Page 1

Nokia Customer Care
7 - RF Description and
Troubleshooting
Issue 1 11/05 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL
Copyright © 2005 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 2

RA-8
7 - RF Description and Troubleshooting Nokia Customer Care
[This page intentionally blank]
Issue 1 11/05 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL 2
Copyright © 2005 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 3

RA-8
7 - RF Description and Troubleshooting Nokia Customer Care
Table of Contents
Page No
CMT RF................................................................................................................. 5
Top-level description.......................................................................................... 5
RA-8 test point locations................................................................................... 6
Test points ......................................................................................................... 7
RF implementation in RA-8.............................................................................. 11
Frequency plan ..............................................................................................11
RF block diagram ...........................................................................................12
Antenna switch module (ASM) .......................................................................13
DC characteristics ..........................................................................................13
RF characteristics ............................................................................................ 16
Channel numbers and frequencies ................................................................ 16
RF Troubleshooting..........................................................................................17
Receiver description and troubleshooting........................................................ 17
Rx front end ...................................................................................................17
Antenna .........................................................................................................17
Receiver characteristics .................................................................................18
General instructions for Rx troubleshooting ...................................................19
Transmitter description and troubleshooting.................................................... 26
Power amplifier ..............................................................................................26
RF ASIC Honi ................................................................................................26
AFC function ..................................................................................................27
Transmitter characteristics .............................................................................27
General instructions for Tx troubleshooting ................................................... 27
Additional information for EDGE troubleshooting ............................................ 34
Pictures of EDGE transmitter signals .............................................................38
Synthesizer description and troubleshooting................................................... 42
Frequency synthesizers .................................................................................42
General instructions for synthesizer troubleshooting .....................................42
Frequency Lists ..............................................................................................47
RF tunings after repairs ................................................................................... 50
Issue 1 11/05 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL 3
Copyright © 2005 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 4

RA-8
Nokia Customer Care 7 - RF Description and Troubleshooting
[This page intentionally blank]
4 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 1 11/05
Copyright © 2005 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 5

RA-8
7 - RF Description and Troubleshooting Nokia Customer Care
CMT RF
■ Top-level description
The RF module performs the necessary high frequency operations of theEGSM900/1800/1900
tripleband (EDGE) engine. Both the transmitter and receiver have been implemented by using
direct conversion architecture which means that the modulator and demodulator operate at the
channel frequency.
The core of the RF is an application-specific integrated circuit, Honi. Another co re component
is a power amplifier module which includes two amplifier chains, one fo r EGSM900 and the other for GSM1800/GSM1900.
Other key components include
• 26 MHz VCTCXO for frequency reference
• 3296-3980 MHz SHF VCO (super high frequency voltage controlled oscillator)
• Antenna switch module (ASM)
• Three SAW filters
• BAW-LNA module
The control information for the RF is coming from the baseband section of the engine through
a serial bus, referred later on as RFBus.
The whole RF circuitry is located on one side of the 8-layer PWB.
EMC leakage is prevented by using a metal shield with gasket. The RF circuits are separated
into two blocks.
• PA, ASM, TK balun
• Honi RF IC, VCO + balun, VCTCXO, BAW-LNA, Rx filter, Tx filter
The RF transmission lines constitute of striplines and microstriplines after PA.
Issue 1 11/05 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL 5
Copyright © 2005 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 6
RA-8
Nokia Customer Care 7 - RF Description and Troubleshooting
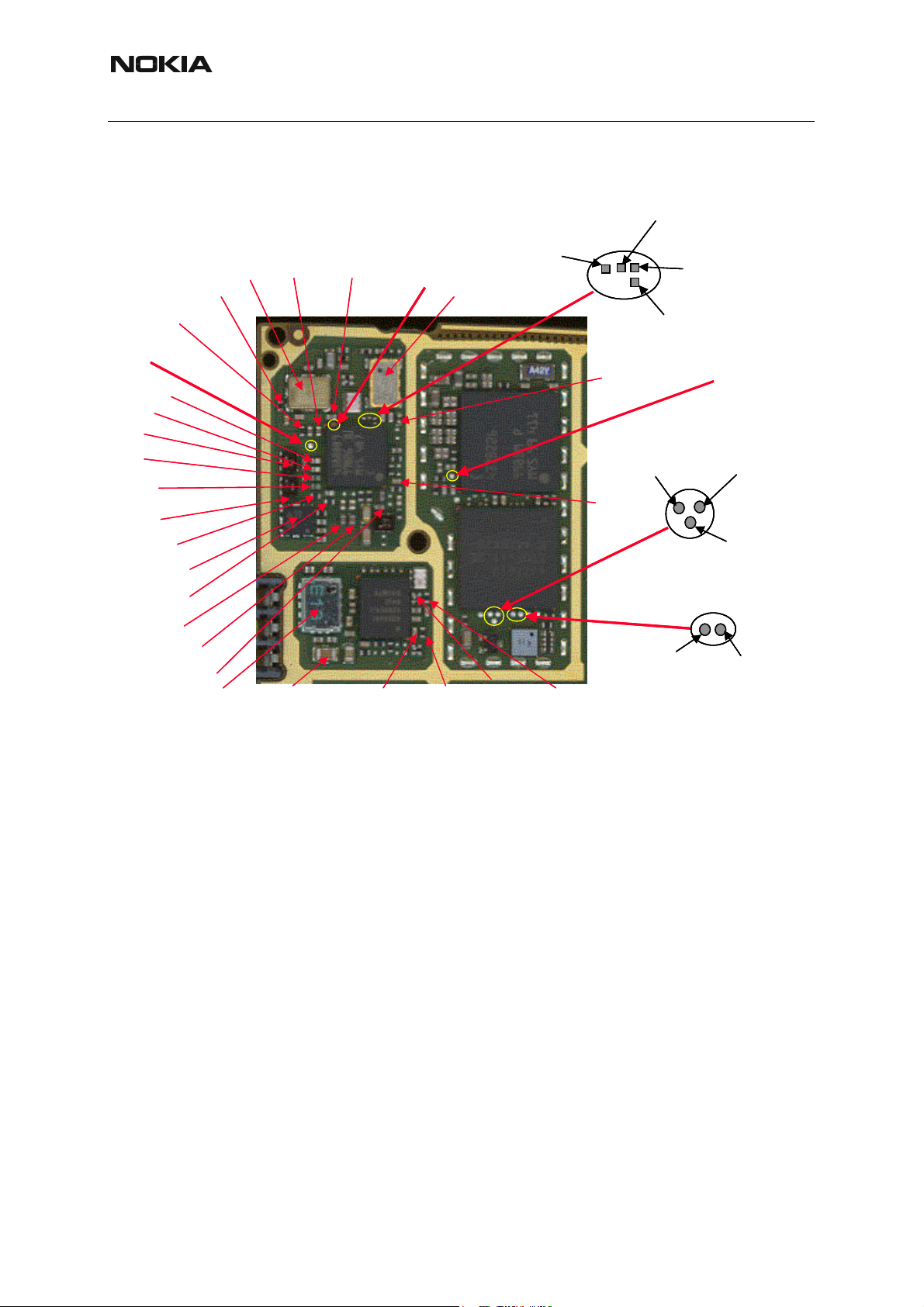
■ RA-8 test point locations
Figure 1: Top view
J7510
J7510
J7510
TXQM
TXQM
TXQM
J7511
J7511
J7511
TXIM
TXIM
TXIM
J7503
J7503
J7503
RFBusClk
RFBusClk
RFBusClk
J7512
J7512
J7512
TXIP
TXIP
TXIP
J7501
J7501
RXQ
RXQ
J7504
J7504
J7504
RFBusEna1
RFBusEna1
RFBusEna1
J7502
J7502
J7502
RFBusData
RFBusData
RFBusData
J7508
J7508
TXC
TXC
L7603
L7603
Z7601
Z7601
L7602
L7602
L7601
L7601
Z7602
Z7602
R7503
R7503
L7604
L7604
R7602
R7602
Z7603
Z7603
R7500
R7500
G7500
G7500
C7506
C7506
C7505
C7505
J7500
J7500
RXI
RXI
G7501
G7501
J7509
J7509
J7509
TXQP
TXQP
TXQP
L7500
L7500
C7516
C7516
R7601
R7601
C7706
C7706
C7705
C7705
C7721
C7721
Z7600
Z7600
C7702
C7702
R7705
R7705
R7707
R7707
R7710
R7710
R7712
R7712
J7506
J7506
J7506
TXA
TXA
TXA
J7505
J7505
J7505
Reset
Reset
Reset
6 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 1 11/05
Copyright © 2005 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 7
RA-8
7 - RF Description and Troubleshooting Nokia Customer Care
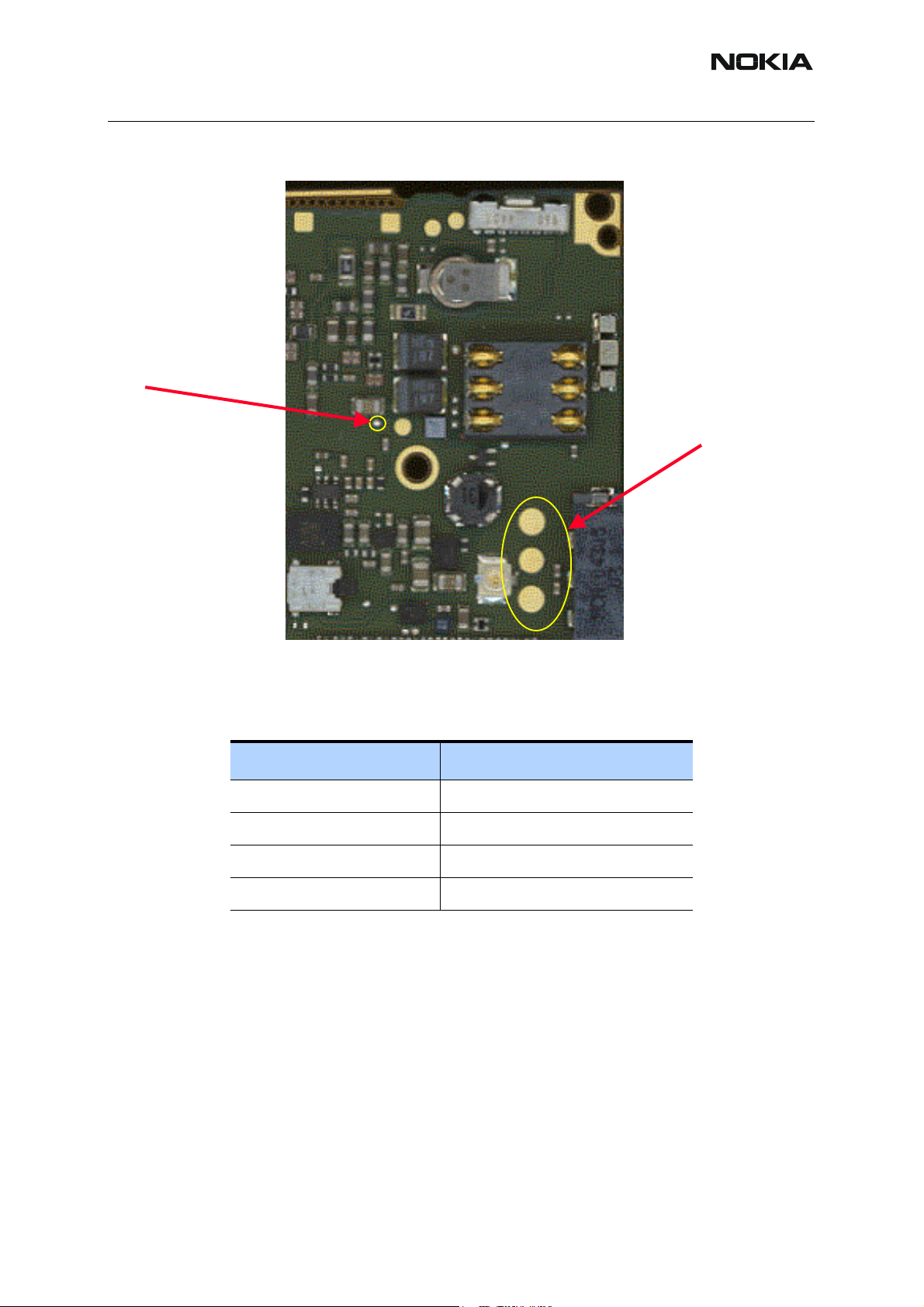
Figure 2: Bottom view
J7507
TXP
RF test
connection
■ Test points
Table 1: Rx test points
Signal name: Ref:
LNAB_P Z7603
LNA_P Z7603
RXI J7500
RXQ J7501
Issue 1 11/05 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL 7
Copyright © 2005 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 8
RA-8
Nokia Customer Care 7 - RF Description and Troubleshooting
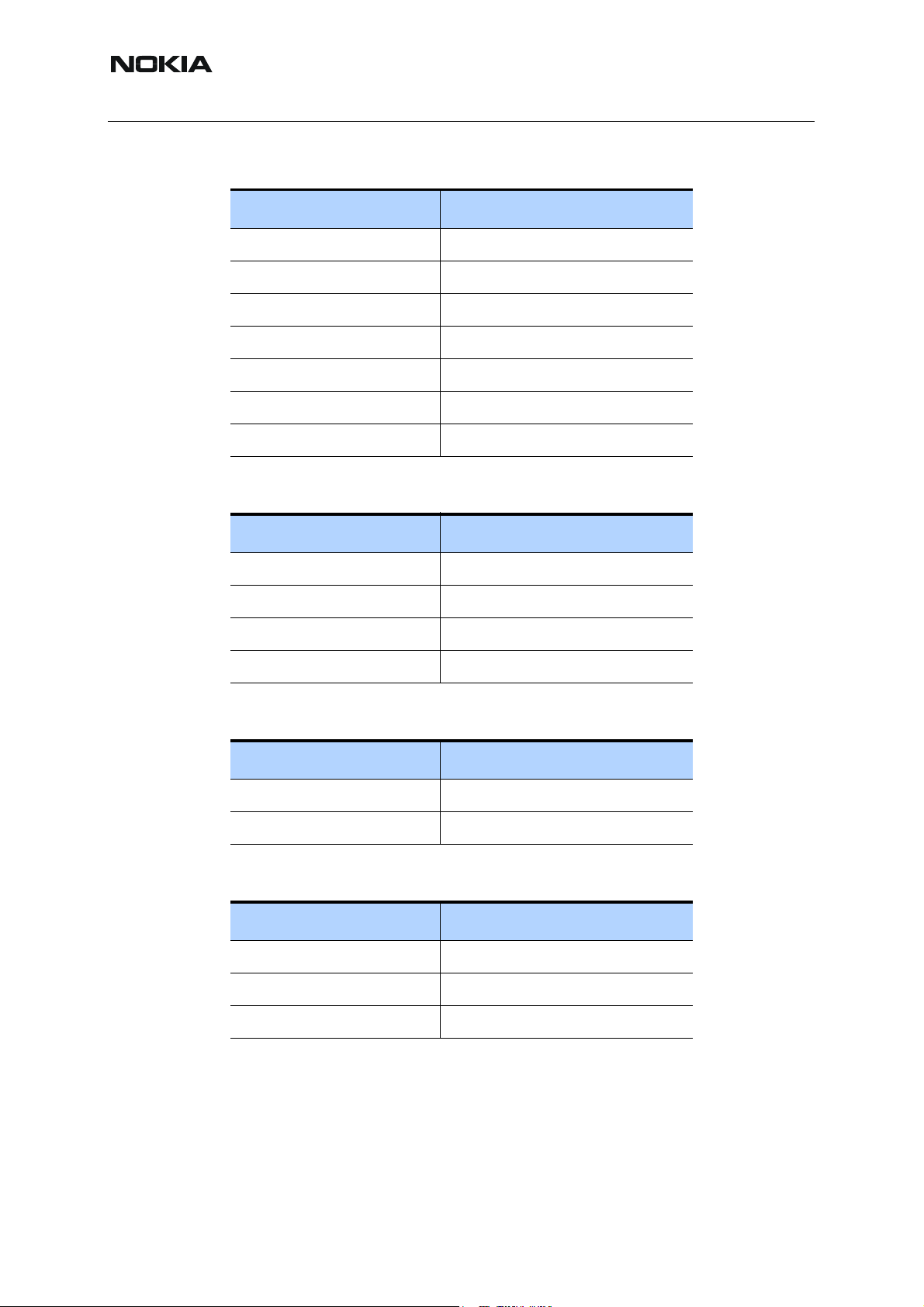
Table 2: Antenna switch test points
Signal name: Ref:
VANT_1 Z7600
VANT_2 Z7600
VANT_3 Z7600
GSM_Rx Z7600
DCS_Rx Z7600
PCS_Rx Z7600
TX_IN_EGSM Z7600
Table 3: Honi serial interface test points
Signal name: Ref:
RFBusClk J7503
RFBusEna1 J7504
RFBusData J7502
Reset J7505
Table 4: Synthesizer test points
Signal name: Ref:
VCO_out G7500
VCTCXO_out G7501
Table 5: GSM900 Rx Honi input test points
RX filter Z7601
Ref:
Inductor L7603
Inductor L7604
8 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 1 11/05
Copyright © 2005 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 9
RA-8
7 - RF Description and Troubleshooting Nokia Customer Care
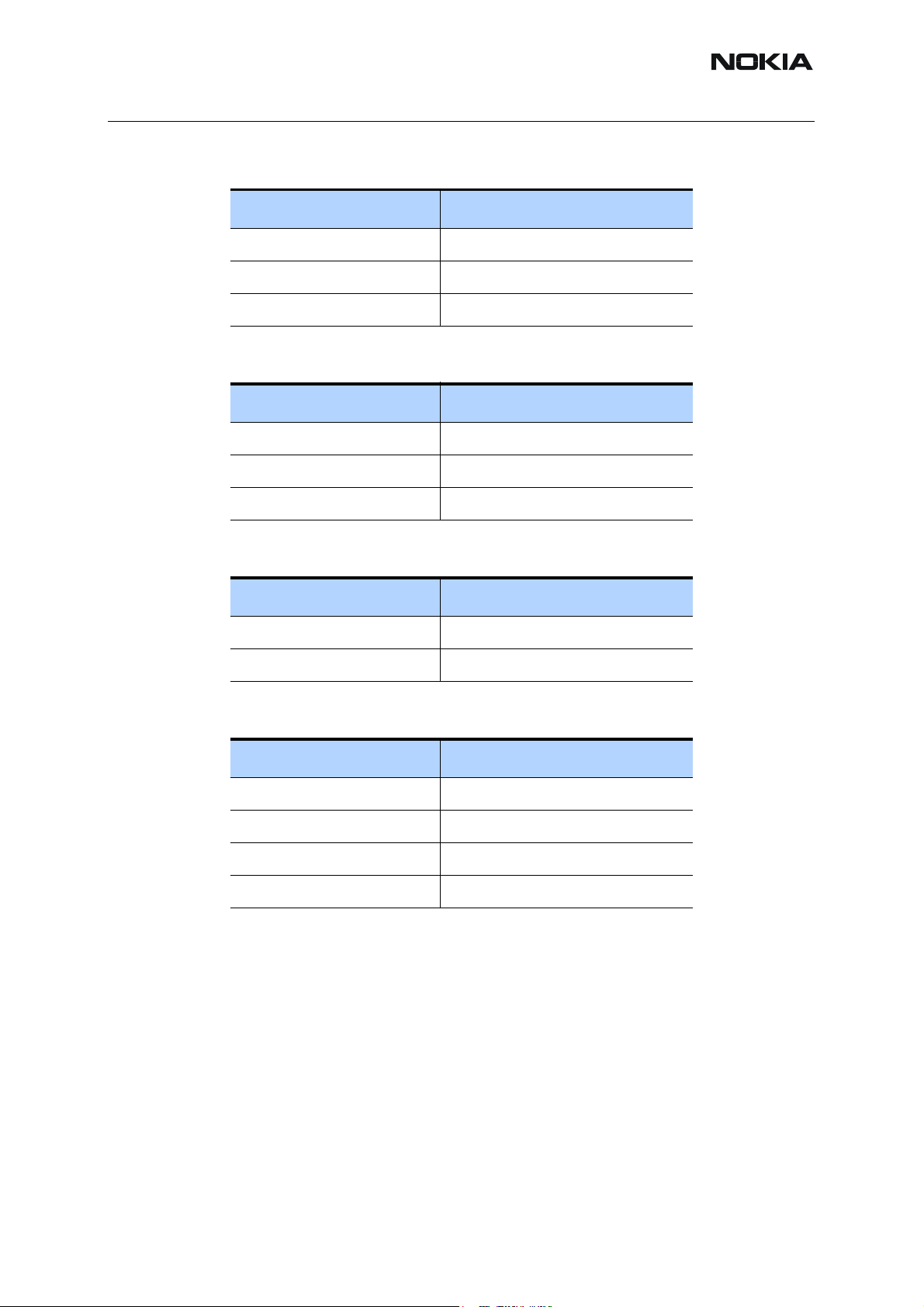
Table 6: GSM1800 Rx Honi input test points
Ref:
Filter Z7602
Inductor L7601
Inductor L7602
Table 7: GSM1900 Rx Honi input test points
Ref:
BAW-LNA Z7603 pin 7
Resistor R7601
Resistor R7602
Table 8: Tx PA input test points
Signal name: Ref:
Rfin_900 R7705
Rfin_1800/190 R7710
Table 9: Tx filter/balun input test points
Signal name: Ref:
RfinP_900 C7721
RfinM_900 C7721
RfinP_1800_1900 C7705
RfinM_1800_1900 C7706
Issue 1 11/05 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL 9
Copyright © 2005 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 10
RA-8
Nokia Customer Care 7 - RF Description and Troubleshooting
Table 10: PA control signal test points
Signal name: Ref:
VPCTRL_900 R7707
VPCTRL_1800_1900 R7712
TXIM J7511
TXIP J7512
TXQM J7510
TXQP J7509
TXC J7508
TXP J7507 (test pad)
TXA J7506
Table 11: Rx test points
Signal name: Ref:
VR1
VR2 C7516
VR3 L7500
VR4
VR5 C7505
VR6 C7506
VR7 R7500
VrefRF01 R7503
VBAT C7702
10 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 1 11/05
Copyright © 2005 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 11
RA-8
7 - RF Description and Troubleshooting Nokia Customer Care
■ RF implementation in RA-8
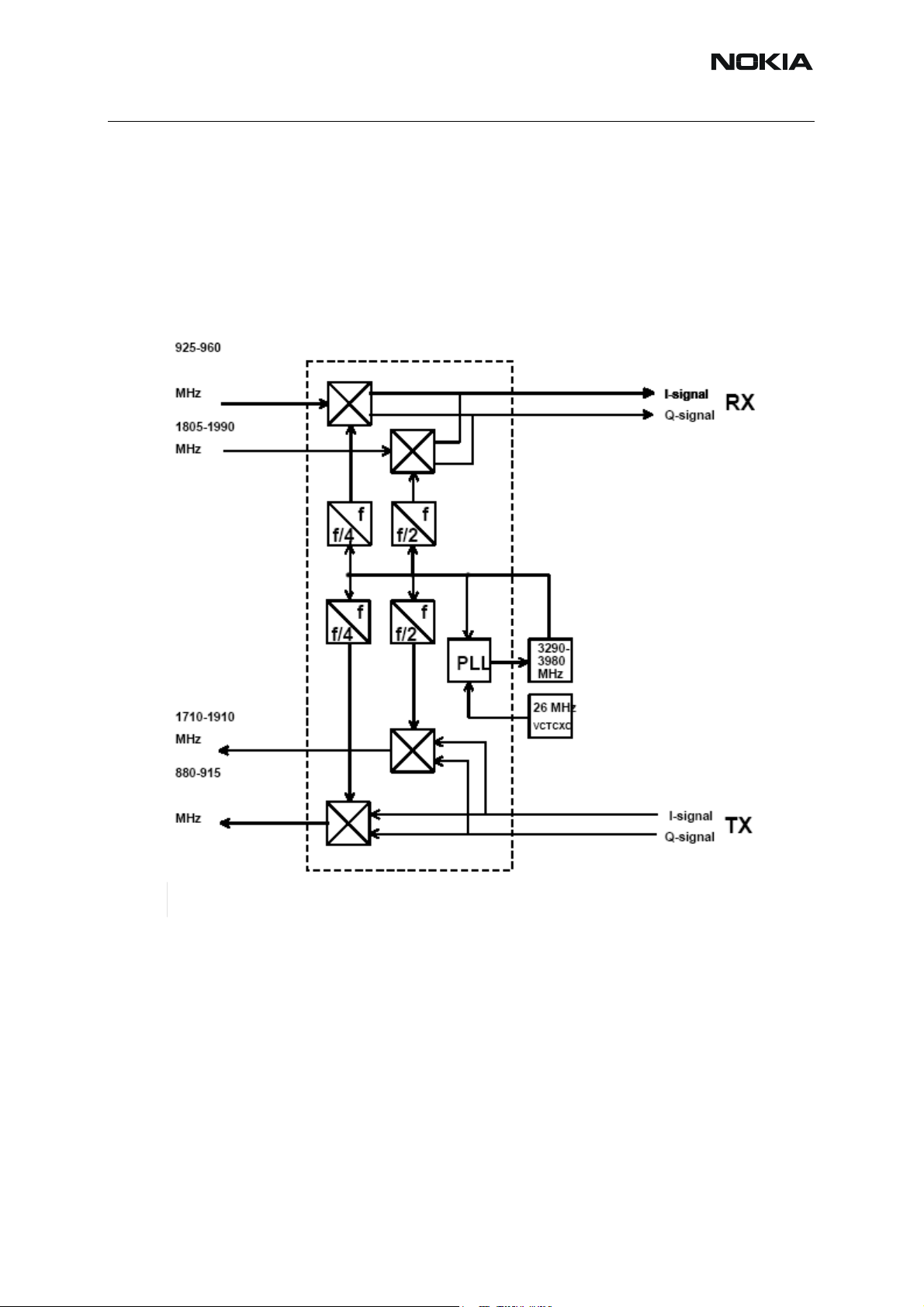
Frequency plan
The RF frequency plan is shown below. The VCO operates at the channel fre quency multiplied
by two or four depending on the frequency band of operation. This means that the baseband
modulated signals are directly converted up to the transmission frequency and the received RF
signals directly down to the baseband frequency.
Figure 3: RF frequency plan
HONI
Issue 1 11/05 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL 11
Copyright © 2005 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 12
RA-8
Nokia Customer Care 7 - RF Description and Troubleshooting
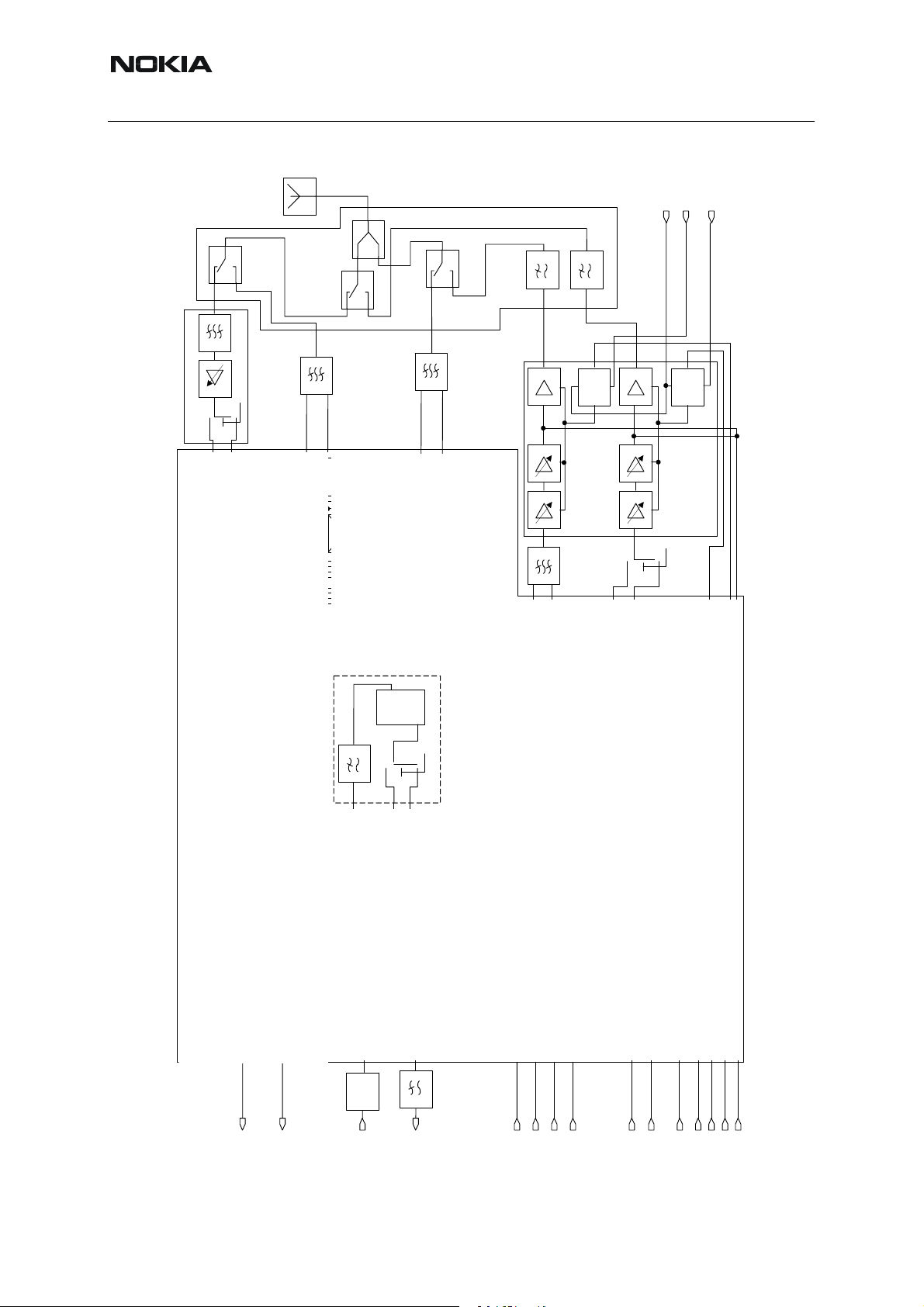
RF block diagram
IN
Antenna
IN
OUT2
OUT1
Front end
INOUT
INOUT
AGC
PCS1900
1
3
BAW-LNA
2
5
4
INOUT
SAW
DCS1800
INOUT
RF
IF
RF
LO
LO
IF
INOUT
AGC
RF
LO
IF
module
OUT1
RF
IF
IN
SAW
IN
IN OUT
OUT2
OUT1
INOUT
IN OUT
INOUT
BIAS
IN OUT
Mode (GSM/EDGE)
IN OUT
OUT2
OUT1
IN
OUT2
EGSM 900
INOUT
AGC
RF
LO
IF
f/2
OUT
f
IN
RF
LO
LO
IF
OUT
f
IN
AGC
IN OUT
AGC
IN OUT
IN OUT
AGC
IN OUT
AGC
IN OUT
1
2
5
3
4
f/4
AGC
IN OUT
AGC
IN OUT
IPA2
IPA1
INOUT
BIAS
Pwr det
Power amplifier
INOUT
HONI
INOUT
HONI
INOUT
AGC
INOUT
INOUT
AGC
IN
MODPLL
VCO
SYNT_MIX
RX-MIX
1
2
5
3
INOUT
INOUT
IN OUT
IN
4
3420 - 3980 MHz
INOUT
EGSM900
DtoS
INOUT
AGC
INOUT
INOUT
AGC
PLL
OUT
REF LE1 CLK DATA
12 dB
AGC
f
IN
IN OUT
f
OUT1
42 dB / 6dB step
VCTCXO
26 Mhz
IN
OUT2
f/2
OUT
IN
OUT1
OUT2
IN
OUTAFC
INOUT
f/4
OUT
IN OUT
RF
LO
IF
f
IN
15 dB
OUT
RF
LO
IF
CNTR
IN OUT
TXP
TXP
OUT
OUT
DCS1800/PCS1900
IN
TXC
f/2
RF
LO
IF
IN
TXC
AGC
15 dB
IN OUT
RF
LO
IF
RXI
RXQ
AFC
Sys.clock
Data
Clock
Reset
Enable
TXIP
TXIM
TXQP
TXA
TXQM
TXP
TXC
12 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 1 11/05
Copyright © 2005 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 13
RA-8
7 - RF Description and Troubleshooting Nokia Customer Care
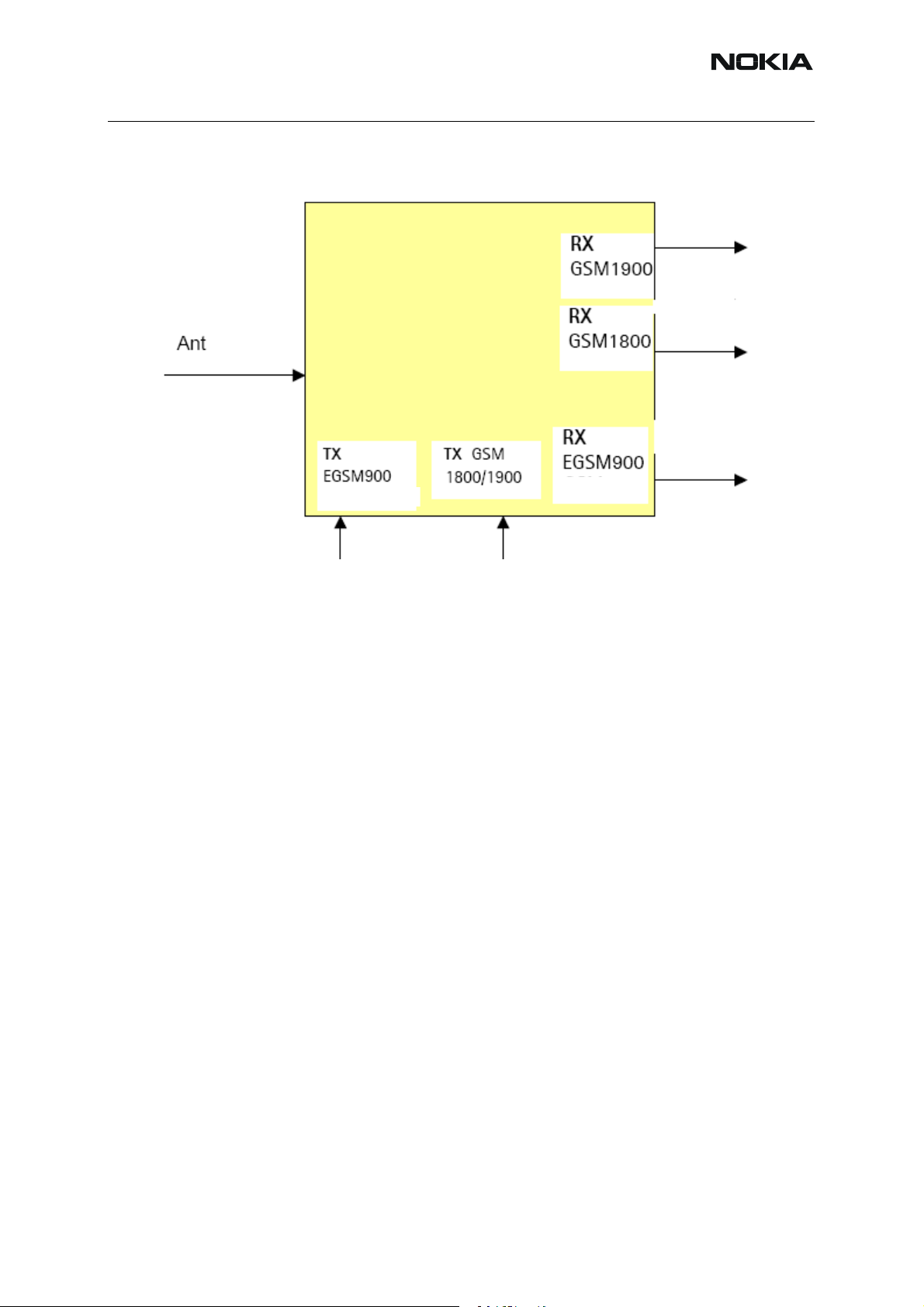
Antenna switch module (ASM)
Figure 4: ASM
DC characteristics
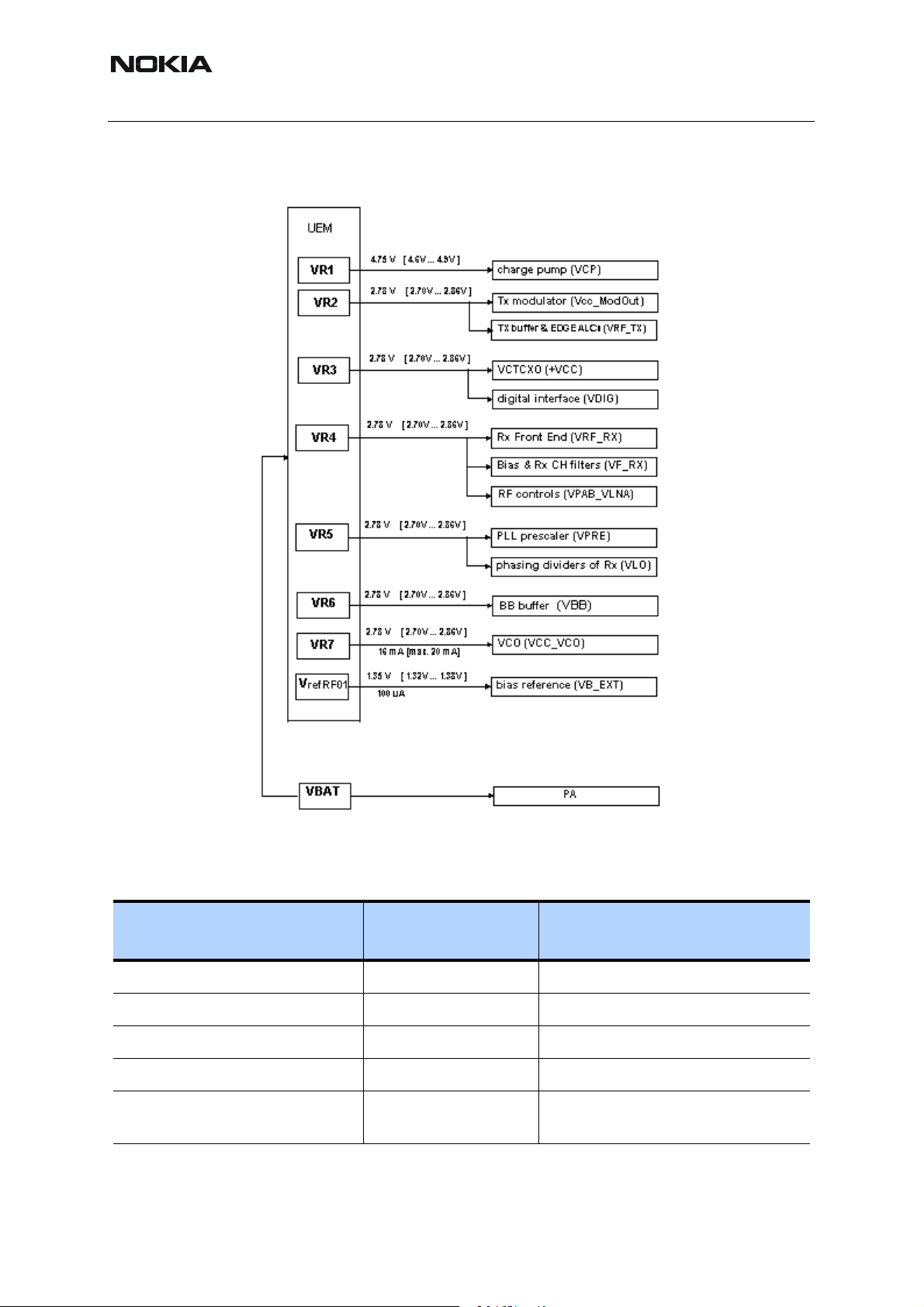
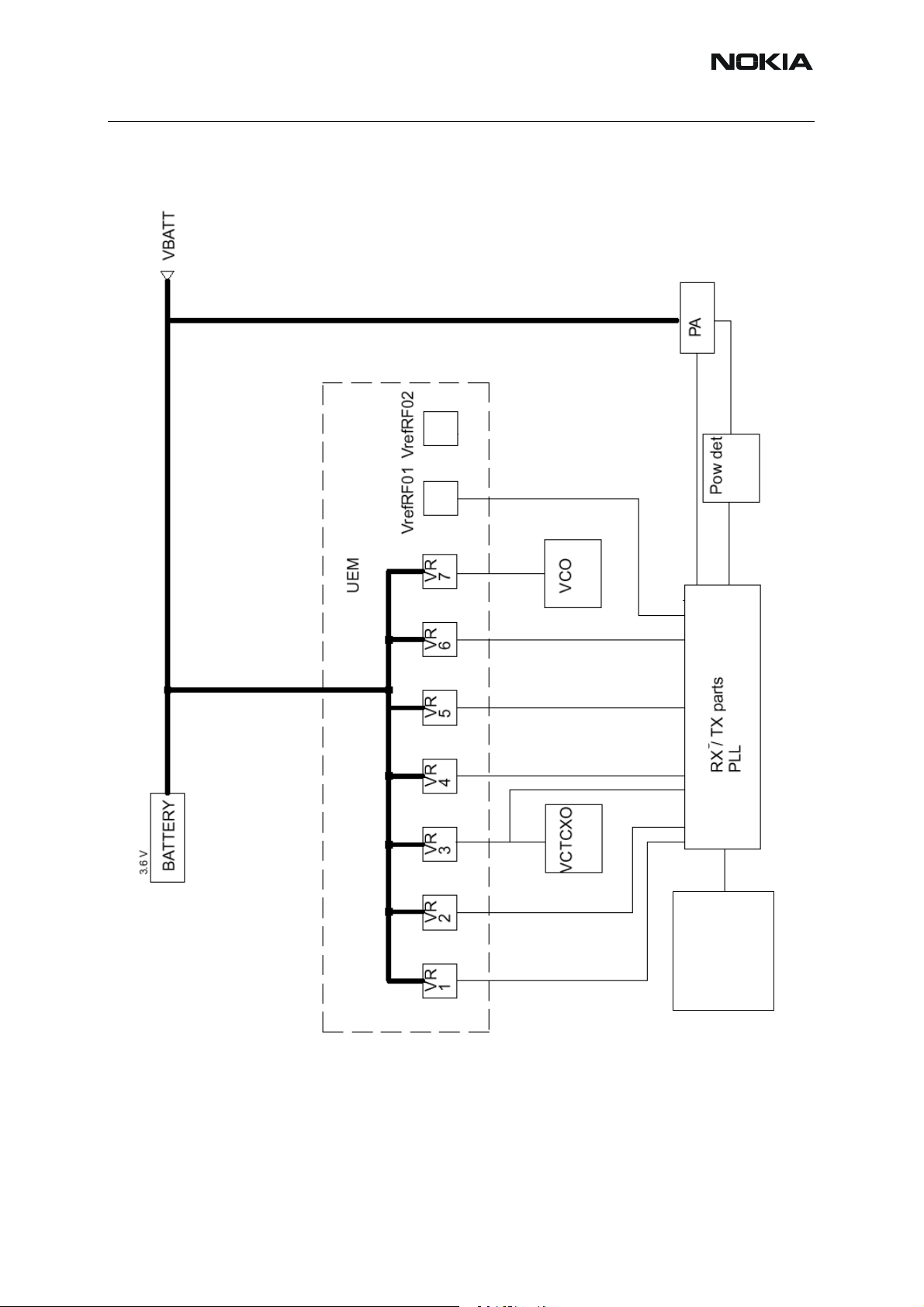
Regulators
The transceiver baseband section has a multi function analog ASIC, UEM, which contains
among other functions six pieces of 2.78 V linear regulators and a 4.8 V switch ing regulator. All
the regulators can be controlled individually by the 2.78 V logic directly or through a control register. Normally, direct control is needed because of switching speed requirement: the regulators are used to enable the RF-functions which means that the controls must be fast enough.
The use of the regulators can be seen in the power distribution diagram which is p resented in
Figure 6, “Power distribution diagram,” on page 15.
The seven regulators are named VR1 to VR7. VrefRF01 is used as a reference voltage for Honi.
The regulators (except for VR7) are connected to the Honi. Different modes of operation can
be selected inside the Honi according to the control information coming through the RFBus.
Issue 1 11/05 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL 13
Copyright © 2005 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 14
RA-8
Nokia Customer Care 7 - RF Description and Troubleshooting
DC supply currents
Figure 5: DC power supplies
Typical current consumption
The table shows the typical current consumption in different operation modes.
Operation mode
Power OFF < 10 uA Leakage current (triple band PA)
Rx, EGSM900 75 mA, peak
Rx, GSM1800/GSM1900 70 mA, peak
Tx, power level 5, EGSM900 1700 mA, peak
Tx, power level 0, GSM1800/
GSM1900
14 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 1 11/05
Copyright © 2005 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
1000 mA, peak
Current
consumption
Notes
Page 15
RA-8
7 - RF Description and Troubleshooting Nokia Customer Care
Power distribution diagram
Figure 6: Power distribution diagram
Honi
LNA
GSM1900
Issue 1 11/05 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL 15
Copyright © 2005 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 16

RA-8
Nokia Customer Care 7 - RF Description and Troubleshooting
■ RF characteristics
Channel numbers and frequencies
System Channel number TX frequency RX frequency Unit
EGSM 0 <= n <=124 F = 890 + 0.2 * n F = 935 + 0.2 * n MHz
975 <= n <= 1023 F= 890+0.2* (n -1024) F= 935+0.2* (n -1024) MHz
DCS1800 512 <= n <= 885 F=1710.2+0.2*(n-512) F=1805.2+0.2*(n-512) MHz
PCS1900 512 <= n <=810 F=1850.2+0.2*(n-512) F=1930.2+0.2*(n-512) MHz
16 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 1 11/05
Copyright © 2005 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 17

RA-8
7 - RF Description and Troubleshooting Nokia Customer Care
RF Troubleshooting
All measurements should be done using a spectrum analyzer with a high-frequency high-impedance passive probe (LO-/reference frequencies and RF power levels) and an oscilloscope
with a 10:1 probe (DC-voltages and low frequency signals).
The RF section is build around one RF ASIC (Honi N7500). For easier troubleshooting, this RF
troubleshooting document is divided into sections.
Before changing Honi, please check that both supply voltages and serial communication coming from baseband to Honi are OK. Please note that the grounding of the PA module is directly
below the PA module, so it is difficult to check or change.
Most RF semiconductors are static discharge sensitive! Therefore ESD protection must be taken care of during repair (ground straps and ESD soldering irons). Honi and PA are moisture
sensitive and thus must be handled as described in the Special Component Handling Document.
Apart from key components described in this document there are a lot of discrete components
(resistors, inductors and capacitors) of which troubleshooting is done by checking if the sold ering of the component is done properly (for factory repairs checking if it is missing from the
PWB). You can check capacitors for shortening and resistors for value by means of an ohmmeter, but be aware in-circuit measurements should be evaluated carefully.
Please be aware that all measured voltages or RF levels in this document are rough figures.
Especially RF levels vary due to different measuring equipment or different grounding of the
probe used. When using an RF probe use a pair of metallic tweezers to connect the probe
ground to the PWB ground as close to the measurement point as possible.
■ Receiver description and troubleshooting
Each receiver path is a direct conversion linear receiver. From the antenna, the received RFsignal is fed to a front end module where a diplexer first divides the signal into two separate
paths according to the band of operation: either lower, EGSM900 or upper, GSM1800/
GSM1900 path.
Most of the receiver circuitry is included in Honi.
Rx front end
The front end features include:
• Antenna 50 ohm input
• RXs single outputs
• TXs single 50 ohm inputs
• 3 control lines from Honi
Antenna
The RA-8 EGSM900/GSM1800/GSM1900 transceiver features an internal antenna.
Issue 1 11/05 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL 17
Copyright © 2005 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 18

RA-8
Nokia Customer Care 7 - RF Description and Troubleshooting
Receiver characteristics
Item Values (GSM9 00/180 0/190 0)
Type Direct conversion, Linear, FDMA/TDMA
LO frequencies 3700...3840 MHz / 3610...3760 MHz /
3860…3980 MHz
Typical 3 dB bandwidth +/- 91 kHz
Sensitivity min. - 102 dBm
Total typical receiver voltage gain (from
antenna
to RX ADC )
Receiver output level (RF level -95 dBm ) 230 mVpp, single-ended I/Q signals to RX
Typical AGC dynamic range 83 dB
Accurate AGC control range 60 dB
Typical AGC step in LNA 30 dB GSM1800/GSM1900, 25 dB GSM900
Usable input dynamic range -102 ... -10 dBm
RSSI dynamic range -110 ... -48 dBm
Compensated gain variation in receiving
band
86 dB
ADCs
+/- 1.0 dB
18 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 1 11/05
Copyright © 2005 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 19

RA-8
7 - RF Description and Troubleshooting Nokia Customer Care
General instructions for Rx troubleshooting
To start Rx troubleshooting:
1. Connect test jig to a computer with a DAU-9S cable or to a FPS-8 flash prommer with an XCS-4 modular cable.
Make sure that you have PKD-1 dongle connected to the computer’s parallel port.
2. Connect a DC power supply to the module test jig with an FLC-2 cable.
3. Set the DC supply voltage to 6 V.
4. Connect an RF cable to the RF connector of the module test jig (MJ-83) and to
RF signal generator.
5. Set the phone module to test jig and start Phoenix service software.
6. Initialize connection to the phone. (Use FBUS driver when using DAU-9S and
COMBOX driver when using FPS-8).
7. From the File menu, choose “Choose Product”.
8. From the list, select RA-8.
9. From the toolbar, set operating mode to "Local".
10.From the Testing menu, choose “RF Controls”.
11.In the “RF Controls” window:
- Select band “GSM 900", "GSM 1800" or “GSM1900” (Default = "GSM900")
- Set Active unit to "Rx" (Default = "Rx")
- Set Operation mode to "Burst" (Default = "Burst")
For continuous mode:
- Set Operation mode to "Continuous"
- Set AGC to "12: FEG_ON + DTOS_ON + BB_30=Vgain60” (maximum gain setting used in normal mode) (Default = "14: FEG_ON + DTOS_ON +
BB_42=Vgain72")
- Set Rx/Tx channel to 37 on GSM900 band, 700 on GSM1800 band or 661on
GSM1900 (Defaults)
12.Apply
942.46771 MHz (channel 37 + 67.710 kHz offset),
1842.86771 MHz (channel 700 + 67.710 kHz offset) or
1960.06771 MHz (channel 661 + 67.71 kHz) –90 dBm signal
to the RF connector (remember to compensate for cable attenuation).
When measuring with an oscilloscope on "RXI" or "RXQ", you should se e the fol-
lowing screens on a working GSM900, GSM1800 or GSM1900 receiver:
Issue 1 11/05 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL 19
Copyright © 2005 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 20

RA-8
Nokia Customer Care 7 - RF Description and Troubleshooting
Figure 7: Rx I/Q signal, burst mode, input level –90dBm
• Receiver I or Q burst mode signal (channel 37) measured from test point RXI
or RXQ with 942.46771 MHz signal, input level –90dBm at RF-connector.
Correct signal amplitudes approximately:
GSM900~170mVpp
GSM1800~140mVpp
GSM1900~160mVpp
Signal part frequency 67.7kHz sine.
DC level of signal part is 1.35V. DC level can vary about +/-100mV between I
20 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 1 11/05
Copyright © 2005 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 21

RA-8
7 - RF Description and Troubleshooting Nokia Customer Care
and Q signals and between different bands as well.
GSM1900 receiver burst mode I or Q signal at ch 661 with input signal
1960.067MHz, level –90 dBm at RF-connector.
Trace2: With wider time scaling both monitoring and own Rx bursts are seen,
1
st burst (shorter) is monitoring and 2nd burst (longer) is own Rx burst.
Trace1: External LNA VCC supply voltage at burst mod e, input leve l –90 dBm.
Measured from test point LNA_VCC
Issue 1 11/05 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL 21
Copyright © 2005 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 22

RA-8
Nokia Customer Care 7 - RF Description and Troubleshooting
Figure 8: GSM1900 Rx I or Q signal (trace2), burst mode.
Detailed view of GSM900 continuous mode Rx I and Q signals measured from test points RXI
and RXQ simultaneously.
Used channel 37, input signal 942.46771 MHz, level –90 dBm at antenna port, AGC settin g 12.
Phase difference should be 90 degrees between Rx I and Q signals at all bands.
22 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 1 11/05
Copyright © 2005 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 23

RA-8
7 - RF Description and Troubleshooting Nokia Customer Care
Troubleshooting diagram for GSM900 receiver
Phone in “Continuous” mode, AGC setting “12”.
HONI
HONI
HONI
Z7600
Check Z7601,
L7603, L7604
HONI
HONI
Issue 1 11/05 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL 23
Copyright © 2005 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 24

RA-8
Nokia Customer Care 7 - RF Description and Troubleshooting
T roubleshooting diagram for GSM1800 receiver
Phone in “Continuous” mode, AGC setting “12.
HONI
HONI
Z7600
Z7602, L7601,
L7602
HONI
HONI
HONI
24 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 1 11/05
Copyright © 2005 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 25

RA-8
7 - RF Description and Troubleshooting Nokia Customer Care
T roubleshooting diagram for GSM1900 receiver
Phone in “Continuous” mode, AGC setting “12.
HONI
HONI
HONI
LNAB_P 2.6V
LNA_P 0V
Check Z7603
Z7600
HONI
HONI
HONI
Check Z7603, R7601,
R7602, L7600
HONI
Issue 1 11/05 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL 25
Copyright © 2005 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 26

RA-8
/
/
GS
/
Nokia Customer Care 7 - RF Description and Troubleshooting
■ Transmitter description and troubleshooting
The transmitter consists of:
• two final frequency IQ-modulators
• two power amplifiers, for the lower and upper bands separately
• power control loop.
The IQ-modulators are integrated in Honi, as well as the operational amplifiers of the power
control loop. The two power amplifiers are located in a single module with a power detector. In
the GMSK mode, the power is controlled by adjusting the DC bias levels of the power amplifiers.
Power amplifier
The power amplifier features include:
• 50 ohm input and output, EGSM900/GSM1800/GSM1900
• internal power detector
• EDGE mode
RF ASIC Honi
The RF ASIC features include
Figure 9: Power amplifier
EGSM900
EGSM
out
GSM1800
DCS/
1900
PCS
out
GSM1800
EGSM900
EGSM
Power
control
1900
DCS/PCS
Power
control
EGSM900
EGSM
in
M1800
DCS/
1900
PCS
in
Power
detector
Mode
• Package LFGBGA88
• Balanced I/Q demodulator and balanced I/Q modulator
• Power control operational amplifier, acts as an error amplifier
• The signal from VCO is balanced, frequencies 3296 to 3980 MHz
26 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 1 11/05
Copyright © 2005 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 27

RA-8
7 - RF Description and Troubleshooting Nokia Customer Care
• EGSM900 and GSM1800 low noise amplifier (LNA) are integrated.
• IPAD substrate, including integrated coils, resistors and capacitors
The Honi can be tested by test points only.
AFC function
AFC is used to lock the transceiver’s clock to the frequency of the base station.
Transmitter characteristics
Item Values (EGSM900/1800/1900)
Type Direct conversion, nonlinear, FDMA/TDMA
LO frequency range 3520…3660 MHz / 3420…3570 MHz /
3700…3820 MHz
Output power GMSK 33 / 30 / 30 dBm 2 W / 1W peak
Output power 8-PSK 27 / 26 / 26 dBm 0.5 W / 0.4 W peak
Gain control range min. 30 dB
Maximum phase error (RMS/peak) GMSK
Maximum EVM (RMS/peak) 8-PSK
max 5 deg./20 deg. Peak
max 10% / 30%
General instructions for Tx troubleshooting
Please refer to section Service Concepts in Chapter 3, Service Software Instructions.
To start Tx troubleshooting:
1. Connect the test jig MJ-83 to a computer with a DAU-9S cable or to an FPS-8
flash prommer with an XCS-4 modular cable.
Make sure that you have a PKD-1 dongle connected to the computer’s parallel port.
2. Connect a DC power supply to the module test jig (MJ-83) with an FLC-2 cable.
Note: When repairing or tuning the transmitter use external DC supply with at least
3A current capability. Set the DC supply voltage to 3.9V and set the jumpe r connector on test jig to "bypass" position.
3. Connect an RF cable to the RF connector of the module test jig (MJ-83) and
measurement equipment; or at least a 10dB attenuator, otherwise the PA may be
damaged. Use a spectrum analyzer as measurement equipment.
Note: The maximum input power of a spectrum analyzer is +30dBm. It is recommended to use 10dB attenuator on the spectrum analyzer input to prevent any damage.
4. Set the phone module to test jig and start Phoenix service software.
5. Initialize connection to the phone. (Use FBUS driver when using DAU-9S and
COMBOX driver when using FPS-8).
Issue 1 11/05 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL 27
Copyright © 2005 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 28

RA-8
Nokia Customer Care 7 - RF Description and Troubleshooting
6. To choose a product in Phoenix:
From the File menu, choose “Choose Product” and select RA-8 from the list
or
from the File menu, choose “Scan Product”.
7. From the toolbar, set operating mode to "Local".
8. From the Testing menu, choose “RF Controls”.
9. In the “RF Controls” window:
- Select band "GSM900" or "GSM 1800" or "GSM1900" (Default = "GSM900").
- Set Active unit to "Tx" (Default = "Rx").
- Set Operation mode to "Burst" (Default = "Burst").
- Set Tx data type to "Random" (Default = "All1").
- Set Rx/Tx channel to 37 on GSM900 band or 700 on GSM1800 band or 661 on
GSM1900 (Defaults).
- Set Tx PA mode to "Free" (Default).
- Set power level to 5 (Default = 19) on GSM900 or to 0 (Default = 15) on GSM1800
or GSM1900.
28 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 1 11/05
Copyright © 2005 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 29

RA-8
7 - RF Description and Troubleshooting Nokia Customer Care
T ransmitter troubleshooting diagram
Honi
Replace Honi
Issue 1 11/05 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL 29
Copyright © 2005 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 30

RA-8
Nokia Customer Care 7 - RF Description and Troubleshooting
Honi IC troubleshooting diagram
Honi
- VR2, VR5, VR6 = 2.8V
- Honi serial interface
Replace Honi
30 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 1 11/05
Copyright © 2005 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 31

RA-8
7 - RF Description and Troubleshooting Nokia Customer Care
PA and antenna switch troubleshooting diagram
Honi
Issue 1 11/05 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL 31
Copyright © 2005 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 32

RA-8
4
Nokia Customer Care 7 - RF Description and Troubleshooting
Pictures of transmitter signals
VPCTRL 850/900 power level 5 at R7703/C7703
VPCRTL_1800/1900 power level 0 at R7704/C7704
VTXB 850/900 at C7713 VTXB_1800/1900 at C771
TXI/TXQ TX signals at R7516/R7515/C7535/C7536
I
TXC 850/900 power level 5 at R7522
VANT_1 at C7805 VANT_2 at C7804
VANT_3 at C7538
32 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 1 11/05
Copyright © 2005 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 33

RA-8
7 - RF Description and Troubleshooting Nokia Customer Care
Figure 10: Tx out signal, 900 band burst mode, channel 37
Issue 1 11/05 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL 33
Copyright © 2005 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 34

RA-8
Nokia Customer Care 7 - RF Description and Troubleshooting
■ Additional information for EDGE troubleshooting
Note! EDGE mode troubleshooting differs slightly from basic GSM troubleshooting.
To start EDGE troubleshooting:
1. Initialize a connection to the phone (see GSM900/1800/1900 troubleshooting
instructions).
2. To select a product in Phoenix:
From the File menu, choose “Choose Product “and select RA-8 from the list
or
from the File menu, choose “Scan Product”.
3. From the toolbar, set operating mode to “Local”
4. From the Testing menu, choose “RF Controls”.
5. In the “RF Controls” window:
- Select Band “GSM900” or “GSM1800” or “GSM1900” (Default = "GSM900").
- Set Active unit to “Tx” (Default=”Rx”).
- Set Edge “On” (Default=”Off”).
- Set Operation mode to “Burst” (Default=”Burst”).
- Set Tx data type to “Alternate PN9” (Default=”All1”).
- Set Rx/Tx channel to 37 on GSM900 or 700 on GSM1800 or 661 on GSM1900
(Defaults).
- Set power level to 8 (Default = 19) on GSM900 or to 2 (Default = 0) on GSM1800
or GSM1900.
Note! For GSM900 Edge power levels 5, 6 and 7 are not in use and for
GSM1800&1900 Edge power levels 0 and 1 are not in use.
34 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 1 11/05
Copyright © 2005 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 35

RA-8
7 - RF Description and Troubleshooting Nokia Customer Care
T ransmitter EDGE troubleshooting diagram
Honi EDGE
Replace HONI
Issue 1 11/05 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL 35
Copyright © 2005 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 36

RA-8
Nokia Customer Care 7 - RF Description and Troubleshooting
Honi EDGE troubleshooting diagram
Check with oscilloscope:
-TXI/TXQ signals
- VR2, VR5, VR6 = 2.8V
No
-VR1, VR2, VR4, VR5, VR6 =2.8V
-VrefRF01 = 1.35V
-Honi serial interface
-Helgo serial interface
-TXP & TXC & TXA
OK?
Yes
Check with RF probe:
4G VCO signal output:
No
-3346.4MHz(GSM850)
-3589.6MHz (GSM900)
-3589.6MHz(GSM900)
-3495.6MHz (GSM1800)
-3495.6MHz(GSM1800)
-3760MHz (GSM1900)
-3760MHz(GSM1900)
Level > - 10dBm
Level > - 10dBm
OK?
Yes
Yes
Check modulator output components
No
HONI EDGE
Helgo EDGE
troubleshooting
OK?
OK?
Replace faulty
component(s)
Baseband
troubleshooting
Synthesizer
troubleshooting
Replace HELGO
HONI
36 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 1 11/05
Copyright © 2005 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 37

RA-8
7 - RF Description and Troubleshooting Nokia Customer Care
PA and antenna switch EDGE troubleshooting diagram
HONI
Issue 1 11/05 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL 37
Copyright © 2005 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 38

RA-8
Nokia Customer Care 7 - RF Description and Troubleshooting
Pictures of EDGE transmitter signals
Figure 11: I_ref_1800/1900 power level 2 at R7700/C7700
Figure 12: VTXB 1800/1900 power level 2 at C7714
38 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 1 11/05
Copyright © 2005 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 39

RA-8
7 - RF Description and Troubleshooting Nokia Customer Care
Figure 13: TXI/TXQ signal at C7535/C7536/R7516/R7517
Figure 14: TXA 900/1800/1900 at C7538
Issue 1 11/05 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL 39
Copyright © 2005 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 40

RA-8
Nokia Customer Care 7 - RF Description and Troubleshooting
Figure 15: VTXB 900 power level 8 at C7713
Figure 16: I_ref 900 power level 8 at R7701/C7701
40 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 1 11/05
Copyright © 2005 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 41

RA-8
7 - RF Description and Troubleshooting Nokia Customer Care
Figure 17: TXC 900 power level 8 at 7522
Issue 1 11/05 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL 41
Copyright © 2005 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 42

RA-8
Nokia Customer Care 7 - RF Description and Troubleshooting
■ Synthesizer description and troubleshooting
Frequency synthesizers
The VCO frequency is locked by a PLL (phase locked loop) in to a stable frequency so urce given by a VCTCXO which is running at 26 MHz. The frequency of the VCTCXO is in turn locked
into the frequency of the base station with the help of an AFC voltage which is generated in
UEM by an 11 bit D/A converter. The PLL is located in Honi and it is controlled through the RFBus.
The required frequency dividers for modulator and demodulator mixers are integrated in Honi.
Loop filter filters out the comparison pulses of the phase detector and generates a DC control
voltage to the VCO. The loop filter determines the step response of the PLL (settling time) and
contributes to the stability of the loop.
The frequency synthesizer is integrated in Honi except for the VCTCXO, VCO, and the loop
filter.
General instructions for synthesizer troubleshooting
To start synthesizer troubleshooting:
1. Connect the test jig (MJ-83) to a computer with a DAU-9S cable or to an FPS-8
flash prommer with an XCS-4 modular cable.
Make sure that you have a PKD-1 dongle connected to the computer’s parallel port.
2. Connect a DC power supply or FPS-8 to the module test jig with a PCS-1 cable.
3. Set the DC supply voltage to 3.6V and set the jumper connector on test jig to "bypass" position.
4. Set the phone module to test jig and start Phoenix service software
5. Initialize connection to the phone. (Use FBUS driver when using DAU-9S and
COMBOX driver when using FPS-8).
6. From the File menu, choose “Choose Product”.
7. From the list, select RA-8.
8. From the toolbar, set operating mode to "Local"
9. From the Testing menu, choose “RF Controls”.
10.In the “RF Controls” window:
- Select band "GSM900", "GSM 1800" or "GSM1900" (Default = "GSM900").
- Set Active unit to "Rx" (Default = "Rx").
- Set Operation mode to "Continuous" (Default = "Burst").
- Set Rx/Tx channel to 37 on GSM900 band, 700 on GSM1800 band, 661 on
GSM1900 band (Defaults).
42 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 1 11/05
Copyright © 2005 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 43

RA-8
A
y
y
7 - RF Description and Troubleshooting Nokia Customer Care
Troubleshooting diagram for synthesizer
Setup with Phoenix:
ctive Unit: Rx
Mode: Continuous
Channel:
190 (GSM850)
37 (GSM900)
700 (GSM1800)
661 (GSM1900)
Troubleshooting diagram for synthesi zer
Spectrum analyzer
Check with RF probe
VCO (G7500) out signal:
-3526.4MHz(GSM850)
-3769.6MHz(GSM900)
-3685.6MHz(GSM1800)
-3920MHz(GSM1900)
Level > -10dBm *
OK?
Yes
PLL Block is functional
Oscilloscope
No
VCTCXO Suppl
VR3=2.78V
Oscilloscope
VCTCXO output at G7501
26MHz,app.0.8Vpp
Oscilloscope
VCO suppl
VR7 = 2.78V, VR5=2.78V,
VR1=4.7V
Spectrum analyzer
VCO (G7500) out
Some signal 3-4.4 GHz
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
No
No
No
Check supply filter components :
Fault is in non-reworkable
C2232, C7590.
component. Refer to
Check UEM and SW.
current BR handling guidance.
G7501 defective or short
Circuit to GND
Check supply filter components:
R7500, C7501, C7560, C2230, C7551,
R7500, C7501, C7500, C7505
C7552, C7553
Check UEM and Software.
Check VCO G7500,
Balun T7500
Yes
Check loop filter components:
C7503, C7504, C7505, R7501, R7502
R7501, R7502
Wrong writing on RFBus (see BB part)
Wrong writing on RFBus (see BB part)
If ok change RF ASIC N7500
If ok, change RF ASIC N7500
C7502, C7519,
* When 1 kOhm passive probe is used,
Correct the measurement by +26dB
Issue 1 11/05 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL 43
Copyright © 2005 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 44

RA-8
Nokia Customer Care 7 - RF Description and Troubleshooting
Pictures of synthesizer signals
Figure 18: 26MHz at G501 pin out
Figure 19: 26MHz RFCLK at R420/C420
44 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 1 11/05
Copyright © 2005 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 45

RA-8
7 - RF Description and Troubleshooting Nokia Customer Care
Figure 20: 1800 Tx, channel 512, burst mode
Figure 21: 1900 Rx, channel 810, continuous mode
Issue 1 11/05 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL 45
Copyright © 2005 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 46

RA-8
m
W
Nokia Customer Care 7 - RF Description and Troubleshooting
Figure 22: VCO output, 1800 band, ch700, Rx on, continuous output
-12
-20
-30
-40
-50
-60
-70
Ref Lvl
-12 dBm
-12 dBm
1VIE
Marker 1 [T1]
-15.59 dBm
3.68560301 GHz
RBW 10 kHz
VBW 10 kHzRef Lvl
SWT 25 ms
1
RF Att 10 dB
Unit dB
A
1MA
-80
-90
-100
-112
Date: 29.APR.2003 13:41:26
100 kHz/Center 3.6856 GHz Span 1 MHz
46 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 1 11/05
Copyright © 2005 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 47

RA-8
7 - RF Description and Troubleshooting Nokia Customer Care
Frequency Lists
GSM900 (including EGSM900)
CH TX RX VCO TX VCO RX CH TX RX VCO TX VCO RX CH TX RX VCO TX VCO RX
975 880.2 925.2 3520.8 3700.8 1 890.2 935.2 3560.8 3740.8 63 902.6 947.6 3610.4 3790.4
976 880.4 925.4 3521.6 3701.6 2 890.4 935.4 3561.6 3741.6 64 902.8 947.8 3611.2 3791.2
977 880.6 925.6 3522.4 3702.4 3 890.6 935.6 3562.4 3742.4 65 903.0 948.0 3612.0 3792.0
978 880.8 925.8 3523.2 3703.2 4 890.8 935.8 3563.2 3743.2 66 903.2 948.2 3612.8 3792.8
979 881.0 926.0 3524.0 3704.0 5 891.0 936.0 3564.0 3744.0 67 903.4 948.4 3613.6 3793.6
980 881.2 926.2 3524.8 3704.8 6 891.2 936.2 3564.8 3744.8 68 903.6 948.6 3614.4 3794.4
981 881.4 926.4 3525.6 3705.6 7 891.4 936.4 3565.6 3745.6 69 903.8 948.8 3615.2 3795.2
982 881.6 926.6 3526.4 3706.4 8 891.6 936.6 3566.4 3746.4 70 904.0 949.0 3616.0 3796.0
983 881.8 926.8 3527.2 3707.2 9 891.8 936.8 3567.2 3747.2 71 904.2 949.2 3616.8 3796.8
984 882.0 927.0 3528.0 3708.0 10 892.0 937.0 3568.0 3748.0 72 904.4 949.4 3617.6 3797.6
985 882.2 927.2 3528.8 3708.8 11 892.2 937.2 3568.8 3748.8 73 904.6 949.6 3618.4 3798.4
986 882.4 927.4 3529.6 3709.6 12 892.4 937.4 3569.6 3749.6 74 904.8 949.8 3619.2 3799.2
987 882.6 927.6 3530.4 3710.4 13 892.6 937.6 3570.4 3750.4 75 905.0 950.0 3620.0 3800.0
988 882.8 927.8 3531.2 3711.2 14 892.8 937.8 3571.2 3751.2 76 905.2 950.2 3620.8 3800.8
989 883.0 928.0 3532.0 3712.0 15 893.0 938.0 3572.0 3752.0 77 905.4 950.4 3621.6 3801.6
990 883.2 928.2 3532.8 3712.8 16 893.2 938.2 3572.8 3752.8 78 905.6 950.6 3622.4 3802.4
991 883.4 928.4 3533.6 3713.6 17 893.4 938.4 3573.6 3753.6 79 905.8 950.8 3623.2 3803.2
992 883.6 928.6 3534.4 3714.4 18 893.6 938.6 3574.4 3754.4 80 906.0 951.0 3624.0 3804.0
993 883.8 928.8 3535.2 3715.2 19 893.8 938.8 3575.2 3755.2 81 906.2 951.2 3624.8 3804.8
994 884.0 929.0 3536.0 3716.0 20 894.0 939.0 3576.0 3756.0 82 906.4 951.4 3625.6 3805.6
995 884.2 929.2 3536.8 3716.8 21 894.2 939.2 3576.8 3756.8 83 906.6 951.6 3626.4 3806.4
996 884.4 929.4 3537.6 3717.6 22 894.4 939.4 3577.6 3757.6 84 906.8 951.8 3627.2 3807.2
997 884.6 929.6 3538.4 3718.4 23 894.6 939.6 3578.4 3758.4 85 907.0 952.0 3628.0 3808.0
998 884.8 929.8 3539.2 3719.2 24 894.8 939.8 3579.2 3759.2 86 907.2 952.2 3628.8 3808.8
999 885.0 930.0 3540.0 3720.0 25 895.0 940.0 3580.0 3760.0 87 907.4 952.4 3629.6 3809.6
1000 885.2 930.2 3540.8 3720.8 26 895.2 940.2 3580.8 3760.8 88 907.6 952.6 3630.4 3810.4
1001 885.4 930.4 3541.6 3721.6 27 895.4 940.4 3581.6 3761.6 89 907.8 952.8 3631.2 3811.2
1002 885.6 930.6 3542.4 3722.4 28 895.6 940.6 3582.4 3762.4 90 908.0 953.0 3632.0 3812.0
1003 885.8 930.8 3543.2 3723.2 29 895.8 940.8 3583.2 3763.2 91 908.2 953.2 3632.8 3812.8
1004 886.0 931.0 3544.0 3724.0 30 896.0 941.0 3584.0 3764.0 92 908.4 953.4 3633.6 3813.6
1005 886.2 931.2 3544.8 3724.8 31 896.2 941.2 3584.8 3764.8 93 908.6 953.6 3634.4 3814.4
1006 886.4 931.4 3545.6 3725.6 32 896.4 941.4 3585.6 3765.6 94 908.8 953.8 3635.2 3815.2
1007 886.6 931.6 3546.4 3726.4 33 896.6 941.6 3586.4 3766.4 95 909.0 954.0 3636.0 3816.0
1008 886.8 931.8 3547.2 3727.2 34 896.8 941.8 3587.2 3767.2 96 909.2 954.2 3636.8 3816.8
1009 887.0 932.0 3548.0 3728.0 35 897.0 942.0 3588.0 3768.0 97 909.4 954.4 3637.6 3817.6
1010 887.2 932.2 3548.8 3728.8 36 897.2 942.2 3588.8 3768.8 98 909.6 954.6 3638.4 3818.4
1011 887.4 932.4 3549.6 3729.6 37 897.4 942.4 3589.6 3769.6 99 909.8 954.8 3639.2 3819.2
1012 887.6 932.6 3550.4 3730.4 38 897.6 942.6 3590.4 3770.4 100 910.0 955.0 3640.0 3820.0
1013 887.8 932.8 3551.2 3731.2 39 897.8 942.8 3591.2 3771.2 101 910.2 955.2 3640.8 3820.8
1014 888.0 933.0 3552.0 3732.0 40 898.0 943.0 3592.0 3772.0 102 910.4 955.4 3641.6 3821.6
1015 888.2 933.2 3552.8 3732.8 41 898.2 943.2 3592.8 3772.8 103 910.6 955.6 3642.4 3822.4
1016 888.4 933.4 3553.6 3733.6 42 898.4 943.4 3593.6 3773.6 104 910.8 955.8 3643.2 3823.2
1017 888.6 933.6 3554.4 3734.4 43 898.6 943.6 3594.4 3774.4 105 911.0 956.0 3644.0 3824.0
1018 888.8 933.8 3555.2 3735.2 44 898.8 943.8 3595.2 3775.2 106 911.2 956.2 3644.8 3824.8
1019 889.0 934.0 3556.0 3736.0 45 899.0 944.0 3596.0 3776.0 107 911.4 956.4 3645.6 3825.6
1020 889.2 934.2 3556.8 3736.8 46 899.2 944.2 3596.8 3776.8 108 911.6 956.6 3646.4 3826.4
1021 889.4 934.4 3557.6 3737.6 47 899.4 944.4 3597.6 3777.6 109 911.8 956.8 3647.2 3827.2
1022 889.6 934.6 3558.4 3738.4 48 899.6 944.6 3598.4 3778.4 110 912.0 957.0 3648.0 3828.0
1023 889.8 934.8 3559.2 3739.2 49 899.8 944.8 3599.2 3779.2 111 912.2 957.2 3648.8 3828.8
0 890.0 935.0 3560.0 3740.0 50 900.0 945.0 3600.0 3780.0 112 912.4 957.4 3649.6 3829.6
51 900.2 945.2 3600.8 3780.8 113 91 2.6 957.6 3 650.4 3830.4
52 900.4 945.4 3601.6 3781.6 114 91 2.8 957.8 3 651.2 3831.2
53 900.6 945.6 3602.4 3782.4 115 91 3.0 958.0 3 652.0 3832.0
54 900.8 945.8 3603.2 3783.2 116 91 3.2 958.2 3 652.8 3832.8
55 901.0 946.0 3604.0 3784.0 117 91 3.4 958.4 3 653.6 3833.6
56 901.2 946.2 3604.8 3784.8 118 91 3.6 958.6 3 654.4 3834.4
57 901.4 946.4 3605.6 3785.6 119 91 3.8 958.8 3 655.2 3835.2
58 901.6 946.6 3606.4 3786.4 120 91 4.0 959.0 3 656.0 3836.0
59 901.8 946.8 3607.2 3787.2 121 91 4.2 959.2 3 656.8 3836.8
60 902.0 947.0 3608.0 3788.0 122 91 4.4 959.4 3 657.6 3837.6
61 902.2 947.2 3608.8 3788.8 123 91 4.6 959.6 3 658.4 3838.4
62 902.4 947.4 3609.6 3789.6 124 91 4.8 959.8 3 659.2 3839.2
Issue 1 11/05 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL 47
Copyright © 2005 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 48

RA-8
Frequency list GSM1800
Nokia Customer Care 7 - RF Description and Troubleshooting
GSM1800
CH TX RX VCO TX VCO RX CH TX RX VCO TX VCO RX CH TX RX VCO TX VC O RX CH TX RX VCO TX VCO RX
512
1710.2 1805.2 3420.4 3610.4
513
1710.4 1805.4 3420.8 3610.8
514
1710.6 1805.6 3421.2 3611.2
515
1710.8 1805.8 3421.6 3611.6
516
1711.0 1806.0 3422.0 3612.0
517
1711.2 1806.2 3422.4 3612.4
518
1711.4 1806.4 3422.8 3612.8
519
1711.6 1806.6 3423.2 3613.2
520
1711.8 1806.8 3423.6 3613.6
521
1712.0 1807.0 3424.0 3614.0
522
1712.2 1807.2 3424.4 3614.4
523
1712.4 1807.4 3424.8 3614.8
524
1712.6 1807.6 3425.2 3615.2
525
1712.8 1807.8 3425.6 3615.6
526
1713.0 1808.0 3426.0 3616.0
527
1713.2 1808.2 3426.4 3616.4
528
1713.4 1808.4 3426.8 3616.8
529
1713.6 1808.6 3427.2 3617.2
530
1713.8 1808.8 3427.6 3617.6
531
1714.0 1809.0 3428.0 3618.0
532
1714.2 1809.2 3428.4 3618.4
533
1714.4 1809.4 3428.8 3618.8
534
1714.6 1809.6 3429.2 3619.2
535
1714.8 1809.8 3429.6 3619.6
536
1715.0 1810.0 3430.0 3620.0
537
1715.2 1810.2 3430.4 3620.4
538
1715.4 1810.4 3430.8 3620.8
539
1715.6 1810.6 3431.2 3621.2
540
1715.8 1810.8 3431.6 3621.6
541
1716.0 1811.0 3432.0 3622.0
542
1716.2 1811.2 3432.4 3622.4
543
1716.4 1811.4 3432.8 3622.8
544
1716.6 1811.6 3433.2 3623.2
545
1716.8 1811.8 3433.6 3623.6
546
1717.0 1812.0 3434.0 3624.0
547
1717.2 1812.2 3434.4 3624.4
548
1717.4 1812.4 3434.8 3624.8
549
1717.6 1812.6 3435.2 3625.2
550
1717.8 1812.8 3435.6 3625.6
551
1718.0 1813.0 3436.0 3626.0
552
1718.2 1813.2 3436.4 3626.4
553
1718.4 1813.4 3436.8 3626.8
554
1718.6 1813.6 3437.2 3627.2
555
1718.8 1813.8 3437.6 3627.6
556
1719.0 1814.0 3438.0 3628.0
557
1719.2 1814.2 3438.4 3628.4
558
1719.4 1814.4 3438.8 3628.8
559
1719.6 1814.6 3439.2 3629.2
560
1719.8 1814.8 3439.6 3629.6
561
1720.0 1815.0 3440.0 3630.0
562
1720.2 1815.2 3440.4 3630.4
563
1720.4 1815.4 3440.8 3630.8
564
1720.6 1815.6 3441.2 3631.2
565
1720.8 1815.8 3441.6 3631.6
566
1721.0 1816.0 3442.0 3632.0
567
1721.2 1816.2 3442.4 3632.4
568
1721.4 1816.4 3442.8 3632.8
569
1721.6 1816.6 3443.2 3633.2
570
1721.8 1816.8 3443.6 3633.6
606
1729.0 1824.0 3458.0 3648.0
607
1729.2 1824.2 3458.4 3648.4
608
1729.4 1824.4 3458.8 3648.8
609
1729.6 1824.6 3459.2 3649.2
610
1729.8 1824.8 3459.6 3649.6
611
1730.0 1825.0 3460.0 3650.0
612
1730.2 1825.2 3460.4 3650.4
613
1730.4 1825.4 3460.8 3650.8
614
1730.6 1825.6 3461.2 3651.2
615
1730.8 1825.8 3461.6 3651.6
616
1731.0 1826.0 3462.0 3652.0
617
1731.2 1826.2 3462.4 3652.4
618
1731.4 1826.4 3462.8 3652.8
619
1731.6 1826.6 3463.2 3653.2
620
1731.8 1826.8 3463.6 3653.6
621
1732.0 1827.0 3464.0 3654.0
622
1732.2 1827.2 3464.4 3654.4
623
1732.4 1827.4 3464.8 3654.8
624
1732.6 1827.6 3465.2 3655.2
625
1732.8 1827.8 3465.6 3655.6
626
1733.0 1828.0 3466.0 3656.0
627
1733.2 1828.2 3466.4 3656.4
628
1733.4 1828.4 3466.8 3656.8
629
1733.6 1828.6 3467.2 3657.2
630
1733.8 1828.8 3467.6 3657.6
631
1734.0 1829.0 3468.0 3658.0
632
1734.2 1829.2 3468.4 3658.4
633
1734.4 1829.4 3468.8 3658.8
634
1734.6 1829.6 3469.2 3659.2
635
1734.8 1829.8 3469.6 3659.6
636
1735.0 1830.0 3470.0 3660.0
637
1735.2 1830.2 3470.4 3660.4
638
1735.4 1830.4 3470.8 3660.8
639
1735.6 1830.6 3471.2 3661.2
640
1735.8 1830.8 3471.6 3661.6
641
1736.0 1831.0 3472.0 3662.0
642
1736.2 1831.2 3472.4 3662.4
643
1736.4 1831.4 3472.8 3662.8
644
1736.6 1831.6 3473.2 3663.2
645
1736.8 1831.8 3473.6 3663.6
646
1737.0 1832.0 3474.0 3664.0
647
1737.2 1832.2 3474.4 3664.4
648
1737.4 1832.4 3474.8 3664.8
649
1737.6 1832.6 3475.2 3665.2
650
1737.8 1832.8 3475.6 3665.6
651
1738.0 1833.0 3476.0 3666.0
652
1738.2 1833.2 3476.4 3666.4
653
1738.4 1833.4 3476.8 3666.8
654
1738.6 1833.6 3477.2 3667.2
655
1738.8 1833.8 3477.6 3667.6
656
1739.0 1834.0 3478.0 3668.0
657
1739.2 1834.2 3478.4 3668.4
658
1739.4 1834.4 3478.8 3668.8
659
1739.6 1834.6 3479.2 3669.2
660
1739.8 1834.8 3479.6 3669.6
661
1740.0 1835.0 3480.0 3670.0
662
1740.2 1835.2 3480.4 3670.4
663
1740.4 1835.4 3480.8 3670.8
664
1740.6 1835.6 3481.2 3671.2
700
1747.8 1842.8 3495.6 3685.6
701
1748.0 1843.0 3496.0 3686.0
702
1748.2 1843.2 3496.4 3686.4
703
1748.4 1843.4 3496.8 3686.8
704
1748.6 1843.6 3497.2 3687.2
705
1748.8 1843.8 3497.6 3687.6
706
1749.0 1844.0 3498.0 3688.0
707
1749.2 1844.2 3498.4 3688.4
708
1749.4 1844.4 3498.8 3688.8
709
1749.6 1844.6 3499.2 3689.2
710
1749.8 1844.8 3499.6 3689.6
711
1750.0 1845.0 3500.0 3690.0
712
1750.2 1845.2 3500.4 3690.4
713
1750.4 1845.4 3500.8 3690.8
714
1750.6 1845.6 3501.2 3691.2
715
1750.8 1845.8 3501.6 3691.6
716
1751.0 1846.0 3502.0 3692.0
717
1751.2 1846.2 3502.4 3692.4
718
1751.4 1846.4 3502.8 3692.8
719
1751.6 1846.6 3503.2 3693.2
720
1751.8 1846.8 3503.6 3693.6
721
1752.0 1847.0 3504.0 3694.0
722
1752.2 1847.2 3504.4 3694.4
723
1752.4 1847.4 3504.8 3694.8
724
1752.6 1847.6 3505.2 3695.2
725
1752.8 1847.8 3505.6 3695.6
726
1753.0 1848.0 3506.0 3696.0
727
1753.2 1848.2 3506.4 3696.4
728
1753.4 1848.4 3506.8 3696.8
729
1753.6 1848.6 3507.2 3697.2
730
1753.8 1848.8 3507.6 3697.6
731
1754.0 1849.0 3508.0 3698.0
732
1754.2 1849.2 3508.4 3698.4
733
1754.4 1849.4 3508.8 3698.8
734
1754.6 1849.6 3509.2 3699.2
735
1754.8 1849.8 3509.6 3699.6
736
1755.0 1850.0 3510.0 3700.0
737
1755.2 1850.2 3510.4 3700.4
738
1755.4 1850.4 3510.8 3700.8
739
1755.6 1850.6 3511.2 3701.2
740
1755.8 1850.8 3511.6 3701.6
741
1756.0 1851.0 3512.0 3702.0
742
1756.2 1851.2 3512.4 3702.4
743
1756.4 1851.4 3512.8 3702.8
744
1756.6 1851.6 3513.2 3703.2
745
1756.8 1851.8 3513.6 3703.6
746
1757.0 1852.0 3514.0 3704.0
747
1757.2 1852.2 3514.4 3704.4
748
1757.4 1852.4 3514.8 3704.8
749
1757.6 1852.6 3515.2 3705.2
750
1757.8 1852.8 3515.6 3705.6
751
1758.0 1853.0 3516.0 3706.0
752
1758.2 1853.2 3516.4 3706.4
753
1758.4 1853.4 3516.8 3706.8
754
1758.6 1853.6 3517.2 3707.2
755
1758.8 1853.8 3517.6 3707.6
756
1759.0 1854.0 3518.0 3708.0
757
1759.2 1854.2 3518.4 3708.4
758
1759.4 1854.4 3518.8 3708.8
794
1766.6 1861.6 3533.2 3723.2
795
1766.8 1861.8 3533.6 3723.6
796
1767.0 1862.0 3534.0 3724.0
797
1767.2 1862.2 3534.4 3724.4
798
1767.4 1862.4 3534.8 3724.8
799
1767.6 1862.6 3535.2 3725.2
800
1767.8 1862.8 3535.6 3725.6
801
1768.0 1863.0 3536.0 3726.0
802
1768.2 1863.2 3536.4 3726.4
803
1768.4 1863.4 3536.8 3726.8
804
1768.6 1863.6 3537.2 3727.2
805
1768.8 1863.8 3537.6 3727.6
806
1769.0 1864.0 3538.0 3728.0
807
1769.2 1864.2 3538.4 3728.4
808
1769.4 1864.4 3538.8 3728.8
809
1769.6 1864.6 3539.2 3729.2
810
1769.8 1864.8 3539.6 3729.6
811
1770.0 1865.0 3540.0 3730.0
812
1770.2 1865.2 3540.4 3730.4
813
1770.4 1865.4 3540.8 3730.8
814
1770.6 1865.6 3541.2 3731.2
815
1770.8 1865.8 3541.6 3731.6
816
1771.0 1866.0 3542.0 3732.0
817
1771.2 1866.2 3542.4 3732.4
818
1771.4 1866.4 3542.8 3732.8
819
1771.6 1866.6 3543.2 3733.2
820
1771.8 1866.8 3543.6 3733.6
821
1772.0 1867.0 3544.0 3734.0
822
1772.2 1867.2 3544.4 3734.4
823
1772.4 1867.4 3544.8 3734.8
824
1772.6 1867.6 3545.2 3735.2
825
1772.8 1867.8 3545.6 3735.6
826
1773.0 1868.0 3546.0 3736.0
827
1773.2 1868.2 3546.4 3736.4
828
1773.4 1868.4 3546.8 3736.8
829
1773.6 1868.6 3547.2 3737.2
830
1773.8 1868.8 3547.6 3737.6
831
1774.0 1869.0 3548.0 3738.0
832
1774.2 1869.2 3548.4 3738.4
833
1774.4 1869.4 3548.8 3738.8
834
1774.6 1869.6 3549.2 3739.2
835
1774.8 1869.8 3549.6 3739.6
836
1775.0 1870.0 3550.0 3740.0
837
1775.2 1870.2 3550.4 3740.4
838
1775.4 1870.4 3550.8 3740.8
839
1775.6 1870.6 3551.2 3741.2
840
1775.8 1870.8 3551.6 3741.6
841
1776.0 1871.0 3552.0 3742.0
842
1776.2 1871.2 3552.4 3742.4
843
1776.4 1871.4 3552.8 3742.8
844
1776.6 1871.6 3553.2 3743.2
845
1776.8 1871.8 3553.6 3743.6
846
1777.0 1872.0 3554.0 3744.0
847
1777.2 1872.2 3554.4 3744.4
848
1777.4 1872.4 3554.8 3744.8
849
1777.6 1872.6 3555.2 3745.2
850
1777.8 1872.8 3555.6 3745.6
851
1778.0 1873.0 3556.0 3746.0
852
1778.2 1873.2 3556.4 3746.4
48 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 1 11/05
Copyright © 2005 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 49

RA-8
Frequency list NPL 2 GSM1900
7 - RF Description and Troubleshooting Nokia Customer Care
GSM1900
CH TX RX VCO TX VCO RX CH TX RX VCO TX VCO RX CH TX RX VCO TX VCO RX CH TX RX VCO TX VCO RX
512
1850.2 1930.2 3700.4 3860.4
513
1850.4 1930.4 3700.8 3860.8
514
1850.6 1930.6 3701.2 3861.2
515
1850.8 1930.8 3701.6 3861.6
516
1851.0 1931.0 3702.0 3862.0
517
1851.2 1931.2 3702.4 3862.4
518
1851.4 1931.4 3702.8 3862.8
519
1851.6 1931.6 3703.2 3863.2
520
1851.8 1931.8 3703.6 3863.6
521
1852.0 1932.0 3704.0 3864.0
522
1852.2 1932.2 3704.4 3864.4
523
1852.4 1932.4 3704.8 3864.8
524
1852.6 1932.6 3705.2 3865.2
525
1852.8 1932.8 3705.6 3865.6
526
1853.0 1933.0 3706.0 3866.0
527
1853.2 1933.2 3706.4 3866.4
528
1853.4 1933.4 3706.8 3866.8
529
1853.6 1933.6 3707.2 3867.2
530
1853.8 1933.8 3707.6 3867.6
531
1854.0 1934.0 3708.0 3868.0
532
1854.2 1934.2 3708.4 3868.4
533
1854.4 1934.4 3708.8 3868.8
534
1854.6 1934.6 3709.2 3869.2
535
1854.8 1934.8 3709.6 3869.6
536
1855.0 1935.0 3710.0 3870.0
537
1855.2 1935.2 3710.4 3870.4
538
1855.4 1935.4 3710.8 3870.8
539
1855.6 1935.6 3711.2 3871.2
540
1855.8 1935.8 3711.6 3871.6
541
1856.0 1936.0 3712.0 3872.0
542
1856.2 1936.2 3712.4 3872.4
543
1856.4 1936.4 3712.8 3872.8
544
1856.6 1936.6 3713.2 3873.2
545
1856.8 1936.8 3713.6 3873.6
546
1857.0 1937.0 3714.0 3874.0
547
1857.2 1937.2 3714.4 3874.4
548
1857.4 1937.4 3714.8 3874.8
549
1857.6 1937.6 3715.2 3875.2
550
1857.8 1937.8 3715.6 3875.6
551
1858.0 1938.0 3716.0 3876.0
552
1858.2 1938.2 3716.4 3876.4
553
1858.4 1938.4 3716.8 3876.8
554
1858.6 1938.6 3717.2 3877.2
555
1858.8 1938.8 3717.6 3877.6
556
1859.0 1939.0 3718.0 3878.0
557
1859.2 1939.2 3718.4 3878.4
558
1859.4 1939.4 3718.8 3878.8
559
1859.6 1939.6 3719.2 3879.2
560
1859.8 1939.8 3719.6 3879.6
561
1860.0 1940.0 3720.0 3880.0
562
1860.2 1940.2 3720.4 3880.4
563
1860.4 1940.4 3720.8 3880.8
564
1860.6 1940.6 3721.2 3881.2
565
1860.8 1940.8 3721.6 3881.6
566
1861.0 1941.0 3722.0 3882.0
567
1861.2 1941.2 3722.4 3882.4
568
1861.4 1941.4 3722.8 3882.8
569
1861.6 1941.6 3723.2 3883.2
570
1861.8 1941.8 3723.6 3883.6
606
1869.0 1949.0 3738.0 3898.0
607
1869.2 1949.2 3738.4 3898.4
608
1869.4 1949.4 3738.8 3898.8
609
1869.6 1949.6 3739.2 3899.2
610
1869.8 1949.8 3739.6 3899.6
611
1870.0 1950.0 3740.0 3900.0
612
1870.2 1950.2 3740.4 3900.4
613
1870.4 1950.4 3740.8 3900.8
614
1870.6 1950.6 3741.2 3901.2
615
1870.8 1950.8 3741.6 3901.6
616
1871.0 1951.0 3742.0 3902.0
617
1871.2 1951.2 3742.4 3902.4
618
1871.4 1951.4 3742.8 3902.8
619
1871.6 1951.6 3743.2 3903.2
620
1871.8 1951.8 3743.6 3903.6
621
1872.0 1952.0 3744.0 3904.0
622
1872.2 1952.2 3744.4 3904.4
623
1872.4 1952.4 3744.8 3904.8
624
1872.6 1952.6 3745.2 3905.2
625
1872.8 1952.8 3745.6 3905.6
626
1873.0 1953.0 3746.0 3906.0
627
1873.2 1953.2 3746.4 3906.4
628
1873.4 1953.4 3746.8 3906.8
629
1873.6 1953.6 3747.2 3907.2
630
1873.8 1953.8 3747.6 3907.6
631
1874.0 1954.0 3748.0 3908.0
632
1874.2 1954.2 3748.4 3908.4
633
1874.4 1954.4 3748.8 3908.8
634
1874.6 1954.6 3749.2 3909.2
635
1874.8 1954.8 3749.6 3909.6
636
1875.0 1955.0 3750.0 3910.0
637
1875.2 1955.2 3750.4 3910.4
638
1875.4 1955.4 3750.8 3910.8
639
1875.6 1955.6 3751.2 3911.2
640
1875.8 1955.8 3751.6 3911.6
641
1876.0 1956.0 3752.0 3912.0
642
1876.2 1956.2 3752.4 3912.4
643
1876.4 1956.4 3752.8 3912.8
644
1876.6 1956.6 3753.2 3913.2
645
1876.8 1956.8 3753.6 3913.6
646
1877.0 1957.0 3754.0 3914.0
647
1877.2 1957.2 3754.4 3914.4
648
1877.4 1957.4 3754.8 3914.8
649
1877.6 1957.6 3755.2 3915.2
650
1877.8 1957.8 3755.6 3915.6
651
1878.0 1958.0 3756.0 3916.0
652
1878.2 1958.2 3756.4 3916.4
653
1878.4 1958.4 3756.8 3916.8
654
1878.6 1958.6 3757.2 3917.2
655
1878.8 1958.8 3757.6 3917.6
656
1879.0 1959.0 3758.0 3918.0
657
1879.2 1959.2 3758.4 3918.4
658
1879.4 1959.4 3758.8 3918.8
659
1879.6 1959.6 3759.2 3919.2
660
1879.8 1959.8 3759.6 3919.6
661
1880.0 1960.0 3760.0 3920.0
662
1880.2 1960.2 3760.4 3920.4
663
1880.4 1960.4 3760.8 3920.8
664
1880.6 1960.6 3761.2 3921.2
700
1887.8 1967.8 3775.6 3935.6
701
1888.0 1968.0 3776.0 3936.0
702
1888.2 1968.2 3776.4 3936.4
703
1888.4 1968.4 3776.8 3936.8
704
1888.6 1968.6 3777.2 3937.2
705
1888.8 1968.8 3777.6 3937.6
706
1889.0 1969.0 3778.0 3938.0
707
1889.2 1969.2 3778.4 3938.4
708
1889.4 1969.4 3778.8 3938.8
709
1889.6 1969.6 3779.2 3939.2
710
1889.8 1969.8 3779.6 3939.6
711
1890.0 1970.0 3780.0 3940.0
712
1890.2 1970.2 3780.4 3940.4
713
1890.4 1970.4 3780.8 3940.8
714
1890.6 1970.6 3781.2 3941.2
715
1890.8 1970.8 3781.6 3941.6
716
1891.0 1971.0 3782.0 3942.0
717
1891.2 1971.2 3782.4 3942.4
718
1891.4 1971.4 3782.8 3942.8
719
1891.6 1971.6 3783.2 3943.2
720
1891.8 1971.8 3783.6 3943.6
721
1892.0 1972.0 3784.0 3944.0
722
1892.2 1972.2 3784.4 3944.4
723
1892.4 1972.4 3784.8 3944.8
724
1892.6 1972.6 3785.2 3945.2
725
1892.8 1972.8 3785.6 3945.6
726
1893.0 1973.0 3786.0 3946.0
727
1893.2 1973.2 3786.4 3946.4
728
1893.4 1973.4 3786.8 3946.8
729
1893.6 1973.6 3787.2 3947.2
730
1893.8 1973.8 3787.6 3947.6
731
1894.0 1974.0 3788.0 3948.0
732
1894.2 1974.2 3788.4 3948.4
733
1894.4 1974.4 3788.8 3948.8
734
1894.6 1974.6 3789.2 3949.2
735
1894.8 1974.8 3789.6 3949.6
736
1895.0 1975.0 3790.0 3950.0
737
1895.2 1975.2 3790.4 3950.4
738
1895.4 1975.4 3790.8 3950.8
739
1895.6 1975.6 3791.2 3951.2
740
1895.8 1975.8 3791.6 3951.6
741
1896.0 1976.0 3792.0 3952.0
742
1896.2 1976.2 3792.4 3952.4
743
1896.4 1976.4 3792.8 3952.8
744
1896.6 1976.6 3793.2 3953.2
745
1896.8 1976.8 3793.6 3953.6
746
1897.0 1977.0 3794.0 3954.0
747
1897.2 1977.2 3794.4 3954.4
748
1897.4 1977.4 3794.8 3954.8
749
1897.6 1977.6 3795.2 3955.2
750
1897.8 1977.8 3795.6 3955.6
751
1898.0 1978.0 3796.0 3956.0
752
1898.2 1978.2 3796.4 3956.4
753
1898.4 1978.4 3796.8 3956.8
754
1898.6 1978.6 3797.2 3957.2
755
1898.8 1978.8 3797.6 3957.6
756
1899.0 1979.0 3798.0 3958.0
757
1899.2 1979.2 3798.4 3958.4
758
1899.4 1979.4 3798.8 3958.8
794
1906.6 1986.6 3813.2 3973.2
795
1906.8 1986.8 3813.6 3973.6
796
1907.0 1987.0 3814.0 3974.0
797
1907.2 1987.2 3814.4 3974.4
798
1907.4 1987.4 3814.8 3974.8
799
1907.6 1987.6 3815.2 3975.2
800
1907.8 1987.8 3815.6 3975.6
801
1908.0 1988.0 3816.0 3976.0
802
1908.2 1988.2 3816.4 3976.4
803
1908.4 1988.4 3816.8 3976.8
804
1908.6 1988.6 3817.2 3977.2
805
1908.8 1988.8 3817.6 3977.6
806
1909.0 1989.0 3818.0 3978.0
807
1909.2 1989.2 3818.4 3978.4
808
1909.4 1989.4 3818.8 3978.8
809
1909.6 1989.6 3819.2 3979.2
810
1909.8 1989.8 3819.6 3979.6
Issue 1 11/05 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL 49
Copyright © 2005 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 50

RA-8
Nokia Customer Care 7 - RF Description and Troubleshooting
■ RF tunings after repairs
The following tunings have to be performed after repairs:
• Repairs in the Tx part require "Tx Power Level Tuning".
• When component replacements around the modulator area (RF path from
UEM via RF ASIC to RF PA) have been done, "Tx IQ Tuning" is additionally
required.
• In general Rx repairs, the front-end always requires "Rx Calibration" and “Rx
Band Filter Calibration” for all three bands.
• Repairs in the PLL circuit always require "Rx Calibration" of the low band.
• If the RF ASIC is replaced, all calibrations mentioned above have to be done.
Refer to Chapter 3, Service Software Instructions, for instructions on the above-mentioned tunings.
50 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL Issue 1 11/05
Copyright © 2005 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
 Loading...
Loading...