Page 1

Nokia Customer Care
7 — RF Troubleshooting and
Manual Tuning Guide
Issue 1 Company Confidential Page 7–1
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 2

RM-1
Nokia Customer Care RF Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
(This page left intentionally blank.)
Page 7–2 Company Confidential Issue 1
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 3

RM-1
RF Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide Nokia Customer Care
Table of Contents
Introduction to RF troubleshooting.........................................................................................................................................7–5
RM-1 RF key component placement.........................................................................................................................................7–5
RM-1 fault finding test point locations....................................................................................................................................7–7
Receiver troubleshooting............................................................................................................................................................7–9
Introduction to Rx troubleshooting...................................................................................................................................7–9
GSM Rx chain activation for manual measurements / GSM RSSI measurement................................................7–10
WCDMA Rx chain activation for manual measurement.............................................................................................7–11
WCDMA RSSI measurement.................................................................................................................................................7–12
Transmitter troubleshooting...................................................................................................................................................7–12
General instructions for Tx troubleshooting.................................................................................................................7–12
Checking antennae functionality......................................................................................................................................7–15
RF manual tuning guide............................................................................................................................................................7–17
Introduction to RF tunings.................................................................................................................................................7–17
RF autotuning with CMU200...............................................................................................................................................7–18
System mode independent manual tunings......................................................................................................................7–25
RF channel filter calibration...............................................................................................................................................7–25
PA detection............................................................................................................................................................................7–26
Temperature sensor calibration ......................................................................................................................................7–26
GSM receiver tunings..................................................................................................................................................................7–27
Rx calibration (GSM)..............................................................................................................................................................7–27
Rx band filter response compensation (GSM)...............................................................................................................7–30
Rx AM suppression (GSM).....................................................................................................................................................7–34
GSM transmitter tunings...........................................................................................................................................................7–35
Tx IQ tuning (GSM).................................................................................................................................................................7–35
Tx power level tuning (GSM)..............................................................................................................................................7–37
WCDMA receiver tunings............................................................................................................................................................7–41
Rx AGC alignment (WCDMA)................................................................................................................................................7–41
Rx band response calibration (WCDMA)..........................................................................................................................7–43
WCDMA transmitter tunings.....................................................................................................................................................7–46
Tx AGC & power detector (WCDMA)..................................................................................................................................7–46
Tx band response calibration (WCDMA)..........................................................................................................................7–51
Tx LO leakage (WCDMA)........................................................................................................................................................7–52
List of Tables
Table 4 RF channel filter calibration tuning limits.............................................................................................................7–25
Table 5 Temperature sensor calibration tuning limits.....................................................................................................7–27
Table 6 RF tuning limits in Rx calibration.............................................................................................................................7–29
List of Figures
Figure 63 RF key component placement.................................................................................................................................7–6
Figure 64 Test point locations for spectrum analyzer.........................................................................................................7–7
Figure 65 Test points for oscilloscope - bottom....................................................................................................................7–8
Figure 66 Test points for oscilloscope - top............................................................................................................................7–9
Figure 67 RSSI Reading window..............................................................................................................................................7–10
Figure 68 Activating Rx Control window in Phoenix.........................................................................................................7–11
Figure 69 Rx Control window...................................................................................................................................................7–11
Figure 70 RF Controls window..................................................................................................................................................7–14
Figure 71 Tx Control window....................................................................................................................................................7–15
Issue 1 Company Confidential Page 7–3
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 4

RM-1
Nokia Customer Care RF Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
Figure 72 Main antenna, GSM and WCDMA...........................................................................................................................7–16
Figure 73 Feed and GND spots of the main antenna.........................................................................................................7–16
Figure 74 RF channel filter calibration typical values.......................................................................................................7–26
Figure 75 High burst measurement........................................................................................................................................7–49
Page 7–4 Company Confidential Issue 1
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 5

RM-1
RF Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide Nokia Customer Care
Introduction to RF troubleshooting
All measurements should be done using:
• spectrum analyser with a high-frequency high-impedance passive probe (LO-/reference frequencies and RF
power levels)
• oscilloscope with a 10:1 probe (DC-voltages and low frequency signals)
Caution: A mobile phone WCDMA transmitter should never be tested with full Tx power, if there is no
possibility to perform the measurements in a good performance RF-shielded room. Even low power
WCDMA transmitters may disturb nearby WCDMA networks and cause problems to 3G cellular phone
communication in wide area. WCDMA Tx measurements should be performed at least in an RF-shielded
box and never with higher Tx power level than 0 dBm! Test full WCDMA Tx power only in RF-shielded
environment.
The RF section of the phone is build around two RF ASICS: Rx ASIC N7500 and Tx ASIC N7501. There are also two
PA’s on board, one for GSM (N7502) and another for WCDMA (N7503).
The WCDMA PA needs variable supply voltage to work properly and therefore there is a switched mode power
supply component (N7504) added to the PWB.
Please note that the grounding of the PA module is directly below the PA module. Therefore, it is difficult to
check or change the module.
Most RF semiconductors are static discharge sensitive! ESD protection must be taken care of during repair
(ground straps and ESD soldering irons). N7501, N7500, both PAs and SMPS are moisture sensitive, so parts must
be pre-baked prior to soldering.
In addition to key components, there are lot of discrete components (resistors, inductors and capacitors) which
troubleshooting is done mainly by checking if the soldering of the component is done properly.
Capacitor can be checked for shorts and resistors for value by means of an ohmmeter, but be aware in-circuit
measurements should be evaluated carefully.
Keep in mind that all measured voltages or RF levels depicted in the service manual are rough figures. Especially
RF levels vary because of different measuring equipment or different grounding of the probe used.
When using an RF probe, use a pair of metallic tweezers to connect the probe ground to the PWB ground as
close to the measurement point as possible. If measurements are performed in a product specific module jig
then “GND” pads should be used for the probe ground.
For additional RF troubleshooting instructions, see Appendix A. These instructions include descriptions/
instructions for RF self-tests as well as troubleshooting instructions for various fault cases.
RM-1 RF key component placement
The RF section of the phone is build around two RF ASICs, Rx ASIC N7500 and Tx ASIC N7501.
There are also two PAs on the board, one for GSM (N7502) and one for WCDMA (N7503). The WCDMA PA needs
variable supply voltage to work power efficiently and therefore there is a Switched Mode Power Supply (SMPS)
component (N7504) added to the PWB.
Issue 1 Company Confidential Page 7–5
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 6

RM-1
Nokia Customer Care RF Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
Figure 63 RF key component placement
Page 7–6 Company Confidential Issue 1
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 7
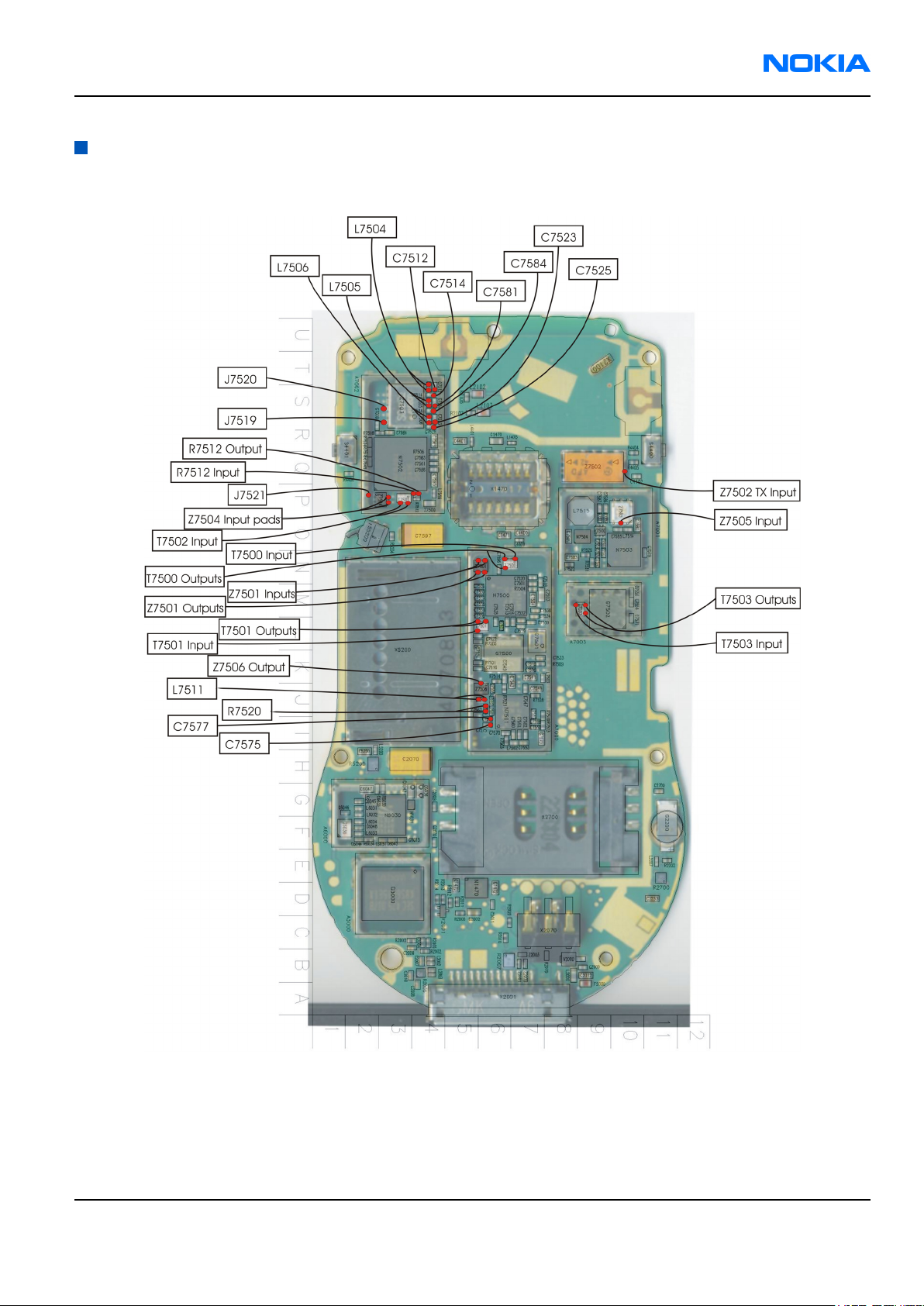
RM-1
RF Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide Nokia Customer Care
RM-1 fault finding test point locations
Test points for spectrum analyzer
Figure 64 Test point locations for spectrum analyzer
Issue 1 Company Confidential Page 7–7
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 8
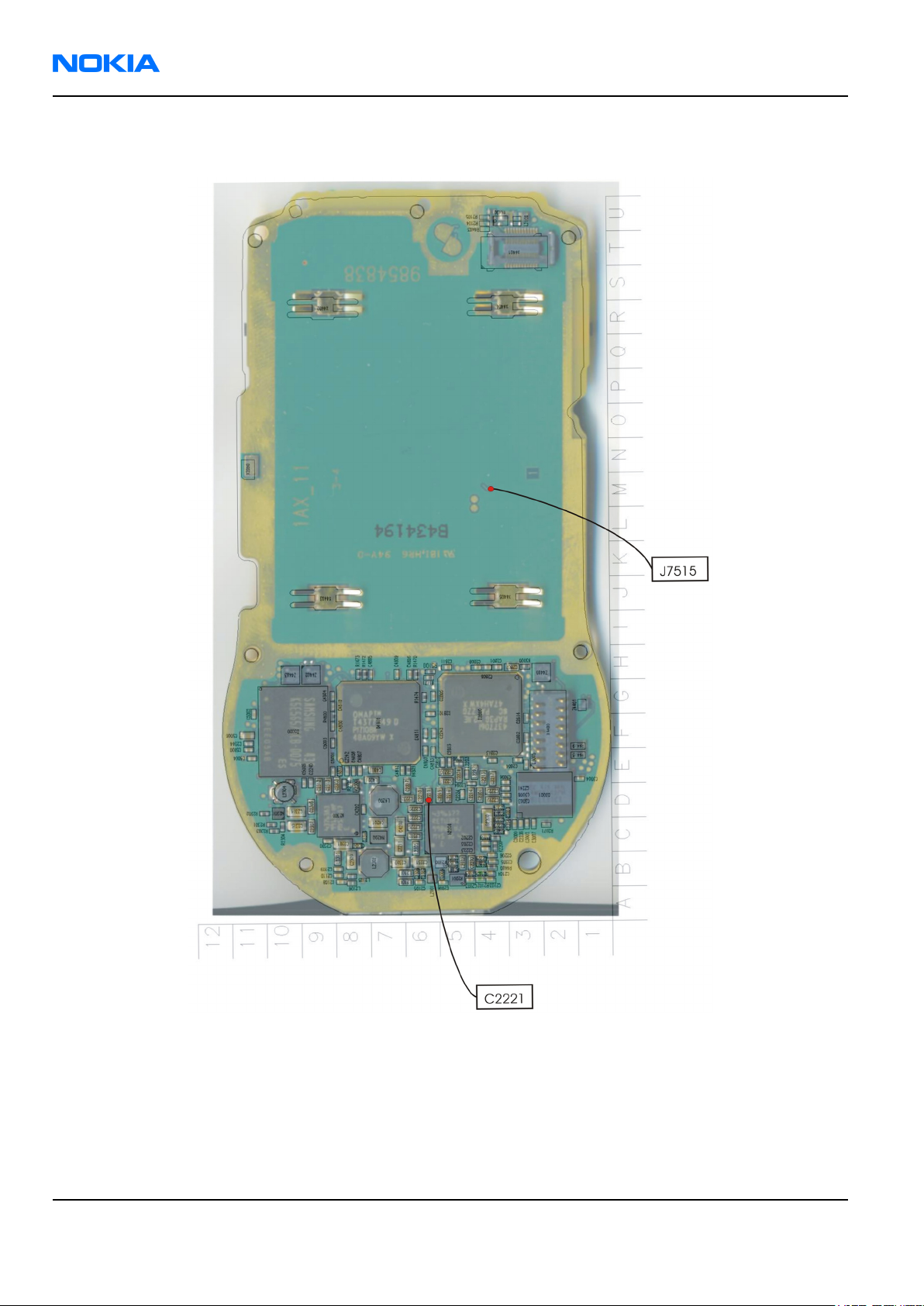
RM-1
Nokia Customer Care RF Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
Test points for oscilloscope
Figure 65 Test points for oscilloscope - bottom
Page 7–8 Company Confidential Issue 1
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 9

RM-1
RF Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide Nokia Customer Care
Figure 66 Test points for oscilloscope - top
Receiver troubleshooting
Introduction to Rx troubleshooting
Rx can be tested by making a phone call or in the local mode. For the local mode testing, use Phoenix service
software.
Issue 1 Company Confidential Page 7–9
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 10

RM-1
Nokia Customer Care RF Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
The main Rx troubleshooting measurement is RSSI measurement. This test measures the signal strength of the
received signal. I and Q branches can be measured separately. For GSM RSSI measurement, see GSM Rx chain
activation for manual measurements / GSM RSSI measurement (Page 7–10), and for the same measurement
in WCDMA, see WCDMA RSSI measurement (Page 7–12).
In GSM, the input signal can be either a real GSM signal or a CW signal that is 67.771kHz up from the carrier
frequency.
For service tool usage instructions, refer to section Service Tools and Service Concepts.
See Also
• WCDMA Rx chain activation for manual measurement (Page 7–11)
GSM Rx chain activation for manual measurements / GSM RSSI measurement
Context
RSSI signal measurement is the main Rx troubleshooting measurement. The test measures the strength of the
received signal.
I and Q branches can be measured separately. In GSM, the input signal can be either real GSM signal or CW signal
that is 67.771kHz up from the carrier frequency.
Steps
1. Start Phoenix service software.
2. From the Testing menu, choose GSM and RSSI Reading.
3. Setup RF signal generator for channel frequency +67.771kHz CW mode with –80dBm signal.
Alternatively set cellular tester downlink channel to an appropriate channel.
4. In the RSSI Reading window, select the appropriate band and channel.
Figure 67 RSSI Reading window
5. To start measurement/activate GSM Rx chain, click the Start button.
Results
RSSI reading values of the selected band and channel are displayed.
Page 7–10 Company Confidential Issue 1
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 11

RM-1
RF Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide Nokia Customer Care
WCDMA Rx chain activation for manual measurement
Steps
1. Start Phoenix service software.
2. From the Testing menu, choose WCDMA and Rx Control.
Figure 68 Activating Rx Control window in Phoenix
3. In the Rx Control window:
Figure 69 Rx Control window
• From the AGC Mode pane, select Algorithm.
• Set AFC Algorithm to OFF (Default = OFF).
• Set Channel to 10700.
Next action
When settings are ready, click Update to activate them.
If settings are changed later on (for example, you give a new channel number), you will need to click RF Stop
and Update again.
Note: Clicking RF Stop also disables Tx Control if that was active!
Issue 1 Company Confidential Page 7–11
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 12

RM-1
Nokia Customer Care RF Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
WCDMA RSSI measurement
Before you begin
WCDMA Rx must be activated before RSSI can be measured. See WCDMA Rx chain activation for manual
measurement (Page 7–11).
Steps
1. From the Testing menu in Phoenix, choose WCDMA -> Rx Power Measurement.
2. In the Rx Power Measurement window, choose the following settings:
• Mode: RSSI
• Continuous Mode
3. To perform the measurement, click Start.
Transmitter troubleshooting
General instructions for Tx troubleshooting
Context
• Tx troubleshooting requires Tx operation.
• Do not transmit on frequencies that are in use!
• Transmitter can be controlled in the local mode for diagnostic purposes.
• The most useful Phoenix tool for GSM transmitter testing is "RF Controls" and in WCDMA transmitter testing
the best tool is "Tx Control"..
• Tx IQ tuning and Tx power tuning can be also used in some cases.
• Remember that retuning is not a fix! Phones are tuned correctly in production.
The first set of steps instructs how to assemble the test setup. This setup is general for all Tx troubleshooting
tasks.
Alternative steps provide specific troubleshooting instructions for Phoenix service software. The first section is
for the EGSM900/GSM1800/GSM1900 bands and the latter for WCDMA.
Caution: Never activate the GSM or WCDMA transmitter without a proper antenna load. There should
be always 50 ohm load connected to the RF connector (antenna, RF-measurement equipment or at
least 2 watts dummy load), otherwise GSM or WCDMA PA may be damaged.
Steps
1. Connect a test jig to a computer with a DAU-9S cable or to a FPS-8 flash prommer with a modular cable.
Page 7–12 Company Confidential Issue 1
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 13

RM-1
RF Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide Nokia Customer Care
Make sure that you have a PKD-1 dongle connected to the computer's parallel port.
2. Connect a DC power supply to a module jig (MJ-26).
Note: When repairing or tuning a transmitter, use an external DC supply with at least 3 A current
capability.
Set the DC supply voltage to 3.9 V and set the jumper connector on the test jig's reg.pass switch to
“ON” position.
3. Connect an RF cable between the RF connector of the module test jig (MJ-26) and measurement equipment
or alternatively use a 50 ohms (at least 2 W) dummy load in the module test jig RF connector, otherwise GSM
or WCDMA PA may be damaged.
Note: There are three antenna connectors in the module jig:
• one for GSM
• one for WCDMA
• one for Bluetooth
Make sure that all connections are made to the correct RF connector.
Normally a spectrum analyser is used as measurement equipment.
Note: The maximum input power of a spectrum analyser is +30 dBm.
To prevent any damage, it is recommended to use 10 dB attenuator on the spectrum analyzer input.
4. Set Tx on.
i Set the phone module to the test jig and start Phoenix service software.
ii Initialize connection to the phone. (With FPS-8 use FBUS driver when using DAU-9S and COMBOX driver).
iii From the File menu, choose product: File -> Choose Product -> xx-x*(* = type designator of the phone).
iv From the toolbar, set operating mode to “Local”.
Alternative steps
• EGSM900/DCS1800/PCS1900 troubleshooting
i From the toolbar, set system to “GSM”.
ii From the Testing menu, activate the RF Controls window: Maintenance -> Testing -> GSM -> RF Controls.
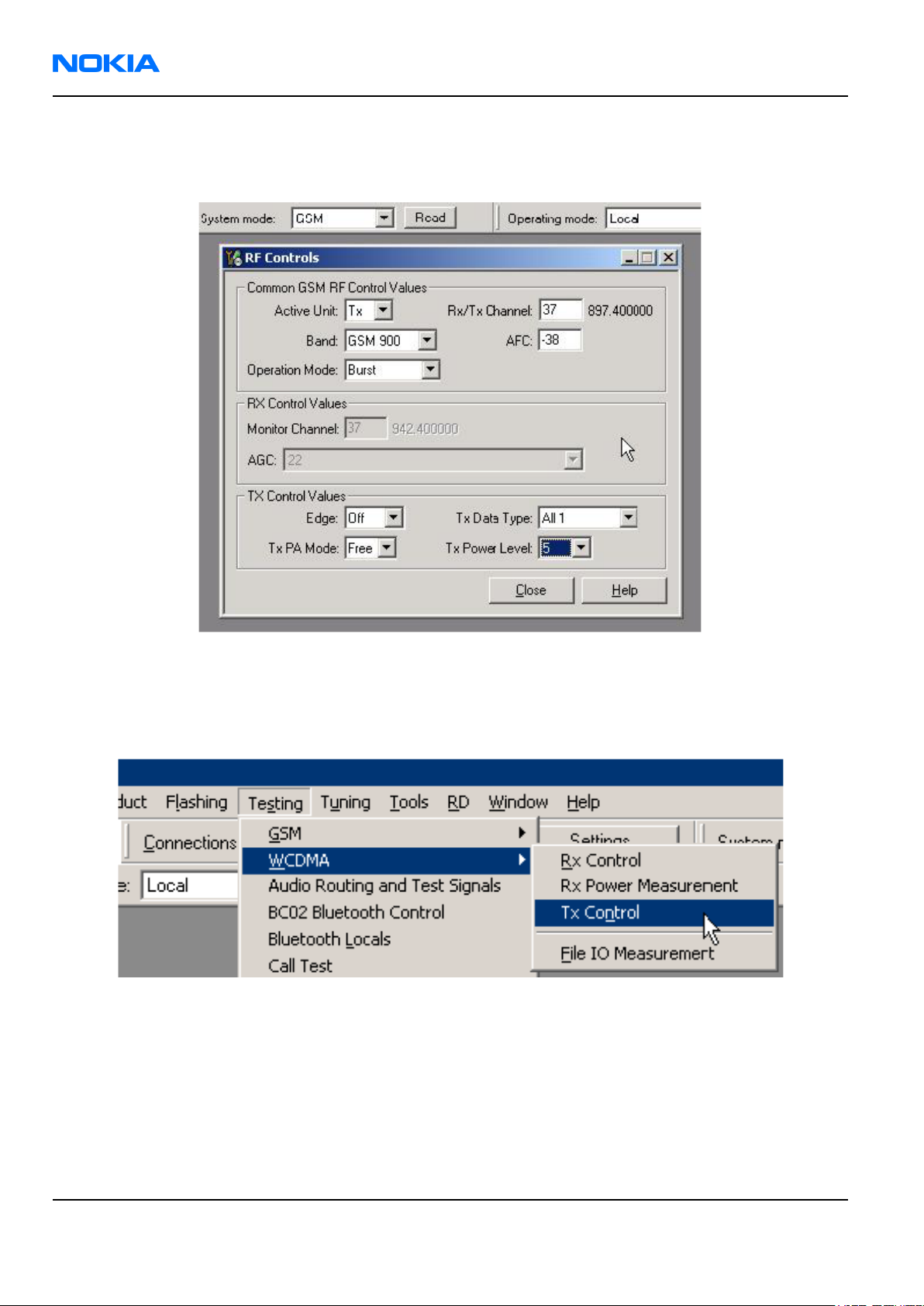
iii In the RF Controls window:
• Select band “GSM900” or “GSM1800” or “GSM1900” (Default = “GSM900”).
• Set Active unit to “Tx” (Default = “Rx”).
• Set Operation mode to “Burst” (Default = “Burst”).
• Set Tx data type to “All1” (Default = “All1”).
• Set Rx/Tx channel to 37 on GSM900 band or 700 on GSM1800 band or 661 on GSM1900 (Defaults).
Issue 1 Company Confidential Page 7–13
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 14
RM-1
Nokia Customer Care RF Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
• Set Edge to “Off” (Default).
• Set Tx PA mode to “Free” (Default).
• Set power level to 5 (Default = 19) on GSM900 or to 0 (Default = 15) on GSM1800 or GSM1900.
Figure 70 RF Controls window
• WCDMA troubleshooting
i From the toolbar, set system to "WCDMA".
ii From the Testing menu, activate the Tx Control window: Maintenance -> Testing -> WCDMA -> Tx Control.
iii In the Tx Control window:
• Select the Algorithm mode tab.
• Set Start level to “0” dBm (Default = “0”).
• Set Step size, Step count and Sequence to “0” (Default = “0”).
• Set Scrambling code class to “LONG” (Default = “LONG”).
• Set Scrambling code to “16” (Default = “16”).
• Set DPDCH Code number to “0”, Code class to “2” and Weight to “15” (Defaults).
• Set DPCCH Code number to “0”, Code class to "2" and Weight to “8” (Defaults).
• Set DPDCH enabled (Default).
Page 7–14 Company Confidential Issue 1
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 15

RM-1
RF Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide Nokia Customer Care
• Set Channel to 9750.
Figure 71 Tx Control window
Next action
When settings are done, click “Send” to enable them.
If you change the settings (e.g. give a new channel number), you need to click “Stop” and “Send” again.
Checking antennae functionality
The main antenna has two separate antenna elements: GSM and WCDMA.
In the GSM antenna, there is one Feed and two GND contacts.
In the WCDMA antenna, there is one Feed and one GND contact.
Issue 1 Company Confidential Page 7–15
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 16

RM-1
Nokia Customer Care RF Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
The contacts of the GSM antenna are separated in the (RDC = 0 ohm) short-circuit. The contacts of the WCDMA
antenna are in the (RDC = 0 ohm) short-circuit.
Figure 73 Feed and GND spots of the main antenna
Figure 72 Main antenna, GSM and WCDMA
The antenna is functioning normally when the contacts function (RDC = 0 ohm) and the antenna is visually intact.
BT antenna
BT antenna has one Feed and two GND contacts. The antenna is functioning normally when the contacts function
(RDC = 0 ohm) and the antenna is visually intact.
Page 7–16 Company Confidential Issue 1
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 17

RM-1
RF Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide Nokia Customer Care
RF manual tuning guide
Introduction to RF tunings
Phone RF is tuned in production. There is no reason to do the re-calibration unless:
• One or more of the RF components is changed
• FLASH Memory chip (D3000) is changed or otherwise corrupted.
RF calibration is always performed with the help of module jig MJ-26. Whenever possible, automatic tuning
system should be used.
If manual tuning is used, only relevant tunings should be performed. Refer to the table below:
Changed component Perform following tunings
Tx RF ASIC Vinku (N7501) RF Channel Filter Calibration, Tx IQ Tuning, Tx Power
Level Tuning, Temperature Sensor Calibration, TX AGC
& Power Detector, Tx Band Response Calibration, Tx
LO Leakage
RX RF ASIC Hinku (N7500) RF Channel Filter Calibration, Rx Calibration, Rx Band
Filter Response Compensation, Rx AM Suppression, Rx
AGC Alignment, Rx Band Response Calibration
Any component in the GSM TX RF chain before the PA Tx IQ Tuning, Tx Power Level Tuning
Any component in the GSM TX RF chain after the PA
or PA
Any component in the WCDMA TX RF chain before thePATx AGC & Power Detector, Tx Band Response
Any component in the WCDMA TX RX chain after the
PA, PA, power detector or PA switch mode power
supply
Any component in the GSM RX chain Rx Calibration, RX Band Filter Response
Any component in the WCDMA RX chain Rx AGC Alignment, RX Band Response Calibration
Tx Power Level Tuning
Calibration, Tx LO Leakage
Tx AGC & Power Detector, Tx Band Response
Calibration, PA Detection
Compensation, RX AM Suppression
Cable and adapter losses
RF cables and adapters have some losses. They have to be taken in account when the phone is tuned. As all the
RF losses are frequency dependent, the user have to be very careful and understand the measurement setup.
In the following table there are RF attenuations of the module jig, MJ-26:
Band Attenuation
GSM900 0.2 dB
GSM1800 0.3 dB
GSM1900 0.3 dB
WCDMA 2100
(WCDMA connector)
Issue 1 Company Confidential Page 7–17
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
0.5 dB
Page 18

RM-1
Nokia Customer Care RF Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
RF autotuning with CMU200
Before you begin
Recommended test set-up:
• Windows 2000 PC
• CMU200 communication tester
• USB to GPIB converter from National Instruments. Order information: 778416-01 GPIB-USB-B, NI-488.2 for
Windows 2000/XP/Me/98.
Before you can use the auto-tune feature, the GPIB driver from the GPIB card vendor must be installed and
running.
Then the auto tune .ini file must be in a correct place: C:\Program Files\Nokia\Phoenix\products\xx-x*
\autotune_xx-x*.ini (*= indicates the type designator of the phone, e.g. RM-1)
Context
It is possible to perform an automatic RF tuning with the aid of CMU200. Autotuning covers all RF tunings that
are needed to perform after RF component repairs.
Note: Do not perform RF autotuning “just for sure”. Phones are tuned in the production and RF tuning
may performed only after component repairs or if the RF tuning information is lost.
Steps
1. Connect CMU200 to the GPIB bus.
2. From the Tools menu in Phoenix, choose Options -> GPIB Card.
3. In the Card Type line, select CEC8Bit, then click Start.
After clicking Start, the name of the CMU200 communication tester appears in the list of found Listeners.
Page 7–18 Company Confidential Issue 1
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 19

RM-1
RF Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide Nokia Customer Care
4. To specify the cable loss from module jig to CMU200, choose Set Loss from the Tuning menu..
5. In the Set Loss window, click the Jig tab and select the right jig for the phone.
Issue 1 Company Confidential Page 7–19
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 20

RM-1
Nokia Customer Care RF Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
6. Click the Cable tab and add the extra cable attenuation.
Page 7–20 Company Confidential Issue 1
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 21

RM-1
RF Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide Nokia Customer Care
7. To start autotuning, choose Auto-Tune from the Tuning menu.
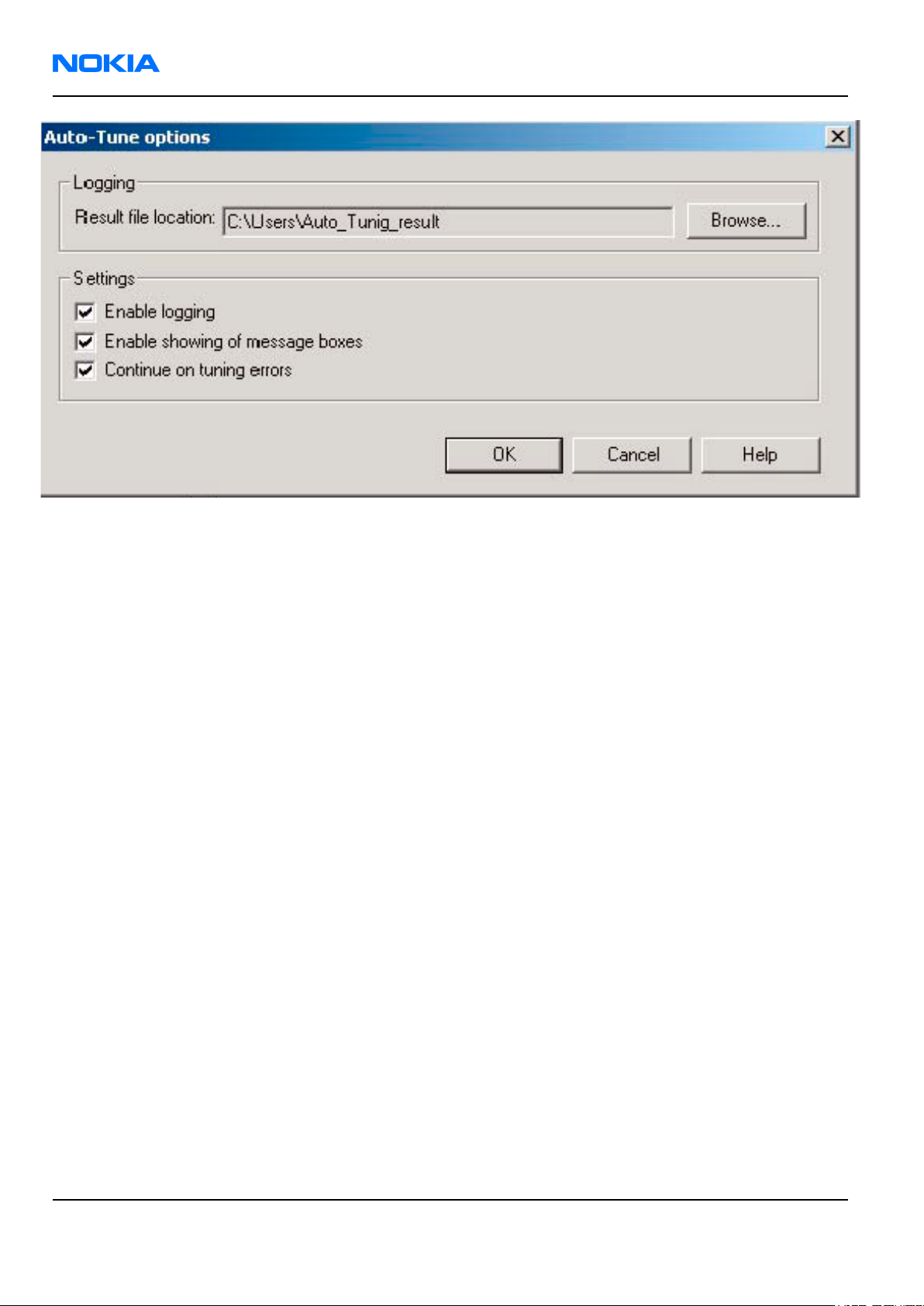
8. In the Auto-Tune window, click Options.
9. In the Auto-Tune options window, see that the "Enable showing of messages" check box is checked. Then
click OK.
Issue 1 Company Confidential Page 7–21
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 22
RM-1
Nokia Customer Care RF Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
10. Connect the phone's WCDMA RF port to CMU200 and click Tune.
Page 7–22 Company Confidential Issue 1
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 23

RM-1
RF Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide Nokia Customer Care
11. Change the phone's RF adapter from WCDMA port to GSM port.
To complete the RF autotuning, click OK.
Issue 1 Company Confidential Page 7–23
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 24

RM-1
Nokia Customer Care RF Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
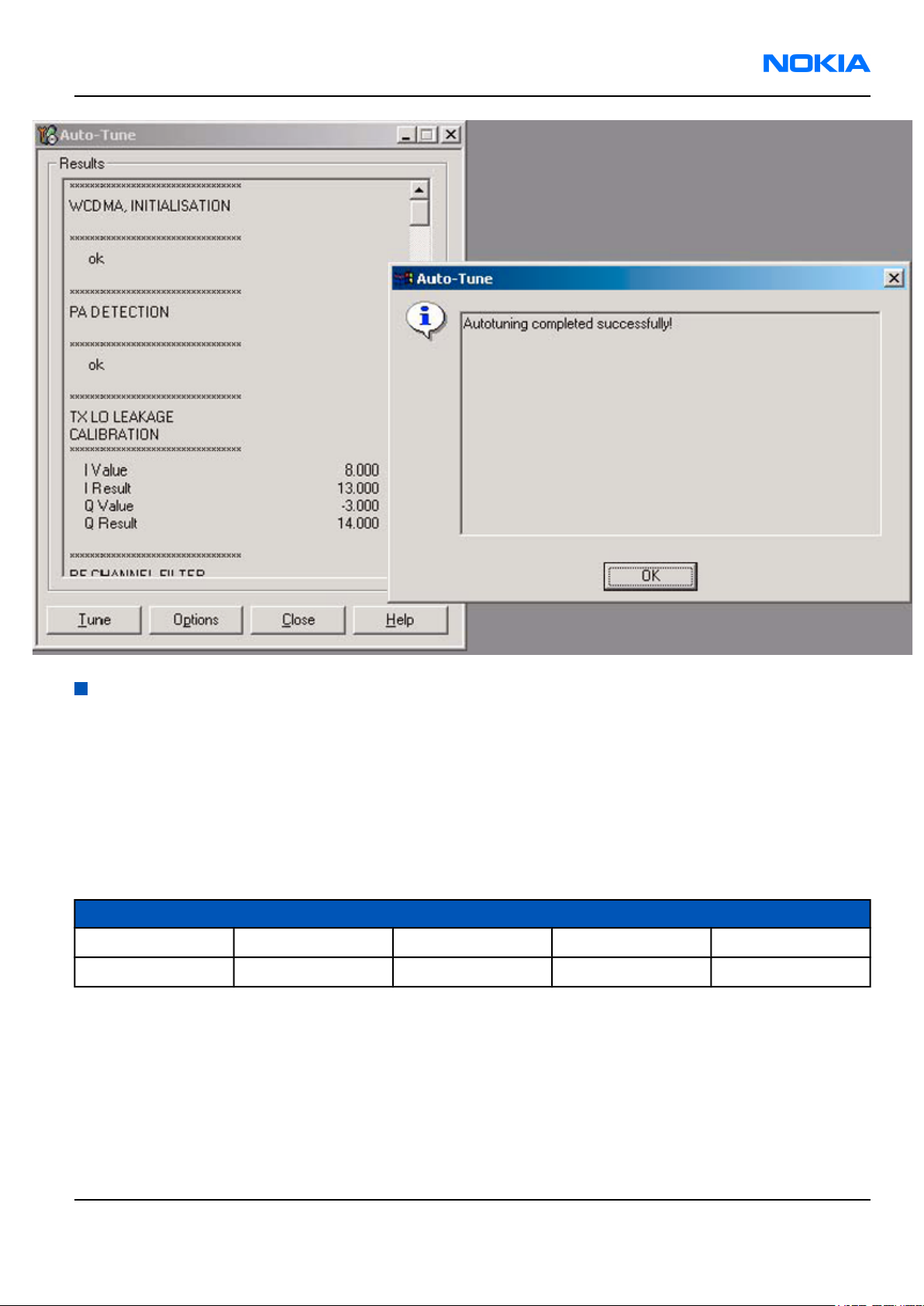
Results
"Autotuning completed successfully" message appears.
Page 7–24 Company Confidential Issue 1
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 25
RM-1
RF Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide Nokia Customer Care
System mode independent manual tunings
RF channel filter calibration
Context
Rx channel filter calibration tunes Rx and Tx ASICs' internal low pass filters that limit the bandwidth of BB IQ
signals.
One common calibration is made for GSM and WCDMA.
Table 4 RF channel filter calibration tuning limits
Min Typ Max Unit
TX filter 0 10 31
RX filter 0 16 31
Steps
1. From the dropdown menus, set "System mode" to Local and "Operating mode" to WCDMA, GSM or Dual.
2. From the Tuning menu, choose RF Channel Filter Calibration.
3. Click Tune.
4. Click Write.
Saves tuned values to the PMM area.
5. To close the tuning window, click Close.
Issue 1 Company Confidential Page 7–25
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 26

RM-1
Nokia Customer Care RF Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
Results
Figure 74 RF channel filter calibration typical values
PA detection
Context
PA detection procedure asks DSP to detect which PA manufacturer is used for GSM and WCDMA PAs.
If PA is changed or if PMM data is corrupted, PA detection has to be performed before Tx tunings.
Steps
1. From the dropdown menus, set "System mode" to Local and "Operating mode" to WCDMA, GSM or Dual.
2. From the Tuning menu, choose PA Detection.
3. Click Tune.
4. Check that the detected PA manufacturers are corresponding to the actual chips on the board.
5. To end the procedure, click Close.
Temperature sensor calibration
Context
There is a temperature sensor integrated into VINKU ASIC. VINKU provides DC-voltage, which is temperature
dependent.
Temperature sensor calibration is done in room temperature, in which offset caused by VINKU variation and
AD-converter inside RETU are nullified.
The module is able to do this calibration by itself, no external equipment is needed.
The temperature of the module and components must be 23 +/-2 degrees.
Steps
1. From the dropdown menus, set "Operating mode" to Local and "System mode" to WCDMA, GSM or Dual.
2. From the Tuning menu, choose WCDMA -> Temperature Sensor Calibration.
Page 7–26 Company Confidential Issue 1
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 27

RM-1
RF Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide Nokia Customer Care
3. Click Tune.
Table 5 Temperature sensor calibration tuning limits
Min Typ Max Unit
-20 -4 20
A popup window appears asking: “Save Values to PM”. Click “Yes”
4. To finish the calibration, click Close.
0
C
GSM receiver tunings
Rx calibration (GSM)
Context
Rx Calibration is used to find out the real gain values of the GSM Rx AGC system and tuning response of the AFC
system (AFC D/A init value and AFC slope)
Steps
1. Connect module jig’s GSM connector to signal generator.
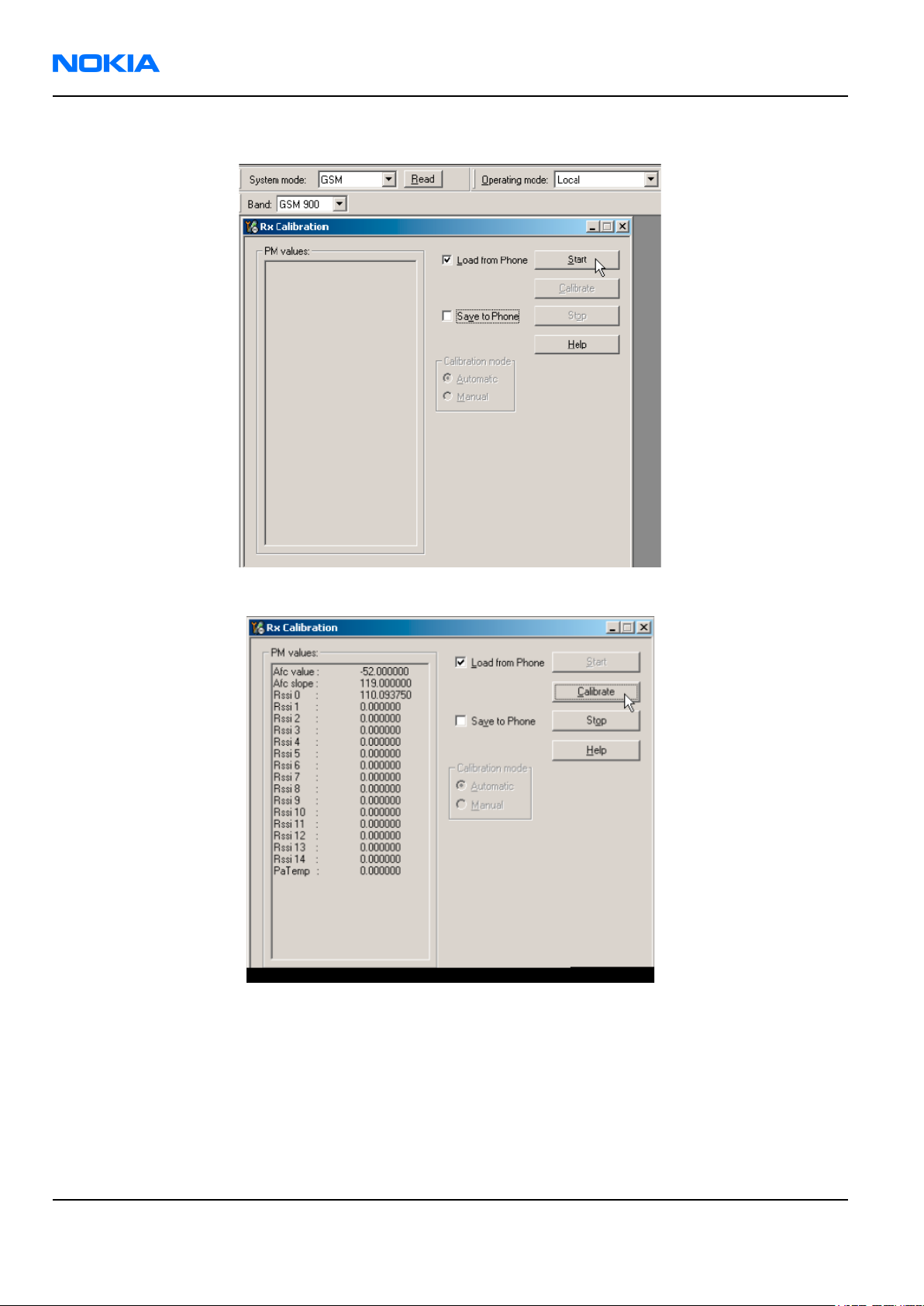
2. From the dropdown menus, set "Operating mode" to Local, "System mode" to GSM, and Band to GSM900.
3. From the Tuning menu, choose GSM -> Rx Calibration.
4. Check the “Load from Phone” check box and clear the “Save to Phone” checkbox.
5. From the Band dropdown menu, choose GSM900.
Issue 1 Company Confidential Page 7–27
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 28
RM-1
Nokia Customer Care RF Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
6. Click Start (if it not active already).
7. Click Calibrate.
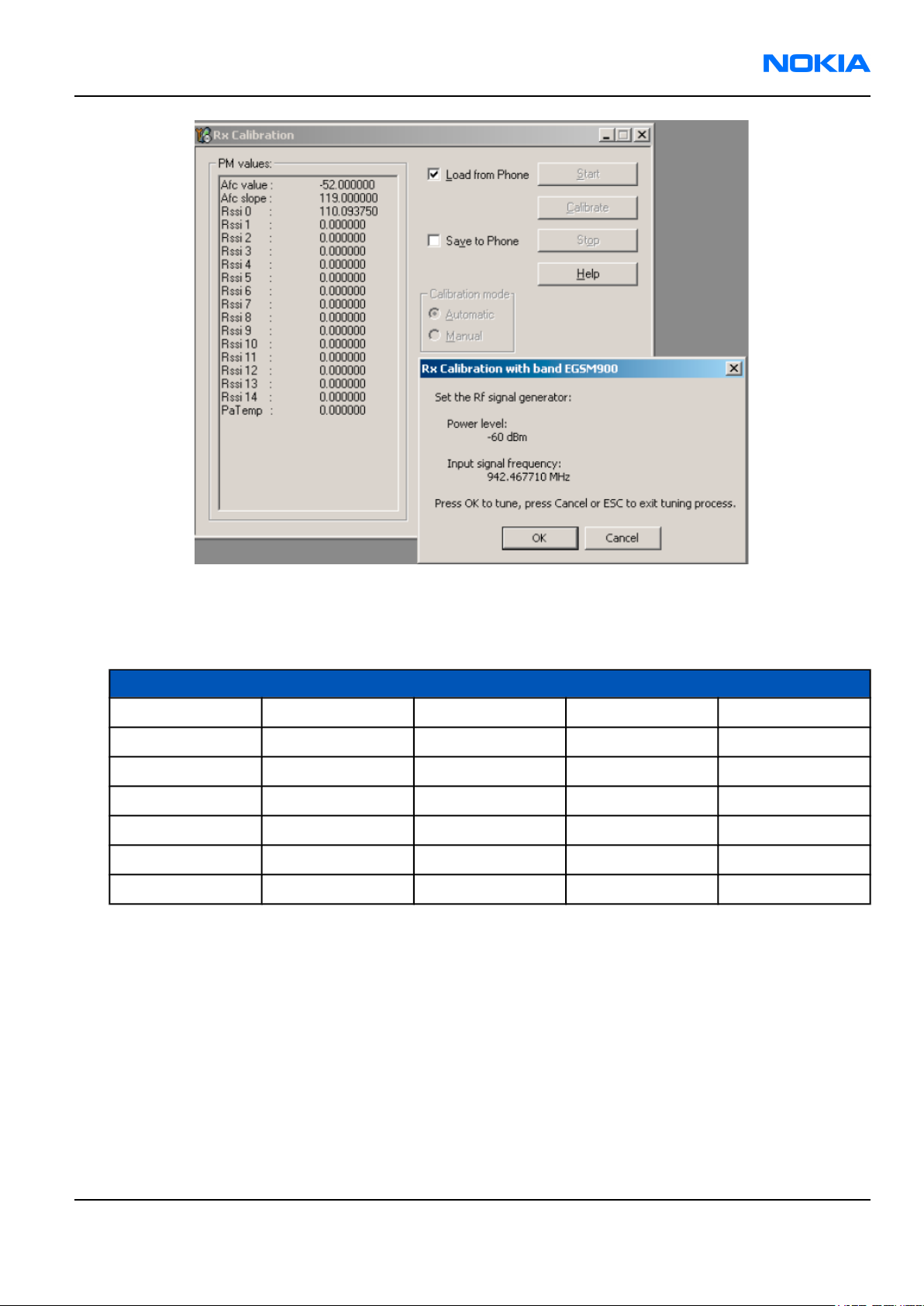
8. Connect signal generator to the phone and set frequency and amplitude as instructed in the "Rx Calibration
with band EGSM900" popup window.
The calibration uses a non-modulated CW signal. Increase the signal generator level by cable attenuation
and module jig probe attenuation!
Page 7–28 Company Confidential Issue 1
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 29
RM-1
RF Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide Nokia Customer Care
9. To perform tuning, click OK.
10. Check that the tuning values are within the limits specified in this table:
Table 6 RF tuning limits in Rx calibration
GSM900 Min Typ Max Unit
AFC Value -200 -105 62 200
AFC slope 0 122 200
RSSI0 106 107 110 114 dB
GSM1800
RSSI0 104 104 109 114 dB
GSM1900
RSSI0 104 104 109 114 dB
Issue 1 Company Confidential Page 7–29
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 30
RM-1
Nokia Customer Care RF Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
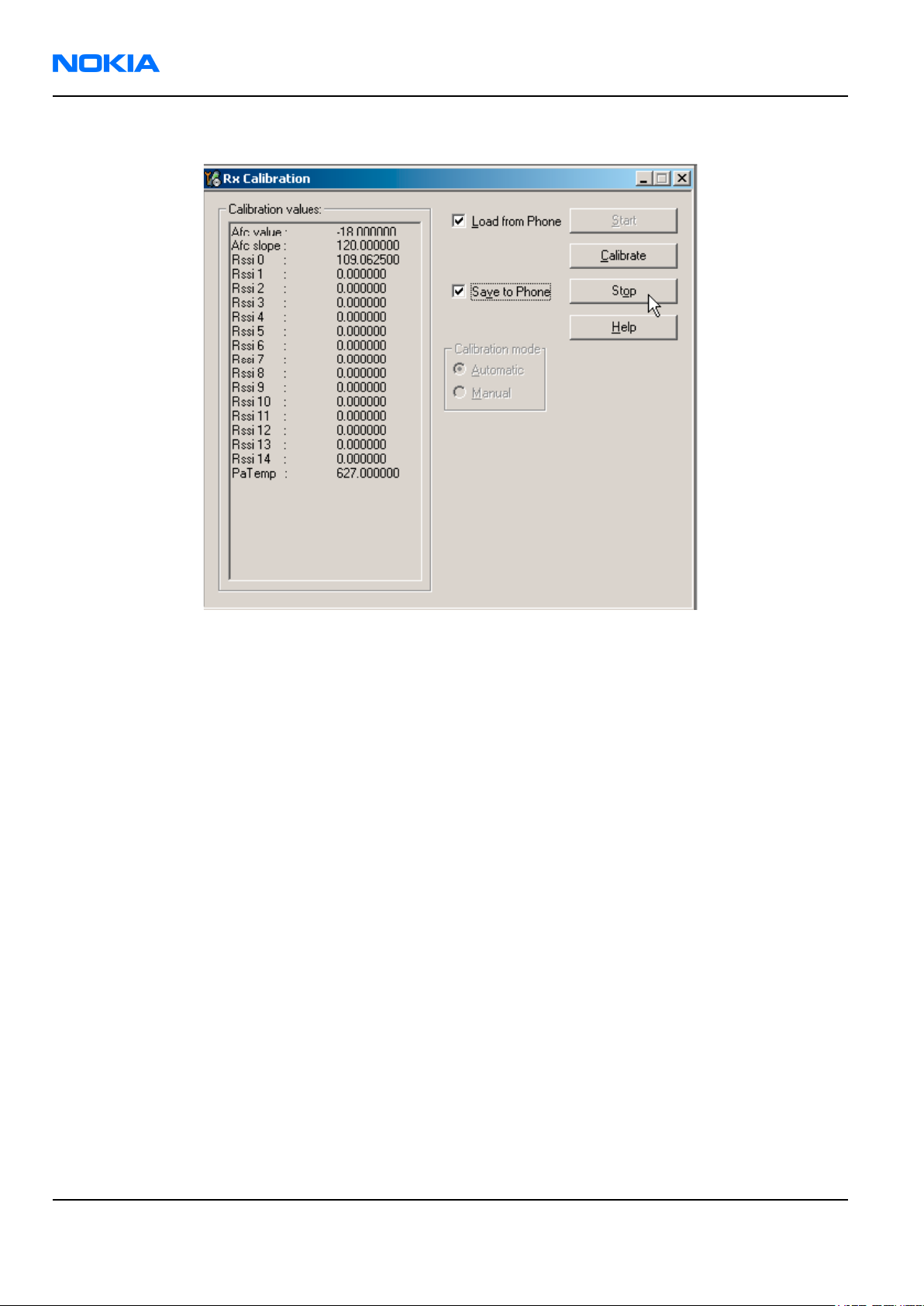
11. To save values to the phone, check the "Save to Phone" check box and click Stop.
Next action
Repeat steps 3 to 8 for GSM1800 and GSM1900
Rx band filter response compensation (GSM)
Before you begin
Rx calibration must be done before the Rx Band Filter Response Compensation
Context
In each GSM Rx band, there’s a band rejecting filter in front of HINKU front end. The amplitude ripple caused by
these filters causes ripple to the RSSI measurement and therefore calibration is needed.
The calibration has to be repeated for each GSM band.
Steps
1. Connect module jig’s GSM connector to signal generator.
2. From the dropdown menus, set "Operating mode" to Local, "System mode" to GSM, and Band to GSM900.
Page 7–30 Company Confidential Issue 1
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 31

RM-1
RF Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide Nokia Customer Care
3. From the Tuning menu, choose GSM -> Rx Band Filter Response Compensation.
4. Check “Manual” and “Load from Phone” check boxes. Clear “Save to Phone” check box
5. Click Start.
6. Click Tune.
Issue 1 Company Confidential Page 7–31
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 32

RM-1
Nokia Customer Care RF Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
7. Connect signal generator to the phone and set frequency and amplitude as instructed in the "Rx Band Filter
Response Compensation for EGSM900" popup window.
8. To perform tuning, click OK.
9. Go through all 9 frequencies.
10. Check that the tuning values are within the limits specified in this table:
Min Typ Max Unit
GSM900
Ch. 965 /
923.26771 MHz
Ch. 975 /
925.26771 MHz
Ch. 987 /
927.66771 MHz
Ch. 1009 /
932.06771 MHz
Ch. 37 / 942.46771
MHz
Ch. 90 / 953.06771
MHz
Ch. 114 /
957.86771 MHz
-10 -1 5 dB
-3 0 5 dB
-3 0 5 dB
-3 0 5 dB
-3 0 5 dB
-3 0 5 dB
-3 0 5 dB
Page 7–32 Company Confidential Issue 1
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 33

RM-1
RF Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide Nokia Customer Care
Min Typ Max Unit
Ch. 124 /
959.86771 MHz
Ch. 136 /
962.26771 MHz
GSM1800
Ch. 497 /
1802.26771 MHz
Ch. 512 /
1805.26771 MHz
Ch. 535 /
1809.86771 MHz
Ch. 606 /
1824.06771 MHz
Ch. 700 /
1842.86771 MHz
Ch. 791 /
1861.06771 MHz
Ch. 870 /
1876.86771 MHz
-3 0 5 dB
-10 -1 5 dB
-10 -1 5 dB
-3 0 5 dB
-3 0 5 dB
-3 0 5 dB
-3 0 5 dB
-3 0 5 dB
-3 0 5 dB
Ch. 885 /
1879.86771 MHz
Ch. 908 /
1884.46771 MHz
GSM1900
Ch. 496 /
1927.06771 MHz
Ch. 512 /
1930.26771 MHz
Ch. 537 /
1935.26771 MHz
Ch. 586 /
1945.06771 MHz
Ch. 661 /
1960.06771 MHz
Ch. 736 /
1975.06771 MHz
Ch. 794 /
1986.66771 MHz
-3 0 5 dB
-10 -1 5 dB
-10 -1 5 dB
-3 0 5 dB
-3 0 5 dB
-3 0 5 dB
-3 0 5 dB
-3 0 5 dB
-3 0 5 dB
Ch. 810 /
1989.86771 MHz
Issue 1 Company Confidential Page 7–33
-3 0 5 dB
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 34

RM-1
Nokia Customer Care RF Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
Min Typ Max Unit
Ch. 835 /
1994.86771 MHz
11. Check the "Save to Phone" check box and click Stop if the values are within the limits.
-10 -1 5 dB
Next action
Repeat the steps 4 to 10 for GSM1800 and GSM1900.
Rx AM suppression (GSM)
Context
Rx AM suppression is used to tune the AM suppression capabilities of the GSM receiver.
AM suppression is related to ability of the receiver to operate when there is disturbing AM modulated signal
near the received channel signal frequency.
RFIC has tunable compensation circuit which has an effect on the AM suppression ability.
In the tuning, a continuous useful signal + AM modulated signal 10MHz above current channel is fed to the
antenna. RFIC control word values are iterated until a minimum RSSI signal is found.
Steps
1. Connect module jig’s GSM connector to signal generator.
2. From the dropdown menus, set "Operating mode" to Local, "System mode" to GSM, and Band to GSM900.
3. From the Tuning menu, choose GSM -> Rx AM Suppression.
4. Check the Automatic check box.
5. Connect signal generator to phone according to the frequency and modulation parameters displayed in the
tuning window:
Frequency 952.46771MHz / 1852.86771MHz / 1970.06771 MHz
(depending on the band used)
Page 7–34 Company Confidential Issue 1
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 35

RM-1
RF Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide Nokia Customer Care
Power level -25 dBm / -26 dBm / -29 dBm (increase by cable and
jig attenuations)
Modulation AM
AM modulation depth 90%
Modulation signal 50 kHz sinewave (or 15 kHz if 50 kHz is not available)
6. Click Start.
7. Click Tune.
8. Check that RSSI level value is between the limits presented in this table. If not, try clicking the Tune button
again.
GSM900 Min Typ Max Unit
RSSI level -115 -90 dB
GSM1800
RSSI level -115 -85 dB
GSM1900
RSSI level -115 -100 dB
9. Make sure that the "Save to Phone" check box is checked and click Stop.
Next action
Repeat steps 3 to 7 for GSM1800 and GSM1900
GSM transmitter tunings
Tx IQ tuning (GSM)
Context
The Tx path branches to I and Q signals at RF I/Q modulator. Modulator and analog hardware located after it
cause unequal amplitude and phase disturbance to I and Q signal paths. Tx IQ tuning tuning balances the I and
Q branches.
Tx IQ tuning must be performed on all GSM bands. GSM1900 uses the same values as GSM1800.
Steps
1. From the dropdown menus, set "Operating mode" to Local, "System mode" to GSM, and Band to GSM900.
Issue 1 Company Confidential Page 7–35
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 36

RM-1
Nokia Customer Care RF Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
2. From the Tuning menu, choose GSM -> Tx IQ Tuning.
3. Set Mode to Automatic and Edge to Off.
4. Click Start.
Wait until automatic tuning has finished and moved the sliders.
Values are written to the phone memory automatically.
5. When the values have been written to the phone memory, click the Finish button to end the tuning.
6. Change band to GSM1800 and repeat steps 4 to 5.
Page 7–36 Company Confidential Issue 1
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 37

RM-1
RF Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide Nokia Customer Care
7. Change band to GSM1900 and repeat steps 4 to 5.
8. To close the tuning window, click Close.
Next action
Tuning sliders should be close to the center of the scale after the tuning and within the limits specified in the
table below. If they are not within the limits, check Tx IQ quality manually.
GSM900 Min Typ Max Unit
I DC offset / Q DC
offset
Ampl -1 0 1 dB
Phase 85 90 95 dB
GSM1800/GSM1900 dB
I/Q DC -6 0.5 6 dB
Ampl -1 0 1 dB
Phase 95 100 110 dB
-6 -4 4 6 dB
Tx power level tuning (GSM)
Context
Because of variations at IC process and discrete component values, actual transmitter RF gain of each phone is
different. Tx power level tuning is used to find out mapping factors called 'power coefficients’. These adjust the
GSM transmitter output power to fulfill the specifications.
For EDGE transmission the bias settings of the GSM PA are adjusted in order to improve linearity. This affects
the PA gain and hence the power levels have to be aligned separately for EDGE transmission.
Tx power level tuning has to be performed on all GSM bands.
Steps
1. Connect the phone to a spectrum analyzer.
2. From the dropdown menus, set "Operating mode" to Local, "System mode" to GSM, and Band to GSM900.
3. From the Tuning menu, choose GSM -> Tx Power Level Tuning.
4. Set Mode to Automatic and Edge to Off.
5. Set the spectrum analyzer for power level tuning:
Frequency channel frequency (897.4MHz GSM900, 1747.8MHz
GSM1800, 1880MHz GSM1900)
Span 0 Hz
Sweep time 2ms
Issue 1 Company Confidential Page 7–37
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 38

RM-1
Nokia Customer Care RF Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
Trigger Video triggering (-10dBm)
Resolution BW 3MHz
Video BW 3MHz
Reference level offset sum cable attenuation with module jig
attenuation
Reference level 33dBm
A power meter with a peak power detector can be also used. Remember to take the attenuations in the
account!
6. Click Start.
Page 7–38 Company Confidential Issue 1
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 39

RM-1
RF Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide Nokia Customer Care
7. Adjust power levels 5, 15 and 19 to correspond the "Target dBm" column by pressing + or – keys.
8. Click Calculate Coefficients.
9. Check that the coeffiecient values are within the limits specified in the table below.
Min Typ Max Unit
GSM900 EDGE off
PL5 coefficient 0.45 0.626 0.73
PL15 coefficient 0.234
Issue 1 Company Confidential Page 7–39
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 40

RM-1
Nokia Customer Care RF Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
Min Typ Max Unit
PL19 coefficient 0.12 0.195 0.3
GSM900 EDGE on
PL8 coefficient 0.35 0.419 0.6
PL15 coefficient 0.247
PL19 coefficient 0.12 0.204 0.3
GSM1800 EDGE off
PL0 coefficient 0.45 0.51 0.7
PL11 coefficient 0.219
PL15 coefficient 0.12 0.185 0.3
GSM1800 EDGE on
PL2 coefficient 0.35 0.394 0.6
PL11 coefficient 0.23
PL15 coefficient 0.12 0.194 0.3
GSM1900 EDGE off
PL0 coefficient 0.45 0.482 0.7
PL11 coefficient 0.218
PL15 coefficient 0.12 0.184 0.3
GSM1900 EDGE on
PL2 coefficient 0.35 0.377 0.6
PL11 coefficient 0.23
PL15 coefficient 0.12 0.193 0.3
If the values are within the limits, check that the "Save to Phone Permanent Memory" check box is checked
and click Stop.
Page 7–40 Company Confidential Issue 1
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 41

RM-1
RF Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide Nokia Customer Care
10. Set Edge mode on and start tuning again. Change video averaging to 50.
11. Tune EDGE power levels to the corresponding target power levels.
Only power levels 8, 15 and 19 are tuned in GSM900 and 2, 10 and 15 in GSM1800/1900. The rest are
calculated by clicking the Calculate Coefficients button. Check the coefficients against the RF tuning limits
table presented in Step 9.
12. When the tuning is completed, click Stop.
Next action
Repeat steps 4 to 9 for GSM1800 and GSM1900. On those bands only power levels 0, 11 and 15 need to be tuned.
WCDMA receiver tunings
Rx AGC alignment (WCDMA)
Context
Rx AGC alignment tuning is used to find out the real gain values of the WCDMA Rx AGC system and converters.
Issue 1 Company Confidential Page 7–41
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 42

RM-1
Nokia Customer Care RF Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
Steps
1. From the dropdown menus, set "Operating mode" to Local and "System mode" to WCDMA.
2. From the Tuning menu, choose WCDMA -> Rx AGC Alignment.
3. Click Start and Tune.
4. Setup the signal generator to correspond the values in the "RX AGC Calibration" pop-up window and click OK:
Frequency: 2141MHz
Level: –51 dBm + cable and adapter attenuations
Modulation: FM
Deviation: 500 kHz
Modulation frequency: 50 kHz
Page 7–42 Company Confidential Issue 1
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 43

RM-1
RF Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide Nokia Customer Care
5. Check that the “Rx Chain” value in “Tuning Results” is within the limits presented in the table below.
Min Typ Max Unit
RX chain -6 1.5 3.5 6 dB
Low freq -5 -0.7 4.0 5
High freq -5 -0.7 4.0 5
i If the Rx gain is acceptable, click Yes to save the results to the phone.
6. To close the tuning window, click Close.
Rx band response calibration (WCDMA)
Context
There is a band rejecting filter for each WCDMA Rx band between the front end LNA and the mixer of HINKU. The
amplitude ripple caused by this filter causes ripple to the RSSI measurement and therefore Rx band response
calibration is needed.
Rx band response calibration can be done in two different ways. If the signal generator in use supports frequency
sweep table, the calibration can be done as a part of Rx calibration. If not, it is possible to calibrate all the
necessary frequencies one by one.
The first set of steps shows how to perform the calibration without the signal generator sweep feature and the
alternative steps give instructions how to perform the calibration if the signal generator supports frequency
sweeps and the calibration can be performed within Rx AGC calibration.
Steps
1. From the dropdown menus, set "Operating mode" to Local and "System mode" to WCDMA.
2. From the Tuning menu choose WCDMA -> Rx Band Response Calibration.
Issue 1 Company Confidential Page 7–43
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 44

RM-1
Nokia Customer Care RF Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
3. Click Start and Tune.
4. Setup the signal generator to correspond the values in the pop-up window:
Frequency: 2113.4MHz
Level: –51 dBm + cable and adapter attenuations
Modulation: FM
Deviation: 500 kHz
Modulation frequency: 50 kHz
5. Click OK.
6. Change frequency to 2166.6 MHz and click OK.
7. Check that the tuned values are within the limits specified in the table below:
Min Max
Frequency compensation low -5 +5
Frequency compensation high -5 +5
Page 7–44 Company Confidential Issue 1
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 45

RM-1
RF Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide Nokia Customer Care
i If the values are OK, click Yes to save the values.
8. Close the tuning window.
Alternative steps
• From the dropdown menus, set "Operating mode" to Local and "System mode" to WCDMA.
• From the Tuning menu, choose WCDMA -> Rx AGC Alignment.
• Click Start.
• Check the “Tune Rx Band Response” check box and click Tune.
• Setup the signal generator according to the values in the pop-up window:
Frequency list: 2113.4 MHz, 2141 MHz and 2166.6 MHz
Dwell time: 2 ms
Sweep control: Automatic continuous sweep
Level: –51 dBm + cable and adapter attenuations
Modulation: FM
Deviation: 500 kHz
Modulation frequency: 50 kHz
• Click OK.
• Check that the “Rx chain” , “Low freq.” and “High freq.” values in the Tuning Results window are within the
limits presented in the table below.
Issue 1 Company Confidential Page 7–45
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 46

RM-1
Nokia Customer Care RF Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
Min Typ Max Unit
Rx chain -6 1.5 3.5 6 dB
Low freq -5 -0.7 4.0 5
High freq -5 -0.7 4.0 5
• If the Rx gain is acceptable, click Yes to save the results to the phone.
• To close the window, click Close.
WCDMA transmitter tunings
Tx AGC & power detector (WCDMA)
Context
Tx AGC & power detector tuning has two purposes:
• to enable the phone to select the correct TxC value accurately in order to produce the required RF level
• to enable the phone to measure its own transmitter power accurately
There are two ways to perform the tuning. For an alternative method, see Alternative steps.
Steps
1. From the dropdown menus, set "Operating mode" to Local and "System mode" to WCDMA.
2. From the Tuning menu, choose WCDMA -> Tx AGC & Power Detector.
3. Click Start.
4. In the "Wide Range" pane, click Tune (the leftmost Tune button).
5. Setup the spectrum analyzer in the following way:
Center frequency: 1950.3 MHz
Span: 0 Hz
Reference level offset: Cable attenuations + adapter attenuation
Reference level: 14 dBm
Input attenuation: (20 dB) Manually select as small value as possible
for the mentioned reference level to minimize the
noise floor.
Resolution bandwidth: 30 kHz
Video bandwidth: 30 kHz
Sweep time: 20 ms
Detector: RMS detector
Page 7–46 Company Confidential Issue 1
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 47

RM-1
RF Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide Nokia Customer Care
Average: No
Trigger: Video
Trigger level: 0 dBm
Marker: 250 us
Marker step: 500 us
6. After setting the spectrum analyzer, click OK.
7. Measure the power levels with a marker.
Take the first measurement from 250 us after the trigger, the second from 750 us, the third on 1225 us
and so on in every 500 us until the table is filled.
Note: It must be possible to measure power levels down to –68 dBm. The measured power levels must
be monotonously decreasing.
Make sure that the marker is not measuring the level of noise spike on lower levels.
Issue 1 Company Confidential Page 7–47
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 48

RM-1
Nokia Customer Care RF Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
8. Fill in the power level values (in dBm) to the Wide Range table.
9. In the Wide Range pane, click Calculate.
10. In the High Burst pane, click Tune.
11. Setup the spectrum analyzer with the following settings:
Center frequency: 1950 MHz
Span: 0 Hz
Reference level offset: Cable attenuations + adapter attenuation
Reference level: 24 dBm
Input attenuation: Automatic
Resolution bandwidth: 5 MHz
Video bandwidth: 5 MHz
Sweep time: 20 ms
Detector: RMS detector
Average: No
Trigger: Video
Trigger level: 0 dBm
Marker: 250 us
Marker step: 500 us
Page 7–48 Company Confidential Issue 1
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 49

RM-1
RF Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide Nokia Customer Care
12. Measure the power levels with a marker.
Take the first measurement from 250 us after the trigger, the second from 750 us, third on 1225 us and
so on in every 500 us until the table is filled.
Figure 75 High burst measurement
13. In the High Burst pane, click Calculate.
14. Check that the calculated values are within the limits specified in the table below:
Min Typ Max Unit
C0-high -0.5 5
C1-high -50 50
C2-high 400 900
C0-mid -0.7 0.7
C1-mid 0 50
C2-mid 400 900
C0-low -4 4
C1-low -400 440
C2-low -10000 15000
Det-k 0 800
Det-b -1000 1000
15. To save the coefficients to the phone, click Write.
16. To close the tuning window, click Close.
17. From the Testing menu, choose WCDMA -> Tx Control.
Issue 1 Company Confidential Page 7–49
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 50

RM-1
Nokia Customer Care RF Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
18. Select the Algorithm mode tab.
19. Write the target power level 25 dBm to the "Start level" line and check the "Max power limit" check box
(detector calibration check).
20. Setup the spectrum analyzer with the following settings:
Center frequency: 1947.4 MHz
Span: 0 Hz
Reference level offset: Cable attenuations + adapter attenuation
Reference level: 24 dBm or -20 dBm depending on the
measured level
Input attenuation: Automatic
Resolution bandwidth: 5 MHz
Video bandwidth: 5 MHz
Sweep time: 20 ms
Detector: RMS detector
Average: No
Trigger: Free run
21. Click Send.
22. Measure the WCDMA output power.
It should be around 21 dBm.
23. Click RF Stop and uncheck the "Max power limit" check box.
24. Repeat steps 19 to 23 for levels +19, +7, 0, -20 and –40 dBm levels.
The measured output power may not differ more than +-2 dB from the requested value at level +19dBm
and no more than +-4dB on lower levels.
Page 7–50 Company Confidential Issue 1
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 51

RM-1
RF Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide Nokia Customer Care
Remember to stop the RF before sending new data.
Alternative steps
• Measure the wide range levels normally and write down the levels that are possible to measure.
• Click Finish.
• Click Options.
• Change the first wide range DAC value to 573 and change the number of tuning steps to 21.
• Change the spectrum analyzer reference level to –20 dBm and adjust the input attenuator to the lowest
value possible.
• In the Wide Range pane, click Tune and fill in the rest of values starting from the 19th level.
Tx band response calibration (WCDMA)
Context
Tx band response calibration is required to get compensation parameters for DSP algorithm in order for it to
handle frequency response variations (caused by SAW filter, PA and duplexer unidealities) in open loop power
control and maximum power limitation situations.
Steps
1. From the dropdown menus, set "Operating mode" to Local and "System mode" to WCDMA.
2. From the Tuning menu, choose WCDMA -> Tx Band Response Calibration.
3. Setup the spectrum analyzer according to the following settings:
Frequency: 1950.3 MHz
Span: 100 MHz
Reference level offset: Cable attenuations + adapter attenuation
Reference level: 30 dBm
Input attenuation: Default
Resolution bandwidth: more than 4.7 MHz (i.e. 5MHz)
Video bandwidth: more than 4.7 MHz (i.e. 5MHz)
Trigger: Free run
Markers: 1922.4 MHz, 1950.0 MHz and 1977.6 MHz
4. Click Start and OK.
5. In the "Mid Channel Power Level" pane, adjust the power level to 21.0 dBm.
6. Click Accept and OK.
7. Read the marker power level on the low channel and fill it in to the “Low Power Level” line.
8. Click Accept and OK.
9. Read the marker power level on the high channel and fill it in to the “High Power Level” line.
10. Check that the tuned values are within the limits presented in the table below. If they are OK, click yes.
Min Max
TX Freq Comp (the first and last
value)
11. Close the tuning window.
Issue 1 Company Confidential Page 7–51
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
-4 +4
Page 52

RM-1
Nokia Customer Care RF Troubleshooting and Manual Tuning Guide
Tx LO leakage (WCDMA)
Context
The purpose of Tx LO leakage tuning is to minimize the carrier leakage of the IQ-modulator which is caused by
the DC offset voltages in the Tx IQ-signal lines and in the actual IQ-modulator. The tuning improves WCDMA Tx
AGC dynamics at low power levels. A self-calibration routine selects the best combination for internal control
words in order to produce minimum LO leakage.
Steps
1. From the dropdown menus, set "Operating mode" to Local and "System mode" to WCDMA.
2. From the Tuning menu, choose WCDMA -> Tx LO Leakage.
3. Click Tune.
4. To end the tuning, click Close.
Page 7–52 Company Confidential Issue 1
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 53

Nokia Customer Care
Appendix A: Additional RF
Troubleshooting Instructions
Company Confidential
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All rights reserved
Page 54

Nokia Customer Care
RM-1
RF Troubleshooting
Table of Contents
1. Using these instructions ..................................................................................................................5
2. RF Self tests .....................................................................................................................................6
2.1 RX PLL phase lock self test (ST_CDSP_RX_PLL_PHASE_LOCK_TEST)................................................... 7
2.2 RF-BB interface (ST_CDSP_RF_BB_IF_TEST)....................................................................................8
2.3 RX IQ loop back self test (ST_CDSP_RX_IQ_LOOP_BACK_TEST) .......................................................10
2.4 TX IQ self test (ST_CDSP_TX_IQ_TEST) .........................................................................................11
2.5 TX PLL phase lock self test (ST_CDSP_TX_PLL_PHASE_LOCK_TEST) .................................................11
2.6 WCDMA power detector biasing self test (ST_CDSP_PWR_DETECTOR_BIAS_TEST)..........................12
2.6.1 WCDMA power detector ok? .............................................................................................13
2.7 WCDMA transmitter self test (ST_CDSP_WCDMA_TX_POWER_TEST)...............................................14
2.8 GSM transmitter self test (ST_CDSP_GSM_TX_POWER_TEST)......................................................... 15
2.9 Supply test for Hinku and Vinku (ST_CDSP_RF_SUPPLY_TEST) ......................................................15
2.10 TXC Data test (ST_TXC_DATA_TEST) ........................................................................................19
2.11 Error Code Interpretation Examples .....................................................................................19
2.11.1 Example 1........................................................................................................................ 19
2.11.2 Example 2........................................................................................................................ 20
2.11.3 Example 3........................................................................................................................ 20
3. Does the phone register to the network and make a call (GSM)?..................................................... 22
3.1 GSM transmitter power levels and transmit frequency ok? .......................................................22
3.1.1 Does GSM TX transmit RF-power at all? .............................................................................23
3.1.2 Does GSM TX transmit enough RF-power and power levels otherwise ok? .........................34
3.1.3 GSM transmitter frequency correct?..................................................................................43
3.2 Does the phone give realistic RSSI-values?............................................................................... 47
3.2.1 Is Hinku (N7500) ASIC receiving RF-power correctly from the GSM-antenna connector? .....48
3.2.2 Are RX-IQ signal waveforms and levels correct? ................................................................51
3.2.3 Is RAP3G ASIC getting ok VREFCM-signal from Hinku (N7500)? Signal level ok?...................59
3.2.4 RAP3G faulty? ..................................................................................................................60
3.3 GSM Transmitter phase error ok? .............................................................................................60
3.3.1 Are capacitors in Vinku REG1 and REG2 lines in place?....................................................... 60
3.3.2 Are capacitors in GSM PA power supply line in place?........................................................61
3.3.3 Are TX-IQ signals ok?........................................................................................................61
3.3.4 Is TX VCO signal level in the T7503 output high enough? .................................................. 61
3.3.5 VCTCXO frequency and output level correct? .....................................................................61
3.4 GSM (GMSK) modulation spectrum ok?..................................................................................... 62
3.4.1 Are components in GSM power control loop in place and working ok? ..............................63
3.4.2 Does GSM PA (N7502) get correct bias currents? Is the level of bias currents ok? ...............63
3.4.3 Are TX-IQ signals ok?........................................................................................................64
3.4.4 Is TX VCO signal level in the T7503 output high enough? .................................................. 64
3.4.5 Replace Vinku (N7501) or GSM PA (N7502) or both............................................................ 64
3.5 TX power vs. time ok? .............................................................................................................65
3.5.1 Is the TXC-signal coming to Vinku ASIC (N7501) OK?..........................................................65
3.5.2 Does GSM PA (N7502) get correct bias currents? Is the level of bias currents ok? ...............66
3.5.3 Does GSM PA (N7502) get correct DET_SW_G -voltage from Vinku ASIC (N7501)?................. 66
3.5.4 Are components in GSM power control loop in place and working ok? ..............................66
Issue 1
7A - 2
Company Confidential
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All rights reserved
Page 55

Nokia Customer Care
Does the phone register to the network and make a call (WCDMA)?................................................68
4.
4.1 WCDMA TX power and transmit frequency ok? .........................................................................68
4.1.1 Does the WCDMA TX transmit RF-power at all?.................................................................. 68
4.1.2 Does WCDMA TX transmit enough RF-power and power levels otherwise ok?.................... 80
4.1.3 WCDMA transmitter frequency correct?.............................................................................88
4.2 Does the phone give realistic RSSI-values?............................................................................... 91
4.2.1 Is Hinku ASIC (N7500) receiving RF-power correctly from the WCDMA-antenna connector? 92
4.2.2 Hinku WCDMA LNA output ok? ..........................................................................................93
4.2.3 WCDMA SAW Z7501 in place and working correctly?..........................................................93
4.2.4 Are RX-IQ signal waveforms and levels correct? ................................................................93
4.2.5 Does RAP3G ASIC get ok VREFCM-signal from Hinku (N7500)? Signal level ok? ..................101
4.2.6 RAP3G faulty? ................................................................................................................102
4.3 WCDMA modulation spectrum and ACLR ok? ..........................................................................102
4.3.1 Does N7504 give correct voltage level (Vcc11) to the WCDMA PA (N7503)? ...................... 102
4.3.2 Does WCDMA PA (N7503) get correct bias currents Icont11 and Icont12?.........................102
4.3.3 Are TX-IQ signals ok?......................................................................................................103
4.3.4 Is TX VCO signal level in the T7503 output high enough? ................................................ 103
4.3.5 Replace Vinku (N7501) or WCDMA PA (N7503) or both .................................................... 104
5. Does the phone have a reliable connection to the network (GSM)? ...............................................104
5.1 GSM receiver Bit Error Rate (BER) ok? .....................................................................................104
5.1.1 Does the phone give realistic RSSI-values?......................................................................104
5.1.2 Hinku (N7500) or RAP3G (D2800) faulty? ........................................................................ 104
5.2 GSM transmitter power levels and transmit frequency ok? .....................................................104
5.3 GSM Transmitter phase error ok? ...........................................................................................104
5.4 GSM (GMSK) modulation spectrum ok?................................................................................... 105
5.5 TX power vs. time ok? ...........................................................................................................105
6. Does the phone have a reliable connection to the network (WCDMA)? ..........................................105
6.1 WCDMA receiver Bit Error Rate (BER) ok? ................................................................................105
6.1.1 Does the phone give realistic RSSI-values?......................................................................105
6.1.2 Hinku (N7500) or RAP3G (D2800) faulty? ........................................................................ 105
6.2 WCDMA TX power and transmit frequency ok? .......................................................................106
6.3 WCDMA Transmitter error vector magnitude ok?....................................................................106
6.3.1 Is capacitor C7579 in WCDMA PA (N7503) bias line in place?............................................ 106
6.3.2 Are capacitors in Vinku REG1 and REG2 lines in place?..................................................... 106
6.3.3 Are capacitors in WCDMA PA power supply lines in place? ...............................................106
6.3.4 Are TX-IQ signals ok?......................................................................................................106
6.3.5 Is TX VCO signal level in the T7503 output high enough? ................................................ 107
6.3.6 VCTCXO frequency and output level correct? ...................................................................107
6.4 WCDMA modulation spectrum and ACLR ok? ..........................................................................107
6.5 Troubleshooting pictures ......................................................................................................108
6.5.1 VCTCXO Output (DC Offset 1.24 V) ....................................................................................108
6.5.2 TXC in GSM mode (DC Offset 0 V) .....................................................................................108
6.5.3 TX VC in GSM mode (DC Offset 1.8 V)................................................................................109
6.5.4 Icont_21/Icont_22 (DC Offset 1.2 V) .................................................................................109
6.5.5 Icont_31/Icont_32 (DC Offset 1.2 V) .................................................................................110
6.5.6 GSM RX IQ (DC Offset 0.4 V) .............................................................................................111
6.5.7 RX VC in GSM mode (DC Offset 1.5 V)................................................................................112
Issue 1
RM-1
RF Troubleshooting
7A - 3
Company Confidential
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All rights reserved
Page 56

Nokia Customer Care
TX Modulation spectrum (GSM).......................................................................................113
6.5.8
6.5.9 RFBUS ............................................................................................................................114
RM-1
RF Troubleshooting
Issue 1
7A - 4
Company Confidential
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All rights reserved
Page 57

Nokia Customer Care
RM-1
RF Troubleshooting
1. USING THESE INSTRUCTIONS
The following sections include lots of headings and subheadings that are asking simple positive style
questions.
For example heading 4.2 asks if the phone does measure RSSI-values correctly in GSM-bands. If the answer is
“Yes” then user should go to the next heading on the same level (heading number that has as many decimal
numbers as the heading 4.2) In our example case moving to the chapter 4.3. If the answer is “No” then user
should go to one heading level deeper in hierarchical system meaning the chapter 4.2.1 in our example case.
Figure 1 Use of this troubleshooting manual presented with an example. Notice that real chapter numbers are not
used.
Issue 1
7A - 5
Company Confidential
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All rights reserved
Page 58

Nokia Customer Care
RM-1
RF Troubleshooting
2. RF SELF TESTS
The RF part of Nokia 6630 is equipped with self test functionality which tests most of RF-BB interface signals
and some parts of RF circuitry. Self-tests are designed to detect faults on some critical parts, but they cannot
prove that everything is OK even if all the self-tests are passed.
Self-tests can be run with Phoenix service software. Tests can return pass/fail result and detailed
measurement data and error codes in fail case. Select “Testing” -> “Self Tests” from the Phoenix menu. Select
appropriate RF self tests and run them with “Start”-button. Notice that self tests should be run in “Local”mode (change “Operating Mode” to “Local” in Phoenix before running self tests). For service tool usage
instructions refer to the chapter “Service Tools and Service Concepts”.
Issue 1
Company Confidential
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All rights reserved
7A - 6
Page 59

Nokia Customer Care
If one or more self tests show fail results (for example: “minor” or “fatal”) more detailed error codes can be
read from the phone with “Details” button. Error codes are shown in hexadecimal format, but notice that all
returned hexadecimal values are not necessarily useful in RF troubleshooting because some of the self-tests
return also different kind of measurement information together with “real” error codes. If self-tests are not
passed, please refer to following subchapters for detailed troubleshooting information.
IMPORTANT! ST_CDSP_RF_SUPPLY_TEST is the most important self-test and the reason for the supply voltage
self test fail should always be found before reasons for other self test fails are checked!
2.1 RX PLL phase lock self test (ST_CDSP_RX_PLL_PHASE_LOCK_TEST)
This self-test verifies the functionality of the RX VCO (G7500) and Hinku (N7500) synthesizer.
Test can fail if communication with Hinku is not working, Hinku, RX VCO, balun (T7501) or loop
filter components are broken or poorly soldered.
Tested signals: VBAT_ASIC, VDIG, VR1, VR1RX, VCP1, RFBUSDAT, RFBUSCLK, RFBUSENA, RXRESETX
RM-1
RF Troubleshooting
Error code for this self-test is given in format:
• 0xyy, 0xzz
,where 0xyy, 0xzz part is the total error code: 0xyyzz
Error
code
0x0001 ---------------1
0x0002 --------------1-
0x0004 -------------1-- Hinku PLL is not locked. See section 3.1.1.1.1 “RF operating
Bit mask Reason Actions
Communication with Hinku
failed.
See section 3.1.1.1.1 “
voltage VBAT_ASIC?”
See section 3.2.2.3 “
regulator voltage VR1 ok?”
Does RF-BB interface self test also fail?
See section 3.1.1.1.2 “
ok?”
Faulty Hinku (N7500) or RAP3G
(D2800)?
voltage VBAT_ASIC?”
See section 3.2.2.3 “
regulator voltage VR1 ok?”
RX VCO, balun T7501 or loop filter
faulty?
Check following steps: See section
RF operating
Hinku (N7500)
RFBUS signals
Hinku (N7500)
Issue 1
7A - 7
Company Confidential
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All rights reserved
Page 60

Nokia Customer Care
3.2.2.7
“Is there RF power in the RX VCO
output at all?”
RX VCO RF-signal coming to the Hinku
at all?”
See section 3.2.2.9 “
frequency as expected?”
Faulty Hinku (N7500) or RAP3G
(D2800)?
and section 3.2.2.8 “Is
RM-1
RF Troubleshooting
Is RX VCO
Please, refer to chapter 2.11 “
error code interpretation is needed.
2.2 RF-BB interface (ST_CDSP_RF_BB_IF_TEST)
RF-BB interface self test verifies if the RF control bus is functional and the functionality of
digital parts of the RF ASICs is ok.
Tested signals: VBAT_ASIC, VDIG, VREFRF01, VXO, RFBUSDAT, RFBUSCLK, RFBUSENA, RXRESETX,
TXRESETX
Error code for this self-test is given in format:
• 0xyy, 0xzz
,where 0xyy, 0xzz part is the total error code: 0xyyzz
Error
code
0x0001 ---------------1 Incorrect version number
0x0002 --------------1- RX IC is not reset correctly. See section 3.1.1.1.1 “RF operating
Issue 1
Bit mask Reason Actions
read from the RX IC.
Error Code Interpretation Examples”, if more information about
See section 3.1.1.1.1 “RF operating
voltage VBAT_ASIC?”
See section 3.1.1.1.2 “
ok?”
Faulty Hinku (N7500) or RAP3G
(D2800)?
voltage VBAT_ASIC?”
Check RXRESETX signal.
See section 3.1.1.1.2 “
ok?”
RFBUS signals
RFBUS signals
7A - 8
Company Confidential
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All rights reserved
Page 61

Nokia Customer Care
0x0004 -------------1-- Register write-read cycle
0x0008 ------------1--- Incorrect version number
0x0010 -----------1---- TX IC is not reset correctly. See section 3.1.1.1.1 “RF operating
0x0012 ----------1----- Register write-read cycle
All six error codes:
failed.
read from the TX IC.
failed.
Faulty Hinku (N7500) or RAP3G
(D2800)?
See section 3.1.1.1.1 “RF operating
voltage VBAT_ASIC?”
Check RXRESETX signal.
See section 3.1.1.1.2 “
ok?”
Faulty Hinku (N7500) or RAP3G
(D2800)?
See section 3.1.1.1.1 “RF operating
voltage VBAT_ASIC?”
Check RFBUS signal levels, see section
3.1.1.1.2 “
Faulty Vinku (N7501) or RAP3G
(D2800)?
voltage VBAT_ASIC?”
Check TXRESETX signal
See section 3.1.1.1.2 “
ok?”
Faulty Vinku (N7501) or RAP3G
(D2800)?
See section 3.1.1.1.1 “RF operating
voltage VBAT_ASIC?”
Check TXRESETX signal
See section 3.1.1.1.2 “
ok?”
Faulty Vinku (N7501) or RAP3G
(D2800)?
RFBUS signals ok?”
RM-1
RF Troubleshooting
RFBUS signals
RFBUS signals
RFBUS signals
Issue 1
=> If VBAT_ASIC voltage is correct: Most probably caused by faulty RAP3G (D2800) but also
faulty Hinku (N7500) or Vinku (N7501) can cause this
error.
Please, refer to chapter 2.11 “
error code interpretation is needed.
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All rights reserved
Error Code Interpretation Examples”, if more information about
7A - 9
Company Confidential
Page 62

Nokia Customer Care
2.3 RX IQ loop back self test (ST_CDSP_RX_IQ_LOOP_BACK_TEST)
This test verifies if the RX-IQ signal path from Hinku (N7500) to the baseband circuitry is
operational.
Tested signals: VBAT_ASIC, RXQP, RXQN, RXIP, RXIN, VREFCM, TXIP, TXIN, RFBUS
Error code for this self-test is given in format:
• 0xyy, 0xzz, MeasResult1, MeasResult2
,where 0xyy, 0xzz part is the main part of the error code: 0xyyzz
RM-1
RF Troubleshooting
Error
code
0x0001 ---------------1
0x0002 --------------1-
0x0004 -------------1--
0x0008 ------------1--0x0010 -----------1---- Measured IQ power is
Bit mask Reason Actions
Test can not be executed
under limit
Internal SW error. Should not happen.
Does RF-BB interface self test also fail?
See section 3.1.1.1.2 “
ok?”
Check TXIP, TXIN, RXQP, RXQN, RXIP,
RXIN, VREFCM signals.
Check following steps: See section
3.2.2
Are RX-IQ signal waveforms and levels
“
correct?”
See section 3.2.3 “I
getting ok VREFCM-signal from Hinku
(N7500)? Signal level ok?”
Hinku (N7500), Vinku (N7501) or
RAP3G faulty?
Check the following steps if
TX IQ self test
2.4. “
(ST_CDSP_TX_IQ_TEST)”shows also fail:
see section 3.1.1.1.1
RF operating voltage VBAT_ASIC?”
“
Vinku (N7501) or RAP3G (D2800) faulty
or soldering not ok? Retu (N2200) AD
converter?
RFBUS signals
s RAP3G ASIC
Issue 1
7A - 10
Company Confidential
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All rights reserved
Page 63

Nokia Customer Care
Please, refer to chapter 2.11 “
error code interpretation is needed.
2.4 TX IQ self test (ST_CDSP_TX_IQ_TEST)
This test verifies if TX-IQ lines from RAP3G (D2800) to Vinku (N7501). Test returns pass of fail
result and measured test voltages from each of four lines. The voltage should be equal on each
line and more than 1.2V.
Tested signals: VBAT_ASIC, TXIP, TXIQ, TXQP, TXQN, DAC_REF1, RFBUS
Error code for this self-test is given in format:
• 0xyy, 0xzz, MeasResult1, MeasResult2, …
,where 0xyy, 0xzz is the main part of the error code: 0xyyzz
Error Code Interpretation Examples”, if more information about
RM-1
RF Troubleshooting
Error
code
0x0001 ---------------1 TXIP signal level under
0x0002 --------------1- TXIN signal level under
0x0004 -------------1-- TXQP signal level under
0x0008 ------------1--- TXQN signal level under
0x0010 -----------1---- CBUS read or write access
2.5 TX PLL phase lock self test (ST_CDSP_TX_PLL_PHASE_LOCK_TEST)
Bit mask Reason Actions
If only one of the signals is faulty,
threshold
threshold
threshold
threshold
failed
Please, refer to chapter 2.11 “
error code interpretation is needed.
Error Code Interpretation Examples”, if more information about
check Vinku (N7501) and RAP3G
(D2800) soldering.
If the result is fail with all four IQsignals check following steps: 3.1.1.1.1
“
Retu (N2200) AD converter can be
faulty, RAP3G (D2800) faulty or
soldering bad, Vinku (N7501) faulty,
(DAC_REF1 signal)?
Retu access problem. Internal SW
error. Should not happen.
RF operating voltage VBAT_ASIC?”
Issue 1
This self-test verifies the functionality of the TX VCO (G7502) and Vinku (N7501) synthesizer.
Test can fail if communication with Vinku is not working, Vinku, TX VCO, balun (T7503) or loop
filter components are broken or poorly soldered.
Tested signals: VBAT_ASIC, VDIG, VR1, VCP2, RFBUSDAT, RFBUSCLK, RFBUSENA, TXRESETX
Error code for this self-test is given in format:
• 0xyy, 0xzz
7A - 11
Company Confidential
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All rights reserved
Page 64

Nokia Customer Care
,where 0xyy, 0xzz part is the total error code: 0xyyzz
RM-1
RF Troubleshooting
Error
code
0x0001 ---------------1
0x0002 --------------1-
0x0004 -------------1-- Vinku PLL is not locked. 3.1.1.1.1 “RF operating voltage
Bit mask Reason Actions
Communication with Vinku
failed.
3.1.1.1.1 “
VBAT_ASIC?”
3.1.1.1.3 “
voltages VREG1, VREG2 ok?”
Is RF-BB interface self-test result also
fail? 3.1.1.1.2 “
Faulty Vinku (N7501) or RAP3G
(D2800)?
VBAT_ASIC?”
3.1.1.1.3 “
voltages VREG1, VREG2 ok?”
TX VCO, balun T7503 or loop filter
faulty?
Check following steps: 3.1.1.1.6
Is there RF power in the TX VCO output
at all?
signal coming to the Vinku at all?”,
3.1.3.1 “
expected?”
Faulty Vinku (N7501)?
RF operating voltage
Vinku (N7501) regulator
RFBUS signals ok?”
Vinku (N7501) regulator
And 3.1.1.1.7 “Is TX VCO RF-
Is TX VCO frequency as
Please, refer to chapter 2.11 “
error code interpretation is needed
2.6 WCDMA power detector biasing self test (ST_CDSP_PWR_DETECTOR_BIAS_TEST)
This self-test is used to check if the biasing of the WCDMA power detector circuit is ok.
Test covers: Vinku (N7501) WCDMA power detector biasing circuit functionality, Retu (N2200)
WTXDET input. RFBUS, VBAT_ASIC
Error code for this self-test is given in format:
• 0xyy, 0xzz, MeasResult1, MeasResult2
Issue 1
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All rights reserved
Error Code Interpretation Examples”, if more information about
Company Confidential
7A - 12
Page 65

Nokia Customer Care
,where 0xyy, 0xzz part is the main part of the error code: 0xyyzz
RM-1
RF Troubleshooting
Error
code
0x0001 ---------------1
0x0002 --------------10x0008 ------------1--0x0010 -----------1---0x0004 -------------1-- Power detector reading is
Bit mask Reason Actions
Test cannot be executed.
outside limits.
Internal SW error. Should not happen.
Does RF-BB interface self test also fail?
3.1.1.1.2 “
3.1.1.1.1. “RF operating voltage
VBAT_ASIC?”
Check WCDMA power detector circuitry:
Follow troubleshooting in section
4.1.2.3.2.4 “
control voltage from the WCDMA
power detector (signal Vcontrol)?”
Measure also WTXDET-signal: 2.6.1.
WCDMA power detector ok?”
“
If ok => Retu AD converter faulty?
RFBUS signals ok?”
Does SMPS get correct
Please, refer to chapter 2.11 “
error code interpretation is needed.
2.6.1 WCDMA power detector ok?
Follow these instructions if it’s needed to check WCDMA power detector functionality. Please
notice that WCDMA power detector is used only in maximum TX power limiting and WCDMA PA
supply voltage controlling purposes.
• WCDMA transmitter has to be active before measurements. Procedure is explained in
chapter “General instructions for TX troubleshooting”.
• Measurement can be done with an oscilloscope and a probe.
• Connect the probe to R7531.
• WTXDET signal should be constant DC-voltage. Voltage level should change if TX power is
changed. Vcontrol is lower on lower power levels and higher if higher power levels are
used.
Issue 1
Error Code Interpretation Examples”, if more information about
7A - 13
Company Confidential
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All rights reserved
Page 66

Nokia Customer Care
• WTXDET should be about 325 mV with power level +10 dBm, about 1.03 V with power level
+21 dBm and about 150 mV when power levels below 0 dBm are used.
• NOTICE: Perform WCDMA transmitter tests with > 0 dBm power only in RF shielded
environment.
• If WTXDET –signal is not as expected follow the same troubleshooting instructions as in:
4.1.2.3.2.4 “
Vcontrol)?”
2.7 WCDMA transmitter self test (ST_CDSP_WCDMA_TX_POWER_TEST)
This test transmits one WCDMA slot with full TX power and measures the output power with
power detector. This information is used to judge if WCDMA TX parts are faulty.
The phone must be in a shield box, when this test is run to prevent network interference!
Test covers: Modulator, Vinku (N7501) IC gain stages, IC output supply components, TX filter,
WCDMA PA (N7503), DCDC-converter (N7504), RFBUS, VBAT_ASIC, VBAT_PA
Does SMPS get correct control voltage from the WCDMA power detector (signal
RM-1
RF Troubleshooting
Test does not cover: Circulator (Z7505), duplexer (Z7502), antenna
Error code for this self-test is given in format:
• 0xyy, 0xzz, MeasResult1, MeasResult2
,where 0xyy, 0xzz part is the main part of the error code: 0xyyzz
Error
code
0x0001 ---------------1
0x0002 --------------1-
0x0004 -------------1--
0x0008 ------------1---
0x0010 -----------1---- Measured output power
Bit mask Reason Actions
Test execution failed. Internal SW error. Should not happen.
too low.
Does RF-BB interface self test also fail?
3.1.1.1.2 “
Something is faulty in the WCDMA TX
chain (Power detector, Vinku, WCDMA
PA, DCDC-converter…).
Check TX chain manually: 4.1. “
TX power and transmit frequency ok?”
RFBUS signals ok?”
WCDMA
Issue 1
Please, refer to chapter 2.11 “
error code interpretation is needed.
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All rights reserved
Error Code Interpretation Examples”, if more information about
Company Confidential
7A - 14
Page 67

Nokia Customer Care
2.8 GSM transmitter self test (ST_CDSP_GSM_TX_POWER_TEST)
This test verifies if GSM transmitter can transmit power.
Test covers: RFIC Vinku (N7501), modulator, IC gain control stages, filter/balun solder joints,
GSM PA (N7502), PA bias lines & DACs, RFBUS, TX power detector functionality, VBAT_ASIC,
VBAT_PA.
Test does not cover: Antenna functionality, RX/TX-switch functionality, TX signal quality
Error code for this self-test is given in format:
• 0xyy, 0xzz, MeasResult1, MeasResult2, …
,where 0xyy, 0xzz part is the main part of the error code: 0xyyzz
RM-1
RF Troubleshooting
Error
code
0x0001 ---------------1 GSM900 Tx power is under
0x0002 --------------1- GSM1800 Tx power is under
0x0004 -------------1-- GSM1900 Tx power is under
2.9 Supply test for Hinku and Vinku (ST_CDSP_RF_SUPPLY_TEST)
Bit mask Reason Actions
threshold.
threshold.
threshold.
Please, refer to chapter 2.11 “
error code interpretation is needed.
This self test tests supply voltage connections of RF ASICs Vinku (N7501) and Hinku (N7500).
The signals supported to be measured are:
- Reference voltage supply to each ASIC
- Regulator connections of each ASICs
Error Code Interpretation Examples”, if more information about
Check following steps: 3.1 “
transmitter power levels and transmit
frequency ok?”
GSM
Issue 1
- Supply voltage routings to each functional block of each ASIC.
Error code for this self-test is given in format:
• 0xyy, 0xyy, 0xzz, 0xzz, MeasResult1, MeasResult2, …
,where 0xyy, 0xyy part is the main part of the error code for Vinku TX ASIC: 0xyyyy
and 0xzz, 0xzz is the main part of the error code for Hinku TX ASIC: 0xzzzz
7A - 15
Company Confidential
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All rights reserved
Page 68

Nokia Customer Care
NOTICE: There are two error code tables for this self-test, one for Vinku and one for Hinku
Error code table for Vinku supply voltage errors (0xyyyy):
supply voltage troubleshooting.
RM-1
RF Troubleshooting
Error
code
0x0001 ---------------1 VB_EXT line (RX ASIC Hinku,
0x0002 --------------1- VXO supply (RX ASIC Hinku,
0x0004 -------------1-- VBAT1 or VR1 pins of Vinku
0x0008 ------------1--- VBAT2 or VR2 pins of Vinku
0x0010 -----------1---- VRFTX pin of TX ASIC 3.1.1.1.1 “RF operating voltage
0x0020 ----------1----- VVGA pin of TX ASIC 3.1.1.1.1 “RF operating voltage
0x0040 ---------1------ VVCO pin of TX ASIC Poor soldering in Vinku ASIC (N7501)?
Bit mask Reason Actions
3.1.1.1.3.1 “
TX ASIC Vinku or RETU) or
TX_MUXOUT line (Vinku or
RETU)
TX ASIC Vinku, RETU or
VCTCXO G7501)
TX ASIC or Vinku internal
regulator(1)
TX ASIC or Vinku internal
regulator(2)
voltage ok?”
Poor soldering in Vinku ASIC (N7501)?
3.1.3.3.1 “
Poor soldering in Vinku ASIC (N7501)?
3.1.1.1.1 “
VBAT_ASIC?”
3.1.1.1.3 “
voltages VREG1, VREG2 ok?”
Poor soldering in Vinku ASIC (N7501)?
3.1.1.1.1 “
VBAT_ASIC?”
3.1.1.1.3 “Vinku (N7501) regulator
voltages VREG1, VREG2 ok?”
Poor soldering in Vinku ASIC (N7501)?
VBAT_ASIC?”
3.1.1.1.3 “Vinku (N7501) regulator
voltages VREG1, VREG2 ok?”
Poor soldering in Vinku ASIC (N7501)?
VBAT_ASIC?”
3.1.1.1.3 “Vinku (N7501) regulator
voltages VREG1, VREG2 ok?”
Poor soldering in Vinku ASIC (N7501)?
Vinku (N7501) RB_EXT
VXO-voltage ok? (=Vdig)”
RF operating voltage
Vinku (N7501) regulator
RF operating voltage
Issue 1
0x0080 --------1------- VLO pin of TX ASIC 3.1.1.1.1 “RF operating voltage
VBAT_ASIC?”
3.1.1.1.3 “
voltages VREG1, VREG2 ok?”
Poor soldering in Vinku ASIC (N7501)?
Company Confidential
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All rights reserved
Vinku (N7501) regulator
7A - 16
Page 69

(
Nokia Customer Care
0x0100 -------1--------
0x0200 ------1--------- RB_EXT pin of TX ASIC or
0x0800 ----1----------- Temperature sensor 3.1.1.1.1 “RF operating voltage
RM-1
RF Troubleshooting
VPRE pin of TX ASIC 3.1.1.1.1 “RF operating voltage
VBAT_ASIC?”
Vinku (N7501) regulator
Vinku (N7501) RB_EXT
Vinku (N7501) regulator
Vinku internal bias block
3.1.1.1.3 “
voltages VREG1, VREG2 ok?”
Poor soldering in Vinku ASIC (N7501)?
3.1.1.1.1 “RF operating voltage
VBAT_ASIC?”
3.1.1.1.3.1 “
voltage ok?”
Poor soldering in Vinku ASIC (N7501)?
VBAT_ASIC?”
3.1.1.1.3 “
voltages VREG1, VREG2 ok?”
Faulty Vinku ASIC (N7501)
NOTE! ST_CDSP_RF_SUPPLY_TEST error code: 0x0B, 0xBC, 0x00, 0x00, … means typically that
there is no VBAT_ASIC voltage coming to the Vinku TX ASIC at all or the ASIC is poorly
soldered to the PWB (All voltages that are somehow related to VBAT_ASIC are causing
errors).
Error code table for Hinku supply voltage errors (0xzzzz):
Error
Bit mask Reason Actions
code
0x0001 ---------------1 VB_EXT pin of Hinku RX ASIC
(VB_EXT line tested before
with TX ASIC) or CALOUT CALIN line between RX ASIC
and TX ASIC
0x0002 --------------1- VDIG pin of RX ASIC (VXO
line tested before with TX
ASIC)
0x0004 -------------1-- VBAT1 or VR1 pins of Hinku
RX ASIC or Hinku internal
regulator(1)
If this test didn’t failed with Vinku ASIC
(N7501) then there has to be poor
soldering in Hinku ASIC (N7500).
Otherwise: 3.2.2.3.1 “
Hinku (N7500)
RB_EXT voltage ok?”
If VXO supply test with Vinku TX ASIC
(N7501) has not been failed => Poor
soldering in Hinku ASIC (N7500).
Otherwise: 3.1.3.3.1 “
VXO-voltage ok?
(=Vdig)”
3.1.1.1.1 “
RF operating voltage
VBAT_ASIC?”
If supply test with Vinku TX ASIC
N7501) has not been failed => Poor
Issue 1
7A - 17
Company Confidential
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All rights reserved
Page 70

Nokia Customer Care
0x0008 ------------1--- VMIX pin of Hinku RX ASIC 3.1.1.1.1 “RF operating voltage
0x0010 -----------1---- VDDLNA1 & VDDLNA2 pin of
0x0020 ----------1----- VDDLNA2 pin of Hinku RX
0x0040 ---------1------ VLO pin of Hinku RX ASIC 3.1.1.1.1 “RF operating voltage
0x0080 --------1------- VPRE pin of Hinku RX ASIC 3.1.1.1.1 “RF operating voltage
0x0100 -------1-------- RB_EXT pin of Hinku RX ASIC
0x0200 ------1--------- Temperature sensor 3.1.1.1.1 “RF operating voltage
Hinku RX ASIC
ASIC
or Hinku internal bias
block
soldering in Hinku RX ASIC (N7500) or
faulty Hinku ASIC:
3.2.2.3 “
voltage VR1 ok?”
VBAT_ASIC?”
3.2.2.3 “
voltage VR1 ok?”
Poor soldering in Hinku ASIC (N7500)?
3.1.1.1.1 “RF operating voltage
VBAT_ASIC?”
3.2.2.3 “
voltage VR1 ok?”
Poor soldering in Hinku ASIC (N7500)?
3.1.1.1.1 “RF operating voltage
VBAT_ASIC?”
3.2.2.3 “
voltage VR1 ok?”
Poor soldering in Hinku ASIC (N7500)?
VBAT_ASIC?”
3.2.2.3 “
voltage VR1 ok?”
Poor soldering in Hinku ASIC (N7500)?
VBAT_ASIC?
3.2.2.3 “
voltage VR1 ok?”
Poor soldering in Hinku ASIC (N7500)?
3.1.1.1.1 “
VBAT_ASIC?”
3.2.2.3.1 “
voltage ok?”
VBAT_ASIC?”
3.2.2.3 “
voltage VR1 ok?”
Faulty Hinku ASIC (N7500)
Hinku (N7500) regulator
Hinku (N7500) regulator
Hinku (N7500) regulator
Hinku (N7500) regulator
Hinku (N7500) regulator
”
Hinku (N7500) regulator
RF operating voltage
Hinku (N7500) RB_EXT
Hinku (N7500) regulator
RM-1
RF Troubleshooting
Issue 1
7A - 18
Company Confidential
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All rights reserved
Page 71

Nokia Customer Care
NOTE! ST_CDSP_RF_SUPPLY_TEST error code: 0x00, 0x00, 0x03, 0xBF, … means typically that
there is no VBAT_ASIC voltage coming to the Hinku RX ASIC at all or the ASIC is poorly
soldered to the PWB (All voltages that are somehow related to VBAT_ASIC are
causing errors).
RM-1
RF Troubleshooting
Please, refer to chapter 2.11 “
error code interpretation is needed.
2.10 TXC Data test (ST_TXC_DATA_TEST)
This self-test is used to check if the TXC-signal is coming correctly from Retu (N2200) to Vinku
(N7501).
Test covers: TxC power control signal, Retu (N2200), RFBUS, Vinku (N7501), VBAT_ASIC
Error code for this self-test is given in format:
• 0xyy, 0xzz, MeasResult1, MeasResult2, …
,where 0xyy, 0xzz part is the main part of the error code: 0xyyzz
Error
code
0x0001 ---------------1 TxC voltage too high with
0x0002 --------------1- TxC voltage too low with
Bit mask Reason Actions
minimum input.
maximum input.
Error Code Interpretation Examples”, if more information about
Retu (or Vinku) faulty…Replace the
component.
3.1.1.1.1 “RF operating voltage
VBAT_ASIC?”
3.1.1.1.3 “Vinku (N7501) regulator
voltages VREG1, VREG2 ok?”
Check following step:
3.1.1.1.9 “
Vinku ASIC (N7501)?”
Is there TXC-signal coming to
Please, refer to chapter 2.11 “
error code interpretation is needed.
2.11 Error Code Interpretation Examples
This chapter presents three different examples of RF error code interpretation.
2.11.1 Example 1
ST_CDSP_RX_PLL_PHASE_LOCK self test gives “Fatal” result with error code: 0x00, 0x04
This means that the total error code is 0x004 and if we look an error code table in Chapter 2.1
RX PLL phase lock self test” the meaning for the code is “Hinku PLL is not locked”.
“
Issue 1
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All rights reserved
Error Code Interpretation Examples”, if more information about
7A - 19
Company Confidential
Page 72

Nokia Customer Care
There is also another way to do the error code interpretation in this case:
0x004 hexadecimal value is “100” in binary format. If we look the error code table (bit mask
column) again it can be seen that the results is the same “Hinku PLL is not locked”.
2.11.2 Example 2
Some of the self-tests can return multiple errors at the same time.
For example: ST_CDSP_TX_IQ_TEST self test gives “Fatal” result with error code: 0x00, 0x0F, …
RM-1
RF Troubleshooting
This means that the error code without measurement values is 0x000F
is explained in chapter 2.4 “
look an error code table (bit mask column) in Chapter 2.4 “
errors found:
Bit mask ---------------1: “TXIP signal level under threshold”
Bit mask --------------1-: “TXIN signal level under threshold”
Bit mask -------------1--: “TXQP signal level under threshold”
Bit mask ------------1---: “TXQN signal level under threshold”
But there is no error with:
Bit mask -----------1----: “CBUS read or write access”
2.11.3 Example 3
Supply test for Hinku and Vinku (ST_CDSP_RF_SUPPLY_TEST) is slightly different self-test from
others because there are both Vinku and Hinku errors shown in the same error code (
for error code is explained in chapter2.9 “
For example: ST_CDSP_RF_SUPPLY_TEST gives “Fatal” result with error code: 0x0B, 0xBC, 0x00,
(The format for error code
TX IQ self test”) and this is the same as “1111” in binary format. If we
TX IQ self test” there are multiple
The format
Supply test for Hinku and Vinku”).
0x00, …
Issue 1
This error code means that there are probably no errors in Hinku RX ASIC supply voltages
because the main part of the error code for Hinku is 0x00, 0x00 (=0x0000) and means the same
as “no errors”.
Anyway, there are many errors with Vinku TX ASIC supply voltages. The main part of the error
code for Vinku is 0x0B, 0xBC and that’s the same as “101110111100” in binary format. If we
look an error code table (bit mask column) in chapter 2.9 “
Supply test for Hinku and Vinku“
there are multiple errors found:
Bit mask -------------1--: “ST_TX_VBAT1_OR_VR1_REG1”
Bit mask ------------1---: “ST_TX_VBAT2_OR_VR2_OR_REG2”
Bit mask -----------1----: “ST_TX_VRFTX”
7A - 20
Company Confidential
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All rights reserved
Page 73

Nokia Customer Care
Bit mask ----------1-----: “ST_TX_VVGA”
Bit mask --------1-------: “ST_TX_VLO”
Bit mask -------1--------: “ST_TX_VPRE”
Bit mask ------1---------: “ST_TX_RBEXT_OR_BIAS”
Bit mask ----1-----------: “ST_TX_TEMP_SENSOR”
But there are no errors with:
Bit mask ---------------1: “ST_VBEXT_OR_TXMUXOUT”
Bit mask --------------1-: “ST_VXO_SUPPLY”
Bit mask ---------1------: “ST_TX_VVCO”
Bit mask -----1----------: “No error defined for this bit mask”
RM-1
RF Troubleshooting
Typically this kind of error occurs if there is no VBAT_ASIC voltage coming to the Vinku TX ASIC
at all or the ASIC is poorly soldered to the PWB (All voltages that are somehow related to
VBAT_ASIC are causing errors).
Issue 1
7A - 21
Company Confidential
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All rights reserved
Page 74

Nokia Customer Care
3. DOES THE PHONE REGISTER TO THE NETWORK AND MAKE A CALL (GSM)?
• Test against a GSM communication tester or real GSM network with a proper SIM.
3.1 GSM transmitter power levels and transmit frequency ok?
• Attach the phone to the product specific test jig (AD-23) and a spectrum analyser to the
RF-coupler. Remember that there are two antenna connectors in the coupler, one for GSM
and one for WCDMA. Coupler attenuation should be also taken into account during
measurements.
• Set GSM Tx ON. Procedure is explained in chapter “General instructions for TX
troubleshooting”.
• Spectrum analyser centre frequency should be set according the used TX channel (See
chapter “Frequency mappings”).
RM-1
RF Troubleshooting
• Spectrum analyser RBW = VBW = 1 MHz, Span 0 MHz, sweep time 1 ms. Notice that GSM
transmission has pulsed nature and power should be measured during TX burst (triggering
needed). Another possibility is to use following settings: RBW = VBW = 1 MHz, Span 200 kHz
and sweep time at least 2.5 seconds.
• Test at least the maximum and minimum power levels:
- EGSM900: The maximum power level is “5” (31 – 34 dBm, typ. value +33 dBm)
The minimum power level is “19” (3 – 7 dBm, typ. value +5 dBm)
- DCS1800: The maximum power level is “0” (28 – 32 dBm, typ. value +30 dBm)
The minimum power level is “15” (-2 - +2 dBm, typ. value +0 dBm)
- PCS1900: The maximum power level is “0” (28 – 32 dBm, typ. value +30 dBm)
The minimum power level is “15” (-2 - +2 dBm, typ. value +0 dBm)
• If power is not as expected separate the phone into parts and place to the MJ-26 module
jig. Connect the spectrum analyser to the module jig GSM RF connector and measure power
levels again (Notice that there are three antenna connectors in the module jig, one for GSM,
one for WCDMA and one for Bluetooth. Make sure that all connections are made to the correct
RF-connector).
Issue 1
- Power levels ok in the module jig: Antenna or antenna connection bad. Replace the
antenna
- Power levels still wrong or no TX signal found at all: Continue troubleshooting
7A - 22
Company Confidential
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All rights reserved
Page 75

Nokia Customer Care
• If TX signal is not found at all use wider span setting and check if the transmitter is
transmitting on wrong frequency. If the signal is found to be on wrong frequency or
frequency is not stabile,
3.1.1 Does GSM TX transmit RF-power at all?
• If TX signal is not found at all use wider span setting and check if the transmitter is
transmitting on wrong frequency. If signal is found to be on wrong frequency or frequency
is not stabile,
3.1.1.1 Is Vinku (N7501) transmitting RF-power at all?
• GSM transmitter has to be active before Vinku’s output level can be measured. Procedure is
explained in chapter “General instructions for TX troubleshooting”.
• Measurements can be done with a spectrum analyser and an RF probe. RBW and VBW =
1 MHz, Span = 0, sweep time 1 ms. Spectrum analyser centre frequency should be set
according the used TX channel (see chapter “Frequency mappings”). Notice that GSM
transmission has pulsed nature and power should be measured during TX burst (triggering
needed). Another possibility is to use following settings: RBW = VBW = 1 MHz, Span 200 kHz
and sweep time at least 2.5 seconds.
see section 3.1.3. "GSM transmitter frequency correct".
see section 3.1.3. "GSM transmitter frequency correct".
RM-1
RF Troubleshooting
• EGSM900:
- Connect the RF probe to Z7504 input. The level should be about the same on both input
pins. Check output level with at least the maximum (5) and the minimum (19) power
levels.
- Maximum power level – Output level should be about -15…-25 dBm
- Minimum power level – Output level should be about -45…-55 dBm
• DCS1800/PCS1900:
- Connect the RF probe to C7577 or C7575. The level should be about the same on both
capacitors. Check output level with at least the maximum (0) and the minimum (15) power
levels.
- Maximum power level – Output level should be about -25…-35 dBm
- Minimum power level – Output level should be about -55…-65 dBm
• Check if output levels of Vinku are as expected.
• NOTE! If VINKU output RF-power is totally missing just in one or two GSM-bands,
typically this means that Vinku ASIC (N7501) is faulty or the ASIC is badly soldered. For
example: VINKU is not transmitting at all in EGSM900-band but TX-power is ok in other
GSM-bands. Then it’s quite clear that VINKU (N7501) is faulty or badly soldered and the
component should be replaced.
Issue 1
7A - 23
Company Confidential
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All rights reserved
Page 76

Nokia Customer Care
3.1.1.1.1 RF operating voltage VBAT_ASIC?
• Measurement can be done with an oscilloscope and a probe.
• Connect the probe to C7503 (or C7501, C7541)
• VBAT_ASIC voltage level should be 3.05 – 5.4 V. Typical value is 4.0 V.
3.1.1.1.1.1 Ferrite inductor L7503 ok?
• Check that component is in place and solder joints are ok
• Measure voltage from the both ends of L7503. Is it faulty or is there short circuit in RF end?
• Disconnect the power supply from the phone and use an ohmmeter to check that inductor
is conducting DC.
3.1.1.1.2 RFBUS signals ok?
RM-1
RF Troubleshooting
• GSM receiver has to be active before RFBUS signals can be measured. Procedure is
explained in chapter “GSM RX chain activation for manual measurements”. Also
WCDMA/GSM transmitter and WCDMA receiver activation can be used for the measurement
but then RFBUS -signals don’t necessarily look like in figures mentioned below.
• Measurements can be performed with an oscilloscope and a probe. Check all five RF BUS
signals:
- RFBUSDAT: Connect the probe to J7504. Typical RFBUSDAT -signal is shown in section 6.5.9.3
RFBUSDAT (GSM RX)”
“
- RFBUSCLK: Connect the probe to J7505. Typical RFBUSCLK -signal is shown in sections 6.5.9.1
RFUSCLK (GSM RX)” and 6.5.9.2 “RFBUSCLK and RFBUSENA (GSM RX)”
“
- RFBUSENA: Connect the probe to J7506. Typical RFBUSENA -signal is shown in section 6.5.9.2
RFBUSCLK and RFBUSENA (GSM RX)”
“
- RXRESETX: Connect the probe to J7515. RXRESETX -signal is a constant 2 V DC-signal after
GSM or WCDMA transceiver has been activated the first time after phone boot up. The level
of this signal should be about 0 V before transceiver activation.
- TXRESETX: Connect the probe to J7517. TXRESETX -signal is a constant 2 V DC-signal after
GSM or WCDMA transceiver has been activated the first time after phone boot up. The level
of this signal should be about 0 V before transceiver activation.
3.1.1.1.2.1 RAP3G (or Vinku or Hinku) faulty?
• RAP3G (D2800) can not be replaced
Issue 1
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All rights reserved
7A - 24
Company Confidential
Page 77

Nokia Customer Care
3.1.1.1.3 Vinku (N7501) regulator voltages VREG1, VREG2 ok?
• GSM transmitter has to be active before VREG1 and VREG2 voltages can be measured.
Procedure is explained in chapter “General instructions for TX troubleshooting.”
• Measurements can be done with an oscilloscope and a probe.
• VREG1: Connect the probe to C7543
• VREG2: Connect the probe to C7548 (or C7547)
• VREG1 and VREG2 voltage levels should be 2.65 – 2.86 V. Typical value is 2.7 V.
3.1.1.1.3.1 Vinku (N7501) RB_EXT voltage ok?
• GSM transmitter has to be active before Vinku’s RB_EXT voltage can be measured.
Procedure is explained in chapter “General instructions for TX troubleshooting”.
RM-1
RF Troubleshooting
• Measurement can be done with an oscilloscope and a probe.
• Connect the probe to R7521.
• RB_EXT voltage should be 1.325 – 1.375 V.
3.1.1.1.3.1.1 VREFRF01-voltage ok?
• Measurement can be done with an oscilloscope and a probe.
• Connect the probe to R7503.
• VREFRF01 voltage should be 1.325 – 1.375 V. Typical value is 1.35 V.
3.1.1.1.3.1.1.1 Desolder R7503. Is VREFRF01 voltage still wrong?
• Remember to solder a new component to R7503 pads after the measurement.
3.1.1.1.3.1.2 R7521 and R7504 in place and working correctly?
• Check that components are in place and solder joints are ok
• Disconnect the power supply from the phone and check R7521 and R7504 resistance
values with an ohmmeter.
3.1.1.1.3.1.3 VB_EXT voltage ok?
• Measurement can be done with an oscilloscope and a probe.
• Connect the probe to C7518.
• VB_EXT voltage should be 1.325 – 1.375 V. Typical value is 1.35 V.
Issue 1
7A - 25
Company Confidential
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All rights reserved
Page 78

Nokia Customer Care
3.1.1.1.3.1.3.1 Is R7503 in place and working correctly?
• Check that the component is in place and solder joints are ok
• Disconnect the power supply from the phone and check R7503 resistance value with an
ohmmeter
3.1.1.1.3.1.3.2 Capacitors C7518, C7520 and C7570 working correctly?
• Check that components are in place and solder joints are ok
• Disconnect the power supply from the phone and use an ohmmeter to check that
capacitors are not short-circuited. If short-circuit is found replace capacitors mentioned
above. If this does not help go to the next step.
3.1.1.1.3.1.3.3 Replace Vinku (N7501) or Hinku (N7500) or both
3.1.1.1.3.1.4 Replace Vinku (N7501)
RM-1
RF Troubleshooting
3.1.1.1.3.2 Are capacitors in Vinku (N7501) regulator lines working correctly?
VREG1: C7543
VREG2: C7547, C7548, C7554, C7555, C7553, C7552, C7558 and C7567
• Check that components are in place and solder joints are ok
• Disconnect the power supply from the phone and use an ohmmeter to check that regulator
lines are not short-circuited to the ground. If short-circuit is found replace capacitors
mentioned above. If this does not help go to the next step.
3.1.1.1.3.3 TX VCO (G7502) ok?
3.1.1.1.3.4 Replace Vinku (N7501)
3.1.1.1.4 VXO-voltage ok? (=Vdig).
• Measurement can be done with an oscilloscope and a probe
• Connect the probe to C7560 (or C7526, C7513)
• VXO-voltage should be about 2.5 V
3.1.1.1.5 VCP2-voltage ok?
• GSM transmitter has to be active before VCP2 voltage can be measured. Procedure is
explained in chapter “General instructions for TX troubleshooting”.
• Measurement can be done with an oscilloscope and a probe.
• Connect the probe to C2221 (or C7550).
Issue 1
7A - 26
Company Confidential
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All rights reserved
Page 79

Nokia Customer Care
• VCP2 voltage should be about 4.75 V.
3.1.1.1.5.1 C7550 and C2221 working correctly?
• Check that components are in place and solder joints are ok
• Disconnect the power supply from the phone and use an ohmmeter to find out if the VCP2-
line is short-circuited to the ground. If short-circuit is found replace C7550 and C2221. If
this does not help go to the next steps.
3.1.1.1.5.2 Retu ok?
3.1.1.1.5.3 Vinku (N7501) ok?
3.1.1.1.6 Is there RF power in the TX VCO output at all?
• GSM transmitter has to be active before TX VCO’s output frequency and output level can be
measured. Procedure is explained in chapter “General instructions for TX troubleshooting”.
RM-1
RF Troubleshooting
• Measurements can be done with a spectrum analyser and an RF probe. Spectrum analyser
centre frequency should be set according the used TX channel (see chapter “Frequency
mappings”).
• Spectrum analyser RBW and VBW = 1 MHz, Span = 0, sweep time 1 ms. Notice that GSM
transmission has pulsed nature and VCO output power should be measured during TX
burst (triggering needed). Another possibility is to use following settings: RBW = VBW = 1
MHz, Span 200 kHz and sweep time at least 2.5 seconds.
• Connect the RF probe to the T7503 input. VCO shield has to be removed before
measurement. Remember to solder the shield back after the phone repairing. Quick VCO
alive check can be done also without removing the RF shield. The RF probe should be placed
as near the TX VCO output as possible (Put the head of the probe carefully inside the VCO can
through the holes of the shield). Remember to use low RF Attenuator value in the spectrum
analyser with this method.
• Check if the frequency of the TX VCO is as expected. If the VCO signal is not found try to use
wider span setting. The correct VCO frequency can be found in chapter “Frequency
mappings”. The output level of the VCO should be about -25 dBm during GSM TX burst.
3.1.1.1.6.1 TX VCO operating voltage VREG2 (VR2) ok?
• GSM transmitter has to be active before VREG1 and VREG2 voltages can be measured.
Procedure is explained in chapter “General instructions for TX troubleshooting”.
Issue 1
• Measurements can be done with an oscilloscope and a probe.
• VREG1: Connect the probe to C7543
• VREG2: Connect the probe to C7548 (or C7547)
7A - 27
Company Confidential
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All rights reserved
Page 80

Nokia Customer Care
• VREG1 and VREG2 voltage levels should be 2.65 – 2.86 V. Typical value is 2.7 V.
3.1.1.1.6.2 Replace TX VCO (G7502)
3.1.1.1.7 Is TX VCO RF-signal coming to the Vinku at all?
• GSM transmitter has to be active before TX VCO’s output level can be measured. Procedure
is explained in chapter “General instructions for TX troubleshooting”.
• Measurements can be done with a spectrum analyser and an RF probe. Spectrum analyser
centre frequency should be set according the used TX channel (see chapter “Frequency
mappings”).
• Spectrum analyser RBW and VBW = 1 MHz, Span = 0, sweep time 1 ms. Notice that GSM
transmission has pulsed nature and VCO output power should be measured during TX
burst (triggering needed). Another possibility is to use following settings: RBW = VBW = 1
MHz, Span 200 kHz and sweep time at least 2.5 seconds.
RM-1
RF Troubleshooting
• Check the level of the TX VCO frequency in T7503 outputs. The level should be about
-30…-35 dBm in both output lines. If the signal level is correct in the input (about -25 dBm)
but output level is not as expected then replace T7503. VCO shield has to be removed
before measurement. Remember to solder the shield back after the phone repairing.
3.1.1.1.7.1 Replace balun T7503
3.1.1.1.8 Are TX-IQ signals ok?
• These current mode signals are not possible to measure, but are tested with self-tests. So if
there is no fail in 2.4. “
(N7501) or RAP3G (D2800) is faulty. Notice that it is not possible to replace RAP3G ASIC.
3.1.1.1.9 Is there TXC-signal coming to Vinku ASIC (N7501)?
• GSM transmitter has to be active before TX control voltage TXC can be measured. Procedure
is explained in chapter “General instructions for TX troubleshooting”.
• Set TX power level first to the maximum (“5” in EGSM900 and “0” in DCS1800/PCS1900)
• Measurement can be done with an oscilloscope and a probe.
• Connect the probe to C7549
ST_CDSP_TX_IQ_TEST” these signals should be ok. Otherwise Vinku
Issue 1
• Typical TX control voltage TXC timing should look somehow similar to figure 6.5.2
(EGSM900 TX power level 5) and voltage levels should be roughly:
- EGSM900: 1.8 V while TX burst and 0 V otherwise.
- DCS1800/PCS1900: 1.8 V while TX burst and 0 V otherwise.
• Change the TX to the minimum power level (“19” in EGSM and “15” in DCS1800/PCS1900)
7A - 28
Company Confidential
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All rights reserved
Page 81

Nokia Customer Care
• Typical TX control voltage TXC levels should be now about:
- EGSM900: 1.0 V while TX burst and 0 V otherwise.
- DCS1800/PCS1900: 0.7 V while TX burst and 0 V otherwise.
3.1.1.1.9.1 R7514 in place?
• Check that the component is in place and solder joints are ok
• Disconnect the power supply from the phone and check R7514 resistance value with an
ohmmeter
3.1.1.1.9.2 C7549 working correctly?
• Check that the component is in place and solder joints are ok
• Disconnect the power supply from the phone and use an ohmmeter to check that C7549is
not short-circuited. If short-circuit is found replace the capacitor.
RM-1
RF Troubleshooting
3.1.1.1.9.3 Retu ok?
3.1.1.1.10 VCTCXO frequency and output level correct?
• Measurement can be done with an oscilloscope and a probe.
• Connect the probe to C7529 (or C7582)
• The frequency of the VCTCXO should be quite exactly 38.4 MHz and level about 0.5 - 0.9 Vpp.
Example of the correct VCTCXO output signal is presented in figure
(DC Offset 1.24 V)"..
3.1.1.1.10.1 VXO-voltage ok? (=Vdig).
Measurement can be done with an oscilloscope and a probe
•
Connect the probe to C7560 (or C7526, C7513)
•
VXO-voltage should be about 2.5 V
•
3.1.1.1.10.2 BB AFC-voltage ok?
• Measurement can be done with an oscilloscope and a probe
6.5.1. "VCTCXO Output
Issue 1
• Connect the probe to R7509 (or C7533)
• AFC-voltage may vary between 0.1 - 2.3 V. Typical value is 1.2 V. Phoenix “RF Controls” tool
can be used to change the AFC value. Voltage level should be about 0.1 V with AFC value 1024 and about 2.3 V with AFC value 1023.
7A - 29
Company Confidential
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All rights reserved
Page 82

Nokia Customer Care
3.1.1.1.10.3 Replace VCTCXO G7501
3.1.1.1.11 Replace Vinku (N7501)
3.1.1.2 Is there RF-power in the GSM PA (N7502) input at all?
• GSM transmitter has to be active before measurements. Procedure is explained in chapter
“General instructions for TX troubleshooting”.
• Set TX power level to the maximum (“5” in EGSM900 and “0” in DCS1800/PCS1900)
• Measurements can be done with a spectrum analyser and an RF probe. Remember to make
correct frequency settings to the spectrum analyser. Spectrum analyser centre frequency
should be set according the used TX channel (see chapter “Frequency mappings”).
• Spectrum analyser RBW and VBW = 1 MHz, Span = 0, sweep time 1 ms. Notice that GSM
transmission has pulsed nature and power should be measured during TX burst (triggering
needed). Another possibility is to use following settings: RBW = VBW = 1 MHz, Span 200 kHz
and sweep time at least 2.5 seconds.
RM-1
RF Troubleshooting
• EGSM900: Connect the probe to J7521 (test point). The RF level should be roughly
-15…-20 dBm.
• DCS1800 or PCS1900: Connect the probe to R7512 output. The RF level should be roughly 20…-30 dBm.
3.1.1.2.1 EGSM900: Replace SAW Z7504
3.1.1.2.2 DCS1800/PCS1900: Is Vinku (N7501) output RF-signal coming to the T7502 (Balun)?
• GSM transmitter has to be active before measurements. Procedure is explained in chapter
“General instructions for TX troubleshooting”. Set TX power level to the maximum (“0” in
DCS1800/PCS1900)
• Measurements can be done with a spectrum analyser and an RF probe. Spectrum analyser
centre frequency should be set according the used TX channel (see chapter “Frequency
mappings”).
• Spectrum analyser RBW and VBW = 1 MHz, Span = 0, sweep time 1 ms. Notice that GSM
transmission has pulsed nature and power should be measured during TX burst (triggering
needed). Another possibility is to use following settings: RBW = VBW = 1 MHz, Span 200 kHz
and sweep time at least 2.5 seconds.
Issue 1
• DCS1800 or PCS1900: Connect the probe to T7502 input. There are two input ports in T7502
because the input port is balanced. The RF level should be roughly -25 dBm in both inputs.
7A - 30
Company Confidential
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All rights reserved
Page 83

Nokia Customer Care
3.1.1.2.2.1 Matching components ok?
DCS1800/PCS1900: C7575 and C7577
• Check that components are in place and solder joints are ok
• DCS1800 and PCS1900: Disconnect the power supply from the phone and use an ohmmeter
to check that capacitors C7575 and C7577 are not short-circuited. If short-circuit is found
replace the faulty capacitor.
3.1.1.2.3 DCS1800/PCS1900: Is there RF power in the balun (T7502) output at all?
• GSM transmitter has to be active before measurements. Procedure is explained in chapter
“General instructions for TX troubleshooting”. Set TX power level to the maximum (“0” in
DCS1800/PCS1900)
• Measurements can be done with a spectrum analyser and an RF probe. Remember to make
correct frequency settings to the spectrum analyser. Spectrum analyser centre frequency
should be set according the used TX channel (see chapter “Frequency mappings”).
RM-1
RF Troubleshooting
• Spectrum analyser RBW and VBW = 1 MHz, Span = 0, sweep time 1 ms. Notice that GSM
transmission has pulsed nature and power should be measured during TX burst (triggering
needed). Another possibility is to use following settings: RBW = VBW = 1 MHz, Span 200 kHz
and sweep time at least 2.5 seconds.
• DCS1800 or PCS1900: Connect the probe to R7512 input. The RF level should be roughly 20…-30 dBm.
3.1.1.2.3.1 Replace balun T7502
3.1.1.2.4 DCS1800/PCS1900: Replace attenuator R7512
3.1.1.3 Does GSM PA (N7502) transmit RF-power at all?
• GSM transmitter has to be active before measurements. Procedure is explained in chapter
“General instructions for TX troubleshooting”.
• Set TX power level to the minimum (“19” in EGSM900 and “15” in DCS1800/PCS1900)
• Measurements can be done with a spectrum analyser and an RF probe. Spectrum analyser
centre frequency should be set according the used TX channel (see chapter “Frequency
mappings”).
Issue 1
• Spectrum analyser RBW and VBW = 1 MHz, Span = 0, sweep time 1 ms. Notice that GSM
transmission has pulsed nature and power should be measured during TX burst (triggering
needed). Another possibility is to use following settings: RBW = VBW = 1 MHz, Span 200 kHz
and sweep time at least 2.5 seconds.
7A - 31
Company Confidential
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All rights reserved
Page 84

Nokia Customer Care
• EGSM900: Connect the probe to J7520 (test point). The RF level should be about
-16…-17 dBm.
• DCS1800 or PCS1900: Connect the probe to J7519 (test point). The RF level should be
roughly -29…-30 dBm in both bands.
3.1.1.3.1 GSM PA (N7502) operating voltage ok?
• Measurement can be done with an oscilloscope and a probe.
• Connect the probe to C7593
• Voltage level should be 3.05 – 5.4 V. Typical value is 4.0 V
3.1.1.3.1.1 PA operating voltage VBAT_PA ok?
• Measurement can be done with an oscilloscope and a probe.
RM-1
RF Troubleshooting
• Connect the probe to C7569 (or C7564, C7583)
• Voltage level should be 3.05 – 5.4 V. Typical value is 4.0 V.
3.1.1.3.1.1.1 Ferrite Z7500 ok?
• Check that component is in place and solder joints are ok
• Disconnect the power supply from the phone and use an ohmmeter to check that inductor
is conducting DC.
3.1.1.3.1.2 C7593 ok?
• Check that the component is in place and solder joints are ok
• Disconnect the power supply from the phone and use an ohmmeter to check that the
capacitor is not short-circuited. If short-circuit is found replace the capacitor.
3.1.1.3.1.3 Replace inductor L7516
• If replacing doesn’t help then replace GSM PA (N7502)
3.1.1.3.2 Are bias currents coming correctly to the GSM PA (N7502)?
EGSM: Icont_21 and Icont_22
DCS1800/PCS1900: Icont_31 and Icont_32
• GSM transmitter has to be active before measurements. Procedure is explained in chapter
“General instructions for TX troubleshooting”.
• Set TX power level to the maximum (“5” in EGSM900 and “0” in DCS1800/PCS1900)
Issue 1
Company Confidential
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All rights reserved
7A - 32
Page 85

Nokia Customer Care
• Measurements can be done with an oscilloscope and a VOLTAGE probe.
• EGSM900:
- Connect the probe to C7545 or C7544. Notice: C7544 is a non-assembled component so the
probe should be connected to the pad that can be still found from the PWB.
- Typical full TX power bias currents (Icont_21 and Icont_22) should look somehow similar to
figure 6.5.4 when measured with an oscilloscope and a probe. Check both currents.
• DCS1800 or PCS1900:
- Connect the probe to C7561 or C7556. Notice: C7556 is a non-assembled component so the
probe should be connected to the pad that can be still found from the PWB.
- Typical full TX power bias currents (Icont_31 and Icont_32) should look somehow similar to
figure 6.5.5 when measured with an oscilloscope and a probe. Check both currents.
RM-1
RF Troubleshooting
3.1.1.3.2.1 Vinku (N7501) RB_EXT voltage ok?
• GSM transmitter has to be active before Vinku’s RB_EXT voltage can be measured.
Procedure is explained in section “General instructions for TX troubleshooting”.
• Measurement can be done with an oscilloscope and a probe.
• Connect the probe to R7521.
• RB_EXT voltage should be 1.325 – 1.375 V.
3.1.1.3.2.2 Are capacitors in GSM PA (N7502) bias lines working correctly?
EGSM: Icont_21 missing – Replace Vinku
Icont_22 missing – C7545 short-circuited?
DCS1800/PCS1900: Icont_31 missing – C7556 short-circuited?
Icont_32 missing – C7561 short-circuited?
• Check that components are in place and solder joints are ok
• Disconnect the power supply from the phone and use an ohmmeter to check that
capacitors are not short-circuited. If short-circuit is found replace capacitors mentioned
above. If this does not help go to the next step.
3.1.1.3.2.3 Replace Vinku (N7501)
3.1.1.3.3 Replace PA (N7502)
3.1.1.4 Are control voltages VC1, VC2 and VC3 coming correctly to the antenna switch (Z7503)?
• Use “RF Controls” window in Phoenix test software to activate the GSM transmitter and to
select the wanted GSM band. Procedure is explained in chapter “General instructions for TX
Issue 1
Company Confidential
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All rights reserved
7A - 33
Page 86

Nokia Customer Care
troubleshooting”. GSM RX activation is described in chapter “GSM RX chain activation for
manual measurements”.
• Use an oscilloscope and probe to find out if antenna switch control lines are working
according to table shown below. “Hi” means that there is 2.4 – 2.8 V control voltage level
in the corresponding control line. “Lo” means levels 0 – 0.2 V. Remember to trigger the
oscilloscope because control voltages VC1, VC2 and VC3 are pulsed
• Connect the probe to correct test points to measure VC1, VC2 and VC3 voltages (check test
point locations from chapter “Test point locations”). Notice: these test points are PWB pads
for three non-assembled capacitors.
RM-1
RF Troubleshooting
3.1.1.4.1 Replace Hinku (N7500)
3.1.1.5 Replace antenna Switch Z7503
3.1.2 Does GSM TX transmit enough RF-power and power levels otherwise ok?
3.1.2.1 Is Vinku ASIC (N7501) transmitting correct RF-power?
• GSM transmitter has to be active before Vinku’s output level can be measured. Procedure is
explained in chapter “General instructions for TX troubleshooting”.
• Measurements can be done with a spectrum analyser and an RF probe. RBW and VBW =
1 MHz, Span = 0, sweep time 1 ms. Spectrum analyser centre frequency should be set
according the used TX channel (see chapter “Frequency mappings”). Notice that GSM
transmission has pulsed nature and power should be measured during TX burst (triggering
needed). Another possibility is to use following settings: RBW = VBW = 1 MHz, Span 200 kHz
and sweep time at least 2.5 seconds.
• EGSM900:
- Connect the RF probe to Z7504 input. The level should be about the same on both input
pins. Check output level with at least the maximum (5) and the minimum (19) power
levels.
Issue 1
- Maximum power level – Output level should be about -15…-25 dBm
- Minimum power level – Output level should be about -45…-55 dBm
7A - 34
Company Confidential
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All rights reserved
Page 87

Nokia Customer Care
• DCS1800/PCS1900:
- Connect the RF probe to C7577 or C7575. The level should be about the same on both
capacitors. Check output level with at least the maximum (0) and the minimum (15) power
levels.
- Maximum power level – Output level should be about -25…-35 dBm
- Minimum power level – Output level should be about -55…-65 dBm
• Check if output levels of Vinku are as expected.
• NOTE! If VINKU ASIC is transmitting wrong TX power just in one or two GSM-bands,
typically this means that Vinku ASIC (N7501) is faulty or the ASIC is badly soldered. Of
course SAW-filter Z7504 or balun T7502 can be also faulty/badly soldered and causing
shortcircuit, but probability to this is quite low. For example: VINKU is transmitting too low
power in EGSM900-band but TX-power is ok in other GSM-bands. Then it’s almost clear that
VINKU (N7501) is faulty or badly soldered and the component should be replaced.
RM-1
RF Troubleshooting
3.1.2.1.1 RF operating voltage VBAT_ASIC ok?
• Measurement can be done with an oscilloscope and a probe.
• Connect the probe to C7503 (or C7501, C7541)
• VBAT_ASIC voltage level should be 3.05 – 5.4 V. Typical value is 4.0 V.
3.1.2.1.2 Are Vinku (N7501) regulator voltages VREG1, VREG2 ok?
• GSM transmitter has to be active before VREG1 and VREG2 voltages can be measured.
Procedure is explained in section “General instructions for TX troubleshooting”.
• Measurements can be done with an oscilloscope and a probe.
• VREG1: Connect the probe to C7543
• VREG2: Connect the probe to C7548 (or C7547)
• VREG1 and VREG2 voltage levels should be 2.65 – 2.86 V. Typical value is 2.7 V.
3.1.2.1.3 Are TX-IQ signal waveforms looking correct?
• These current mode signals are not possible to measure, but are tested with self-tests. So
if there is no fail in 2.4
(N7501) or RAP3G (D2800) is faulty. Notice that it is not possible to replace RAP3G ASIC.
ST_CDSP_TX_IQ_TEST these signals should be ok. Otherwise Vinku
Issue 1
7A - 35
Company Confidential
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All rights reserved
Page 88

Nokia Customer Care
3.1.2.1.4 Is the TXC-signal coming to Vinku ASIC (N7501) OK? Is signal level correct?
• GSM transmitter has to be active before TX control voltage TXC can be measured.
Procedure is explained in section “General instructions for TX troubleshooting”.
• Set TX power level first to the maximum (“5” in EGSM900 and “0” in DCS1800/PCS1900)
• Measurement can be done with an oscilloscope and a probe.
• Connect the probe to C7549
RM-1
RF Troubleshooting
• Typical TX control voltage TXC timing should look somehow similar to figure 6.5.2 “
GSM mode (DC offset 0 V)” (EGSM900 TX power level 5) and voltage levels should be
roughly:
- EGSM900: 1.8 V while TX burst and 0 V otherwise.
- DCS1800/PCS1900: 1.8 V while TX burst and 0 V otherwise.
• Change the TX to the minimum power level (“19” in EGSM and “15” in DCS1800/PCS1900)
• Typical TX control voltage TXC levels should be now about:
- EGSM900: 1.0 V while TX burst and 0 V otherwise.
• DCS1800/PCS1900: 0.7 V while TX burst and 0 V otherwise.
3.1.2.1.4.1 R7514 in place and working correctly?
• Check that the component is in place and solder joints are ok
• Disconnect the power supply from the phone and check R514 resistance value with an
ohmmeter
3.1.2.1.4.2 C7549 working correctly?
TXC in
• Check that the component is in place and solder joints are ok
• Disconnect the power supply from the phone and check with an ohmmeter that C7549 is
not short-circuited.
3.1.2.1.4.3 Retu ok?
3.1.2.1.5 Does GSM PA (N7502) get correct DET_SW_G -voltage from Vinku ASIC (N7501)?
• GSM transmitter has to be active before DET_SW_G voltage can be measured. Procedure is
explained in chapter “General instructions for TX troubleshooting”.
• Measurement can be done with an oscilloscope and a probe.
Issue 1
Company Confidential
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All rights reserved
7A - 36
Page 89

Nokia Customer Care
• Connect the probe to C7595 pad. Notice: C7595 is a non-assembled component so the
probe should be connected to the pad that can be still found from the PWB.
• DET_SW_G voltage should be about 2.8 V while TX burst and 0 V otherwise.
3.1.2.1.5.1 C7595 working correctly?
• Check that the component is in place and solder joints are ok
• Disconnect the power supply from the phone and check with an ohmmeter that C7595 is
not short-circuited.
3.1.2.1.5.2 Replace Vinku (N7501)
3.1.2.1.6 Are components in GSM power control loop in place and working ok?
R7516 and C7559
• Disconnect the power supply from the phone and use an ohmmeter to check that C7559 is
not short-circuited. If short-circuit is found replace the capacitor.
RM-1
RF Troubleshooting
• Check R7516 resistance value with an ohmmeter and replace resistor if needed.
3.1.2.1.7 Is TX VCO signal level in the T7503 output high enough?
• GSM transmitter has to be active before TX VCO’s output level can be measured. Procedure
is explained in chapter “General instructions for TX troubleshooting”.
• Measurements can be done with a spectrum analyser and an RF probe. RBW and VBW =
1 MHz, Span = 0, sweep time 1 ms. Spectrum analyser centre frequency should be set
according the used TX channel (see chapter “Frequency mappings”). Notice that GSM
transmission has pulsed nature and VCO output power should be measured during TX
burst (triggering needed). Another possibility is to use following settings: RBW = VBW = 1
MHz, Span 200 kHz and sweep time at least 2.5 seconds.
• Check the level of the VCO frequency in T7503 outputs. The level should be about
-30…-35 dBm in both output lines during GSM TX burst. If the signal level is correct in the
input (about -25 dBm) but output level is not as expected then replace T7503. VCO shield
has to be removed before measurement. Remember to solder the shield back after the
phone repairing.
3.1.2.1.7.1 TX VCO G7502 output level high enough?
• GSM transmitter has to be active before TX VCO’s output frequency and output level can be
measured. Procedure is explained in chapter “General instructions for TX troubleshooting”.
Issue 1
• Measurements can be done with a spectrum analyser and an RF probe. Spectrum analyser
centre frequency should be set according the used TX channel (see chapter “Frequency
mappings”).
7A - 37
Company Confidential
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All rights reserved
Page 90

Nokia Customer Care
• Spectrum analyser RBW and VBW = 1 MHz, Span = 0, sweep time 1 ms. Notice that GSM
transmission has pulsed nature and VCO output power should be measured during TX
burst (triggering needed). Another possibility is to use following settings: RBW = VBW = 1
MHz, Span 200 kHz and sweep time at least 2.5 seconds.
• Connect the RF probe to the T7503 input. VCO shield has to be removed before
measurement. Remember to solder the shield back after the phone repairing.
• Check if the frequency of the TX VCO is as expected. If the VCO signal is not found try to use
wider span setting. The output level of the VCO should be about -25 dBm during GSM TX
burst.
3.1.2.1.7.1.1 Replace TX VCO G7502
3.1.2.1.7.2 Replace balun T7503
3.1.2.1.8 Replace Vinku (N7501) or GSM PA (N7502)
RM-1
RF Troubleshooting
• If the output level of Vinku is higher than wanted then replace GSM PA (N7502). Otherwise
replace TX ASIC Vinku (N7501).
3.1.2.2 Does GSM PA (N7502) have enough RF-power in its input?
• GSM transmitter has to be active before measurements. Procedure is explained in chapter
“General instructions for TX troubleshooting”.
• Set TX power level to the maximum (“5” in EGSM900 and “0” in DCS1800/PCS1900)
• Measurements can be done with a spectrum analyser and an RF probe. Remember to make
correct frequency settings to the spectrum analyser. Spectrum analyser centre frequency
should be set according the used TX channel (see chapter “Frequency mappings”).
• Spectrum analyser RBW and VBW = 1 MHz, Span = 0, sweep time 1 ms. Notice that GSM
transmission has pulsed nature and power should be measured during TX burst (triggering
needed). Another possibility is to use following settings: RBW = VBW = 1 MHz, Span 200 kHz
and sweep time at least 2.5 seconds.
• EGSM900: Connect the probe to J7521 (test point). The RF level should be roughly
-15…-20 dBm.
• DCS1800 or PCS1900: Connect the probe to R7512 output. The RF level should be roughly 20…-30 dBm.
3.1.2.2.1 EGSM900: Replace SAW Z7504
3.1.2.2.2 DCS1800/PCS1900: Is Vinku (N7501) output RF-signal coming correctly to the T7502 (Balun)?
• GSM transmitter has to be active before measurements Procedure is explained in chapter
“General instructions for TX troubleshooting”.
Issue 1
Company Confidential
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All rights reserved
7A - 38
Page 91

Nokia Customer Care
• Set TX power level to the maximum (“0” in DCS1800/PCS1900)
• Measurements can be done with a spectrum analyser and an RF probe. Spectrum analyser
centre frequency should be set according the used TX channel (see chapter “Frequency
mappings”).
• Spectrum analyser RBW and VBW = 1 MHz, Span = 0, sweep time 1 ms. Notice that GSM
transmission has pulsed nature and power should be measured during TX burst (triggering
needed). Another possibility is to use following settings: RBW = VBW = 1 MHz, Span 200 kHz
and sweep time at least 2.5 seconds.
• DCS1800 or PCS1900: Connect the probe to T7502 input. There are two input ports in T7502
because the input port is balanced. The RF level should be roughly -25 dBm in both inputs.
3.1.2.2.2.1 Matching components ok?
DCS1800/PCS1900: C7575 and C7577
• Check that components are in place and solder joints are ok
RM-1
RF Troubleshooting
• DCS1800 and PCS1900: Disconnect the power supply from the phone and use an ohmmeter
to check that capacitors C7575 and C7577 are not short-circuited. If short-circuit is found
replace the faulty capacitor.
3.1.2.2.3 DCS1800/PCS1900: Is there correct RF power in the balun (T7502) output?
• GSM transmitter has to be active before measurements. Procedure is explained in chapter
“General instructions for TX troubleshooting”.
• Set TX power level to the maximum (“0” in DCS1800/PCS1900)
• Measurements can be done with a spectrum analyser and an RF probe. Remember to make
correct frequency settings to the spectrum analyser. Spectrum analyser centre frequency
should be set according the used TX channel (see chapter “Frequency mappings”).
• Spectrum analyser RBW and VBW = 1 MHz, Span = 0, sweep time 1 ms. Notice that GSM
transmission has pulsed nature and power should be measured during TX burst (triggering
needed). Another possibility is to use following settings: RBW = VBW = 1 MHz, Span 200 kHz
and sweep time at least 2.5 seconds.
• DCS1800 or PCS1900: Connect the probe to R7512 input. The RF level should be roughly 20…-30 dBm.
3.1.2.2.3.1 Replace balun T7502
3.1.2.2.4 DCS1800/PCS1900: Replace attenuator R7512
Issue 1
Company Confidential
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All rights reserved
7A - 39
Page 92

Nokia Customer Care
3.1.2.3 GSM PA (N7502) transmitting correct RF-power?
• GSM transmitter has to be active before measurements. Procedure is explained in chapter
“General instructions for TX troubleshooting”.
• Set TX power level to the minimum (“19” in EGSM900 and “15” in DCS1800/PCS1900)
• Measurements can be done with a spectrum analyser and an RF probe. Spectrum analyser
centre frequency should be set according the used TX channel (see chapter “Frequency
mappings”).
• Spectrum analyser RBW and VBW = 1 MHz, Span = 0, sweep time 1 ms. Notice that GSM
transmission has pulsed nature and power should be measured during TX burst (triggering
needed). Another possibility is to use following settings: RBW = VBW = 1 MHz, Span 200 kHz
and sweep time at least 2.5 seconds.
• EGSM900: Connect the probe to J7520 (test point). The RF level should be about
-16…-17 dBm.
RM-1
RF Troubleshooting
• DCS1800 or PCS1900: Connect the probe to J7519 (test point). The RF level should be
roughly -29…-30 dBm in both bands.
3.1.2.3.1 GSM PA (N7502) operating voltage ok?
• Measurement can be done with an oscilloscope and a probe.
• Connect the probe to C7593
• Voltage level should be 3.05 – 5.4 V. Typical value is 4.0 V.
3.1.2.3.1.1 PA operating voltage VBAT_PA ok?
• Measurement can be done with an oscilloscope and a probe.
• Connect the probe to C7569 (or C7564, C7583)
• Voltage level should be 3.05 – 5.4 V. Typical value is 4.0 V.
3.1.2.3.1.1.1 Ferrite Z7500 ok?
• Check that component is in place and solder joints are ok
• Disconnect the power supply from the phone and use an ohmmeter to check that inductor
is conducting DC.
3.1.2.3.1.2 C7593 ok?
• Check that the component is in place and solder joints are ok
Issue 1
7A - 40
Company Confidential
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All rights reserved
Page 93

Nokia Customer Care
• Disconnect the power supply from the phone and use an ohmmeter to check that the
capacitor is not short-circuited. If short-circuit is found replace the capacitor.
3.1.2.3.1.3 Replace inductor L7516
• If replacing doesn’t help then replace GSM PA (N7502)
3.1.2.3.2 Are bias currents coming correctly to the GSM PA (N7502)? Level ok?
EGSM: Icont_21 and Icont_22
DCS1800/PCS1900: Icont_31 and Icont_32
• GSM transmitter has to be active before measurements. Procedure is explained in chapter
“General instructions for TX troubleshooting”.
• Set TX power level to the maximum (“5” in EGSM900 and “0” in DCS1800/PCS1900)
• Measurements can be done with an oscilloscope and a VOLTAGE probe.
RM-1
RF Troubleshooting
• EGSM900:
- Connect the probe to C7545 or C7544. Notice: C7544 is a non-assembled component so the
probe should be connected to the pad that can be still found from the PWB
- Typical full TX power bias currents (Icont_21 and Icont_22) should look somehow similar to
figure
a probe. Check both currents.
• DCS1800 or PCS1900:
- Connect the probe to C7561 or C7556. Notice: C7556 is a non-assembled component so the
probe should be connected to the pad that can be still found from the PWB
- Typical full TX power bias currents (Icont_31 and Icont_32) should look somehow similar to
figure
a probe. Check both currents.
3.1.2.3.2.1 Vinku (N7501) RB_EXT voltage ok?
• GSM transmitter has to be active before Vinku’s RB_EXT voltage can be measured.
Procedure is explained in chapter “General instructions for TX troubleshooting”.
6.5.4 "Icont_21/Icont_22 (DC Offset 1.2 V)" when measured with an oscilloscope and
6.5.5 "Icont_31/Icont_32 (DC Offset 1.2 V)" when measured with an oscilloscope and
Issue 1
• Measurement can be done with an oscilloscope and a probe.
• Connect the probe to R7521.
• RB_EXT voltage should be 1.325 – 1.375 V.
7A - 41
Company Confidential
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All rights reserved
Page 94

Nokia Customer Care
3.1.2.3.2.2 Are capacitors in GSM PA (N7502) bias lines working correctly?
EGSM: Icont_21 missing – Replace Vinku
Icont_22 missing – C7545 short-circuited?
DCS1800/PCS1900: Icont_31 missing – C7556 short-circuited?
Icont_32 missing – C7561 short-circuited?
• Check that components are in place and solder joints are ok
• Disconnect the power supply from the phone and use an ohmmeter to check that
capacitors are not short-circuited. If short-circuit is found replace capacitors mentioned
above.
3.1.2.3.2.3 Replace Vinku (N7501) or GSM PA (N7502)
3.1.2.3.3 Replace GSM PA (N7502)
3.1.2.4 Are control voltages VC1, VC2 and VC3 coming correctly to the antenna switch (Z7503)?
RM-1
RF Troubleshooting
• Use “RF Controls” window in Phoenix test software to activate the GSM transmitter and to
select the wanted GSM band. Procedure is explained in chapter “General instructions for TX
troubleshooting”. GSM RX activation is described in chapter “GSM RX chain activation for
manual measurements”.
• Use an oscilloscope and probe to find out if antenna switch control lines are working
according to table shown below. “Hi” means that there is 2.4 – 2.8 V control voltage level
in the corresponding control line. “Lo” means levels 0 – 0.2 V. Remember to trigger the
oscilloscope because control voltages VC1, VC2 and VC3 are pulsed
• Connect the probe to correct test points to measure VC1, VC2 and VC3 voltages (check test
point locations, see chapter “Test point locations). Notice: these test points are PWB pads
for three non-assembled capacitors.
3.1.2.5 Replace antenna switch Z503
Issue 1
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All rights reserved
7A - 42
Company Confidential
Page 95

Nokia Customer Care
3.1.3 GSM transmitter frequency correct?
• Connect a spectrum analyser to the module test jig (MJ-26) RF connector.
• Set GSM Tx ON. Procedure is explained in chapter “General instructions for TX
troubleshooting”.
• Check if the frequency of the GSM transmitter is as expected. If output signal is not found
try to use 500 MHz span setting.
The correct TX frequency is shown in Phoenix “RF Controls (GSM)” window and can be
found also in chapter “Frequency mappings”. If the frequency is not found at all then go to
Does GSM TX transmit RF-power at all?”
3.1.1 “
3.1.3.1 Is TX VCO frequency as expected?
• GSM transmitter has to be active before TX VCO’s output frequency and output level can be
measured. Procedure is explained in chapter “General instructions for TX troubleshooting”.
RM-1
RF Troubleshooting
• Measurements can be done with a spectrum analyser and an RF probe. Spectrum analyser
centre frequency should be set according the used TX channel (see chapter “Frequency
mappings”).
• Spectrum analyser RBW and VBW = 1 MHz, Span = 0, sweep time 1 ms. Notice that GSM
transmission has pulsed nature and VCO output power should be measured during TX
burst (triggering needed). Another possibility is to use following settings: RBW = VBW = 1
MHz, Span 200 kHz and sweep time at least 2.5 seconds.
• Connect the RF probe to the T7503 input. VCO shield has to be removed before
measurement. Remember to solder the shield back after the phone repairing. Quick VCO
alive check can be done without removing the RF shield. The RF probe should be placed as
near the TX VCO output as possible (Put the head of the probe carefully inside the VCO can
through the holes of the shield). This method can be used only to check that the TX VCO is
alive. It won’t expose if the T7503 is broken or the output level of the VCO is too low.
Remember to use low RF Attenuator value in the spectrum analyser with this method.
• Check if the frequency of the TX VCO is as expected. If the VCO signal is not found try to use
wider span setting. The output level of the VCO should be about -25 dBm during GSM TX
burst.
3.1.3.1.1 C7543, C7548 and L7517 ok?
Issue 1
• These components should be checked if TX VCO frequency is not stable and TX PLL
frequency not locked.
• Check that components are in place and solder joints are ok
• Disconnect the power supply from the phone and use an ohmmeter to check that inductor
is conducting DC.
7A - 43
Company Confidential
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All rights reserved
Page 96

Nokia Customer Care
3.1.3.1.2 TX VCO control voltage VC ok?
• GSM transmitter has to be active before TX VCO control voltage VC can be measured.
Procedure is explained in chapter “General instructions for TX troubleshooting”.
• Measurement can be done with an oscilloscope and a probe.
• Connect the probe to R7519.
• Typical TX VCO control voltage VC should look somehow similar to figure 6.5.3. DC voltage
level should change if TX channel is changed. VC is lower on lower channels and higher if
higher channel numbers are used.
3.1.3.1.2.1 VCP2-voltage ok?
• GSM transmitter has to be active before VCP2 voltage can be measured. Procedure is
explained in chapter “General instructions for TX troubleshooting”.
RM-1
RF Troubleshooting
• Measurement can be done with an oscilloscope and a probe.
• Connect the probe to C2221 (or C7550).
• VCP2 voltage should be about 4.75 V.
3.1.3.1.2.2 Vinku (N7501) RB_EXT voltage ok?
• GSM transmitter has to be active before Vinku’s RB_EXT voltage can be measured.
Procedure is explained in chapter “General instructions for TX troubleshooting”.
• Measurement can be done with an oscilloscope and a probe.
• Connect the probe to R7521.
• RB_EXT voltage should be 1.325 – 1.375 V.
3.1.3.1.2.3 Balun T7503 ok?
• GSM transmitter has to be active before TX VCO’s output level can be measured. Procedure
is explained in chapter “General instructions for TX troubleshooting”.
• Measurements can be done with a spectrum analyser and an RF probe. Spectrum analyser
centre frequency should be set according the used TX channel (see chapter “Frequency
mappings”).
Issue 1
• Spectrum analyser RBW and VBW = 1 MHz, Span = 0, sweep time 1 ms. Notice that GSM
transmission has pulsed nature and VCO output power should be measured during TX
burst (triggering needed). Another possibility is to use following settings: RBW = VBW = 1
MHz, Span 200 kHz and sweep time at least 2.5 seconds.
7A - 44
Company Confidential
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All rights reserved
Page 97

Nokia Customer Care
• Check the level of the TX VCO frequency in T7503 outputs. The level should be about
-30…-35 dBm in both output lines. If the signal level is correct in the input (about -25 dBm)
but output level is not as expected then replace T7503. VCO shield has to be removed
before measurement. Remember to solder the shield back after the phone repairing.
3.1.3.1.2.4 Components near TX VCO ok?
C7571, R7519, R7523, C7573 and C7568 working correctly?
• Check that components are in place and solder joints are ok
• Disconnect the power supply from the phone and check resistors resistance values with an
ohmmeter.
• Use an ohmmeter to check also that capacitors are not short-circuited
3.1.3.1.2.5 Replace Vinku (N7501) or TX VCO (G7502) or both
RM-1
RF Troubleshooting
3.1.3.1.3 Replace TX VCO G7502
3.1.3.2 Is TX VCO signal level in the T7503 output high enough?
• GSM transmitter has to be active before TX VCO’s output level can be measured. Procedure
is explained in chapter “General instructions for TX troubleshooting”.
• Measurements can be done with a spectrum analyser and an RF probe. Spectrum analyser
centre frequency should be set according the used TX channel (see chapter “Frequency
mappings”).
• Spectrum analyser RBW and VBW = 1 MHz, Span = 0, sweep time 1 ms. Notice that GSM
transmission has pulsed nature and VCO output power should be measured during TX
burst (triggering needed). Another possibility is to use following settings: RBW = VBW = 1
MHz, Span 200 kHz and sweep time at least 2.5 seconds.
• Check the level of the VCO frequency in T7503 outputs. The level should be about
-30…-35 dBm in both output lines during GSM TX burst. If the signal level is correct in the
input (about -25 dBm) but output level is not as expected then replace T7503. VCO shield
has to be removed before measurement. Remember to solder the shield back after the
phone repairing.
3.1.3.2.1 TX VCO G7502 output level high enough?
Issue 1
• GSM transmitter has to be active before TX VCO’s output frequency and output level can be
measured. Procedure is explained in chapter “General instructions for TX troubleshooting”.
• Measurements can be done with a spectrum analyser and an RF probe. Spectrum analyser
centre frequency should be set according the used TX channel (see chapter “Frequency
mappings”).
7A - 45
Company Confidential
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All rights reserved
Page 98

Nokia Customer Care
• Spectrum analyser RBW and VBW = 1 MHz, Span = 0, sweep time 1 ms. Notice that GSM
transmission has pulsed nature and VCO output power should be measured during TX
burst (triggering needed). Another possibility is to use following settings: RBW = VBW = 1
MHz, Span 200 kHz and sweep time at least 2.5 seconds.
• Connect the RF probe to the T7503 input. VCO shield has to be removed before
measurement. Remember to solder the shield back after the phone repairing.
• Check if the frequency of the TX VCO is as expected. If the VCO signal is not found try to use
wider span setting. The output level of the VCO should be about -25 dBm during GSM TX
burst.
3.1.3.2.1.1 Replace TX VCO G7502
3.1.3.2.2 Replace balun T7503
3.1.3.3 VCTCXO frequency and output level ok?
RM-1
RF Troubleshooting
• Measurement can be done with an oscilloscope and a probe.
• Connect the probe to C7529 (or C7582)
• The frequency of the VCTCXO should be quite exactly 38.4 MHz and level about 0.5 - 0.9 Vpp.
Example of the correct VCTCXO output signal is presented in figure
(DC Offset 1.24 V)".
3.1.3.3.1 VXO-voltage ok? (=Vdig).
• Measurement can be done with an oscilloscope and a probe
• Connect the probe to C7560 (or C7526, C7513)
• VXO-voltage should be about 2.5 V
3.1.3.3.1.1 C7560, C7513, C7526 and C2214 ok?
• Check that components are in place and solder joints are ok
• Disconnect the power supply from the phone and use an ohmmeter to find out if the VXO-
line is short-circuited to the ground. If short-circuit is found replace C7560, C7513, C7526
and C2214. If replacing does not help then go to the next steps.
6.5.1 "VCTCXO Output
3.1.3.3.1.2 Replace Retu
3.1.3.3.1.3 Replace Hinku (N7500) or Vinku (N7501) or VCTCXO (G7501) or all three components
Issue 1
Company Confidential
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All rights reserved
7A - 46
Page 99

Nokia Customer Care
3.1.3.3.2 BB AFC-voltage ok?
• Measurement can be done with an oscilloscope and a probe
• Connect the probe to R7509 (or C7533)
• AFC-voltage may vary between 0.1 - 2.3 V. Typical value is 1.2 V. Phoenix “RF Controls” tool
can be used to change the AFC value. Voltage level should be about 0.1 V with AFC value 1024 and about 2.3 V with AFC value 1023.
3.1.3.3.2.1 Low pass filter components R7509 and C7533 ok?
• Check that components are in place and solder joints are ok
• Disconnect the power supply from the phone and check R7509 resistance value with an
ohmmeter.
• Use an ohmmeter to find out also if the AFC-line is short-circuited to the ground. If shortcircuit is found replace C7533. If this does not help then go to the next steps.
RM-1
RF Troubleshooting
3.1.3.3.2.2 VCTCXO ok?
• Remove R7509. If AFC-voltage is correct after removing then replace faulty VCTCXO G7501
and solder R7509 (new component) back to the PWB
3.1.3.3.2.3 Replace Retu
3.1.3.3.3 Replace VCTCXO G7501
3.2 Does the phone give realistic RSSI-values?
Attach the phone to the product specific test jig (AD-23) and a signal generator to the
RF-coupler. Remember that there are two antenna connectors in the coupler, one for GSM and
one for WCDMA. Coupler attenuation should be also taken into account during measurements.
Use the signal generator to supply -90 dBm RF-level (unmodulated signal) to the phone via the
antenna coupler. Set generator RF-level to -90 dBm + Cable and coupler attenuation. This
measurement should be performed in a RF-shielded environment because existing GSMnetwork base stations can disturb this measurement otherwise.
• Set RF-generator frequency as following:
Issue 1
- EGSM900: 942.46771 MHz (channel 37)
- DCS1800: 1842.86771 MHz (channel 700)
- PCS1900: 1960.06771 MHz (channel 661)
7A - 47
Company Confidential
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All rights reserved
Page 100

Nokia Customer Care
• Use Phoenix testing & tuning software to perform GSM receiver activation and RSSI
measurement for proper channels. Procedure is explained in chapter “GSM RX chain
activation for manual measurements” (Start “Testing” -> “GSM” -> “RSSI Reading” tool in
Phoenix. Select the correct band and channel).
• “RSSI Reading” -tool should show quite exact -90 dBm RSSI level. Remember to take into
account attenuation between the phone and signal generator. Test also Q and I branches
separately. Signal level in both I and Q lines should be about -93 dBm
• Increase signal generator RF level to -60 dBm. Phoenix ”RSSI Reading” tool should show
now quite exact RSSI level -60 dBm. Test also Q and I branches separately. Signal level in
both I and Q lines should be about -63 dBm
• If RSSI-levels are not as expected separate the phone into parts and place to the MJ-26
module jig. Connect the signal generator to the module jig GSM RF connector (Notice that
there are three antenna connectors in the module jig, one for GSM, one for WCDMA and one
for Bluetooth. Make sure that all connections are made to the correct RF-connector).
RM-1
RF Troubleshooting
3.2.1 Is Hinku (N7500) ASIC receiving RF-power correctly from the GSM-antenna connector?
• GSM receiver has to be active before measurements. Procedure is explained in chapter
“GSM RX chain activation for manual measurements.”
• Connect an RF-generator to the GSM-antenna connector
• Set RF-generator frequency as following:
- EGSM900: 942.46771 MHz
- DCS1800: 1842.86771 MHz
- PCS1900: 1960.06771 MHz
• Measurements can be done with a spectrum analyser and an RF probe. Remember to make
correct frequency settings to the spectrum analyser (Centre frequency should be set to the
same frequency as the RF-generator). RBW and VBW = 10 kHz, Span = 0 kHz, sweep time 5
ms.
• RF-signals in this measurement are pulsed and video triggering is needed in the spectrum
analyser (software dependent issue. With some phone softwares these signals are
constant in “Local” mode and triggering is not needed)
Issue 1
• EGSM900: Connect the probe to C7512 or C7514. The RF level should be roughly -85 dBm
during RX period when input signal in GSM antenna connector is -50 dBm. RF-levels should
be about the same on both capacitors. Remember to select the correct band also in
Phoenix.
• DCS1800: Connect the probe to C7581 or C7584. The RF level should be roughly -85…90 dBm during RX period when input signal in GSM antenna connector is -50 dBm.
7A - 48
Company Confidential
Copyright © 2004 Nokia. All rights reserved
 Loading...
Loading...