx Applica-
tion 1 code, executed in FPS–4 box.’x.xxx’ is the vesion number. (update
from setup utility or FPS4 menus.
FPS4 may need to run with ’–S’ setup parameter)
BOOT2.BIN Secondary boot, executed in target phone (update from
setup utility or FPS4 menus)
28F008.BIN Flash algorithm file for Intel 28F00x memories, executed in
target phone. (update from setup utility or FPS4 menus)
Tuning and Flashing Instructions
DEV_LIST.FPS This DOS text file includes Flash descriptions and Flash
alias data. (file can be modified by user with ASCII text editor)
HELP.FPS FPS4 help file. File is in hyper text format and it can give
case sensitive help.
RELEASES.FPS This DOS text file includes list of current MCUSW release versions for all HW versions individually. The User must update this
file with any DOS ASCII text editor. Main Menu selection ’F2 Program
Phone by Type’ needs this file.
SETUP.FPS Prommer creates this DOS text file automatically. File includes all prommer settings.
FLASH.LOG Prommer creates this DOS text file with –tn parameters
automatically. File is appended with prommer M2BUS messages. This file
is very useful if something fails...
Issue 3 02/2000
Page 23
Page 24

THF-12
PAMS
Tuning and Flashing Instructions
Technical Documentation
Appendix B: FPS–4 Front plate
+–––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––+
| o o |
| FPS4 FLASH PROMMER NOKIA |
| MODE1 |
| | MODE2 |
| | | M2BUS |
| DAU2 | | | VPP_TARGET |
| +––––+ | | | | FPGA_LOADED |
| | | | | | | | POWER |
| | | o o o o o o |
| +––––+ |
| o o |
+–––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––+
MODE1 & MODE 2 LEDS
These LEDs display prommer status.
– MODE1 & MODE2 LEDs are toggled slowly (once / second)
Prommer is in IDLE state, DAU2 connector can be used for M2BUS com-
munication.
– MODE1 & MODE2 LEDs are toggled very fast (5 times / second)
Prommer is in WAIT BOOT COMMAND state.
This state has 20 second time–out.. After time–out prommer returns to
the IDLE state.
– MODE1 LED is ON
Prommer runs DCT Application (not available yet).
– MODE2 LED is ON
Prommer runs DCT2 Application.
– MODE2 LEDs blinks slowly (once / second)
M2BUS LED
This LED light up when M2BUS is used.
VPP TARGET LED
This LED light up when target Vpp is switched on.
Page 24
FPGA LOADED LED
This LED should always light up when prommer software is running.
POWER LED
This LED should always light up when prommer has power on.
Issue 3 02/2000
Page 25

PAMS
THF-12
Technical Documentation
Appendix C, Vocabulary
Abbreviation Description
Application code Prommer software, executed in prommer
ASIC–boot Bootstrap code
Bootstrap code Code that resides in target hardware, either in
RAM.
DAU–9P M2BUS – RS–232 adapter
Download code Highest level Flash programming code; executed
Tuning and Flashing Instructions
hardware
ASIC ROM or in MCU internal ROM. Bootstrap
code loads secondary bootstrap code into target
in target hardware
EEPROM Memory for adjustment parameters (Electrically
Erasable and Programmable Read Only
Memory)
FLASH Nonvolatile electronically erasable memory ,data
is not lost even when power down
FPS4 Name of second generation Flash prommer
M2BUS Serial communication bus which can be con
nected to accessory devices and test PC
MCU Master Control Unit
ME Mobile Equipment
MS Mobile Station
OTP Once Time Programmable device (Mask PROM
or non erasable EPROM)
PC IBM PS/AT or compatible personal computer
PKD Parallel Port Software Protection Device
RF Radio Frequency parts
Secondary boot Second bootstrap code, loads download code
SRAM Random access memory, data is lost when power
SW Software
Target Phone hardware
Issue 3 02/2000
into target RAM. Executed in target hardware.
down
Page 25
Page 26

THF-12
PAMS
Tuning and Flashing Instructions
Technical Documentation
This page intentionally left blank.
1
[]
Page 26
Issue 3 02/2000
 Loading...
Loading...