Netgear FVS318N Installation Manual

ProSafe Wireless-N 8-Port Gigabit VPN Firewall FVS318N
CLI Reference Manual
350 East Plumeria Drive
San Jose, CA 95134
USA
August 2012
202-10827-01
v3.0
ProSafe Wireless-N 8-Port Gigabit VPN Firewall FVS318N
© 2012 NETGEAR, Inc. All rights reserved.
No part of this publication may be reproduced, transmitted, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, or translated
into any language in any form or by any means without the written permission of NETGEAR, Inc.
NETGEAR, the NETGEAR logo, and Connect with Innovation are trademarks and/or registered trademarks of
NETGEAR, Inc. and/or its subsidiaries in the United States and/or other countries. Information is subject to change
without notice. Other brand and product names are registered trademarks or trademarks of their respective
holders. © 2012 All rights reserved.
Technical Support
Thank you for choosing NETGEAR. To register your product, get the latest product updates, get support online, or
for more information about the topics covered in this manual, visit the Support website at
http://support.netgear.com.
Phone (US & Canada only): 1-888-NETGEAR
Phone (Other Countries): Check the list of phone numbers at
http://support.netgear.com/app/answers/detail/a_id/984.
Statement of Conditions
To improve internal design, operational function, and/or reliability, NETGEAR reserves the right to make changes
to the products described in this document without notice. NETGEAR does not assume any liability that may occur
due to the use, or application of, the product(s) or circuit layout(s) described herein.
Revision History
Publication Part Number Version Publish Date Comments
202-10827-01 3.0 August 2012 Many commands changed and some commands
added
202-10827-01 2.0 May 2012 Minor corrections
202-10827-01 1.0 April 2012 First publication
2

Contents
Chapter 1 Introduction
Chapter 2 Overview of the Configuration Commands
Command Syntax and Conventions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
Command Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
Description of a Command. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
Common Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
The Four Categories of Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
The Five Main Modes for Configuration Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
Save Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
Global Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
The Three Basic Types of Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
Command Autocompletion and Command Abbreviation . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
CLI Line-Editing Conventions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
Access the CLI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
Network Settings (Net Mode) Configuration Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
Security Settings (Security Mode) Configuration Commands . . . . . . . . . .21
Administrative and Monitoring Settings (System Mode)
Configuration Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .24
Wireless Settings (Dot11 Mode) Configuration Commands. . . . . . . . . . . .25
VPN Settings (VPN Mode) Configuration Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
Chapter 3 Net Mode Configuration Commands
General WAN Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30
IPv4 WAN Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .32
IPv6 WAN Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .38
IPv6 Tunnel Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41
Dynamic DNS Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .44
IPv4 LAN Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .45
IPv6 LAN Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .55
IPv4 DMZ Setup Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .66
IPv6 DMZ Setup Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .68
IPv4 Routing Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .75
IPv6 Routing Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .80
Chapter 4 Security Mode Configuration Commands
Security Services Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .83
Security Schedules Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .85
3

ProSafe Wireless-N 8-Port Gigabit VPN Firewall FVS318N
IPv4 Add Firewall Rule and Edit Firewall Rule Commands . . . . . . . . . . . .87
IPv4 General Firewall Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .125
IPv6 Firewall Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .126
Attack Check Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .134
Session Limit, Time-Out, and Advanced Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .137
Address Filter and IP/MAC Binding Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .140
Port Triggering Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .145
UPnP Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .147
Bandwidth Profile Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .148
Content Filtering Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .151
Chapter 5 System Mode Configuration Commands
Remote Management Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .158
SNMP Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .162
Time Zone Command. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .164
WAN Traffic Meter Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .167
Firewall Logs and Email Alerts Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .171
Chapter 6 Dot11 Mode Configuration Commands
Wireless Radio Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .178
Wireless Profile Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .186
Chapter 7 VPN Mode Configuration Commands
IPSec VPN Wizard Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .196
IPSec IKE Policy Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .198
IPSec VPN Policy Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .205
IPSec VPN Mode Config Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .216
SSL VPN Portal Layout Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .219
SSL VPN Authentication Domain Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .223
SSL VPN Authentication Group Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .227
SSL VPN User Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .229
SSL VPN Port Forwarding Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .236
SSL VPN Client Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .238
SSL VPN Resource Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .242
SSL VPN Policy Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .246
RADIUS Server Command. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .253
L2TP Server Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .255
Chapter 8 Overview of the Show Commands
Network Settings (Net Mode) Show Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .256
Security Settings (Security Mode) Show Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .258
Administrative and Monitoring Settings (System Mode)
Show Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .259
Wireless Settings (Dot11 Mode) Show Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .260
VPN Settings (VPN Mode) Show Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .261
4

ProSafe Wireless-N 8-Port Gigabit VPN Firewall FVS318N
Chapter 9 Show Commands
Network Settings (Net Mode) Show Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .264
WAN (IPv4 and IPv6) Show Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .264
IPv6 Mode and IPv6 Tunnel Show Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .266
LAN DHCP Show Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .267
Dynamic DNS Show Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .268
IPv4 LAN Show Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .268
IPv6 LAN Show Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .271
DMZ Show Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .273
Routing Show Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .274
Network Statistics Show Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .275
Security Settings (Security Mode) Show Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .276
Services Show Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .276
Schedules Show Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .277
Firewall Rules Show Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .277
Attack Checks Show Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .279
Session Limits Show Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .281
Advanced Firewall Show Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .281
Address Filter Show Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .282
Port Triggering Show Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .283
UPnP Show Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .283
Bandwidth Profiles Show Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .284
Content Filtering Show Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .284
Administrative and Monitoring Settings (System Mode)
Show Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .286
Remote Management Show Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .286
SNMP Show Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .287
Time Show Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .287
Firmware Version Show Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .288
Status Show Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .288
Traffic Meter Show Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .291
Logging Configuration Show Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .292
Logs Show Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .294
Wireless Settings (Dot11 Mode) Show Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .296
Radio Show Command. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .296
Profile Show Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .297
Wireless Statistics Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .299
VPN Settings (VPN Mode) Show Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .299
IPSec VPN Show Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .299
SSL VPN Show Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .301
SSL VPN User Show Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .304
RADIUS Server Show Command. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .307
L2TP Server Show Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .308
Chapter 10 Utility Commands
Overview Util Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .309
Firmware Backup, Restore, and Upgrade Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .310
5

ProSafe Wireless-N 8-Port Gigabit VPN Firewall FVS318N
Diagnostic Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .311
CLI Command Index
6

1. Introduction
This document describes the command-line interface (CLI) for the NETGEAR ProSafe
Wireless-N 8-Port Gigabit VPN Firewall FVS318N.
This chapter introduces the CLI interface. It includes the following sections:
• Command Syntax and Conventions
• The Four Categories of Commands
• The Five Main Modes for Configuration Commands
• Global Commands
• The Three Basic Types of Commands
• Command Autocompletion and Command Abbreviation
• Access the CLI
Note: For more information about the topics covered in this manual, visit
the support website at http://support.netgear.com.
1
Note: For more information about the features that you can configure
using the CLI, see the ProSafe Wireless-N 8-port Gigabit VPN
Firewall FVS318N Reference Manual.
Note: You cannot generate and upload a certificate through the CLI. You
need to access the web management interface to manage these
tasks.
7
ProSafe Wireless-N 8-Port Gigabit VPN Firewall FVS318N
Command Syntax and Conventions
A command is one or more words that can be followed by one or more keywords and
parameters. Keywords and parameters can be required or optional:
• A keyword is a predefined string (word) that narrows down the scope of a command. A
keyword can be followed by an associated parameter or by associated keywords. In
many cases, these associated keywords are mutually exclusive, so you need to select
one of them. In some cases, this manual refers to a group of words as a keyword.
• A parameter is a variable for which you need to type a value. You need to replace the
parameter name with the appropriate value, which might be a name or number. A
parameter can be associated with a command or with a keyword.
This manual lists each command by its full command name and provides a brief description
of the command. In addition, for each command, the following information is provided:
• Format. Shows the command keywords and the required and optional parameters.
• Mode. Identifies the command mode you need to be in to access the command. (With
some minor exceptions, the mode is always described using lowercase letters.)
• Related show command or commands. Identifies and links to the show command or
commands that can display the configured information.
For more complicated commands, in addition to the format, mode, and related show
command or commands, the following information is provided:
• Table. Explains the keywords and parameters that you can use for the command.
• Example. Shows a CLI example for the command.
Command Conventions
In this manual, the following type font conventions are used:
• A command name is stated in bold font.
• A keyword name is stated in bold font.
• A parameter name is stated in italic font.
The keywords and parameters for a command might include mandatory values, optional
values, or choices. The following table describes the conventions that this manual uses to
distinguish between value types:
Table 1. Command conventions
Symbol Example Description
< > angle brackets <value> Indicate that you need to enter a value in place of the
brackets and text inside them. (value is the parameter.)
[ ] square brackets [value] Indicate an optional parameter that you can enter in place of
the brackets and text inside them. (value is the parameter.)
Introduction
8
ProSafe Wireless-N 8-Port Gigabit VPN Firewall FVS318N
Table 1. Command conventions (continued)
Symbol Example Description
{ } curly braces {choice1 | choice2} Indicate that you need to select a keyword from the list of
choices. (choice1 and choice1 are keywords.)
| vertical bars choice1 | choice2 Separate the mutually exclusive choices. (choice1 and
choice1 are keywords.)
[ { } ] braces within
square brackets
[{choice1 | choice2}] Indicate a choice within an optional element. (choice1 and
choice1 are keywords.)
Description of a Command
The following example describes the net radvd pool lan edit <row id> command:
net radvd pool lan edit is the command name.
<row id> is the required parameter for which you need to enter a value after you type
the command words.
The command lets you enter the net-config [radvd-pool-lan] mode, from which you can
issue the following keywords and parameters:
prefix_type {6To4 {sla_id <id number>} | {Global-Local-ISATAP}
{prefix_address <ipv6-address>} {prefix_length
<prefix length>}}
prefix_life_time <seconds>
Explanation of the keywords and parameters:
prefix_type is a keyword. The required associated keyword that you need to
select is either 6To4 or Global-Local-ISATAP.
• If you select 6To4, you also need to issue the sla_id keyword and enter a
value for the <id number> parameter.
• If you select Global-Local-ISATAP, you also need to issue the
prefix_address keyword and enter a value for the <ipv6-address>
parameter, and you need to issue the prefix_length keyword and enter a
value for the <prefix length> parameter.
prefix_life_time is a keyword. <seconds> is the required parameter for which
you need to enter a value.
Command example:
FVS318N> net radvd pool lan edit 12
net-config[radvd-pool-lan]> prefix_type Global-Local-ISATAP
net-config[radvd-pool-lan]> prefix_address 10FA:2203:6145:4201::
net-config[radvd-pool-lan]> prefix_length 10
net-config[radvd-pool-lan]> prefix_life_time 3600
net-config[radvd-pool-lan]> save
Introduction
9
ProSafe Wireless-N 8-Port Gigabit VPN Firewall FVS318N
Common Parameters
Parameter values might be names (strings) or numbers. To use spaces as part of a name
parameter, enclose the name value in double quotes. For example, the expression “System
Name with Spaces” forces the system to accept the spaces. Empty strings (“”) are not valid
user-defined strings. The following table describes common parameter values and value
formatting:
Table 2. Common parameters
Parameter Description
ipaddr This parameter is a valid IPv4 address. You need to enter the IP address in the a.b.c.d
format, in which each octet is a number in the range from 0 to 255 (both inclusive), for
example, 10.12.140.218.
The CLI accepts decimal, hexadecimal, and octal formats through the following input
formats (where n is any valid decimal, hexadecimal, or octal number):
• 0xn (CLI assumes hexadecimal format)
• 0n (CLI assumes octal format with leading zeros)
• n (CLI assumes decimal format)
ipv6-address This parameter is a valid IPv6 address. You can enter the IPv6 address in the following
formats:
• FE80:0000:0000:0000:020F:24FF:FEBF:DBCB, or
• FE80:0:0:0:20F:24FF:FEBF:DBCB, or
• FE80::20F:24FF:FEBF:DBCB, or
• FE80:0:0:0:20F:24FF:128:141:49:32
For additional information, see RFC 3513.
Character strings Use double quotation marks to identify character strings, for example, “System Name with
Spaces”. An empty string (“”) is not valid.
The Four Categories of Commands
There are four CLI command categories:
• Configuration commands with five main configuration modes. For more information, see
the following section, The Five Main Modes for Configuration Commands). Save
commands also fall into this category (see Save Commands on page 13).
• Show commands that are available for the five main configuration modes (see Chapter 8,
Overview of the Show Commands and Chapter 9, Show Commands).
• Utility commands (see Chapter 10, Utility Commands).
• Global commands (see Global Commands on page 14).
Introduction
10
ProSafe Wireless-N 8-Port Gigabit VPN Firewall FVS318N
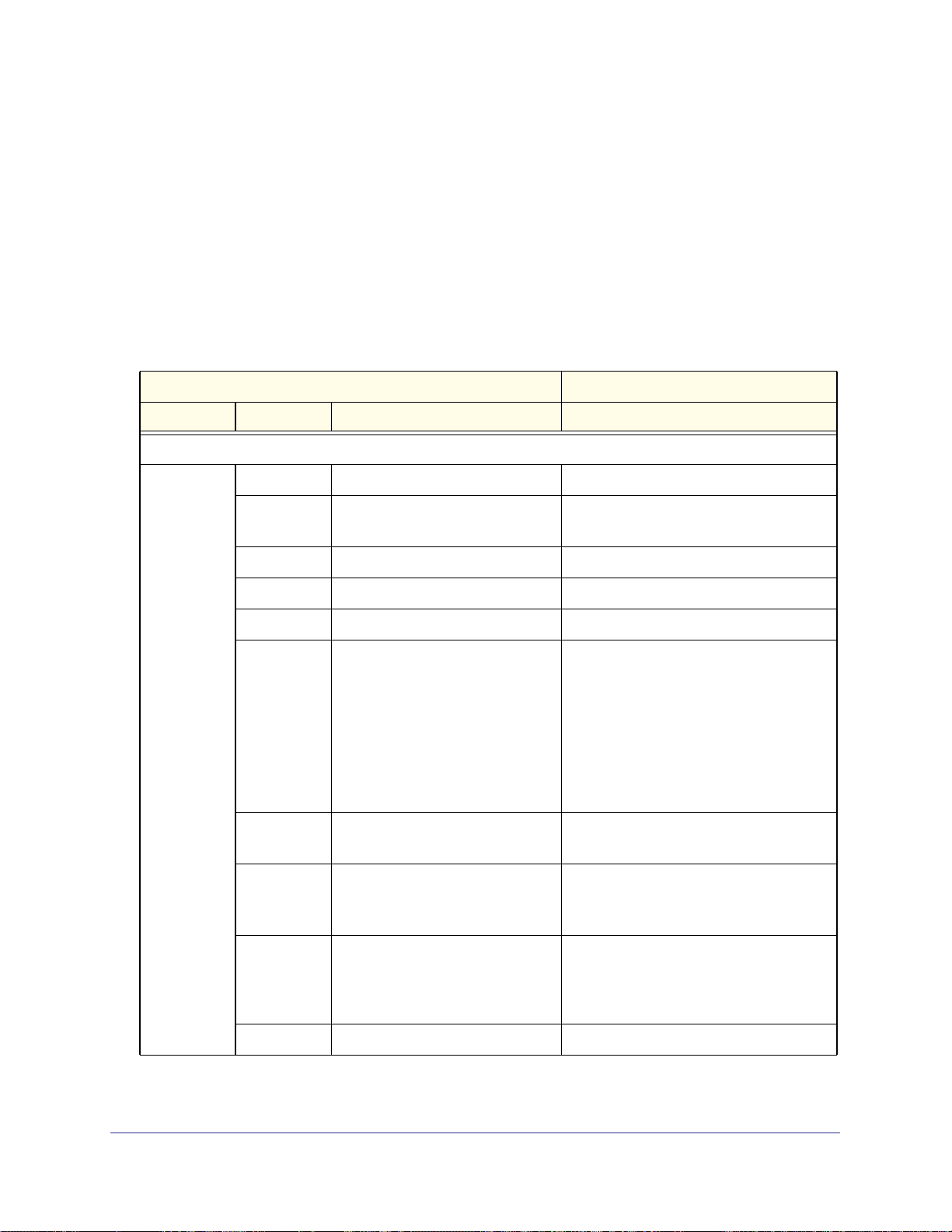
The Five Main Modes for Configuration Commands
For the configuration commands, there are five main modes in the CLI: net, security, system,
dot11, and vpn.
these modes, and each of these modes is described in detail in a separate chapter (see
Chapter 3 through Chapter 7).
The following table lists the main configuration modes, the configuration modes, the features
that you can configure in each configuration mode, and, for orientation, the basic web
management interface (GUI) path to the feature.
Table 3. Main configuration modes
__________________________CLI________________________ ___Web Management Interface (GUI)___
Main Mode Submode Feature That You Can Configure Basic Path
Network configuration commands
net ddns Dynamic DNS Network Configuration > Dynamic DNS
Chapter 2, Overview of the Configuration Commands lists all commands in
dmz DMZ for IPv4
DMZ for IPv6
ethernet VLAN assignment to LAN interface Network Configuration > LAN Setup
ipv6 IPv4 or IPv4/IPv6 mode Network Configuration > WAN Settings
ipv6_tunnel IPv6 tunnels Network Configuration > WAN Settings
lan IPv4 LAN settings and VLANs
LAN groups for IPv4
Secondary IPv4 addresses
Advanced IPv4 LAN settings
IPv6 LAN settings
Secondary IPv6 addresses
IPv6 LAN DHCP address pools
IPv6 prefix delegation for the LAN
radvd IPv6 RADVD and pools for the LAN
IPv6 RADVD and pools for the DMZ
routing Dynamic IPv4 routes
Static IPv4 routes
Static IPv6 routes
wan IPv4 WAN (Internet) settings
IPv6 WAN (Internet) settings
MTU, port speed, and MAC
address
Network Configuration > DMZ Setup
Network Configuration > LAN Setup
Network Configuration > LAN Setup
Network Configuration > DMZ Setup
Network Configuration > Routing
Network Configuration > WAN Settings
wan_settings NAT or Classical Routing Network Configuration > WAN Settings
Introduction
11
ProSafe Wireless-N 8-Port Gigabit VPN Firewall FVS318N
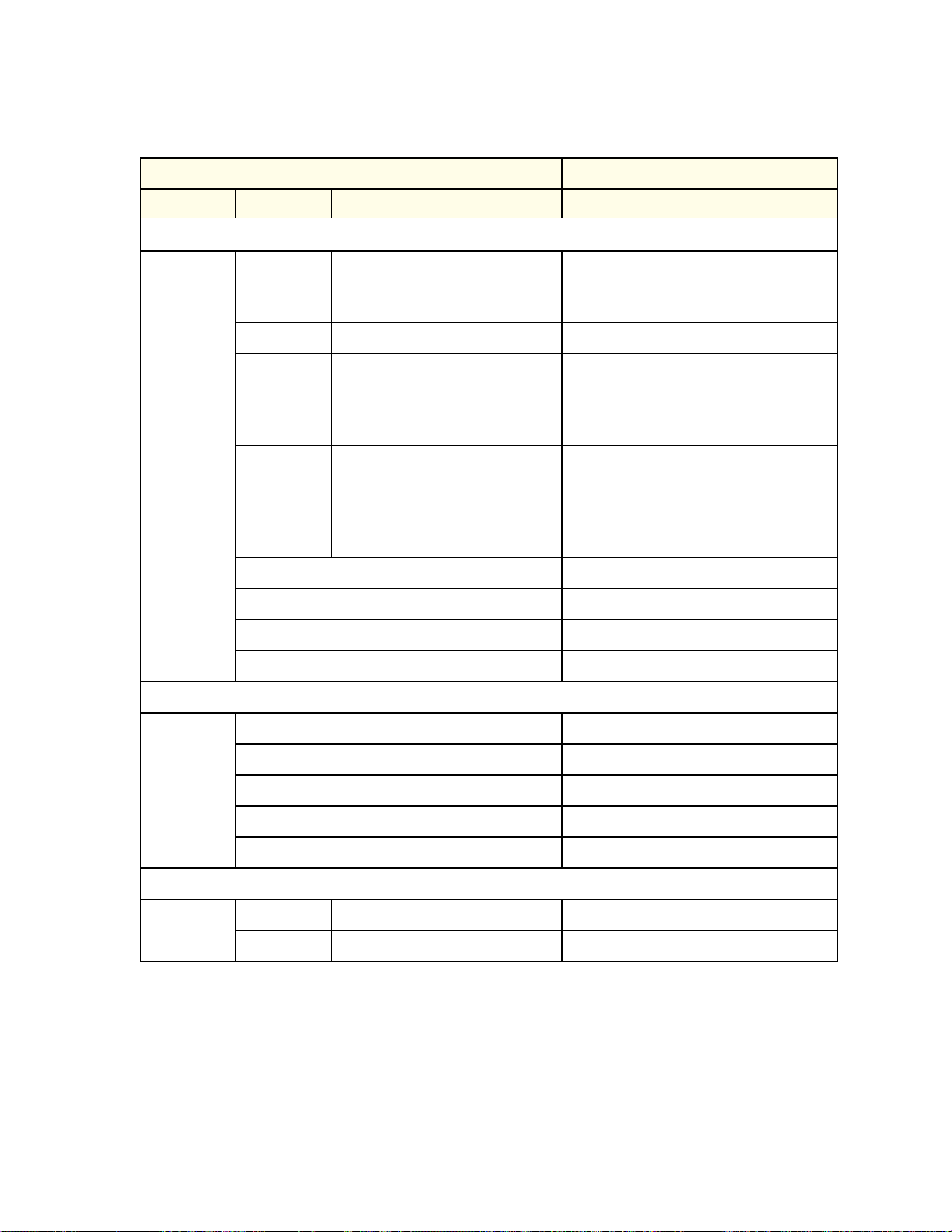
Table 3. Main configuration modes (continued)
__________________________CLI________________________ ___Web Management Interface (GUI)___
Main Mode Submode Feature That You Can Configure Basic Path
Security configuration commands
security address_filter Source MAC filters
IP/MAC bindings for IPv4
IP MAC bindings for IPv6
bandwidth Bandwidth profiles Security > Bandwidth Profile
content_filter Group filtering
Blocked keywords
Web components
Trusted domains
firewall All IPv4 firewall rules
All IPv6 firewall rules
Attack checks
Session limits and time-outs
SIP ALG
porttriggering_rules Security > Port Triggering
schedules Security > Schedule
services Security > Services
upnp Security > UPnP
Administration and monitoring configuration commands
Security > Address Filter
Security > Content Filtering
Security > Firewall
system logging Monitoring > Firewall Logs & E-mail
remote_management Administration > Remote Management
snmp Administration > SNMP
time Administration > Time Zone
traffic_meter Monitoring > Traffic Meter
Wireless configuration commands
dot11 profile Wireless profiles Network Configuration > Wireless Settings
radio Wireless radio Network Configuration > Wireless Settings
Introduction
12
ProSafe Wireless-N 8-Port Gigabit VPN Firewall FVS318N
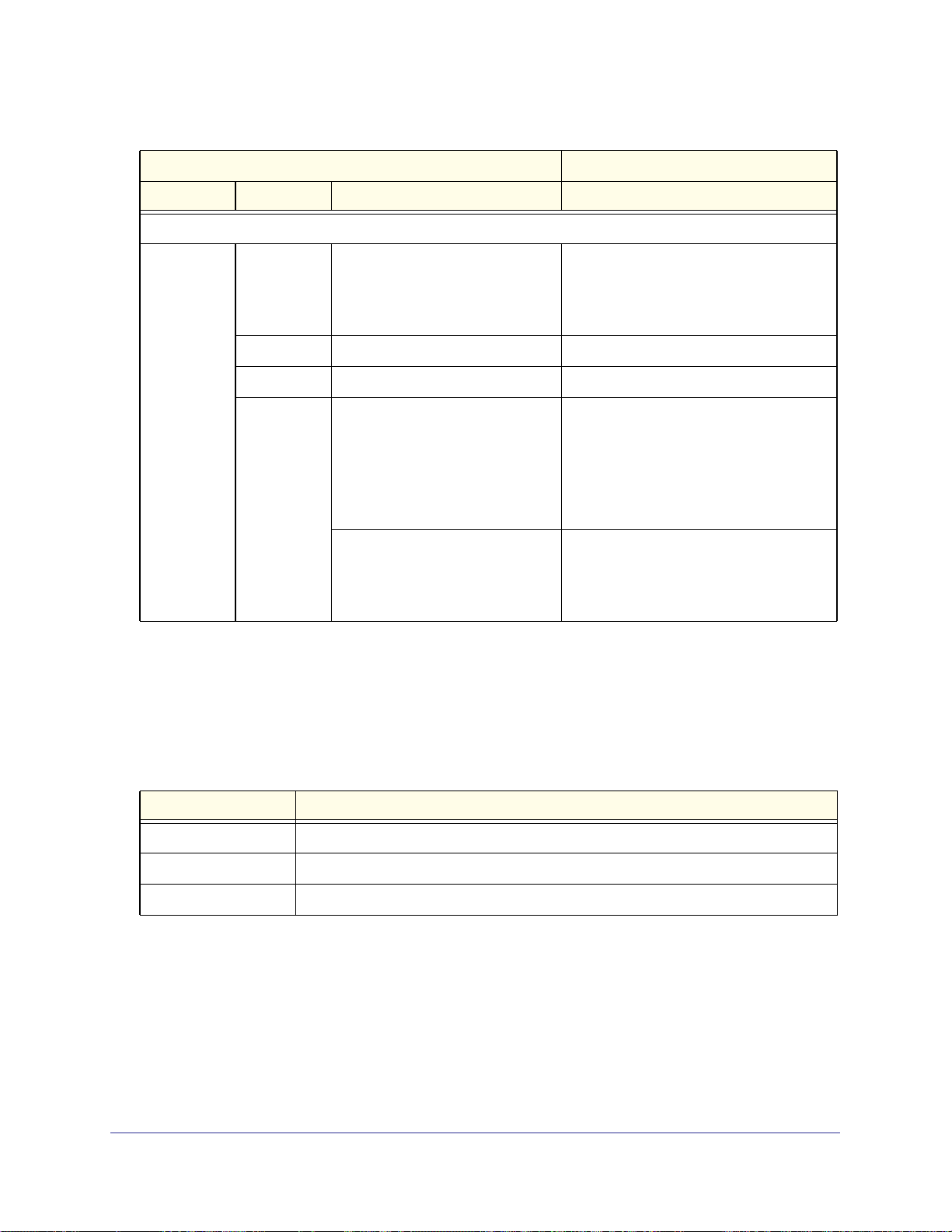
Table 3. Main configuration modes (continued)
__________________________CLI________________________ ___Web Management Interface (GUI)___
Main Mode Submode Feature That You Can Configure Basic Path
VPN configuration commands
vpn ipsec IKE policies
VPN policies
VPN IPSec Wizard
Mode Config records
l2tp L2TP server VPN > L2TP Server
radius RADIUS servers for VPN VPN > IPSec VPN > RADIUS Client
sslvpn SSL policies
Resources
Portal layouts
SSL VPN clients
Client routes
Port forwarding
Domains
Groups
User accounts
User login and IP policies
VPN > IPSec VPN
VPN > SSL VPN
Users
Save Commands
The following table describes the configuration commands that let you save or cancel
configuration changes in the CLI. You can use these commands in any of the five main
configuration modes. These commands are not preceded by a period.
Table 4. Save commands
Command Description
save Save the configuration changes.
exit Save the configuration changes and exit the current configuration mode.
cancel Roll back the configuration changes.
Commands That Require Saving
After you have issued a command that includes the word configure, add, or edit, you
enter a configuration mode from which you can issue keywords and associated parameters.
Introduction
13
ProSafe Wireless-N 8-Port Gigabit VPN Firewall FVS318N
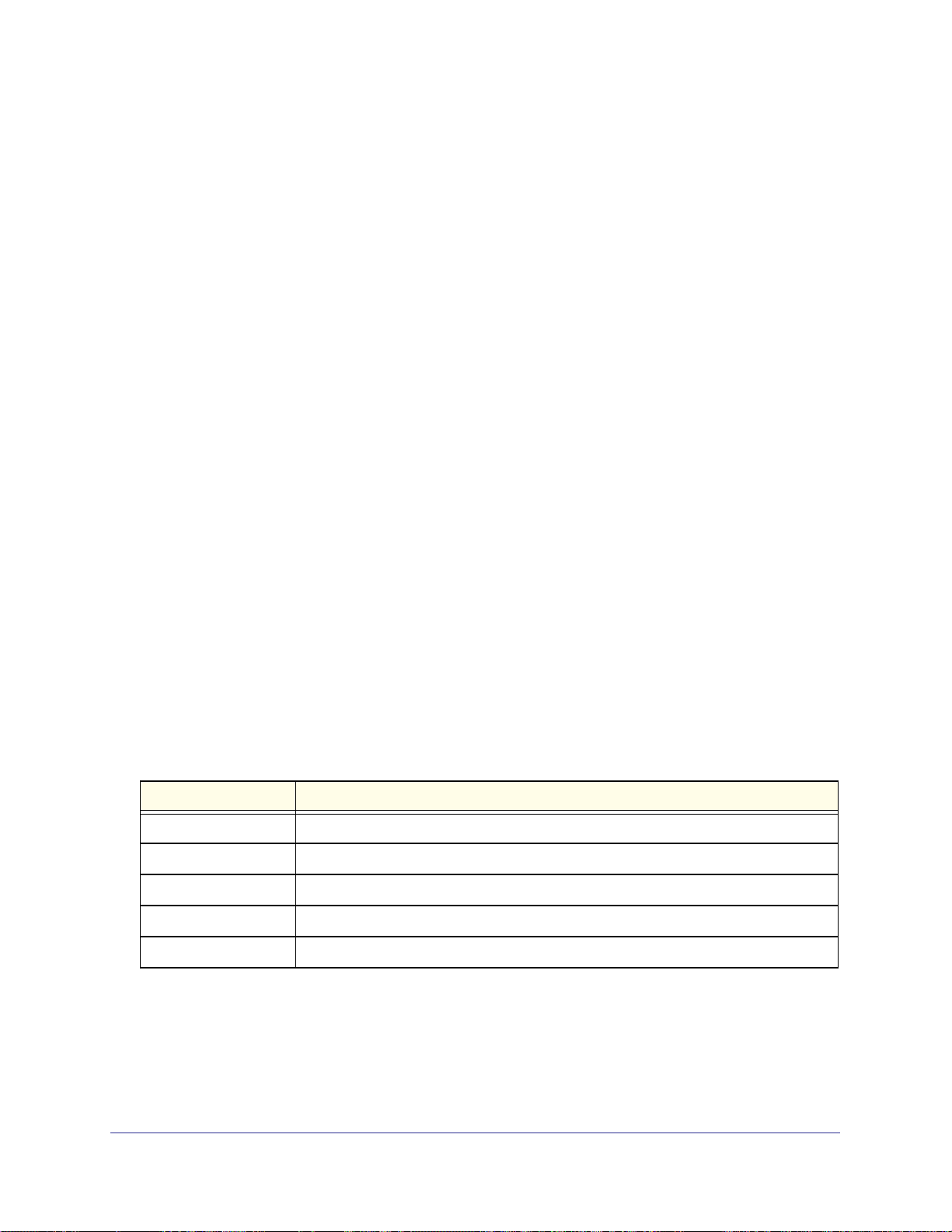
These are examples of commands for which you need to save your changes:
• net lan ipv4 configure <vlan id> lets you enter the net-config [lan-ipv4]
configuration mode. After you made your changes, issue save or exit to save your
changes.
• security content_filter trusted_domain add lets you enter the
security-config [approved-urls] configuration mode. After you made your changes, issue
save or exit to save your changes.
• dot11 profile configure <profile name> lets you enter the dot11-config
[profile] configuration mode. After you made your changes, issue save or exit to save
your changes.
Commands That Do Not Require Saving
You do not need to save your changes after you have issued a command that deletes,
disables, or enables a row ID, name, IP address, or MAC address, or that lets you make a
configuration change without entering another configuration mode.
These are examples of commands that you do not need to save:
• net lan dhcp reserved_ip delete <mac address>
• dot11 profile disable <profile name>
• security firewall ipv4 enable <row id>
• security firewall ipv4 default_outbound_policy {Allow | Block}
Global Commands
The following table describes the global commands that you can use anywhere in the CLI.
These commands need to be preceded by a period.
Table 5. Global CLI commands
Command Description
.exit Exit the current session.
.help Display an overview of the CLI syntax.
.top Return to the default command mode or root.
.reboot Reboot the system.
.history Display the command-line history of the current session.
Introduction
14

ProSafe Wireless-N 8-Port Gigabit VPN Firewall FVS318N
The Three Basic Types of Commands
You can encounter the following three basic types of commands in the CLI:
• Entry commands to enter a configuration mode. Commands that let you enter a
configuration mode from which you can configure various keywords and associated
parameters and keywords. For example, the net wan wan1 ipv4 configure
command lets you enter the net-config [wan1-ipv4] mode, from which you can configure
the IPv4 WAN settings.
This type of command is the most common in the CLI and is always indicated by two
steps in this manual, each one showing the format and mode:
Step 1 Format
Mode net
Step 2 Format This section shows the keywords and associated parameters, for example:
Mode net-config [wan1-ipv4]
net wan wan1 ipv4 configure
isp_connection_type {STATIC | DHCPC | PPPoE | PPTP}
Sometimes, you need to enter a parameter to enter a configuration mode. For example,
security schedules edit <row id> requires you to enter the row ID parameter to
enter the security-config [schedules] mode, from which you can modify various keywords
and associated parameters and keywords.
• Commands with a single parameter. Commands that require you to supply one or more
parameters and that do not let you enter another configuration mode. The parameter is
usually a row ID or a name. For example, security firewall ipv4 delete
<row id> requires you to enter the row ID parameter to delete the firewall rule.
For this type of command, the format and mode are shown in this manual:
Format
Mode security
security firewall ipv4 delete <row id>
• Commands without parameters. Commands that do not require you to supply a
parameter after the command and that do not let you enter another configuration mode.
For example, util restore_factory_defaults does not require parameters.
For this type of command also, the format and mode are shown in this manual:
Format
Mode util
util restore_factory_defaults
Introduction
15
ProSafe Wireless-N 8-Port Gigabit VPN Firewall FVS318N
Command Autocompletion and Command Abbreviation
Command autocompletion finishes spelling the command when you type enough letters of a
command to uniquely identify the command keyword. You need to type all of the required
keywords and parameters before you can use autocompletion.
The following keys both perform autocompletion for the current command. If the command
prefix is not unique, a subsequent repeat of the key displays possible completions.
• Enter or Return key. Autocompletes, syntax-checks, and then executes the command. If
there is a syntax error, the offending part of the command is highlighted and explained.
• Spacebar. Autocompletes, or if the command is already resolved, inserts a space.
CLI Line-Editing Conventions
The following table describes the key combinations that you can use to edit commands or
increase the speed of command entry. Access this list from the CLI by issuing .help.
Table 6. CLI editing conventions
Key or Key Sequence Description
Invoking context-sensitive help
? Displays context-sensitive help. The information that displays consists either of a list of
possible command completions with summaries or of the full syntax of the current
command. When a command has been resolved, a subsequent repeat of the help key
displays a detailed reference.
Autocompleting
Note: Command autocompletion finishes spelling the command when you type enough letters of a command
to uniquely identify the command keyword. However, you need to type all of the required keywords and
parameters before you use autocompletion.
Enter (or Return) Autocompletes, syntax-checks, and then executes a command. If there is a syntax
error, the offending part of the command line is highlighted and explained. If the
command prefix is not unique, a subsequent repeat of the key displays possible
completions.
Spacebar Autocompletes, or if the command is already resolved, inserts a space. If the command
prefix is not unique, a subsequent repeat of the key displays possible completions.
Moving around
Ctrl-A Go to the beginning of the line.
Ctrl-E Go to the end of the line.
Up arrow Go to the previous line in the history buffer.
Down arrow Go to the next line in the history buffer.
Left arrow Go backward one character.
Introduction
16
ProSafe Wireless-N 8-Port Gigabit VPN Firewall FVS318N
Table 6. CLI editing conventions (continued)
Key or Key Sequence Description
Right arrow Go forward one character.
Deleting
Ctrl-C Delete the entire line.
Ctrl-D Delete the next character.
Ctrl-K Delete all characters to the end of the line from where the cursor is located.
Backspace Delete the previous character.
Invoking escape sequences
!! Substitute the previous line.
!N Substitute the Nth line, in which N is the absolute line number as displayed in the
output of the history command.
!-N Substitute the line that is located N lines before the current line, in which N is a relative
number in relation to the current lint.
Access the CLI
You can access the CLI by logging in with the same user credentials (user name and
password) that you use to access the web management interface. FVS318N> is the CLI
prompt.
FVS318N login: admin
Password:
************************************************
Welcome to FVS318N Command Line Interface
************************************************
FVS318N>
Introduction
17
2. Overview of the Configuration
Commands
This chapter provides an overview of all configuration commands in the five configuration
command modes. The keywords and associated parameters that are available for these
commands are explained in the following chapters. The chapter includes the following sections:
• Network Settings (Net Mode) Configuration Commands
• Security Settings (Security Mode) Configuration Commands
• Administrative and Monitoring Settings (System Mode) Configuration Commands
• Wireless Settings (Dot11 Mode) Configuration Commands
• VPN Settings (VPN Mode) Configuration Commands
2
Network Settings (Net Mode) Configuration Commands
Enter the net ? command at the CLI prompt to display the submodes in the net mode. The
following table lists the submodes and their commands in alphabetical order:
Table 7. Net mode configuration commands
Submode Command Name Purpose
ddns net ddns configure Enable, configure, or disable Dynamic
DNS (DDNS) service.
net dmz ipv4 configure Enable, configure, or disable the IPv4
DMZ.
net dmz ipv6 configure Enable, configure, or disable the IPv6
dmz
net dmz ipv6 pool configure <ipv6 address> Configure a new or existing IPv6 DMZ
net dmz pool ipv6 delete < ipv6 address> Delete an IPv6 DMZ DHCP address pool.
ethernet net ethernet configure <interface name or number> Configure a VLAN for a LAN interface.
ipv6 net ipv6 ipmode configure Configure the IP mode (IPv4 only or
18
DMZ.
DHCP address pool.
IPv4/IPv6).
ipv6_tunnel
net ipv6_tunnel isatap delete <row id> Delete an IPv6 ISATAP tunnel.
net ipv6_tunnel isatap edit <row id> Configure an existing IPv6 ISATAP tunnel.
net ipv6_tunnel six_to_four configure Enable or disable automatic (6to4)
tunneling.
net lan dhcp reserved_ip configure <mac address> Bind a MAC address to an IP address for
DHCP reservation or change an existing
binding, and assign a LAN group.
net lan dhcp reserved_ip delete <mac address> Delete the binding of a MAC address to
an IP address.
net lan ipv4 advanced configure Configure advanced LAN settings such as
the MAC address for VLANs and ARP
broadcast.
net lan ipv4 configure <vlan id> Configure a new or existing VLAN.
net lan ipv4 default_vlan Configure the default VLAN for each port.
net lan ipv4 delete <vlan id> Delete a VLAN.
net lan ipv4 disable <vlan id> Disable a VLAN.
net lan ipv4 enable <vlan id> Enable a VLAN.
lan
net lan ipv4 multi_homing add Configure a new secondary IPv4 address.
net lan ipv4 multi_homing delete <row id> Delete a secondary IPv4 address.
net lan ipv4 multi_homing edit <row id> Configure an existing secondary IPv4
address.
net lan ipv6 configure Configure the IPv6 LAN address settings
and DHCPv6.
net lan ipv6 multi_homing add Configure a new secondary IPv6 address.
net lan ipv6 multi_homing delete <row id> Delete a secondary IPv6 address.
net lan ipv6 multi_homing edit <row id> Configure an existing secondary IPv6
address.
net lan ipv6 pool configure Configure a new IPv6 LAN DHCP address
pool.
net lan ipv6 pool delete <row id> Delete an IPv6 LAN DHCP address pool.
net lan ipv6 pool edit <row id> Configure an existing IPv6 LAN DHCP
address pool.
Overview of the Configuration Commands
19
lan
(continued)
delegation.
net lan ipv6 prefix_delegation delete <row id> Delete a prefix for IPv6 LAN prefix
delegation.
net lan ipv6 prefix_delegation edit <row id> Configure an existing prefix for IPv6 LAN
prefix delegation.
net lan lan_groups edit <row id> <new group name> Change an existing LAN default group
name.
net radvd configure dmz Configure the IPv6 RADVD for the DMZ.
net radvd configure lan Configure the IPv6 RADVD for the LAN.
net radvd pool dmz add Configure a new IPv6 RADVD pool for the
DMZ.
net radvd pool dmz delete <row id> Delete an IPv6 RADVD pool from the
DMZ.
radvd
routing
net radvd pool dmz edit <row id> Configure an existing IPv6 RADVD pool
for the DMZ.
net radvd pool lan add Configure a new IPv6 RADVD pool for the
LAN.
net radvd pool lan delete <row id> Delete an IPv6 RADVD pool from the
LAN.
net radvd pool lan edit <row id> Configure an existing IPv6 RADVD pool
for the LAN.
net routing dynamic configure Configure RIP and the associated MD5
key information.
net routing static ipv4 configure <route name> Configure a new or existing IPv4 static
route.
net routing static ipv4 delete <route name> Delete an IPv4 static route.
net routing static ipv4 delete_all Delete all IPv4 routes.
net routing static ipv6 configure <route name> Configure a new or existing IPv6 static
route.
net routing static ipv6 delete <route name> Delete an IPv6 static route.
net routing static ipv6 delete_all Delete all IPv6 routes.
siit
net siit configure Configure Stateless IP/ICMP Translation
Overview of the Configuration Commands
20
wan
wan_settings net wan_settings wanmode configure Configure the mode of IPv4 routing (NAT
net wan wan1 ipv4 configure Configure the IPv4 settings of the WAN
interface.
net wan wan1 ipv6 configure Configure the IPv6 settings of the WAN
interface.
or classical routing) between the WAN
interface and LAN interfaces.
Security Settings (Security Mode) Configuration Commands
Enter the security ? command at the CLI prompt to display the submodes in the security
mode. The following table lists the submodes and their commands in alphabetical order:
Table 8. Security mode configuration commands
Submode Command Name Purpose
security address_filter ip_or_mac_binding add Configure a new IP/MAC
binding rule.
security address_filter ip_or_mac_binding delete <row id> Delete an IP/MAC binding
rule.
address_filter
bandwidth
security address_filter ip_or_mac_binding edit <row id> Configure an existing IP/MAC
binding rule.
security address_filter ip_or_mac_binding
enable_email_log {IPv4 | IPv6}
security address_filter mac_filter configure Configure the source MAC
security address_filter mac_filter source add Configure a new MAC source
security address_filter mac_filter source delete <row id> Delete a MAC source
security bandwidth profile add Configure a new bandwidth
security bandwidth profile delete <row id> Delete a bandwidth profile.
security bandwidth profile edit <row id> Configure an existing
Overview of the Configuration Commands
21
Configure the email log for
IP/MAC Binding violations.
address filter.
address.
address.
profile.
bandwidth profile.
groups.
security content_filter block_group enable Apply content filtering to
groups.
security content_filter blocked_keywords add Configure a new blocked
keyword.
security content_filter blocked_keywords delete <row id> Delete a blocked keyword.
content_filter
firewall
security content_filter blocked_keywords edit <row id> Configure an existing blocked
keyword.
security content_filter content_filtering configure Configure web content
filtering.
security content_filter trusted_domain add Configure a new trusted
domain.
security content_filter trusted_domain delete <row id> Delete a trusted domain.
security content_filter trusted_domain edit <row id> Configure an existing trusted
domain.
security firewall advanced algs Configure SIP support for the
ALG.
security firewall attack_checks configure ipv4 Configure WAN and LAN
security attack checks for IPv4
traffic.
security firewall attack_checks configure ipv6 Configure WAN security
attack checks for IPv6 traffic.
security firewall attack_checks igmp configure Enable or disable multicast
pass-through for IPv4 traffic.
security firewall attack_checks jumboframe configure Enable or disable jumbo
frames for IPv4 traffic.
security firewall attack_checks vpn_passthrough configure Configure VPN pass-through
for IPv4 traffic.
security firewall ipv4 add_rule dmz_wan inbound Configure a new IPv4 DMZ
WAN inbound firewall rule.
security firewall ipv4 add_rule dmz_wan outbound Configure a new IPv4 DMZ
WAN outbound firewall rule.
security firewall ipv4 add_rule lan_dmz inbound Configure a new IPv4 LAN
DMZ inbound firewall rule.
security firewall ipv4 add_rule lan_dmz outbound Configure a new IPv4 LAN
DMZ outbound firewall rule.
Overview of the Configuration Commands
22
security firewall ipv4 add_rule lan_wan outbound Configure a new IPv4 LAN
WAN outbound firewall rule.
firewall
(continued)
security firewall ipv4 default_outbound_policy {Allow |
Block}
security firewall ipv4 delete <row id> Delete an IPv4 firewall rule.
security firewall ipv4 disable <row id> Disable an IPv4 firewall rule.
security firewall ipv4 edit_rule dmz_wan inbound <row id> Configure an existing IPv4
security firewall ipv4 edit_rule dmz_wan outbound <row id> Configure an existing IPv4
security firewall ipv4 edit_rule lan_dmz inbound <row id> Configure an existing IPv4
security firewall ipv4 edit_rule lan_dmz outbound <row id> Configure an existing IPv4
security firewall ipv4 edit_rule lan_wan inbound <row id> Configure an existing IPv4
Configure the default
outbound policy for IPv4
traffic.
DMZ WAN inbound firewall
rule.
DMZ WAN outbound firewall
rule.
LAN DMZ inbound firewall
rule.
LAN DMZ outbound firewall
rule.
LAN WAN inbound firewall
rule.
security firewall ipv4 edit_rule lan_wan outbound <row id> Configure an existing IPv4
LAN WAN outbound firewall
rule.
security firewall ipv4 enable <row id> Enable an IPv4 firewall rule.
security firewall ipv6 configure Configure a new IPv6 firewall
rule.
security firewall ipv6 default_outbound_policy {Allow |
Block}
security firewall ipv6 delete <row id> Delete an IPv6 firewall rule.
security firewall ipv6 disable <row id> Disable an IPv6 firewall rule.
security firewall ipv6 edit <row id> Configure an existing IPv6
security firewall ipv6 enable <row id> Enable an IPv6 firewall rule.
Configure the default
outbound policy for IPv6
traffic.
firewall rule.
Overview of the Configuration Commands
23
firewall
(continued)
porttriggering_rules security porttriggering_rules add Configure a new port
security firewall session_settings configure Configure global session
security porttriggering_rules delete <row id> Delete a port triggering rule.
security porttriggering_rules edit <row id> Configure an existing port
limits.
time-outs.
triggering rule.
triggering rule.
schedules
services
upnp security upnp configure Configure UPnP.
security schedules edit {1 | 2 | 3} Configure one of the three
security schedules.
security services add Configure a new custom
service.
security services delete <row id> Delete a custom service.
security services edit <row id> Configure an existing custom
service.
Administrative and Monitoring Settings (System Mode) Configuration Commands
Enter the system ? command at the CLI prompt to display the submodes in the system
mode. The following table lists the submodes and their commands in alphabetical order:
Table 9. System mode configuration commands
Submode Command Name Purpose
system logging configure Configure routing logs for accepted and
dropped IPv4 and IPv6 packets.
logging
system logging remote configure Configure email logs and alerts,
schedule email logs and alerts, and
configure a syslog server.
remote_management
system remote_management https configure Configure remote management over
HTTPS.
system remote_management telnet configure Configure remote management over
Telnet.
Overview of the Configuration Commands
24
snmp
time system time configure Configure the system time, date, and
traffic_meter system traffic_meter configure Configure the WAN traffic meter.
system snmp trap configure <ip address> Configure an SNMP agent and
community.
system snmp trap delete <ipaddress> Delete an SNMP agent.
NTP servers.
Wireless Settings (Dot11 Mode) Configuration Commands
Enter the dot11 ? command at the CLI prompt to display the submodes in the dot11 mode.
The following table lists the submodes and their commands in alphabetical order:
Table 10. Dot11 mode configuration commands
Submode Command Name Purpose
dot11 profile acl configure <row id > Configure an ACL for a specific profile.
dot11 profile add Configure a new wireless profile.
dot11 profile delete <row id> Delete a wireless profile.
profile
radio
dot11 profile disable <row id> Disable a wireless profile.
dot11 profile enable <row id> Enable a wireless profile.
dot11 profile edit <row id> Configure an existing wireless profile.
dot11 profile wps configure Configure Wi-Fi Protected Setup™ (WPS).
dot11 radio advanced configure Configure advanced radio settings.
dot11 radio configure Configure basic radio settings.
Overview of the Configuration Commands
25
Table 11. Configuration commands: vpn mode
Submode Command Name Purpose
vpn ipsec ikepolicy configure <ike policy name> Configure a new or existing manual IPSec
IKE policy.
vpn ipsec ikepolicy delete <ike policy name> Delete an IPSec policy.
vpn ipsec mode_config configure <record name> Configure a new or existing Mode Config
record.
vpn ipsec mode_config delete <record name> Delete a Mode Config record.
vpn ipsec radius configure Configure the RADIUS servers.
vpn ipsec vpnpolicy configure <vpn policy name> Configure a new or existing auto IPSec
ipsec
vpn ipsec vpnpolicy connect <vpn policy name> Establish a VPN connection.
vpn ipsec vpnpolicy delete <vpn policy name> Delete an IPSec VPN policy.
vpn ipsec vpnpolicy disable <vpn policy name> Disable an IPSec VPN policy.
vpn ipsec vpnpolicy drop <vpn policy name> Terminate an IPSec VPN connection.
vpn ipsec vpnpolicy enable <vpn policy name> Enable an IPSec VPN policy.
VPN policy or manual IPSec VPN policy.
vpn ipsec wizard configure <Gateway | VPN_Client> Configure the IPSec VPN wizard for a
gateway-to-gateway or gateway-to-VPN
client connection.
l2tp vpn l2tp server configure Configure the L2TP server.
vpn sslvpn client ipv4 Configure the SSL client IPv4 address
range.
vpn sslvpn client ipv6 Configure the SSL client IPv6 address
range.
vpn sslvpn policy add Configure a new SSL VPN policy.
sslvpn
vpn sslvpn policy delete <row id> Delete an SSL VPN policy.
vpn sslvpn policy edit <row id> Configure an existing SSL VPN policy.
vpn sslvpn portal_layouts add Configure a new SSL VPN portal layout.
vpn sslvpn portal_layouts delete <row id> Delete an SSL VPN portal layout.
vpn sslvpn portal_layouts edit <row id> Configure an existing SSL VPN portal
layout.
Overview of the Configuration Commands
26
vpn sslvpn portforwarding appconfig add Configure a new SSL port forwarding
application.
vpn sslvpn portforwarding appconfig delete <row id> Delete an SSL VPN port forwarding
application.
vpn sslvpn portforwarding hostconfig add Configure a new host name for an SSL
port forwarding application.
vpn sslvpn portforwarding hostconfig delete <row id> Delete a host name for an SSL port
forwarding application.
vpn sslvpn resource add Add a new SSL VPN resource.
vpn sslvpn resource configure add <resource name> Configure an SSL VPN resource object.
vpn sslvpn resource configure delete <row id> Delete an SSL VPN resource object.
vpn sslvpn resource delete <row id> Delete an SSL VPN resource.
vpn sslvpn route add Add an SSL VPN client route.
vpn sslvpn route delete <row id> Delete an SSL VPN client route.
sslvpn
(continued)
vpn sslvpn users domains add Configure a new authentication domain.
vpn sslvpn users domains delete <row id> Delete an authentication domain.
vpn sslvpn users domains
disable_Local_Authentication {Y | N}
vpn sslvpn users domains edit <row id> Configure an existing authentication
vpn sslvpn users groups add Configure a new authentication group.
vpn sslvpn users groups delete <row id> Delete an authentication group.
vpn sslvpn users groups edit <row id> Configure an existing authentication
vpn sslvpn users users add Add a new user account.
vpn sslvpn users users browser_policies <row id> Configure the client browsers from which
vpn sslvpn users users delete <row id> Delete a user account.
vpn sslvpn users users edit <row id> Configure an existing user account.
vpn sslvpn users users ip_policies configure <row id> Configure source IP addresses from
Enable or disable local authentication for
users.
domain.
group.
a user is either allowed or denied access.
which a user is either allowed or denied
access.
Overview of the Configuration Commands
27

(continued)
vpn sslvpn users users login_policies <row id> Configure the login policy for a user.
Overview of the Configuration Commands
28

3. Net Mode Configuration Commands
This chapter explains the configuration commands, keywords, and associated parameters in the
net mode. The chapter includes the following sections:
• General WAN Commands
• IPv4 WAN Commands
• IPv6 WAN Commands
• IPv6 Tunnel Commands
• Dynamic DNS Commands
• IPv4 LAN Commands
• IPv6 LAN Commands
• IPv4 DMZ Setup Commands
• IPv6 DMZ Setup Commands
• IPv4 Routing Commands
• IPv6 Routing Commands
3
IMPORTANT:
After you have issued a command that includes the word
configure, add, or edit, you need to save (or cancel) your
changes. For more information, see
29
Save Commands on page 13.
This command configures the MTU, port speed, and MAC address of the wireless VPN
firewall. After you have issued the net wan port_setup configure command, you
enter the net-config [port_setup] mode, and then you can configure the MTU, port speed, and
MAC address.
Step 1 Format
Mode net
Step 2 Format
Mode net-config [port_setup]
Keyword Associated Keyword to
def_mtu Default or Custom Specifies whether the default MTU or a custom MTU is
mtu_size number The size of the default MTU in bytes for the WAN port:
net wan port_setup configure
def_mtu {Default | Custom {mtu_size <number>}}
port_speed {Auto_Sense | 10_BaseT_Half_Duplex |
10_BaseT_Full_Duplex | 100_BaseT_Half_Duplex |
100_BaseT_Full_Duplex | 1000_BaseT_Half_Duplex |
1000_BaseT_Full_Duplex}
mac_type {Use-Default-Mac | Use-This-Computers-Mac |
Use-This-Mac {mac_address <mac address>}}
Description
Select or Parameter to Type
used. If you select Custom, you need to issue the
mtu_size keyword and specify the size of the MTU.
• If you have configured IPv4 mode, type a number between
68 and 1500 bytes.
• If you have configured IPv4/IPv6 mode, type a number
between 1280 and 1500 bytes.
port_speed Auto_Sense,
10_BaseT_Half_Duplex,
10_BaseT_Full_Duplex,
100_BaseT_Half_Duplex,
100_BaseT_Full_Duplex,
1000_BaseT_Half_Duplex,
or
1000_BaseT_Full_Duplex
Specifies the port speed and duplex mode of the WAN port.
The keywords are self-explanatory.
Net Mode Configuration Commands
30
 Loading...
Loading...