Page 1

Customer Care Solutions
Technical Documentation
6(b) - RF T roubleshooting and
Manual T uning Guide
ISSUE 2 01/2004 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL 1
Copyright © 2003 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 2

NHL-10
CCS Technical Documentation RF Troubleshooting
This page has been deliberately left blank
2 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL ISSUE 2 01/2004
Copyright © 2003 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 3

NHL-10
RF Troubleshooting CCS Technical Documentation
Table of Contents
Page No
Introduction ...................................................................................................................5
General troubleshooting ................................................................................................6
RF Key Component Placement ..................................................................................... 7
Receiver Troubleshooting ............................................................................................. 9
General Description .................................................................................................... 9
General Instructions for RX Troubleshooting .......................................................... 10
Measuring RX I/Q signals using RSSI ...................................................................10
Measuring RX performance using SNR measurement ........................................... 11
Measuring the RX module manually using Oscilloscope and Spectrum Analyzer 12
GSM900 ..................................................................................................................12
GSM1800 ................................................................................................................14
GSM1900 ................................................................................................................15
Measurement points in the Receiver ...................................................................... 17
Tuning of the RX Using Phoenix ................................................................................19
RX Channel Select Filter Calibration .......................................................................19
RX Calibration .......................................................................................................... 19
RX Band Filter Response Compensation .................................................................. 22
Transmitter Troubleshooting .......................................................................................25
General Description .................................................................................................. 25
Preparation for Fault Finding .................................................................................... 26
Fault-finding chart: TX-BB interface and control signals ...................................... 28
Fault-finding chart: RF side of transmitter .............................................................29
Transmitter Tuning ...................................................................................................... 30
Introduction ...............................................................................................................30
TX IQ Tuning ............................................................................................................ 30
TX Power Level Tuning ........................................................................................... 34
ISSUE 2 01/2004 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL 3
Copyright © 2003 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 4

NHL-10
CCS Technical Documentation RF Troubleshooting
This page has been deliberately left blank
4 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL ISSUE 2 01/2004
Copyright © 2003 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 5

NHL-10
RF Troubleshooting CCS Technical Documentation
Introduction
This document describes the troubleshooting and RF tuning of Nokia 6600 (NHL-10). In general, two types of measurements have to be performed during the troubleshooting and repair
of phones:
• RF measurements shall be done with a spectrum analyzer, either connected directly
to the RF connector of the board (“antenna point”), or used together with a high-frequency probe to measure RF signals at points along the TX or RX chain.
• LF (Low-Frequency) and DC measurements shall be done either with a multimeter, or
with an oscilloscope together with a 10:1 probe.
All tuning must be done with Phoenix Service Software, version A9 2003.15.2.25, or later.
Always make sure that the measurement set-up has been calibrated when measuring RF pa-
rameters at the RF connector. Remember to include the correct losses in the module repair jig
and the connecting cable when realigning the phone.
Most RF semiconductors are static discharge sensitive. ESD protection must be taken into
account during repair (ground straps and ESD soldering irons).
Mjølner RF ASIC is moisture sensitive. Therefore, Mjølner RF ASIC must be pre-baked prior
to soldering.
RF calibration done via Phoenix software is temperature sensitive because of calibration of 26MHz reference oscillator (VCXO). According to the Mjølner specification, ambient
temperature has to be in the range of 22 to 36
o
C.
ISSUE 2 01/2004 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL 5
Copyright © 2003 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 6

NHL-10
CCS Technical Documentation RF Troubleshooting
General troubleshooting
The first step of fault-finding should always be a visual inspection. Carefully inspect the RF area
using a microscope and look for cracks, solder bridges, dry joints, missing components, components that have partially come off and other anomalies. Capacitors can be checked to see
that they are not short-circuited, and inductors that they are not open circuits. Also check that
power supply lines are not short-circuited, i.e. not 0Ω to ground.
Instruments needed for trouble-shooting (minimum requirement):
• Oscilloscope
• Multimeter
• Spectrum analyzer (SA)
Note:
Use an attenuator at the spectrum analyzer input to ensure that the SA will not become damaged by
excessive input power from the phone. Check the spectrum analyzer for maximum allowable input
power.
• Power supply that can deliver at least 2Adc
• Nokia 6600 module jig (also called test jig)
• PC with Phoenix installed
Note:
In this text the following terms are used interchangeably:
GSM900 = EGSM900 = EGSM
GSM1800 = DCS band
GSM1900 = PCS band
6 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL ISSUE 2 01/2004
Copyright © 2003 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 7

NHL-10
RF Troubleshooting CCS Technical Documentation
RF Key Component Placement
The following figure shows the key components of the RF section.
Figure 1: RF Key Components
shows key components of the RF section.
ᵱᵟᵵ
ᵐ
ᵥᵱ ᵫᵏᵖᵎᵎ
E-GSM900
ᵢᶓᵿᶊ
ᵡᶍᶓᶎᶊᶃᶐ
ᵟᶌᶒᶃᶌᶌᵿ
ᵱᶕᶇᶒᶁᶆ
ᵏ
ᵏᵑ
ᵠᶓᶄᶄᶃᶐ
ᵟᶋᶎᶊᶇᶄᶃ ᶐ
ᵮᶍᶕᶃᶐ
ᵟᶋᶎᶊᶇᶄᶃ ᶐ
ᵏᵎ
ᵱᵟᵵ
ᵑ
ᵥᵱ ᵫᵏᵗᵎᵎ
ᵱᵟᵵ
ᵒ
GSM1800
ᵣᵋ ᵥ ᵱᵫ ᵗᵎᵎ
ᵱᵟᵵ
ᵗ
ᵓ
ᵠᵟᵪᵳᵬ
ᵏᵒ
ᵡᶃ ᶊᶊᶓᶊᵿᶐ
ᵲᶐᵿᶌᶑᶁᶃᶇᶔᶃᶐ
ᵧᵡ
ᵔ
ᵠᶓᶄᶄᶃᶐ
ᵟᶋᶎᶊᶇᶄ ᶃᶐ
ᵏᵏ
ᵴᵡᵭ
ᵶᵲᵟᵪ
ᵕ
ᵖ
ᵠᶊᶓᶃᶒᶍᶍᶒᶆ
ᵲᶐᵿᶌᶑᶁᶃᶇᶔᶃᶐ
ᵏᵐ
Figure 2: RF Key Components
ISSUE 2 01/2004 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL 7
Copyright © 2003 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 8

NHL-10
CCS Technical Documentation RF Troubleshooting
Figure 3: RF Key Components
8 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL ISSUE 2 01/2004
Copyright © 2003 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 9

NHL-10
RF Troubleshooting CCS Technical Documentation
Receiver Troubleshooting
General Description
Figure 4: Receiver Signal Path
The receiver is a direct conversion, triple-band linear receiver. NHL-10 uses Mjølner RFIC with
external VCO.
The received RF signal from the antenna/RF connector goes into the RF antenna switch where
the signal is fed to the E-GSM900, GSM1800 or GSM1900 path. For each band, a RX bandpass SAW filter with unbalanced input and balanced output follows. All blocks are specified as
50Ω single ended, only the SAW filter output to the Mjølner input is differentially matched to
LNA G
gain nominally 12 dB, the second one is about 30 dB below max. gain. The gain selection control of the LNAs is done via the serial interface.
The differential RX signals are further amplified in the “pre-gain” stage and then mixed down to
baseband inside Mjølner using two Mixers with a 90° phase shift in the LO signal resulting in
an in- and quadrature phase paths. Local oscillator signal is generated with the external VCO.
The VCO signal is buffered and divided by 2 (DCS/PCS) or by 4 (EGSM). Accurate phasing is
generated in LO dividers.
The Rx BB chain incorporates AGC, channel select filter and DC compensation. The AGC is
adjusted in 6 dB steps in Mjølner. The DCN1 gain can be adjusted to +24/+18/+12/+6/0 dB.
The attenuator gain can step from 0/-6/-12/-18/-24/-30/-36/-42/-48dB. Other BB amplifiers have
a nominal summed gain of 58dB. The total dynamic range of AGC alone is 72dB. The 3
active channel filters in Mjølner defines the channel selectivity (flat response up to +/-90kHz
typical). Integrated base band filters are based on active RC filters with on-chip capacitors. The
baseband filters are distributed to following stages: BBAMP1, LPF1, LPF2. DC compensation
is split to DCN1 and DCN2. DCN1 is used to compensate DC offset from RF front-end imper-
. The LNAs are integrated in Mjølner and have two gain levels. The first one is max.
opt
rd
order
ISSUE 2 01/2004 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL 9
Copyright © 2003 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 10

NHL-10
CCS Technical Documentation RF Troubleshooting
fections. DCN2 centres the differential signal with respect to the common mode reference voltage of 1.35V. Differential, filtered I/Q-signals are finally fed to the sigma-delta ADC’s in the
UEM. Further filtering in the digital domain occurs in the sinc decimation filter and DSP based
FIR filters
General Instructions for RX Troubleshooting
Connect the phone to a PC with DAU-9S cable and dongle and follow the following instructions.
Measuring RX I/Q signals using RSSI
• Start Phoenix Service Software and establish a connection to the phone.
• Select File -> Scan Product Ctrl R.
• Wait until the phone software version is shown in the lower part of the screen.
• Select Testing -> RF controls.
• Select Band -> GSM900/GSM1800/GSM1900.
• Active unit -> RX.
• Operation mode -> Burst.
• RX/TX channel -> 37/700/661.
• Select RF Alt-M
Testing -> T
RSSI -> R
The set-up now looks like this:
10 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL ISSUE 2 01/2004
Copyright © 2003 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 11

NHL-10
RF Troubleshooting CCS Technical Documentation
• Apply a signal with frequency of:
EGSM: 942.467MHz (channel 37 + 67.710KHz offset),
GSM1800: 1842.867MHz (channel 700 + 67.710KHz offset),
GSM1900: 1960.067MHz (channel 661 + 67.710KHz offset),
and a power level of –80dBm to the RF connector (remember to compensate for the
cable loss).
•In RSSI reading click Read now.
The resulting RSSI level should be –80dBm in each band.
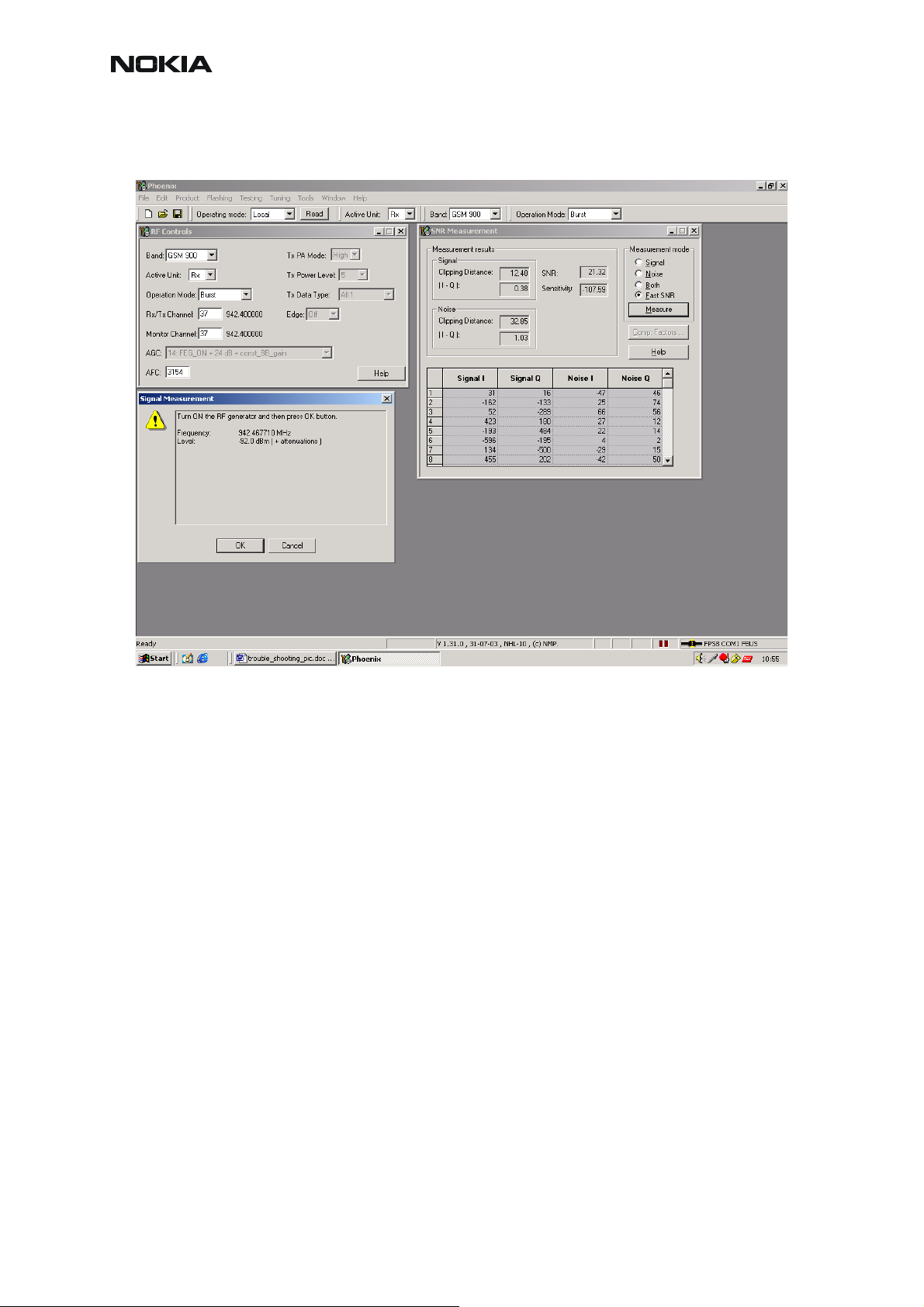
Measuring RX performance using SNR measurement
Note: This measurement also provides an indication of the conducted sensitivity.
• Start Phoenix Service Software and establish a connection to the phone.
• Select File -> Scan Product Ctrl R.
• Wait until the phone software version is shown in the lower part of the screen.
• Select Testing -> RF controls.
• Select Band -> GSM900/GSM1800/GSM1900.
• Active unit -> RX.
• Operation mode -> Burst.
• RX/TX channel -> 37/700/661.
• Select Maintenance Alt-M
Testing -> T
SNR Measurement -> M
• Select Fast SNR.
• Choose the respective band (EGSM900, GSM1800, GSM1900).
• Press Measure.
• Follow the instructions for Signal generator set–up in the pop–up window.
• Press OK.
• Read the SNR result. The SNR should be: EGSM900: > 20dB
GSM1800: > 18dB
GSM1900: > 18dB
• Check the sensitivity value.
The set-up should now look as shown in the following figure. The icon also includes a pop-up
window for reference.
ISSUE 2 01/2004 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL 11
Copyright © 2003 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 12
NHL-10
CCS Technical Documentation RF Troubleshooting
Measuring the RX module manually using Oscilloscope and Spectrum Analyzer
Spectrum Analyzer level values depend on the probe type and should be validated using a
known good NHL-10 sample. The levels that are given here are measured using a high frequency probe.
Measuring with Oscilloscope on RXINN or RXQINN (J606 –608) and RXID or RXQD (J211 –
J212) is recommended only if RSSI reading does not provide enough information. No dedicated test points exist for RX I/Q signals, however, they can be accessed by probing on a via hole
plating.
GSM900
• Start Phoenix Service Software and establish a connection to the phone.
• Select File -> Scan Product Ctrl R.
• Wait until the phone software version is shown in the lower part of the screen.
• Select Testing -> RF controls.
• Select Band -> GSM900.
• Active unit -> RX.
• Operation mode -> Continuous.
• RX/TX channel -> 7.
• AGC -> 9.
12 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL ISSUE 2 01/2004
Copyright © 2003 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 13

NHL-10
RF Troubleshooting CCS Technical Documentation
The input freq/level of the signal generator is 942.467710MHz, -60dBm.
Figure 5: Fault finding chart for GSM900
Apply -60 dBm
942.4 MHz, offset
67.71 kHz
from generator to
antenna connector
YES
EGSM chain
functional
Check RSSI using
Phoenix Does it
match Sig Gen
Output level ?
NO
Replace UPP
YES
Is L.O running ?
YES
Probe J606 -609
RX I &Q Does
waveform look like
example given
earlier ?
YES
Probe J211 &J212
Is digital data
visable ?
visible
NO
Replace UEM
NO
Synthesiser Fault -
NO
Refer to
finding chart
Check RX/TX
switch at RX 900
Z601
Input -63 dBm
Output -63dbm
Spectrum analyzer
EGSM SAW filter
Z604
output -66 dBm
YES
Spectrum analyzer
Check signal after
inductors L606 and
L607
-66 dBm
YES
Oscilloscope
VRX 2.7 V on
Mjoelner
YES
NO NO
NO
NO
NO
Oscilloscope
check Vc1, Vc2,
Vc3 at Z601 signal
0V
Check RX/TX
switch
Check SAW filter
Check inductors
L606, L607
Check Base band
Z604
Check Mjoelner
YES
ISSUE 2 01/2004 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL 13
Copyright © 2003 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 14

NHL-10
CCS Technical Documentation RF Troubleshooting
Probed RX I/Q signals J606 - 609 with signal setting to 942.467710MHz, -60dBm. Note that
the display is the same for both GSM1800/1900 bands as well.
• Signal amplitude: 456mV
• DC offset: 1.36V
• Frequency: approx 67KHz
GSM1800
• Start Phoenix Service Software and establish a connection to the phone.
• Select File -> Scan Product Ctrl R.
• Wait until the phone software version is shown in the lower part of the screen.
• Select Testing -> RF controls.
• Select Band -> GSM1800.
• Active unit -> RX.
• Operation mode -> Continuous.
• RX/TX channel -> 700.
• AGC -> 9.
The input freq/level of the signal generator is 1842.867710MHz, -60dBm.
14 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL ISSUE 2 01/2004
Copyright © 2003 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 15

NHL-10
RF Troubleshooting CCS Technical Documentation
Figure 6: Fault finding chart for GSM1800
Apply -60 dBm
1842.8 MHz, offset
67.71 kHz
from generator to
antenna connector
YES
EGSM chain
functional
Check RSSI using
Phoenix Does it
match Sig Gen
Output le vel ?
NO
Replace UPP
YES
Is L.O running ?
YES
Probe J606 -609
RX I &Q Does
waveform look like
example given
earlier ?
YES
Probe J211 &J212
Is digital data
visible
visable ?
NO
Replace UEM
NO
Synthesiser Fault -
NO
Refer to
finding chart
Check RX/TX
switch at RX 1800
Z601
Input -63 dBm
Output -65dBm
Spectrum analyzer
EGSM SAW filter
Z602
output -70 dBm
YES
Spectrum analyzer
Check signal after
inductors L603 and
L604
-73 dBm
YES
Oscilloscope
VRX 2.7 V on
Mjoelner
YES
NO NO
NO
NO
NO
Oscilloscope
check Vc1, Vc2,
Vc3 at Z601 signal
0V
Check RX/TX
switch
Check SAW filter
Check inductors
L603, L604
Check Base band
Z602
Check Mjoelner
YES
GSM1900
• Start Phoenix Service Software and establish a connection to the phone.
• Select File -> Scan Product Ctrl R.
• Wait until the phone software version is shown in the lower part of the screen.
• Select Testing -> RF controls.
• Select Band -> GSM1900.
• Active unit -> RX.
• Operation mode -> Continuous.
• RX/TX channel -> 661.
• AGC -> 9.
ISSUE 2 01/2004 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL 15
Copyright © 2003 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 16

NHL-10
CCS Technical Documentation RF Troubleshooting
The input freq/level of signal generator is 1960.067710MHz, -60dBm
Figure 7: Fault finding chart for GSM1900
Apply -60 dBm
1960 MHz, offset
67.71 kHz
from generator to
antenna connector
YES
EGSM chain
functional
Check RSSI using
Phoenix Does it
match Sig Gen
Output level ?
NO
Replace UPP
YES
Is L.O running ?
YES
Probe J606 -609
RX I &Q Does
waveform look like
example given
earlier ?
YES
Probe J211 &J212
Is digital data
visable ?
visible
NO
Replace UEM
NO
Synthesiser Fault -
NO
Refer to
finding chart
Check RX/TX
switch at RX 1900
Z601
Input -63 dBm
Output -65 dBm
Spectrum analyzer
EGSM SAW filter
Z603
output -70 dBm
YES
Spectrum analyzer
Check signal after
inductors L608 and
L609
-73 dBm
YES
Oscilloscope
VRX 2.7 V on
Mjoelner
YES
NO NO
NO
NO
NO
Oscilloscope
check Vc1, Vc2,
Vc3 at Z601 signal
Vc1, Vc3 =0V
Vc2=2.7V
Check RX/TX
switch
Check SAW filter
Check inductors
L608, L609
Check Base band
Z603
Check Mjoelner
YES
16 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL ISSUE 2 01/2004
Copyright © 2003 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 17

NHL-10
RF Troubleshooting CCS Technical Documentation
Measurement points in the Receiver
Figure 8: Measurement points at the RX SAW filters –Z602, Z603, Z604
Figure 9: Measurement points for I/Q baseband signals
ISSUE 2 01/2004 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL 17
Copyright © 2003 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 18

NHL-10
CCS Technical Documentation RF Troubleshooting
Figure 10: Measurement points for RX I/Q digital signals
Figure 11: Measurement points at the Antenna switch
18 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL ISSUE 2 01/2004
Copyright © 2003 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 19

NHL-10
RF Troubleshooting CCS Technical Documentation
Tuning of the RX Using Phoenix
RX Channel Select Filter Calibration
This calibration is calibrating the Baseband filter inside Mjølner ASIC. It is done by internally
measuring a prototype filter, for this reason the calibration is done once, not separately for all
three bands.
• Select Tuning -> RX Channel Select Filter Calibration.
• Press Tune.
RX channel select filter calibration is finished.
RX Calibration
The RX Calibration is used to determine the gain at different gain settings for the front-end and
the Mjølner ASIC and needs to be done in all three bands.
RX-calibration requires an external signal generator.
• Select Tuning -> RX calibration.
• Select band: GSM900.
ISSUE 2 01/2004 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL 19
Copyright © 2003 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 20

NHL-10
CCS Technical Documentation RF Troubleshooting
• Press Start.
• Follow the instructions in the pop–up window.
• Press OK.
20 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL ISSUE 2 01/2004
Copyright © 2003 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 21

NHL-10
RF Troubleshooting CCS Technical Documentation
• Press Save & Continue.
• Press OK and continue.
For GSM1900 just repeat the same procedure as for GSM900/GSM1800. If the calibration is
OK, you should see “RX calibration was completed successfully” on the display.
ISSUE 2 01/2004 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL 21
Copyright © 2003 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 22

NHL-10
CCS Technical Documentation RF Troubleshooting
RX Band Filter Response Compensation
The Rx Band Filter Response Compensation has nine steps for each band.
The RF Band Filter Response Compensation requires an external signal generator.
• Select Tuning -> RX Band Filter Response Compensation.
• Select Manual.
22 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL ISSUE 2 01/2004
Copyright © 2003 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 23

NHL-10
RF Troubleshooting CCS Technical Documentation
• Follow the instructions given in the following pop-up window . There are nine steps in
all.
• After completing the nine steps of calibration at nine frequencies, press Save & Con-
tinue.
ISSUE 2 01/2004 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL 23
Copyright © 2003 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 24

NHL-10
CCS Technical Documentation RF Troubleshooting
Repeat all steps as for GSM900 for the GSM1800 band. Follow all the instructions in the popup window. Repeat the procedure for GSM1900.
The tuning is completed.
24 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL ISSUE 2 01/2004
Copyright © 2003 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 25

NHL-10
RF Troubleshooting CCS Technical Documentation
Transmitter Troubleshooting
General Description
A simple block diagram of the TX part of the phone is shown in the fo llowing figure. The voice
or data signals to be transmitted come from the UEME IC in the BB (Base Band) area, and go
to the Mjølner IC, where they are up-converted to RF. The TX signals going from UEME to Mjølner are called the IQ signals, and consist of two balanced signals { TXIN, TXIP } and { TXQN,
TXQP }, i.e. a total of four signal lines. In addition to the IQ-signals, there are also control signals going between BB and RF.
Figure 1: TX RF Block Diagram
BB-RF
Interface
Signals:
From UEME:
TXIQ
TXC
From UPP:
TXP
RFBUSCLK
RFBUSEN1
RFBUSDA
RESET
Mjølner
4
4
1/2
4
1/4
2
1800 / 1900MHz
900MHz
SAW
2
VPD_900
VPD_1800
V_BAT
VTXB_900 (BUFFER BIAS)
Discrete
TX buffer/amp
PA
Coupler Ant-Switch
VBD (DIODE BIAS)
Power
Detect
Power Loop Filter
DET
Synthesizer
LO
(LO=Local Oscillator)
The picture below shows the two shielding cans where the TX circuitry is located (the lid has
been removed). The shielding can on the right side contains BB-RF interface cir cuitry, the Mjølner RF system IC, a SAW filter for the EGSM band, and a balun for the DCS/PCS band. The
shielding can on the left side contains the power amplifier (PA), the EGSM pre-amplifier, the
directional coupler, the power detector, and the Antenna Switch Module (ASM).
ISSUE 2 01/2004 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL 25
Copyright © 2003 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 26

NHL-10
CCS Technical Documentation RF Troubleshooting
Figure 2: GSM RF area
Directional
Coupler
Power
Detector
Circuit
Power
Amplifier
Preparation for Fault Finding
1 Place phone (mechanics removed) on module jig.
2 Connect the module jig to the PC via a DAU-9S cable.
3 Connect the module jig to the power supply (4.2V).
ASM
EGSM
Pre-Amp
DCS/PCS
Balun
Up-mixer bias
networks
(EGSM/DCS/PCS)
EGSM
SAW Filter
Mjolner
4 Connect the RF output to a spectrum analyzer or another measurement instru-
ment.
Use a 10dB attenuator at the input to spectrum analyzer to avoid damaging it.
5 Make sure the dongle is connected and start Phoenix.
6 In Phoenix, select File -> Open Product -> NHL-10 6600 Product Menu.
7 Select Testing -> RF Controls.
8 From the toolbar, set Operating Mode to Local.
9 Select band: GSM900, GSM1800 or GSM1900.
10 Set Operation Mode to Burst.
11 Set Active Unit to TX.
12 Set TX Data Type to All1.
26 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL ISSUE 2 01/2004
Copyright © 2003 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 27

NHL-10
RF Troubleshooting CCS Technical Documentation
13 Set RX/TX Channel to 37 for GSM900, 700 for GSM1800 or 661 for GSM1900.
14 Set TX PA Mode to Free.
15 Set TX Power Level to 5 in GSM900, otherwise to 0.
Phoenix should now look as shown in the following figure.
ISSUE 2 01/2004 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL 27
Copyright © 2003 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 28

NHL-10
CCS Technical Documentation RF Troubleshooting
Fault-finding chart: TX-BB interface and control signals
Figure 3: Fault finding chart of BB-TX interface & some control signals
Start
Using a multimeter, check power supply lines to Mjolner:
Line
VR1a 4.75V J612
VR2 2.78V J613
VR3 2.78V J614 (J601)
VR5 2.78V J616
VR6 2.78V J617
VR7 2.78V J618
Using the oscilloscope, check TXC and TX IQ lines from UEME to Mjolner:
TXIOUTP R715 1.1Vdc 0.4Vp-p 67kHz
TXIOUTN R715 1.1Vdc 0.4Vp-p 67kHz
TXQOUTP R716 1.1Vdc 0.4Vp-p 67kHz
TXQOUTN R716 1.1Vdc 0.4Vp-p 67kHz
Using the oscilloscope, check TXP from UPP:
Using the oscilloscope, check control signals from Mjolner to ASM1:
1
Testpoint DC Voltage AC Voltage Frequency
Line
TXC J611 Depends on the power level 217Hz
Line
TXP J610 1.8V 217Hz
Testpoint GSM900 GSM1800 GSM1900 Period
Line
Cont1 R702 0V 2.7V 2.7V 4.615ms
Cont2 R703 0V 2.7V 2.7V 4.615ms
Cont3 R701 2.7V 0V 0V 4.615ms
=
Use Phoenix to set TX_Data_Type to 'Random'
Voltage Test Points
OK
OK
Testpoint Vpp Frequency
OK
OK
and to set TX Power Level to '5'
Not OK
Check UEME
(D190) in BB area
Not OK
Not OK
(D100) in BB area
Not OK
Check UEME
(D190) in BB area
Check UPP
Check serial
interface between
Mjolner & UPP
VR3
VR6
Mjolner output
bias network
VR7
VR2
TXIOUTP
TXIOUTN
VR5
VR1A
TXC
TXQOUTP
TXQOUTN
Cont1Cont2Cont3
TXP
Use the oscilloscope to check the voltage supply line to
the transistorized pre-amplifier: VTXB_900
Typical oscilloscope plots
of the four TXIQ-lines:
TXC-signal
EGSM900
channel = 37
PL = 5
Check serial
Not OK
interface between
Mjolner & UPP
Figure 4: Oscilloscope screen shots
zoom
1.1Vdc
~67kHz
TXP-signal
6
0.5Vpp
waveform for all 1's
4.615ms
VTXB_900
2.7V
Ctrl signals to ASM:
( DCS/PCS )
Cont1
Cont2
4.615ms
2.7V
4.615ms
4.
28 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL ISSUE 2 01/2004
Copyright © 2003 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 29

NHL-10
RF Troubleshooting CCS Technical Documentation
Fault-finding chart: RF side of transmitter
In Phoenix select:
Active unit=TX, Operation Mode=Burst, TxPA Mode=Free,
TxData Type=Random, and for each band:
GSM900, channel=37, PL5
GSM1800, channel=700, PL0
GSM1900, channel=661, PL0
Measure power at RF connec tor:
GSM900: Power between 31 & 35dBm
GSM1800 & GSM1900: Power between 28 & 32dBm
NOK
Signal found?
Yes
Check power
control loop
OK
Correct signal at
ASM output?
No
Correct signal at
ASM input?
No
Correct signal at
directional coupler
input?
No
Correct signal at
power amplifier
input?
EGSM => check pre-amp & SAW
Check bias network at output of Mjolner IC
(Discrete components: R's, L's & C's)
Check fault finding chart of
No
DCS/PCS => check balun
OK
OK
TX-BB interface
OK
Mjolner broken?
Replace it & retune RF
Search for output signal with
No
500MHz span. Signal found
on incorrect frequency?
Yes
RF connector broken?
Yes
ASM broken?
Yes
Yes
directional coupler broken?
Yes
Check power
control loop
Spectrum analyzer screen shots
Measurements done at RF connector
OK
Transmitter is OK
OK
Check all
power levels
OK
power amplifier broken?
Tune TX power
synthesizer
4.615ms
OK
VPD_900 R818
Check power
control loop
Check power
control loop
Testpoint
Line
VBD R801
DET R802
Note:
2.7V
NOK NOK
Yes
Trouble-shoot
Using the oscilloscope, check power control loop signals
(Compare to oscilloscope screen plots shown below)
When using the SA to check if a signal is 'correct' at a certain
point (at input/output of ASM, directional coupler, PA, SAW-
filter, balun, etc.), the best way to do so is to compare with the
signal of a working sample of a phone. The reason for this is
that the level seen on the SA screen will vary depending on the
type of probe, the impedance of the measurement point, etc.
VBD: bias to pwr detector
EGSM
input
EGSM
output
PA
VPD_900
SAW
VPD_1800
DCS/PCS
PA
input
DCS/PCS
VTXB_900
(pre-amp bias)
Balun
output
ASM
DCS/PCS
input
ASM
TX
output
EGSM
output
PA
DCS/PCS
output
PA
ASM
EGSM
input
DET
VBD
Span = 3MHz
EGSM900
channel = 37
PL = 5
Span = 0Hz
DET: output of pwr detector
GSM900, PL=5
VPD_900: input voltage ctrl signal to PA
GSM900, PL=5
ISSUE 2 01/2004 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL 29
Copyright © 2003 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 30

NHL-10
CCS Technical Documentation RF Troubleshooting
Transmitter Tuning
Introduction
In the transmitter, there are two kinds of tunings that can be performed. These are IQ-tuning
and power level tuning. In general, different repairs require different tunings. In order to decide
which tuning is necessary after a repair, it is important to understand well the functionality of
the repaired circuit. In general, it is recommended that if any TX component is changed, both
these tunings are done.
Note: All tunings are done in local mode using Phoenix to control the phone.
TX IQ Tuning
The tuning must be carried out in all three bands. In addition to Phoenix, a spectrum analyzer
(SA) is needed. Connect the SA to the RF connector of the module jig. The settings of the spectrum analyzer will depend on the band to be tuned. The following table summarizes the settings
for each of the three bands.
Center frequency
Frequency span
Resolution
Bandwidth
Video Bandwidth
Sweep Time
Trace Type
Detector Type
Reference Level
Marker 1
Table 1: Spectrum Analyzer Settings
EGSM900 GSM1800 GSM1900
897.4MHz 1747.8MHz 1880MHz
300kHz 300kHz 300kHz
3kHz 3kHz 3kHz
3kHz 3kHz 3kHz
3 sec 3 sec 3 sec
Clear/Write Clear/Write Clear/Write
Max Peak Max Peak Max Peak
35dBm 35dBm 35dBm
897.33229 MHz 1747.73229 MHz 1879.93229 MHz
Marker 2
Marker 3
For this tuning, two windows of Phoenix must be open: (1) Testing -> RF Controls, and (2)
Tuning -> TX IQ Tuning, as seen in figures below.
30 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL ISSUE 2 01/2004
897.4MHz 1747.8MHz 1880MHz
897.46771MHz 1747.86771MHz 1880.06771MHz
Copyright © 2003 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 31

NHL-10
RF Troubleshooting CCS Technical Documentation
Figure 1: Phoenix set-up
Figure 2: Phoenix set-up
After opening the two before-mentioned windows, Phoenix should look as shown in the following figure.
ISSUE 2 01/2004 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL 31
Copyright © 2003 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 32

NHL-10
CCS Technical Documentation RF Troubleshooting
Figure 3: Phoenix set-up
The following table summarises the settings of the RF control window for the IQ tuning of the
three bands.
Table 2: RF Control Window Settings
Band
TX Data
Type
TX Power
Level
RX/TX
Channel
GSM900 All 1 5 37
GSM1800 All 1 0 700
GSM1900 All 1 0 661
To start the IQ tuning, press Start in the IQ Tuning window.
32 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL ISSUE 2 01/2004
Copyright © 2003 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 33

NHL-10
A
5
5
RF Troubleshooting CCS Technical Documentation
The spectrum analyzer screen should now look similar to that of the figure below (GSM900
case).
Figure 4: Spectrum analyzer screen shot when performing IQ tuning
Ref Lvl
Ref Lvl
35 dBm
35 dBm
3
27.5 dB Offset
30
20
10
0
-10
-20
-30
-40
-50
Marker 1 [T1]
33.35 dBm
897.33229000 MHz
1
RBW 3 kHz
VBW 3 kHz
SWT 3 s
2
RF Att 30 dB
Unit dBm
1 [T1] 33.35 dBm
897.33229000 MHz
2 [T1] -6.76 dBm
897.40000000 MHz
3 [T1] -10.74 dBm
897.46771000 MHz
3
A
1M
-60
-6
30 kHz/Center 897.4 MHz Span 300 kHz
Date: 14.JAN.2002 13:11:55
The purpose of this tuning is to reduce the frequency components at marker 2 (carrier leakage)
and marker 3 (+67kHz / upper sideband) as much as possible. Adjust the TXI DC Offset and
the TXQ DC Offset buttons in the TX IQ Tuning window so that the carrier level (marker 2)
reaches a minimum. After this adjustment, the carrier (marker 2) should be at least 40dB below
the lower side band (marker 1).
Next, use the Amplitude difference and the Phase difference buttons in the TX IQ Tuning
window to adjust the upper side band (marker 3) to a minimum. Now, marker 3 should also be
at least 40dB below marker 1.
At this point, the spectrum analyzer screen should look similar to that of the figure below.
ISSUE 2 01/2004 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL 33
Copyright © 2003 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 34

NHL-10
CCS Technical Documentation RF Troubleshooting
After reducing the amplitude of the frequency components at marker 2 and 3 to a minimum,
press Save & Continue. The EGSM tuning has now been completed.
Now, using the spectrum analyzer settings of Table 1, and the RF control settings of Table 2,
follow exactly the same procedure to perform IQ tuning in the GSM1800 and GSM1900 bands.
TX Power Level Tuning
This tuning is done separately in all three bands, and requires a spectrum analyzer to measure
the burst power of the GSM RF signal. When measuring the RF output (burst) power on a spectrum analyzer, use the settings found in the following table:
34 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL ISSUE 2 01/2004
Copyright © 2003 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 35

NHL-10
RF Troubleshooting CCS Technical Documentation
Table 3: Spectrum Analyzer Settings
EGSM900 GSM1800 GSM1900
Center frequency 897.4MHz 1747.8MHz 1880MHz
Frequency span Zero-span Zero-span Zero-span
Resolution Bandwidth 1MHz 1MHz 1MHz
Video Bandwidth 1MHz 1MHz 1MHz
Sweep Time 1ms 1ms 1ms
Trigger Type Video Video Video
Trace Type Clear/Write Clear/Write Clear/Write
Detector Type Max Peak Max Peak Max Peak
In Phoenix, select Tuning -> TX Power Level Tuning.
Figure 5: Phoenix menu select
Phoenix should now as shown in the figure below.
ISSUE 2 01/2004 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL 35
Copyright © 2003 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 36

NHL-10
CCS Technical Documentation RF Troubleshooting
Figure 6: Phoenix power level tuning menu
Connect the module jig RF output to the measurement instrument. In the EGSM band the power must be tuned in both high and low TX PA mode. In the two upper bands (GSM1800 and
GSM1900) there is only one mode.
For each band, tune the power by adjusting the coefficient in the Tx Power Level Tuning window in Phoenix until the target level is reached (measured on the spectrum analyzer). Re member to take into account the external power loss, i.e. the loss of the cable and the external
attenuator at the spectrum analyzer input. The coefficient must be tuned for the base level and
other levels, marked with bold letters in Phoenix (GSM900: PL19/15/7/5, GSM1800/1900:
PL15, 11, 0).
When the tuning has been completed, press Save & Continue to save the new tuning values
into the phone memory.
The following figure shows the power level tuning at the GSM900 band.
36 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL ISSUE 2 01/2004
Copyright © 2003 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 37

NHL-10
RF Troubleshooting CCS Technical Documentation
Figure 7: Phoenix screen shot
The next figure shows the spectrum analyzer screen shot associated with the above Phoenix
screen shot.
Figure 8: Spectrum analyzer screen short during power level tuning
ISSUE 2 01/2004 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL 37
Copyright © 2003 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
Page 38

NHL-10
CCS Technical Documentation RF Troubleshooting
This page has been deliberately left blank
38 COMPANY CONFIDENTIAL ISSUE 2 01/2004
Copyright © 2003 Nokia. All Rights Reserved.
 Loading...
Loading...