Page 1

Technical
Information
1X SC480 BTS HARDWARE
INSTALLATION, OPTIMI ZATION/ATP, AND
FRU
SOFTWARE RELEASE 2.16.4.X
800 MHZ
CDMA2000 1X
PRELIMINARY
ENGLISH
MAY 2004
68P09260A11–7
Page 2

Notice
While reasonable efforts have been made to assure the accuracy of this document, Motorola, Inc. assumes no liability resulting from any
inaccuracies or omissions in this document, or from use of the information obtained herein. The information in this document has been
carefully checked and is believed to be entirely reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed for inaccuracies or omissions. Motorola,
Inc. reserves the right to make changes to any products described herein and reserves the right to revise this document and to make
changes from time to time in content hereof with no obligation to notify any person of revisions or changes. Motorola, Inc. does not
assume any liability arising out of the application or use of any product, software, or circuit described herein; neither does it convey
license under its patent rights or the rights of others.
It is possible that this publication may contain references to, or information about Motorola products (machines and programs),
programming, or services that are not announced in your country. Such references or information must not be construed to mean
that Motorola intends to announce such Motorola products, programming, or services in your country.
Copyrights
This instruction manual, and the Motorola products described in this instruction manual may be, include or describe copyrighted
Motorola material, such as computer programs stored in semiconductor memories or other media. Laws in the United States and
other countries preserve for Motorola and its licensors certain exclusive rights for copyrighted material, including the exclusive
right to copy, reproduce in any form, distribute and make derivative works of the copyrighted material. Accordingly, any
copyrighted material of Motorola and its licensors contained herein or in the Motorola products described in this instruction manual
may not be copied, reproduced, distributed, merged or modified in any manner without the express written permission of Motorola.
Furthermore, the purchase of Motorola products shall not be deemed to grant either directly or by implication, estoppel, or
otherwise, any license under the copyrights, patents or patent applications of Motorola, as arises by operation of law in the sale of a
product.
SPECIFICATIONS SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE
Usage and Disclosure Restrictions
License Agreement
The software described in this document is the property of Motorola, Inc and its licensors. It is furnished by express license
agreement only and may be used only in accordance with the terms of such an agreement.
Copyrighted Materials
Software and documentation are copyrighted materials. Making unauthorized copies is prohibited by law. No part of the software or
documentation may be reproduced, transmitted, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, or translated into any language or
computer language, in any form or by any means, without prior written permission of Motorola, Inc.
High Risk Activities
Components, units, or third–party products used in the product described herein are NOT fault–tolerant and are NOT designed,
manufactured, or intended for use as on–line control equipment in the following hazardous environments requiring fail–safe
controls: the operation of Nuclear Facilities, Aircraft Navigation or Aircraft Communication Systems, Air Traffic Control, Life
Support, or Weapons Systems (“High Risk Activities”). Motorola and its supplier(s) specifically disclaim any expressed or implied
warranty of fitness for such High Risk Activities.
Trademarks
MOTOROLA and the Stylized M Logo are registered in the US Patent & Trademark Office. All other product or service names are
the property of their respective owners.
© Copyright 2003, 2004 Motorola, Inc.
Javat Technology and/or J2MEt: Java and all other Java–based marks are trademarks or registered trademarks of Sun
Microsystems, Inc. in the U.S. and other countries.
R
: UNIX is a registered trademark of The Open Group in the United States and other countries.
UNIX
PRELIMINARY
REV091302
Page 3

1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
List of Figures vi . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
List of Tables xii . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Foreword xx . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
FCC Requirements xxiv . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
General Safety xxvii . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Revision History xxix . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Chapter 1: Introduction
Introduction 1-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table of Contents
Software Release 2.16.4.X
Content xxiv . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
FCC Part 15 Requirements xxiv . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Part 68 Requirements xxv . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Required Documents 1-5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
800 MHz CDMA Frequencies and Channels 1-8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation Tools and Materials 1-11 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
ATP Tools and Materials 1-14 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
BTS Equipment Identification 1-20 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Outdoor Enclosure Equipment Identification 1-30 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation and ATP Order 1-33 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Chapter 2: Site Preparation
Site Preparation Overview 2-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Site Inspections 2-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Prepare Site for the Arrival of the Equipment 2-5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Unpacking the Equipment 2-7 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Dimensions and Clearances 2-14 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Chapter 3: BTS Cables
Cable Description 3-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Power, Earth Ground, and Battery Cabling 3-4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Antenna Cabling 3-6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
MAY 2004 1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU i
PRELIMINARY
Page 4

Table of Contents – continued
Span Line and RGPS Cabling 3-7 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Remote GPS Head 3-9 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Local GPS (RF–GPS) Antenna Cabling 3-11 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Chapter 4: BTS and Cabling Installation
Installation Overview 4-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Connector Locations 4-3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Attaching BTS to Mounting Rack 4-5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Compact Combined Linear Power Amplifier Installation 4-10 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Thermal Management Enclosure Installation 4-21 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Compact BTS and HMS Installation 4-28 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Power Distribution Enclosure Installation 4-32 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Earth Ground Cabling 4-46 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
BTS DC Power Cabling 4-53 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
AC / DC Power Cabling Installation 4-57 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Antenna Cabling 4-59 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Span Line, RGPS, and RF GPS Cabling 4-63 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Customer Input / Output Cables 4-74 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Site Cleanup 4-76 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation Completion Checklist 4-77 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Chapter 5: Power Installation
Frame Configuration DIP Switch 5-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Pre–Power Up Test (Indoor) 5-4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
AC Power Input (Outdoor Configuration) 5-7 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Battery Backup DC Power Input (Outdoor Configuration) 5-9 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Initial Power–Up Test 5-11 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Remove Power 5-14 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Chapter 6: Optimization and Calibration
Preliminary Operations: Overview 6-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Preliminary Operations: Overview 6-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Ethernet LAN 6-3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Introduction to Optimization and Calibration 6-4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Preparing the LMF 6-7 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Span Lines – Interface and Isolation 6-16 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
LMF to BTS Connection 6-17 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Using the LMF 6-18 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
ii 1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU MAY 2004
PRELIMINARY
Page 5

Table of Contents – continued
Pinging the Processors 6-33 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Download the BTS 6-36 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
CSA System Time – GPS & HSO/MSO Verification 6-43 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Test Equipment Setup 6-51 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Test Set Calibration 6-65 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Bay Level Offset Calibration 6-76 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Chapter 7: Automated Acceptance Test Procedure (ATP)
Automated Acceptance Test Procedure – Introduction 7-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Acceptance Tests – Test Set Up 7-4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Abbreviated (All–inclusive) Acceptance Tests 7-5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Individual Acceptance Tests–Introduction 7-9 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
TX Spectral Purity Transmit Mask Acceptance Test 7-11 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
TX Waveform Quality (Rho) Acceptance Test 7-14 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
TX Pilot Time Offset Acceptance Test 7-16 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
TX Code Domain Power/Noise Floor Acceptance Test 7-18 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
RX FER Acceptance Test 7-21 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Generating an ATP Report 7-23 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Chapter 8: Leave the Site
Updating Calibration Data Files 8-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Prepare to Leave the Site 8-3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Chapter 9: Field Replaceable Unit
Introduction 9-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fan Module 9-4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
High and Medium Stability Oscillator Module 9-7 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Global Positioning System (GPS) Receivers 9-11 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
RF–GPS Module 9-14 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Power Supply Module (PSM) 9-18 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Clock Synchronization Alarms Card 9-21 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Group Line Interface Card 9-24 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Multi–Channel CDMA Card 9-28 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Broadband Transceiver Card 9-32 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Compact BTS Multi–Coupler Preselector Card 9-36 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
MCC Data Only (MCC–DO) Card 9-41 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Compact BTS Input and Output Board 9-45 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SDCX Module 9-50 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
MAY 2004 1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU iii
PRELIMINARY
Page 6

Table of Contents – continued
RF Filter Tray 9-55 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Compact Combined Linear Power Amplifier 9-67 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
TME Power Distribution Assembly 9-70 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Heat Management System 9-75 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Thermal Management Enclosure 9-83 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Power Distribution Enclosure 9-86 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Master Item Number Failure List 9-87 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Chapter 10: Reference Procedures Performed At OMC–R
Reference Procedures Performed At OMC–R 10-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Accessing OMC–R CLI Window 10-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Circuit BTS Shut Down Procedures 10-3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Circuit BTS Start–Up Procedures 10-23 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Packet BTS Shut Down Procedures 10-32 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Packet BTS Start–Up Procedures 10-53 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Chapter 11: Basic Troubleshooting
Basic Troubleshooting 11-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Appendix A: MCC–Data Only
MCC–DO Tests A-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Appendix B: Test Equipment Preparation
Test Equipment Preparation B-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Verifying and Setting GPIB Addresses B-5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Test Equipment Connection, Testing, and Control B-17 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Equipment Calibration B-28 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Manual Cable Calibration B-32 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Appendix C: Download ROM Code
Downloading ROM Code C-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Appendix D: MMI Cable Fabrication
MMI Cable Fabrication D-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Appendix E: Multiple BTS Configurations
Compact BTS Expansion Configuration (Indoor) E-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Multiple Compact BTS Configuration (Outdoor) E-22 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Appendix F: Logical BTS Configuration
Logical BTS LAN Configuration for Compact BTS (Indoor) F-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
iv 1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU MAY 2004
PRELIMINARY
Page 7

Table of Contents – continued
Appendix G: Integrated BTS Router Preliminary Operations
Integrated BTS Router Preliminary Operations – Introduction G-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Verify GLI3 Software Version and Span Parameter Settings G-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Change GLI3 Span Parameter Settings G-6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Appendix H: Integrated BTS Router Installation
Integrated BTS Router Installation – Introduction H-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
New Packet BTS Installation with IBR H-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
BTS Span Connections for IBR H-4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
BTS Span Connections for IBR – One Span H-5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Appendix I: Packet Backhaul Configuration
Packet Backhaul BTS I-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Index
MAY 2004 1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU v
PRELIMINARY
Page 8

List of Figures
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
Software Release 2.16.4.X
Figure 1-1: Mounted BTS and Rack 1-4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 1-2: CDMA Frequency Spectrum 1-10 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 1-3: RS232–IEEE488 Converter Serial Cable Configuration 1-16 . . . . . . . . .
Figure 1-4: Front View of Compact BTS 1-22 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 1-5: Rear View of Compact BTS 1-23 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 1-6: CCP2 Shelf Layout 1-24 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 1-7: CBIO Board 1-27 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 1-8: –48 VDC RF Connectors, Circuit Breaker, DC Power Terminal
Strip, and Ground Studs 1-28 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 1-9: +27VDC RF Connectors, Circuit Breaker, DC Power Terminal
Strip, and Ground Studs 1-29 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 1-10: Thermal Managment Enclosure and Heat Manaagement
System 1-30 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 1-11: Power Distribution Assembly 1-31 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 1-12: Power Distribution Enclosure and Heat Exchanger 1-32 . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 1-13: Compact Combined Linear Power Amplifier 1-32 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 2-1: Securing Lights with Tape 2-5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 2-2: Wood Shipping Container 2-9 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 2-3: Cardboard Shipping Container 2-10 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 2-4: Overall Dimensions of BTS 2-15 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 2-5: cCLPA Dimensions and Functional Clearances 2-17 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 2-6: Indoor Functional Clearances for BTS 2-18 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 2-7: Indoor Functional Clearances for BTS Side–By–Side
Configuration 2-19 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 2-8: TME 2-20 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 2-9: Overall Dimensions of the Thermal Management Enclosure 2-21 . . . . .
Figure 2-10: Functional Clearances for TME 2-22 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 2-11: PDE 2-23 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 2-12: PDE Overall Dimensions 2-24 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 2-13: Functional Clearances for PDE 2-25 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
vi 1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU MAY 2004
PRELIMINARY
Page 9

List of Figures – continued
Figure 2-14: Mulitple Pole Installation and Functional Clearances for
Enclosures and PA 2-26 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 2-15: Multiple Wall Installation and Functional Clearances for
TME and HMS, PDE, and cCLPA 2-27 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 3-1: Antenna Cabling Details 3-6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4-1: Rear View of BTS 4-3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4-2: Detail of Antenna Connectors and DC Power (Rear of BTS) 4-4 . . . . .
Figure 4-3: Attaching Mounting Plate to Rack 4-6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4-4: Attaching Mounting Bracket to BTS 4-7 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4-5: Attaching BTS to Mounting Plate 4-8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4-6: BTS Rear Attachment 4-9 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4-7: Bottom View of cCLPA 4-11 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4-8: cCLPA Mounting to Rack 4-12 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4-9: cCLPA Grounding 4-13 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4-10: DC Power Connection to cCLPA 4-15 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4-11: CBIO–to–cCLPA Data Cable RJ45 Connector 4-16 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4-12: Data Cable Connection Diagram for Compact BTS to cCLPA 4-18 . . .
Figure 4-13: Pole Mounting BracketAssembly 4-20 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4-14: Wall Mounting Bracket and cCLPA 4-20 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4-15: Thermal Management Enclosure and Heat Management
System 4-21 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4-16: Bottom View of TME 4-22 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4-17: Wall Mounting Bracket and Pole Mounting Bracket
Assembly 4-25 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4-18: TME Screw Mounting Location 4-27 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4-19: Thermal Management Enclosure and BTS 4-29 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4-20: Heat Management System (HMS) 4-30 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4-21: HMS Installation 4-31 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4-22: PDE and Heat Exchanger 4-32 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4-23: PDE Conduit Location 4-33 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4-24: PDE Detail 4-35 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4-25: Wall Mounting Bracket and Pole Mounting Bracket
Assembly 4-36 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4-26: PDE Mounting Screw Locations 4-38 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4-27: PDE Heat Exchanger Dimensions 4-39 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4-28: PDE Heat Exchanger Detail 4-40 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4-29: PDE and Heat Exchanger 4-41 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4-30: Detail Location of Ground Studs 4-47 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4-31: Grounding Location on BTS 4-48 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
MAY 2004 1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU vii
PRELIMINARY
Page 10

List of Figures – continued
Figure 4-32: Typical Outdoor Grounding Configuration 4-50 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4-33: Typical Multiple Outdoor Grounding Configuration 4-51 . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4-34: Rear View of PDE 4-52 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4-35: DC Power Terminal Strip 4-54 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4-36: TME Power Distribution Assembly for –48VDC 4-55 . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4-37: TME Power Distribution Assembly for +27VDC 4-56 . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4-38: Antenna Cabling (With cCLPA) 4-60 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4-39: Antenna Cabling with 2 cCLPAs 4-61 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4-40: Antenna Cabling (Without cCLPA) 4-62 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4-41: Span and RGPS Cabling Details 4-64 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4-42: Connector Pins Numbering for Cables C and C1 4-66 . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4-43: Installing the Remote GPS Head 4-68 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4-44: RGPS Head 4-69 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4-45: RGPS to SC480 Connection Diagram 4-69 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4-46: RGPS Lightning Arrestor Wiring 4-70 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4-47: RF–GPS Installation and Components 4-72 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4-48: Span and RF–GPS Cabling Details 4-73 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 5-1: DIP Switch Configuration 5-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 5-2: Expansion Frames DIP Switch Configuration 5-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 5-3: Location of Circuit Breaker for –48 VDC 5-5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 5-4: Bottom View of cCLPA 5-6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 6-1: LAN Connectors 6-3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 6-2: WinLMF Folder Structure 6-9 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 6-3: WinLMF Connection Detail 6-17 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 6-4: BTS Login Screen – Identifying Circuit and Packet BTS Files 6-20 . . .
Figure 6-5: Self–Managed Network Elements (NEs) State of a Packet
Mode 6-21 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 6-6: Available Packet Mode Commands 6-22 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 6-7: Packet Mode Site with MCC–1 and BBX–1 under LMF
Control 6-23 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 6-8: LMF Computer Common MMI Connections – Motorola MMI
Interface Kit, SLN2006A 6-31 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 6-9: MMI Connection Detail – Fabricated MMI Cable 6-32 . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 6-10: BTS Ethernet LAN Termination Diagram 6-33 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 6-11: CSA MMI Terminal Connection 6-46 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 6-12: IS–95A/B and CDMA 2000 1X Cable Calibration Test Setup –
Agilent E4406A/E4432B and Advantest R3267/R3562 6-56 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 6-13: IS–95A/B and CDMA 2000 1X Cable Calibration Test Setup –
Agilent E4406A/E4432B and Advantest R3267/R3562 6-57 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
viii 1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU MAY 2004
PRELIMINARY
Page 11

List of Figures – continued
Figure 6-14: TX Calibration Test Setup –
CyberTest (IS–95A/B) and Agilent 8935 (IS–95A/B and CDMA2000 1X) 6-58 . . .
Figure 6-15: TX Calibration Test Setup – Using Power Meter 6-59 . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 6-16: TX Calibration Test Setup –
Agilent E4406A and Advantest R3567 (IS–95A/B and CDMA2000 1X) 6-60 . . . . .
Figure 6-17: IS–95A/B ATP Test Set–up–
CyberTest, Advantest R3465, and Agilent 8935 6-61 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 6-18: IS–95A/B ATP Test Setup – HP 8921A 6-62 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 6-19: IS–95A/B and CDMA2000 1X ATP Test Setup Agilent Test
Equipment 6-63 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 6-20: IS–95A/B and CDMA2000 1X Optimization/ATP Test Setup –
Agilent E4432B/8935 Series E6380A and E4432B/E4406A Test Equipment 6-64 .
Figure 6-21: Cal Setup for TX/Duplexed RX Test Cabling
Using Signal Generator & Spectrum Analyzer 6-72 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 6-22: Cal Setup for Non–Duplexed RX Test Cabling Using Signal
Generator & Spectrum Analyzer 6-73 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 7-1: TX Mask Verification Spectrum Analyzer Display 7-13 . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 7-2: Code Domain Analyzer CD Power/Noise Floor Display
Examples 7-20 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 9-1: Compact BTS Front Panel Layout without Front Panel Cover 9-2 . . . .
Figure 9-2: Compact BTS Fan and CCP2 Shelf Layout 9-3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 9-3: Fan Module 9-5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 9-4: HSO or MSO Module 9-9 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 9-5: HSO or MSO Location 9-10 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 9-6: RGPS Head and Mounting Pipe/Conduit 9-13 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 9-7: RF–GPS Module 9-16 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 9-8: RF–GPS Placement on CBIO Board 9-17 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 9-9: Power Supply Module (PSM) 9-20 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 9-10: Clock Synchronization and Alarm Card 9-23 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 9-11: Group Line Interface 3 Card 9-27 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 9-12: MCC 1X Card 9-31 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 9-13: BBX–1X Card 9-35 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 9-14: Compact Multi–Coupler Preselector Card 9-39 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 9-15: Compact Multi–Coupler Preselector Card Jumper Connection 9-40 . .
Figure 9-16: MCC–DO Card 9-44 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 9-17: CBIO Board with SDCX Removed 9-49 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 9-18: SDCX Module 9-52 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 9-19: CBIO Board with SDCX 9-53 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 9-20: CBIO Board with SDCX Removed 9-54 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 9-21: cMPC Cable Clip 9-58 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
MAY 2004 1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU ix
PRELIMINARY
Page 12

List of Figures – continued
Figure 9-22: Filter Tray Connectors and Cable Part Numbers 9-61 . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 9-23: Filter Tray Connectors and Cable Part Numbers (SGLN6223) 9-62 . . .
Figure 9-24: Filter Tray Connectors and Cable Part Numbers (SGLN6222) 9-66 . . .
Figure 9-25: Compact Combined Linear Power Amplifier 9-69 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 9-26: PDA Location 9-71 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 9-27: Power Distribution Assembly for –48VDC 9-72 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 9-28: Power Distribution Assembly for +27VDC 9-74 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 9-29:Heat Management System 9-76 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 9-30: HMS Heater Elements 9-79 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 9-31: HMS Controller 9-80 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 9-32: Blower Fan 9-82 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 11-1: TME and BTS Cable Routing 11-9 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 11-2: TX Output Fault Isolation Flowchart 11-35 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 11-3: CSM Front Panel Indicators & Monitor Ports 11-51 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 11-4: GLI3 Front Panel 11-54 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 11-5: MCC24 and MCC–1X Front Panel LEDs and LED
Indications 11-56 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 11-6: MGLI/GLI Board MMI Connection Detail 11-58 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure B-1: Agilent E7495A Pre–Power Sensor Calibration Connection B-4 . . . . .
Figure B-2: Agilent E7495A Power Sensor Calibration Connection B-4 . . . . . . . . .
Figure B-3: Setting Agilent E4406A GPIB Address B-5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure B-4: Setting Agilent E4432B GPIB Address B-6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure B-5: Setting Advantest R3267 GPIB Address B-8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure B-6: Advantest R3562 GPIB Address Switch Setting B-9 . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure B-7: Agilent 8935 Test Set B-9 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure B-8: HP 8921A and HP 83236A/B B-11 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure B-9: R3465 Communications Test Set B-12 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure B-10: HP 437 Power Meter B-14 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure B-11: Gigatronics 8541C Power Meter Detail B-15 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure B-12: RS232 GPIB Interface Adapter B-16 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure B-13: HP 8921A/600 Cable Connections for 10 MHz Signal and
GPIB without Rubidium Reference B-18 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure B-14: HP 8921A Cable Connections for 10 MHz Signal and GPIB
with Rubidium Reference B-20 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure B-15: Cable Connections for Test Set without 10 MHz Rubidium
Reference B-23 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure B-16: Cable Connections for Test Set with 10 MHz Rubidium
Reference B-24 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure B-17: Agilent 8935/E4432B 10MHz Reference and Even Second
Tick Connections B-26 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
x 1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU MAY 2004
PRELIMINARY
Page 13

List of Figures – continued
Figure B-18: Agilent 10 MHz Reference Connections B-26 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure B-19: Advantest 10 MHz Reference and Serial I/O Connections B-27 . . . . . .
Figure B-20: Performing Agilent E4406A Self–alignment (Calibration) B-28 . . . . .
Figure B-21: Power Meter Detail B-29 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure B-22: Gigatronics 8541C Power Meter Detail B-31 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure B-23: Cable Calibration Using HP8921 with PCS Interface B-35 . . . . . . . . .
Figure B-24: Cable Calibration Using Advantest R3465 B-38 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure D-1: Fabricated MMI Cable Details D-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure E-1: Three Expansion BTSes Cabling Diagram with Two cCLPAs E-4 . . .
Figure E-2: Two Expansion BTSes Cabling Diagram with Two cCLPAs E-6 . . . . .
Figure E-3: One Expansion BTS Cabling Diagram with Two cCLPAs E-8 . . . . . . .
Figure E-4: Three Expansion BTSes Cabling Diagram with One cCLPA E-11 . . . . .
Figure E-5: Two Expansion BTSes Cabling Diagram with One cCLPA E-13 . . . . . .
Figure E-6: One Expansion BTS Cabling Diagram with One cCLPA E-15 . . . . . . . .
Figure E-7: Three Expansion BTSes Cabling Diagram E-17 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure E-8: Two Expansion BTSes Cabling Diagram E-18 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure E-9: One Expansion BTS Cabling Diagram E-19 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure E-10: Three Expansion BTSes Cabling Diagram E-24 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure E-11: Outdoor Two Expansion BTSes Cabling Diagram E-25 . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure E-12: Outdoor One Expansion BTS Cabling Diagram E-26 . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure F-1: Three Expansion BTSes LAN Cabling Diagram F-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure F-2: Two Expansion BTSes LAN Cabling Diagram F-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure F-3: One Expansion BTSes LAN Cabling Diagram F-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure H-1: Cabling Compact BTS Packet Operation Integrated BTS
Router Spans – One Span H-5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
MAY 2004 1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU xi
PRELIMINARY
Page 14

List of Tables
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
Software Release 2.16.4.X
FCC Part 68 Registered Devices xxv . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 1-1: Abbreviations and Acronyms 1-5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 1-2: Regular Band Class 0 TX and RX Frequency vs Channel 1-9 . . . . . . . .
Table 1-3: China A–Band TX and RX Frequency vs Channel 1-9 . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 1-4: Recommended Tools and Materials for Rack Mounting 1-11 . . . . . . . . . .
Table 1-5: CCP2 Shelf Card/Module Device ID Numbers for Logical BTS 1-21 . . .
Table 1-6: Shelf Device ID Numbers 1-24 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-1: Procedure to Prepare the Site for the BTS 2-6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-2: Recommended Unpacking Tools 2-8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-3: Unpacking Equipment from a Cardboard or Wood Container 2-11 . . . . .
Table 2-4: Procedure to Remove Outdoor Equipment from Container 2-11 . . . . . . .
Table 2-5: Procedure to Remove Indoor Equipment from Container 2-13 . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-6: Installation Dimensions for the BTS 2-14 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-7: Minimum Clearances for the BTS 2-14 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-8: Installation Dimensions for the cCLPA 2-16 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-9: Minimum Clearances for the cCLPA 2-16 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-10: Installation Dimensions for the TME 2-20 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-11: Minimum Clearances for the TME 2-20 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-12: Installation Dimensions for the PDE 2-23 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-13: Minimum Clearances for the PDE 2-23 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 3-1: Cable Descriptions and Part Numbers 3-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 3-2: Cables Needed for Antenna Connections 3-6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 3-3: Pin and Signal Information for Cable B (Antenna Cable) 3-6 . . . . . . . .
Table 3-4: Cables Needed for Span/RGPS Connections 3-7 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 3-5: Pin/Signal Information for Span Cable 3-8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 3-6: RGPS Pin/Signal Name Information 3-8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 3-7: Cabling for Local GPS 3-11 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 3-8: Local GPS Antenna Mounting Considerations 3-12 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 4-1: Procedure to Attach Mounting Plate to Rack 4-6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
xii 1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU MAY 2004
PRELIMINARY
Page 15

List of Tables – continued
Table 4-2: Procedure to Attach BTS Mounting Bracket 4-7 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 4-3: Procedure to Attach BTS to Mounting Plate 4-8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 4-4: DC Input Cable Description and Part Number 4-10 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 4-5: Procedure to Mount the Power Amplifier 4-11 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 4-6: Ground Cable and Lug Description and Part Number 4-12 . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 4-7: Procedure to Ground the cCLPA 4-13 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 4-8: Procedure to Attach DC Power Cable to the cCLPA 4-14 . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 4-9: Data Cable Description and Part Number 4-16 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 4-10: Data Cable Wiring Scheme 4-16 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 4-11: Procedure to Attach BTS Data Cable to cCLPA 4-17 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 4-12: Procedure to Pole or Wall Mount the cCLPA 4-19 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 4-13: TME Conduit Sizes 4-23 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 4-14: Procedure to Pole Mount the TME 4-24 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 4-15: Procedure to Install Mounting Bracket on a Wall 4-26 . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 4-16: Procedure to Install Compact BTS in a TME 4-28 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 4-17: Procedure to Install the HMS 4-30 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 4-18: Conduit Sizes 4-33 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 4-19: Procedure to Install Mounting Bracket Assembly on a Pole 4-37 . . . . .
Table 4-20: Procedure to Install the Wall Mounting Bracket on a Wall 4-38 . . . . . . .
Table 4-21: Procedure to Install the Heat Exchanger 4-40 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 4-22: PDE Punchblock Wiring Descriptions 4-41 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 4-23: Ground Cable and Lug Description and Part Number 4-46 . . . . . . . . . .
Table 4-24: Procedure to Attach the Earth Ground Cable 4-47 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 4-25: Procedure to Ground an Outdoor Site 4-49 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 4-26: DC Input Cable Description and Part Number 4-53 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 4-27: Procedure to Connect DC Power to the BTS 4-53 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 4-28: Procedure to Connect DC Power to the BTS 4-55 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 4-29: AC Input Cable Description and Part Number 4-57 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 4-30: Cable Descriptions and Part Numbers 4-59 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 4-31: Procedure to Install Antenna Cables 4-59 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 4-32: List of Required Cables 4-63 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 4-33: Pin/Signal Information for Span Cable 4-65 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 4-34: Procedure to Install 1X or DO Span Cable 4-65 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 4-35: Pinout for Cables C and C1 4-66 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 4-36: Procedure for Installing the RGPS Head and Cabling 4-67 . . . . . . . . . .
Table 4-37: Procedure for Installing RF–GPS Antenna and Cabling 4-70 . . . . . . . . .
Table 4-38: Cable Descriptions and Part Numbers 4-74 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
MAY 2004 1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU xiii
PRELIMINARY
Page 16

List of Tables – continued
Table 4-39: Customer Input Connector Pinouts 4-74 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 4-40: Customer Input Connector Pinouts 4-75 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 4-41: Procedure for Using Ferrite Core on Customer Input and
Output Wires 4-75 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 4-42: Indoor Installation Completion Checklist 4-77 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 5-1: Frame ID Switch Position – Single/Starter Frame 5-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 5-2: Frame ID Switch Position – Expansion 1 Frame 5-3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 5-3: Frame ID Switch Position – Expansion 2 Frame 5-3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 5-4: Frame ID Switch Position – Expansion 3 Frame 5-3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 5-5: BTS DC Pre–Power Test 5-4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 5-6: cCLPA DC Pre–Power Test 5-6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 5-7: PDE Initial Power –Up Test 5-7 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 5-8: Cable Descriptions and Part Numbers 5-9 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 5-9: Procedure to Verify Battery Backup DC Power Test 5-9 . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 5-10: Procedure for BTS Initial Power–Up 5-11 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 5-11: Procedure cCLPA Initial Power–Up 5-11 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 5-12: TME DC Initial Power–Up Test 5-12 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 5-13: Procedure to Remove Power to BTS 5-14 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 5-14: Procedure to Remove Power to cCLPA 5-14 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 5-15: Procedure to Remove Power to PDE 5-14 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 6-1: Initial Installation of Boards/Modules 6-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 6-2: Install WinLMF using CD ROM 6-11 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 6-3: Copying CDF or NECF Files to the WinLMF Computer 6-12 . . . . . . . . .
Table 6-4: Create HyperTerminal Connection 6-14 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 6-5: T1/E1 Span Isolation 6-16 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 6-6: Connecting the WinLMF to the BTS 6-17 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 6-7: BTS GUI Login Procedure 6-25 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 6-8: BTS CLI Login Procedure 6-27 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 6-9: BTS GUI Logout Procedure 6-28 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 6-10: BTS CLI Logout Procedure 6-29 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 6-11: Establishing MMI Communication 6-30 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 6-12: Pinging the Processors 6-34 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 6-13: Verify GLI ROM Code Loads 6-38 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 6-14: Download and Enable GLI Device 6-39 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 6-15: Download RAM Code and Data to Non–GLI Devices 6-40 . . . . . . . . . .
Table 6-16: Select CSA Clock Source 6-41 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 6-17: Enable CSA 6-41 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
xiv 1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU MAY 2004
PRELIMINARY
Page 17

List of Tables – continued
Table 6-18: Enable MCCs 6-42 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 6-19: Test Equipment Setup (GPS & HSO/MSO Verification) 6-45 . . . . . . . .
Table 6-20: GPS Initialization/Verification 6-47 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 6-21: IS–95A/B–only Test Equipment Interconnection 6-53 . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 6-22: CDMA2000 1X/IS–95A/B Test Equipment Interconnection 6-54 . . . . .
Table 6-23: Procedure for Selecting Test Equipment Manually in the
Serial Connection Tab 6-67 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 6-24: Procedure for Selecting Test Equipment Using Auto-Detect 6-68 . . . . .
Table 6-25: Procedure for Test Equipment Calibration 6-69 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 6-26: Procedure to Test Cabling Calibration using Communication
System Analyzer 6-70 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 6-27: Procedure to Calibrate TX/Duplexed RX Test Cabling Using
Signal Generator & Spectrum Analyzer 6-71 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 6-28: Procedure for Calibrating Non–Duplexed RX Test Cabling Using
Signal Generator & Spectrum Analyzer 6-72 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 6-29: Procedure for Setting Cable Loss Values 6-73 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 6-30: Procedure for Setting TX and RX Directional Coupler Loss
Values 6-74 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 6-31: Procedure to Set Up Test Equipment for RF Path Calibration 6-78 . . . .
Table 6-32: Maximum and Minimum Power 6-79 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 6-33: Test Patterns with Channels and Gain Settings Used 6-81 . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 6-35: Procedure for All Cal/Audit and TX Calibration 6-83 . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 6-36: Procedure to Download BLO 6-85 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 6-37: Procedure for BTS TX Path Audit 6-86 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 6-38: Create CAL File 6-88 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 7-1: Set Up Test Equipment – TX Output Verify/Control Tests 7-4 . . . . . . . .
Table 7-2: All TX/RX ATP Test Procedure 7-6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 7-3: All TX ATP Test Procedure 7-7 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 7-4: All RX ATP Test Procedure 7-8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 7-5: Test Spectral Purity Transmit Mask 7-11 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 7-6: Test Waveform Quality (Rho) 7-14 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 7-7: Test Pilot Time Offset 7-16 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 7-8: Test Code Domain Power/Noise Floor 7-19 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 7-9: Test FER 7-21 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 7-10: Generating an ATP Report 7-23 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 8-1: Copying CAL Files to a Diskette 8-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 8-2: Copying CAL Files from Diskette to the CBSC 8-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 8-3: Remove External Test Equipment 8-3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 8-4: Bring Modules into Service 8-3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
MAY 2004 1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU xv
PRELIMINARY
Page 18

List of Tables – continued
Table 8-5: Terminate the WinLMF Session and Remove the WinLMF 8-4 . . . . . . .
Table 8-6: Connect T1 or E1 Spans 8-4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 8-7: Check Before Leaving the Site 8-5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 8-8: Reset BTS Devices and Remote Site Initialization 8-5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-1: Procedure to Remove Fan Module 9-5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-2: Procedure to Install Fan Module 9-6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-3: Procedure to Remove HSO or MSO Module 9-8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-4: Procedure to Install HSO or MSO Module 9-8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-5: Procedure to Remove RGPS Head 9-12 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-6: Procedure to Install RGPS Head 9-12 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-7: Procedure to Remove RF–GPS 9-15 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-8: Procedure to Install RF–GPS 9-15 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-9: Procedure to Remove Power Supply Module 9-19 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-10: Procedure to Install Power Supply Module 9-19 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-11: Procedure to Remove CSA Module 9-21 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-12: Procedure to Install CSA Module 9-22 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-13: Procedure to Remove GLI3 Card 9-25 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-14: Procedure to Install GLI3 Card 9-25 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-15: Procedure to Recover GLI3 Card 9-26 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-16: Procedure to Remove MCC–1X Card 9-29 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-17: Procedure to Install MCC–1X Card 9-30 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-18: Procedure to Remove BBX–1X Card 9-34 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-19: Procedure to Install BBX–1X Card 9-34 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-20: cMPC PWR/ALM LED State 9-36 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-21: Procedure to Remove cMPC 9-37 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-22: Procedure to Install cMPC 9-38 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-23: MCC–DO LED States 9-41 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-24: Procedure to Remove MCC–DO Card 9-42 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-25: Procedure to Install MCC–DO Card 9-43 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-26: Procedure to Remove CBIO Board 9-46 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-27: Procedure to Install CBIO Board 9-47 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-28: Procedure to Remove SDCX 9-50 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-29: Procedure to Install SDCX 9-51 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-30: Preparation Procedure for Removing the Filter Tray 9-56 . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-31: Procedure to Remove Filter Tray Kit SGLF4152 9-57 . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-32: Procedure to Remove cMPC Cable Clip 9-57 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-33: Procedure to Install cMPC Cable Clip 9-58 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
xvi 1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU MAY 2004
PRELIMINARY
Page 19

List of Tables – continued
Table 9-34: Procedure to Install Filter Tray Kit SGLF4152 9-58 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-35: Procedure to Remove Filter Tray Kit SGLN6223 9-61 . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-36: Procedure to Install Filter Tray Kit SGLN6223 9-63 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-37: Procedure to Remove Filter Tray Kit SGLN6222 9-65 . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-38: Procedure to Install Filter Tray Kit SGLN6222 9-65 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-39: Procedure to Remove cCLPA 9-67 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-40: Procedure to Install cCLPA 9-68 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-41: Procedure to Remove PDA 9-71 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-42: Procedure to Install PDA 9-73 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-43: Procedure to Remove HMS 9-77 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-44: Procedure to Re–install HMS 9-77 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-45: Procedure to Replace Heater Elements 9-78 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-46: Procedure to Install Heater Elements 9-78 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-47: Procedure to Replace HMS Controller 9-79 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-48: Procedure to Install HMS Controller 9-80 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-49: Procedure to Replace Blower Fan 9-81 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-50: Procedure to Install Blower Fan 9-81 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-51: Procedure to Remove TME 9-83 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-52: Procedure to Install TME 9-84 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-53: Fan Module Item Number List 9-87 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-54: HSO or MSO Module Item Number List 9-87 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-55: RGPS Item Number List 9-87 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-56: RF GPS Module Item Number List 9-87 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-57: PSM Item Number List 9-88 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-58: CSA Card Item Number List 9-88 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-59: GLI3 Card Item Number List 9-88 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-60: MCC–1X Card Item Number List 9-88 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-61: BBX–1X Card Item Number List 9-89 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-62: Compact MPC Item Number List 9-89 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-63: MCC–DO Card Item Number List 9-89 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-64: CBIO Board Item Number List 9-89 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-65: SDCX Module Item Number List 9-89 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-66: Filter Tray Kit Item Number List 9-90 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-67: cCLPA Item Number List 9-90 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-68: TME PDA Item Number List 9-90 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-69: TME HMS Item Number List 9-90 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-70: TME HMS Heater Element Item Number List 9-91 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
MAY 2004 1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU xvii
PRELIMINARY
Page 20

List of Tables – continued
Table 9-71: TME HMS Controller Item Number List 9-91 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 9-72: TME HMS Blower Fan Item Number List 9-91 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 10-1: Login and Access Alarm Window Procedure 10-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 10-2: Shut Down Site Signaling Functions Procedure For a
Circuit BTS 10-3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 10-3: Shut Down Sector Signaling Functions Procedure For a
Circuit BTS 10-9 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 10-4: Shut Down Carrier Signaling Functions Procedure For a
Circuit BTS 10-16 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 10-5: Restore Site Signaling Operations Procedure For a
Circuit BTS 10-23 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 10-6: Restore Sector Signaling Operations Procedure For a
Circuit BTS 10-26 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 10-7: Restore Carrier Signaling Operations Procedure For a
Circuit BTS 10-29 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 10-8: Shut Down Site Signaling Functions Procedure For a
Packet BTS 10-33 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 10-9: Shut Down Sector Signaling Functions Procedure For a
Packet BTS 10-40 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 10-10: Shut Down Carrier Signaling Functions Procedure For a
Packet BTS 10-47 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 10-11: Restore Site Signaling Operations Procedure For a
Packet BTS 10-53 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 10-12: Restore Sector Signaling Operations Procedure For a
Packet BTS 10-56 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 10-13: Restore Carrier Signaling Operations Procedure For a
Packet BTS 10-59 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 11-1: Login Failure Troubleshooting Procedures 11-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 11-2: Force Ethernet LAN A to Active State as Primary LAN 11-2 . . . . . . . .
Table 11-3: GLI IP Address Setting 11-3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 11-4: Troubleshooting a Power Meter Communication Failure 11-5 . . . . . . . .
Table 11-5: Troubleshooting a Communications System Analyzer
Communication Failure 11-5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 11-6: Troubleshooting a Signal Generator Communication Failure 11-6 . . . . .
Table 11-7: Troubleshooting Code Download Failure 11-6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 11-8: Troubleshooting Data Download Failure 11-7 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 11-9: Troubleshooting Device Enable (INS) Failure 11-7 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 11-10: cCLPA Errors 11-8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 11-11: Restore Site Signaling Operations Procedure For a
Packet BTS 11-10 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 11-12: Restore Sector Signaling Operations Procedure For a
Packet BTS 11-13 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 11-13: Restore Carrier Signaling Operations Procedure For a
Packet BTS 11-16 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
xviii 1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU MAY 2004
PRELIMINARY
Page 21

List of Tables – continued
Table 11-14: Login Failure Troubleshooting Procedures 11-21 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 11-15: Force Ethernet LAN A to Active State as Primary LAN 11-22 . . . . . . .
Table 11-16: GLI IP Address Setting 11-23 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 11-17: Troubleshooting a Power Meter Communication Failure 11-25 . . . . . . .
Table 11-18: Troubleshooting a Communications System Analyzer
Communication Failure 11-25 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 11-19: 11-26 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 11-20: Troubleshooting Code Download Failure 11-27 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 11-21: Troubleshooting Data Download Failure 11-27 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 11-22: Troubleshooting Device Enable (INS) Failure 11-28 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 11-23: LPA Errors 11-28 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 11-24: Troubleshooting BLO Calibration Failure 11-30 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 11-25: Troubleshooting Calibration Audit Failure 11-31 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 11-26: Troubleshooting Forward Link Failure (BTS Passed
Reduced ATP) 11-36 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 11-27: Troubleshooting TX Mask Measurement Failure 11-36 . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 11-28: Troubleshooting Rho and Pilot Time Offset Measurement
Failure 11-36 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 11-29: Troubleshooting Code Domain Power and Noise Floor
Measurement Failure 11-38 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 11-30: Troubleshooting Multi-FER Failure 11-39 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 11-31: CSM Reference (Clock) Sources by GPS Type and
Kit Number 11-41 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 11-32: No GLI Control Through LMF (All GLIs) 11-44 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 11-33: No GLI Control Through Span Line Connection (Both GLIs) 11-44 . . .
Table 11-34: MGLI Control Good – No Control Over Co–located GLI 11-44 . . . . . .
Table 11-35: MGLI Control Good – No Control Over AMR 11-44 . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 11-36: MGLI Control Good – No Control over Co–located BBXs 11-45 . . . . .
Table 11-37: BBX Control Good – No (or Missing) Span Line Traffic 11-45 . . . . . . .
Table 11-38: No MCC–1X/MCC24E/MCC8E Channel Elements 11-45 . . . . . . . . . .
Table 11-39: No DC Input Voltage to Power Supply Module 11-46 . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 11-40: No DC Input Voltage to any SCCP Shelf Module 11-47 . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 11-41: TX and RX Signal Routing Problems 11-47 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 11-42: RFDS Fault Isolation – All Tests Fail 11-48 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 11-43: RFDS Fault Isolation – All Tests Fail on Single Antenna Path 11-49 . .
Table 11-44: Troubleshoot Control Link Failure 11-57 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 11-45: Set BTS Span Parameter Configuration 11-59 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table A-1: Procedure to Test MCC–DO Code Domain Power A-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table A-2:Procedure to Test the MCC–DO TX Mask A-4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
MAY 2004 1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU xix
PRELIMINARY
Page 22

List of Tables – continued
Table A-3: Procedure to Test MCC–DO Pilot Time Offset A-6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table A-4: Procedure to Test MCC–DO Rho A-8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table A-5: Procedure to Test MCC–DO Packet Error Rate A-10 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table B-1: Set IP Address on Agilent E7495A test set B-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table B-2: Detecting Agilent E7495A Test Equipment B-3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table B-3: E7495A Power Sensor Calibration B-3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table B-4: Verify and Change Agilent E4406A GPIB Address B-5 . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table B-5: Verify and Change Agilent E4432B GPIB Address B-7 . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table B-6: Verify and Change Advantest R3267 GPIB Address B-8 . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table B-7: Verify and/or Change Agilent 8935 (formerly HP 8935)
GPIB Address B-10 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table B-8: Verify and/or Change HP 8921A and HP 83236A
GPIB Addresses B-11 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table B-9: Verify and/or Change Advantest R3465 GPIB Address B-12 . . . . . . . . . .
Table B-10: Verify and/or Change Motorola CyberTest GPIB Address B-13 . . . . . .
Table B-11: Verify and/or Change HP 437 Power Meter GPIB Address B-14 . . . . . .
Table B-12: Verify and/or Change Gigatronics 8541C Power Meter
GPIB Address B-15 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table B-13: HP 8921A/600 Communications Test Set Rear Panel
Connections Without Rubidium Reference B-17 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table B-14: HP 8921A/600 Communications Test Set Rear Panel
Connections With Rubidium Reference B-19 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table B-15: System Connectivity B-21 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table B-16: Pretest Setup for HP 8921A B-22 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table B-17: Pretest Setup for Agilent 8935 B-22 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table B-18: Advantest R3465 Clock Setup B-24 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table B-19: Pretest Setup for Advantest R3465 B-25 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table B-20: Perform Agilent E4406A Self–alignment (Calibration) B-28 . . . . . . . . .
Table B-21: HP 437 Power Meter Calibration Procedure B-29 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table B-22: Calibrate Gigatronics 8541C Power Meter B-31 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table B-23: Calibrating Test Cable Setup (using the HP PCS Interface) B-32 . . . . .
Table B-24: Procedure for Calibrating Test Cable Setup Using Advantest
R3465 B-36 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table C-1: Download ROM and RAM Code to Devices C-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table D-1: Parts Required to Fabricate MMI Cable D-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table D-2: Fabricated MMI Cable Wire Run List D-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table E-1: Combiner and Directional Coupler Specifications E-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table E-2: Procedure for Installing Expansion Compact BTS with Dual
cCLPA E-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
xx 1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU MAY 2004
PRELIMINARY
Page 23

List of Tables – continued
Table E-3: Starter and Three Expansion BTS Interconnect Cabling
for Circuit or Packet Configuration with Dual cCLPA E-3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table E-4: Starter and Two Expansion BTS Interconnect Cabling
for Circuit or Packet Configuration with Dual cCLPA E-5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table E-5: Starter and One Expansion BTS Interconnect Cabling
for Circuit or Packet Configuration with Dual cCLPA E-7 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table E-6: Procedure for Installing Expansion Compact BTS with Single
cCLPA E-9 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table E-7: Starter and Three Expansion BTS Interconnect Cabling
for Circuit or Packet Configuration with Single cCLPA E-10 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table E-8: Starter and Two Expansion BTS Interconnect Cabling
for Circuit or Packet Configuration with Single cCLPA E-12 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table E-9: Starter and One Expansion BTS Interconnect Cabling
for Circuit or Packet Configuration with Single cCLPA E-14 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table E-10: Procedure for Installing Expansion Compact BTS without
cCLPA E-16 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table E-11: BBX (Carrier) to cCLPA Via RS485 E-20 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table E-12: Starter and Three Expansion BTS Cabling for
Circuit or Packet to Dual cCLPAs E-20 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table E-13: Starter and Two Expansion BTS Cabling for
Circuit or Packet to Dual cCLPAs E-21 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table E-14: Starter and One Expansion BTS Cabling for
Circuit or Packet to Dual cCLPAs E-21 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table E-15: Combiner and Directional Coupler Specifications E-22 . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table E-16: Procedure for Installing Expansion Compact BTSes E-23 . . . . . . . . . . .
Table F-1: Procedure for Installing LAN Cabling for Logical BTS F-3 . . . . . . . . . .
Table G-1: Suggested Preliminary Verification Locations G-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table G-2: Verify GLI3 Software Version and Span Parameter Settings G-3 . . . . . .
Table G-3: Set GLI3 Span Parameter Configuration G-6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table H-1: Implement IBR Functionality in New BTS H-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table H-2: BTS Span Cables H-4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
MAY 2004 1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU xxi
PRELIMINARY
Page 24
Foreword
Scope of manual
Obtaining manuals
This manual is intended for use by cellular telephone system
craftspersons in the day-to-day operation of Motorola cellular system
equipment and ancillary devices.
This manual is not intended to replace the system and equipment
training offered by Motorola, although it can be used to supplement or
enhance the knowledge gained through such training.
To view, download, or order manuals (original or revised), visit the
Motorola Lifecycles Customer web page at
https://mynetworksupport.motorola.com/
account representative.
If Motorola changes the content of a manual after the original printing
date, Motorola publishes a new version with the same part number but a
different revision character.
, or contact your Motorola
Text conventions
The following special paragraphs are used in this manual to point out
information that must be read. This information may be set-off from the
surrounding text, but is always preceded by a bold title in capital letters.
The four categories of these special paragraphs are:
NOTE
Presents additional, helpful, non-critical information that
you can use.
IMPORTANT
*
Presents information to help you avoid an undesirable
situation or provides additional information to help you
understand a topic or concept.
CAUTION
Presents information to identify a situation in which
damage to software, stored data, or equipment could occur,
thus avoiding the damage.
WARNING
Presents information to warn you of a potentially
hazardous situation in which there is a possibility of
personal injury.
xxii 1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU MAY 2004
PRELIMINARY
Page 25

Foreword – continued
Reporting manual errors
The following typographical conventions are used for the presentation of
software information:
S In text, sans serif BOLDFACE CAPITAL characters (a type style
without angular strokes: for example, SERIF versus SANS SERIF)
are used to name a command.
S In text, typewriter style characters represent prompts and the
system output as displayed on an operator terminal or printer.
S In command definitions, sans serif boldface characters represent
those parts of the command string that must be entered exactly as
shown and typewriter style characters represent command output
responses as displayed on an operator terminal or printer.
S In the command format of the command definition, typewriter
style characters represent the command parameters.
To report a documentation error, call the CNRC (Customer Network
Resolution Center) and provide the following information to enable
CNRC to open an SR (Service Request):
– the document type
– the manual title, part number, and revision character
– the page number(s) with the error
– a detailed description of the error and if possible the proposed solution
Motorola appreciates feedback from the users of our manuals.
Contact us
Manual banner definitions
24-hour support service
Send questions and comments regarding user documentation to the email
address below:
cdma.documentation@motorola.com
Motorola appreciates feedback from the users of our information.
A banner (oversized text on the bottom of the page, for example,
PRELIMINARY) indicates that some information contained in the
manual is not yet approved for general customer use.
If you have problems regarding the operation of your equipment, please
contact the Customer Network Resolution Center (CNRC) for immediate
assistance. The 24 hour telephone numbers are:
North America +1–800–433–5202
Europe, Middle East, Africa +44– (0) 1793–565444
Asia Pacific +86–10–88417733
Japan & Korea +81–3–5463–3550. . . . . . . . . . .
For further CNRC contact information, contact your Motorola account
representative.
MAY 2004 1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU xxiii
PRELIMINARY
Page 26
FCC Requirements
Content
FCC Part 15 Requirements
This section presents the Federal Communications Commission (FCC)
Rules Parts 15 and 68 requirements and compliance information for the
SC480 domestic series Radio Frequency Base TransceiverStations.
Part 15.19a(3) – Information to User
NOTE
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules.
Operationis subject to the following two conditions:
1. This device may not cause harmful interference, and
2. This device must accept any interference received,
includinginterference that may cause undesired
operation.
Part 15.21 – Information to User
CAUTION
Changes or modifications not expressly approved by
Motorolacould void your authority to operate the
equipment.
xxiv 1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU MAY 2004
PRELIMINARY
Page 27
FCC Requriements – continued
Part 15.105(b) – Information to User
NOTE
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with
thelimits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15
of theFCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide
reasonableprotection against harmful interference in a
residentialinstallation. This equipment generates, uses and
can radiate radiofrequency energy and, if not installed and
used in accordancewith the instructions, may cause harmful
interference to radiocommunications. However, there is no
guarantee thatinterference will not occur in a particular
installation. If thisequipment does cause harmful
interference to radio or televisionreception, which can be
determined by turning the equipmentOFF and ON, the user
is encouraged to try to correct theinterference by one or
more of the following measures:
S Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
S Increase the separation between the equipment and
receiver.
S Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit
different from that to which the receiver is connected.
S Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV
technician for help.
Part 68 Requirements
This equipment complies with Part 68 of the Federal
CommunicationsCommission (FCC) Rules. A label on the GLI3 board,
easily visiblewith the board removed, contains the FCC Registration
Number for thisequipment. If requested, this information must be
provided to the telephone company.
FCC Part 68 Registered Devices
Device FCC Part 68 ID
SC480–800MHz 1X/EVDO See Note US: IHEDENANSC4801XDO
NOTE
The SC480–800MHz 1X/EVDO BTS is registered with an FCC part number
(US: IHEDENANSC4801XDO) which will cover all the internal cards and
modules.
The telephone company may make changes in its facilities, equipment,
operations, or procedures that could affect the operation of your T1. If
this happens, the telephone company will provide advance notice so that
you can modify your equipment as required to maintain uninterrupted
service.
MAY 2004 1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU xxv
PRELIMINARY
Page 28
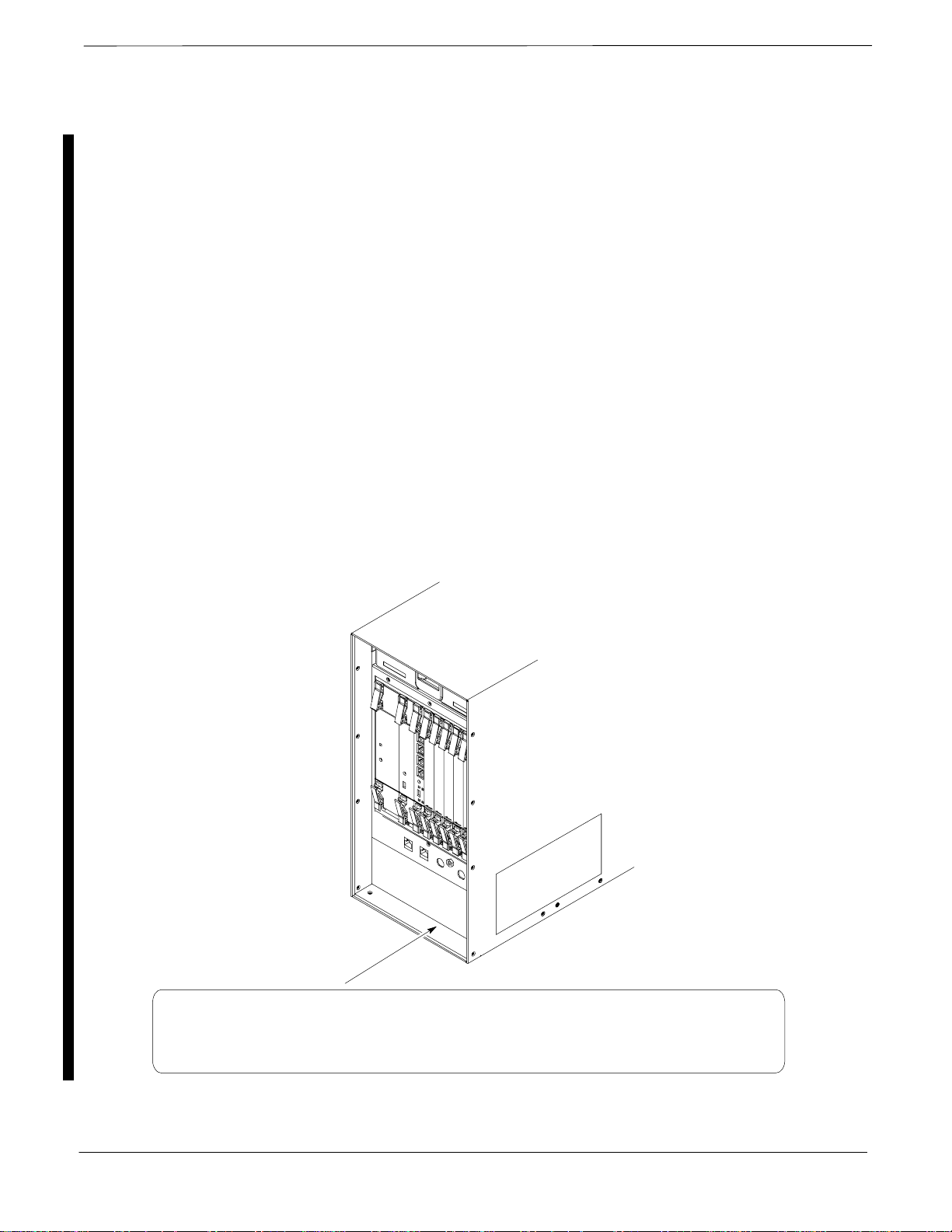
FCC Requirements – continued
If this equipment causes harm to the telephone network, the telephone
company will notify you in advance that temporary discontinuance of
service may be required. If advance notice is not practical, the telephone
company will notify you as soon as possible. Also, you will be advised
of your right to file a complaint with the FCC if you believe it is
necessary.
If you experience trouble operating this equipment with the T1, please
contact:
Global Customer Network Resolution Center (CNRC)
1501 W. Shure Drive, 3436N
Arlington Heights, Illinois 60004
Phone Number: (847) 632–5390
for repair and/or warranty information. You should not attempt to repair
this equipment yourself. This equipment contains no customer or
user–serviceable parts.
Changes or modifications not expressly approved by Motorola could
void your authority to operate this equipment.
FCC Label and Location
LABEL SHOWN ISFOR
DISPLAY PURPOSES
ONLY.
LABEL PLACED HERE
Model No. Motorola
Model No. ___________
MOTOROLA
SERIAL NO.
FCC ID IHET5EJ1
FCC ID: IHET5EJ1
Complies with Part 68, FCC Rules
FCC Reg. No.
US: IHEDENANSC4801XDO
xxvi 1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU MAY 2004
PRELIMINARY
Page 29
General Safety
Remember! . . . Safety
depends on you!!
Ground the instrument
The following general safety precautions must be observed during all
phases of operation, service, and repair of the equipment described in
this manual. Failure to comply with these precautions or with specific
warnings elsewhere in this manual violates safety standards of design,
manufacture, and intended use of the equipment. Motorola, Inc. assumes
no liability for the customer’s failure to comply with these requirements.
The safety precautions listed below represent warnings of certain dangers
of which we are aware. You, as the user of this product, should follow
these warnings and all other safety precautions necessary for the safe
operation of the equipment in your operating environment.
To minimize shock hazard, the equipment chassis and enclosure must be
connected to an electrical ground. If the equipment is supplied with a
three-conductor ac power cable, the power cable must be either plugged
into an approved three-contact electrical outlet or used with a
three-contact to two-contact adapter. The three-contact to two-contact
adapter must have the grounding wire (green) firmly connected to an
electrical ground (safety ground) at the power outlet. The power jack and
mating plug of the power cable must meet International Electrotechnical
Commission (IEC) safety standards.
Do not operate in an explosive
atmosphere
Keep away from live circuits
NOTE
Refer to Grounding Guideline for Cellular Radio
Installations – 68P81150E62.
Do not operate the equipment in the presence of flammable gases or
fumes. Operation of any electrical equipment in such an environment
constitutes a definite safety hazard.
Operating personnel must:
S not remove equipment covers. Only Factory Authorized Service
Personnel or other qualified maintenance personnel may remove
equipment covers for internal subassembly, or component
replacement, or any internal adjustment.
S not replace components with power cable connected. Under certain
conditions, dangerous voltages may exist even with the power cable
removed.
S always disconnect power and discharge circuits before touching them.
MAY 2004 1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU xxvii
PRELIMINARY
Page 30
General Safety – continued
Do not service or adjust alone
Do not substitute parts or
modify equipment
Dangerous procedure
warnings
Do not attempt internal service or adjustment, unless another person,
capable of rendering first aid and resuscitation, is present.
Because of the danger of introducing additional hazards, do not install
substitute parts or perform any unauthorized modification of equipment.
Contact Motorola Warranty and Repair for service and repair to ensure
that safety features are maintained.
Warnings, such as the example below, precede potentially dangerous
procedures throughout this manual. Instructions contained in the
warnings must be followed. You should also employ all other safety
precautions that you deem necessary for the operation of the equipment
in your operating environment.
WARNING
Dangerous voltages, capable of causing death, are present in this
equipment. Use extreme caution when handling, testing, and
adjusting.
xxviii 1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU MAY 2004
PRELIMINARY
Page 31

Revision History
Manual Number
Manual Title
Version Information
68P09260A11–7
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
Software Release 2.16.4.X
The following table lists the manual version, date of version, and
remarks on the version.
Version
Level
–1 Feb 4, 2004 DRAFT – For General engineering review
–2 Feb 23, 2004 PRELIMINARY – Incorporated Engineering review comments.
–3 Mar 16, 2004 First Order Application – Incorporated comments from engineering and
–4 Apr 10, 2004 FOA updated. Corrected text and illustrations due to SRs
–5 Apr 29, 2004 FOA updated, corrected grounding information and other minor text
–6 May 7, 2004 FOA for indoor circuit configuration
–7 May 27, 2004 Preliminary for Packet configuration
Date of Issue Remarks
test groups.
errors, added in AC/DC power cabling information for outdoor
enclosures.
MAY 2004 1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU xxix
PRELIMINARY
Page 32

Revision History – continued
Notes
xxx 1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU MAY 2004
PRELIMINARY
Page 33

Chapter 1: Introduction
Table of Contents
Introduction 1-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Scope of this Document 1-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Manual Order 1-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Site Cleanliness 1-3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Site Manager 1-3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
System Diagrams 1-3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Configurations 1-3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Required Documents 1-5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 1-5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Abbreviations and acronyms 1-5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1
800 MHz CDMA Frequencies and Channels 1-8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
800 MHz Center Frequencies 1-8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
China 800 MHz Frequencies 1-9 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation Tools and Materials 1-11 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Introduction 1-11 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Tools and Materials for Installation 1-11 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
ATP Tools and Materials 1-14 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Policy 1-14 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Test equipment calibration 1-14 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Test cable calibration 1-14 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Equipment Warm–up 1-14 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Test Equipment List 1-15 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Optional Equipment 1-19 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
BTS Equipment Identification 1-20 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Overview 1-20 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Shelf Device ID Numbers for Stand–Alone 1-24 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
HSO and MSO 1-26 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Modem 1-26 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
BTS Rear Panel 1-26 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Outdoor Enclosure Equipment Identification 1-30 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Outdoor Enclosure Equipment Identification 1-30 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Thermal Management Enclosure 1-30 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Power Distribution Enclosure 1-31 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Combined Compact Linear Power Amplifier 1-32 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation and ATP Order 1-33 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
MAY 2004 1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
Page 34

1
Table of Contents – continued
Indoor Installation Order 1-33 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Outdoor Installation Order 1-33 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
ATP Order 1-33 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU MAY 2004
PRELIMINARY
Page 35

Introduction
Scope of this Document
Manual Order
1
This document provides information pertaining to the hardware
installation, cabling installation, ATP and Field Replaceable Unit (FRU)
procedures of the Motorola SCt480 CDMA Base Transceiver
Subsystem (BTS), 800 MHz, –48 and +27 VDC versions. Information
on Circuit and Packet Backhaul, Expansion, and Logical BTS are also
included
The FRU procedures cover all components that are considered
replaceable.
An individual SCt480 BTS will be referred to as the “BTS” for the
remainder of this document.
For detailed installation information of non-Motorola equipment, refer to
the vendor manuals provided with such equipment.
The installation order is the order of the manual starting at Chapter 1 and
continuing through Chapter 5. After hardware installation has been
completed, run the ATP for the system by following the procedures
defined in Chapter 6 of this manual.
Chapter 1
“Introduction” — This is a brief outline of the manual. Also provided is
a list of additional documents and tools necessary to complete the
procedures.
Chapter 2
“Site Preparation” — This chapter contains the necessary information to
verify the condition of the site.
Chapter 3
“BTS Cables” — This chapter contains the general information on the
cables required for the Compact BTS.
Chapter 4
“Installation of Equipment, Cables, and GPS” — This chapter contains
procedures for installing the equipment, external AC, DC, data, ground
antenna, and GPS cabling.
Chapter 5
“Pre–Power–Up, Initial Power, and Removal of Power” — This chapter
contains procedures for performing electrical power checks.
MAY 2004
Chapter 6
“Optimization and Calibration Procedures” – This chapter contains
general information and procedures for optimizing the BTS.
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
1-1
Page 36

1
Introduction – continued
Chapter 7
“Acceptance Test Procedures” – This chapter contains general
information and procedures for testing the BTS.
Chapter 8
“Leaving the Site” – This chapter contains general information and
procedures for preparing to leave and departing the site.
Chapter 9
“Field Replaceable Units” – This chapter contains general information
and procedures for removing and installing boards, cards and modules of
the BTS.
Chapter 10
“Reference Procedures Performed at OMC–R ” – This chapter contains
general information and procedures to be followed by the OMC–R
operator.
Appendix A
“MCC–Data Only ” – This appendix contains general information and
test procedures for the DO card.
Appendix B
“Test Equipment Preparation ” – This appendix contains general
information and procedures for setting up the test equipment.
Appendix C
“Download ROM Code ” – This appendix contains general information
and procedures for the loading ROM code into the BTS cards.
Appendix D
“MMI Cable ” – This appendix contains general information and
procedures for making an MMI cable.
Appendix E
“Expansion BTS Configuration” – This appendix contains general
information and interconnect diagrams for expansion configuration.
Appendix F
1-2
“Logical BTS LAN Configuration for Compact BTS (Indoor) ” – This
appendix contains general information and interconnect diagrams for
logical BTS.
Appendix G
“Integrated BTS Router Preliminary Operations” – This appendix
contains general information and procedures IBR and span line
verification.
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
MAY 2004
Page 37

Introduction – continued
Site Cleanliness
1
Appendix H
“Integrated BTS Router Installation ” – This appendix contains general
information and procedures IBR and span line installation.
Appendix I
“Packet Backhaul BTS ” – This appendix contains general information
and procedures for packet backhaul operation with LMF Help.
While performing the procedures provided in this document, ensure
that:
S for an internal installation, the site is kept clean and free of tracked-in
dirt
S all packing material has been removed from the equipment.
S all tools not currently in use are picked-up as the installation
progresses.
Site Manager
System Diagrams
Configurations
S all trash is removed from the site at the end of each day and after the
installation is complete.
S equipment is covered with a tarpaulin whenever possible.
S use a shop-vac whenever you perform an internal installation
procedure that generates dust, such as drilling or cutting.
The site manager is the person in charge of and responsible for the full
site. The installer will be verifying a variety of conditions with the site
manager.
Figure 1-1 shows the BTS mounted on a rack. The configuration is for
indoor operation.
The BTS supports the omni configuration.
The power configuration for the BTS is:
MAY 2004
S DC power only
The synchronization configurations for the BTS are:
S Remote GPS Receiver – synchronous operation
S RF GPS
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
1-3
Page 38

1
Introduction – continued
Figure 1-1: Mounted BTS and Rack
NOTE:
SIngle BTS setup shown.
Compact PA and RGPS Head
are not shown
Rack
BTS
Location for
Second BTS
Mounting Plate
Mounting
Bracket
ti–cdma–wp–00303–v01–ildoc–ah
1-4
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
MAY 2004
Page 39

Required Documents
Installation
1
The following documents are required to perform the installation, ATP
and FRU procedures of the cell site equipment:
S SCt480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP and FRU –
68P09260A11 (This manual)
S Standards and Guidelines for Communication Sites
– Hard copy (Motorola Part Number 6881089E50–A)
– CD–ROM (Motorola Part Number 9882904Y01)
S Grounding Guidelines for Cellular Radio Installations
(Motorola part number 68P81150E62) or
– Appendix C of Standards and Guidelines for Communication Sites
S Site Document (generated by Motorola Systems Engineering), which
includes:
– site specific documentation
– channel allocation
– contact list (customer)
– ancillary/expendable equipment list
– site wiring lists
– contact list (Motorola support)
– job box inventory
S Demarcation Document (Scope of Work agreement)
S Installation manuals for non-Motorola equipment (for reference
purposes).
Abbreviations and acronyms
MAY 2004
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
Table 1–1 contains a list of the abbreviations and acronyms used in this
manual.
Table 1-1: Abbreviations and Acronyms
Acronym Description
ACT Active
ALM Alarm
ATP Acceptance Test Procedure
AUX Auxiliary
BLO Bay Level Offset
BSS Base Station System
BTS Base Transceiver Station or Subsystem
BBX Broad Band Transceiver
table continued on next page
1-5
PRELIMINARY
Page 40

1
Required Documents – continued
Table 1-1: Abbreviations and Acronyms
Acronym Description
CAL Calibration
CBIO Compact BTS Input/Output
CBSC Centralized Base Station Controller
cCLPA Compact Combined Linear Power Amplifier
CCP2 CDMA Channel Processor 2
CDF Configuration Data File
CDMA Code Division Multiple Access
cMPC Compact Multi–coupler Preselector Card
CRMS Cellular Remote Monitoring System
CSA Clock Synchronization Alarms
DLM Download Manager
EMPC Expansion Compact Mulit–Preselector Card
ERP Effective Rated Power
ESD Electrostatic Discharge
EXP Expansion
FREQ Frequency
FRU Field Replaceable Unit
FTP File Transfer Protocol
GLI 3 Group Line Interface III
GPS Global Positioning System or Satellite
HMS Heat Management System
HSO High Stability Oscillator
HX Heat Exchanger
INS In–Service
INS_ACT In–Service Active
INS_SBY In–Service Standby
1-6
LAN Local Area Network
LIF Load Information File
LMF Local Maintenance Facility
table continued on next page
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
MAY 2004
Page 41

Required Documents – continued
LMT Local Maintenance Tool
MCC Multi–Channel CDMA
MCC–DO Multi–Channel CDMA Data Only
MMI Man–Machine Interface
MON Monitor
MSO Medium Stability Oscillator
NECB Network Element Configuration Base
NECF Network Element Configuration File
NECJ Network Element Change Journal
OMC–R Operations and Maintenance Center – Radio
OOS Out–of–Service
1
Table 1-1: Abbreviations and Acronyms
Acronym Description
PDE Power Distribution Enclosure
PSM Power Supply Module
PWR Power
RAM Random Access Memory
ROM Read Only Memory
RF GPS Radio Frequency Global Positioning System
RGPS Remote Global Positioning System
RX Receive
SDCX Synchronization Daisy–Chaining and
eXpansion
STA Status
SYNC Synchronization
TME Thermal Management Enclosure
TX Transmit
MAY 2004
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
1-7
Page 42

1
800 MHz CDMA Frequencies and Channels
800 MHz Center Frequencies
Table 1-2 lists the selected 800 MHz CDMA candidate operating
channels and the corresponding transmit and receive frequencies for
Regular Band Class 0 (North America). Figure 1-2 shows the CDMA
Frequency Spectrum for Table 1-2. Center frequencies (in MHz) for
channels not shown in the table may be calculated as follows:
For Channels 1 – 799
S For TX
TX = 870 + (0.03 * Channel #)
Example: Channel 262
TX = 870 +0.03 * 262
TX = 877.86 MHz
S For RX
RX = 825 + (0.03 * Channel#)
Example: Channel 262
RX = 825 + (0.03 * 262)
RX = 832.860 MHz
For Channels 991 – 1023
S For TX
TX = 870 + [0.03 *(Channel# – 1023)]
Example: Channel 1015
TX = 870 + [0.03 * (1015 – 1023)]
TX = 870.240 MHz
S For RX
RX = 825 + [0.03 * (Channel# – 1023)]
Example: Channel 262
RX = 825 + [0.03 * (262–1023)]
RX = 847.830 MHz
NOTE
Conditionally Valid – Valid channels in TIA/EIA–97–D
that are <885 kHz from the operator’s band edge. If the
operator’s system must coexist with another system that
uses an adjacent frequency band, it is recommended that
the operator coordinate with the other operator to
determine if the usage of the Reduced–Sideband Spectral
Mask is required for Conditionally Valid channels. The
Reduced–Sideband Spectral Mask is in addition to other
spectral masks that apply.
1-8
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
MAY 2004
Page 43

800 MHz CDMA Frequencies and Channels – continued
CAUTION
Certain widely–spaced combinations of A–Band transmit
frequencies, when combined to drive one antenna, can
produce 3rd order intermodulation products that are within
the receive band. During system planning, the proper
selection of combined frequencies or the use of multiple
transmit antennas will prevent this situation. Additional
receive filtering at a particular cell site can also help. China
A Band is used in the China SC480–800 BTS in
conjunction with a GSM Elimination Filter.
Table 1-2: Regular Band Class 0 TX and RX Frequency vs Channel
1
System
Designator
A (1 MHz) Conditional Valid 1013 – 1019 824.700 – 824.880 869.700 – 869.880
A (10 MHz) Valid 1 – 303 825.030 – 834.090 870.030 – 879.090
B (10 MHz) Conditional Valid 356 – 362 836.680 – 835.860 880.680 – 880.860
A (1.5 MHz) Conditional Valid 689 – 694 845.670 – 845.820 890.670 – 890.820
B (2.5 MHz) Conditional Valid 739 – 746 847.170 – 847.380 892.170 – 892.380
China 800 MHz Frequencies
CDMA Channel
Validity
Valid 1020 – 1023 824.910 – 825.000 869.910 – 870.000
Conditional Valid 304 – 311 834.120 – 834.330 879.120 – 879.330
Valid 363 – 637 835.890 – 844.110 880.890 – 889.110
Conditional Valid 638 – 644 844.140 – 844.320 889.140 – 889.320
Valid 747 – 770 847.410 – 848.100 892.410 – 893.100
Conditional Valid 771 – 777 848.130 – 848.310 893.130 – 893.310
CDMA Channel
Number
Transmit Center
Frequency (MHz)
Receive Center
Frequency (MHz)
System
Designator
China
A–Band
MAY 2004
The receive and transmit frequency ranges (A–Band) for China are as
follows:
S RX – 825.5000 MHz – 834.1000 MHz
S TX – 870.5000 MHz – 879.1000 MHz
Table 1-3 lists the China A–Band frequencies and channels.
Table 1-3: China A–Band TX and RX Frequency vs Channel
CDMA Channel
Validity
Valid 37 – 283 826.110 – 833.490 871.110 – 878.490
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
CDMA Channel
Number
Transmit Center
Frequency (MHz)
Receive Center
Frequency (MHz)
PRELIMINARY
1-9
Page 44

1
800 MHz CDMA Frequencies and Channels – continued
Figure 1-2: CDMA Frequency Spectrum
(MHz)
TX
824.700
824.880
824.910
825.000
825.030 870.030
RX
869.700
869.880
869.910
870.000
CHANNELS
1013
1019
1020
1023
1
870.110
833.490
F R E Q U E N C Y I N C R E A S E
834.090
834.120 879.120
834.330
835.680
835.860
835.890 880.890 363
844.110
844.140
844.320
845.820 890.820
878.490
879.090
897.330
880.680
880.860 362
889.110
889.140
889.320
890.670845.670
37825.110
283
303
304
311
356
637
638
644
689
694
CHINA A–BAND
1-10
847.170
847.380
847.410
848.100 893.100
848.130 893.130
848.330 893.330
892.170
892.380
892.410
739
746
747
770
771
777
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
MAY 2004
Page 45

Installation Tools and Materials
Introduction
Many of the tools and materials depend on the style of the wall, pole, or
rack on which the mounting bracket is being installed. The tools and
materials required to install the BTS hardware are specified for each
mounting style. Due to the variability of mounting styles, additional
tools and materials may be required to meet specific site needs.
Tools and Materials for
Installation
The tools and materials listed in Table 1-4 are recommended to properly
and safely perform the installation procedures.
Table 1-4: Recommended Tools and Materials for Rack Mounting
Hand Tools Materials Purpose
1
Adjustable Torque ratchet and socket
set
T10, T20, T30, Security T20,
Security T30 Torx, cross–recess,
flathead bits, 1/4–in. hex
Torque driver wrench, 1/4–in. hex
female drive, 0–10 N–M
Power Drill, 1/4–in or 3/8–in drive Appropriate wood and
Hammer Drill Appropriate masonry drill
Adjustable Wrench Customer Supplied General purpose use
Mechanical lifting device Customer Supplied For lifting equipment
Bucklestrap Cutting Tool (Motorola P/N
Tape Measure Customer Supplied General purpose measurement
Heavy Gloves Customer Supplied Hand Safety
Customer Supplied General torquing of screws and nuts.
Customer Supplied General purpose use
(Utica P/N TCI–150 R/A
3/8–in. or equivalent)
Customer Supplied
masonry drill bits (Standard
set may be adequate)
Customer Supplied
bits (Customer Supplied)
6604809N01)
General torquing of screws and nuts.
Drill holes in wood and light concrete
Rack installation to floor and RGPS
to wall
Pole Mounting
Safety Glasses Customer Supplied Eye Safety
Tin Snips Customer Supplied General purpose metal cutting
Hacksaw Various blades
(Customer Supplied)
Metal File Fine cut
(Customer Supplied)
Flashlight Customer Supplied General purpose use
Utility Knife Customer Supplied General purpose cutting
Small Flathead Screwdriver Customer Supplied General purpose use
MAY 2004
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
Cutting large coax cable
Coax cable preparation
PRELIMINARY
1-11
Page 46

1
Installation Tools and Materials – continued
Table 1-4: Recommended Tools and Materials for Rack Mounting
Hand Tools PurposeMaterials
Small Phillips Screwdriver Customer Supplied General purpose use
Hex Crimping Tool Various die sets
(Customer Supplied)
RJ45 Crimping Tool (Tyco P/N 2–231652–1,
853400–0, 853400–1,
853400–7 or equivalent)
Customer Supplied
5/16 Breakaway Torque Wrench,
9–in. lb
13/16 Breakaway Torque Wrench
38–in. lb
Volt/Ohmmeter or Digital Multimeter Customer Supplied Voltage and continuity testing
Label Maker Customer Supplied General purpose marking
cCLPA Installation Handles Motorola P/N:
Wire Strippers Customer Supplied Accommodates 6 AWG to 26 AWG
Customer Supplied SMA Connectors
Customer Supplied N Connectors
5587763T01
RTV Sealant
(Customer Supplied)
electrical tape
(Customer Supplied)
Fine Grit Sandpaper
(Customer Supplied)
Cable Tie–wraps various
sizes.
(Customer Supplied)
Create RF cabling and power/ground
cabling
Create RJ11/RJ45 cabling
For installing the cCLPA
Weatherproofing openings for cable
pass through
General purpose use
Finishing coax cable surfaces
General purpose dressing of cables
1-12
15–pin D–sub plug and
termination equipment
(Customer Supplied)
BNC male style connectors
(Customer Supplied)
N–male and N–female style
connectors for 1/2–in Heliax
(Customer Supplied)
7/16 DIN connector for
1/2–in and 7/8–in Heliax
(Customer Supplied)
RF Cabling, 1/2–in and
7/8–in Heliax
Braided Coax
(Customer Supplied)
10AWG two–wire stranded
(Customer Supplied)
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
For RGPS cabling
Coaxial span cable, interframe
cabling
Cabling between BTS, PA, and
Antenna
Antenna cabling
Cabling between BTS, PA, and
Antenna
Coaxial span cable, interframe
cabling
Power cabling
PRELIMINARY
MAY 2004
Page 47
Installation Tools and Materials – continued
Table 1-4: Recommended Tools and Materials for Rack Mounting
Hand Tools PurposeMaterials
1
6 AWG stranded
(Customer Supplied)
Assorted ground lugs
(6AWG, 10 AWG) ring style
(Customer Supplied)
Assortment of flat washers,
lock washers
(Customer Supplied)
Assortment of nuts M3 – M6
(Customer Supplied)
Rack screws (depends on
rack style used)
(Customer Supplied)
T1/E1 span cabling (4 or 8
wire TP style)
(Customer Supplied)
ILSCO p/n CRB–6L2–14–58
two–hole ground lugs or
equiv. Hole spacing 5/8”,
hole sizes for 1/4” bolt, tang
width 13/32”.
(Customer Supplied)
Chalk or marker to mark
location on rack
(Customer Supplied)
Ground cabling
Site ground cabling, Core power
input
Mounting equipment to racks and for
general purpose
Mounting equipment to racks and for
general purpose
Rack mounting
Span and cCLPA signal cabling
Ground Lugs
MAY 2004
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
1-13
Page 48

1
ATP Tools and Materials
Policy
To ensure consistent, reliable, and repeatable test results, test equipment
meeting the following technical criteria should be used to perform the
ATP on the BTS equipment.
NOTE
During manual testing, you can substitute supported test
equipment with other test equipment models not supported
by the LMF. However, they must meet the same technical
specifications.
It is the responsibility of the customer to account for any measurement
variances and /or additional losses / inaccuracies that can be introduced
as a result of these substitutions. Before beginning the ATP, make sure
that the test equipment needed is on hand and operating properly.
Test equipment calibration
Test cable calibration
Equipment Warm–up
Optimal system performance and capacity depend on regular test
equipment service, calibration, and characterization. Follow the original
equipment manufacture (OEM) recommended maintenance and
calibration schedules closely.
Equipment test cables are very important in the ATP. It is recommended
that the cable calibration be run at every BTS with the test cables
attached. This method compensates for test cable insertion loss within
the test equipment itself. No other allowance for test cable insertion loss
needs to be made during the performance of tests.
Another method is to account for the loss by entering it into the Local
Maintenance Facility (LMF) during the optimization procedure. This
method requires accurate test cable characterization in a lab
environment. The cable should be tagged with the characterization
information prior to field optimization.
After arriving at the a site, the test equipment should be plugged in and
turned on to allow warm up and stabilization to occur for as long as
possible. The following pieces of test equipment must be warmed–up for
a minimum of 60 minutes prior to the ATP.
1-14
S Communications Test Set
S Power Meter
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
MAY 2004
Page 49

ATP Tools and Materials – continued
Test Equipment List
The following pieces of test equipment are required during the ATP.
Common assorted tools like screwdrivers and keys are not listed, but are
still required. Read the owners manual on all of the following major
pieces of test equipment to understand their individual operation prior to
use in optimization.
CDMA LMF Hardware Requirements
A CDMA LMF computer platform that meets the following
requirements (or better) is recommended:
S Notebook computer
S PCMCIA to Serial I/O Adapter
1
NOTE
Always refer to specific OEM test equipment
documentation for detailed operating instructions.
S 266 MHz (32 bit CPU) Pentium processor
S 4 GigaByte internal hard disk drive
S SVGA 12.1 inch active matrix color display with 1024 x 768
(recommended) or 800 x 600 pixel resolution and capability to display
more than 256 colors
S 128 MB RAM minimum (98SE) or 256 (Windows 2000)
S 20X CD ROM drive
S 3–1/2 inch floppy drive
S Serial port (COM 1)
S Serial Port (COM 2)
S Parallel port (LPT 1)
S PCMCIA Ethernet interface card (for example, 3COM Etherlink III)
with a 10Base–T–to–coax adapter
S Windows 98 SE or higher operating system
NOTE
If 800 x 600 pixel resolution is used, the CDMA LMF
window must be maximized after it is displayed.
MAY 2004
Ethernet LAN Transceiver (part of all LMF kits)
S PCMCIA Ethernet Adapter + Ethernet UTP Adapter 3COM Model –
Etherlink III 3C589B
used with
S Transition Engineering Model E–CX–TBT–03 10BaseT/10Base 2
Converter
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
1-15
Page 50

1
ATP Tools and Materials – continued
CDMA LMF Software
The Local maintenance Facility (LMF) application program is a
graphical user interface (GUI)–based software tool. This product is
specifically designed to provide cellular communication field personnel
with the capability to support the following CDMA Base Transceiver
Station (BTS) operations:
S Installation
S Maintenance
S Calibration
S Optimization
RS232 to GPIB Interface
One National Instruments GPIB–232–CT with Motorola
CGDSEDN04X RS232 serial cable or equivalent; used to interface the
LMF to the test equipment.
A Standard RS–232 cable can be used with the following modifications:
S Pin 8 (CTS) does not have to be jumpered/shorted to the others as
it is a driver output. The DTR is already a driver output signal.
The other pins are to receivers. Short pins 7, 1, 4, 6 on each cable end:
Figure 1-3: RS232–IEEE488 Converter Serial Cable Configuration
9–pin D (female) 9–pin D (female)
GND 5 5 GND
RX 3
RTS 7 7 RTS
CTS 8
RSD/DCD 1 1 RSD/DCD
DTR 4 4 DTR
DSR 6 6 DSR
ON BOTH CONNECTORS SHORT
PINS 7 AND 8;
SHORT PINS 1, 4 AND 6
Communications system analyzer CDMA/analog
2 TX
3 RXTX 2
8 CTS
1-16
IS–95A/B–only test capability – The following communications system
analyzers which provide only IS–95A/B test capability are supported by
the LMF:
S Motorola CyberTest
S Hewlett Packard Model HP 8921A/600 Analyzer including 83203B
CDMA Interface, manual control system card, and, for 1900 MHz
BTSs, 83236A/B PCS Interface
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
MAY 2004
Page 51

ATP Tools and Materials – continued
S Advantest R3465 Analyzer with R3561L signal generator
CDMA2000 1X and IS–95A/B test capability – The following
communications system analyzers which provide both CDMA2000 1X
and IS–95A/B test capability are supported by the LMF:
S Agilent 8935 series E6380A communications test set (formerly HP
8935) with option 200 or R2K for CDMA2000 1X support
S Agilent E4406A
S Advantest R3267 spectrum analyzer with Advantest R3562 Generator
for IS–95 and cdma200 1X testing
A combination of test equipment supported by the LMF may also be
used during optimization and testing of the RF communications portion
of BTS equipment when the communications system analyzer does not
perform all of the following functions:
S Frequency counter
S Deviation meter
1
S RF power meter (average and code domain)
S RF signal generator (capable of DSAT/CDMA modulation)
S Audio signal generator
S AC voltmeter (with 600–ohm balanced audio input and high
impedance input mode)
S Noise measurement meter
S C–Message filter
S Spectrum analyzer
S CDMA code domain analyzer
NOTE
Advantest R3267 with Advantest R3562 Generator are
capable of performing IS–95B and cdma2000 1X tests, if
the required options are installed.
GPIB cables
MAY 2004
Two Hewlett Packard 10833A or equivalent; 1 or 2 meters long used to
interconnect test equipment and LMF terminal.
Power meter
Gigatronics Model 8541C with 80601A power sensor capable of
measuring from –70 dBm to +23 dBm; supported by the LMF to
perform BTS Total Power measurement.
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
1-17
Page 52

1
ATP Tools and Materials – continued
Model SLN2006A MMI Interface Kit
S Motorola Model TRN9666A null modem board. Connectors on
opposite sides of the board must be used as this performs a null
modem transformation between cables. This board can be used for
10–pin to 8–pin, 25–pin to 25–pin and 10–pin to 10–pin conversions.
S Motorola 30–09786R01 MMI cable or equivalent; used to interface
the LMF serial port connection to GLI, CSA and cCLPA debug serial
ports.
CDMA2000 1X signal generators
S Agilent E4432B signal generator (required for use with Agilent
E4406A when performing Frame Erasure Rate acceptance testing)
or
S Advantest R3562 signal generator (required for use with Advantest
R3267 when performing Frame Erasure Rate acceptance testing)
Power meter
S Hewlett Packard Model HP437B with HP8481A power sensor capable
of measuring from –30 dBm to 20 dBm
or
S Gigatronics 8542B power meter
Timing Reference Cables
S Two BNC–male to BNC–male RG316 cables; 3.04 m. (10 ft.) long,
Two BNC–male to BNC–male RG316 cables; 0.61 m. (2 ft.) long
with Two BNC “T” connectors, used to interconnect the
Communications Analyzer to CSA front panel timing references in the
BTS.
RF Attenuators
S 30 dB Fixed in–line attenuators, 150 W (Narda 769–30) used in
conjunction with calibration of test cables.
S 50 dB attenuator for connection to 30 dB directional coupler
Misc. Components (RF Adaptors, Loads, Cables, etc.)
S As required to interface test cables and BTS equipment and for
various test set ups. Should include at least (2) 50–Ohm loads (type
N) for calibration, (1) RF short, (2) RF cables, (1) GPIB Box, and (1)
ethernet cable.
RF Load
S 150W non–radiating RF load; used (as required) to provide dummy
RF loading during BTS transmit tests.
1-18
High–Impedance Conductive Wrist Strap
S Motorola Model 42–80385A59; used to prevent damage from
Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) when handling or working with
modules.
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
MAY 2004
Page 53

ATP Tools and Materials – continued
Directional Coupler
S 30 dB attenuation
Optional Equipment
Digital Multimeter
S Fluke Model 8062A with Y8134 test lead kit or equivalent; used for
precision dc and ac measurements, requiring 4–
Frequency Counter
S Stanford Research Systems SR620 or equivalent. If direct
measurement of the 3 MHz or 19.6608 MHz references are required.
NOTE
Not all optional equipment specified here will be supported
by the LMF in automated tests or when executing various
measure type commands. It is meant to serve as a list of
additional equipment that might be required during
maintenance and troubleshooting operations.
1
/2 digits.
1
Spectrum Analyzer
S Spectrum Analyzer (HP8594E with CDMA personality card) or
equivalent; required for manual tests other than standard Receive
band spectral purity and TX cCLPA IM reduction verification tests
performed by the LMF.
LAN Tester
S Model NETcat 800 LAN troubleshooter (or equivalent); Used to
supplement LAN tests using the ohm meter.
Span Line (T1 or E1) Verification Equipment
S As required for local application
RF Test Cable (if not provided with test equipment)
S Motorola Model TKN8231A; used to connect test equipment to the
BTS transmitter output during optimization procedures.
Oscilloscope
S Tektronics Model 2445 or equivalent; used for waveform viewing,
timing, and measurements procedures.
CDMA Subscriber Mobile or Portable Radiotelephone
S CDMA compatible with power supply and antenna; used to provide
test transmission and reception during BTS maintenance. Two radios
will be required for system and drive around testing after optimization
and BTS ATP is completed.
MAY 2004
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
1-19
Page 54

1
BTS Equipment Identification
Overview
Stand–Alone BTS
The 1X SC480 BTS consists of one shelf of cards and modules within a
metal cabinet. Depending on configuration the BTS may be powered by:
S Converted AC to –48 VDC
S Converted AC to +27 VDC
S Battery (–48 or +27 VDC)
S +27 VDC
S –48 VDC
The BTS can support up to two carriers in a non–redundant omni
configuration.
Figure 1-4 shows the two different front vies and Figure 1-5 shows the
rear view of the BTS.
Exapnsion BTS
When more than two carriers are desired, up to 3 additional BTSes may
be added. Up to 8 carriers can be supported in this configuration. The
Starter BTS has the Compact Multi–Preselector Card (cMPC) and the
expansion BTSes contain Expansion Compact Multi–Preselector Cards
(EMPC) in place of the cMPC. In expansion the BTSes are identified as
individual BTSes, (i.e.; BTS–100, BTS–200, BTS–300, BTS–400).
LAN connections are not used. The BTSes will share TX and RX
antennas. Reference Appendix E for interconnect diagrams.
Logical BTS
The BTS software implements the logical BTS capability. Previously, all
BTS frames co–located at a single site had to be identified in the
network with separate and distinct BTS ID numbers. In the Logical BTS
feature, all BTSes located at a single BTS site are identified with unique
Frame ID numbers (Frame ID Numbers 1, 101, 201, 301) under a single
(site) BTS ID number. A logical BTS can consist of up to three BTSes
(up to 8 carriers). When the LMF is connected to the Starter of a logical
BTS, you can access all devices in all of the BTSes that make up the
logical BTS. A logical BTS requires a CDF/NECF file that includes
equipage information for all of the logical BTSes and their devices and a
CBSC file that includes channel data for all of the logical BTSes.
1-20
In this configuration LAN connections are used. The Starter BTS has the
Compact Multi–Preselector Card (cMPC) and the expansion BTSes
contain Expansion Compact Multi–Preselector Cards (EMPC) in place
of the cMPC. The BTSes will share TX and RX antennas. Reference
Appendix F for interconnect diagrams.
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
MAY 2004
Page 55

BTS Equipment Identification – continued
CCP2 Shelf Card/Module Device ID Numbers Logical
BTS
All cards/modules/boards in the BTSes at a single site, assigned to a
single BTS number, are also identified with unique Device ID numbers
dependent upon the Frame ID number in which they are located. Refer to
Table 1-5 for specific device ID numbers. See Figure 1-6 for shelf
layout.
Table 1-5: CCP2 Shelf Card/Module Device ID Numbers for Logical BTS
BTS # PSM CSA GLI3 MCC BBX cMPC/E
1 – 1 1 1 2 3 1 4 –
101 – 101 101 101 102 103 101 104 –
201 – 201 201 201 202 203 201 204 –
301 – 301 301 301 302 303 301 304 –
1
MPC
MAY 2004
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
1-21
Page 56

1
BTS Equipment Identification – continued
Figure 1-4: Front View of Compact BTS
Front Panel
Cover
Standard CCP2 Shelf
Front Panel cover
removed
CCP2 Shelf with
MCC–DO card
Front Panel cover
removed
1-22
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
MAY 2004
Page 57

BTS Equipment Identification – continued
Figure 1-5: Rear View of Compact BTS
RF GPS not shown and
SDCX Module is shown.
1
MAY 2004
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
1-23
Page 58

1
BTS Equipment Identification – continued
Shelf Device ID Numbers for
Stand–Alone
All cards/modules/boards in the BTS at a single site assigned to a single
BTS are also identified with unique Device ID numbers. Refer to
Table 1-6 for the Device ID Numbers. Reference Figure 1-6 or
Figure 9-2 for the layout of the shelf.
Table 1-6: Shelf Device ID Numbers
BTS # PS1 CSA GLI MCC BBX cMPC
1 1 1 1 1 2 3 1 4 –
Figure 1-6: CCP2 Shelf Layout
SYNC MONITOR
STA/ALM
FREQ. MONITOR
MMI
When used, the MCC–DO
is seated in MCC slots 1
and 2. MCC slot 3 can be
an MCC–1X or a filler
panel.
ti–cdma–wp–00310–v01–ildoc–ah
The following is a list of the cards/modules in CCP 2 Shelf and a brief
description.
1. Power Supply Module
2. CSA
1-24
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
MAY 2004
Page 59

BTS Equipment Identification – continued
3. GLI3
4. MCC–1X (or MCC–DO)
5. MCC–1X (or MCC–DO)
6. MCC–1X or Filler Panel
7. BBX–1X (Carrier 1)
8. BBX–1X (Carrier 2)
9. cMPC
Power Supply Module
Occupies the first slot. The same assembly used in the SC48XX series.
Provides power to the cards on the CCP2 shelf.
CSA Card
Occupies the second slot. The Clock Synchronization Alarm card,
combines the functions of the SC4812’s CSM and AMR cards into one.
The CSA timing circuit receives a 1pps signal from the GPS. The CSA
timing circuit generates the CDMA timing signal to the BBX and MCC
cards.
1
During normal operation the CSA is set up to select the GPS as the first
reference source. With an HSO or MSO as backup, the CSA is set up to
select the HSO or MSO 1 pps as the backup reference source should the
GPS signal fail. .
GLI3 Card
Occupies the third slot. The same card used in the SC48XX series.
Provides interfaces, inter–card communications, operation, and
maintenance functions for all the devices in the CCP2 shelf.
MCC–1X Cards and MCC–DO
Occupies the fourth through sixth slots (MCC slots 1, 2, & 3).
Depending on configuration they will be MCC–1X cards (16s, 32s, 48s,
or 64s). MCC–1X 64s require packet backhaul configuration. This
implements the traffic and control (sync, paging, access) channels of the
BTS.
If the BTS is configured for MCC–Data Only (DO), then MCC slots 1
and 2 will be used with slot 3 containing an MCC–1X card or a filler
panel.
BBX–1X Cards
Occupies the seventh and eighth slots (BBX slots 1 & 4). The same
BBX–1X cards used in the SC48XX series. Provides the RF to digital
signal functions for the reverse and forward links.
MAY 2004
cMPC
Occupies the ninth slot. Compact BTS Multicoupler Preselector Card.
Provides low–noise amplification for all RX path signals. DC voltages
are monitored on the RF devices and regulators and are used to generate
hard and soft alarms.
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
1-25
Page 60

1
BTS Equipment Identification – continued
HSO and MSO
The High Stability and Medium Stability Oscillator module provide a
backup reference source should the Global Positioning System (GPS)
fail. The HSO is capable of providing up to 24 hours and the MSO is
capable of providing up to 8 hours.
Only one of either the HSO or MSO is available in the Compact BTS.
The module is located in front, behind a cover, underneath the CCP2
Shelf. The unit slides into the top slot of the two that are present.
Modem
The slot underneath the HSO/MSO slot is reserved for a Modem
module, however it is not supported for the SC480.
BTS Rear Panel
LAN connectors, RF Connectors, circuit breaker, DC Power connection,
RF GPS, and SDCX are found at the rear of the BTS.
CBIO Board
Figure 1-7 shows the RF GPS, SDC, TME, PDE, cPA, Customer I/O
connectors, and Status indicators.
RF GPS
The optional Radio Frequency Global Positioning System (RF–GPS) is
contained in a module that plugs in to the CBIO board at the rear of the
BTS. It can be used in place of the RGPS. See Figure 1-7.
SDCX
The Synchronization Daisy–Chaining and eXpansion (SDCX) module is
only used when there are expansion BTSs at the site. It supports timing
distribution for up to three expansion frames, and also supports
synchronization daisy–chaining feature. See Figure 1-7.
LAN Connectors
LAN input and out put connectors for 10BaseT connection are found at
the upper right rear of the BTS. See Figure 1-7. There are LAN output
connectors on the front panel below the CCP2 Shelf. See Figure 1-4.
1-26
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
MAY 2004
Page 61

BTS Equipment Identification – continued
Figure 1-7: CBIO Board
TME Alarm
1
RF–GPS
Expansion
TX
Customer
Input/Output
Expansion RX
Main
Expansion RX
Diversity
PWR
RF–GPD IN
EXPANSION FRAME SYNC – OUT
DAISY–CHAIN POWER
SDCX POWER
SDCX KIT NO.
SDCX SERIAL NO.
LAN
PDE Alarm
CBIO LEDs
Network Span
1X–A, –B, & –C
Group 1 Span
DO–A, –B, & –C
SDCX
cCLPA
Data A & B
Directional
Coupler
Frame ID
Switch
MAY 2004
DAISY–CHAIN SYNC – OUT
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
See
Figure 1-8 or
Figure 1-9
ti–cdma–wp–00311–v01–ildoc–ah
1-27
Page 62
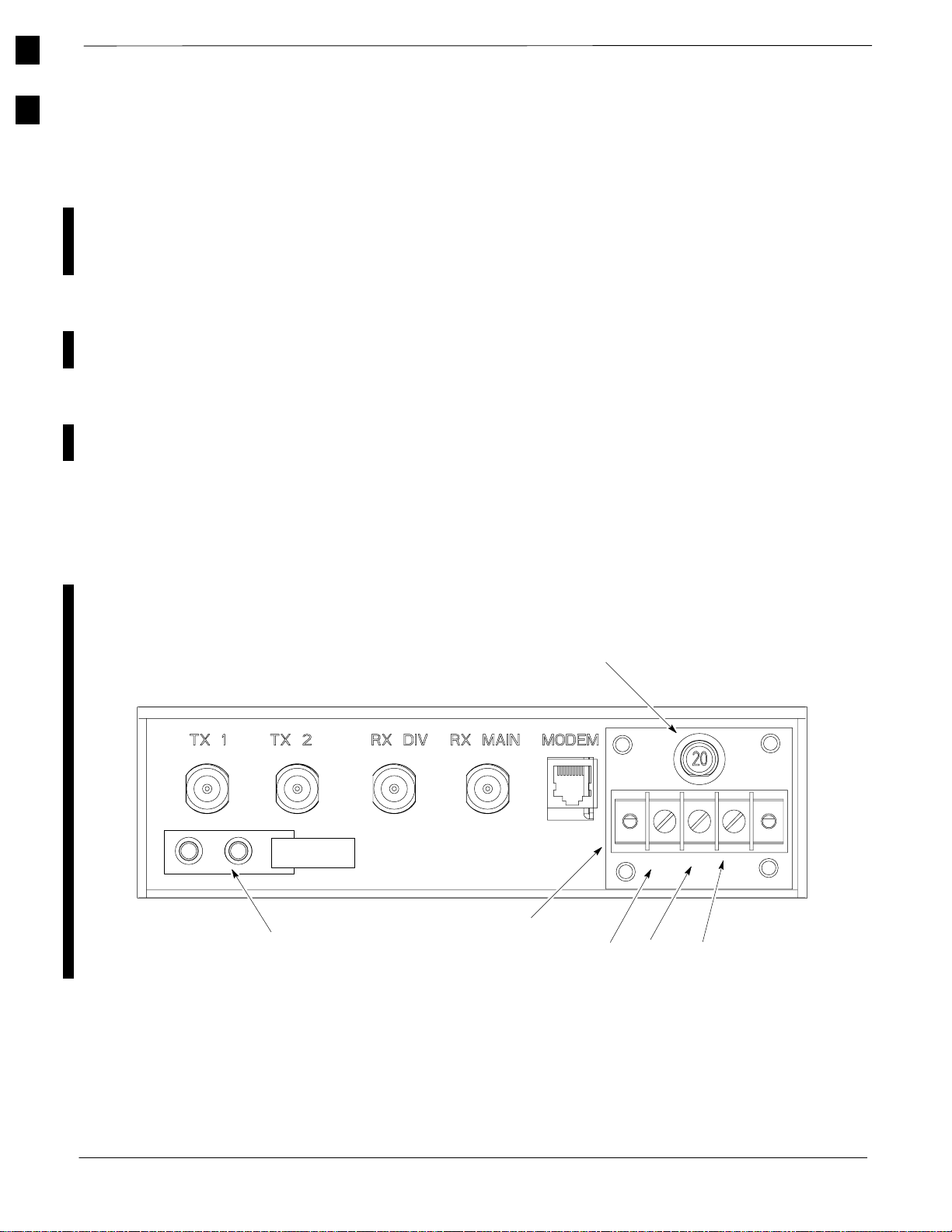
1
BTS Equipment Identification – continued
RF Connectors
Figure 1-8 shows the RF connectors at the rear of the Compact BTS.
Modem Connector
Figure 1-8 shows the Modem connector at the rear of the Compact BTS
(not supported in SC480).
Circuit Breaker
Figure 1-8 and Figure 1-9 show the location of the –48VDC 20A circuit
breaker and +27VDC 25A circuit breaker, respectively.
DC Power Connection
Figure 1-8 and Figure 1-9 shows the location of the DC Power Terminal
Strip.
Ground
Figure 1-8 shows the location of the two ground screw holes for the
Compact BTS.
Figure 1-8: –48 VDC RF Connectors, Circuit Breaker, DC Power Terminal Strip, and
Ground Studs
20A Circuit
Breaker
20A
–48V
DC Power
GROUND
(Screw Holes)
Terminal Strip
–48 V
+0 V
TME
+0V
TME
1-28
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
MAY 2004
Page 63

BTS Equipment Identification – continued
Figure 1-9: +27VDC RF Connectors, Circuit Breaker, DC Power Terminal Strip, and
Ground Studs
25A Circuit
Breaker
1
GROUND
(Screw Holes)
DC Power
Terminal Strip
+27 V
25A
RETURN
25
TME
TME
MAY 2004
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
1-29
Page 64

1
Outdoor Enclosure Equipment Identification
Outdoor Enclosure Equipment
Identification
Figure 1-10 shows the TME and HMS outdoor enclosures.
Figure 1-10: Thermal Managment Enclosure and Heat Manaagement System
Wall Mounting
Bracket
Heat Management
Thermal
Management
Enclosure
System
Compact BT S
Thermal Management
Enclosure
1-30
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
The following are brief descriptions of the components of the TME.
TME
The Thermal Management Enclosure surrounds the Compact BTS,
affording it protection against the weather. See Figure 1-10.
HMS
The Heat Management System attaches to the TME and provides
temperature regulation of the Compact BTS. See Figure 1-10.
PDA
The Power Distribution Assembly is the connection point for the –48
and +27 VDC. Also, it contains circuit breakers for the TME and 1U
(optional module). Connections to the HMS and BTS are also provided
at the rear of the unit.. See Figure 1-11.
MAY 2004
PRELIMINARY
Page 65

BTS Equipment Identification – continued
Figure 1-11: Power Distribution Assembly
(–48V version shown)
1
ti–cdma–wp–00350–v01–ildoc–ah
Power Distribution Enclosure
The following are brief descriptions of the components of the PDE.
PDE
The Power Distribution Enclosure converts AC voltage to DC voltage
for use by the TME and Compact Combined Linear Power Amplifier
(cCLPA). Battery backup is routed through the PDE. See Figure 1-12.
S AC Load Center (ACLC) – Where the AC voltage is connected to the
PDE. Also contains AC surge protection.
S Power Supply Module (PSM) – Converts the 220–240 VAC to –48 V
DC for use by the TME, BTS, and cCLPA.
S Power Management Alarm Card (PMAC) – Monitors alarms for PDE
and battery backup.
S Circuit Breakers (CB) – Provides DC surge and DC short circuit
protection.
S Punch Block (PB) – Distribution point for incoming and outgoing
data signal lines.
S Multiple ground connections at the reaar of the PDE
MAY 2004
S Antenna surge arrestors slots
HX
The Heat Exchanger attaches to the PDE and provides temperature
regulation.
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
1-31
Page 66

1
Outdoor Enclosure Equipment Identification – continued
Figure 1-12: Power Distribution Enclosure and Heat Exchanger
Power
Management
Enclosure
Antenna Surge
Arrestor Location
Ground
Location
Heat Exchanger
Combined Compact Linear
Power Amplifier
Figure 1-13: Compact Combined Linear Power Amplifier
1-32
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
ti–cdma–wp–00300–v01–ildoc–ah
MAY 2004
Page 67

Installation and ATP Order
Indoor Installation Order
Outdoor Installation Order
1
The pieces of the BTS should be installed in the following order.
1. Unpack and inspect hardware
2. Install mounting hardware and bracket (s)
3. Attach and secure unit to mounting bracket
4. Install GPS
5. Prepare site cabling
6. Attach all ground cabling to unit(s)
7. Attach all cables to unit(s)
The pieces of the BTS should be installed in the following order.
1. Unpack and inspect hardware
2. Install mounting hardware
3. Attach and secure units to mounting bracket(s).
4. Attach all ground cabling to unit(s).
5. Prepare site cabling
6. Install GPS.
7. Install antennas
8. Attach AC power cable to PDE
9. Connect DC Power cables between PDE and TME
10. Connect DC power cables between PDE and cCLPA
11. Connect optional Battery Backup cable to PDE
12. Attach all interconnection cables to unit(s).
ATP Order
MAY 2004
The following should already be installed on the laptop computer
S WinLMF
The ATP for the BTS is performed in the following sequence:
1. BTS preparation
2. Connecting the LMF computer to the BTS
3. Connecting test equipment to the BTS and LMF
4. Establishing an MMI communications session
5. Setting customer operating channel
6. Synchronization verification
7. Start WinLMF and log on to BTS
8. Update BTS–specific CDF file device load version
9. Download and enable MCC
10. Test equipment setup (Calibration/GPIB address & clock setup)
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
1-33
Page 68

1
Installation and ATP Order – continued
11. Test equipment selection
12. Power meter calibration
13. Test cable calibration
14. Create CAL file
15. RF path audit
16. TX and RX Acceptance tests
17. Generate an ATP Report
18. Copy WinLMF CAL file to Floppy Disc
19. Terminate LMF session/leave the site
1-34
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
MAY 2004
Page 69

Chapter 2: Site Preparation
Table of Contents
Site Preparation Overview 2-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Overview 2-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation 2-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Verifications and procedures 2-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Site manager 2-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Verifications and inspections 2-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Site Inspections 2-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Inspection overview 2-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Deficiencies 2-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
What to Inspect 2-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Antenna and Transmission Line Inspections 2-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Structural Inspections and Verifications 2-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Grounding Inspections 2-4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2
Prepare Site for the Arrival of the Equipment 2-5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Description 2-5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Equipment Arrival 2-5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Securing Fluorescent Lights 2-5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Procedure to Prepare the Site for the Equipment 2-6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Unpacking the Equipment 2-7 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Description 2-7 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
How Equipment is Shipped 2-7 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
How Equipment Arrives 2-7 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Securing Fluorescent Lights 2-7 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Unpacking Process 2-7 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Recommended Tools 2-7 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Unpacking Diagrams 2-8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Unpacking a Cardboard or Wood Container 2-11 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removing Outdoor Equipment from a Container 2-11 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Removing Indoor Equipment from a Container 2-13 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Dimensions and Clearances 2-14 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
BTS Overview 2-14 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Dimensions and Clearances 2-14 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
BTS Dimensions 2-15 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
cCLPA Dimensions and Clearances 2-16 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Unit Clearances 2-18 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
TME Dimensions and Clearances 2-20 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
MAY 2004 1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
Page 70

Table of Contents – continued
TME Clearances 2-22 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PDE Dimensions and Clearances 2-23 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2
PDE Clearances 2-25 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Outdoor Clearances 2-25 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU MAY 2004
PRELIMINARY
Page 71

Site Preparation Overview
Overview
Installation
Verifications and procedures
Site manager
This chapter provides the procedures and information to verify that the
site is ready to have the equipment installed. It also provides procedures
to ensure the safety of the installation personnel, protect the equipment
from damage, and verify the site layout parameters.
This SCt480 BTS can be installed indoors. The site preparation
depends on the type of installation and the site characteristics. Battery
back up is optional and provided by the customer.
The verifications and procedures provided in this chapter are:
S Internal site inspections
S Preparing site for the arrival of equipment
S Site layout verification
The site manager is the person in charge of and responsible for the full
site.
2
Verifications and inspections
Verifications typically have the installer check with the site manager that
a condition has been previously checked or procedure previously
performed and meets a stated specification.
Inspections typically have the installer personally checking that a
condition or item meets stated specifications.
MAY 2004
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
2-1
Page 72

Site Inspections
Inspection overview
2
Deficiencies
What to Inspect
Inspect the site to verify that the necessary equipment has been properly
installed. Also, as part of the inspection, verify that the equipment is
adequate to support the Motorola equipment. Not all inspections may
apply to every site. The site characteristics determine which inspections
apply.
NOTE
Installation of ancillary equipment (e.g., power supplies,
terminal blocks, etc.) may be the responsibility of the
installer. Refer questions to your Motorola Program
Manager.
Notify responsible personnel of any deficiencies as soon as possible, if
the installer is not responsible for correcting the noted deficiencies.
Deficiencies may need to be corrected before any installation can start.
The following external items should be inspected and compared against
any related site-specific documentation.
S Antennas
S External ground systems
S Clearances for units
S Mounting Structures
Antenna and Transmission
Line Inspections
Structural Inspections and
Verifications
Additionally, for all sites the incoming power should be inspected and
compared against any related site-specific documentation.
Documentation
The vendor(s) responsible for supplying other equipment have left
installation documentation at the site. Review this documentation and
compare it with any related site-specific documents.
Inspection
Inspect the following:
S Antenna and transmission line installation
S Grounding.
Site power
Verify with the site manager that site power has been previously checked
and meets the specifications stated in the site-specific documentation.
2-2
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
MAY 2004
Page 73

Site Inspections – continued
Cabling rack
Inspect the cable rack for proper installation. The cable racks should be
at least 7 ft from the floor. The cable racks should be electrically tied
together with 6 AWG wire, except cable racks that are in an isolated
ground zone.
Fire protection
For indoor installations verify with the site manager that some type of
fixed fire suppression equipment is installed. The possible types are:
S Halon gas system, recommended for cell sites because:
– Halon extinguishes a fire without removing oxygen from a room.
– Halon is clean, allowing for quick cleanup after a fire.
– Halon will not damage the cell site equipment.
2
S CO
(carbon dioxide) system.
S Sprinkler system. “Dry pipe” sprinkler systems that remove all power
to a room before filling the overhead sprinklers with water are
recommended.
2
WARNING
In addition to the fixed fire suppression equipment, there
should be at least two 5-lb ABC class portable fire
extinguishers on the premises before equipment installation
begins.
Fire Fighting Procedures
Cellular infrastructure equipment contains various materials which can
decompose into toxic compounds during intense heat. When fire
fighting conditions are severe, wear full protective clothing, including
helmet, self–contained, positive pressure or pressure demand breathing
apparatus, bunker coat and pants, bands around arms, waist and legs,
face mask, and protective covering for exposed areas of the head.
Antenna cables and ports
Inspect the antenna cables and ports to verify that:
S All antenna cables have been properly labeled.
S Antenna ports have been properly weatherproofed.
S An adequate number of ports exist to handle all of the required
antenna runs.
MAY 2004
S Lightning arrestors have been installed at the building or shelter entry
point.
S For some systems, special ports may be required (refer to the
site-specific information for further details).
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
2-3
Page 74

Site Inspections – continued
Grounding Inspections
2
Indoor installations
For indoor installations refer to the Grounding Guideline for Cellular
Radio Installations (68P81150E62) for all grounding inspection
procedures.
Verify the following:
S All ground cables have a bend radius of 20 cm (8 inches) or more.
S Metallic lines (span, phone[modem], RGPS, power and antenna) that
enter or leave the site should be equipped with a 3-electrode gas tube
protector. The ground side of the gas tubes should be tied to the
Master Ground Bus (MGB).
S All installed cable racks (in the same ground zone) are jumpered
together.
WARNING
Cable racks in an Isolated Ground Zone (IGZ) are not to be
connected to a cable rack in a non-IGZ. For more
information on IGZ, see Grounding Guideline for Cellular
Radio Installations, Motorola part number 68P81150E62
or Appendix C of Standards and Guidelines for
Communications Sites (Motorola part number
9882904Y01)
Outdoor Installations
For outdoor installations refer to the Grounding Guideline for Cellular
Radio Installations (Motorola part number 68P81150E62) or Appendix
C of Standards and Guidelines for Communications Sites (Motorola part
number 9882904Y01) for all grounding inspection procedures.
Verify the following:
S All outdoor enclosures are grounded to system masrter ground.
S All enclosures have conduit attached.
S It is recommended that all metallic lines (span, RGPS, power, and
antenna) that enter or leave the site are be equipped with a surge
suppression device (lightning arrestor).
2-4
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
MAY 2004
Page 75

Prepare Site for the Arrival of the Equipment
Description
Equipment Arrival
Securing Fluorescent Lights
Figure 2-1: Securing Lights with Tape
This information covers various topics not all of which are needed at
every site. Based on the site characteristics execute the steps that apply
to your site. Before installing the equipment, do the following to ensure
the safety of installation personnel and to protect the equipment.
Before the equipment arrives, indicate to the transport company an area
at the site where the equipment can be unloaded and, if necessary,
unpacked. The equipment should be carefully delivered to the site, along
with all equipment dollies and padding required to safely move the
equipment from the unloading area to the cell site. The following should
also be provided, outdoor weather protection, temporary lighting and
power for lighting and power tools.
Figure 2-1 illustrates the use of tape to secure fluorescent tubes. Secure
any fluorescent tubes that may be hit or damaged by any unit, cable, or
personnel.
2
MAY 2004
Apply masking tape to keep
fluorescent tubes in place in
the fixtures.
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
0150–O_IL.doc
2-5
Page 76

Prepare Site for the Arrival of the Equipment – continued
Procedure to Prepare the Site
for the Equipment
2
Step Action
1 If some type of protective padding is available install it around any existing equipment at the site that
could be damaged during installation of the unit(s).
2 Hang plastic sheets around intended work areas to prevent dust and debris from damaging co-located
equipment during installation.
3 Secure any fluorescent tubes in place using masking tape. (Refer to Figure 2-1.)
Table 2-1: Procedure to Prepare the Site for the BTS
NOTE
This will prevent the tubes from being inadvertently jarred from the fixtures during the installation of
equipment or cables.
4 Locate the demarcation blocks for external utilities.
Verify that they are shown on the Site Engineering documents, and determine the required cable
routing back to the equipment frames.
5 Verify the following:
S DC power is available and meets the site documentation specifications (if applicable).
S Cable rack is installed per site document specifications.
S Outdoor cable runs are installed and meet local building codes.
S Span line termination tie points are available.
S Customer input termination tie points are available.
S There is clear access to move the equipment to the desired mounting area.
S There is sufficient space for installation and service access to the equipment.
S Customer supplied shelters are installed.
2-6
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
MAY 2004
Page 77

Unpacking the Equipment
Description
How Equipment is Shipped
How Equipment Arrives
The Purpose of this section is to describe how the SC480 Compact BTS,
TME, PDE, and cCLPA are packaged for shipping and how to correctly
unpack the units in preparation for installation.
The equipment are shipped in either cardboard or wood containers. The
equipment are shipped with all internal cabling installed. For an indoor
installation, the BTS is shipped in a single container. BTS accessories
are shipped in their own container. If used, the cCLPA and accessories
are shipped in a single container. Also, the Mounting Plate and BTS
Mounting Bracket are shipped in a separate container.
For an outdoor configuration, the Thermal Management Enclosure
(TME) and Wall Mounting Bracket are shipped in a single containter.
The Base Transceiver Station (BTS) is shipped in a separate container.
BTS accessories are packed separately and shipped in a container. The
Power Distribution Enclosure (PDE), and Compact Combined Linear
Power Amplifier (cCLPA) with their respective accessories, are shipped
in separate containers.
Conduit piping and batteries for backup power are customer supplied.
2
Securing Fluorescent Lights
Unpacking Process
Recommended T ools
Before the equipment arrives, indicate to the transport company an area
at the site where the equipment can be unloaded and, if necessary,
unpacked. The equipment should be carefully delivered to the site, along
with all equipment dollies and padding required to safely move the
equipment from the unloading area to the cell site. The following should
also be provided, outdoor weather protection, temporary lighting and
power for lighting and power tools.
For indoor configuration, Figure 2-1 illustrates the use of tape to secure
fluorescent tubes. Secure any fluorescent tubes that may be hit or
damaged by any unit, cable, mechanical lift, or personnel.
The unpacking process requires that the following procedures be
completed in the order shown:
1. Unpack the shipping container
2. Inventory the shipping container
3. Inspect equipment for damage
MAY 2004
The tools in Table 2-2 are recommended to assist in opening the
containers housing the equipment.
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
2-7
Page 78

Unpacking the Equipment – continued
Table 2-2: Recommended Unpacking Tools
Qty Description
2
Unpacking Diagrams
1 Tin Snips
2 Knife, Box Cutter, or Scissors
The following diagrams show how to unpack the equipment.
WARNING
The steel bands surrounding the container can spring out
from the container when the bands are cut. To avoid
personal injury, stand safely to one side of the bands while
cutting.
The approximate weights of the containers (with
packaging):
TME: 50 kgs (100 lbs)
BTS: 30 kgs (150 lbs)
PDE :40 kgs (85 lbs)
cCLPA: 22 kgs (48 lbs).
Mounting Plate/BTS Mounting Bracket: 7 kgs (15 lbs).
2-8
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
MAY 2004
Page 79

Unpacking the Equipment – continued
Figure 2-2: Wood Shipping Container
Wood Crate
Top
Wall Mounting
Bracket
container
Styrofoam
Packing
Styrofoam
Packing
TME
NOTE:
1. Normally this styrofoam
packing is attached to the
pallet. it is shown exploded
for clarity
2. This example shows the TME
shipping container.
2
MAY 2004
Wood Crate
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
ti–cdma–wp–00347–v02–ildoc–ah
2-9
Page 80

Unpacking the Equipment – continued
Figure 2-3: Cardboard Shipping Container
2
Wall Mounting
Bracket
cardboard Box
Insert with
Packing
Styrofoam
Packing
Cardboard Lid
NOTE:
1. Normally this styrofoam
packing is attached to the
pallet. it is shown exploded
for clarity
2. This example shows the TME
shipping container.
Styrofoam
Packing
Cardboard
Box
Wood Pallet
TME
1
2-10
ti–cdma–wp–00347–v01–ildoc–ah
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
MAY 2004
Page 81

Unpacking the Equipment – continued
Unpacking a Cardboard or
Wood Container
Follow the procedure in Table 2-3 to unpack equipment from a container.
Table 2-3: Unpacking Equipment from a Cardboard or Wood Container
Step Action
1 Inspect the container for damage.
Cardboard Container
2 Open container using tin snips to cut each outer steel band or a knife (or equivalent) to cut the plastic
wrap that surrounds the container.
3 Remove equipment door key from top of container.
4 Lift off the cardboard cover.
5 Proceed to Table 2-4 or Table 2-5.
Wood Container
6 Perform step 1.
7 Loosen latches at the bottom of the container.
8 Remove clips holding the top pallet , and remove pallet from the container.
9 Remove equipment door key from pallet.
2
10 Proceed to Table 2-4 or Table 2-5.
Removing Outdoor Equipment
from a Container
Follow the procedure in Table 2-4 to remove the outdoor equipment
from a container. The following procedure starts with the TME removal
and continues through to the Pole Mounting Assembly. The order of
opening containers is not important, it is just for demonstration
purposes. The procedure is written for one set. Perform procedure as
many times as required to accommodate the site configuration.
Table 2-4: Procedure to Remove Outdoor Equipment from Container
Step Action
1 Open shipping container holding TME. Perform Table 2-3.
2 Remove the box containing the Wall Mounting Bracket from the insert.
3 Remove insert.
4 Remove cage style packing material surrounding the TME.
5 Using a knife or equivalent, carefuly cut through protective bag enclosing TME.
MAY 2004
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
2-11
Page 82

Unpacking the Equipment – continued
Table 2-4: Procedure to Remove Outdoor Equipment from Container
Step Action
2
n W ARNING
The TME and HMS are shipped as one unit. Together they weigh 39 kg (86 lbs). It is recommended
that the HMS be removed first; otherwise, two people are required to remove the TME with HMS
installed.
6 Use the key to unlock the HMS and open.
7 Use a wrench to remove two nuts and washers securing ground cable to HMS.
8 Disconnect signal cable from TME.
9 Remove HMS from TME hinges and place on a flat surface.
10 Remove TME and place on its backside on a flat surface.
11 Open shipping container holding PDE. Perform Table 2-3.
12 Remove box containing the Wall Mounting Bracket from insert.
13 Remove insert.
n W ARNING
The PDE and HX are shipped as one unit. Together they weigh 52 kg (115 lbs). It is recommended
that a minimum of two people be required to remove the PDE with HX installed.
13a Remove PDE and place on its backside on a flat surface.
14 Open shipping container holding cCLPA. Perform Table 2-3.
! CAUTION
Be careful not to damage the cooling fins on the cCLPA.
14a Remove cCLPA and place on its backside on a flat surface.
15 Remove associated accessories and place on a flat surface.
16 Open shipping container holding BTS. Perform Table 2-3.
17 Remove box containing RGPS or Local GPS (RF–GPS) antenna and cabling, and place on a flat
surface.
NOTE
RGPS or RF–GPS may have been shipped in a separate container.
18 Remove packing surrounding BTS.
19 Remove BTS and place on a flat surface.
20 If system is to be pole mounted proceed to step 21; otherwise, proceed to step 23.
21 Open shipping container holding Pole Mounting Assembly.
22 Remove Pole Mounting Bracket Assembly from container and set on a flat surface.
23 Take inventory of equipment received. Report the extent of any equipment damage to the transport
company and to appropriate management personnel.
2-12
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
MAY 2004
Page 83

Unpacking the Equipment – continued
Removing Indoor Equipment
from a Container
Follow the procedure in Table 2-5 to remove the indoor equipment from
a container. The following procedure starts with the BTS removal and
continues through to the Mounting Plate. The order of opening
containers is not important, it is just for demonstration purposes. The
procedure is written for one set. Perform procedure as many times as
required to accommodate the site configuration.
Table 2-5: Procedure to Remove Indoor Equipment from Container
Step Action
1 Inspect containers for damage. Use tin snips or knife to cut straps holding Mounting Plate container to
the BTS container.
2 Open container holding Mounting Plate and accessories.
3 Remove Mounting Plate and accessories and place on a flat surface.
4 Open shipping container holding BTS.
5 Remove box containing RGPS or Local GPS (RF–GPS) antenna and cabling, and place on a flat
surface.
6 Remove insert.
7 Remove packing surrounding BTS.
2
8 Remove BTS and place on a flat surface.
NOTE
If a cCLPA has also been shipped, proceed to step 9; otherwise, proceed to step 12.
9 Open shipping container holding cCLPA. Perform Table 2-3.
10 Remove packing surrounding cCLPA.
! CAUTION
Be careful not to damage the cooling fins on the cCLPA.
11 Remove cCLPA and place on a flat surface.
12 Take inventory of equipment received. Report the extent of any equipment damage to the transport
company and to appropriate management personnel.
MAY 2004
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
2-13
Page 84

Dimensions and Clearances
BTS Overview
2
Dimensions and Clearances
Item Front Back Left Right Top Bottom
Installation and
Maintenance
Requirements
680 mm
(27 in.)
This information covers the dimensions and clearances associated with
the BTS for indoor configurations.
Table 2-6, Table 2-7, and Figure 2-4 through Figure 2-7 show the
installed dimensions and recommended clearances for each item.
Table 2-6: Installation Dimensions for the BTS
Item Height Width Depth Weight
BTS
(fully
installed)
Table 2-7: Minimum Clearances for the BTS
400 mm
(16 in.)
425 mm
50 mm
(2 in.)
(17 in.)
218 mm
(9 in.)
50 mm
(2 in.)
626 mm
(25 in.)
50 mm
(2 in.)
23 kg
(50 lbs)
0 mm
(0 in.)
Functional
Requirements
50 mm
(2 in.)
50 mm
(2 in.)
50 mm
(2 in.)
50 mm
(2 in.)
50 mm
(2 in.)
0 mm
(0 in.)
2-14
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
MAY 2004
Page 85

Dimensions and Clearances – continued
BTS Dimensions
The BTS dimensions are shown below.
Figure 2-4: Overall Dimensions of BTS
Front cover installed
2
218 mm
425 mm
626 mm
ti–cdma–wp–00302–v01–ildoc–ah
MAY 2004
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
2-15
Page 86

Dimensions and Clearances – continued
cCLPA Dimensions and
Clearances
2
Table 2-9: Minimum Clearances for the cCLPA
Item Front Back Left Right Top Bottom
Installation and
Maintenance
Requirements
Functional
Requirements
* Dimension shown accommodates the handles. Without handles 0 mm is the minimum.
** Minimum of 1 M (40 in) for ground clearance.
680 mm
(27 in.)
680 mm
(27 in.)
Table 2-8, Table 2-9, and Figure 2-5 show the installed dimensions and
recommended clearances for each item.
Table 2-8: Installation Dimensions for the cCLPA
Item Height Length Width Weight
cCLPA 261 mm
0 mm
(0 in.)
0 mm
(0 in.)
*150 mm
(6 in.)
150 mm
(6 in.)
(10 in.)
495 mm
(19 in.)
*150 mm
(6 in.)
150 mm
(6 in.)
295 mm
(12 in.)
100 mm
(4 in.)
100 mm
(4 in.)
20 kg
(44 lbs)
**500 mm
(20 in.)
500 mm
(20 in.)
2-16
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
MAY 2004
Page 87

Dimensions and Clearances – continued
Figure 2-5: cCLPA Dimensions and Functional Clearances
Side Clearance
150 mm minimum
295.0 m m
Top Clearance
100 mm minimum
487.0 mm
Bottom Clearance
500 mm minimum
NOTE:
Overall length of cCLPA is from
mounting flange to mounting
flange.
Side Clearance
150 mm minimum
Bottom Clearance
1 M minimum above
ground
2
260.0 mm
Front Clearance
680 mm minimum
Rear Clearance
0 mm minimum
ti–cdma–wp–00301–v01–ildoc–ah
MAY 2004
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
2-17
Page 88

Dimensions and Clearances – continued
Unit Clearances
The unit clearances are shown below.
2
Figure 2-6: Indoor Functional Clearances for BTS
Side Clearance
Front Clearance
50 mm minimum
50 mm minimum
Mounting Plate
Compact BTS
Top View
Rear Clearance
50 mm minimum
NOTE:
For access to RF filter
tray, remove BTS from
the shelf.
Side Clearance
50 mm minimum
NOTE:
If there is only one cCLPA, then
the top clearance is 100 mm (4
in.) minimum. The clearance
above a single BTS is 125 mm (5
in.) minimum.
For two BTSs the clearance is
250 mm (10 in.) minimum. See
Figure 2-7.
If two cCLPAs are used, the
clearance between them is 625
mm (20 in.) minimum. See
Figure 2-7.
100 mm minimum
clearance
125 mm minimum
clearance
BTS can be mounted
on either side of the
mounting plate
2-18
Side View
Front View
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
MAY 2004
Page 89

Dimensions and Clearances – continued
Figure 2-7: Indoor Functional Clearances for BTS Side–By–Side Configuration
NOTE:
For access to RF filter tray
remove BTS from the shelf.
Seated side–by–side on the
mounting plate does not interfere
with BTS ventilation.
Front Clearance
50 mm minimum
Side Clearance
50 mm minimum
Side Clearance
50 mm minimum
NOTE:
The 100 mm (4 in.) clearance above
the cCLPA only applies if there is a
single cCLPA present.
If two cCLPAs are used, the clearance
between the cCLPAs is 625 mm (25 in. )
minimum.
2
Top View
Rear Clearance
50 mm minimum
Top Clearance
100 mm minimum
625 mm minimum
clearance
Side View
NOTE:
Normal clearance for cCLPA above
BTS is 125 mm (5 in.) minimum.
If two BTSs are used, the clearance
is 250 mm (10 in.) minimum.
250 mm minimum
clearance
Front View
MAY 2004
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
2-19
Page 90

Dimensions and Clearances – continued
TME Dimensions and
Clearances
2
Table 2-11: Minimum Clearances for the TME
Item Front Back Left Right Top Bottom
Installation and
Maintenance
Requirements
Functional
Requirements
* Minimum of 1 Meter for ground clearance.
Figure 2-8: TME
705 mm
(30 in.)
100 mm
(30 in.)
Table 2-10, Table 2-11, Figure 2-9, and Figure 2-10 show the TME
installed dimensions and recommended clearances.
Table 2-10: Installation Dimensions for the TME
Item Height Length Width Weight
TME 530 mm
51 mm
(2 in.)
51 mm
(2 in.)
600 mm
(24 in.
300 mm
(12 in.)
(21 in.)
738 mm
(29 in.)
600 mm
(24 in.)
300 mm
(12 in.)
448 mm
(18 in.)
80 mm
(3 in.)
80 mm
(3 in.)
34 kg
(75 lbs)
*1000 mm
(39 in.)
*1000 mm
(39 in.)
2-20
ti–cdma–wp–00357–v01–ildoc–ah
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
MAY 2004
Page 91

Dimensions and Clearances – continued
Figure 2-9: Overall Dimensions of the Thermal Management Enclosure
530 mm
738 mm
448 mm
2
ti–cdma–wp–00354–v01–ildoc–ah
MAY 2004
ti–cdma–wp–00353–v01–ildoc–ah
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
2-21
PRELIMINARY
Page 92

Dimensions and Clearances – continued
TME Clearances
Figure 2-10 shows the recommended clearances for the TME.
2
Figure 2-10: Functional Clearances for TME
Rear Clearance
51 mm
Side Clearance
300 mm
Side Clearance
300 mm
Front Clearance
100 mm
Top Clearance
80 mm
Bottom Clearance
1 M
2-22
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
MAY 2004
Page 93

Dimensions and Clearances – continued
PDE Dimensions and
Clearances
Table 2-12, Table 2-13, and Figure 2-11 and Figure 2-12 show the
installed dimensions and recommended clearances for each item.
Table 2-12: Installation Dimensions for the PDE
Item Height Length Width Weight
PDE *350 mm
(14 in.)
* Mounting Bracket extends an additional 186 mm (7 in) beyond
bottom of TME.
Table 2-13: Minimum Clearances for the PDE
Item Front Back Left Right Top Bottom
Installation and
Maintenance
Requirements
Functional
Requirements
760 mm
(30 in.)
300 mm
(12 in.)
51 mm
(2 in.)
51 mm
(2 in.)
334 mm
(13 in.)
150 mm
(6 in.)
810 mm
(32 in.)
334 mm
(13 in.)
150 mm
(6 in.)
473 mm
(19 in.)
150 mm
(6 in.)
150 mm
(6 in.)
2
52 kg
(115 lbs)
*150 mm
(6 in.)
*150 mm
(6 in.)
* Minimum of 1 Meter for ground clearance.
Figure 2-11: PDE
MAY 2004
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
ti–cdma–wp–00336–v01–ildoc–ah
2-23
Page 94

Dimensions and Clearances – continued
Figure 2-12: PDE Overall Dimensions
2
350 mm
186 mm
810 mm
760 mm
473 mm
444 mm
305mm
ti–cdma–wp–00270–v01–ildoc–ah
2-24
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
MAY 2004
Page 95

Dimensions and Clearances – continued
PDE Clearances
Figure 2-13 shows the recommended clearances for the PDE.
Figure 2-13: Functional Clearances for PDE
Rear Clearance
51 mm
2
Side Clearance
150 mm
Side Clearance
150 mm
Front Clearance
300 mm
Top Clearance
150 mm
Bottom Clearance
1 M
Outdoor Clearances
MAY 2004
Figure 2-14 and Figure 2-15 show the minimum clearances for the
outdoor configuration.
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
2-25
Page 96

Dimensions and Clearances – continued
Figure 2-14: Mulitple Pole Installation and Functional Clearances for Enclosures and PA
2
BTS with TME/HMS, PDE HX, & PA
Electrical connections
not shown
PA 2
PA 1
TME 2&4, PDE 2, and
PA2 are attached on
the opposite side of the
pole.
Front View
Partial
Side View
10 Meters
PDE 2
TME 2
TME 3
1000 mm
Minimum
PDE 1
1000 mm
Minimum
TME 1
2-26
Ground Level
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
1000 mm
Minimum
MAY 2004
Page 97

Dimensions and Clearances – continued
Figure 2-15: Multiple Wall Installation and Functional Clearances for TME and HMS, PDE, and
cCLPA
A possible layout is
shown.
Electrical connections
not shown
Battery Backup not
shown. Batteries are
connected through
the PDE.
Wall
TME #2
1000 mm
Minimum
PA #2
2
PA #1
10 Meters
Ground Level
TME #1
1000 mm
Minimum
TME #3
1000 mm
minimum
PDE #2PDE #1
1000 mm
Minimum
Front View
MAY 2004
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
2-27
Page 98

Dimensions and Clearances – continued
Notes
2
2-28
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
MAY 2004
Page 99

Chapter 3: BTS Cables
Table of Contents
Cable Description 3-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Overview 3-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Configurations Supported 3-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cabling Installation Order 3-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cable Labels 3-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Ground Lug Specification 3-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Customer I/O Connector 3-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cable Descriptions and Part Numbers 3-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cabling for EV–DO 3-3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Power, Earth Ground, and Battery Cabling 3-4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Objective 3-4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Grounding Considerations 3-4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Indoor Power Considerations 3-5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Outdoor Power Considerations 3-5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3
Antenna Cabling 3-6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cable Labels 3-6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Required Cables 3-6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Antenna Cable Pin and Signal Information 3-6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Span Line and RGPS Cabling 3-7 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cable Labels 3-7 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Required Tools and Materials 3-7 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cable Pin and Signal Information for Span Cabling 3-7 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cable Pin and Signal Information for RGPS Cabling 3-8 . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Remote GPS Head 3-9 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Objective 3-9 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Required Tools and Materials 3-9 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
RGPS Mounting Considerations 3-9 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Local GPS (RF–GPS) Antenna Cabling 3-11 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Objective 3-11 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cable labels 3-11 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cabling diagram 3-11 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Equipment needed 3-11 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Mounting Considerations 3-12 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
MAY 2004 1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU
PRELIMINARY
Page 100

Table of Contents – continued
Notes
3
1X SC480 BTS Hardware Installation, Optimization/ATP, and FRU MAY 2004
PRELIMINARY
 Loading...
Loading...