Page 1

Nokia MetroSite EDGE Base Station
DN98621958 © Nokia Corporation Internal Copy 1 (30)
Issue 3-0 en Nokia Proprietary and Confidential
Warnings and Cautions
Page 2

Warnings and Cautions
2 (30) © Nokia Corporation Internal Copy DN98621958
Nokia Proprietary and Confidential Issue 3-0 en
The information in this documentation is subject to change without notice and describes only
the product defined in the introduction of this documentation. This documentation is intended
for the use of Nokia's customers only for the purposes of the agreement under which the
documentation is submitted, and no part of it may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or
means without the prior written permission of Nokia. The documentation has been prepared to
be used by professional and properly trained personnel, and the customer assumes full
responsibility when using it. Nokia welcomes customer comments as part of the process of
continuous development and improvement of the documentation.
The information or statements given in this documentation concerning the suitability, capacity,
or performance of the mentioned hardware or software products cannot be considered binding
but shall be defined in the agreement made between Nokia and the customer. However, Nokia
has made all reasonable efforts to ensure that the instructions contained in the documentation
are adequate and free of material errors and omissions. Nokia will, if necessary, explain issues
which may not be covered by the documentation.
Nokia's liability for any errors in the documentation is limited to the documentary correction of
errors. NOKIA WILL NOT BE RESPONSIBLE IN ANY EVENT FOR ERRORS IN THIS
DOCUMENTATION OR FOR ANY DAMAGES, INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL
(INCLUDING MONETARY LOSSES), that might arise from the use of this documentation or
the information in it.
This documentation and the product it describes are considered protected by copyright
according to the applicable laws.
NOKIA logo is a registered trademark of Nokia Corporation.
Other product names mentioned in this documentation may be trademarks of their respective
companies, and they are mentioned for identification purposes only.
Copyright © Nokia Corporation 2002. All rights reserved.
Page 3

DN98621958 © Nokia Corporation Internal Copy 3 (30)
Issue 3-0 en Nokia Proprietary and Confidential
Hereby, Nokia Corporation, declares that this product is in compliance with the
essential requirements and other relevant provisions of Directive: 1999/5/EC.
The product is marked with the CE marking and Notified Body number according to the
Directive 1999/5/EC
FCC FCC §15.21 - Information to user - This product is used as an intentional radiated
equipment and any changes or modifications on the equipment without any approval
by Nokia could void the user's authority to operate the equipment.
FCC §15.105 - Information to user - This equipment has been tested and found to
comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC
Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful
interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and can
radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the
instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there
is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this
equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can
be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to
correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the
receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
0523
Page 4

Warnings and Cautions
4 (30) © Nokia Corporation Internal Copy DN98621958
Nokia Proprietary and Confidential Issue 3-0 en
Page 5

DN98621958 © Nokia Corporation Internal Copy 5 (30)
Issue 3-0 en Nokia Proprietary and Confidential
Contents
Contents 5
List of tables 6
List of figures 7
1 About this document 11
1.1 Safety guidelines 11
2 Warnings 13
2.1 Personnel 13
2.2 Dangerous voltage 13
2.3 Weight 16
2.4 High temperatures 16
2.5 Toxic hazards 17
2.5.1 Beryllium oxide 17
2.6 Electromagnetic fields and RF power 18
2.6.1 General guidelines 18
2.6.2 Formula for minimum safety distances 19
2.6.3 Safety distance calculation examples 19
3 Cautions 23
3.1 Handling the BTS 23
3.1.1 Storage and transportation 23
3.1.2 Weight 23
3.1.3 Heat management 24
3.1.4 Grounding 24
3.1.5 Electro-static discharge protection 24
3.2 BTS power supply 26
3.2.1 AC and DC connectors 26
3.2.2 Grounding of AC power supply units 27
Index 29
Page 6

Warnings and Cautions
6 (30) © Nokia Corporation Internal Copy DN98621958
Nokia Proprietary and Confidential Issue 3-0 en
List of tables
Table 1. Description for distance calculations in controlled and uncontrolled
environments 20
Table 2. Safety distance calculation example 20
Page 7

DN98621958 © Nokia Corporation Internal Copy 7 (30)
Issue 3-0 en Nokia Proprietary and Confidential
List of figures
Figure 1. Dangerous voltage symbol 14
Figure 2. Stand-by symbol on the power supply unit 15
Figure 3. Hot surface symbol 17
Figure 4. Beryllium Oxide label 17
Figure 5. Hot surface label 24
Figure 6. Electro-static sensitive device label 25
Figure 7. Using the antistatic wrist strap 26
Page 8

Warnings and Cautions
8 (30) © Nokia Corporation Internal Copy DN98621958
Nokia Proprietary and Confidential Issue 3-0 en
Page 9

DN98621958 © Nokia Corporation Internal Copy 9 (30)
Issue 3-0 en Nokia Proprietary and Confidential
Summary of Changes
Version 1, 12th November 1999.
Version 2, 2
nd
June 2000:
• added GSM references to the title and body text
• added EC marking
• changed maximum power in Table 2 to 5W
Version 3, 30th June 2001:
• updated for EDGE
Page 10

Warnings and Cautions
10 (30) © Nokia Corporation Internal Copy DN98621958
Nokia Proprietary and Confidential Issue 3-0 en
Page 11

About this document
DN98621958 © Nokia Corporation Internal Copy 11 (30)
Issue 3-0 en Nokia Proprietary and Confidential
WARNING
Caution
1 About this document
This document details the safety precautions to be followed when working with
the Nokia MetroSite EDGE Base Station. The instructions in Nokia MetroSite
EDGE Base Station: Installation and Nokia MetroSite EDGE Base Station:
Maintenance must be followed when installing the Nokia MetroSite EDGE Base
Station and performing any maintenance on it. Failure to follow these instructions
may be dangerous to the installation and maintenance personnel.
1.1 Safety guidelines
The safety guidelines are designed as follows:
• Warnings alert the reader to dangers which may cause loss of life, physical
injury or ill health. The symbol denoting a warning is presented below.
This is a warning!
• Cautions are used to denote possible damage to equipment but not dangers
to personnel. The symbol denoting a caution is presented below.
This is a caution!
Page 12

Warnings and Cautions
12 (30) © Nokia Corporation Internal Copy DN98621958
Nokia Proprietary and Confidential Issue 3-0 en
Page 13

Warnings
DN98621958 © Nokia Corporation Internal Copy 13 (30)
Issue 3-0 en Nokia Proprietary and Confidential
WARNING
2 Warnings
2.1 Personnel
Installation, commissioning and maintenance measures for any Nokia Base
Station (BTS) may be performed only by trained and authorized personnel. The
Nokia MetroSite EDGE Base Station must be installed so that only authorized
personnel have access to its sensitive parts.
Always prevent unauthorized personnel from accessing the Nokia MetroSite
EDGE Base Station.
2.2 Dangerous voltage
Potentially lethal voltages are present within this system. For more information
on grounding and on the power supply, refer to Nokia MetroSite EDGE Base
Station: Requirements for Installation and Operation.
The symbol shown in Figure 1 denotes dangerous voltage. The Nokia MetroSite
EDGE Base Station is labelled with this symbol.
Page 14

Warnings and Cautions
14 (30) © Nokia Corporation Internal Copy DN98621958
Nokia Proprietary and Confidential Issue 3-0 en
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
Figure 1. Dangerous voltage symbol
Make sure that applicable high voltage safety precautions are taken before
attempting to work on the system with the power connected!
Potentially lethal voltages can be induced if the equipment is not grounded
correctly. Ensure that all ground connections are secure and nonremovable!
An electrical plug with a ground connection is not sufficient as it can be
pulled off. There is a possibility of surge voltage through the transmission
lines in the case of lightning.
Connect the Nokia MetroSite BTS to the main grounding busbar of the site!
Electrical currents from power and communication cables is dangerous.
Page 15

Warnings
DN98621958 © Nokia Corporation Internal Copy 15 (30)
Issue 3-0 en Nokia Proprietary and Confidential
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
Ensure that the ground connection is established before an AC or DC power
outlet is connected to the BTS! Ensure that the ground connection is
removed only after the AC or DC power outlet is disconnected!
The power switch of the Nokia MetroSite EDGE Base Station does not
disconnect it from the power network (AC/DC). The power switch of the
Nokia MetroSite EDGE Base Station power supply unit has two positions:
ON and stand-by.
A separate main switch on the site is considered to be the disconnect device
for safety and service purposes.
The symbol shown in Figure 2 is used to denote the stand-by position of the power
supply unit power switch.
Figure 2. Stand-by symbol on the power supply unit
Do not rely on the power switch alone to isolate a supply. When switching
OFF the Nokia MetroSite EDGE Base Station, make sure that the power
supply is completely isolated by setting the power switch to OFF (including
the site mains power switch), disconnecting all relevant connectors, and
removing all relevant fuses!
Page 16

Warnings and Cautions
16 (30) © Nokia Corporation Internal Copy DN98621958
Nokia Proprietary and Confidential Issue 3-0 en
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
The site mains power switch must be turned OFF before connecting the
mains power cable to the Nokia MetroSite EDGE Base Station!
Do not disconnect the antenna connectors when the Nokia MetroSite EDGE
Base Station is powered ON!
When using an external synchronisation source, make sure that the ground for the
Nokia MetroSite EDGE Base Station and for the device supplying the
synchronisation signal are at the same ground potential. If this is not the case,
make sure that the synchronisation cable shield is capacitively grounded at the
supply end.
2.3 Weight
The Nokia MetroSite EDGE Base Station weighs 28 to 40 kg (62 to 88 lb)
depending on the number of TRXs. Lifting of the fully equipped BTS
requires at least two people.
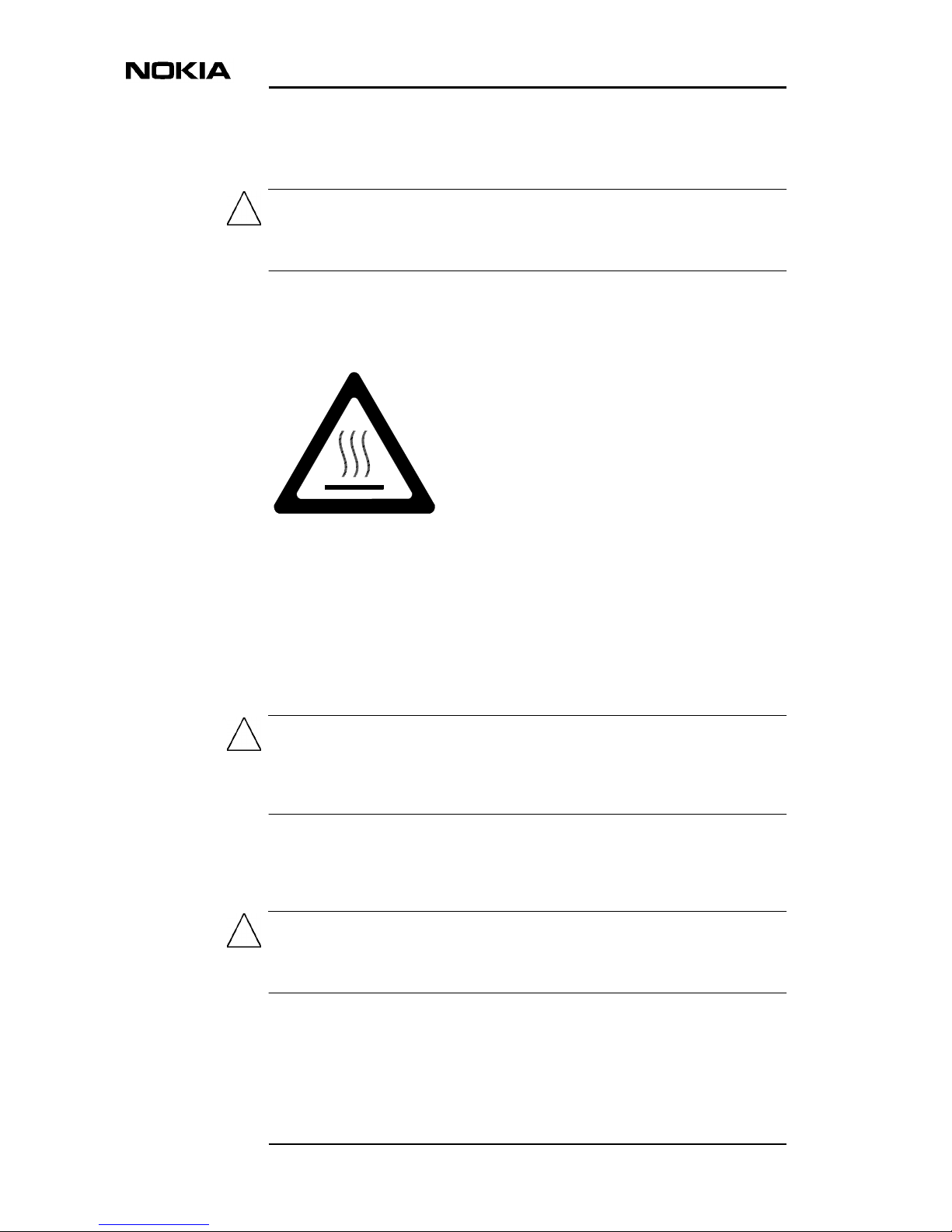
2.4 High temperatures
The symbol shown in Figure 3denotes a hot surface. Equipment whose surface
reaches high temperatures is labelled with this symbol.
Page 17

Warnings
DN98621958 © Nokia Corporation Internal Copy 17 (30)
Issue 3-0 en Nokia Proprietary and Confidential
WARNING
Figure 3. Hot surface symbol
During operation, the interior of the Nokia MetroSite EDGE Base Station
reaches a temperature of 60° to 70°C (140° to 158°F).
2.5 Toxic hazards
2.5.1 Beryllium oxide
The Nokia MetroSite EDGE Base Station uses beryllium oxide (BeO), which can
be harmful to human health.
Beryllium oxide is used in:
• Power amplifiers
• RF transistors (isolator internal load)
The equipment containing BeO carries a Beryllium Oxide label, as shown in
Figure 4.
Figure 4. Beryllium Oxide label
BERYLLIUM OXIDE
(TOXIC) IS USED
IN SOME COMPONENTS.
REFER TO MANUAL.
Page 18

Warnings and Cautions
18 (30) © Nokia Corporation Internal Copy DN98621958
Nokia Proprietary and Confidential Issue 3-0 en
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
Personnel who handle, use or dispose of components containing BeO should
be aware of its nature and of the necessary safety precautions. Beryllium
oxide is released into the air if the components containing it are damaged.
The sub assemblies or components in units containing BeO must not under
any circumstances be subjected to mechanical strain that might damage the
components and thereby release beryllium oxide into the air.
The components containing BeO must never be thrown out with general or
domestic waste. Dispose of the equipment in the manner appropriate to
chemical or special waste, and according to the local regulations!
2.6 Electromagnetic fields and RF power
The Nokia MetroSite EDGE Base Station generates electromagnetic radiation.
This can exceed safety levels very close to the antennas. Personnel must observe
the general guidelines presented in Section 2.6.1, and apply the minimum
distance calculation formula presented in Section 2.6.2.
2.6.1 General guidelines
This equipment generates electromagnetic radiation which can exceed safety
levels when a person is working in very close proximity to the antennas.
Observe the minimum distance precautions shown in Table 1 when working
in close proximity to antennas operating at full power!
Page 19

Warnings
DN98621958 © Nokia Corporation Internal Copy 19 (30)
Issue 3-0 en Nokia Proprietary and Confidential
WARNING
WARNING
Do not install the Nokia MetroSite EDGE Base Station or its antennas in
areas where there is a potential risk for interference with inadequately
shielded medical equipment, such as life supporting devices, hearing aids or
other electrically or magnetically sensitive devices!
When installing the Nokia MetroSite EDGE Base Station or its antennas, the
emission of other antennas nearby must be known beforehand so that
ambient emissions can be managed properly.
2.6.2 Formula for minimum safety distances
This section presents the formula for calculating the minimum safety distances
using the specifications of the particular antenna.
Equation 1. Formula for calculating minimum safety distance (r
min
)
Equation 1 refers to the following factors:
• G is the antenna gain (in dB) compared to isotropically radiating antenna
• P is the power delivered to the antenna (W)
• L is the total loss (in dB) between the transmitter and the antenna input
• N is the number of transmitters combined to the antenna
• S is the maximum allowed power density in air (W/m
2
)
2.6.3 Safety distance calculation examples
Table 1 describes how the minimum distances for controlled and uncontrolled
environments have been calculated.
r
min
=
N
10
P
(
G-L
)
10
S
4
Page 20

Warnings and Cautions
20 (30) © Nokia Corporation Internal Copy DN98621958
Nokia Proprietary and Confidential Issue 3-0 en
Using the formula for minimum safety distances and the appropriate information
for each factor, safety distances can be calculated as in the following calculations
(Table 2) for a particular environment.
Table 1. Description for distance calculations in controlled and uncontrolled
environments
Limit Description
Minimum Distance in Controlled
Environments*
The minimum distances are calculated
using the reference levels for power density
as presented in the CENELEC
prestandard; f/40 W/m
2
, in the frequency
range 400 to 2000 MHz, averaged over any
6 min. time interval. This is in agreement
with other guidelines (IEEE/ANSI, IRPA,
NCRP, FCC) or stricter.
Minimum Distance in Uncontrolled
Environments*
The minimum distances are calculated
using the reference levels for power density
as presented in the CENELEC
prestandard; f/200 W/m
2
, in the frequency
range 400 to 2000 MHz, averaged over any
6 min. time interval. This is in agreement
with other guidelines (IEEE/ANSI, IRPA,
NCRP, FCC) or stricter.
* Controlled environments refer to locations where there is exposure to persons aware
of the potential exposure. Uncontrolled environments refer to locations where there is
exposure to persons not aware of the potential exposure and who have no control over
it.
Table 2. Safety distance calculation example
Factor Unit GSM/E
DGE
900
GSM/E
DGE
1800
GSM/ED
GE 1900
Frequency f [MHz] 900 1800 1900
Maximum TX power P
out
[W] 5 5 5
Minimum losses: cable L [dB] 1 1 1
Maximum antenna gain (dependent on user
choices)
G [dB] 10 10 10
* CENELEC prestandard ENV50166-2
Page 21

Warnings
DN98621958 © Nokia Corporation Internal Copy 21 (30)
Issue 3-0 en Nokia Proprietary and Confidential
Maximum number of TRXs/antenna (dependent
on user choices)
N 222
Power Density / Controlled environment*
S [W/m
2
]
22.50 45 47.5
Power Density / Uncontrolled environment*
S [W/m
2
]
4.5 9 9.5
Safety distance / Controlled environment r
min
[m] 0.3 m 0.2 m 0.2 m
(0.66 ft)
Safety distance / Uncontrolled environment r
min
[m] 0.6 m 0.4 m 0.4 m
(1.32 ft)
Table 2. Safety distance calculation example (Continued)
Factor Unit GSM/E
DGE
900
GSM/E
DGE
1800
GSM/ED
GE 1900
* CENELEC prestandard ENV50166-2
Page 22

Warnings and Cautions
22 (30) © Nokia Corporation Internal Copy DN98621958
Nokia Proprietary and Confidential Issue 3-0 en
Page 23

Cautions
DN98621958 © Nokia Corporation Internal Copy 23 (30)
Issue 3-0 en Nokia Proprietary and Confidential
Caution
Caution
Caution
3 Cautions
3.1 Handling the BTS
3.1.1 Storage and transportation
During storage and transportation, the Nokia MetroSite EDGE Base Station must
remain in its original package in order to:
• avoid mechanical damage
• maintain traceability
• protect the units against static electricity
Handle the Nokia MetroSite EDGE Base Station with care. Do not drop the base
station or the package containing it.
3.1.2 Weight
Persons in charge of the transportation and installation of the Nokia MetroSite
EDGE Base Station must note that a fully equipped Nokia MetroSite base station
weighs 28 to 40 kg (62 to 88 lb).
Page 24
Warnings and Cautions
24 (30) © Nokia Corporation Internal Copy DN98621958
Nokia Proprietary and Confidential Issue 3-0 en
Caution
Caution
Caution
3.1.3 Heat management
During operation, the interior of the Nokia MetroSite EDGE Base Station may
reach high temperatures (60° to 70°C).
The power supply unit of the Nokia MetroSite EDGE Base Station carries a hot
surface label, as shown in Figure 5.
Figure 5. Hot surface label
3.1.4 Grounding
The Nokia MetroSite EDGE Base Station may receive damaging over voltages
through the antenna equipment, communication cables or power supply lines.
Sufficient protective grounding is required. An electrical power plug with ground
connection is not sufficient: the grounding of the Nokia MetroSite EDGE Base
Station must be based on a fixed grounding cable.
3.1.5 Electro-static discharge protection
Always wear a close-fitting antistatic wrist strap around your uncovered wrist
when handling the Nokia MetroSite EDGE Base Station!
Page 25

Cautions
DN98621958 © Nokia Corporation Internal Copy 25 (30)
Issue 3-0 en Nokia Proprietary and Confidential
The Nokia MetroSite EDGE Base Station contains electro-static sensitive
devices, which means that they may be permanently damaged by electro-static
discharges encountered in routine handling, testing and transportation. The Nokia
MetroSite EDGE Base Station is labelled with an electro-static sensitive device
symbol as shown in Figure 6.
Figure 6. Electro-static sensitive device label
Electro-static discharges are caused by direct contact or by an electro-static field.
If a charged body approaches an electrically conducting surface, the acquired
potential is discharged. An equalizing current can then flow in the associated
circuitry and generate permanently damaging voltages by induction. The human
body should be grounded at the same potential as the component or equipment
being handled. A wrist strap creates an equipotential electrical connection
between the object and the human.
The Nokia MetroSite EDGE Base Station has a grounding point (ESD stud) to
which a wrist strap must be connected. The wrist strap should be used and
connected to the ESD stud as shown in Figure 7.
Page 26

Warnings and Cautions
26 (30) © Nokia Corporation Internal Copy DN98621958
Nokia Proprietary and Confidential Issue 3-0 en
Caution
Caution
Figure 7. Using the antistatic wrist strap
3.2 BTS power supply
3.2.1 AC and DC connectors
Ensure the correct polarity. Incorrect polarity causes damage to the equipment.
The Nokia MetroSite BTS power switch does not disconnect the base station from
the power network (AC or DC). The separate main switch on the site is considered
to be the power disconnect device for safety and service purposes.
ESD stud
to ESD stud
Wrist strap
Page 27

Cautions
DN98621958 © Nokia Corporation Internal Copy 27 (30)
Issue 3-0 en Nokia Proprietary and Confidential
Caution
Caution
Do not connect AC or DC power until you have verified that the line voltage is
correct!
3.2.2 Grounding of AC power supply units
Ensure that the Nokia MetroSite EDGE Base Station is connected to a grounded
power outlet!
Page 28

Warnings and Cautions
28 (30) © Nokia Corporation Internal Copy DN98621958
Nokia Proprietary and Confidential Issue 3-0 en
Page 29

DN98621958 ©Nokia Corporation Internal Copy 29 (30)
Issue 3-0 en Nokia Proprietary and Confidential
Index
B
beryllium oxide 17
D
dangerous voltage 13
E
electromagnetic radiation 18
electro-static discharge (ESD) protection 24
G
grounding 24
H
heat control 24
P
power switch 15
S
safety distance calculation 19
safety distances 19
stand-by mode 15
storage 23
T
toxic hazards 17
transportation 23
Page 30

Warnings and Cautions
30 (30) © Nokia Corporation Internal Copy DN98621958
Nokia Proprietary and Confidential Issue 3-0 en
 Loading...
Loading...