Page 1
SDI-TD-MUX-4 / SDI-TD-DMUX-4
4 x SD-SDI / DVB-ASI over HD-SDI
Time Division Multiplexer / De-Multiplexer
User manual
Rev. N
Nevion
Nordre Kullerød 1
3241 Sandefjord
Norway
Tel: +47 33 48 99 99
nevion.com
Page 2
SDI-TD-MUX-4 / SDI-TD-DMUX-4 Rev. N
Nevion Europe
P.O. Box 1020
3204 Sandefjord, Norway
Support phone 1: +47 33 48 99 97
Support phone 2: +47 90 60 99 99
Nevion USA
1600 Emerson Avenue
Oxnard, CA 93033, USA
Toll free North America: (866) 515-0811
Outside North America: +1 (805) 247-8560
E-mail: support@nevion.com
See http://www.nevion.com/support/ for service hours for customer support globally.
Rev.
Repl.
Date
Sign
Change description
N
12
2015-05-14
MB
Cover page update; DoC removed; no other
changes to content
12
11
2012-04-04
TB
Clarified the ASI data rate in the specification lists
(updated chapters 1, 2 and 3).
11
10
2011-04-15
TB
Corrected error in the description of the DIPs for
fallback to internal video generator.
10 - 2011-01-31
TB
Based on version 5.4 of MUX and DMUX codes and
combined from earlier FLP3 versions of the manual.
Nevion Support
Revision history
Current revision of this document is the uppermost in the table below.
nevion.com | 2
Page 3

SDI-TD-MUX-4 / SDI-TD-DMUX-4 Rev. N
Contents
1 The SDI-TD-MUX-4 and SDI-TD-DMUX-4 at a glance ............................................ 4
1.1 Product versions .............................................................................................................. 4
2 Multiplexer specifications ......................................................................................... 5
3 De-multiplexer specifications ................................................................................... 6
4 Description ............................................................................................................... 7
5 Configuration ........................................................................................................... 9
5.1 Multicon GYDA mode ...................................................................................................... 9
5.2 MUX DIP switches ..........................................................................................................16
5.3 DMUX DIP switches .......................................................................................................17
6 Connections ........................................................................................................... 18
6.1 Power connections .........................................................................................................18
6.2 Backplane ......................................................................................................................18
6.3 The main board ..............................................................................................................19
7 Operation ................................................................................................ ............... 21
7.1 Front panel LED indicators .............................................................................................21
7.2 GPI alarms .....................................................................................................................22
7.3 RS422 commands ..........................................................................................................22
8 Laser safety precautions ........................................................................................ 27
General environmental requirements for Nevion equipment..................................... 28
Product Warranty ...................................................................................................... 29
Appendix A Materials declaration and recycling information..................................... 30
nevion.com | 3
Page 4

SDI-TD-MUX-4 / SDI-TD-DMUX-4 Rev. N
SDI-TD-MUX-4
4xSD-SDI/DVB-ASI multiplexer with electrical HD-SDI output.
SDI-TD-MUX-4-T
4xSD-SDI/DVB-ASI multiplexer with simultaneous electrical and
optical HD-SDI outputs.1
SDI-TD-DMUX-4
HD-SDI to 4xSD-SDI/DVB-ASI de-multiplexer with electrical input.
SDI-TD-DMUX-4-R
HD-SDI to 4xSD-SDI/DVB-ASI de-multiplexer with both electrical
and high sensitivity 9/125µm single mode optical input.
1
1 The SDI-TD-MUX-4 and SDI-TD-DMUX-4 at a glance
The SDI-TD-MUX-4 is a Flashlink time-division multiplexer (TDM) that allows any
combination of four SD-SDI or DVB-ASI inputs to be transported over a single HD-SDI link
according to the SMPTE 346M-2000 standard.
The SDI-TD-DMUX-4 is a Flashlink time division de-multiplexer that recovers the four SDSDI or DVB-ASI input signals from the SMPTE 346M-2000 compliant transport signal.
The key features of the combination SDI-TD-MUX-4 / SDI-TD-DMUX-4 include:
Accepts any synchronous or asynchronous SD-SDI 270 Mbps input format as well as
270 Mbps DVB-ASI.
Automatic input format detection for each channel.
Mix of input formats allowed and correct format recovered at the de-multiplexer side.
Built-in routing switcher at both ends.
Separate stream clock reference data for each channel is transferred for remote clock
regeneration.
The four streams embedded in the HD-SDI are completely independent, no
contamination of remaining streams when one or more inputs are lost.
High performance optics for short and long haul applications available, including
CWDM laser option.
Optical and electrical 1.485 Gbps HD output TDM available simultaneously.
Change-over functionality between de-multiplexer electrical and optical inputs.
The transport signal is compliant with the SMPTE-346M-2000 standard, allowing use
of a standard HD infrastructure for transport and switching of the multiplexed signal.
EDH handling for the SD-SDI signals.
Multicon interface allows remote control, status monitoring, error reporting and SNMP
support.
1.1 Product versions
Several wavelength/power options exist. From a control perspective all these versions are identical,
but the laser control block reports its parameters to the system controller.
nevion.com | 4
Page 5

SDI-TD-MUX-4 / SDI-TD-DMUX-4 Rev. N
Number of inputs
4 independent SD-SDI, DVB-ASI or SDTI
Data rates
270 Mbps, any DVB-ASI payload data rate2
Equalization
Automatic up to 300m
Impedance
75 ohm
Return loss
>15dB @ 270MHz
Connector
BNC
Output signal
HD-SDI with TDM payload according to SMPTE 346M-2000
Data rate
1485 Mbps
Impedance
75 ohm
Return loss
>15dB @ 1485MHz
Jitter (UI = Unit Interval)
Max. 0.2UI
Peak to peak signal level
0.8V ±0.1V
Signal polarity
Non-inverting
Connector
BNC
Output signal
HD-SDI, TDM payload according to SMPTE 346M-2000
Transmission circuit fiber
Single Mode
Light source
F-P / DFB laser
Optical power
-7.5dBM @ 1310nm (F-P laser), 0 dBm (DFB laser)
Optical center wavelength
1310nm, 1550nm, CWDM according to ITU-T G.694.2
Max. wavelength drift
±20nm (F-P lasers), ±6nm (DFB lasers)
Jitter (UI = Unit Interval)
Max. 0.2UI @ 1485Mbps
Connector return loss
better than 40dB w/ SM fiber
Connector
SC/UPC
Temperature range
0 to +45 °C
Power consumption
+5V/3.5 W, +15V/1.0W
(4.5W when running on a single +5V supply)
Control
RS-422, Multicon GYDA enabled, SNMP
Electrical and optical delay
Less than 100 us (combined through MUX and DEMUX)
In addition comes 5 us/km of fiber signal propagation time
SMPTE
SMPTE 346M-2000, SMPTE 292M, SMPTE 259M,
SMPTE 305.2M, SMPTE 297M, SMPTE RP165
DVB-ASI
EN50083-9
2
2 Multiplexer specifications
Electrical input
Electrical output (standard)
Optical output (optional)
Electrical
Latency
Supported standards for electrical and optical ports
Early versions of the MUX/DMUX modules were limited to DVB-ASI payload data rates ≤ 35 Mbps.
nevion.com | 5
Page 6

SDI-TD-MUX-4 / SDI-TD-DMUX-4 Rev. N
Input signal
HD-SDI, TDM payload according to SMPTE 346M-2000
Sensitivity
Better than -25dBm
Max multi mode fiber length
300m (version SDI-TD-DMUX-4-RM)
Detector overload threshold
Min. -6dBm
Detector damage threshold
> +1dBm
Optical wavelength
1200 - 1620nm
Transmission circuit fiber
Single Mode 9/125µm or multimode 50/125µm
Connector return loss
better than 40dB w/ SM fiber
Connector
SC/UPC
Output signal
HD-SDI with TDM payload according to SMPTE 346M2000
Data rate
1485 Mbps
Equalization
Automatic up to 100m
Impedance
75 ohm
Return loss
>15dB @ 270MHz
Signal level
Nom. 800mV
Connector
BNC
Number of outputs
4 independent SD-SDI, DVB-ASI or SDTI
Data rates
270 Mbps (see footnote on the previous page)
Impedance
75 ohm
Return loss
>15dB @ 270MHz
Jitter (UI = Unit Interval)
Max. 0.2UI
Peak to peak signal level
0.8V ±0.1V
Signal polarity
Non-inverting
Connector
BNC
Temperature range
0 to +45 °C
Power consumption
+5V/3.5 W, +15V /1.8W
(5.2W when running on a single +5V supply)
Control
RS-422, Multicon GYDA enabled, SNMP
Electrical and optical delay
Less than 100μs (combined through MUX and DEMUX) In
addition comes 5us/km of fiber signal propagation time
SMPTE
SMPTE 346M-2000, SMPTE 292M, SMPTE 259M,
SMPTE 305.2M, SMPTE 297M, SMPTE RP165
DVB-ASI
EN50083-9
3 De-multiplexer specifications
Optical input
Electrical input
Electrical output
Electrical
Latency
Supported standards for electrical and optical ports
nevion.com | 6
Page 7
SDI-TD-MUX-4 / SDI-TD-DMUX-4 Rev. N
4 Description
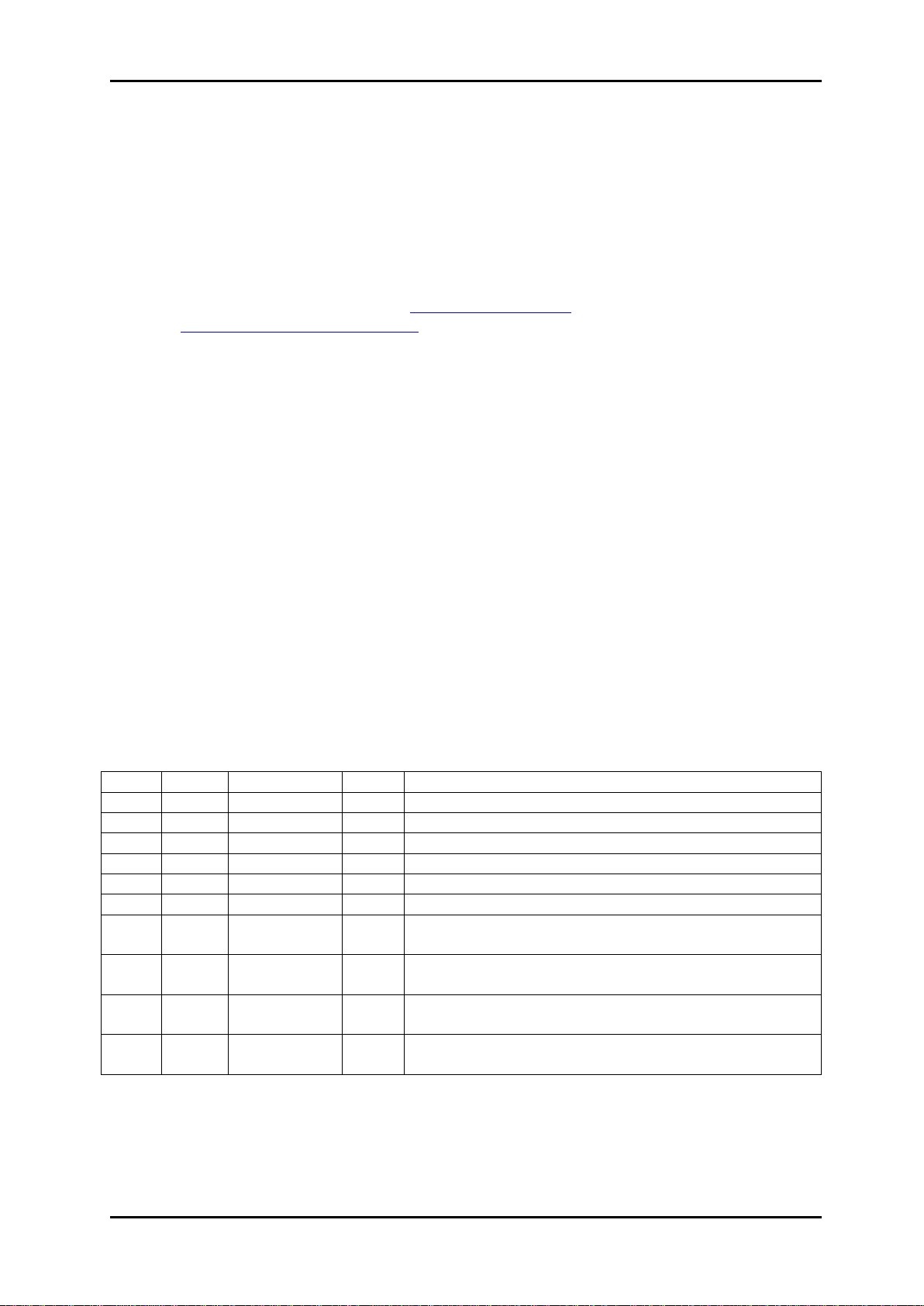
Figure 1: Logical building blocks for SDI-TD-MUX-4(-T)
Figure 2: Logical building blocks for SDI-TD-DMUX-4(-R)
The SDI-TD-MUX-4 board transfers any or all of the four 270 Mbps input signals via an
optical or electrical HD interface according to SMPTE 346M-2000. An SDI-TD-DMUX-4
board is required to reconstruct the four 270 Mbps signals, normally at a remote location and
linked via an optical fiber or an electrical coax cable. The inputs to the SDI-TD-MUX-4 can be
any combination of 270 Mbps SD-SDI or DVB-ASI (188 or 204 word packets).
The output from the SDI-TD-MUX-4 module is either electrical HD according to the SMPTE
346M-2000 standard, or simultaneous electrical and optical HD according to the same
standard if an optional laser module is purchased (in which case the module will identify itself
as an SDI-TD-MUX-4-T).
nevion.com | 7
Page 8

SDI-TD-MUX-4 / SDI-TD-DMUX-4 Rev. N
The SDI-TD-DMUX-4 board receives any combination of four 270 Mbps time division
multiplexed SD-SDI or DVB-ASI signals embedded in the 1.485 Mbps HD signal according to
SMPTE 346M-2000. If the customer has purchased an optional pin diode module for optical
input (in which case the module will identify itself as an SDI-TD-DMUX-4-R), there will be an
option available to select either input manually, or to select between them automatically.
All outputs can be either 270 Mbps SD-SDI or DVB-ASI (188 or 204 word packets). Channel
swapping (“shuffler”) is available either from DIP-switches or remotely via the standard
Multicon GYDA interface. Shuffling is available in both modules, in case the two modules are
on different control networks, or only one of the modules is even connected to the control
network. I cases where fewer than four SD signal are transported, the shuffling feature can
also be used to duplicate channels on the outputs, potentially saving a distribution amplifier.
The SD-SDI clocks for each recovered SD channel will be regenerated based on a frequently
received SCR counter (Stream Clock Reference – refer to the SMPTE 346M-2000 standard).
This ensures a stable, low-jitter output.
There are four signal generators available on the board. Each can be set to color bar 525,
color bar 625, black 525 or black 625 from Multicon GYDA. Since the SDI-TD-DMUX-4 does
not have a local clock reference input, a valid SD signal must be present in the HD stream
from the SDI-TD-MUX-4 (i.e. at least one SD signal must be connected to one of the SDI-TDMUX-4 SD inputs) in order to guarantee that the output signals from the test signal
generators in the SDI-TD-DMUX-4 are compliant with the SD clock requirements. The
module will still generate an output based on the video signal that was lost, but without a
clock reference there’s no guarantee that equipment down the signal chain will be able to
lock (or remain locked) to that output.
By default, there is no fallback for missing SD streams. If fallback is set to black or color bar,
the video format (SD-SDI, 525 vs. 625 lines) will be selected automatically based on the
signal that was lost. If the lost signal was DVB-ASI, no fallback will be available, regardless
of the setting.
The board measures the RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indicator) from the optical input.
Normally, the readout (in the Multicon GYDA GUI) shows the signal strength within ±1-2 dB.
However, the measurement is NOT calibrated and the readout should be used as an
indication only. Also, while the readout is fairly linear within a range from -15 dBm to -30
dBm, outside this range the meter will just “bottom out” at -15dBm or -30dBm. If that occurs,
disregard the actual readout but know that the signal is either strong enough with good
margins or too weak to be detectable.
nevion.com | 8
Page 9
SDI-TD-MUX-4 / SDI-TD-DMUX-4 Rev. N
5 Configuration
Both multiplexer and de-multiplexer cards are self-configuring in the sense that they will start
working according to default factory settings once power and input signals are applied.
Signals will be routed straight through without swapping/duplication and SD-SDI/DVB-ASI
will be detected and handled automatically.
Configuration parameters can be changed in two ways, via changes to the DIP switches or
via the system controller Multicon. The 8th DIP from the top of the module is labeled OVR. If
this DIP is set to the ON position, DIP switches 1-7 will control the module. Conversely, if it is
set to the OFF position, DIPs 1-7 are disregarded altogether and the module is controlled
from Multicon GYDA. Default settings as delivered from factory should be all DIPs in the Off
position. The module will then be under Multicon GYDA control.
5.1 Multicon GYDA mode
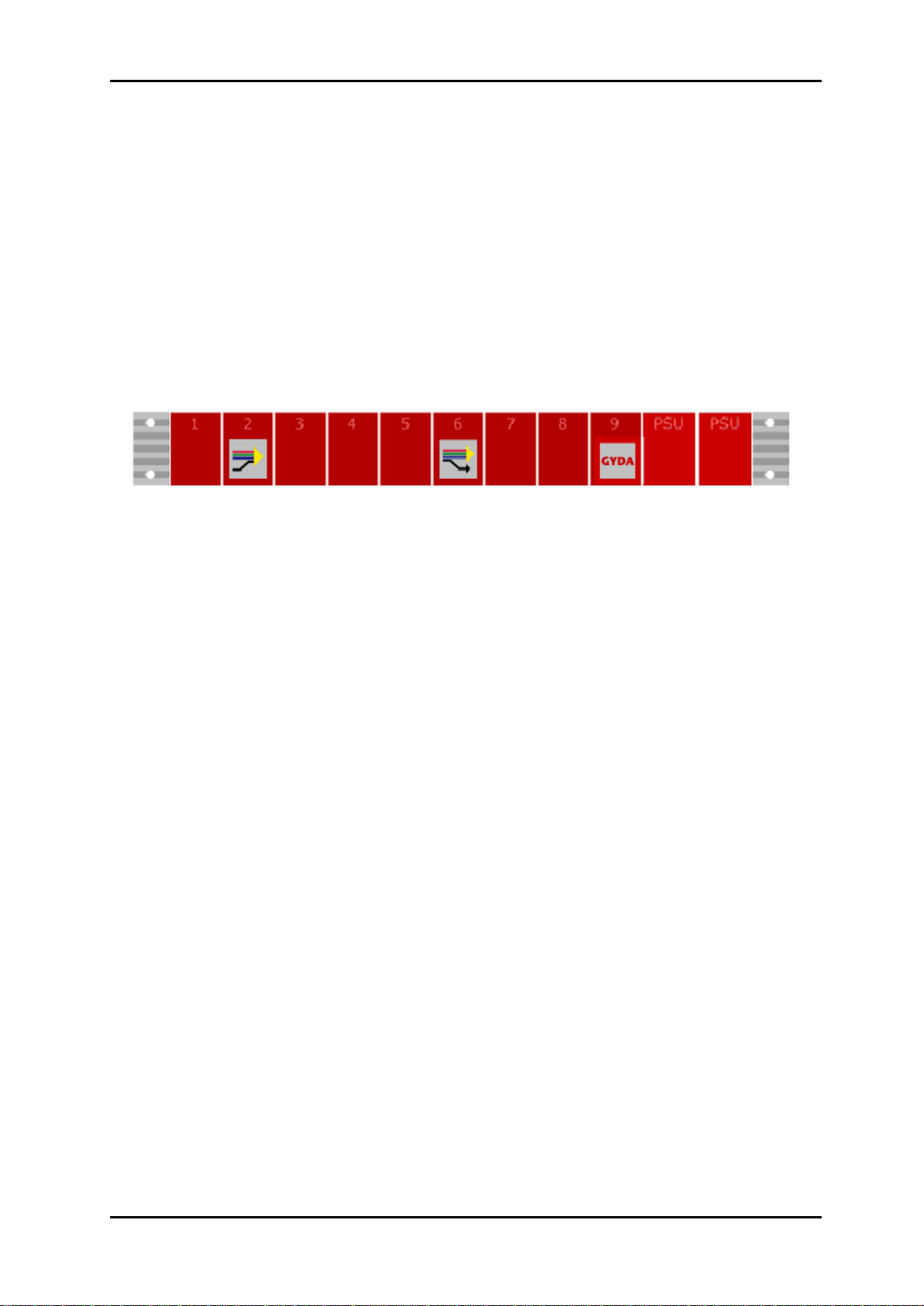
Figure 3: Multicon GYDA presentation of rack with an SDI-TD-MUX-4 module in position 2
Figure 3 shows how Multicon GYDA will present a rack equipped with an SDI-TD-MUX-4
module in rack position 2, an SDI-TD-DMUX-4 module in rack position 6, a Multicon GYDA
module in rack position 9 and a power supply unit in rack positions 10 and 11.
All functions of the card can be controlled through the Multicon GYDA control system. The
Multicon GYDA interface has an information page and a configuration page.
5.1.1 Information page
The information page shows a dynamic block diagram of the board and some additional
information text. The block diagram updates with the board status, showing missing signals
(by red crosses over the appropriate signal lines).
The text table on the information page gives additional information not easily conveyed in a
graphical manner.
nevion.com | 9
Page 10

SDI-TD-MUX-4 / SDI-TD-DMUX-4 Rev. N
Figure 4: The MUX info page in Multicon GYDA.
From the text table, we can read the following: All four cable equalizers are enabled
(“Normal”), as opposed to “Bypassed”. Of the four reclockers, only reclocker 1 has been able
to lock to an input signal. That reclockers 2-4 are unlocked can also be seen from the three
red crosses in the block representation. The locked input is indicated as 270Mbps SD-SDI.
The error counter has found no errors for input 1 (at least not errors of the types that should
be counted), but plenty of errors for inputs 2-4. We can also tell that the voltages are
reasonably close to their nominal values. And last, since this is a board with the laser option,
we can see that the laser is powered and what kind of laser it is (wavelength, power and
type).
nevion.com | 10
Page 11

SDI-TD-MUX-4 / SDI-TD-DMUX-4 Rev. N
Figure 5: The DMUX info page in Multicon GYDA.
From the text table, we can read the following: The electrical input has been manually
selected. This (and the name of the module) also indicates that this board has the optional
optical input installed. No carrier is detected on the optical input. Of the four streams, only
stream 4 can be locked to and recovered. The locked stream is indicated to contain an
270Mbps SD-SDI. The line that says “Routing” is a list of how the streams are routed to the
outputs. In this case we can see that output 1 is routed from stream 4, output 2 from stream
3 and so on. If fallback had been selected for the missing streams, “Stream3”, “Stream 2”
and “Stream 1“ would have been replaced with the texts “Black” or “Cbar”.
The error counter has found no errors for the HD input (at least not errors of the types that
should be counted). We can also see that the voltages are reasonably close to their nominal
values (It is quite normal for the 5V supply to be 0.2V – 0.3V under its nominal value).
nevion.com | 11
Page 12

SDI-TD-MUX-4 / SDI-TD-DMUX-4 Rev. N
5.1.2 Configuration page
Figure 6: The MUX config page in Multicon GYDA.
Starting from the top of the page, the following things can be set/adjusted:
Card label: This field enables the user to set a name for each module (Actually, it’s the slot
in the frame, as the label will persist even if the card/backplane combination is replaced by a
completely different module.) The name will show up above the card type on the info page
and on the conf page, and it will also be shown as a mouse-over text when the mouse cursor
is held over the card’s icon in the pictured rack.
Locate card: Flashes the 4 LEDs on the front of the module at about 0.5Hz for the number
of seconds the user specifies.
Firmware upgrade: The firmware for the onboard microcontroller and the FPGA can both be
upgraded, if needed. This line only shows up if the Multicon GYDA system controller has
found a folder containing Flashlink firmware files. Contact Nevion support if you need an
updated firmware.
nevion.com | 12
Page 13

SDI-TD-MUX-4 / SDI-TD-DMUX-4 Rev. N
Cable equalizers: (Stored setting) ‘Normal’ means that the cable equalizer is enabled. ‘Eq
bypass’ means that the cable equalizer is bypassed (disabled).
Shuffler: (Stored setting) this is where each transport stream (in the SMPTE 346M-2000
compatible HD video) has a physical input assigned to it. In this particular case a reversediagonal is formed; all four inputs are transported, but they have all changed places.
Input 1…4 integrity: (Stored setting) sets the maximum error rate or the maximum number
of errors that can be present before Multicon GYDA sets off an alarm.
Input 1-4 integrity: (Stored setting) This setting is common for all the four error counters and
sets which types of errors should be counted and which should be ignored.
Laser: (Stored setting) this control is only available for boards with the optional optical
output. The only setting available for the laser is power On or Off. All other settings should be
done at the factory.
Figure 7: The DMUX config page in Multicon GYDA.
Starting from the top of the page, the following things can be set/adjusted:
Card label: See MUX description.
nevion.com | 13
Page 14

SDI-TD-MUX-4 / SDI-TD-DMUX-4 Rev. N
Locate card: See MUX description.
Firmware upgrade: See MUX description.
Input selector: (Stored setting). This control is only available for boards with the optional
optical input. Here the user can select to force the input to be taken from either the electrical
or the optical input, or allow the card to automatically select between them.
In “Auto (pri opt)”, the operation is like this:
1. If there is a carrier on the optical input, this input will always be preferred.
2. If there is no carrier on the optical input, the electrical input will only be selected if it
has got a carrier.
3. There is no check for signal lock and there are no significant delays before swapping
to the other input.
In “Auto (latch)” mode, the operation is like this:
1. On power-on, the board will start with selecting the optical input as default.
2. If, at any time, the lock is lost on the presently selected input, after a ~one second
delay, the board will first check if there is a carrier on the other input. If it isn’t, the
input select will remain unchanged. If there is a carrier on the other input, the board
will swap to that input and try to lock to it.
3. If both inputs have a carrier, but the board is incapable of locking to any of the
signals, the board will toggle between the two inputs until a lockable signal is applied
to either of the two inputs. Then, this input will be selected. The toggling rate is about
once per second while searching for a lockable signal.
4. If none of the inputs has a carrier, the board will remain at its present input selection
(the last one it successfully locked to or tried to lock to).
5. If there is a carrier on only one of the inputs, only this input will be selected as long as
this is the case (no toggling).
6. There will always be a one second delay before giving up the presently selected
signal on loss of lock.
7. There will be no non-volatile memory for keeping the last selected input when in auto
mode. The above algorithm will always start working to find a signal when starting the
board. This means that, after power-on, the optical input will always win if there is a
lockable signal present at that input.
Shuffler: (Stored setting) Each SD output is here assigned to one of the transport streams
(in the SMPTE 346M-2000 compatible HD video) or to one of the onboard generators. Note
that in this particular case a reverse-diagonal is formed, and when combined with the
reverse-diagonal we saw in the MUX, this means that input 1 on the MUX side is routed out
as output 1 on the DMUX side, input 2 is routed out as output 2, and so forth.
The option also exists to force one or more of the outputs to internal generators. This is
primarily useful during site installation, to validate parts of the signal chain.
Fallback (for SD-SDI only): If/when the SD-SDI is lost on the MUX side, or if the HD link
between the MUX and the DMUX breaks down, the DMUX has optional fallback to internal
generators. The video format (525 vs. 625 lines) will then be determined by the last valid
video to be seen by that particular output, while the user selects the video pattern (black
picture or color bars). If no fallback is selected, the output driver will simply be turned off
when the card can no longer output a valid SD signal. This is also the behavior when
transporting DVB-ASI: Since the card has no onboard DVB-ASI generators, and thus no valid
fallback for DVB-ASI, the fallback logic will always treat a DVB-ASI gone missing as if the
fallback option for that particular output was “None”. In other words, when a DVB-ASI
nevion.com | 14
Page 15

SDI-TD-MUX-4 / SDI-TD-DMUX-4 Rev. N
transport stream disappears, the outputs connected to that stream will simply be turned off,
until a valid stream (SD-SDI or DVB-ASI) reappears.
Signal integrity: (Stored setting) sets the maximum error rate or the maximum number of
errors that can be present before Multicon GYDA sets off an alarm. Also sets which types of
errors should be counted and which should be ignored.
nevion.com | 15
Page 16

SDI-TD-MUX-4 / SDI-TD-DMUX-4 Rev. N
Switch #
Function name
Function DIPs
Comment
1 - 3
Shuffler
Input to stream allocation:
RD0 RD1 RD2 S1 S2 S3 S4
[OFF][OFF][OFF]: 1 2 3 4
[ON ][OFF][OFF]: 1 1 3 4
[OFF][ON ][OFF]: 1 1 3 3
[ON ][ON ][OFF]: 1 1 1 4
[ ---- ][ ---- ][ON ]: 1 1 1 1
( ---- means “Don’t care”. As long as
RD2=ON, any combination of
values for RD0 and RD1 will give
the same result.)
Changing the
shuffler DIPs to
something other than
[OFF][OFF][OFF] will
substitute one or
more of the inputs 24 for a duplicate of
input 1 or 3. Usually
this should rather be
done on the DMUX
side.
4 - 6
Cable equalizer
bypass
EQ0 EQ1 EQ2
[OFF][OFF][OFF]: Bypassed: none
[ON ][OFF][OFF]: Bypassed: 1
[OFF][ON ][OFF]: Bypassed: 1+2
[ON ][ON ][OFF]: Bypassed: 1+2+3
[ ---- ][ ---- ][ON ]: Bypassed: all
( ---- means “Don’t care”. As long as
EQ2=ON, any combination of
values for EQ0 and EQ1 will give
the same result.)
Changing the cable
equalizer DIPs to
something other than
[OFF][OFF][OFF] will
bypass one or more
of the cable
equalizers. This will
normally result in
reduced
performance. Only
use this feature if
you understand why
you would want to do
it. 7 ---
---
Reserved
8
OVR
Off: Multicon GYDA mode
On: Manual mode
This DIP is only read
at power up.
OVR is short term for
Multicon GYDA
override.
Switch 1 (’off’ / 0)
Switch 2 (’off’ / 0)
Switch 3 (’off’ / 0)
Switch 4 (’off’ / 0)
Switch 5 (’on’ / 1)
Switch 6 (’off’ / 0)
Switch 7 (’on’ / 1)
Switch 8 (’on’ / 1)
Remote Distribution
Shown: 1=>1 , 2=>2 , 3=>3 , 4=>4
Cable Equalisers
Shown: 1 and 2 bypass, 3 and 4 enabled
Spare (not in use).
Override. Shown: DIP switch control only
(Upper left corner of board)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
RD0
RD1
RD2
EQ0
EQ1
EQ2
---
OVR
OFF ON
5.2 MUX DIP switches
nevion.com | 16
Table 1: MUX DIP switch functions
Figure 8: MUX DIP switch settings exemplified
Page 17

SDI-TD-MUX-4 / SDI-TD-DMUX-4 Rev. N
Switch #
Function name
Function DIPs
Comment
1 - 3
Shuffler
Stream to output allocation:
1 2 3 O1 O2 O3 O4
[OFF][OFF][OFF]: 1 2 3 4
[ON ][OFF][OFF]: 1 1 3 4
[OFF][ON ][OFF]: 1 1 3 3
[ON ][ON ][OFF]: 1 1 1 4
[ ---- ][ ---- ][ON ]: 1 1 1 1
( ---- means “Don’t care”. As long as
RD2=ON, any combination of
values for RD0 and RD1 will give
the same result.)
Changing the
shuffler DIPs to
something other than
[OFF][OFF][OFF] will
substitute one or
more of the inputs 24 for a duplicate of
input 1 or 3. This
means that the card
can be used as a
distribution amplifier.
4 - 5
Input selector
4 5 INPUT
[OFF][OFF]: Optical (manually)
[ON ][OFF]: Electrical (manually)
[OFF][ON ]: Auto (pri. optical)
[ON ][ON ]: Auto (latching)
For boards without
the optional optical
input, electrical input
will always be
selected and these
DIPs have no
function.
6 - 7
Video fallback
6 7 Output video
[OFF][OFF]: Black, auto vstd.
[ON][OFF ]: Color bar, auto vstd.
[OFF ][ON]: No fallback
[ON ][ON ]: No fallback
(auto vstd. = automatic standard
detection - 525/625 lines according
to the lost SD-SDI signal)
There is no on-board
DVB-ASI signal
generator available.
When losing a DVBASI signal, no
fallback is available.
The output will
simply be lost,
regardless of the
fallback setting.
8
OVR
Off: Multicon GYDA mode
On: Manual mode
This DIP is only read
at power up.
OVR is short term for
Multicon GYDA
override.
Switch 1 (’off’ / 0)
Switch 2 (’off’ / 0)
Switch 3 (’off’ / 0)
Switch 4 (’off’ / 0)
Switch 5 (’off’ / 0)
Switch 6 (’off’ / 0)
Switch 7 (’off’ / 0)
Switch 8 (’off’ / 0)
Routing
Shown: 1=>1 , 2=>2 , 3=>3 , 4=>4
Input Select
Shown: Auto, priority optical
Output Select (when no input)
Shown: black picture, auto video standard
Mode. Shown: GYDA control enabled
(Upper left corner of board)
OFF ON
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
5.3 DMUX DIP switches
nevion.com | 17
Table 2: DMUX DIP switch functions
Figure 9: DMUX DIP switches exemplified
Page 18

SDI-TD-MUX-4 / SDI-TD-DMUX-4 Rev. N
SD2 Input
HD Optical Output
SD3 Input
SD1 Input
SD4 Input
GPI Outputs
HD Electrical Output
Name
Description
Connector Type
SD1
Input (Output) for 270 Mbps SD-SDI or DVB-ASI.
BNC
SD2
Input (Output) for 270 Mbps SD-SDI or DVB-ASI.
BNC
SD3
Input (Output) for 270 Mbps SD-SDI or DVB-ASI.
BNC
SD4
Input (Output) for 270 Mbps SD-SDI or DVB-ASI.
BNC
6 Connections
6.1 Power connections
Power is applied to the board via the backplane board, which in turn is plugged into the
power distribution bus in the Flashlink rack.
The SDI-TD-MUX-4 board consumes slightly more than the full maximum of 3 watts from the
+5V supply and slightly more than the full maximum of 1.5 watts from the +15V supply
available at the backplane. The SDI-TD-DMUX-4 consumes 3.5W from the +5V supply and
1.8W from the +15V supply. In both cases this limits the number of boards in a rack to 8
boards plus Multicon GYDA, when using a standard single power supply.
Note that both boards can run on a single 5V supply, but then the full power of about 4.5
watts will be drawn from the 5V supply. The boards automatically adapts to sharing the load
between +5V and +15V when 15V is available.
6.2 Backplane
The SDI-TD-MUX-4 and SDI-TD-DMUX-4 boards use the same backplane.
Figure 10 shows the backplane rear view. The signal directions indicated are for the SDI-TD-
MUX-4 card, with the DMUX in parentheses. When the backplane is used for the SDI-TDDMUX-4, the directions of SD1-SD4, HD electrical and HD optical will be reversed.
The SD1 to SD4 connectors are for 270 Mbps SD-SDI or DVB-ASI signals.
The HD output carries the electrical HD-signal with the four input signals time division
multiplexed according to the SMPTE 346M-2000 standard.
The optical and electrical outputs both carry the same HD-signal.
The GPI outputs are alarm signals for driving external alarm devices.
Figure 10: Rear view of the backplane
The following connectors are available:
nevion.com | 18
Page 19

SDI-TD-MUX-4 / SDI-TD-DMUX-4 Rev. N
HD
Output (Input) for 1.485 Gbps HD-SDI
(Multiplexed according to SMPTE 346M-2000).
BNC
OPT
Optical output (input) for 1.485 Gbps HD-SDI.
SC/UPC
GPI
General Purpose Interface (transistor drivers for
external alarm devices).
RJ-45
RJ45 Pin Number
Description
8
GND
7
Not Used
6
Not Used
5
Not Used
4
GPI2
3
GPI3
2
GPI0
1
GPI1
Unused inputs should be terminated to avoid alarms triggered by noise.
6.2.1 GPI/ Data connections RJ45
Figure 11: RJ45 Connector for GPI Signals
The below table show the signals available on the GPI connector on the backplane.
6.3 The main board
There are also a number of connectors on the board itself. None of these are intended for the
end-user. For proper operation, make sure there is a jumper in the lower position of the
connector located behind the DIP-switches (see Figure 12 and Figure 13 below).
The rear end of the boards (with the connector that mates to the backplane) is towards the
right side of the board. The boards must be mounted in a Flashlink FR-2RU-10-2 frame with
dedicated backplanes. Avoid inserting the SDI-TD-MUX-4 or SDI-TD-DMUX-4 board into a
wrong backplane, as this may cause electrical and/or mechanical damage to the main
boards and/or the backplanes.
nevion.com | 19
Page 20

SDI-TD-MUX-4 / SDI-TD-DMUX-4 Rev. N
DIP switches
OFF ON
’0’ ’1’
Jumper needed
for proper
operation
Optical
backplane
connector
Electrical backplane
connector with signals
and power lines
LED
indicators
DIP switches
OFF ON
’0’ ’1’
Jumper needed
for proper
operation
Optical
backplane
connector
LED
indicators
Electrical backplane
connector with signals
and power lines
Figure 12: MUX main board overview
nevion.com | 20
Figure 13: DMUX main board overview
Page 21

SDI-TD-MUX-4 / SDI-TD-DMUX-4 Rev. N
Diode
Description
Red LED
Orange LED
Green LED
No light
1
Card status
Power on,
FPGA not
configured
Not applicable
Power on and
FPGA
configured
No power
to board
2
Status of SD
inputs/streams
1 and 2
Both SD
inputs/streams
(1 and 2)
In error
One of the
inputs/streams
(1 or 2)
in error
Both
inputs/streams
(1 and 2)
operating
normally
No power
to board
3
Status of SD
inputs/streams
3 and 4
Both SD
inputs/streams
(3 and 4)
in error
One of the
inputs/streams
(3 or 4)
in error
Both
inputs/streams
(3 and 4)
operating
normally
No power
to board
4
(MUX)
Status of
HD OUT
Output failure
Laser failure
Output OK and
laser working
No power
to board
4
(DMUX)
Status of
HD IN
Input failure
N/A
Input OK
No power
to board
7 Operation
7.1 Front panel LED indicators
Figure 14 shows how the LEDs are located on the front panel.
Figure 14: Front panel view for the MUX. The DMUX LEDs are identical, except that the lower
LED refers to the HD input.
The table below shows how the front panel LEDs are to be interpreted. The four LEDs
correspond closely to the four GPI alarms explained in chapter 7.2.
Note that the term “in error” in the table means that there is either a missing signal (no carrier
detect) AND/OR the reclocker has not been able to lock to the incoming signal.
The term “operating normally” means that a signal has been detected (carrier detect on the
cable equalizer) AND the reclocker has been able to lock to the signal.
nevion.com | 21
Page 22

SDI-TD-MUX-4 / SDI-TD-DMUX-4 Rev. N
Block
Blk# Commands
Example
Response
Control
- - ?
?
product name\
SW rev n.m\
FW rev r.s\
protocol ver 4.0\
Hello command.
Note 1: No other commands will be
available until the card has received
this hello.
Note 2: This command will also
enable checksums.
Note 3: Cards are designed to be
hot-swappable. To sync with the start
of a new command, the cards will
wait for a <lf> character before
looking for a valid command.
conf 0 -
conf 0
*too long to list*
Configuration settings
Retrieves the card's configurable
settings. Each addressable block is
represented by a single line. Dynamic
status may be included in response,
but is usually reported in info only.
- - info
info
*too long to list*
Dynamic status info
Blocks with static settings only will
usually not be included, see conf
above.
- - chk off
chk off
ok
Checksum off
If issued twice in succession, this
command will disable checksums.
Note: Responses will still have the
checksums appended.
NOTE1:? command turns the
checksum on again
- - locate on <seconds>
locate on 3
ok
Card locator
This command will cause all the
3
7.2 GPI alarms
Four alarms are present on the RJ45 connector. These four GPI signals indicate the same
status as the LEDs (see above):
GPI0: On => Power on, FPGA not configured
Off => Power on, FPGA configured
GPI1: On => One of the channels (1 or 2) in error
Off => Both channels (1 and 2) are OK
GPI2: On => One of the channels (3 or 4) in error
Off => Both channels (3 and 4) are OK
GPI3: On => For SDI-TD-MUX-4: Laser failure, for SDI-TD-DMUX-4: No HD input
Off => For SDI-TD-MUX-4: Laser OK, for SDI-TD-DMUX-4: Locked to an HD
electrical or optical input signal.3
An active alarm condition means that the transistor is conducting.
7.3 RS422 commands
7.3.1 FLP4.0 required commands
When optical input is selected by Multicon GYDA, alarm status is indicated only for optical
input. When electrical input is selected from Multicon GYDA, status is indicated only for
electrical input. When Multicon GYDA control is disabled or auto-select is chosen from
Multicon GYDA, an alarm will be indicated only when both input HD signals are lost.
nevion.com | 22
Page 23

SDI-TD-MUX-4 / SDI-TD-DMUX-4 Rev. N
Block
Blk# Commands
Example
Response
Control
locate off
locate off
LEDs to flash for a user specified
number of seconds. If omitted, the
value <seconds> will be set to a
default of 120 seconds. The flashing
can be terminated at any time with
locate off.
- - address
Address
address <address>
Card address
This command will force the module
to check and update its current rack
and slot address. This is normally
only done at start-up.
- - filename
filename tdmux103.ffw
filename tddmx321.ffw
<name>'.'<extensio
n>
Firmware update
The <name> part must match the
card's hardware and include a
revision number, and the extension
must be either 'ffw' for FPGA
firmware or 'mfw' for microcontroller
firmware. After running this
command, the board will be ready to
receive its new firmware in Intel-hex
format.
- - fin
Fin
ok
Finalize
Finalize the programming of the
microcontroller. See description of
the uC boot loader (separate
document).
misc
0 - STATUS NOT
AVAILABLE BY
SEPARATE
COMMAND,
ONLY FOUND in conf
0 AND info
RESPONSES!
prog | fin
' ' | ovr
' ' | err
Misc info
prog if the card is freshly
programmed by the boot loader and
the program is still un-finalized. fin is
the normal condition.
ovr if DIP-switch 16 is set to the ON
position and the card is under DIPswitch control.
Note 1: The info part of misc has
additional functionality when locate is
used: locating <remaining seconds>.
This enables a visible countdown
clock in Multicon GYDA, but is not a
required part of FLP4.
nevion.com | 23
Page 24

SDI-TD-MUX-4 / SDI-TD-DMUX-4 Rev. N
Block
Blk# Commands
Example(s)
Response
Control
ceq
0-3
(0)
-
ceq 0
ceq 3
cd | ncd
Cable equalizer
No control; only used to report carrier
detected or no carrier detected.
The DMUX has only one (ceq 0) for
its HD electrical input, the MUX has
one for each SD input, 4 in total.
gpi 0 act
inact
gpi 0 inact
act | inact
Free-running vs. Locked to SD
(MUX only)
This gpi control is normally hidden to
the end user. See the ‘cal’ command
under ch. 7.3.3. ‘act’ means that the
frequency of the HD output from the
MUX is locked to one of the SD
inputs, while ‘inact’ means that it is
free-running. By locking to incoming
SD, frequency drift is eliminated, but
glitches will occur in all 4 outputs on
the DMUX side if/when the MUX
board must change its reference to a
different SD input.
lsr 0 on | off
lambda <wavelen>
lpwr <laser_pwr>
type ( c | t | n )
lsr 0 off
lsr 0 lambda 1310
lsr 0 lpwr 0
lsr 0 type c
on type C 1310nm
0dBm
Laser control (MUX only)
Only on/off is directly available from
Multicon. The other commands does
not affect the laser itself, they just
provide a tool to set information
about the laser fitted to the board.
C=CWDM
T=DWDM
N=None
mtx 0 <input> <output>
mtx 0 0 2
size 4:4 <in1>
<in2> <in3> <in4>
Input/stream shuffler
mtx 0 controls which input is routed
to which stream (MUX) or which
stream is routed to each output
(DMUX).
mtx 1 <input> <output>
mtx 0 0 2
size 4:1 <in1>
Input selector (DMUX)
0: Always optical input
1: Always electrical input
2: Auto (pri optical)
3: Auto (latching)
mtx 2 <input> <output>
Fallback generators (DMUX)
Do not use, not fully implemented per
SW 5.3.
mtx 3 - size 2:1 <in1>
Currently selected input (DMUX)
0: optical input
1: electrical input
mtx 4 - size 6:4 < in1>
<in2> <in3> <in4>
Output status (DMUX)
Reports the current status of all
four outputs:
0: stream 1
1: stream 2
2: stream 3
3: stream 4
4: color bar
5: black
Note that per SW 5.3, the fallbacks
are not yet implemented and used.
pin
(0) - pin 0
cd | ncd
Pin diode status (DMUX only)
No control. Only used to report
7.3.2 Normal control blocks
nevion.com | 24
Page 25

SDI-TD-MUX-4 / SDI-TD-DMUX-4 Rev. N
Block
Blk# Commands
Example(s)
Response
Control
carrier detected or no carrier
detected.
pwr
0-5 -
<nom>Vnom
<volt>V
Power supply monitors
pwr 0 = 5.0V
pwr 1 = 3.3V
pwr 2 = 2.5V
pwr 3 = 1.8V
pwr 4 = 1.2V
rcl
0-3
(4)
-
rcl 0
lock | lol
Reclocker
No commands available, only used to
report lock status. The MUX board
has one rcl block for each SD input,
while the DMUX board has one rcl
block for the HD input (rcl 0) and one
rcl block for each recovered stream
(rcl 1 – rcl 4).
vmon
0-3
reset
vmon 3 reset
vmon N cnt
<errors> edh
<edh_bits> err
<error_bits>
Video monitor (MUX)
The vmon blocks 0-3 consist of an
error counter for each SD input. Each
error counter can be reset with the
reset command.
vmon
4
msk <bit_mask>
vmon 4 msk 1
vmon 4 msk
<bit_mask>
Video monitor (MUX)
Which errors are to be counted is set
for all 4 error counters at once with
the msk command. See the chapter
on Signal integrity for explanation on
the bit values.
vmon
0
reset
msk <bit_msk>
reset
msk 0x7b
vmon 0 msk
<bit_mask>
vmon 0 cnt
<errors> edh
<edh_bits> err
<error_bits>
Video monitor (DMUX)
The DMUX has one vmon block to
monitor the incoming HD signal. See
the chapter on Signal integrity for
explanation on the bit values.
Block
Commands
example
Response
Control
cal
gpi sesame
cal gpi sesame
ok
Toggles the visibility of normally
hidden control blocks.
rdp
<page_number>
rdp 4
*too long to list*
Will list the contents of one page
of the flash memory holding the
FPGA program.
rdr
<address>
rdr 0x0679
r<bits> <value>
Ex: r16 0x0001
Reads a register value. Register
value is returned as a hexadecimal
numbers, and it’s preceded by
either r8 or r16 to show if the
rgister is 8 bit or 16 bit.
MUX addresses:
0100-01FF: Deserializer 1
0200-02FF: Deserializer 2
0300-03FF: Deserializer 3
0400-04FF: Deserializer 4
0600-06FF: FPGA
0700-07FF: MCU EEPROM
0800-08FF: Serializer
0900-09FF: LED
1000-10FF: FPGA program flash
7.3.3 Commands intended for debug/lab use only
nevion.com | 25
Page 26

SDI-TD-MUX-4 / SDI-TD-DMUX-4 Rev. N
Block
Commands
example
Response
Control
DMUX addresses:
0100-01FF: Serializer 1
0200-02FF: Serializer 2
0300-03FF: Serializer 3
0400-04FF: Serializer 4
0600-06FF: FPGA
0700-07FF: MCU EEPROM
0800-08FF: Deserializer
0900-09FF: LED
1000-10FF: FPGA program flash
rst
<number>
rst 1
ok
<number>=0: Restarts all chips
except MCU and FPGA.
<number>=1: (DMUX only)
Restarts deserializer
<number>=2: Restarts MCU,
thereby reinitializing entire board.
<number>=4: Restarts FPGA only
wrr
<address> <value>
wrr 0x0679 1
ok
Write to register. See description
of the ‘rdr’ command for valid
address ranges. Note that the
LEDs are read-only; all other
registers are writable, even if the
written value in some cases will be
overwritten almost immediately.
nevion.com | 26
Page 27

SDI-TD-MUX-4 / SDI-TD-DMUX-4 Rev. N
4
8 Laser safety precautions
These are guidelines to limit hazards from laser exposure.
All the available EO (including ETH100) units in the Flashlink range include a laser.
Therefore this note on laser safety should be read thoroughly.
The lasers emit light at wavelengths from 1270 nm up to 1610 nm. This means that the
human eye cannot see the beam, and the blink reflex cannot protect the eye. (The human
eye can see light between 400 nm to 700 nm).
A laser beam can be harmful to the human eye (depending on laser power and exposure
time). Therefore:
Be careful when connecting / disconnecting fiber pigtails (ends).
Never look directly into the pigtail of the laser/fiber.
Never use microscopes, magnifying glasses or eye loupes to look into a fiber
end.
Use laser safety goggles blocking light at 1310 nm and at 1550 nm
Instruments exist to verify light output power: Power meters, IR-cards etc.
Flashlink features:
All the laser module cards in the Flashlink product range, are Class 1 laser products
according to IEC 825-1 1993, and class I according to 21 CFR 1040.10 when used in normal
operation.
Maximum output power4: 5 mW
Operating wavelengths: > 1270 nm
Max power is for safety analysis only and does not represent device performance.
nevion.com | 27
Page 28

SDI-TD-MUX-4 / SDI-TD-DMUX-4 Rev. N
1.
The equipment will meet the guaranteed performance specification under the following
environmental conditions:
-
Operating room temperature range:
0°C to 45°C
-
Operating relative humidity range:
<90% (non-condensing)
2.
The equipment will operate without damage under the following environmental
conditions:
-
Temperature range:
-10°C to 55°C
-
Relative humidity range:
<95% (non-condensing)
General environmental requirements for Nevion equipment
nevion.com | 28
Page 29

SDI-TD-MUX-4 / SDI-TD-DMUX-4 Rev. N
Product Warranty
The warranty terms and conditions for the product(s) covered by this manual follow the
General Sales Conditions by Nevion, which are available on the company web site:
www.nevion.com
nevion.com | 29
Page 30

SDI-TD-MUX-4 / SDI-TD-DMUX-4 Rev. N
組成名稱
Part Name
Toxic or hazardous substances and elements
鉛
Lead
(Pb)
汞
Mercury
(Hg)
镉
Cadmium
(Cd)
六价铬
Hexavalent
Chromium
(Cr(VI))
多溴联苯
Polybrominated
biphenyls
(PBB)
多溴二苯醚
Polybrominated
diphenyl ethers
(PBDE)
SDI-TD-DMUX-4(-R)
SDI-TD-MUX-4(-T)
O O O O O
O
O: Indicates that this toxic or hazardous substance contained in all of the homogeneous materials for
this part is below the limit requirement in SJ/T11363-2006.
X: Indicates that this toxic or hazardous substance contained in at least one of the homogeneous
materials used for this part is above the limit requirement in SJ/T11363-2006.
Appendix A Materials declaration and recycling information
A.1 Materials declaration
For product sold into China after 1st March 2007, we comply with the “Administrative
Measure on the Control of Pollution by Electronic Information Products”. In the first stage of
this legislation, content of six hazardous materials has to be declared. The table below
shows the required information.
This is indicated by the product marking:
A.2 Recycling information
Nevion provides assistance to customers and recyclers through our web site
http://www.nevion.com/. Please contact Nevion’s Customer Support for assistance with
recycling if this site does not show the information you require.
Where it is not possible to return the product to Nevion or its agents for recycling, the
following general information may be of assistance:
Before attempting disassembly, ensure the product is completely disconnected from
power and signal connections.
All major parts are marked or labeled to show their material content.
Depending on the date of manufacture, this product may contain lead in solder.
Some circuit boards may contain battery-backed memory devices.
nevion.com | 30
 Loading...
Loading...