Page 1

DATA SHEET
MOS INTEGRATED CIRCUIT
µ
PD75P3116
4-BIT SINGLE-CHIP MICROCONTROLLER
The µPD75P3116 replaces the µPD753108’s internal mask ROM with a one-time PROM, and features expanded
ROM capacity.
µ
Because the
development stage using the
Detailed information about functions is provided in the following User’s Manual. Be sure to read it before
designing:
PD75P3116 supports programming by users, it is suitable for use in evaluation of systems in the
µ
PD753104, 753106, or 753108, and for use in small-scale production.
µ
PD753108 User’s Manual: U10890E
FEATURES
Compatible with µPD753108
Memory capacity:
• PROM: 16384 × 8 bits
• RAM: 512 × 4 bits
Can be operated in same power supply voltage range as the mask version µPD753108
• VDD = 1.8 to 5.5 V
On-chip LCD controller/driver
QTOPTM microcontroller
Remark QTOP microcontrollers are microcontrollers with on-chip one-time PROM that are totally supported by NEC.
This support includes writing application programs, marking, screening, and verification.
ORDERING INFORMATION
Part Number Package
µ
PD75P3116GC-AB8 64-pin plastic QFP (14 × 14)
µ
PD75P3116GK-8A8 64-pin plastic LQFP (12 × 12)
µ
PD75P3116GC-8BS 64-pin plastic LQFP (14 × 14)
Caution This device does not provide an internal pull-up resistor connection function by means of mask
option.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. Before using this document, please
confirm that this is the latest version.
Not all devices/types available in every country. Please check with local NEC representative for
availability and additional information.
Document No. U11369EJ3V0DS00 (3rd edition)
Date Published March 2002 N CP(K)
Printed in Japan
The mark shows major revised points.
1994
Page 2

µ
PD75P3116
FUNCTION OUTLINE
Item Function
Instruction execution time • 0.95, 1.91, 3.81, or 15.3 µs (main system clock: @ 4.19 MHz)
• 0.67, 1.33, 2.67, or 10.7 µs (main system clock: @ 6.0 MHz)
• 122 µs (subsystem clock: @ 32.768 kHz)
Internal memory PROM 16384 × 8 bits
RAM 512 × 4 bits
General-purpose registers • 4-bit manipulation: 8 × 4 banks
• 8-bit manipulation: 4 × 4 banks
I/O ports CMOS input 8 Internal pull-up resistor connection can be specified by software setting: 7
CMOS I/O 20
N-ch open-drain I/O 4 13 V withstanding voltage
Total 32
LCD controller/driver • Segment number selection: 16/20/24 segments (switchable to CMOS I/O ports
Timers 5 channels: • 8-bit timer/event counter: 3 channels
Serial interface • 3-wire serial I/O mode ··· MSB/LSB first switchable
Bit sequential buffer (BSB) 16 bits
Clock output (PCL) Φ, 524, 262, and 65.5 kHz (main system clock: @ 4.19 MHz)
Buzzer output (BUZ) • 2, 4, and 32 kHz (
Vectored interrupts • External: 3
Test inputs • External: 1
System clock oscillator • Ceramic/crystal oscillator for main system clock
Standby function STOP/HALT mode
Power supply voltage VDD = 1.8 to 5.5 V
Package • 64-pin plastic QFP (14 × 14)
Internal pull-up resistor connection can be specified by software setting: 12
Shared with segment pins: 8
in a batch of 4 pins, max. 8 pins)
• Display mode selection: Static, 1/2 duty (1/2 bias), 1/3 duty (1/2 bias),
1/3 duty (1/3 bias), 1/4 duty (1/3 bias)
(Can be used as 16-bit timer/event counter, carrier generator,
and timer with gate)
• Basic interval timer/watchdog timer: 1 channel
• Watch timer: 1 channel
• 2-wire serial I/O mode
• SBI mode
Φ, 750, 375, and 93.8 kHz (main system clock: @ 6.0 MHz)
main system clock: @ 4.19 MHz or subsystem clock: @ 32.768 kHz
• 2.93, 5.86, 46.9 kHz (main system clock: @ 6.0 MHz)
• Internal: 5
• Internal: 1
• Crystal oscillator for subsystem clock
• 64-pin plastic LQFP (12 × 12)
• 64-pin plastic LQFP (14 × 14)
)
2
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
Page 3

µ
PD75P3116
CONTENTS
1. PIN CONFIGURATION (TOP VIEW)................................................................................................. 4
2. BLOCK DIAGRAM ............................................................................................................................ 6
3. PIN FUNCTIONS ............................................................................................................................... 7
3.1 Port Pins ................................................................................................................................................... 7
3.2 Non-Port Pins ........................................................................................................................................... 9
3.3 Pin I/O Circuits ......................................................................................................................................... 11
3.4 Recommended Connection of Unused Pins ......................................................................................... 13
4. Mk I AND Mk II MODE SELECTION FUNCTION ............................................................................. 14
4.1 Differences Between Mk I Mode and Mk II Mode................................................................................... 14
4.2 Setting of Stack Bank Selection (SBS) Register ................................................................................... 15
5. DIFFERENCES BETWEEN µPD75P3116 AND µPD753104, 753106, 753108 ............................... 16
6. MEMORY CONFIGURATION ........................................................................................................... 17
7. INSTRUCTION SET .......................................................................................................................... 19
8. ONE-TIME PROM (PROGRAM MEMORY) WRITE AND VERIFY ................................................... 28
8.1 Operation Modes for Program Memory Write/Verify ............................................................................ 28
8.2 Program Memory Write Procedure......................................................................................................... 29
8.3 Program Memory Read Procedure ......................................................................................................... 30
8.4 One-Time PROM Screening .................................................................................................................... 31
9. ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS .....................................................................................................32
10. CHARACTERISTIC CURVES (REFERENCE VALUES).................................................................. 47
11. PACKAGE DRAWINGS ................................................................................................................... 49
12. RECOMMENDED SOLDERING CONDITIONS ................................................................................ 52
APPENDIX A. LIST OF µPD75308B, 753108, AND 75P3116 FUNCTIONS......................................... 54
APPENDIX B. DEVELOPMENT TOOLS................................................................................................ 56
APPENDIX C. RELATED DOCUMENTS ............................................................................................... 65
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
3
Page 4

1. PIN CONFIGURATION (TOP VIEW)
• 64-pin plastic QFP (14 × 14):µPD75P3116GC-AB8
µ
• 64-pin plastic LQFP (12 × 12):
• 64-pin plastic LQFP (14 × 14):
PD75P3116GK-8A8
µ
PD75P3116GC-8BS
COM363COM262COM161COM060S059S158S257S356S455S554S653S752S851S950S1049S11
µ
PD75P3116
BIAS
LC0
V
LC1
V
LC2
V
P30/LCDCL/MD0
P31/SYNC/MD1
P32/MD2
P33/MD3
Vss
P50/D4
P51/D5
P52/D6
P53/D7
P60/KR0/D0
P61/KR1/D1
P62/KR2/D2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
Note Always connect the V
64
17
18
19
21
22X123X224
25
26
27
28
29
Note
VPP
VDD
P00/INT4
P01/SCK
P03/SI/SB1
P02/SO/SB0
XT120XT2
RESET
P63/KR3/D3
PP pin directly to VDD during normal operation.
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
30
31
32
P13/TI0
P10/INT0
P11/INT1
P12/INT2/TI1/TI2
S12
S13
S14
S15
P93/S16
P92/S17
P91/S18
P90/S19
P83/S20
P82/S21
P81/S22
P80/S23
P23/BUZ
P22/PCL/PTO2
P21/PTO1
P20/PTO0
4
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
Page 5

µ
PD75P3116
PIN IDENTIFICATIONS
P00 to P03: Port 0 COM0 to COM3: Common output 0 to 3
P10 to P13: Port 1 V
P20 to P23: Port 2 BIAS: LCD power supply bias control
P30 to P33: Port 3 LCDCL: LCD clock
P50 to P53: Port 5 SYNC: LCD synchronization
P60 to P63: Port 6 TI0 to TI2: Timer input 0 to 2
P80 to P83: Port 8 PTO0 to PTO2: Programmable timer output 0 to 2
P90 to P93: Port 9 BUZ: Buzzer clock
KR0 to KR3: Key return 0 to 3 PCL: Programmable clock
SCK: Serial clock INT0, 1, 4: External vectored interrupt 0, 1, 4
SI: Serial input INT2: External test input 2
SO: Serial output X1, X2: Main system clock oscillation 1, 2
SB0, SB1: Serial data bus 0, 1 XT1, XT2: Subsystem clock oscillation 1, 2
RESET: Reset V
MD0 to MD3: Mode selection 0 to 3 V
D0 to D7: Data bus 0 to 7 Vss: Ground
S0 to S23: Segment output 0 to 23
LC0 to VLC2: LCD power supply 0 to 2
PP: Programming power supply
DD: Positive power supply
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
5
Page 6

2. BLOCK DIAGRAM
µ
PD75P3116
BUZ/P23
PTO0/P20
TI1/TI2/
P12/INT2
PTO1/P21
PTO2/
PCL/P22
TOUT0
SI/SB1/P03
SO/SB0/P02
SCK/P01
INT0/P10
INT1/P11
INT4/P00
INT2/P12/TI1/TI2
P60/KR0 to
P63/KR3
TI0/P13
timer/event
counter #1
timer/event
counter #2
INTT1
8-bit
8-bit
INTT2
4
Watch
timer
INTW f
Basic
interval
timer/
watchdog
timer
INTBT
8-bit
timer/event
counter #0
INTT0 TOUT0
Cascaded
16-bit
timer/
event
counter
Clocked
serial
interface
INTCSI
INT1
Interrupt
control
Bit sequential
buffer (16)
LCD
TOUT0
Program
counter (14)
Program
memory
(PROM)
16384 × 8 bits
Clock
output
control
PCL/PTO2/P22
fx/2
Clock
divider
Decode
control
N
System clock
generator
Main Sub
X2X1 XT2XT1
ALU
and
CPU clock Φ
CY
General-
512 × 4 bits
Standby
control
SP (8)
SBS
Bank
purpose
register
Data
memory
(RAM)
V
DD
Port 0
Port 1
Port 2
Port 3
Port 5
Port 6
Port 8
Port 9 P90 to P93
f
LCD
V
PP
RESETVss
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
LCD
controller/driver
P00 to P03
P10 to P13
P20 to P23
P30/MD0 to
P33/MD3
P50/D4 to
P53/D7
P60/D0 to
P63/D3
P80 to P83
S0 to S1516
S16/P93 to
S19/P90
S20/P83 to
S23/P80
COM0 to COM34
BIAS
V
LC0
V
LC1
V
LC2
SYNC/P31
LCDCL/P30
6
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
Page 7
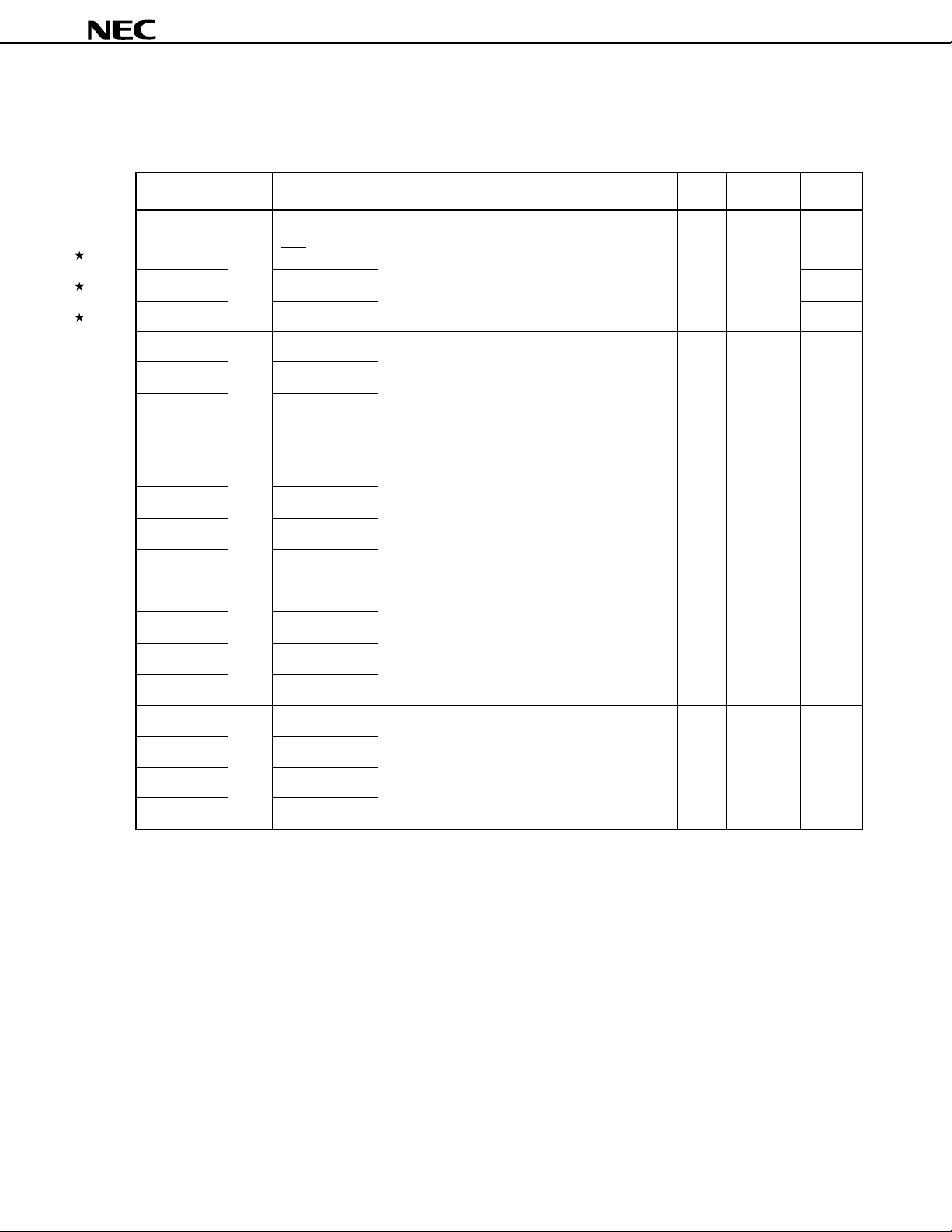
3. PIN FUNCTIONS
3.1 Port Pins (1/2)
µ
PD75P3116
Pin Name I/O Alternate Function 8-Bit Status I/O Circuit
Function I/O After Reset Type
P00 Input INT4 4-bit input port (Port 0) — Input <B>
Connection of an internal pull-up resistor can be
P01 SCK specified by a software setting in 3-bit units. <F>-A
P02 SO/SB0 <F>-B
P03 SI/SB1 <M>-C
P10 Input INT0 4-bit input port (Port 1) — Input <B>-C
Connection of an internal pull-up resistor can be
P11 INT1 specified by a software setting in 4-bit units.
P10/INT0 can be used to select a noise eliminator.
P12 TI1/TI2/INT2
P13 TI0
P20 I/O PTO0 4-bit I/O port (Port 2) — Input E-B
Connection of an internal pull-up resistor can be
P21 PTO1 specified by a software setting in 4-bit units.
P22 PCL/PTO2
P23 BUZ
P30 I/O LCDCL/MD0 Programmable 4-bit I/O port (Port 3) — Input E-B
Input and output can be specified in 1-bit units.
P31 SYNC/MD1 Connection of an internal pull-up resistor can be
specified by a software setting in 4-bit units.
P32 MD2
Note 1
P33 MD3
Note 2
P50
P51
P52
P53
Note 2
Note 2
Note 2
I/O D4 N-ch open-drain 4-bit I/O port (Port 5) — High M-E
When set to open-drain, the withstanding voltage impedance
D5 is 13 V.
D6
D7
Notes 1. Circuit types enclosed in angle brackets indicate Schmitt-triggered input.
2. The low-level input leakage current increases when input instructions or bit manipulation instructions are
executed.
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
7
Page 8

3.1 Port Pins (2/2)
µ
PD75P3116
Pin Name I/O Alternate Function 8-Bit Status I/O Circuit
P60 I/O KR0/D0 Programmable 4-bit I/O port (Port 6) — Input <F>-A
P61 KR1/D1 Connection of an internal pull-up resistor can be
P62 KR2/D2
P63 KR3/D3
P80 I/O S23 4-bit I/O port (Port 8) √ Input H
P81 S22 specified by a software setting in 4-bit units
P82 S21
P83 S20
P90 I/O S19 Programmable 4-bit I/O port (Port 9) Input H
P91 S18 specified by a software setting in 4-bit units
P92 S17
P93 S16
Function I/O After Reset Type
Input and output can be specified in 1-bit units.
specified by a software setting in 4-bit units.
Connection of an internal pull-up resistor can be
Connection of an internal pull-up resistor can be
Note 2
Note 2
.
.
Notes 1. Circuit types enclosed in angle brackets indicate Schmitt-triggered input.
2. Do not connect an internal pull-up resistor by software when these pins are used as segment signal outputs.
Note 1
8
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
Page 9

3.2 Non-Port Pins (1/2)
µ
PD75P3116
Pin Name I/O Alternate Function Status I/O Circuit
Function After Reset Type
TI0 Input P13 External event pulse input to timer/event counter Input <B>-C
TI1 P12/INT2/TI2
TI2 P12/INT2/TI1
PTO0 Output P20 Timer/event counter output Input E-B
PTO1 P21
PTO2 P22/PCL
PCL P22/PTO2 Clock output
BUZ P23 Frequency output (for buzzer or system clock trimming)
SCK I/O P01 Serial clock I/O Input <F>-A
SO/SB0 P02 Serial data output <F>-B
Serial data bus I/O
SI/SB1 P03 Serial data input <M>-C
Serial data bus I/O
INT4 Input P00 Edge detection vectored interrupt input <B>
(valid for detecting both rising and falling edges)
INT0 Input P10 Edge detection vectored interrupt
input (detection edge is selectable) asynchronous is
INT0/P10 can be used to select a selectable
INT1 P11
INT2 Input P12/TI1/TI2 Rising edge detection testable input Asynchronous
KR0 to KR3 I/O P60 to P63 Parallel falling edge detection testable input Input <F>-A
X1 Input — Ceramic/crystal resonator connection for main system — —
X2 —
XT1 Input — Crystal resonator connection for subsystem clock oscillation. — —
XT2 —
RESET Input — System reset input (low-level active) — <B>
MD0 to MD3 Input P30 to P33 Mode selection for program memory (PROM) write/verify Input E-B
D0 to D3 I/O
D4 to D7 P50 to P53 M-E
Note 2
VPP
VDD — — Positive power supply — —
Vss — — Ground potential — —
P60/KR0 to P63/KR3
— — Programmable power supply voltage applied for program — —
noise eliminator.
clock oscillation. If using an external clock, input the signal
to X1 and input the inverted signal to X2.
If using an external clock, input the signal to XT1 and input
the inverted signal to XT2. XT1 can be used as a 1-bit (test)
input.
Data bus for program memory (PROM) write/verify Input <F>-A
memory (PROM) write/verify.
During normal operation, connect directly to VDD.
Apply +12.5 V for PROM write/verify.
With noise eliminator/
Asynchronous
Input <B>-C
Note 1
Notes 1. Circuit types enclosed in angle brackets indicate Schmitt-triggered input.
2. The V
PP pin does not operate correctly when it is not connected to the VDD pin during normal operation.
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
9
Page 10

µ
PD75P3116
3.2 Non-Port Pins (2/2)
Pin Name I/O Alternate Function Status I/O Circuit
Function After Reset Type
S0 to S15
S16 to S19
S20 to S23
COM0 to COM3
VLC0 to VLC2 — — Power supply for driving LCD — —
BIAS Output — Output for external split resistor cut Note 2 —
Note 3
LCDCL
Note 3
SYNC
Output — Segment signal output Note 1 G-A
Output P93 to P90 Segment signal output Input H
Output P83 to P80 Segment signal output Input H
Output — Common signal output Note 1 G-B
Output P30/MD0 Clock output for driving external expansion driver Input E-B
Output P31/MD1 Clock output for synchronization of external expansion driver Input E-B
Notes 1. VLCX (X = 0, 1, 2) is selected as the input source for the display outputs as shown below.
S0 to S23: V
LC1, COM0 to COM2: VLC2, COM3: VLC0
2. When the split resistor is incorporated: Low level
When the split resistor is not incorporated: High impedance
3. These pins are provided for future system expansion. Currently, only P30 and P31 are used.
10
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
Page 11

3.3 Pin I/O Circuits
The I/O circuits for the µPD75P3116’s pins are shown in abbreviated form below.
Type A Type D
V
DD
µ
PD75P3116
V
DD
IN
P-ch
N-ch
CMOS standard input buffer
IN
Data
Output
disable
Push-pull output that can be set to high impedance output
(with both P-ch and N-ch OFF).
Type E-BType B
P.U.R.
enable
Data
Type D
Output
disable
P-ch
N-ch
V
DD
OUT
P.U.R.
P-ch
IN/OUT
Schmitt-triggered input with hysteresis characteristics.
Type B-C Type F-A
V
DD
P.U.R.
P-ch
IN
P.U.R. : Pull-Up Resistor
P.U.R.
enable
Data
Output
disable
Type A
P.U.R. : Pull-Up Resistor
P.U.R.
enable
Type D
Type B
P.U.R. : Pull-Up Resistor
V
DD
P.U.R.
P-ch
IN/OUT
(Continued)
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
11
Page 12
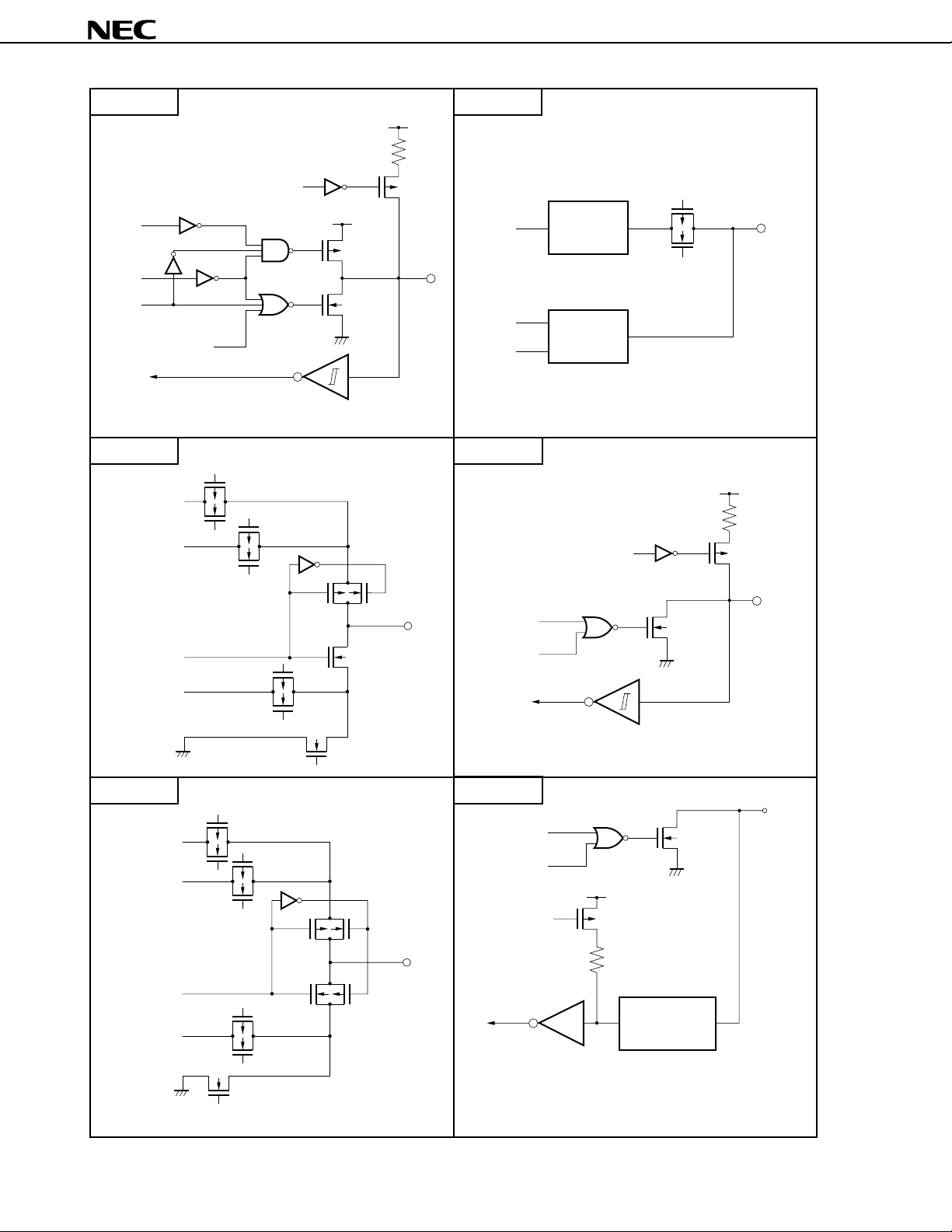
Type F-B Type H
VDD
P.U.R.
µ
PD75P3116
(Continued)
Output
disable
(P)
Data
Output
disable
Output
disable
(N)
P.U.R. : Pull-Up Resistor
VLC0
VLC1
SEG
data
V
LC2
P-ch
N-ch
P-ch
N-ch
enable
P-ch
N-ch
P.U.R.
VDD
P-ch
N-ch
N-chP-ch
N-ch
P-ch
IN/OUT
OUT
SEG
data
Data
Output
disable
Type M-CType G-A
Output
disable
Data
Type G-A
Type E-B
P.U.R.
enable
N-ch
P-ch
N-ch
IN/OUT
VDD
P.U.R.
P-ch
IN/OUT
Type G-B
COM
V
LC0
VLC1
data
VLC2
P-ch
N-ch
N-ch
P-ch
N-ch
P-ch
N-ch
N-ch
P.U.R. : Pull-Up Resistor
Type M-E
IN/OUT
Data
Output
disable
N-chP-ch
P-chN-ch
OUT
Input instruction
Pull-up resistor that operates only when an input
Note
instruction is executed. (The current flows from
VDD to a pin when the pin is at low level.)
VDD
P-ch
P.U.R.
N-ch
Note
Voltage
controller
(+13 V
withstanding
voltage)
(+13 V
withstanding
voltage)
12
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
Page 13

3.4 Recommended Connection of Unused Pins
Table 3-1. List of Unused Pin Connections
Pin Recommended Connection
P00/INT4 Connect to Vss or VDD.
P01/SCK Input: Independently connect to Vss or VDD via a resistor.
P02/SO/SB0 Output: Leave open.
P03/SI/SB1 Connect to Vss.
P10/INT0 and P11/INT1 Connect to Vss or VDD.
P12/TI1/TI2/INT2
P13/TI0
P20/PTO0 Input: Independently connect to Vss or VDD via a resistor.
P21/PTO1 Output: Leave open.
P22/PTO2/PCL
P23/BUZ
P30/LCDCL/MD0
P31/SYNC/MD1
P32/MD2
P33/MD3
P50/D4 to P53/D7 Input: Connect to Vss.
P60/KR0/D0 to P63/KR3/D3 Input: Independently connect to Vss or VDD via a resistor.
S0 to S15 Leave open.
COM0 to COM3
S16/P93 to S19/P90 Input: Independently connect to Vss or VDD via a resistor.
S20/P83 to S23/P80 Output: Leave open.
VLC0 to VLC2 Connect to Vss.
BIAS Connect to Vss only when none of VLC0, VLC1 or VLC2 is used.
Note
XT1
Note
XT2
VPP Always connect to VDD directly.
Output: Connect to Vss.
Output: Leave open.
In other cases, leave open.
Connect to Vss.
Leave open.
µ
PD75P3116
Note When the subsystem clock is not used, select SOS.0 = 1 (on-chip feedback
resistor not used).
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
13
Page 14
µ
PD75P3116
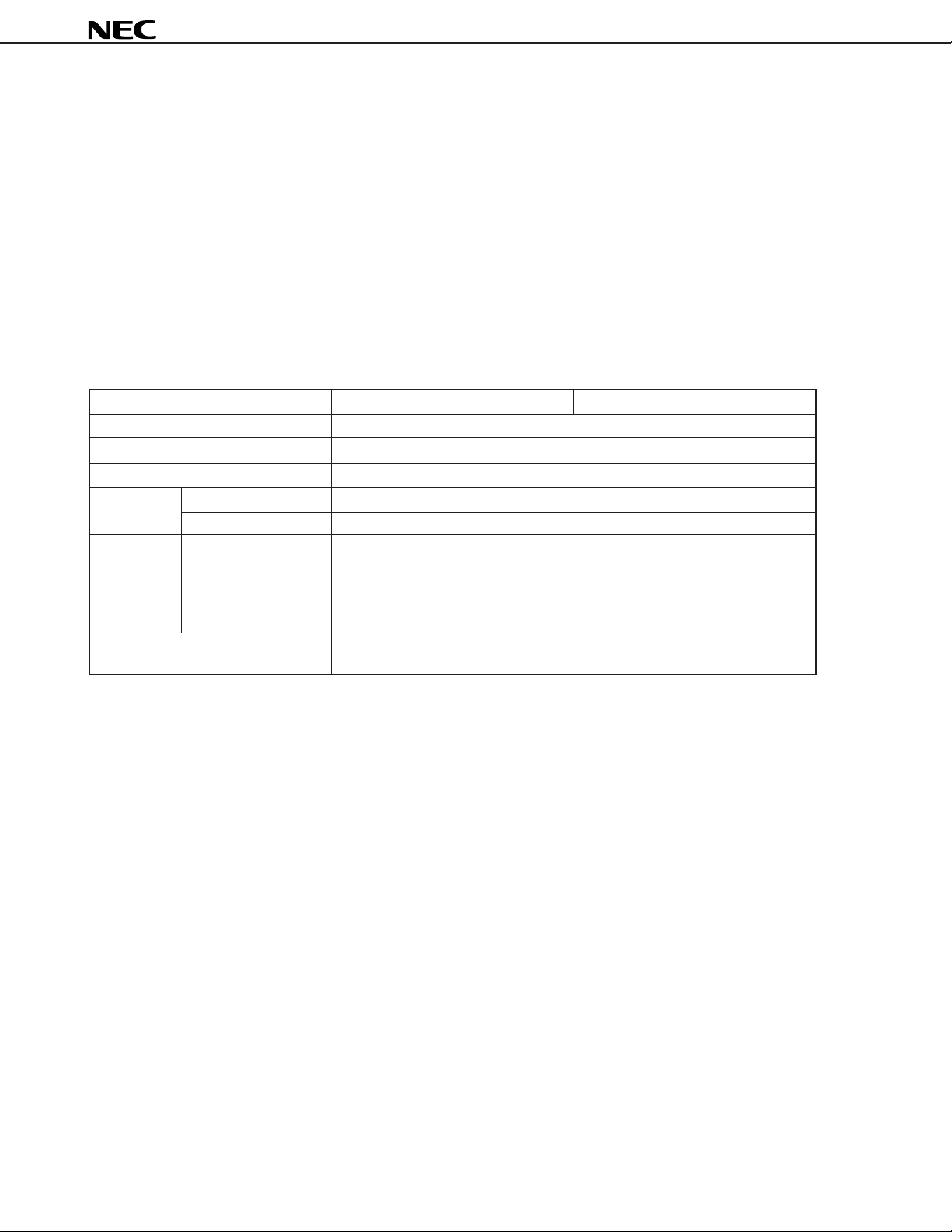
4. Mk I AND Mk II MODE SELECTION FUNCTION
Setting the stack bank selection (SBS) register for the µPD75P3116 enables the program memory to be switched
between the Mk I mode and Mk II mode. This function is applicable when using the
µ
PD753104, 753106, or 753108.
When bit 3 of SBS is set to 1: Sets the Mk I mode (supports the Mk I mode for the
When bit 3 of SBS is set to 0: Sets the Mk II mode (supports the Mk II mode for the µPD753104, 753106, and 753108)
4.1 Differences Between Mk I Mode and Mk II Mode
Table 4-1 lists the differences between the Mk I mode and the Mk II mode for the
Table 4-1. Differences Between Mk I Mode and Mk II Mode
Item Mk I Mode Mk II Mode
Program counter PC13-0
Program memory (bytes) 16384
Data memory (bits) 512 × 4
Stack Stack bank Selectable via memory banks 0 and 1
No. of stack bytes 2 bytes 3 bytes
Instruction BRA !addr1 instruction Not available Available
CALLA !addr1 instruction
Instruction CALL !addr instruction 3 machine cycles 4 machine cycles
execution time CALLF !faddr instruction 2 machine cycles 3 machine cycles
Supported mask ROM products When set to Mk I mode: When set to Mk II mode:
µ
PD753104, 753106, and 753108
µ
µ
PD75P3116 to evaluate the
µ
PD753104, 753106, and 753108)
µ
PD75P3116.
PD753104, 753106, and 753108
Caution The Mk II mode supports a program area exceeding 16 KB for the 75X and 75XL Series. Therefore, this
mode is effective for enhancing software compatibility with products that have a program area of more
than 16 KB.
With regard to the number of stack bytes during execution of subroutine call instructions, the usable
area increases by 1 byte per stack compared to the Mk I mode when the Mk II mode is selected.
However, when the CALL !addr and CALLF !faddr instructions are used, the machine cycle becomes
longer by 1 machine cycle. Therefore, if more emphasis is placed on RAM use efficiency and
processing performance than on software compatibility, the Mk I mode should be used.
14
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
Page 15

µ
PD75P3116
4.2 Setting of Stack Bank Selection (SBS) Register
Use the stack bank selection register to switch between the Mk I mode and Mk II mode. Figure 4-1 shows the format
of the stack bank selection register.
The stack bank selection register is set using a 4-bit memory manipulation instruction. When using the Mk I mode, be
Note
sure to initialize the stack bank selection register to 100×B
Note
be sure to initialize it to 000×B
.
at the beginning of the program. When using the Mk II mode,
Note Set the desired value for ×.
Figure 4-1. Format of Stack Bank Selection Register
Address 3 2 1 0
SBS3 SBS2 SBS1 SBS0F84H
Symbol
SBS
Stack area specification
0
0
Memory bank 0
0
1
Memory bank 1
1
0
Setting prohibited
1
1
0 Be sure to enter “0” for bit 2.
Mode selection specification
01Mk II mode
Mk I mode
Caution SBS3 is set to 1 after RESET input, and consequently the CPU operates in the Mk I mode. When using
instructions for the Mk II mode, set SBS3 to 0 and set the Mk II mode before using the instructions.
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
15
Page 16

µ
PD75P3116
5. DIFFERENCES BETWEEN µPD75P3116 AND µPD753104, 753106, 753108
The µPD75P3116 replaces the internal mask ROM in the µPD753104, 753106, and 753108 with a one-time PROM
and features expanded ROM capacity. The
and 753108 and the µPD75P3116’s Mk II mode supports the Mk II mode in the µPD753104, 753106, and 753108.
Table 5-1 lists differences between the
differences between these products before using them with PROMs for debugging or prototype testing of application
systems or, later, when using them with a mask ROM for full-scale production.
For details of the CPU functions and internal hardware, refer to the User’s Manual.
Table 5-1. Differences Between
µ
PD75P3116’s Mk I mode supports the Mk I mode in the µPD753104, 753106,
µ
PD75P3116 and the µPD753104, 753106, and 753108. Be sure to check the
µ
PD75P3116 and µPD753104, 753106, and 753108
Item
Program counter 12 bits 13 bits 14 bits
Program memory (bytes) Mask ROM Mask ROM Mask ROM One-time PROM
Data memory (× 4 bits) 512
Mask options Pull-up resistor for Available Not available
Port 5 (On chip/not on chip can be specified.) (Not on chip)
Split resistor for
LCD driving power supply
Wait time after Available Not available
RESET (Selectable between 217/fX and 215/fX)
Feedback resistor Available Not available
of subsystem clock (Use/not use can be selected.) (Enable)
Pin configuration Pins 5 to 8 P30 to P33
Pins 10 to 13 P50 to P53 P50/D4 to P53/D7
Pins 14 to 17 P60/KR0 to P63/KR3
Pin 21 IC VPP
Other Noise resistance and noise radiation may differ due to the different circuit sizes and mask
µ
PD753104
4096 6144 8192 16384
layouts.
µ
PD753106
Note
µ
PD753108
µ
(Fixed to 215/fX)
P30/MD0 to P33/MD3
P60/KR0/D0 to P63/KR3/D3
PD75P3116
Note 217/fX: 21.8 ms at 6.0 MHz operation, 31.3 ms at 4.19 MHz operation
215/fX: 5.46 ms at 6.0 MHz operation, 7.81 ms at 4.19 MHz operation
Note
Caution There are differences in the amount of noise tolerance and noise radiation between flash memory
versions and mask ROM versions. When considering changing from a flash memory version to a mask
ROM version during the process from experimental manufacturing to mass production, make sure to
sufficiently evaluate commercial samples (CS) (not engineering samples (ES)) of the mask ROM
versions.
16
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
Page 17

6. MEMORY CONFIGURATION
765 0
MBE
RBE
0000H
0002H
0004H
0006H
0008H
000AH
000CH
MBE
MBE
MBE
MBE
MBE
MBE
Internal reset start address (higher 6 bits)
Internal reset start address (lower 8 bits)
RBE
INTBT/INT4 start address (higher 6 bits)
INTBT/INT4 start address (lower 8 bits)
RBE
INT0 start address (higher 6 bits)
INT0 start address (lower 8 bits)
RBE
INT1 start address (higher 6 bits)
INT1 start address (lower 8 bits)
RBE
INTCSI start address (higher 6 bits)
INTCSI start address (lower 8 bits)
RBE
INTT0 start address (higher 6 bits)
INTT0 start address (lower 8 bits)
RBE
INTT1/INTT2 start address (higher 6 bits)
INTT1/INTT2 start address (lower 8 bits)
Figure 6-1. Program Memory Map
CALLF
!faddr instruction
entry address
BRCB
!caddr instruction
branch address
µ
PD75P3116
Branch addresses for
the following instructions
• BR !addr
• CALL !addr
• BRA !addr1
• CALLA !addr1
• BR BCDE
• BR BCXA
Note
Note
Branch/call
0020H
007FH
0080H
07FFH
0800H
0FFFH
1000H
1FFFH
2000H
2FFFH
3000H
3FFFH
Reference table for GETI instruction
BRCB
!caddr instruction
branch address
BRCB
!caddr instruction
branch address
BRCB
!caddr instruction
branch address
address
by GETI
BR $addr instruction
relative branch address
(–15 to –1,
+2 to +16)
Note Can only be used in the Mk II mode.
Remark For instructions other than those noted above, the BR PCDE and BR PCXA instructions can be used to branch
to addresses with changes in the PC’s lower 8 bits only.
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
17
Page 18

Figure 6-2. Data Memory Map
µ
PD75P3116
Data area
static RAM
(512 × 4)
Stack area
Note
Display data memory
General-purpose register area
000H
01FH
020H
0FFH
100H
1DFH
1E0H
1F7H
1F8H
1FFH
Data memory
(32 × 4)
256 × 4
(224 × 4)
256 × 4
(224 × 4)
(24 × 4)
(8 × 4)
Not incorporated
Memory bank
0
1
F80H
Peripheral hardware area
FFFH
Note Memory bank 0 or 1 can be selected as the stack area.
128 × 4
15
18
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
Page 19

µ
PD75P3116
7. INSTRUCTION SET
(1) Representation and coding formats for operands
In the instruction’s operand area, use the following coding format to describe operands corresponding to the
instruction’s operand representations (for further details, refer to the RA75X Assembler Package Language User’s
Manual (U12385E)). When there are several codes, select and use just one. Codes that consist of uppercase letters and
+ or – symbols are keywords that should be entered as they are.
For immediate data, enter an appropriate numerical value or label.
Enter register flag symbols as label descriptors instead of mem, fmem, pmem, bit, etc. (for further details, refer to the
User’s Manual). The number of labels that can be entered for fmem and pmem are restricted.
Representation Coding Format
reg X, A, B, C, D, E, H, L
reg1 X, B, C, D, E, H, L
rp XA, BC, DE, HL
rp1 BC, DE, HL
rp2 BC, DE
rp’ XA, BC, DE, HL, XA’, BC’, DE’, HL’
rp’1 BC, DE, HL, XA’, BC’, DE’, HL’
rpa HL, HL+, HL–, DE, DL
rpa1 DE, DL
n4 4-bit immediate data or label
n8 8-bit immediate data or label
mem 8-bit immediate data or label
bit 2-bit immediate data or label
fmem FB0H to FBFH, FF0H to FFFH immediate data or label
pmem FC0H to FFFH immediate data or label
addr 0000H to 3FFFH immediate data or label
addr1 0000H to 3FFFH immediate data or label (Mk II mode only)
caddr 12-bit immediate data or label
faddr 11-bit immediate data or label
taddr 20H to 7FH immediate data (however, bit 0 = 0) or label
PORTn Port 0 to Port 3, Port 5, Port 6, Port 8, Port 9
IE××× IEBT, IECSI, IET0 to IET2, IE0 to IE2, IE4, IEW
RBn RB0 to RB3
MBn MB0, MB1, MB15
Note
Note When processing 8-bit data, only even-numbered addresses can be specified.
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
19
Page 20

(2) Operation conventions
A: A register; 4-bit accumulator
B: B register
C: C register
D: D register
E: E register
H: H register
L: L register
X: X register
XA: Register pair (XA); 8-bit accumulator
BC: Register pair (BC)
DE: Register pair (DE)
HL: Register pair (HL)
XA’: Expansion register pair (XA’)
BC’: Expansion register pair (BC’)
DE’: Expansion register pair (DE’)
HL’: Expansion register pair (HL’)
PC: Program counter
SP: Stack pointer
CY: Carry flag; bit accumulator
PSW: Program status word
MBE: Memory bank enable flag
RBE: Register bank enable flag
PORTn: Port n (n = 0 to 3, 5, 6, 8, 9)
IME: Interrupt master enable flag
IPS: Interrupt priority selection register
IE×××: Interrupt enable flag
RBS: Register bank selection register
MBS: Memory bank selection register
PCC: Processor clock control register
.: Delimiter for address and bit
(××): Data addressed with ××
××H: Hexadecimal data
µ
PD75P3116
20
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
Page 21
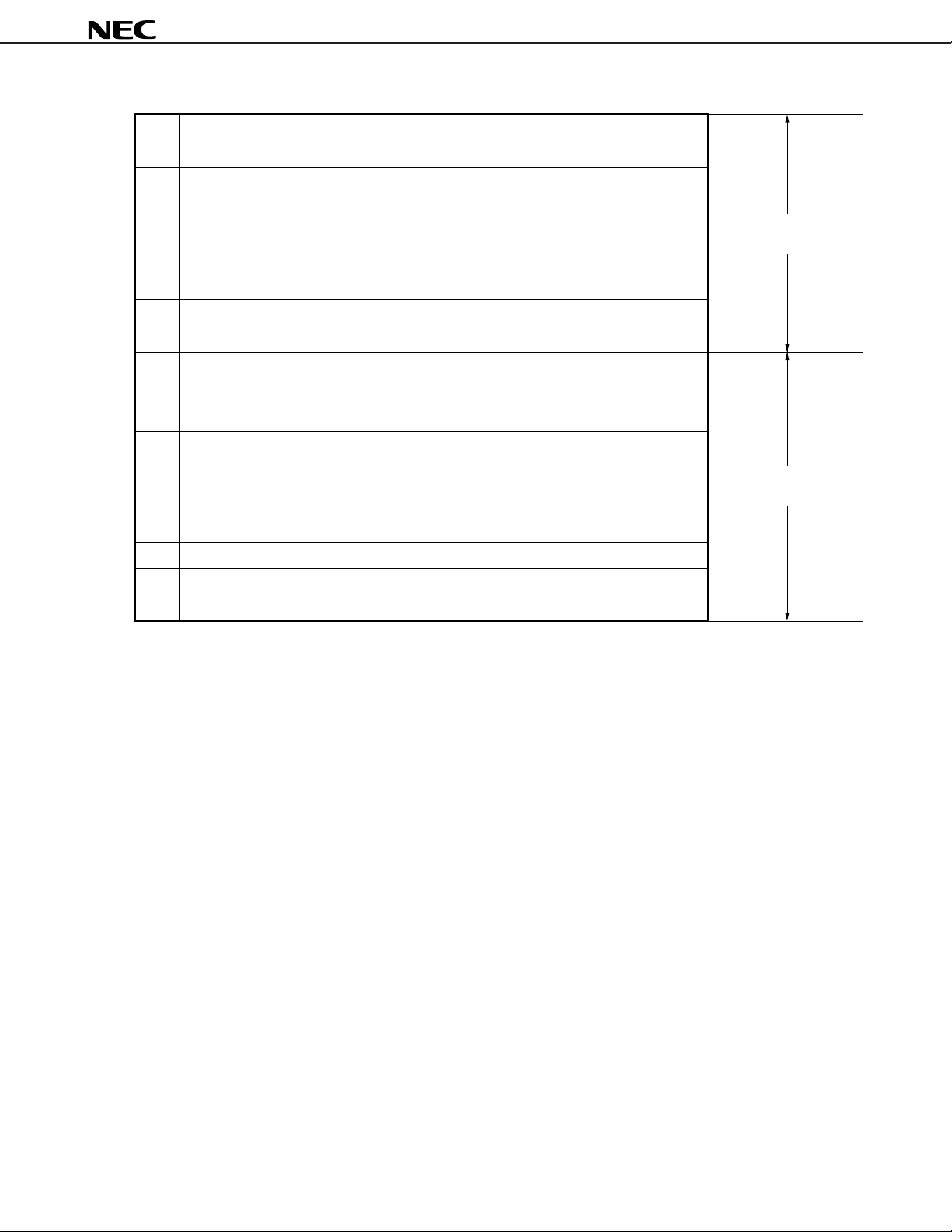
(3) Description of symbols used in addressing area
MB = MBE • MBS
*1
MB = 0
*2
MBE = 0:
*3
MBE = 1:
MB = 15, fmem = FB0H to FBFH, FF0H to FFFH
*4
MB = 15, pmem = FC0H to FFFH
*5
addr = 0000H to 3FFFH
*6
addr, addr1 =*7(Current PC) – 15 to (Current PC) – 1
caddr = 0000H to 0FFFH (PC
*8
MBS = 0, 1, 15
MB = 0 (000H to 07FH)
MB = 15 (F80H to FFFH)
MB = MBS
MBS = 0, 1, 15
(Current PC) + 2 to (Current PC) + 16
13,12
= 00B) or
1000H to 1FFFH (PC
2000H to 2FFFH (PC
3000H to 3FFFH (PC
13,12
13,12
13,12
= 01B) or
= 10B) or
= 11B)
µ
PD75P3116
Data memory
addressing
Program memory
addressing
faddr = 0000H to 07FFH
*9
taddr = 0020H to 007FH
*10
addr1 = 0000H to 3FFFH (Mk II mode only)
*11
Remarks 1. MB indicates access-enabled memory banks.
2. In area *2, MB = 0 for both MBE and MBS.
3. In areas *4 and *5, MB = 15 for both MBE and MBS.
4. Areas *6 to *11 indicate corresponding address-enabled areas.
(4) Description of machine cycles
S indicates the number of machine cycles required for skipping skip-specified instructions. The value of S varies as
shown below.
• No skip ..................................................................... S = 0
• Skipped instruction is 1-byte or 2-byte instruction .... S = 1
Note
• Skipped instruction is 3-byte instruction
.............. S = 2
Note 3-byte instructions: BR !addr, BRA !addr1, CALL !addr, and CALLA !addr1
Caution The GETI instruction is skipped for one machine cycle.
One machine cycle equals one cycle (= t
times.
CY) of the CPU clock Φ. Use the PCC setting to select from among four cycle
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
21
Page 22

µ
PD75P3116
Instruction Mnemonic Operand
Group
Transfer MOV A, #n4 1 1 A ← n4 String-effect A
reg1, #n4 2 2 reg1 ← n4
XA, #n8 2 2 XA ← n8 String-effect A
HL, #n8 2 2 HL ← n8 String-effect B
rp2, #n8 2 2 rp2 ← n8
A, @HL 1 1 A ← (HL) *1
A, @HL+ 1 2+S A ← (HL), then L ← L+1 *1 L = 0
A, @HL– 1 2+S A ← (HL), then L ← L–1 *1 L = FH
A, @rpa1 1 1 A ← (rpa1) *2
XA, @HL 2 2 XA ← (HL) *1
@HL, A 1 1 (HL) ← A*1
@HL, XA 2 2 (HL) ← XA *1
A, mem 2 2 A ← (mem) *3
XA, mem 2 2 XA ← (mem) *3
mem, A 2 2 (mem) ← A*3
mem, XA 2 2 (mem) ← XA *3
A, reg 2 2 A ← reg
XA, rp’ 2 2 XA ← rp’
reg1, A 2 2 reg1 ← A
rp’1, XA 2 2 rp’1 ← XA
XCH A, @HL 1 1 A ←→ (HL) *1
A, @HL+ 1 2+S A ←→ (HL), then L ← L+1 *1 L = 0
A, @HL– 1 2+S A ←→ (HL), then L ← L–1 *1 L = FH
A, @rpa1 1 1 A ←→ (rpa1) *2
XA, @HL 2 2 XA ←→ (HL) *1
A, mem 2 2 A ←→ (mem) *3
XA, mem 2 2 XA ←→ (mem) *3
A, reg1 1 1 A ←→ reg1
XA, rp’ 2 2 XA ←→ rp’
Table MOVT XA, @PCDE 1 3 XA ← (PC13-8+DE)ROM
reference XA, @PCXA 1 3 XA ← (PC13-8+XA)ROM
XA, @BCDE
XA, @BCXA
No. of Machine
Bytes Cycle Area
Note
1 3 XA ← (BCDE)ROM *6
Note
1 3 XA ← (BCXA)ROM *6
Operation
Addressing
Skip
Condition
Note Only the lower 3 bits in the B register are valid.
22
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
Page 23

µ
PD75P3116
Instruction Mnemonic Operand
Group
Bit transfer MOV1 CY, fmem.bit 2 2 CY ← (fmem.bit) *4
CY, pmem.@L 2 2 CY ← (pmem7-2+L3-2.bit(L1-0)) *5
CY, @H+mem.bit 2 2 CY ← (H+mem
fmem.bit, CY 2 2 (fmem.bit) ← CY *4
pmem.@L, CY 2 2 (pmem7-2+L3-2.bit(L1-0)) ← CY *5
@H+mem.bit, CY 2 2 (H+mem
Arithmetic ADDS A, #n4 1 1+S A ← A+n4 carry
XA, #n8 2 2+S XA ← XA+n8 carry
A, @HL 1 1+S A ← A+(HL) *1 carry
XA, rp’ 2 2+S XA ← XA+rp’ carry
rp’1, XA 2 2+S rp’1 ← rp’1+XA carry
ADDC A, @HL 1 1 A, CY ← A+(HL)+CY *1
XA, rp’ 2 2 XA, CY ← XA+rp’+CY
rp’1, XA 2 2 rp’1, CY ← rp’1+XA+CY
SUBS A, @HL 1 1+S A ← A–(HL) *1 borrow
XA, rp’ 2 2+S XA ← XA–rp’ borrow
rp’1, XA 2 2+S rp’1 ← rp’1–XA borrow
SUBC A, @HL 1 1 A, CY ← A–(HL)–CY *1
XA, rp’ 2 2 XA, CY ← XA–rp’–CY
rp’1, XA 2 2 rp’1, CY ← rp’1–XA–CY
AND A, #n4 2 2 A ← A ^ n4
A, @HL 1 1 A ← A ^ (HL) *1
XA, rp’ 2 2 XA ← XA ^ rp’
rp’1, XA 2 2 rp’1 ← rp’1 ^ XA
OR A, #n4 2 2 A ← A v n4
A, @HL 1 1 A ← A v (HL) *1
XA, rp’ 2 2 XA ← XA v rp’
rp’1, XA 2 2 rp’1 ← rp’1 v XA
XOR A, #n4 2 2 A ← A v n4
A, @HL 1 1 A ← A v (HL) *1
XA, rp’ 2 2 XA ← XA v rp’
rp’1, XA 2 2 rp’1 ← rp’1 v XA
Accumulator RORC A 1 1 CY ← A0, A3 ← CY, An-1 ← An
manipulation NOT A 2 2 A ← A
Increment/ INCS reg 1 1+S reg ← reg+1 reg = 0
decrement rp1 1 1+S rp1 ← rp1+1 rp1 = 00H
@HL 2 2+S (HL) ← (HL)+1 *1 (HL) = 0
mem 2 2+S (mem) ← (mem)+1 *3 (mem) = 0
DECS reg 1 1+S reg ← reg–1 reg = FH
rp’ 2 2+S rp’ ← rp’–1 rp’ = FFH
No. of Machine
Bytes Cycle Area
Operation
3-0.bit) *1
3-0.bit) ← CY *1
Addressing
Skip
Condition
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
23
Page 24

µ
PD75P3116
Instruction Mnemonic Operand
Group
Comparison SKE reg, #n4 2 2+S Skip if reg=n4 reg = n4
@HL, #n4 2 2+S Skip if (HL)=n4 *1 (HL) = n4
A, @HL 1 1+S Skip if A=(HL) *1 A = (HL)
XA, @HL 2 2+S Skip if XA=(HL) *1 XA = (HL)
A, reg 2 2+S Skip if A=reg A = reg
XA, rp’ 2 2+S Skip if XA=rp’ XA = rp’
Carry flag SET1 CY 1 1 CY ← 1
manipulation CLR1 CY 1 1 CY ← 0
SKT CY 1 1+S Skip if CY=1 CY = 1
NOT1 CY 1 1 CY ← CY
Memory bit SET1 mem.bit 2 2 (mem.bit) ← 1*3
manipulation fmem.bit 2 2 (fmem.bit) ← 1*4
pmem.@L 2 2 (pmem7-2+L3-2.bit(L1-0)) ← 1*5
@H+mem.bit 2 2 (H+mem3-0.bit) ← 1*1
CLR1 mem.bit 2 2 (mem.bit) ← 0*3
fmem.bit 2 2 (fmem.bit) ← 0*4
pmem.@L 2 2 (pmem7-2+L3-2.bit(L1-0)) ← 0*5
@H+mem.bit 2 2 (H+mem3-0.bit) ← 0*1
SKT mem.bit 2 2+S Skip if(mem.bit)=1 *3 (mem.bit) = 1
fmem.bit 2 2+S Skip if(fmem.bit)=1 *4 (fmem.bit) = 1
pmem.@L 2 2+S Skip if(pmem7-2+L3-2.bit(L1-0))=1 *5 (pmem.@L) = 1
@H+mem.bit 2 2+S Skip if(H+mem3-0.bit)=1 *1
SKF mem.bit 2 2+S Skip if(mem.bit)=0 *3 (mem.bit) = 0
fmem.bit 2 2+S Skip if(fmem.bit)=0 *4 (fmem.bit) = 0
pmem.@L 2 2+S Skip if(pmem7-2+L3-2.bit(L1-0))=0 *5 (pmem.@L) = 0
@H+mem.bit 2 2+S Skip if(H+mem3-0.bit)=0 *1
SKTCLR fmem.bit 2 2+S Skip if(fmem.bit)=1 and clear *4 (fmem.bit) = 1
pmem.@L 2 2+S
@H+mem.bit 2 2+S Skip if(H+mem3-0.bit)=1 and clear *1
AND1 CY, fmem.bit 2 2 CY ← CY ^ (fmem.bit) *4
CY, pmem.@L 2 2 CY ← CY ^ (pmem7-2+L3-2.bit(L1-0)) *5
CY, @H+mem.bit 2 2 CY ← CY ^ (H+mem3-0.bit) *1
OR1 CY, fmem.bit 2 2 CY ← CY v (fmem.bit) *4
CY, pmem.@L 2 2 CY ← CY v (pmem7-2+L3-2.bit(L1-0)) *5
CY, @H+mem.bit 2 2 CY ← CY v (H+mem3-0.bit) *1
XOR1 CY, fmem.bit 2 2 CY ← CY v (fmem.bit) *4
CY, pmem.@L 2 2 CY ← CY v (pmem7-2+L3-2.bit(L1-0)) *5
CY, @H+mem.bit 2 2 CY ← CY v (H+mem3-0.bit) *1
No. of Machine
Bytes Cycle Area
Skip if(pmem
Operation
7-2+L3-2
.bit(L
1-0
))=1 and clear
Addressing
*5 (pmem.@L) = 1
Skip
Condition
(@H+mem.bit) = 1
(@H+mem.bit) = 0
(@H+mem.bit) = 1
24
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
Page 25

µ
PD75P3116
Instruction Mnemonic Operand
Group
Branch BR
Note 1
BRA
BRCB !caddr 2 2 PC13-0 ← PC13, 12+caddr11-0 *8
addr ——PC13-0 ← addr *6
addr1 ——PC13-0 ← addr1 *11
!addr 3 3 PC13-0 ← addr *6
$addr 1 2 PC13-0 ← addr *7
$addr1 1 2 PC13-0 ← addr1
PCDE 2 3 PC13-0 ← PC13-8+DE
PCXA 2 3 PC13-0 ← PC13-8+XA
BCDE 2 3 PC13-0 ← BCDE
BCXA 2 3 PC13-0 ← BCXA
Note 1
!addr1 3 3 PC13-0 ← addr1 *11
No. of Machine
Bytes Cycle Area
Use the assembler to select the
most appropriate instruction
among the following.
• BR !addr
• BRCB !caddr
• BR $addr
Use the assembler to select
the most appropriate instruction
among the following.
• BRA !addr1
• BR !addr
• BRCB !caddr
• BR $addr1
Operation
Note 2
Note 2
Addressing
*6
*6
Skip
Condition
Notes 1. The sections in double boxes are only supported in the Mk II mode. The other sections are only supported in
the MK I mode.
2. Only the lower two bits in the B register are valid.
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
25
Page 26

µ
PD75P3116
Instruction Mnemonic Operand
Group
Subroutine CALLA
Note
!addr1 3 3
No. of Machine
Operation
Bytes Cycle Area
(SP–6)(SP–3)(SP–4)
←
stack control (SP–5) ← 0, 0, PC13, 12
(SP–2)
← X, X, MBE, RBE
PC13-0 ← addr1, SP ← SP–6
Note
CALL
!addr 3 3 (SP–4)(SP–1)(SP–2) ← PC11-0 *6
(SP–3) ← MBE, RBE, PC13, 12
PC13-0 ← addr, SP ← SP–4
4 (SP–6)(SP–3)(SP–4) ← PC11-0
(SP–5) ← 0, 0, PC13, 12
(SP–2) ← X, X, MBE, RBE
PC13-0 ← addr, SP ← SP–6
Note
CALLF
!faddr 2 2 (SP–4)(SP–1)(SP–2) ← PC11-0 *9
(SP–3) ← MBE, RBE, PC13, 12
PC13-0 ← 000+faddr, SP ← SP–4
3
(SP–6)(SP–3)(SP–4)
←
(SP–5) ← 0, 0, PC13, 12
(SP–2) ← X, X, MBE, RBE
PC13-0 ← 000+faddr, SP ← SP–6
Note
RET
1 3 MBE, RBE, PC13, 12 ← (SP+1)
PC11-0 ← (SP)(SP+3)(SP+2)
SP ← SP+4
X, X, MBE, RBE ← (SP+4)
PC11-0 ← (SP)(SP+3)(SP+2)
0, 0, PC13, 12 ← (SP+1)
SP ← SP+6
Note
RETS
1 3+S MBE, RBE, PC13, 12 ← (SP+1) Unconditional
PC11-0 ← (SP)(SP+3)(SP+2)
SP ← SP+4
then skip unconditionally
X, X, MBE, RBE ← (SP+4)
PC11-0 ← (SP)(SP+3)(SP+2)
0, 0, PC13, 12 ← (SP+1)
SP ← SP+6
then skip unconditionally
Note
RETI
1 3 MBE, RBE, PC13, 12 ← (SP+1)
PC11-0 ← (SP)(SP+3)(SP+2)
PSW ← (SP+4)(SP+5)
SP ← SP+6
0, 0, PC13, 12 ← (SP+1)
PC11-0 ← (SP)(SP+3)(SP+2)
PSW ← (SP+4)(SP+5), SP ← SP+6
PC11-0
PC11-0
Addressing
*11
Skip
Condition
Note
The sections in double boxes are only supported in the Mk II mode. The other sections are only supported in the Mk I mode.
26
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
Page 27

µ
PD75P3116
Instruction Mnemonic Operand
Group
Subroutine PUSH rp 1 1 (SP–1)(SP–2) ← rp, SP ← SP–2
stack control BS 2 2 (SP–1) ← MBS, (SP–2) ← RBS,
POP rp 1 1 rp ← (SP+1)(SP), SP ← SP+2
BS 2 2
Interrupt EI 2 2 IME(IPS.3) ← 1
control IE××× 22IE××× ← 1
DI 2 2 IME(IPS.3) ← 0
IE××× 22IE××× ← 0
I/O IN
CPU control HALT 2 2 Set HALT Mode(PCC.2 ← 1)
Special SEL RBn 2 2 RBS ← n (n=0 to 3)
Note 1
OUT
STOP 2 2 Set STOP Mode(PCC.3 ← 1)
NOP 1 1 No Operation
GETI
A, PORTn 2 2 A ← PORTn
XA, PORTn 2 2 XA ← PORTn+1, PORTn (n=8)
Note 1
PORTn, A 2 2 PORTn ← A
PORTn, XA 2 2 PORTn+1, PORTn ← XA (n=8)
MBn 2 2 MBS ← n (n=0, 1, 15)
Notes 2, 3
taddr 1 3 • When using TBR instruction *10
No. of Machine
Bytes Cycle Area
SP ← SP–2
MBS ← (SP+1), RBS ← (SP), SP ← SP+2
PC13-0 ← (taddr)5-0+(taddr+1)
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
• When using TCALL instruction
(SP–4)(SP–1)(SP–2) ← PC11-0
(SP–3)
PC13-0 ← (taddr)5-0+(taddr+1)
SP ← SP–4
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
• When using instruction other than Determined by
TBR or TCALL referenced
Execute (taddr)(taddr+1) instructions instruction
1 3 • When using TBR instruction *10
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
PC13-0 ← (taddr)5-0+(taddr+1)
4 • When using TCALL instruction
(SP–6)(SP–3)(SP–4) ← PC11-0
(SP–5) ← 0, 0, PC13, 12
(SP–2) ← X, X, MBE, RBE
PC13-0 ← (taddr)5-0+(taddr+1)
SP ← SP–6
3 • When using instruction other than Determined by
TBR or TCALL referenced
Execute (taddr)(taddr+1) instructions instruction
Operation
(n=0 to 3, 5, 6, 8, 9)
(n=2 to 3, 5, 6, 8, 9)
←
MBE, RBE, PC13, 12
Addressing
Skip
Condition
- - - - - - - - - - - -
Notes 1. Setting MBE = 0 or MBE = 1, MBS = 15 is required during the execution of the IN or OUT instruction.
2. The TBR and TCALL instructions are assembler quasi-directives for the GETI instruction table definitions.
3. The sections in double boxes are only supported in the Mk II mode. The other sections are only supported in
the Mk I mode.
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
27
Page 28

µ
PD75P3116
8. ONE-TIME PROM (PROGRAM MEMORY) WRITE AND VERIFY
The program memory contained in the µPD75P3116 is a 16384 × 8-bit one-time PROM that can be electrically written
one time only. The pins listed in the table below are used for this PROM’s write/verify operations. Clock input from the
X1 pin is used instead of address input as a method for updating addresses.
Pin Function
VPP Pin where program voltage is applied during program memory
X1, X2 Clock input pins for address updating during program memory
MD0 to MD3 Operation mode selection pin for program memory write/verify
D0/P60 to D3/P63 8-bit data I/O pins for program memory write/verify
(lower 4 bits)
D4/P50 to D7/P53
(higher 4 bits)
DD Pin where power supply voltage is applied. Apply 1.8 to 5.5 V
V
Caution Pins not used for program memory write/verify should be connected to Vss.
write/verify (usually VDD potential)
write/verify. Input the X1 pin’s inverted signal to the X2 pin.
in normal operation mode and +6 V for program memory write/
verify.
8.1 Operation Modes for Program Memory Write/Verify
When +6 V is applied to the V
DD pin and +12.5 V to the VPP pin, the
µ
PD75P3116 enters the program memory write/
verify mode. The following operation modes can be specified by setting pins MD0 to MD3 as shown below.
Operation Mode Specification Operation Mode
VPP VDD MD0 MD1 MD2 MD3
+12.5 V +6 V H L H L Zero-clear program memory address
L H H H Write mode
L L H H Verify mode
H × H H Program inhibit mode
×: L or H
28
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
Page 29

8.2 Program Memory Write Procedure
Program memory can be written at high speed using the following procedure.
(1) Pull down unused pins to Vss via resistors. Set the X1 pin to low.
(2) Supply 5 V to the V
DD and VPP pins.
(3) Wait 10 µs.
(4) Select the program memory address zero-clear mode.
(5) Supply 6 V to V
DD and 12.5 V to VPP.
(6) Write data in the 1 ms write mode.
(7) Select the verify mode. If the data is written, go to (8) and if not, repeat (6) and (7).
(8) Additional write. (X: Number of write operations from (6) and (7)) × 1 ms
(9) Apply four pulses to the X1 pin to increment the program memory address by one.
(10) Repeat (6) to (9) until the end address is reached.
(11) Select the program memory address zero-clear mode.
(12) Return the V
DD- and VPP-pin voltages to 5 V.
(13) Turn off the power.
The following figure shows steps (2) to (9).
µ
PD75P3116
V
PP
VDD + 1
V
DD
X1
D0/P60 to D3/P63
D4/P50 to D7/P53
MD0/P30
MD1/P31
MD2/P32
X repetitions
Additional
Write Verify
V
PP
V
DD
DD
V
Data input
Data
output
write
Data input
Address
increment
MD3/P33
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
29
Page 30

µ
PD75P3116
8.3 Program Memory Read Procedure
µ
PD75P3116 can read program memory contents using the following procedure.
The
(1) Pull down unused pins to V
(2) Supply 5 V to the V
(3) Wait 10
µ
s.
DD and VPP pins.
SS via resistors. Set the X1 pin to low.
(4) Select the program memory address zero-clear mode.
(5) Supply 6 V to V
DD and 12.5 V to VPP.
(6) Select the verify mode. Apply four pulses to the X1 pin. The data stored in one address will be output every four
clock pulses.
(7) Select the program memory address zero-clear mode.
(8) Return the V
DD- and VPP-pin voltages to 5 V.
(9) Turn off the power.
The following figure shows steps (2) to (7).
VPP
VDD
D0/P60 to D3/P63
D4/P50 to D7/P53
VPP
VDD
VDD + 1
V
DD
X1
MD0/P30
MD1/P31
MD2/P32
MD3/P33
Data output Data output
“L”
30
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
Page 31

µ
PD75P3116
8.4 One-Time PROM Screening
Due to its structure, the one-time PROM cannot be fully tested before shipment by NEC. Therefore, NEC recommends
that after the required data is written and the PROM is stored under the temperature and time conditions shown below,
the PROM should be verified via screening.
Storage Temperature Storage Time
125˚C 24 hours
NEC offers QTOP microcontrollers for which one-time PROM writing, marking, screening, and verification are provided
at additional cost. For further details, contact an NEC sales representative.
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
31
Page 32

µµ
µ
PD75P3116
µµ
9. ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
Absolute Maximum Ratings (TA = 25˚C)
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions Rating Unit
Power supply voltage VDD –0.3 to +7.0 V
PROM power supply V
voltage
Input voltage V
Output voltage V
Output current, high I
Output current, low IOL Per pin 30 mA
Operating ambient TA –40 to +85
temperature
Storage temperature Tstg –65 to +150 ˚C
PP –0.3 to +13.5 V
I1 Except port 5 –0.3 to VDD + 0.3 V
VI2 Port 5 (N-ch open drain) –0.3 to +14 V
O –0.3 to VDD + 0.3 V
OH Per pin –10 mA
Total of all pins –30 mA
Total of all pins 220 mA
Note
˚C
Note When LCD is driven in normal mode: TA = –10 to +85˚C
Caution Product quality may suffer if the absolute maximum rating is exceeded even momentarily for any
parameter. That is, the absolute maximum ratings are rated values at which the product is on
the verge of suffering physical damage, and therefore the product must be used under conditions
that ensure that the absolute maximum ratings are not exceeded.
Capacitance (T
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
Input capacitance CIN f = 1 MHz 15 pF
Output capacitance COUT Unmeasured pins returned to 0 V. 15 pF
I/O capacitance CIO 15 pF
A = 25˚C, VDD = 0 V)
32
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
Page 33

µµ
µ
PD75P3116
µµ
Main System Clock Oscillator Characteristics (TA = –40 to +85°C, VDD = 1.8 to 5.5 V)
Resonator Recommended Constant Parameter Test Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
Note 2
Ceramic Oscillation 1.0
X1
resonator frequency (fx)
C1
Crystal Oscillation 1.0
X1
resonator frequency (fx)
C1
X2
Note 1
C2
V
DD
X2
C2
DD
V
Oscillation After VDD reaches oscil- 4 ms
stabilization time
Note 1
Note 3
lation voltage range MIN.
Oscillation VDD = 4.5 to 5.5 V 10 ms
stabilization time
Note 3
VDD = 1.8 to 5.5 V 30
External X1 input 1.0
clock frequency (fx)
X1
X2
Note 1
X1 input 83.3 500 ns
high-/low-level width
(t
XH, tXL)
6.0
6.0
6.0
Note 2
Note 2
MHz
MHz
MHz
Notes 1. Indicates only oscillator characteristics. Refer to AC Characteristics for instruction execution time.
2. When the power supply voltage is 1.8 V ≤ V
DD < 2.7 V and the oscillation frequency is 4.19 MHz < fx
≤ 6.0 MHz, setting the processor clock control register (PCC) to 0011 makes 1 machine cycle less than
the required 0.95 µs. Therefore, set PCC to a value other than 0011.
3. The oscillation stabilization time is necessary for oscillation to stabilize after applying V
DD or releasing
the STOP mode.
Caution When using the main system clock oscillator, wire as follows in the area enclosed by the broken
lines in the above figures to avoid an adverse effect from wiring capacitance.
• Keep the wiring length as short as possible.
• Do not cross the wiring with the other signal lines.
• Do not route the wiring near a signal line through which a high fluctuating current flows.
• Always make the ground point of the oscillator capacitor the same potential as V
DD.
• Do not ground the capacitor to a ground pattern through which a high current flows.
• Do not fetch signals from the oscillator.
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
33
Page 34

µ
PD75P3116
Subsystem Clock Oscillator Characteristics (TA = –40 to +85˚C, VDD = 1.8 to 5.5 V)
Resonator Recommended Constant Parameter Test Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
Crystal Oscillation 32 32.768 35 kHz
XT1
resonator frequency (fXT)
C3
XT2
R
C4
DD
V
Oscillation VDD = 4.5 to 5.5 V 1.0 2 s
stabilization time
Note 1
Note 2
VDD = 1.8 to 5.5 V 10
External XT1 input frequency 32 100 kHz
clock (fXT)
XT1
XT2
Note 1
XT1 input high-/low-level
515
µ
s
width (tXTH, tXTL)
Notes 1. Indicates only oscillator characteristics. Refer to AC Characteristics for instruction execution time.
2. The oscillation stabilization time is necessary for oscillation to stabilize after applying V
DD.
Caution When using the subsystem clock oscillator, wire as follows in the area enclosed by the broken lines
in the above figures to avoid an adverse effect from wiring capacitance.
• Keep the wiring length as short as possible.
• Do not cross the wiring with the other signal lines.
• Do not route the wiring near a signal line through which a high fluctuating current flows.
• Always make the ground point of the oscillator capacitor the same potential as V
DD.
• Do not ground the capacitor to a ground pattern through which a high current flows.
• Do not fetch signals from the oscillator.
The subsystem clock oscillator is designed as a low amplification circuit to provide low consumption
current, and is more liable to misoperation by noise than the main system clock oscillator. Special
care should therefore be taken regarding the wiring method when the subsystem clock is used.
34
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
Page 35

DC Characteristics (TA = –40 to +85˚C, VDD = 1.8 to 5.5 V)
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
µµ
µ
PD75P3116
µµ
Output current, low I
Input voltage, high V
Input voltage, low VIL1 Ports 2, 3, 5, 8, and 9 2.7 ≤ VDD ≤ 5.5 V 0 0.3VDD V
Output voltage, high VOH
Output voltage, low VOL1
OL Per pin 15 mA
Total of all pins 150 mA
IH1 Ports 2, 3, 8, and 9 2.7 ≤ VDD ≤ 5.5 V 0.7VDD VDD V
DD < 2.7 V 0.9VDD VDD V
1.8 ≤ V
V
IH2 Ports 0, 1, 6, RESET 2.7 ≤ VDD ≤ 5.5 V 0.8VDD VDD V
DD < 2.7 V 0.9VDD VDD V
1.8 ≤ V
V
IH3 Port 5 2.7 ≤ VDD ≤ 5.5 V 0.7VDD 13 V
(N-ch open-drain) 1.8 ≤ VDD < 2.7 V 0.9VDD 13 V
VIH4 X1, XT1
DD < 2.7 V 0 0.1VDD V
1.8 ≤ V
V
IL2 Ports 0, 1, 6, RESET 2.7 ≤ VDD ≤ 5.5 V 0 0.2VDD V
1.8 ≤ VDD < 2.7 V 0 0.1VDD V
VIL3 X1, XT1 0 0.1 V
SCK, SO, Ports 2, 3, 6, 8, and 9 IOH = –1.0 mA
SCK, SO, Ports 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, and 9
IOL = 15 mA, 0.2 2.0 V
VDD =
4.5 to 5.5 V
IOL = 1.6 mA 0.4 V
VDD – 0.1
VDD – 0.5
VDD V
V
VOL2 SB0, SB1 When N-ch open-drain 0.2VDD V
pull-up resistor ≥ 1 kΩ
Input leakage ILIH1 VIN = VDD Pins other than X1, XT1 3
current, high ILIH2 X1, XT1 20
ILIH3 VIN = 13 V Port 5 (N-ch open-drain) 20
Input leakage ILIL1 VIN = 0 V Pins other than X1, XT1, and Port 5 –3
current, low ILIL2 X1, XT1 –20
ILIL3 Port 5 (N-ch open-drain) –3
When another instruction than input
instruction is executed
Port 5
(N-ch open-drain)
When input
instruction is
executed
Output leakage ILOH1 VOUT = VDD
current, high ILOH2 VOUT = 13 V Port 5 (N-ch open-drain) 20
Output leakage ILOL VOUT = 0 V –3
current, low
On-chip pull-up resistor RL VIN = 0 V Ports 0, 1, 2, 3, 6, 8, and 9 50 100 200 kΩ
SCK, SO/SB0, SB1, Ports 2, 3, 6, 8, and 9
(Excluding P00 pin)
VDD = 1.8 to 5.5 V –30
VDD = 5.0 V –10 –27
VDD = 3.0 V –3 –8
µ
µ
µ
µ
µ
µ
µ
µ
µ
3
µ
µ
µ
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
35
Page 36

µµ
µ
PD75P3116
µµ
DC Characteristics (TA = –40 to +85˚C, VDD = 1.8 to 5.5 V)
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
LCD drive voltage VLCD VAC0 = 0 TA = –40 to +85°C 2.7 VDD V
A = –10 to +85°C 2.2 VDD V
T
VAC0 = 1 1.8 V
VAC current
Note 1
IVAC VAC0 = 1, VDD = 2.0 V ±10% 1 4
LCD output voltage VODC lo = ±1.0 µAVLCD0 = VLCD 0 ±0.2 V
deviation
LCD output voltage VODS lo = ±0.5 µA
deviation
Supply current
Note 2
(common)
VLCD1 = VLCD × 2/3
VLCD2 = VLCD × 1/3
Note 2
(segment) 1.8 V ≤ VLCD ≤ VDD
Note 3
IDD1 6.00 MHz
Crystal oscillation
DD2
I
C1 = C2 = 22 pF
IDD1 4.19 MHz
Crystal oscillation
IDD2
C1 = C2 = 22 pF
Note 4
Note 4
VDD = 5.0 V ±10%
VDD = 3.0 V ±10%
HALT mode VDD = 5.0 V ±10% 0.7 2.0 mA
VDD = 5.0 V ±10%
VDD = 3.0 V ±10%
HALT mode VDD = 5.0 V ±10% 0.65 1.8 mA
0 ±0.2 V
Note 5
Note 6
V
DD = 3.0 V ±10% 0.25 0.8 mA
Note 5
Note 6
3.2 9.5 mA
0.55 1.6 mA
2.5 7.5 mA
0.45 1.35 mA
VDD = 3.0 V ±10% 0.22 0.7 mA
IDD3 32.768 kHz
Crystal oscillation
IDD4 HALT mode
IDD5 XT1 = 0 V
Note 7
Low-voltage VDD = 3.0 V ±10% 45 130
Note 8
mode
VDD = 2.0 V ±10% 20 55
VDD = 3.0 V, TA = 25˚C
Low current
consumption
Note 9
mode
Note 10
VDD = 5.0 V ±10% 0.05 10
VDD = 3.0 V ±10% 42 120
VDD = 3.0 V, TA = 25˚C
Note 8
VDD = 3.0 V ±10%
VDD = 2.0 V ±10%
VDD = 3.0 V, TA = 25˚C
VDD = 3.0 V ±10%
VDD = 3.0 V,
TA = 25˚C
Lowvoltage
mode
Low
current
consumption mode
Note 9
45 90
42 85
5.5 18
2.2 7
5.5 12
4.0 12
4.0 8
STOP mode VDD = 3.0 V TA = –40 to +85˚C 0.02 5
±10%
TA = 25˚C 0.02 3
DD V
µ
A
µ
A
µ
A
µ
A
µ
A
µ
A
µ
A
µ
A
µ
A
µ
A
µ
A
µ
A
µ
A
µ
A
Notes 1. Set to VAC0 = 0 when the low current consumption mode and the stop mode are used. If VAC0 = 1
µ
is set, the current increases for approx. 1
A.
2. The voltage deviation is the difference from the output voltage corresponding to the ideal value of the
segment and common outputs (VLCDn; n = 0, 1, 2).
3. Not including currents flowing through on-chip pull-up resistors.
4. Including oscillation of the subsystem clock.
5. When the processor clock control register (PCC) is set to 0011 and the device is operated in the high-
speed mode.
6. When PCC is set to 0000 and the device is operated in the low-speed mode.
7. When the system clock control register (SCC) is set to 1001 and the device is operated on the
subsystem clock, with main system clock oscillation stopped.
8. When the sub-oscillator control register (SOS) is set to 0000.
9. When SOS is set to 0010.
10. When SOS is set to 00 ×1 and the feedback resistor of the sub-oscillator is not used (×: Don’t care).
36
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
Page 37

AC Characteristics (TA = –40 to +85˚C, VDD = 1.8 to 5.5 V)
y
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
µ
PD75P3116
CPU clock cycle t
Note 1
time
(Min. instruction execution
time = 1 machine cycle)
TI0, TI1, TI2 input fTI VDD = 2.7 to 5.5 V 0 1.0 MHz
frequency V
TI0, TI1, TI2 input t
high-/low-level width VDD = 1.8 to 5.5 V 1.8
Interrupt input high-/
low-level width IM02 = 1 10
RESET low-level width tRSL 10
Notes 1. The cycle time (minimum instruction
execution time) of the CPU clock
(Φ) is determined by the oscillation
frequency of the connected
CY Operating on VDD = 2.7 to 5.5 V 0.67 64
main system clock VDD = 1.8 to 5.5 V 0.95 64
Operating on subsystem clock 114 122 125
DD = 1.8 to 5.5 V 0 275 kHz
TIH, tTIL VDD = 2.7 to 5.5 V 0.48
tINTH, tINTL
INT0 IM02 = 0 Note 2
INT1, 2, 4 10
KR0 to KR7 10
CY
vs. V
DD
t
(Main system clock operation)
64
60
resonator (and external clock), the
system clock control register (SCC)
and the processor clock control
register (PCC). The figure on the
right indicates the cycle time t
versus supply voltage VDD
characteristics with the main system
clock operating.
CY or 128/fx is set by setting the
2. 2t
CY
6
5
4
[µs]
3
CY
2
Cycle time t
Guaranteed operation
range
interrupt mode register (IM0).
1
µ
s
µ
s
µ
s
µ
s
µ
s
µ
s
µ
s
µ
s
µ
s
µ
s
0.5
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
10 23456
voltage VDD [V]
Suppl
37
Page 38

Serial Transfer Operation
µµ
µ
PD75P3116
µµ
2-wire and 3-wire serial I/O mode (SCK...Internal clock output): (T
A = –40 to +85˚C, VDD = 1.8 to 5.5 V)
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
SCK cycle time t
SCK high-/low-level t
width V
Note 1
SI
setup time tSIK1 VDD = 2.7 to 5.5 V 150 ns
KCY1 VDD = 2.7 to 5.5 V 1300 ns
V
DD = 1.8 to 5.5 V 3800 ns
KL1, tKH1 VDD = 2.7 to 5.5 V
DD = 1.8 to 5.5 V
tKCY1/2–50
tKCY1/2–150
(to SCK↑)VDD = 1.8 to 5.5 V 500 ns
Note 1
SI
hold time tKSI1 VDD = 2.7 to 5.5 V 400 ns
(from SCK↑)V
Note 1
SO
output delay tKSO1 RL = 1 kΩ,VDD = 2.7 to 5.5 V 0 250 ns
time from SCK↓ CL = 100 pF
DD = 1.8 to 5.5 V 600 ns
Note 2
VDD = 1.8 to 5.5 V 0 1000 ns
Notes 1. In 2-wire serial I/O mode, read this parameter as SB0 or SB1 instead.
L and CL are the load resistance and load capacitance of the SO output lines, respectively.
2. R
2-wire and 3-wire serial I/O mode (SCK...External clock input): (TA = –40 to +85˚C, VDD = 1.8 to 5.5 V)
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
SCK cycle time tKCY2 VDD = 2.7 to 5.5 V 800 ns
ns
ns
VDD = 1.8 to 5.5 V 3200 ns
SCK high-/low-level tKL2, tKH2 VDD = 2.7 to 5.5 V 400 ns
width VDD = 1.8 to 5.5 V 1600 ns
Note 1
SI
setup time tSIK2 VDD = 2.7 to 5.5 V 100 ns
(to SCK↑)VDD = 1.8 to 5.5 V 150 ns
Note 1
SI
hold time tKSI2 VDD = 2.7 to 5.5 V 400 ns
(from SCK↑)VDD = 1.8 to 5.5 V 600 ns
Note 1
SO
output delay tKSO2 RL = 1 kΩ,VDD = 2.7 to 5.5 V 0 300 ns
time from SCK↓ CL = 100 pF
Note 2
VDD = 1.8 to 5.5 V 0 1000 ns
Notes 1. In 2-wire serial I/O mode, read this parameter as SB0 or SB1 instead.
2. RL and CL are the load resistance and load capacitance of the SO output lines, respectively.
38
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
Page 39

µµ
µ
µµ
SBI mode (SCK...Internal clock output (master)): (TA = –40 to +85˚C, VDD = 1.8 to 5.5 V)
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
PD75P3116
SCK cycle time t
SCK high-/low-level tKL3, tKH3 VDD = 2.7 to 5.5 V
width V
SB0, 1 setup time t
(to SCK↑)V
SB0, 1 hold time (from SCK↑)
SB0, 1 output delay tKSO3 RL = 1 kΩ,VDD = 2.7 to 5.5 V 0 250 ns
time from SCK↓ CL = 100 pF
SB0, 1↓ from SCK↑ tKSB tKCY3 ns
SCK↓ from SB0, 1↓ t
SB0, 1 low-level width t
SB0, 1 high-level width tSBH tKCY3 ns
KCY3 VDD = 2.7 to 5.5 V 1300 ns
V
DD = 1.8 to 5.5 V 3800 ns
tKCY3/2–50
DD = 1.8 to 5.5 V
SIK3 VDD = 2.7 to 5.5 V 150 ns
DD = 1.8 to 5.5 V 500 ns
tKSI3 tKCY3/2 ns
Note
SBK tKCY3 ns
SBL tKCY3 ns
VDD = 1.8 to 5.5 V 0 1000 ns
tKCY3/2–150
ns
ns
Note RL and CL are the load resistance and load capacitance of the SB0 and SB1 output lines, respectively.
SBI mode (SCK...External clock input (slave)): (T
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
SCK cycle time tKCY4 VDD = 2.7 to 5.5 V 800 ns
A = –40 to +85˚C, VDD = 1.8 to 5.5 V)
VDD = 1.8 to 5.5 V 3200 ns
SCK high-/low-level tKL4, tKH4 VDD = 2.7 to 5.5 V 400 ns
width VDD = 1.8 to 5.5 V 1600 ns
SB0, 1 setup time tSIK4 VDD = 2.7 to 5.5 V 100 ns
(to SCK↑)VDD = 1.8 to 5.5 V 150 ns
SB0, 1 hold time (from SCK↑)
SB0, 1 output delay tKSO4 RL = 1 kΩ,VDD = 2.7 to 5.5 V 0 300 ns
time from SCK↓ CL = 100 pF
SB0, 1↓ from SCK↑ tKSB tKCY4 ns
SCK↓ from SB0, 1↓ tSBK tKCY4 ns
SB0, 1 low-level width tSBL tKCY4 ns
SB0, 1 high-level width tSBH tKCY4 ns
tKSI4 tKCY4/2 ns
Note
VDD = 1.8 to 5.5 V 0 1000 ns
Note RL and CL are the load resistance and load capacitance of the SB0 and SB1 output lines, respectively.
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
39
Page 40

AC Timing Test Points (Excluding X1, XT1 Input)
µ
PD75P3116
Clock Timing
X1 input
VIH (MIN.)
IL (MAX.)
V
VOH (MIN.)
OL (MAX.)
V
tXL
1/fX
1/fXT
tXH
V
IH (MIN.)
IL (MAX.)
V
V
OH (MIN.)
OL (MAX.)
V
V
DD – 0.1 V
0.1 V
XT1 input
TI0, TI1, TI2 Timing
TI0, TI1, TI2
tXTL
tXTH
V
DD – 0.1 V
0.1 V
1/f
TI
t
TIL
t
TIH
40
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
Page 41

Serial Transfer Timing
3-wire serial I/O mode
SCK
tKCY1, 2
tKL1, 2 tKH1, 2
tSIK1, 2 tKSI1, 2
µ
PD75P3116
SI
SO
2-wire serial I/O mode
SCK
SB0, 1
tKSO1, 2
Input data
tKL1, 2
tSIK1, 2
Output data
tKCY1, 2
tKH1, 2
tKSI1, 2
tKSO1, 2
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
41
Page 42

Serial Transfer Timing
Bus release signal transfer
SCK
tKL3, 4
tKCY3, 4
tKH3, 4
µ
PD75P3116
SB0, 1
Command signal transfer
SCK
SB0, 1
tSBKtSBHtSBLtKSB
tKCY3, 4
tKL3, 4
tSBKtKSB
tKH3, 4
tSIK3, 4
tKSO3, 4
tSIK3, 4
tKSO3, 4
tKSI3, 4
tKSI3, 4
Interrupt input timing
INT0, 1, 2, 4
RESET input timing
42
tINTL tINTH
KR0 to 7
tRSL
RESET
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
Page 43

µ
PD75P3116
Data Memory Stop Mode Low Supply Voltage Data Retention Characteristics (TA = –40 to +85˚C)
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
Release signal set time tSREL 0
Oscillation stabilization tWAIT Release by RESET
wait time
Note 1
Release by interrupt request
215/f
Note 2
X
µ
ms
ms
s
Notes 1. The oscillation stabilization wait time is the time during which the CPU operation is stopped to prevent
unstable operation at the start of oscillation.
2. Depends on the basic interval timer mode register (BTM) settings (see the table below).
BTM3 BTM2 BTM1 BTM0 Wait Time
fx = 4.19 MHz fx = 6.0 MHz
—0002
—0112
—1012
—1112
20
/fx (approx. 250 ms) 220/fx (approx. 175 ms)
17
/fx (approx. 31.3 ms) 217/fx (approx. 21.8 ms)
15
/fx (approx. 7.81 ms) 215/fx (approx. 5.46 ms)
13
/fx (approx. 1.95 ms) 213/fx (approx. 1.37 ms)
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
43
Page 44

Data Retention Timing (STOP Mode Release by RESET)
STOP mode
Data retention mode
Internal reset operation
HALT mode
µ
PD75P3116
Operating mode
VDD
tSREL
STOP instruction execution
RESET
tWAIT
Data Retention Timing (Standby Release Signal: STOP Mode Release by Interrupt Signal)
HALT mode
STOP mode
Data retention mode
VDD
tSREL
STOP instruction execution
Standby release signal
(Interrupt request)
Operating mode
44
tWAIT
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
Page 45

µµ
µ
PD75P3116
µµ
DC Programming Characteristics (TA = 25 ±5˚C, VDD = 6.0 ±0.25 V, VPP = 12.5 ±0.3 V, VSS = 0 V)
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
Input voltage, high VIH1 Except X1 and X2 pins 0.7VDD VDD V
VIH2 X1, X2 VDD – 0.5 VDD V
Input voltage, low VIL1 Except X1 and X2 pins 0 0.3VDD V
VIL2 X1, X2 0 0.4 V
Input leakage current ILI VIN = VIL or VIH 10
Output voltage, high VOH IOH = –1 mA VDD – 1.0 V
Output voltage, low V
VDD power supply current IDD 30 mA
V
PP power supply current IPP MD0 = VIL, MD1 = VIH 30 mA
OL IOL = 1.6 mA 0.4 V
Cautions 1. Do not exceed +13.5 V for VPP, including the overshoot.
DD must be applied before VPP, and cut after VPP.
2. V
µ
A
AC Programming Characteristics (T
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
Address setup time
MD1 setup time (to MD0↓)tM1S 2
Data setup time (to MD0↓)tDS 2
Address hold time
Data hold time (from MD0↑)tDH 2
Data output float delay time from MD0↑ tDF 0 130 ns
VPP setup time (to MD3↑)tVPS 2
VDD setup time (to MD3↑)tVDS 2
Initial program pulse width tPW 0.95 1.0 1.05 ms
Additional program pulse width tOPW 0.95 21.0 ms
MD0 setup time (to MD1↑)tM0S 2
Data output delay time from MD0↓ tDV MD0 = MD1 = VIL 1
MD1 hold time (from MD0↑)tM1H tM1H + tM1R ≥ 50 µs2
MD1 recovery time (from MD0↓)tM1R 2
Program counter reset time tPCR 10
X1 input high-/low-level width tXH, tXL 0.125
X1 input frequency fX 4.19 MHz
Initial mode set time tI 2
MD3 setup time (to MD1↑)tM3S 2
MD3 hold time (from MD1↓)tM3H 2
MD3 setup time (to MD0↓)tM3SR
Data output delay time from Address
Data output hold time from Address
MD3 hold time (from MD0↑)tM3HR
Data output float delay time from MD3↓ tDFR
Note
(to MD0↓)tAS 2
Note
(from MD0↑)tAH 2
A = 25 ±5˚C, VDD = 6.0 ±0.25 V, VPP = 12.5 ±0.3 V, VSS = 0 V)
Note
Note
tDAD
tHAD
During program memory read
During program memory read
During program memory read
During program memory read
During program memory read
2
0 130 ns
2
µ
s
µ
s
µ
s
µ
s
µ
s
µ
s
µ
s
µ
s
µ
s
µ
s
µ
s
µ
s
µ
s
µ
s
µ
s
µ
s
µ
s
2
2
µ
s
µ
s
µ
s
Note The internal address signal is incremented by 1 at the rising edge of the fourth X1 input and is not connected to
a pin.
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
45
Page 46

Program Memory Write Timing
t
VPS
V
PP
V
PP
V
DD
t
VDS
VDD + 1
V
DD
DD
V
X1
D0/P60 to D3/P60
D4/P50 to D7/P53
MD0/P30
MD1/P31
MD2/P32
MD3/P33
t
I
t
PCR
t
M3S
Data input
t
DS
t
t
M1S
µ
PD75P3116
t
XH
t
Data output
t
DH
PW
t
M1H
t
M1R
t
DVtDF
t
M0S
Data input
t
DS
t
OPW
XL
t
DH
t
AH
t
AS
Data input
t
M3H
Program Memory Read Timing
tVPS
VPP
VPP
VDD
VDD + 1
VDD
VDD
X1
D0/P60 to D3/P60
D4/P50 to D7/P53
tI
MD0/P30
MD1/P31
tPCR
MD2/P32
tVDS
tXH
tXL
tHAD
tDAD
Data output Data output
tDV
tM3HR
tDFR
46
tM3SR
MD3/P33
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
Page 47

10. CHARACTERISTIC CURVES (REFERENCE VALUES)
DD
vs VDD (Main System Clock: 6.0 MHz Crystal Resonator)
I
10
5.0
1.0
0.5
µµ
µ
PD75P3116
µµ
(T
A
= 25°C)
PCC = 0011
PCC = 0010
PCC = 0001
PCC = 0000
Main system clock
HALT mode + 32 kHz oscillation
(mA)
DD
0.1
Supply current I
0.05
0.01
0.005
Subsystem clock operation
mode (SOS.1 = 0)
Main system clock STOP
mode + 32 kHz oscillation
(SOS.1 = 0) and
subsystem clock HALT mode
(SOS.1 = 0)
Main system clock STOP
mode + 32 kHz oscillation
(SOS.1 = 1) and subsystem
clock HALT mode (SOS.1 = 1)
XT1 XT2X1 X2
Crystal resonator
6.0 MHz
22 pF 22 pF 22 pF 22 pF
Crystal resonator
32.768 kHz
330 kΩ
V
V
0.001
012345678
Supply voltage V
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
DD
(V)
DD
DD
47
Page 48

10
5.0
1.0
0.5
IDD vs VDD (Main System Clock: 4.19 MHz Crystal Resonator)
PCC = 0011
PCC = 0010
PCC = 0001
PCC = 0000
Main system clock
HALT mode + 32 kHz oscillation
µµ
µ
PD75P3116
µµ
(T
A
= 25°C)
(mA)
DD
0.1
Supply current I
0.05
0.01
0.005
Subsystem clock operation
mode (SOS.1 = 0)
Subsystem clock HALT mode
(SOS.1 = 0) and
main system clock STOP mode
+ 32 kHz oscillation (SOS.1 = 0)
Main system clock STOP
mode + 32 kHz oscillation
(SOS.1 = 1)
and subsystem
mode (SOS.1 = 1)
XT1 XT2X1 X2
Crystal resonator
4.19 MHz
22 pF 22 pF 22 pF 22 pF
clock HALT
Crystal resonator
32.768 kHz
330 kΩ
48
V
V
DD
0.001
012345678
Supply voltage VDD (V)
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
DD
Page 49

11. PACKAGE DRAWINGS
64-PIN PLASTIC QFP (14x14)
µ
PD75P3116
A
B
49
48
33
32
detail of lead end
S
C D
64
Q
1
16
17
R
F
G
M
I
H
P
J
K
S
SN
L
M
NOTE
Each lead centerline is located within 0.15 mm of
its true position (T.P.) at maximum material condition.
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
ITEM MILLIMETERS
A
17.6±0.4
B
14.0±0.2
C 14.0± 0.2
D
17.6±0.4
F 1.0
G
1.0
H 0.37
I 0.15
J
K
L
M 0.17
N
P
Q
R
S
+0.08
-0.07
0.8 (T.P.)
1.8±0.2
0.8±0.2
+0.08
-0.07
0.10
2.55±0.1
0.1±0.1
5°±5°
2.85 MAX.
P64GC-80-AB8-5
49
Page 50

64-PIN PLASTIC LQFP (12x12)
A
B
µ
PD75P3116
48
49
33
32
detail of lead end
S
C D
R
64
Q
1
16
17
F
G
M
I
H
P
J
K
S
SN
L
M
NOTE
Each lead centerline is located within 0.13 mm of
its true position (T.P.) at maximum material condition.
ITEM MILLIMETERS
14.8±0.4
A
12.0±0.2
B
C 12.0± 0.2
14.8±0.4
D
F 1.125
1.125
G
H 0.32± 0.08
0.13
I
J
0.65 (T.P.)
K
1.4±0.2
L
0.6±0.2
M 0.17
N
P
Q
R
S
+0.08
-0.07
0.10
1.4±0.1
0.125±0.075
5°±5°
1.7 MAX.
P64GK-65-8A8-3
50
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
Page 51

64-PIN PLASTIC LQFP (14x14)
A
B
48 33
49
32
µ
PD75P3116
detail of lead end
S
P
64
1
16
F
G
M
I
H
SN
NOTE
Each lead centerline is located within 0.20 mm of
its true position (T.P.) at maximum material condition.
17
C D
R
T
L
U
Q
J
ITEM MILLIMETERS
17.2±0.2
A
14.0±0.2
K
S
M
B
C 14.0± 0.2
17.2±0.2
D
F 1.0
1.0
G
H 0.37
I 0.20
J
K
L
M 0.17
N
P
Q
R
S
T 0.25
U 0.886± 0.15
+0.08
-0.07
0.8 (T.P.)
1.6±0.2
0.8
+0.03
-0.06
0.10
1.4±0.1
0.127±0.075
+4°
3°
-3°
1.7 MAX.
P64GC-80-8BS
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
51
Page 52

µ
PD75P3116
12. RECOMMENDED SOLDERING CONDITIONS
The µPD75P3116 should be soldered and mounted under the conditions recommended in the table below.
For details of recommended soldering conditions, refer to the information document Semiconductor Device
Mounting Technology Manual (C10535E).
For soldering methods and conditions other than those recommended below, contact an NEC Sales representative.
Table 12-1. Surface Mounting Type Soldering Conditions (1/2)
µ
PD75P3116GC-AB8: 64-pin plastic QFP (14 × 14)
(1)
Soldering Soldering Conditions Recommended
Method Condition Symbol
Infrared reflow Package peak temperature: 235°C, Time: 30 seconds max. (at 210°C or higher), IR35-00-3
Count: Three times or less
VPS Package peak temperature: 215°C, Time: 40 seconds max. (at 200°C or higher), VP15-00-3
Count: Three times or less
Wave soldering Solder bath temperature: 260°C max., Time: 10 seconds max., Count: Once, WS60-00-1
Preheating temperature: 120°C max. (package surface temperature)
Partial heating Pin temperature: 300° C max., Time: 3 seconds max. (per pin row) —
Caution Do not use different soldering methods together (except for partial heating).
(2)
µ
PD75P3116GK-8A8: 64-pin plastic LQFP (12 × 12)
Soldering Soldering Conditions Recommended
Method Condition Symbol
Infrared reflow Package peak temperature: 235°C, Time: 30 seconds max. (at 210°C or higher), IR35-107-2
Count: Twice or less
Exposure limit: 7 days
VPS Package peak temperature: 215°C, Time: 40 seconds max. (at 200°C or higher), VP15-107-2
Count: Twice or less
Exposure limit: 7 days
Wave soldering Solder bath temperature: 260°C max., Time: 10 seconds max., Count: Once, WS 60-107-1
Preheating temperature: 120°C max. (package surface temperature)
Exposure limit: 7 days
Partial heating Pin temperature: 300°C max., Time: 3 seconds max. (per pin row) —
Note
(after that, prebake at 125°C for 10 hours)
Note
(after that, prebake at 125°C for 10 hours)
Note
(after that, prebake at 125°C for 10 hours)
Note After opening the dry pack, store it at 25°C or less and 65% RH or less for the allowable storage period.
Caution Do not use different soldering methods together (except for partial heating).
52
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
Page 53

µ
PD75P3116
Table 12-1. Surface Mounting Type Soldering Conditions (2/2)
(3)
µ
PD75P3116GC-8BS: 64-pin plastic LQFP (14 × 14)
Soldering Soldering Conditions Recommended
Method Condition Symbol
Infrared reflow Package peak temperature: 235°C, Time: 30 seconds max. (at 210°C or higher), IR35-00-2
Count: Twice or less
VPS Package peak temperature: 215°C, Time: 40 seconds max. (at 200°C or higher), VP15-00-2
Count: Twice or less
Wave soldering Solder bath temperature: 260°C max., Time: 10 seconds max., Count: Once, WS60-00-1
Preheating temperature: 120°C max. (package surface temperature)
Partial heating Pin temperature: 300° C max., Time: 3 seconds max. (per pin row) —
Caution Do not use different soldering methods together (except for partial heating).
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
53
Page 54

APPENDIX A. LIST OF µPD75308B, 753108, AND 75P3116 FUNCTIONS
µ
PD75P3116
Parameter
Program memory Mask ROM Mask ROM One-time PROM
Data memory 000H to 1FFH
CPU 75X Standard 75XL CPU
Instruction When main system 0.95, 1.91, 15.3 µs • 0.95, 1.91, 3.81, 15.3 µs (during 4.19 MHz operation)
execution clock is selected
time
Stack SBS register None SBS.3 = 1: Mk I mode selection
Instruction BRA !addr1 Unavailable When Mk I mode: Unavailable
I/O ports CMOS input 8 8
LCD controller/driver
Timer 3 channels 5 channels
When subsystem 122 µs (during 32.768 kHz operation)
clock is selected
Stack area 000H to 0FFH 000H to 1FFH
Subroutine call instruc- 2-byte stack When Mk I mode: 2-byte stack
tion stack operation When Mk II mode: 3-byte stack
CALLA !addr1 When Mk II mode: Available
MOVT XA, @BCDE Available
MOVT XA, @BCXA
BR BCDE
BR BCXA
CALL !addr 3 machine cycles Mk I mode: 3 machine cycles
CALLF !faddr 2 machine cycles Mk I mode: 2 machine cycles
CMOS I/O 16 20
Bit port output 8 0
N-ch open-drain I/O 8 4
Total 40 32
µ
PD75308B
0000H to 1F7FH 0000H to 1FFFH 0000H to 3FFFH
(8064 × 8 bits) (8192 × 8 bits) (16384 × 8 bits)
(during 4.19 MHz operation)
Segment selection: 24/28/32
(can be changed to CMOS (can be changed to CMOS I/O port in 4-bit units; max. 8)
I/O port in 4-bit units; max.
8)
Display mode selection: Static, 1/2 duty (1/2 bias), 1/3 duty (1/2 bias), 1/3 duty
(1/3 bias), 1/4 duty (1/3 bias)
On-chip split resistor for LCD driver can be specified by No on-chip split resistor
using mask option. for LCD driver
• Basic interval timer: • Basic interval timer/watchdog timer: 1 channel
1 channel • 8-bit timer/event counter: 3 channels
• 8-bit timer/event counter: (can be used as 16-bit timer/event counter)
1 channel • Watch timer: 1 channel
• Watch timer: 1 channel
µ
PD753108
(512 × 4 bits)
• 0.67, 1.33, 2.67, 10.7 µs (during 6.0 MHz operation)
SBS.3 = 0: Mk II mode selection
Mk II mode: 4 machine cycles
Mk II mode: 3 machine cycles
Segment selection: 16/20/24 segments
µ
PD75P3116
54
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
Page 55

µ
PD75P3116
Parameter
Clock output (PCL) Φ , 524, 262, 65.5 kHz • Φ, 524, 262, 65.5 kHz
BUZ output (BUZ) 2 kHz • 2, 4, 32 kHz
Serial interface 3 modes are available
SOS register Feedback resistor None Contained
cut flag (SOS.0)
Sub-oscillator current None Contained
cut flag (SOS.1)
Register bank selection register (RBS) None Yes
Standby release by INT0 No Yes
Vectored interrupts External: 3, Internal: 3 External: 3, Internal: 5
Supply voltage VDD = 2.0 to 6.0 V VDD = 1.8 to 5.5 V
Operating ambient temperature TA = –40 to +85°C
Package • 80-pin plastic QFP • 64-pin plastic QFP • 64-pin plastic QFP
µ
PD75308B
(Main system clock: (Main system clock: during 4.19 MHz operation)
during 4.19 MHz operation) • Φ, 750, 375, 93.8 kHz
(Main system clock: (Main system clock: during 4.19 MHz operation or
during 4.19 MHz operation) subsystem clock: during 32.768 kHz operation)
• 3-wire serial I/O mode ··· MSB/LSB can be selected for transfer first bit
• 2-wire serial I/O mode
• SBI mode
(14 × 20) (14 × 14) (14 × 14)
• 80-pin plastic QFP • 64-pin plastic LQFP • 64-pin plastic LQFP
(14 × 14) (12 × 12) (12 × 12)
• 80-pin plastic TQFP • 64-pin plastic TQFP • 64-pin plastic LQFP
(Fine pitch) (12 × 12) (12 × 12) (14 × 14)
µ
PD753108
(Main system clock: during 6.0 MHz operation)
• 2.93, 5.86, 46.9 kHz
(Main system clock: during 6.0 MHz operation)
• 64-pin plastic LQFP
(14 × 14)
µ
PD75P3116
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
55
Page 56

µ
PD75P3116
APPENDIX B. DEVELOPMENT TOOLS
The following development tools have been provided for system development using the µPD75P3116.
In the 75XL Series, a common relocatable assembler is used in combination with a device file dedicated to each model.
RA75X relocatable assembler Host Machine Part Number
OS Supply Medium
PC-9800 Series MS-DOS
IBM PC/AT™ Refer to OS for 3.5" 2HC
or compatibles IBM PCs
Device file Host Machine Part Number
OS Supply Medium
PC-9800 Series MS-DOS 3.5" 2HD
IBM PC/AT Refer to OS for 3.5" 2HC
or compatibles IBM PCs
TM
Ver.3.30 to
Note
Ver.6.2
Ver.3.30 to
Note
Ver.6.2
3.5" 2HD
(Product Name)
µ
S5A13RA75X
µ
S7B13RA75X
(Product Name)
µ
S5A13DF753108
µ
S7B13DF753108
Note Ver. 5.00 and later include a task swapping function, but this function cannot be used in this software.
Remark Operation of the assembler and device file is guaranteed only when using the host machine and OS described
above.
56
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
Page 57

µ
PD75P3116
PROM Write Tools
Hardware PG-1500 This is a PROM writer that can program a single-chip microcontroller with PROM in stand-alone
mode or under the control of a host machine when connected with the supplied accessory board
and optional programmer adapter.
It can also program typical PROMs in capacities ranging from 256 Kb to 4 Mb.
PA-75P3116GC This is a PROM programmer adapter for the µPD75P3116GC-AB8.
It can be used when connected to the PG-1500.
PA-75P3116GK This is a PROM programmer adapter for the µPD75P3116GK-8A8.
It can be used when connected to the PG-1500.
PA-75P3116GC-8BS This is a PROM programmer adapter for the µPD75P3116GC-8BS.
It can be used when connected to the PG-1500.
Software PG-1500 controller Connects the PG-1500 to the host machine via serial and parallel interfaces and controls the
PG-1500 on the host machine.
Host machine Part number
OS Supply medium
PC-9800 Series MS-DOS 3.5" 2HD
Ver.3.30 to
Note
Ver.6.2
IBM PC/AT Refer to OS for 3.5" 2HD
or compatible IBM PCs
(Product name)
µ
S5A13PG1500
µ
S7B13PG1500
Note Ver. 5.00 and later include a task swapping function, but this function cannot be used in this software.
Remark Operation of the PG-1500 controller is guaranteed only when using the host machine and OS described above.
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
57
Page 58

Debugging Tools
An in-circuit emulator (IE-75001-R) is provided as a program debugging tool for the µPD75P3116.
The system configuration using this in-circuit emulator is shown below.
µ
PD75P3116
Hardware IE-75001-R The IE-75001-R is an in-circuit emulator to be used for hardware and software debugging during
IE-75300-R-EM This is an emulation board for evaluating application systems using the µPD75P3116.
EP-753108GC-R This is an emulation probe for the µPD75P3116GC.
EV-9200GC-64 It includes a 64-pin conversion socket (EV-9200GC-64) to facilitate connection with the target
EP-753108GK-R This is an emulation probe for the
TGK-064SBW It includes a 64-pin conversion adapter (TGK-064SBW) to facilitate connection with the target
Note 1
Software IE control program This program can control the IE-75001-R on a host machine when connected to the IE-75001-R
development of application systems using the 75X or 75XL Series products.
The IE-75001-R is used in combination with an emulation board (IE-75300-R-EM) and
emulation probe (EP-753108GC-R or EP-753108GK-R) (both sold separately).
Highly efficient debugging can be performed when connected to the host machine and PROM
programmer.
It is used in combination with the IE-75001-R.
When being used, it is connected with the IE-75001-R and the IE-75300-R-EM.
system.
µ
PD75P3116GK.
When being used, it is connected with the IE-75001-R and the IE-75300-R-EM.
system.
via an RS-232C or Centronics interface.
Host machine Part number
OS Supply medium
PC-9800 Series MS-DOS 3.5" 2HD
Ver.3.30 to
Note 2
Ver.6.2
IBM PC/AT Refer to OS for 3.5" 2HC
or compatible IBM PCs
(Product name)
µ
S5A13IE75X
µ
S7B13IE75X
Notes 1. This is a product of TOKYO ELETECH CORPORATION.
Contact: Daimaru Kogyo, Ltd. Tokyo Electronic Department (TEL: +81-3-3820-7112)
Osaka Electronic Department (TEL: +81-6-6244-6672)
2. Ver. 5.00 and later include a task swapping function, but this function cannot be used in this software.
Remarks 1. Operation of the IE control program is guaranteed only when using the host machine and OS
described above.
µ
2. The
PD753104, 753106, 753108, and 75P3116 are generically called the µPD753108 Subseries.
58
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
Page 59

µ
PD75P3116
OS for IBM PCs
The following operating systems for IBM PCs are supported.
OS Version
PC DOS
TM
MS-DOS Ver.5.0 to 6.2
IBM DOS
TM
Note Only English mode is supported.
Caution Ver. 5.0 and later include a task swapping function, but this function cannot be used in this software.
Ver.3.1 to 6.3
Note
J6.1/V
5.0/V
J5.02/V
Note
to 6.2/V
Note
to J6.3/V
Note
Note
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
59
Page 60

Package Drawing and Recommended Footprint of Conversion Socket (EV-9200GC-64)
Figure B-1. EV-9200GC-64 Package Drawing (For Reference Only)
µ
PD75P3116
E
D
No.1 pin index
A
B
C
EV-9200GC-64
1
G
H
I
F
ITEM MILLIMETERS INCHES
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
M
N
O
P
Q
R
S
T
M
N
18.8
14.1
14.1
18.8
4-C 3.0
0.8
6.0
15.8
18.5
6.0
15.8
18.5
8.0
7.8
2.5
2.0
1.35
0.35±0.1
φ
2.3
φ
1.5
O
R
S
J
P
EV-9200GC-64-G0E
φ
φ
Q
T
L
K
0.74
0.555
0.555
0.74
4-C 0.118
0.031
0.236
0.622
0.728
0.236
0.622
0.728
0.315
0.307
0.098
0.079
0.053
+0.004
0.014
–0.005
0.091
0.059
60
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
Page 61

µ
PD75P3116
Figure B-2. EV-9200GC-64 Recommended Footprint (For Reference Only)
G
J
K
F
E
D
HI
L
C
B
A
EV-9200GC-64-P1E
ITEM MILLIMETERS INCHES
A
19.5
0.768
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
Caution
14.8
0.8±0.02 × 15=12.0±0.05
0.8±0.02 × 15=12.0±0.05
14.8
19.5
6.00±0.08
6.00±0.08
0.5±0.02
φ
2.36±0.03
φ
2.2±0.1
φ
1.57±0.03
Dimensions of mount pad for EV-9200 and that for target
device (QFP) may be different in some parts. For the
recommended mount pad dimensions for QFP, refer to
"SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE MOUNTING
TECHNOLOGY MANUAL" (C10535E).
0.583
+0.002
0.031 × 0.591=0.472
–0.001
+0.002
0.031 × 0.591=0.472
–0.001
0.583
0.768
+0.004
0.236
–0.003
+0.004
0.236
–0.003
+0.001
0.197
–0.002
φ
0.093
φ
0.087
φ
0.062
+0.001
–0.002
+0.004
–0.005
+0.001
–0.002
+0.003
–0.002
+0.003
–0.002
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
61
Page 62

Package Drawing of Conversion Adapter (TGK-064SBW)
Figure B-3. TGK-064SBW Package Drawing (For Reference Only)
µ
PD75P3116
K
G F E D
e
d
c
b
A
B
C
L
M
X
S
V
U
T
H
I J
Protrusion height
Q
W
R
Z
a
N
O
P
Y
k
h
j
i
f
g
ITEM MILLIMETERS INCHES
A 18.4 0.724
B
0.65x15=9.75 0.026x0.591=0.384
C 0.65 0.026
D
7.75
E 10.15 0.400
F 12.55
G 14.95 0.589
H
0.65x15=9.75 0.026x0.591=0.384
I 11.85 0.467
J 18.4 0.724
K C 2.0 C 0.079
L 12.45 0.490
10.25
M
N 7.7 0.303
O 10.02
P 14.92 0.587
Q 11.1 0.437
R 1.45 0.057
S 1.45 0.057
φ
T 4- 1.3 4- 0.051
U 1.8
V 5.0 0.197
φ
W 5.3 0.209
X 4-C 1.0 4-C 0.039
φ
Y 3.55 0.140
φ
Z 0.9 0.035
0.305
0.494
0.404
0.394
φ
0.071
φ
φ
φ
ITEM MILLIMETERS INCHES
φφ
a 0.3 0.012
b 1.85 0.073
c 3.5 0.138
d 2.0 0.079
e 3.9 0.154
f 1.325
g 1.325 0.052
h 5.9 0.232
i 0.8 0.031
j 2.4 0.094
k 2.7 0.106
0.052
TGK-064SBW-G1E
62
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
Page 63

µ
PD75P3116
Notes on Target System Design
The following shows a diagram of the connection conditions between the emulation probe, conversion connector
and conversion socket or conversion adapter.
Design your system making allowances for conditions such as the form of parts mounted on the target system,
as shown below.
Table B-1. Distance Between In-Circuit Emulator and Conversion Socket
Emulation Probe Conversion Socket/ Distance Between In-Circuit Emulator
Conversion Adapter and Conversion Socket or
Conversion Adapter
EP-753108GC-R EV-9200GC-64 700 mm
EP-753108GK-R TGK-064SBW 700 mm
Figure B-4. Distance Between In-Circuit Emulator and Conversion Socket or Conversion Adapter (1)
In-circuit emulator
IE-75001-R
700 mm
Emulation probe
EP-753108GC-R
DIN connector
(CN5)
Target system
Conversion socket
EV-9200GC-64
Figure B-5. Distance Between In-Circuit Emulator and Conversion Socket or Conversion Adapter (2)
In-circuit emulator
IE-75001-R
700 mm
Target system
DIN connector
(CN5)
Emulation probe
EP-753108GK-R
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
Conversion adapter
TGK-064SBW
63
Page 64

In-circuit emulator
IE-75001-R
Figure B-6. Connection Conditions of Target System (1)
Ground clip
External sense clips
µ
PD75P3116
64-pin GC
EP-753108GC-R
8 mm
35 mm
In-circuit emulator
IE-75001-R
Conversion socket
EV-9200GC-64
35 mm
18.5 mm
Target system
Figure B-7. Connection Conditions of Target System (2)
Ground clip
9 mm
External sense clips
Conversion adapter
TGK-064SBW
18.5 mm
64-pin GK
EP-753108GK-R
Notch
13.8 mm
64
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
34 mm
Target system
18.4 mm
34 mm
18.4 mm
Notch
Page 65

µ
PD75P3116
APPENDIX C. RELATED DOCUMENTS
The related documents indicated in this publication may include preliminary versions. However, preliminary
versions are not marked as such.
Documents Related to Devices
Document Name Document No.
µ
PD753104, 753106, 753108 Data Sheet U10086E
µ
PD75P3116 Data Sheet This document
µ
PD753108 User’s Manual U10890E
75XL Series Selection Guide U10453E
Documents Related to Development Tools (Software) (User’s Manuals)
Document Name Document No.
RA75X Assembler Package Operation U12622E
Language U12385E
Structured Assembler Preprocessor U12598E
Documents Related to Development Tools (Hardware) (User’s Manuals)
Document Name Document No.
IE-75000-R, IE-75001-R In-Circuit Emulator EEU-1455
IE-75300-R-EM Emulation Board U11354E
EP-753108GC-R, EP-753108GK-R Emulation Probe EEU-1495
Documents Related to PROM Writing (User’s Manuals)
Document Name Document No.
PG-1500 PROM Programmer U11940E
PG-1500 Controller PC-9800 Series (MS-DOS) Based EEU-1291
IBM PC Series (PC DOS) Based U10540E
Caution The related documents listed above are subject to change without notice. Be sure to use the
latest version of each document for designing.
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
65
Page 66

µ
PD75P3116
Other Related Documents
Document Name Document No.
SEMICONDUCTOR SELECTION GUIDE – Products & Packages – X13769E
Semiconductor Device Mounting Technology Manual C10535E
Quality Grades on NEC Semiconductor Devices C11531E
NEC Semiconductor Device Reliability/Quality Control System C10983E
Guide to Prevent Damage for Semiconductor Devices by Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) C11892E
Caution The related documents listed above are subject to change without notice. Be sure to use the
latest version of each document for designing.
66
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
Page 67

[MEMO]
µ
PD75P3116
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
67
Page 68

NOTES FOR CMOS DEVICES
1 PRECAUTION AGAINST ESD FOR SEMICONDUCTORS
Note:
Strong electric field, when exposed to a MOS device, can cause destruction of the gate oxide and
ultimately degrade the device operation. Steps must be taken to stop generation of static electricity
as much as possible, and quickly dissipate it once, when it has occurred. Environmental control
must be adequate. When it is dry, humidifier should be used. It is recommended to avoid using
insulators that easily build static electricity. Semiconductor devices must be stored and transported
in an anti-static container, static shielding bag or conductive material. All test and measurement
tools including work bench and floor should be grounded. The operator should be grounded using
wrist strap. Semiconductor devices must not be touched with bare hands. Similar precautions need
to be taken for PW boards with semiconductor devices on it.
2 HANDLING OF UNUSED INPUT PINS FOR CMOS
Note:
No connection for CMOS device inputs can be cause of malfunction. If no connection is provided
to the input pins, it is possible that an internal input level may be generated due to noise, etc., hence
causing malfunction. CMOS devices behave differently than Bipolar or NMOS devices. Input levels
of CMOS devices must be fixed high or low by using a pull-up or pull-down circuitry. Each unused
DD
pin should be connected to V
being an output pin. All handling related to the unused pins must be judged device by device and
related specifications governing the devices.
or GND with a resistor, if it is considered to have a possibility of
µ
PD75P3116
3 STATUS BEFORE INITIALIZATION OF MOS DEVICES
Note:
Power-on does not necessarily define initial status of MOS device. Production process of MOS
does not define the initial operation status of the device. Immediately after the power source is
turned ON, the devices with reset function have not yet been initialized. Hence, power-on does
not guarantee out-pin levels, I/O settings or contents of registers. Device is not initialized until the
reset signal is received. Reset operation must be executed immediately after power-on for devices
having reset function.
68
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
Page 69

µ
PD75P3116
Regional Information
Some information contained in this document may vary from country to country. Before using any NEC
product in your application, pIease contact the NEC office in your country to obtain a list of authorized
representatives and distributors. They will verify:
•
Device availability
•
Ordering information
•
Product release schedule
•
Availability of related technical literature
•
Development environment specifications (for example, specifications for third-party tools and
components, host computers, power plugs, AC supply voltages, and so forth)
•
Network requirements
In addition, trademarks, registered trademarks, export restrictions, and other legal issues may also vary
from country to country.
NEC Electronics Inc. (U.S.)
Santa Clara, California
Tel: 408-588-6000
800-366-9782
Fax: 408-588-6130
800-729-9288
NEC do Brasil S.A.
Electron Devices Division
Guarulhos-SP, Brasil
Tel: 11-6462-6810
Fax: 11-6462-6829
NEC Electronics (Europe) GmbH
Duesseldorf, Germany
Tel: 0211-65 03 01
Fax: 0211-65 03 327
•
Branch The Netherlands
Eindhoven, The Netherlands
Tel: 040-244 58 45
Fax: 040-244 45 80
•
Branch Sweden
Taeby, Sweden
Tel: 08-63 80 820
Fax: 08-63 80 388
NEC Electronics (France) S.A.
Vélizy-Villacoublay, France
Tel: 01-3067-58-00
Fax: 01-3067-58-99
NEC Electronics (France) S.A.
Representación en España
Madrid, Spain
Tel: 091-504-27-87
Fax: 091-504-28-60
NEC Electronics Italiana S.R.L.
Milano, Italy
Tel: 02-66 75 41
Fax: 02-66 75 42 99
NEC Electronics (UK) Ltd.
Milton Keynes, UK
Tel: 01908-691-133
Fax: 01908-670-290
NEC Electronics Hong Kong Ltd.
Hong Kong
Tel: 2886-9318
Fax: 2886-9022/9044
NEC Electronics Hong Kong Ltd.
Seoul Branch
Seoul, Korea
Tel: 02-528-0303
Fax: 02-528-4411
NEC Electronics Shanghai, Ltd.
Shanghai, P.R. China
Tel: 021-6841-1138
Fax: 021-6841-1137
NEC Electronics Taiwan Ltd.
Taipei, Taiwan
Tel: 02-2719-2377
Fax: 02-2719-5951
NEC Electronics Singapore Pte. Ltd.
Novena Square, Singapore
Tel: 253-8311
Fax: 250-3583
J02.3
Data Sheet U11369EJ3V0DS
69
Page 70

µ
PD75P3116
QTOP is a trademark of NEC Corporation.
MS-DOS is either a registered trademark or a trademark of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and/or
other countries.
IBM DOS, PC/AT, and PC DOS are trademarks of International Business Machines Corporation.
The export of this product from Japan is regulated by the Japanese government. To export this product may be prohibited
without governmental license, the need for which must be judged by the customer. The export or re-export of this product
from a country other than Japan may also be prohibited without a license from that country. Please call an NEC sales
representative.
•
The information in this document is current as of November, 2001. The information is subject to
change without notice. For actual design-in, refer to the latest publications of NEC's data sheets or
data books, etc., for the most up-to-date specifications of NEC semiconductor products. Not all
products and/or types are available in every country. Please check with an NEC sales representative
for availability and additional information.
•
No part of this document may be copied or reproduced in any form or by any means without prior
written consent of NEC. NEC assumes no responsibility for any errors that may appear in this document.
•
NEC does not assume any liability for infringement of patents, copyrights or other intellectual property rights of
third parties by or arising from the use of NEC semiconductor products listed in this document or any other
liability arising from the use of such products. No license, express, implied or otherwise, is granted under any
patents, copyrights or other intellectual property rights of NEC or others.
•
Descriptions of circuits, software and other related information in this document are provided for illustrative
purposes in semiconductor product operation and application examples. The incorporation of these
circuits, software and information in the design of customer's equipment shall be done under the full
responsibility of customer. NEC assumes no responsibility for any losses incurred by customers or third
parties arising from the use of these circuits, software and information.
•
While NEC endeavours to enhance the quality, reliability and safety of NEC semiconductor products, customers
agree and acknowledge that the possibility of defects thereof cannot be eliminated entirely. To minimize
risks of damage to property or injury (including death) to persons arising from defects in NEC
semiconductor products, customers must incorporate sufficient safety measures in their design, such as
redundancy, fire-containment, and anti-failure features.
•
NEC semiconductor products are classified into the following three quality grades:
"Standard", "Special" and "Specific". The "Specific" quality grade applies only to semiconductor products
developed based on a customer-designated "quality assurance program" for a specific application. The
recommended applications of a semiconductor product depend on its quality grade, as indicated below.
Customers must check the quality grade of each semiconductor product before using it in a particular
application.
"Standard": Computers, office equipment, communications equipment, test and measurement equipment, audio
and visual equipment, home electronic appliances, machine tools, personal electronic equipment
and industrial robots
"Special": Transportation equipment (automobiles, trains, ships, etc.), traffic control systems, anti-disaster
systems, anti-crime systems, safety equipment and medical equipment (not specifically designed
for life support)
"Specific": Aircraft, aerospace equipment, submersible repeaters, nuclear reactor control systems, life
support systems and medical equipment for life support, etc.
The quality grade of NEC semiconductor products is "Standard" unless otherwise expressly specified in NEC's
data sheets or data books, etc. If customers wish to use NEC semiconductor products in applications not
intended by NEC, they must contact an NEC sales representative in advance to determine NEC's willingness
to support a given application.
(Note)
(1) "NEC" as used in this statement means NEC Corporation and also includes its majority-owned subsidiaries.
(2) "NEC semiconductor products" means any semiconductor product developed or manufactured by or for
NEC (as defined above).
M8E 00. 4
 Loading...
Loading...