Page 1

Installation Guide
NCT240
IP DSLAM
Page 2

NetComm NCT240 Installation Guide Release 1.0
Table of Content
1. INTRODUCTION................................................................................................................................3
FEATURES.................................................................................................................................................... 4
2. SYSTEM APPLICA TION (UPDATE PICTURE!!!)......................................................................... 5
3. SYSTEM REQUIREMENT................................................................................................................ 6
LED DEFINITION......................................................................................................................................... 6
HARDWARE ................................................................................................................................................. 6
SOFTWARE FEATURE ................................................................................................................................... 7
4. INSTALLATION PROCEDURE........................................................................................................ 9
EQUIPMENT CHECKLIST .............................................................................................................................. 9
MOUNTING................................................................................................................................................ 10
INSTALLING OPTIONAL MODULES..............................................................................................................11
DESKTOP OR SHELF MOUNTING ................................................................................................................ 13
WALL MOUNT MOUNTING ......................................................................................................................... 14
PROPER GROUNDING (EARTH).................................................................................................................... 15
INSTALLING AN SFP TRANSCEIVER ........................................................................................................... 16
CONNECTING TO THE 1000BASE-T AND 10/100BASE-TX INTERFACE .................................................... 16
CONNECTING RJ-21 CABLES..................................................................................................................... 17
CONSOLE MANAGEMENT........................................................................................................................... 18
5. TROUBLESHOOTING..................................................................................................................... 23
TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE........................................................................................................................ 23
ALARM DEFINITION................................................................................................................................... 24
6. CABLE AND PIN ASSIGNMENT.................................................................................................... 28
10BASE-T/100BASE-TX PIN ASSIGNMENTS .......................................................................................... 28
1000BASE-T PIN ASSIGNMENTS .............................................................................................................. 29
RJ-21 PORT PIN ASSIGNMENTS ................................................................................................................. 29
CONSOLE PORT PIN ASSIGNMENTS............................................................................................................ 30
7. OBTAINING TECHNICAL ASSIST ANCE..................................................................................... 32
ACCESSORIES FOR NETCOMM NCT240 .................................................................................................... 32
8. SPECIFICATION............................................................................................................................... 33
HARDWARE ............................................................................................................................................... 33
SOFTWARE FEATURE ................................................................................................................................. 34
9. GLOSSARY........................................................................................................................................ 35
Page 3

NetComm NCT240 Installation Guide Release 1.0
1. Introduction
This document is intended for First Office Acceptance test plan for NetComm’s ADSL2+
Broadband Access Switch solution (BAS). The Netcomm NCT240 Broadband Access Switch
contains 24 ADSL2/2+ circuits to deliver high-speed data, video and voice service over traditional
twisted copper pairs by using DSL technology.
To meet the increasing demand for high-speed internet access and triple play application
services. The next generation network offers a feasible functionality of integrated ser vices with
the most cost effective architecture. Next generation broadband access networks are designed
to provide rich video contents, DSL, POTS and VoIP services over traditional copper wire
infrastructure. These types of services will be supported on NGN architecture simultaneously.
DSL is used as the data service platform for traditional POTS technology which is used for voice
services. The multimedia and local content-rich applications can also be easily implemented on
this NGN architecture.
xDSL (Digital Subscriber Line) is a technology for delivering high-bandwidth information over
copper telephone lines. xDSL service can deliver POTS and high date rate services simultaneously
over a single twisted-wire pair. The POTS and data service are simultaneous and independent;
the xDSL data service does not affect the POTS service. xDSL uses the bandwidth above the 4-kHz
POTS frequency to transmit duplex data using digital modulation techniques from the C.O side to
the Customer Premises Equipment (CPE).
ADSL is a form of xDSL service that delivers an asymmetric data rate over a twisted copper pair.
ADSL delivers a higher rate downstream, towards the customer premises and lower rate
upstream, from the customer premises. ITU standard compliant Full-Rate ADSL2+ can deliver
data rates up to 25 Mbps downstream and 1 Mbps upstream; Full-Rate ADSL can deliver data rates
up to 8 Mbps downstream and 800 kbps upstream; G.Lite ADSL can deliver up to 1.5 Mbps
downstream and 512 kbps upstream. The actual data rate depends on the length, gauge, and
condition of the twisted-wire pair, the bandwidth of the uplink depends on the data network,
and the capacity of the network service provider.
Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) dominates broadband market. The position of national telecom
operators in most countries has given the advantage in reaching out to customers with
broadband services over DSL.
The NCT240 Access system contains 24 ADSL2/2+ circuits to deliver high-speed data service over
twisted copper pairs using industry standard Discrete Multi-Tone (DMT) line coding technology.
The NCT240 complies with full-rate ADSL in accordance with ANSI T1.413 Issue 2, ITU-T G.992.1
(G.dmt), ITU-T G.992.2 (G.lite)ITU-T G.992.3 ( ADSL2) and ITU G.992.5 (G.ADSL2+) protocols.
The NCT240 greatly expand broadband capabilities in the access network, enhancing the
infrastructure for emerging servic es. With simple in-service upgrades, service provid ers obtain
the capacity and Quality of Service (QoS) to support larger populations of narrowband and
broadband users. For management, NCT240 can be easily configured by SNMP, T elnet, SSH, HTTP,
HTTPS and RS-232 console.
Page 4

NetComm NCT240 Installation Guide Release 1.0
Features
Complete Intelligent L2 switch feature
Intelligent DSL interworking feature
RFC2684 MpoA
VPN pass-through
RFC2516 PPPoE packet forwarding.
Advanced L2+/higher layer protocol & policy control
GVRP (IEEE 802.1q)
STP/RSTP (IEEE 802.1d/w)
IGMP Snooping
DHCP relay and relay agent option 82
Packet inspection and do policy control (filtering, forwarding..)
Security of authentication mechanism and encryption
SSH/SSL
Rich user interface for management including security
CLI/Telnet/SSH/SNMP/HTTP/S-HTTP
Variety of uplink interface
SFP for 1000 Base-SX, LX, LHX and ZX.
RJ45 for 1000 Base-TX.
Remote software upgrade
Page 5
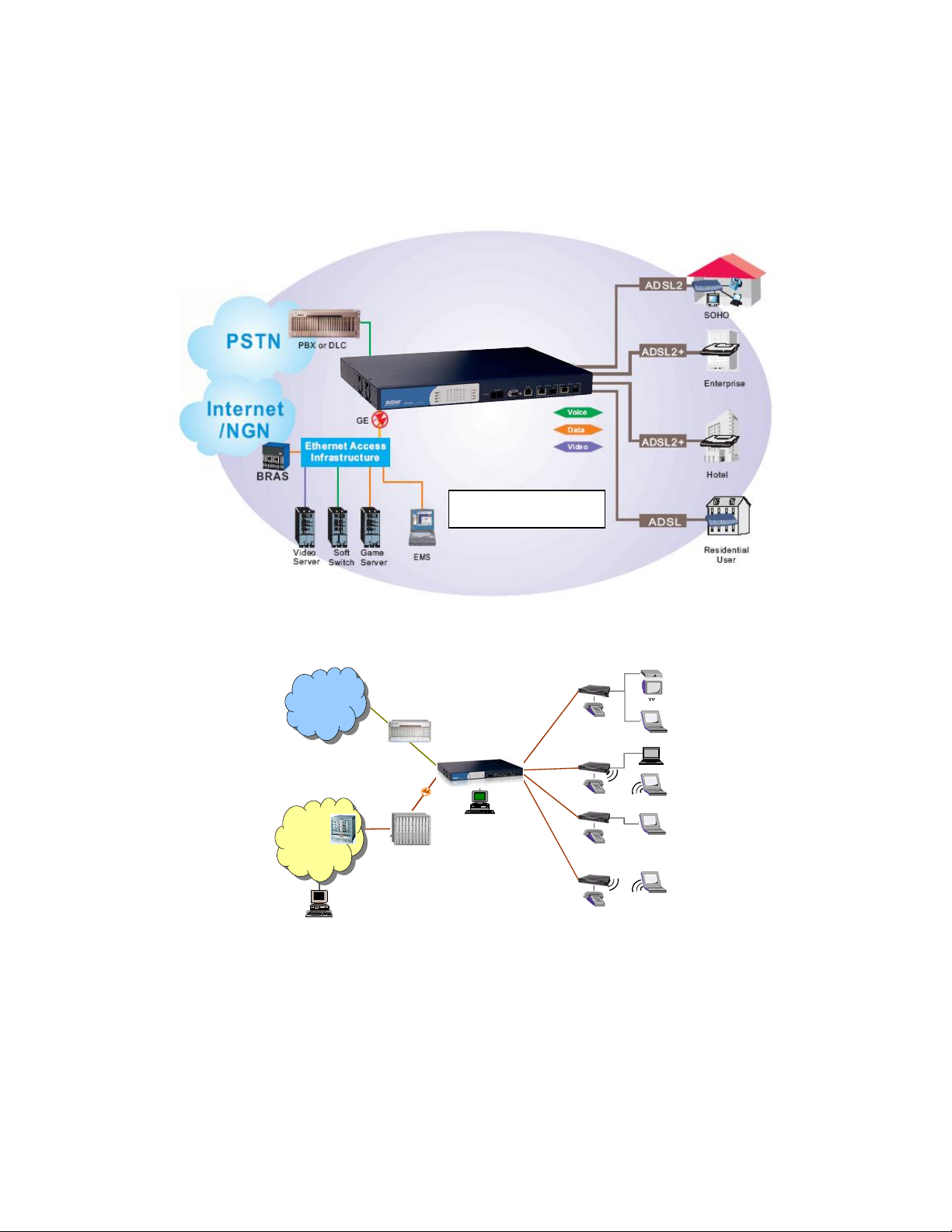
NetComm NCT240 Installation Guide Release 1.0
2. System Application
The following figures present the system application in the access network. NCT240 provides
video, voice and data service for different users, such as Hotels, SOHOs, residential users and
enterprises. The end user can use DSL for Various applications such as Telecommuting, Video
streaming, On-line game, IPTV, Distance learning, Telemedicine, Voice over IP and Video
conferencing...etc.
EMS: Element Management
Switch
Internet
EMS
Basic System Application
PSTN
BRAS
PBX or DLC
Aggregator
Switch
ADSL2+ (1)
BAS-8124
ADSL2+ (2)
CIT
ADSL2 (24)
ADSL (3)
.
.
ADSL2+
Modem
.
.
PC
PC
PC
PC
Page 6
NetComm NCT240 Installation Guide Release 1.0
3. System Requirement
LED Definition
Items LED color Function
PWR (power)
SYS (system)
SYS (system) - When the
ACO/RST button is pressed
MAJ (Major alarm )
GREEN – SOLID Power on
GREEN – SOLID
Flashing GREEN – 2Hz System is booting up
Flashing GREEN – 4Hz
Flashing GREEN – 1Hz
RED Major alarm reporting
System finished initializing
stage
System is ready to restart –
release the ACO/RST button
to restart
System is ready to reset to
Factory default – release the
ACO/RST button to reset to
factory default
MIN ( Minor alarm )
ADSL link
GE-FX Link
GE-TX Link
Hardware
Dimensions & Capacity
1. 19” wide rack mount available.
2. 1U height
3. Provide 24 DSL ports and built-in splitters.
Uplink Interfaces
1. The connector is SFP type at optical interface port.
2. The connector is RJ-45 at copper interface port.
3. When plug in SFP, the work interface will select optical interface automatic and
copper interface is assistant interface. And when plug out SFP, the copper interface
will change to work interface automatic.
4. Supported SFP optical module types have 1000 Base-SX, 1000 Base-LX, 1000
Base-LHX and 1000 Base-ZX.
Line Interfaces
1. Support 24 ports ADSL2+ line interface module (ATU-C).
2. Build in Splitter/Filter inte rnal.
3. The connectors are wire-wrapping; a converter device can be connected in
between interfaces and user device at both ADSL2+ line interface and PSTN
interface.
Management Interfaces
AMBER Minor alarm reporting
GREEN ADSL link is UP
Flashing GREEN DSL line is training (to linkup)
AMBER Ethernet Fiber port is UP
Flashing AMBER Dataflow activity in the port
GREEN Ethernet Copper port is UP
Flashing GREEN Dataflow activity in the port
Page 7

NetComm NCT240 Installation Guide Release 1.0
1. One Ethernet interface (RJ45) support Full Duplex and Half Duplex transceiver
function, conforms to IEEE 802.3 Auto-Negotiation standard and comply with
IEEE802.3 Ethernet, IEEE802.3u Fast Ethernet.
2. One RS232 console interface (DB9) support Full Duplex, 1、2 stop bits and odd、
even、none parity check. The baud rate range :12 00 baud rate ~ 921000 baud rate.
Power Supply
1. 60Wt. (input 90~260 VAC(10%), 50~60Hz)
2. 60Wt. (input –36~-72 VDC)
Operating Requirement
1. Temperature: -10ºC ~ 60ºC.
2. Humidity: 10~90% (non-condensing).
3. EMC/ESD Certification: FCC Part15 Class A.
4. Safety Certification : UL60950
ADSL/ADSL2+ Interface
1. ITU-T G.992.1 (G.dmt) [Annex A], ITU-T G.992.2 (G.lite) [Annex A]
2. ITU-T G.992.3 (ADSL2) [A,L], ITU-T G.992.5 (ADSL2+) [A,L]
3. OAM functionality according to ITU-T G.997.1 (G.ploam)
4. ANSI T1.413 Issue 2
5. Line loop back and diagnostic
Software Feature
L2/L3 Functionality
1. Switch capability: IEEE802.3x flow control, IEE E802.1d bridging.
2. VLAN: IEEE802.1p/q VLAN (4094), stacked VLAN, Port-based and Tag-based.
3. Multicasting: IGMP snooping, 250 groups , Dynamic & Static Configuration.
4. QoS: IEEE802.1p based COS, 4 priority output queue per port, RFC 2475
DiffServ/TOS.
5. DHCP: DHCP relay and relay agent option 82.
6. Rate Limitation: from 64K to Maximum rate, the ste p is 64K.
7. Security: Packet policy control (filtering/forwarding) and ACL function.
Interworking
1. RFC2684 MPoA LLC/VCMUX.
2. VPN pass-through
3. RFC2516 PPPoE packet forwarding.
Trouble Shooting
1. LED indicator for power, varied interfaces and system alar ms.
2. Cable labeling
3. Local and remote management by using serial and u plink interface
¾ On-line show link status, quality and traffic counters
¾ Loop back test
¾ Log event/alarm of system level
¾ Log event/alarm of GE and ADSL2+ interfaces
Management
1. CLI support for local management
2. SNMP V1/V2c
3. Telnet/SSH
Page 8

NetComm NCT240 Installation Guide Release 1.0
4. Web-based
5. Support FCAPS management for EMS
6. Syslog
7. SNTP
8. Remote software upgrade
9. Remote file backup and restore
Page 9

NetComm NCT240 Installation Guide Release 1.0
4. Installation Procedure
Equipment Checklist
Before installing the access switch please verify that you have received all the items listed u nder
“Package Contents.” If any of the items are missing or damaged, contact your local distributor.
Also, be sure you have all the necessary tools and cabling before installing the switch and splitter.
Note that these devices can be installed on any suitably large flat surface or in a standard EIA
19-inch rack.
Package Contents
1. A NCT240 ADSL2+ IP DSLAM
2. A Bracket Mounting Kit containing two brackets and four screws for attaching the brackets
to the DSLAM
3. One Power Cord
4. Four adhesive foot pads
5. One CD containing installation Guide and Management Guide
6. One RS-232 console cable (Optional)
7. Two RJ-21 cables (Optional)
Page 10

NetComm NCT240 Installation Guide Release 1.0
Mounting
The NCT240 may be mounted on any flat surface, such as a shelf, or in a rack. Before you start
installing the access switch, make sure you can provide the right operating environment,
including power requirements, sufficient physical space, and proxim ity to other network devices
that are to be connected. Verify the following installation requirements:
• Power requirements: 100 to 240 VAC (± 10%) at 50 to 60 Hz (± 3 Hz). The access switch power
supplies automatically adjust to the input voltage level. Make sure that a properly grounded
power outlet is within 2.5 m (8 ft) of the access switch.
• The access switch should be located in a cool dry place, with at least 10 cm (4 in.)of space on
the sides for ventilation.
• Place the access switch out of direct sunlight, and away from heat sources or areas with a high
amount of electromagnetic interference. The temperature and humidity should be within the
ranges listed in the specifications.
• If you intend to mount the access switch in a rack, make sure you have all the necessary
mounting screws, brackets, bolts and nuts, and the right tools.
• Check if network cables and connectors needed for installation are available.
• Be sure the access switch is within reach of the punch-down blocks for rear panel connections
that include DSL and splitter interface.
Page 11
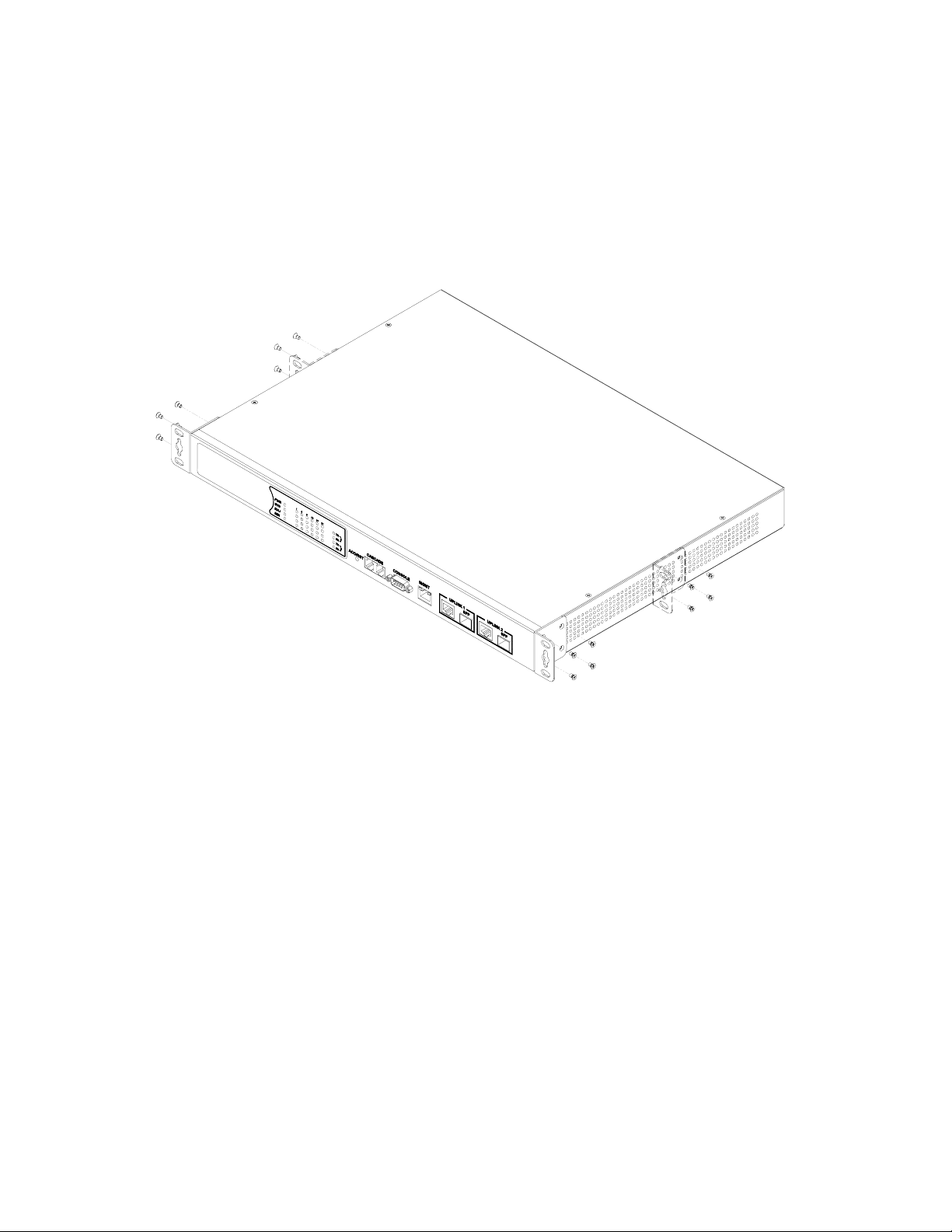
NetComm NCT240 Installation Guide Release 1.0
Installing Optional Modules
Before mounting the switch, be sure you install any optional modules. If you have purchased an
optional slide-in 1000BASE-T, SFP 1000BASE-X, install it now, and following the instructions
below.
To rack-mount devices:
1. Attach the brackets to the device using the screws provided in the Bracket Mounting Kit.
Figure 4-1. Attaching the Brackets
2. Mount the device in the rack, using four rack-mounting screws.
Page 12
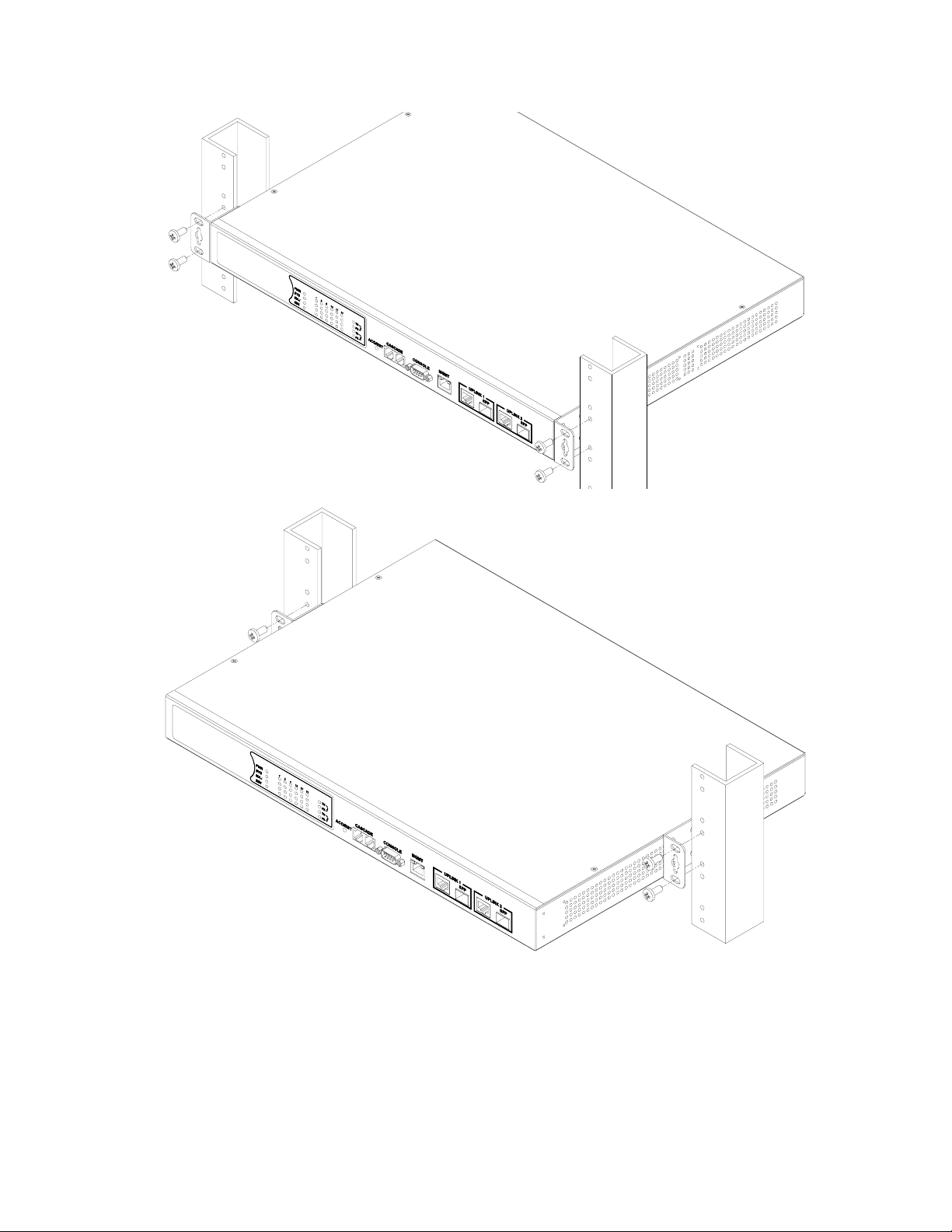
NetComm NCT240 Installation Guide Release 1.0
Figure 4-2. Installing the Switch in a Rack
3. If installing a single switch only, turn to “Powering On the Switch” at the end of this chapter.
4. If installing several devices, we recommend using one stack for the switch, and another for
the others. This will keep the cabling straight and easy to maintain.
Page 13

NetComm NCT240 Installation Guide Release 1.0
Desktop or Shelf Mounting
1. Attach the four adhesive feet to the bottom of the first switch.
Figure 4-3. Attaching the Adhesive Feet
2. Set the device on a flat surface near an AC power source, making sure there are at least two
inches of space on all sides for proper air flow.
3. If installing a single switch only, go to “Powering On the Switch” at the end of this chapter.
4. If installing multiple switches, attach four adhesive feet to each one. Place each device
squarely on top of the one below, in any order.
Page 14

NetComm NCT240 Installation Guide Release 1.0
Wall mount Mounting
1. Attach the four adhesive feet to the bottom of the first switch.
Figure 4-4. Installing the Switch on a Wall
2. Set the device on a flat surface near an AC power source, making sure there are at least two
inches of space on all sides for proper air flow.
3. If installing a single switch only, go to “Powering On the Switch” at the end of this chapter.
4. If installing multiple switches, attach four adhesive feet to each one. Place each device
squarely on top of the one below, in any order.
Page 15

NetComm NCT240 Installation Guide Release 1.0
Proper grounding (earth)
Proper Grounding is a very important part of the electrical installation for NCT240, if
noise is present in the Electrical ground this noise can leak to the ADSL circuit through
the Surge protectors and interfere with the proper operation of ADSL links.
*** both AC/DC power supplies are isolated from the NCT240 ground therefore the
Grounding procedure is the same regardless of what the power supply is .
NCT240 Ground:
Grounding procedure: (FIX Picture)
NCT240
NCT240
Page 16

NetComm NCT240 Installation Guide Release 1.0
Installing an SFP Transceiver
NCT240
Figure 4-5. Inserting an SFP Transceiver into the Slot
To install an SFP transceiver, do the following:
1. Use your cabling requirements to select an appropriate SFP transceiver type.
2. Insert the transceiver with the LC connector facing outward and the slot connector facing
down.
Note: SFP transceivers are keyed so they can only be installed in one orientation.
3. Slide the SFP transceiver into the slot until it clicks into place.
Notes:
1. If the stacking ports are connected, the SFP port will be disabled.
2. SFP transceivers are hot-swappable. You do not need to power off the switch before
installing or removing a transceiver. However, you should always first disconnect the
network cable before removing a transceiver.
Connecting to the 1000BASE-T and 10/100BASE-TX Interface
Each device requires an unshielded twisted-pair (UTP) cable with RJ-45 connectors at both ends.
For 1000BASE-T connections, Category 5, 5e or better cable is required; for 100BASE-TX
connections, Category 5 cable is required; for 10BASE-TX, Category 3,4, or 5 cable can be used.
The RJ-45 ports on the NCT240 modules support automatic MDI/MDI-X operation, so you can use
standard straight-through twisted-pair cables to connect to any other network device (PCs,
servers, switches, routers, or hubs).
Note: Auto-negotiation must be enabled for automatic MDI/MDI-X pin out configuration. See
Appendix B for further information on cabling.
Page 17

NetComm NCT240 Installation Guide Release 1.0
Connecting RJ-21 Cables
For incoming phone lines, a splitter can connect directly to a PBX or can be connected via a
punch-down block. The particular connection method used will depend on the type of
connectors and cables supported on the PBX, and on the existing cabling in the building.
The EE lines from the splitter interface of NCT240 are connected to the punch-down block that
connects the phone lines that run up to the end users. If the NCT240 is installed in a rack, it may
be convenient to use a patch panel between the splitter interface and the punch-down block.
For all connections to the splitter interface, cables with standard Telco RJ-21 connectors must
be used. Some punch-down blocks can be pre-wired with an RJ-21 connector provided, making
the connection simple. Otherwise, a cable with an RJ-21 on one end and free wi ring on the other
end will be required.
Figure 4-6. Connecting to the Punch-down Blocks
Follow the steps below to connect an EE Splitter to a building’s phone-line system using a
punch-down block:
1. Connect one RJ-21 flat cable from the PBX to the connector on the splitter’s rear panel
labeled “PBX/MDF.”
Note: Some installations may also have a separate punch-down block between the PBX and the
EE Splitter. In this case, connect an RJ-21 cable from the splitter’s “PBX/MDF” connector
to the punch-down block.
2. Connect another RJ-21 flat cable from the RJ-21 connector on the front of the splitter labeled
“Line” to the building’s phone-line punch-down block. Note that the connection to the
punch-down block usually requires punching down the free wires from the RJ-21 cable.
Note: If you use pre-wired punch-down blocks with RJ-21 connectors, be sure they are wired to
match the pin assignments of ports on the back of the splitter. To ensure that your cables
are properly wired, refer to “RJ-21 Port Pin Assignments” on page B-6.
Page 18

NetComm NCT240 Installation Guide Release 1.0
Console management
1. HyperTerminal setting
2. Bootloader startup
If you not press any key in the below state, system will load the default startup sequence to
do boot our system.
U-Boot 1.1.3 (Jun 29 2006 - 16:38:55) BAS ver:1.00.07
U-Boot code: 00200000 -> 0021CBCC BSS: -> 0022120C
RAM Configuration:
Bank #0: 00000000 128 MB
Flash: 32 MB
In: serial
Out: serial
Err: serial
Net: No ethernet found.
Hit any key to stop autoboot: 3
RTC clock initial start !!!
RTC clock initial end !!!
Scanning JFFS2 FS:
U-Boot 1.1.3 (Jun 29 2006 - 16:38:55) BAS ver:1.00.07
U-Boot code: 00200000 -> 0021CBCC BSS: -> 0022120C
RAM Configuration:
Page 19

NetComm NCT240 Installation Guide Release 1.0
Bank #0: 00000000 128 MB
Flash: 32 MB
In: serial
Out: serial
Err: serial
Net: No ethernet found.
Hit any key to stop autoboot: 3
Please choose booting method:
1--Startup from old kernel and old ramdisk
2--Startup from new kernel and old ramdisk
3--Startup from old kernel and new ramdisk
4--Startup from new kernel and new ramdisk
5--Startup from NFS
6--Startup from RAM
7--U-boot command line
Please choose booting method by pressing the option number:
Your choice is: 4--Startup from new kernel and new ramdisk
Do you want to save it as default booting method? y/n
RTC clock initial start !!!
RTC clock initial end !!!
Scanning JFFS2 FS: |
If you press a key during this state, there is a menu for you to do a choice the startup
sequence you prefer. After you choice a startup sequence this time, system will ask you whether
save this choice for next time startup.
Your choice is: 4--Startup from new kernel and new ramdisk
Do you want to save it as default booting method? y/n
RTC clock initial start !!!
RTC clock initial end !!!
Scanning JFFS2 FS: done.
-rw------- 8068015 Thu Jan 05 12:03:55 2006 uImage.ramdisk
-rw------- 1081250 Thu Jan 05 12:03:48 2006 uimage.kernel
drwx------ 0 Thu Jun 08 03:08:47 2006 config
drwxr-xr-x 0 Thu Jan 05 12:26:25 2006 aa
-rw------- 1187 Thu Jan 05 19:28:29 2006 telnet_info1
drwx------ 0 Thu Jan 05 12:01:20 2006 update
### JFFS2 loading 'update/newkernel.image' to 0x3000000
### JFFS2 load complete: 1081262 bytes loaded to 0x3000000
### JFFS2 loading 'update/newramdisk.image' to 0x5000000
In this state, system will take two~three minutes to do system initialize, so please have patience
with this procedure.
BAS>
Before you connect PC to NCT240 system, you should configure Ethernet first.
BAS>ip
Page 20

NetComm NCT240 Installation Guide Release 1.0
BAS/ip>?
help Display command list
? Display command list
show Display the management ip adress settings
arp Display, flush the device ARP table
set Set the management ip address and subnet mask
gateway Set the default gateway of the device's default gateway
ping Ping a remote host
root Return to the root directory.
exit Return to upper level
BAS/ip>set
Set the management ip address and subnet mask
set <ip|netmask>
ip .
netmask .
BAS/ip>set ip ixp0 192.168.1.1
Done
BAS/ip>set netmask ixp0 255.255.255.0
BAS/ip>show
ixp0 ip addr: 192.168.1.1
mac addr: 00:05:ca:00:42:11
gateway: 0.0.0.0
net mask: 255.255.255.0
eth0 ip addr: 192.168.0.1
mac addr: 00:05:ca:00:42:15
gateway: 0.0.0.0
net mask: 255.255.255.0
After configuring IP and Netmask, you should also configuring gateway of your network.
When the console starts, it will show the command prompt.
BAS>
You can type help or ?, and it will show all the command groups in this program. This program has
seven groups: sys, adsl, switch, isolation, ip, staticsti cs, and config . User can type end to termi nate
this program, or to type test to enter the test program.
BAS>help
Page 21

NetComm NCT240 Installation Guide Release 1.0
help Display command list
? Display command list
< sys >
< adsl >
< status >
< switch >
< ip >
< statistics >
< config >
exit Return to upper level
BAS0>
Type sys to enter the sys group, and then type help or ? to show the information about the sys.
User can also type “help argument” to display that how to execute this argument.
BAS/sys>help
help Display command list
? Display command list
daisycontrol The management of daisy chain
update Update system version
info Show general system information
user Setup user information
reboot Reboot the system
snmp SNMP information
server The device's service status and port numbers information
syslog Log the system status and exception
time The system's current time
date The system's current date
timeserver The system's time server
alarm The recorded system alarm
exit Return to upper level
BAS0/sys>
Ex. type “help info” command, system will show the message about this argument of info. Like
following figure, program will display the command of info and its arguments.
BAS/sys>help info
Show general system information.
info <show|switchname|location|contact|phone>
show Display general system information.
switchname Set the switch name.
location Set the location information.
contact Set the contact person information.
phone Set the contact phone number.
Page 22

NetComm NCT240 Installation Guide Release 1.0
And we can type the command of exit to leave the group sys, and this program will show following
figure
BAS>
If our location is in top of the level, and we want to terminate this program. We can type end to
terminate the program, like following figure.
BAS>end
BAS comand line program ended !
Above description, we only tell user the method about group sys, and the methods of other groups
like the same way. And we can type help to show the purpose of each group and its command.
Page 23
NetComm NCT240 Installation Guide Release 1.0
5. Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting guide
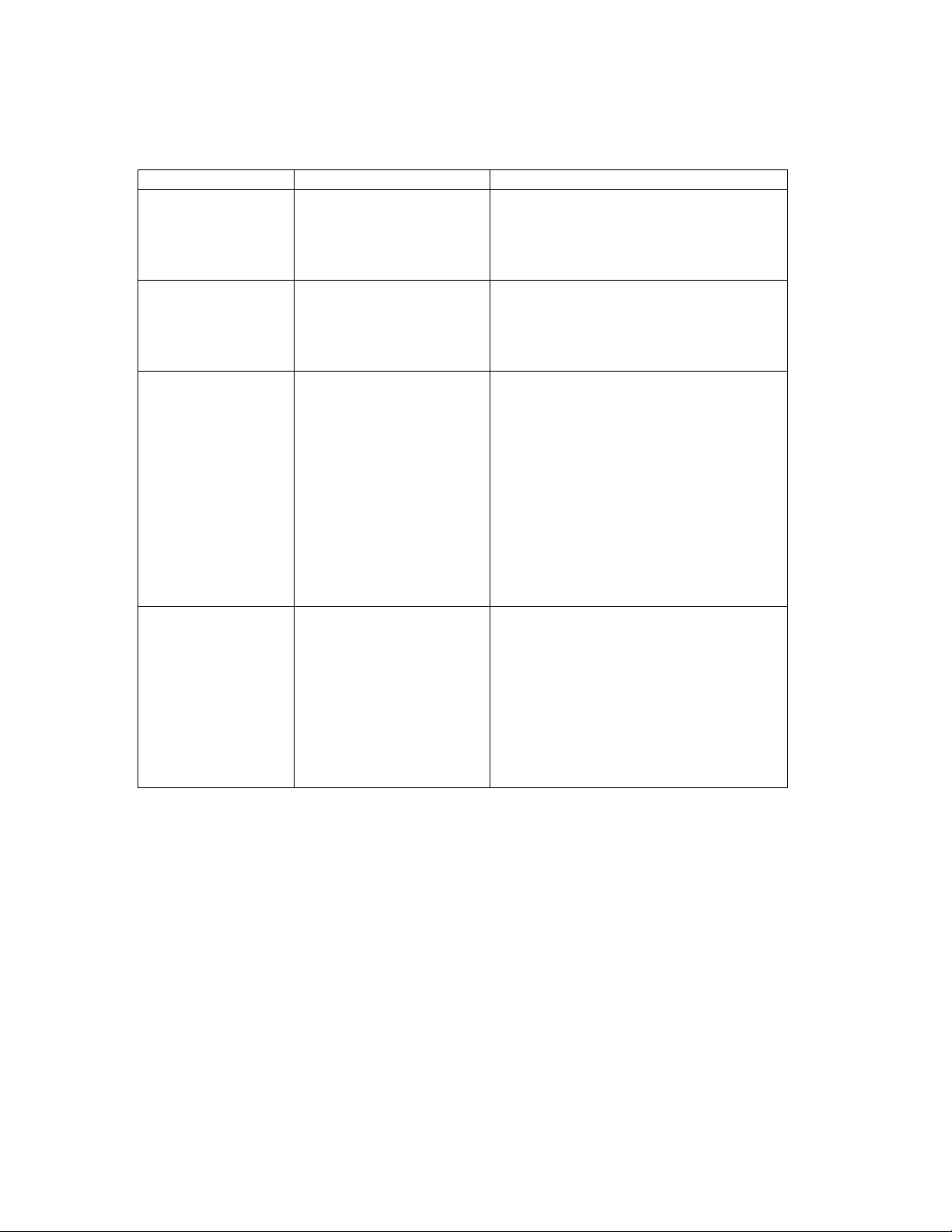
Trouble Possible cause Solution
PWR indicator does
not light up after
Turning on the
power.
SYS indicator does
not light up after
startup.
ADSL2+ LINK
indicator does not
light up after making
a connection.
UP LINK indicator
does not light up
after making a
connection.
Power outlet, power cord,
or internal power supply
may be defective.
Microprocessor, SDRAM,
Flash or Software may be
defective.
NCT240 Switch, cabling,
ADSL Line, or ADSL Switch
Ports may be defective.
Network cable or Ethernet
device attached to this
port may be defective.
• Check the power outlet by plugging in
another device that is functioning
properly.
• Check the power cord with another
device.
• Verify that the switch are powered on.
• Check the boot-up statement from
console. The boot up procedure is Boot
-> kernel->application
•
• Verify that the Access Switch and
attached CPE are powered on.
• Be sure the RJ-21 cables are plugged
into the Access Switch from ADSL2+
modem through the Phone-line
punch-down block.
• Verify that the cable length does not
exceed specified limits.
• Check the cable connections on the
access Switch, punch-down block/patch
panel, and the Extended Ethernet CPE
for possible defects. Replace the
defective cable if necessary.
• Verify that the access switch and
attached device are powered on.
• Be sure an Ethernet cable is plugged into
both the switch and attached device.
• Verify that the proper cable type is used
and its length does not exceed specified
limits.
• Check the network cable connections
for possible defects. Replace the
defective cable if necessary.
Page 24
NetComm NCT240 Installation Guide Release 1.0
Alarm definition
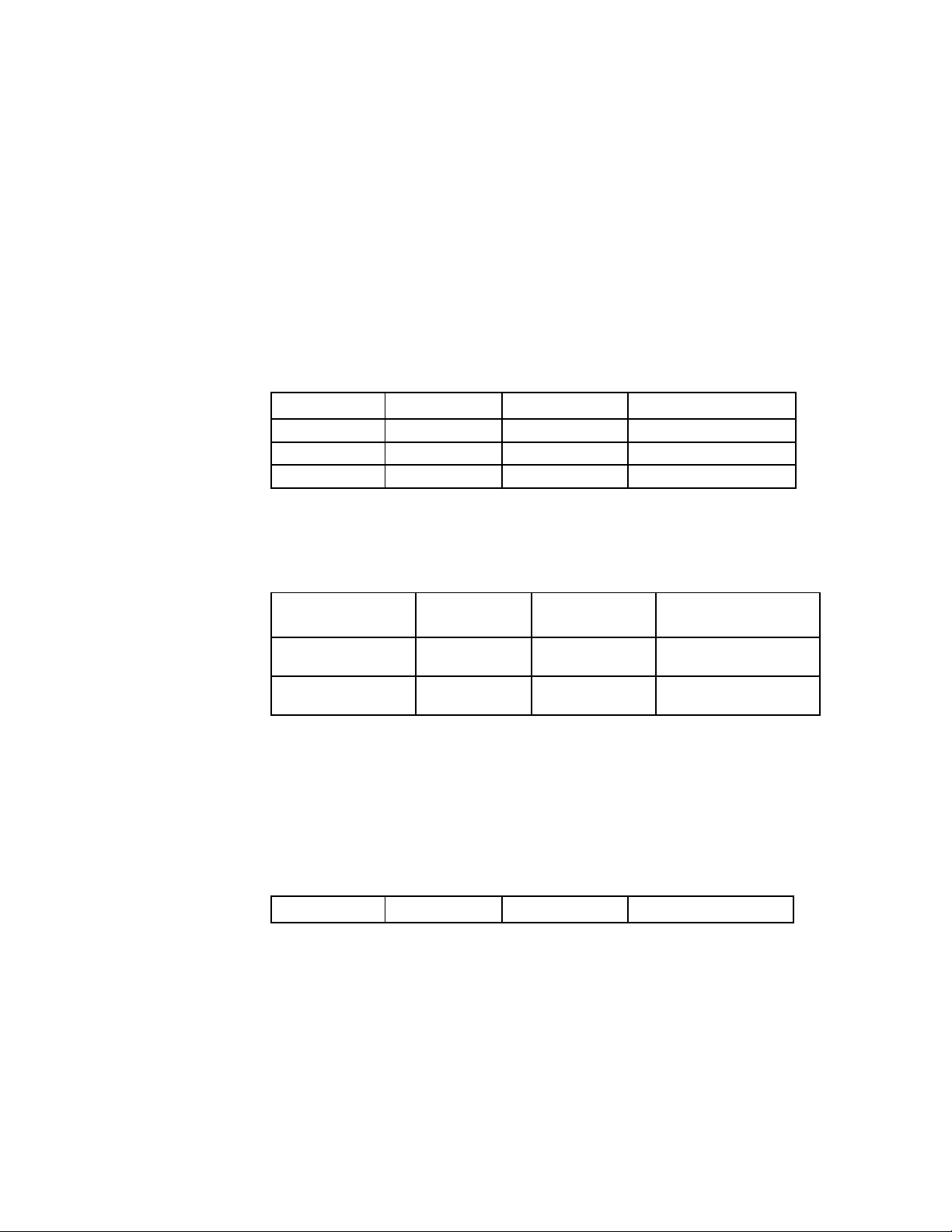
1. Information about this Alarm Definition.
The NCT240 alarm system have two ways that to make a sound by external alarm
out or LED signal on faceplate to indicate an error condition. In this document, we
declare the alarm as follow format:
Alarm Type Alarm Level Alarm Group Alarm Description
Alarm Level: Major/Minor
Alarm Group: System/CGC group/GEMINAX Group
2. System alarm
The system alarms are triggered by ALARM OUT or kernel oops.
Alarm Type Alarm Level Alarm Group Alarm Description
DoorOpen Major sys Device has been opend
PowerFail Major Sys Power failure
TemDetect Major Sys Fire/ High temperature
Table 1 System Alarm
3. CGC alarm
The CGC alarms are including the GE ports errors.
Alarm Type Alarm
Level
GE port0 link
down
GE port1 link
down
Major CGC GE port0 link down
Major CGC GE port1 link down
Table 2 CGC Alarm
4. GEMINAX alarm
The GEMINAX alarm includes the alarms on the ports.
Alarm Type Alarm Level Alarm Group Alarm Description
Alarm
Group
Alarm
Description
Page 25
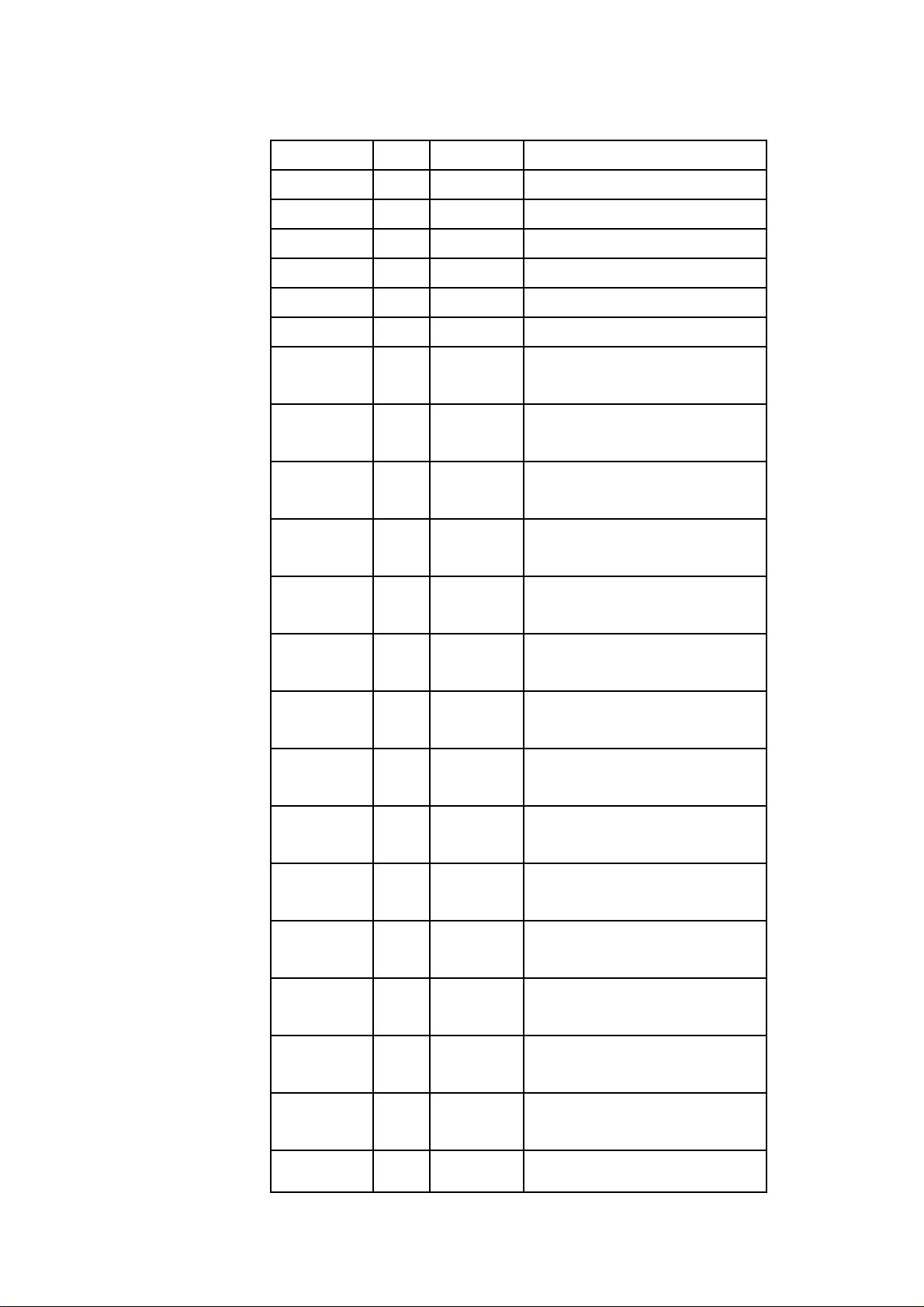
NetComm NCT240 Installation Guide Release 1.0
LPR Major GEMINAX Loss-of-power
LOF Major GEMINAX Loss-of-frame
LOS Major GEMINAX Loss-of-signal
LOM Major GEMINAX loss-of-margin
LOL Major GEMINAX Loss of Link
NCD Major GEMINAX No Cell Delineation
LCD Major GEMINAX Loss of Cell Delineation
15M FECS Major GEMINAX 15 minutes threshold error
Forward Error Correction Seconds
15M ES Major GEMINAX 15 minutes threshold error
Errored Seconds
15M SES Major GEMINAX 15 minutes threshold error
Severely Errored Seconds.
15M UAS Major GEMINAX 15 minutes threshold error
Unavailable Seconds.
15M LOSS Major GEMINAX 15 minutes threshold error
Loss of Signal Seconds.
15M LOFS Major GEMINAX 15 minutes threshold error
Loss of Frame Seconds.
15M LOLS Major GEMINAX 15 minutes threshold error
Loss of Link Seconds.
15M LPRS Major GEMINAX 15 minutes threshold error
Loss of Power Seconds.
15M FIFAIL Major GEMINAX 15 minutes threshold error
Failed full initializations
15M SIFAIL Major GEMINAX 15 minutes threshold error
Failed short initializations
1D FECS Major GEMINAX 1 Day threshold error
Forward Error Correction Seconds
1D ES Major GEMINAX 1 Day threshold error
Errored Seconds
1D SES Major GEMINAX 1 Day threshold error
Severely Errored Seconds
1D UAS Major GEMINAX 1 Day threshold error
Unavailable Seconds.
1D LOSS Major GEMINAX 1 Day threshold error
Page 26

NetComm NCT240 Installation Guide Release 1.0
Loss of Signal Seconds
1D LOFS Major GEMINAX 1 Day threshold error
Loss of Frame Seconds
1D LOLS Major GEMINAX 1 Day threshold error
Loss of Link Seconds.
1D LPRS Major GEMINAX 1 Day threshold error
Loss of Power Seconds.
1D FIFAIL Major GEMINAX 1 Day threshold error
Failed full initializations
1D SIFAIL Major GEMINAX 1 Day threshold error
Failed short initializations
15M FEC Major GEMINAX 15 minutes threshold error
Forward Error Corrections.
15M CV Major GEMINAX 15 minutes threshold error
Coding Violations
1D FEC Major GEMINAX 1 Day threshold error
Forward Error Corrections.
1D CV Major GEMINAX 1 Day threshold error
Coding Violations
15M HEC Major GEMINAX 15 minutes threshold error
Header Error Control
15M
TOTALCELL
15M
USERCELL
15M IBE Major GEMINAX 15 minutes threshold error
15M CRC_P Major GEMINAX 15 minutes threshold error
Major GEMINAX 15 minutes threshold error
Total cells
Major GEMINAX 15 minutes threshold error
User cells
Cell Bit Error
non pre-emptive packets with CRC
error in the bearer channel threshold
crossing.
15M CRCP_P Major GEMINAX 15 minutes threshold error
Pre-emptive packets with CRC error
in the bearer channel threshold
crossing.
Page 27

NetComm NCT240 Installation Guide Release 1.0
15M CV_P Major GEMINAX 15 minutes threshold error
non pre-emptive packets with coding
violation in the bearer channel
threshold crossing.
15M CVP_P Major GEMINAX 15 minutes threshold error
pre-emptive packets with coding
violation in the bearer channel
threshold crossing.
1D HEC Major GEMINAX 1 Day threshold error
Header Error Control
1D
TOTALCELL
1D
USERCELL1D
Major GEMINAX 1 Day threshold error
Total cells
Major GEMINAX 1 Day threshold error
User cells
1D IBE Major GEMINAX 1 Day threshold error
Cell Bit Error
1D CRC_P Major GEMINAX 1 Day threshold error
non pre-emptive packets with CRC
error in the bearer channel threshold
crossing.
1D CRCP_P Major GEMINAX 1 Day threshold error
Pre-emptive packets with CRC error
in the bearer channel threshold
crossing.
1D CV_P Major GEMINAX 1 Day threshold error
non pre-emptive packets with coding
violation in the bearer channel
threshold
crossing.
1D CVP_P Major GEMINAX 1 Day threshold error
pre-emptive packets with coding
violation in the bearer channel
threshold crossing.
Table 3 GEMINAX Alarm
Page 28

NetComm NCT240 Installation Guide Release 1.0
6. Cable and Pin Assignment
Following illustrates how the pins on the RJ-45 connector are numbered. Be sure to hold the
connectors in the same orientation when attaching the wires to the pins.
Figure 5-1. Connecting to the Punch-down Blocks
10BASE-T/100BASE-TX Pin Assignments
For 100BASE-TX/10BASE-T connections, a twisted-pair cable must have two pairs of wires. Each wire
pair is identified by two different colors. For example, one wire might be red and the other, red with white
stripes. Also, an RJ-45 connector must be attached to both ends of the cable.
With 100BASE-TX/10BASE-T cable, pins 1 and 2 are used for transmitting data, and pins 3 and 6 for
receiving data.
Pin Number Assignment
1 Tx+
2 Tx3 Rx+
6 Rx-
Because the ports on the NCT240 support automatic MDI/MDI-X operation, you can use
straight-through cables for all network connections to PCs or servers, or to other switches or hubs. In
straight-through cable, pins 1, 2, 3, and 6, at one end of the cable, are connected straight through to pins 1,
2, 3 and 6 at the other end of the cable. The table below shows the 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX MDI and
MDI-X port pin outs.
Page 29

NetComm NCT240 Installation Guide Release 1.0
Pin MDI-X Assignment MDI Assignment
1
2
3
6
Input Receive Data + Output Transmit Data +
Input Receive Data - Output Transmit Data -
Output Transmit Data + Input Receive Data +
Output Transmit Data - Input Receive Data -
Note: Auto-negotiation must be enabled for automatic MDI/MDI-X pinout configuration.
1000BASE-T Pin Assignments
1000BASE-T ports support automatic MDI/MDI-X operation, so you can use straight-through cables for
all network connections to PCs or servers, or to other switches or hubs. The table below shows the
1000BASE-T MDI and MDI-X port pinouts. These ports require that all four pairs of wires be connected.
Note that for 1000BASE-T operation, all four pairs of wires are used for both transmit and receive. Use
100-ohm Category 5, 5e or better unshielded twisted-pair (UTP) or shielded twisted-pair (STP) cable for
1000BASE-T connections. Also be sure that the length of any twisted-pair connection does not exceed 100
meters (328 feet).
Pin MDI Signal Name MDI-X Signal Name
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Transmit Data plus (TD1+) Transmit Data plus (TD2 +)
Receive Data minus (RD1-) Receive Data minus (RD2-)
Transmit Data plus (TD2+) Transmit Data plus (TD1+)
Transmit Data plus (TD3+) Transmit Data plus (TD4+)
Receive Data minus (RD3-) Receive Data minus (RD4-)
Receive Data minus (RD2-) Receive Data minus (RD1-)
Transmit Data plus (TD4+) Transmit Data plus (TD3+)
Receive Data minus (RD4-) Receive Data minus (RD3-)
RJ-21 Port Pin Assignments
The PBX/MDF connector is designed to aggregate 24 POTS/ISDN ports. Each wire pair must be
attached to the RJ-21 connector in a specific orientation detailed below. The following table shows the pin
assignments.
Page 30

NetComm NCT240 Installation Guide Release 1.0
Pins Circuit Pins Circuit Pins Circuit Pins Circuit
1,26 1,Ring/Tip 7,32 7,Ring/Tip 13,38 13,Ring/Tip 19,44 19,Ring/Tip
2,27 2,Ring/Tip 8,33 8,Ring/Tip 14,39 14,Ring/Tip 20,45 20,Ring/Tip
3,28 3,Ring/Tip 9,34 9,Ring/Tip 15,40 15,Ring/Tip 21,46 21,Ring/Tip
4,29 4,Ring/Tip 10,35 10,Ring/Tip 16,41 16,Ring/Tip 22,47 22,Ring/Tip
5,30 5,Ring/Tip 11,36 11,Ring/Tip 17,42 17,Ring/Tip 23,28 23,Ring/Tip
6,31 6,Ring/Tip 12,37 12,Ring/Tip 18,43 18,Ring/Tip 24,49 24,Ring/Tip
The Extended Ethernet Line connector is designed to aggregate 24 Ethernet ports. The following table
shows the pin assignments.
Pins Circuit Pins Circuit Pins Circuit Pins Circuit
1,26 Port 1 7,32 Port 7 13,38 Port 13 19,44 Port 19
2,27 Port 2 8,33 Port 8 14,39 Port 14 20,45 Port 20
3,28 Port 3 9,34 Port 9 15,40 Port 15 21,46 Port 21
4,29 Port 4 10,35 Port 10 16,41 Port 16 22,47 Port 22
5,30 Port 5 11,36 Port 11 17,42 Port 17 23,28 Port 23
6,31 Port 6 12,37 Port 12 18,43 Port 18 24,49 Port 24
Console Port Pin Assignments
The DB-9 serial port on the switch’s rear panel is used to connect to the switch for out-of-band console
configuration. The on-board menu-driven configuration program can be accessed from a terminal, or a PC
running a terminal emulation program. The pin assignments used to connect to the serial port are provided
in the following tables.
Page 31

NetComm NCT240 Installation Guide Release 1.0
Figure 5-1. Connecting to the Punch-down Blocks
DB-9 Port Pin Assignments
EIA Circuit CCITT Signal
Description Switch’s DB-9
PC DB-9 DTE Pin
DTE Pin #
BB 104
BA 103
AB 102
RxD (Received Data)
TxD (Transmitted Data)
SGND (Signal Ground)
2 2
3 3
5 5
Console Port to 9-Pin DTE Port on PC
Switch’s 9-pin Serial Port CCITT Signal PC’s 9-pin DTE Port
2 RxD <----------RXD ------------ 3 TxD
3 TxD -------------TXD -----------> 2 RxD
5 SGND ------------SGND ----------- 5 SGND
#
Page 32

NetComm NCT240 Installation Guide Release 1.0
7. Obtaining Technical Assistance
For this NCT240 installation procedures, please contact NetComm Limited.
Accessories for NetComm NCT240
1. A Bracket Mounting Kit
It contains two brackets and four screws for attaching the brackets to the DSLAM
2. One Power Cord
3. Four adhesive foot pads
4. One CD containing installation Guide and Management Guide
5. One RS-232 console cable (Optional)
6. Two RJ-21 cables which consist of 24-pair Category 3 telephone lines (Optional).
Page 33

NetComm NCT240 Installation Guide Release 1.0
8. Specification
Hardware
Dimensions
(WxDxH): 440 x 320 x 44.4 mm
Weight
5.2 Kg
LED
System: Power, System, Major and Minor alarm.
ADSL port: link
Uplink Port: TX link and FX link.
Interfaces
One RS232 Serial port for management
One RJ21 for DSL port
One RJ21 for Splitter port
ACO/RST for alarm cut off and system reset
Two RJ45 1000 Base-TX and One SFP interface (w/o optical module) for uplink
port
Remark: 1000 Base-SX, 1000 Base-LX, 1000 Base-LHX and 1000 Base-ZX.
Ethernet interface comply with IEEE802.3ab Gigabit Ethernet, IEEE802.3z
Gigabit Ethernet.
Power Supply
60Wt. (input 90~260 VAC(10%), 50~60Hz)
60Wt. (input –36~-72 VDC)
Operating Requirement
Temperature: -10ºC ~ 60ºC.
Humidity: 0~95% (non-condensing).
EMC/ESD Certification: FCC Part15 Class A.
Safety Certification: UL60950
ADSL/ADSL2+ Interface
ITU-T G.992.1 (G.dmt) [Annex A], ITU-T G.992.2 (G.lite) [Annex A]
ITU-T G.992.3 (ADSL2) [A,L], ITU-T G.992.5 (ADSL2+) [A,L]
OAM functionality according to ITU-T G.997.1 (G.ploam)
Page 34

NetComm NCT240 Installation Guide Release 1.0
ANSI T1.413 Issue 2
Line loop back and diagnostic
Software Feature
L2/L3 Functionality
Switch capability: IEEE802.3x flow control, IEEE802.1d brid ging.
VLAN: IEEE802.1p/q VLAN (4094), stacked VLAN, Port-based and Tag-based.
Multicasting: IGMP snooping, 250 groups, Dynamic&Static Configuration.
QoS: IEEE802.1p based COS, 4 priority output queue per port, RFC 2475
DiffServ/TOS.
DHCP: DHCP relay and relay agent option 82.
Rate Limitation: from 64K to Maximum rate, the step is 64K.
Interworking
RFC2684 MPoA LLC/VCMUX.
VPN pass-through
RFC2516 PPPoE packet forwarding.
Trouble Shooting
LED indicator for power, varied interfaces and system alarms.
Local and remote management by using serial and uplink interface
Cable labeling
Management
CLI support for local management
SNMP V1/V2c
¾ On-line show link status monitor, quality and traffic counters
¾ Loop back test
¾ Log event/alarm of system level
¾ Log event/alarm of GE and ADSL2+ interfaces
Telnet/SSH
Web-based
Support FCAPS management for EMS
Syslog
SNTP
Remote software upgrade
Remote file backup and restore
Page 35

NetComm NCT240 Installation Guide Release 1.0
9. Glossary
10BASE-T
IEEE 802.3 specification for 10 Mbps Ethernet over two pairs of Category 3, 4, or 5 UTP cable.
100BASE-TX
IEEE 802.3u specification for 100 Mbps Fast Ethernet over two pairs of Catego ry 5 UTP cable.
100BASE-FX
IEEE 802.3u specification for 100 Mbps Fast Ethernet over two stra nds of 50/125, 62.5/125 or
9/125 micron core fiber cable.
1000BASE-T
IEEE 802.3ab specification for Gigabit Ethernet over 100-ohm Category 5 or 5e twisted-pair
cable (using all four wire pairs).
Auto-Negotiation
Signaling method allowing each node to select its optimu m operational mode (e.g., 10 Mbps
or 100 Mbps and half or full duplex) based on the capability of the node to which it is
connected.
Bandwidth
The difference between the highest and lowest frequencies available for network signals.
Also synonymous with wire speed, the actual speed of the data transmission along the cable.
Collision
A condition in which packets transmitted over the cable interferes with each other. Their
interference makes both signals unintelligible.
Collision Domain
Single CSMA/CD LAN segment.
CSMA/CD
CSMA/CD (Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detect) is the communication method
employed by Ethernet, Fast Ethernet, or Gigabit Ethernet.
End Station
A workstation, server, or other device that does not forward traffic.
Ethernet
A network communication system developed and standardized by DEC, Intel, and Xerox,
using baseband transmission, CSMA/CD access, logical bus topology, and coaxial cable. The
successor IEEE 802.3 standard provides for integration into the OSI model and extends the
physical layer and media with repeaters and implementations that operate on fiber, thin
coax and twisted-pair cable.
Fast Ethernet
A 100 Mbps network communication system based on Ethernet and the CSMA/CD acce ss
method.
Gigabit Ethernet
Page 36

NetComm NCT240 Installation Guide Release 1.0
A 1000 Mbps network communication system based on Ethernet and the CSMA/CD access
method.
Full-Duplex
Transmission method that allows two network devices to transmit and receive concurrently,
effectively doubling the bandwidth of that link.
IEEE
Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers.
IEEE 802.3
Defines carrier sense multiple access with collision detection (CSMA/CD) access method and
physical layer specifications.
IEEE 802.3ab
Defines CSMA/CD access method and physical layer specifications for 1000BASE-T Fast
Ethernet.
IEEE 802.3u
Defines CSMA/CD access method and physical layer specifications for 100BASE-TX Fast
Ethernet.
IEEE 802.3x
Defines Ethernet frame start/stop requests and timers used for flow control on full-duplex
links.
IEEE 802.3z
Defines CSMA/CD access method and physical layer specifications for 1000BASE Gigabit
Ethernet.
Local Area Network (LAN)
A group of interconnected computer and support devices.
LAN Segment
Separate LAN or collision domain.
LED
Light emitting diode used for monitoring a device or network condition.
Local Area Network
A group of interconnected computers and support devices.
Media Access Control (MAC)
A portion of the networking protocol that governs access to the transmission medium,
facilitating the exchange of data between network nodes.
MDF (Main Distribution Frame)
Equipment where outside telephone lines are terminated at a building or site.
MIB
An acronym for Management Information Base. It is a set of database objects that contains
information about the device.
Page 37

NetComm NCT240 Installation Guide Release 1.0
MPOE (Minimum or Main Point of Entry)
The location in a building where cables from the telephone service provider are terminated.
Network Diameter
Wire distance between two end stations in the same collision domain.
Private Branch Exchange (PBX)
A telephone exchange local to a particular organization who use, rather than provide,
telephone services.
POTS
Plain Old Telephone Service.
Redundant Power Unit (RPU)
A backup power supply that automatically takes over in case the primary power supply should
fail.
RJ-45 Connector
A connector for twisted-pair wiring.
Splitter
A filter to separate DSL signals from POTS signals to prevent mutual interferen ce.
Switched Ports
Ports that are on separate collision domains or LAN segments.
Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
Protocol suite that includes TCP as the primary transport protocol, and I P as the network
layer protocol.
UTP
Unshielded twisted-pair cable.
ADSL
asymmetric data rate Digital Subscriber Line: A family of digital telecommunications
protocols designed to allow high speed data communication at data rates deliver data rates
up to 25 Mbps downstream and 1 Mbps upstream with corresponding maximum reach 18K feet
of 24 gauge twisted pair cable over the existing copper telephone lines between end-users
and telephone companies.
Virtual LAN (VLAN)
A Virtual LAN is a collection of network nodes that share the same collision domain re gardle ss
of their physical location or connection point in the network. A VLAN serves as a logical
workgroup with no physical barriers, allowing users to share information and resources as
though located on the same LAN.
Page 38

Product Warranty
NetComm products have a standard 12 months warranty from date of purchase. However some products have an extended
registering your product online at the NetComm website www.netcomm.com.au. Refer to the Management Guide
conditions, limitations of warranty and other legal and regulatory information.
for complete product warranty
warranty option, via
Contact Information
If you have any technical difficulties with your product, please do not hesitate to contact NetComm’s Customer Support Department.
Email: support@netcomm.com.au
www.netcomm.com.au
Note: NetComm Technical Support for this product only covers the basic installation and features outlined in the Quick Start Guide. For further information regarding the advanced features of this
product, please refer to the configuring sections in the User Guide or contact a Network Specialist.
NetComm Limited ABN 85 002 490 486
PO Box 1200, Lane Cove NSW 2066 Australia
E – sales@netcomm.com.au W – www.netcomm.com.au
 Loading...
Loading...