Page 1

Technical
Information
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware
Installation
Software Release R2.16.1.x
800 MHz
CDMA
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
ENGLISH
Mar 2003
68P64115A19–4
Page 2

Notice
While reasonable efforts have been made to assure the accuracy of this document, Motorola, Inc. assumes no liability resulting from any
inaccuracies or omissions in this document, or from use of the information obtained herein. The information in this document has been
carefully checked and is believed to be entirely reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed for inaccuracies or omissions. Motorola,
Inc. reserves the right to make changes to any products described herein and reserves the right to revise this document and to make
changes from time to time in content hereof with no obligation to notify any person of revisions or changes. Motorola, Inc. does not
assume any liability arising out of the application or use of any product, software, or circuit described herein; neither does it convey
license under its patent rights or the rights of others.
It is possible that this publication may contain references to, or information about Motorola products (machines and programs),
programming, or services that are not announced in your country. Such references or information must not be construed to mean
that Motorola intends to announce such Motorola products, programming, or services in your country.
Copyrights
This instruction manual, and the Motorola products described in this instruction manual may be, include or describe copyrighted
Motorola material, such as computer programs stored in semiconductor memories or other media. Laws in the United States and
other countries preserve for Motorola certain exclusive rights for copyrighted material, including the exclusive right to copy,
reproduce in any form, distribute and make derivative works of the copyrighted material. Accordingly, any copyrighted Motorola
material contained herein or in the Motorola products described in this instruction manual may not be copied, reproduced,
distributed, merged or modified in any manner without the express written permission of Motorola. Furthermore, the purchase of
Motorola products shall not be deemed to grant either directly or by implication, estoppel, or otherwise, any license under the
copyrights, patents or patent applications of Motorola, as arises by operation of law in the sale of a product.
SPECIFICATIONS SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE
Usage and Disclosure Restrictions
License Agreement
The software described in this document is the property of Motorola, Inc. It is furnished by express license agreement only and may
be used only in accordance with the terms of such an agreement.
Copyrighted Materials
Software and documentation are copyrighted materials. Making unauthorized copies is prohibited by law. No part of the software or
documentation may be reproduced, transmitted, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, or translated into any language or
computer language, in any form or by any means, without prior written permission of Motorola, Inc.
High Risk Activities
Components, units, or third–party products used in the product described herein are NOT fault–tolerant and are NOT designed,
manufactured, or intended for use as on–line control equipment in the following hazardous environments requiring fail–safe
controls: the operation of Nuclear Facilities, Aircraft Navigation or Aircraft Communication Systems, Air Traffic Control, Life
Support, or Weapons Systems (“High Risk Activities”). Motorola and its supplier(s) specifically disclaim any expressed or implied
warranty of fitness for such High Risk Activities.
CONTROLLED
Page 3

Trademarks
and Motorola are registered trademarks of Motorola, Inc.
Product and service names profiled herein are trademarks of Motorola, Inc. Other manufacturers’ products or services profiled
herein may be referred to by trademarks of their respective companies.
Copyright 2003 Motorola, Inc.
SPECIFICATIONS SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE
Printed on
Recyclable Paper
REV012501
CONTROLLED
Page 4
68P64115A19–4
5
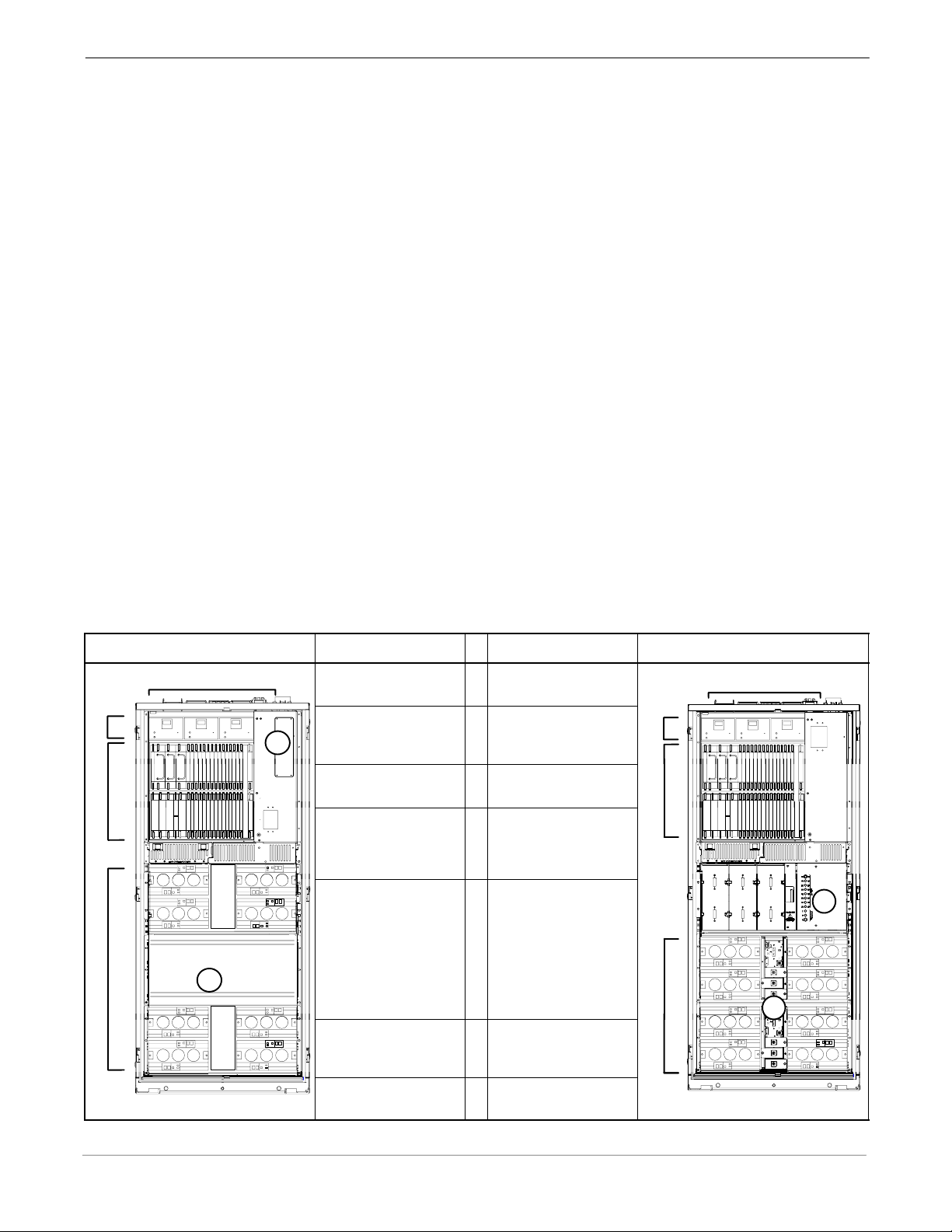
SC 4812T-MC vs SC 4812T BTS Read Me First (Comparison)
Read Me First
SC 4812T-MC vs SC 4812T BTS Read Me First (Comparison)
This Read-me-first document describes a summary of changes between
the existing SCt4812T BTS and the SC 4812T-MC (Multicarrier) BTS.
The SC 4812T-MC is based on the existing SC 4812T platform and
employs similar hardware and architecture. The differences between
these products are briefly described and illustrated below. This section is
not intended to replace the SC 4812T-MC manual set.
Multicarrier provides the capability for all PAs in all quadrants to
provide trunked power across all sector/carriers. This differs from the
previous architecture in which PA modules within a quadrant provided
trunked power to only one carrier. Furthermore, in SC 4812T-MC,
adjacent channels can be combined onto one antenna versus being
transmitted on separate antennas in SC 4812T.
An overview of the BTS differences is illustrated in the following table
and in illustrations on the following pages (Figure 1 thru Figure 4).
SC 4812T
2
3
4
5
6
ti-CDMA-WP-00098-v01-ildoc-ftw
1
7
Description # Description SC 4812T-MC
3x3 DC Power Input
(see Figure 1)
I/O Plate supporting
3x3 DC Power Input
(see Figure 2)
CCCP Fan Tray
C-CCP Cage:
S CIO (3- or 6-Sector)
S BBX-1X
S Switch
PA Shelves:
S SC 4812T LPA
S 4x4 TX Backplane
S PA Location and
Mapping (see Figure 3)
2:1 or 4:1 Combiners or
Dual Bandpass TX
Filters
PA Breaker Mapping
(see Figure 4)
2x2 DC Power Input
1
(see Figure 1)
I/O Plate supporting
2
2x2 DC Power Input
(see Figure 2)
CCCP Speed
3
Controlled Fan Tray
C-CCP Cage:
4
S MCIO (3- or 6-Sector)
S High Power BBX-1X
S High Power Switch
PA Shelves:
5
S SC 4812T CLPA
S Multicarrier module
S Parallel PA Combiner
S Enhanced Trunking
Module
S LPA/PLC Filler Panel
S PA Location and
Mapping (see Figure 3)
TX Bandpass Filters
6
7
and/or
TX Output Terminator
PA Breaker Mapping
(see Figure 4)
3
4
5
ti-CDMA-WP-00196-v01-ildoc-ftw
2
1
7
6
Mar 2003 1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
RMF-1
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
Page 5
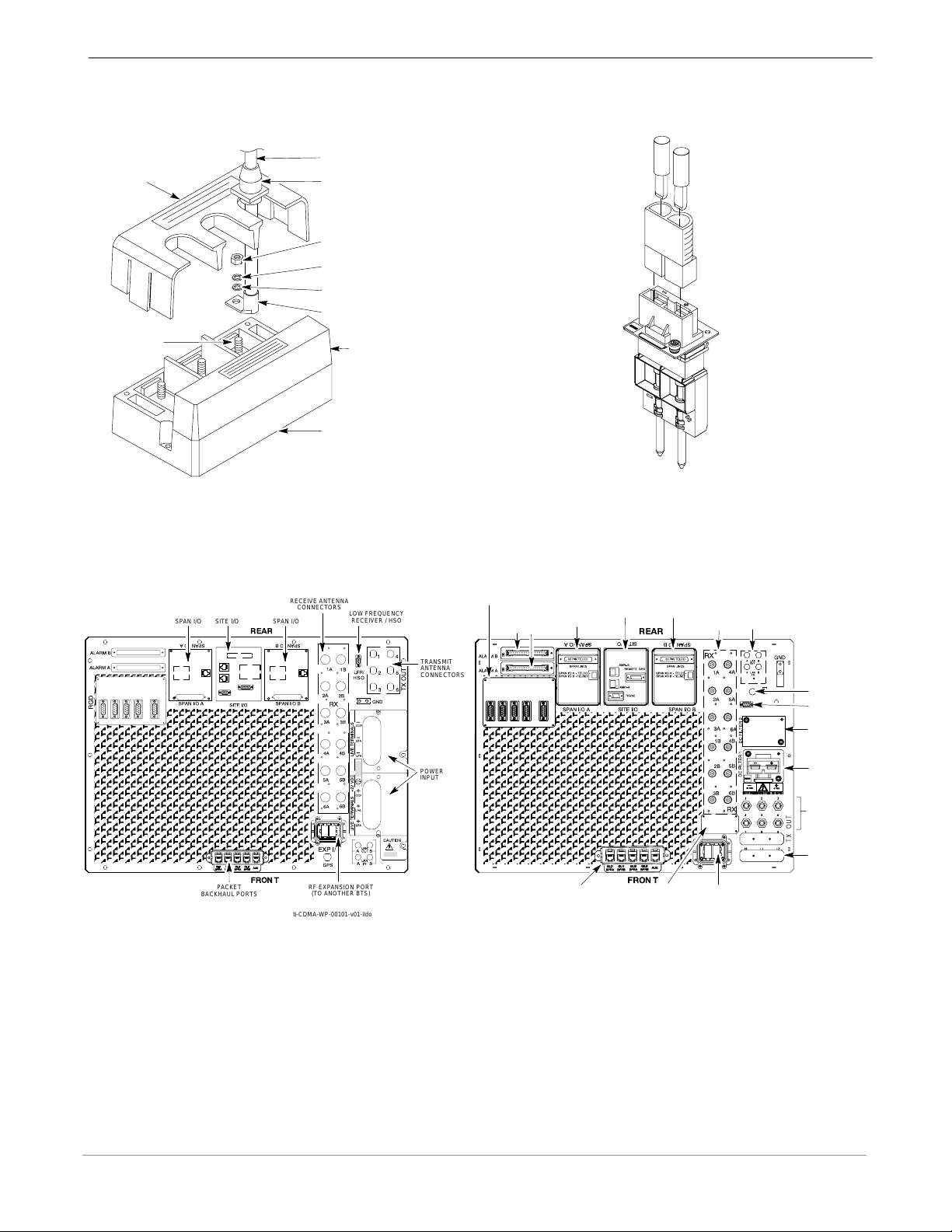
SC 4812T-MC vs SC 4812T BTS Read Me First (Comparison)
Figure 1: DC Power Input Connector Comparison
68P64115A19–4
SC 4812T
LUG COVER
(1509789V01)
POWER
INPUT STUD
CABLE
GROMMET
(0509591Y02)
M10 NUT
(0210971A09)
M10 LOCK WASHER
(0410985A02)
M10 FLAT WASHER
(0410983B28)
CRIMP LUG
FEED COVER
(DO NOT REMOVE)
ENCLOSURE
BASE
ti-CDMA-WP-00024-v01-ildoc-ftw
DC CABLE (–)
DC
CONTACT
Input
Connector/
DC Filter
(–)
(+) DC CABLE
DC
CONTACT
Connector
Housing
(+)
ti-CDMA-WP-00074-v01-ildoc-ftw
SC 4812T–MC
DC
Figure 2: I/O Plate Comparison
SC 4812T SC 4812T–MC
REMOTE GPS DISTRIBUTION (RGD) MODULE –
RECEIVE ANTENNA
SITE I/OSPAN I/O
CONNECTORS
SPAN I/O
LOW FREQUENCY
RECEIVER / HSO
USED ONLY IF EXPANSION FRAME(S) INSTALLED
ALARM
CONNECTORS
SITE I/O
SPAN I/O
SPAN I/O
RECEIVE
ANTENNA
CONNECTORS
LAN
CONNECTIONS
PACKET
BACKHAUL PORTS
RF EXPANSION PORT
(TO ANOTHER BTS)
ti-CDMA-WP-00101-v01-ildoc-ftw
TRANSMIT
ANTENNA
CONNECTORS
POWER
INPUT
ETHERNET ROUTER (IF USED;
OTHERWISE, FILLER PLATE)
EXP IN FILLER
PLATE
RF EXPANSION PORT TO ANOTHER
BTS (USED ONLY IF EXPANSION
FRAME INSTALLED; OTHERWISE,
FILLER PLATE INSTALLED)
ti-CDMA-WP-00188-v01-ildoc-ftw
GPS IN
HSO/LFR
FILLER PLATE
INPUT
CONNECTOR/
DC FILTER
3 to 6 TX
ANTENNA
CONNECTORS
(depending on
configuration)
2 to 3 TX
ANTENNA
FILLER PLATES
(depending on
configuration)
RMF-2
Mar 20031X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
Page 6
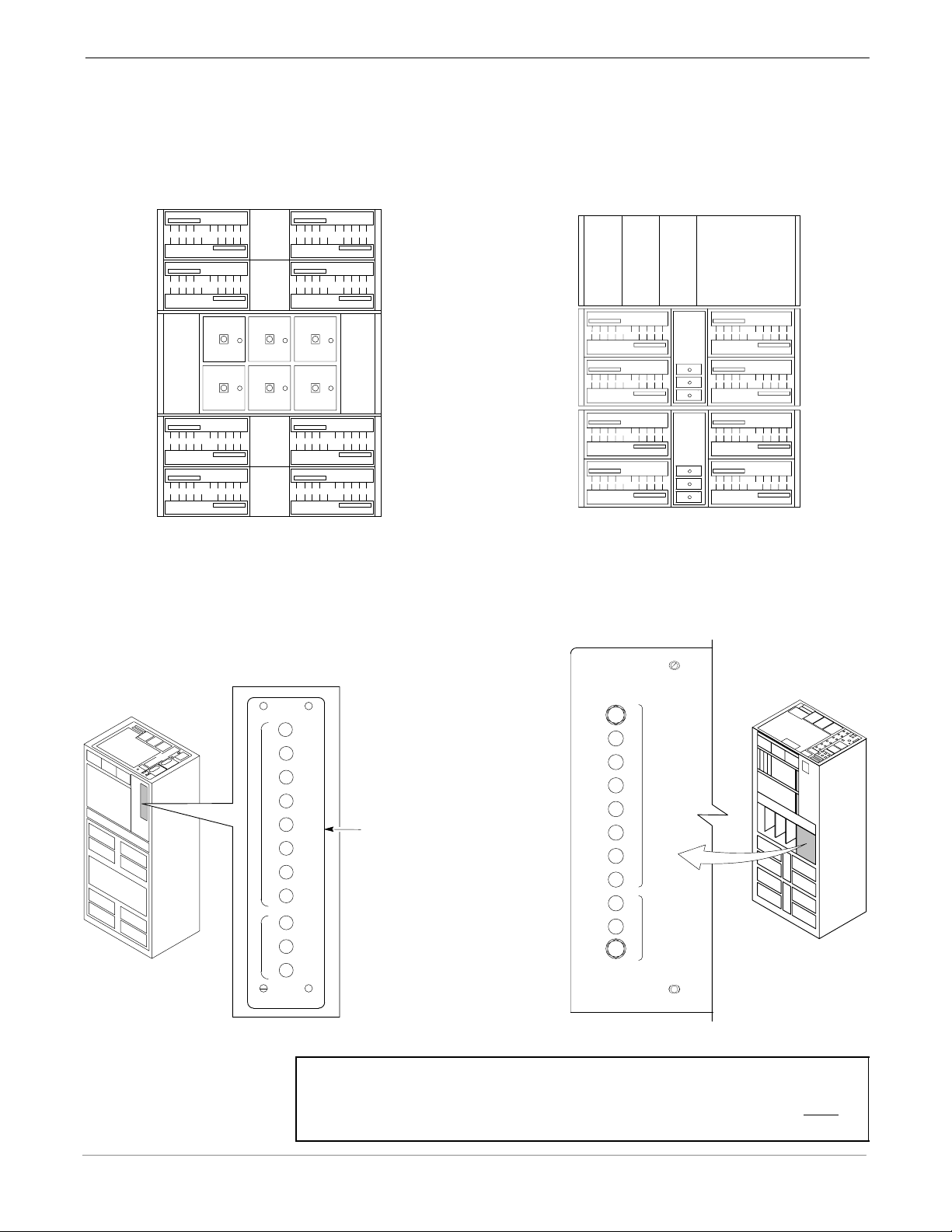
68P64115A19–4
SC 4812T-MC vs SC 4812T BTS Read Me First (Comparison)
Figure 3: PA Location Comparison
SC 4812T SC 4812T–MC
Sector
Numbering
3 Sector
(6 Sector)
2 to 1 Combiner
3 Sector or 6 Sector
LPA 1A
LPA 2A
Sector
Numbering
3 Sector
(6 Sector)
Carrier
Numbering
3 Sector
(6 Sector)
3 Sector and 6 Sector
Carrier
Numbering
3 Sector
(6 Sector)
C1, S1–3
(C1, S1–3)
C3, S1–3
(C1, S4–6)
LPA 1B
LPA 1C
LPA 1D
123
456
LPA 3A
LPA 3B
LPA 3C
LPA 3D
LPA 2B
LPA 2D
LPA 4B
LPA 4D
LPA 2C
LPA 4A
LPA 4C
FW00297 REF.
C2, S1–3
(C2, S1–3)
C4, S1–3
(C2, S4–6)
C1 (C1)
C2 (C2)
C3 (C1)
C4 (C2)
C1 (C1)
C2 (C2)
C3 (C1)
C4 (C2)
CLPA
CLPA
CLPA
CLPA
1A 1B
MCM
3A
1C
3C
1
S3
S2
S1
MCM
2
S6
S5
S4
2A
CLPA
4A
CLPA
2C
CLPA
4C
CLPACLPA
CLPA
2B
CLPA
4B
CLPA
CLPA
CLPA
2D
CLPA
4D
CLPA
ti-CDMA-WP-00197-v01-ildoc-ftw
3B
1D
3D
C1 (C1)
C2 (C2)
C3 (C1)
C4 (C2)
C1 (C1)
C2 (C2)
C3 (C1)
C4 (C2)
Figure 4: PA Breaker Mapping Comparison
SC 4812T SC4812T–MC
50
1A
30
1A
1B
1D
30
1C
30
2A
L
P
A
C
C
C
P
2B
30
2C
2D
3B
30
3A
30
3C
3D
30
4B
4A
4C
30
4D
50
1
2
50
3
50
NOTE
CIRCUIT
BREAKER
PANEL
FW00380 REF.
IMPORTANT: A breaker supports a pair of PAs. In
2A
3A
4A
1B
2B
3B
1C
3C
1D
3D
1
2
3
L
4B
P
2C
A
4C
2D
4D
C
C
50 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 50
C
P
50
ti-CDMA-WP-00224-v01-ildoc-ftw
SC4812T–MC, disengaging (pulling) a PA breaker while the
BTS is operational will degrade the TX Output power of ALL
sector–carriers, not just a specific carrier as in SC4812T.
Mar 2003 1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
RMF-3
Page 7

SC 4812T-MC vs SC 4812T BTS Read Me First (Comparison)
Notes
68P64115A19–4
RMF-4
Mar 20031X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
Page 8

Table of Contents
.
.
.
Mar 2003
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
i
Page 9

Table of Contents
SC 4812T-MC vs SC 4812T BTS Read Me First (Comparison) RMF-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
68P64115A19–4
Contents
FCC Requirements xi . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Content xi . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
FCC Part 15 Requirements xi . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
FCC Part 68 Requirements xii . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Foreword xiii . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
General Safety xv . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Revision History xvii . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Chapter 1 Manual Overview and BTS General Information 1-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Manual Overview, Abbreviations and Acronyms 1-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Manual Overview 1-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Manual Structure 1-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Abbreviations and Acronyms 1-3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Required Documentation and Environmental Specifications 1-5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Required Documentation 1-5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Specifications 1-6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
BTS Frame Site Layout 1-7 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Base Transceiver Station (BTS) Frame Identification 1-8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
BTS Frame 1-8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
I/O Plate 1-9 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Site I/O 1-9 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Span I/O 1-9 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Combined CDMA Channel Processor (C-CCP) Shelf 1-9 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Power Distribution Cage MC Configuration 1-10 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
MC CLPA Cage 1-10 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
MC Module 1-10 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
In-Frame Components 1-10 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
External Components 1-10 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Chapter 2 Inter-Frame Cabling 2-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Inter-Frame Cabling 2-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Overview 2-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Review the Material 2-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Configurations Supported 2-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cabling Installation Order 2-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cable Labels 2-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cable Connections 2-3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
BTS Frame Description 2-3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Top I/O (Interconnect) Plate (Figure 2-1 and Figure 2-2) 2-3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Expansion Frame I/O Plate 2-5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Site I/O and Span I/O Boards 2-6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Remote GPS Distribution (RGD) Card 2-6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cabling Diagrams and Descriptions 2-7 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cable Descriptions and Part Numbers 2-7 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Overall Cabling Diagram (Single Frame) 2-9 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Alarm / Span Cabling 2-10 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Objective 2-10 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
ii
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
Mar 2003
Page 10

68P64115A19–4
Cable Labels 2-10 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Equipment Needed 2-10 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cabling Diagram 2-11 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cable Run List 2-11 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Install Span and Alarm Cables 2-12 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Alarm Signal Specifications 2-13 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Span Line Cable Pin Numbering 2-14 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Alarm Connectors Pin and Signal Information 2-15 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Equipment Compliance 2-18 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
BTS System Timing Options 2-19 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Timing Sources 2-19 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
RF Global Positioning Satellite (RF GPS) Cabling 2-20 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
RF GPS Cabling Diagram 2-20 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cable Run List 2-21 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
RF GPS Cabling Installation Procedure 2-21 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Remote Global Positioning Satellite (RGPS) Cabling 2-22 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
RGPS Cabling Diagrams 2-22 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cabling Run List 2-23 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Install RGPS Cable 2-23 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Low Frequency Receiver / High Stability Oscillator (LFR/HSO) Cabling 2-24 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Overview 2-24 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cable Labels 2-24 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cable Run List 2-24 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Procedure 2-24 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
LFR Cable (Cable L) Pin/Signal Information 2-25 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
BTS Antenna Configuration 2-26 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Overview 2-26 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
RX Antenna Configurations 2-26 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
TX Antenna Configurations 2-27 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
BTS 60 Degree Sector (6 Sector) Transmit Path Cabling 2-28 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Objective 2-28 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cable Labels 2-28 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cabling Diagram 2-28 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
60 Degree Sector Configuration 2-30 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
TX Ports for 6 Sector Configuration 2-30 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Procedure 2-30 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
BTS 60 Degree Sector (6 Sector) Receive Path Cabling 2-31 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Objective 2-31 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cable Labels 2-31 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cabling Diagram 2-31 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Procedure 2-32 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
BTS 120 Degree Sector (3 Sector) Transmit Path Cabling 2-33 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Objective 2-33 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cable Labels 2-33 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cabling Diagram 2-33 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Procedure 2-35 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
BTS 120 Degree Sector (3 Sector) Receive Path Cabling 2-36 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Objective 2-36 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cable Labels 2-36 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cabling Diagram 2-36 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cabling Procedure 2-38 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table of Contents
Mar 2003
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
iii
Page 11

Table of Contents
Earth Ground Cabling 2-39 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Objective 2-39 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Earth Grounding Diagram 2-39 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cable Labels 2-39 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Equipment Needed 2-39 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Install Earth Grounding Cables 2-40 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
BTS Power Cabling 2-41 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Objective 2-41 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Important Guidelines 2-41 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Option A. Power Distribution Cabling for +27 V BTS Configuration with One Power Feed 2-44 . . . . . .
Option B. Power Distribution Cabling for +27 V BTS Configuration with Two Power Feeds 2-45 . . . . .
Tools and Equipment Required 2-46 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Pre-connection Checklist 2-47 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installing Power Cables 2-47 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
BTS Power Cabling 2-48 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
68P64115A19–4
Chapter 3 Expansion Frame Cabling and Installation 3-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Expansion Frame (+27 V BTS Configuration) 3-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation Procedures 3-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Inter-frame Cables 3-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Before You Begin 3-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Expansion Frame and Expansion I/O Plate 3-3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cable Labels 3-6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Expansion Frame Cabling Diagram 3-6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Expansion Frame Inter-Frame Cabling 3-7 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Remote GPS Distribution (RGD) Board Diagram 3-7 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Expansion of the +27 V Frame 3-8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Antenna Sharing 3-8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Tools Required 3-8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Expansion Procedure 3-8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
RF GPS Expansion Installation 3-10 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
GPS Expansion 3-10 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Customer Equipment Considerations and System Constrains 3-10 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
RF RGPS Expansion Installation Considerations 3-10 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Remote GPS Distribution Expansion 3-12 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Configuration 3-12 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Tools Required 3-12 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Remote GPS (RGD) Expansion Procedure 3-12 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
High Stability Oscillator Expansion (HSOX) 3-13 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Configuration 3-13 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Tools Required 3-13 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
HSO Expansion Procedure 3-13 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Local Area Network (LAN) Expansion Installation 3-14 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Configuration 3-14 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Tools Required 3-14 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Torque Specifications 3-14 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
LAN Expansion Installation Procedure 3-14 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Setting Frame C-CCP Shelf Configuration Switch 3-16 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Chapter 4 Optional Equipment 4-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Optional BTS Equipment Identification 4-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
iv
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
Mar 2003
Page 12

68P64115A19–4
Overview 4-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Directional Couplers 4-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Duplex Directional Couplers (DDC) and Mounting Bracket 4-3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
RFDS 4-4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
RF Interfaces 4-4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
RFDS Function 4-4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
RFDS Cabling to the BTS 4-6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
BTS Antenna Configuration 4-7 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Overview 4-7 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
BTS 60 Degree Sector (6 Sector) Transmit Path Cabling 4-8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Objective 4-8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cable Labels 4-8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cabling Diagram 4-8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
60 Degree Sector Configuration 4-9 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Procedure 4-9 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
BTS 60 Degree Sector (6 Sector) Receive Path Cabling 4-10 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Objective 4-10 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cable Labels 4-10 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cabling Diagram 4-10 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Procedure 4-11 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
BTS 120 Degree Sector (3 Sector) Transmit Path Cabling 4-12 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Objective 4-12 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cable Labels 4-12 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cabling Diagram 4-12 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Procedure 4-13 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
BTS 120 Degree Sector (3 Sector) Receive Path Cabling 4-14 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Objective 4-14 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cable Labels 4-14 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cabling Diagram 4-14 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cabling Procedure 4-16 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3 Sector Non–Duplexed Cabling 4-17 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Objective 4-17 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cabling Diagram 4-17 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3 Sector Duplexed 4-20 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Objective 4-20 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cabling Diagram 4-20 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6 Sector Duplexed 4-22 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Objective 4-22 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cabling Diagram 4-22 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table of Contents
4-17 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Chapter 5 What’s Next and Site Cleanup 5-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
What’s Next 5-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Introduction 5-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Clean Up the Site 5-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fill Out Checklist 5-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Optimize the System 5-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Site Cleanup 5-3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Remove Protective Covering 5-3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Lighting Fixtures 5-3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Tools 5-3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Mar 2003
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
v
Page 13

Table of Contents
Materials 5-3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Remove Debris 5-3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Environment 5-3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation Completion Checklist 5-4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Directions 5-4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation Completion Checklist 5-4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
68P64115A19–4
Appendix A Carrier Add Instructions A-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Carrier Add Instructions A-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Overview A-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Tool & Torque Requirements A-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
T– Options A-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Carrier Add Matrix (3 Sector) A-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Adding a Carrier (3 Sector) A-3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Carrier Add (6 Sector) A-5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Carrier Add Matrix (6 Sector) A-5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installing a Second Carrier A-5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Index Index-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
vi
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
Mar 2003
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
Page 14

68P64115A19–4
Figure 1: DC Power Input Connector Comparison RMF-3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 2: I/O Plate Comparison RMF-3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 3: PA Location Comparison RMF-4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4: PA Breaker Mapping Comparison RMF-4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 1-1:Dimensions and Clearances for the BTS 1-7 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 1-2: SC 4812T–MC BTS Frame 1-8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 2-1: SC4812T–MC Starter Frame I/O Plate 2-4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 2-2: SC4812T–MC Expansion Frame I/O Plate 2-5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 2-3: Site I/O and Span I/O Boards 2-6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 2-4: RGD Board Cables Connection 2-6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 2-5: Overall Signal Cabling Diagram for CDMA Systems 2-9 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 2-6: Alarm and Span Line Cabling Details 2-11 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 2-7: Cable A (Span Line) Pin Numbering 2-14 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 2-8: Cable B (Alarm) Pin Numbering 2-15 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table of Contents
List of Figures
Figure 2-9: RF GPS Cabling Detail 2-20 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 2-10: Remote GPS Mounting Detail 2-22 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 2-11: Remote GPS Cabling Diagram 2-23 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 2-12: 60 Degree Sector (6 Sector) Transmit Path Cabling Details (Outside Frame) 2-28 . . . . . .
Figure 2-13: 60 Degree Sector (6 Sector) Transmit Path Cabling Details (Inside frame) 2-29 . . . . . . . .
Figure 2-14: 60 Degree Sector (6 Sector) Receive Path Cabling Details 2-31 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 2-15: 120 Degree Sector (3 Sector) Transmit Path Cabling Details (outside the frame) 2-33 . . .
Figure 2-16: 120 Degree Sector (3 Sector) Transmit Path Cabling Details (inside the frame) 2-34 . . . .
Figure 2-17: 120 Degree Sector (3 Sector) Receive Path Cabling Details 2-37 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 2-18: Earth Ground Cabling Details 2-39 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 2-19: Breaker Panel Identification 2-42 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 2-20: Length and Tie-Down Requirements for BTS Power Cables 2-43 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 2-21: BTS Power Cabling for the +27 V BTS Configuration using One Power Feed 2-44 . . . . .
Figure 2-22: BTS Power Cabling for the + 27 V BTS Configuration using TwoPower Feeds 2-45 . . . . .
Figure 2-23: DC Power Connector/Filter 2-46 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 3-1:BTS MC Expansion Frame (+27 V Configuration) 3-3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 3-2: Expansion Frame I/O Plate (+27 V Configuration) 3-4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 3-3: Starter Frame I/O Plate 3-5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Mar 2003
Figure 3-4: Expansion Frame Cabling Details 3-6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 3-5: RGD Board Cable Connections 3-7 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 3-6: RX Antenna Sharing with an Expansion Frame 3-8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 3-7: System to Feed Multiple BTS’s from One RF GPS Antenna 3-11 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 3-8: HSOX Cable (3086458H01) for Expansion Frame 3-13 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 3-9: LAN Grounding Stud 3-15 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 3-10: Backplane DIP Switch Settings 3-16 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
vii
Page 15

Table of Contents
Figure 4-1: Directional Couplers 4-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4-2: DDC (Duplexers – Directional Couplers) 4-3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4-3: RFDS (Rack Mount Unit) 4-5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4-4: RFDS (Block Diagram) 4-6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4-5: 60 Degree Sector (6 Sector) Transmit Path Cabling Details 4-8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4-6: 60 Degree Sector (6 Sector) Receive Path Cabling Details 4-10 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4-7: 120 Degree Sector (3 Sector) Transmit Path Cabling Details 4-12 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4-8: 120 Degree Sector (3 Sector) Receive Path Cabling Details 4-15 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4-9: 3-Sector Non–Duplexed Cabling Configurations 4-18 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4-10: 3–Sector Duplexed Cabling Configurations 4-20 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 4-11: 6-Sector Duplexed Cabling Configurations 4-23 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure A-1: PLC Filler Plate Location (3X3 Enhanced Trunking Module) A-4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure A-2: PLC Filler Plate Location (4X4 Enhanced Trunking Module) A-4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure A-3: PLC Filler Plate Locations 6 Sector (3X3 Enhanced Trunking Module) A-6 . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure A-4: PLC Filler Plate Locations (4X4 Enhanced Trunking Module) A-6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
68P64115A19–4
viii
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
Mar 2003
Page 16

68P64115A19–4
FCC Part 68 Registered Devices xii . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 1-1: Abbreviations and Acronyms 1-3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 1-2: Environmental Specifications 1-6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-1: Cable Descriptions and Part Numbers 2-7 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-2: Cables Needed for Alarm and Span Line Cabling 2-10 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-3: Cable Run List for Alarm and Span Line Cabling 2-11 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-4: Procedure to Install Span Line A Cable 2-12 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-5: Procedure to Install Span Line B Cable 2-12 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-6: Procedure to Install Alarm Cables 2-12 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-7: External Alarm Connector Characteristics and Requirements 2-13 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-8: Span I/O Connector 2-14 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-9: Pin and Signal Information for ALARM A Connectors 2-16 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-10: Pin and Signal Information for ALARM B Connectors 2-17 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-11: Cable Run List for GPS and LFR Cabling 2-21 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table of Contents
List of Tables
Table 2-12: Procedure to Install the RF GPS Cabling 2-21 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-13: Remote GPS Cable Descriptions and Part Numbers 2-23 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-14: Installing the RGPS Cabling 2-23 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-15: Cable Run List for GPS and LFR Cabling 2-24 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-16: Procedure to Install LFR Cabling 2-24 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-17: Pin /Signal Information for LFR Cable (Cable C) 2-25 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-18: RX Antenna Configuration 2-26 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-19: Multicarrier BTS TX Antenna Configuration 2-27 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-20: Cable Run List for 60 Degree Sector TX Configuration 2-30 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-21: Cable Run List for 60 Degree Sector Receive Path Cabling 2-30 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-22: Installing the 60 Degree Sector TX Path Cables 2-30 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-23: Cables Needed for 120 Degree Sector Receive Path 2-32 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-24: Cable Run List for 60 Degree Sector Receive Path Cabling 2-32 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-25: Installing the 60 Degree Sector Receive Path Cables 2-32 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-26: Cables Needed for 120 Degree Sector Transmit Path 2-34 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-27: Cable Run List for 120 Degree Sector TX Configuration 2-34 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-28: Installing the 120 Degree Sector TX Path Cables 2-35 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-29: Cables Needed for 120 Degree Sector Receive Path 2-36 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Mar 2003
Table 2-30: Cable Run List for 120 Degree Sector Receive Path Cabling 2-36 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-31: Installing the 120 Degree Sector Receive Path Cables 2-38 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-32: Items Required for Earth Grounding 2-39 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-33: Procedure to Install Earth Grounding Cables 2-40 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-34: DC Filter Power Feed Configurations 2-41 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-35: Maximum Cable Length 2-43 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-36: Lug Part Numbers 2-46 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
ix
Page 17

Table of Contents
Table 2-37: Procedure to Install BTS +27 V Power Cables 2-48 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 3-1: Expansion Cable/Hardware Descriptions and Part Numbers 3-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 3-2: Installing an Expansion BTS 3-8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 3-3: Installing Remote GPS (RGD) Expansion 3-12 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 3-4: Installing the HSOX Cable and Card 3-13 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 3-5: Installing LAN Expansion 3-14 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 4-1: CDMA Frequency Spectrum in MHz 4-4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 4-2: Cable Run List for 60 Degree Sector TX Configuration 4-9 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 4-3: Installing the 60 Degree Sector TX Path Cables 4-9 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 4-4: Cables Needed for 120 Degree Sector Receive Path 4-11 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 4-5: Cable Run List for 60 Degree Sector Receive Path Cabling 4-11 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 4-6: Installing the 60 Degree Sector Receive Path Cables 4-11 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 4-7: Cables Needed for 120 Degree Sector Transmit Path 4-12 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 4-8: Cable Run List for 120 Degree Sector Configuration 4-13 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 4-9: Installing the 120 Degree Sector TX Path Cables 4-13 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 4-10: Cables Needed for 120 Degree Sector Receive Path 4-14 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
68P64115A19–4
Table 4-11: Cable Run List for 120 Degree Sector Receive Path Cabling 4-14 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 4-12: Installing the 120 Degree Sector Receive Path Cables 4-16 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 4-13: 3-Sector Non-Duplexed Directional Coupler to RFDS Cabling Table 4-19 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 4-14: Installing RF Cables in a 3-Sector Non-Duplexed System 4-19 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 4-15: 3-Sector Duplexed Directional Coupler to RFDS Cabling Table 4-21 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 4-16: Installing RF Cables in a 3-Sector Duplexed System 4-21 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 4-17: 6-Sector Duplexed Directional Coupler to RFDS Cabling Table 4-24 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 4-18: Installing RF Cables in a 6-Sector Duplexed System 4-24 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 5-1: Installation Completion Checklist 5-4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table A-1: 3 Sector Carrier Add Matrix A-3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table A-3: Adding a Carrier A-3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table A-4: Six Sector Carrier Add Matrix A-5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table A-5: Installing a Second Carrier A-5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
x
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
Mar 2003
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
Page 18

68P64115A19–4
FCC Requirements
Content
FCC Part 15 Requirements
FCC Requirements
This section presents Federal Communications Commission (FCC)
Rules Parts 15 and 68 requirements and compliance information for the
SCt4812T/ET/ET Lite series Radio Frequency Base Transceiver
Stations.
Part 15.19a(3) – INFORMATION TO USER
NOTE
CAUTION
NOTE
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation
is subject to the following two conditions:
1. This device may not cause harmful interference, and
2. This device must accept any interference received, including
interference that may cause undesired operation.
Part 15.21 – INFORMATION TO USER
Changes or modifications not expressly approved by Motorola
could void your authority to operate the equipment.
15.105(b) – INFORMATION TO USER
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the
limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the
FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable
protection against harmful interference in a residential
installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio
frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance
with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio
communications. However, there is no guarantee that
interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this
equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television
reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment
OFF and ON, the user is encouraged to try to correct the
interference by one or more of the following measures:
S Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
Mar 2003
S Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
S Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different
from that to which the receiver is connected.
S Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for
help.
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
xi
Page 19

FCC Requirements
FCC Part 68 Requirements
68P64115A19–4
This equipment complies with Part 68 of the Federal Communications
Commission (FCC) Rules. A label on the GLI board, easily visible with
the board removed, contains the FCC Registration Number for this
equipment. If requested, this information must be provided to the
telephone company.
FCC Part 68 Registered Devices
Device FCC Part 68 ID
Group Line Interface (GLI2) US: IHEUSA–32769–XD–E
Group Line Interface (GLI3) US: IHEXDNANGLI3–1X
The telephone company may make changes in its facilities, equipment,
operations, or procedures that could affect the operation of your T1. If
this happens, the telephone company will provide advance notice so that
you can modify your equipment as required to maintain uninterrupted
service.
If this equipment causes harm to the telephone network, the telephone
company will notify you in advance that temporary discontinuance of
service may be required. If advance notice is not practical, the telephone
company will notify you as soon as possible. Also, you will be advised
of your right to file a complaint with the FCC if you believe it is
necessary.
If you experience trouble operating this equipment with the T1, please
contact:
Global Customer Network Resolution Center (CNRC)
1501 W. Shure Drive, 3436N
Arlington Heights, Illinois 60004
Phone Number: (847) 632–5390
for repair and/or warranty information. You should not attempt to repair
this equipment yourself. This equipment contains no customer or
user-serviceable parts.
Changes or modifications not expressly approved by Motorola could
void your authority to operate this equipment.
xii
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
Mar 2003
Page 20
68P64115A19–4
Foreword
Scope of manual
Obtaining Manuals
Foreword
This manual is intended for use by cellular telephone system
craftspersons in the day-to-day operation of Motorola cellular system
equipment and ancillary devices.
This manual is not intended to replace the system and equipment
training offered by Motorola, although it can be used to supplement or
enhance the knowledge gained through such training.
To view, download, order manuals (original or revised), visit the
Motorola Lifecycles Customer web page at http://services.motorola.com,
or contact your Motorola account representative.
If Motorola changes the content of a manual after the original printing
date, Motorola publishes a new version with the same part number but a
different revision character.
Text conventions
NOTE
CAUTION
WARNING
The following special paragraphs are used in this manual to point out
information that must be read. This information may be set-off from the
surrounding text, but is always preceded by a bold title in capital letters.
The three categories of these special paragraphs are:
Presents additional, helpful, non-critical information that you can
use.
Bold-text notes indicate information to help you avoid
an undesirable situation or provides additional information
to help you understand a topic or concept.
Presents information to identify a situation in which equipment
damage could occur, thus avoiding damage to equipment.
Presents information to warn you of a potentially hazardous
situation in which there is a possibility of personal injury.
The following typographical conventions are used for the presentation of
software information:
S In text, sans serif BOLDFACE CAPITAL characters (a type style
without angular strokes: i.e., SERIF versus SANS SERIF) are used to
name a command.
Mar 2003
S In text, typewriter style characters represent prompts and the
system output as displayed on an operator terminal or printer.
S In command definitions, sans serif boldface characters represent those
parts of the command string that must be entered exactly as shown and
typewriter style characters represent command output responses
as displayed on an operator terminal or printer.
S In the command format of the command definition, typewriter
style characters represent the command parameters.
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
xiii
Page 21

Foreword
Reporting manual errors
Contact us
Manual banner definitions
68P64115A19–4
To report a documentation error, call the CNRC (Customer Network
Resolution Center) and provide the following information to enable
CNRC to open an MR (Modification Request):
– the document type
– the manual title, part number, and revision character
– the page number(s) with the error
– a detailed description of the error and if possible the proposed solution
Motorola appreciates feedback from the users of our manuals.
Send questions and comments regarding user documentation to the email
address below:
cdma.documentation@motorola.com
Motorola appreciates feedback from the users of our information.
A banner (oversized text on the bottom of the page, for example,
PRELIMINARY) indicates that some information contained in the
manual is not yet approved for general customer use.
24-hour support service
If you have problems regarding the operation of your equipment, please
contact the Customer Network Resolution Center for immediate
assistance. The 24 hour telephone numbers are:
NA CNRC +1–800–433–5202
EMEA CNRC +44– (0) 1793–565444
ASPAC CNRC +86–10–88417733
Japan & Korea CNRC +81–3–5463–3550
LAC CNRC +51–1–212–4020
For further CNRC contact information, contact your Motorola account
representative.
xiv
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
Mar 2003
Page 22
68P64115A19–4
General Safety
Remember! . . . Safety
depends on you!!
Ground the instrument
General Safety
The following general safety precautions must be observed during all
phases of operation, service, and repair of the equipment described in
this manual. Failure to comply with these precautions or with specific
warnings elsewhere in this manual violates safety standards of design,
manufacture, and intended use of the equipment. Motorola, Inc. assumes
no liability for the customer’s failure to comply with these requirements.
The safety precautions listed below represent warnings of certain dangers
of which we are aware. You, as the user of this product, should follow
these warnings and all other safety precautions necessary for the safe
operation of the equipment in your operating environment.
To minimize shock hazard, the equipment chassis and enclosure must be
connected to an electrical ground. If the equipment is supplied with a
three-conductor ac power cable, the power cable must be either plugged
into an approved three-contact electrical outlet or used with a
three-contact to two-contact adapter. The three-contact to two-contact
adapter must have the grounding wire (green) firmly connected to an
electrical ground (safety ground) at the power outlet. The power jack and
mating plug of the power cable must meet International Electrotechnical
Commission (IEC) safety standards.
NOTE
Do not operate in an explosive
atmosphere
Keep away from live circuits
Refer to Grounding Guideline for Cellular Radio Installations –
68P81150E62.
Do not operate the equipment in the presence of flammable gases or
fumes. Operation of any electrical equipment in such an environment
constitutes a definite safety hazard.
Operating personnel must:
S not remove equipment covers. Only Factory Authorized Service
Personnel or other qualified maintenance personnel may remove
equipment covers for internal subassembly, or component
replacement, or any internal adjustment.
S not replace components with power cable connected. Under certain
conditions, dangerous voltages may exist even with the power cable
removed.
S always disconnect power and discharge circuits before touching them.
Do not service or adjust alone
Mar 2003
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
Do not attempt internal service or adjustment, unless another person,
capable of rendering first aid and resuscitation, is present.
xv
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
Page 23
General Safety
Use caution when exposing or
handling the CRT
Do not substitute parts or
modify equipment
Dangerous procedure
warnings
68P64115A19–4
Breakage of the Cathode–Ray Tube (CRT) causes a high-velocity
scattering of glass fragments (implosion). To prevent CRT implosion,
avoid rough handling or jarring of the equipment. The CRT should be
handled only by qualified maintenance personnel, using approved safety
mask and gloves.
Because of the danger of introducing additional hazards, do not install
substitute parts or perform any unauthorized modification of equipment.
Contact Motorola Warranty and Repair for service and repair to ensure
that safety features are maintained.
Warnings, such as the example below, precede potentially dangerous
procedures throughout this manual. Instructions contained in the
warnings must be followed. You should also employ all other safety
precautions that you deem necessary for the operation of the equipment
in your operating environment.
WARNING
Dangerous voltages, capable of causing death, are present in this
equipment. Use extreme caution when handling, testing, and
adjusting.
xvi
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
Mar 2003
Page 24
68P64115A19–4
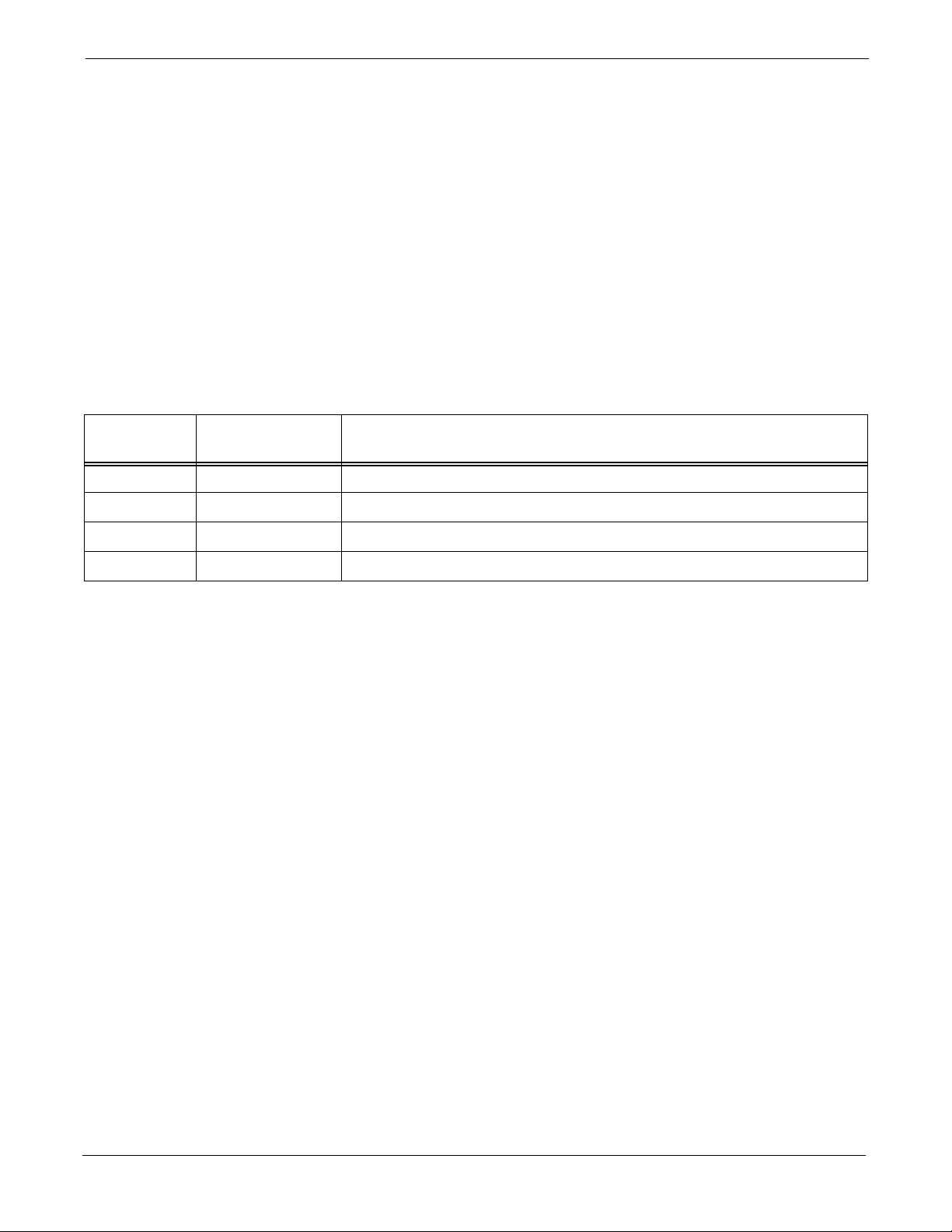
Revision History
Manual Number
Manual Title
Version Information
Version
Level
1 Jan 2003 DRAFT Manual submitted for engineering markup
Date of Issue Remarks
Revision History
68P64115A19–4
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release
R2.16.1.x
The following table lists the manual version, date of version, and
remarks on the version. Revision bars printed in page margins (as shown
to the side) identify material which has changed from the previous
release of this publication.
2 Feb 2003 Preliminary Manual submitted for engineering review
3 Feb 2003 DV&V Test Review
4 Mar 2003 CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
Mar 2003
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
xvii
Page 25

Revision History
Notes
68P64115A19–4
xviii
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
Mar 2003
Page 26

Chapter 1
Manual Overview and BTS General
1
Information
Mar 2003
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
1-1
Page 27

Manual Overview, Abbreviations and Acronyms
68P64115A19–4
1
Manual Overview, Abbreviations and Acronyms
Manual Overview
NOTE
The SC 4812T-MC Base Transceiver Station can be a stand alone BTS,
or can be co-located with an SC 4812T for use as an expansion frame. In
a single stand alone configuration, the SC4812T-MC system is capable
of supporting a maximum of 4 carriers in 3-sector configuration or 2
carriers in 6-sector configuration. With the addition of one expansion
frame, the maximum carrier capacity becomes 8 in a 3-sector
configuration or 4 in a 6-sector configuration.
This document provides information pertaining to the specific hardware
and cable installation of the Motorola 1X SCt4812T–MC BTS
Multicarrier frame.
The basic frame installation procedure is described in the SC Product
Family Frame Mounting Guide – 68P09226A18. For detailed
installation information on non-Motorola equipment, refer to the vendor
manuals provided with such equipment.
This document supports Software Version Release 16.1.
Manual Structure
Chapter 1 – Overview
This chapter provides the following information:
S Overview of manual content (including Abbreviations and Acronyms)
S Required documents
S Site layout
S Frame Identification
Chapter 2 – Inter-frame Cabling
This chapter contains procedures for cabling the BTS frame
configuration and cabling instruction for optional equipment.
Chapter 3 – Expansion Frame Cabling
This chapter contains procedures for cabling the Expansion frame
associated with the configuration of the BTS.
Chapter 4 – Optional Equipment
This chapter provides identification of optional BTS equipment and the
procedures to install the equipment.
Chapter 5 – What’s Next and Cleanup
1-2
This chapter includes site cleanup and a pre-optimization checklist.
Appendix A – Carrier Add
Provides detailed instructions for installing one or more additional
carriers to a BTS frame.
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
Mar 2003
Page 28

68P64115A19–4
Manual Overview, Abbreviations and Acronyms
Abbreviations and Acronyms
Table 1-1 identifies the equipment related abbreviations and acronyms
used in this manual.
1
Table 1-1: Abbreviations and Acronyms
Acronym Definition
AMR Alarm Monitor Reporting
ATP Acceptance Test Procedure or Plan
BBX Broadband Transceiver
BLO Bay Level Offset
BTS Base Transceiver Station
CBSC Centralized Base Station Controller
C-CCP Combined CDMA Channel Processor
CCD CDMA Clock Distribution
CDMA Code Division Multiple Access
CE Channel Element
CLI Command Line Interface
CLPA Higher Power Linear Power Amplifier
CM Channel Module
CMR Cellular Manual Revision
CSM Clock Synchronization Manager
DBPF Dual Bandpass Filter
DBM Debug Monitor
DDC Duplexer/Directional Coupler
DSP Digital Signal Processor
EMPC Expansion Multicoupler Preselector Card
ETM Enhanced Trunking Module
FRU Field Replaceable Unit
FSI Frame Status Indicator
GLI Group Line Interface
GPS Global Positioning System
HSO High Stability Oscillator
I&Q In–phase and Quadrature
LAPD Link Access Protocol “D”
LFR Low Frequency Receiver
LMF Local Maintenance Facility
LORAN Long Range Navigational
LPA Linear Power Amplifier
MC Multicarrier
MCC Multi-channel CDMA
MCIO Multicarrier Combiner Input/Output
. . . continued on next page
Mar 2003
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
1-3
Page 29
Manual Overview, Abbreviations and Acronyms
68P64115A19–4
1
Table 1-1: Abbreviations and Acronyms
Acronym Definition
MCM Multicarrier Module
MGLI Master Group Line Interface
MM Mobility Manager
MMI Man Machine Interface
MPC Multicoupler Preselector Card
MSC Mobile Switching Center
OMCR Operations Maintenance Center – Radio
PAC Power Alarms Card
PCS Personal Communication System
PLC Parallel LPA Combiner
PN Pseudo-random Noise
PSTN Public Switched Telephone Network
PSM Power Supply Module
PWM Pulse Width Monitor
QPSK Quadrature Phase Shift Keyed
RGD Remote GPS Distribution Card
RFDS Radio Frequency Diagnostic Subsystem
RSSI Received Signal Strength Indicator
SCAP Super Cell Application Protocol
TCH Traffic Channel
TSI Time Slot Interchanger
1-4
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
Mar 2003
Page 30

Required Documentation and Environmental Specifications
Required Documentation and Environmental Specifications
Required Documentation
The following documents are required to perform the installation of the
cell site equipment:
S SC Product Family Frame Mounting Guide (Motorola part number
68P09226A18)
NOTE
The Frame Mounting Guide manual is a generic manual
designed to provide specific information needed to install any
SC frame at a variety of sites.
Instructions for installing certain optional material, (i.e.,
directional couplers, circulators, etc.) is also contained in the
Frame Mounting Guide. If your site includes such options, use
the information provided therein.
However, some material in the Frame Mounting Guide may not
apply to your site. The RFDS shown in the Frame Mounting
Guide is for analog cell sites. The Frame Mounting Guide will
be revised to include new options as they become available.
Other optional material, such as duplexers, is contained in this
manual. If your site includes the duplexer option, use the
information provided later in this manual.
1
S 1X SC 4812T-MC BTSOptimization/ATP (Motorola part number
68P64115A21)
S 1X SC 4812T-MC BTS FRU Guide (Motorola part number
68P64115A20)
S Site Document (generated by Motorola Systems Engineering) which
includes:
– trial specific documentation
– channel allocation
– contact list (customer)
– ancillary/expendable equipment list
– site wiring lists
– card placement
– contact list (Motorola support)
– job box inventory
S Demarcation Document (Scope of Work agreement)
S Grounding Guidelines for Cellular Radio Installations (Motorola part
number 68P81150E62)
Mar 2003
S Installation manuals for non-Motorola equipment (for reference
purposes)
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
1-5
Page 31

Required Documentation and Environmental Specifications
68P64115A19–4
1
Specifications
Table 1-2 describes the environmental specifications for the 1X
SCt4812T–MC BTS configuration.
Table 1-2: Environmental Specifications
Specification Description
Operating Temperature 0 Deg C to +50 Deg C
Humidity:
Operating
0 Deg C to +35 Deg C: 20 to 90 percent relative humidity
35Deg C to +50 Deg C: 20 to 80 percent relative humidity
Storage 10 to 95 percent relative humidity non-condensing
Max Absolute Operating/storage humidity not to exceed 0.024 gram H2O/gram dry
air
Storage Temperature –40 Deg C to 60 Deg C
Operating Altitude –61 to 1524 meters above sea level
Seismic per Bellcore GR-63-CORE Zone 3 without top bracing
Zone 4 with top bracing (HILTIHSL M12/25 anchors, or equivalent;
are required for seismic integrity). Note: For raised floor mounting
consult a licensed civil engineer regarding site-specific requirements
and/or consult the Frame Mounting Guide.
3
Airborne Particulate per Bellcore
0 to 25 mg/m
average yearly concentration
GR-63-CORE
Electromagnetic Susceptibility Withstand an electric field due to AC power, having field strength
5 V/m at 50–60 Hz, measured 1 meter from the frame.
Sound Level per Bellcore
GR-63-CORE
75 dBA maximum
56 dBA for 1 carrier/3 sectors at 25 Deg C
1-6
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
Mar 2003
Page 32

68P64115A19–4
BTS Frame Site Layout
BTS Frame Site Layout
Figure 1-1 provides an illustration of the dimensions and clearances for
the BTS.
Figure 1-1:Dimensions and Clearances for the BTS
94.5 in.
(2400 mm)
(recommended
for lighting,
cable trays, etc.)
70.9 in.
(1800 mm)
for BTS
ttti
RECOMMENDED BTS CLEARANCES
5.9 in. (150 mm)
Rear Clearance
0.12 in. (3 mm) spacing
between frames.
1
FRONT VIEW
31.5 in.
(800 mm)
52.4 in.
(1330 mm)
24.2 in.
(615 mm)
TOP VIEW
(Optional
2nd BTS)
FRONT
ti–CDMA–WP–00043–02–ildoc–ftw
23.6 in. (600 mm)
minimum front clearance
for service access
Mar 2003
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
1-7
Page 33

Base Transceiver Station (BTS) Frame Identification
68P64115A19–4
1
Base Transceiver Station (BTS) Frame Identification
BTS Frame
The Motorola SC 4812T–MC BTS (1800 mm) BTS frame contains RX
front-end and CLPAs housed in one frame. For increased channel
capacity, a second frame (called an “Expansion” frame) may be added to
the Starter Frame.
Figure 1-2: SC 4812T–MC BTS Frame
I/O Interconnect
Plate
Fan Module
C–CCP Cage
Power
Amplifier
Cage
C–CCP Cage
and PA Breakers
Enhanced
Trunking Module
TX Filter
ti-CDMA-WP-00196-v01-ildoc-ftw
1-8
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
Mar 2003
Page 34

68P64115A19–4
Base Transceiver Station (BTS) Frame Identification
I/O Plate
1
The I/O plate for the SC4812T–MC BTS Configuration (see Figure 2-1)
contains the following:
S Alarm connectors (2)
S Site I/O
S Span I/O (2)
S RX antenna ports (1–12)
S TX antenna ports (1–12)
S Local Area Network (LAN) A and B Out
S LAN A and B In
S Ground (GND) connection
S RF connector for expansion
S DC power inputs
S Global Positioning Satellite (GPS) connector
S Low Frequency Receiver/High Stability Oscillator (LFR/HSO)
S Remote GPS Distribution (RGD) card (required for expansion only)
S Air Exhaust Region
Site I/O
The Site I/O (see Figure 2-3) contains the following:
S Alarm Monitoring and Reporting connectors (AMR A & AMR B)
S Remote Global Positioning Satellite System (RGPS) connector
S Man Machine Interface (MMI) connector
Span I/O
The Span I/O (see Figure 2-3) contains the following:
S Telco interface to network
S POTS line interface to modem
Combined CDMA Channel Processor (C-CCP) Shelf
The C-CCP shelf (see Figure 1-2) contains the following:
S Low Frequency Receiver/High Stability Oscillator (LFR/HSO)
S Clock Synchronization Manager (CSM) and CSM with GPS
S CDMA Clock Distribution (CCD) cards (2)
S Power Supply cards (2 minimum, 3 maximum)
S Multicoupler Preselector Cards (MPC) (2)
S Alarm Monitoring and Reporting (AMR) cards (2)
S Multi Channel CDMA (MCC8E/MCC24E or MCC–1X) cards
(up to 12)
S Broadband Transceiver (BBX2 or BBX–1X) cards (up to 13)
Mar 2003
NOTE
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
MC uses only BBX–1X or above. BBX2 or lower cards will not
satisfy the Multicarrier requirements.
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
1-9
Page 35

Base Transceiver Station (BTS) Frame Identification
68P64115A19–4
1
S Group Line Interface (GLI) cards (2)
S BBX Switch card
S CCP Fans (3)
S Modem (optional)
Power Distribution Cage MC Configuration
The power distribution cage contains:
S Breaker Assembly
MC CLPA Cage
The MC CLPA cage contains:
S Higher Power Linear Power Amplifiers (CLPAs – 8 maximum per
cage; 16 maximum per frame)
S Fan Modules (4 maximum per cage; 8 maximum per frame)
S PLC (2 maximum per cage; 4 maximum per frame)
S PLC Fillers Panel (2 maximum per cage; 4 maximum per frame)
– Only required in 1–Carrier, 3–Sector MC Operation
S Multicarrier Module (1 maximum per cage; 2 maximum per frame)
MC Module
In-Frame Components
External Components
The Multicarrier Module contains:
S Enhanced Trunking Module (1 maximum per module; 2 maximum
per frame)
S Transmit Filters (3 maximum per module; 6 maximum per frame)
The In-Frame components are:
S Receive Bandpass filters
The external components are:
S Directional Couplers
S Duplexer Directional Couplers (DDCs)
S Radio Frequency Diagnostic Subsystem (RFDS)
1-10
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
Mar 2003
Page 36

Chapter 2
Inter-Frame Cabling
2
Mar 2003
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
2-1
Page 37

Inter-Frame Cabling
68P64115A19–4
Inter-Frame Cabling
Overview
This chapter provides the BTS inter-frame cabling procedures for the SC
2
4812T–MC BTS configuration.
NOTE
Review the Material
Configurations Supported
Cabling Installation Order
Cabling is one of the most noticeable aspects of workmanship.
Straight runs and proper turns are critical for a positive
evaluation of the work. Power and signal cables should be run
with sharp corners, while grounds and antenna lines require
gentle corners.
Before installing cables, it is recommended that you become familiar
with the equipment and the cable connection locations. Start by
reviewing “Connection Locations” topic in this chapter and Table 2-1,
BTS Cable Descriptions and part numbers.
This chapter supports Inter-Frame cabling installation for a Standalone
Base Transceiver Station (BTS) in the following configurations:
S 120 Degree Sector/Sector (3 Sector)
S 60 Degree Sector/Sector (6 Sector)
Cable Labels
To install BTS inter-frame cabling, perform the following procedures in
the order shown:
1. Alarm and Span Line
2. Modem/TELCO (optional)
3. GPS and optional LFR
4. Transmit path – perform one of the following based on site
specifications:
– 120 Degree Sector Transmit Path
– 60 Degree Sector Transmit Path
5. Receive path – Perform one of the following based on site
specifications:
– 120 Degree Sector Receive Path
– 60 Degree Sector Receive Path
6. Earth ground
7. DC power cables
The “Overall Cabling Diagrams and Description” area provides
generalized cabling diagrams and cable descriptions. The labels used to
designate the cables in this area are used throughout this chapter.
2-2
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
Mar 2003
Page 38

68P64115A19–4
Cable Connections
BTS Frame Description
The BTS is the interface between the span lines to/from the Centralized
Base Station Controller (CBSC) and the site antennas. This frame is
described in three sections:
S The top interconnect plate where all connections are made.
S The upper portion of the frame which houses circuit breakers, cooling
fans, and the C–CCP shelf.
S The lower portion of the frame which houses the PA fans, PAs, and
TX filter.
Top I/O (Interconnect) Plate (Figure 2-1 and Figure 2-2)
All cabling to and from the BTS equipment frames is via the I/O
(interconnect) panel on the top of each frame. Connections made here
include:
S Span lines
Cable Connections
2
S RX antennas
S TX antenna
S Alarm connections
S Power input
S LAN connections
S GPS input or Remote Global Positioning System (RGPS) on the Site
I/O Board
S Remote Global Positioning System Distribution (RGD)
S LORAN–C Low Frequency Receiver (LFR) input
S Expansion frame connection
S Ground connections
Mar 2003
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
2-3
Page 39

Cable Connections
68P64115A19–4
Figure 2-1: SC4812T–MC Starter Frame I/O Plate
REMOTE GPS DISTRIBUTION (RGD) MODULE –
USED ONLY IF EXPANSION FRAME(S) INSTALLED
SITE I/O
2
ALARM
CONNECTORS
SPAN I/O
REAR
SPAN I/O A
SPAN I / O
RGPS
SITE I/O
RECEIVE
ANTENNA
CONNECTORS
SPAN I/O B
LAN
CONNECTIONS
ALARM B
ALARM A
ETHERNET ROUTER (IF USED;
OTHERWISE, FILLER PLATE)
SPAN I/O A SITE I/O SPAN I/O B
FRONT
EXP IN FILLER
PLATE
RX
4A
1A
2A
5A
GND
RF GPS IN
HSO/LFR
3A
6A
4B
1B
2B
3B
DC FILTER 2
5B
DC FILTER 1
6B
RX
FILLER PLATE
INPUT
CONNECTOR/
DC FILTER
3 TO 6 TRANSMIT
ANTENNA
CONNECTORS
DEPENDING ON
CONFIGURATION
2 TO 3
TRANSMIT
ANTENNA FILLER
PLATES
DEPENDING ON
CONFIGURATION
RF EXPANSION PORT TO ANOTHER
BTS (USED ONLY IF EXPANSION FRAME
INSTALLED; OTHERWISE, FILLER PLATE
INSTALLED)
ti-CDMA-WP-00188-v01-ildoc-ftwREF
2-4
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
Mar 2003
Page 40

68P64115A19–4
Expansion Frame I/O Plate
Cable Connections
Figure 2-2 provides a detailed view of the connections associated with
the SC4812T–MC Expansion Frame I/O Plate.
Figure 2-2: SC4812T–MC Expansion Frame I/O Plate
SITE I/O
ALARM
CONNECTORS
ALARM B
ALARM A
SPAN I/O
REAR
SPAN I/O A
SPAN I/O A SITE I/O SPAN I/O B
RGPS
SITE I/O
SPAN I / O
RECEIVE
ANTENNA
COVERS
SPAN I/O B
RX
2
LAN
CONNECTIONS
GND
4A
1A
2A
5A
3A
6A
4B
1B
2B
3B
DC FILTER 2
5B
DC FILTER 1
6B
RX
RF GPS IN
HSO/LFR
FILLER PLATE
INPUT
CONNECTOR/
DC FILTER
3 TO 6 TRANSMIT
ANTENNA
CONNECTORS
DEPENDING ON
CONFIGURATION
ETHERNET ROUTER (IF USED;
OTHERWISE, FILLER PLATE)
FRONT
FILLER PLATE
EXP OUT
RF EXPANSION PORT
FROM STAR TER BTS
2 TO 3
TRANSMIT
ANTENNA FILLER
PLATES
DEPENDING ON
CONFIGURATION
ti-CDMA-WP-00189-v01-ildoc-ftw–REF
Mar 2003
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
2-5
Page 41

Cable Connections
Site I/O and Span I/O Boards
Figure 2-3: Site I/O and Span I/O Boards
68P64115A19–4
Figure 2-3 provides a detailed view of the Site I/O and Span I/O boards.
2
50–Pin Telco
SURGE
PROTECTION
SPAN IN
Span I/O
SPAN A TELCO
SPAN B TELSET
ti-CDMA-WP-00009-v01-ildoc-ftw
6–Pin Jack
37–Pin
D–sub
50–Pin
D–sub
8–Pin Jack
8–Pin Jack
AMR B
AMR A
MMI
9–Pin D
Site I/O
REMOTE GPS IN
15–Pin D
OVER VOLTAGE
PROTECTION
Remote GPS Distribution (RGD) Card
Figure 2-4 provides a detailed view of the Remote GPS Distribution
(RGD) card which is used with a Starter BTS to provide signal to the
Expansion frame.
Figure 2-4: RGD Board Cables Connection
Surge Protected
Punch block
RGD
NOTE:
RGD card is required on the Starter frame only.
It provides Remote GPS signal to the Expansion frame.
Site I/O
Remote GPS
Antenna
Expansion 1
Not Used
Not Used
(Main out)
ti-CDMA-WP-00010-v01-ildoc-ftwREF
2-6
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
Mar 2003
Page 42
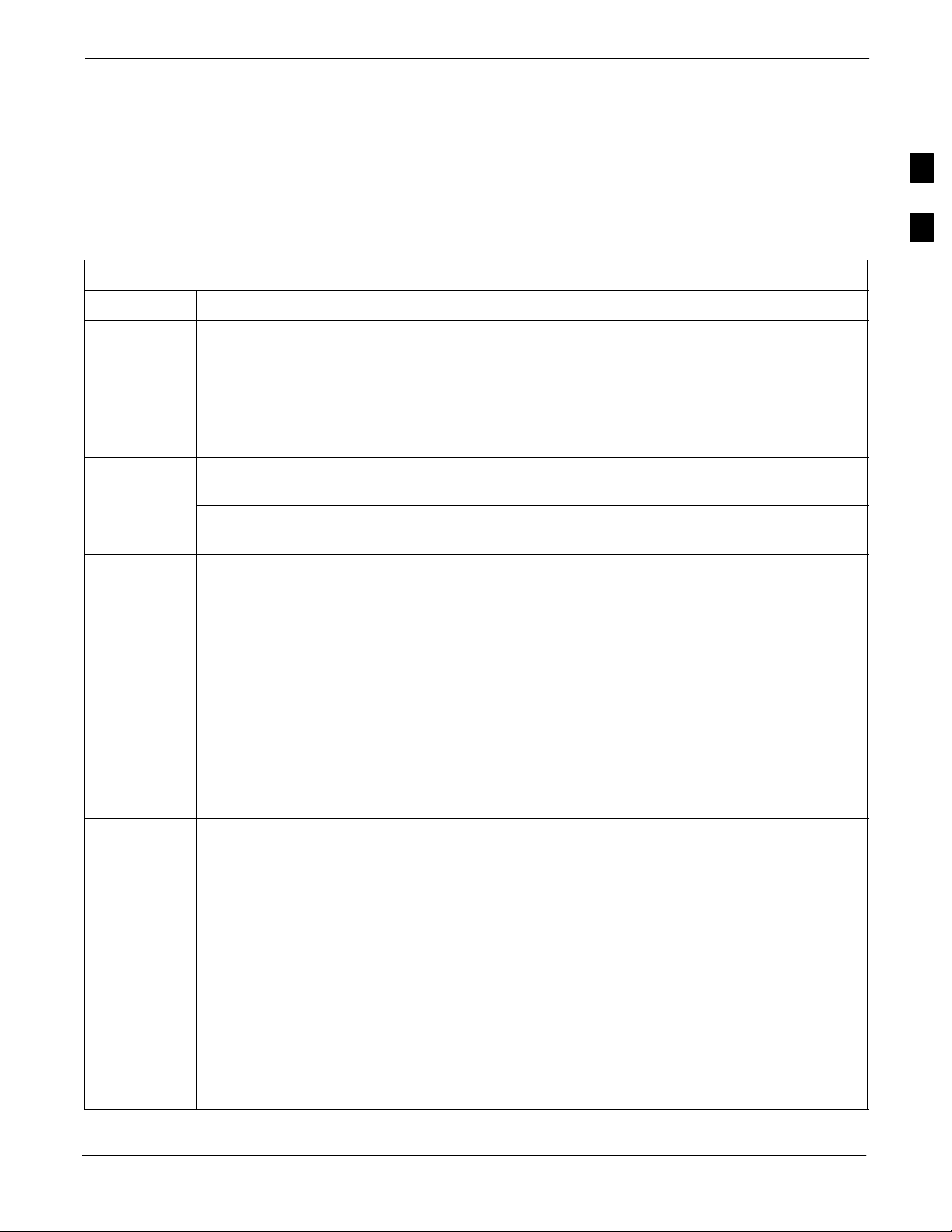
68P64115A19–4
Cabling Diagrams and Descriptions
Cabling Diagrams and Descriptions
Cable Descriptions and Part Numbers
Table 2-1 lists the cable descriptions and part numbers. The letter listed
under the cable label column is used as a reference for ALL cabling
procedures and diagrams in this manual. This information also applies to
all system configurations.
Table 2-1: Cable Descriptions and Part Numbers
Cable Label Part Number Description
A CGDS1583461 Cable, 50-wire, shielded twisted 25 pair, 100 ohm, 24-AWG, 7.6 m
(25 ft), one male TELCO connector attached. One end of cable has
shielded twisted pairs, no connector.
CGDS1583462 Cable, 50-wire, shielded twisted 25 pair, 100 ohm, 24-AWG, 15.2 m
(50 ft), one male TELCO connector attached. One end of cable has
shielded twisted pairs, no connector.
B CGDS1583451 Cable, 60-wire, 100 ohm, 24-AWG, 7.6 m (25 ft), one 60-pin D
connector. One end of cable has shielded twisted pairs.
2
CGDS1583452 Cable, 60-wire, 100 ohm, 24-AWG, 15.2 m (50 ft), one 60-pin D
connector. One end of cable has shielded twisted pairs.
C CGDSMCXNJACK Cable, GPS antenna adapter, OSX connector and female N-type
connector. Mounts inside antenna assembly (assembly #
SGAN4000A)
E CGDS997264 Coaxial cable (RG-58), 50 ohm, shielded, 26 m (85.3 ft), 18 BNC
connectors included.
CGDS997265 Coaxial cable (RG-58), 50 ohm, shielded, 13 m (42.6 ft), 10 BNC
connectors included.
G CGDS2212602 15 ft. Jumper cable, N/M–N/M (only one end of the cable is
terminated with an N connector).
J CGDSGFEL04MS82 Cable, 4-wire, 26-AWG, 25 m (82 ft), two 4-pin RJ-11 connectors
attached to cable.
K N/A Cable, 50 ohm coaxial, two male N-type connectors. Maximum Loss:
< 4.5 dB at 1575 MHz for all cabling and connections between the
GPS antenna and the BTS frame.
Cable style and length is determined by the site configuration. Refer
to the site specific documentation for information about this cable.
The following are maximum suggested cable lengths for three
common cable types:
S RG-393U – with adapter cable and connectors; will accommodate
distances up to 12.5 m (41 ft).
S Andrew FT5-50T – Heliax with adapter cable and connectors; will
accommodate distances up to 39.6 m (130 ft).
S Andrew LDF7-50A – Heliax with adapter cable and connectors;
will accommodate distances up to 100.6 m (330 ft).
Mar 2003
...continued on next page
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
2-7
Page 43

Cabling Diagrams and Descriptions
68P64115A19–4
Table 2-1: Cable Descriptions and Part Numbers
Cable Label DescriptionPart Number
L CGDS315SA038 Cable, 5-wire, 100 ohm, 24-AWG, shielded twisted pair, 91.5 m
(300 ft). One 9-pin sub-miniature D-connector and one 5-pin circular
2
connector.
M N/A Power cable – See Power Cable section for detailed information on
cable termination lugs. Customer supplied cable.
N N/A Ground cable, 6-AWG, insulated copper wire, loop connectors.
Customer supplied cable.
2-8
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
Mar 2003
Page 44
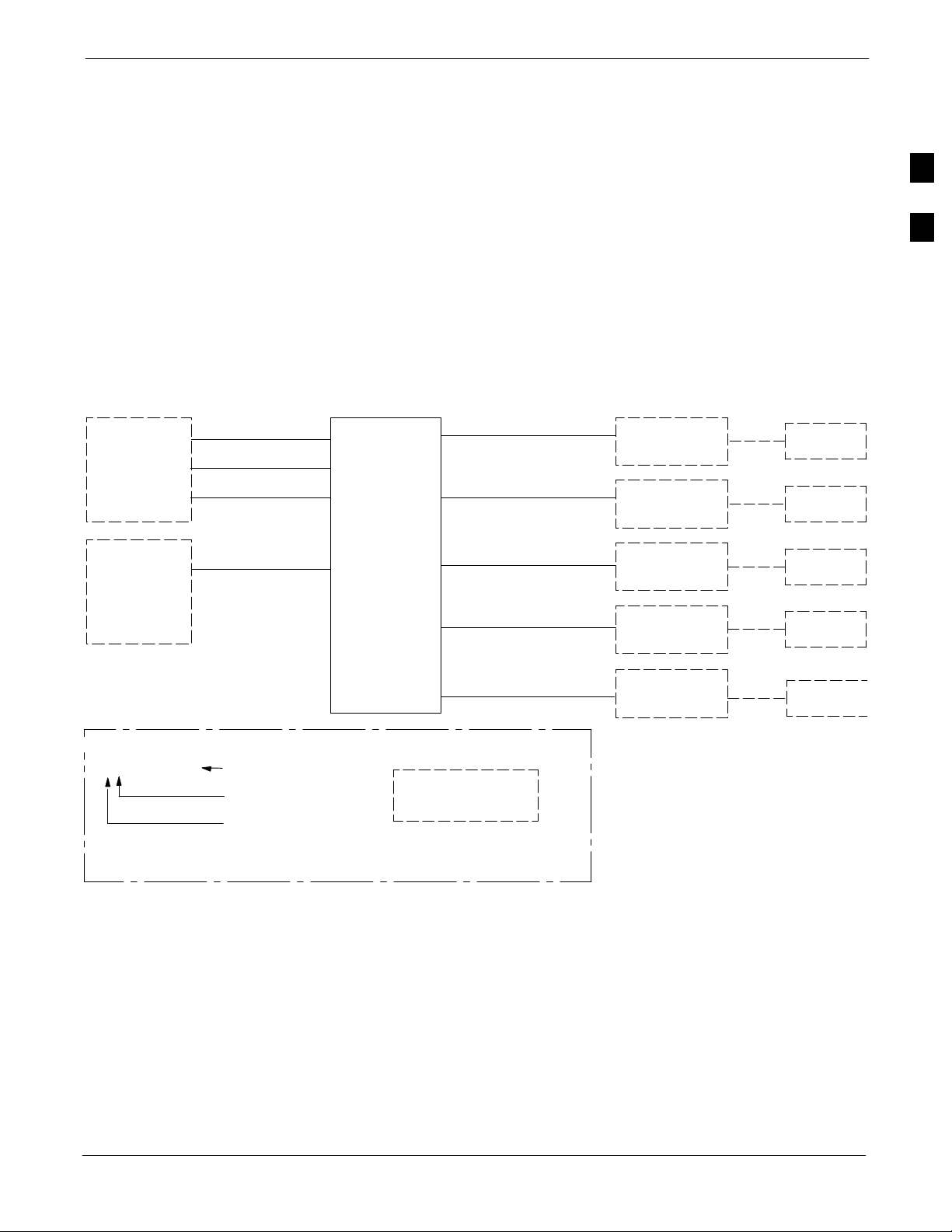
68P64115A19–4
Overall Cabling Diagram (Single Frame)
Omni Systems
The following diagram shows the overall BTS cabling (power and
ground cables are not shown) for an Omni/Omni system. Table 2-1
contains the detailed cable descriptions.
3 and 6 Sector Systems
Figure 2-5 also represents the overall BTS cabling (power and ground
cables are not shown) for a 3 and 6 sector CDMA system. Refer to the
legend in the following diagram and Table 2-1 for detailed cable
descriptions.
Figure 2-5: Overall Signal Cabling Diagram for CDMA Systems
Cabling Diagrams and Descriptions
2
TERMINATION
EQUIPMENT
PHONE
LEGEND
B/2 (ALARMS)
J/1 (MODEM/TELCO)
A/2 (SPAN LINES)
B/2 (ALARMS)
J/1 (TELSET)
NAME
NUMBER OF CABLES
CABLE LABEL
(OMNI) = OMNI/OMNI SYSTEMS
(SECTOR) = 60/120 DEGREE SECTOR/SECTOR SYSTEMS
BTS
FRAME
Indicates equipment
existing prior to this
(CDMA ONLY)
(CDMA ONLY)
G/3 (3Sectors 1–4 CARRIER)
G/6 (6Sectors 1–2 CARRIER)
TX ANTENNAS
G/6 (3 SECTORS)
G/12 (6 SECTORS)
RX ANTENNAS
installation.
K/1 (GPS)
L/1 (LFR)
LIGHTNING
ARRESTOR
LIGHTNING
ARRESTOR
LIGHTNING
ARRESTOR
LIGHTNING
ARRESTORS
LIGHTNING
ARRESTORS
GPS
ANTENNA
LFR
ANTENNA
TX
ANTENNA
RX
ANTENNA
REMOTE
GPS
ti-CDMA-WP-00045-v01-ildoc-ftw
Mar 2003
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
2-9
Page 45

Alarm / Span Cabling
68P64115A19–4
Alarm / Span Cabling
Objective
The objective of this procedure is to install the BTS alarm and span line
2
Cable Labels
Equipment Needed
Table 2-2: Cables Needed for Alarm and Span Line Cabling
Cable Qty. Part Number Description
A 1 or 2 CGDS1583461 Cable, 50-wire, shielded twisted 25 pair, 100 ohm, 24-AWG, 7.6 m
cabling.
The cable designations are referenced to Table 2-1 in the “Overall
Cabling Diagrams and Description” area.
Table 2-2 lists the quantity and description of the required cables.
(25 ft), one male TELCO connector attached. One end of cable has
shielded twisted pairs, no connector.
CGDS1583462 Cable, 50-wire, shielded twisted 25 pair, 10 ohm, 24-AWG, 15.2 m
(50 ft), one male TELCO connector attached. One end of cable has
shielded twisted pairs, no connector.
B 2 CGDS1583451 Cable, 60-wire, 100 ohm, 24 AWG, 7.6 m (25 ft), one 60-pin
connector. One end of cable has shielded twisted pairs.
CGDS1583452 Cable, 60-wire, 100 ohm, 24 AWG, 15.2 m (50 ft), one 60-pin
connector. One end of cable has shielded twisted pairs.
2-10
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
Mar 2003
Page 46

68P64115A19–4
T
Cabling Diagram
Figure 2-6 illustrates the recommended BTS span and alarm cabling.
Figure 2-6: Alarm and Span Line Cabling Details
TERMINATION
EQUIPMENT
BB
ALARM_B
ALARM_A
Alarm / Span Cabling
2
A
50–Pin Telco
SPAN IN
SC 4812T–MC
Cable Run List
SPAN
I/O A
SPAN
I/O B
SURGE
PROTECTION
SPAN A TELCO
SPAN B TELSET
Span I/O
ti-CDMA-WP-00046-v02 ildoc–ftw
Table 2-3 provides the cable run list for alarm and span line cabling.
Table 2-3: Cable Run List for Alarm and Span Line Cabling
6–Pin Jack
37–Pin
D–sub
Cable From BTS Connector To
A SPAN LINE (on Span I/O board) Termination Equipment
B ALARM A
ermination Equipment
ALARM B
* IMPORTANT
Site I/O and Span I/O boards are located on the top of the BTS frame.
Mar 2003
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
2-11
Page 47

Alarm / Span Cabling
Install Span and Alarm Cables
Install the cables by using the cable run list provided in Table 2-3, by
referencing Figure 2-6, and by following the procedures in Table 2-4
through Table 2-6.
68P64115A19–4
2
Table 2-4: Procedure to Install Span Line A Cable
Step Action
1 Connect the TELCO connector of cable A to the SPAN LINE connector of Span I/O board A.
2 Route the cable to the termination equipment.
3 Cut the cable to length, and connect it to the termination equipment. Refer to Figure 2-7 and Table 2-8
for pin and signal information.
Span I/O Board (A) Installation
Perform the following procedure to connect cable A, to Span I/O board
A.
Span I/O Board (B) Installation
Perform the following procedure to connect cable A, to Span I/O board
B.
Table 2-5: Procedure to Install Span Line B Cable
Step Action
1 Connect the TELCO connector of cable A to the SPAN LINE connector of Span I/O board B.
2 Route the cable to the termination equipment.
3 Cut the cable to length, and connect it to the termination equipment. Refer to Figure 2-7 and Table 2-8
for pin and signal information.
Alarm Cable Installation
Perform the following procedure to install the alarm cables.
Table 2-6: Procedure to Install Alarm Cables
Step Action
1 Connect the 60-pin connector of one cable B to the ALARM A connector.
2 Route the cable to the termination equipment.
3 Cut the cable to length and connect it to the termination equipment. Refer to Figure 2-8, and Table 2-9
for pin and signal information. Alarm signal specifications are described on the following page.
4 Repeat Steps 1 through 3, using the other cable B and the ALARM B connector.
2-12
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
Mar 2003
Page 48

68P64115A19–4
Alarm Signal Specifications
Alarm / Span Cabling
There are two ALARM connectors, A and B. A connector is always
functional; B is only functional when an AMR module is equipped in the
AMR 2 slot in the Combined CDMA Channel Processing Shelf
(C-CCP).
2
Function
ALARM connectors provide for Customer Defined Alarm Inputs and
Outputs. The customer can connect BTS site alarm input sensors and
output devices to the BTS, thus providing alarm reporting of active
sensors as well controlling output devices.
ALARM A connector provides 18 inputs and 8 outputs. ALARM B
connector provides 17 inputs and 8 outputs. If both AMR cards are
present, 35 inputs and 16 outputs are available.
Power Alarms Card (PAC)
The PAC combines alarms from five (5) power supply modules in the
BTS, generating one alarm output. The alarm signal is output through
the Alarm B connector, as follows:
NOTE
CAUTION
S Major alarm – pin 29
S Major alarm return – pin 30
Alarm B pin connections above are for –48V frame application
only. These pins ar not used in the +27V application.
These pins are NOT to be used as a customer defined input or
the PSM alarms will not function correctly.
Internal Connections
Both ALARM A and B connectors are cabled to the C-CCP shelf
backplane CUSTOMER I/O connector via a single 120-wire (twisted
pair) shielded cable. The inputs/outputs of ALARM A connector are
supported by the control interface module AMR 1. The input/outputs of
ALARM B connector are supported by the optional control interface
module AMR 2. The AMR detects signals from input sensors and
provides relay controlled switched contacts to output devices.
External Connections
Table 2-7 describes the characteristics and requirements for the inputs
(each of which consists of a wire/pin pair) and outputs (each of which
consists of 3-wires/pins–COM, NC, and NO).
Mar 2003
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
2-13
Page 49

Alarm / Span Cabling
Table 2-7: External Alarm Connector Characteristics and Requirements
68P64115A19–4
Inputs Outputs
To ensure proper operation, each pair to be used must be
connected to an external sensor that provides a dry-contact
2
closure. The customer sensor output contacts between an
optically isolated 9V DC signal and an isolated return.
S 10k ohms or greater across the input pair is detected as an
open contact.
S 1k ohms or less across the input pair is detected as a closed
contact.
Either of the above states can be defined by the customer in
system software as an alarm condition.
The customer output device control inputs
connect between the common (COM) and
either the normally closed (NC) or normally
open (NO) contacts of a relay.
S Relay contacts are load rated for a
maximum of 1 A @ 24 Vdc and 0.5 A @
48 Vdc.
The toggling of the relay contacts to the
opposite state is controlled by system
software.
2-14
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
Mar 2003
Page 50

68P64115A19–4
Span Line Cable Pin Numbering
Figure 2-7 shows the pin numbering for Cable A – CGDS1583461,
CGDS1583462. Table 2-8 provides the Telco connector pin out
designators on the Span I/O PCB.
Alarm / Span Cabling
Figure 2-7: Cable A (Span Line) Pin Numbering
50
26
(MALE 50–PIN TELCO)
25
1
Table 2-8: Span I/O Connector
Span
I/O
T1 Signal
Name
A B
RX1 RX_TIP_1 1 BLU/WHT RX_RING_1 26 WHT/BLU
Span # 1 2
TX1 TX_TIP_1 2 ORG/WHT TX_RING_1 27 WHT/ORG
CABLES CGDS1583461 AND CGDS1583462
LOOSE WIRES, NO CONNECTOR
ti-CDMA-WP-00013-v01-ildoc-ftw
Input
Wire Color Signal Name Input
Pin
2
Wire Color
Pin
Span # 3 4
Span # 5 6
RX2 RX_TIP_2 3 GRN/WHT RX_RING_2 28 WHT/GRN
TX2 TX_TIP_2 4 BRN/WHT TX_RING_2 29 WHT/BRN
RX3 RX_TIP_3 5 SLT/WHT RX_RING_3 30 WHT/SLT
TX3 TX_TIP_3 6 BLU/RED TX_RING_3 31 RED/BLU
Mar 2003
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
2-15
Page 51

Alarm / Span Cabling
Alarm Connectors Pin and Signal Information
Figure 2-8 shows the Alarm A and B pin numbering for Cable B CGDS1583451, CGDS1583452, respectively. Pin and signal information
are described in Table 2-9 for Alarm A and Table 2-10 for Alarm B.
68P64115A19–4
2
Figure 2-8: Cable B (Alarm) Pin Numbering
60
4
2
(FEMALE 60-PIN)
59
5758
3
1
CABLES CGDS1583451 AND CGDS1583452
LOOSE WIRES, NO CONNECTOR
ti-CDMA-WP-00014-v01-ildoc-ftw
2-16
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
Mar 2003
Page 52

68P64115A19–4
Table 2-9: Pin and Si
l Inf
ALARM A C
Alarm / Span Cabling
gna
ormation for
onnectors
Pin Wire Color Signal Name Pin Wire Color Signal Name
1 BLU/WHT A CDO1 NC 16 RED/GRN A CDO6 NC
2 WHT/BLU A CDO1 COM 17 BRN/RED A CDO6 COM
3 ORG/WHT A CDO1 NO 18 RED/BRN A CDO6 NO
4 WHT/ORG A CDO2 NC 19 SLT/RED A CDO7 NC
5 GRN/WHT A CDO2 COM 20 RED/SLT A CDO7 COM
6 WHT/GRN A CDO2 NO 21 BLU/BLK A CDO7 NO
7 BRN/WHT A CDO3 NC 22 BLK/BLU A CDO8 NC
8 WHT/BRN A CDO3 COM 23 ORG/BLK A CDO8 COM
9 SLT/WHT A CDO3 NO 24 BLK/ORG A CDO8 NO
10 WHT/SLT A CDO4 NC 25 GRN/BLK Cust Retn 1
11 BLU/RED A CDO4 COM 26 BLK/GRN A CDI 1
12 RED/BLU A CDO4 NO 27 BRN/BLK Cust Retn 2
13 ORG/RED A CDO5 NC 28 BLK/BRN A CDI 2
14 RED/ORG A CDO5 COM 29 SLT/BLK Cust Retn 3
15 GRN/RED A CDO5 NO 30 BLK/SLT A CDI 3
Pin Wire Color Signal Name Pin Wire Color Signal Name
2
31 BLU/YEL CUST RTRN 4 46 VIO/GRN A CDI 11
32 YEL/BLU A CDI 4 47 BRN/VIO CUST RTRM 12
33 ORG/YEL CUST RTRN 5 48 VIO/BRN A CDI 12
34 YEL/ORG A CDI 5 49 SLT/VIO CUST RTRM 13
35 GRN/YEL CUST RTRN 6 50 VIO/SLT A CDI 13
36 YEL/GRN A CDI 6 51 RED/WHT CUST RTRM 14
37 BRN/YEL CUST RTRN 7 52 WHT/RED A CDI 14
38 YEL/BRN A CDI 7 53 BLK/WHT CUST RTRM 15
39 SLT/YEL CUST RTRN 8 54 WHT/BLK A CDI 15
40 YEL/SLT A CDI 8 55 YEL/WHT CUST RTRM 16
41 BLU/VIO CUST RTRN 9 56 WHT/YEL A CDI 16
42 VIO/BLU A CDI 9 57 VIO/WHT CUST RTRM 17
43 ORG/VIO CUST RTRN 10 58 WHT/VIO A CDI 17
44 VIO/ORG A CDI 10 59 BLK/RED CUST RTRM 18
45 GRN/VIO CUST RTRN 11 60 RED/BLK A CDI 18
NC – normally closed, NO – normally open, Com – common, CDO – Customer Defined Output,
CDI – Customer Defined Input
All Cust Rtrm 1–18 are electronically tied together at the RFMF.
The A CDI numbering is from the LMF/OMCR/CBSC perspective. LMF/OMCR/CBSC starts the numbering at 1 (giving
1 – 18). Actual cable hardware starts the numbering at 0 (giving 0–17)
Mar 2003
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
2-17
Page 53

Alarm / Span Cabling
68P64115A19–4
Table 2-10: Pin and Signal Information for ALARM B Connectors
Pin Wire Color Signal Name Pin Wire Color Signal Name
1 BLU/WHT B CDO9 NC 16 RED/GRN B CDO14 NC
2 WHT/BLU B CDO9 COM 17 BRN/RED B CDO14 COM
2
3 ORG/WHT B CDO9 NO 18 RED/BRN B CDO14 NO
4 WHT/ORG B CDO10 NC 19 SLT/RED B CDO15 NC
5 GRN/WHT B CDO10 COM 20 RED/SLT B CDO15 COM
6 WHT/GRN B CDO10 NO 21 BLU/BLK B CDO15 NO
7 BRN/WHT B CDO11 NC 22 BLK/BLU B CDO16 NC
8 WHT/BRN B CDO11 COM 23 ORG/BLK B CDO16 COM
9 SLT/WHT B CDO11 NO 24 BLK/ORG B CDO16 NO
10 WHT/SLT B CDO12 NC 25 GRN/BLK B CDI 19
11 BLU/RED B CDO12 COM 26 BLK/GRN Cust Retn 19
12 RED/BLU B CDO12 NO 27 BRN/BLK B CDI 20
13 ORG/RED B CDO13 NC 28 BLK/BRN Cust Retn 20
14 RED/ORG B CDO13 COM 29 Power Supply Module Alarm*
15 GRN/RED B CDO13 NO 30 Power Supply Module Alarm Return*
Pin Wire Color Signal Name Pin Wire Color Signal Name
31 BLU/YEL B CDI 22 46 VIO/GRN CUST RTRM 29
32 YEL/BLU CUST RTRN 22 47 BRN/VIO B CDI 30
33 ORG/YEL B CDI 23 48 VIO/BRN CUST RTRM 30
34 YEL/ORG CUST RTRN 23 49 SLT/VIO B CDI 31
35 GRN/YEL B CDI 24 50 VIO/SLT CUST RTRM 31
36 YEL/GRN CUST RTRN 24 51 RED/WHT B CDI 32
37 BRN/YEL B CDI 25 52 WHT/RED CUST RTRM 32
38 YEL/BRN CUST RTRN 25 53 BLK/WHT B CDI 33
39 SLT/YEL B CDI 26 54 WHT/BLK CUST RTRM 33
40 YEL/SLT CUST RTRN 26 55 YEL/WHT B CDI 34
41 BLU/VIO B CDI 27 56 WHT/YEL CUST RTRM 34
42 VIO/BLU CUST RTRN 27 57 VIO/WHT B CDI 35
43 ORG/VIO B CDI 28 58 WHT/VIO CUST RTRM 35
44 VIO/ORG CUST RTRN 28 59 BLK/RED B CDI 36
45 GRN/VIO B CDI 29 60 RED/BLK CUST RTRM 36
NC – normally closed, NO – normally open, Com – common, CDO – Customer Defined Output,
CDI – Customer Defined Input
All Cust Rtrm 19–36 are electronically tied together at the RFMF.
The A CDI numbering is from the LMF/OMCR/CBSC perspective. LMF/OMCR/CBSC starts the numbering at 19 (giving
19 – 36). Actual cable hardware starts the numbering at 0 (giving 0–17)
*CAUTION
Reserved for PSM Alarm signal (–48V application ONLY). DO NOT use these pins for CDOs or CDIs.
2-18
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
Mar 2003
Page 54

68P64115A19–4
Equipment Compliance
Equipment Compliance
This equipment complies with Part 68 of the Federal communications
commission (FCC) Rules and regulations. On the top of the Frame is a
label, located inside the cabinet frame on the top, left side, that contains,
among other information, the FCC Registration Number and Ringing
Equivalence Number (REN) for this equipment. If requested, this
information must be provided to the telephone company.
The REN is useful to determine the quantity of the devices which may
connect to the telephone line. Excessive REN’s on the telephone line
may result in the devices not ringing in response to incoming call. In
most, but not all areas, the sum of the REN’s should not exceed five
(5.0). To be certain of the number of devices that may be connected to
the line as determined by the total REN’s, contact the telephone
company to determine the maximum REN for the calling area.
If the dial-in site access modem causes harm to the telephone network,
the telephone company will notify you in advance that temporary
discontinuance of service may be required. If advance notice is not
practical, the telephone company will notify you of the discontinuance as
soon as possible. Also, you will be advised of your right to file a
complaint with the FCC if you believe it is necessary.
2
The telephone company may make changes in its facilities, equipment,
operations, or procedures that could affect the operation of your dial-in
site access modem. If this happens, the telephone company will provide
advance notice so that you can modify your equipment as required to
maintain uninterrupted service.
If you experience trouble with the dial-in site access modem, contact
Motorola Service Center for repair and/or warranty information:
Motorola Cellular Service Center (MCSC)
1501 W. Shure Drive
Arlington Heights, Illinois 60004
Phone Number: (847) 632–5390
If the trouble is causing harm to the telephone network, the telephone
company may request you to disconnect the equipment from the network
until the problem is solved. You should not attempt to repair this
equipment yourself. This equipment contains no customer or
user-serviceable parts.
Changes or modifications not expressly approved by Motorola could
void your authority to operate this equipment.
Mar 2003
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
2-19
Page 55

BTS System Timing Options
BTS System Timing Options
Timing Sources
68P64115A19–4
2
The BTS is able to receive timing information from the following
sources:
S RF Global Positioning Satellite (RF GPS)
S Remote GPS (RGPS)
S Low Frequency Receiver (LFR)
S High Stability Oscillator (HSO)
Customers have the option of installing either an RF GPS or Remote
GPS. Site characteristics determine the cabling to be installed (GPS,
LFR or HSO, if any).
Timing sources can be used independently. However, in typical
applications, sites are outfitted in pairs so that if a failure occurs in the
main source, a backup system will provide timing to keep the cell site in
operation.
Typical installations include:
S RF GPS with LFR backup
S Remote GPS with LFR backup
S GPS with LFR or HSO backup
Each of these cabling installations are described in the following
sections.
2-20
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
Mar 2003
Page 56

68P64115A19–4
RF Global Positioning Satellite (RF GPS) Cabling
RF Global Positioning Satellite (RF GPS) Cabling
RF GPS Cabling Diagram
Figure 2-9 shows a detailed diagram of RF GPS cabling in the Starter
frame. Refer to Table 2-1 for a description of the cables required for
installing the RF GPS.
Figure 2-9: RF GPS Cabling Detail
2
Starter BTS
NOTE: Surge protection for the GPS
antenna must pass 5 Vdc.
K
Surge Protector
K
Cable C is mounted
inside the antenna
assembly.
C
RF GPS
ANTENNA
Mar 2003
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
2-21
Page 57

RF Global Positioning Satellite (RF GPS) Cabling
Cable Run List
Table 2-11 lists the cable runs for the BTS GPS and LFR cables. If
lightning arrestors are used with the LFR antenna, refer to the site
specific documentation for cabling information.
68P64115A19–4
2
Cable From Connector To
Table 2-11: Cable Run List for GPS and LFR Cabling
K GPS GPS Antenna
RF GPS Cabling Installation Procedure
Install each cable by referring to the cable run list in Table 2-1, the
cabling diagram in Figure 2-9, and the procedure in Table 2-12. If
lightning arrestors are used with the RF GPS antenna, refer to the site
specific documentation for cabling information.
NOTE
Table 2-12: Procedure to Install the RF GPS Cabling
Step Action
1 Follow the OEM information to disassemble the GPS antenna and gain access to the OSX connector.
2 Connect the the OSX connector of cable C to the antenna.
3 Follow the OEM information to assemble the GPS antenna with cable C attached.
Site specific characteristics determine the GPS/LFR cabling that
is installed.
4 Connect one end of cable K to the N-type connector of cable C.
5 Connect the other end of cable K to the GPS connector on the BTS.
2-22
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
Mar 2003
Page 58

68P64115A19–4
Remote Global Positioning Satellite (RGPS) Cabling
Remote Global Positioning Satellite (RGPS) Cabling
RGPS Cabling Diagrams
Figure 2-10 depicts the detail for mounting the RGPS antenna and the
cable leading to the BTS. Figure 2-11 shows the detailed remote GPS
cabling diagram.
2
NOTE
Figure 2-10: Remote GPS Mounting Detail
The Remote GPS cable is comprised of 6-twisted pairs of wires.
For proper Remote GPS operation, each black wire in this cable
is unique and MUST be paired with its proper mate.
Mar 2003
CLAMP
BRACKETS (2)
WALL MOUNTING
BRACKETS (2)
CABLE TO BTS
ti-CDMA-WP-00016-v01-ildoc-ftw
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
2-23
Page 59

Remote Global Positioning Satellite (RGPS) Cabling
Figure 2-11: Remote GPS Cabling Diagram
Remote GPS
Antenna
68P64115A19–4
2
Surge
Protected
Punchblock
(Customer
supplied)
A1
AMR A
A2
MMI
Cabling Run List
Table 2-13 provides a listing of the cables need for installing the Remote
GPS option.
Table 2-13: Remote GPS Cable Descriptions and Part Numbers
Cable
Label
A
A
Part Number Description
1
T472Ax
RGD Antenna to Punchblock Cable; x=A–F for
different A1 cable length 50 feet to 2000 feet
2
3086433H07 Punchblock to Site I/O board
Install RGPS Cable
Install each cable by referring to the cable run list in Table 2-13, the
cabling diagram in Figure 2-11, and the procedure in Table 2-14. If
lightning arrestors are used with the RGPS, refer to the site specific
documentation for cabling information.
NOTE
Table 2-14: Installing the RGPS Cabling
Step Action
1 Connect cables A1 and A2 into the punch block, as if they were part of the same cable, cut in the
middle maintaining color code and signal integrity..
2 Connect the same corresponding color on both sides of the punchblock (see Figure 2-11).
Site specific characteristics determine the GPS/LFR cabling that
is installed.
2-24
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
Mar 2003
Page 60

68P64115A19–4
Low Frequency Receiver / High Stability Oscillator (LFR/HSO) Cabling
Low Frequency Receiver / High Stability Oscillator (LFR/HSO)
Cabling
Overview
Cable Labels
Cable Run List
Procedure
This section provides the information to install the Low Frequency
Receiver/High Stability Oscillator (LFR/HSO) cabling for CDMA
systems.
The cable designations are referenced in Table 2-1 on 2-7 in the “Overall
Cabling Diagrams and Description” area.
Table 2-15 lists the cable runs for the BTS GPS and LFR cables. If
lightning arrestors are used with the LFR antenna, refer to the site
specific documentation for cabling information.
Table 2-15: Cable Run List for GPS and LFR Cabling
Cable From Connector To
L LFR LFR Antenna
Install each cable by referring to the cable run list in Table 2-15, the
cabling diagram in Figure 2-9, and the procedure in Table 2-16. If
lightning arrestors are used with the LFR antenna, refer to the site
specific documentation for cabling information.
2
NOTE
Table 2-16: Procedure to Install LFR Cabling
Step Action
1 Attach the 9-pin subminiature connector of cable L to the LFR connector of the BTS.
2 Attach the 5-pin circular connector of cable L to the LFR antenna.
Mar 2003
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
Site specific characteristics determine the GPS/LFR cabling that
is installed.
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
2-25
Page 61

Low Frequency Receiver / High Stability Oscillator (LFR/HSO) Cabling
68P64115A19–4
LFR Cable (Cable L) Pin/Signal Information
The pin/signal information for the LFR cable is presented in Table 2-17.
This information applies to the standard LFR cable.
Table 2-17: Pin /Signal Information for LFR Cable (Cable C)
2
9-Pin D Connector
Pin Number for Connector Type
5-Pin Circular
(for antenna/preamplifier)
Wire Color Description
1 D Red Antenna +
(power and signal)
6 E Black
(paired with red)
Antenna –
(power and signal)
5 A White Calibrator +
9 B Black
Calibrator –
(paired with white)
3 C Bare Drain from shield
2-26
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
Mar 2003
Page 62

68P64115A19–4
RX Antenna Connections
1A
4A
1A
4A
RXRX
I/O Plat
2B
5B
2B
5B
BTS Antenna Configuration
Overview
This section provides detail on the antenna configurations supported by
the BTS, including:
S 3 Sector
S 6 Sector
RX Antenna Configurations
Table 2-18 provides the RX antenna configurations for the BTS.
Table 2-18: RX Antenna Configuration
BTS Antenna Configuration
2
Configuration
3 Sector 6 Sector
1A S1 Main S1 Main
1B S1 Div S1 Div
2A S2 Main S2 Main
2B S2 Div S2 Div
3A S3 Main S3 Main
3B S3 Div S3 Div
4A S4 Main
4B S4 Div
5A S5 Main
5B S5 Div
6A S6 Main
6B S6 Div
RX Antenna Connections
2A
5A
6A
3A
RX
1B
4B
e
2B
5B
6B
3B
3 Sector 6 Sector
2A
3A
1B
2B
3B
5A
6A
RX
4B
5B
6B
Mar 2003
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
2-27
Page 63

BTS Antenna Configuration
4
D
TX Antenna Configurations
68P64115A19–4
Table 2-19, show configurations for a fully populated SC 4812T–MC
frame with 4X4 ETM. For a SC 4812T–MC frame populated with a 3X3
ETM the lower right quadrant will not be populated.
2
Table 2-19, also displays the I/O plate for 3 to 6 Transmit Antenna
Connectors (depending on configuration) and
2 to 3 Transmit Antenna
Filler plates (depending on configuration).
Table 2-19: Multicarrier BTS TX Antenna Configuration
TX Filter
Sector/Carrier
BTS TX Ports
3 Sector 6 Sector
TX 1 S1/C1–C4 S1/C1–C2
I/O Plate
1
3
2
TX
56
TX 2 S2/C1–C4 S2/C1–C2
TX 3 S3/C1–C4 S3/C1–C2
7
8
9
TX 4 S4/C1–C2
TX 5 S5/C1–C2
TX 6 S6/C1–C2
FILLER PLATE
Max No. Carriers 4 2
SC4812T–MC
Carrier
Numbering
3 Sector
(6 Sector)
3 Sector and 6 Sector
Carrier
Numbering
3 Sector
(6 Sector)
CLPA
CLPA
CLPA
CLPA
2B
4B
2D
4D
CLPACLPA
CLPA
CLPA
CLPA
3B
1D
3D
C1 (C1)
C2 (C2)
C3 (C1)
C4 (C2)
C1 (C1)
C2 (C2)
C3 (C1)
C4 (C2)
C1 (C1)
C2 (C2)
C3 (C1)
C4 (C2)
C1 (C1)
C2 (C2)
C3 (C1)
C4 (C2)
CLPA
CLPA
CLPA
CLPA
1A 1B
MCM
3A
1C
3C
1
S3
S2
S1
MCM
2
S6
S5
S4
2A
CLPA
4A
CLPA
2C
CLPA
4C
NOTES:
1. C1, C2, C3 and C4 denote carriers 1, 2, 3 and 4, respectively.
2. The maximum number of CLPAs for a given carrier is shown.
3. SC 4812T–MC frames with a 3 X 3 ETM, the lower right quadrant will not be populated.
4. SC 4812T–MC frame with a 3 Sector configuration only one MCM is used.
2-28
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
Mar 2003
ti-C
Page 64

68P64115A19–4
BTS 60 Degree Sector (6 Sector) Transmit Path Cabling
BTS 60 Degree Sector (6 Sector) Transmit Path Cabling
Objective
The objective of this procedure is to install the BTS transmit path
cabling.
Cable Labels
The cable designations referenced in Table 2-20, provide the quantities
and descriptions of the cables required for the procedure.
Cabling Diagram
Figure 2-12 and Figure 2-13 shows direct connect cable configurations
(both inside and outside the BTS frame). Table 2-21 describes the
antenna cable connection ports.
Figure 2-12: 60 Degree Sector (6 Sector) Transmit Path Cabling Details (Outside Frame)
2
1
.
.
6
ANTENNA
LIGHTNING
ARRESTOR
DIRECT CONNECT
1
.
.
6
6
CARRIER 1 & 2
G (See Table 2-20)
I/O PLATE
123
456
789
10 11 12
ti-CDMA-WP-00048-v04-ildoc-ftw–REF
TX OUT
Mar 2003
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
2-29
Page 65

BTS 60 Degree Sector (6 Sector) Transmit Path Cabling
Figure 2-13: 60 Degree Sector (6 Sector) Transmit Path Cabling Details (Inside frame)
68P64115A19–4
TX1 TX2 TX3
BBX–1
S1 C1
2
BBX–2
S2 C1
BBX–3
S3 C1
BBX–4
S1 C3
BBX–5
S2 C3
BBX–6
S3 C3
BBX–7
S1 C2
BBX–8
S2 C2
BBX–9
S3 C2
BBX–10
S1 C4
BBX–11
S2 C4
BBX–12
S3 C4
J1
TX1
TX2
TX3
TX4
HARTING 6–PACKHARTING 6–PACK
TX5
TX6
6–Sector
MCPA CIO
J5
TX7
TX8
TX9
TX10
TX11
TX12
HARTING 6–PACK
J7
C–CCP BACKPLANE
J14
PA1PA2PA3PA4PA5PA6 HARTING 6–PACK
S1
C1 & C2
S2
C1 & C2
S3
C1 & C2
C1 & C2
S5
C1 & C2
S6
C1 & C2
S4
SMB
SMB
SMB
SMB
SMB
SMB
MULTITONE
MODULE
MULTITONE
MODULE
BPF
BPF
BPF
BPF
BPF
BPF
N–F N–F N–F
S1
C1 & C2
S2
C1 & C2
S3
C1 & C2
C1 & C2
C1 & C2
C1 & C2
TX4 TX5 TX6
N–F N–F N–F
S4
S5
S6
BBX–R
ti-CDMA-WP-00243-v01-ildoc-ftw
2-30
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
Mar 2003
Page 66

68P64115A19–4
BTS 60 Degree Sector (6 Sector) Transmit Path Cabling
60 Degree Sector Configuration
Table 2-20 provides the Cable Run List for 60 degree sector transmit
paths.
Table 2-20: Cable Run List for 60 Degree Sector TX Configuration
Cable Cable Parts Connecting Lightning Arrestors To BTS TX Connectors
G Direct
Quantity 6
TX Ports for 6 Sector Configuration
Table 2-21: Cable Run List for 60 Degree Sector Receive Path Cabling
Cable Cable path connecting Lightning Arrestors to BTS TX connectors TX Ports Used
Quantity 6 TX 1A–6A
Procedure
Install each cable by using the cable run list in Table 2-20, the cabling
diagram in Figure 2-12, and the procedure in Table 2-22. Each cable is
installed the same way.
2
Table 2-22: Installing the 60 Degree Sector TX Path Cables
Step Action
1 Attach the connector–equipped end of the cables to the BTS TX connectors.
2 Route the cables to the lightning arrestors.
3 Cut the cables to length and label them accordingly. Install connectors on the cables and attach the
cables to the Lightning Arrestors.
Mar 2003
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
2-31
Page 67

BTS 60 Degree Sector (6 Sector) Receive Path Cabling
68P64115A19–4
BTS 60 Degree Sector (6 Sector) Receive Path Cabling
Objective
The objective of this procedure is to install the BTS transmit path
2
Cable Labels
Cabling Diagram
Figure 2-14: 60 Degree Sector (6 Sector) Receive Path Cabling Details
cabling.
The cable designations are referenced in Table 2-1 the “Overall Cabling
Diagrams and Description” area. Table 2-23, and Table 2-24 provide the
quantities and descriptions of the cables required for this procedure.
Figure 2-14 shows RX (Main/Diversity) antenna configurations.
Table 2-24 describes the antenna cable connection ports.
MAIN
1A, 2A, 3A
4A, 5A, 6A
DIV
1B, 2B, 3B
4B, 5B, 6B
DIRECT CONNECTION
LIGHTNING
ARRESTORS
LIGHTNING
ARRESTORS
RX
1A
4A
2A
G
G
1A, 2A, 3A, 4A, 5A, 6A
1B, 2B, 3B, 4B, 5B, 6B
MAIN
DIVERSITY
5A
3A
6A
4B
1B
5B
2B
3B
RX
6B
123
456
789
10 11 12
2-32
I/O PLATE
ti-CDMA-WP-00049-v04-ildoc-ftw–REF
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
Mar 2003
Page 68

68P64115A19–4
Q
BTS 60 Degree Sector (6 Sector) Receive Path Cabling
Table 2-23: Cables Needed for 120 Degree Sector Receive Path
Cable Qty. Part Number Description
G 12 CGDS2212602 15 ft. Jumper Cable, N/M–N/M.
Table 2-24: Cable Run List for 60 Degree Sector Receive Path Cabling
2
Cable
uantity
Cable path connecting Lightning Arrestors
to BTS RX connectors
6 MAIN RX 1A–6A
6 DIVERSITY RX 1B–6B
RX CONNECT
Procedure
Install each cable by using the cable run list in Table 2-23, the cabling
diagram in Figure 2-14, and the procedure in Table 2-25. Each cable is
installed the same way.
Table 2-25: Installing the 60 Degree Sector Receive Path Cables
Step Action
1 Attach the connector–equipped end of the cables to the BTS RX connectors.
2 Route the cables to the lightning arrestors.
3 Cut the cables to length and label them accordingly. Install connectors on the cables.
RX Ports Used
Mar 2003
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
2-33
Page 69

BTS 120 Degree Sector (3 Sector) Transmit Path Cabling
68P64115A19–4
BTS 120 Degree Sector (3 Sector) Transmit Path Cabling
Objective
The objective of this procedure is to install the 120 degree BTS transmit
2
Cable Labels
Cabling Diagram
Figure 2-15: 120 Degree Sector (3 Sector) Transmit Path Cabling Details (outside the frame)
path cabling.
The cable designations are referenced to Table 2-1 in the “Cabling
Diagrams and Description” area. Table 2-26 and Table 2-27 provide the
quantities and descriptions of the cables required for this procedure.
Figure 2-15 and Figure 2-16 shows both inside and outside cable
connections for 3 Sector direct connect configurations. Table 2-26 and
Table 2-27, describes the antenna cable connection ports.
ANTENNA
DIRECT CONNECTION
LIGHTNING
ARRESTOR
G
I/O PLATE
S3 C1–C4
S2 C1–C4
S1 C1–C4
123
456
789
10 11 12
TX OUT
2-34
ti-CDMA-WP-00050-v04-ildoc-ftw
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
Mar 2003
Page 70

68P64115A19–4
BTS 120 Degree Sector (3 Sector) Transmit Path Cabling
Figure 2-16: 120 Degree Sector (3 Sector) Transmit Path Cabling Details (inside the frame)
BBX–1
S1 C1
BBX–2
S2 C1
BBX–3
S3 C1
BBX–4
S1 C3
BBX–5
S2 C3
BBX–6
S3 C3
TX1
TX2
TX3
TX4
TX5
TX6
TX7
TX8
J1
3–Sector
MCPA CIO
J5
J14
PA1PA2PA3PA4PA5PA6 HARTING 6–PACK
S1
C1–C4
S2
C1–C4
S3
C1–C4
SMB
SMB
SMB
MULTITONE
MODULE
BPF
BPF
BPF
TX1 TX2 TX3
N–F N–F N–F
S1
C1–C4
S2
C1–C4
S3
C1–C4
2
BBX–7
S1 C2
BBX–8
S2 C2
BBX–9
S3 C2
BBX–10
S1 C4
BBX–11
S2 C4
BBX–12
S3 C4
TX9
TX10
TX11
TX12
SMB
NOT USED
C–CCP BACKPLANE
BBX–R
Table 2-26: Cables Needed for 120 Degree Sector Transmit Path
Cable Qty. Part Number Description
G (see Table 2-27) CGDS2212602 15 ft Jumper Cable, N/M–N/M.
ti-CDMA-WP-00242-v01-ildoc-ftw
Table 2-27: Cable Run List for 120 Degree Sector TX Configuration
Cable Cable Parts Connecting Lightning Arrestors To BTS TX Connectors
G Direct BTS TX Ports
Quantity (TX–only path) 3 TX1, TX2, TX3
Mar 2003
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
2-35
Page 71

BTS 120 Degree Sector (3 Sector) Transmit Path Cabling
Procedure
Install each cable by using the cable run list in Table 2-27, the cabling
diagram in Figure 2-15, and the procedure in Table 2-28. Each cable is
installed the same way.
68P64115A19–4
2
Table 2-28: Installing the 120 Degree Sector TX Path Cables
Step Action
1 Attach the connector–equipped end of the cables to the BTS TX connectors.
2 Route the cables to the lightning arrestors.
3 Cut the cables to length and label them accordingly. Install connectors on the cables and attach the
cables to the Lightning Arrestors.
2-36
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
Mar 2003
Page 72

68P64115A19–4
Q
6
BTS 120 Degree Sector (3 Sector) Receive Path Cabling
BTS 120 Degree Sector (3 Sector) Receive Path Cabling
Objective
The objective of this procedure is to install the BTS RX Port receive
path cabling. 120-degree sector receive path cabling is used for CDMA
systems.
Cable Labels
The cable designations are referenced to Table 2-1 in the “Cabling
Diagrams and Description” area. Table 2-29 and Table 2-30 provide the
quantities and descriptions of the cables required for this procedure.
Table 2-29: Cables Needed for 120 Degree Sector Receive Path
Cable Qty. Part Number Description
G (see Table 2-30) CGDS2212602 15 ft. Jumper Cable, N/M–N/M.
Cabling Diagram
2
Cable
uantity
Figure 2-17 shows RX antenna (Direct Connect) configuration.
Table 2-30 describes the antenna cable connection ports.
Table 2-30: Cable Run List for 120 Degree Sector Receive Path Cabling
Cable path connecting Lightning Arrestors
to BTS RX connectors
RX Antenna Ports
RX 1A
RX 2A
RX 3A
RX 1B
RX 2B
RX 3B
Mar 2003
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
2-37
Page 73

BTS 120 Degree Sector (3 Sector) Receive Path Cabling
Figure 2-17: 120 Degree Sector (3 Sector) Receive Path Cabling Details
68P64115A19–4
ANTENNA
MAIN / A / 1A
2
MAIN / B / 2A
MAIN / G / 3A
ANTENNA
LIGHTNING
ARRESTOR
LIGHTNING
ARRESTOR
G
MAIN
DIVERSITY
G
DIV / A / 1B
DIV / B / 2B
DIV / G / 3B
DIRECT CONNECTION
RX
1A
4A
2A
5A
3A
6A
4B
1B
5B
2B
3B
6B
123
456
RX
789
10 11 12
ti-CDMA-WP-00185-v01-ildoc-ftw
TX OUT
2-38
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
Mar 2003
Page 74

68P64115A19–4
Cabling Procedure
BTS 120 Degree Sector (3 Sector) Receive Path Cabling
Install each cable by referring to the cable run list in Table 2-30, the
cabling diagram in Figure 2-17, and the procedure in Table 2-31. Each
cable is installed the same way.
Table 2-31: Installing the 120 Degree Sector Receive Path Cables
Step Action
1 Attach the connector-equipped end of the cables to the BTS RX connectors.
2 Route the cables to the lightning arrestors.
3 Cut the cables to length and label them accordingly. Install connectors on the cables, and attach the
cables to the lightning arrestors.
2
Mar 2003
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
2-39
Page 75

Earth Ground Cabling
68P64115A19–4
Earth Ground Cabling
Objective
The objective of this procedure is to install the BTS earth ground cables.
2
This manual describes only general procedures for grounding the site.
Refer to the Grounding Guidelines for Cellular Radio Installations,
Motorola part no. 68P81150E62, for detailed grounding information.
WARNING
Earth Grounding Diagram
Figure 2-18 illustrates the earth ground cable.
Figure 2-18: Earth Ground Cabling Details
BTS
Each cabinet must be grounded separately and NOT daisy
chained together!
GND
N
MASTER GROUND BAR
ti-CDMA-WP-00052-v02–ildoc–ftw
Cable Labels
Equipment Needed
2-40
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
The cable designations are referenced in Table 2-1, in the “Cabling
Diagrams and Description” section of this manual.
Table 2-32 describes the cable and ring lugs required for earth
grounding.
NOTE
Two-hole (Thomas & Betts part no. 54207; or equivalent) are
recommended.
Table 2-32: Items Required for Earth Grounding
Item Qty Description
Cable
(N)
Ring
Lugs
1 Ground cable, 6-AWG, insulated copper wire, loop
connectors. Customer supplied cable.
1 Ring lugs to attach to the BTS end of the cable.
Customer supplied item.
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
Mar 2003
Page 76

68P64115A19–4
Install Earth Grounding Cables
Install the earth ground cables according to the procedures in Table 2-33
(see Figure 2-18).
Earth Ground Cabling
WARNING
S Do NOT wear a wrist strap when servicing the power
supplies or power distribution cabling! Serious personal
injury can result.
S Before starting the procedure, ensure that the BTS power
cables are not connected to the main DC source.
Table 2-33: Procedure to Install Earth Grounding Cables
Step Action
1 Route the ground cables (cable N) between the Master
Ground Bar (MGB) and the BTS frames.
NOTE
Ground cables must not have sharp bends.
2 Strip insulation from the BTS end of each cable.
3 Attach a ring lug to the BTS end of each cable.
4 Connect a ground cable (cable N) to the ground stud of each
BTS frame.
5 Connect the ground lugs to directional coupler bracket,
duplexer bracket, and RFDS (if used).
2
6 Attach the ground cables to the MGB using the appropriate
connectors.
Mar 2003
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
2-41
Page 77

BTS Power Cabling
68P64115A19–4
BTS Power Cabling
Objective
The objective of this procedure is to define the BTS’s site power
2
Important Guidelines
distribution system requirements, and install the DC power input
cabling.
Several guidelines must be followed in the design of the site power
distribution system. Depending on site requirements and specific
guidelines, two different cabling choices are offered in this section,
Option A or Option B. Read this entire section before power cabling the
BTS.
Inrush Current
When the frame is powered on, there is the potential for an inrush
current which exceeds the steady state current draw of the frame. In
order to prevent this inrush current from affecting other equipment,
power feeds and circuit breakers should NOT be shared between the
BTS and any other equipment. This BTS is designed to comply with the
ETS 300-132-2 standard for DC inrush current.
Feeds and Breaker Sizes
Table 2-34 lists different site configurations, depending on the number of
carriers. Select a power distribution system configuration that is most
appropriate for your site. Figure 2-19 identifies the BTS Breaker Panel.
Table 2-34: DC Filter Power Feed Configurations
Number of
Number of
Carriers
1–2 1 125A A
3–4 1 250A A
3–4 2 125A B
Feeds Required
(+ and – pair)
Breaker Size
(per Feed)
Utilize
Cable Option
2-42
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
Mar 2003
Page 78

68P64115A19–4
Figure 2-19: Breaker Panel Identification
1A
3A
1B
3B
1C
3C
1D
3D
BTS Power Cabling
2
50
2A
4A
2B
L
4B
P
2C
A
4C
2D
4D
1
2
3
C
C
50 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 50
C
50
P
ti-CDMA-WP-00227-v01-ildoc-ftw–REF
Source Impedance
The frame power interface supports AWG 2/0, AWG 3/0, and AWG 4/0
cable sizes.
In order to limit the voltage drop due to cable resistance, the length of
the cable runs from power source to BTS must be less than the
maximum distance for each cable size shown in the Table 2-35. These
values apply for both single feed and two feed configurations.
Mar 2003
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
2-43
Page 79

BTS Power Cabling
68P64115A19–4
In the + 27 V configuration the power supply input “+” and “–”
terminals are isolated from the BTS chassis ground. In order to control
the inductance at the BTS power input due to the feed cables, the
positive and negative cables (feed and return) must be bound together at
intervals of 1 meter or less (see Figure 2-20).
2
Meeting these limits will ensure a voltage drop of less than 2% due to
cable resistance, and will control the source impedance to ensure
stability of the power supply.
Table 2-35: Maximum Cable Length
Maximum
Number of
Carriers
Number of
Feeds
Cable Type
Length in
meters
1–2 1 AWG 2/0 22
1–2 1 AWG 3/0 28*
1–2 1 AWG 4/0 28*
3–4 1 AWG 2/0 12.2
3–4 1 AWG 3/0 15.4
3–4 1 AWG 4/0 19.4
3–4 2 AWG 2/0 22
3–4 2 AWG 3/0 28
3–4 2 AWG 4/0 28*
* Limited by inductance rather than voltage drop.
Figure 2-20: Length and Tie-Down Requirements for BTS Power Cables
BTS
TIE ALL CABLES
AT 1 METER INTER VALS
2
1
See Table 2-35
for cable length
POWER SOURCE
BREAKER 2
GROUND
BREAKER 1
ti-CDMA-WP-00077-v02–ildoc–ftw REF.
2-44
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
Mar 2003
Page 80

68P64115A19–4
BTS Power Cabling
Current Sharing
For installations with one power feed (2 carrier system cabling) use
Option A (see Figure 2-21).
For installations with two feeds (e.g., 3 carrier or 4 carrier systems using
cabling Option B, (see Figure 2-22), the total current will be shared
between the two feeds. If the current becomes greatly unbalanced
between the two feeds, the circuit breaker carrying the greater current
may be tripped. In this case, all current will flow in the remaining feed,
causing the breaker to be tripped, and the BTS to go out-of-service. In
order to minimize the current imbalance between the feeds, it is
necessary to:
S ensure the cable lengths and sizes of the cables are the same,
S the breakers on the two feeds are the same (same manufacturer, same
part number, etc.), and
S contacts and connectors are identical.
For short cable runs with two feeds, it is recommended that 2/0 cable be
used rather than 3/0 or 4/0.
2
Option A. Power Distribution Cabling for +27 V BTS Configuration with One Power Feed
Figure 2-21: BTS Power Cabling for the +27 V BTS Configuration using One Power Feed
+27 VOLTS
GROUND (0 VOLTS)
M/1
M/1
SC4812T–MC
Mar 2003
ti-CDMA-WP-00190-v01-ildoc-ftw–REF
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
2-45
Page 81

BTS Power Cabling
68P64115A19–4
Option B. Power Distribution Cabling for +27 V BTS Configuration with Two Power Feeds
Figure 2-22: BTS Power Cabling for the + 27 V BTS Configuration using TwoPower Feeds
2
+ 27 VOLT
GROUND (0 VOLT)
M/2
M/2
SC4812T–MC
ti-CDMA-WP-00193-v01-ildoc-ftw–REF
2-46
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
Mar 2003
Page 82

68P64115A19–4
Figure 2-23: DC Power Connector/Filter
BTS Power Cabling
2nd DC FIL TER
OPTIONAL
DC CABLE (–)
DC
CONTACT
Input
Connector/
DC Filter
(+) DC CABLE
DC
CONTACT
DC
Connector
(–)
(+)
ti-CDMA-WP-00194-v01-ildoc-ftw
Housing
2
Tools and Equipment Required
The following tools are required to install the power cable on the BTS:
Cable M – The cable diameter and lug style depend on the length of
cable required. Appropriate codes and standards must be followed to
determine the correct wire size and type (see Table 2-35). A variety of
lug sizes are available from Motorola for the various cable sizes and
types that may be selected (see Table 2-36).
NOTE
Table 2-36: Lug Part Numbers
Lug Part Numbers Cable Type
CGDS6320G1 AWG 2/0
CGDS6320G5 AWG 3/0
CGDS6320G2 AWG 4/0
The cable diameter and lug style depend on the length of cable
required. Appropriate codes and standards MUST be followed to
determine the correct wire size and type. A variety of lug sizes
are available from Motorola for the various cable sizes and types
that may be selected. Lug size is dependent on the gauge and
type of cable selected for the frame power feed.
Mar 2003
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
2-47
Page 83

BTS Power Cabling
Recommended Crimper Tool – The following three crimper tools
are recommended to assemble the customer-side connector for the DC
cables. Choose one of the following crimper tools, according to site
requirements and preferences.
68P64115A19–4
S AMP 600850 – maximum cable size of #4/0 (mechanical hand tool)
2
S SMH p/n SY283 – maximum cable size of #4/0 (mechanical hand
tool)
S Anderson Power Products (APP) p/n 1368 – can accommodate cable
sizes up to 300 MCM (hydralic hand crimp tool).
Pre-connection Checklist
At this point in the installation ensure that the cabinet is NOT already
connected to the main dc power source.
Installing Power Cables
Read the Power Cable Installation WARNINGS and CAUTIONS before
going to Table 2-37 (+27 V Power Cable Installation) also review
Figure 2-23.
WARNING
CAUTION
S Failure to observe these warnings could cause electrical
shock to personnel and/or damage to equipment!
S Do NOT wear a wrist strap when servicing the power
supplies or power distribution cabling! Serious personal
injury can result.
S The external converter supplying the cabinet must have
double or reinforced insulation between its primary and
secondary circuits, and must conform to Safety Standard
EN60 950.
S Ensure the source for the DC voltage is in the OFF position
prior to attempting to connect the dc voltage.
S Ensure all frame power supply circuit breakers are OFF.
S Perform any adjustments recommended by the manufacturer
on the main power supply equipment before connecting dc
power cables to the main dc power source.
S Input to the base station must remain between +34 V and
+21 V dc for +27 V dc operation.
BTS Power Cabling for + 27 V Configuration
The cable connections for powering a +27 V BTS are presented in
Table 2-37.
Table 2-37: Procedure to Install BTS +27 V Power Cables
Step Action
1 Ensure the DC power cables are NOT connected to the main DC power source.
2 Remove the components from the dc connector package shipped with the BTS.
3 Strip 35 mm of insulation from the negative (–) and positive (+) power cables.
2-48
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
Mar 2003
Page 84

68P64115A19–4
Table 2-37: Procedure to Install BTS +27 V Power Cables
Step Action
4 Place a dc contact on the negative (–) and positive (+) dc cables.
BTS Power Cabling
5 Using the appropriate crimping tool, crimp the dc contact to the dc cables.
6 Observe the negative (–) and positive (+) cables and insert the dc contacts into the dc connector
housing(s) until an audible click is heard.
7 Verify the positive (+) cable is installed in the positive position and the negative (–) cable is installed
in the negative (–) position on the connector housing(s).
8 Ensure the cables are firmly fastened to the dc connector housing(s).
9 Connect the DC connector housing to the mating input connector/DC filter on the BTS (see
Figure 2-23).
10 Connect the DC connector housing to the mating input connector/DC filter on the BTS for the second
dc filter feed, if required (see Figure 2-23).
11 Are there additional frames that require cable installation?
– If YES, repeat the above procedure for the additional frame(s).
– If NO, this procedure is complete.
2
Mar 2003
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
2-49
Page 85

Chapter 3
Expansion Frame Cabling and
Installation
3
Mar 2003
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
3-1
Page 86

Expansion Frame (+27 V BTS Configuration)
Expansion Frame (+27 V BTS Configuration)
This chapter provides the procedures for installing an Expansion frame
to either a SC4812T or SC 4812T–MC Starter frame.
Installation Procedures
This chapter includes installation and setup procedures for the following:
S RF Cabling (TX & RX)
S RF GPS
68P64115A19–4
3
S Remote GPS Distribution (RGD)
S HSOX
S Local Area Network (LAN)
S C-CCP Cage Dip Switch Settings
Inter-frame Cables
Sites utilizing Expansion frames require certain procedures to be
completed (depending on site requirements) before proper operation can
be obtained. The BTS cable description and part numbers for certain
different procedures are listed in Table 3-1. The letters, referenced under
the Cable Label column in Table 3-1, are used as a reference for all
cabling procedures and diagrams in this manual. This information
applies to all system configurations.
Table 3-1: Expansion Cable/Hardware Descriptions and Part Numbers
Cable
Label
A
1
A
2
Part
Number
T472Ax
3086433H07 Punch block to RGD Site I/O board cable
RGD Antenna punch block cable; where x=A–F for different A1 cable lengths
(50 to 2000 ft).
Description
B 3086433H02 RGD Expansion cable
C 3086433H01 RGD to Site I/O cable
D 3086458H01 HSOX cable
E 3086412H01 RF Expansion cable
F 1586370H01 Harting; 12 pack
M N.A. Power cable – See Power Cable section, for detailed information on cable
termination lugs. Customer supplied cable.
Before You Begin
Ensure each Starter and/or Expansion frame has been properly powered
off before performing any installation procedures.
3-2
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
Mar 2003
Page 87

68P64115A19–4
Expansion Frame (+27 V BTS Configuration)
Expansion Frame and Expansion I/O Plate
Figure 3-1 shows the SC 4812T–MC BTS that can be used as an
expansion frame and Figure 3-2 that shows a detailed version of the
Expansion I/O plate for the +27 V configuration.
Figure 3-1:BTS MC Expansion Frame (+27 V Configuration)
Fan Module
C–CCP Cage
C–CCP Cage
and PA Breakers
I/O Interconnect
Plate
3
Mar 2003
Power
Amplifier
Cage
For clarity, doors are not shown.
ti-CDMA-WP-00205-v01-ildoc-ftw
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
3-3
Page 88

Expansion Frame (+27 V BTS Configuration)
Figure 3-2: Expansion Frame I/O Plate (+27 V Configuration)
68P64115A19–4
CONNECTORS
ALARM B
ALARM A
ALARM
SPAN I/O
REAR
SPAN I/O A
SITE I/O
SPAN I / O
RGPS
SITE I/O
RECEIVE
ANTENNA
COVERS
SPAN I/O B
RX
LAN
CONNECTIONS
GND
4A
1A
RF GPS IN
2A
5A
3
SPAN I/O A SITE I/O SPAN I/O B
3A
6A
4B
1B
2B
3B
DC FILTER 2
5B
DC FILTER 1
6B
RX
HSO/LFR
FILLER PLATE
INPUT
CONNECTOR/
DC FILTER
3 TO 6 TRANSMIT
ANTENNA
CONNECTORS
DEPENDING ON
CONFIGURATION
2 TO 3
TRANSMIT
ANTENNA FILLER
PLATES
DEPENDING ON
CONFIGURATION
ti-CDMA-WP-00189-v01-ildoc-ftw–REF
ETHERNET ROUTER (IF USED;
OTHERWISE, FILLER PLATE)
FRONT
FILLER PLATE
EXP OUT
RF EXPANSION PORT
FROM STAR TER BTS
3-4
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
Mar 2003
Page 89

68P64115A19–4
Figure 3-3: Starter Frame I/O Plate
REMOTE GPS DISTRIBUTION (RGD) MODULE –
USED ONLY IF EXPANSION FRAME(S) INSTALLED
ALARM
CONNECTORS
SPAN I/O
REAR
SPAN I/O A
SITE I/O
RGPS
SITE I/O
Expansion Frame (+27 V BTS Configuration)
SPAN I / O
RECEIVE
ANTENNA
CONNECTORS
SPAN I/O B
LAN
CONNECTIONS
ALARM B
ALARM A
ETHERNET ROUTER (IF USED;
OTHERWISE, FILLER PLATE)
SPAN I/O A SITE I/O SPAN I/O B
FRONT
EXP IN FILLER
PLATE
RX
4A
1A
2A
5A
GND
RF GPS IN
HSO/LFR
3A
6A
4B
1B
2B
3B
DC FILTER 2
5B
DC FILTER 1
6B
RX
FILLER PLATE
INPUT
CONNECTOR/
DC FILTER
3 TO 6 TRANSMIT
ANTENNA
CONNECTORS
DEPENDING ON
CONFIGURATION
2 TO 3
TRANSMIT
ANTENNA FILLER
PLATES
DEPENDING ON
CONFIGURATION
RF EXPANSION PORT TO ANOTHER
BTS (USED ONLY IF EXPANSION FRAME
INSTALLED; OTHERWISE, FILLER PLATE
INSTALLED)
ti-CDMA-WP-00188-v01-ildoc-ftwREF
3
Mar 2003
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
3-5
Page 90

Expansion Frame (+27 V BTS Configuration)
Cable Labels
The cable designations are referenced to Table 2-13 in “Cable
Description and Part Numbers”.
Expansion Frame Cabling Diagram
Figure 3-4 illustrates the BTS Expansion Frame cabling details with the RF
GPS or Remote GPS option.
Figure 3-4: Expansion Frame Cabling Details
68P64115A19–4
3
Lighting Protected
Punch block
RGD PCB
Remote GPS
Antenna
A
1
A
2
C
Starter
Frame
E
RF Expansion Cable
Harting 12 PK
LFR/HSO
(9 Pin D)
Site I/O
D
B
LFR/HSO
(9 Pin D)
Remote GPS
Expansion
Frame
3-6
ti-CDMA-WP-00088-v01-ildoc-ftw
REF
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
Mar 2003
Page 91

68P64115A19–4
Expansion Frame Inter-Frame Cabling
Expansion Frame Inter-Frame Cabling
This section describes the connections between an expansion frame with
a starter frame.
Remote GPS Distribution (RGD) Board Diagram
Figure 3-5 shows the RGD board cable connections. Both RGD and Site
I/O boards are on the strater BTS. Table 3-1 provides a description of all
cables associated with the installation of RGD.
Figure 3-5: RGD Board Cable Connections
Remote GPS Antenna
3
Site I/O
Surge Protected
A1
Punch block
A2
RGD
(Main out)
NOTE:
RGD card is required on the Starter frame only.
It provides Remote GPS signal to the Expansion frame.
NOTE
B
To Expansion Frame
Not used
Not used
C
ti-CDMA-WP-00087-v01-ildoc-ftw–REF
S Cables A1 and A2 must be punched into the punch block as
if they were part of the same cable, cut in the middle. The
same colors must be punched on both sides of the punch
block.
S Frame MUST be equipped with CSM2 for Remote GPS
operations.
S Remote GPS is NOT supported in all Motorola 4-digit
frames.
Mar 2003
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
3-7
Page 92

Expansion of the +27 V Frame
68P64115A19–4
Expansion of the +27 V Frame
Site configurations can include a +27 V SC 4812T–MC BTS Starter
Frame using either a +27 V SC 4812T–MC BTS frame or a +27 V SC
4812T BTS as an Expansion frame.
Another site configuration can include a +27 V SC 4812T BTS Starter
Frame using a +27 V SC 4812T–MC BTS frame as an Expansion frame.
Antenna Sharing
Separate TX antennas are used in each frame. One Expansion frame can
3
Figure 3-6: RX Antenna Sharing with an Expansion Frame
share RX antennas with the Starter Frame. RX antenna sharing is shown
in Figure 3-6.
Tools Required
TX
Starter Frame
S T10 and T30 Torx bits and driver
S Flat head screwdriver or 5/16” Hex socket
S Torque driver
NOTE
RX
TX
RX
EXP.
OUT
RX
EXP.
IN
Expansion Frame
ti-CDMA-WP-00056-v01-ildoc-ftw–REFREF
Use the following procedures to add an Expansion frame to a
Starter frame. The instructions are identical when connecting a
SC 4812T–MC BTS “Expansion” frame to either a SC 4812T or
SC4812T–MC BTS “Starter” frame.
Expansion Procedure
Table 3-2 provides the procedures necessary to install a SC 4812T–MC
BTS Expansion Frame to a Starter frame.
Table 3-2: Installing an Expansion BTS
Step Action
1 Confirm the BTS is powered down.
2 Locate the Expansion I/O Filler Plate on the Starter Frame I/O plate (see Figure 3-3).
3 Using the Torx T10 bit, remove four M3 screws attaching the Expansion I/O Filler Plate to the I/O
plate. (The filler plate can be discarded.)
. . . continued on next page
3-8
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
Mar 2003
Page 93

68P64115A19–4
Expansion of the +27 V Frame
Table 3-2: Installing an Expansion BTS
Step Action
4 Install the Expansion I/O Housing on the Starter I/O in the same area as the filler plate.
5 Secure the housing to the I/O plate by using four M3x10 screws, T10 Torx bit and torque to
10–12 in-lb. The label FRONT on the Expansion I/O housing should face EXP I/O text on the
I/O plate.
6 Using the T30 bit, remove the eight M6 screws attaching the front cosmetic panel to the cabinet.
7 Locate the two Expansion OUT cables tie-wrapped behind the front cosmetic panel.
8 Remove Harting terminators, if present, on the Expansion out cables.
9 Carefully cut the tie-wrap, taking care as not to cut cables, and insert the cables into the Expansion
I/O housing from below the I/O plate. Note the cables are keyed, and can only be installed one way in
the Expansion I/O housing. Confirm the cables are fully snapped into place in the Expansion I/O
housing.
10 Attach the front cosmetic panel to the cabinet using the eight M6 screws torqued to 45 in-lb.
11 Install one end of the RF expansion cable (see Figure 3-4) to the Starter frame by plugging the end of
the cable labeled SC 4812T into the Expansion I/O housing labeled EXP I/O, located on the Starter
frame I/O plate (see Figure 3-3). The cable is keyed and can only be installed one way.
12 Secure the connection by fastening the four retention screws of the cable into the Expansion I/O
housing. The screws should be fastened to 20 in-lb torque using a flat head screwdriver or a 5/16”
socket and ratchet.
13 Following the same procedure, install the other end of the RF expansion cable, labeled SC 4812T
EXP to the expansion housing labeled EXP I/O on the +27 V SC 4812T (1800 mm) Expansion
frame I/O plate (see Figure 3-2).
3
Mar 2003
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
3-9
Page 94

RF GPS Expansion Installation
RF GPS Expansion Installation
GPS Expansion
The Global Positioning System (GPS) is used by Motorola as the
primary means to synchronize all base stations in a CDMA cellular
system. The GPS signal is the input to the CSM, which develops the
timing references for the Base Transceiver system (BTS). Every BTS at
a site requires a GPS input.
On some versions of the SC 4812T product, GPS timing is provided by
3
Customer Equipment Considerations and System Constrains
a built-in dedicated RF GPS receiver module installed on the CSM. On
BTSs equipped with redundancy, two (2) CSMs are installed.
On some versions of the SC 4812T product, GPS timing is provided by
an optional Remote GPS receiver (RGPS). The RGD card accepts timing
information in digital format from the RGPS head and distributes it
within the BTS, and to other Expansion cabinets by a small digital cable.
The procedure for RGPS is covered in a separate section.
In order to share RF GPS signals, customer equipment external to the
BTS must be carefully designed to ensure that overall performance is not
degraded. Both the gain and the noise of the complete system affect the
performance and the A/D converter in the GPS receiver. A typical
diagram of a system to feed multiple BTSs from one GPS antenna is
shown in Figure 3-7.
RF RGPS Expansion Installation Considerations
Following are recommendations for the RF GPS distributing amplifier
method:
S The maximum GPS system NF is 4 dB, per OnCore Technical
Application Note (CSM GPS Vendor).
S GPS distributed amplifier is acceptable, but only with Motorola
recommended parts.
S Recommended amplifier model number is HP58516A (4–way).
S Must have surge protection before the distribution amplifier
(PolyPhaser number is IS–MR50LNZ–6–MA).
S Maximum cable loss between GPS antenna and BTS is 4.5 dB.
S Maximum cable length difference between the 4:1 splitter to any
cabinet is 8 meters.
3-10
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
Mar 2003
Page 95

68P64115A19–4
Figure 3-7: System to Feed Multiple BTS’s from One RF GPS Antenna
BTS
GPS
Receiver
BTS
RF GPS Expansion Installation
GPS
Receiver
GPS
Receiver
GPS
Receiver
BTS
BTS
NOTE
DC
Block
DC
Block
DC
Block
4-Way
Splitter
Preamp
w/ DC Pass
Through
Lightning
Arrestor
Note: Motorola P/N is CGDSHP58516A
(HP P/N is HP58516A). Can be used to
replace all parts in box.
ti-CDMA-WP-00028-v01-ildoc-ftw
Antenna /
LNA
– Maximum cable loss is 4.5 dB with or without 4:1 splitter.
– HP58516A replaces all three components (DC Block,
Splitter, and Pre-amplifier.
3
Mar 2003
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
3-11
Page 96

Remote GPS Distribution Expansion
Remote GPS Distribution Expansion
Configuration
RGD and Remote GPS Expansion
Tools Required
S T10 Torx bit
S Flat head screwdriver
68P64115A19–4
3
S Torque driver
Remote GPS (RGD) Expansion Procedure
The Remote GPS Expansion procedure is listed in Table 3-3 and
Figure 3-8 shows the RGD board cable connections.
Table 3-3: Installing Remote GPS (RGD) Expansion
Step Action
1 Install the RGD board on the I/O plate of the MC Starter frame of the cell site. The RGD board
mounting area on the frame I/O plate is shown in Figure 2-1 and Figure 2-2. Align the RGD board to
the I/O plate using six M3 screws, fastening the screws to 8–10 in-lb (0.9 – 1.1 N-m) using the T10
Torx bit and torque driver.
2 Install the RGD cover over the board. Align the connector ports on the cover with the connectors on
the RGD board. The cover will snap into place.
3 Install the Remote GPS IN cable. Plug the 15-pin D-sub end of the cable into the RGD board
connector labeled REMOTE GPS IN. This cable may have to be unplugged from the Starter frame
remote GPS connector on the Site I/O board (see Figure 3-3).
4 Unfasten the cable connector retention screws using the flat head screwdriver to remove the cable.
5 Secure the cable to the RGD board connector by fastening the cable connector retention screws using
the flat head screwdriver.
6 Install the RGD to Site I/O cable (15 pin D-sub to 15-pin D-sub short ribbon cable). Plug either end of
the cable into the RGD board connector labeled MAIN OUT.
7 Fasten the cable connector retention screws to 4–6 in-lbs (0.4 – 0.7 N-m) using the screwdriver.
8 Fasten the other end of the cable to connector labeled REMOTE GPS on the Site I/O board (see
Figure 3-3).
9 Fasten cable connector retention screws to 4–6 in-lbs (0.4 – 0.7 N-m) using the screwdriver.
10 Install the RGD expansion cable (15 pin D-sub to 15 pin D-sub long ribbon cable). Plug either end of
the cable into the RGD board connector labeled EXP 1 (see Figure 2-1).
11 Fasten cable connector retention screws to 4–6 in-lbs (0.4 – 0.7 N–m) using the screwdriver.
12 Plug the opposite end of the cable into the SC 4812T–MC Expansion Frame Remote GPS connector
on the Site I/O board (see Figure 2-2).
3-12
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
Mar 2003
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
Page 97

68P64115A19–4
High Stability Oscillator Expansion (HSOX)
High Stability Oscillator Expansion (HSOX)
Configuration
High Stability Oscillator Expansion (HSOX)
Tools Required
S Flat head screwdriver
HSO Expansion Procedure
Install the HSOX cable and card per instructions in Table 3-4.
Table 3-4: Installing the HSOX Cable and Card
Step Action
1 Disconnect the LFR antenna cable from the HSO/LFR connector on the Starter Frame I/O plate, if
necessary.
2 Install the HSO expansion cable (9-pin D-sub “Y” ribbon cable). Plug connector “B” of the HSO
expansion cable (see Figure 3-8) into the Starter Frame HSO/LFR input/output port on the I/O plate
(see Figure 2-1).
3
3 Fasten the cable connector retention screws to 4–6 in-lb (0.4 – 0.7 N-m) using the flat head
screwdriver.
4 If an LFR antenna is used, connect the LFR antenna cable to connector “C” (see Figure 3-8) of the
HSO expansion cable.
5 Plug connector “A” of the HSO expansion cable (see Figure 3-8) into the Expansion Frame HSO/LFR
input/output port on the I/O plate (see Figure 2-2).
6 Fasten the cable connector retention screws to 4–6 in-lbs (0.4 – 0.7 N-m) using the flat head
screwdriver.
7 Attach a static wrist strap to your wrist and to the ESD plug on the BTS.
8 Install the HSO expansion card into the appropriate HSO/LFR slot. Latch the top and bottom latches
at the same time to properly seat the card.
Figure 3-8: HSOX Cable (3086458H01) for Expansion Frame
CONNECTOR
LFR
LFR /
HSO
CONN B
CONN C
RETENTION
SCREW
CONN A
LFR /
HSO
STARTER FRAME
Mar 2003
I/O PLATE
TO LFR
ANTENNA
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
EXPANSION
FRAME
ti-CDMA-WP-00029-v01-ildoc-ftw
3-13
Page 98

Local Area Network (LAN) Expansion Installation
Local Area Network (LAN) Expansion Installation
Configuration
The LAN is only connected between frames in a BTS if the system is
running software revision 2.9 or later, and the site is configured as a
logical BTS.
NOTE
3
Tools Required
C-CCP dip switch changes are required to reflect frame ID (refer
to Figure 3-10).
S 5.5 mm Hex socket
Torque Specifications
Terminator grounding stud nut: 10–12 in-lbs (1.1 – 1.3 N-m).
LAN Expansion Installation Procedure
Table 3-5 provides the procedure to install LAN Expansion.
Table 3-5: Installing LAN Expansion
Step Action
1 Remove the LAN OUT A and LAN OUT B terminators (BNC) located on the Starter frame I/O plate.
2 Remove the LAN IN A and LAN IN B terminators (BNC) located on the Expansion frame I/O plate
through a conductive tether and lug attached to a grounding stud (see Figure 3-9).
3 To remove the lug of the tether from the grounding stud, remove the nut and washer from the
grounding stud using a 5.5 mm hex socket and ratchet. Slide the lug off the stud.
4 Reinstall the nut and washer on the grounding stud, tightening the nut to 8–10 in-lbs using the 5.5 mm
hex socket and torque ratchet.
5 Install the frame-to-frame LAN cables by plugging one end of a BNC cable into the LAN OUT B
connector on the Starter Frame I/O plate. Plug the opposite ends of the cables into the appropriate
LAN IN (A and B) connector on the Expansion Frame I/O plate.
3-14
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
Mar 2003
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
Page 99

68P64115A19–4
Figure 3-9: LAN Grounding Stud
I/O PLATE
Local Area Network (LAN) Expansion Installation
3
LAN GROUND
STUD
LAN
CONNECTIONS
ti-CDMA-WP-00215-v01-ildoc-ftw
Mar 2003
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
3-15
Page 100

Setting Frame C-CCP Shelf Configuration Switch
Setting Frame C-CCP Shelf Configuration Switch
When the frame is a Starter BTS, the backplane switch settings behind
the fan module nearest the breaker panel must be set to the ON position
(see Figure 3-10).
68P64115A19–4
NOTE
The switch setting must be verified and set before power is
applied to the BTS equipment!
NOTE
Dip switch settings are only changed in the Expansion frame if
the system is running software release 2.9 or later, AND the site
3
is configured as a logical BTS.
Figure 3-10: Backplane DIP Switch Settings
ON
OFF
RIGHT / LEFT
BOTTOM / TOP
EXPANSION
FRAME
SETTING
MODEM_FRAME_ID_1
MODEM_FRAME_ID_0
REAR
FRONT
ON
OFF
SPEED
CONTROLLED
FAN
MODULE
PWR/ALM
RIGHT / LEFT
BOTTOM / TOP
SPEED
CONTROLLED
FAN
MODULE
REAR
PWR/ALM
FRONT
MODEM_FRAME_ID_1
STARTER
FRAME
SETTING
FAN MODULE
MODEM_FRAME_ID_0
REMOVED
3-16
Power Supply
Power Supply
19 mm Filter Panel
HSO
CSM
CSM
AMR / MACH
Power Supply
AMR / MACH
CCD CCD
39 mm Filter Panel
GLI–1GLI–2
MCC–2
MCC–1
MCC–8
MCC–7
MCC–4
MCC–3
MCC–9
MCC–10
MCC–6
MCC–5
MCC–11
MCC–12
BBX–1
BBX–2
BBX–7
BBX–8
BBX–3
BBX–4
BBX–9
BBX–10
BBX–5
BBX–6
BBX–11
BBX–12
BBX–R
MCIO
Switch
SC 4812T–MC C–CCP SHELF
1X SC 4812T-MC BTS Hardware Installation - Software Release R2.16.1.x
CONTROLLED INTRODUCTION
MPCMPC
ti-CDMA-WP-00211-v01-ildoc-ftw
Mar 2003
 Loading...
Loading...