Page 1

Beta Draft 2
March 2006
NETGEAR, Inc.
4500 Great America Parkway
Santa Clara, CA 95054 USA
Command Line Interface
Reference for the ProSafe
7200 Series Layer-2
Switches, Software
Version 4.0
Page 2

ii
v1.0, March 2006
© 2006 by NETGEAR, Inc. All rights reserved. FullManual.
Trademarks
NETGEAR and Auto Uplink are trademarks or registered trademarks of NETGEAR , Inc. .
Microsoft, Windows, and Windows NT are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Other brand and product names are registered trademarks or trademarks of their respective holders. Portions of this
document are copyright Intoto, Inc.
March 2006
Statement of Conditions
In the interest of improving internal design, operational function, and/or reliability, NETGEAR reserves the right to
make changes to the products described in this document without notice.
NETGEAR does not assume any liability that may occur due to the use or application of the product(s) or circuit
layout(s) described herein.
EN 55 022 Declaration of Conformance
This is to certify that the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Managed Switch is shielded against the generation of radio
interference in accordance with the application of Council Directive 89/336/EEC, Article 4a. Conformity is declared by
the application of EN 55 022 Class B (CISPR 22).
Certificate of the Manufacturer/Importer
It is hereby certified that the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Managed Switch has been suppressed in accordance with the
conditions set out in the BMPT-AmtsblVfg 243/1991 and Vfg 46/1992. The operation of some equipment (for example,
test transmitters) in accordance with the regulations may, ho wever, be subject to certain restrictions. Please refer to the
notes in the operating instructions.
The Federal Office for Telecommunications Approvals has been notified of the placing of this equipment on the market
and has been granted the right to test the series for compliance with the regulations.
Bestätigung des Herstellers/Importeurs
Es wird hiermit bestätigt, daß dasProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Managed Switch gemäß der im BMPT-AmtsblVfg 243/
1991 und Vfg 46/1992 aufgeführten Bestimmungen entstört ist. Das vorschriftsmäßige Betreiben einiger Geräte (z.B.
Testsender) kann jedoch gewissen Beschränkungen unterliegen. Lesen Sie dazu bitte die Anmerkungen in der
Betriebsanleitung.
Das Bundesamt für Zulassungen in der Telekommunikation wurde davon unterrichtet, daß dieses Gerät auf den Markt
gebracht wurde und es ist berechtigt, die Serie auf die Erfüllung der Vorschriften hin zu überprüfen.
Voluntary Control Council for Interference (VCCI) Statement
This equipment is in the Class B category (information equipment to be used in a residential area or an adjacent area
thereto) and conforms to the standards set by the Voluntary Control Council for Interference by Data Processing
Equipment and Electronic Office Machines aimed at preventing radio interference in such residential are as . When used
near a radio or TV receiver, it may become the cause of radio interference. Read instructions for correct handling.
Page 3

v1.0, March 2006
iii
Product and Publication Details
Model Number: FSM72xx/GSM72xx
Publication Date: March 2006
Product Family: managed switch
Product Name: ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Managed Switch
Home or Business Product: Business
Language: English
Publication Part Number: Beta Draft 2
Publication Version Number 1.0
Page 4

v1.0, March 2006
iv
Page 5

v
v1.0, March 2006
Contents
Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2
Switches, Software Version 4.0
Chapter 1
About This Manual
1.1 Audience ............................. ...................... ....................... ...................... ............1-1
1.2 Scope ................................................................................................................1-1
1.3 Typographical Conventions ...............................................................................1-2
1.4 Special Message Format s .................................................................................1-2
1.5 How to Use This Manual ...................................................................................1-3
1.6 How to Print this Manual ....................................................................................1-3
1.7 Revision History ........................................... .... ... ... .................................... ... ... ..1-4
Chapter 2
Overview
2.1 Scope ................................................................................................................2-1
2.2 Using the Command-Line Interface ...................................................................2-1
2.2.1 Command Syntax .....................................................................................2-2
2.2.2 Command Conventions ............................................................................2-2
2.2.3 Unit-Slot-Port Naming Convention ...........................................................2-4
2.2.4 Using the “No” Form of a Command ........................................................2-5
2.2.5 Command Modes .....................................................................................2-5
2.2.6 Entering CLI Commands ........ ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .................................... ... ..2-8
2.2.7 Using CLI Help .......................................................................................2-10
2.2.8 Accessing the CLI ...................................................................................2-11
Chapter 3
Administrative Access Commands
3.1 Network Interface Commands ........................................................................... 3-1
3.1.1 enable ................................. ....................................... ............................... 3-2
3.1.2 serviceport ip ...... ... .... ... ... .................................... ................................... ..3-2
Page 6

vi
v1.0, March 2006
3.1.3 serviceport protocol ................................................................... ... ............3-2
3.1.4 network parms ..........................................................................................3-2
3.1.5 network mgmt_vlan ..................................................................................3-2
3.1.6 network protocol .......................................................................................3-3
3.1.7 show network ............................................................................................3-3
3.1.8 show serviceport .......................................................................................3-4
3.2 Console Port Access Commands ......................................................................3-5
3.2.1 configuration ............................................................................................. 3-5
3.2.2 lineconfig ..................................................................................................3-5
3.2.3 serial baudrate ..........................................................................................3-6
3.2.4 serial timeout ............................................................................................3-6
3.2.5 show serial ................................................................................................3-7
3.3 Telnet Commands ..................... ... .... ... ... ... ... .................................... ... ... .... ... ... ..3-8
3.3.1 telnet ................................... .......................................... ............................ 3-8
3.3.2 transport input telnet .................................................................................3-8
3.3.3 transport output telnet ...............................................................................3-9
3.3.4 session-limit .................................. .......................................... .................. 3-9
3.3.5 session-timeout ......................................................................................3-10
3.3.6 telnetcon maxsessions ...........................................................................3-10
3.3.7 telnetcon timeout ....................................................................................3-11
3.3.8 show telnet .............................................................................................3-11
3.3.9 show telnetcon ........................................................................................3-12
3.4 Secure Shell (SSH) Command ........................................................................3-13
3.4.1 ip ssh ............ ... ... ... .................................................................................3-13
3.4.2 ip ssh protocol .................... .... ... ................................... .... ... ... ................3-13
3.4.3 sshcon maxsessions ..............................................................................3-14
3.4.4 sshcon timeout .......................................................................................3-14
3.4.5 show ip ssh .............................................................................................3-14
3.5 Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) Commands ............................. ................3-15
3.5.1 ip http secure-port ...................................................................................3-15
3.5.2 ip http secure-protocol ............................................................................ 3-16
3.5.3 ip http secure-server ........................ .......................................... ............. 3-16
3.5.4 ip http server .................... ... .... ................................................................3-16
3.5.5 network javamode ..................................................................................3-17
3.5.6 show ip http ............................................................................................3-17
Page 7

vii
v1.0, March 2006
3.6 User Account Commands ......... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ...................................3-18
3.6.1 users name .............................................................................................3-18
3.6.2 users passwd ..........................................................................................3-19
3.6.3 users snmpv3 accessmode ....................................................................3-19
3.6.4 users snmpv3 authentication ..................................................................3-20
3.6.5 users snmpv3 encryption ........................................................................3-20
3.6.6 show loginsession ..................................................................................3-21
3.6.7 show users .............................................................................................3-21
3.6.8 disconnect ..............................................................................................3-22
Chapter 4
Port and System Setup Commands
4.1 Port Configuration Commands ..................................................................... ... ..4-1
4.1.1 interface ........................... ....................................... .................................. 4-1
4.1.2 cablestatus ...............................................................................................4-2
4.1.3 auto-negotiate .................................. .......... .......... ......... .......... .......... ........4-2
4.1.4 auto-negotiate all ......................................................................................4-2
4.1.5 mtu ............................. ......... .......... .......... ......... .......... .......... ......... .......... ..4-3
4.1.6 shutdown ..................................................................................................4-3
4.1.7 shutdown all ..................... ... .... ... ... ... ... .................................... ..................4-4
4.1.8 speed ............................... .......................................... ............................... 4-4
4.1.9 speed all ...................................................................................................4-5
4.1.10 monitor session ..... .... ................................... .................................... ... .....4-5
4.1.11 no monitor .................................................................................................4-6
4.1.12 show monitor session ...............................................................................4-6
4.1.13 show port ..................................................................................................4-6
4.1.14 show port protocol ....................................................................................4-7
4.2 Pre-login Banner and System Prompt Commands ............................................4-8
4.2.1 copy .......................................................................................................... 4-8
4.2.2 set prompt .................................................................................................4-8
4.3 Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) Commands ..........................................4-9
4.3.1 sntp broadcast client poll-interval .............................................................4-9
4.3.2 sntp client mode .......................................................................................4-9
4.3.3 sntp client port ..........................................................................................4-9
4.3.4 sntp unicast client poll-interval ................................................................4-10
4.3.5 sntp unicast client poll-timeout ...............................................................4-10
Page 8

viii
v1.0, March 2006
4.3.6 sntp unicast client poll-retry ....................................................................4-11
4.3.7 sntp multicast client poll-interval .............................................................4-11
4.3.8 sntp server ..............................................................................................4-12
4.3.9 show sntp ...............................................................................................4-12
4.3.10 show sntp client ......................................................................................4-12
4.3.11 show sntp server ....................................................................................4-13
4.4 MAC Address and MAC Database Commands ......................... ...................... 4-14
4.4.1 network mac-address .............................................................................4-14
4.4.2 network mac-type ...................................................................................4-14
4.4.3 macfilter .................................................................................................. 4-15
4.4.4 macfilter adddest ....................................................................................4-15
4.4.5 macfilter adddest all ................................................................................4-16
4.4.6 macfilter addsrc ......................................................................................4-16
4.4.7 macfilter addsrc all ..................................................................................4-17
4.4.8 bridge aging-time ....................................................................................4-17
4.4.9 show forwardingdb agetime ....................................................................4-18
4.4.10 show mac-address-table multicast .........................................................4-18
4.4.11 show mac-address-table static ...............................................................4-19
4.4.12 show mac-address-table staticfiltering ...................................................4-20
4.4.13 show mac-address-table stats ................................................................4-20
Chapter 5 Spanning Tree Protocol Commands
5.1 STP Configuration Commands ..........................................................................5-1
5.1.1 spanning-tree .......................................... ................... ................... ............5-1
5.1.2 spanning-tree bpdumigrationcheck ..........................................................5-2
5.1.3 spanning-tree configuration name ............................................................5-2
5.1.4 spanning-tree configuration revision ....................................... ..................5-3
5.1.5 spanning-tree edgeport ............................................................................5-3
5.1.6 spanning-tree forceversion .......................................................................5-3
5.1.7 spanning-tree forward-time .......................................................................5-4
5.1.8 spanning-tree hello-time ...........................................................................5-4
5.1.9 spanning-tree max-age .............................................................................5-5
5.1.10 spanning-tree max-hops ...........................................................................5-5
5.1.11 spanning-tree mst .....................................................................................5-6
5.1.12 spanning-tree mst instance ......................................................................5-7
5.1.13 spanning-tree mst priority ......................................................................... 5-7
Page 9

ix
v1.0, March 2006
5.1.14 spanning-tree mst vlan .............................................................................5-8
5.1.15 spanning-tree port mode ..........................................................................5-8
5.1.16 spanning-tree port mode all ................ .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... .....................5-9
5.2 STP Show Commands ......................................................................................5-9
5.2.1 show spanning-tree ..................................................................................5-9
5.2.2 show spanning-tree summary ................................................................5-11
5.2.3 show spanning-tree interface .................................................................5-12
5.2.4 show spanning-tree mst port detailed ..................................... ................ 5-13
5.2.5 show spanning-tree mst port summary ..................................................5-15
5.2.6 show spanning-tree mst summary ..........................................................5-15
5.2.7 show spanning-tree vlan .........................................................................5-16
Chapter 6
VLAN Commands
6.1 VLAN Configuration Commands .......................................................................6-1
6.1.1 vlan database ............... ................................... .... ... ... ...............................6-1
6.1.2 network mgmt_vlan ..................................................................................6-1
6.1.3 vlan ........................................................................................................... 6-2
6.1.4 vlan acceptframe ....... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... .................................... ... ... ..6-2
6.1.5 vlan ingressfilter .................. .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ................................... .... ... ... ..6-3
6.1.6 vlan makestatic .......................................................... ... .... ........................6-3
6.1.7 vlan name ........................................ ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ...............................6-3
6.1.8 vlan participation ................. .... ... ... ... ... .................................... ... ... .... ........6-4
6.1.9 vlan participation all ......................................... .... ... ..................................6-4
6.1.10 vlan port acceptframe all ........................................... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ........6-5
6.1.11 vlan port pvid all ........................................................................................6-5
6.1.12 vlan port tagging all ..................................................................................6-6
6.1.13 vlan port ingressfilter all ............................................................................6-6
6.1.14 Global Config ...................... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ................................... .... ... ... ..6-7
6.1.15 vlan protocol group ................. ... ... .................................... ... .....................6-7
6.1.16 vlan protocol group add protocol ...................................... ........................6-7
6.1.17 vlan protocol group remove ...................................................................... 6-7
6.1.18 protocol group .................................................. .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ........6-8
6.1.19 protocol vlan group .................... ... ... .................................... ... ..................6-8
6.1.20 protocol vlan group all ..... ... .... ... ................................... .... ... ... ..................6-9
6.1.21 vlan pvid ....... ... .........................................................................................6-9
Page 10

x
v1.0, March 2006
6.1.22 vlan tagging .. ... ... ... .... ................................... ... .... ... ..................................6-9
6.2 VLAN Show Commands ..................................................................................6-10
6.2.1 show vlan ................................................................................................6-10
6.2.2 show vlan brief ........................................................................................6-11
6.2.3 show vlan port ........................................................................................6-12
6.3 Provisioning (IEEE 802.1p) Commands ..........................................................6-13
6.3.1 vlan port priority all .................................................................................6-13
6.3.2 vlan priority ......... ... .... ... ... ... .................................... ................................6-13
Chapter 7
DHCP Commands
7.1 DHCP Server Commands (DHCP Config Pool Mode) ......................................7-2
7.1.1 ip dhcp pool ............... ... ... ... .... ... ................................... .... ........................7-2
7.1.2 client-identifier ..........................................................................................7-2
7.1.3 client-name ............................................................................................... 7-3
7.1.4 default-router ............................................................................................7-3
7.1.5 dns-server ............................... ......... .......... .......... ......... .......... .......... ........7-4
7.1.6 hardware-address ................................... ......... ............. ............. ............. ..7-4
7.1.7 host ............................ ...................................... ....................................... ..7-4
7.1.8 lease ......................................................................................................... 7-5
7.1.9 network ..................................................................................................... 7-5
7.1.10 bootfile ......................................................................................................7-6
7.1.11 domain-name ...................... ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. .....7-6
7.1.12 netbios-name-server ............................................................ ............. ........7-6
7.1.13 netbios-node-type ............................................................. ........................ 7-7
7.1.14 next-server .............................................................. ............. ............. ........7-7
7.1.15 option ............................................................ ....................................... ..... 7-8
7.2 DHCP Server Commands (Global Config Mode) ..............................................7-8
7.2.1 ip dhcp excluded-address .......................... ... ... .................................... ... ..7-9
7.2.2 ip dhcp ping packets .................................................................................7-9
7.2.3 service dhcp ....... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... .................................... ... ...................7-10
7.2.4 ip dhcp bootp automatic .........................................................................7-10
7.2.5 ip dhcp conflict logging ...........................................................................7-10
7.3 DHCP Server Clear and Show Commands .....................................................7-11
7.3.1 clear ip dhcp binding ...............................................................................7-11
7.3.2 clear ip dhcp server statistics .................................................................7-11
Page 11

xi
v1.0, March 2006
7.3.3 clear ip dhcp conflict ...............................................................................7-11
7.3.4 show ip dhcp binding ..............................................................................7-12
7.3.5 show ip dhcp global configuration ..........................................................7-12
7.3.6 show ip dhcp pool configuration .............................................................7-12
7.3.7 show ip dhcp server statistics .................................................................7-13
7.3.8 show ip dhcp conflict ..............................................................................7-14
7.4 DHCP and BOOTP Relay Commands ............................................................7-14
7.4.1 bootpdhcprelay cidoptmode ...................................................................7-15
7.4.2 bootpdhcprelay enable ...........................................................................7-15
7.4.3 bootpdhcprelay maxhopcount ................................................................7-15
7.4.4 bootpdhcprelay minwaittime ...................................................................7-16
7.4.5 bootpdhcprelay serverip .........................................................................7-16
7.4.6 show bootpdhcprelay ..............................................................................7-17
Chapter 8
GARP, GVRP, and GMRP Commands
8.1 GARP Commands .............................................................................................8-2
8.1.1 set garp timer join .....................................................................................8-2
8.1.2 set garp timer leave ..................................................................................8-3
8.1.3 set garp timer leaveall ..............................................................................8-4
8.1.4 show garp .................................................................................................8-4
8.2 GVRP Commands .............................................................................................8-5
8.2.1 set gvrp adminmode .................................................................................8-5
8.2.2 set gvrp interfacemode .............................................................................8-5
8.2.3 show gvrp configuration ............................................................................8-6
8.3 GMRP Commands ............................................................................................8-7
8.3.1 set gmrp adminmode ................................................................................8-7
8.3.2 set gmrp interfacemode ............................................................................8-8
8.3.3 show gmrp configuration ..........................................................................8-8
8.3.4 show mac-address-table gmrp .................................................................8-9
Chapter 9
Port-Based Traffic Control Commands
9.1 Port Security Commands ....... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... .................................... ... ... ..9-1
9.1.1 port-security ............................ .......................................... ........................ 9-2
9.1.2 port-security max-dynamic ........... ............................................................9-2
9.1.3 port-security max-static .......... ................................... ... .... ... ... ... ... ............9-2
Page 12

xii
v1.0, March 2006
9.1.4 port-security mac-address ...................................... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... ............9-3
9.1.5 port-security mac-address move ............ ... ... ... .... ................................... ..9-3
9.1.6 show port-security ....................................................................................9-3
9.1.7 show port-security ....................................................................................9-4
9.1.8 show port-security dynamic ......................................................................9-4
9.1.9 show port-security static ...........................................................................9-4
9.1.10 show port-security violation ......................................................................9-4
9.2 Storm Control Commands .................................................................................9-5
9.2.1 storm-control broadcast ............................................................................9-5
9.2.2 storm-control flowcontrol ..........................................................................9-6
9.2.3 show storm-control ...................................................................................9-6
Chapter 10
SNMP Commands
10.1 SNMP Configuration Commands ....................................................................10-1
10.1.1 snmp-server .................................. ..........................................................10-1
10.1.2 snmp-server community .........................................................................10-2
10.1.3 snmp-server community ipaddr ..............................................................10-2
10.1.4 snmp-server community ipmask .............................................................10-3
10.1.5 snmp-server community mode ...............................................................10-3
10.1.6 snmp-server community ro ..................................................................... 10-4
10.1.7 snmp-server community rw ....................................................................10-4
10.1.8 snmp-server enable traps violation .........................................................10-4
10.1.9 snmp-server enable traps .................................... ................................... 10-5
10.1.10 snmp-server enable traps bcaststorm ....................................................10-5
10.1.11 snmp-server enable traps linkmode .......................................................10-5
10.1.12 snmp-server enable traps multiusers .....................................................10-6
10.1.13 snmp-server enable traps stpmode ........................................................10-6
10.1.14 snmptrap .................................................................................................10-7
10.1.15 snmptrap snmpversion ...........................................................................10-7
10.1.16 snmptrap ipaddr ......................................................................................10-8
10.1.17 snmptrap mode ............................. ............. ............. .......... ............ ..........10-8
10.1.18 snmp trap link-status ..............................................................................10-8
10.1.19 snmp trap link-status all ..........................................................................10-9
10.2 SNMP Show Commands .................................................................................10-9
10.2.1 show snmpcommunity ..........................................................................10-10
Page 13

xiii
v1.0, March 2006
10.2.2 show snmptrap .....................................................................................10-10
10.2.3 show trapflags ......................................................................................10-11
Chapter 11
Port-Based Access and Authentication Commands
11.1 Port-Based Network Access Control Commands ............................................11-1
11.1.1 authentication login .................................................................................11-1
11.1.2 clear dot1x statistics ...............................................................................11-3
11.1.3 clear radius statistics ..............................................................................11-3
11.1.4 dot1x defaultlogin ................................................................................... 11-3
11.1.5 dot1x initialize .................................. ... .................................... ... ... .... ... ...11-3
11.1.6 dot1x login .... ... ... ... .... ................................... .................................... ... ...11-3
11.1.7 dot1x max-req ......................... ......... ............. ............. ............. ............. ...11-4
11.1.8 dot1x port-control ....................................................................................11-4
11.1.9 dot1x port-control all ...............................................................................11-5
11.1.10 dot1x re-authenticate ....................... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ...11-5
11.1.11 dot1x re-authentication ........................................... ................................11-5
11.1.12 dot1x system-auth-control ...... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ...................................11-6
11.1.13 dot1x timeout ............................................. ... ... .... ... ... ... ..........................11-6
11.1.14 dot1x user ........................ ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ................................... ... .... ... ...11-7
11.1.15 users defaultlogin ...................................................................................11-8
11.1.16 users login ..............................................................................................11-8
11.1.17 show authentication ................................................................................11-8
11.1.18 show authentication users ......................................................................11-9
11.1.19 show dot1x .............................................................................................11-9
11.1.20 show dot1x users ..................................................................................11-12
11.1.21 show users authentication .................................................................... 11-12
11.2 RADIUS Commands ......................................................................................11-13
11.2.1 radius accounting mode ..... .... ... ...........................................................11-13
11.2.2 radius server host .................................................................................11-13
11.2.3 radius server key .......... ... ... .... ... ...........................................................11-15
11.2.4 radius server msgauth ......................................... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... .11-15
11.2.5 radius server primary ....................... ............................................. ........ 11-15
11.2.6 radius server retransmit .......................... ..............................................11-16
11.2.7 radius server timeout ............................................................................11-16
11.2.8 show radius ..........................................................................................11-16
Page 14

xiv
v1.0, March 2006
11.2.9 show radius accounting ........................................................................11-17
11.2.10 show radius statistics ............................................................................11-19
Chapter 12
Port-Channel/LAG (802.3ad) Commands
12.1 Port-Channel Configuration Commands ..........................................................12-1
12.1.1 addport ...................................................................................................12-2
12.1.2 deleteport (Interface Config) ...................................................................12-2
12.1.3 deleteport (Global Config) ......................................................................12-2
12.1.4 port-channel ............................... .............................................................12-2
12.1.5 clear port-channel ...................................................................................12-3
12.1.6 port-channel staticcapability ...................................................................12-3
12.1.7 port lacpmode .........................................................................................12-3
12.1.8 port lacpmode all ....................................................................................12-4
12.1.9 port-channel adminmode ........................................................................12-4
12.1.10 port-channel name ..................................................................................12-4
12.1.11 port-channel linktrap ...............................................................................12-5
12.2 Port-Channel Show Commands ......................................................................12-5
12.2.1 show port-channel brief ..........................................................................12-5
12.2.2 show port-channel ..................................................................................12-6
Chapter 13
IGMP Snooping Commands
13.1 IGMP Snooping Configuration Commands .....................................................13-1
13.1.1 set igmp ..................................................................................................13-1
13.1.2 set igmp interfacemode ..........................................................................13-2
13.1.3 set igmp fast-leave .................................................................................13-3
13.1.4 set igmp groupmembership-interval .......................................................13-3
13.1.5 set igmp maxresponse ...........................................................................13-4
13.1.6 set igmp mcrtexpiretime .........................................................................13-5
13.1.7 set igmp mrouter .....................................................................................13-5
13.1.8 set igmp mrouter interface ......................................................................13-6
13.2 IGMP Snooping Show Commands ..................................................................13-6
13.2.1 show igmpsnooping ................................................................................13-6
13.2.2 show igmpsnooping mrouter interface ....................................................13-8
13.2.3 show igmpsnooping mrouter vlan ...........................................................13-8
13.2.4 show mac-address-table igmpsnooping .................................................13-8
Page 15

xv
v1.0, March 2006
Chapter 14
Quality of Service (QoS) Commands
14.1 Class of Service (CoS) Commands (GSM7248 only) ......................................14-2
14.1.1 classofservice dot1p-mapping ................................................................ 14-2
14.1.2 classofservice ip-precedence-mapping ..................................................14-2
14.1.3 classofservice ip-dscp-mapping .............................................................14-3
14.1.4 classofservice trust ................................................................................. 14-3
14.1.5 cos-queue min-bandwidth ......................................................................14-4
14.1.6 cos-queue strict ......................................................................................14-4
14.1.7 traffic-shape .................................. .................................................... ......14-4
14.1.8 show classofservice dot1p-mapping .......................................................14-5
14.1.9 show classofservice ip-precedence-mapping .........................................14-5
14.1.10 show classofservice ip-dscp-mapping .................................................... 14-6
14.1.11 show classofservice trust .................... ............. ............. ............. .............14-6
14.1.12 show interfaces cos-queue .....................................................................14-7
14.2 Differentiated Services (DiffServ) Commands ................................................. 14-7
14.2.1 diffserv ....................................................................................................14-9
14.3 DiffServ Class Commands (GSM7248 only) ...................................................14-9
14.3.1 class-map .............................................................................................14-10
14.3.2 class-map rename ................................................................................14-10
14.3.3 match any ........................................ .................................... ... ... ... ........14-11
14.3.4 match class-map ............. ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ................................... ... .... ... .14-11
14.3.5 match dstip ...... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ................................... ... .... ... .................14-12
14.3.6 match dstl4port .................................................................... ... ... ... ........14-12
14.3.7 match ip dscp ......................................... ................................... ... ........14-12
14.3.8 match ip precedence ............................................................................14-13
14.3.9 match ip tos ........ ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... .................................... ... ... ... ...........14-13
14.3.10 match protocol ........................... ...........................................................14-14
14.3.11 match srcip ... ... ... ... .... ... ........................................................................14-14
14.3.12 match srcl4port .....................................................................................14-14
14.4 DiffServ Policy Commands (GSM7248 only) ............................. .................... 14-15
14.4.1 assign-queue ........................................................................................ 14-15
14.4.2 drop ......................................................................................................14-16
14.4.3 conform-color ........................................................................................14-16
14.4.4 class .....................................................................................................14-16
Page 16

xvi
v1.0, March 2006
14.4.5 mark cos ...............................................................................................14-17
14.4.6 mark ip-dscp .........................................................................................14-17
14.4.7 mark ip-precedence ..............................................................................14-18
14.4.8 police-simple .........................................................................................14-18
14.4.9 policy-map ............................................................................................14-19
14.4.10 policy-map rename ...............................................................................14-19
14.5 DiffServ Service Commands (GSM7248 only) ..............................................14-19
14.5.1 service-policy ................ .......................................... .............................. 14-20
14.6 DiffServ Show Commands .............................................................................14-21
14.6.1 show class-map (GSM7248 only) .........................................................14-21
14.6.2 show diffserv .........................................................................................14-22
14.6.3 show policy-map (GSM7248 only) ........................................................14-23
14.6.4 show diffserv service (GSM7248 only) .................................................14-25
14.6.5 show diffserv service brief (GSM7248 only) .........................................14-26
14.6.6 show policy-map interface (GSM7248 only) ........ ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... .14-26
14.6.7 show service-policy (GSM7248 only) ...................................................14-27
14.7 MAC Access Control List (ACL) Commands (GSM7248 only) ......................14-27
14.7.1 mac access-list extended .....................................................................14-28
14.7.2 mac access-list extended rename ........................................................14-28
14.7.3 {deny|permit} ........................................................................................14-29
14.7.4 mac access-group ................................................................................14-30
14.7.5 show mac access-lists ..........................................................................14-31
14.8 IP Access Control List (ACL) Commands (GSM7248 only) ..........................14-32
14.8.1 access-list ............................... ..............................................................14-32
14.8.2 ip access-group ....................................................................................14-33
14.8.3 show ip access-lists ......................... ..................................................... 14-34
14.8.4 show access-lists ................................ ....................... ....................... .... 14-35
Chapter 15
System Maintenance Commands
15.1 System Information and Statistics Commands ................................................ 15-1
15.1.1 show arp switch ......................................................................................15-1
15.1.2 show eventlog .........................................................................................15-2
15.1.3 show hardware .......................................................................................15-2
15.1.4 show interface ........................................................................................15-3
15.1.5 show interface ethernet ..........................................................................15-5
Page 17

xvii
v1.0, March 2006
15.1.6 show logging .........................................................................................15-14
15.1.7 show mac-addr-table ............................................................................15-14
15.1.8 clear mac-addr-table .............................................................................15-15
15.1.9 show running-config .............................................................................15-16
15.1.10 terminal length ........................................ ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... .................15-16
15.1.11 show sysinfo .........................................................................................15-16
15.2 System Utility Commands .................. ... ... ... .... ... ... .................................... ... .15-17
15.2.1 traceroute .............................................................................................15-17
15.2.2 clear config ...........................................................................................15-17
15.2.3 clear counters .......................................................................................15-18
15.2.4 clear igmpsnooping ..............................................................................15-18
15.2.5 clear pass .............................................................................................15-18
15.2.6 enable passwd ......................................................................................15-18
15.2.7 clear port-channel .................................................................................15-18
15.2.8 clear traplog ..........................................................................................15-18
15.2.9 clear vlan ..............................................................................................15-19
15.2.10 copy ...................................................................................................... 15-19
15.2.11 logout ............................ ....................................... ................................. 15-20
15.2.12 ping .................................. ....................................... .............................. 15-21
15.2.13 reload .................................. .......... .......... ......... .......... .......... ......... ........15-21
15.3 Logging Commands ......................................................................................15-21
15.3.1 logging buffered ....................................................................................15-21
15.3.2 logging buffered wrap ...........................................................................15-22
15.3.3 logging console .....................................................................................15-22
15.3.4 logging host ..........................................................................................15-23
15.3.5 logging host remove .............................................................................15-23
15.3.6 logging port ...........................................................................................15-23
15.3.7 logging syslog .......................................................................................15-23
15.3.8 show logging .........................................................................................15-24
15.3.9 show logging buffered ..........................................................................15-25
15.3.10 clear logging buffered .......................................... ... ... ...........................15-25
15.3.11 show logging hosts ...............................................................................15-25
15.3.12 show logging traplogs ...........................................................................15-26
15.4 CLI Command Logging Command ................................................................15-26
15.4.1 logging cli-command .............................................................................15-26
Page 18

xviii
v1.0, March 2006
15.5 Configuration Scripting Commands ...............................................................15-27
15.5.1 script apply ...........................................................................................15-28
15.5.2 script delete ..........................................................................................15-28
15.5.3 script list ................................................................................................15-28
15.5.4 script show ............................................................................................15-28
15.5.5 script validate ........................................................................................15-29
Page 19
About This Manual 1-1
Publication Version 1.0, March 200 6
Chapter 1
About This Manual
This chapter introduces the Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200
Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Version 4.0. It describes the command-line interface
(CLI) commands used to view and configure the 7200 Series Managed Switch software.
You can access the CLI by using a direct connection to the serial port or by using telnet or
SSH over a remote network connection.
1.1 Audience
This document is for system administrators who configure and operate systems using 7200
Series Managed Switch software. Software engineers who integrate 7200 Series Managed
Switch software into their hardware platform can also benefit from a description of the
configuration options.
This document assumes that the reader has an understanding of the 7200 Series Managed
Switch software base and has read the appropriate specification for the relevant
networking device platform. It also assumes that the reader has a basic knowledge of
Ethernet and networking concepts.
1.2 Scope
This manual is written for the 7200 Series Managed Switch according to these
specifications:
Table 1-1. Manual Specifications
Product ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Managed Switch
Product Final Assembly Number
Firmware Version Number
Manual Part Number Beta Draft 2
Manual Publication Date March 2006
Page 20
Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
1-2 About This Manual
Publication Version 1.0, March 2006
1.3 Typographical Conventions
This guide uses the following typographical conventions:
1.4 Special Message Formats
This guide uses the following formats to highlight special messages:
Note: Product updates are available on the NETGEAR Web site at
http://kbserver.netgear.com/products/.
Table 1-2. Typographical conventions
italics Emphasis.
bold User input.
Small Caps DOS file and directory names.
Note: This format is used to highlight of importance or special interest.
Tip: A time-saving or resource-saving procedural step.
Warning: Ignoring a warning could result in damage to the equipment or
software malfunction.
Danger: Ignoring this type of warning could result in personal injury or death.
Page 21

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
About This Manual 1-3
Publication Version 1.0, March 200 6
1.5 How to Use This Manual
The HTML version of this manual includes the following:
•Buttons, and , for browsing forwards or backwards through the manual
one page at a time
•A button that displays the table of contents and possibly an button.
Double-click on a link in the table of contents or index to navigate directly to where
the topic is described in the manual.
•A button to access the full NETGEAR, Inc. online knowledge base for
the product model.
• Links to PDF versions of the full manual and individual chapters.
1.6 How to Print this Manual
To print this manual you can choose one of the following several options, according to
your needs.
• Printing a Page in the HTML View.
Each page in the HTML version of the manual is dedicated to a major topic. Use the
Print button on the browser toolbar to print the page contents.
• Printing a Chapter.
Use the PDF of This Chapter link at the top left of any page.
— Click the PDF of This Chapter link at the top right of any page in the chapter you
want to print. The PDF version of the chapter you were viewing opens in a
browser window.
Your computer must have the free Adobe Acrobat reader installed in order to view
and print PDF files. The Acrobat reader is available on the Adobe Web site at
http://www.adobe.com.
— Click the print icon in the window toolbar.
Tip: If your printer supports printing of two or more pages on a single sheet
of paper, you can save paper and printer ink by clicking the printer
Properties button and increasing the number of pages per sheet.
Page 22
Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
1-4 About This Manual
Publication Version 1.0, March 2006
• Printing the Full Manual.
Use the Complete PDF Manual link at the top left of any page.
— Click the Complete PDF Manual link at the top left of any page in the manual.
The PDF version of the complete manual opens in a browser window.
— Click the print icon in the window toolbar.
1.7 Revision History
Table 1-3 lists the revision history of this manual.
Tip: If your printer supports printing of two or more pages on a single sheet
of paper, you can save paper and printer ink by clicking the printer
Properties button and increasing the number of pages per sheet.
Table 1-3. Revision History of This Manual
Revision Change Description
Page 23
Overview 2-1
v1.0, March 2006
Chapter 2
Overview
The 7200 Series Managed Switch software has two purposes:
• Assist attached hardware in switching frames, based on Layer 2, 3, or 4 inform ation
contained in the frames.
• Provide a complete device management portfolio to the network administrator.
2.1 Scope
7200 Series Managed Switch software encompasses both hardware and software support.
It software is partitioned to run in the following processors:
• CPU—This code runs the networking device management portfolio and controls the
overall networking device hardware. It also assists in frame forwarding, as needed and
specified. This code is designed to run on multiple platforms with minimal changes
from platform to platform.
• Networking Device Processor—This code does the majority of the packet switching,
usually at wire speed. This code is platform dependent, and substantial changes might
exist across products.
2.2 Using the Command-Line Interface
The command-line interface (CLI) is a text-based way to manage and monitor the system.
You can access the CLI by using a direct serial connection or by using a remote logical
connection with telnet or SSH.
This section describes the CLI syntax, conventions, and modes. It contains the following
topics:
• Section 2.2.1 “Command Syntax” on page 2-2
• Section 2.2.2 “Command Conventions” on page 2-2
• Section 2.2.3 “Unit-Slot-Port Naming Convention” on page 2-4
• Section 2.2.4 “Using the “No” Form of a Command” on page 2-5
Page 24

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
2-2 Overview
v1.0, March 2006
• Section 2.2.5 “Command Modes” on page 2-5
• Section 2.2.6 “Entering CLI Commands” on page 2-8
• Section 2.2.7 “Using CLI Help” on page 2-10
• Section 2.2.8 “Accessing the CLI” on page 2-11
2.2.1 Command Syntax
A command is one or more words that might be followed by one or more parameters.
Parameters can be required or optional values.
Some commands, such as
show network or clear vlan, do not require parameters.
Other commands, such as
network parms, require that you supply a value after the
command. You must type the parameter values in a specific order, and optional parameters
follow required parameters. The following example describes the
network parms
command syntax:
Format
network parms <ipaddr> <netmask> [gateway]
• network parms is the command name.
•
<ipaddr> and <netmask> are parameters and represent required values that you must
enter after you type the command keywords.
•
[gateway] is an optional parameter, so you are not required to enter a value in place
of the parameter.
The CLI Command Reference lists each command by the command name and provides a
brief description of the command. Each command reference also contains the following
information:
• Format shows the command keywords and the req uired and optional parameters.
• Mode identifies the command mode you must be in to access the command.
• Default shows the default value, if any, of a configurable setting on the device.
The
show commands also contain a description of the information that the command
displays.
2.2.2 Command Conventions
In this document, the command name is in bold font. Parameters are in italic font. You
must replace the parameter name with an appropriate value, which might be a name or
number. Parameters are order dependent.
Page 25
Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
Overview 2-3
v1.0, March 2006
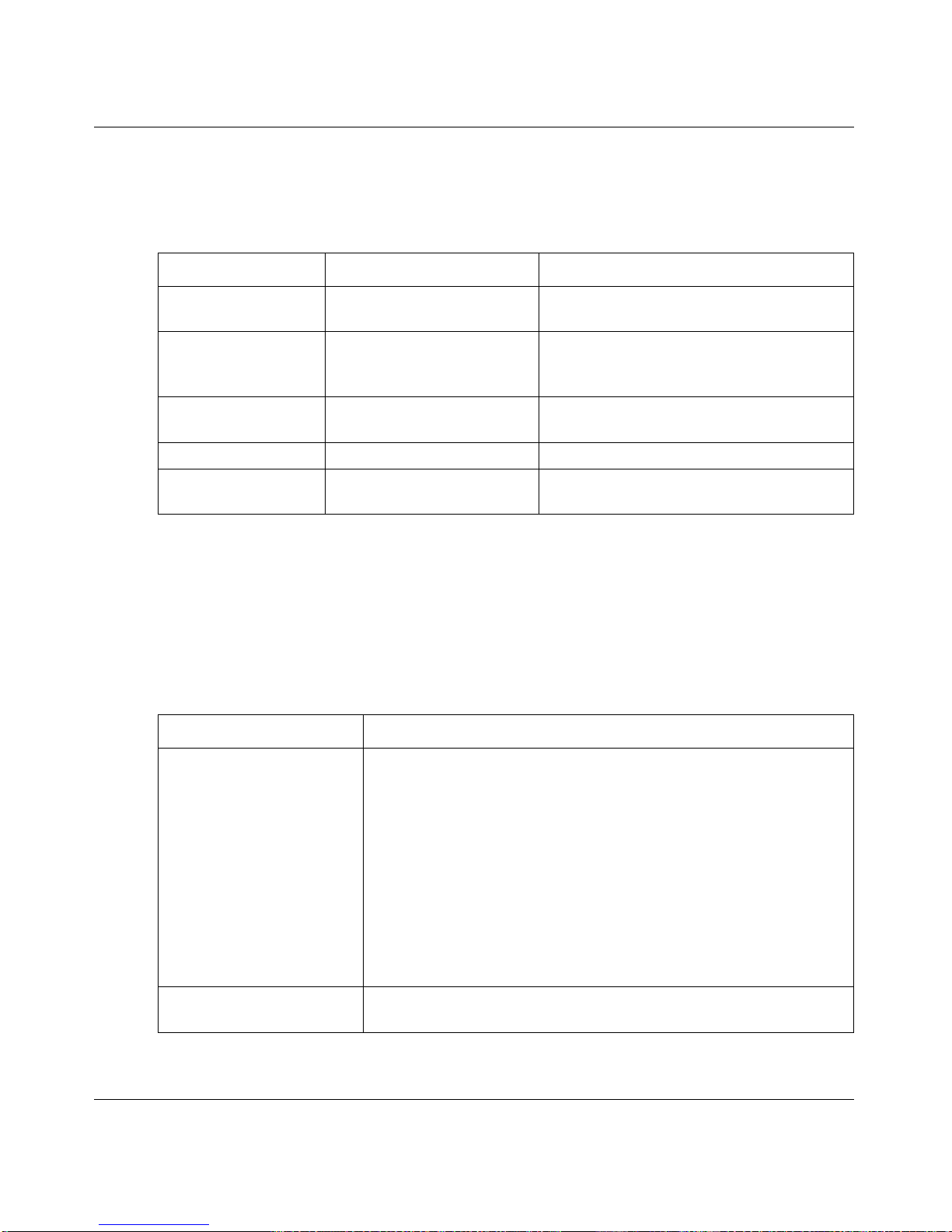
The parameters for a command might include mandatory values, optional values, or
keyword choices. Table 2-1 describes the conventions this document uses to distinguish
between value types.
2.2.2.1 Common Parameter Values
Parameter values might be names (strings) or numbers. To use spaces as part of a name
parameter, enclose the name value in double quotes. For example, the expression “System
Name with Spaces” forces the system to accept the spaces. Empty strings (“ ”) are not
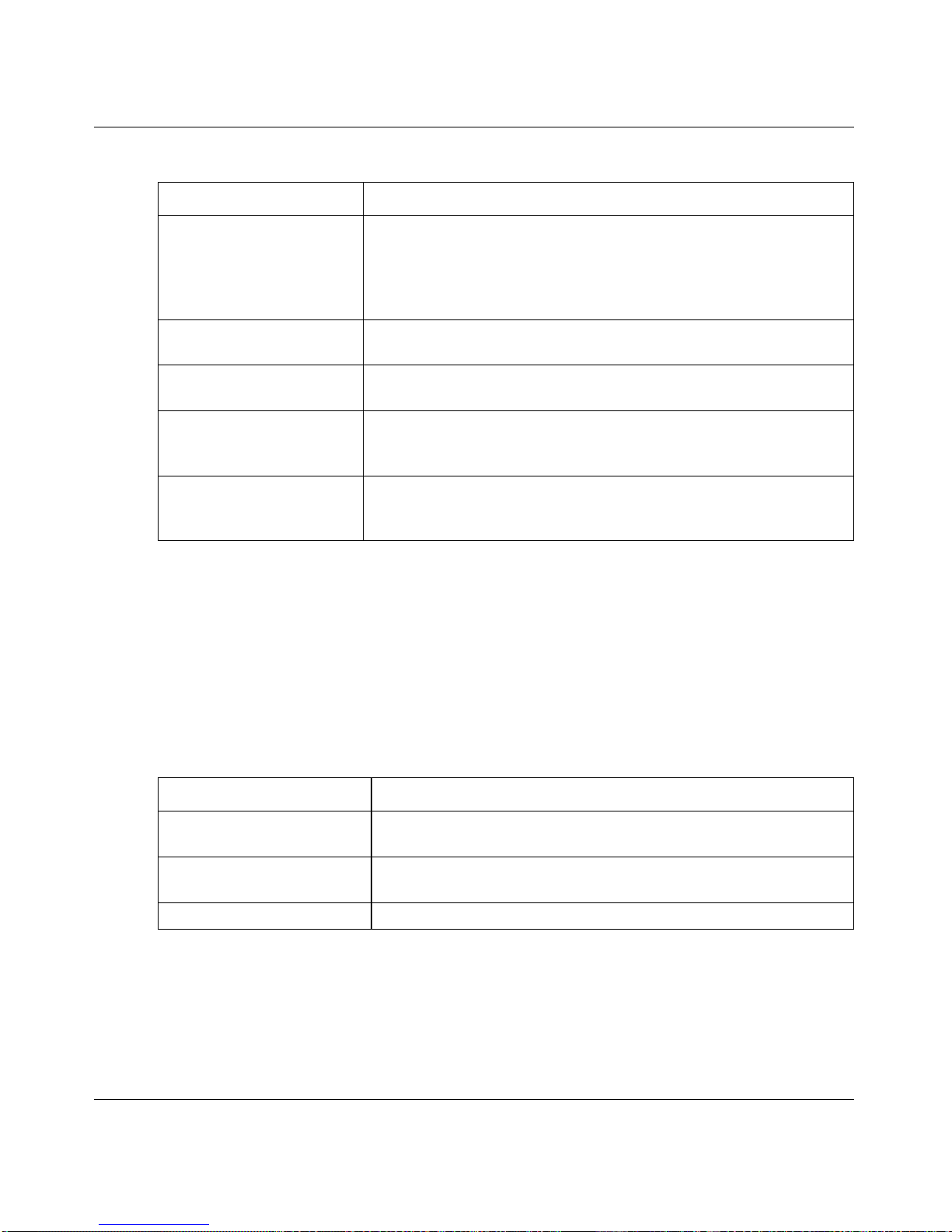
valid user-defined strings. Table 2-2 describes common parameter values and value
formatting.
Table 2-1. Parameter Conventions
Symbol Example Description
<> angle brackets <value> Indicates that you must enter a value in
place of the brackets and text inside them.
[] square brackets [value] Indicates an optional parameter that you
can enter in place of the brackets and text
inside them.
{} curly braces {choice1 | choice2} Indicates that you must select a
parameter from the list of choices.
| Vertical bars choice1 | choice2 Separates the mutually exclusive choices.
[{}] Braces within
square brackets
[{choice1} choice2}] Indicate a choice within an optional
element.
Table 2-2. Parameter Descriptions
Parameter Description
ipaddr This parameter is a valid IP address. You can enter the IP address
in the following formats:
a (32 bits)
a.b (8.24 bits)
a.b.c (8.8.16 bits)
a.b.c.d
(8.8.8.8)
In addition to these formats, the CLI accepts decimal, hexidecimal
and octal formats through the following input formats (where n is
any valid hexidecimal, octal or decimal number):
0xn (CLI assumes hexidecimal format)
0n (CLI assumes octal format with leading zeros)
n (CLI assumes decimal format)
macaddr The MAC address format is six hexadecimal numbers separated by
colons, for example 00:06:29:32:81:40.
Page 26
Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
2-4 Overview
v1.0, March 2006
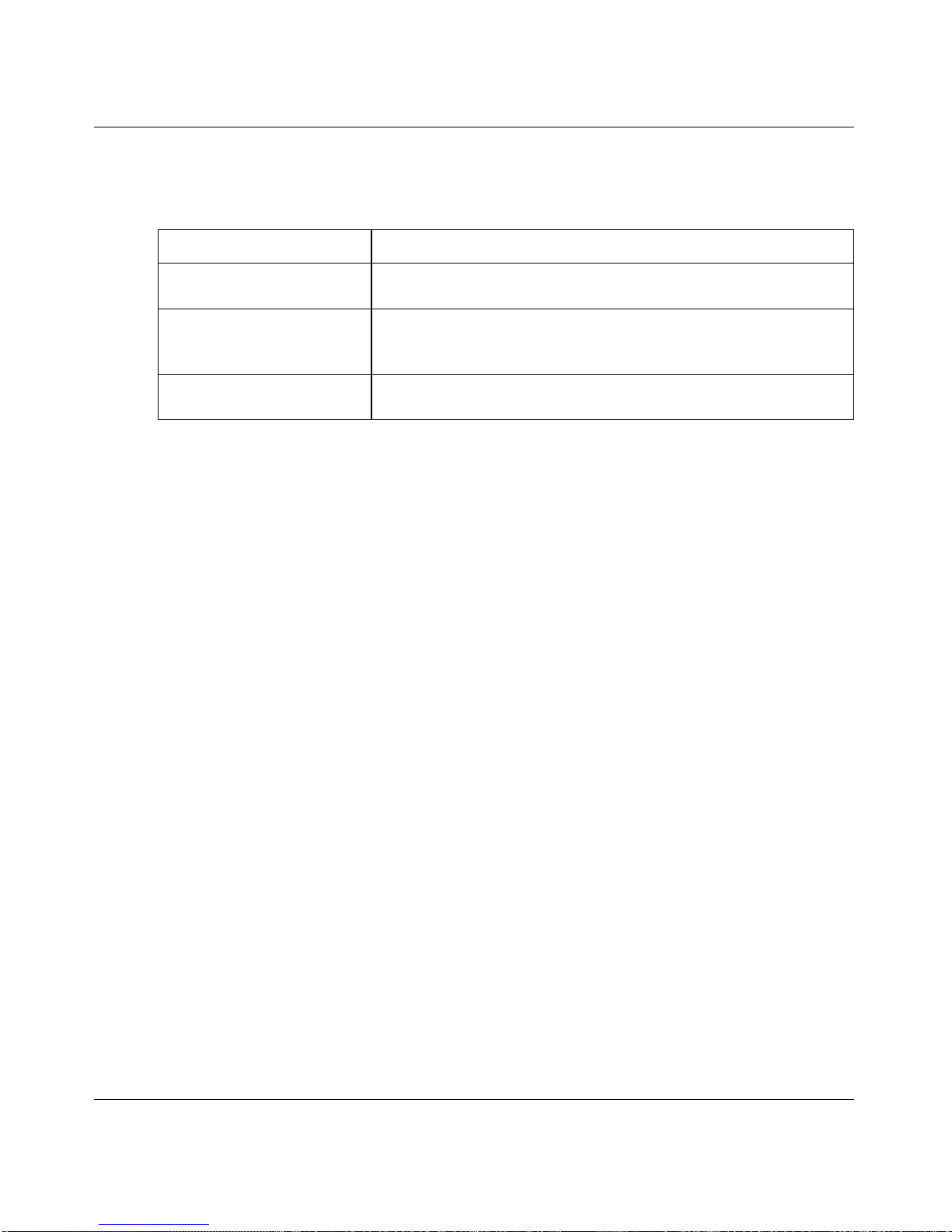
2.2.3 Unit-Slot-Port Naming Convention
7200 Series Managed Switch software references physical entities such as cards and ports
by using a Unit-Slot-Port (USP) naming convention. The software also uses this
convention to identify certain logical entities, such as port-channel interfaces.
The slot number has two uses. In the case of physical ports, it identifies the card
containing the ports. In the case of logical and CPU ports it also identifies the type of
interface or port.
areaid Enter area IDs in dotted-decimal notation (for example, 0.0.0.1). An
area ID of 0.0.0.0 is reserved for the backbone. Area IDs have the
same format as IP addresses but are distinct from IP addresses.
You can use the IP network number of the sub-netted network for
the area ID.
routerid Enter the value of <routerid> in dotted-decimal notation, such as
0.0.0.1. A router ID of 0.0.0.0 is invalid.
Interface or slot/port Valid slot and port number separated by forward slashes. For
example, 0/1 represents slot number 0 and port number 1.
Logical Interface Logical slot and port number. This is applicable in the case of a
port-channel (LAG). You can use the logical slot/port to configure
the port-channel.
Character strings Use double quotation marks to identify character strings, for
example, “System Name with Spaces”. An empty string (“”) is not
valid.
Table 2-3. Type of Slots
Slot Type Description
Physical slot numbers Physical slot numbers begin with zero, and are allocated up to the
maximum number of physical slots.
Logical slot numbers Logical slots immediately follow physical slots and identify port-
channel (LAG) or router interfaces.
CPU slot numbers The CPU slots immediately follow the logical slots.
Table 2-2. Parameter Descriptions
Parameter Description
Page 27
Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
Overview 2-5
v1.0, March 2006
The port identifies the specific physical port or logical interface being managed on a given
slot.
2.2.4 Using the “No” Form of a Command
The no keyword is a specific form of an existing command and does not represent a new
or distinct command. Almost every configuration command has a
no form. In general, use
the
no form to reverse the action of a command or reset a value back to the default. For
example, the
no shutdown configuration command reverses the shutdown of an interface.
Use the command without the keyword
no to re-enable a disabled feature or to enable a
feature that is disabled by default.
Only the configuration commands are available in the
no form.
2.2.5 Command Modes
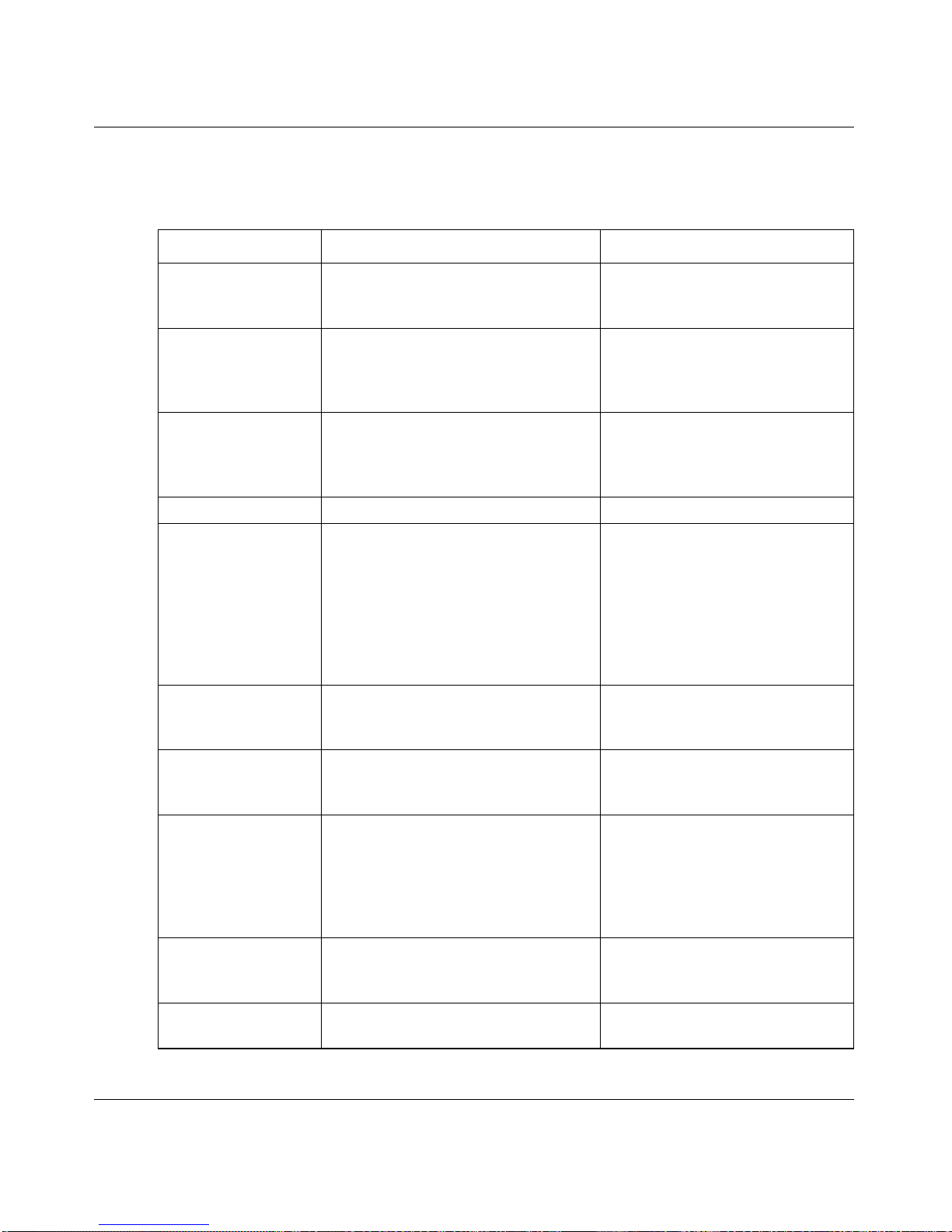
The CLI groups commands into modes according to the command function. Each of the
command modes supports specific 7200 Series Managed Switch software commands. The
commands in one mode are not available until you switch to that particular mode, with the
exception of the User EXEC mode commands. You can execute the User EXEC mode
commands in the Privileged EXEC mode.
Table 2-4. Type of Ports
Port Type Description
Physical Ports The physical ports for each slot are numbered sequentially starting
from zero.
Logical Interfaces Port-channel or Link Aggregation Group (LAG) interfaces are
logical interfaces that are only used for bridging functions.
VLAN routing interfaces are only used for routing functions.
CPU ports CPU ports are handled by the driver as one or more physical
entities located on physical slots.
Page 28
Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
2-6 Overview
v1.0, March 2006
The command prompt changes in each command mode to help you identify the current
mode. Table 2-5 describes the command modes and the prompts visible in that mode.
Table 2-5. CLI Command Modes
Command Mode Prompt Mode Description
User EXEC
Switch>
Contains a limited set of
commands to view basic system
information.
Privileged EXEC
Switch#
Allows you to issue any EXEC
command, enter the VLAN
mode, or enter the
Global
Configuration mode.
Global Config
Switch (Config)#
Groups general setup commands
and permits you to make
modifications to the running
configuration.
VLAN Config
Switch (Vlan)#
Groups all the VLAN commands.
Interface Config
Switch (Interface <unit/slot/
port>)#
Allows you to enable or modify
the operation of an interface and
provides access to the router
interface configuration
commands.
Use this mode to set up a
physical port for a specific logical
connection operation.
Line Config
Switch (line)#
Allows you to configure various
telnet settings and the console
interface.
Policy Map Config
Switch (Config policy-map)#
Allows you to access the QoS
Policy-Map configuration mode
to configure the QoS Policy-Map.
Policy Class Config
Switch (Config policy-class-map)#
Consists of class creation,
deletion, and matching
commands. The class match
commands specify Layer 2,
Layer 3, and general match
criteria.
Class Map Config
Switch (Config class-map)#
Allows you to access the QoS
Class-Map configuration mode to
configure QoS class maps.
Router OSPF
Config
Switch (Config router)#
Allows you to access the router
OSPF configuration commands.
Page 29
Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
Overview 2-7
v1.0, March 2006
Table 2-6 explains how to enter or exit each command mode.
Router RIP Config
Switch (Config router)#
Allows you to access the router
RIP configuration commands.
Router BGP Config
Switch (Config router)#
Allows you to access the router
BGP4 configuration commands.
MAC Access-list
Config
Switch (Config mac-access-list)#
Allows you to create a MAC
Access-List and to enter the
mode containing Mac AccessList configuration commands.
DHCP Pool Config
Switch (Config dhcp-pool)#
Allows you to access the DHCP
Pool configuration.
Stack Global
Config Mode
Switch (Config stack)#
Allows you to access the Stack
Global Config Mode.
Table 2-6. CLI Mode Access and Exit
Command Mode Access Method Exit or Access Previous Mode
User EXEC This is the first level of access. To exit, enter logout.
Privileged EXEC From the User EXEC mode, enter
enable.
To exit to the User EXEC mode, enter
exit or press Ctrl-Z.
Global Config From the Privileged EXEC mode, enter
configure.
To exit to the Privileged EXEC mode,
enter exit, or press Ctrl-Z.
VLAN Config From the Privileged EXEC mode, enter
vlan database.
To exit to the Privileged EXEC mode,
enter exit, or press Ctrl-Z.
Interface Config From the Global Config mode, enter
interface <slot/port>.
To exit to the Global Config mode,
enter exit. To return to the Privileged
EXEC mode, enter Ctrl-Z.
Line Config From the Global Config mode, enter
lineconfig.
To exit to the Global Config mode,
enter exit. To return to the Privileged
EXEC mode, enter Ctrl-Z.
Policy-Map
Config
From the Global Config mode, enter
policy-map.
To exit to the Global Config mode,
enter exit. To return to the Privileged
EXEC mode, enter Ctrl-Z.
Policy-Class-Map
Config
From the Policy Map mode enter
class.
To exit to the Policy Map mode, enter
exit. To return to the Privileged
EXEC
mode, enter Ctrl-Z.
Table 2-5. CLI Command Modes (continued)
Command Mode Prompt Mode Description
Page 30
Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
2-8 Overview
v1.0, March 2006
2.2.6 Entering CLI Commands
The 7200 Series Managed Switch supports several features to help you enter commands.
2.2.6.1 Command Completion and Abbreviation
Command completion finishes spelling the command when you type enough letters of a
command to uniquely identify the command keyword. Once you have entered enough
letters, press the SPACEBAR or TAB key to complete the word.
Command abbreviation allows you to execute a command when you type enough letters of
a command to uniquely identify the command. You must enter all of the required
keywords and parameters before you enter the command.
Class-Map
Config
From the Global Config mode, enter
class-map.
To exit to the Global Config mode,
enter exit. To return to the Privileged
EXEC mode, enter Ctrl-Z.
Router OSPF
Config
From the Global Config mode, enter
router ospf.
To exit to the Global Config mode,
enter exit. To return to the Privileged
EXEC mode, enter Ctrl-Z.
Router RIP
Config
From the Global Config mode, enter
router rip.
To exit to the Global Config mode,
enter exit. To return to the Privileged
EXEC mode, enter Ctrl-Z.
Router BGP
Config
From the Global Config mode, enter
router bgp <asnumber>.
To exit to the Global Config mode,
enter exit. To return to the Privileged
EXEC mode, enter Ctrl-Z.
MAC Access-list
Config
From the Global Config mode enter
mac access-list extended
<name>.
To exit to the Global Config mode,
enter exit. To return to the Privileged
EXEC mode, enter Ctrl-Z.
DHCP Pool
Config
From the Global Config mode, enter
ip dhcp pool
<name>.
To exit to the Global Config mode,
enter exit. To return to the Privileged
EXEC mode, enter Ctrl-Z.
Stack Global
Config Mode
From the Global Config mode, enter the
stack command.
To exit to the Global Config mode,
enter the exit command. To re turn
to the Privileged EXEC mode, enter
Ctrl-Z.
Table 2-6. CLI Mode Access and Exit (continued)
Command Mode Access Method Exit or Access Previous Mode
Page 31

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
Overview 2-9
v1.0, March 2006
2.2.6.2 CLI Error Messages
If you enter a command and the system is unable to execute it, an error message appears.
Table 2-7 describes the most common CLI error messages.
2.2.6.3 CLI Line-Editing Conventions
Table 2-8 describes the key combinations you can use to edit commands or increase the
speed of command entry. You can access this list from the CLI by entering
help from the
User or Privileged EXEC modes.
Table 2-7. CLI Error Messages
Message Text Description
% Invalid input detected at '^'
marker.
Indicates that you entered an incorrect or
unavailable command. The carat (^) shows
where the invalid text is detected. This message
also appears if any of the parameters or values
are not recognized.
Command not found / Incomplete
command. Use ? to list commands.
Indicates that you did not enter the required
keywords or values.
Ambiguous command Indicates that you did not enter enough letters to
uniquely identify the command.
Table 2-8. CLI Editing Conventions
Key Sequence Description
DEL or Backspace Delete previous character
Ctrl-A Go to beginning of line
Ctrl-E Go to end of line
Ctrl-F Go forward one character
Ctrl-B Go backward one character
Ctrl-D Delete current character
Ctrl-U, X Delete to beginning of line
Ctrl-K Delete to end of line
Ctrl-W Delete previous word
Ctrl-T Transpose previous character
Ctrl-P Go to previous line in history buffer
Ctrl-R Rewrites or pastes the line
Ctrl-N Go to next line in history buffer
Ctrl-Y Prints last deleted character
Ctrl-Q Enables serial flow
Page 32

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
2-10 Overview
v1.0, March 2006
2.2.7 Using CLI Help
Enter a question mark (?) at the command prompt to display the commands available in
the current mode.
(switch) >?
enable Enter into user privilege mode.
help Display help for various special keys.
logout Exit this session. Any unsaved changes are lost.
ping Send ICMP echo packets to a specified IP address.
show Display switch options and settings.
Enter a question mark (?) after each word you enter to display available command
keywords or parameters.
(switch) #network ?
javamode Enable/Disable.
parms Configure Network Parameters of the router.
protocol Select DHCP, BootP, or None as the network con fig
protocol.
mgmt_vlan Configure the Management VLAN ID of the switch.
If the help output shows a parameter in angle brackets, you must replace the parameter
with a value.
(switch) #network parms ?
<ipaddr> Enter the IP Address.
If there are no additional command keywords or parameters, or if additional parameters
are optional, the following message appears in the output:
<cr> Press Enter to execute the command
Ctrl-S Disables serial flow
Ctrl-Z Return to root command prompt
Tab, <SPACE> Command-line completion
Exit Go to next lower command prompt
? List available commands, keywords, or parameters
Table 2-8. CLI Editing Conventions
Key Sequence Description
Page 33

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
Overview 2-11
v1.0, March 2006
You can also enter a question mark (?) after typing one or more characters of a word to list
the available command or parameters that begin with the letters, as shown in the following
example:
(switch) #show m?
mac-addr-table mac-address-table monitor
2.2.8 Accessing the CLI
You can access the CLI by using a direct console connection or by using a telnet or SSH
connection from a remote management host.
For the initial connection, you must use a direct connection to the console port. You
cannot access the system remotely until the system has an IP address and subnet mask.
You can set the network configuration information manually, or you can configure the
system to accept these settings from a BOOTP or DHCP server on your network. For more
information, see Section 3.1 “Network Interface Commands” on page 3-1.
Page 34

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
2-12 Overview
v1.0, March 2006
Page 35

Administrative Access Commands 3-1
v1.0, March 2006
Chapter 3
Administrative Access Commands
This section describes the management access and basic port configuration commands
available in the 7200 Series Managed Switch CLI.
This section contains the following topics:
• Section 3.1 “Network Interface Commands” on page 3-1
• Section 3.2 “Console Port Access Commands” on page 3-5
• Section 3.3 “Telnet Commands” on page 3-8
• Section 3.4 “Secure Shell (SSH) Command” on page 3-13
• Section 3.5 “Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) Commands” on page 3-15
• Section 3.6 “User Account Commands” on page 3-18
The commands in this section are divided into two functional groups:
• Show commands display switch settings, statistics, and other information.
• Configuration commands configure features and options of the switch. For every
configuration command, there is a show command that displays the configuration
setting.
To manage the device by using SNMP, see “SNMP Commands” in Chapter 10.
3.1 Network Interface Commands
This section describes the commands you use to configure a logical interface for
management access.
Note: The service port commands are for out-of-band network management
using the dedicated service port on the platform. The network commands
are used for in-band management using the data ports.
Page 36

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
3-2 Administrative Access Commands
v1.0, March 2006
3.1.1 enable
This command gives you access to the Privileged EXEC mode. From the Privileged
EXEC mode, you can configure the network interface.
Format
enable
Mode User EXEC
3.1.2 serviceport ip
This command sets the IP address, the netmask and the gateway of the network
management port.
Format
serviceport ip <ipaddr> <netmask> [gateway]
Mode Privileged EXEC
3.1.3 serviceport protocol
This command specifies the network management port configuration protocol. If you
modify this value, the change is effective immediately. If you use the
bootp parameter,
the switch periodically sends requests to a BootP server until a response is received. If you
use the
dhcp parameter, the switch periodically sends requests to a DHCP server until a
response is received. If you use the
none parameter, you must configure the network
information for the switch manually.
Format
serviceport protocol {none | bootp | dhcp}
Mode Privileged EXEC
3.1.4 network parms
This command sets the IP Address, subnet mask and gateway of the device. The IP
Address and the gateway must be on the same subnet.
Format
network parms <ipaddr> <netmask> [<gateway>]
Mode Privileged EXEC
3.1.5 network mgmt_vlan
This command configures the Management VLAN ID.
Default 1
Format
network mgmt_vlan <1-4069>
Mode Privileged EXEC
Page 37

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
Administrative Access Commands 3-3
v1.0, March 2006
3.1.5.1 no network mgmt_vlan
This command sets the Management VLAN ID to the default.
Format
no network mgmt_vlan
Mode Privileged EXEC
3.1.6 network protocol
This command specifies the network configuration protocol to be used. If you modify this
value, change is effective immediately. If you modify this value, the change is effective
immediately. If you use the
bootp parameter, the switch periodically sends requests to a
BootP server until a response is received. If you use the
dhcp parameter, the switch
periodically sends requests to a DHCP server until a response is received. If you use the
none parameter, you must configure the network information for the switch manually.
Default none
Format
network protocol {none | bootp | dhcp}
Mode Privileged EXEC
3.1.7 show network
This command displays configuration settings associated with the switch's network
interface. The network interface is the logical interface used for in-band connectivity with
the switch via any of the switch's front panel ports. The configuration parameters
associated with the switch's network interface do not affect the configuration of the front
panel ports through which traffic is switched or routed.
Format
show network
Modes Privileged EXEC
User EXEC
IP Address The IP address of the interface. The factory default value is
0.0.0.0
Subnet Mask The IP subnet mask for this interface. The factory default
value is 0.0.0.0
Default Gateway The default gateway for this IP interface. The factory default
value is 0.0.0.0
Burned In MAC
Address The burned in MAC address used for in-band connectivity.
Page 38

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
3-4 Administrative Access Commands
v1.0, March 2006
Locally
Administered
MAC Address If desired, a locally administered MAC address can be con-
figured for in-band connectivity. To take effect, 'MAC
Address Type' must be set to 'Locally Administered'. Enter
the address as twelve hexadecimal digits (6 bytes) with a
colon between each byte. Bit 1 of byte 0 must be set to a 1
and bit 0 to a 0, i.e. byte 0 should have the following mask
'xxxx xx10'. The MAC address used by this bridge when it
must be referred to in a unique fashion. It is recommended
that this be the numerically smallest MAC address of all ports
that belong to this bridge. However it is only required to be
unique. When concatenated with dot1dStpPriority a unique
BridgeIdentifier is formed which is used in the Spanning Tree
Protocol.
MAC Address
Type Specifies which MAC address should be used for in-band
connectivity. The choices are the burned in or the Locally
Administered address. The factory default is to use the
burned in MAC address.
Network
Configuration
Protocol Current Indi cates which network protocol is being used. The options
are bootp | dhcp | none.
Java Mode Specifies if the switch should allow access to the Java applet
in the header frame. Enabled means the applet can be viewed.
The factory default is disabled.
Web Mode Specifies if the switch should allow access to the Web Inter-
face.
3.1.8 show serviceport
This command displays service port configuration information.
Format
show serviceport
Mode Privileged EXEC
IP Address The IP address of the interface. The factory default value is
0.0.0.0
Page 39

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
Administrative Access Commands 3-5
v1.0, March 2006
Subnet Mask The IP subnet mask for this interface. The factory default
value is 0.0.0.0
Default Gateway The default gateway for this IP interface. The factory default
value is 0.0.0.0
ServPort
Configuration
Protocol Current Indicates what network protocol was used on the last, or cur-
rent power-up cycle, if any.
Burned in MAC
Address The burned in MAC address used for in-band connectivity.
3.2 Console Port Access Commands
This section describes the commands you use to configure the console port. Y ou can use a
serial cable to connect a management host directly to the console port of the switch.
3.2.1 configuration
This command gives you access to the Global Config mode. From the Global Config
mode, you can configure a variety of system settings, including user accounts. From the
Global Config mode, you can enter other command modes, including Line Config mode.
Format
configuration
Mode Privileged EXEC
3.2.2 lineconfig
This command gives you access to the Line Config mode, which allows you to configure
various telnet settings and the console port.
Format
lineconfig
Mode Global Config
Page 40

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
3-6 Administrative Access Commands
v1.0, March 2006
3.2.3 serial baudrate
This command specifies the communication rate of the terminal interface. The supported
rates are 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200, 38400, 57600, 115200.
Default 9600
Format
serial baudrate {1200 | 2400 | 4800 | 9600 | 19200
| 38400 | 57600 | 115200}
Mode Line Config
3.2.3.1 no serial baudrate
This command sets the communication rate of the terminal interface.
Format
no serial baudrate
Mode Line Config
3.2.4 serial timeout
This command specifies the maximum connect time (in minutes) without console activity.
A value of 0 indicates that a console can be connected indefinitely. The time range is 0 to
160.
Default 5
Format
serial timeout <0-160>
Mode Line Config
3.2.4.1 no serial timeout
This command sets the maximum connect time (in minutes) without console activity.
Format
no serial timeout
Mode Line Config
Page 41

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
Administrative Access Commands 3-7
v1.0, March 2006
3.2.5 show serial
This command displays serial communication settings for the switch.
Format
show serial
Modes Privileged EXEC
User EXEC
Serial Port Login
Timeout
(minutes) Specifies the time, in minutes, of inactivity on a Serial port
connection, after which the Switch will close the connection.
Any numeric value between 0 and 160 is allowed, the factory
default is 5. A value of 0 disables the timeout.
Baud Rate (bps) The default baud rate at which the serial port will try to con-
nect. The available values are 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600,
19200, 38400,57600, and 1 15 200 baud. The factory default is
9600 baud.
Character Size
(bits) The number of bits in a character. The number of bits is
always 8.
Flow Control Whether Hardware Flow-Control is enabled or disabled.
Hardware Flow Control is always disabled.
Stop Bit s The number of Stop bits per character. The number of Stop
bits is always 1.
Parity Type The Parity Method used on the Serial Port. The Parity
Method is always None.
Page 42

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
3-8 Administrative Access Commands
v1.0, March 2006
3.3 Telnet Commands
This section describes the commands you use to configure and view telnet settings. You
can use telnet to manage the device from a remote management host.
3.3.1 telnet
This command establishes a new outbound telnet connection to a remote host. The host
value must be a valid IP address. Valid values for port should be a valid decimal integer in
the range of 0 to 65535, where the default value is 23. If [debug] is used, the current telnet
options enabled is displayed. The optional line parameter sets the outbound telnet
operational mode as ‘linemode’, where by default, the operational mode is ‘character
mode’. The noecho option disables local echo.
Format
telnet <host> <port> [debug] [line] [noecho]
Modes Privileged EXEC
User EXEC
3.3.2 transport input telnet
This command regulates new telnet sessions. If sessions are enabled, new telnet sessions
can be established until there are no more sessions available. If sessions are disabled, no
new telnet sessions are established. An established session remains active until the session
is ended or an abnormal network error ends the session.
Default enabled
Format
transport input telnet
Mode Line Config
3.3.2.1 no transport input telnet
This command disables telnet sessions. If sessions are disabled, no new telnet sessions are
established.
Format
no transport input telnet
Mode Line Confi g
Page 43

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
Administrative Access Commands 3-9
v1.0, March 2006
3.3.3 transport output telnet
This command regulates new outbound telnet connections. If enabled, new outbound
telnet sessions can be established until it reaches the maximum number of simultaneous
outbound telnet sessions allowed. If disabled, no new outbound telnet session can be
established. An established session remains active until the session is ended or an
abnormal network error ends it.
Default enabled
Format
transport output telnet
Mode Line Confi g
3.3.3.1 no transport output telnet
This command disables new outbound telnet connections. If disabled, no new outbound
telnet connection can be established.
Format
no transport output telnet
Mode Line Confi g
3.3.4 session-limit
This command specifies the maximum number of simultaneous outbound telnet sessions.
A value of 0 indicates that no outbound telnet session can be established.
Default 5
Format
session-limit <0-5>
Mode Line Confi g
3.3.4.1 no session-limit
This command sets the maximum number of simultaneous outbound telnet sessions to the
default value.
Format
no session-limit
Mode Line Confi g
Page 44

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
3-10 Administrative Access Commands
v1.0, March 2006
3.3.5 session-timeout
This command sets the telnet session timeout value.The timeout value unit of time is
minutes. A value of 0 indicates that a session remains active indefinitely.
Default 0
Format
session-timeout <0-160>
Mode Line Config
3.3.5.1 no session-timeout
This command sets the telnet session timeout value to the default. The timeout value unit
of time is minutes.
Format
no session-timeout
Mode Line Config
3.3.6 telnetcon maxsessions
This command specifies the maximum number of telnet connection sessions that can be
established. A value of 0 indicates that no telnet connectio n can be established. The range
is 0 to 5.
Default 5
Format
telnetcon maxsessions <0-5>
Mode Privileged EXEC
3.3.6.1 no telnetcon maxsessions
This command sets the maximum number of telnet connection sessions that can be
established to the default value.
Format
no telnetcon maxsessions
Mode Privileged EXEC
Page 45

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
Administrative Access Commands 3-11
v1.0, March 2006
3.3.7 telnetcon timeout
This command sets the telnet connection session timeout value, in minutes. A session is
active as long as the session has not been idle for the value you set, which ranges from 1160 minutes.
Default 5
Format
telnetcon timeout <1-160>
Mode Privileged EXEC
3.3.7.1 no telnetcon timeout
This command sets the telnet connection session timeout value to the default.
Format
no telnetcon timeout
Mode Privileged EXEC
3.3.8 show telnet
This command displays the current outbound telnet settings.
Format
show telnet
Modes Privileged EXEC
User EXEC
Outbound Telnet
Login Timeout Indicates the number of minutes an outbound telnet session is
allowed to remain inactive before being logged off.
Maximum Number
of Outbound
Telnet Sessions Indicates the number of simultaneous outbound telnet con-
nections allowed.
Note: Changing the timeout value for active sessions does not become effective
until the session is reaccessed. Also, any keystroke activates the new
timeout duration.
Note: Changing the timeout value for active sessions does not become effective
until the session is reaccessed. Also, any keystroke activates the new
timeout duration.
Page 46

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
3-12 Administrative Access Commands
v1.0, March 2006
Allow New
Outbound Telnet
Sessions Indicates whether outbound telnet sessions are allowed.
3.3.9 show telnetcon
This command displays telnet settings.
Format
show telnetcon
Modes Privileged EXEC
User EXEC
Remote
Connection Login
Timeout
(minutes) This object indicates the number of minutes a remote connec-
tion session is allowed to remain inactive before being logged
off. May be specified as a number from 1 to 160. The factory
default is 5.
Maximum Number
of Remote
Connection
Sessions This object indicates the number of simultaneous remote con-
nection sessions allowed. The factory default is 5.
Allow New Telnet
Sessions Indicates that new telnet sessions will not be allowed when
set to no. The factory default value is yes.
Page 47

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
Administrative Access Commands 3-13
v1.0, March 2006
3.4 Secure Shell (SSH) Command
This section describes the commands you use to configure SSH access to the switch. Use
SSH to access the switch from a remote management host.
3.4.1 ip ssh
This command is used to enable SSH.
Default disabled
Format
ip ssh
Mode Privileged EXEC
3.4.1.1 no ip ssh
This command is used to disable SSH.
Format
no ip ssh
Mode Privileged EXEC
3.4.2 ip ssh protocol
This command is used to set or remove protoc ol levels (or versions) for SSH. Either SSH1
(1), SSH2 (2), or both SSH 1 and SSH 2 (1 and 2) can be set.
Default 1 and 2
Format
ip ssh protocol [1] [2]
Mode Privileged EXEC
Note: The system allows a maximum of 5 SSH sessions.
Page 48

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
3-14 Administrative Access Commands
v1.0, March 2006
3.4.3 sshcon maxsessions
This command specifies the maximum number of SSH connection sessions that can be
established. A value of 0 indicates that no ssh connection can be established. The range is
0 to 5.
Default 5
Format
sshcon maxsessions <0-5>
Mode Privileged EXEC
3.4.3.1 no sshcon maxsessions
This command sets the maximum number of allowed SSH connection sessions to the
default value.
Format
no sshcon maxsessions
Mode Privileged EXEC
3.4.4 sshcon timeout
This command sets the SSH connection session timeout value, in minutes. A session is
active as long as the session has been idle for the value set. The time is a decimal value
from 1 to 160.
Changing the timeout value for active sessions does not become effective until the session
is re accessed. Also, any keystroke activates the new timeout duration.
Default 5
Format
sshcon timeout <1-160>
Mode Privileged EXEC
3.4.4.1 no sshcon timeout
This command sets the SSH connection session timeout value, in minutes, to the default.
Changing the timeout value for active sessions does not become effective until the session
is re accessed. Also, any keystroke activates the new timeout duration.
Format
no sshcon timeout
Mode Privileged EXEC
3.4.5 show ip ssh
This command displays the ssh settings.
Page 49

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
Administrative Access Commands 3-15
v1.0, March 2006
Format show ip ssh
Mode Privileged EXEC
Administrative
Mode This field indicates whether the administrative mode of SSH
is enabled or disabled.
Protocol Level The protocol level may have the values of version 1, version
2 or both versions 1 and version 2.
Connections This field specifies the current SSH connections.
3.5 Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) Commands
This section describes the commands you use to configure HTTP access to the switch.
Access to the switch by using a Web browser is enabled by default. Everything you can
view and configure by using the CLI is also available by using the Web.
3.5.1 ip http secure-port
This command is used to set the SSL port where port can be 1-65535 and the default is
port 443.
Default 443
Format
ip http secure-port <portid>
Mode Privileged EXEC
3.5.1.1 no ip http secure-port
This command is used to reset the SSL port to the default value.
Format
no ip http secure-port
Mode Privileged EXEC
Page 50

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
3-16 Administrative Access Commands
v1.0, March 2006
3.5.2 ip http secure-protocol
This command is used to set protocol levels (versions). The protocol level can be set to
TLS1, SSL3 or to both TLS1 and SSL3.
Default SSL3 and TLS1
Format
ip http secure-protocol [SSL3] [TLS1]
Mode Privileged EXEC
3.5.3 ip http secure-server
This command is used to enable the secure socket layer for secure HTTP.
Default disabled
Format
ip http secure-server
Mode Privileged EXEC
3.5.3.1 no ip http secure-server
This command is used to disable the secure socket layer for secure HTTP.
Format
no ip http secure-server
Mode Privileged EXEC
3.5.4 ip http server
This command enables access to the switch through the Web interface. When access is
enabled, you can login to the switch from the Web interface. When access is disabled, you
cannot login to the switch's Web server. Disabling the Web interface takes effect
immediately and affects all interfaces.
Default enabled
Format
ip http server
Mode Privileged EXEC
3.5.4.1 no ip http server
This command disables access to the switch through the Web interface. When access is
disabled, you cannot login to the switch's Web server.
Format
no ip http server
Mode Privileged EXEC
Page 51

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
Administrative Access Commands 3-17
v1.0, March 2006
3.5.5 network javamode
This command specifies whether or not the switch should allow access to the Java applet
in the header frame of the Web interface. When access is enabled, the Java applet can be
viewed from the Web interface. When access is disabled, the user cannot view the Java
applet.
Default enabled
Format
network javamode
Mode Privileged EXEC
3.5.5.1 no network javamode
This command disallows access to the Java applet in the header frame of the Web
interface. When access is disabled, the user cannot view the Java applet.
Format
no network javamode
Mode Privileged EXEC
3.5.6 show ip http
This command displays the http settings for the switch.
Format
show ip http
Mode Privileged EXEC
Secure-Server
Administrative
Mode Indicates whether the administrative mode of secure HTTP is
enabled or disabled.
Secure Protocol
Level Possible values are SSL3, TSL1, or both SSL3 and TSL1.
Secure Port This field specifies the port configured for SSLT.
HTTP Mode This field indicates whether the HTTP mode is enabled or
disabled.
Page 52

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
3-18 Administrative Access Commands
v1.0, March 2006
3.6 User Account Commands
This section describes the commands you use to add, manage, and delete system users.
The 7200 Series Managed Switch has two default users: admin and guest. The admin user
can view and configure system settings, and the guest user can view settings.
3.6.1 users name
This command adds a new user account, if space permits. The account <username> can be
up to eight characters in length. You can use alphanumeric char acters as well as the dash
(‘-’) and underscore (‘_’). The
<username> is not case-sensitive.
You can define up to six user names.
Format
users name <username>
Mode Global Config
3.6.1.1 no users name
This command removes a user account.
Format
no users name <username>
Mode Global Config
Note: You cannot delete the admin user, and there is only one user allowed with
read/write privileges. You can configure up to five read-only users on the
system.
Note: You cannot delete the “admin” user account.
Page 53

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
Administrative Access Commands 3-19
v1.0, March 2006
3.6.2 users passwd
Use this command to change a password. Passwords are a maximum of eight
alphanumeric characters. If a user is authorized for authentication or encryption is
enabled, the password length must be at least eight alphanumeric characters. The
username and password are not case-sensitive. When you change a password, a prompt
asks for the old password. If there is no password, press enter.
Default no password
Format
users passwd <username>
Mode Global Config
3.6.2.1 no users passwd
This command sets the password of an existing user to blank. When you change a
password, a prompt asks for the old password. If there is no password, press enter.
Format
no users passwd <username>
Mode Global Config
3.6.3 users snmpv3 accessmode
This command specifies the snmpv3 access privileges for the specified login user. The
valid accessmode values are
readonly or readwrite. The <username> is the login user
name for which the specified access mode applies. The default is
readwrite for the
“admin” user and
readonly for all other users
Default admin - readwrite; other - readonly
Format
users snmpv3 accessmode <username> {readonly |
readwrite}
Mode Global Config
3.6.3.1 no users snmpv3 accessmode
This command sets the snmpv3 access privileges for the specified user as readwrite for
the “admin” user and readonly for all other users. The
<username> value is the user name
for which the specified access mode will apply.
Format
no users snmpv3 accessmode <username>
Mode Global Config
Page 54

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
3-20 Administrative Access Commands
v1.0, March 2006
3.6.4 users snmpv3 authentication
This command specifies the authentication protocol to be used for the specified user . The valid authentication
protocols are none, md5 or sha. If you specify md5 or sha, the login password is also used as
the snmpv3 authentication password and therefore must be at least eight characters in
length. The
<username> is the user name associated with the authentication protocol.
Default no authentication
Format
users snmpv3 authentication <username> {none | md5
| sha}
Mode Global Config
3.6.4.1 no users snmpv3 authentication
This command sets the authentication protocol to be used for the specified user to none.
The
<username> is the user name for which the specified authentication protocol is used.
Format
users snmpv3 authentication <username>
Mode Global Config
3.6.5 users snmpv3 encryption
This command specifies the encryption protocol used for the specified user. The valid
encryption protocols are
des or none.
If you select
des, you can specify the required key on the command line. The encryption
key
must be 8 to 64 characters long. If you select the des protocol but do not provide a
key, the user is prompted for the key. When you use the
des protocol, the login password
is also used as the snmpv3 encryption password, so it must be a minimum of eight
characters. If you select
none, you do not need to provide a key.
The
<username> value is the login user name associated with the specified encryption.
Default no encryption
Format
users snmpv3 encryption <username> {none |
des[key]}
Mode Global Config
Page 55

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
Administrative Access Commands 3-21
v1.0, March 2006
3.6.5.1 no users snmpv3 encryption
This command sets the encryption protocol to none. The
<username> is the login user
name for which the specified encryption protocol will be used.
Format
no users snmpv3 encryption <username>
Mode Global Config
3.6.6 show loginsession
This command displays current telnet and serial port connections to the switch.
Format
show loginsession
Mode Privileged EXEC
ID Login Session ID
User Name The name the user will use to login using the serial port or
Telnet.
Connection From IP address of the Telnet client machine or EIA-232 for the
serial port connection.
Idle Time Time this session has been idle.
Session Time Total time this session has been connected.
3.6.7 show users
This command displays the configured user names and their settings. This command is
only available for users with Read/Write privileges.
The SNMPv3 fields will only be displayed if
SNMP is available on the system.
Format show users
Mode Privileged EXEC
User Name The name the user enters to login using the serial port, Telnet
or Web.
Access Mode Shows whether the user is able to change parameters on the
switch (Read/Write) or is only able to view them (Read
Only). As a factory default, the “admin” user has Read/W rite
access and the “guest” has Read Only access. There can only
be one Read/Write user and up to five Read Only users.
SNMPv3 Access
Mode This field displays the SNMPv3 Access Mode. If the value is
set to
ReadWrite, the SNMPv3 user is able to set and
Page 56

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
3-22 Administrative Access Commands
v1.0, March 2006
retrieve parameters on the system. If the value is set to Rea-
dOnly,
the SNMPv3 user is only able to retrieve parameter
information. The SNMPv3 access mode may be different
than the CLI and Web access mode.
SNMPv3
Authentication This field displays the authentication protocol to be used for
the specified login user.
SNMPv3
Encryption This field displays the encryption protocol to be used for the
specified login user.
3.6.8 disconnect
This command closes a telnet session.
Format
disconnect {<sessionID> | all}
Mode Privileged EXEC
Page 57

Port and System Setup Commands 4-1
v1.0, March 2006
Chapter 4
Port and System Setup Commands
This section describes general port and system setup commands available in the 7200
Series Managed Switch CLI.
This section contains the following topics:
• Section 4.1 “Port Configuration Commands” on page 4-1
• Section 4.2 “Pre-login Banner and System Prompt Commands” on page 4-8
• Section 4.3 “Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) Commands” on page 4-9
• Section 4.4 “MAC Address and MAC Database Commands” on page 4-14
The commands in this section are in one of three functional groups:
• Show commands display switch settings, statistics, and other information.
• Configuration commands configure features and options of the switch. For every
configuration command, there is a show command that displays the configuration
setting.
• Copy commands transfer or save configuration and informational files to and from the
switch.
4.1 Port Configuration Commands
This section describes the commands you use to view and configure port settings.
4.1.1 interface
This command gives you access to the Interface Config mode, which allows you to enable
or modify the operation of an interface.
Format
interface <slot/port>
Mode Global Config
Page 58

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
4-2 Port and System Setup Commands
v1.0, March 2006
4.1.2 cablestatus
This command tests the status of the cable attached to an interface.
Format
cablestatus <slot/port>
Mode Privileged EXEC
4.1.3 auto-negotiate
This command enables automatic negotiation on a port.
Default enabled
Format
auto-negotiate
Mode Interface Config
4.1.3.1 no auto-negotiate
This command disables automatic negotiation on a port.
Format
no auto-negotiate
Mode Interface Config
4.1.4 auto-negotiate all
This command enables automatic negotiation on all ports. The default value is enable.
Format
auto-negotiate all
Mode Global Config
4.1.4.1 no auto-negotiate all
This command disables automatic negotiation on all ports.
Format
no auto-negotiate all
Mode Global Config
Note: Automatic sensing is disabled when automatic negotiation is disabled.
Page 59

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
Port and System Setup Commands 4-3
v1.0, March 2006
4.1.5 mtu
This command sets the maximum transmission unit (MTU) size, in bytes, for physical and
port-channel (LAG) interfaces. For the standard implementation, the MTU size is a valid
integer between 1522 - 9216 for tagged packets and a valid integer between 1518 - 9216
for untagged packets.
Default 1518 (untagged)
Format
mtu <1518-9216>
Mode Interface Config
4.1.5.1 no mtu
This command sets the default MTU size (in bytes) for the interface.
Format
no mtu
Mode Interface Config
4.1.6 shutdown
This command disables a port.
Default enabled
Format
shutdown
Mode Interface Config
Note: To receive and process packets, the Ethernet MTU must include any extra
bytes that Layer-2 headers might require. To configure the IP MTU size,
which is the maximum size of the IP packet (IP Header + IP payload), see
Section 14.2.9 “ip mtu” on page 14-11.
Note: You can use the shutdown command on physical and port-channel (LAG)
interfaces, but not on VLAN routing interfaces.
Page 60

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
4-4 Port and System Setup Commands
v1.0, March 2006
4.1.6.1 no shutdown
This command enables a port.
Format
no shutdown
Mode Interface Config
4.1.7 shutdown all
This command disables all ports.
Default enabled
Format
shutdown all
Mode Global Config
4.1.7.1 no shutdown all
This command enables all ports.
Format
no shutdown all
Mode Global Config
4.1.8 speed
This command sets the speed and duplex setting for the interface.
Format
speed {<100 | 10> <half-duplex | full-duplex>}
Mode Interface Config
Note: You can use the no shutdown command on physical and port-channel
(LAG) interfaces, but not on VLAN routing interfaces.
Note: You can use the shutdown command on physical and port-channel (LAG)
interfaces, but not on VLAN routing interfaces.
Note: You can use the shutdown command on physical and port-channel (LAG)
interfaces, but not on VLAN routing interfaces.
Page 61

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
Port and System Setup Commands 4-5
v1.0, March 2006
Acceptable values are:
100h 100BASE-T half duplex
100f 100BASE-T full duplex
10h 10BASE-T half duplex
10f 10BASE-T full duplex
4.1.9 speed all
This command sets the speed and duplex setting for all interfaces.
Format
speed all {<100 | 10> <half-duplex | full-duplex>}
Mode Global Config
Acceptable values are:
100h 100BASE-T half-duplex
100f 100BASE-T full duplex
10h 10BASE-T half duplex
10f 10BASE-T full duplex
4.1.10 monitor session
This command configures a probe port and a monitored port for monitor session (port
monitoring). To enable port monitoring, you must add a source interface, destination
interface, and enable the mode. If enabled, the probe port monitors all the traffic received
and transmitted on the physical monitored port.
Format
monitor session <session-id> {source interface
<slot/port> | destination interface <slot/port> |
mode}
Mode Global Config
4.1.10.1 no monitor session
This command removes the monitor session (port monitoring) designation from the source
probe port, the destination monitored port and all VLANs. Once the port is removed from
the VLAN, the user must manually add the port to any desired VLANs.
Note: This command sets the monitor session (port monitoring) mode to disable
and removes the source and destination interfaces.
Page 62

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
4-6 Port and System Setup Commands
v1.0, March 2006
Format no monitor session <session-id>
Mode Global Config
4.1.11 no monitor
This command removes all the source ports and a destination port and restores the default
value for mirroring session mode for all the configured sessions.
Default enabled
Format
no monitor
Mode Global config
4.1.12 show monitor session
This command displays the port monitoring information for the system. The <sessionid>
parameter is an integer.
Format
show monitor session <sessionid>
Mode Privileged EXEC
Session ID The session identifying number.
Admin Mode Indicates whether the Port Monitoring feature is enabled or
disabled. The possible values are enable and disable.
Probe Port The interface configured as the probe port.
Mirrored Port
The interface configured as the mirrored port.
4.1.13 show port
This command displays port information.
Format
show port {<slot/port> | all}
Mode Privileged EXEC
Interface Valid slot and port number separated by forward slashes.
Type If not blank, this field indicates that this port is a special type
of port. The possible values are:
Note: This is a stand-alone “no” command. This command does not have a
“normal” form.
Page 63

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
Port and System Setup Commands 4-7
v1.0, March 2006
Mon - this port is a monitoring port. Look at the Port Monitoring screens to find out more information.
Lag - this port is a member of a port-channel (LAG).
Probe - this port is a probe port.
Admin Mode Selects the Port control administration state. The port must be
enabled in order for it to be allowed into the network. - May
be enabled or disabled. The factory default is enabled.
Physical Mode Selects the desired port speed and duplex mode. If auto-nego-
tiation support is selected, then the duplex mode and speed is
set from the auto-negotiation process. Note that the maximum capability of the port (full duplex -100M) is advertised.
Otherwise, this object determines the port's duplex mode and
transmission rate. The factory default is Auto.
Physical Status Indicates the port speed and duplex mode.
Link Status Indicates whether the Link is up or down.
Link Trap This object determines whether or not to send a trap when
link status changes. The factory default is enabled.
LACP Mode Displays whether LACP is enabled or disabled on this port.
4.1.14 show port protocol
This command displays the Protocol-Based VLAN information for either the entire
system, or for the indicated group.
Format
show port protocol {<groupid> | all}
Mode Privileged EXEC
Group Name This field displays the group name of an entry in the Proto-
col-based VLAN table.
Group ID This field displays the group identifier of the protocol group.
Protocol(s) This field indicates the type of protocol(s) for this group.
VLAN This field indicates the VLAN associated with this Protocol
Group.
Interface(s) This field lists the slot/port interface(s) that are associated
with this Protocol Group.
Page 64

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
4-8 Port and System Setup Commands
v1.0, March 2006
4.2 Pre-login Banner and System Prompt Commands
This section describes the commands you use configure the pre-login banner and the
system prompt. The pre-login banner is the text that displays before you login at the
User:
prompt.
4.2.1 copy
The copy command includes the option to upload or down l oad the CLI Bann er t o o r from
the switch. You can specify local URLs by using TFTP, Xmodem, Ymodem, or Zmodem.
Default none
Format
copy <Code Sample Variable><tftp://<ipaddr>/<filepath>/
<filename>><Code Sample Variable>
nvram:clibanner
copy nvram:clibanner <Code Sample Variable><tftp://
<ipaddr>/<filepath>/<filename>><Code Sample Variable>
Mode Privileged EXEC
4.2.2 set prompt
This command changes the name of the prompt. Th e length of name may be up to 64
alphanumeric characters.
Format
set prompt <prompt_string>
Mode Privileged EXEC
Page 65

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
Port and System Setup Commands 4-9
v1.0, March 2006
4.3 Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) Commands
This section describes the commands you use to automatically configure the system time
and date by using SNTP.
4.3.1 sntp broadcast client poll-interval
This command sets the poll interval for SNTP broadcast clients in seconds as a power of
two where <poll-interval> can be a value from 6 to 16.
Default 6
Format
sntp broadcast client poll-interval <poll-interval>
Mode Global Config
4.3.1.1 no sntp broadcast client poll-interval
This command resets the poll interval for SNTP broadcast client back to the default value.
Format
no sntp broadcast client poll-interval
Mode Global Config
4.3.2 sntp client mode
This command enables Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) client mode and may set
the mode to either broadcast or unicast.
Default disabled
Format
sntp client mode [broadcast | unicast]
Mode Global Config
4.3.2.1 sntp client mode
This command disables Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) client mode.
Format
no sntp client mode
Mode Global Config
4.3.3 sntp client port
This command sets the SNTP client port id to a value from 1-65535.
Default 123
Page 66

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
4-10 Port and System Setup Commands
v1.0, March 2006
Format sntp client port <portid>
Mode Global Config
4.3.3.1 no sntp client port
This command resets the SNTP client port back to its default value.
Format
no sntp client port
Mode Global Config
4.3.4 sntp unicast client poll-interval
This command sets the poll interval for SNTP unicast clients in seconds as a power of two
where
<poll-interval> can be a value from 6 to 16.
Default 6
Format
sntp unicast client poll-interval <poll-interval>
Mode Global Config
4.3.4.1 no sntp unicast client poll-interval
This command resets the poll interval for SNTP unicast clients to its default value.
Format
no sntp unicast client poll-interval
Mode Global Config
4.3.5 sntp unicast client poll-timeout
This command sets the poll timeout for SNTP unicast clients in seconds to a value from 1-
30.
Default 5
Format
sntp unicast client poll-timeout <poll-timeout>
Mode Global Config
4.3.5.1 no sntp unicast client poll-timeout
This command resets the poll timeout for SNTP unicast clients to its default value.
Format
no sntp unicast client poll-timeout
Mode Global Config
Page 67

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
Port and System Setup Commands 4-11
v1.0, March 2006
4.3.6 sntp unicast client poll-retry
This command will set the poll retry for SNTP unicast clients to a value from 0 to 10.
Default 1
Format
sntp unicast client poll-retry <poll-retry>
Mode Global Config
4.3.6.1 no sntp unicast client poll-retry
This command will reset the poll retry for SNTP unicast clients to its default value.
Format
no sntp unicast client poll-retry
Mode Global Config
4.3.7 sntp multicast client poll-interval
This command will set the poll interval for SNTP multicast clients in seconds as a power
of two where
<poll-interval> can be a value from 6 to 16.
Default 6
Format
sntp multicast client poll-interval <poll-interval>
Mode Global Config
4.3.7.1 no sntp multicast client poll-interval
This command resets the poll interval for SNTP multicast clients to its default value.
Format
no sntp multicast client poll-interval
Mode Global Config
Page 68

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
4-12 Port and System Setup Commands
v1.0, March 2006
4.3.8 sntp server
This command configures an SNTP server (a maximum of three). The optional priority
can be a value of 1-3, the version a value of 1-4, and the port id a value of 1-65535.
Format
sntp server <ipaddress> [<priority> [<version>
[<portid>]]]
Mode Global Config
4.3.8.1 no sntp server
This command deletes an server from the configured SNTP servers.
Format
no sntp server remove <ipaddress>
Mode Global Config
4.3.9 show sntp
This command is used to display SNTP settings and status.
Format
show sntp
Mode Privileged EXEC
Last Update Time Time of last clock update.
Last Attempt
Time Time of last transmit query (in unicast mode).
Last Attempt
Status Status of the last SNTP request (in unicast mode) or unsolic-
ited message (in broadcast mode).
Broadcast Count Current number of unsolicited broadcast messages that have
been received and processed by the SNTP client since last
reboot.
Multicast Count Current number of unsolicited multicast messages that have
been received and processed by the SNTP client since last
reboot
4.3.10 show sntp client
This command is used to display SNTP client settings.
Format
show sntp client
Mode Privileged EXEC
Page 69

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
Port and System Setup Commands 4-13
v1.0, March 2006
Client Supported
Modes Supported SNTP Modes (Broadcast, Unicast, or Multicast).
SNTP Version The highest SNTP version the client supports
Port SNTP Client Port
Client Mode Configured SNTP Client Mode
Poll Interval Poll interval value for SNTP clients in seconds as a power of
two.
Poll Timeout Poll timeout value in seconds for SNTP clients.
Poll Retry Poll retry value for SNTP clients.
4.3.11 show sntp server
This command is used to display SNTP server settings and configured servers.
Format
show sntp server
Mode Privileged EXEC
Server IP
Address IP Address of configured SNTP Server
Server Type Address Type of Server.
Server Stratum Claimed stratum of the server for the last received valid
packet.
Server Reference
ID Reference clock identifier of the server for the last received
valid packet.
Server Mode SNTP Server mode.
Server Max
Entries Total number of SNTP Servers allowed.
Server Current
Entries Total number of SNTP configured.
For each configured server:
IP Address IP Address of configured SNTP Server.
Address Type Address Type of configured SNTP server.
Priority IP priority type of the configured server.
Version SNTP Version number of the server. The protocol version
used to query the server in unicast mode.
Page 70

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
4-14 Port and System Setup Commands
v1.0, March 2006
Port Server Port Number
Last Attempt
Time Last server attempt time for the specified server.
Last Attempt
Status Last server attempt status for the server.
Total Unicast
Requests Number of requests to the server.
Failed Unicast
Requests Number of failed requests from server.
4.4 MAC Address and MAC Database Commands
This section describes the commands you use to configure and view information about the
system MAC address and the MAC address table.
4.4.1 network mac-address
This command sets locally administered MAC addresses. The following rules apply:
• Bit 6 of byte 0 (called the U/L bit) indicates whether the address is universally
administered (b'0') or locally administered (b'1').
• Bit 7 of byte 0 (called the I/G bit) indicates whether the destination address is an
individual address (b'0') or a group address (b'1').
• The second character, of the twelve character macaddr, must be 2, 6, A or E.
A locally administered address must have bit 6 On (b'1') and bit 7 Off (b'0').
Format
network mac-address <macaddr>
Mode Privileged EXEC
4.4.2 network mac-type
This command specifies whether the switch uses the burned in MAC address or the
locally-administered MAC address.
Default burnedin
Format
network mac-type {local | burnedin}
Mode Privileged EXEC
Page 71

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
Port and System Setup Commands 4-15
v1.0, March 2006
4.4.2.1 no network mac-type
This command resets the value of MAC address to its default.
Format
no network mac-type
Mode Privileged EXE
4.4.3 macfilter
This command adds a static MAC filter entry for the MAC address <macaddr> on the
VLAN <
vlanid>. The <macaddr> parameter must be specified as a 6-byte hexadecimal
number in the format of b1:b2:b3:b4:b5:b6.
The restricted MAC Addresses are: 00:00:00:00:00:00, 01:80:C2:00:00:00 to
01:80:C2:00:00:0F, 01:80:C2:00:00:20 to 01:80:C2:00:00:21, and FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF.
The <
vlanid> parameter must identify a valid VLAN.
Up to 100 static MAC filters may be created.
Format
macfilter <macaddr> <vlanid>
Mode Global Config
4.4.3.1 no macfilter
This command removes all filtering restrictions and the static MAC filter entry for the
MAC address
<macaddr> on the VLAN <vlanid>. The <macaddr> parameter must be
specified as a 6-byte hexadecimal number in the format of b1:b2:b3:b4:b5:b6.
The
<vlanid> parameter must identify a valid VLAN.
Format
no macfilter <macaddr> <vlanid>
Mode Global Config
4.4.4 macfilter adddest
This command adds the interface to the destination filter set for the MAC filter with the
given
<macaddr> and VLAN of <vlanid>. The <macaddr> parameter must be specified as
a 6-byte hexadecimal number in the format of b1:b2:b3:b4:b5:b6.
The
<vlanid> parameter must identify a valid VLAN.
Format
macfilter adddest <macaddr> <vlanid>
Mode Interface Config
Page 72

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
4-16 Port and System Setup Commands
v1.0, March 2006
4.4.4.1 no macfilter adddest
This command removes a port from the destination filter set for the MAC filter with the
given
<macaddr> and VLAN of <vlanid>. The <macaddr> parameter must be specified as
a 6-byte hexadecimal number in the format of b1:b2:b3:b4:b5:b6.
The
<vlanid> parameter must identify a valid VLAN.
Format
no macfilter adddest <macaddr> <vlanid>
Mode Interface Config
4.4.5 macfilter adddest all
This command adds all interfaces to the destination filter set for the MAC filter with the
given
<macaddr> and VLAN of <vlanid>. The <macaddr> parameter must be specified
as a 6-byte hexadecimal number in the format of b1:b2:b3:b4:b5:b6.
The
<vlanid> parameter must identify a valid VLAN.
Format
macfilter adddest {all | <macaddr> <vlanid>}
Mode Global Config
4.4.5.1 no macfilter adddest all
This command removes all ports from the destination filter set for the MAC filter with the
given
<macaddr> and VLAN of <vlanid>. The <macaddr> parameter must be specified
as a 6-byte hexadecimal number in the format of b1:b2:b3:b4:b5:b6.
The
<vlanid> parameter must identify a valid VLAN.
Format
no macfilter adddest {all | <macaddr> <vlanid>}
Mode Global Config
4.4.6 macfilter addsrc
This command adds the interface to the source filter set for the MAC filter with the MAC
address of
<macaddr> and VLAN of <vlanid>. The <macaddr> parameter must be
specified as a 6-byte hexadecimal number in the format of b1:b2:b3:b4:b5:b6.
The
<vlanid> parameter must identify a valid VLAN.
Format
macfilter addsrc <macaddr> <vlanid>
Mode Interface Config
Page 73

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
Port and System Setup Commands 4-17
v1.0, March 2006
4.4.6.1 no macfilter addsrc
This command removes a port from the source filter set for the MAC filter with the MAC
address of
<macaddr> and VLAN of <vlanid>. The <macaddr> parameter must be
specified as a 6-byte hexadecimal number in the format of b1:b2:b3:b4:b5:b6.
The
<vlanid> parameter must identify a valid VLAN.
Format
no macfilter addsrc <macaddr> <vlanid>
Mode Interface Config
4.4.7 macfilter addsrc all
This command adds all interfaces to the source filter set for the MAC filter with the MAC
address of
<macaddr> and <vlanid>. You must specify the <macaddr> parameter as a 6-
byte hexadecimal number in the format of b1:b2:b3:b4:b5:b6. The
<vlanid> parameter
must identify a valid VLAN.
Format
macfilter addsrc {all | <macaddr> <vlanid>}
Mode Global Config
4.4.7.1 no macfilter addsrc all
This command removes all interfaces to the source filter set for the MAC filter with the
MAC address of
<macaddr> and VLAN of <vlanid>. You must specify the <macaddr>
parameter as a 6-byte hexadecimal number in the format of b1:b2:b3:b4:b5:b6.
The
<vlanid> parameter must identify a valid VLAN.
Format
no macfilter addsrc {all | <macaddr> <vlanid>}
Mode Global Config
4.4.8 bridge aging-time
This command configures the forwarding database address aging timeout in seconds. In an
IVL system, the
[fdbid | all] parameter is required.
Default 300
Format
bridge aging-time <10-1,000,000> [fdbid | all]
Mode Global Config
Seconds The
<seconds> parameter must be within the range of 10 to
1,000,000 seconds.
Page 74

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
4-18 Port and System Setup Commands
v1.0, March 2006
Forwarding
Database ID The forwarding database ID (
fdbid) indicates which for-
warding database's aging timeout is being configured. Use
the
all option to configure the agetime of all forwarding
databases.
4.4.8.1 no bridge aging-time
This command sets the forwarding database address aging timeout to 300 seconds. In an
IVL system, the
[fdbid | all] parameter is required.
Format
no bridge aging-time [fdbid | all]
Mode Global Config
Forwarding
Database ID Fdbid (Forwarding database ID) indicates which forwarding
database's aging timeout is being configured. All is used to
configure all forwarding database's agetime.
4.4.9 show forwardingdb agetime
This command displays the timeout for address aging. In an IVL system, the [fdbid |
all] parameter is required.
Default all
Format
show forwardingdb agetime [fdbid | all]
Mode Privileged EXEC
Forwarding DB
ID Forwarding database ID indicates the forwarding database
whose aging timeout is to be shown. The all option is used to
display the aging timeouts associated with all forwarding
databases.
Agetime In an IVL system, this parameter displays the address aging
timeout for the associated forwarding database.
4.4.10 show mac-address-table multicast
This command displays the Multicast Forwarding Database (MFDB) information. If you
enter the command with no parameter, the entire table is displayed. You can display the
table entry for one MAC Address by specifying the MAC address as an optional
parameter.
Page 75

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
Port and System Setup Commands 4-19
v1.0, March 2006
Format show mac-address-table multicast <macaddr>
Mode Privileged EXEC
MAC Address A multicast MAC address for which the switch has forward-
ing and or filtering information. The format is two-digit hexadecimal numbers separated by colons, for example
01:23:45:67:89:AB. In an IVL system the MAC address will
be displayed as a MAC address and VLAN ID combination
of 8 bytes.
Type This displays the type of the entry . S tatic entries are those that
are configured by the end user. Dynamic entries are added to
the table as a result of a learning process or protocol.
Component The component that is responsible for this entry in the Multi-
cast Forwarding Database. Possible values are IGMP Snooping, GMRP, and Static Filtering.
Description The text description of this multicast table entry.
Interfaces The list of interfaces that are designated for forwarding
(Fwd:) and filtering (Flt:).
Forwarding
Interfaces The resultant forwarding list is derived from combining all
the component’s forwarding interfaces and removing the
interfaces that are listed as the static filtering interfaces.
4.4.11 show mac-address-table static
This command displays the Static MAC Filtering information for all Static MAC Filters. If
you select
<all>, all the Static MAC Filters in the system are displayed. If you supply a
value for
<macaddr>, you must also enter a value for <vlanid>, and the system displays
Static MAC Filter information only for that MAC address and VLAN.
Format
show mac-address-table static {<macaddr> <vlanid>
| all}
Mode Privileged EXEC
MAC Address Is the MAC Address of the static MAC filter entry.
VLAN ID Is the VLAN ID of the static MAC filter entry.
Source Port(s) Indicates the source port filter set's slot and port(s).
Destination
Port(s) Indicates the destination port filter set's slot and port(s).
Page 76

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
4-20 Port and System Setup Commands
v1.0, March 2006
4.4.12 show mac-address-table staticfiltering
This command displays the Static Filtering entries in the Multicast Forwarding Database
(MFDB) table.
Format
show mac-address-table staticfiltering
Mode Privileged EXEC
Mac Address A unicast MAC address for which the switch has forwarding
and or filtering information. The format is 6 or 8 two-digit
hexadecimal numbers that are separated by colons, for example 01:23:45:67:89:AB. In an IVL system the MAC address
will be displayed as 8 bytes.
Type Displays the type of the entry. Static entries are those that are
configured by the end user. Dynamic entries are added to the
table as a result of a learning process or protocol.
Description The text description of this multicast table entry.
Interfaces The list of interfaces that are designated for forwarding
(Fwd:) and filtering (Flt:).
4.4.13 show mac-address-table stats
This command displays the Multicast Forwarding Database (MFDB) statistics.
Format
show mac-address-table stats
Mode Privileged EXEC
Total Entries Displays the total number of entries that can possibly be in
the Multicast Forwarding Database table.
Most MFDB
Entries Ever
Used Displays the largest number of entries that have been present
in the Multicast Forwarding Database table. This value is also
known as the MFDB high-water mark.
Current Entries Displays the current number of entries in the MFDB.
Page 77

Spanning Tree Protocol Commands 5-1
v1.0, March 2006
Chapter 5 Spanning Tree Protocol Commands
This section describes the spanning tree protocol (STP) commands available in the 72 00
Series Managed Switch CLI. STP helps prevent network loops, duplicate messages, and
network instability.
The STP Commands section includes the following topics:
• Section 5.1 “STP Configuration Commands” on page 5-1
• Section 5.2 “STP Show Commands” on page 5-9
The commands in this section are in one of two functional groups:
• Show commands display switch settings, statistics, and other information.
• Configuration commands configure features and options of the switch. For every
configuration command, there is a show command that displays the configuration
setting.
5.1 STP Configuration Commands
This section describes the commands you use to configure Spanning Tree Protocol (STP).
5.1.1 spanning-tree
This command sets the spanning-tree operational mode to enabled.
Default disabled
Format
spanning-tree
Mode Global Config
Note: STP is disabled by default. When you enable STP on the switch, STP is
still disabled on each port.
If STP is disabled, the system does not forward BPDU messages.
Page 78

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
5-2 Spanning Tree Protocol Commands
v1.0, March 2006
5.1.1.1 no spanning-tree
This command sets the spanning-tree operational mode to disabled. While disabled, the
spanning-tree configuration is retained and can be changed, but is not activated.
Format
no spanning-tree
Mode Global Config
5.1.2 spanning-tree bpdumigrationcheck
This command enables BPDU migration check on a given interface. The all option
enables BPDU migration check on all interfaces.
Format
spanning-tree bpdumigrationcheck {<slot/port> |
all}
Mode Global Config
5.1.2.1 no spanning-tree bpdumigrationcheck
This command disables BPDU migration check on a given interface. The all option
disables BPDU migration check on all interfaces.
Format
no spanning-tree bpdumigrationcheck {<slot/port> |
all}
Mode Global Config
5.1.3 spanning-tree configuration name
This command sets the Configuration Identifier Name for use in identifying the
configuration that this switch is currently using. The
<name> is a string of up to 32
characters.
Default base MAC address in hexadecimal notation
Format
spanning-tree configuration name <name>
Mode Global Config
5.1.3.1 no spanning-tree configuration name
This command resets the Configuration Identifier Name to its default.
Format
no spanning-tree configuration name
Mode Global Config
Page 79

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
Spanning Tree Protocol Commands 5-3
v1.0, March 2006
5.1.4 spanning-tree configuration revision
This command sets the Configuration Identifier Revision Level for use in identifying the
configuration that this switch is currently using. The Configuration Identifier Revision
Level is a number in the range of 0 to 65535.
Default 0
Format
spanning-tree configuration revision <0-65535>
Mode Global Config
5.1.4.1 no spanning-tree configuration revision
This command sets the Configuration Identifier Revision Level for use in identifying the
configuration that this switch is currently using to the default value, i.e. 0.
Format
no spanning-tree configuration revision
Mode Global Config
5.1.5 spanning-tree edgeport
This command specifies that this port is an Edge Port within the common and internal
spanning tree. This allows this port to transition to Forwarding State without delay.
Format
spanning-tree edgeport
Mode Interface Config
5.1.5.1 no spanning-tree edgeport
This command specifies that this port is not an Edge Port within the common and internal
spanning tree.
Format
no spanning-tree edgeport
Mode Interface Config
5.1.6 spanning-tree forceversion
This command sets the Force Protocol Version parameter to a new value. The Force
Protocol Version can be one of the following:
• 802.1d - ST BPDUs are transmitted rather than MST BPDUs (IEEE 802.1d
functionality supported)
• 802.1w - RST BPDUs are transmitted rather than MST BPDUs (IEEE 802.1w
functionality supported)
Page 80

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
5-4 Spanning Tree Protocol Commands
v1.0, March 2006
• 802.1s - MST BPDUs are transmitted (IEEE 802.1s functionality supported)
Default 802.1s
Format
spanning-tree forceversion <802.1d | 802.1w |
802.1s>
Mode Global Config
5.1.6.1 no spanning-tree forceversion
This command sets the Force Protocol Version parameter to the default value, i.e. 802.1s.
Format
no spanning-tree forceversion
Mode Global Config
5.1.7 spanning-tree forward-time
This command sets the Bridge Forward Delay parameter to a new value for the common
and internal spanning tree. The forward-time value is in seconds within a range of 4 to 30,
with the value being greater than or equal to “(Bridge Max Age / 2) + 1”.
Default 15
Format
spanning-tree forward-time <4-30>
Mode Global Config
5.1.7.1 no spanning-tree forward-time
This command sets the Bridge Forward Delay parameter for the common and internal
spanning tree to the default value of 15.
Format
no spanning-tree forward-time
Mode Global Config
5.1.8 spanning-tree hello-time
This command sets the Admin Hello Time parameter to a new value for the common and
internal spanning tree. The hello time
<value> is in whole seconds within a range of 1 to
10, with the value being less than or equal to (Bridge Max Age / 2) - 1.
Default 2
Format
spanning-tree hello-time <1-10>
Mode Interface Config
Page 81

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
Spanning Tree Protocol Commands 5-5
v1.0, March 2006
5.1.8.1 no spanning-tree hello-time
This command sets the admin Hello Time parameter for the common and internal
spanning tree to the default value.
Format
no spanning-tree hello-time
Mode Interface Config
5.1.9 spanning-tree max-age
This command sets the Bridge Max Age parameter to a new value for the common and
internal spanning tree. The max-age value is in seconds within a range of 6 to 40, with the
value being less than or equal to 2 x (Bridge Forward Delay - 1).
Default 20
Format
spanning-tree max-age <6-40>
Mode Global Config
5.1.9.1 no spanning-tree max-age
This command sets the Bridge Max Age parameter for the common and internal spanning
tree to the default value of 20.
Format
no spanning-tree max-age
Mode Global Config
5.1.10 spanning-tree max-hops
This command sets the MSTP Max Hops parameter to a new value for the common and
internal spanning tree. The max-hops value is a range from 1 to 127.
Default 20
Format
spanning-tree max-hops <1-127>
Mode Global Config
5.1.10.1 no spanning-tree max-hops
This command sets the Bridge Max Hops parameter for the common and internal spanning
tree to the default value.
Format
no spanning-tree max-hops
Mode Global Config
Page 82

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
5-6 Spanning Tree Protocol Commands
v1.0, March 2006
5.1.11 spanning-tree mst
This command sets the Path Cost or Port Priority for this port within the multiple spanning
tree instance or in the common and internal spanning tree. If you specify an
<mstid>
parameter that corresponds to an existing multiple spanning tree instance, the
configurations are done for that multiple spanning tree instance. If you specify 0 (defined
as the default CIST ID) as the
<mstid>, the configurations are done for the common and
internal spanning tree instance.
If you specify the cost option, the command sets the path cost for this port within a
multiple spanning tree instance or the common and internal spanning tree instance,
depending on the
<mstid> parameter . You can set the path cost as a number in the range of
1 to 200000000 or auto. If you select auto the path cost value is set based on Link Speed.
If you specify the external-cost option, this command sets the external-path cost for MST
instance ‘0’ i.e. CIST instance. You can set the external cost as a number in the range of 1
to 200000000 or auto. If you specify au to, the external path cost value is set based on Link
Speed.
If you specify the port-priority option, this command sets the priority for this port within
a specific multiple spanning tree instance or the common and internal spanning tree
instance, depending on the
<mstid> parameter. The port-priority value is a number in the
range of 0 to 240 in increments of 16.
Default cost: auto; external-cost: auto; port-priority: 128
Format
spanning-tree mst <mstid> {{cost <1-200000000> |
auto} |
{external-cost <1-200000000> | auto}| port-prior-
ity <0-240>}
Mode Interface Config
5.1.11.1 no spanning-tree mst
This command sets the Path Cost or Port Priority for this port within the multiple spanning
tree instance, or in the common and internal spanning tree to the respective default values.
If you specify an
<mstid> parameter that corresponds to an existing multiple spanning tree
instance, you are configuring that multiple spanning tree instance. If you specify 0
(defined as the default CIST ID) as the
<mstid>, you are configuring the common and
internal spanning tree instance.
If the you specify cost, this command sets the path cost for this port within a multiple
spanning tree instance or the common and internal spanning tree instance, depending on
the
<mstid> parameter, to the default value, i.e. a path cost value based on the Link Speed.
Page 83

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
Spanning Tree Protocol Commands 5-7
v1.0, March 2006
If you specify external-cost, this command sets the external path cost for this port for mst
‘0’ instance, to the default value, i.e. a path cost value based on the Link Speed.
If you specify port-priority, this command sets the priority for this port within a specific
multiple spanning tree instance or the common and internal spanning tree instance,
depending on the
<mstid> parameter, to the default value, i.e. 128.
Format
no spanning-tree mst <mstid> <cost | external-cost
| port-priority>
Mode Interface Config
5.1.12 spanning-tree mst instance
This command adds a multiple spanning tree instance to the switch. The parameter
<mstid> is a number within a range of 1 to 4094, that corresponds to the new instance ID
to be added. The maximum number of multiple instances supported by the switch is 4.
Format
spanning-tree mst instance <mstid>
Mode Global Config
5.1.12.1 no spanning-tree mst instance
This command removes a multiple spanning tree instance from the switch and reallocates
all VLANs allocated to the deleted instance to the common and internal spanning tree. The
parameter
<mstid> is a number that corresponds to the desired existing multiple spanning
tree instance to be removed.
Format
no spanning-tree mst instance <mstid>
Mode Global Config
5.1.13 spanning-tree mst priority
This command sets the bridge priority for a specific multiple spanning tree instance. The
parameter
<mstid> is a number that corresponds to the desired existing multiple spanning
tree instance. The priority value is a number within a range of 0 to 61440 in increments of
4096.
If you specify 0 (defined as the default CIST ID) as the
<mstid>, this command sets the
Bridge Priority parameter to a new value for the common and internal spanning tree. The
bridge priority value is a number within a range of 0 to 61440. The twelve least significant
bits are masked according to the 802.1s specification. This causes the priority to be
rounded down to the next lower valid priority.
Default 32768
Page 84

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
5-8 Spanning Tree Protocol Commands
v1.0, March 2006
Format spanning-tree mst priority <mstid> <0-61440>
Mode Global Config
5.1.13.1 no spanning-tree mst priority
This command sets the bridge priority for a specific multiple spanning tree instance to the
default value, i.e. 32768. The parameter
<mstid> is a number that corresponds to the
desired existing multiple spanning tree instance.
If 0 (defined as the default CIST ID) is passed as the
<mstid>, this command sets the
Bridge Priority parameter for the common and internal spanning tree to the default value,
i.e. 32768.
Format
spanning-tree mst priority <mstid>
Mode Global Config
5.1.14 spanning-tree mst vlan
This command adds an association between a multiple spanning tree instance and a VLAN
so that the VLAN is no longer associated with the common and internal spanning tree.
The parameter
<mstid> is a number that corresponds to the desired existing multiple
spanning tree instance. The
<vlanid> corresponds to an existing VLAN ID.
Format
spanning-tree mst vlan <mstid> <vlanid>
Mode Global Config
5.1.14.1 no spanning-tree mst vlan
This command removes an association between a multiple spanning tree instance and a
VLAN so that the VLAN is again be associated with the common and internal spanning
tree. The parameter
<mstid> is a number that corresponds to the desired existing multiple
spanning tree instance. The
<vlanid> corresponds to an existing VLAN ID.
Format
no spanning-tree mst vlan <mstid> <vlanid>
Mode Global Config
5.1.15 spanning-tree port mode
This command sets the Administrative Switch Port State for this port to enabled.
Default disabled
Format
spanning-tree port mode
Mode Interface Config
Page 85

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
Spanning Tree Protocol Commands 5-9
v1.0, March 2006
5.1.15.1 no spanning-tree port mode
This command sets the Administrative Switch Port State for this port to disabled.
Format
no spanning-tree port mode
Mode Interface Config
5.1.16 spanning-tree port mode all
This command sets the Administrative Switch Port State for all ports to enabled.
Default disabled
Format
spanning-tree port mode all
Mode Global Config
5.1.16.1 no spanning-tree port mode all
This command sets the Administrative Switch Port State for all ports to disabled.
Format
no spanning-tree port mode all
Mode Global Config
5.2 STP Show Commands
This section describes the commands you use to view information about STP
configuration and status.
5.2.1 show spanning-tree
This command displays spanning tree settings for the common an d inter nal spanni ng tree,
when the optional parameter “brief” is not included in the command. The following details
are displayed.
Format
show spanning-tree <brief>
Modes Privileged EXEC
User EXEC
Bridge Priority Specifies the bridge priority for the Common and Internal
Spanning tree (CST). The value lies between 0 and 61440. It
is displayed in multiples of 4096.
Bridge Identifier The bridge identifier for the CST. It is made up using the
bridge priority and the base MAC address of the bridge.
Page 86

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
5-10 Spanning Tree Protocol Commands
v1.0, March 2006
Time Since
Topology
Change Time in seconds.
Topology Change
Count Number of times changed.
Topology
Change Boolean value of the Topology Change parameter for the
switch indicating if a topology change is in progress on any
port assigned to the common and internal spanning tree.
Designated Root The bridge identifier of the root bridge. It is made up from the
bridge priority and the base MAC address of the bridge.
Root Path Cost Value of the Root Path Cost parameter for the common and
internal spanning tree.
Root Port
Identifier Identifier of the port to access the Designated Root for the
CST.
Root Port Max
Age Derived value.
Root Port Bridge
Forward Delay Derived value.
Hello Time Configured value of the parameter for the CST.
Bridge Hold Time Minimum time between transmission of Configuration
Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs)
Bridge Max Hops Bridge max-hops count for the device.
CST Regional
Root Bridge Identifier of the CST Regional Root. It is made up
using the bridge priority and the base MAC address of the
bridge.
Regional Root
Path Cost Path Cost to the CST Regional Root.
Associated FIDs List of forwarding database identifiers currently associated
with this instance.
Associated
VLANs List of VLAN IDs currently associated with this instance.
Page 87

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
Spanning Tree Protocol Commands 5-11
v1.0, March 2006
When you include the brief keyword, this command displays spanning tree settings for
the bridge and the following information appears.
Bridge Priority Configured value.
Bridge Identifier The bridge identifier for the selected MST instance. It is
made up using the bridge priority and the base MAC address
of the bridge.
Bridge Max Age Configured value.
Bridge Max Hops Bridge max-hops count for the device.
Bridge Hello
Time Configured value.
Bridge Forward
Delay Configured value.
Bridge Hold Time Minimum time between transmission of Configuration
Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs)
5.2.2 show spanning-tree summary
This command displays spanning tree settings and parameters for the switch. The
following details are displayed on execution of the command.
Format
show spanning-tree summary
Modes Privileged EXEC
User EXEC
Spanning Tree
Adminmode Enabled or disabled.
Spanning Tree
Version Version of 802.1 currently supported (IEEE 802.1s, IEEE
802.1w, or IEEE 802.1d) based upon the Force Protocol Version parameter.
Configuration
Name Identifier used to identify the configuration currently being
used.
Configuration
Revision Level Identifier used to identify the configuration currently being
used.
Page 88

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
5-12 Spanning Tree Protocol Commands
v1.0, March 2006
Configuration
Digest Key Identifier used to identify the configuration currently being
used.
MST Instances List of all multiple spanning tree instances configured on the
switch
5.2.3 show spanning-tree interface
This command displays the settings and parameters for a specific switch port within the
common and internal spanning tree. The
<slot/port> is the desired switch port. The
following details are displayed on execution of the command.
Format
show spanning-tree interface <slot/port>
Modes Privileged EXEC
User EXEC
Hello Time Admin hello time for this port.
Port mode Enabled or disabled.
Port Up Time
Since Counters
Last Cleared Time since port was reset, displayed in days, hours, minutes,
and seconds.
STP BPDUs
Transmitted Spanning Tree Protocol Bridge Protocol Data Units sent
STP BPDUs
Received Spanning Tree Protocol Bridge Protocol Data Units received.
RST BPDUs
Transmitted Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol Bridge Protocol Data Units
sent
RST BPDUs
Received Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol Bridge Protocol Data Units
received.
MSTP BPDUs
Transmitted Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol Bridge Protocol Data Units
sent
MSTP BPDUs
Received Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol Bridge Protocol Data Units
received.
Page 89

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
Spanning Tree Protocol Commands 5-13
v1.0, March 2006
5.2.4 show spanning-tree mst port detailed
This command displays the detailed settings and parameters for a specific switch port
within a particular multiple spanning tree instance. The parameter
<mstid> is a number
that corresponds to the desired existing multiple spanning tree instance. The
<slot/port>
is the desired switch port.
Format
show spanning-tree mst port detailed <mstid>
<slot/port>
Mode Privileged EXEC
User EXEC
MST Instance ID The ID of the existing MST instance.
Port Identifier The port identifier for the specified port within the selected
MST instance. It is made up from the port priority and the
interface number of the port.
Port Priority The priority for a particular port within the selected MST
instance. The port priority is displayed in multiples of 16.
Port Forwarding
State Current spanning tree state of this port.
Port Role Each enabled MST Bridge Port receives a Port Role for each
spanning tree. The port role is one of the following values:
Root Port, Designated Port, Alternate Port, Backup Port,
Master Port or Disabled Port
Auto-Calculate
Port Path Cost This indicates whether auto calculation for port path cost is
enabled.
Port Path Cost Configured value of the Internal Port Path Cost parameter.
Auto-Calculate
External Port Path
Cost This indicates whether auto calculation for external port path
cost is enabled.
External Port Path
Cost Configured value of the external Port Path Cost parameter.
Designated Root The Identifier of the designated root for this port.
Designated Port
Cost Path Cost offered to the LAN by the Designated Port
Page 90

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
5-14 Spanning Tree Protocol Commands
v1.0, March 2006
Designated
Bridge
Bridge Identifier of the bridge with the Designated Port.
Designated Port
Identifier Port on the Designated Bridge that offers the lowest cost to
the LAN.
If you specify 0 (defined as the default CIST ID) as the
<mstid>, this command displays
the settings and parameters for a specific switch port within the common and internal
spanning tree. The
<slot/port> is the desired switch port. In this case, the following are
displayed.
Port Identifier The port identifier for this port within the CST.
Port Priority The priority of the port within the CST.
Port Forwarding
State The forwarding state of the port within the CST.
Port Role The role of the specified interface within the CST.
Port Path Cost The configured path cost for the specified interface.
Designated Root Identifier of the designated root for this port within the CST.
Designated Port
Cost Path Cost offered to the LAN by the Designated Port.
Designated
Bridge The bridge containing the designated port
Designated Port
Identifier Port on the Designated Bridge that offers the lowest cost to
the LAN
Topology Change
Acknowledgement Value of flag in next Configuration Bridge Protocol Data
Unit (BPDU) transmission indicating if a topology change is
in progress for this port.
Hello Time The hello time in use for this port.
Edge Port The configured value indicating if this port is an edge port.
Edge Port Status The derived value of the edge port status. True if operating as
an edge port; false otherwise.
Point To Point
MAC Status Derived value indicating if this port is part of a point to point
link
.
Page 91

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
Spanning Tree Protocol Commands 5-15
v1.0, March 2006
CST Regional
Root The regional root identifier in use for this port.
CST Port Cost The co nfig ured path cost for this port.
5.2.5 show spanning-tree mst port summary
This command displays the settings of one or all ports within the specified multiple
spanning tree instance. The parameter
<mstid> indicates a particular MST instance. The
parameter {
<slot/port> | all} indicates the desired switch port or all ports.
If you specify 0 (defined as the default CIST ID) as the
<mstid>, the status summary
displays for one or all ports within the common and internal spanning tree.
Format
show spanning-tree mst port summary <mstid> {<sl ot/
port> | all}
Modes Privileged EXEC
User EXEC
MST Instance ID The MST instance associated with this port.
Interface Valid slot and port number separated by forward slashes.
Type Currently not used.
STP State The forwarding state of the port in the specified spanning tree
instance
Port Role The role of the specified port within the spanning tree.
Link Status The operational status of the link. Possible values are “Up” or
“Down”.
Link Trap The link trap configuration for the specified interface.
5.2.6 show spanning-tree mst summary
This command displays summary information about all multiple spanning tree instances in
the switch. On execution, the following details are displayed.
Format
show spanning-tree mst summary
Modes Privileged EXEC
User EXEC
MST Instance ID
List List of multiple spanning trees IDs currently configured.
For each MSTID:
Page 92

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
5-16 Spanning Tree Protocol Commands
v1.0, March 2006
Associated FIDs List of forwarding database identifiers associated with this
instance.
Associated
VLANs List of VLAN IDs associated with this instance.
5.2.7 show spanning-tree vlan
This command displays the association between a VLAN and a multiple spanning tree
instance. The
<vlanid> corresponds to an existing VLAN ID.
Format
show spanning-tree vlan <vlanid>
Modes Privileged EXEC
User EXEC
VLAN Identifier The VLANs associated with the selected MST instance.
Associated
Instance Identifier for the associated multip le spanning tree instance or
“CST” if associated with the common and internal spanning
tree.
Page 93

VLAN Commands 6-1
v1.0, March 2006
Chapter 6
VLAN Commands
This section describes the VLAN commands available in the 7200 Series Managed Switch
CLI. VLANs allow users located on different physical networks to be on the same logical
network.
The VLAN Commands section includes the following topics:
• Section 6.1 “VLAN Configuration Commands” on page 6-1
• Section 6.2 “VLAN Show Commands” on page 6-10
• Section 6.3 “Provisioning (IEEE 802.1p) Commands” on page 6-13
The commands in this section are in one of two functional groups:
• Show commands display switch settings, statistics, and other information.
• Configuration commands configure features and options of the switch. For every
configuration command, there is a show command that displays the configuration
setting.
6.1 VLAN Configuration Commands
This section describes the commands you use to configure VLAN settings.
6.1.1 vlan database
This command gives you access to the VLAN Config mode, which allows you to
configure VLAN characteristics.
Format
vlan database
Mode Privileged EXEC
6.1.2 network mgmt_vlan
This command configures the Management VLAN ID.
Default 1
Format
network mgmt_vlan <1-4069>
Page 94

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
6-2 VLAN Commands
v1.0, March 2006
Mode Privileged EXEC
6.1.2.1 no network mgmt_vlan
This command sets the Management VLAN ID to the default.
Format
no network mgmt_vlan
Mode Privileged EXEC
6.1.3 vlan
This command creates a new VLAN and assigns it an ID. The ID is a valid VLAN
identification number (ID 1 is reserved for the default VLAN). VLAN range is 2-4094.
Format
vlan <2-4094>
Mode VLAN Config
6.1.3.1 no vlan
This command deletes an existing VLAN. The ID is a valid VLAN identification number
(ID 1 is reserved for the default VLAN). The VLAN range is 2-4094.
Format
no vlan <2-4094>
Mode VLAN Config
6.1.4 vlan acceptframe
This command sets the frame acceptance mode per interface. For VLAN Only mode,
untagged frames or priority frames received on this interface are discarded. For Admit All
mode, untagged frames or priority frames received on this interface are accepted and
assigned the value of the interface VLAN ID for this port. With either option, VLAN
tagged frames are forwarded in accordance with the IEEE 802.1Q VLAN Specification.
Default all
Format
vlan acceptframe {vlanonly | all}
Mode Interface Config
6.1.4.1 no vlan acceptframe
This command sets the frame acceptance mode per interface to Admit All. For Admit All
mode, untagged frames or priority frames received on this interface are accepted and
assigned the value of the interface VLAN ID for this port. With either option, VLAN
tagged frames are forwarded in accordance with the IEEE 802.1Q VLAN Specification.
Page 95

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
VLAN Commands 6-3
v1.0, March 2006
Format vlan acceptframe {vlanonly | all}
Mode Interface Config
6.1.5 vlan ingressfilter
This command enables ingress filtering. If ingress filtering is disabled, frames received
with VLAN IDs that do not match the VLAN membership of the receiving interface are
admitted and forwarded to ports that are members of that VLAN.
Default disabled
Format
vlan ingressfilter
Mode Interface Config
6.1.5.1 no vlan ingressfilter
This command disables ingress filtering. If ingress filtering is disabled, frames received
with VLAN IDs that do not match the VLAN membership of the receiving interface are
admitted and forwarded to ports that are members of that VLAN.
Format
no vlan ingressfilter
Mode Interface Config
6.1.6 vlan makestatic
This command changes a dynamically created VLAN (one that is created by GVRP
registration) to a static VLAN (one that is permanently configured and defined). The ID is
a valid VLAN identification number. VLAN range is 2-4094.
Format
vlan makestatic <2-4094>
Mode VLAN Config
6.1.7 vlan name
This command changes the name of a VLAN. The name is an alphanumeric string of up to
32 characters, and the ID is a valid VLAN identification number. ID range is 1-4094.
Default VLAN ID 1 - default; other VLANS - blank string
Format
vlan name <2-4094> <name>
Mode VLAN Config
Page 96

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
6-4 VLAN Commands
v1.0, March 2006
6.1.7.1 no vlan name
This command sets the name of a VLAN to a blank string.
Format
no vlan name <2-4094>
Mode VLAN Config
6.1.8 vlan participation
This command configures the degree of participation for a specific interface in a VLAN.
The ID is a valid VLAN identification number, and the interface is a valid interface
number
.
Format vlan participation {exclude | include | auto} <1-
4094>
Mode Interface Config
Participation options are:
include The interface is always a member of this VLAN. This is
equivalent to registration fixed.
exclude The interface is never a member of this VLAN. This is equiv-
alent to registration forbidden.
auto The interface is dynamically registered in this VLAN by
GVRP. The interface will not participate in this VLAN unless
a join request is received on this interface. This is equivalent
to registration normal.
6.1.9 vlan participation all
This command configures the degree of participation for all interfaces in a VLAN. The ID
is a valid VLAN identification number
.
Format vlan participation all {exclude | include | auto}
<1-4094>
Mode Global Config
Participation options are:
include The interface is always a member of this VLAN. This is
equivalent to registration fixed.
exclude The interface is never a member of this VLAN. This is equiv-
alent to registration forbidden.
Page 97

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
VLAN Commands 6-5
v1.0, March 2006
auto The interface is dynamically registered in this VLAN by
GVRP. The interface will not participate in this VLAN unless
a join request is received on this interface. This is equivalent
to registration normal.
6.1.10 vlan port acceptframe all
This command sets the frame acceptance mode for all interfaces. The modes defined as
follows:
• VLAN Only mode - Untagged frames or priority frames received on this interface are
discarded.
• Admit All mode - Untagged frames or priority frames received on this interface are
accepted and assigned the value of the interface VLAN ID for this port.
With either option, VLAN tagged frames are forwarded in accordance with the IEEE
802.1Q VLAN Specification.
Default all
Format
vlan port acceptframe all {vlanonly | all}
Mode Global Config
6.1.10.1 no vlan port acceptframe all
This command sets the frame acceptance mode for all interfaces to Admit All. For Admit
All mode, untagged frames or priority frames received on this interface are accepted and
assigned the value of the interface VLAN ID for this port. With either option, VLAN
tagged frames are forwarded in accordance with the IEEE 802.1Q VLAN Specification.
Format
no vlan port acceptframe all
Mode Global Config
6.1.11 vlan port pvid all
This command changes the VLAN ID for all interface.
Default 1
Format
vlan port pvid all <1-4094>
Mode Global Config
6.1.11.1 no vlan port pvid all
This command sets the VLAN ID for all interfaces to 1.
Page 98

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
6-6 VLAN Commands
v1.0, March 2006
Format no vlan port pvid all
Mode Global Config
6.1.12 vlan port tagging all
This command configures the tagging behavior for all interfaces in a VLAN to enabled. If
tagging is enabled, traffic is transmitted as tagged frames. If tagging is disabled, traffic is
transmitted as untagged frames. The ID is a valid VLAN identification number.
Format
vlan port tagging all <1-4094>
Mode Global Config
6.1.12.1 no vlan port tagging all
This command configures the tagging behavior for all interfaces in a VLAN to disabled. If
tagging is disabled, traffic is transmitted as untagged frames. The ID is a valid VLAN
identification number.
Format
no vlan port tagging all
Mode Global Config
6.1.13 vlan port ingressfilter all
This command enables ingress filtering for all ports. If ingress filtering is disabled, frames
received with VLAN IDs that do not match the VLAN membership of the receiving
interface are admitted and forwarded to ports that are members of that VLAN.
Default disabled
Format
vlan port ingressfilter all
Mode Global Config
6.1.13.1 no vlan port ingressfilter all
This command disables ingress filtering for all ports. If ingress filtering is disabled, frames
received with VLAN IDs that do not match the VLAN membership of the receiving
interface are admitted and forwarded to ports that are members of that VLAN.
Format
no vlan port ingressfilter all
Page 99

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
VLAN Commands 6-7
v1.0, March 2006
Mode 6.1.14 Global Config
6.1.15 vlan protocol group
This command adds protocol-based VLAN group to the system. The <groupName> is a
character string of 1 to 16 characters. When it is created, the protocol group will be
assigned a unique number that will be used to identify the group in subsequent commands.
Format
vlan protocol group <groupname>
Mode Global Config
6.1.16 vlan protocol group add protocol
This command adds the <protocol> to the protocol-based VLAN identified by
<groupid>. A group may have more than one protocol associated with it. Each interface
and protocol combination can only be associated with one group. If adding a protocol to a
group causes any conflicts with interfaces currently associated with the group, this
command will fail and the protocol will not be added to the group. The possible values for
protocol are
ip, arp, and ipx.
Default none
Format
vlan protocol group add protocol <groupid> <protocol>
Mode Global Config
6.1.16.1 no vlan protocol group add protocol
This command removes the <
protocol> from this protocol-based VLAN group that is
identified by this <
groupid>. The possible values for protocol are ip, arp, and ipx.
Format
no vlan protocol group add protocol <groupid>
<protocol>
Mode Global Config
6.1.17 vlan protocol group remove
This command removes the protocol-based VLAN group that is identified by this
<groupid>.
Format
vlan protocol group remove <groupid>
Mode Global Config
Page 100

Command Line Interface Reference for the ProSafe 7200 Series Layer-2 Switches, Software Ver-
6-8 VLAN Commands
v1.0, March 2006
6.1.18 protocol group
This command attaches a <vlanid> to the protocol-based VLAN identified by <groupid>.
A group may only be associated with one VLAN at a time, however the VLAN
association can be changed.
The referenced VLAN should be created prior to the creation of the protocol-based VLAN
except when GVRP is expected to create the VLAN.
Default none
Format
protocol group <groupid> <vlanid>
Mode VLAN Config
6.1.18.1 no protocol group
This command removes the
<vlanid> from this protocol-based VLAN group that is
identified by this
<groupid>.
Format
no protocol group <groupid> <vlanid>
Mode VLAN Config
6.1.19 protocol vlan group
This command adds the physical interface to the protocol-based VLAN identified by
<groupid>. You can associate multiple interfaces with a group, but you can only associate
each interface and protocol combination with one group. If adding an interface to a group
causes any conflicts with protocols currently associated with the group, this command
fails and the interface(s) are not added to the group.
Create the referenced VLAN before you create the protocol-based VLAN except when
you configure GVRP to create the VLAN.
Format
protocol vlan group <groupid>
Mode Interface Config
6.1.19.1 no protocol vlan group
This command removes the interface
from this protocol-based VLAN group that is
identified by this
<groupid>.
Format
no protocol vlan group <groupid>
Mode Interface Config
 Loading...
Loading...