Netgear FSM726S Brochure

Page 1 of 110

© 2002 by NETGEAR, Inc. All rights reserved.
Trademarks
NETGEAR® is a registered trademark of NETGEAR, Inc. in the United States and other countries. Auto Uplink™ is a trademark of NETGEAR, Inc.
All other trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Statement of Conditions
In the interest of improving internal design, operational function, and/or reliability, NETGEAR reserves the right to make changes to the products
described in this document without notice. NETGEAR does not assume any liability that may occur due to the use or application of the product(s) or
circuit layout(s) described herein.
Certificate of the Manufacturer/Importer
It is hereby certified that the NETGEAR Model FSM726S Managed Stackable Switch has been suppressed in accordance with the conditions set
out in the BMPT-AmtsblVfg 243/1991 and Vfg 46/1992.The operation of some equipment (for example, test transmitters) in accordance with the
regulations may, however, be subject to certain restrictions. Please refer to the notes in the operating instructions.
Federal Office for Telecommunications Approvals has been notified of the placing of this equipment on the market and has been granted the right
to test the series for compliance with the regulations.
Voluntary Control Council for Interference (VCCI) Statement
This equipment is in the first category (information equipment to be used in commercial and/or industrial areas) and conforms to the standards set
by the Voluntary Control Council for Interference by Data Processing Equipment and Electronic Office Machines that are aimed at preventing radio
interference in commercial and/or industrial areas.
Consequently, when this equipment is used in a residential area or in an adjacent area thereto, radio interference may be caused to equipment
such as radios and TV receivers.
Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Compliance Notice: Radio Frequency Notice
This device complies with part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
This device may not cause harmful interference.
This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
Note: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC Rules. These
limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses, and
can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio
communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful
interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct
the interference by one or more of the following measures:
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that which the receiver is connected.
Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
EN 55 022 Declaration of Conformance
This is to certify that the NETGEAR Model FSM726S Managed Stackable Switch is shielded against the generation of radio interference in
accordance with the application of Council Directive 89/336/EEC, Article 4a. Conformity is declared by the application of EN 55024 Class A (CISPR
22).
EN 55 022 and EN 55 024 Statements
This is to certify that the NETGEAR Model FSM726S Managed Stackable Switch is shielded against the generation of radio interference in
accordance with the application of Council Directive 89/336/EEC, Article 4a. Conformity is declared by the application of EN 55 022 Class A
(CISPR 22) and EN 55 024.
Page 2 of 110
Warning: This is a Class A product. In a domestic environment, this product may cause radio interference, in which case the user may
be required to take appropriate measures.
Canadian Department of Communications Radio Interference Regulations
This digital apparatus (NETGEAR Model FSM726S Managed Stackable Switch) do not exceed the Class A limits for radio-noise emissions from
digital apparatus as set out in the Radio Interference Regulations of the Canadian Department of Communications.
Règlement sur le brouillage radioélectrique du ministère des Communications
Cet appareil numérique (NETGEAR Model FSM726S Managed Stackable Switch) respecte les limites de bruits radioélectriques visant les
appareils numériques de classe A prescrites dans le Règlement sur le brouillage radioélectrique du ministère des Communications du Canada.
Customer Support
For assistance with installing and configuring your NETGEAR system or with questions or problems following installation:
• Check the NETGEAR Web page at http://www.NETGEAR.com.
• Call Technical Support in North America at 1-888-NETGEAR. If you are outside North America, please refer to the phone numbers listed
on the Support Information Card that shipped with your switch.
• Email Technical Support at support@NETGEAR.com.
Defective or damaged merchandise can be returned to your point-of-purchase representative.
Internet/World Wide Web
NETGEAR maintains a World Wide Web home page that you can access at the uniform resource locator (URL) http://www.NETGEAR.com. A
direct connection to the Internet and a Web browser such as Internet Explorer or Netscape are required.
Page 3 of 110

CONTENTS
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION ....................................................................................................................................................................... 9
Overview ...................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 9
Features..................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 10
Package Contents .................................................................................................................................................................................................... 11
Verify that your package contains the following: .................................................................................................................................................. 11
CHAPTER 2: PHYSICAL DESCRIPTION............................................................................................................................................... 12
Front Panels .............................................................................................................................................................................................................. 12
10/100 Mbps RJ-45 Ports........................................................................................................................................................................................ 12
Gigabit Ethernet Ports (RJ-45 and GBIC module bay)........................................................................................................................................ 13
LED Descriptions...................................................................................................................................................................................................... 14
Console Port.............................................................................................................................................................................................................. 14
Stacking Ports ........................................................................................................................................................................................................... 14
CHAPTER 3: APPLICATIONS ...................................................................................................................................................................... 16
Desktop Switching.................................................................................................................................................................................................... 16
Stacked Switching .................................................................................................................................................................................................... 17
CHAPTER 4: INSTALLATION....................................................................................................................................................................... 18
Step 1: Preparing the Site ....................................................................................................................................................................................... 18
Step 2: Installing the Switch.................................................................................................................................................................................... 18
Step 3: Installing a GBIC Module ........................................................................................................................................................................... 19
Step 4: Connecting Switches to the Stack’s Backplane...................................................................................................................................... 19
Step 5: Checking the Installation............................................................................................................................................................................ 20
Step 6: Applying AC Power..................................................................................................................................................................................... 20
Step 7: Connecting to the Console Port to Manage the Switch (initial configuration)..................................................................................... 20
Step 8: Connecting Devices to the Switch ............................................................................................................................................................ 25
Adding or Removing Switches to the stack........................................................................................................................................................... 25
CHAPTER 5: SWITCH MANAGEMENT OVERVIEW..................................................................................................................... 26
Management Access Overview .............................................................................................................................................................................. 26
SNMP Access ........................................................................................................................................................................................................... 26
Protocols .................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 27
Software Upgrade Procedure ................................................................................................................................................................................. 27
CHAPTER 6: ADMINISTRATION CONSOLE ACCESS ............................................................................................................... 29
Main Menu ................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 32
Main Menu> System ................................................................................................................................................................................................ 33
Main Menu> Status .................................................................................................................................................................................................. 34
Main Menu> Set-Up ................................................................................................................................................................................................. 36
Main Menu> Tools.................................................................................................................................................................................................... 39
Main Menu> Security ............................................................................................................................................................................................... 42
Main Menu> Advanced Menu ................................................................................................................................................................................. 43
CHAPTER 7: WEB MANAGEMENT ACCESS ................................................................................................................................... 61
System ....................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 63
Status ......................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 64
Set-up............................................................................................................................... .......................................................................................... 70
Tools............................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................ 74
Security ...................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 77
Advanced................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 78
APPENDIX A: GLOSSARY.............................................................................................................................................................................. 93
APPENDIX B: TROUBLESHOOTING ...................................................................................................................................................... 96
Troubleshooting Chart.............................................................................................................................................................................................. 96
Additional Troubleshooting Suggestions............................................................................................................................................................... 96
Page 4 of 110

APPENDIX C: VIRTUAL LOCAL AREA NETWORK (VLAN)................................................................................................... 97
APPENDIX D: TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS............................................................................................................................... 104
APPENDIX E: CONNECTOR PIN ASSIGNMENTS....................................................................................................................... 106
APPENDIX F: CABLING GUIDELINES................................................................................................................................................. 107
Page 5 of 110

Figures
FIGURE 1-1. PACKAGE CONTENTS................................................................................................................................................................................................. 11
FIGURE 2-1. FRONT PANEL OF THE FSM726S MANAGED STACKABLE SWITCH..................................................................................................... 12
FIGURE 2-2. BACK PANEL OF THE FSM726S MANAGED STACKABLE SWITCH........................................................................................................ 12
FIGURE 2-3 CREATING REDUNDANT PATHS BETWEEN NETWORK DEVICES ........................................................................................................ 13
FIGURE 3-1. EXAMPLE OF DESKTOP SWITCHING .................................................................................................................................................................. 16
FIGURE 3-2. EXAMPLE OF SWITCHED STACKING .................................................................................................................................................................. 17
FIGURE 4-1. ATTACHING MOUNTING BRACKETS ................................................................................................................................................................... 19
FIGURE 4-2. INSTALLING A GIGABIT ETHERNET MODULE ................................................................................................................................................. 19
FIGURE 4-3. CABLING THREE FSM726S STACKED SWITCHES ........................................................................................................................................ 20
FIGURE 4-4 SYSTEM DESCRIPTION............................................................................................................................................................................................... 22
FIGURE 4-5 MAIN MENU ....................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 22
FIGURE 4-6 SET-UP ................................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 23
FIGURE 4-7 IP CONFIGURATION ...................................................................................................................................................................................................... 23
FIGURE 4-8: TOOLS PAGE................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 24
FIGURE 4-9. CONNECTING DEVICES TO THE SWITCH......................................................................................................................................................... 25
FIGURE 5-1. SNMP-BASED MANAGEMENT METHOD ............................................................................................................................................................. 27
FIGURE 5-2. ADMINISTRATION CONSOLE ACCESS ............................................................................................................................................................... 27
FIGURE 6-1. ADMINISTRATION CONSOLE MANAGEMENT METHOD ............................................................................................................................. 29
FIGURE 6-2 INITIAL WELCOME SCREEN OF USER INTERFACE (PASSWORD ENABLED)................................................................................... 31
FIGURE 6-3: MAIN MENU ...................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 32
FIGURE 6-4: SYSTEM MANAGER: SYSTEM INFO ..................................................................................................................................................................... 33
FIGURE 6-5: STATISTICS ...................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 34
FIGURE 6-6: ADDRESS MANAGER: MAC ADDRESS TABLE ................................................................................................................................................ 35
FIGURE 6-7: PORT CONFIGURATION............................................................................................................................................................................................. 37
FIGURE 6-8: SET-UP MANAGER: IP CONFIGURATION........................................................................................................................................................... 38
FIGURE 6-9: SOFTWARE UPDATE ...................................................................................................................................................................................................39
FIGURE 6-10: RESTORE FACTORY VALUES............................................................................................................................................................................... 40
FIGURE 6-11: RESET .............................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 41
FIGURE 6-12: SECURITY ADMIN ....................................................................................................................................................................................................... 42
FIGURE 6-13: PORT MIRRORING...................................................................................................................................................................................................... 43
FIGURE 6-14: PORT TRUNKING ........................................................................................................................................................................................................ 44
FIGURE 6-15: MULTIMEDIA SUPPORT (IGMP)............................................................................................................................................................................ 45
FIGURE 6-16: CLASS OF SERVICE .................................................................................................................................................................................................. 46
FIGURE 6-17: VLAN SET-UP............................................................................................................................................................................................................... 47
FIGURE 6-18: VLAN ADMINISTRATION .......................................................................................................................................................................................... 48
FIGURE 6-19: VLAN MEMBERSHIP .................................................................................................................................................................................................. 49
FIGURE 6-20: PVID SETTINGS ........................................................................................................................................................................................................... 50
FIGURE 6-21: SPANNING TREE......................................................................................................................................................................................................... 51
FIGURE 6-22: SPANNING TREE: BRIDGE SETTINGS .............................................................................................................................................................. 52
FIGURE 6-23: SPANNING TREE: PORT SETTINGS................................................................................................................................................................... 53
FIGURE 6-24: ADDRESS MANAGER................................................................................................................................................................................................ 54
FIGURE 6-25: ADDRESS MANAGER: ADDRESS AGING......................................................................................................................................................... 55
FIGURE 6-26: ADDRESS MANAGER: STATIC ADDRESSES ................................................................................................................................................. 56
FIGURE 6-27: SNMP MANAGEMENT ...............................................................................................................................................................................................57
FIGURE 6-28: SNMP MANAGEMENT: COMMUNITY TABLE .................................................................................................................................................. 58
FIGURE 6-29: SNMP MANAGEMENT: HOST TABLE .................................................................................................................................................................59
FIGURE 6-31: SNMP MANAGEMENT: TRAP SETTINGS.......................................................................................................................................................... 60
FIGURE 7-1. WEB MANAGEMENT METHOD ................................................................................................................................................................................ 61
FIGURE 7-2: PASSWORD...................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 61
FIGURE 7-3: SYSTEM ............................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 63
FIGURE 7-4: STATISTICS: SWITCH STATISTICS ....................................................................................................................................................................... 65
FIGURE 7-5: STATISTICS: PORT STATISCIS ............................................................................................................................................................................... 66
FIGURE 7-6: PORT CONFIGURATION: PORT SETTINGS....................................................................................................................................................... 67
FIGURE 7-7: STATUS MANAGER: MAC ADDRESS TABLE .................................................................................................................................................... 68
FIGURE 7-8: STATISTICS: ERROR STATISTICS......................................................................................................................................................................... 69
FIGURE 7-9: SYSTEM CONFIGURATION ....................................................................................................................................................................................... 70
FIGURE 7-10: SYSTEM MANAGER: IP CONFIGURATION ...................................................................................................................................................... 71
FIGURE 7-11: SETUP: PORT CONFIGURATION ......................................................................................................................................................................... 72
FIGURE 7-12: SETUP: GBIC ................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 73
FIGURE 7-13: SOFTWARE UPGRADE............................................................................................................................................................................................. 74
FIGURE 7-14: SAVE CONFIGURATION........................................................................................................................................................................................... 75
FIGURE 7-15: DEVICE RESET............................................................................................................................................................................................................. 76
FIGURE 7-16: SYSTEM MANAGER: PASSWORD ADMIN ....................................................................................................................................................... 77
Page 6 of 110

FIGURE 7-17: PORT MIRRORING...................................................................................................................................................................................................... 79
FIGURE 7-18: PORT TRUNKING ........................................................................................................................................................................................................ 80
FIGURE 7-19: IGMP.................................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 81
FIGURE 7-20: TRAFFIC PRIORTIZATION SETTINGS................................................................................................................................................................ 82
FIGURE 7-21: VLANS: VLAN’S AND PRIMARY VLAN................................................................................................................................................................ 83
FIGURE 7-22: VLAN VLAN PORTSSETTINGS .............................................................................................................................................................................. 84
FIGURE 7-23: SPANNING TREE: BRIDGE SETTINGS .............................................................................................................................................................. 86
FIGURE 7-24: SPANNING TREE: PORT SETTINGS................................................................................................................................................................... 87
FIGURE 7-25: ADDRESS MANAGER: ADDRESS AGING......................................................................................................................................................... 88
FIGURE 7-26: ADDRESS MANAGER: STATIC ADDRESSES ................................................................................................................................................. 89
FIGURE 7-27: SNMP MANAGEMENT: COMMUNITY TABLE .................................................................................................................................................. 90
FIGURE 7-28: SNMP MANAGEMENT: HOST TABLE .................................................................................................................................................................91
FIGURE 7-29: SNMP MANAGEMENT: TRAP SETTINGS.......................................................................................................................................................... 92
FIGURE E-1. RJ-45 PLUG AND RJ-45 CONNECTOR WITH BUILT-IN LEDS.................................................................................................................. 106
FIGURE F-1. STRAIGHT-THROUGH TWISTED-PAIR CABLE .............................................................................................................................................. 108
FIGURE F-2. CROSSOVER TWISTED-PAIR CABLE ................................................................................................................................................................ 108
FIGURE F-3. CATEGORY 5 UTP CABLE WITH MALE RJ-45 PLUG AT EACH END .................................................................................................... 108
Page 7 of 110

Tables
TABLE 2-1. FRONT PANEL LEDS:.................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 14
TABLE 4-1. SITE REQUIREMENTS................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 18
TABLE 5-1. COMPARING SWITCH MANAGEMENT METHODS................................................................................................................................................................... 26
TABLE 6-1 STP PORT SETTING PARAMETERS........................................................................................................................................................................................... 53
TABLE 7-1. STP PORT SETTING PARAMETERS.......................................................................................................................................................................................... 87
TABLE B-1. TROUBLESHOOTING CHART.................................................................................................................................................................................................... 96
TABLE E-1. 10/100 MBPS RJ-45 PLUG AND RJ-45 CONNECTOR PIN ASSIGNMENTS.......................................................................................................................... 106
TABLE E-2. 100/1000 MBPS RJ-45 PLUG AND RJ-45 CONNECTOR PIN ASSIGNMENTS...................................................................................................................... 106
TABLE F-1. ELECTRICAL REQUIREMENTS OF CATEGORY 5 CABLE ....................................................................................................................................................107
Page 8 of 110

CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION
Congratulations on your purchase of the NETGEAR Model FSM726S Managed Stackable, Fast Ethernet Switch! Your NETGEAR Switch is a stateof-the-art, high-performance, IEEE-compliant network solution designed for users who require a large number of ports and want the power of
management to eliminate bottlenecks, boost performance, and increase productivity. In addition to providing easy, straightforward management,
your switch is expandable and comes with two stacking ports that can connect to other NETGEAR Model FSM726S Managed Stackable Switches.
Additionally, your switch provides flexible Gigabit speed connections to servers and other Gigabit Ethernet switches. There are two Gigabit
Ethernet ports on the switch that can be used either by the built-in RJ-45 ports or by the Gigabit Interface Converter (GBIC) module bays, both
located on the front panel. To simplify installation, the switch is shipped ready for use. Everything necessary for setup comes in the box.
This chapter serves as the introduction for using your NETGEAR FSM726S Stackable Switch and provides the following information:
Overview
Switch Features
Package contents
Overview
Your NETGEAR Model FSM726S Managed Stackable Switch provides the benefit of management with a complete package of features for the
observation, configuration, and control of your network. With a web-based Graphical User Interface (GUI), the switch’s many capabilities can be
viewed and used in a simple and intuitive manner. For those who prefer a more traditional interface, there is a Command Menu Interface available
through the console port on the front. The switch’s management features include SNMP and RMON for port and switch information, VLAN for
traffic control, port trunking for increased bandwidth, and Class of Service (CoS) for traffic prioritization. These features and more will allow you to
better understand and better control your network.
Your NETGEAR Model FSM726S Managed Stackable Switch includes two bi-directional stacking ports, which can connect to other NETGEAR
Model FSM726 Manageable Switches. This built-in stackability gives you the flexibility to buy the number of ports you need now to meet your
immediate needs, then add ports to your system later as your networking requirements grow.
Your NETGEAR Model FSM726S Managed Stackable Switch also provides two Gigabit Ethernet ports that are used either by the built-in RJ-45
ports or by the GBIC module bays, both located on the front panel. The GBIC module bays will accept any standard GBIC module, including the
AGM721F 1000BASE-SX module from NETGEAR. Using these Gigabit ports, you can create high-speed connections to a server or network
backbone. For example, you can:
• Connect switches to each other with high-speed links
• Link up to high-speed servers
• Connect fiber and copper networks
Your NETGEAR Model FSM726S Managed Stackable Switch can be free-standing, or rack mounted in a wiring closet or equipment room. It is
IEEE-compliant and offers low latency for high-speed networking. It includes 24 auto-sensing 10/100 Ethernet/Fast Ethernet ports. The 10/100
ports are shielded RJ-45 ports that automatically negotiate to the highest speed. This capability makes the switch ideal for environments that have
a mix of Ethernet and Fast Ethernet devices. In addition, all 10/100 Mbps ports operate in half- or full-duplex mode, increasing the maximum
bandwidth of each connection up to 20 Mbps or 200 Mbps, respectively. The maximum segment length is 328 feet (100 meters) over Category 5
unshielded twisted-pair (UTP) cable.
Page 9 of 110

Features
The following list identifies the key features of the NETGEAR Model FSM726S Managed Stackable Switch.
• Twenty-four 10/100 Mbps auto sensing Fast Ethernet switching ports
• Two Gigabit Ethernet ports that can be used either through the built-in RJ-45 ports for 10/100/1000 Mbps connectivity or through the GBIC
modules for a variety of fiber connections
• Two, built-in gigabit speed stacking ports for network expandability and scalability up to six stacked units
• Full Layer 2 switch management including:
o SNMP
o RMON (groups 1,2,3 and 9)
o IEEE 802.1Q (up to 64 Static VLAN groups)
o IEEE 802.1p (Class of Service)
o IEEE 802.1ad (Link Aggregation)
o IEEE 802.1D (Spanning Tree)
o IGMP snooping
o Port Mirroring
o Password access control
o TFTP firmware upgrade
o Multiple interfaces: Browser-based, Telnet, or SNMP application
• Full compatibility with IEEE standards:
o IEEE 802.3i, (10BASE-T)
o IEEE 802.3u (100BASE-TX)
o IEEE 802.3ab (1000BASE-T)
o IEEE 802.3x (full-duplex flow control)
• Auto-sensing and auto-negotiating capabilities for all ports
• Auto Uplink™ on all ports to make the right connection
• Automatic address learning function to build the packet-forwarding information table. The table contains up to 8,000 media access control
(MAC) addresses (that is, the switch can support networks with as many as 8,000 devices).
• Full- and half-duplex functions for all 10/100 ports
• Store-and-Forward transmission to remove bad packets from the network
• Active flow control to minimize packet loss/frame drops:
o Half-duplex back-pressure control
o Full-duplex IEEE 802.3x pause frame flow control
• LED indicators for port status monitoring:
o Power LED to indicate power on/off status
o Link LED to indicate link status and activity
o Dual-color Mode LED to indicate speed, activity, duplex mode, and collision
o Stacking LED to indicate link status, activity, and master/slave status
• Easy migration from existing 10 Mbps network to 100 Mbps Fast Ethernet network
• Easy upgrade path to add gigabit technology to your network
• Flexible installation:
o Standalone desktop installation
o 19-inch standard rack-mount
• Standard 1U case size
Page 10 of 110
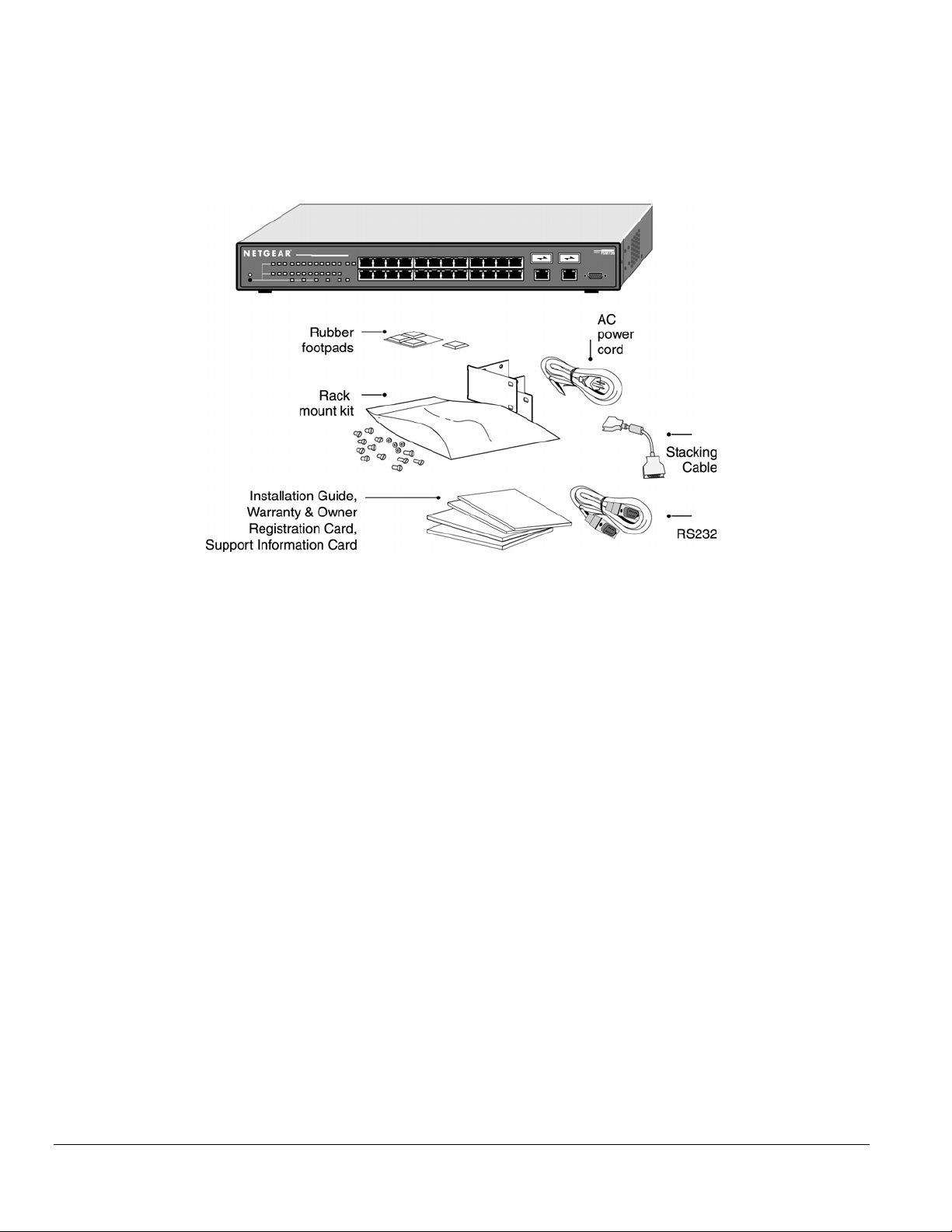
Package Contents
Figure 1-1 shows the package contents of the NETGEAR Model FSM726S Managed Stackable Switch.
Figure 1-1. Package Contents
Verify that your package contains the following:
One FSM726S Managed Stackable Switch
Rubber footpads for tabletop installation
Power cord
One null-modem cable
One stacking cable
Rack-mount kit for installing the switch in a 19-inch rack
This user’s guide
Support Information Card
Warranty & Owner Registration Card
If you ordered additional GBIC modules with your switch, they are provided in a separate package.
If any item is missing or damaged, contact your place of purchase immediately.
Page 11 of 110

CHAPTER 2: PHYSICAL DESCRIPTION
This chapter describes the hardware features of the NETGEAR Model FSM726S Managed Stackable Switch. Topics include:
Front and back panels
10/100 Mbps auto-sensing RJ-45 ports
Gigabit Ethernet Ports (RJ-45 and GBIC module bay)
LED descriptions
Console port
Stacking ports
Front Panels
Figures 2-1 and 2-2 show the key components on the front and back panels of the NETGEAR Model FSM726S Managed Stackable Switch.
The front panel contains LEDs, RJ-45 jacks, GBIC module bays, and a console port. The back panel has two stacking ports and a standard AC
power receptacle for accommodating the supplied power cord.
Figure 2-1. Front Panel of the FSM726S Managed Stackable Switch
Figure 2-2. Back Panel of the FSM726S Managed Stackable Switch
10/100 Mbps RJ-45 Ports
As Figure 2-1 shows, the FSM726S Managed Stackable Switch has 24 10/100 Mbps RJ-45 ports. These ports are auto-sensing 10/100 Mbps
ports: When you insert a cable into an RJ-45 port, the switch automatically ascertains the maximum speed (10 or 100 Mbps) and duplex mode
(half- or full-duplex) of the attached device. The 10/100 Mbps ports support only unshielded twisted-pair (UTP) cable terminated with an 8-pin RJ45 plug.
To simplify the procedure for attaching devices, all RJ-45 ports support Auto Uplink. This technology lets you attach devices to the RJ-45 ports
using either straight-through or crossover cables. When you insert a cable into the switch’s RJ-45 port, the switch automatically:
• Senses whether the cable is a straight-through or crossover cable, and
• Determines whether the link to the attached device requires a “normal” connection (such as when connecting the port to a PC) or an
“uplink” connection (such as when connecting the port to a router, switch, or hub).
• After ascertaining this information, the switch automatically configures the RJ-45 port to enable communications with the attached
device, without requiring user intervention. In this way, the Auto Uplink technology compensates for setting uplink connections, while
eliminating concern about whether to use crossover or straight-through cables when attaching devices.
Warning! You must use Link Aggregation (a.k.a. Port Trunking) to create multiple links between switches. Using Auto Uplink to create multiple
active paths between any two network devices can cause undesirable loops in the network, resulting in an endless broadcast traffic that disables
your network. Loops occur when there are alternate routes between two network devices. In Figure 2-3, for example, a loop is created by
connecting two RJ-45 ports on a NETGEAR Model FSM726S Managed Stackable Switch to a router containing a 4-port switch. The Spanning Tree
protocol will prevent loops, if that advanced feature is enabled.
Page 12 of 110

Figure 2-3 Creating Redundant Paths between Network Devices
Gigabit Ethernet Ports (RJ-45 and GBIC module bay)
Your NETGEAR Model FSM726S Managed Stackable Switch has two Gigabit Ethernet ports that can be used as either a 1000BASE-T port or as a
GBIC module bay. The default setting for port 25 and port 26 is for the built-in RJ-45 connector to be active, but they can be independently
configured to activate either the RJ-45 or the GBIC module, enabling multiple combinations of fiber and copper connections. The Gigabit Ethernet
ports provide a full-duplex 1000 Mbps (1 Gbps) connection that effectively doubles throughput to 2 Gbps.
The GBIC bay accommodates a standard GBIC module, such as the NETGEAR AGM721F 1000BASE-SX GBIC module. This module has an SC
connector that is compatible with the IEEE 802.3z 1000BASE-SX standard.
Page 13 of 110
LED Descriptions
The front panel of the NETGEAR Model FSM726S Managed Stackable Switch has LEDs that provide a quick and accurate display of port speed,
activity, collisions, and duplex mode. For stacked use, there are additional LEDs for link status and master unit status (to indicate master/slave
status in a stack). The Gigabit Ethernet ports also have LEDs that show link and mode status. Table 2-1 summarizes the LEDs on the switch and
Gigabit Ethernet module.
Table 2-1. Front Panel LEDs:
Label Color Activity Description
Power Green
Link
(the port number)
LED Mode in (Three LEDs)
Max Spd
ACT
FDX
Stack In Green On
Stack Out Green On
Master Green On
Yellow
Green On
Green
Green
Green
Yellow
Blinking
Blinking
Blinking
On
On
Off
Off
On
Off
Off
On
On
Off
Off
Off
Power is supplied to the switch.
Power On Self Test (POST) in progress
Hardware failure during POST
Power is disconnected
Port has a valid link connection.
A valid link has not been established on the port.
Port has made a connection at the fastest speed possible for that port. For
10/100 Mbps ports, it indicates a 100 Mbps connection. For a 10/100/1000
Mbps port, it indicates a 1 Gbps connection.
Port is not operating at the fastest speed possible.
Data transmission is occurring on the port.
No data transmission is occurring on the port.
Port is operating in full-duplex mode.
Port is operating in half-duplex mode.
Collision is occurring.
Stack In port has a valid link connection.
Stack In port does not have a valid link connection
Stack Out port has a valid link connection.
Stack Out port does not have a valid link connection
Switch acts as a master unit in a stack of FSM726S switches.
Switch acts as a slave unit in a stack of FSM726S switches.
Console Port
Your NETGEAR Model FSM726S Managed Stackable Switch has a console port on the front panel. This port is labeled Console and is required
for initial configuration of the switch. It also lets you manage the switch using a directly connected VT-100 terminal, personal computer (PC),
Apple Macintosh, or UNIX workstation. The terminal, computer, or workstation connects to the console port using
the null-modem cable supplied with
your switch.
The console port is configured to use the following settings:
• Baud rate: 9,600 bps
• Data bits: 8
• Parity: none
• Stop bit: 1
• Flow control: none
These settings appear below the connector on the switch front panel.
In addition to using the console port, you can manage the switch using a Web browser and/or a Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
management program.
Note: You must use the console port for the initial switch configuration.
For more information about console-port connections, see “Connecting to the Console Port” on page 20. For more information about managing the
switch, see Chapter 5.
Stacking Ports
Your NETGEAR Model FSM726S Managed Stackable Switch has two stacking ports on the back panel, each with a full-duplex throughput of 2.6
gigabit per second (Gbps). These ports are labeled Stack In and Stack Out. You can use the stacking ports to cascade NETGEAR Model
FSM726S Managed Stackable Switches as your network grows to a maximum of six FSM726S Switches. The front panel of the switch contains
Stack In and Stack Out LEDs that show link on these stacking ports. For more information about stacking switches, see “Connecting Switches to
the Stack’s Backplane” on page 19.
Page 14 of 110

Page 15 of 110
CHAPTER 3: APPLICATIONS
Your NETGEAR Model FSM726S Managed Stackable Switch is designed to provide flexibility in configuring your network connections. It can be
used as stand-alone devices or used with 10 Mbps, 100 Mbps, 10/100 Mbps, and 1000 Mbps hubs and switches. It can also be stacked with other
FSM726S Switches to create one large virtual switch. This chapter shows how the switch can be used in various network environments.
Topics include:
Desktop switching
Stacked Switching
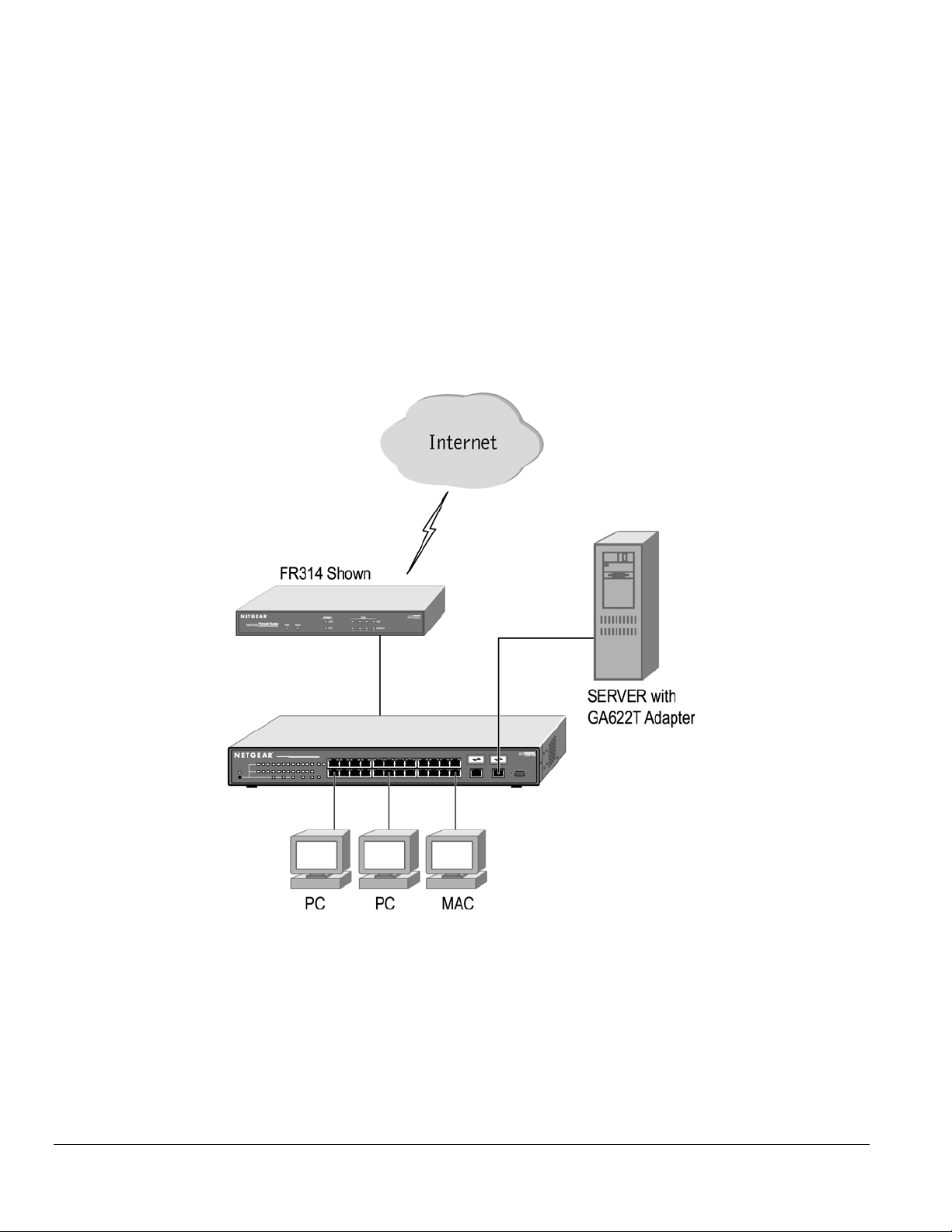
Desktop Switching
Your NETGEAR Model FSM726S Managed Stackable Switch can be used as desktop switch to build a small network that enables users to have
1000 Mbps access to a file server. With full-duplex enabled, the switch port connected to the server or PC can provide 2000 Mbps throughput.
Figure 3-1. Example of Desktop Switching
Page 16 of 110

Stacked Switching
Your NETGEAR Model FSM726S Managed Stackable Switch has two bi-directional stacking ports on the back panel. Using these ports, you can
build a full-duplex, switched network for large numbers of users simply by stacking units together. The high-speed stacking ports deliver 2 Gbps of
throughput across the stacking backplane.
A total of 6 switches can be put into a single stack. Stacked FSM726S Managed Stackable Switches can be assigned a single IP address using
the switch’s management software. The stack can then be treated as a single manageable unit with one IP address.
Figure 3-2. Example of Switched Stacking
Page 17 of 110
CHAPTER 4: INSTALLATION
This chapter describes the installation procedures for your NETGEAR Model FSM726S Managed Stackable Switch. Switch installation involves the
following steps:
Step 1: Preparing the site
Step 2: Installing the switch
Step 3: Installing a GBIC module Connecting devices to the switch
Step 4: Connecting Switches to the Stack’s Backplane
Step 5: Checking the installation
Step 6: Applying AC power
Step 7: Connecting to the console port to manage the switch (initial configuration)
Step 8: Connecting devices to the switch
This chapter also discusses how to add or remove switches to your stack
Step 1: Preparing the Site
Before you install your switch, be sure your operating environment meets the operating environment requirements in Table 4-1.
Table 4-1. Site Requirements
Characteristics Requirements
Mounting
Desktop installations:
Rack-mount installations:
Provide a flat table or shelf surface.
Use a 19-inch (48.3-centimeter) EIA standard equipment rack that is grounded and physically
secure. You also need the rack-mount kit supplied with your switch.
Access Locate the switch in a position that lets you access the front panel RJ-45 ports, view the front
Power source Provide a power source within 6 feet (1.8 meters) of the installation location. Power specifications
Environmental
Temperature: Install the switch in a dry area, with ambient temperature between 0 and 40ºC (32 and 104ºF).
Operating humidity: The installation location should have a maximum relative humidity of 90%, non-condensing.
Ventilation: Do not restrict airflow by covering or obstructing air inlets on the sides of the switch. Keep at least
Operating conditions: Keep the switch at least 6 ft (1.83 m) away from nearest source of electromagnetic noise, such as
Stacking If you intend to stack two or more switches, be sure the mounting surface can safely support the
panel LEDs, and access the rear-panel stacking port(s) and power connector.
for the switch is shown in Appendix C. Be sure the AC outlet is not controlled by a wall switch,
which can accidentally turn off power to the outlet and the switch.
Keep the switch away from heat sources such as direct sunlight, warm air exhausts, hot-air vents,
and heaters.
2 inches (5.08 centimeters) free on all sides for cooling.
Be sure there is adequate airflow in the room or wiring closet where you intend to install the
switch.
a photocopy machine.
switch stack. Also, be sure there is adequate space around the stack for ventilation and cooling.
Step 2: Installing the Switch
You can install your NETGEAR Model FSM726S Managed Stackable Switch on a flat surface or in a standard 19-inch rack.
Installing the Switch on a Flat Surface
The switch ships with four self-adhesive rubber footpads. Stick one rubber foot pad on each of the four concave spaces on the bottom of the switch.
The rubber footpads cushion the switch against shock/vibrations. They also provide space between each stacked switch for ventilation.
Installing the Switch in a Rack
Page 18 of 110

To install the switch in a rack, use the following procedure (and refer to Figure 4-1). To perform this procedure, you need the 19-inch rack-mount kit
supplied with your switch.
1. Attach the supplied mounting brackets to the side of the switch.
2. Insert the screws provided in the rack-mount kit through each bracket and into the bracket mounting holes in the switch.
3. Tighten the screws with a #1 Phillips screwdriver to secure each bracket.
4. Align the mounting holes in the brackets with the holes in the rack, and insert two pan-head screws with nylon washers through each bracket
and into the rack.
5. Tighten the screws with a #2 Phillips screwdriver to secure the switch in the rack.
6. If you want to install a GBIC module, proceed to “Step 3: Installing a GBIC Module,” next. If you want to stack switches, proceed to “Step 4:
Connecting Switches to the Stack’s Backplane,” Otherwise, skip to “Step 5: Checking the Installation.”
Figure 4-1. Attaching Mounting Brackets
Step 3: Installing a GBIC Module
The following procedure describes how to install a GBIC Gigabit Ethernet module, such as the NETGEAR AGM721F, in the switch’s Gigabit
module bays. The AGM721F is sold separately from the FMS726S. If you do not want to install a GBIC module at this time, skip this procedure.
To install a GBIC module:
7. Insert the GBIC module into the GBIC module bay. Press firmly to ensure the module seats into the connector.
8. After the switch has been powered on, use one of the management interfaces (web browser or console interface) to configure the Gigabit
Ethernet port with the GBIC module installed to the GBIC option.
9. To install a second Gigabit Ethernet module, repeat this procedure using the second module and the unoccupied module bay.
10. If you want to stack switches, proceed to “Step 4: Connecting Switches to the Stack’s Backplane,” next. Otherwise, skip to “Step 5: Checking
the Installation.”
Figure 4-2. Installing a Gigabit Ethernet Module
Step 4: Connecting Switches to the Stack’s Backplane
Your NETGEAR Model FSM726S Managed Stackable Switch provides two stacking connectors. You can use these connectors to cascade up to
six switches together to create one large virtual switch (for more information, see “Stacked Switching” on page 17).
Observe the following guidelines when installing the switches in a stacked configuration.
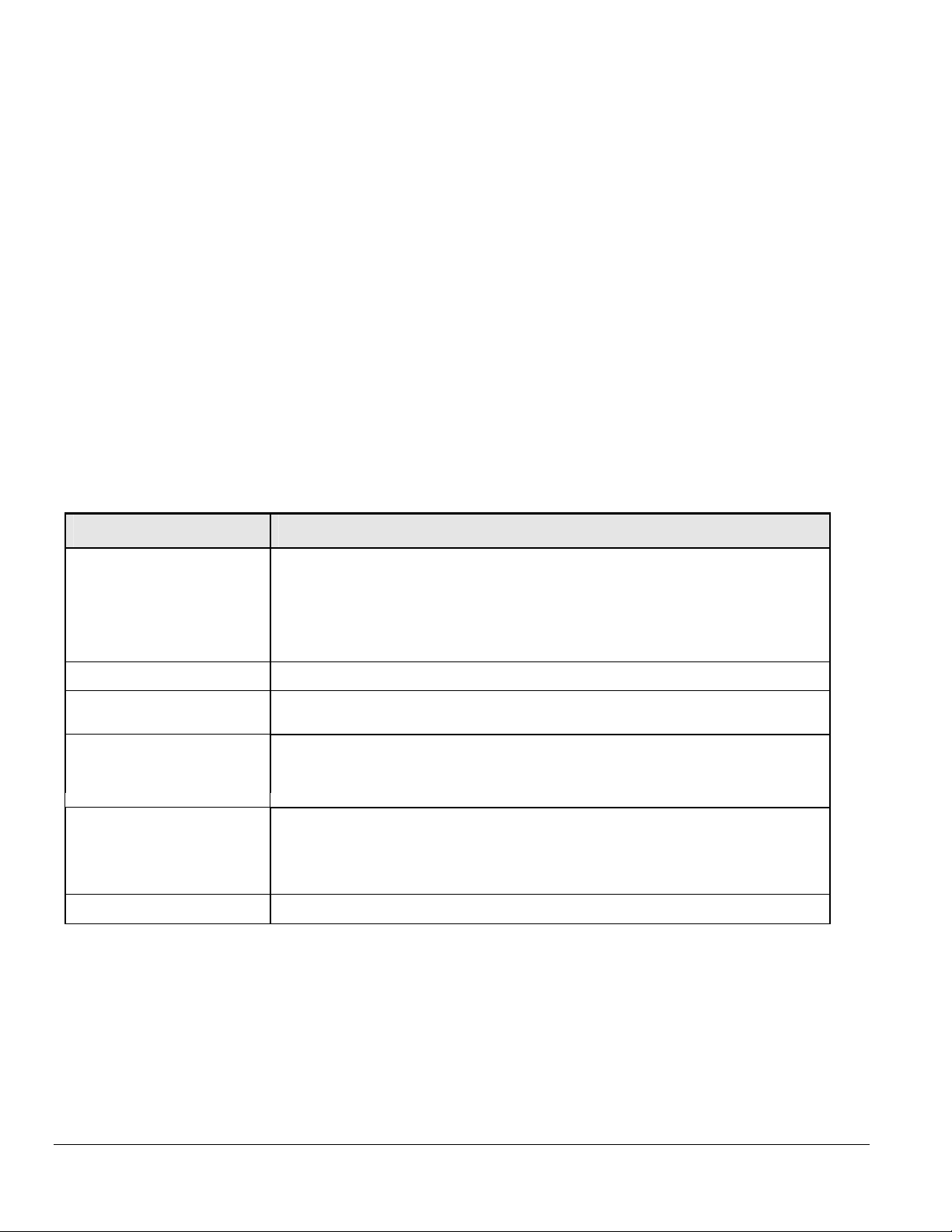
Connecting Stacking Ports
When connecting two FSM726S Managed Stackable Switches, one stacking cable connects the stacking port on one switch to the stacking port on
the other switch.
Page 19 of 110
Connect Straight-in
To prevent bent pins, do not install the stack port cable connector at an angle. Use extra care to insert the cable connector straight into the switch’s
stacking connector.
The following procedure describes how to stack three FSM726S Managed Stackable Switches and Figure 4-3 shows these connections:
11. Connect either end of the supplied stacking cable to the Stack In connector on the first switch. Connect the other end of the cable to the Stack
Out connector on the second switch.
12. Connect either end of another stacking cable to the Stack In connector on the second switch. Connect the other end of the cable to the Stack
Out connector on the third switch. The third switch will be the master switch.
Note: Stacked FSM726S Switches can be assigned a single IP address using the switches’ management software. The stack can then be treated
as a single manageable unit with one IP address. The switch with that IP address is considered the master unit, while the other switches in the
stack are called slave units.
Note: The switch that is acting as the master unit should have the Stack In port empty.
Figure 4-3. Cabling Three FSM726S Stacked Switches
Step 5: Checking the Installation
Before you apply power:
o Inspect the equipment thoroughly.
o Verify that all cables are installed correctly.
o Check cable routing to make sure cables are not damaged or create a safety hazard.
o Be sure all equipment is mounted properly and securely.
Step 6: Applying AC Power
NETGEAR Model FSM726S Managed Stackable Switches do not have an ON/OFF switch; the only method of applying or removing AC power is
by connecting or disconnecting the power cord. Before you connect the power cord, select an AC outlet that is not controlled by a wall switch, which
can turn off power to the switch. After you select an appropriate outlet, use the following procedure to apply AC power.
13. Connect the female end of the supplied AC power adapter cable to the power receptacle on the back of the switch.
14. Connect the 3-pronged end of the AC power adapter cable to a grounded 3-pronged AC outlet.
When you apply power, the Power LED on the switch’s front panel will be Yellow, as it conducts a Power On Self Test (POST). After the switch
passes the POST, the Power LED will change to Green and the switch is functional and ready to pass data.
If the Power LED does not go on, check that the power cable is plugged in correctly and that the power source is good. If this does not resolve the
problem, refer to Appendix B, Troubleshooting.
Note: If you are powering up stacked FSM762 switches, power up the master unit last.
Step 7: Connecting to the Console Port to Manage the Switch (initial configuration)
Your NETGEAR Model FSM726S Managed Stackable Switch contains software for viewing, changing, and monitoring the way it works. This
management software is not required for the switch to work. You can use the 10/100 Mbps ports, the built-in RJ-45 Gigabit ports, and the stacking
ports without using the management software. However, the management software can let you improve the efficiency of the switch and, as a
result, improve its overall performance as well as the performance of your network. The remainder of this section describes how to initialize the
management software to the first time you use the management features.
Page 20 of 110

After you power-up the switch for the first time, you can configure it using a VT100/ANSI terminal or a PC, Apple Macintosh, or UNIX workstation
that is directly connected to the switch’s console port. Thereafter, you can assign an IP address, subnet mask, and gateway address to the switch
and manage it through a Web browser, Telnet session, or SNMP management application. For more information about using the console, see
Chapter 6, Administration Console Access.
To connect a console to the switch:
15. Connect a VT100/ANSI terminal or a PC, Apple Macintosh, or UNIX workstation to the switch’s console port, labeled Console, using the nullmodem cable supplied with the switch. The supplied null-modem cable has 9-pin connectors on each end.
Note: you must connect the console cable to the master switch. Connecting the console cable a slave switch will not allow configuration
Note: If you are stacking your switches, you only have to configure the Master unit via the Console port. Once you have assigned an IP address to
the master unit, you can use the browser interface to configure the other units.
16. If you attached a PC, Apple Macintosh, or UNIX workstation, start a terminal-emulation program.
Microsoft Windows users can use HyperTerminal, which comes with the Windows operating systems.
Macintosh users can use ZTerm.
UNIX users can use a terminal emulator such as TIP.
17. Configure the terminal-emulation program to use the following settings:
Baud rate: 9,600 bps
Data bits: 8
Parity: none
Stop bit: 1
Flow control: none
Page 21 of 110
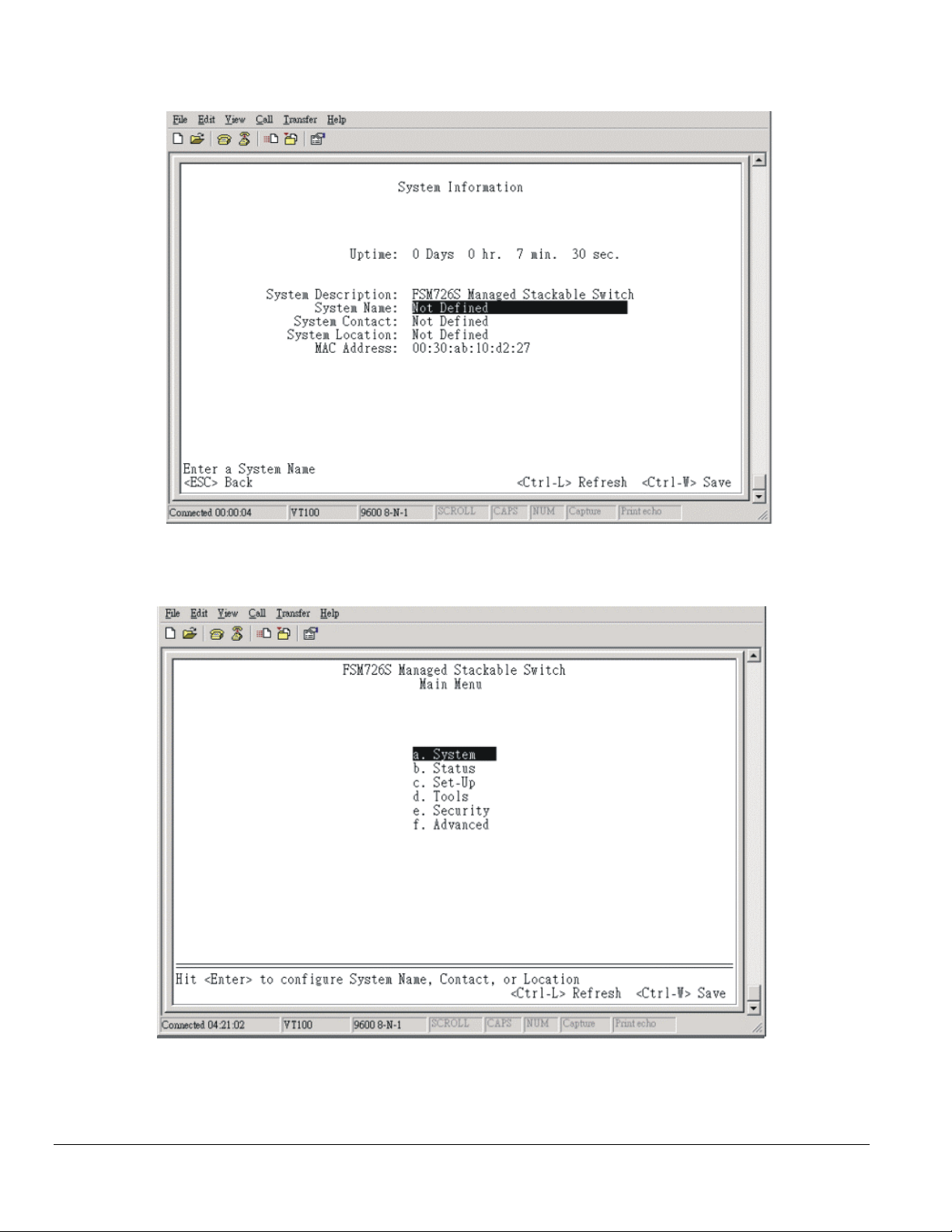
Figure 4-4 System Description
18. The terminal-emulation program should display the System Description page. Hit the ‘ESC’ key to get to the Main Menu page.
Figure 4-5 Main Menu
19. On the Main Menu page, hit the ‘C’ key to select the Set Up page
Page 22 of 110
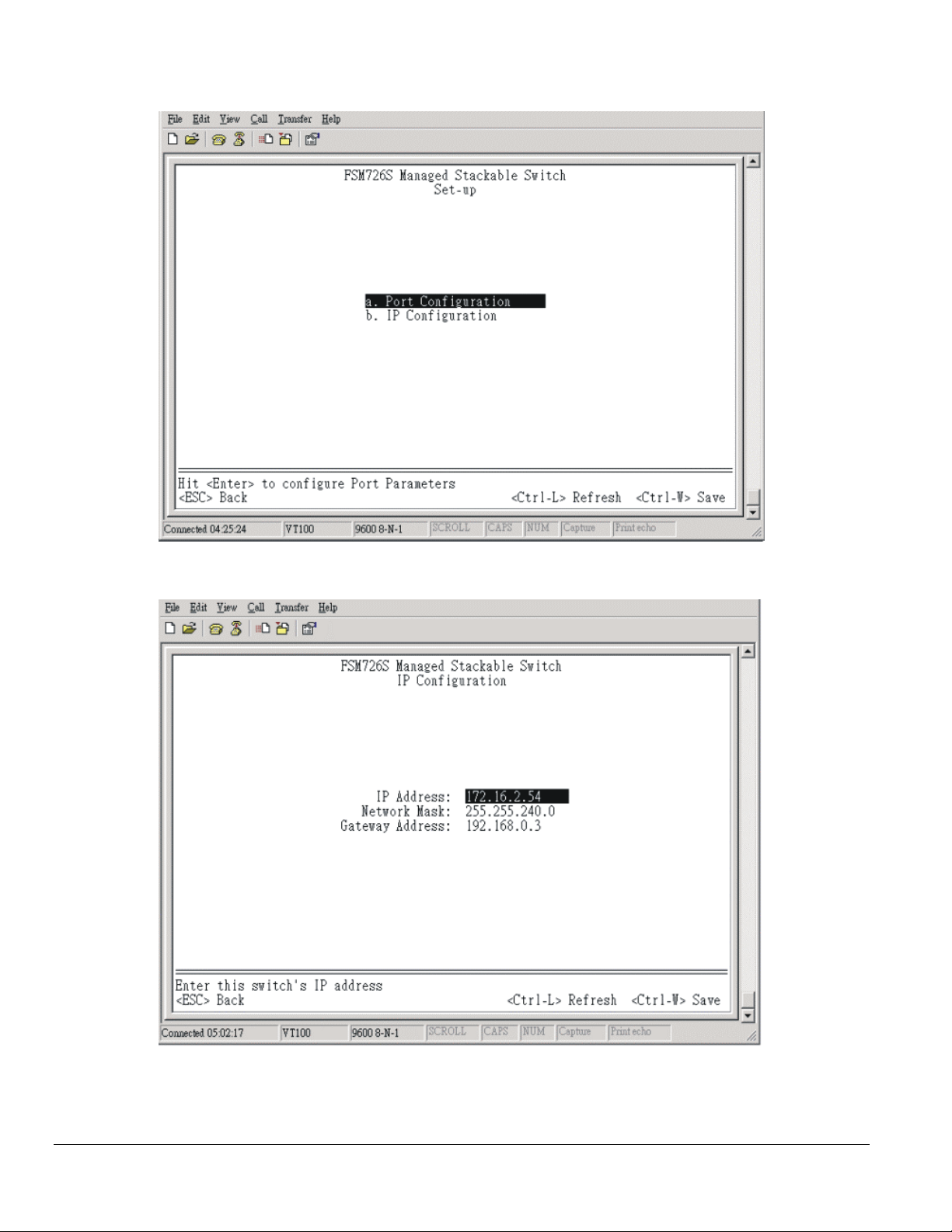
Figure 4-6 Set-Up
20. On the Set Up page, hit the ‘B’ key to select the IP Configuration page.
Figure 4-7 IP Configuration
Page 23 of 110
21. On the IP Configuration page, type in the desired IP Address for this switch, followed by the ‘Enter’ key.
Note: this switch is not DHCP client capable. You must assign a static IP address to the master switch.
22. Now type in the desired Network Mask, followed by the ‘Enter’ key.
23. Now type in the desired Default Gateway, followed by the ‘Enter’ key.
24. Use Ctrl-W to save these new settings. Hit the ‘Y’ key or ‘Enter’ to confirm saving the new settings to NVRAM.
25. Now hit the ‘ESC’ key twice to return to the Main Menu.
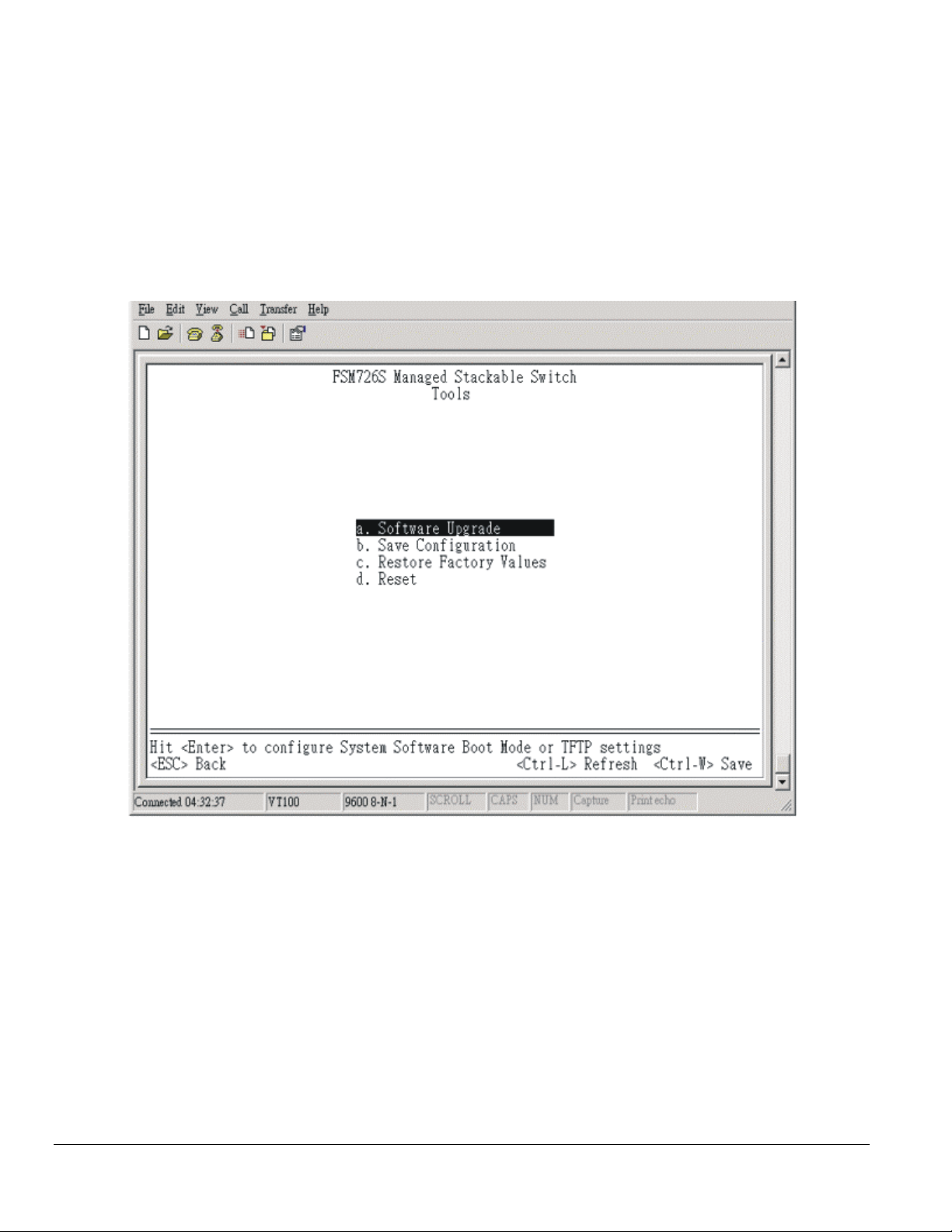
26. On the Main Menu page, hit the ‘D’ key to select the Tools page.
Figure 4-8: Tools page
27. On the Tools page, hit the ‘D’ key to Reset the switch. Hit the ‘Y’ key or ‘Enter’ to confirm resetting the switch.
The switch will now reset, loading the new IP address. At this point you can use your web browser to manage your switch through the network.
After you have connected your computer to the switch via one of the network ports, simply launch your web browser and type the IP address in the
Address Bar to use the Graphical User Interface (GUI) for configuration, observation, and management of your switch.
Page 24 of 110

Step 8: Connecting Devices to the Switch
The following procedure describes how to connect devices to the switch’s RJ-45 ports. Your NETGEAR Model FSM726S Managed Stackable
Switch contains Auto Uplink™ technology, which allows you to attach devices using either straight-through or crossover cables.
Figure 4-9. Connecting Devices to the Switch
28. Connect each device to an RJ-45 network port on the switch’s front panel (see Figure 4-9). Use Category 5 (Cat5) unshielded twisted-pair
(UTP) cable terminated with an RJ-45 connector to make these connections.
Note: Ethernet specifications limit the cable length between the switch and the attached device to 100 m (328 ft).
Adding or Removing Switches to the stack
For the master unit to properly manage the stack, we recommend the following steps when adding or removing a switch from the stack
1. Power down all switches in
Note: Do not add or remove stacking cables while the switch is powered up.
2. Remove/Add the necessary switches
Note: the Stack In port on the master unit is always empty.
3. Power up the slave units in the stack.
4. Power up the master unit
the stack.
Page 25 of 110
CHAPTER 5: SWITCH MANAGEMENT OVERVIEW
This chapter gives an overview of switch management, including the methods you can use to manage your NETGEAR Model FSM726S Managed
Stackable Switch. Topics include:
Management Access Overview
SNMP Access
Protocols
Software Upgrade Procedure
Management Access Overview
Your NETGEAR Model FSM726S Managed Stackable Switch gives you the flexibility to access and manage the switch using any or all of the
following methods:
An administration console
Web browser interface
External SNMP-based network-management application
The administration console and Web browser interface support are embedded in the switch’s firmware and available for immediate use. Each of
these management methods has advantages. Table 5-1 compares the three management methods.
Table 5-1. Comparing Switch Management Methods
Management Method Advantages Disadvantages
Administration console Out-of-band access via direct cable connection
Web browser Can be accessed from any location via the switch’s
SNMP Agent Communicates with switch functions at the
means network bottlenecks, crashes, and downtime
do not slow or prevent access
No IP address or subnet needed
Menu-based
HyperTerminal access to full functionality
(HyperTerminal are built into Microsoft Windows
95/98/NT/2000 operating systems)
Secure – MAKE SURE THE AREA WHERE THE
SWITCH IS INSTALLED IS A SECURE AREA
IP address
Ideal for configuring the switch remotely
Compatible with Internet Explorer and Netscape
Navigator Web browsers
Familiar browser interface
Graphical data available
Most visually appealing
Management Information Base (MIB) level
Based on open standards
.
Must be near switch or use dial-up connection
Not convenient for remote users
Not graphical
Security can be compromised (hackers need
only know IP address and subnet mask)
May encounter lag times on poor connections
Displaying graphical objects over a browser
interface may slow navigation
Requires SNMP manager software
Least visually appealing of all three methods
Limited amount of information available
Some settings require calculations
Security can be compromised (hackers need
only know the community name)
For a more detailed discussion of the Administration Console, see chapter 6. For a more detailed discussion of the Web Browser Interface, see
chapter 7.
SNMP Access
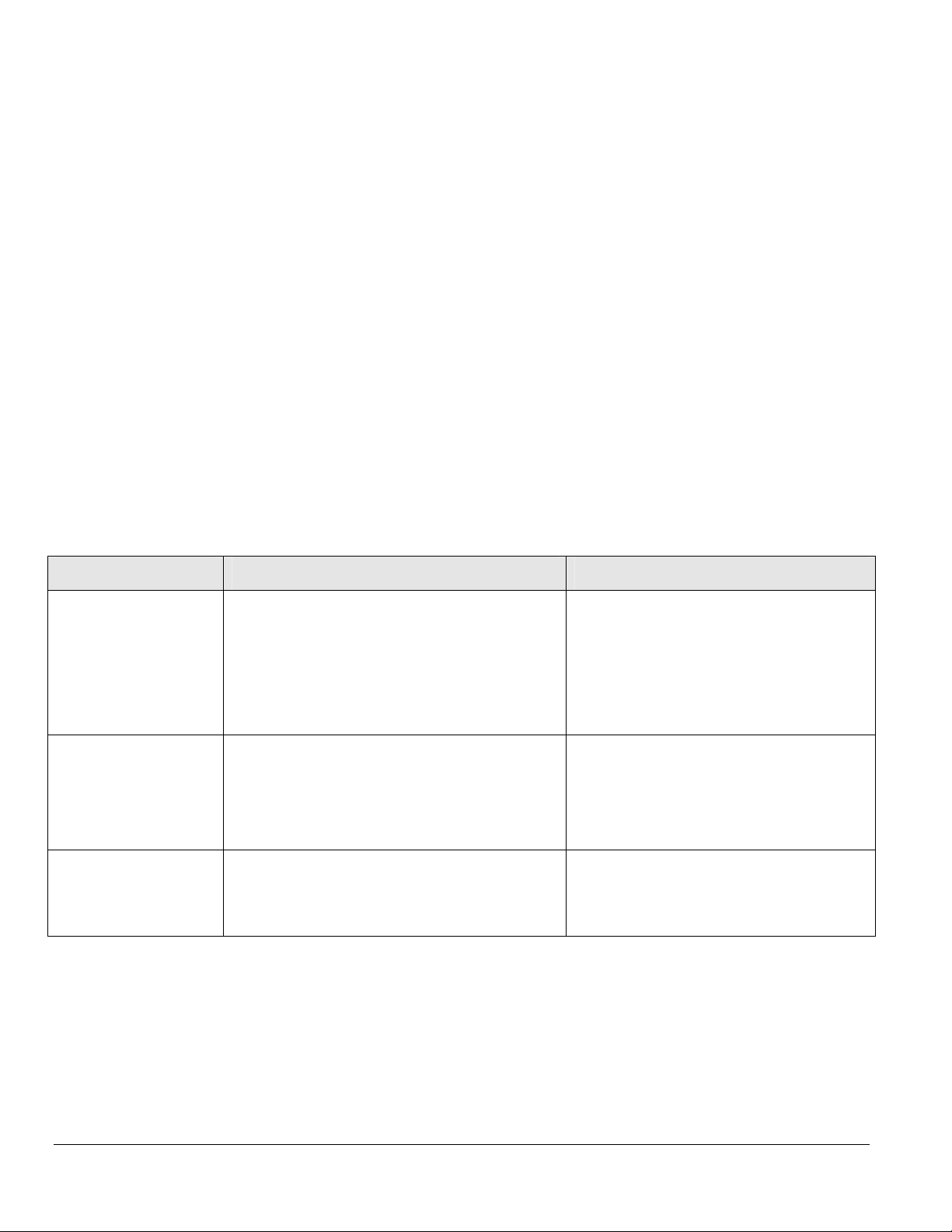
With this access method, you can use an external Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) -based application to manage your NETGEAR
Model FSM726S Managed Stackable Switch. Figure 5-1 shows an example of this management method.
This management method requires the SNMP agent on the switch and the SNMP Network Management Station to use the same community string.
This management method, in fact, uses two community strings: the GET community string and the SET community string. If the SNMP Network
Page 26 of 110
management Station only knows the SET community string, it can read from and write to the MIBs. However, if it only knows the GETcommunity
string, it can only read MIBs. The default GET community string for the switch is ‘public’.
Figure 5-1. SNMP-Based Management Method
Protocols
Your NETGEAR Model FSM726S Managed Stackable Switch supports the following protocols:
Virtual terminal protocols, such as Telnet
SNMP
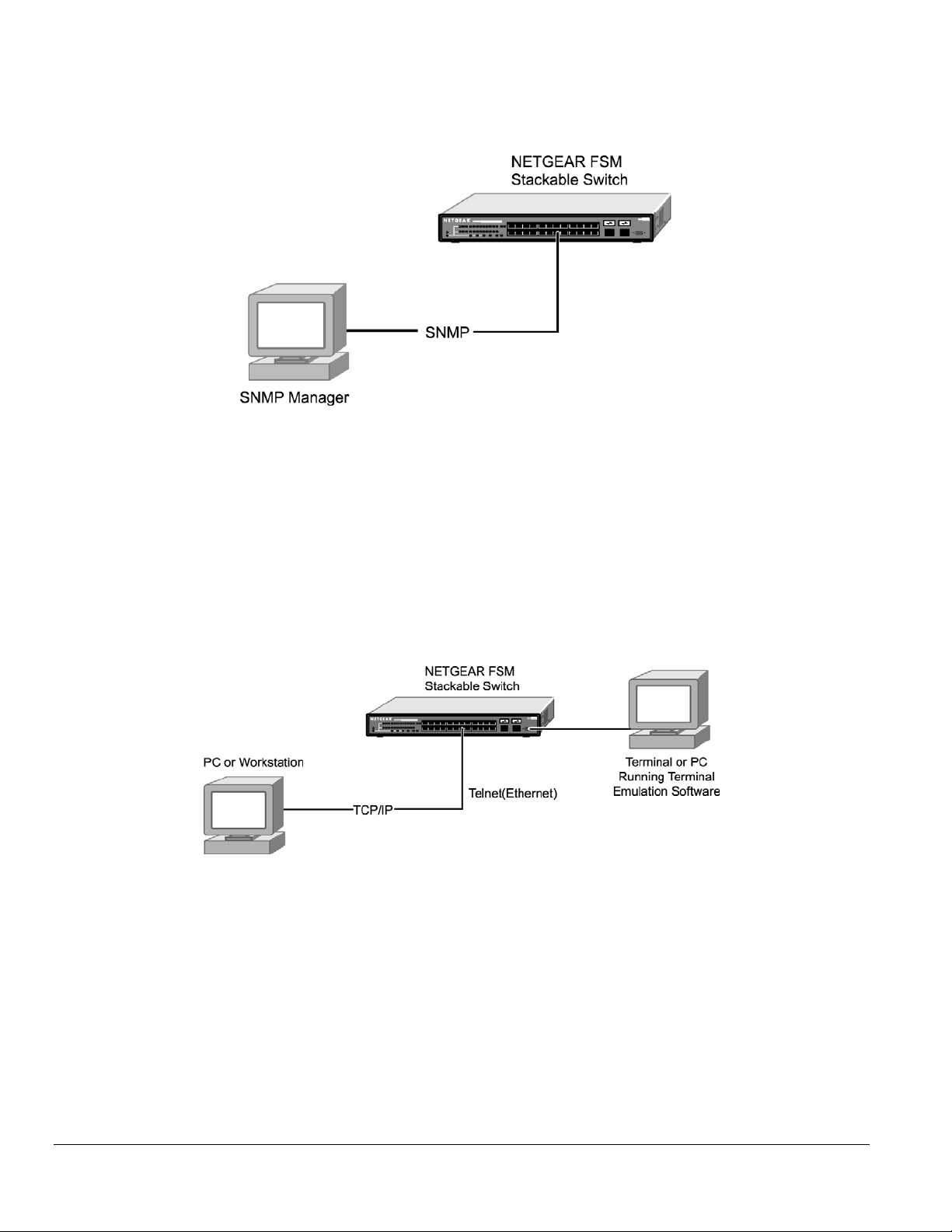
Virtual Terminal Protocols
A virtual terminal protocol is a software program, such as Telnet, that allows you to establish a management session from a Macintosh, a PC, or a
UNIX workstation. Because Telnet runs over TCP/IP, you must have at least one IP address configured on the NETGEAR Model FSM726S
Managed Stackable Switch before you can establish access to it with a virtual terminal protocol.
Terminal emulation differs from a virtual terminal protocol in that you must connect a terminal or PC directly to the console port. Figure 5-2 shows a
UNIX workstation connected to the system through a virtual terminal protocol (Telnet), and a terminal connecting directly to the console port
through a null-modem cable.
Figure 5-2. Administration Console Access
SNMP Protocol
SNMP is the standard management protocol for multi-vendor IP networks. SNMP supports transaction-based queries that allow the protocol to
format messages and to transmit information between reporting devices and data-collection programs. SNMP runs on top of the User Datagram
Protocol (UDP), offering a connectionless-mode service.
Software Upgrade Procedure
The application software is field upgradeable. The upgrade procedure and the required equipment is described in the following section.
Note that once the system is up, it is controlled by an executing application image residing in non-volatile memory. No software upgrade is possible
during this mode. The upgrade can only be done when the system is resetting. To initiate this sequence, the user must set the ‘Next Boot From’
configuration parameter to ‘Boot from Net’ during normal operation, and then perform a ‘reset’. When the ‘Boot from Net’ option is set, the switch
will start using an image residing on a TFTP server on the network. Be sure that the TFTP server residing on the network is accessible by the
switch. Once completed, the software version should be verified in the System page.
Page 27 of 110

Note: It is highly recommended, though not necessary, to use a RS-232 serial port connection to the switch during the software upgrading
procedure. When using a Telnet Session or web interface alone, your connection to the switch will not be available until the switch has entered
forwarding mode. This takes approximately three minutes.
The upgrade procedure is as follow:
Go to Main Menu>Tools>Software Upgrade (in the Web or Console Interface).
1.
2. Select ‘Boot from Net’ option.
3. Verify information such as the IP address for the TFTP Server, Gateway IP address, and the file name and its path of the new image.
4. Save the setting in non-volatile memory. In the Browser interface, use the ‘Apply’ button, and the Tools> Save Configuration screen. In the
console interface, use Ctrl-W and confirm the change to NVRAM.
5. Restart the system via the Tools>Reset command
6. Bootstrap will retrieve the new image then pass control to it.
7. The system executes the new software image.
Note: the previous image in non-volatile memory will not be replaced by the new image using this option. The image in non-volatile memory will
only be over-written if ‘Boot from Net and Save’ option is selected.
8. Test your switch to make sure the new image is working correctly. If you decide to keep the new image, go to Software Download again.
Select ‘Boot from Net & Save’ option.
9. Save the setting in non-volatile memory. In the Browser interface, use the ‘Apply’ button, and the Tools> Save Configuration screen. In the
console interface, use Ctrl-W and confirm the change to NVRAM.
10. Restart the system via the Tools>Reset command
11. The new image should over-write the old image in non-volatile memory. Verify it by going to the Software Download screen and checking the
Software Release information.
Note: IP address, Network Mask, and Default Gateway are not affected by upgrading the software. The settings will still be in non-volatile memory.
Page 28 of 110
CHAPTER 6: ADMINISTRATION CONSOLE ACCESS
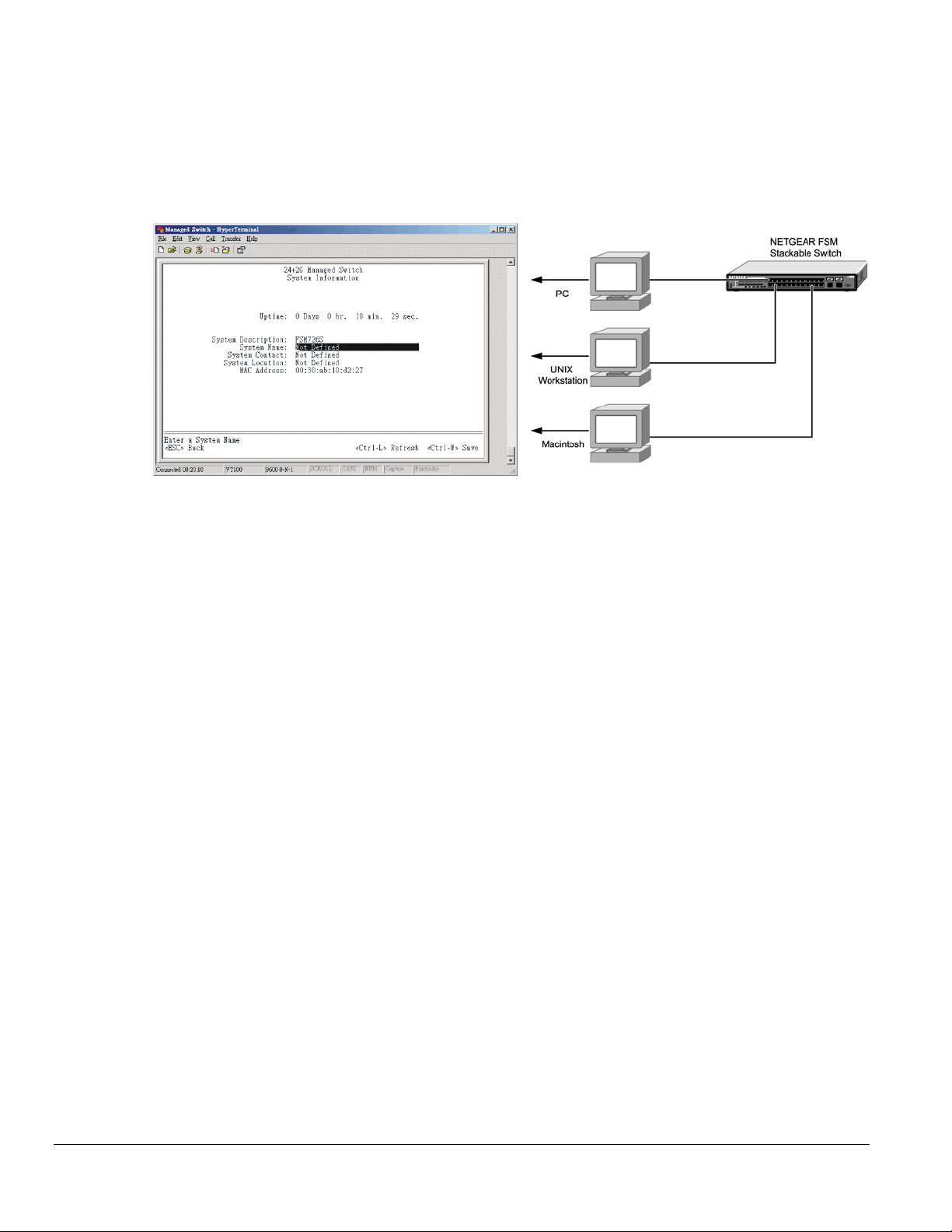
The administration console is an internal, character-oriented, VT-100/ANSI menu-driven user interface for performing management activities. Using
this method, you can view the administration console from a terminal, PC, Apple Macintosh, or UNIX workstation connected to the switch’s console
port. Figure 6-1 shows an example of this management method.
Figure 6-1. Administration Console Management Method
Direct Access
Direct access to the switch console is achieved by connecting the switch’s console port to a VT-100 or compatible terminal or to a PC, Apple
Macintosh, or UNIX workstation equipped with a terminal-emulation program. This connection is made using the null-modem cable supplied with
the switch.
The following list provides examples of terminal-emulation programs:
HyperTerminal (which is built into the Microsoft Windows operating systems)
ZTerm (Apple Macintosh)
TIP (UNIX workstation)
The terminal-emulation program should use the following settings:
Baud rate: 9,600 bps
Data bits: 8
Parity: none
Stop bit: 1
Flow control: none
The direct access management method is required when you configure the switch for the first time. Thereafter, we recommend you use the Web
management access method (described in chapter 7) to manage the switch.
The console, using VT100 terminal emulation, can be accessed from the RS-232 serial port or a telnet connection. The switch offers password
protection for this interface. All of the following examples of the Console’s User Interface show a screen capture from a telnet session.
Page 29 of 110

When attached to the User Interface via a Telnet Session, the following must be set in order to use the arrow keys: Under the terminal pull down
menu choose Properties and make sure the VT100 Arrows option is turned on.
User Interface
The switch offers a menu-driven interface.
Characteristics
There are several characteristics to the User Interface pages that are necessary to know before proceeding to use it. The TAB key or the arrow
keys may be used to move within menus and sub-screens. At the bottom of every screen are some key commands available to the user for that
particular screen, as well as some helpful information.
The common keystrokes and their definitions and intricacies are listed below:
ESC Return to the previous menu or screen, or abort editing
Tab Select field
Ctrl-L Refresh the screen
Ctrl-D Log off (password enabled)
Ctrl-M Move to field (Switch Statistics and Port Configuration menus only)
Ctrl-W Saves current configuration to Non-Volatile RAM (NVRAM)
Spacebar Toggles between possible settings for a field
Enter Select a menu item, edit a field, or accept a value after editing a field
Ctrl-X Delete a table entry
Page 30 of 110
 Loading...
Loading...