Page 1

ProSafe Managed Switch
Command Line Interface (CLI)
User Manual
10.0.1
M7100-24X
M4100-24G-POE+
M4100-26G
M4100-26-POE
M4100-26G-POE
M4100-50G
M4100-50-POE
M4100-50G-POE+
350 East Plumeria Drive
San Jose, CA 95134
USA
February 2013
202-11166-02
1.0
M4100-12GF
M4100-12G-POE+
M4100-D12G
M4100-D10-POE
M4100-D12G-POE+
Page 2

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Support
Thank you for selecting NETGEAR products.
After installing your device, locate the serial number on the label of your product and use it to register your product
at https://my.netgear.com. You must register your product before you can use NETGEAR telephone support.
NETGEAR recommends registering your product through the NETGEAR website. For product updates and web
support, visit http://support.netgear.com.
Phone (US & Canada only): 1-888-NETGEAR.
Phone (Other Countries): Check the list of phone numbers at
http://support.netgear.com/general/contact/default.aspx.
Trademarks
NETGEAR, the NETGEAR logo, and Connect with Innovation are trademarks and/or registered trademarks of
NETGEAR, Inc. and/or its subsidiaries in the United States and/or other countries. Information is subject to change
without notice. © NETGEAR, Inc. All rights reserved.
Revision History
Publication Part Number Version Publish Date Comments
202-11166-02 1.0 February 2013 Updated document.
202-11166-01 1.0 October 2012 First publication.
2
Page 3

Contents
Chapter 1 Using the Command-Line Interface
Chapter 2 Switching Commands
Licensing and Command Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
Command Syntax. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
Command Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
Common Parameter Values. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
Slot/Port Naming Convention. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
Using a Command’s “No” Form . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
Managed Switch Modules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
Command Modes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
Command Completion and Abbreviation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
CLI Error Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
CLI Line-Editing Conventions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
Using CLI Help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
Accessing the CLI. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
Port Configuration Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
Loopback Interface Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30
VLAN Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .47
Double VLAN Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .60
Voice VLAN Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .63
Provisioning (IEEE 802.1p) Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .65
Protected Ports Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .65
Private VLAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .68
GARP Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .71
GVRP Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .73
GMRP Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .75
Port-Based Network Access Control Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .77
802.1X Supplicant Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .91
Storm-Control Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .94
Flow Control Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .104
Port-Channel/LAG (802.3ad) Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .105
Port Mirroring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .121
Static MAC Filtering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .123
DHCP L2 Relay Agent Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .127
DHCP Client Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .131
DHCP Snooping Configuration Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .132
Dynamic ARP Inspection Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .141
3
Page 4

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
IGMP Snooping Configuration Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .148
IGMP Snooping Querier Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .157
MLD Snooping Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .161
MLD Snooping Querier Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .168
set mld querier . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .168
set mld querier query_interval . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .169
set mld querier timer expiry . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .169
set mld querier election participate. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .170
show mldsnooping querier . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .170
Port Security Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .171
LLDP (802.1AB) Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .175
LLDP-MED Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .184
Denial of Service Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .193
MAC Database Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .203
ISDP Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .205
Priority-Based Flow Control Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .210
Chapter 3 Multicast VLAN Registration (MVR)
About MVR. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .214
MVR Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .214
Chapter 4 Routing Commands
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .222
IP Routing Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .227
Router Discovery Protocol Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .244
Virtual LAN Routing Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .248
Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .249
DHCP and BOOTP Relay Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .257
IP Helper Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .259
Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .263
OSPF Graceful Restart Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .304
nsf. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .305
nsf restart-interval. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .305
nsf helper . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .306
nsf helper disable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 307
nsf [ietf] helper strict-lsa-checking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .307
OSPF Interface Flap Dampening Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .309
Routing Information Protocol (RIP) Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .311
ICMP Throttling Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .318
Chapter 5 IP Multicast Commands
Multicast Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .321
DVMRP Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .326
PIM Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .331
Internet Group Message Protocol (IGMP) Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . .342
IGMP Proxy Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .349
4
Page 5

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Chapter 6 IPv6 Commands
Tunnel Interface Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .356
IPv6 Routing Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .357
OSPFv3 Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .380
OSPFv3 Graceful Restart Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .411
DHCPv6 Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .413
Chapter 7 IPv6 Multicast Commands
IPv6 Multicast Forwarder Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .422
IPv6 PIM Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .424
IPv6 MLD Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .431
IPv6 MLD-Proxy Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .437
Chapter 8 Quality of Service (QoS) Commands
Class of Service (CoS) Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .444
Differentiated Services (DiffServ) Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .451
DiffServ Class Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .452
DiffServ Policy Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .461
DiffServ Service Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .466
DiffServ Show Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .468
MAC Access Control List (ACL) Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .473
IP Access Control List (ACL) Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .478
IPv6 Access Control List (ACL) Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .484
Time Range Commands for Time-Based ACLs. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .488
AutoVOIP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .490
iSCSI Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .494
Chapter 9 Power over Ethernet (PoE) Commands
About PoE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .501
PoE Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .502
Chapter 10 Utility Commands
Auto Install Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .513
Dual Image Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .515
System Information and Statistics Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .517
Logging Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .534
Email Alerting and Mail Server Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .539
System Utility and Clear Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .546
Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .556
DHCP Server Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .564
DNS Client Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .575
Packet Capture Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .580
Serviceability Packet Tracing Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .583
Cable Test Command. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .603
sFlow Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .604
5
Page 6

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Software License Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .609
IP Address Conflict Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .610
Link Local Protocol Filtering Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .611
RMON Stats and History Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .612
UDLD Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .618
USB commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .620
Chapter 11 Management Commands
Configuring the Switch Management CPU. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .624
Network Interface Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .626
Console Port Access Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .629
Telnet Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .631
Secure Shell (SSH) Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .636
Management Security Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .639
Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .640
Access Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .647
User Account Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .647
SNMP Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .670
RADIUS Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .680
TACACS+ Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 693
Configuration Scripting Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .698
Pre-Login Banner and System Prompt Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .700
Switch Database Management (SDM) Templates. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .701
IPv6 Management Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .703
Chapter 12 Log Messages
Core . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .709
Utilities . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .711
Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .713
Switching . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .717
QoS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .723
Routing/IPv6 Routing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .724
Multicast. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .727
Stacking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .729
Technologies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .730
O/S Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .732
Chapter 13 Green Ethernet Commands
Energy-Detect Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .735
Energy Efficient Ethernet (EEE). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .735
Chapter 14 Command List
6
Page 7

1. Using the Command-Line Interface
The command-line interface (CLI) is a text-based way to manage and monitor the system.
You can access the CLI by using a direct serial connection or by using a remote logical
connection with telnet or SSH.
This chapter describes the CLI syntax, conventions, and modes. It contains the following
sections:
• Licensing and Command Support
• Command Syntax
• Command Conventions
• Common Parameter Values
• Slot/Port Naming Convention
• Using a Command’s “No” Form
• Managed Switch Modules
• Command Modes
• Command Completion and Abbreviation
• CLI Error Messages
• CLI Line-Editing Conventions
• Using CLI Help
• Accessing the CLI
1
7
Page 8

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Licensing and Command Support
As shown in the following table, some command groups, or commands, require a license and
some are supported on particular switch models. For those requiring a license, license keys
are available from your VAR or NETGEAR authorized e-commerce portal. License activation
is described in the Software Setup Manual.
Command Group or Command M4100 M7100
Router Discovery Protocol Commands Not supported Not supported
Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol Commands Not supported Not supported
Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) Commands Not supported Not supported
OSPF Graceful Restart Commands Not supported Not supported
Routing Information Protocol (RIP) Commands Not supported Not supported
Tunnel Interface Commands Not supported Not supported
IPv6 Routing Commands Not supported Not supported
OSPFv3 Commands Not supported Not supported
OSPFv3 Graceful Restart Commands Not supported Not supported
DHCPv6 Commands Not supported Not supported
Multicast Commands Not supported Not supported
DVMRP Commands Not supported Not supported
PIM Commands Not supported Not supported
Internet Group Message Protocol (IGMP) Commands Not supported Not supported
IGMP Proxy Commands Not supported Not supported
IPv6 Multicast Forwarder Commands Not supported Not supported
IPv6 PIM Commands Not supported Not supported
IPv6 MLD Commands Not supported Not supported
IPv6 MLD-Proxy Commands Not supported Not supported
PoE Commands Supported on PoE
models only
MVR Commands Supported Supported
Link Local Protocol Filtering Commands Not supported Supported
Not supported
Priority-Based Flow Control Commands Not Supported Not supported
cos-queue random-detect Supported Supported
no cos-queue random-detect Supported Supported
random-detect exponential weighting-constant Supported Supported
no random-detect exponential weighting-constant Supported Supported
Using the Command-Line Interface
8
Page 9

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Command Group or Command M4100 M7100
random-detect queue-parms Supported Supported
no random-detect queue-parms Supported Supported
Command Syntax
A command is one or more words that might be followed by one or more parameters.
Parameters can be required or optional values.
Some commands, such as show network or clear vlan, do not require parameters.
Other commands, such as network parms, require that you supply a value after the
command. You must type the parameter values in a specific order, and optional parameters
follow required parameters. The following example describes the network parms
command syntax:
Format network parms <ipaddr> <netmask> [gateway]
• network parms is the command name.
• <ipaddr> and <netmask> are parameters and represent required values that you
must enter after you type the command keywords.
• [gateway] is an optional parameter, so you are not required to enter a value in place of
the parameter.
The New Template User Manual lists each command by the command name and provides a
brief description of the command. Each command reference also contains the following
information:
• Format shows the command keywords and the required and optional parameters.
• Mode identifies the command mode you must be in to access the command.
• Default shows the default value, if any, of a configurable setting on the device.
The show commands also contain a description of the information that the command shows.
Command Conventions
In this document, the command name is in bold font. Parameters are in italic font. Y ou
must replace the parameter name with an appropriate value, which might be a name or
number. Parameters are order-dependent.
Using the Command-Line Interface
9
Page 10
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
The parameters for a command might include mandatory values, optional values, or keyword
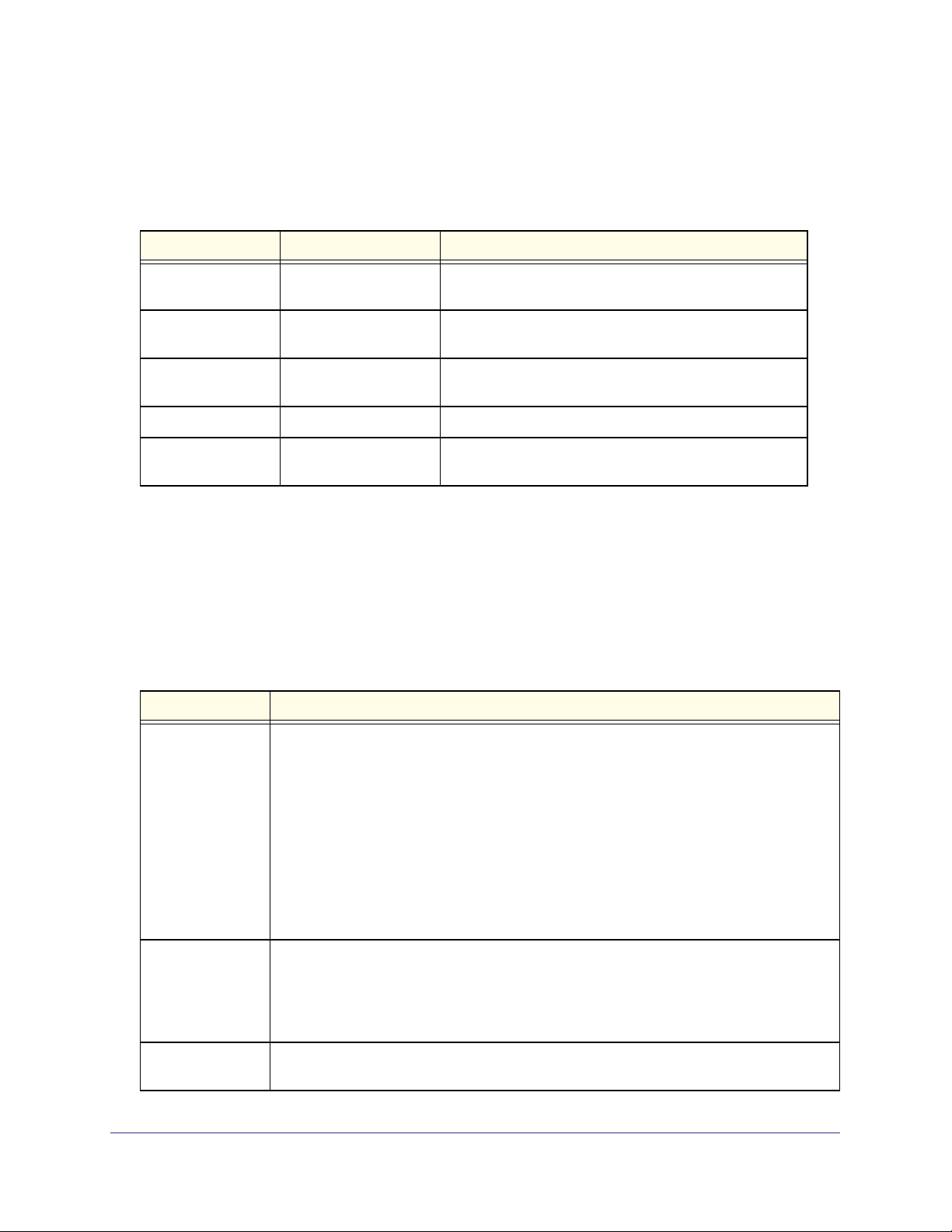
choices. Table 1 describes the conventions this document uses to distinguish between value
types.
Table 1. Parameter Conventions
Symbol Example Description
<> angle brackets
[] square brackets Indicates an optional parameter that you can enter in
{} curly braces Indicates that you must select a parameter from the list of
| V
ertical bars Separates the mutually exclusive choices.
[{}] Braces within
square brackets
<value>
[value]
{choice1 |
choice2}
choice1 | choice2
[{choice1 |
choice2}]
Indicates that you must enter a value in place of the
brackets and text inside them.
place of the brackets and text inside them.
choices.
Indicates a choice within an optional element.
Common Parameter Values
Parameter values might be names (strings) or numbers. To use spaces as part of a name
parameter, enclose the name value in double quotes. For example, the expression “System
Name with Spaces” forces the system to accept the spaces. Empty strings (““) are not valid
user-defined strings. Table 2 describes common parameter values and value formatting.
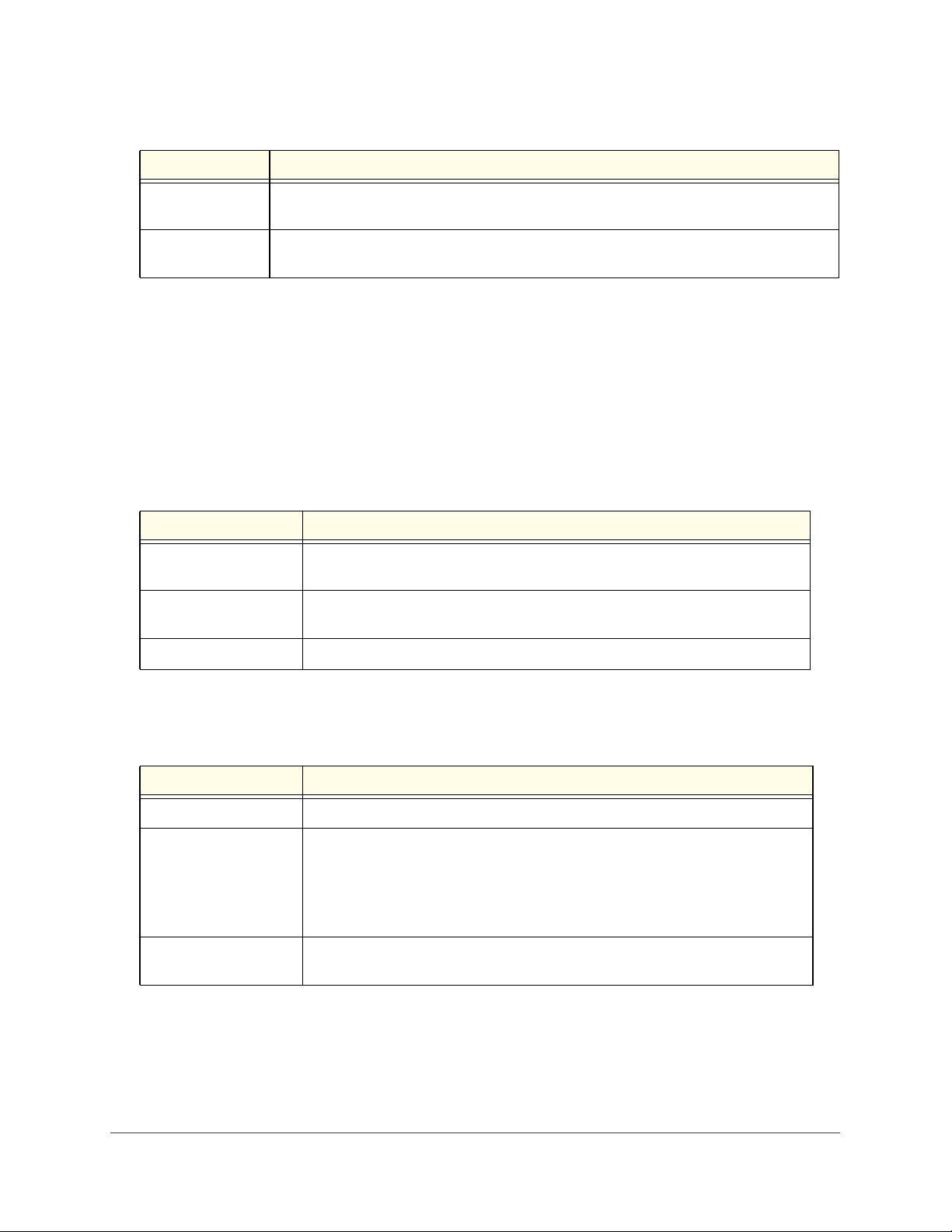
Table 2. Parameter Descriptions
Parameter Description
ipaddr This parameter is a valid IP address. You can enter the IP address in the following formats:
a (32 bits)
a.b (8.24 bits)
a.b.c (8.8.16 bits)
a.b.c.d (8.8.8.8)
In addition to these formats, the CLI accepts decimal, hexadecimal, and octal formats
through the following input formats (where n is any valid hexadecimal, octal, or decimal
number):
0xn (CLI assumes hexadecimal format)
0n (CLI assumes octal format with leading zeros)
n (CLI assumes decimal format)
ipv6-address
FE80:0000:0000:0000:020F:24FF:FEBF:DBCB, or
FE80:0:0:0:20F:24FF:FEBF:DBCB, or
FE80::20F24FF:FEBF:DBCB, or
FE80:0:0:0:20F:24FF:128:141:49:32
Interface or
slot/port
For more information, refer to RFC 3513.
V
alid slot and port number separated by forward slashes. For example, 0/1 represents slot
number 0 and port number 1.
Using the Command-Line Interface
10
Page 11
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Table 2. Parameter Descriptions (Continued)
Parameter Description
Logical Interface Represents a logical slot and port number. This is applicable in the case of a port-channel
(LAG). You can use the logical slot/port to configure the port-channel.
Character strings Use double quotation marks to identify character strings, for example, “System Name with
Spaces”. An empty string (“”) is not valid.
Slot/Port Naming Convention
Managed switch software references physical entities such as cards and ports by using a
slot/port naming convention. The software also uses this convention to identify certain logical
entities, such as Port-Channel interfaces.
The slot number has two uses. In the case of physical ports, it identifies the card containing
the ports. In the case of logical and CPU ports it also identifies the type of interface or port.
Table 3. Type of Slots
Slot Type Description
Physical slot numbers Physical slot numbers begin with zero, and are allocated up to the maximum
number of physical slots.
Logical slot numbers Logical slots immediately follow physical slots and identify port-channel (LAG) or
router interfaces.
CPU slot numbers The CPU slots immediately follow the logical slots.
The port identifies the specific physical port or logical interface being managed on a given
slot.
Table 4. Type of Ports
Port Type Description
Physical Ports The physical ports for each slot are numbered sequentially starting from zero.
Logical Interfaces Port-channel or link aggregation group (LAG) interfaces are logical interfaces that
are only used for bridging functions.
VLAN routing interfaces are only used for routing functions.
Loopback interfaces are logical interfaces that are always up.
Tunnel interfaces are logical point-to-point links that carry encapsulated packets.
CPU ports CPU ports are handled by the driver as one or more physical entities located on
physical slots.
Using the Command-Line Interface
11
Page 12

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Note: In the CLI, loopback and tunnel interfaces do not use the slot/port
format. To specify a loopback interface, you use the loopback ID. To
specify a tunnel interface, you use the tunnel ID.
Using a Command’s “No” Form
The no keyword is a specific form of an existing command and does not represent a new or
distinct command. Almost every configuration command has a no form. In general, use the
no form to reverse the action of a command or reset a value back to the default. For example,
the no shutdown configuration command reverses the shutdown of an interface. Use the
command without the keyword no to reenable a disabled feature or to enable a feature that
is disabled by default. Only the configuration commands are available in the no form.
Managed Switch Modules
Managed switch software consists of flexible modules that can be applied in various
combinations to develop advanced Layer 2/3/4+ products. The commands and command
modes available on your switch depend on the installed modules. Additionally, for some show
commands, the output fields might change based on the modules included in the software.
The software suite includes the following modules:
• Switching (Layer 2)
• Routing (Layer 3)
• IPv6—IPv6 routing
• Multicast
• Quality of Service
• Management (CLI, web UI, and SNMP)
• IPv6 Management—Allows management of the device through an IPv6 through an IPv6
address without requiring the IPv6 Routing package in the system. The management
address can be associated with the network port (front-panel switch ports) and a routine
interface (port or VLAN).
• Stacking
Not all modules are available for all platforms or software releases.
Command Modes
The CLI groups commands into modes according to the command function. Each of the
command modes supports specific software commands. The commands in one mode are not
available until you switch to that particular mode, except for the User EXEC mode
Using the Command-Line Interface
12
Page 13

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
commands. You can execute the User EXEC mode commands in the Privileged EXEC
mode.
The command prompt changes in each command mode to help you identify the current
mode.
Table 5 describes the command modes and the prompts visible in that mode.
Note: The command modes available on your switch depend on the
software modules that are installed. For example, a switch that does
not support BGPv4 does not have the Router BGPv4 Command
Mode.
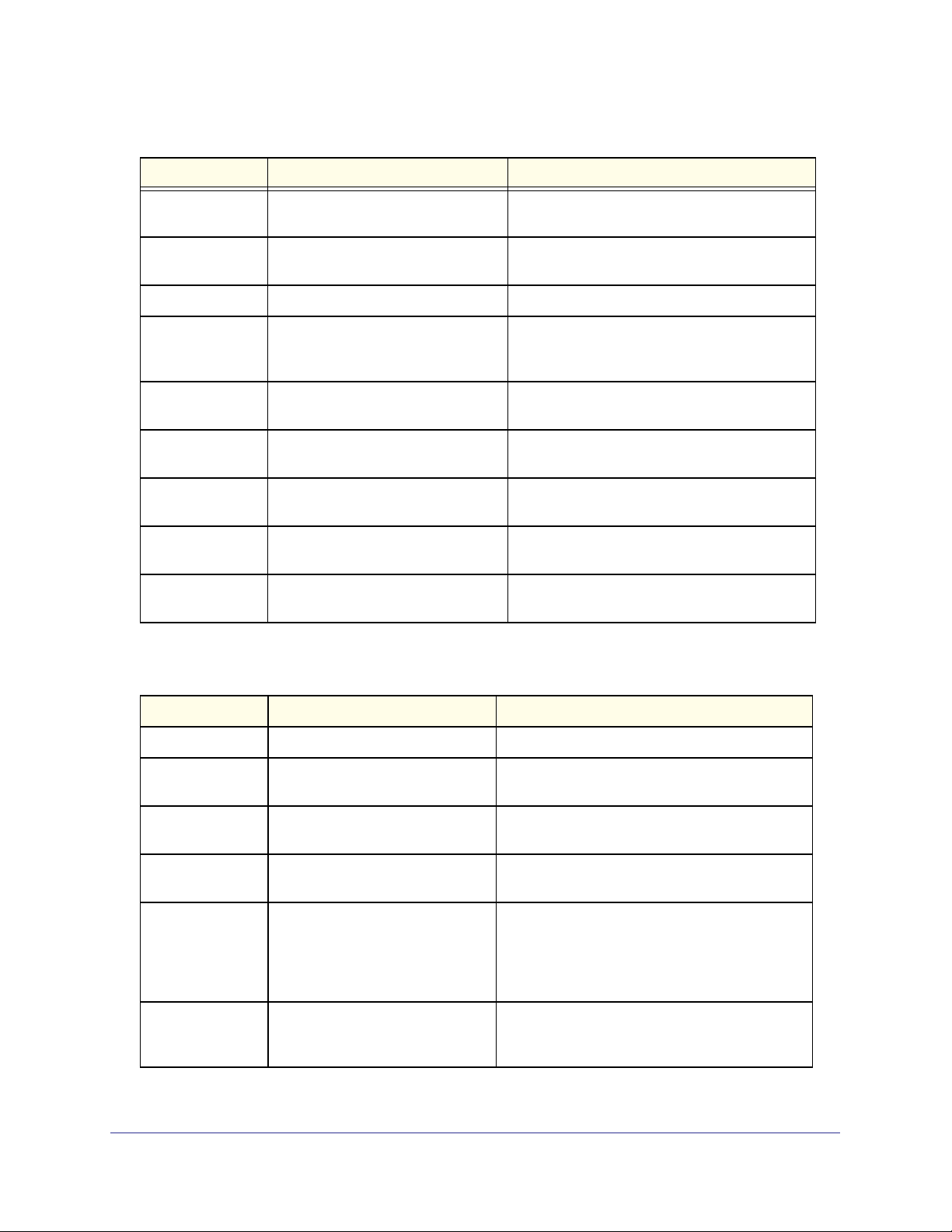
Table 5. CLI Command Modes
Command Mode Prompt Mode Description
User EXEC
Privileged EXEC
Global Config
VLAN Config
Switch>
Switch#
Switch (Config)#
Switch (Vlan)#
Contains a limited set of commands to view
basic system information.
Allows you to issue any EXEC command, enter
the VLAN mode, or enter the Global
Configuration mode.
Groups general setup commands and permits
you to make modifications to the running
configuration.
Groups all the VLAN commands.
Interface Config Switch (Interface <slot/port>)#
Switch (Interface Loopback <id>)#
Switch (Interface Tunnel <id>)#
Line Config Switch (line)# Contains commands to configure outbound
Policy Map
Config
Policy Class
Config
Class Map Config Switch (Config-class-map)# Contains the QoS class map configuration
Ipv6_Class-Map
Config
Switch (Config-policy-map)# Contains the QoS Policy-Map configuration
Switch (Config-policy-class-map)# Consists of class creation, deletion, and
Switch (Config-class-map)# Contains the QoS class map configuration
Manages the operation of an interface and
provides access to the router interface
configuration commands.
Use this mode to set up a physical port for a
specific logical connection operation.
telnet settings and console interface settings.
commands.
matching commands. The class match
commands specify Layer 2, Layer 3, and
general match criteria.
commands for IPv4.
commands for IPv6.
Using the Command-Line Interface
13
Page 14
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Table 5. CLI Command Modes (Continued)
Command Mode Prompt Mode Description
Router OSPF
Config
Router OSPFv3
Config
Router RIP Config Switch (Config-router)# Contains the RIP configuration commands.
MAC Access-list
Config
TACACS Config Switch (Tacacs)# Contains commands to configure properties for
DHCP Pool
Config
DHCPv6 Pool
Config
Stack Global
Config Mode
ARP Access-List
Config Mode
Switch (Config-router)# Contains the OSPF configuration commands.
Switch (Config rtr)# Contains the OSPFv3 configuration commands.
Switch (Config-mac-access-list)# Allows you to create a MAC Access-List and to
enter the mode containing MAC Access-List
configuration commands.
the T ACACS servers.
Switch (Config dhcp-pool)# Contains the DHCP server IP address pool
configuration commands.
Switch (Config dhcp6-pool)# Contains the DHCPv6 server IPv6 address pool
configuration commands.
Switch (Config stack)# Allows you to access the Stack Global Config
Mode.
Switch (Config-arp-access-list)# Contains commands to add ARP ACL rules in
an ARP Access List.
Table 6 explains how to enter or exit each mode.
Table 6. CLI Mode Access and Exit
Command Mode Access Method Exit or Access Previous Mode
User EXEC This is the first level of access. To exit, enter logout.
Privileged EXEC From the User EXEC mode, enter
enable.
Global Config From the Privileged EXEC mode,
enter configure.
VLAN Config From the Privileged EXEC mode,
enter vlan database.
Interface Config From the Global Config mode,
enter
interface <slot/port> or
interface loopback <id> or
interface tunnel <id>
Line Config From the Global Config mode,
enter
lineconfig.
To exit to the User EXEC mode, enter exit or
press Ctrl-Z.
To exit to the Privileged EXEC mode, enter exit,
or press Ctrl-Z.
To exit to the Privileged EXEC mode, enter exit,
or press Ctrl-Z.
To exit to the Global Config mode, enter exit. T o
return to the Privileged EXEC mode, enter
Ctrl-Z.
To exit to the Global Config mode, enter exit. T o
return to the Privileged EXEC mode, enter
Ctrl-Z.
Using the Command-Line Interface
14
Page 15
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
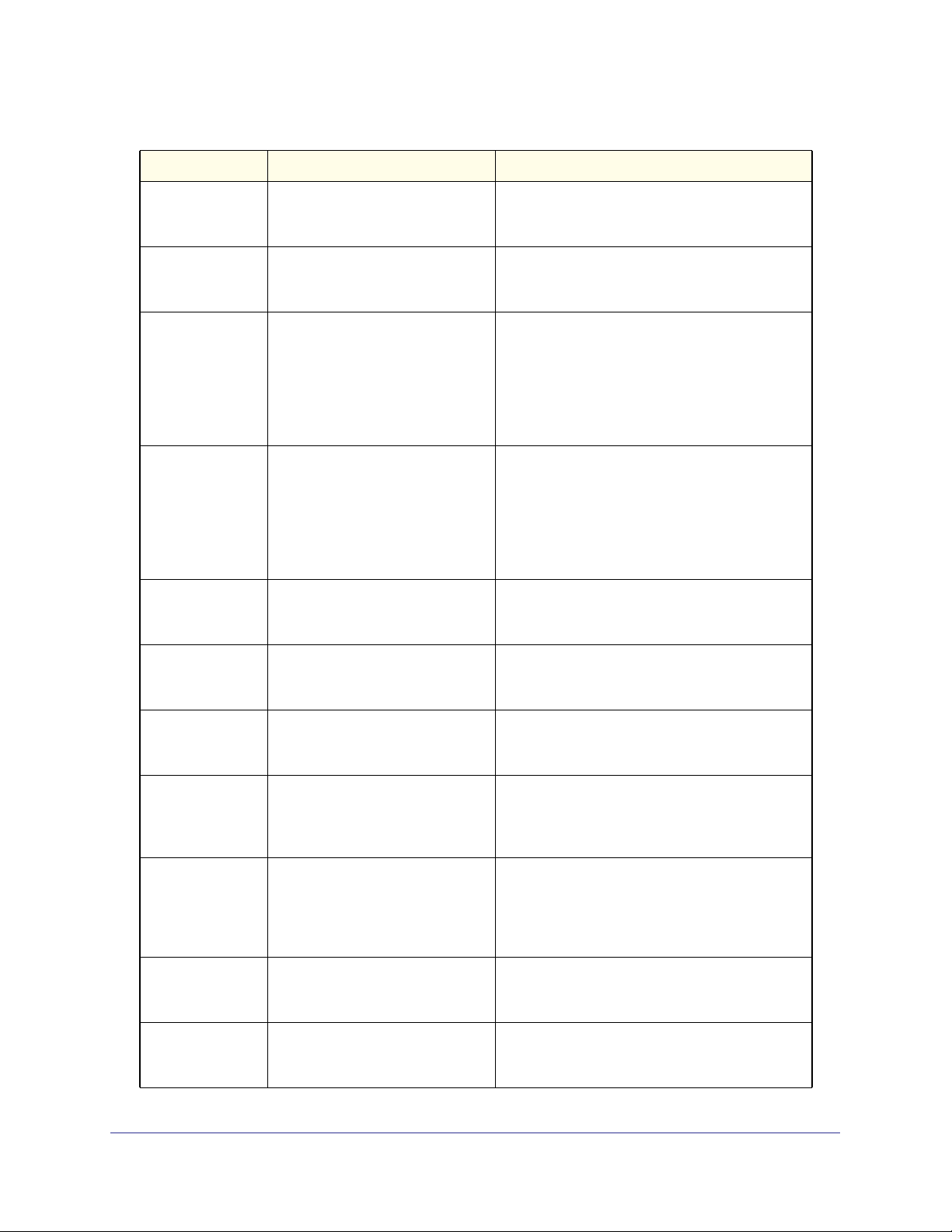
Table 6. CLI Mode Access and Exit (Continued)
Command Mode Access Method Exit or Access Previous Mode
Policy-Map
Config
Policy-Class-Map
Config
Class-Map
Config
Ipv6-Class-Map
Config
Router OSPF
Config
From the Global Config mode,
enter
policy-map <name> in.
From the Policy Map mode enter
class.
From the Global Config mode,
enter
class-map, and specify the
optional keyword ipv4 to specify
the Layer 3 protocol for this class.
See class-map on page 453 for
more information.
From the Global Config mode,
enter
class-map and specify the
optional keyword ipv6 to specify
the Layer 3 protocol for this class.
See class-map on page 453 for
more information.
From the Global Config mode,
enter
router ospf.
To exit to the Global Config mode, enter exit. T o
return to the Privileged EXEC mode, enter
Ctrl-Z.
To exit to the Policy Map mode, enter exit. T o
return to the Privileged EXEC mode, enter
Ctrl-Z.
To exit to the Global Config mode, enter exit. T o
return to the Privileged EXEC mode, enter
Ctrl-Z.
To exit to the Global Config mode, enter exit. T o
return to the Privileged EXEC mode, enter
Ctrl-Z.
To exit to the Global Config mode, enter exit. T o
return to the Privileged EXEC mode, enter
Ctrl-Z.
Router OSPFv3
Config
Router RIP
Config
MAC Access-list
Config
TACACS Config From the Global Config mode,
DHCP Pool
Config
DHCPv6 Pool
Config
From the Global Config mode,
enter
ipv6 router ospf.
From the Global Config mode,
enter
router rip.
From the Global Config mode,
enter
mac access-list extended
<name>.
enter tacacs-server host
<ip-addr>, where <ip-addr> is
the IP address of the TACACS
server on your network.
From the Global Config mode,
enter
ip dhcp pool <pool-name>.
From the Global Config mode,
enter
ip dhcpv6 pool <pool-name>.
To exit to the Global Config mode, enter exit. T o
return to the Privileged EXEC mode, enter
Ctrl-Z.
To exit to the Global Config mode, enter exit. T o
return to the Privileged EXEC mode, enter
Ctrl-Z.
To exit to the Global Config mode, enter exit. T o
return to the Privileged EXEC mode, enter
Ctrl-Z.
To exit to the Global Config mode, enter exit. T o
return to the Privileged EXEC mode, enter
Ctrl-Z.
To exit to the Global Config mode, enter exit. T o
return to the Privileged EXEC mode, enter
Ctrl-Z.
To exit to the Global Config mode, enter exit. T o
return to the Privileged EXEC mode, enter
Ctrl-Z.
Using the Command-Line Interface
15
Page 16
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Table 6. CLI Mode Access and Exit (Continued)
Command Mode Access Method Exit or Access Previous Mode
Stack Global
Config Mode
ARP Access-List
Config Mode
From the Global Config mode,
enter the stack command.
From the Global Config mode,
enter the
command.
arp access-list
T o exit to the Global Config mode, enter the exit
command. To return to the Privileged EXEC
mode, enter Ctrl-Z.
To exit to the Global Config mode, enter the
exit command. To return to the Privileged
EXEC mode, enter
Ctrl-Z.
Command Completion and Abbreviation
Command completion finishes spelling the command when you type enough letters of a
command to uniquely identify the command keyword. Once you have entered enough letters,
press the SPACEBAR or TAB key to complete the word.
Command abbreviation allows you to execute a command when you have entered there are
enough letters to uniquely identify the command.
You must enter all of the required keywords
and parameters before you enter the command.
CLI Error Messages
If you enter a command and the system is unable to execute it, an error message appears.
Table 7 describes the most common CLI error messages.
Table 7. CLI Error Messages
Message Text Description
% Invalid input detected at '^' marker. Indicates that you entered an incorrect or unavailable command.
The carat (^) shows where the invalid text is detected. This
message also appears if any of the parameters or values are not
recognized.
Command not found / Incomplete
command. Use a question mark (?) to
list commands.
Ambiguous command Indicates that you did not enter enough letters to uniquely identify
Indicates that you did not enter the required keywords or values.
the command.
Using the Command-Line Interface
16
Page 17
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
CLI Line-Editing Conventions
Table 8 describes the key combinations you can use to edit commands or increase the
speed of command entry. You can access this list from the CLI by entering help from the
User or Privileged EXEC modes.
Table 8. CLI Editing Conventions
Key Sequence Description
DEL or Backspace Delete previous character
Ctrl-A Go to beginning of line
Ctrl-E Go to end of line
Ctrl-F Go forward one character
Ctrl-B Go backward one character
Ctrl-D Delete current character
Ctrl-U, X Delete to beginning of line
Ctrl-K Delete to end of line
Ctrl-W Delete previous word
Ctrl-T Transpose previous character
Ctrl-P Go to previous line in history buffer
Ctrl-R Rewrites or pastes the line
Ctrl-N Go to next line in history buffer
Ctrl-Y Prints last deleted character
Ctrl-Q Enables serial flow
Ctrl-S Disables serial flow
Ctrl-Z Return to root command prompt
Tab, <SPACE> Command-line completion
Exit Go to next lower command prompt
? List available commands, keywords, or parameters
Using CLI Help
Enter a question mark (?) at the command prompt to display the commands available in the
current mode.
(switch) >?
Using the Command-Line Interface
17
Page 18

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
enable Enter into user privilege mode.
help Display help for various special keys.
logout Exit this session. Any unsaved changes are lost.
ping Send ICMP echo packets to a specified IP address.
quit Exit this session. Any unsaved changes are lost.
show Display Switch Options and Settings.
telnet Telnet to a remote host.
Enter a question mark (?) after each word you enter to display available command keywords
or parameters.
(switch) #network ?
javamode Enable/Disable.
mgmt_vlan Configure the Management VLAN ID of the switch.
parms Configure Network Parameters of the router.
protocol Select DHCP, BootP, or None as the network config
protocol.
If the help output shows a parameter in angle brackets, you must replace the parameter with
a value.
(switch) #network parms ?
<ipaddr> Enter the IP address.
If there are no additional command keywords or parameters, or if more parameters are
optional, the following message appears in the output:
<cr> Press Enter to execute the command
You can also enter a question mark (?) after typing one or more characters of a word to list
the available command or parameters that begin with the letters, as shown in the following
example:
(switch) #show m?
mac-addr-table mac-address-table monitor
Accessing the CLI
You can access the CLI by using a direct console connection or by using a telnet or SSH
connection from a remote management host.
For the initial connection, you must use a direct connection to the console port. You cannot
access the system remotely until the system has an IP address, subnet mask, and default
gateway. You can set the network configuration information manually, or you can configure
the system to accept these settings from a BOOTP or DHCP server on your network. For
more information, see
Network Interface Commands on page 626.
Using the Command-Line Interface
18
Page 19

2. Switching Commands
This chapter describes the switching commands available in the managed switch CLI.
This chapter contains the following sections:
• Port Configuration Commands
• Loopback Interface Commands
• Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) Commands
• VLAN Commands
• Double VLAN Commands
• Voice VLAN Commands
• Provisioning (IEEE 802.1p) Commands
• Protected Ports Commands
• Private VLAN
• GARP Commands
• GVRP Commands
• GMRP Commands
• Port-Based Network Access Control Commands
• 802.1X Supplicant Commands
• Storm-Control Commands
• Flow Control Commands
• Port Mirroring
• Static MAC Filtering
• DHCP L2 Relay Agent Commands
• DHCP Client Commands
2
• DHCP Snooping Configuration Commands
• Dynamic ARP Inspection Commands
• IGMP Snooping Configuration Commands
• IGMP Snooping Querier Commands
• MLD Snooping Commands
• MLD Snooping Querier Commands
19
Page 20

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
• Port Security Commands
• LLDP (802.1AB) Commands
• LLDP-MED Commands
• Denial of Service Commands
• MAC Database Commands
• ISDP Commands
• Priority-Based Flow Control Commands
The commands in this chapter are in three functional groups:
• Show commands display switch settings, statistics, and other information.
• Configuration commands configure features and options of the switch. Every switch
command has a show command that displays the configuration setting.
• Clear commands clear some or all of the settings to factory defaults.
Switching Commands
20
Page 21

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Port Configuration Commands
This section describes the commands you use to view and configure port settings.
interface
This command gives you access to the Interface Config mode, which allows you to enable or
modify the operation of an interface (port).
Format interface <slot/port>
Mode
interface vlan
This command gives you access to the vlan virtual interface mode, which allows certain port
configurations (for example, the IP address) to be applied to the VLAN interface. Type a
question mark (?) after entering the interface configuration mode to see the available options.
Global Config
Format interface vlan <vlan id>
Mode
Global Config
interface lag
This command gives you access to the LAG (link aggregation, or port channel) virtual
interface, which allows certain port configurations to be applied to the LAG interface. Type a
question mark (?) after entering the interface configuration mode to see the available options.
Note: The IP address cannot be assigned to a LAG virtual interface. The
interface must be put under a VLAN group and an IP address
assigned to the VLAN group.
Format interface lag <lag id>
Mode
Global Config
auto-negotiate
This command enables automatic negotiation on a port.
Default
Format auto-negotiate
Mode
enabled
Interface Config
Switching Commands
21
Page 22

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
no auto-negotiate
This command disables automatic negotiation on a port.
Note: Automatic sensing is disabled when automatic negotiation is
disabled.
auto-negotiate all
This command enables automatic negotiation on all ports.
Default
Format auto-negotiate all
Mode
enabled
Global Config
no auto-negotiate all
This command disables automatic negotiation on all ports.
Format no auto-negotiate all
Mode
Global Config
description
Use this command to create an alpha-numeric description of the port.
Format description <description>
Mode
Interface Config
mtu
Use the mtu command to set the maximum transmission unit (MTU) size, in bytes, for frames
that ingress or egress the interface. You can use the mtu command to configure jumbo frame
support for physical and port-channel (LAG) interfaces. For the standard 7000 series
implementation, the MTU size is a valid integer between 1522–9216 for tagged packets and
a valid integer between 1518–9216 for untagged packets.
Note: To receive and process packets, the Ethernet MTU must include
any extra bytes that Layer-2 headers might require. To configure the
IP MTU size, which is the maximum size of the IP packet (IP Header
+ IP payload), see ip mtu on page 233.
Switching Commands
22
Page 23
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Default
Format mtu <1518-9216>
Mode
1518 (untagged)
Interface Config
no mtu
This command sets the default MTU size (in bytes) for the interface.
Format no mtu
Mode
Interface Config
shutdown
This command disables a port.
Note: You can use the shutdown command on physical and port-channel
(LAG) interfaces, but not on VLAN routing interfaces.
Format shutdown
Mode
Interface Config
no shutdown
This command enables a port.
Format no shutdown
Mode
Interface Config
shutdown all
This command disables all ports.
Note: You can use the shutdown all command on physical and
port-channel (LAG) interfaces, but not on VLAN routing interfaces.
Format shutdown all
Mode
Global Config
Switching Commands
23
Page 24
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
no shutdown all
This command enables all ports.
Format no shutdown all
Mode
Global Config
speed
This command sets the speed and duplex setting for the interface.
Format speed [{auto}] [{<100 | 10 | 10G> {<half-duplex | full-duplex>}}]
Mode
Interface Config
Acceptable
Values
100h
100f
10h
10f
10Gh
10Gf
Definition
100BASE-T half duplex
100BASE-T full duplex
10BASE-T half duplex
10BASE-T full duplex
10GBase-T full duplex
10Gbase-T half duplex
speed all
This command sets the speed and duplex setting for all interfaces.
Format speed all [{auto}] [{<100 | 10> {<half-duplex | full-duplex>}}]
Mode
Acceptable
Values
100h
100f
10h
10f
10Gh
10Gf
Global Config
Definition
100BASE-T half duplex
100BASE-T full duplex
10BASE-T half duplex
10BASE-T full duplex
10GBase-T full duplex
10Gbase-T half duplex
Switching Commands
24
Page 25

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
show port advertise
Use this command to display the local administrative link advertisement configuration, local
operational link advertisement, and the link partner advertisement for an interface. It also
displays priority Resolution for speed and duplex as per 802.3 Annex 28B.3. It displays the
autonegotiation state, Phy Master/Slave Clock configuration, and Link state of the port.
If the link is down, the Clock is displayed as No Link, and a dash is displayed against the
Oper Peer advertisement, and Priority Resolution. If autonegotiation is disabled, the admin
Local Link advertisement, operational local link advertisement, operational peer
advertisement, and Priority resolution fields are not displayed.
If this command is executed without the optional slot/port parameter, it displays the
autonegotiation state and operational Local link advertisement for all the ports. Operational
link advertisement will display speed only if it is supported by both local as well as link
partner
Format show port advertise [slot/port]
Mode
. If autonegotiation is disabled, operational local link advertisement is not displayed.
Privileged EXEC
Example: The following commands show the command output with and without the optional
parameter:
(switch)#show port advertise 0/1
Port: 0/1
Type: Gigabit - Level
Link State: Down
Auto Negotiation: Enabled
Clock: Auto
1000f 1000h 100f 100h 10f 10h
----- ----- ---- ---- --- --Admin Local Link Advertisement no no yes no yes no
Oper Local Link Advertisement no no yes no yes no
Oper Peer Advertisement no no yes yes yes yes
Priority Resolution - - yes - - -
(Netgear Switch)#show port advertise
Port Type Neg Operational Link Advertisement
--------- ------------------------------ ----------- ------------------------------
0/1 Gigabit - Level Enabled 1000f, 100f, 100h, 10f, 10h
0/2 Gigabit - Level Enabled 1000f, 100f, 100h, 10f, 10h
0/3 Gigabit - Level Enabled 1000f, 100f, 100h, 10f, 10h
show port
This command displays port information.
Format show port {<slot/port> | all}
Mode
Privileged EXEC
Switching Commands
25
Page 26

Term Definition
Interface
Type
Admin Mode
Physical Mode
Physical Status
Link Status
Link Trap
LACP Mode
Valid slot and port number separated by forward slashes.
If not blank, this field indicates that this port is a special type of port. The possible
values are:
• Mirror - this port is a monitoring port. For more information, see Port Mirroring on
page 121.
• PC Mbr- this port is a member of a port-channel (LAG).
• Probe - this port is a probe port.
The Port control administration state. The port must be enabled in order for it to be
allowed into the network. - May be enabled or disabled.
The desired port speed and duplex mode. If autonegotiation support is selected, the
duplex mode and speed is set from the auto-negotiation process. Note that the
maximum capability of the port (full-duplex -100M) is advertised. Otherwise, this object
determines the port's duplex mode and transmission rate.
The port speed and duplex mode.
The Link is up or down.
This object determines whether to send a trap when link status changes. The factory
default is enabled.
LACP is enabled or disabled on this port.
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
The factory default is enabled.
The factory default is Auto.
show port protocol
This command displays the Protocol-Based VLAN information for either the entire system, or
for the indicated group.
Format show port protocol {<groupid> | all}
Mode
Term Definition
Group Name
Group ID
Protocol(s)
VLAN
Interface(s)
Privileged EXEC
The group name of an entry in the Protocol-based VLAN table.
The group identifier of the protocol group.
The type of protocol(s) for this group.
The VLAN associated with this Protocol Group.
Lists the slot/port interface(s) that are associated with this Protocol Group.
Switching Commands
26
Page 27
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
show port description
This command displays the port description for every port.
Format show port description <slot/port>
Mode
Term Definition
Interface
Description
Privileged EXEC
Valid slot and port number separated by forward slashes
Shows the port description configured via the “description” command
show port status
This command displays the Protocol-Based VLAN information for either the entire system, or
for the indicated group.
Format show port status {<slot/port> | all}
Mode
Privileged EXEC
Term Definition
Interface
Media Type
STP Mode
Physical Mode
Physical Status
Link Status
Loop Status
Partner Flow
Control
Valid slot and port number separated by forward slashes.
“Copper” or “Fiber” for combo port.
Indicate the spanning tree mode of the port.
Either “Auto” or fixed speed and duplex mode.
The actual speed and duplex mode.
Whether the link is Up or Down.
Whether the port is in loop state or not.
Whether the remote side is using flow control or not.
Loopback Interface Commands
The commands in this section describe how to create, delete, and manage loopback
interfaces. A loopback interface is always expected to be up. This interface can provide the
source address for sent packets and can receive both local and remote packets. The
loopback interface is typically used by routing protocols.
To assign an IP address to the loopback interface, see ip address on page 228. To assign an
IPv6 address to the loopback interface, see ipv6 address on page 359.
Switching Commands
27
Page 28
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
interface loopback
Use this command to enter the Interface Config mode for a loopback interface. The range of
the loopback ID is 0–7.
Format interface loopback <loopback-id>
Mode
Global Config
no interface loopback
This command removes the loopback interface and associated configuration parameters for
the specified loopback interface.
Format no interface loopback <loopback-id>
Mode
Global Config
show interface loopback
This command displays information about configured loopback interfaces.
Format show interface loopback [<loopback-id>]
Mode
Privileged EXEC
If you do not specify a loopback ID, the following information appears for each loopback
interface on the system:
Term Definition
Loopback ID
Interface
IP Address
Received
Packets
Sent Packets
IPv6 Address
The loopback ID associated with the rest of the information in the row.
The interface name.
The IPv4 address of the interface.
The number of packets received on this interface.
The number of packets transmitted from this interface.
The IPv6 address of this interface.
If you specify a loopback ID, the following information appears:
Term Definition
Interface Link
Status
IP Address
IPv6 is enabled
(disabled)
Shows whether the link is up or down.
The IPv4 address of the interface.
Shows whether IPv6 is enabled on the interface.
Switching Commands
28
Page 29
Term Definition
IPv6 Prefix is
MTU size
The IPv6 address of the interface.
The maximum transmission size for packets on this interface, in bytes.
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Switching Commands
29
Page 30

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) Commands
This section describes the commands you use to configure Spanning Tree Protocol (STP).
STP helps prevent network loops, duplicate messages, and network instability.
spanning-tree
This command sets the spanning-tree operational mode to enabled.
Default
Format spanning-tree
Mode
enabled
Global Config
no spanning-tree
This command sets the spanning-tree operational mode to disabled. While disabled, the
spanning-tree configuration is retained and can be changed, but is not activated.
Format no spanning-tree
Mode
Global Config
spanning-tree auto-edge
This command enables auto-edge on the interface or range of interfaces. When enabled, the
interface becomes an edge port if it does not see BPDUs for edge delay time.
Default
Format spanning-tree auto-edge
Mode
enabled
Interface Config
no spanning-tree auto-edge
This command disables auto-edge on the interface or range of interfaces.
Format no spanning-tree auto-edge
Mode
Interface Config
spanning-tree bpdufilter
Use this command to enable BPDU Filter on an interface or range of interfaces.
Default
Format spanning-tree bpdufilter
Mode
disabled
Interface Config
Switching Commands
30
Page 31

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
no spanning-tree bpdufilter
Use this command to disable BPDU Filter on the interface or range of interfaces.
Default
Format no spanning-tree bpdufilter
Mode
disabled
Interface Config
spanning-tree bpdufilter default
Use this command to enable BPDU Filter on all the edge port interfaces.
Default
Format spanning-tree bpdufilter
Mode
no spanning-tree bpdufilter default
Use this command to disable BPDU Filter on all the edge port interfaces.
Default
Format no spanning-tree bpdufilter default
Mode
disabled
Global Config
enabled
Global Config
spanning-tree bpduflood
Use this command to enable BPDU Flood on the interface.
Default
Format spanning-tree bpduflood
Mode
no spanning-tree bpduflood
Use this command to disable BPDU Flood on the interface.
Format no spanning-tree bpduflood
Mode
disabled
Interface Config
Interface Config
Switching Commands
31
Page 32

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
spanning-tree bpduguard
Use this command to enable BPDU Guard on the switch.
Default
Format spanning-tree bpduguard
Mode
disabled
Global Config
no spanning-tree bpduguard
Use this command to disable BPDU Guard on the switch.
Format no spanning-tree bpduguard
Mode
Global Config
spanning-tree bpdumigrationcheck
Use this command to force a transmission of rapid spanning tree (RSTP) and multiple
spanning tree (MSTP) BPDUs. Use the <slot/port> parameter to transmit a BPDU from a
specified interface, or use the all keyword to transmit BPDUs from all interfaces. This
command forces the BPDU transmission when you execute it, so the command does not
change the system configuration or have a “no” version.
Format spanning-tree bpdumigrationcheck {<slot/port> | all}
Mode
Global Config
spanning-tree configuration name
This command sets the Configuration Identifier Name for use in identifying the configuration
that this switch is currently using. The <name> is a string of up to 32 characters.
Default
Format spanning-tree configuration name
Mode
no spanning-tree configuration name
This command resets the Configuration Identifier Name to its default.
Format no spanning-tree configuration name
Mode
base MAC address in hexadecimal notation
<name>
Global Config
Global Config
Switching Commands
32
Page 33

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
spanning-tree configuration revision
This command sets the Configuration Identifier Revision Level for use in identifying the
configuration that this switch is currently using. The Configuration Identifier Revision Level is
a number in the range of 0–65535.
Default
Format spanning-tree configuration revision
Mode
0
<0-65535>
Global Config
no spanning-tree configuration revision
This command sets the Configuration Identifier Revision Level for use in identifying the
configuration that this switch is currently using to the default value.
Format no spanning-tree configuration revision
Mode
Global Config
spanning-tree edgeport
This command specifies that this port is an Edge Port within the Common and Internal
Spanning Tree. This allows this port to transition to Forwarding State without delay.
Default enabled
Format spanning-tree edgeport
Mode
Interface Config
no spanning-tree edgeport
This command specifies that this port is not an Edge Port within the Common and Internal
Spanning T
Format no spanning-tree edgeport
Mode
ree.
Interface Config
spanning-tree forceversion
This command sets the Force Protocol Version parameter to a new value.
Default
Format spanning-tree forceversion
Mode
• Use 802.1d to specify that the switch transmits ST BPDUs rather than MST BPDUs (IEEE
802.1s
<802.1d | 802.1s | 802.1w>
Global Config
802.1d functionality supported).
Switching Commands
33
Page 34

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
• Use 802.1s to specify that the switch transmits MST BPDUs (IEEE 802.1s functionality
supported).
• Use 802.1w to specify that the switch transmits RST BPDUs rather than MST BPDUs
(IEEE 802.1w functionality supported).
no spanning-tree forceversion
This command sets the Force Protocol Version parameter to the default value.
Format no spanning-tree forceversion
Mode
Global Config
spanning-tree forward-time
This command sets the Bridge Forward Delay parameter to a new value for the Common and
Internal Spanning Tree. The forward-time value is in seconds within a range of 4–30, with the
value being greater than or equal to “(Bridge Max Age / 2) + 1”.
Default
Format spanning-tree forward-time
Mode
15
<4-30>
Global Config
no spanning-tree forward-time
This command sets the Bridge Forward Delay parameter for the Common and Internal
Spanning
Format no spanning-tree forward-time
Mode
Tree to the default value.
Global Config
spanning-tree guard
This command selects whether loop guard or root guard is enabled on an interface. If neither
is enabled, the port operates in accordance with the multiple spanning tree protocol.
Default
Format spanning-tree guard { none | root | loop }
Mode
none
Interface Config
no spanning-tree guard
This command disables loop guard or root guard on the interface.
Format no spanning-tree guard
Mode
Interface Config
Switching Commands
34
Page 35

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
spanning-tree tcnguard
This command enables the propagation of received topology change notifications and topology
changes to other ports.
Default
Format spanning-tree tcnguard
Mode
disable
Interface Config
no spanning-tree tcnguard
This command
disables the propagation of received topology change notifications and topology
changes to other ports.
Format no spanning-tree tcnguard
Mode
Interface Config
spanning-tree max-age
This command sets the Bridge Max Age parameter to a new value for the Common and
Internal Spanning Tree. The max-age value is in seconds within a range of 6–40, with the
value being less than or equal to 2 x (Bridge Forward Delay - 1).
Default
Format spanning-tree max-age
Mode
20
<6-40>
Global Config
no spanning-tree max-age
This command sets the Bridge Max Age parameter for the Common and Internal Spanning
ree to the default value.
T
Format no spanning-tree max-age
Mode
Global Config
spanning-tree max-hops
This command sets the MSTP Max Hops parameter to a new value for the Common and
Internal Spanning Tree. The max-hops value is a range from 6 to 40.
Default
Format spanning-tree max-hops <1-127>
Mode
20
Global Config
Switching Commands
35
Page 36

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
no spanning-tree max-hops
This command sets the Bridge Max Hops parameter for the Common and Internal Spanning
ree to the default value.
T
Format no spanning-tree max-hops
Mode
Global Config
spanning-tree mst
This command sets the Path Cost or Port Priority for this port within the multiple spanning
tree instance or in the Common and Internal Spanning Tree. If you specify an <mstid>
parameter that corresponds to an existing multiple spanning tree instance, the configurations
are done for that multiple spanning tree instance. If you specify 0 (defined as the default CIST
ID) as the <mstid>, the configurations are done for the Common and Internal Spanning Tree
instance.
If you specify the cost option, the command sets the path cost for this port within a multiple
spanning tree instance or the Common and Internal Spanning
the <mstid> parameter . You can set the path cost as a number in the range of 1–200000000
or auto. If you select auto the path cost value is set based on Link Speed.
Tree instance, depending on
If you specify the external-cost option, this command sets the external-path cost for MST
instance ‘0’ that is, CIST instance.
You can set the external cost as a number in the range of
1–200000000 or auto. If you specify auto, the external path cost value is set based on Link
Speed.
If you specify the port-priority option, this command sets the priority for this port within a
specific multiple spanning tree instance or the Common and Internal Spanning
Tree instance,
depending on the <mstid> parameter. The port-priority value is a number in the range of
0–240 in increments of 16.
Default
Format spanning-tree mst
Mode
• cost—auto
• external-cost—auto
• port-priority—128
<mstid> {{cost <1-200000000> | auto} |
{external-cost <1-200000000> | auto} | port-priority <0-240>}
Interface Config
no spanning-tree mst
This command sets the Path Cost or Port Priority for this port within the multiple spanning
tree instance, or in the Common and Internal Spanning
Tree to the respective default values.
If you specify an <mstid> parameter that corresponds to an existing multiple spanning tree
instance, you are configuring that multiple spanning tree instance. If you specify 0 (defined as
the default CIST ID) as the <mstid>, you are configuring the Common and Internal
Spanning Tree instance.
Switching Commands
36
Page 37

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
If you specify cost, this command sets the path cost for this port within a multiple spanning
tree instance or the Common and Internal Spanning Tree instance, depending on the
<mstid> parameter, to the default value, that is, a path cost value based on the Link Speed.
If you specify external-cost, this command sets the external path cost for this port for mst ‘0’
instance, to the default value, that is, a path cost value based on the Link Speed.
If you specify port-priority, this command sets the priority for this port within a specific
multiple spanning tree instance or the Common and Internal Spanning
Tree instance,
depending on the <mstid> parameter, to the default value.
Format no spanning-tree mst <mstid> <cost | external-cost | port-priority>
Mode
Interface Config
spanning-tree mst instance
This command adds a multiple spanning tree instance to the switch. The parameter
<mstid> is a number within a range of 1–4094, that corresponds to the new instance ID to
be added. The maximum number of multiple instances supported by the switch is 4.
Default
Format spanning-tree mst instance <mstid>
Mode
none
Global Config
no spanning-tree mst instance
This command removes a multiple spanning tree instance from the switch and reallocates all
VLANs allocated to the deleted instance to the Common and Internal Spanning
Tree. The
parameter <mstid> is a number that corresponds to the desired existing multiple spanning
tree instance to be removed.
Format no spanning-tree mst instance <mstid>
Mode
Global Config
spanning-tree mst priority
This command sets the bridge priority for a specific multiple spanning tree instance. The
parameter <mstid> is a number that corresponds to the desired existing multiple spanning
tree instance. The priority value is a number within a range of 0–61440 in increments of
4096.
If you specify 0 (defined as the default CIST ID) as the <mstid>, this command sets the
Bridge Priority parameter to a new value for the Common and Internal Spanning
bridge priority value is a number within a range of 0–61440. The twelve least significant bits
Tree. The
Switching Commands
37
Page 38

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
are masked according to the 802.1s specification. This causes the priority to be rounded
down to the next lower valid priority.
Default
Format spanning-tree mst priority
Mode
32768
<mstid> <0-61440>
Global Config
no spanning-tree mst priority
This command sets the bridge priority for a specific multiple spanning tree instance to the
default value.
The parameter <mstid> is a number that corresponds to the desired existing
multiple spanning tree instance.
If 0 (defined as the default CIST ID) is passed as the <mstid>, this command sets the
Bridge Priority parameter for the Common and Internal Spanning
Format no spanning-tree mst priority <mstid>
Mode
Global Config
Tree to the default value.
spanning-tree mst vlan
This command adds an association between a multiple spanning tree instance and one or
more VLANs so that the VLAN(s) are no longer associated with the Common and Internal
Spanning Tree. The parameter <mstid> is a number that corresponds to the desired
existing multiple spanning tree instance. The vlan range can be specified as a list or as a
range of values. To specify a list of VLANs, enter a list of VLAN IDs, each separated by a
comma with no spaces in between. To specify a range of VLANs, separate the beginning and
ending VLAN ID with a dash ("-").
Format spanning-tree mst vlan <mstid> <vlanid>
Mode
Global Config
no spanning-tree mst vlan
This command removes an association between a multiple spanning tree instance and one
or more VLANs so that the VLAN(s) are again associated with the Common and Internal
Spanning T
Format no spanning-tree mst vlan <mstid> <vlanid>
Mode
ree.
Global Config
Switching Commands
38
Page 39

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
spanning-tree port mode
This command sets the Administrative Switch Port State for this port to enabled.
Default
Format spanning-tree port mode
Mode
enabled
Interface Config
no spanning-tree port mode
This command sets the Administrative Switch Port State for this port to disabled.
Format no spanning-tree port mode
Mode
Interface Config
spanning-tree port mode all
This command sets the Administrative Switch Port State for all ports to enabled.
Default
Format spanning-tree port mode all
Mode
no spanning-tree port mode all
enabled
Global Config
This command sets the Administrative Switch Port State for all ports to disabled.
Format no spanning-tree port mode all
Mode
Global Config
spanning-tree edgeport all
This command specifies that every port is an Edge Port within the Common and Internal
Spanning Tree. This allows all ports to transition to Forwarding State without delay.
Format spanning-tree edgeport all
Mode
no spanning-tree edgeport all
This command disables Edge Port mode for all ports within the Common and Internal
Spanning T
Format no spanning-tree edgeport all
Mode
Global Config
ree.
Global Config
Switching Commands
39
Page 40

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
spanning-tree bpduforwarding
Normally a switch will not forward Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) BPDU packets if STP is
disabled. However, if in some network setup, the user wishes to forward BDPU packets
received from other network devices, this command can be used to enable the forwarding.
Default
Format spanning-tree bpduforwarding
Mode
disabled
Global Config
no spanning-tree bpduforwarding
This command will cause the STP BPDU packets received from the network to be dropped if
STP is disabled.
Format no spanning-tree bpduforwarding
Mode
Global Config
show spanning-tree
This command displays spanning tree settings for the Common and Internal Spanning Tree.
The following details are displayed.
Format show spanning-tree
Mode
• Privileged EXEC
• User EXEC
Term Definition
Bridge Priority
Bridge Identifier
Time Since
Topology
Change
Topology
Change Count
Topology
Change
Designated
Root
Root Path Cost
Specifies the bridge priority for the Common and Internal Spanning Tree (CST). The
value lies between 0 and 61440. It is displayed in multiples of 4096.
The bridge identifier for the CST. It is made up using the bridge priority and the base
MAC address of the bridge.
Time in seconds.
Number of times changed.
Boolean value of the Topology Change parameter for the switch indicating if a topology
change is in progress on any port assigned to the Common and Internal Spanning Tree.
The bridge identifier of the root bridge. It is made up from the bridge priority and the base
MAC address of the bridge.
Value of the Root Path Cost parameter for the Common and Internal Spanning Tree.
Switching Commands
40
Page 41
Term Definition
Root Port
Identifier
Root Port Max
Age
Root Port
Bridge Forward
Delay
Hello Time
Bridge Hold
Time
Bridge Max
Hops
CST Regional
Root
Regional Root
Path Cost
Associated
FIDs
Associated
VLANs
Identifier of the port to access the Designated Root for the CST
Derived value.
Derived value.
Configured value of the parameter for the CST
Minimum time between transmission of Configuration Bridge Protocol Data Units
(BPDUs).
Bridge max-hops count for the device.
Bridge Identifier of the CST Regional Root. It is made up using the bridge priority and the
base MAC address of the bridge.
Path Cost to the CST Regional Root.
List of forwarding database identifiers currently associated with this instance.
List of VLAN IDs currently associated with this instance.
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
.
show spanning-tree brief
This command displays spanning tree settings for the bridge. The following information
appears.
Format show spanning-tree brief
Mode
Term Definition
Bridge Priority
Bridge Identifier
Bridge Max Age
Bridge Max Hops
Bridge Hello Time
Bridge Forward Delay
Bridge Hold Time
• Privileged EXEC
• User EXEC
Configured value.
The bridge identifier for the selected MST instance. It is made up using the
bridge priority and the base MAC address of the bridge.
Configured value.
Bridge max-hops count for the device.
Configured value.
Configured value.
Minimum time between transmission of Configuration Bridge Protocol Data
Units (BPDUs).
Switching Commands
41
Page 42

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
show spanning-tree interface
This command displays the settings and parameters for a specific switch port within the
Common and Internal Spanning Tree. The <slot/port> is the desired switch port. The
following details are displayed on execution of the command.
Format show spanning-tree interface <slot/port>
Mode
Term Definition
Hello Time
Port Mode
BPDU Guard Effect
Root Guard
Loop Guard
TCN Guard
BPDU Filter Mode
BPDU Flood Mode
Auto Edge
Port Up Time Since
Counters Last Cleared
STP BPDUs
Transmitted
STP BPDUs Received
RSTP BPDUs
Transmitted
RSTP BPDUs Received
MSTP BPDUs
Transmitted
MSTP BPDUs Received
• Privileged EXEC
• User EXEC
Admin hello time for this port.
Enabled or disabled.
Enabled or disabled.
Enabled or disabled.
Enabled or disabled.
Enable or disable the propagation of received topology change notifications and
topology changes to other ports.
Enabled or disabled.
Enabled or disabled.
To enable or disable the feature that causes a port that has not seen a BPDU for
‘edge delay’ time, to become an edge port and transition to forwarding faster
Time since port was reset, displayed in days, hours, minutes, and seconds.
Spanning Tree Protocol Bridge Protocol Data Units sent.
Spanning Tree Protocol Bridge Protocol Data Units received.
Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol Bridge Protocol Data Units sent.
Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol Bridge Protocol Data Units received.
Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol Bridge Protocol Data Units sent.
Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol Bridge Protocol Data Units received.
.
show spanning-tree mst port detailed
This command displays the detailed settings and parameters for a specific switch port within
a particular multiple spanning tree instance. The parameter <mstid> is a number that
Switching Commands
42
Page 43
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
corresponds to the desired existing multiple spanning tree instance. The <slot/port> is
the desired switch port.
Format show spanning-tree mst port detailed <mstid> <slot/port>
Mode
Term Definition
MST Instance ID
Port Identifier
Port Priority
Port Forwarding
State
Port Role
Auto-Calculate
Port Path Cost
Port Path Cost
Designated
Root
Root Path Cost
Designated
Bridge
Designated Port
Identifier
Loop
Inconsistent
State
Transitions Into
Loop
Inconsistent
State
Transitions Out
of Loop
Inconsistent
State
• Privileged EXEC
• User EXEC
The ID of the existing MST instance.
The port identifier for the specified port within the selected MST instance. It is made up
from the port priority and the interface number of the port.
The priority for a particular port within the selected MST instance. The port priority is
displayed in multiples of 16.
Current spanning tree state of this port.
Each enabled MST Bridge Port receives a Port Role for each spanning tree. The port
role is one of the following values: Root Port, Designated Port,
Port, Master Port, or Disabled Port
Indicates whether auto calculation for port path cost is enabled.
Configured value of the Internal Port Path Cost parameter.
The Identifier of the designated root for this port.
The path cost to get to the root bridge for this instance. The root path cost is zero if the
bridge is the root bridge for that instance.
Bridge Identifier of the bridge with the Designated Port.
Port on the Designated Bridge that offers the lowest cost to the LAN.
The current loop inconsistent state of this port in this MST instance. When in loop
inconsistent state, the port has failed to receive BPDUs while configured with loop guard
enabled. Loop inconsistent state maintains the port in a "blocking" state until a
subsequent BPDU is received.
The number of times this interface has transitioned into loop inconsistent state.
The number of times this interface has transitioned out of loop inconsistent state.
Alternate Port, Backup
Switching Commands
43
Page 44

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
If you specify 0 (defined as the default CIST ID) as the <mstid>, this command displays the
settings and parameters for a specific switch port within the Common and Internal Spanning
Tree. The <slot/port> is the desired switch port. In this case, the following are displayed.
Term Definition
Port Identifier
Port Priority
Port Forwarding
State
Port Role
Auto-Calculate
Port Path Cost
Port Path Cost
Auto-Calculate
External Port
Path Cost
External Port
Path Cost
Designated
Root
Root Path Cost
Designated
Bridge
Designated Port
Identifier
Topology
Change
Acknowledgem
ent
Hello Time
Edge Port
Edge Port
Status
Point To Point
MAC Status
CST Regional
Root
CST Internal
Root Path Cost
Loop
Inconsistent
State
The port identifier for this port within the CST.
The priority of the port within the CST.
The forwarding state of the port within the CST.
The role of the specified interface within the CST.
Indicates whether auto calculation for port path cost is enabled or not (disabled).
The configured path cost for the specified interface.
Indicates whether auto calculation for external port path cost is enabled.
The cost to get to the root bridge of the CIST across the boundary of the region. This
means that if the port is a boundary port for an MSTP region, the external path cost is
used.
Identifier of the designated root for this port within the CST.
The root path cost to the LAN by the port.
The bridge containing the designated port.
Port on the Designated Bridge that offers the lowest cost to the LAN.
Value of flag in next Configuration Bridge Protocol Data Unit (BPDU) transmission
indicating if a topology change is in progress for this port.
The hello time in use for this port.
The configured value indicating if this port is an edge port.
The derived value of the edge port status. True if operating as an edge port; false
otherwise.
Derived value indicating if this port is part of a point to point link.
The regional root identifier in use for this port.
The internal root path cost to the LAN by the designated external port.
The current loop inconsistent state of this port in this MST instance. When in loop
inconsistent state, the port has failed to receive BPDUs while configured with loop guard
enabled. Loop inconsistent state maintains the port in a "blocking" state until a
subsequent BPDU is received.
Switching Commands
44
Page 45

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Term Definition
Transitions Into
Loop
Inconsistent
State
Transitions Out
of Loop
Inconsistent
State
The number of times this interface has transitioned into loop inconsistent state.
The number of times this interface has transitioned out of loop inconsistent state.
show spanning-tree mst port summary
This command displays the settings of one or all ports within the specified multiple spanning
tree instance. The parameter <mstid> indicates a particular MST instance. The parameter
{<slot/port> | all} indicates the desired switch port or all ports.
If you specify 0 (defined as the default CIST ID) as the <mstid>, the status summary
displays for one or all ports within the Common and Internal Spanning
Tree.
Format show spanning-tree mst port summary <mstid> {<slot/port> | all}
Mode
Term Definition
MST Instance ID
Interface
STP Mode
Type
STP State
Port Role
Desc
• Privileged EXEC
• User EXEC
The MST instance associated with this port.
Valid slot and port number separated by forward slashes.
Indicates whether spanning tree is enabled or disabled on the port.
Currently not used.
The forwarding state of the port in the specified spanning tree instance.
The role of the specified port within the spanning tree.
Indicates whether the port is in loop inconsistent state or not. This field is blank if the loop
guard feature is not available.
show spanning-tree mst port summary active
This command displays settings for the ports within the specified multiple spanning tree
instance that are active links.
Format show spanning-tree mst port summary <mstid> active
Mode
• Privileged EXEC
• User EXEC
Switching Commands
45
Page 46

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Term Definition
mstid
Interface
STP Mode
Type
STP State
Port Role
Desc
The ID of the existing MST instance.
slot/port
Indicates whether spanning tree is enabled or disabled on the port.
Currently not used.
The forwarding state of the port in the specified spanning tree instance.
The role of the specified port within the spanning tree.
Indicates whether the port is in loop inconsistent state or not. This field is blank if the loop
guard feature is not available.
show spanning-tree mst summary
This command displays summary information about all multiple spanning tree instances in
the switch. On execution, the following details are displayed.
Format show spanning-tree mst summary
Mode
Term Definition
MST Instance ID
List
For each
MSTID:
• Associated
FIDs
• Associated
VLANs
• Privileged EXEC
• User EXEC
List of multiple spanning trees IDs currently configured.
• List of forwarding database identifiers associated with this instance.
• List of VLAN IDs associated with this instance.
show spanning-tree summary
This command displays spanning tree settings and parameters for the switch. The following
details are displayed on execution of the command.
Format show spanning-tree summary
Mode
• Privileged EXEC
• User EXEC
Switching Commands
46
Page 47

Term Definition
Spanning Tree
Adminmode
Spanning Tree
Version
BPDU Guard
Mode
BPDU Filter
Mode
Configuration
Name
Configuration
Revision Level
Configuration
Digest Key
Configuration
Format Selector
MST Instances
Enabled or disabled.
Version of 802.1 currently supported (IEEE 802.1s, IEEE 802.1w, or IEEE 802.1d) based
upon the Force Protocol V
Enabled or disabled.
Enabled or disabled.
Identifier used to identify the configuration currently being used.
Identifier used to identify the configuration currently being used.
A generated Key used in the exchange of the BPDUs.
Specifies the version of the configuration format being used in the exchange of BPDUs.
The default value is zero.
List of all multiple spanning tree instances configured on the switch.
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
ersion parameter.
show spanning-tree vlan
This command displays the association between a VLAN and a multiple spanning tree
instance. The <vlanid> corresponds to an existing VLAN ID.
Format show spanning-tree vlan <vlanid>
Mode
Term Definition
VLAN Identifier
Associated
Instance
• Privileged EXEC
• User EXEC
The VLANs associated with the selected MST instance.
Identifier for the associated multiple spanning tree instance or “CST” if associated with
the Common and Internal Spanning
Tree.
VLAN Commands
This section describes the commands you use to configure VLAN settings.
Switching Commands
47
Page 48

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
vlan database
This command gives you access to the VLAN Config mode, which allows you to configure
VLAN characteristics.
Format vlan database
Mode
Privileged EXEC
network mgmt_vlan
This command configures the Management VLAN ID.
Default
Format network mgmt_vlan <1-4093>
Mode
1
Privileged EXEC
no network mgmt_vlan
This command sets the Management VLAN ID to the default.
Format no network mgmt_vlan
Mode
Privileged EXEC
vlan
This command creates a new VLAN and assigns it an ID. The ID is a valid VLAN
identification number (ID 1 is reserved for the default VLAN). The vlan-list contains VlanId's in
range <1-4093>. Separate non-consecutive IDs with ',' and no spaces and no zeros in
between the range; Use '-' for range.
Format vlan <vlan-list>
Mode
VLAN Config
no vlan
This command deletes an existing VLAN. The ID is a valid VLAN identification number (ID 1
is reserved for the default VLAN).
The vlan-list contains VlanId's in range <1-4093>.
Separate non-consecutive IDs with ',' and no spaces and no zeros in between the range; Use
'-' for range.
Format no vlan <vlan-list>
Mode
VLAN Config
Switching Commands
48
Page 49

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
vlan acceptframe
This command sets the frame acceptance mode per interface. For VLAN Only mode,
untagged frames or priority frames received on this interface are discarded. For Admit All
mode, untagged frames or priority frames received on this interface are accepted and
assigned the value of the interface VLAN ID for this port. With either option, VLAN tagged
frames are forwarded in accordance with the IEEE 802.1Q VLAN Specification.
Default
Format vlan acceptframe {untaggedonly | vlanonly | all}
Mode
all
Interface Config
no vlan acceptframe
This command resets the frame acceptance mode for the interface to the default value.
Format no vlan acceptframe
Mode
Interface Config
vlan ingressfilter
This command enables ingress filtering. If ingress filtering is disabled, frames received with
VLAN IDs that do not match the VLAN membership of the receiving interface are admitted
and forwarded to ports that are members of that VLAN.
Default
Format vlan ingressfilter
Mode
disabled
Interface Config
no vlan ingressfilter
This command disables ingress filtering. If ingress filtering is disabled, frames received with
VLAN IDs that do not match the VLAN membership of the receiving interface are admitted
and forwarded to ports that are members of that VLAN.
Format no vlan ingressfilter
Mode
Interface Config
Switching Commands
49
Page 50

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
vlan makestatic
This command changes a dynamically created VLAN (one that is created by GVRP
registration) to a static VLAN (one that is permanently configured and defined). The ID is a
valid VLAN identification number. VLAN range is 2-4093.
Format vlan makestatic <2-4093>
Mode
VLAN Config
vlan name
This command changes the name of a VLAN. The name is an alphanumeric string of up to 32
characters, and the ID is a valid VLAN identification number. ID range is 1-4093.
Default
Format vlan name <1-4093> <name>
Mode
• VLAN ID 1 - default
• other VLANS - blank string
VLAN Config
no vlan name
This command sets the name of a VLAN to a blank string.
Format no vlan name <1-4093>
Mode
VLAN Config
vlan participation
This command configures the degree of participation for a specific interface in a VLAN. The
ID is a valid VLAN identification number, and the interface is a valid interface number.
Format vlan participation {exclude | include | auto} <1-4093>
Mode
Participation options are:
Interface Config
Participation
Options
include
exclude
auto
Definition
The interface is always a member of this VLAN. This is equivalent to registration fixed.
The interface is never a member of this VLAN. This is equivalent to registration
forbidden.
The interface is dynamically registered in this VLAN by GVRP. The interface will not
participate in this VLAN unless a join request is received on this interface.
equivalent to registration normal.
Switching Commands
50
This is
Page 51

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
vlan participation all
This command configures the degree of participation for all interfaces in a VLAN. The ID is a
valid VLAN identification number.
Format vlan participation all {exclude | include | auto} <1-4093>
Mode
You can use the following participation options:
Global Config
Participation
Options
include
exclude
auto
Definition
The interface is always a member of this VLAN. This is equivalent to registration fixed.
The interface is never a member of this VLAN. This is equivalent to registration
forbidden.
The interface is dynamically registered in this VLAN by GVRP. The interface will not
participate in this VLAN unless a join request is received on this interface.
equivalent to registration normal.
vlan port acceptframe all
This command sets the frame acceptance mode for all interfaces.
Default
Format vlan port acceptframe all {vlanonly | all}
Mode
The modes defined as follows:
Mode Definition
VLAN Only
mode
Admit All mode
all
Global Config
Untagged frames or priority frames received on this interface are discarded.
Untagged frames or priority frames received on this interface are accepted and assigned
the value of the interface VLAN ID for this port.
This is
With either option, VLAN tagged frames are forwarded in accordance with the IEEE 802.1Q
VLAN Specification.
no vlan port acceptframe all
This command sets the frame acceptance mode for all interfaces to Admit All. For Admit All
mode, untagged frames or priority frames received on this interface are accepted and
Switching Commands
51
Page 52

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
assigned the value of the interface VLAN ID for this port. With either option, VLAN tagged
frames are forwarded in accordance with the IEEE 802.1Q VLAN Specification.
Format no vlan port acceptframe all
Mode
Global Config
vlan port ingressfilter all
This command enables ingress filtering for all ports. If ingress filtering is disabled, frames
received with VLAN IDs that do not match the VLAN membership of the receiving interface
are admitted and forwarded to ports that are members of that VLAN.
Default
Format vlan port ingressfilter all
Mode
disabled
Global Config
no vlan port ingressfilter all
This command disables ingress filtering for all ports. If ingress filtering is disabled, frames
received with VLAN IDs that do not match the VLAN membership of the receiving interface
are admitted and forwarded to ports that are members of that VLAN.
Format no vlan port ingressfilter all
Mode
Global Config
vlan port pvid all
This command changes the VLAN ID for all interface.
Default
Format vlan port pvid all <1-4093>
Mode
1
Global Config
no vlan port pvid all
This command sets the VLAN ID for all interfaces to 1.
Format no vlan port pvid all
Mode
Global Config
Switching Commands
52
Page 53

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
vlan port tagging all
This command configures the tagging behavior for all interfaces in a VLAN to enabled. If
tagging is enabled, traffic is transmitted as tagged frames. If tagging is disabled, traffic is
transmitted as untagged frames. The ID is a valid VLAN identification number.
Format vlan port tagging all <1-4093>
Mode
no vlan port tagging all
This command configures the tagging behavior for all interfaces in a VLAN to disabled. If
tagging is disabled, traf
identification number.
Format no vlan port tagging all
Mode
Global Config
fic is transmitted as untagged frames. The ID is a valid VLAN
Global Config
vlan protocol group
This command adds protocol-based VLAN groups to the system. When it is created, the
protocol group will be assigned a unique number (1-128) that will be used to identify the
group in subsequent commands.
Format vlan protocol group <1-128>
Mode
Global Config
no vlan protocol group
This command removes a protocol group.
Format no vlan protocol group <1-128>
Mode
Global Config
vlan protocol group name
This command assigns a name to a protocol-based VLAN group. The groupname variable
can be a character string of 0–16 characters.
Format vlan protocol group name <1-128> <groupname>
Mode
Global Config
Switching Commands
53
Page 54

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
no vlan protocol group name
This command removes the name from a protocol-based VLAN group.
Format no vlan protocol group name <1-128>
Mode
Global Config
vlan protocol group add protocol
This command adds the protocol to the protocol-based VLAN identified by groupid. A group
may have more than one protocol associated with it. Each interface and protocol combination
can only be associated with one group. If adding a protocol to a group causes any conflicts
with interfaces currently associated with the group, this command fails and the protocol is not
added to the group. The possible values for protocol-list includes the keywords ip, arp, and
ipx and hexadecimal or decimal values ranging from 0x0600 (1536) to 0xFFFF (65535). The
protocol list can accept up to 16 protocols separated by a comma.
Default
Format vlan protocol group add protocol <groupid> ethertype
Mode
none
{<protocol-list>|arp|ip|ipx}
Global Config
no vlan protocol group add protocol
This command removes the <protocol> from this protocol-based VLAN group that is
identified by this <groupid>.
Format no vlan protocol group add protocol <groupid> ethertype
{<protocol-list>|arp|ip|ipx}
Mode
Global Config
The possible values for protocol are ip, arp, and ipx.
protocol group
This command attaches a <vlanid> to the protocol-based VLAN identified by <groupid>.
A group may only be associated with one VLAN at a time, however the VLAN association can
be changed.
Default
Format protocol group <groupid> <vlanid>
Mode
none
VLAN Config
Switching Commands
54
Page 55

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
no protocol group
This command removes the <vlanid> from this protocol-based VLAN group that is
identified by this <groupid>.
Format no protocol group <groupid> <vlanid>
Mode
VLAN Config
protocol vlan group
This command adds the physical interface to the protocol-based VLAN identified by
<groupid>. You can associate multiple interfaces with a group, but you can only associate
each interface and protocol combination with one group. If adding an interface to a group
causes any conflicts with protocols currently associated with the group, this command fails
and the interface(s) are not added to the group.
Default
Format protocol vlan group <groupid>
Mode
none
Interface Config
no protocol vlan group
This command removes the interface from this protocol-based VLAN group that is identified
by this <groupid>.
Format no protocol vlan group <groupid>
Mode
Interface Config
protocol vlan group all
This command adds all physical interfaces to the protocol-based VLAN identified by
<groupid>. You can associate multiple interfaces with a group, but you can only associate
each interface and protocol combination with one group. If adding an interface to a group
causes any conflicts with protocols currently associated with the group, this command will fail
and the interface(s) will not be added to the group.
Default
Format protocol vlan group all <groupid>
Mode
none
Global Config
Switching Commands
55
Page 56

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
no protocol vlan group all
This command removes all interfaces from this protocol-based VLAN group that is identified
by this <groupid>.
Format no protocol vlan group all <groupid>
Mode
Global Config
vlan pvid
This command changes the VLAN ID per interface.
Default
Format vlan pvid <1-4093>
Mode
1
Interface Config
no vlan pvid
This command sets the VLAN ID per interface to 1.
Format no vlan pvid
Mode
Interface Config
vlan tagging
This command configures the tagging behavior for a specific interface in a VLAN to enabled.
If tagging is enabled, traffic is transmitted as tagged frames. If tagging is disabled, traffic is
transmitted as untagged frames. The vlan-list contains VlanId's in range <1-4093>. Separate
non-consecutive IDs with ',' and no spaces and no zeros in between the range; Use '-' for
range.
Format vlan tagging <vlan-list>
Mode
Interface Config
no vlan tagging
This command configures the tagging behavior for a specific interface in a VLAN to disabled.
If tagging is disabled, traf
fic is transmitted as untagged frames. The vlan-list contains VlanId's
in range <1-4093>. Separate non-consecutive IDs with ',' and no spaces and no zeros in
between the range; Use '-' for range.
Format no vlan tagging <vlan-list>
Mode
Interface Config
Switching Commands
56
Page 57

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
vlan association subnet
This command associates a VLAN to a specific IP-subnet.
Format vlan association subnet <ipaddr> <netmask> <1-4093>
Mode
VLAN Config
no vlan association subnet
This command removes association of a specific IP-subnet to a VLAN.
Format no vlan association subnet <ipaddr> <netmask>
Mode
VLAN Config
vlan association mac
This command associates a MAC address to a VLAN.
Format vlan association mac <macaddr> <1-4093>
Mode
VLAN database
no vlan association mac
This command removes the association of a MAC address to a VLAN.
Format no vlan association mac <macaddr>
Mode
VLAN database
show vlan
This command displays a list of all configured VLAN
Format show vlan
Mode
Term Definition
VLAN ID
VLAN Name
VLAN Type
• Privileged EXEC
• User EXEC
A VLAN Identifier (VID) is associated with each VLAN. The range of the VLAN ID is
1–4093.
A string associated with this VLAN as a convenience. It can be up to 32 alphanumeric
characters long, including blanks.
“Default.” This field is optional.
Type of VLAN, which can be Default (VLAN ID = 1) or static (one that is configured and
permanently defined), or Dynamic (one that is created by GVRP registration).
The default is blank. VLAN ID 1 always has a name of
.
Switching Commands
57
Page 58
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
show vlan <vlanid>
This command displays detailed information, including interface information, for a specific
VLAN. The ID is a valid VLAN identification number.
Format show vlan <vlanid>
Mode
Term Definition
VLAN ID
VLAN Name
VLAN Type
Interface
Current
Configured
Tagging
• Privileged EXEC
• User EXEC
A VLAN Identifier (VID) is associated with each VLAN. The range of the VLAN ID is
1–4093.
A string associated with this VLAN as a convenience. It can be up to 32 alphanumeric
characters long, including blanks.
“Default.” This field is optional.
Type of VLAN, which can be Default (VLAN ID = 1) or static (one that is configured and
permanently defined), or Dynamic (one that is created by GVRP registration).
Valid slot and port number separated by forward slashes. It is possible to set the
parameters for all ports by using the selectors on the top line.
The degree of participation of this port in this VLAN. The permissible values are:
• Include fixed in the IEEE 802.1Q standard.
• Exclude forbidden in the IEEE 802.1Q standard.
• Autodetect The port will not participate in this VLAN unless a join request is received on this port.
This is equivalent to registration normal in the IEEE 802.1Q standard.
The configured degree of participation of this port in this VLAN. The permissible values
are:
• Include fixed in the IEEE 802.1Q standard.
• Exclude forbidden in the IEEE 802.1Q standard.
• Autodetect The port will not participate in this VLAN unless a join request is received on this port.
This is equivalent to registration normal in the IEEE 802.1Q standard.
The tagging behavior for this port in this VLAN.
• T
agged - Transmit traffic for this VLAN as tagged frames.
• Untagged -
This port is always a member of this VLAN. This is equivalent to registration
This port is never a member of this VLAN. This is equivalent to registration
To allow the port to be dynamically registered in this VLAN via GVRP.
This port is always a member of this VLAN. This is equivalent to registration
This port is never a member of this VLAN. This is equivalent to registration
To allow the port to be dynamically registered in this VLAN via GVRP.
Transmit traffic for this VLAN as untagged frames.
The default is blank. VLAN ID 1 always has a name of
Switching Commands
58
Page 59
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
show vlan brief
This command displays a list of all configured VLANs.
Format show vlan brief
Mode
Term Definition
VLAN ID
VLAN Name
VLAN Type
• Privileged EXEC
• User EXEC
There is a VLAN Identifier (vlanid) associated with each VLAN. The range of the VLAN
ID is 1–3965.
A string associated with this VLAN as a convenience. It can be up to 32 alphanumeric
characters long, including blanks.
“Default.” This field is optional.
Type of VLAN, which can be Default (VLAN ID = 1) or static (one that is configured and
permanently defined), or a Dynamic (one that is created by GVRP registration).
The default is blank. VLAN ID 1 always has a name of
show vlan port
This command displays VLAN port information.
Format show vlan port {<slot/port> | all}
Mode
Term Definition
Interface
Port VLAN ID
Acceptable
Frame Types
Ingress
Filtering
GVRP
Default Priority
• Privileged EXEC
• User EXEC
Valid slot and port number separated by forward slashes. It is possible to set the
parameters for all ports by using the selectors on the top line.
The VLAN ID that this port will assign to untagged frames or priority tagged frames
received on this port.
The types of frames that may be received on this port. The options are 'VLAN only' and
'Admit
All'. When set to 'VLAN only', untagged frames or priority tagged frames received
on this port are discarded. When set to 'Admit All', untagged frames or priority tagged
frames received on this port are accepted and assigned the value of the Port VLAN ID for
this port. With either option, VLAN tagged frames are forwarded in accordance to the
802.1Q VLAN specification.
May be enabled or disabled. When enabled, the frame is discarded if this port is not a
member of the VLAN with which this frame is associated. In a tagged frame, the VLAN is
identified by the VLAN ID in the tag. In an untagged frame, the VLAN is the Port VLAN ID
specified for the port that received this frame. When disabled, all frames are forwarded in
accordance with the 802.1Q VLAN bridge specification.
May be enabled or disabled.
The 802.1p priority assigned to tagged packets arriving on the port.
The value must be for an existing VLAN. The factory default is 1.
The factory default is disabled.
Switching Commands
59
Page 60

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
show vlan association subnet
This command displays the VLAN associated with a specific configured IP-Address and net
mask. If no IP address and net mask are specified, the VLAN associations of all the
configured IP-subnets are displayed.
Format show vlan association subnet [<ipaddr> <netmask>]
Mode
Term Definition
IP Subnet
IP Mask
VLAN ID
Privileged EXEC
The IP address assigned to each interface.
The subnet mask.
A VLAN Identifier (VID) is associated with each VLAN.
show vlan association mac
This command displays the VLAN associated with a specific configured MAC address. If no
MAC address is specified, the VLAN associations of all the configured MAC addresses are
displayed.
Format show vlan association mac [<macaddr>]
Mode
Term Definition
MAC Address
VLAN ID
Privileged EXEC
A MAC address for which the switch has forwarding and or filtering information. The
format is 6 or 8 two-digit hexadecimal numbers that are separated by colons, for example
01:23:45:67:89:AB. In an IVL system the MAC address will be displayed as 8 bytes.
A VLAN Identifier (VID) is associated with each VLAN.
Double VLAN Commands
This section describes the commands you use to configure double VLAN (DVLAN). Double
VLAN tagging is a way to pass VLAN traffic from one customer domain to another through a
Metro Core in a simple and cost effective manner. The additional tag on the traffic helps
differentiate between customers in the MAN while preserving the VLAN identification of the
individual customers when they enter their own 802.1Q domain.
Switching Commands
60
Page 61

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
dvlan-tunnel ethertype
This command configures the ether-type for all interfaces. The ether-type may have the
values of 802.1Q, vMAN, or custom. If the ether-type has a value of custom, the optional
value of the custom ether type must be set to a value from 0 to 65535.
Default
Format dvlan-tunnel ethertype {802.1Q | vman | custom} [0-65535]
Mode
vman
Global Config
mode dot1q-tunnel
This command is used to enable Double VLAN Tunneling on the specified interface.
Default
Format mode dot1q-tunnel
Mode
no mode dot1q-tunnel
This command is used to disable Double VLAN Tunneling on the specified interface. By
default, Double VLAN
Format no mode dot1q-tunnel
Mode
disabled
Interface Config
Tunneling is disabled.
Interface Config
mode dvlan-tunnel
Use this command to enable Double VLAN Tunneling on the specified interface.
Note: When you use the mode dvlan-tunnel command on an
interface, it becomes a service provider port. Ports that do not have
double VLAN tunneling enabled are customer ports.
Default
Format mode dvlan-tunnel
Mode
disabled
Interface Config
Switching Commands
61
Page 62
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
no mode dvlan-tunnel
This command is used to disable Double VLAN Tunneling on the specified interface. By
default, Double VLAN
Format no mode dvlan-tunnel
Mode
Interface Config
Tunneling is disabled.
show dot1q-tunnel
Use this command without the optional parameters to display all interfaces enabled for
Double VLAN Tunneling. Use the optional parameters to display detailed information about
Double VLAN Tunneling for the specified interface or all interfaces.
Format show dot1q-tunnel [interface {<slot/port> | all}]
Mode
• Privileged EXEC
• User EXEC
Term Definition
Interface
Mode
EtherType
Valid slot and port number separated by forward slashes.
The administrative mode through which Double VLAN Tunneling can be enabled or
disabled.
A 2-byte hex EtherType to be used as the first 16 bits of the DVLAN tunnel. There are
three dif
value of 0x8100. The second is vMAN, which represents the commonly used value of
0x88A8. If EtherType is not one of these two values, it is a custom tunnel value,
representing any value in the range of 0–65535.
The default value for this field is disabled.
ferent EtherType tags. The first is 802.1Q, which represents the commonly used
show dvlan-tunnel
Use this command without the optional parameters to display all interfaces enabled for
Double VLAN Tunneling. Use the optional parameters to display detailed information about
Double VLAN Tunneling for the specified interface or all interfaces.
Format show dvlan-tunnel [interface {<slot/port> | all}]
Mode
Term Definition
Interface
• Privileged EXEC
• User EXEC
Valid slot and port number separated by forward slashes.
Switching Commands
62
Page 63
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Term Definition
Mode
EtherType
The administrative mode through which Double VLAN Tunneling can be enabled or
disabled.
A 2-byte hex EtherType to be used as the first 16 bits of the DVLAN tunnel. There are
three dif
value of 0x8100. The second is vMAN, which represents the commonly used value of
0x88A8. If EtherType is not one of these two values, it is a custom tunnel value,
representing any value in the range of 0–65535.
The default value for this field is disabled.
ferent EtherType tags. The first is 802.1Q, which represents the commonly used
Voice VLAN Commands
This section describes the commands you use for Voice VLAN. Voice VLAN enables switch
ports to carry voice traffic with defined priority to enable separation of voice and data traffic
coming onto the port. The benefits of using V oice VLAN is to ensure that the sound quality of
an IP phone could be safeguarded from deteriorating when the data traffic on the port is high.
Also the inherent isolation provided by VLANs ensures that inter-VLAN traffic is under
management control and that network- attached clients cannot initiate a direct attack on
voice components. QoS-based on IEEE 802.1P Class of Service (CoS) uses classification
and scheduling to sent network traf
uses the source MAC of the traffic traveling through the port to identify the IP phone data
flow.
fic from the switch in a predictable manner. The system
voice vlan (Global Config)
Use this command to enable the Voice VLAN capability on the switch.
Default
Format voice vlan
Mode
disabled
Global Config
no voice vlan (Global Config)
Use this command to disable the Voice VLAN capability on the switch.
Format no voice vlan
Mode
Global Config
voice vlan (Interface Config)
Use this command to enable the Voice VLAN capability on the interface.
Default
disabled
Switching Commands
63
Page 64
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Format voice vlan {<id> | dot1p <priority> | none | untagged}
Mode
Interface Config
You can configure Voice VLAN in any of the following ways:
Parameter Description
vlan-id
dot1p
none
untagged
Configure the IP phone to forward all voice traffic through the specified VLAN. Valid
VLAN IDs are from 1 to 4093 (the maximum supported by the platform).
Configure the IP phone to use 802.1p priority tagging for voice traffic and to use the
default native VLAN (VLAN 0) to carry all traf
Allow the IP phone to use its own configuration to send untagged voice traffic.
Configure the phone to send untagged voice traffic.
fic. Valid <priority> range is 0–7.
no voice vlan (Interface Config)
Use this command to disable the Voice VLAN capability on the interface.
Format no voice vlan
Mode
Interface Config
voice vlan data priority
Use this command to either trust or untrust the data traffic arriving on the Voice VLAN port.
Default
Format voice vlan data priority {untrust | trust}
Mode
trust
Interface Config
show voice vlan
Format show voice vlan [interface {<slot/port> | all}]
Mode
When the interface parameter is not specified, only the global mode of the Voice VLAN is
displayed.
Term Definition
Administrative
Mode
Privileged EXEC
The Global Voice VLAN mode.
Switching Commands
64
Page 65

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
When the interface is specified:
Term Definition
Voice VLAN Interface Mode
Voice VLAN ID
Voice VLAN Priority
Voice VLAN Untagged
Voice VLAN CoS Override
Voice VLAN Status
The admin mode of the Voice VLAN on the interface.
The Voice VLAN ID
The do1p priority for the Voice VLAN on the port.
The tagging option for the Voice VLAN traffic.
The Override option for the voice traffic arriving on the port.
The operational status of Voice VLAN on the port.
.
Provisioning (IEEE 802.1p) Commands
This section describes the commands you use to configure provisioning, which allows you to
prioritize ports.
vlan port priority all
This command configures the port priority assigned for untagged packets for all ports
presently plugged into the device. The range for the priority is 0-7. Any subsequent per port
configuration will override this configuration setting.
Format vlan port priority all <priority>
Mode
Global Config
vlan priority
This command configures the default 802.1p port priority assigned for untagged packets for a
specific interface. The range for the priority is 0–7.
Default
Format vlan priority <priority>
Mode
0
Interface Config
Protected Ports Commands
This section describes commands you use to configure and view protected ports on a switch.
Protected ports do not forward traffic to each other, even if they are on the same VLAN.
However, protected ports can forward traffic to all unprotected ports in their group.
Unprotected ports can forward traffic to both protected and unprotected ports. Ports are
unprotected by default.
Switching Commands
65
Page 66
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
If an interface is configured as a protected port, and you add that interface to a Port Channel
or link aggregation group (LAG), the protected port status becomes operationally disabled on
the interface, and the interface follows the configuration of the LAG port. However, the
protected port configuration for the interface remains unchanged. Once the interface is no
longer a member of a LAG, the current configuration for that interface automatically becomes
effective.
switchport protected (Global Config)
Use this command to create a protected port group. The <groupid> parameter identifies the
set of protected ports. Use the name <name> pair to assign a name to the protected port
group. The name can be up to 32 alphanumeric characters long, including blanks. The
default is blank.
Note: Port protection occurs within a single switch. Protected port
configuration does not affect traffic between ports on two different
switches. No traffic forwarding is possible between two protected
ports.
Format switchport protected <groupid> name <name>
Mode
Global Config
no switchport protected (Global Config)
Use this command to remove a protected port group. The groupid parameter identifies the
set of protected ports. Use the name keyword to remove the name from the group.
Format NO switchport protected <groupid> name
Mode
Global Config
switchport protected (Interface Config)
Use this command to add an interface to a protected port group. The <groupid> parameter
identifies the set of protected ports to which this interface is assigned. You can only configure
an interface as protected in one group.
Note: Port protection occurs within a single switch. Protected port
configuration does not affect traffic between ports on two different
switches. No traffic forwarding is possible between two protected
ports.
Switching Commands
66
Page 67

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Default
Format switchport protected <groupid>
Mode
unprotected
Interface Config
no switchport protected (Interface Config)
Use this command to configure a port as unprotected. The groupid parameter identifies the
set of protected ports to which this interface is assigned.
Format no switchport protected <groupid>
Mode
Interface Config
show switchport protected
This command displays the status of all the interfaces, including protected and unprotected
interfaces.
Format show switchport protected <groupid>
Mode
• Privileged EXEC
• User EXEC
Term Definition
Group ID
Name
List of Physical
Ports
The number that identifies the protected port group.
An optional name of the protected port group. The name can be up to 32 alphanumeric
characters long, including blanks.
List of ports, which are configured as protected for the group identified with <groupid>. If
no port is configured as protected for this group, this field is blank.
The default is blank.
show interfaces switchport
This command displays the status of the interface (protected/unprotected) under the groupid.
Format show interfaces switchport <slot/port> <groupid>
Mode
Term Definition
Name
Protected port
• Privileged EXEC
• User EXEC
A string associated with this group as a convenience. It can be up to 32 alphanumeric
characters long, including blanks. The default is blank. This field is optional.
Indicates whether the interface is protected or not. It shows TRUE or F ALSE. If the group
is a multiple groups then, it shows
TRUE in Group <groupid>.
Switching Commands
67
Page 68

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Private VLAN
The Private VLANs feature separates a regular VLAN domain into two or more subdomains.
Each subdomain is defined (represented) by a primary VLAN and a secondary VLAN. The
primary VLAN ID is the same for all subdomains that belong to a private VLAN. The
secondary VLAN ID differentiates subdomains from each other and provides Layer 2 isolation
between ports of the same private VLAN. The types of VLANs within a private VLAN are as
follows:
• Primary VLAN—Forwards the traf
fic from the promiscuous ports to isolated ports,
community ports, and other promiscuous ports in the same private VLAN. Only one
primary VLAN can be configured per private VLAN. All ports within a private VLAN share
primary VLAN.
• Isolated VLAN—A secondary VLAN that carries traf
fic from isolated ports to promiscuous
ports. Only one isolated VLAN can be configured per private VLAN.
• Community VLAN—A secondary VLAN that forwards traf
fic between ports that belong to
the same community and the promiscuous ports. There can be multiple community
VLANs per private VLAN.
Three types of port designations exist within a private VLAN:
• Promiscuous Ports—An endpoint connected to a promiscuous port is allowed to
communicate with any endpoint within the private VLAN. Multiple promiscuous ports can
be defined for a single private VLAN domain.
• Isolated Ports—An endpoint connected to an isolated port is allowed to communicate with
endpoints connected to promiscuous ports only
. Endpoints connected to adjacent
isolated ports cannot communicate with each other.
• Community Ports—An endpoint connected to a community port is allowed to
communicate with the endpoints within a community and with any configured
promiscuous port.
The endpoints that belong to one community cannot communicate with
endpoints that belong to a different community or with endpoints connected to isolated
ports.
The Private VLANs can be extended across multiple switches through inter-switch/stack links
that transport primary
, community, and isolated VLANs between devices.
switchport private-vlan
This command is used to define a private-VLAN association for an isolated or community port
or a mapping for a promiscuous port.
Format switchport private-vlan {host-association <primary-vlan-id>
<secondary-vlan-id> | mapping <primary-vlan-id> {add | remove}
<secondary-vlan-list>}
Mode
Interface Config
Switching Commands
68
Page 69

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Term Definition
host-association
mapping
primary-vlan-id
secondary-vlan-id
add
remove
secondary-vlan-list
Defines VLAN association for community or host ports.
Defines the private VLAN mapping for promiscuous ports.
Primary VLAN ID of a private VLAN.
Secondary (isolated or community) VLAN ID of a private VLAN.
Associates the secondary VLAN with the primary one.
Deletes the secondary VLANs from the primary VLAN association.
A list of secondary VLANs to be mapped to a primary VLAN.
no switchport private-vlan
This command is used to remove the private-VLAN association or mapping from the port.
Format no switchport private-vlan {host-association | mapping}
Mode
Interface Config
switchport mode private-vlan
This command is used to configure a port as a promiscuous or host private VLAN port. Note
that the properties of each mode can be configured even when the switch is not in that mode.
However, they will only be applicable once the switch is in that particular mode.
Format switchport mode private-vlan {host | promiscuous}
Mode
Default
Term Definition
host
promiscuous
no switchport mode
This command is used to remove the private-VLAN association or mapping from the port.
Format no switchport mode private-vlan
Mode
Interface Config
General
Configures an interface as a private VLAN host port. It can be either isolated or
community port depending on the secondary VLAN it is associated with.
Configures an interface as a private VLAN promiscuous port. The promiscuous ports
are members of the primary VLAN.
Interface Config
Switching Commands
69
Page 70
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
private-vlan
This command is used to configure the private VLANs and to configure the association
between the primary private VLAN and secondary VLANs.
Format private-vlan {association [add | remove] <secondary-vlan-list> |
community | isolated | primary}
Mode
Term Definition
association
secondary-vlan-list
community
isolated
primary
VLAN Config
Associates the primary and secondary VLAN.
A list of secondary VLANs to be mapped to a primary VLAN.
Designates a VLAN as a community VLAN.
Designates a VLAN as the isolated VLAN.
Designates a VLAN as the primary VLAN.
no private-vlan
This command is used to restore normal VLAN configuration.
Format no private-vlan {association}
Mode
VLAN Config
vlan
Use this command to enter the private vlan configuration. The VLAN range is 1-4094.
Format
Mode
vlan <vlan-list>
Global Config
show vlan
This command displays information about the configured private VLANs including primary
and secondary VLAN IDs, type (community , isolated, or primary) and the ports that belong to
a private VLAN.
Format show vlan private-vlan [type]
Mode
• Privileged EXEC
• User EXEC
Switching Commands
70
Page 71

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Term Definition
Private -vlan
type
Primary
Secondary
Type
Ports
Displays information about the configured private VLANs
Displays only private VLAN ID and its type.
Displays primary VLAN ID
Displays secondary VLAN ID
Displays secondary VLAN type
Displays ports which are associated with a private VLAN
show interface ethernet <slot/port > switchport
This command displays the private-VLAN mapping information for the switch interfaces.
Format show interface ethernet <slot/port> switchport
Mode
• Privileged EXEC
• User EXEC
Term Definition
Private-vlan host-association
Private-vlan mapping
Displays VLAN association for the private-VLAN host ports.
Displays VLAN mapping for the private-VLAN promiscuous ports
GARP Commands
This section describes the commands you use to configure Generic Attribute Registration
Protocol (GARP) and view GARP status. The commands in this section affect both GARP
VLAN Registration Protocol (GVRP) and Garp Multicast Registration Protocol (GMRP).
GARP is a protocol that allows client stations to register with the switch for membership in
VLANS (by using GVMP) or multicast groups (by using GVMP).
set garp timer join
This command sets the GVRP join time for one port (Interface Config mode) or all (Global
Config mode) and per GARP. Join time is the interval between the transmission of GARP
Protocol Data Units (PDUs) registering (or re-registering) membership for a VLAN or
multicast group. This command has an effect only when GVRP is enabled. The time is from
10 to 100 (centiseconds). The value 20 centiseconds is 0.2 seconds.
Default
Format set garp timer join <10-100>
Mode
20
• Interface Config
• Global Config
Switching Commands
71
Page 72

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
no set garp timer join
This command sets the GVRP join time (for one or all ports and per GARP) to the default and
only has an ef
Format no set garp timer join
Mode
fect when GVRP is enabled.
• Interface Config
• Global Config
set garp timer leave
This command sets the GVRP leave time for one port (Interface Config mode) or all ports
(Global Config mode) and only has an effect when GVRP is enabled. Leave time is the time
to wait after receiving an unregister request for a VLAN or a multicast group before deleting
the VLAN entry . This can be considered a buffer time for another station to assert registration
for the same attribute in order to maintain uninterrupted service. The leave time is 20–600
(centiseconds). The value 60 centiseconds is 0.6 seconds.
Default
Format set garp timer leave <20-600>
Mode
60
• Interface Config
• Global Config
no set garp timer leave
This command sets the GVRP leave time on all ports or a single port to the default and only
has an ef
Format no set garp timer leave
Mode
fect when GVRP is enabled.
• Interface Config
• Global Config
set garp timer leaveall
This command sets how frequently Leave All PDUs are generated. A Leave All PDU
indicates that all registrations will be unregistered. Participants would need to rejoin in order
to maintain registration. The value applies per port and per GARP participation. The time may
range from 200 to 6000 (centiseconds). The value 1000 centiseconds is 10 seconds. You
can use this command on all ports (Global Config mode) or a single port (Interface Config
mode), and it only has an effect only when GVRP is enabled.
Default
Format set garp timer leaveall <200-6000>
Mode
1000
• Interface Config
• Global Config
Switching Commands
72
Page 73

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
no set garp timer leaveall
This command sets how frequently Leave All PDUs are generated the default and only has
fect when GVRP is enabled.
an ef
Format no set garp timer leaveall
Mode
• Interface Config
• Global Config
show garp
This command displays GARP information.
Format show garp
Mode
• Privileged EXEC
• User EXEC
Term Definition
GMRP Admin Mode
GVRP Admin Mode
The administrative mode of GARP Multicast Registration Protocol (GMRP) for the
system.
The administrative mode of GARP VLAN Registration Protocol (GVRP) for the
system.
GVRP Commands
This section describes the commands you use to configure and view GARP VLAN
Registration Protocol (GVRP) information. GVRP-enabled switches exchange VLAN
configuration information, which allows GVRP to provide dynamic VLAN creation on trunk
ports and automatic VLAN pruning.
Note: If GVRP is disabled, the system does not forward GVRP messages.
set gvrp adminmode
This command enables GVRP on the system.
Default
Format set gvrp adminmode
Mode
disabled
Privileged EXEC
Switching Commands
73
Page 74
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
no set gvrp adminmode
This command disables GVRP.
Format no set gvrp adminmode
Mode
Privileged EXEC
set gvrp interfacemode
This command enables GVRP on a single port (Interface Config mode) or all ports (Global
Config mode).
Default
Format set gvrp interfacemode
Mode
disabled
• Interface Config
• Global Config
no set gvrp interfacemode
This command disables GVRP on a single port (Interface Config mode) or all ports (Global
Config mode). If GVRP is disabled, Join
Time, Leave Time, and Leave All Time have no
effect.
Format no set gvrp interfacemode
Mode
• Interface Config
• Global Config
show gvrp configuration
This command displays Generic Attributes Registration Protocol (GARP) information for one
or all interfaces.
Format show gvrp configuration {<slot/port> | all}
Mode
• Privileged EXEC
• User EXEC
Term Definition
Interface
Join Timer
Valid slot and port number separated by forward slashes.
The interval between the transmission of GARP PDUs registering (or re-registering)
membership for an attribute. Current attributes are a VLAN or multicast group.
an instance of this timer on a per-Port, per-GARP participant basis. Permissible values
are 10–100 centiseconds (0.1 to 1.0 seconds). The factory default is 20 centiseconds
(0.2 seconds). The finest granularity of specification is one centisecond (0.01 seconds).
There is
Switching Commands
74
Page 75
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Term Definition
Leave Timer
LeaveAll Timer
Port GVMRP
Mode
The period of time to wait after receiving an unregister request for an attribute before
deleting the attribute. Current attributes are a VLAN or multicast group.
considered a buffer time for another station to assert registration for the same attribute in
order to maintain uninterrupted service. There is an instance of this timer on a per-Port,
per-GARP participant basis. Permissible values are 20–600 centiseconds (0.2 to 6.0
seconds). The factory default is 60 centiseconds (0.6 seconds).
This Leave All Time controls how frequently LeaveAll PDUs are generated. A LeaveAll
PDU indicates that all registrations will shortly be deregistered. Participants will need to
rejoin in order to maintain registration.
per-GARP participant basis. The Leave All Period Timer is set to a random value in the
range of LeaveAllTime to 1.5*LeaveAllTime. Permissible values are 200–6000
centiseconds (2–60 seconds). The factory default is 1000 centiseconds (10 seconds).
The GVRP administrative mode for the port, which is enabled or disabled (default). If this
parameter is disabled, Join
GMRP Commands
This may be
There is an instance of this timer on a per-Port,
Time, Leave Time, and Leave All Time have no effect.
This section describes the commands you use to configure and view GARP Multicast
Registration Protocol (GMRP) information. Like IGMP snooping, GMRP helps control the
flooding of multicast packets. GMRP-enabled switches dynamically register and deregister
group membership information with the MAC networking devices attached to the same
segment. GMRP also allows group membership information to propagate across all
networking devices in the bridged LAN that support Extended Filtering Services.
Note: If GMRP is disabled, the system does not forward GMRP
messages.
set gmrp adminmode
This command enables GARP Multicast Registration Protocol (GMRP) on the system.
Default
Format set gmrp adminmode
Mode
no set gmrp adminmode
disabled
Privileged EXEC
This command disables GARP Multicast Registration Protocol (GMRP) on the system.
Format no set gmrp adminmode
Mode
Privileged EXEC
Switching Commands
75
Page 76

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
set gmrp interfacemode
This command enables GARP Multicast Registration Protocol on a single interface (Interface
Config mode) or all interfaces (Global Config mode). If an interface which has GARP enabled
is enabled for routing or is enlisted as a member of a port-channel (LAG), GARP functionality
is disabled on that interface. GARP functionality is subsequently re-enabled if routing is
disabled and port-channel (LAG) membership is removed from an interface that has GARP
enabled.
Default
Format set gmrp interfacemode
Mode
disabled
• Interface Config
• Global Config
no set gmrp interfacemode
This command disables GARP Multicast Registration Protocol on a single interface or all
interfaces. If an interface which has GARP enabled is enabled for routing or is enlisted as a
member of a port-channel (LAG), GARP functionality is disabled. GARP functionality is
subsequently re-enabled if routing is disabled and port-channel (LAG) membership is
removed from an interface that has GARP enabled.
Format no set gmrp interfacemode
Mode
• Interface Config
• Global Config
show gmrp configuration
This command displays Generic Attributes Registration Protocol (GARP) information for one
or all interfaces.
Format show gmrp configuration {<slot/port> | all}
Mode
Term Definition
Interface
Join Timer
• Privileged EXEC
• User EXEC
The slot/port of the interface that this row in the table describes.
The interval between the transmission of GARP PDUs registering (or re-registering)
membership for an attribute. Current attributes are a VLAN or multicast group.
an instance of this timer on a per-Port, per-GARP participant basis. Permissible values
are 10–100 centiseconds (0.1 to 1.0 seconds). The factory default is 20 centiseconds
(0.2 seconds). The finest granularity of specification is 1 centisecond (0.01 seconds).
Switching Commands
76
There is
Page 77

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Term Definition
Leave Timer
LeaveAll Timer
Port GMRP
Mode
The period of time to wait after receiving an unregister request for an attribute before
deleting the attribute. Current attributes are a VLAN or multicast group.
considered a buffer time for another station to assert registration for the same attribute in
order to maintain uninterrupted service. There is an instance of this timer on a per-Port,
per-GARP participant basis. Permissible values are 20–600 centiseconds (0.2 to 6.0
seconds). The factory default is 60 centiseconds (0.6 seconds).
This Leave All Time controls how frequently LeaveAll PDUs are generated. A LeaveAll
PDU indicates that all registrations will shortly be deregistered. Participants will need to
rejoin in order to maintain registration.
per-GARP participant basis. The Leave All Period Timer is set to a random value in the
range of LeaveAllTime to 1.5*LeaveAllTime. Permissible values are 200–6000
centiseconds (2–60 seconds). The factory default is 1000 centiseconds (10 seconds).
The GMRP administrative mode for the port. It may be enabled or disabled. If this
parameter is disabled, Join
show mac-address-table gmrp
This may be
There is an instance of this timer on a per-Port,
Time, Leave Time, and Leave All Time have no effect.
This command displays the GMRP entries in the Multicast Forwarding Database (MFDB)
table.
Format show mac-address-table gmrp
Mode
Term Definition
Mac Address
Type
Description
Interfaces
Privileged EXEC
A unicast MAC address for which the switch has forwarding and or filtering information.
The format is 6 or 8 two-digit hexadecimal numbers that are separated by colons, for
example 01:23:45:67:89:AB. In an IVL system the MAC address is displayed as 8 bytes.
The type of the entry. Static entries are those that are configured by the end user.
Dynamic entries are added to the table as a result of a learning process or protocol.
The text description of this multicast table entry.
The list of interfaces that are designated for forwarding (Fwd:) and filtering (Flt:).
Port-Based Network Access Control Commands
This section describes the commands you use to configure port-based network access
control (802.1x). Port-based network access control allows you to permit access to network
services only to and devices that are authorized and authenticated.
Switching Commands
77
Page 78

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
clear dot1x statistics
This command resets the 802.1x statistics for the specified port or for all ports.
Format clear dot1x statistics {<slot/port> | all}
Mode
Privileged EXEC
clear radius statistics
This command is used to clear all RADIUS statistics.
Format clear radius statistics
Mode
Privileged EXEC
dot1x eapolflood
Use this command to enable EAPOL flood support on the switch.
Format
Mode
Default
dot1x eapolflood
Global Config
Disabled
no dot1x eapolflood
This command disables EAPOL flooding on the switch.
Format no dot1x eapolflood
Mode
Global Config
dot1x guest-vlan
This command configures VLAN as guest vlan on a per port basis. The command specifies
an active VLAN as an IEEE 802.1x guest VLAN. The range is 1 to the maximum VLAN ID
supported by the platform.
Default
Format dot1x guest-vlan <vlan-id>
Mode
disabled
Interface Config
Switching Commands
78
Page 79

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
no dot1x guest-vlan
This command disables Guest VLAN on the interface.
Default
Format no dot1x guest-vlan
Mode
disabled
Interface Config
dot1x initialize
This command begins the initialization sequence on the specified port. This command is only
valid if the control mode for the specified port is “auto” or “mac-based”. If the control mode is
not 'auto' or “mac-based”, an error will be returned.
Format dot1x initialize <slot/port>
Mode
Privileged EXEC
dot1x mac-auth-bypass
This command enables MAC-Based Authentication Bypass (MAB) for 802.1x-unaware
clients. MAB provides 802.1x-unaware clients controlled access to the network using the
devices’ MAC address as an identifier. This requires that the known and allowable MAC
address and corresponding access rights be pre-populated in the authentication server. MAB
works only when the port control mode of the port is MAC-based.
Format dot1x mac-auth-bypass
Mode
Interface Config
no dot1x mac-auth-bypass
This command disables MAB for 802.1x-unaware clients.
Format no dot1x mac-auth-bypass
Mode
Interface Config
dot1x max-req
This command sets the maximum number of times the authenticator state machine on this
port will transmit an EAPOL EAP Request/Identity frame before timing out the supplicant.
The <count> value must be in the range 1 - 10.
Default
Format dot1x max-req
Mode
2
<count>
Interface Config
Switching Commands
79
Page 80

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
no dot1x max-req
This command sets the maximum number of times the authenticator state machine on this
port will transmit an EAPOL EAP Request/Identity frame before timing out the supplicant.
Format no dot1x max-req
Mode
Interface Config
dot1x max-users
Use this command to set the maximum number of clients supported on the port when
MAC-based dot1x authentication is enabled on the port. The maximum users supported per
port is dependent on the product. The <count> value is in the range 1 - 48.
Default
Format dot1x max-users
Mode
48
<count>
Interface Config
no dot1x max-users
This command resets the maximum number of clients allowed per port to its default value.
Format no dot1x max-req
Mode
Interface Config
dot1x port-control
This command sets the authentication mode to use on the specified port. Select
force-unauthorized to specify that the authenticator PAE unconditionally sets the
controlled port to unauthorized. Select force-authorized to specify that the authenticator
PAE unconditionally sets the controlled port to authorized. Select auto to specify that the
authenticator PAE sets the controlled port mode to reflect the outcome of the authentication
exchanges between the supplicant, authenticator, and the authentication server. If the
mac-based option is specified, MAC-based dot1x authentication is enabled on the port.
Default
Format dot1x port-control {force-unauthorized | force-authorized | auto |
Mode
auto
mac-based}
Interface Config
Switching Commands
80
Page 81

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
no dot1x port-control
This command sets the 802.1x port control mode on the specified port to the default value.
Format no dot1x port-control
Mode
Interface Config
dot1x port-control all
This command sets the authentication mode to use on all ports. Select
force-unauthorized to specify that the authenticator PAE unconditionally sets the
controlled port to unauthorized. Select force-authorized to specify that the authenticator
PAE unconditionally sets the controlled port to authorized. Select auto to specify that the
authenticator PAE sets the controlled port mode to reflect the outcome of the authentication
exchanges between the supplicant, authenticator, and the authentication server. If the
mac-based option is specified, MAC-based dot1x authentication is enabled on the port.
Default
Format dot1x port-control all {force-unauthorized | force-authorized | auto
Mode
auto
| mac-based}
Global Config
no dot1x port-control all
This command sets the authentication mode on all ports to the default value.
Format no dot1x port-control all
Mode
Global Config
dot1x re-authenticate
This command begins the re-authentication sequence on the specified port. This command is
only valid if the control mode for the specified port is “auto” or “mac-based”. If the control
mode is not “auto” or “mac-based”, an error will be returned.
Format dot1x re-authenticate <slot/port>
Mode
Privileged EXEC
dot1x re-authentication
This command enables re-authentication of the supplicant for the specified port.
Default
Format dot1x re-authentication
Mode
disabled
Interface Config
Switching Commands
81
Page 82

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
no dot1x re-authentication
This command disables re-authentication of the supplicant for the specified port.
Format no dot1x re-authentication
Mode
Interface Config
dot1x system-auth-control
Use this command to enable the dot1x authentication support on the switch. While disabled,
the dot1x configuration is retained and can be changed, but is not activated.
Default
Format dot1x system-auth-control
Mode
disabled
Global Config
no dot1x system-auth-control
This command is used to disable the dot1x authentication support on the switch.
Format no dot1x system-auth-control
Mode
Global Config
dot1x timeout
This command sets the value, in seconds, of the timer used by the authenticator state
machine on this port. Depending on the token used and the value (in seconds) passed,
various timeout configurable parameters are set. The following tokens are supported:
Tokens Definition
guest-vlan-period
reauth-period
quiet-period
tx-period
The time, in seconds, for which the authenticator waits to see if any EAPOL packets are
received on a port before authorizing the port and placing the port in the guest vlan (if
configured).
on that specific port.
The value, in seconds, of the timer used by the authenticator state machine on this port
to determine when re-authentication of the supplicant takes place.
must be a value in the range 1 - 65535.
The value, in seconds, of the timer used by the authenticator state machine on this port
to define periods of time in which it will not attempt to acquire a supplicant.
quiet-period must be a value in the range 0 - 65535.
The value, in seconds, of the timer used by the authenticator state machine on this port
to determine when to send an EAPOL EAP Request/Identity frame to the supplicant.
quiet-period must be a value in the range 1 - 65535.
The guest vlan timer is only relevant when guest vlan has been configured
The reauth-period
The
The
Switching Commands
82
Page 83

Tokens Definition
supp-timeout
server-timeout
The value, in seconds, of the timer used by the authenticator state machine on this port
to timeout the supplicant.
The value, in seconds, of the timer used by the authenticator state machine on this port
to timeout the authentication server
65535.
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
The supp-timeout must be a value in the range 1 - 65535.
. The supp-timeout must be a value in the range 1 -
Default
Format dot1x timeout {{guest-vlan-period <seconds>} |{reauth-period
Mode
• guest-vlan-period: 90 seconds
• reauth-period: 3600 seconds
• quiet-period: 60 seconds
• tx-period: 30 seconds
• supp-timeout: 30 seconds
• server-timeout: 30 seconds
<seconds>} | {quiet-period <seconds>} | {tx-period <seconds>} |
{supp-timeout <seconds>} | {server-timeout <seconds>}}
Interface Config
no dot1x timeout
This command sets the value, in seconds, of the timer used by the authenticator state
machine on this port to the default values. Depending on the token used, the corresponding
default values are set.
Format no dot1x timeout {guest-vlan-period | reauth-period | quiet-period |
tx-period | supp-timeout | server-timeout}
Mode
Interface Config
dot1x unauthenticated-vlan
Use this command to configure the unauthenticated VLAN associated with that port. The
unauthenticated VLAN ID can be a valid VLAN ID from 0-Maximum supported VLAN ID
(4093 for 7000 series). The unauthenticated VLAN must be statically configured in the VLAN
database to be operational. By default, the unauthenticated VLAN is 0, i.e. invalid and not
operational.
Default
Format dot1x unauthenticated-vlan <vlan id>
Mode
0
Interface Config
Switching Commands
83
Page 84

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
no dot1x unauthenticated-vlan
This command resets the unauthenticated-vlan associated with the port to its default value.
Format no dot1x unauthenticated-vlan
Mode
Interface Config
dot1x user
This command adds the specified user to the list of users with access to the specified port or
all ports. The <user> parameter must be a configured user.
Format dot1x user <user> {<slot/port> | all}
Mode
no dot1x user
This command removes the user from the list of users with access to the specified port or all
ports.
Global Config
Format no dot1x user <user> {<slot/port> | all}
Mode
Global Config
clear dot1x authentication-history
This command clears the authentication history table captured during successful and
unsuccessful authentication on all interface or the specified interface.
Format clear dot1x authentication-history [slot/port]
Mode
Global Config
dot1x dynamic-vlan enable
Use this command to enable the switch to create VLANs dynamically when a RADIUS
assigned VLAN does not exist in the switch.
Format dot1x dynamic-vlan enable
Mode
Default
Global Config
Disabled
Switching Commands
84
Page 85

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
no dot1x dynamic-vlan enable
Use this command to disable the switch from creating VLANs dynamically when a RADIUS
assigned VLAN does not exist in the switch.
Format no dot1x dynamic-vlan enable
Mode
Global Config
dot1x system-auth-control monitor
Use this command to enable the 802.1X monitor mode on the switch. The purpose of Monitor
mode is to help troubleshoot port-based authentication configuration issues without
disrupting network access for hosts connected to the switch. In Monitor mode, a host is
granted network access to an 802.1X-enabled port even if it fails the authentication process.
The results of the process are logged for diagnostic purposes.
Format dot1x system-auth-control monitor
Mode
Default
Global Config
Disabled
no dot1x system-auth-control monitor
Use this command to disable the 802.1X monitor on the switch.
Format no dot1x system-auth-control monitor
Mode
Global Config
show dot1x authentication-history
This command displays 802.1X authentication events and information during successful and
unsuccessful Dot1x authentication process for all interfaces or the specified interface. Use
the optional keywords to display only failure authentication events in summary or in detail.
Format show dot1x authentication-history {slot/port | all} [failedauth-only]
[detail]
Mode
Term Definition
Time Stamp
Interface
Mac-Address
VLAN assigned
Privileged EXEC
The exact time at which the event occurs.
Physical Port on which the event occurs.
The supplicant/client MAC address.
The VLAN assigned to the client/port on authentication.
Switching Commands
85
Page 86

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Term Definition
VLAN assigned
Reason
Auth Status
Reason
The type of VLAN ID assigned, which can be Guest VLAN, Unauth, Default, RADIUS
Assigned, or Monitor Mode VLAN ID.
The authentication status.
The actual reason behind the successful or failed authentication.
show authentication methods
This command displays information about the authentication methods.
Format show authentication methods
Mode
The following is an example of this command:
Login Authentication Method Lists
________________________________
Console_Default: None
Network_Default:Local
Enable Authentication Lists
_____________________
Console_Default: Enable None
Network_Default:Enable
Line Login Method List Enable Method Lists
_____________________
Console Console_Default Console_Default
Telnet Network_Default Network_Default
SSH Network_Default Network_Default
http : Local
https : Local
dot1x :
Privileged EXEC
show dot1x
This command is used to show a summary of the global dot1x configuration, summary
information of the dot1x configuration for a specified port or all ports, the detailed dot1x
configuration for a specified port and the dot1x statistics for a specified port - depending on
the tokens used.
Format show dot1x [{summary {<slot/port> | all} | detail <slot/port> |
statistics <slot/port>]
Mode
Privileged EXEC
Switching Commands
86
Page 87

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
If you do not use the optional parameters <slot/port> or <vlanid>, the command
displays the global dot1x mode, the VLAN Assignment mode, and the Dynamic VLAN
Creation mode.
Term Definition
Administrative
Mode
VLAN
Assignment
Mode
Dynamic VLAN
Creation Mode
Monitor Mode
Indicates whether authentication control on the switch is enabled or disabled.
Indicates whether assignment of an authorized port to a RADIUS assigned VLAN is
allowed (enabled) or not (disabled).
Indicates whether the switch can dynamically create a RADIUS-assigned VLAN if it does
not currently exist on the switch.
Indicates whether the Dot1x Monitor mode on the switch is enabled or disabled.
If you use the optional parameter summary {<slot/port> | all}, the dot1x
configuration for the specified port or all ports are displayed.
Term Definition
Interface
Control Mode
Operating
Control Mode
Reauthenticatio
n Enabled
Port Status
The interface whose configuration is displayed.
The configured control mode for this port. Possible values are force-unauthorized |
force-authorized | auto | mac-based | authorized | unauthorized.
The control mode under which this port is operating. Possible values are authorized |
unauthorized.
Indicates whether re-authentication is enabled on this port.
Indicates whether the port is authorized or unauthorized. Possible values are authorized
| unauthorized.
If you use the optional parameter 'detail <slot/port>', the detailed dot1x configuration
for the specified port is displayed.
Term Definition
Port
Protocol Version
PAE Capabilities
Control Mode
Authenticator
PAE State
The interface whose configuration is displayed.
The protocol version associated with this port. The only possible value is 1,
corresponding to the first version of the dot1x specification.
The port access entity (PAE) functionality of this port. Possible values are Authenticator
or Supplicant.
The configured control mode for this port. Possible values are force-unauthorized |
force-authorized | auto | mac-based.
Current state of the authenticator PAE state machine. Possible values are Initialize,
Disconnected, Connecting,
ForceAuthorized, and ForceUnauthorized. When MAC-based authentication is enabled
on the port, this parameter is deprecated.
Authenticating, Authenticated, Aborting, Held,
Switching Commands
87
Page 88

Term Definition
Backend
Authentication
State
Quiet Period
Transmit Period
Guest-VLAN ID
Guest VLAN
Period
Supplicant
Timeout
Server Timeout
Maximum
Requests
VLAN Id
VLAN Assigned
Reason
Reauthentication
Period
Reauthentication
Enabled
Key
Transmission
Enabled
Control Direction
Maximum Users
Unauthenticated
VLAN ID
Current state of the backend authentication state machine. Possible values are
Request, Response, Success, Fail, Timeout, Idle, and Initialize. When MAC-based
authentication is enabled on the port, this parameter is deprecated.
The timer used by the authenticator state machine on this port to define periods of time
in which it will not attempt to acquire a supplicant. The value is expressed in seconds
and will be in the range 0 and 65535.
The timer used by the authenticator state machine on the specified port to determine
when to send an EAPOL EAP Request/Identity frame to the supplicant. The value is
expressed in seconds and will be in the range of 1 and 65535.
The guest VLAN identifier configured on the interface.
The time in seconds for which the authenticator waits before authorizing and placing the
port in the Guest VLAN, if no EAPOL packets are detected on that port.
The timer used by the authenticator state machine on this port to timeout the supplicant.
The value is expressed in seconds and will be in the range of 1 and 65535.
The timer used by the authenticator on this port to timeout the authentication server.
The value is expressed in seconds and will be in the range of 1 and 65535.
The maximum number of times the authenticator state machine on this port will
retransmit an EAPOL EAP Request/Identity before timing out the supplicant. The value
will be in the range of 1 and 10.
The VLAN assigned to the port by the radius server. This is only valid when the port
control mode is not Mac-based.
The reason the VLAN identified in the VLAN Idfield has been assigned to the port.
Possible values are RADIUS, Unauthenticated VLAN, Guest VLAN, default, and Not
Assigned. When the VLAN Assigned Reason is ‘Not Assigned’, it means that the port
has not been assigned to any VLAN by dot1x. This only valid when the port control
mode is not MAC-based.
The timer used by the authenticator state machine on this port to determine when
reauthentication of the supplicant takes place. The value is expressed in seconds and
will be in the range of 1 and 65535.
Indicates if reauthentication is enabled on this port. Possible values are ‘True” or
“False”.
Indicates if the key is transmitted to the supplicant for the specified port. Possible values
are True or False.
The control direction for the specified port or ports. Possible values are both or in.
The maximum number of clients that can get authenticated on the port in the
MAC-based dot1x authentication mode. This value is used only when the port control
mode is not MAC-based.
Indicates the unauthenticated VLAN configured for this port. This value is valid for the
port only when the port control mode is not MAC-based.
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Switching Commands
88
Page 89

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Term Definition
Session Timeout
Session
Termination
Action
Indicates the time for which the given session is valid. The time period in seconds is
returned by the RADIUS server on authentication of the port.
port only when the port control mode is not MAC-based.
This value indicates the action to be taken once the session timeout expires. Possible
values are Default, Radius-Request. If the value is Default, the session is terminated
the port goes into unauthorized state. If the value is Radius-Request, a reauthentication
of the client authenticated on the port is performed. This value is valid for the port only
when the port control mode is not MAC-based.
This value is valid for the
The show dot1x detail <slot/port> command will display the following MAC-based
dot1x fields if the port-control mode for that specific port is MAC-based. For each client
authenticated on the port, the
show dot1x detail <slot/port> command will display the
following MAC-based dot1x parameters if the port-control mode for that specific port is
MAC-based.
Term Definition
Supplicant
MAC-Address
Authenticator
PAE State
Backend
Authentication
State
VLAN-Assigned
Logical Port
The MAC-address of the supplicant.
Current state of the authenticator PAE state machine. Possible values are Initialize,
Disconnected, Connecting,
ForceAuthorized, and ForceUnauthorized.
Current state of the backend authentication state machine. Possible values are Request,
Response, Success, Fail,
The VLAN assigned to the client by the radius server.
The logical port number associated with the client.
Authenticating, Authenticated, Aborting, Held,
Timeout, Idle, and Initialize.
If you use the optional parameter statistics <slot/port>, the following dot1x statistics
for the specified port appear.
Term Definition
Port
EAPOL Frames
Received
EAPOL Frames
Transmitted
EAPOL Start
Frames
Received
EAPOL Logoff
Frames
Received
Last EAPOL
Frame Version
The interface whose statistics are displayed.
The number of valid EAPOL frames of any type that have been received by this
authenticator
The number of EAPOL frames of any type that have been transmitted by this
authenticator
The number of EAPOL start frames that have been received by this authenticator.
The number of EAPOL logoff frames that have been received by this authenticator.
The protocol version number carried in the most recently received EAPOL frame.
.
.
Switching Commands
89
Page 90
Term Definition
Last EAPOL
Frame Source
EAP
Response/Id
Frames
Received
EAP Response
Frames
Received
EAP Request/Id
Frames
Transmitted
EAP Request
Frames
Transmitted
Invalid EAPOL
Frames
Received
EAP Length
Error Frames
Received
The source MAC address carried in the most recently received EAPOL frame.
The number of EAP response/identity frames that have been received by this
authenticator
The number of valid EAP response frames (other than resp/id frames) that have been
received by this authenticator
The number of EAP request/identity frames that have been transmitted by this
authenticator
The number of EAP request frames (other than request/identity frames) that have been
transmitted by this authenticator
The number of EAPOL frames that have been received by this authenticator in which the
frame type is not recognized.
The number of EAPOL frames that have been received by this authenticator in which the
frame type is not recognized.
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
.
.
.
.
show dot1x clients
This command displays 802.1x client information. This command also displays information
about the number of clients that are authenticated using Monitor mode and using 802.1X.
Format show dot1x clients {<slot/port> | all}
Mode
Term Definition
Clients
Authenticated
using Monitor
Mode
Clients
Authenticated
using Dot1x
Logical
Interface
Interface
User Name
Supplicant MAC
Address
Session Time
Privileged EXEC
Indicates the number of the Dot1x clients authenticated using Monitor mode.
Indicates the number of Dot1x clients authenticated using 802.1x authentication process.
The logical port number associated with a client.
The physical port to which the supplicant is associated.
The user name used by the client to authenticate to the server.
The supplicant device MAC address.
The time since the supplicant is logged on.
Switching Commands
90
Page 91
Term Definition
Filter ID
VLAN ID
VLAN Assigned
Session
Timeout
Session
Termination
Action
Identifies the Filter ID returned by the RADIUS server when the client was authenticated.
This is a configured Dif
The VLAN assigned to the port.
The reason the VLAN identified in the VLAN ID field has been assigned to the port.
Possible values are RADIUS, Unauthenticated VLAN, or Default. When the VLAN
Assigned reason is Default, it means that the VLAN was assigned to the port because
the PVID of the port was that VLAN ID.
This value indicates the time for which the given session is valid. The time period in
seconds is returned by the RADIUS server on authentication of the port. This value is
valid for the port only when the port-control mode is not MAC-based.
This value indicates the action to be taken once the session timeout expires. Possible
values are Default and Radius-Request. If the value is Default, the session is terminated
and client details are cleared. If the value is Radius-Request, a reauthentication of the
client is performed.
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
fServ policy name on the switch.
show dot1x users
This command displays 802.1x port security user information for locally configured users.
Format show dot1x users <slot/port>
Mode
Term Definition
Users
Privileged EXEC
Users configured locally to have access to the specified port.
802.1X Supplicant Commands
802.1X (“dot1x”) supplicant functionality is on point-to-point ports. The administrator can
configure the user name and password used in authentication and capabilities of the
supplicant port.
dot1x pae
Use this command to set the port’s dot1x role. The port can serve as either a supplicant or an
authenticator.
Format dot1x pae {supplicant | authenticator}
Mode
Interface Config
Switching Commands
91
Page 92

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
dot1x supplicant port-control
Use this command to set the ports authorization state (Authorized or Unauthorized) either
manually or by setting the port to auto-authorize upon startup. By default all the ports are
authenticators. If the port’s attribute needs to be moved from <authenticator to supplicant> or
<supplicant to authenticator>, use this command.
Format dot1x supplicant port-control {auto | force-authorized |
force_unauthorized}
Mode
Term Description
auto
force-authorized
forceunauthorized
Interface Config
The port is in the Unauthorized state until it presents its user name and password
credentials to an authenticator. If the authenticator authorizes the port, then it is placed
in the Authorized state.
Sets the authorization state of the port to Authorized, bypassing the authentication
process.
Sets the authorization state of the port to Unauthorized, bypassing the authentication
process.
no dot1x supplicant port-control
Use this command to set the port-control mode to the default, auto.
Default
Format no dot1x supplicant port-control
Mode
Auto
Interface Config
dot1x supplicant max-start
Use this command to configure the number of attempts that the supplicant makes to find the
authenticator before the supplicant assumes that there is no authenticator.
Default
Format dot1x supplicant max-start <1-10>
Mode
no dot1x supplicant max-start
Use this command to set the max-start value to the default.
3
Interface Config
Format no dot1x supplicant max-start
Mode
Interface Config
Switching Commands
92
Page 93

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
dot1x supplicant timeout start-period
Use this command to configure the start period timer interval to wait for the EAP identity
request from the authenticator.
Default
Format dot1x supplicant timeout start-period <1-65535 seconds>
Mode
30 seconds
Interface Config
no dot1x supplicant timeout start-period
Use this command to set the start-period value to the default.
Format no dot1x supplicant timeout start-period
Mode
Interface Config
dot1x supplicant timeout held-period
Use this command to configure the held period timer interval to wait for the next
authentication on previous authentication fail.
Default
Format dot1x supplicant timeout held-period <1-65535 seconds>
Mode
30 seconds
Interface Config
no dot1x supplicant timeout held-period
Use this command to set the held-period value to the default value.
Format no dot1x supplicant timeout held-period
Mode
Interface Config
dot1x supplicant timeout auth-period
Use this command to configure the authentication period timer interval to wait for the next
EAP request challenge from the authenticator.
Default
Format dot1x supplicant timeout auth-period <1-65535 seconds>
Mode
30 seconds
Interface Config
Switching Commands
93
Page 94

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
no dot1x supplicant timeout auth-period
Use this command to set the auth-period value to the default value.
Format no dot1x supplicant timeout auth-period
Mode
Interface Config
dot1x supplicant user
Use this command to map the given user to the port.
Format dot1x supplicant user
Mode
Interface Config
Storm-Control Commands
This section describes commands you use to configure storm-control and view storm-control
configuration information. A traffic storm is a condition that occurs when incoming packets
flood the LAN, which creates performance degradation in the network. The Storm-Control
feature protects against this condition.
The 7000 series provides broadcast, multicast, and unicast story recovery for individual
interfaces. Unicast Storm-Control protects against traf
fic whose MAC addresses are not
known by the system. For broadcast, multicast, and unicast storm-control, if the rate of traffic
ingressing on an interface increases beyond the configured threshold for that type, the traffic
is dropped.
To configure storm-control, you will enable the feature for all interfaces or for individual
interfaces, and you will set the threshold (storm-control level) beyond which the broadcast,
multicast, or unicast traf
fic will be dropped. The Storm-Control feature allows you to limit the
rate of specific types of packets through the switch on a per-port, per-type, basis.
Configuring a storm-control level also enables that form of storm-control. Disabling a
storm-control level (using the “no” version of the command) sets the storm-control level back
to the default value and disables that form of storm-control. Using the “no” version of the
“storm-control” command (not stating a “level”) disables that form of storm-control but
maintains the configured “level” (to be active the next time that form of storm-control is
enabled.)
Note: The actual rate of ingress traf fic required to activate storm-control is
based on the size of incoming packets and the hard-coded average
packet size of 512 bytes - used to calculate a packet-per-second
(pps) rate - as the forwarding-plane requires pps versus an absolute
Switching Commands
94
Page 95

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
rate kbps. For example, if the configured limit is 10%, this is
converted to ~25000 pps, and this pps limit is set in forwarding plane
(hardware). You get the approximate desired output when 512bytes
packets are used.
storm-control broadcast
Use this command to enable broadcast storm recovery mode for a specific interface. If the
mode is enabled, broadcast storm recovery is active and, if the rate of L2 broadcast traffic
ingressing on an interface increases beyond the configured threshold, the traffic will be
dropped. Therefore, the rate of broadcast traffic will be limited to the configured threshold.
Default
Format storm-control broadcast
Mode
enabled
Interface Config
no storm-control broadcast
Use this command to disable broadcast storm recovery mode for a specific interface.
Format no storm-control broadcast
Mode
Interface Config
storm-control broadcast level
Use this command to configure the broadcast storm recovery threshold for an interface as a
percentage of link speed and enable broadcast storm recovery. If the mode is enabled,
broadcast storm recovery is active, and if the rate of L2 broadcast traffic ingressing on an
interface increases beyond the configured threshold, the traffic is dropped. Therefore, the
rate of broadcast traffic is limited to the configured threshold.
If the ‘shutdown’ option is selected, and the broadcast traffic increases beyond the threshold,
the interface shuts down instead of dropping packets.
shutdown’ under the port manually.
To recover the port, issue ‘no
Default
Format storm-control broadcast level
Mode
5
Interface Config
Switching Commands
<0-100> {action [ratelimit | shutdown]}
95
Page 96

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
no storm-control broadcast level
This command sets the broadcast storm recovery threshold to the default value for an
interface and disables broadcast storm recovery
Format no storm-control broadcast level
Mode
Interface Config
.
storm-control broadcast rate
Use this command to configure the broadcast storm recovery threshold for an interface in
packets per second. If the mode is enabled, broadcast storm recovery is active, and if the
rate of L2 broadcast traffic ingressing on an interface increases beyond the configured
threshold, the traffic is dropped. Therefore, the rate of broadcast traffic is limited to the
configured threshold.
Default
Format storm-control broadcast rate <0-14880000>
Mode
0
Interface Config
no storm-control broadcast rate
This command sets the broadcast storm recovery threshold to the default value for an
interface and disables broadcast storm recovery
Format no storm-control broadcast rate
Mode
Interface Config
.
storm-control broadcast (Global)
This command enables broadcast storm recovery mode for all interfaces. If the mode is
enabled, broadcast storm recovery is active, and if the rate of L2 broadcast traffic ingressing
on an interface increases beyond the configured threshold, the traffic will be dropped.
Therefore, the rate of broadcast traffic will be limited to the configured threshold.
Default
Format storm-control broadcast
Mode
disabled
Global Config
no storm-control broadcast
This command disables broadcast storm recovery mode for all interfaces.
Format no storm-control broadcast
Mode
Global Config
Switching Commands
96
Page 97

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
storm-control broadcast level (Global)
This command configures the broadcast storm recovery threshold for all interfaces as a
percentage of link speed and enables broadcast storm recovery. If the mode is enabled,
broadcast storm recovery is active, and if the rate of L2 broadcast traffic ingressing on an
interface increases beyond the configured threshold, the traffic will be dropped. Therefore,
the rate of broadcast traffic will be limited to the configured threshold. This command also
enables broadcast storm recovery mode for all interfaces.
If the ‘shutdown’ option is selected, and the broadcast traffic increases beyond the threshold,
the interface shuts down instead of dropping packets.
shutdown’ under the port manually.
To recover the port, issue ‘no
Default
Format storm-control broadcast level
Mode
5
<0-100>
Global Config
no storm-control broadcast level
This command sets the broadcast storm recovery threshold to the default value for all
interfaces and disables broadcast storm recovery
Format no storm-control broadcast level
Mode
Global Config
.
storm-control broadcast rate (Global)
Use this command to configure the broadcast storm recovery threshold for all interfaces in
packets per second. If the mode is enabled, broadcast storm recovery is active, and if the
rate of L2 broadcast traffic ingressing on an interface increases beyond the configured
threshold, the traffic is dropped. Therefore, the rate of broadcast traffic is limited to the
configured threshold.
Default
Format storm-control broadcast rate <0-14880000>
Mode
0
Global Config
no storm-control broadcast rate
This command sets the broadcast storm recovery threshold to the default value for all
interfaces and disables broadcast storm recovery
Format no storm-control broadcast rate
Mode
Global Config
Switching Commands
.
97
Page 98

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
storm-control multicast
This command enables multicast storm recovery mode for an interface. If the mode is
enabled, multicast storm recovery is active, and if the rate of L2 multicast traffic ingressing on
an interface increases beyond the configured threshold, the traffic will be dropped. Therefore,
the rate of multicast traffic will be limited to the configured threshold.
Default
Format storm-control multicast
Mode
disabled
Interface Config
no storm-control multicast
This command disables multicast storm recovery mode for an interface.
Format no storm-control multicast
Mode
Interface Config
storm-control multicast level
This command configures the multicast storm recovery threshold for an interface as a
percentage of link speed and enables multicast storm recovery mode. If the mode is enabled,
multicast storm recovery is active, and if the rate of L2 multicast traffic ingressing on an
interface increases beyond the configured threshold, the traffic will be dropped. Therefore,
the rate of multicast traffic will be limited to the configured threshold.
Default
Format storm-control multicast level <0-100>
Mode
5
Interface Config
no storm-control multicast level
This command sets the multicast storm recovery threshold to the default value for an
interface and disables multicast storm recovery
Format no storm-control multicast level <0-100>
Mode
Interface Config
.
storm-control multicast rate
Use this command to configure the multicast storm recovery threshold for an interface in
packets per second. If the mode is enabled, multicast storm recovery is active, and if the rate
of L2 broadcast traffic ingressing on an interface increases beyond the configured threshold,
Switching Commands
98
Page 99

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
the traffic is dropped. Therefore, the rate of multicast traffic is limited to the configured
threshold.
Default
Format storm-control multicast rate <0-14880000>
Mode
0
Interface Config
no storm-control multicast rate
This command sets the multicast storm recovery threshold to the default value for an
interface and disables multicast storm recovery
Format no storm-control multicast rate
Mode
Interface Config
.
storm-control multicast (Global)
This command enables multicast storm recovery mode for all interfaces. If the mode is
enabled, multicast storm recovery is active, and if the rate of L2 multicast traffic ingressing on
an interface increases beyond the configured threshold, the traffic will be dropped. Therefore,
the rate of multicast traffic will be limited to the configured threshold.
Default
Format storm-control multicast
Mode
disabled
Global Config
no storm-control multicast
This command disables multicast storm recovery mode for all interfaces.
Format no storm-control multicast
Mode
Global Config
storm-control multicast level (Global)
This command configures the multicast storm recovery threshold for all interfaces as a
percentage of link speed and enables multicast storm recovery mode. If the mode is enabled,
multicast storm recovery is active, and if the rate of L2 multicast traffic ingressing on an
interface increases beyond the configured threshold, the traffic will be dropped. Therefore,
the rate of multicast traffic will be limited to the configured threshold.
Default
Format storm-control multicast level
Mode
5
<0-100>
Global Config
Switching Commands
99
Page 100

ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
no storm-control multicast level
This command sets the multicast storm recovery threshold to the default value for all
interfaces and disables multicast storm recovery
Format no storm-control multicast level
Mode
Global Config
.
storm-control multicast rate (Global)
Use this command to configure the multicast storm recovery threshold for all interfaces in
packets per second. If the mode is enabled, multicast storm recovery is active, and if the rate
of L2 broadcast traffic ingressing on an interface increases beyond the configured threshold,
the traffic is dropped. Therefore, the rate of multicast traffic is limited to the configured
threshold.
Default
Format storm-control multicast rate <0-14880000>
Mode
0
Global Config
no storm-control broadcast rate
This command sets the broadcast storm recovery threshold to the default value for all
interfaces and disables broadcast storm recovery
Format no storm-control broadcast rate
Mode
Global Config
.
storm-control unicast
This command enables unicast storm recovery mode for an interface. If the mode is enabled,
unicast storm recovery is active, and if the rate of unknown L2 unicast (destination lookup
failure) traffic ingressing on an interface increases beyond the configured threshold, the traffic
will be dropped. Therefore, the rate of unknown unicast traffic will be limited to the configured
threshold.
Default
Format storm-control unicast
Mode
disabled
Interface Config
Switching Commands
100
 Loading...
Loading...