Page 1

Customer Care Solutions
RM-37 Series Transceivers
6-Troubleshooting Instructions
Issue 1 04/2004 ©Nokia Corporation
Page 2

RM-37 Company confidential
6-Troubleshooting Instructions CCS Technical Document ation
[This page left intentionally blank]
Page 2 ©Nokia Corporation. Issue 1 04/2004
Page 3

Company confidential RM-37
CCS Technical Documentation 6-Troubleshooting Instructions
Table of Contents
Page No
RF Troubleshooting .......................................................................................................4
Introduction to RF troubleshooting .............................................................................4
RF Key component placement .....................................................................................5
RF Measurement points ...............................................................................................6
GSM900 & GSM1800 Transmitter ................................................................................7
General instructions for Tx troubleshooting .............................................................7
Transmitter troubleshooting diagram ........................................................................9
Pictures of transmitter signals .................................................................................12
GSM900, GSM1800 and GSM1900 Receiver .............................................................14
General instructions for Rx troubleshooting ...........................................................14
Troubleshooting diagram for GSM900 receiver .....................................................18
Troubleshooting diagram for GSM1800 receiver ...................................................19
Troubleshooting diagram for GSM1900 receiver ...................................................20
Synthesizer ...................................................................................................................21
General instructions for synthesizer troubleshooting ..............................................21
Synthesizer troubleshooting diagram ......................................................................22
Pictures of synthesizer signals .................................................................................23
Baseband troubleshooting ............................................................................................25
Main Troubleshooting Diagram ................................................................................25
Phone is dead .............................................................................................................26
Flash Programming Fault ..........................................................................................27
Phone is jammed ........................................................................................................28
SIM card fault (Insert SIM / Card rejected) ...............................................................29
Keypad Fault ..............................................................................................................30
Display Fault ..............................................................................................................32
Illumination fault .......................................................................................................33
Charger Fault .............................................................................................................34
Accessory Fault .........................................................................................................35
Camera Troubleshooting ..............................................................................................36
Camera Fault ..............................................................................................................37
Audio Fault ................................................................................................................38
FM Radio troubleshooting ...........................................................................................39
FM Radio component layout .....................................................................................39
FM Radio troubleshooting diagram ...........................................................................41
Notes to "FM Radio troubleshooting diagram" .......................................................41
Issue 1 04/2004 ©Nokia Corporation. Page 3
Page 4

RM-37 Company confidential
6-Troubleshooting Instructions CCS Technical Document ation
RF Troubleshooting
Introduction to RF troubleshooting
Measurements should be done using Spectrum analyzer with high-frequency highimpedance passive probe (LO-/reference frequencies and RF power levels) and Oscilloscope with a 10:1 probe (DC-voltages and low frequency signals)
The RF-section is build around one RF-ASIC (HELGA N500). For easier troubleshooting,
this RF troubleshooting document is divided in to sections.
Before changing HELGA, please check following things: Supply voltages are OK and serial
communication coming from baseband to HELGA.
Please note that the grounding of the PA module is directly below PA-module so it is difficult to check or change. Most RF semiconductors are static discharge sensitive! So
ESD protection must be taken care of duriong repair (ground straps and ESD soldering
irons). HELGA and PA are moisture sensitive so parts must be pre-baked prior to soldering.
Apart from key components described in this document here are a lot of discrete components (resistors, inductors and capacitors) which troubleshooting is done by checking if
soldering of the component is done properly (for factory repairs checking if it is missing
from PWB). Capacitor can be checked for shortening and resistors for value by means of
an ohmmeter, but be aware in-circuit measurements should be evaluated carefully.
Please be aware that all measured voltages or RF levels in this document are rough figures. Especially RF levels varies due to different measuring equipment or different
grounding of the used probe. When using RF probe usually a good way is to use metallic
tweezers to connect probe ground to PWB ground as close to measurement point as possible.
Page 4 ©Nokia Corporation. Issue 1 04/2004
Page 5

Company confidential RM-37
CCS Technical Documentation 6-Troubleshooting Instructions
RF Key component placement
Figure 1: Component placement 1
GSM 1900
rx saw
Antenna
switch
GSM 1900
rx balun
VCTCXO
PA
GSM900tx
Balanced saw
Helga
VCO
VCO balun
Issue 1 04/2004 ©Nokia Corporation. Page 5
Page 6

RM-37 Company confidential
6-Troubleshooting Instructions CCS Technical Document ation
RF Measurement points
Figure 2: Component placement 2
VBATT
RX-saw-out
LNA-P
to antenna
ASM-out-1900RX
LNA-VCC
VANT-3
RFBusEn
RFBusClk
RFBusRes
RFBusData
VCTCXO 26MHz out
VR2
VR3
VR1
VANT-2
VANT-1
ASM-in
1800-1900PA-in
VTXB-1800-1900
PCRTL-1800-1900
VPCTRL-900
VTXB-900
900PA-in
1800RX-in
1900RX-in
900RX-in
VR7
VR6
VR4
TXC
VR5
TXQP
TXIN
TXIP
TXQN
Page 6 ©Nokia Corporation. Issue 1 04/2004
Page 7

Company confidential RM-37
CCS Technical Documentation 6-Troubleshooting Instructions
GSM900 & GSM1800 Transmitter
General instructions for Tx troubleshooting
Kindly refer to the Service Software Section, Service Concept dagram (p.40)
Connect test jig to computer with DAU-9S cable or to FPS-8 Flash Prommer with XCS-4
modular cable.
Make sure that you have PKD-1 dongle connected to computers parallel port.
Connect DC power supply to module test jig with FLC-2 cable.
Attention: When repairing or tuning transmitter use external DC supply with at
least 3A current capability. Set the DC supply voltage to 3.9V and set the jumper con-
nector on test jig to "bypass" position.
Connect a RF-cable to the module test jig (MJS-38) RF connector to and to measurement
equipment or at least 10dB attenuator, otherfwise the PA may be damaged. Normally
Spectrum analyzer is used as measurement equipment.
Attention: Normally Spectrum analyzer maximum input power is +30dBm. It is recommended to use 10dB attenuator on Spectrum analyzer input to prevent damage.
Set the phone module to test jig and start Phoenix service sofware
Initialize connection to phone. (use FBUS driver when using DAU9S and COMBOX driver
when using FPS-8)
Select product from the menu
File -> Choose product -> RM-37
From toolbar set operating mode to "Local"
Activate RF controls window from the menu
Maintenance -> Testing -> RF Controls
From the RF controls window
- Select band "GSM900" or "GSM 1800" or "GSM1900" (Default = "GSM900")
- Set Active unit to "Tx" (Default = "Rx")
- Set Operation mode to "Burst" (Default = "Burst")
- Set Tx data type to "Random" (Default = "All1")
Issue 1 04/2004 ©Nokia Corporation. Page 7
Page 8

RM-37 Company confidential
6-Troubleshooting Instructions CCS Technical Document ation
- Set Rx/Tx channel to 37 on GSM900 band or 700 on GSM1800 band or 661 on
GSM1900 (Defaults)
- Set Tx PA mode to "Free" (Default)
- Set power level to 5 (Default = 19) on GSM900 or to 0 (Default = 15) on GSM1800 or
GSM1900
Page 8 ©Nokia Corporation. Issue 1 04/2004
Page 9

Company confidential RM-37
Transmitter troubleshooting diagram
CCS Technical Documentation 6-Troubleshooting Instructions
Transmitter troubleshooting diagram
Figure 3: Transmitter troubleshooting
TX troubleshooting
Check output signal level:
+32...+33dBm @897.4 MHz (GSM900)
+29...+30dBm @1747.8 MHz
(GSM1800 & GSM1900)
OK ?
TX signal found ?
Yes
Check with RF probe
signal level on
PA input >=0dBm (*
OK ?
Yes
start TX power level
tuning and check
tuned RAC values:
Highest level~700...900
Lowest level ~190...210
Base levle ~160...190
Major differences ?
No
TX OK
Yes
Yes
Check output signal
on 500 MHZ span
Signal found on
incorrect frequency ?
No
*(When 1kOhm passive probe is used,
correct the measurement result by +26dB
Yes
Check
all power
levels,
OK ?
No
HELGA
troubleshooting
Tune Tx DAC values
No
Yes
Tune
TX power
levels,
OK ?
Synthesizer
troubleshooting
No
Check with oscilloscope:
PA ctrl voltage
>1.5V peak OK ?
Yes
PA & ant switch
troubleshooting
Check control loop
components
No
Yes
Replace
faulty
component(s)
OK ?
Yes
Replace HELGA
dead
Issue 1 04/2004 ©Nokia Corporation. Page 9
Page 10

RM-37 Company confidential
6-Troubleshooting Instructions CCS Technical Document ation
Figure 4: HELGA IC troubleshooting
HELGA
troubleshooting
Check with oscilloscope:
-TXI/TXQ signals
--VR1, VR2, VR4, VR5, VR6 = 2.8V
-VrefRF01 = 1.35 V
-HELGA serial interface
-TXP & TXC signals
OK ?
No
Baseband
troubleshooting
Check with RF probe:
-4G VCO out signal
- 3589.6 MHz (GSM900)
-3495.6 MHz (GSM1800)
- 3760 MHz (GSM1900)
Level >-10dBm (*
OK ?
Check modulator
output components
OK ?
Replace
faulty
component(s)
No
*(When 1kOhm passive probe is used,
correct the measurement result by +26dB
Yes
Synthesizer
troubleshooting
Replace HELGA
dead
Page 10 ©Nokia Corporation. Issue 1 04/2004
Page 11
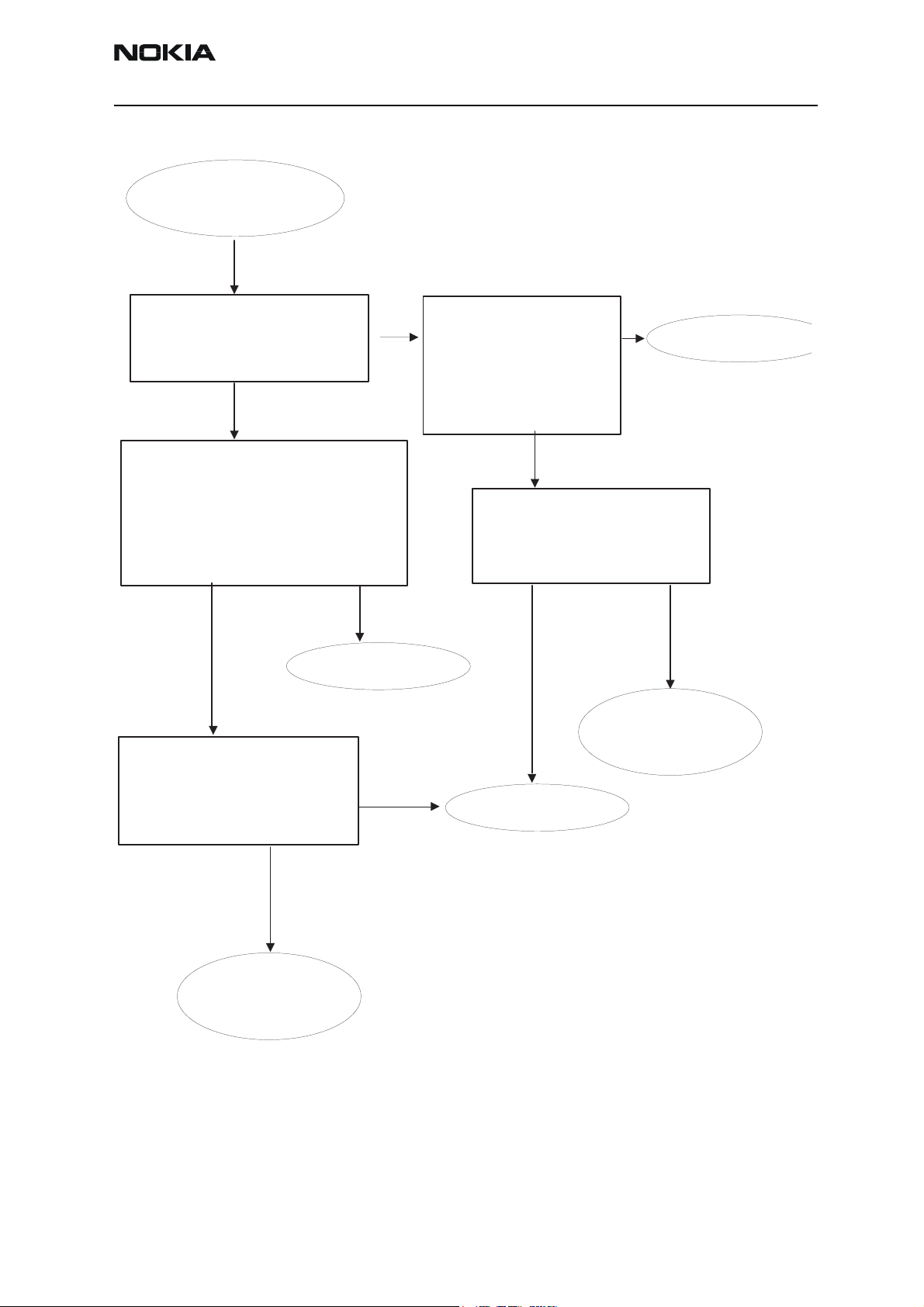
Company confidential RM-37
CCS Technical Documentation 6-Troubleshooting Instructions
Figure 5: PA and Antenna Switch troubleshooting
PA & ant switch
troubleshooting
*(When 1kOhm passive probe is used,
Yes
correct the measurement by +26dB
Check with RF probe
signal level on
PA input >=0dBm (*
OK ?
Yes
Check with
oscilloscope:
-VBATT ~4V
- VTXB = 2.8 V pulsed
- VTxLO_GSM = 0V (GSM900)
OK ?
Yes
No
Replace
PA
Check components
around PA
OK ?
Yes
Yes
Check with
oscilloscope:
-VANT_1 (GSM900)
-VANT_2 (GSM1800)
-VANT_3 (GSM1900)
OK ?
No
Check
VANT lline components
OK ?
Yes
Replace
HELGA
Replace
ant. switch
No
Replace
faulty
component(s)
No
Replace
faulty
component(s)
Issue 1 04/2004 ©Nokia Corporation. Page 11
Page 12
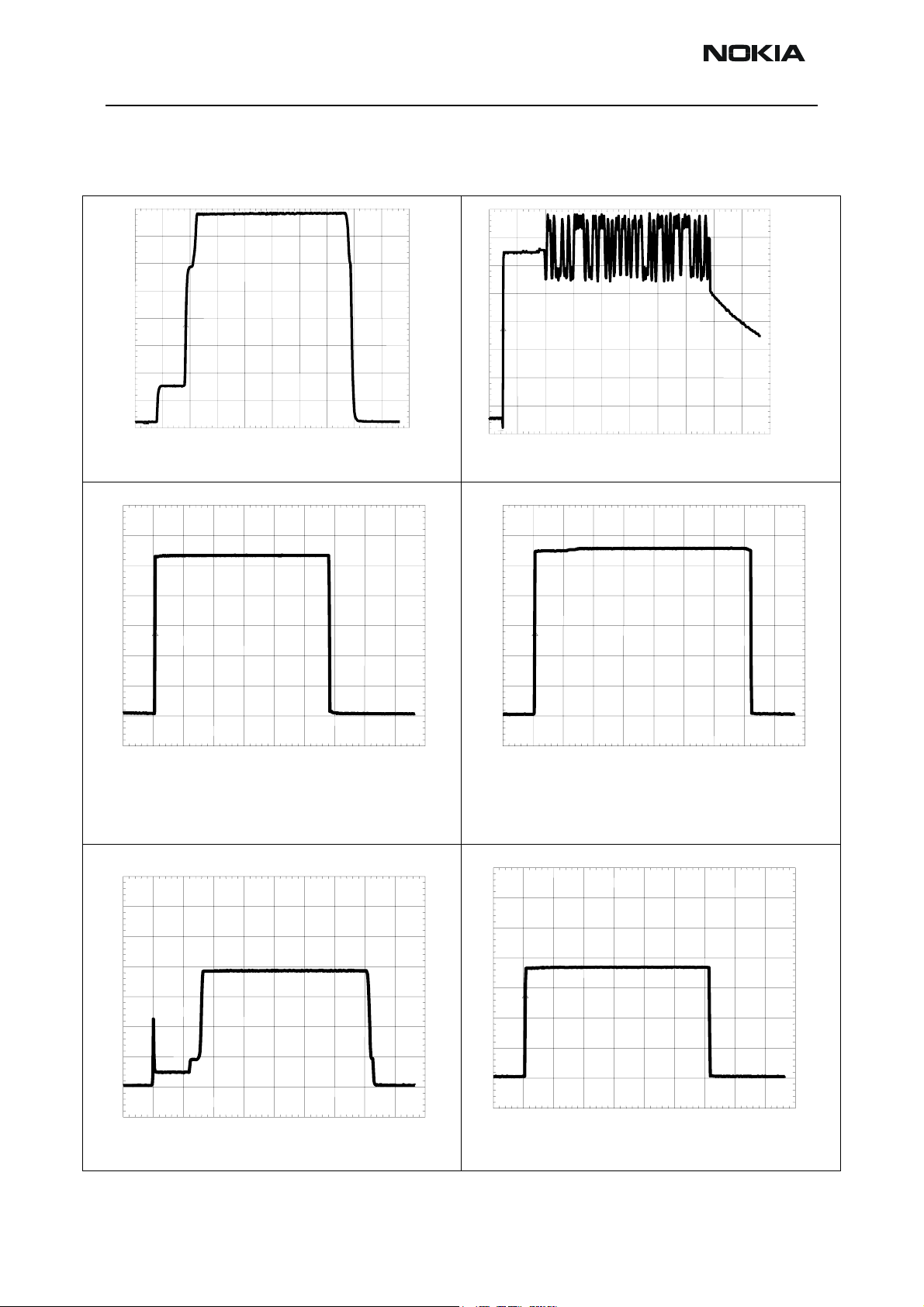
RM-37 Company confidential
v
v
6-Troubleshooting Instructions CCS Technical Documentation
Pictures of transmitter signals
Figure 6: Transmitter signals
TXI
VPC
200mV/di
1
VPCTRL _900 power level high at R703/C703
VPCTRL_1800/1900 power level high at R704/C704
500mV/div 100us/div
VANT_1 / GSM900 TX at C804
VANT_2 / GSM1800 TX at R808
VANT_3 / GSM1900 TX at C805 OV
( no signal/ Flatline on Oscilloscope screen)
100us/di
200mV/div
100us/div
TX I/Q at R516/517 power level high Random data
_
1
500mV/div 100us/div
VANT_1,VANT_2,VANT_3
VTXB_900 at C713
VTXB_1800_1900 at C714
Page 12 ©Nokia Corporation. Issue 1 04/2004
500mV/div 100us/div
500mV/div MTB 100us/div
TXP at J504
Page 13
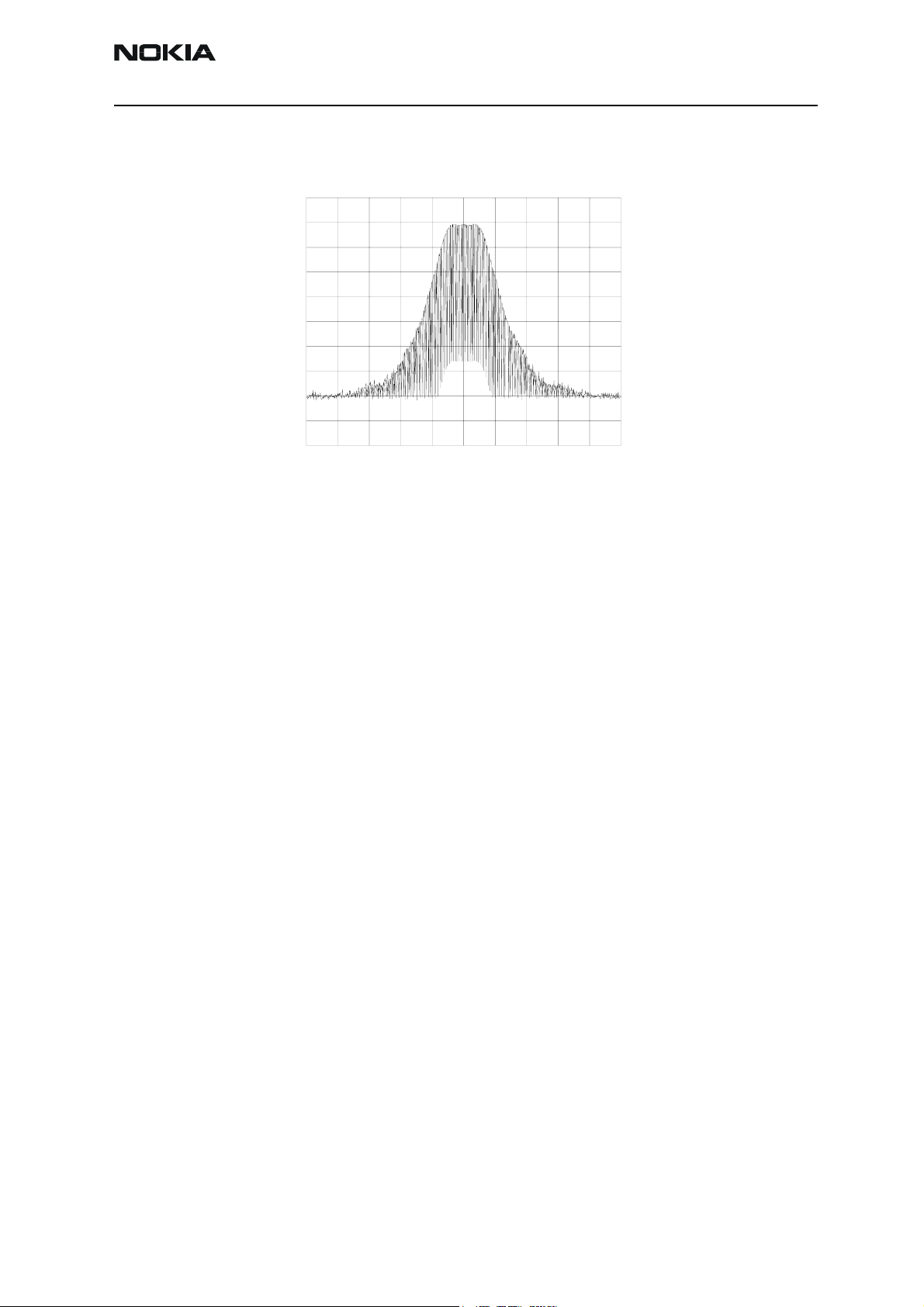
Company confidential RM-37
CCS Technical Documentation 6-Troubleshooting Instructions
Figure 7: TX OUT signal
GS MPOW Tue Sep 25 13: 48 : 59 2001
REF 41. 0 dBm ATT 40 dB
10dB/
REF OFS
11. 0 dB
RBW
100 kHz
VBW
100 kHz
SWP
2. 0 s
CENTER 897. 400 MHz SPAN 2. 000 MHz
Tx out signal, 900 band, burst mode, channel 37
A_ wr i t eB_bl ank
Issue 1 04/2004 ©Nokia Corporation. Page 13
Page 14

RM-37 Company confidential
6-Troubleshooting Instructions CCS Technical Documentation
GSM900, GSM1800 and GSM1900 Receiver
General instructions for Rx troubleshooting
Connect test jig to computer with DAU-9S cable or to FPS-8 Flash Prommer with XCS-4
modular cable.
Make sure that you have PKD-1 dongle connected to computers parallel port.
Connect DC power supply to module test jig with FLC-2 cable.
Set the DC supply voltage to 6V (test jig has internal voltage regulator of output voltage 4V).
Connect an RF-cable to the module test jig (MJS-38) RF connector and to RF signal generator.
Set the phone module to test jig and start Phoenix service sofware.
Initialize connection to phone. (use FBUS driver when using DAU9S and COMBOX driver
when using FPS-8)
Choose product from the menu
File -> Choose product -> RM-37
From toolbar set operating mode to "Local"
Activate RF controls window from the menu
Maintenance -> Testing -> RF Controls
From the RF controls window:
- Select band "GSM900", "GSM 1800" or “GSM1900” (Default = "GSM900")
- Set Active unit to "Rx" (Default = "Rx")
- Set Operation mode to "Burst" (Default = "Burst")
For continuous mode:
- Set Operation mode to "Continuous"
- Set AGC to "12: FEG_ON + DTOS_ON + BB_30=Vgain60” (maximum gain setting used
in normal mode)
(Default = "14: FEG_ON + DTOS_ON + BB_42=Vgain72")
Page 14 ©Nokia Corporation. Issue 1 04/2004
Page 15

Company confidential RM-37
CCS Technical Documentation 6-Troubleshooting Instructions
- Set Rx/Tx channel to 37 on GSM900 band, 700 on GSM1800 band or 661 on GSM1900
(Defaults)
Apply 942.46771 MHz (channel 37 + 67.710 kHz offset), 1842.86771 MHz (channel 700
+ 67.710 kHz offset) or 1960.06771 MHz (channel 661 + 67.71 kHz) –90 dBm signal to
the RF-connector (remember to compensate for cable attenuation).
Measuring with an oscilloscope on "RXI" or "RXQ" following screens should be seen on a
working GSM900 , GSM1800 or GSM1900 receiver:
Figure 8: RX I/Q signal ,burst mode, input level –90dBm.
Figure 8, “RX I/Q signal ,burst mode, input level –90dBm.,” on page 15: Receiver I or Q
burst mode signal (channel 37) measured from testpoint RXI or RXQ with 942.467 MHz
signal, input level –90dBm at RF-connector.
Correct signal amplitudes approximately:
• GSM900~170mVpp
• GSM1800~140mVpp
• GSM1900~160mVpp
Signal part frequency 67.7kHz sine.
Issue 1 04/2004 ©Nokia Corporation. Page 15
Page 16

RM-37 Company confidential
6-Troubleshooting Instructions CCS Technical Documentation
DC level of signal part is 1.35V. DC level can variate about +/-100mV between I and Q
signals and between different bands as well.
Figure 9: GSM1900 RX I or Q signal (trace2), burst mode.
For Figure 9, “GSM1900 RX I or Q signal (trace2), burst mode.,” on page 16 GSM1900
receiver burst mode I or Q signal at ch 661 with input signal 1960.067MHz, level –90
dBm at RF-connector.
st
Trace2: With wider time scaling both monitoring and own RX bursts are seen, 1
burst
(shorter) is monitoring and 2nd burst (longer) is own RX burst.
Trace1: External LNA VCC supply voltage at burst mode, input level –90 dBm. Measured
from testpoint LNA_VCC.
Page 16 ©Nokia Corporation. Issue 1 04/2004
Page 17

Company confidential RM-37
CCS Technical Documentation 6-Troubleshooting Instructions
Figure 10: RX I&Q, phase difference 90 deg between signals.
Figure 10, “RX I&Q, phase difference 90 deg between signals.,” on page 17:
Detailed view of GSM900 continuous mode RX I and Q signals measured from testpoints
RXI and RXQ simultaneously.
Used channel 37, input signal 942.467 MHz, level –90 dBm at antenna port, AGC setting
12.
Phase difference should be 90 degrees between RX I and Q signals at all bands.
Issue 1 04/2004 ©Nokia Corporation. Page 17
Page 18

RM-37 Company confidential
6-Troubleshooting Instructions CCS Technical Documentation
Troubleshooting diagram for GSM900 receiver
Phone in “Continuous” mode, AGC setting “12”
Figure 11: GSM900 receiver troubleshooting
Apply –90dBm
942.46771MHz signal
from generator to antenna connector
Yes
Oscilloscope at RX_I
Signal 700mVpp
DC offset 1.35V***
Frequency 67.7kHz
Yes
900RX chain
functional
No
Change generator level
to –50dBm
Spectrumanalyzer
Antenna Switch
outputs, GSM900
–88 dBm
Yes
Spectrumanalyzer
HELGA inputs
GSM900
–89 dBm
Yes
Oscilloscope
VR1,3...6 2.7V
Check HELGA serial
interface
(burst mode)
NoYes
No
No
Spectrumanalyzer
Antenna Switch
input
–84 dBm
Yes
Oscilloscope
VANT_1...3 0V
Yes
Check Antenna
switch
Z800
Check L809
L810
Check Baseband
No
Check C831,
L811
Oscilloscope :
Check HELGA
serial interface
(burst mode)
Check HELGA
N500
All spectrumanalyzer reading
values are measured with
2.5 kohm passive probe (use
tweezers to connect the
probe ground to the nearest
PWB ground). Reading value
is represented without
+34 dB compensation.
* Spectrumanalyzer
reading with 1 kohm
passive probe (right value add +34 dB)
NoNo
Check Baseband
Yes
Spectrumanalyzer
4G VCO out
3769.6MHz
∼–30 dBm (*
Yes
Check HELGA
N500
No
Synthesiszer troubleshooting
* ** DC–level of RXI/RXQ in
continuous mode will decrease
slowly.
The original level can be restored by rewriting gain set.
Page 18 ©Nokia Corporation. Issue 1 04/2004
Page 19

Company confidential RM-37
CCS Technical Documentation 6-Troubleshooting Instructions
Troubleshooting diagram for GSM1800 receiver
Phone in “Continuous” mode, AGC setting “12
Figure 12: GSM1800 receiver troubleshooting
Apply –90dBm
1842.86771MHz signal
from generator to antenna connector
NoNoYesNoYes
Oscilloscope at RX_I
Signal 140mVpp
DC offset 1.35V ***
Frequency 67.7kHz
Yes
Change generator level
to –50dBm
Spectrumanalyzer
Antenna switch outputs,
1800 LNA out
–61 dBm
Spectrumanalyzer
Antenna Swithc input
-84 dBm
Check C831,
L811
GSM1800 RX chain
functional
Yes
Spectrumanalyzer
HELGA inputs
GSM 1800
–88 dBm
Yes
Oscilloscope
VR1,3...6 2.7V
Check HELGA serial
interface
(burst mode)
Yes
Spectrumanalyzer
4G VCO out
3769.6MHz
∼–30 dBm (*
Yes
Check HELGA
N500
No
No
No
Oscilloscope
VANT_1...3 0V
Check Antenna
Switch Z800
Check C838, C839,
L821. L 872,
C836, C837,
V801
Synthesiszer troubleshooting
Yes
Yes
Check Baseband
Oscilloscope
Check HELGA serial interface (burst
mode)
Yes
Check HELGA
N600
All spectrumanalyzer reading
values are measured with 1
kohm passive probe (use
tweezers to connect the
probe ground to the nearest
PWB ground). Reading value
is represented without +26
dB compensation.
* Spectrumanalyzer
reading with 1 kohm
passive probe (right value add +26 dB)
* ** DC–level of RXI/RXQ in
continuous mode will decrease
slowly.
The original level can be restored by rewriting gain set.
NoNo
Check Baseband
Issue 1 04/2004 ©Nokia Corporation. Page 19
Page 20

RM-37 Company confidential
6-Troubleshooting Instructions CCS Technical Documentation
Troubleshooting diagram for GSM1900 receiver
Phone in “Continuous” mode, AGC setting “12
Figure 13: GSM1900 receiver troubleshooting
Apply –90dBm
1842.86771MHz signal
from generator to antenna connector
NoNoYesNoYes
Oscilloscope at
RX_I /RXQ
Signal 160mVpp
DC offset 1.35V ***
Frequency 67.7kHz
Change generator level
to –50dBm
Spectrumanalyzer
Antenna Switch output, GSM1900
–88 dBm
Spectrumanalyzer
Antenna Switch input
–84 dBm
Check C831,
L811
Yes
GSM1800 RX chain
functional
Spectrumanalyzer
HELGA inputs
GSM1900
–78 dBm
Oscilloscope
VR1,3...6 2.7V
Check HELGA serial
interface
(burst mode)
Yes
Spectrumanalyzer
4G VCO out
3685.6MHz
∼–30 dBm (*
Yes
Check HELGA
N500
Spectrumanalyzer
RX_SAW_out
Yes
–90 dBm
Oscilloscope
LNA_VCC 2.6V
LNA_P 0 V
Check V802,
C826, Z802,
C829, C8097,
C808
Check Baseband
Synthesiszer troubleshooting
Yes
Oscilloscope
VANT_3 2.7VV
VANT_1/2 0V
Check Antenna
switch Z800
Oscilloscope
VR1,3...6 2.7V
Check HELGA serial
interface
(burst mode)
Yes
Yes
Yes
Check HELGA
N500
Oscilloscope
Check HELGA serial interface (burst
mode)
Yes
Check HELGA
N500
Check Baseband
Check Baseband
All spectrumanalyzer reading
values are measured with 1
kohm passive probe (use
tweezers to connect the
probe ground to the nearest
PWB ground). Reading value
is represented without +26
dB compensation.
* Spectrumanalyzer
reading with 1 kohm
passive probe (right value add +26 dB)
* ** DC–level of RXI/RXQ in
continuous mode will decrease
slowly.
The original level can be restored by rewriting gain set.
NoNo
Check Baseband
Page 20 ©Nokia Corporation. Issue 1 04/2004
Page 21

Company confidential RM-37
CCS Technical Documentation 6-Troubleshooting Instructions
Synthesizer
General instructions for synthesizer troubleshooting
Connect test jig to computer with DAU9S cable or to FPS-8 Flash Prommer with XCS-4
modular cable.
Make sure that you have PKD-1 dongle connected to computers parallel port.
Connect DC power supply or FPS-8 to module test jig with PCS-1 cable.
Set the DC supply voltage to 3.9V and set the jumper connector on test jig to "bypass"
position.
Set the phone module to test jig and start Phoenix service sofware
Initialize connection to phone. (use FBUS driver when using DAU9S and COMBOX driver
when using FPS-8)
Select product from the menu
File -> Choose product -> RM-37
From toolbar set operating mode to "Local"
Activate RF controls window from the menu
Maintenance -> Testing -> RF Controls
From the RF controls window
- Select band "GSM900", "GSM 1800" or "GSM1900" (Default = "GSM900")
- Set Active unit to "Rx" (Default = "Rx")
- Set Operation mode to "Continuous" (Default = "Burst")
- Set Rx/Tx channel to 37 on GSM900 band, 700 on GSM1800 band, 661 on GSM1900
band (Defaults)
Issue 1 04/2004 ©Nokia Corporation. Page 21
Page 22

RM-37 Company confidential
6-Troubleshooting Instructions CCS Technical Documentation
Synthesizer troubleshooting diagram
Figure 14:
Synthesizer
troubleshooting
*(When 2.5kOhm passive probe is used,
Yes
correct the measurement by +34 dB
Set with RF controls:
Active Unti = Rx
Operation mode = Continuous
Check with RF probe:
-4G VCO out signal
- 3589.6 MHz (GSM900)
-3495.6 MHz (GSM1800)
- 3760 MHz (GSM1900)
Level >-10dBm (*
OK ?
No
VCO out signal level<-10dBm
No
Check output signal on
1 GHz span
Signal found on
incorrect frequency ?
Yes
Yes
Synthesizer
OK
Yes
Check with oscilloscope:
-4G VCO Vcc = 2.7V
No
Check balun
output levels and
solder joints
OK ?
No
Replace
faulty
component(s)
OK ?
No
Yes
Yes
Baseband
troubleshooting
Replace
VCO
Check with oscilloscope:
VCO control voltage
from VCO pin
0V ?
No
Check with oscilloscope:
VCO control voltage
from VCO pin
>4.0 V ?
Yes
Check balun
output levels and
solder joints
OK ?
Yes
Check VCO control
loop components
Yes
OK ?
Replace
VCO
No
Replace
faulty
component(s)
No
Page 22 ©Nokia Corporation. Issue 1 04/2004
Page 23

Company confidential RM-37
CCS Technical Documentation 6-Troubleshooting Instructions
Pictures of synthesizer signals
Figure 15: 26MHz at G501 pin out
Figure 16:
Figure 17: 1800 TX, channel 512, burst mode
26MHz RFCLK at R420/C420
Issue 1 04/2004 ©Nokia Corporation. Page 23
Page 24

RM-37 Company confidential
/
6-Troubleshooting Instructions CCS Technical Documentation
Figure 18: 1900 RX, channel 810, continuous mode
Figure 19: VCO output, 1800 band, RX on, continuous output
R EF 4. 0 dB m A TT 10 dB
10dB
SPAN
1. 000 MHz
REFOFS
34. 0 dB
RBW
10 kH z
VBW
10 kH z
SWP
50 ms
CE NT ER 3. 685600 GHz S PAN 1. 000 MHz
Wed A ug 21 21: 23: 21 2002
A_vi ew B_bl ank
MARKER
3. 685604 GHz
-3.97 dBm
Page 24 ©Nokia Corporation. Issue 1 04/2004
Page 25

Company confidential RM-37
CCS Technical Documentation 6-Troubleshooting Instructions
Baseband troubleshooting
The following diagrams describe baseband troubleshooting.
Main Troubleshooting Diagram
Figure 20: Baseband general troubleshooting
Issue 1 04/2004 ©Nokia Corporation. Page 25
Page 26

RM-37 Company confidential
6-Troubleshooting Instructions CCS Technical Documentation
Phone is dead
Figure 21: Dead phone troubleshooting
Start
Check X100
Is phone current
0 mA?
No
Yes
(contacts,
solderings). Is it
OK?
Yes
Check L260 -
L265 and C260 -
C265. Are they
OK?
Yes
No
No
Change X100
Change defect
ones
Phone current
< 50 mA
No
Phone current
~54 mA
Yes
Is phone in
LOCAL mode ?
Yes
No
No
Check all
VBATT-lines
Is flash
programming
working OK?
No
Check BSI-line including
X100,C100,C240,R202
and R206. Are they OK?
Yes
Yes
Phone is
jammed
Flash fault
Change UEM
Yes
No
Change defect part
End
Page 26 ©Nokia Corporation. Issue 1 04/2004
Page 27

Company confidential RM-37
CCS Technical Documentation 6-Troubleshooting Instructions
Flash Programming Fault
Figure 22: Flash programming troubleshooting
Start
Is the FBUS
TX-line HIGH
after startup?
Yes
Is FBUSTX-line
set to LOW after
it has been
HIGH?
Yes
Wrong
manufactor ID
and device ID
No
No
No
Measure BSI-pulse
during Flash
operation. Is it OK?
Yes
Measure FBUSTX-line
during Flash operation
(J411). Is it ~1.8V?.
Yes
Yes
No
No
Check BSI-line including
X100,C100,C240,R202
and R206.
Check R104.
If OK, change UEM
Change UPP
Change Flash
Is phone totally
dead?
No
Phone doesn't
start up or it's
jammed?
No
End (retest)
Yes
Yes
Phone is dead
Phone is
jammed
Issue 1 04/2004 ©Nokia Corporation. Page 27
Page 28

RM-37 Company confidential
6-Troubleshooting Instructions CCS Technical Documentation
Phone is jammed
Figure 23: Jammed phone troubleshooting
Start
Measure VIO, VCORE,
VFLASH1,VANA, VR3
voltages. Are they OK?
Yes
Measure 32.6kHz Sleep Clk
from testpoint J404. Is it
OK?
Yes
Measure 26MHz RFClk
from R420. Is it OK?
Yes
Measure PURX-signal from
testpoint J402. Is it ~1.8V?
Yes
Phone shutdown after 30s
No
No
No
No No
No
Yes
Check VBATT1-6, VIO,
VCORE, VANA, VR3
lines. Are they OK?
Yes
Measure Sleep Clk
from B200. Is it OK?
Measure 26MHZ RFClk
from G501. Is it OK?
Measure watchdog signal from
testpoint J414. Is it OK?
No
Yes
Yes
No
Check L260-L265,
C260-C265, BSI/BTEMP
-lines and VBATT-lines
Check BSI/BTEMP-lines. If
OK, UEM regulators are not
working. Change UEM.
Check B200, C209
and C210
Change UEM
Check G501.
If not OK, change.
Check R420, C420.
If OK, change N500.
Change UEM
No
Change UPP
Measure 1MHz Clk signal from
testpoint J413. Is it OK?
Yes
Read phone info. Is it OK?
Yes
Change TB4
module or retest
No
Measure FBUSRX-signal during
No
phone info read from testpoint
J412. Is it OK?
Yes
Measure FBUSTX-signal during
phone info read from testpoint
J411. Is it OK?
Yes
No
Change UEMNo
Change UPP
Change UEM
Page 28 ©Nokia Corporation. Issue 1 04/2004
Page 29

Company confidential RM-37
CCS Technical Documentation 6-Troubleshooting Instructions
SIM card fault (Insert SIM / Card rejected)
Figure 24: SIM card troubleshooting
Start
Insert SIMor
Card rejected
fault?
No
End
Yes
Set phone to LOCAL
mode. Is it OK?
Yes
Measure VSIM voltage
from X386. Is it ~3.0V?
Yes
Check SIM power-up
sequence. Is it OK?
Yes
No
No
No
Check BSI-line including
X100,C100,C240,R202 and
R206. If OK, change UEM.
Check VSIM-line
(X386,C390,R386,C203).
If OK, change R388.
If still fail, change UEM.
Check SIM lines (X386). If
OK, change R388. If still fail,
change UEM.
Change UPP
Issue 1 04/2004 ©Nokia Corporation. Page 29
Page 30

RM-37 Company confidential
6-Troubleshooting Instructions CCS Technical Documentation
Keypad Fault
Figure 25: Keypad troubleshooting 1
Start
Is the power key
working?
Yes
Is the volume
UP key working?
Yes
Measure voltage
No No
from S302. Is it
HIGH?
Yes
Measure voltage
from S302 when
pressed. Is it
HIGH?
Yes
No
Phone is
jammed
Measure ROW0
No No
line from S300.
Is it ~1.8V?
Yes
Measure COL0
from S300 when
pressed. Is there
50us pulse?
No
Check
R306,C310,S30
2 and line. If OK,
change UEM
Check S302. Is
it OK?
Yes
No
Check S300 and line.
If OK, change Z300.If
still FAIL, change
UPP
Check S300 and
COL0 line. If OK,
change Z300.If still
FAIL, change UPP
Phone is
dead
Change S302
Change UPP
Check S301 and line.
If OK, change Z300.If
still FAIL, change
UPP
Is the volume
Down key
working?
Yes
Measure ROW1
No No
line from S301.
Is it ~1.8V?
Yes
Yes
Continue
Measure COL0
from S301 when
pressed. Is there
50us pulse?
No
Yes
Check S301 and
COL0 line. If OK,
change Z300.If still
FAIL, change UPP
Change UPP
Page 30 ©Nokia Corporation. Issue 1 04/2004
Page 31

Company confidential RM-37
CCS Technical Documentation 6-Troubleshooting Instructions
Figure 26: Keypad troubleshooting 2
Continue
Try to change UI
Is the UI-module
keys working?
No
PWB. Are the
keys working
now?
No
Check X301 (solder
joints and spring
contacts). Is it OK?
Yes
No
Retest failing
UI-module
Change X301
Yes
Measure ROW0 - Row4
lines from X301. Are
voltage level ~1.8V?
Yes
Measure
SLEEPX-signal from
testpoin t J403 w hen
key is pressed.
Is voltage level
~1.8V?
Yes
When keypad is
pressed, a r e the
LED's turn ed o n?
No
Check lines ROW0 -
ROW4 from X301.
No
If OK, change Z300. If
still fails, change UPP
No
Illumination
End
fault
Issue 1 04/2004 ©Nokia Corporation. Page 31
Page 32

RM-37 Company confidential
6-Troubleshooting Instructions CCS Technical Documentation
Display Fault
Figure 27: Display troubleshooting
Start
Try to change
Does the display
start?
Yes
No
UI-module. Is
the display
working now?
No
Check X302
(solder joints). Is
it OK?
Yes
No
Retest failing
UI-module
Change X302
Yes
Measure VDD (2.7V)
and VDDI (1.8V). Are
they OK?
Yes
Measure RESX(J306)
and CSX (J304)
signals. Are voltage
levels ~1.8V??
Yes
Measure SDA (J 305)
and SCLK (J307)
signals. Are voltage
levels ~1.8V?
Yes
No
No
No
Check X302 and
lines again. I f OK ,
change UEM
Check X302 and
lines again. I f OK ,
change UPP
Check X302,
R308,R309 and
lines. If OK,
change UPP.
Are the displ ay LED's
working when key is
pressed or enabled by
No
Illumination
fault
Phoenix SW?
End
Page 32 ©Nokia Corporation. Issue 1 04/2004
Page 33

Company confidential RM-37
CCS Technical Documentation 6-Troubleshooting Instructions
Illumination fault
Figure 28: Backlight troubleshooting
Start
Are the display
LED's working?
Yes
Are the
keyboard LED's
working?
Yes
Try to change display.
No
Are the LED's working
now?
No
Check X302 (solder
joints). Is it OK?
Yes
Measur e VLED+ and VL ED-.
VLED+ = ~7.5V and VLED= ~0.5V when LED driver is
enabled. Are they OK?
(Notice: VL ED+=VBATT
when driver is disabled)
Try to change UI PWB.
No
Are the LED's working
now?
No
Check X301 (solder
joints). Is it OK?
Yes
No
No
Yes
No
Retest failing display
Change X302
Check N300, L300, V300, R300,C303,C304.
If not OK, change defect part.
Retest failing UI PWB
Change X301
Yes
End
Measure VLED+. VLED+ =
~7.5V when LED driver is
enabled. Is it OK?
Yes
Check all LED's in UI PWB
(V101 - V106). Are they OK?
Yes
Retest
Check N300, L300, V300, R300,C303,C304.
No
No
If not OK, change defect part.
Change defect parts
Issue 1 04/2004 ©Nokia Corporation. Page 33
Page 34

RM-37 Company confidential
6-Troubleshooting Instructions CCS Technical Documentation
Charger Fault
Figure 29: Charging troubleshooting
Start
Battery bars are
working ( scr o ll)
No
Measure voltage
over V100
(TVS).
Is it > 3.0V?
Yes
Read BTEMP value.
Compare it to ambient
temperature.
Is it ~25C?
Yes
Yes
No
No
Check X102, F100,
L100, V100, C106, C110
and line.
Check X100, C100,
R202, R207, C220
and line. Are they
OK?
Yes
No
Retest
Change defect part (if
any), re-calibrate charge
current/voltage. Retest.
Re-calibrate BTEMP with
Phoenix SW. Retest.
Change defect part,
re-calibrate and retest.
Measure charger
current throug F100.
Is it ~350...390mA
(with ACP-7)?
Yes
Retest
No Yes
Check R200. Is it
OK?
No
Change UEM
Change defect part,
re-calibrate charge
current/voltage. Retest.
Page 34 ©Nokia Corporation. Issue 1 04/2004
Page 35

Company confidential RM-37
CCS Technical Documentation 6-Troubleshooting Instructions
Accessory Fault
Figure 30: Accessory troubleshooting
Start
Is accessory detected
when connected to
system connector?
Yes
No
Check system
connector X101
(solder ings, contact
plates). Is it OK?
Yes
Measure ACI-line
(pin3).
Is it ~0.83...1.13V?
Yes
Measure VOUT
voltage (pin4).
Is it ~2.8V?
Yes
Retest
No
No
No
Repair solderings or check contact
plates if dirty. Retest .
ACI-Accessory
Check ACI- line (L106,R103,R102,R109,C103).
If not OK, change defect part and retest.
Check VOUT-line (N100, L107, R103, C101,
C102, C112).
If not OK, change defect part and retest.
Non-ACI Accessory
End
Measure ACI-line
(pin3).
Is it ~0V?
Yes
Measure VOUT
voltage (pin4).
Is it ~0V?
Yes
Retest
No
No
Check ACI- line (L106,R103,R102,R109,C103).
If not OK, change defect part and retest.
Check that regulator N100 enable-pin is
LOW-state.
If not OK, check ACI-line again
Issue 1 04/2004 ©Nokia Corporation. Page 35
Page 36

RM-37 Company confidential
6-Troubleshooting Instructions CCS Technical Documentation
Camera Troubleshooting
Figure 31: Component placement
Figure 32: Trace layout
Page 36 ©Nokia Corporation. Issue 1 04/2004
Page 37

Company confidential RM-37
CCS Technical Documentation 6-Troubleshooting Instructions
Camera Fault
Figure 33: Camera troubleshooting diagram
Issue 1 04/2004 ©Nokia Corporation. Page 37
Page 38

RM-37 Company confidential
6-Troubleshooting Instructions CCS Technical Documentation
Audio Fault
Figure 34: Audio troubleshooting
Start
Is earpiece working?
Yes
No
Try to change earpiece.
Is it work in g n ow?
Yes
No
Set phone in LOCAL mode. Use Phoenix audio test.
Se t E X T IN , HP O UT , L O OP ON
Measure DC offset
voltage from earpiece
pads. Is it ~1.38V?
No
Yes
Measure MIC2B voltage
from XMICP (L102).
Is it ~2 .2 V ?
Yes
Connect EXT audio signal (1kHz sine,
200mVpp) in XMICP and GND in XMICN.
No
Check L102, C116, R150, C159, R153,
Retest earpiece
Check L150, C155, R151, R152 and
lines. If OK, change UEM .
C150 and line. If OK, change UEM.
Continue
Measure sine signal from
earpiece pads.
Is it~880mVp-p?
Yes
Change UPP and retest
Measure sine signal
No
from R155 (UEM).
Is it ~130mVp-p?
No
Yes
Check C154, R155,
C156, R154 and lines.
Change
UEM
Page 38 ©Nokia Corporation. Issue 1 04/2004
Page 39

Company confidential RM-37
CCS Technical Documentation 6-Troubleshooting Instructions
FM Radio troubleshooting
FM Radio component layout
Figure 35: Component placement
Figure 36: Trace layout.
Issue 1 04/2004 ©Nokia Corporation. Page 39
Page 40

RM-37 Company confidential
6-Troubleshooting Instructions CCS Technical Documentation
Figure 37: FM radio block layout.
Components L103, L104, L105, C107, C108, C109, C117, C162, C163, R164, R165, R166
and R167 are not shown in the picture. Those components are placed in baseband section, near audio amplifier N150.
Page 40 ©Nokia Corporation. Issue 1 04/2004
Page 41

Company confidential RM-37
CCS Technical Documentation 6-Troubleshooting Instructions
FM Radio troubleshooting diagram
Notes to "FM Radio troubleshooting diagram"
Use 1MHz 1X probe when measuring Audio and clock signals with oscilloscope.
Use active RF probe when measuring frequencies with spectrum analyzer.
Note 1. RF test signal parameters:
- Amplitude, A, –67.0 dBm
- Carrier frequency, fc, 98,000 MHz
- Deviation, ∆f, 75 kHz
- Modulating frequency f
, 1,000 kHz (RF generator internal)
m
- FM stereo, mode R=L, pilot state ON
Issue 1 04/2004 ©Nokia Corporation. Page 41
Page 42

RM-37 Company confidential
6-Troubleshooting Instructions CCS Technical Documentation
Figure 38: FM radio troubleshooting diagram
Set phone into local mode.
Start FM radio.
Does
the radio
start ?
YES
Connect RF test signal (note1)
Set radio channel to 98.0 MHz
Set radio volume to max.
Measure
Audio signal
from C162 and
C163.
Is it 1kHz
0.5–0.8Vp–p?
NO
Check
C107, C108,
C109, C117 ,
L105,C367,C378,
C379, L358.
Measure signal
from C162, C163
Is it 1kHz
0.5–0.8
Vp–p?
NO
Check
R359,R360,
V356, V357,
L356,L357,C357,
C358,C362.
Measure
signal from
J103, J104,
OK ?
NO
Change
N356.
Measure signal
from J103 and J104.
Is it
OK ?
Check
NO NO
YES
YES
YES
YES
C374, C375, R375,
R358 and measure
32kHz clock signal
from J359,
retest starting.
Start OK ?
YES
Check
R164,
R165, R166,
R167, L103,L104
Measure
signal from J103
and J104.
Is it
0.015–0.3
Vp–p?
YES
NO
Measure
voltages from
pins 7 and 34,
is it –2.7 V ?
Retest starting.
Start OK now ?
OK, RETEST IN FLALI
Radio and RF generator
to 87.5 and 108.0 MHz.
Measure Audio from
C162 and C163.
Are both cases
1 kHz 0.5 – 0.8 Vp–p ?
V356, V357, L356,
L357, C357, C358, C362,
R359, R360.
T est again with
87.5 and 108.0 MHz.
Measure audio from
C162 and C163.
NO
87.5 and 108.0 MHz.
Measure audio from
C162 and C163.
NO
Set
Check
Both
OK?
Change
V356 and 357.
BOTH !
Retest with
Both OK ?
NO
NO
(pins 5,6,7,8,9,11,
12,13,17,33,34,35,
Check
N356 solders
36, 37.
Start OK
now ?
YESYES
YES
YES
NO
Change
N356.
Radio start
OK
now?
NO
Baseband digital
fault (UPP)
YES
Audio
Amplifier
failure
(N150)
NO
Change
radio module TB4
OK, RETEST IN FLALI
E Nokia Corporation
Page 42 ©Nokia Corporation. Issue 1 04/2004
Page 43

Company confidential RM-37
CCS Technical Documentation 6-Troubleshooting Instructions
Diagrams of FM radio signals
Figure 39: Oscilloscope screen shot, Audio output
Signal 1: Audio output from PWB test points J103 and J104, with FM test signal, volume
100%.
Signal 2: Audio output from FM radio pins 22 and 23(same as in C162 and C163), with
FM test signal
Issue 1 04/2004 ©Nokia Corporation. Page 43
Page 44

RM-37 Company confidential
6-Troubleshooting Instructions CCS Technical Documentation
Figure 40: FM radio clock from test point J359, 32 kHz frequency clock signal, when radio is on.
15:51:49 03 JUL 2002
#AT 0 dBREF -20.0 dBm
PEAK
LOG
10
dB/
WA SB
CORR
SC FS
CENTER 98.0000 MHz SPAN 300.0 kHz
#RES BW 10 kHz VBW 10 kHz #SWP 1.00 sec
MKR 97.9280 MHz
-71.03 dBm
SWEEP
CONT SGL
FREE RUN
VIDEO
LINE
EXTERNAL
SYNC CRD
TV TRIG
Figure 41: FM frequency from FM radio pin 37, the other end of L358, with FM test signal
10:46:24 03 JUL 2002
PEAK
LOG
10
dB/
#AT 10 dBREF .0 dBm
MKR
196.440 MHz
-9.40 dB
MEAS UNCAL
SWEEP
CONT SGL
FREE RUN
VIDEO
LINE
WA SB
CORR
SC FS
CENTER 196.450 MHz SPAN 1.000 MHz
#RES BW 10 kHz #VBW 10 kHz #SWP 20.0 msec
EXTERNAL
SYNC CRD
TV TRIG
Figure 42: VCO frequency from FM radio pins 3 and 4, the other ends of V356 and V357, with FM test signal
Page 44 ©Nokia Corporation. Issue 1 04/2004
 Loading...
Loading...