NEC UPD70216HLP-20, UPD70216HLP-16, UPD70208HLP-10, UPD70208HLP-12, UPD70208HGK-20-9EU Datasheet
...
DATA SHEET
MOS INTEGRATED CIRCUIT
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
V40HLTM, V50HL
TM
16/8, 16-BIT MICROPROCESSOR
DESCRIPTION
The µPD70208H (V40HL) is a high-speed, low-power 16-/8-bit microprocessor based on the µPD70208 (V40TM) with
16-bit architecture, 8-bit data bus, and general-purpose peripheral functions.
µ
PD70216H (V50HL) is a high-speed, low-power 16-bit microprocessor based on the µPD70216 (V50TM) with 16-
The
bit architecture, 16-bit data bus, and general-purpose peripheral functions.
The V40HL and V50HL offer 20 MHz operation, and in addition to the conventional standby functions, also allows the
clock to be stopped by the use of fully static internal circuitry, thus achieving greatly reduced power consumption. It is also
capable of 3 V operation in addition to the previous 5 V operation, making it ideally suited to battery driven systems.
Details are given in the following manuals. Be sure to read when carrying out design work.
• V40HL, V50HL User’s Manual – Hardware (U11610E)
TM
• 16-bit V series
FEATURES
User’s Manual – Instruction (U11301J: Japanese version)
• High-speed, low-power version of V40 and V50
• High-performance CPU (V20
• Minimum instruction execution time: 100 ns (20 MHz, 5 V)
• Memory addressing space: 1M bytes
• High-speed multiply/divide instructions: 0.95 to 2.8
• Maskable (ICU) & non-maskable (NMI) interrupt inputs
•µPD8080AF emulation function
• Standby functions, clock stoppage capability
TM
/V30TM software compatible)
200 ns (10 MHz, 3 V)
1.9 to 5.6 µs (10 MHz, 3 V)
µ
s (20 MHz, 5 V)
• Standard peripheral LSI functions on chip
• Clock generator (CG)
• Programmable wait control unit (WCU)
• Refresh control unit (REFU)
µ
• Timer/counter unit (TCU) ···
• Serial control unit (SCU) ··· µPD71051 subset
• Interrupt control unit (ICU) ··· µPD71059 subset
• DMA control unit (DMAU) ··· µPD71071/71037 subset (functions of either selectable)
PD71054 subset
• Operating frequency: 10/12.5/16/20 MHz (at 5 V, with 20/25/32/40 MHz supplied externally)
5/6.25/8/10 MHz (at 3 V, with 10/12.5/16/20 MHz supplied externally)
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. Before using this document, please
confirm that this is the latest version.
Not all devices/types available in every country. Please check with local NEC representative for availability
and additional information.
Document No. U13225EJ4V0DS00 (4th edition)
Date Published April 1999 N CP(K)
Printed in Japan
The mark shows the the major revised points.
©
1995

µ
PD70208H, 70216H
ORDERING INFORMATION
(1) V40HL
Part Number Package Frequency (MHz)
µ
PD70208HGF-10-3B9 80-pin plastic QFP (14 × 20 mm) 10
(Resin thickness 2.7 mm)
µ
PD70208HGF-12-3B9 80-pin plastic QFP (14 × 20 mm) 12.5
(Resin thickness 2.7 mm)
µ
PD70208HGF-16-3B9 80-pin plastic QFP (14 × 20 mm) 16
(Resin thickness 2.7 mm)
µ
PD70208HGF-20-3B9 80-pin plastic QFP (14 × 20 mm) 20
(Resin thickness 2.7 mm)
µ
PD70208HGK-10-9EU 80-pin plastic TQFP (Fine pitch) (12 × 12 mm) 10
(Resin thickness 1.0 mm)
µ
PD70208HGK-12-9EU 80-pin plastic TQFP (Fine pitch) (12 × 12 mm) 12.5
(Resin thickness 1.0 mm)
µ
PD70208HGK-16-9EU 80-pin plastic TQFP (Fine pitch) (12 × 12 mm) 16
(Resin thickness 1.0 mm)
µ
PD70208HGK-20-9EU 80-pin plastic TQFP (Fine pitch) (12 × 12 mm) 20
(Resin thickness 1.0 mm)
µ
PD70208HLP-10 68-pin plastic QFJ (950 × 950 mil) 10
µ
PD70208HLP-12 68-pin plastic QFJ (950 × 950 mil) 12.5
µ
PD70208HLP-16 68-pin plastic QFJ (950 × 950 mil) 16
µ
PD70208HLP-20 68-pin plastic QFJ (950 × 950 mil) 20
Max. Operating
(2) V50HL
Part Number Package Frequency (MHz)
µ
PD70216HGF-10-3B9 80-pin plastic QFP (14 × 20 mm) 10
(Resin thickness 2.7 mm)
µ
PD70216HGF-12-3B9 80-pin plastic QFP (14 × 20 mm) 12.5
(Resin thickness 2.7 mm)
µ
PD70216HGF-16-3B9 80-pin plastic QFP (14 × 20 mm) 16
(Resin thickness 2.7 mm)
µ
PD70216HGF-20-3B9 80-pin plastic QFP (14 × 20 mm) 20
(Resin thickness 2.7 mm)
µ
PD70216HGK-10-9EU 80-pin plastic TQFP (Fine pitch) (12 × 12 mm) 10
(Resin thickness 1.0 mm)
µ
PD70216HGK-12-9EU 80-pin plastic TQFP (Fine pitch) (12 × 12 mm) 12.5
(Resin thickness 1.0 mm)
µ
PD70216HGK-16-9EU 80-pin plastic TQFP (Fine pitch) (12 × 12 mm) 16
(Resin thickness 1.0 mm)
µ
PD70216HGK-20-9EU 80-pin plastic TQFP (Fine pitch) (12 × 12 mm) 20
(Resin thickness 1.0 mm)
µ
PD70216HLP-10 68-pin plastic QFJ (950 × 950 mil) 10
µ
PD70216HLP-12 68-pin plastic QFJ (950 × 950 mil) 12.5
µ
PD70216HLP-16 68-pin plastic QFJ (950 × 950 mil) 16
µ
PD70216HLP-20 68-pin plastic QFJ (950 × 950 mil) 20
Max. Operating
2
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
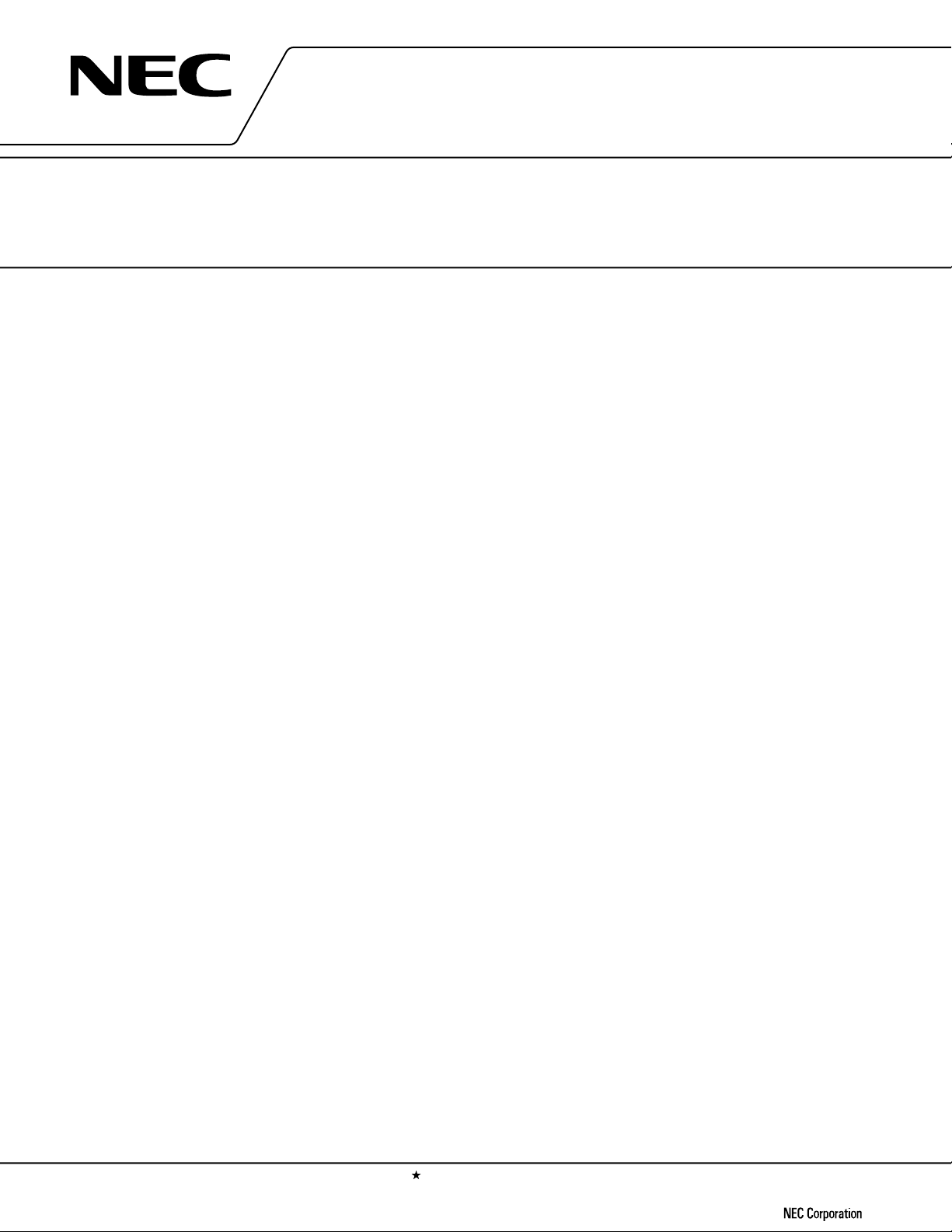
PIN CONFIGURATION (Top View)
(1) V40HL
• 80-pin Plastic QFP (14 × 20 mm)
µ
PD70208HGF-10-3B9
µ
PD70208HGF-12-3B9
µ
PD70208HGF-16-3B9
µ
PD70208HGF-20-3B9
A17/PS1
A18/PS2
A19/PS3
REFRQ
HLDRQ
HLDAK
RESOUT
VDDVDDRESET
READY
NMI
BS2
BS1
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
BS0
MRD
A16/PS0
NC
A15
A14
A13
A12
A11
A10
A9
A8
GND
NC
GND
AD7
AD6
AD5
AD4
AD3
AD2
AD1
AD0
NC
NC
END/TC
80 79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 66 65
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
IORD
NC
MWR
IOWR
BUSLOCK
BUFR/W
BUFEN
CLKOUT
X1
X2
GND
NC
GND
High
ASTB
QS0
QS1
POLL
TCTL2
TOUT2
TCLK
NC
INTP7
INTP6
D
D
IC
X
X
DMAAK1
DMARQ0
DMARQ1
DMAAK0
DMAAK2
DMARQ2
DMARQ3/R
DMAAK3/T
INTAK/SRDY/TOUT1
Caution Leave IC pin open.
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
DD
V
INTP1
INTP2
INTP3
INTP4
INTP5
3
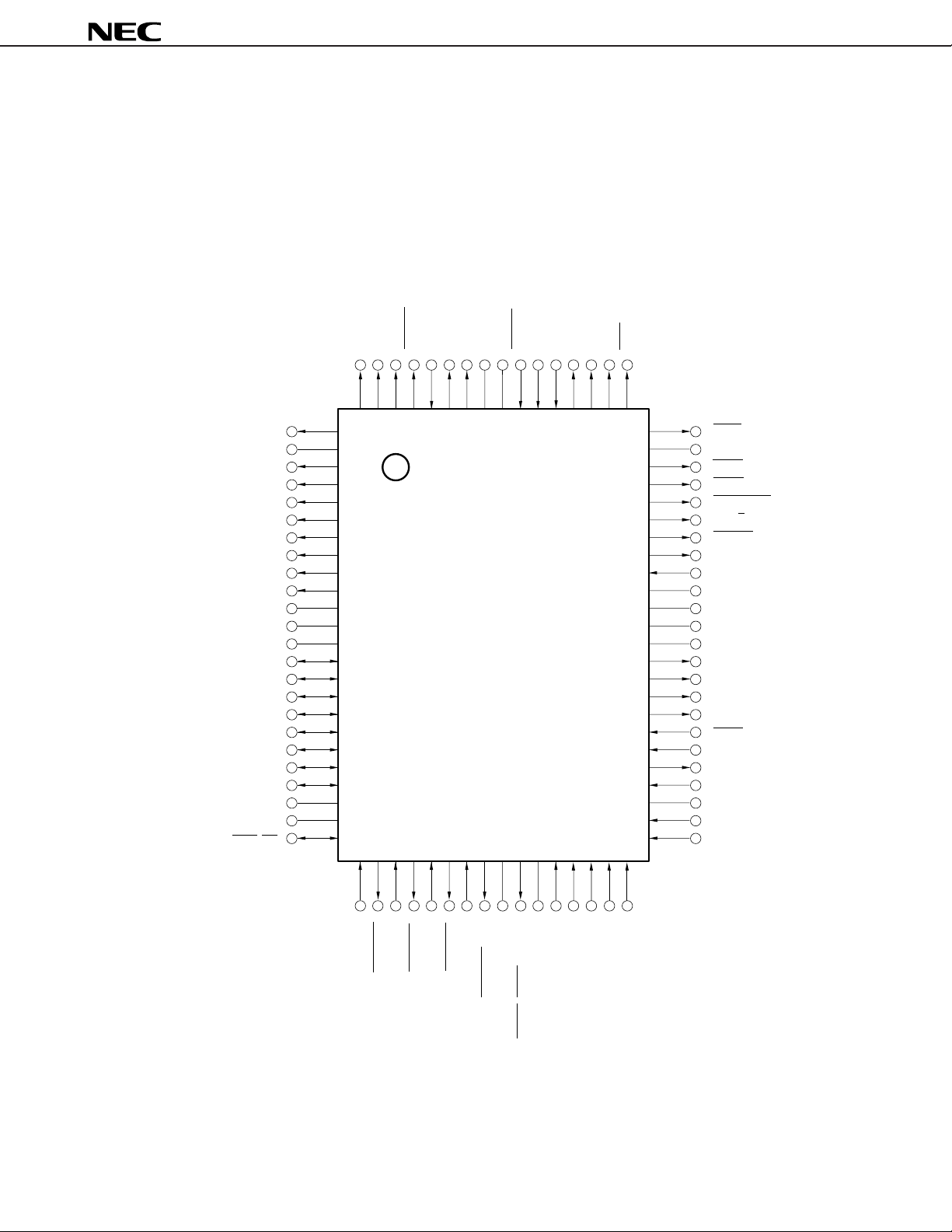
• 80-pin Plastic TQFP (Fine pitch) (12 × 12 mm)
µ
PD70208HGK-10-9EU
µ
PD70208HGK-12-9EU
µ
PD70208HGK-16-9EU
µ
PD70208HGK-20-9EU
NC
A16/PS0
A17/PS1
A18/PS2
A19/PS3
REFRQ
HLDRQ
HLDAK
80 79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 66 65 64 63 62 61
A15
NC
A14
A13
A12
A11
A10
A9
A8
GND
GND
AD7
AD6
AD5
AD4
AD3
AD2
AD1
AD0
NC
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40
RESOUT
VDDVDDRESET
READY
NMI
BS2
BS1
BS0
MRD
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
IORD
NC
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
NC
MWR
IOWR
BUSLOCK
BUFR/W
BUFEN
CLKOUT
X1
X2
GND
GND
High
ASTB
QS0
QS1
POLL
TCTL2
TOUT2
TCLK
NC
D
D
NC
END/TC
DMARQ0
4
DMAAK1
DMARQ1
DMAAK0
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
X
DMAAK2
DMARQ2
DMARQ3/R
DD
X
V
INTP1
INTP2
DMAAK3/T
INTAK/SRDY/TOUT1
INTP3
INTP4
INTP5
INTP6
NC
INTP7
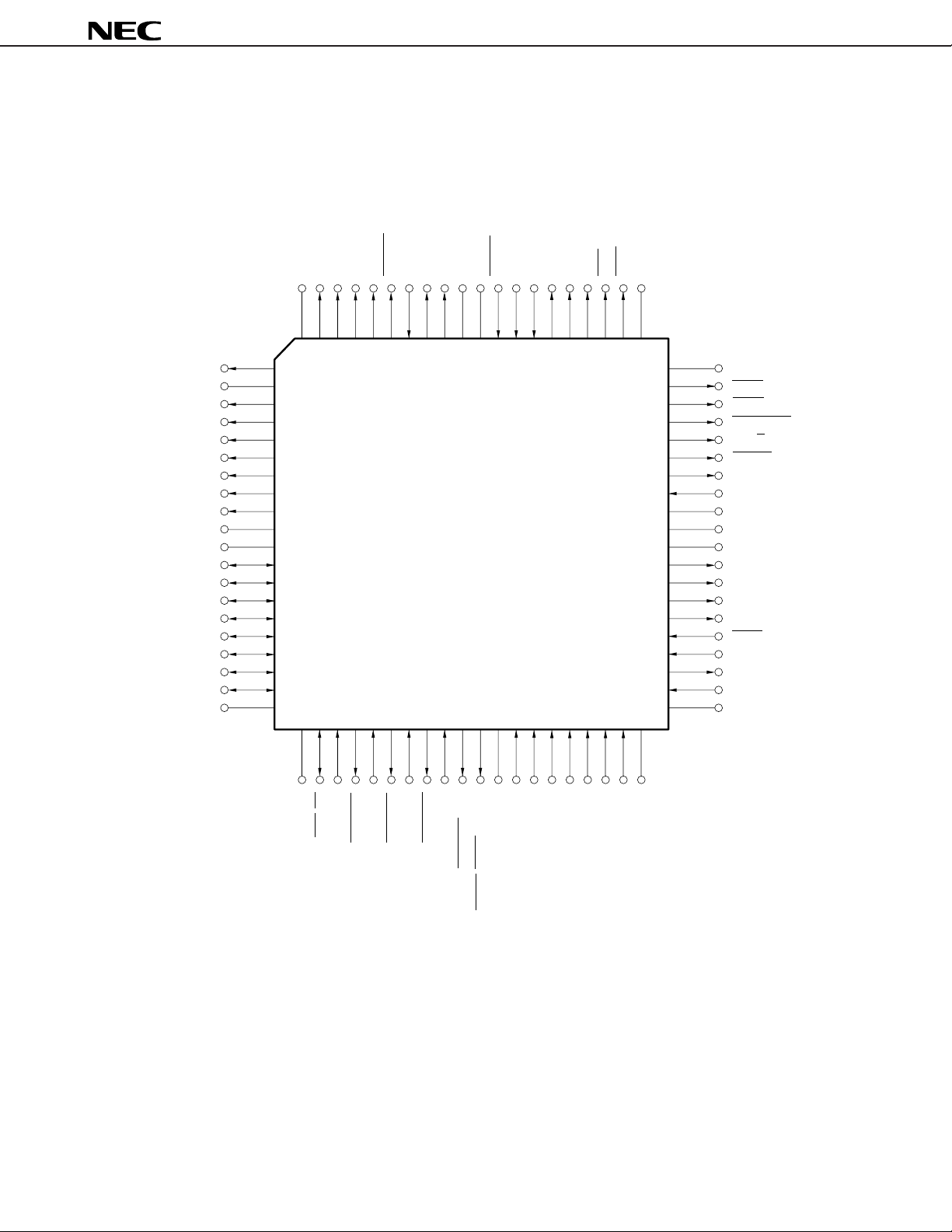
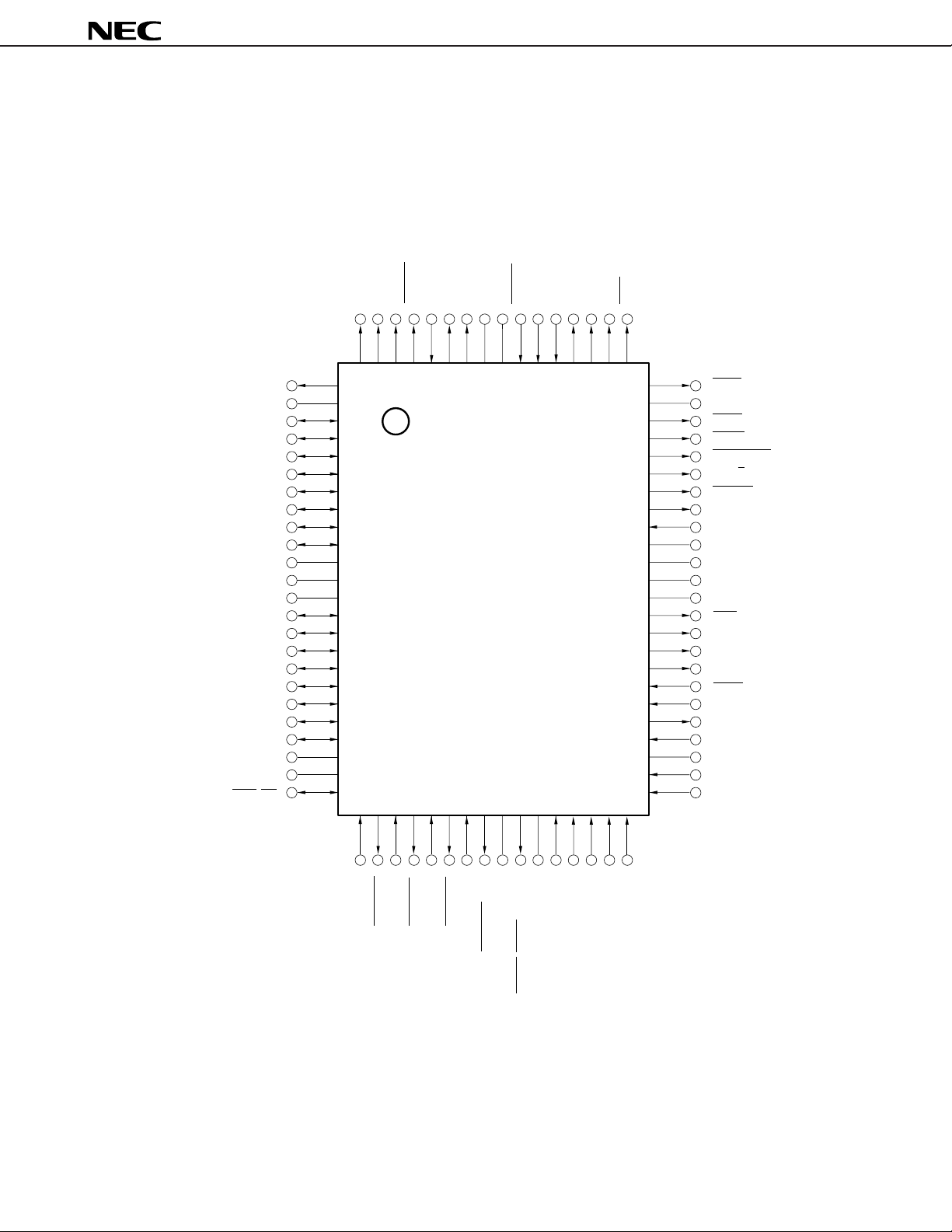
• 68-pin Plastic QFJ (950 × 950 mil)
µ
PD70208HLP-10
µ
PD70208HLP-12
µ
PD70208HLP-16
µ
PD70208HLP-20
A16/PS0
A17/PS1
A18/PS2
A19/PS3
REFRQ
HLDRQ
HLDAK
RESOUT
VDDRESET
READY
NMI
BS2
BS1
BS0
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
MRD
IORD
A15
A14
A13
A12
A11
A10
A9
A8
GND
AD7
AD6
AD5
AD4
AD3
AD2
AD1
AD0
9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 68 67 66 65 64 63 62 61
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43
XD
XD
INTP1
INTP2
END/TC
DMARQ0
DMAAK1
DMARQ1
DMAAK0
DMAAK2
DMARQ2
DMARQ3/R
DMAAK3/T
INTP3
INTP4
INTP5
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
INTP6
INTP7
MWR
IOWR
BUSLOCK
BUFR/W
BUFEN
CLKOUT
X1
X2
GND
High
ASTB
QS0
QS1
POLL
TCTL2
TOUT2
TCLK
INTAK/SRDY/TOUT1
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
5
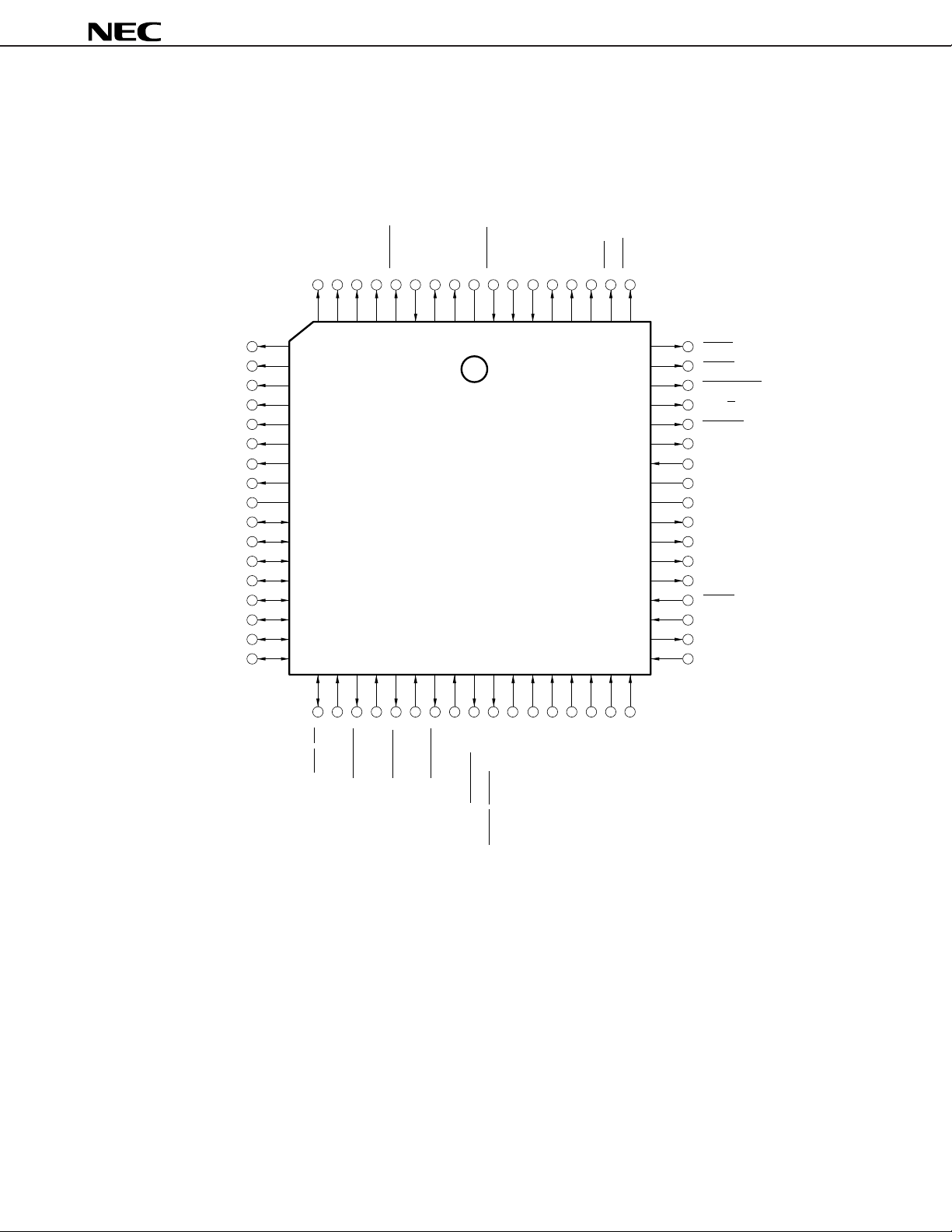
(2) V50HL
• 80-pin Plastic QFP (14 × 20 mm)
µ
PD70216HGF-10-3B9
µ
PD70216HGF-12-3B9
µ
PD70216HGF-16-3B9
µ
PD70216HGF-20-3B9
A17/PS1
A18/PS2
A19/PS3
REFRQ
HLDRQ
HLDAK
RESOUT
VDDVDD
RESET
READY
NMI
BS2
BS1
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
BS0
MRD
A16/PS0
NC
AD15
AD14
AD13
AD12
AD11
AD10
AD9
AD8
GND
NC
GND
AD7
AD6
AD5
AD4
AD3
AD2
AD1
AD0
NC
NC
END/TC
80 79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 66 65
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
IORD
NC
MWR
IOWR
BUSLOCK
BUFR/W
BUFEN
CLKOUT
X1
X2
GND
NC
GND
UBE
ASTB
QS0
QS1
POLL
TCTL2
TOUT2
TCLK
NC
INTP7
INTP6
DD
IC
DMARQ0
DMARQ1
DMAAK0
DMAAK1
DMAAK2
DMARQ2
XD
DMAAK3/T
DMARQ3/RXD
V
INTP1
INTP2
INTP3
INTP4
INTAK/SRDY/TOUT1
INTP5
Caution Leave IC pin open.
6
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
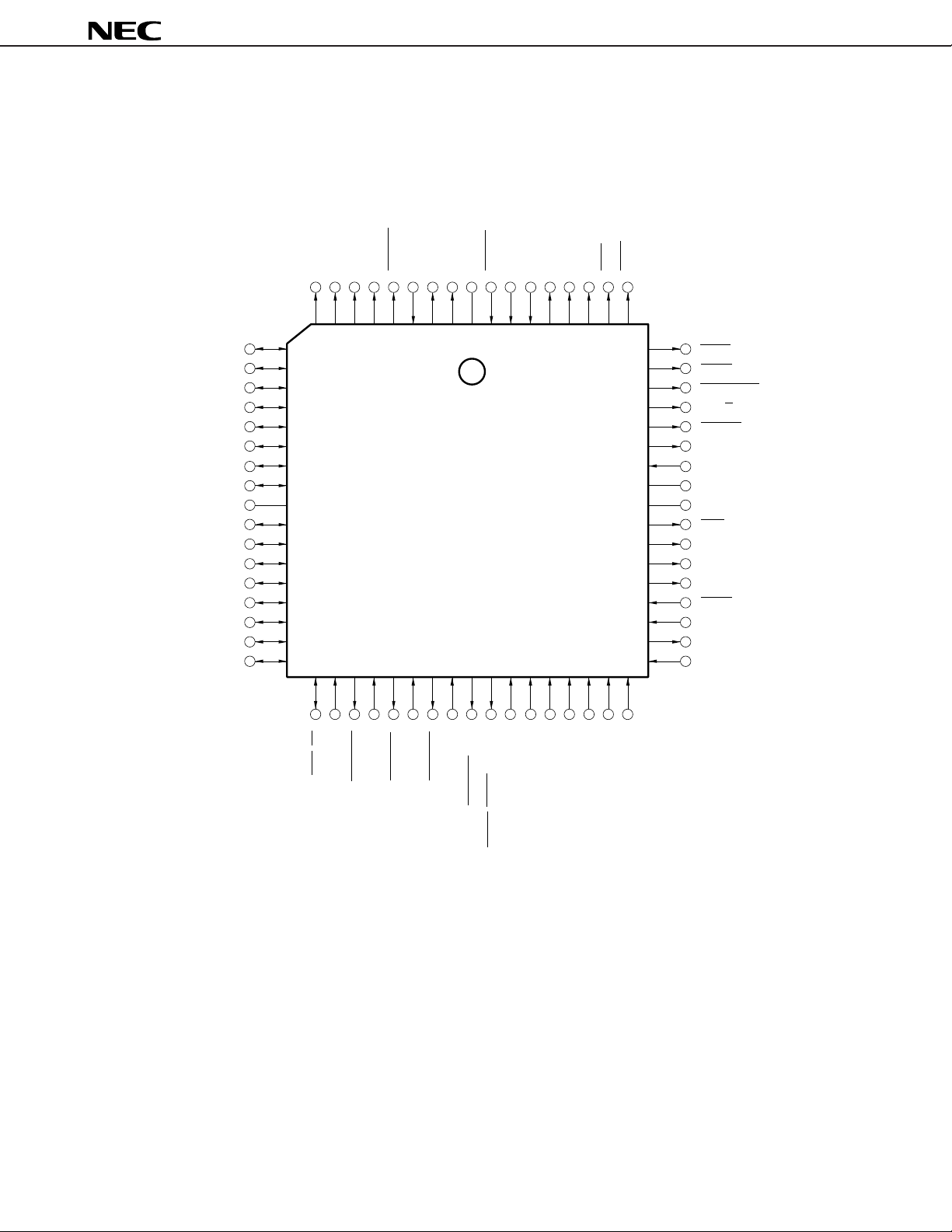
• 80-pin Plastic TQFP (Fine pitch) (12 × 12 mm)
µ
PD70216HGK-10-9EU
µ
PD70216HGK-12-9EU
µ
PD70216HGK-16-9EU
µ
PD70216HGK-20-9EU
NC
A16/PS0
A17/PS1
A18/PS2
A19/PS3
REFRQ
HLDRQ
HLDAK
80 79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 66 65 64 63 62 61
AD15
NC
AD14
AD13
AD12
AD11
AD10
AD9
AD8
GND
GND
AD7
AD6
AD5
AD4
AD3
AD2
AD1
AD0
NC
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40
RESOUT
VDDVDDRESET
READY
NMI
BS2
BS1
BS0
MRD
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
IORD
NC
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
NC
MWR
IOWR
BUSLOCK
BUFR/W
BUFEN
CLKOUT
X1
X2
GND
GND
UBE
ASTB
QS0
QS1
POLL
TCTL2
TOUT2
TCLK
NC
NC
END/TC
DMARQ0
D
D
X
X
DMAAK1
DMARQ1
DMAAK0
DMAAK2
DMARQ2
DMAAK3/T
DMARQ3/R
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
DD
V
INTP1
INTP2
INTP3
INTP4
INTP5
INTAK/SRDY/TOUT1
INTP6
INTP7
NC
7
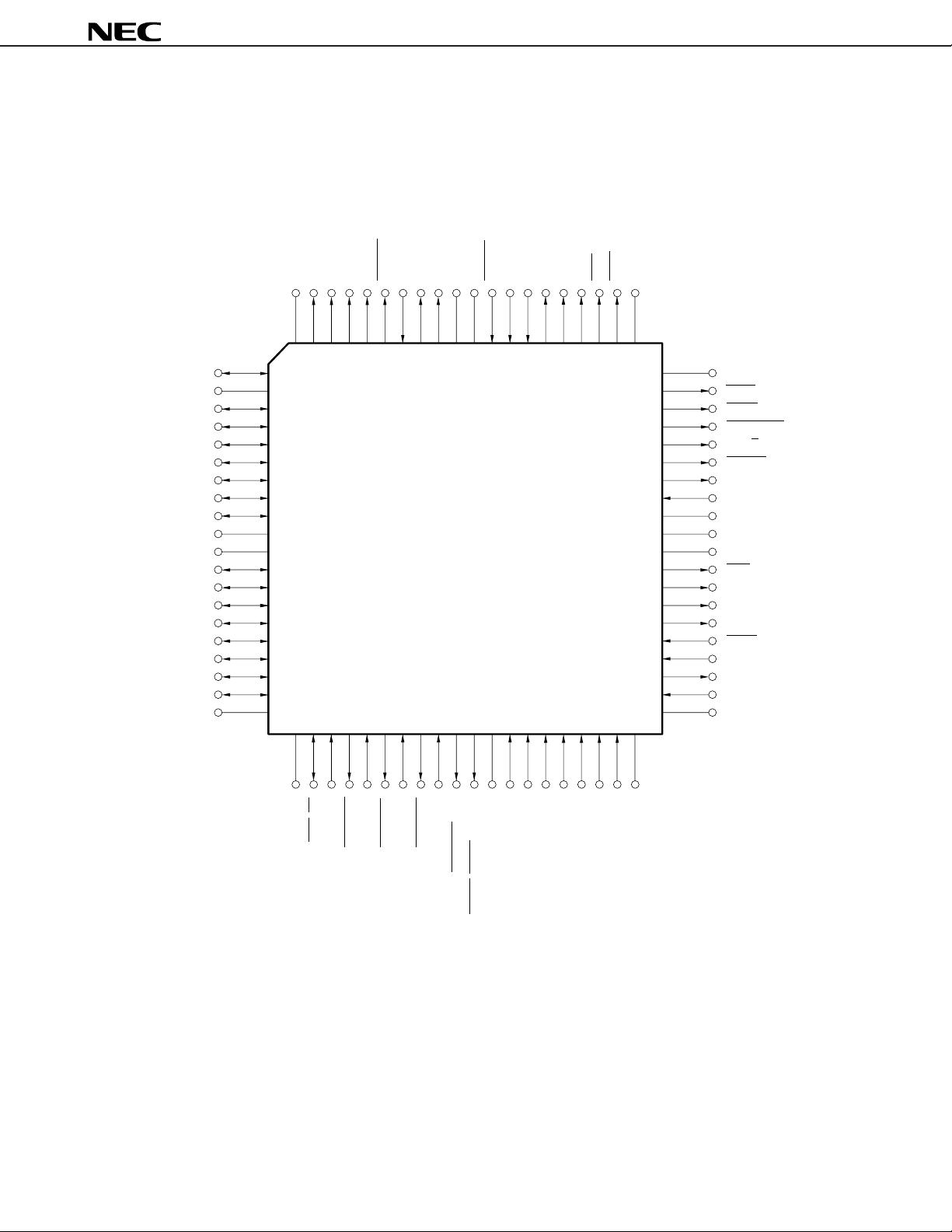
• 68-pin Plastic QFJ (950 × 950 mil)
µ
PD70216HLP-10
µ
PD70216HLP-12
µ
PD70216HLP-16
µ
PD70216HLP-20
A16/PS0
A17/PS1
A18/PS2
A19/PS3
REFRQ
HLDRQ
HLDAK
RESOUT
VDDRESET
READY
NMI
BS2
BS1
BS0
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
MRD
IORD
AD15
AD14
AD13
AD12
AD11
AD10
AD9
AD8
GND
AD7
AD6
AD5
AD4
AD3
AD2
AD1
AD0
9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 68 67 66 65 64 63 62 61
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43
D
D
X
X
INTP1
INTP2
END/TC
DMARQ0
DMAAK1
DMARQ1
DMAAK0
DMAAK2
DMARQ2
DMARQ3/R
DMAAK3/T
INTP3
INTP4
INTP5
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
INTP6
INTP7
MWR
IOWR
BUSLOCK
BUFR/W
BUFEN
CLKOUT
X1
X2
GND
UBE
ASTB
QS0
QS1
POLL
TCTL2
TOUT2
TCLK
INTAK/SRDY/TOUT1
8
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00

PIN NAMES
A8-A15 : Address Bus
A16/PS0-A19/PS3 : Address/Processor Status
AD0-AD15 : Address Bus/Data Bus
ASTB : Address Strobe
BS0-BS2 : Bus Status
BUFEN : Buffer Enable
BUFR/W : Buffer Read/Write
BUSLOCK : Bus Lock
CLKOUT : Clock Output
DMAAK0-DMAAK2 : DMA Acknowledge
DMAAK3/TXD : DMA Acknowledge/Transmit Data
DMARQ0-DMARQ2 : DMA Request
DMARQ3/RXD : DMA Request/Receive Data
END/TC : End/Terminal Count
GND : Ground
High : High Level Output
HLDAK : Hold Acknowledge
HLDRQ : Hold Request
IC : Internally Connected
INTAK/SRDY/TOUT1 : Interrupt Acknowledge/Serial Ready/Timer Output 1
INTP1-INTP7 : Interrupt Request from Peripherals
IORD : I/O Read
IOWR : I/O Write
MRD : Memory Read
MWR : Memory Write
NC : No Connection
NMI : Non-Maskable Interrupt Request
POLL : Poll
QS0, QS1 : Queue Status
READY : Ready
REFRQ : Refresh Request
RESET : Reset
RESOUT : Reset Output
TCLK : Timer Clock
TCTL2 : Timer Control 2
TOUT2 : Timer Output 2
UBE : Upper Byte Enable
DD : Power Supply
V
X1, X2 : Crystal
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
9
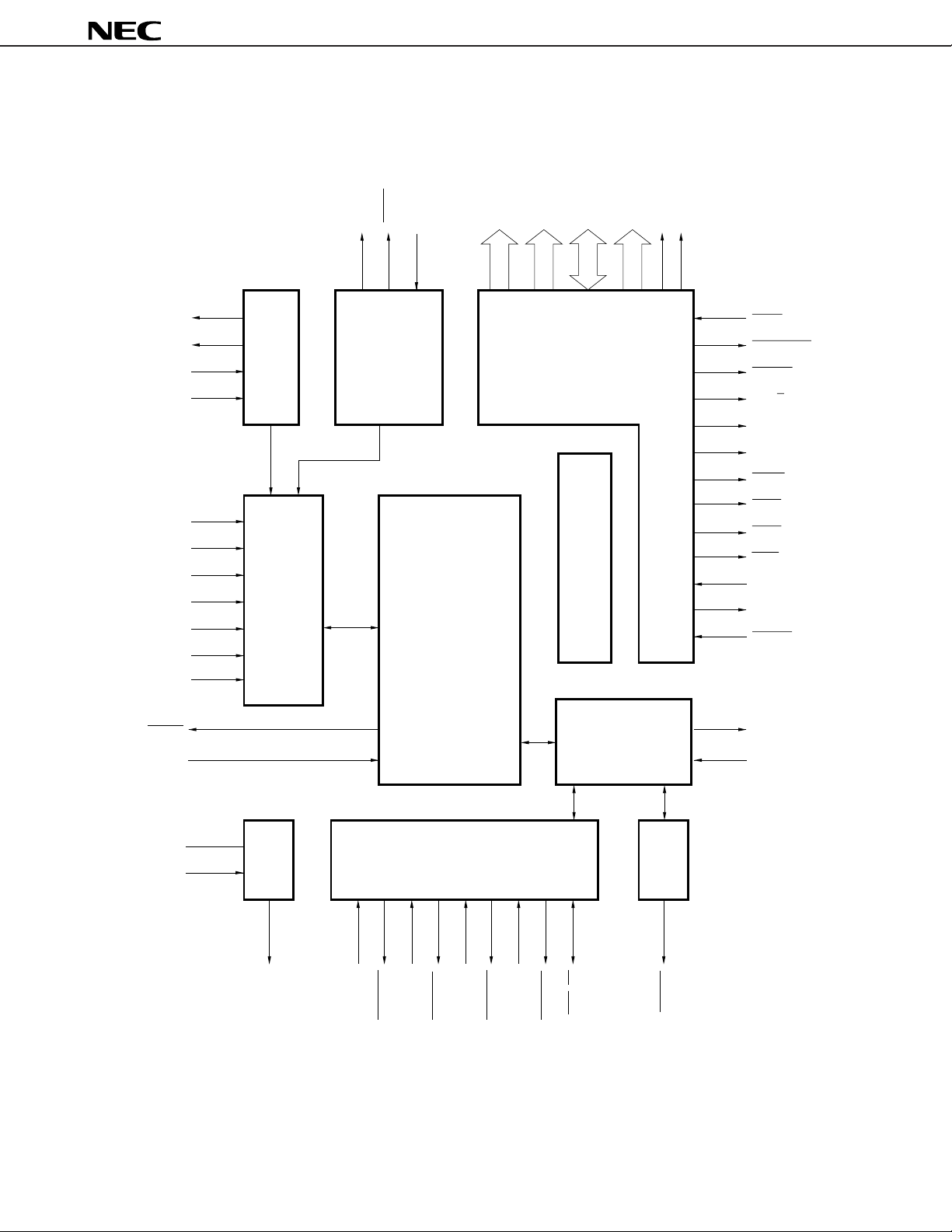
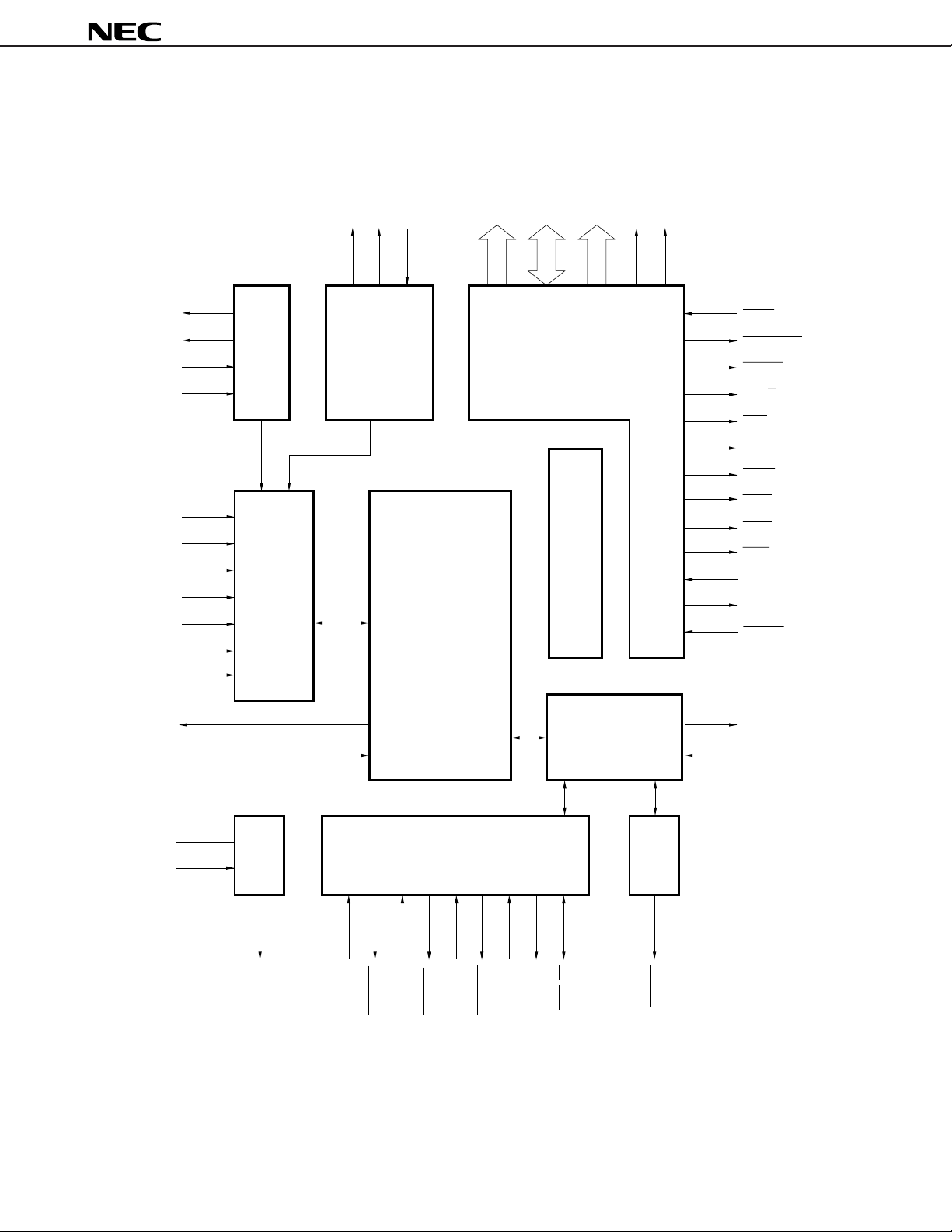
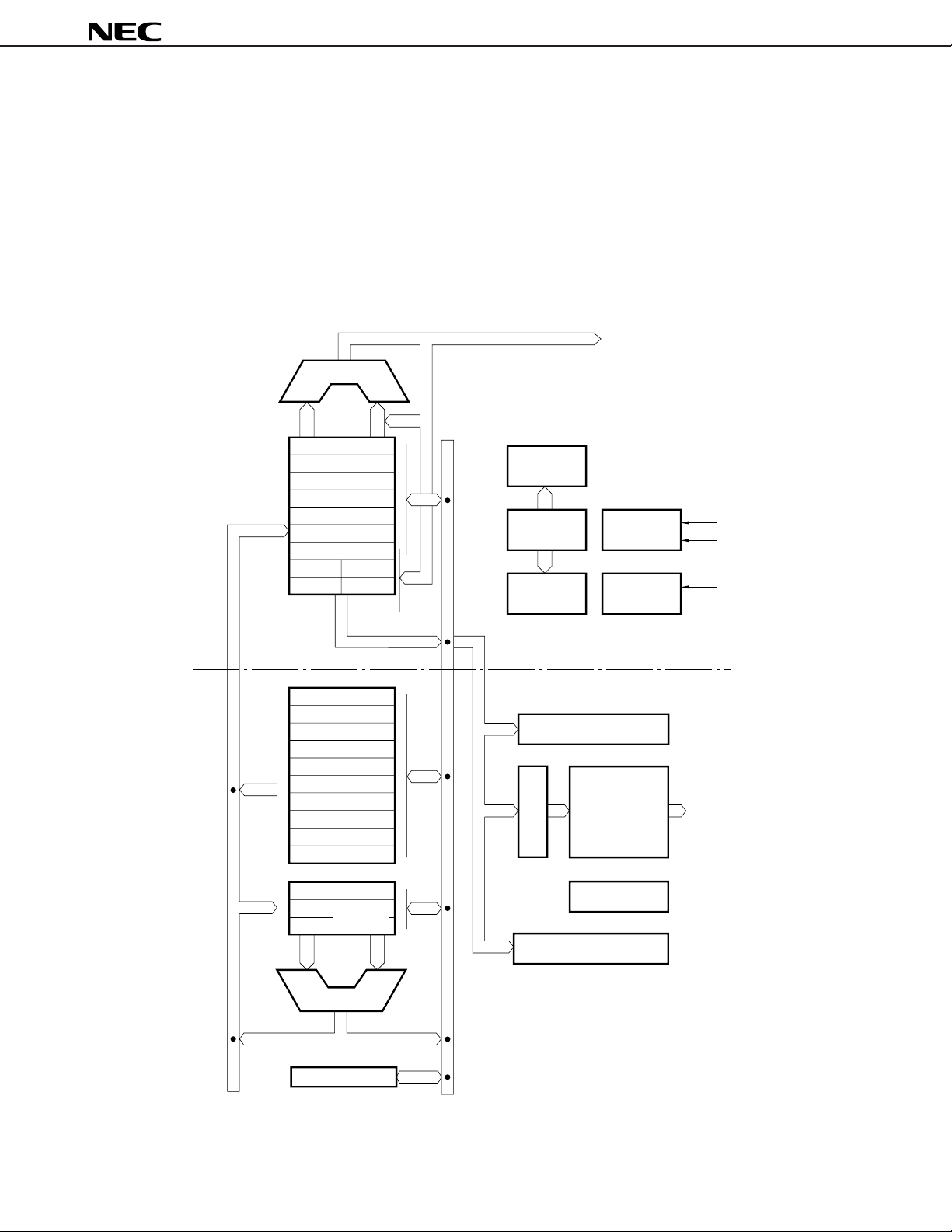
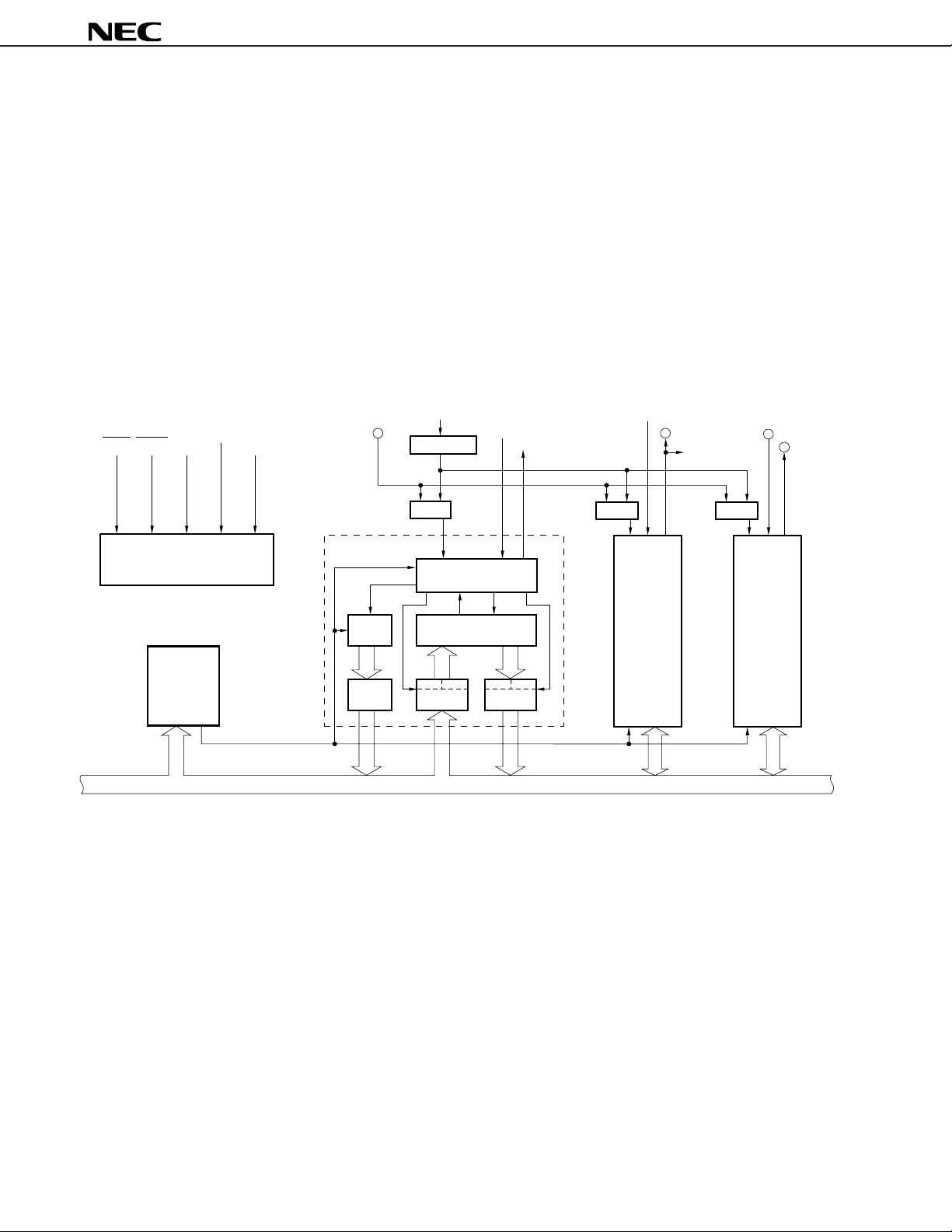
BLOCK DIAGRAM
(1) V40HL
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
TOUT2
TOUT1
TCTL2
TCLK
INTP7
INTP6
INTP5
INTP4
INTP3
INTP2
TCU
ICU
XD
T
SCU
SRDY
XD
R
CPU
A16/PS0-A19/PS3
A8-A15
WCU
AD0-AD7
BIU
QS1
BS0-BS2
QS0
POLL
BUSLOCK
BUFEN
BUFR/W
High
ASTB
IOWR
IORD
MWR
MRD
READY
RESOUT
RESET
INTP1
INTAK
NMI
X2
X1
CG
CLKOUT
DMAAK0
DMARQ0
DMAU
DMAAK1
DMARQ1
DMAAK2
DMARQ2
DMARQ3
CPU : Central Processing Unit REFU : Reflesh Control Unit
CG : Clock Generator TCU : Timer/Count Unit
BIU : Bus Interface Unit SCU : Serial Control Unit
BAU : Bus Arbitration Unit ICU : Interrupt Control Unit
WCU : Wait Control Unit DMAU : DMA Control Unit
10
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
END/TC
DMAAK3
BAU
HLDAK
HLDRQ
REFU
REFRQ
(2) V50HL
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
TOUT2
TOUT1
TCTL2
TCLK
INTP7
INTP6
INTP5
INTP4
INTP3
INTP2
TCU
ICU
XD
T
SCU
SRDY
RXD
CPU
A16/PS0-A19/PS3
AD0-AD15
BIU
WCU
BS0-BS2
QS1
QS0
POLL
BUSLOCK
BUFEN
BUFR/W
UBE
ASTB
IOWR
IORD
MWR
MRD
READY
RESOUT
RESET
INTP1
INTAK
NMI
X2
X1
CG DMAU
CLKOUT
DMAAK0
DMARQ0
DMAAK1
DMARQ1
DMARQ2
DMAAK2
DMARQ3
END/TC
DMAAK3
BAU
HLDAK
HLDRQ
REFU
REFRQ
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
11
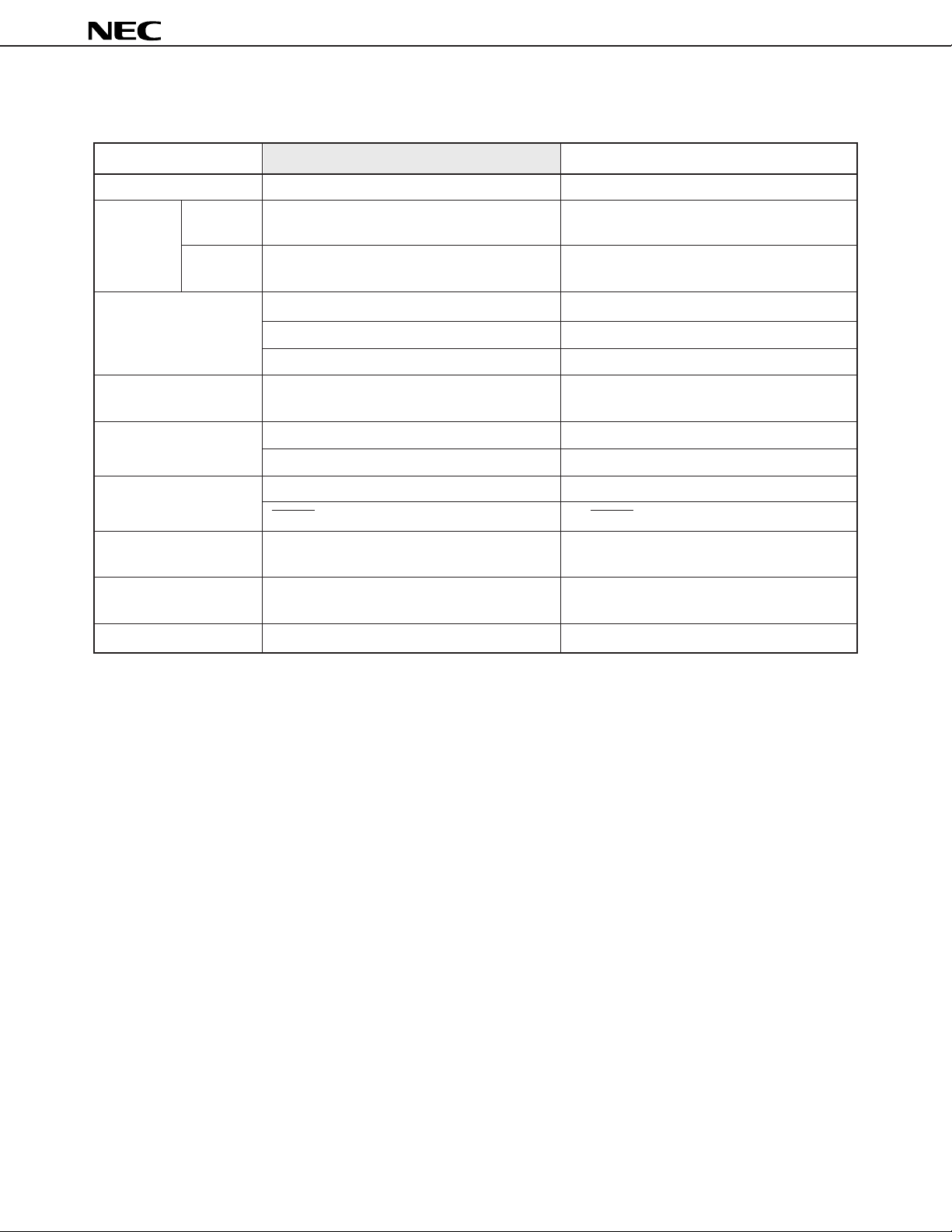
DIFFERENCES FROM V40 AND V50
Item V40, V50V40HL, V50HL
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
Operating supply voltage
Operating
frequency
Clock generator
(CG)
Internal I/O relocation
function
Wait control unit (WCU)
Refresh control unit
(REFU)
Serial control unit (SCU)
DMA control unit (DMAU)
Standby functions
VDD = 5 V
VDD = 3 V
3 V, 5 V
MAX. : 10, 12.5, 16, 20 MHz
MIN. : DC
MAX. : 5, 6.25, 8, 10 MHz
MIN. : DC
Variable scaling factor
Variable instruction cycle time
Maximum input frequency: 40 MHz
Switchable 8-bit boundary or 16-bit boundary
relocation function
Memory space: 5 divisions
I/O space: 3 divisions
Refresh address: 16 bits
REFRQ extended timing supported
Dedicated baud rate generator incorporated
µ
PD71071/71037 subset (either function
selectable)
HALT mode, STOP mode
Note 1
Note 2
5 V
MAX. : 8, 10 MHz
MIN. : 2 MHz
No operation
Fixed scaling factor
Fixed instruction cycle time
Maximum input frequency: 20 MHz
V40: Relocation possible on 8-bit boundary
V50: Relocation possible on 16-bit boundary
Memory space: 3 divisions
I/O space: Not divided
Refresh address: 9 bits
No REFRQ extended timing
No dedicated baund rate generator
incorporated
µ
PD71071 subset
HALT mode only
Notes 1. Divided into 3 when a reset is performed.
2. Not divided when a reset is performed.
12
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00

µ
PD70208H, 70216H
CONTENTS
1. PIN FUNCTIONS ................................................................................................................................... 15
1.1 LIST OF PIN FUNCTIONS........................................................................................................................... 15
1.2 PROCESSING OF UNUSED PINS.............................................................................................................. 17
2. MEMORY AND I/O CONFIGURATION ................................................................................................ 19
2.1 MEMORY SPACE......................................................................................................................................... 19
2.2 I/O SPACE .................................................................................................................................................... 21
3. CPU ........................................................................................................................................................ 22
4. CG (CLOCK GENERATOR) ................................................................................................................. 24
5. BIU (BUS INTERFACE UNIT) .............................................................................................................. 24
6. BAU (BUS ARBITRATION UNIT) ........................................................................................................ 25
7. WCU (WAIT CONTROL UNIT) ................................................................................................................ 27
7.1 FEATURES ................................................................................................................................................... 27
7.2 RELATION BETWEEN WCU AND READY PIN ........................................................................................ 28
8. REFU (REFRESH CONTROL UNIT).................................................................................................... 29
8.1 FEATURES ................................................................................................................................................... 29
8.2 REFRESH OPERATIONS ............................................................................................................................ 29
9. TCU (TIMER/COUNTER UNIT) ............................................................................................................ 30
9.1 FEATURES ................................................................................................................................................... 30
9.2 TCU INTERNAL BLOCK DIAGRAM........................................................................................................... 30
10. SCU (SERIAL CONTROL UNIT) .......................................................................................................... 31
10.1 FEATURES ................................................................................................................................................... 31
10.2 SCU INTERNAL BLOCK DIAGRAM ........................................................................................................... 31
11. ICU (INTERRUPT CONTROL UNIT) .................................................................................................... 32
11.1 FEATURES ................................................................................................................................................... 32
11.2 ICU INTERNAL BLOCK DIAGRAM ............................................................................................................ 32
12. DMAU (DMA CONTROL UNIT) ............................................................................................................ 33
12.1 FEATURES ................................................................................................................................................... 33
12.2 DMAU INTERNAL BLOCK DIAGRAM ....................................................................................................... 33
13. STANDBY FUNCTIONS........................................................................................................................ 34
14. RESET OPERATION ............................................................................................................................. 3 4
15. INSTRUCTION SET............................................................................................................................... 35
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
13

µ
PD70208H, 70216H
16. ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS......................................................................................................... 66
16.1 AT 5 V OPERATION .................................................................................................................................... 66
16.2 AT 3 V OPERATION .................................................................................................................................... 75
17. PACKAGE DRAWINGS ........................................................................................................................ 100
18. RECOMMENDED SOLDERING CONDITIONS ................................................................................... 103
14
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
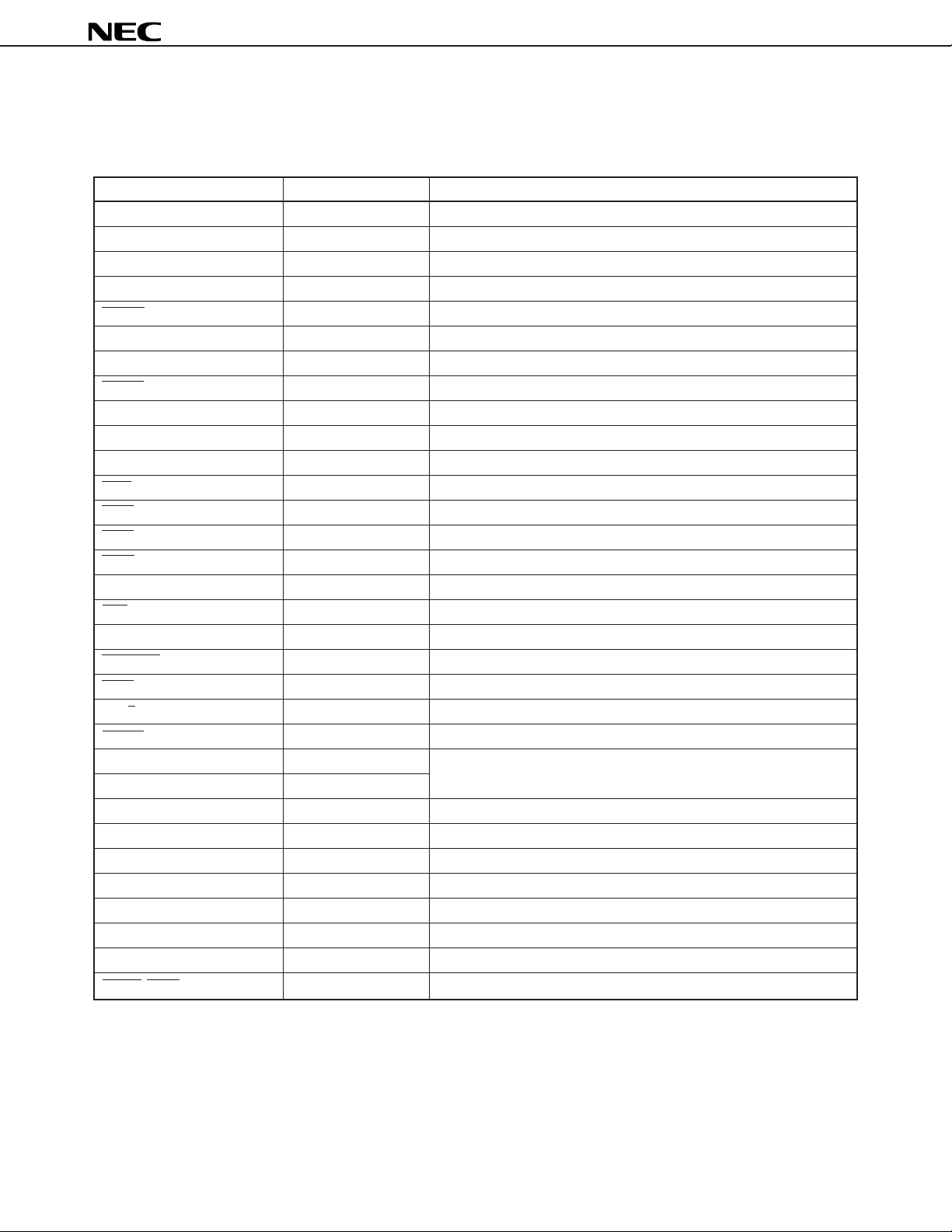
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
1. PIN FUNCTIONS
1.1 LIST OF PIN FUNCTIONS
Pin Name Input/Output Function
Note 3
Note 3
Note 3
Note 3
Note 3
Note 2, 3
Note 2, 3
Note 3
Note 3
Note 3
Note 1, 3
Note 3
3-state I/O Time-division address/data bus
3-state I/O Time-division address/data bus
3-state output Address bus
3-state output Time-division address/processor status
3-state output Memory read strobe
3-state output Memory read strobe
3-state output I/O read strobe
3-state output I/O write strobe
3-state output Data bus upper byte enable
3-state output High level output
3-state output Bus lock
3-state output Buffer read/write
3-state output Buffer enable
3-state output Bus status
AD0 to AD15
AD0 to AD7
A8 to A15
A16/PS0 to A19/PS3
REFRQ Output Refresh request
HLDRQ Input Bus hold request
HLDAK Output Bus hold acknowledge
RESET Input Reset
RESOUT Output System reset output
READY Input Bus cycle end
NMI Input Non-maskable interrupt
MRD
MWR
IORD
IOWR
ASTB Output Address strobe
Note 1, 3
UBE
Note 2
High
BUSLOCK
POLL Input Floating-point operation processor polling
BUFR/W
BUFEN
X1 Input Crystal/external clock
X2 —
CLKOUT Output Clock output
BS0 to BS2
QS0, QS1 Output Queue status
TOUT2 Output Timer 2 output
TCTL2 Input Timer 2 control
TCLK Input Timer clock
INTP1 to INTP7 Input Maskable interrupts
INTAK/SRDY/TOUT1 Output Interrupt acknowledge/serial reception ready/timer 1 output
Notes 1. V50HL only
2. V40HL only
3. These pins are provided with a latch. Therefore, when they go into a high-impedance state, they hold
the status before the high-impedance state until driven by an external device. It is not necessary to pull
up or down the data bus. To invert the level of the pin that goes into a high-impedance state by an
external device, a drive current higher than the latch invert current (I
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
ILH, IILL) is necessary.
15
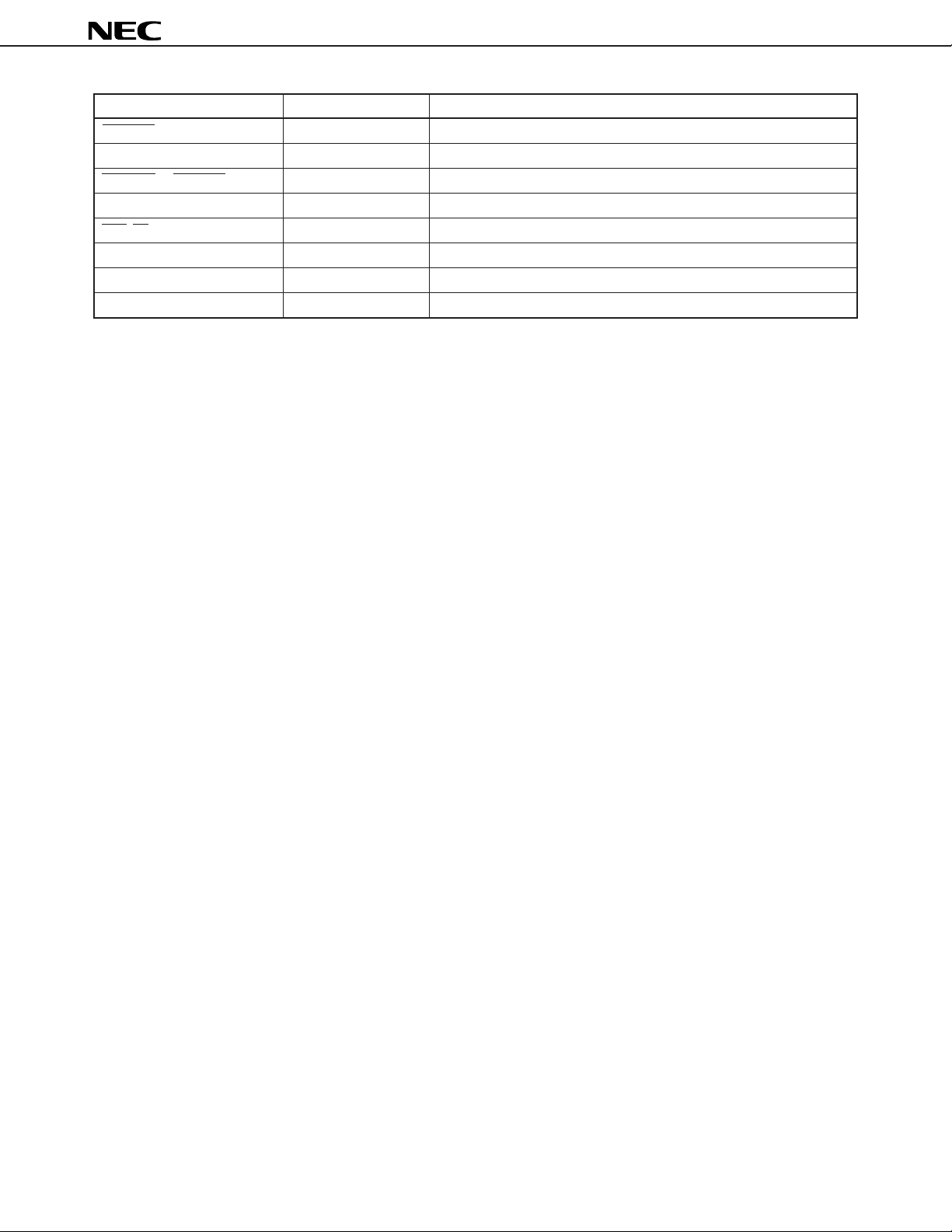
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
Pin Name Input/Output Function
DMAAK3/TXD Output DMA acknowledge 3/serial transmit data
DMARQ3/RXD Input DMA request 3/serial receive data
DMAAK0 to DMAAK2 Output DMA acknowledge
DMARQ0 to DMARQ2 Input DMA request
END/TC I/O DMA service forcible termination/DMA service completion
VDD — Positive power supply pin
GND — Ground potential pin
IC — Internal connection pin (External connection impossible)
16
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
1.2 PROCESSING OF UNUSED PINS
Table 1-1 shows the processing (recommended connection) of the unused pins. Use of a resistor with a resistance of
1 to 10 kΩ is recommended to connect these pins to VDD or GND via resistor.
Table 1-1. Processing of Unused Pins
Pin Name Input/Output Recommended Connection
AD0 to AD15
AD0 to AD7
A8 to A15
A16/PS0 to A19/PS3 3-state output
REFRQ Output
HLDRQ Input Connect to GND via resistor
HLDAK Output Open
RESOUT Output Open
READY Input Connect to VDD via resistor
NMI Input Connect to GND via resistor
MRD 3-state output Open
MWR 3-state output
IORD 3-state output
IOWR 3-state output
ASTB Output
Note 1
UBE
Note 2
High
BUSLOCK 3-state output
POLL Input Connect to GND via resistor
BUFR/W 3-state output Open
BUFEN 3-state output
CLKOUT Output Open
BS0 to BS2 3-state output
QS0, QS1 Output
TOUT2 Output
TCTL2 Input Connect to GND via resistor
TCLK Input
INTP1 to INTP7 Input Open
INTAK/SRDY/TOUT1 Output
DMAAK3/TxD Output
DMARQ3/RxD Input Connect to GND via resistor
DMAAK0 to DMAAK2 Output Open
DMARQ0 to DMARQ2 Input Connect to GND via resistor
END/TC I/O Individually connect to VDD via resistor
Note 1
Note 2
Note 2
3-state I/O Open
3-state I/O
3-state output
3-state output
Output
Notes 1. V50HL only
2. V40HL only
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
17
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
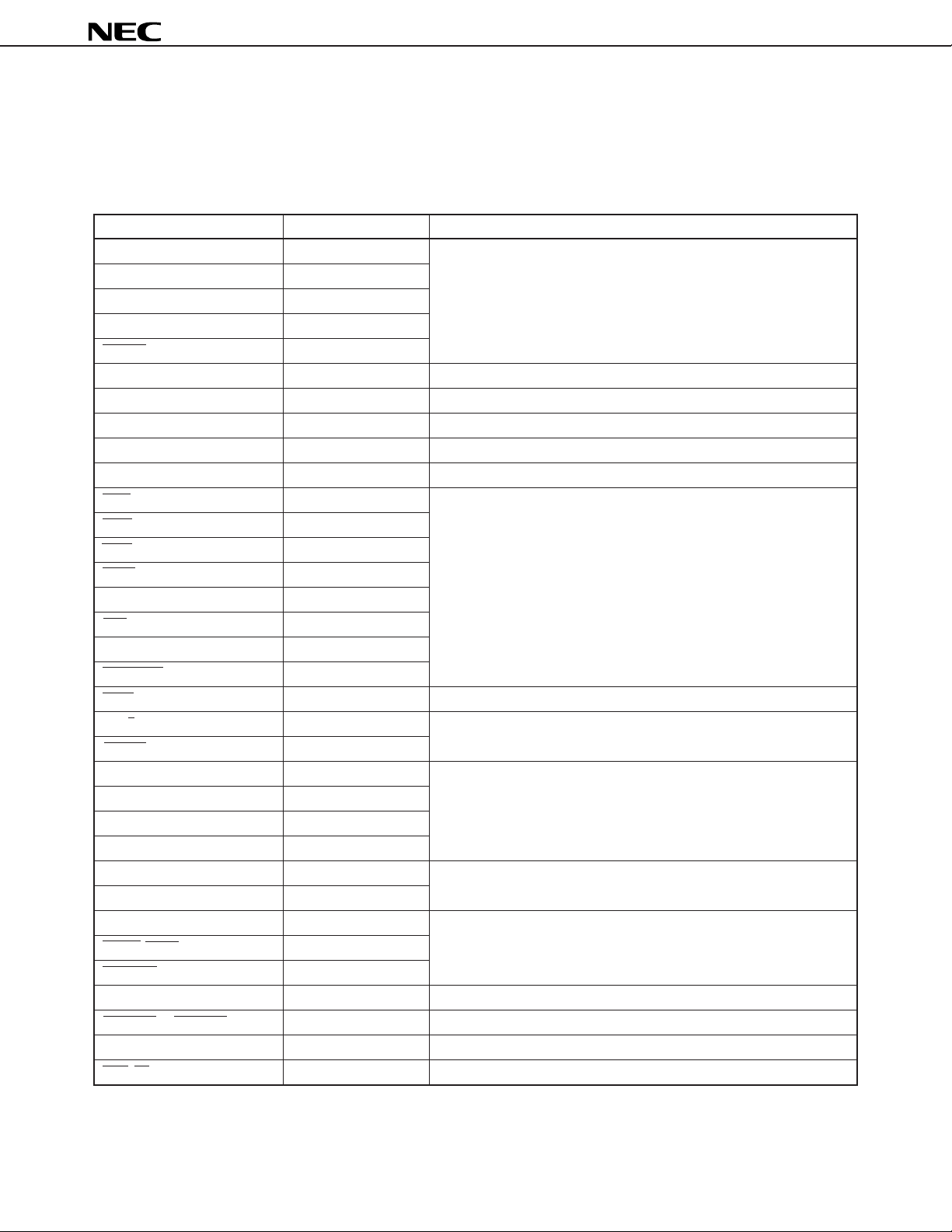
Remark The circuit configuration of the latch is as illustrated below. To invert the level of the pin with a latch, a drive
current higher than the latch invert current is necessary.
(1) Output pin
(2) I/O pin
Hi-Z
control
Hi-Z
control
Output buffer
Output buffer
Input buffer
Latch
Output pin
address bus,
control bus
Latch
I/O pin
(data bus)
18
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
2. MEMORY AND I/O CONFIGURATION
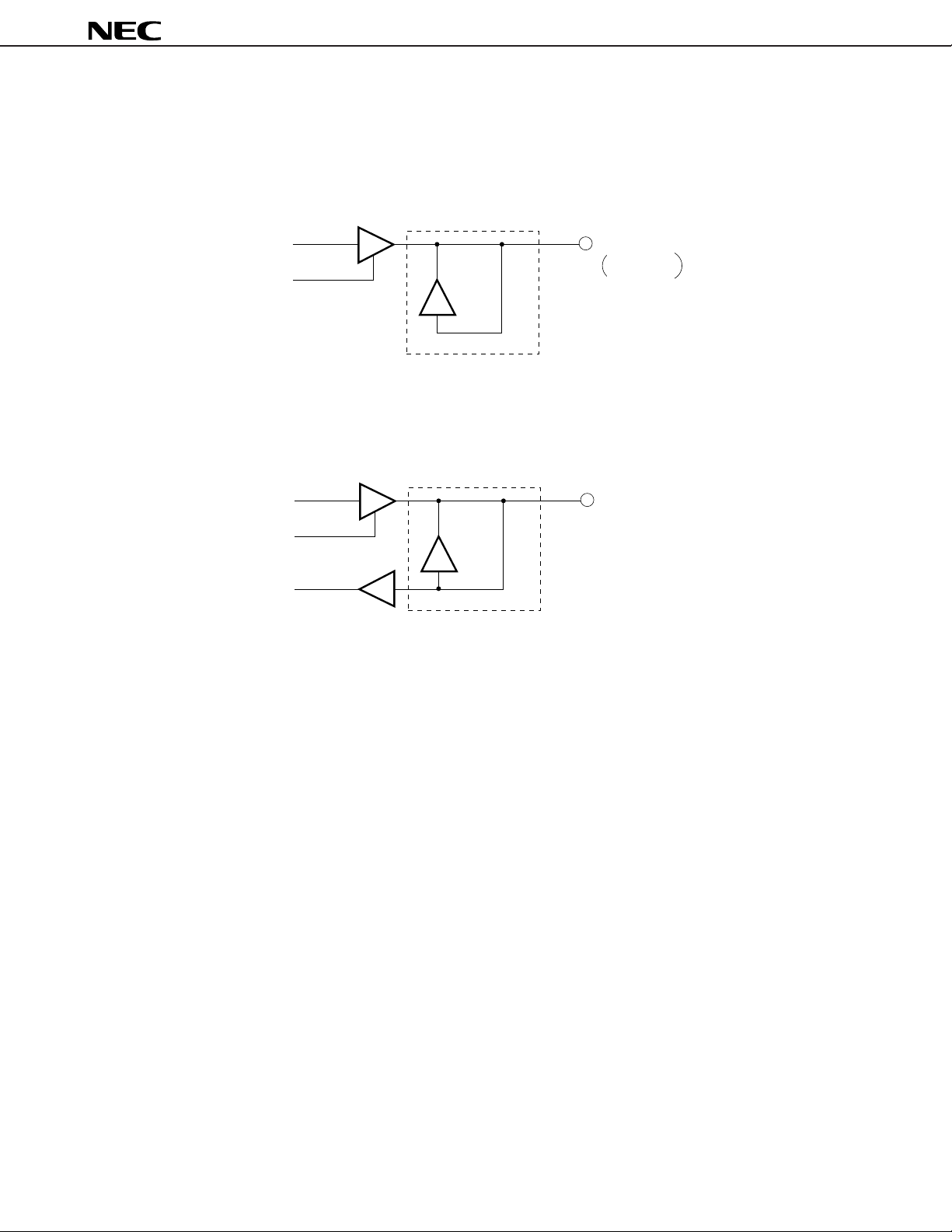
2.1 MEMORY SPACE
The V40HL and V50HL can access a 1M-byte (512K-word) memory space.
Figure 2-1. Memory Map
FFFFFH
Reserved
FFFFCH
FFFFBH
Dedicated
FFFF0H
FFFEFH
General Use
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
A0-A19
00400H
003FFH
Interrupt Vector Table
00000H
Figure 2-2. Interface with Memory (1/2)
(a) V40HL
Address Bus (20)
Memory
1M Byte
8
D0-D7
Data Bus (8)
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
19
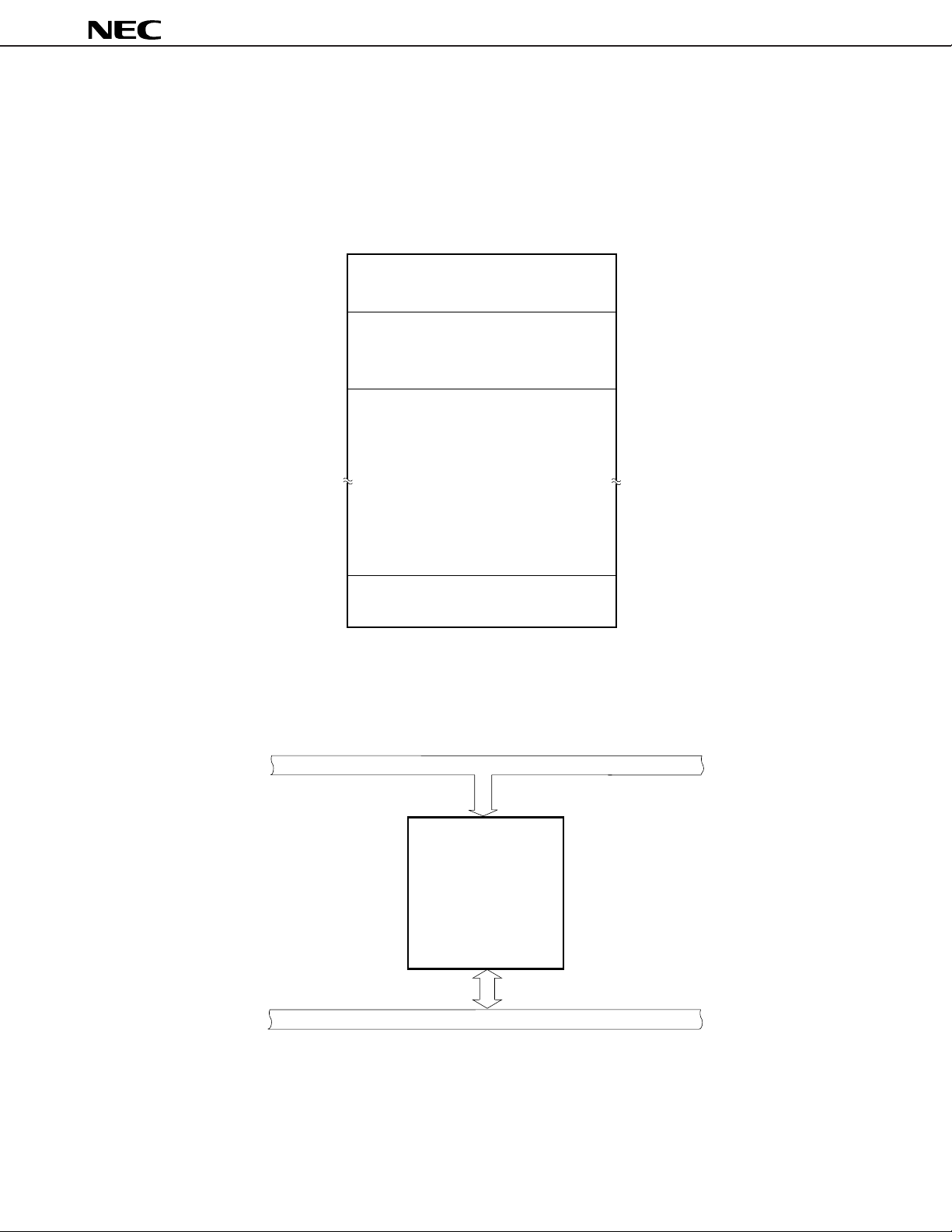
Figure 2-2. Interface with Memory (2/2)
(b) V50HL
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
A1-A19
A0
UBE
D0-D15
Address Bus (19)
19 19
BSEL BSEL
Memory
Upper Bank
512K Byte
D8-D15 D0-D7
8
Data Bus (16)
Memory
Lower Bank
512K Byte
8
20
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
2.2 I/O SPACE
In the V40HL and V50HL, I/Os up to 64K bytes (32K words) can be accessed in an area independent of the memory.
The various on-chip peripheral LSIs are set by accessing the system I/O area.
Extended functions added to those of the V40 and V50 are mapped onto unused V40 and V50 registers and the reserved
area.
The I/O map is shown in Figure 2-3.
Figure 2-3. I/O Map
FFFFH
Area used for setting of I/O boundary,
System I/O Area
FFE0H
FFDFH
Reserved Area
WCU, REFU, baud rate generator, etc.,
and DMAU, ICU, TCU and SCU allocation.
FF00H
FEFFH
256 Bytes
DMAU
ICU
The DMAU, ICU, TCU and SCU
are allocated within any 256 bytes.
TCU
SCU
Internal I/O Area
0000H
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
External I/O Area
21
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
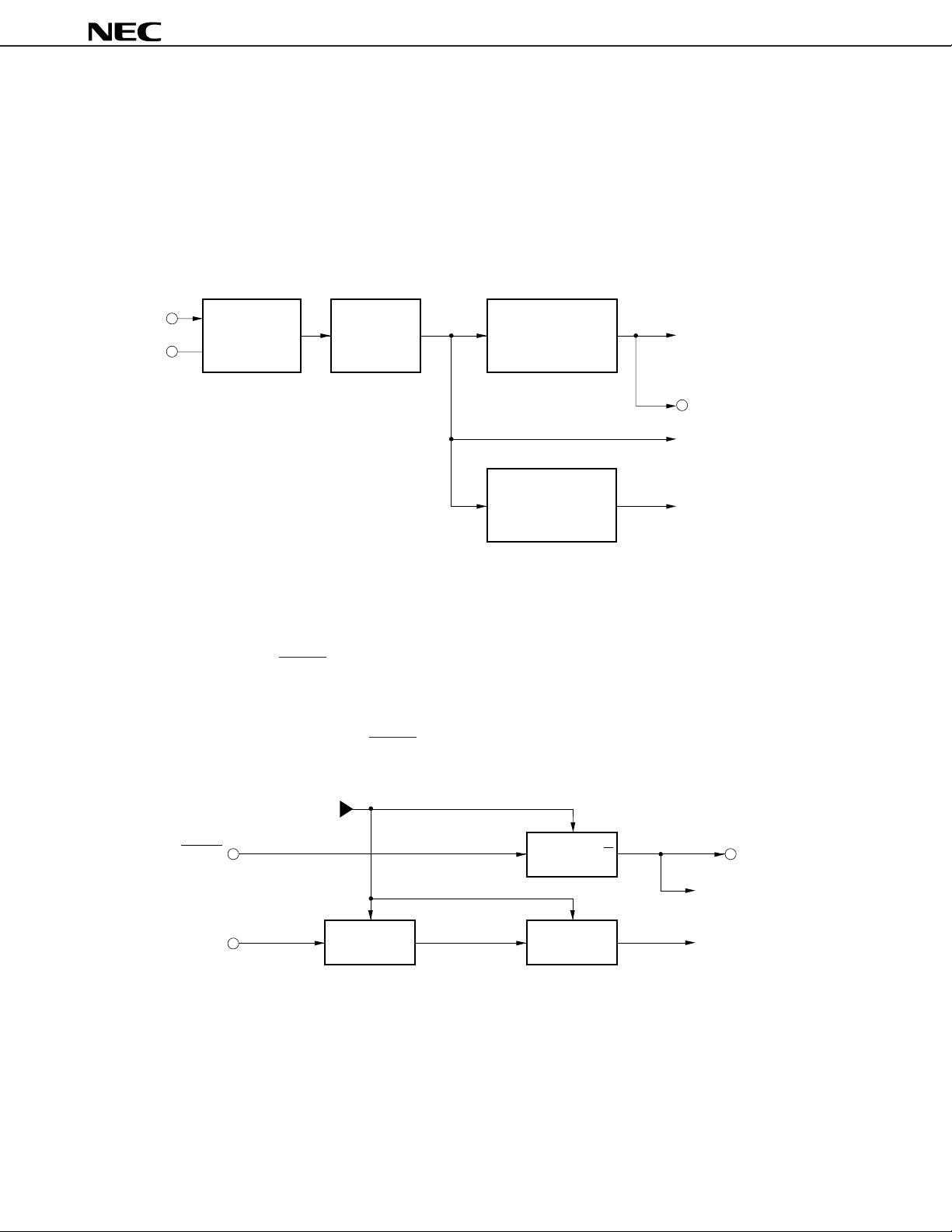
3. CPU
The CPU has the same functions as the V20HLTM and V30HLTM. In hardware terms, there are some changes regarding
the use of the bus with on-chip peripherals, but in software terms the CPU is fully compatible.
The internal block diagram of the CPU is shown in Figure 3-1.
Figure 3-1. Internal Block Diagram of CPU (1/2)
(a) V40HL
Internal Address/Data Bus (20)
To BIU
ADM
TC
TA
TB
Q0
Q2
PS
SS
DS0
DS1
PFP
DP
TEMP
LC
PC
AW
BW
CW
DW
IX
IY
BP
SP
SHIFTER
Q1
Q3
T-STATE
CONTROL
CYCLE
DECISION
QUEUE
CONTROL
EFFECTIVE ADDRESS
GENERATOR
ADDRESS
REGISTER
µ
Queue Data Bus (8)
INSTRUCTION DECODER
INTERRUPT
CONTROL
STANDBY
CONTROL
INSTRUCTION
µ
ROM
SEQUENCE
µ
CONTROL
BCU
EXU
29
Micro Data Bus
NMI
INT
(From ICU)
CLOCK
(From CG)
22
Sub Data Bus
(16)
ALU
PSW
Main Data Bus
(16)
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
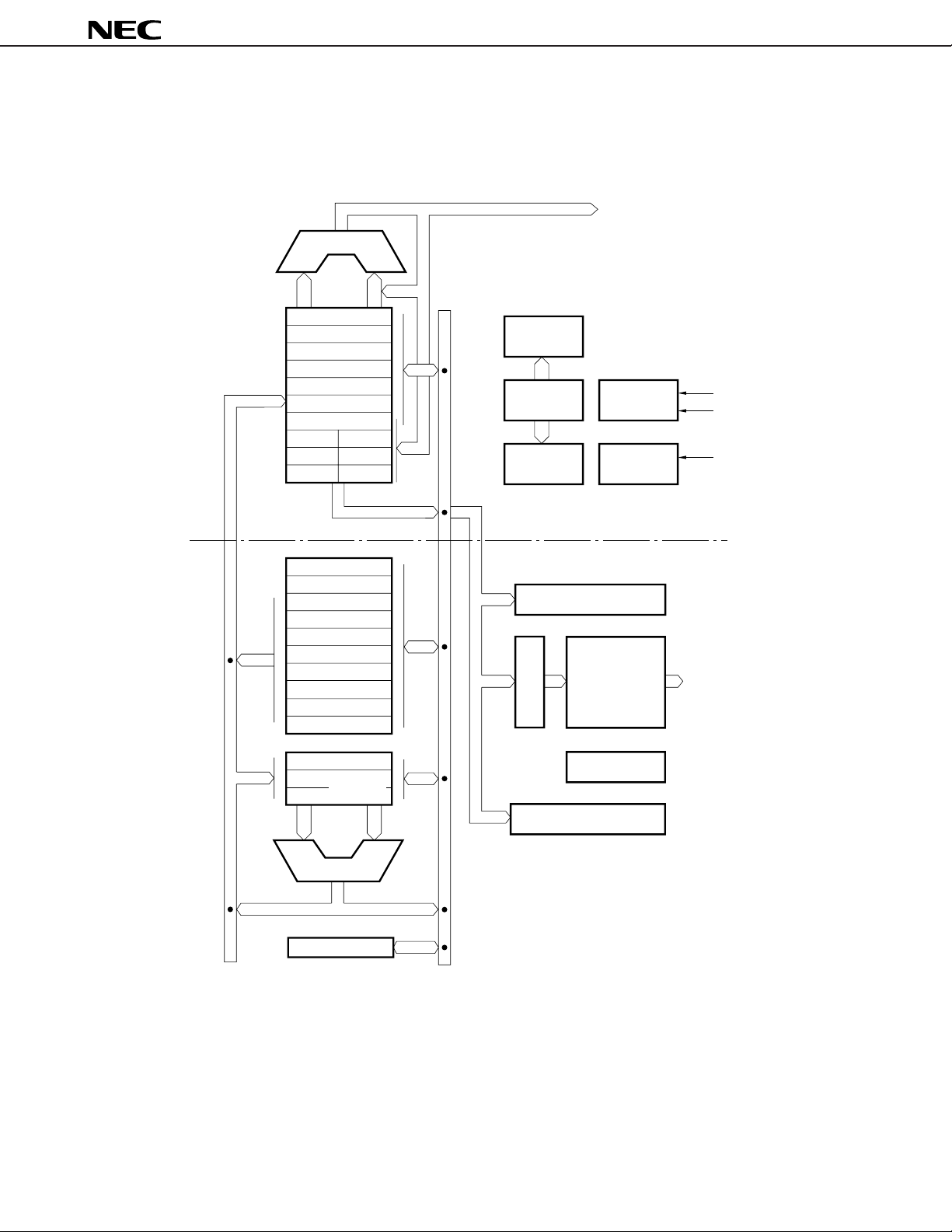
Figure 3-1. Internal Block Diagram of CPU (2/2)
(b) V50HL
Internal Address/Data Bus (20)
To BIU
ADM
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
PS
SS
DS0
DS1
PFP
DP
TEMP
Q0
Q2
Q4 Q5
LC
PC
AW
BW
CW
DW
IX
IY
BP
SP
TC
TA
SHIFTER
TB
Q1
Q3
T-STATE
CONTROL
CYCLE
DECISION
QUEUE
CONTROL
EFFECTIVE ADDRESS
GENERATOR
ADDRESS
REGISTER
µ
Queue Data Bus (8)
INSTRUCTION DECODER
INTERRUPT
CONTROL
STANDBY
CONTROL
INSTRUCTION
µ
ROM
SEQUENCE
µ
CONTROL
BCU
EXU
29
Micro Data Bus
NMI
INT
(From ICU)
CLOCK
(From CG)
Sub Data Bus
(16)
ALU
PSW
Main Data Bus
(16)
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
23
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
4. CG (CLOCK GENERATOR)
The CG generates a clock at a frequency of 1/2, 1/4, 1/8 or 1/16 that of the crystal and oscillator connected to the X1
and X2 pins, supplies it as the CPU operating clock and outputs it externally as the CLKOUT pin output.
The interrupt cycle time can be changed according to the oscillator scaling factor. The scaling factor can be set by a
system I/O area register.
Figure 4-1. Internal Block Diagram of CG
X1
X2
Oscillator
f
XX
Divide-by-2
Scaler
Divide-by-1-to-8
Scaler
Divide-by-2-to-16
Scaler
f
X
CPU, DMAU, REFU, SCU
CLKOUT
Baud Rate Counter (BRC)
TCU
5. BIU (BUS INTERFACE UNIT)
The BIU controls the data bus, address bus and control bus pins. These buses are used by the CPU, DMAU (DMA control
unit) and REFU (refresh control unit).
The BIU synchronizes the RESET input signal and READY input signal using the CLOCK signal generated by the clock
generator (CG). In addition to being supplied to the inside of the V40HL and V50HL, the synchronized reset signal is also
output externally from the RESOUT pin. The synchronized READY signal is supplied to the internal CPU, DMAU and REFU.
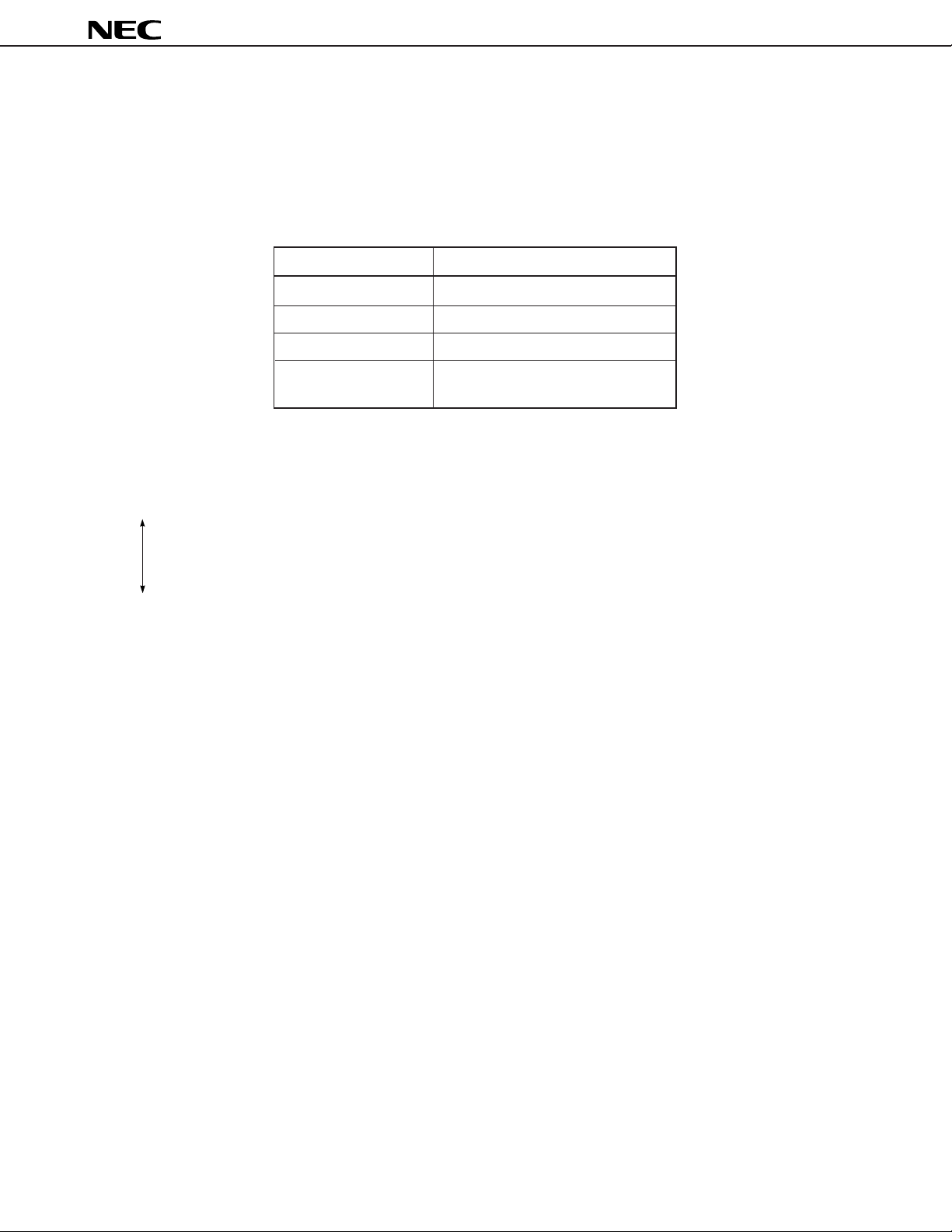
Figure 5-1. RESET and READY Signal Synchronization
24
RESET
READY
CLOCK
CK ↑
QD
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
CK ↓
CK ↓
QD
QD
RESOUT
To Internal Units
To Internal Units
6. BAU (BUS ARBITRATION UNIT)
The BAU performs bus arbitration among bus masters.
A list of bus masters (units which can acquire the bus) is shown below.
Table 6-1. Bus Masters
Bus Master Bus Cycle
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
CPU
DMAU
REFU
External bus master
(HLDRQ pin input)
The relative priorities of the bus masters are shown below.
High CPU (when BUSLOCK prefix is used)
REFU (highest priority: when given number of requests are reached)
DMAU
HLDRQ pin
CPU (normal CPU cycle)
Low REFU (lowest priority: cycle steal)
BAU bus arbitration is performed as follows.
A bus master such as the CPU, DMAU, REFU, etc., incorporated in the V40HL and V50HL normally release the bus at
the end of the bus cycle currently being executed, as shown in Figure 6-1. However, in the case of a bus master connected
to the HLDRQ pin, or cascaded external DMA controllers, for instance, the situation is as shown in Figure 6-2. The V40HL
and V50HL request return of the bus by inactivating the acknowledge signal (HLDAK), and on receiving this request, the
external bus master holding the bus should release the bus by dropping the bus hold request signal (HLDRQ). The V40HL
and V50HL-internal bus master with the highest priority is kept waiting until the bus hold request signal is dropped. This
is called a bus wait operation.
Program fetch, data read/write
DMA cycle
Refresh cycle
Bus cycle driven by external device
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
25
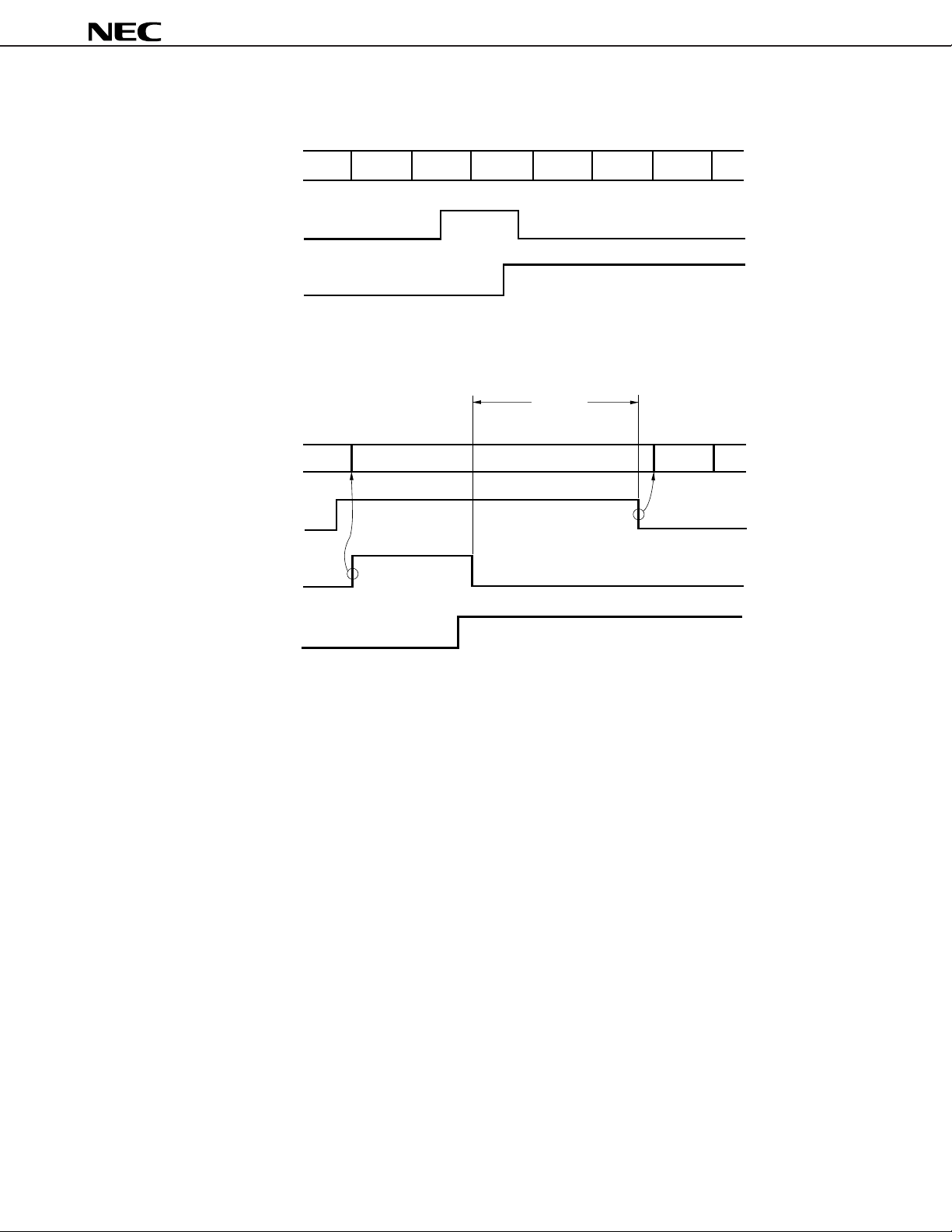
Figure 6-1. Internal Bus Cycles
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
Bus Cycle
Internal DMA Request
Internal Refresh Request
(Highest Priority)
Bus Cycle
HLDRQ Pin
HLDAK Pin
CPU CPU DMA Refresh Refresh Refresh
Figure 6-2. Bus Wait Operation
Bus Wait
Bus Release Refresh
Note
Internal Refresh Request
(Highest Priority)
Note The period in which the external bus master which has been given the bus after its release by the V40HL and
V50HL can use the bus.
26
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
7. WCU (WAIT CONTROL UNIT)
The WCU has the function of automatically inserting a wait state (TW) of 0 to 3 clock cycles in a CPU, DMAU or REFU
bus cycle.
7.1 FEATURES
Automatic setting of 0 to 3 waits for a CPU memory bus cycle
•
1M-byte memory space can be divided into 5
•
64K-byte I/O space can be divided into 3
•
Automatic setting of 0 to 3 waits for an external I/O cycle
•
Automatic setting of 0 to 3 waits for a DMA cycle
•
Automatic setting of 0 to 3 waits for a refresh cycle
•
Same as V40 and V50 directly after a reset (memory space divided into 3, no division of I/O space)
•
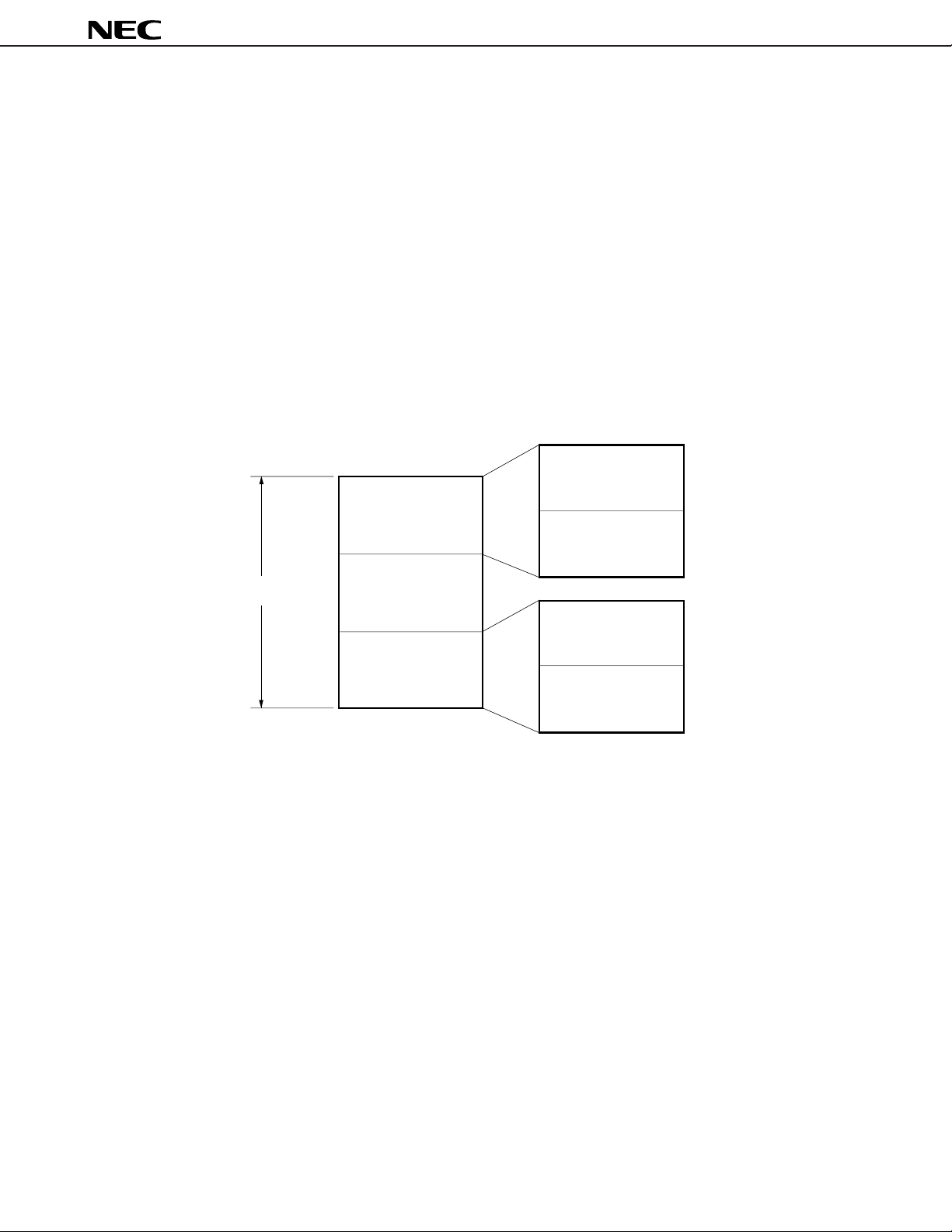
Figure 7-1. Example of Memory Space Division
Upper Sub
FFFFFH
Memory Block
Upper Memory Block
1 M-Byte
Memory Area
00000H
Remark The division specification and the size of each block are set by means of a system I/O area register.
Middle Memory Block
Lower Memory Block
Lower Sub
Memory Block
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
27
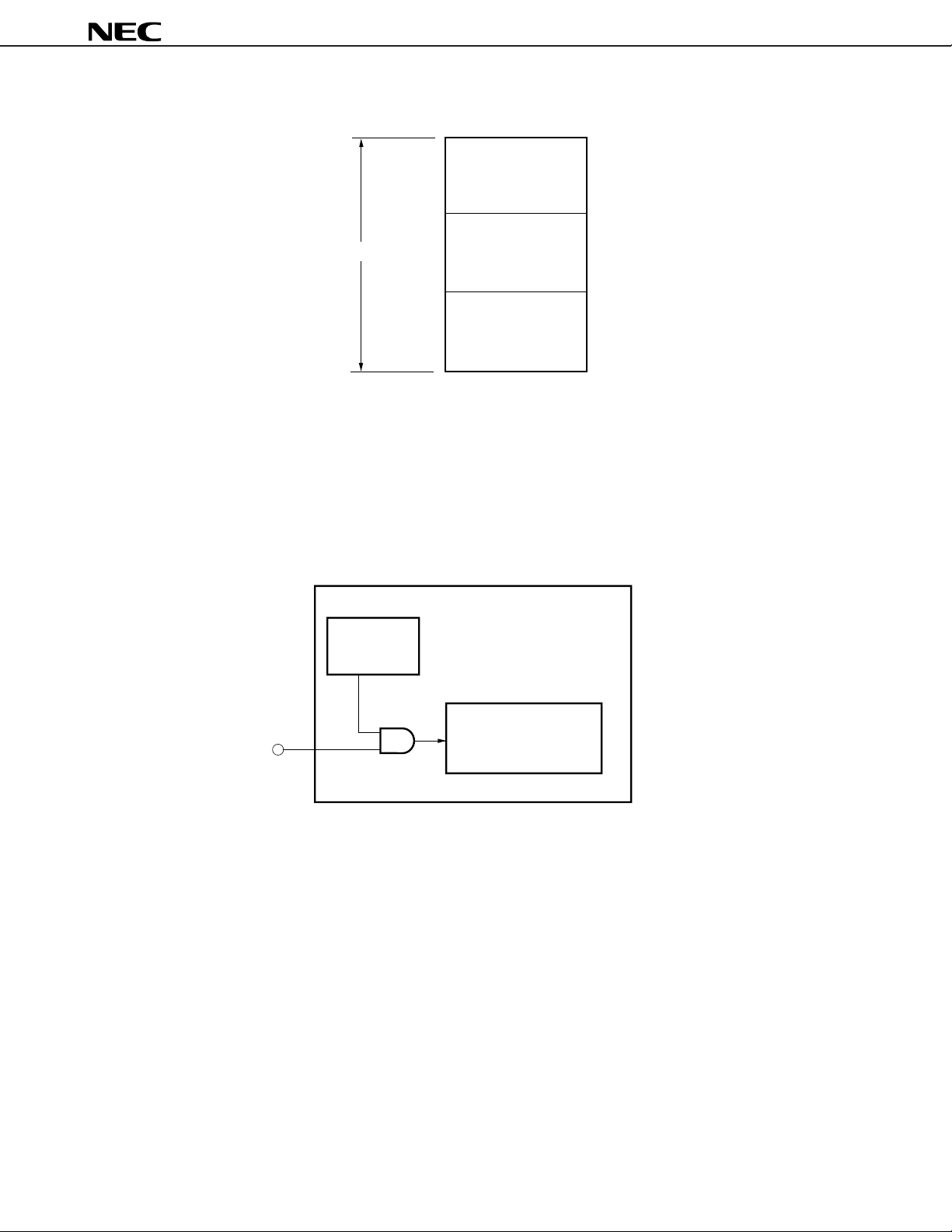
Figure 7-2. Example of I/O Space Division
FFFFH
Upper I/O Block
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
64K-Byte I/O Area
0000H
Remark The division specification and the size of each block are set by means of a system I/O area register.
7.2 RELATION BETWEEN WCU AND READY PIN
When wait cycles exceeding 3 clock cycles are necessary, the WCU and the READY signal pin can be used in
combination. The number of wait cycles specified by the WCU set value or the number of wait cycles under READY control,
whichever is larger, is inserted.
Figure 7-3. WCU and READY Control
WCU
Middle I/O Block
Lower I/O Block
V40HL/V50HL
28
READY
Bus Control
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00

µ
PD70208H, 70216H
8. REFU (REFRESH CONTROL UNIT)
The REFU generates refresh cycles required for refreshing of external DRAM. Refresh enabling/disabling and the refresh
interval can be set programmably.
8.1 FEATURES
Lowest-priority refreshing/highest-priority refreshing
•
7-refresh queue
•
16-bit refresh address
•
REFRQ extended timing supported (REFRQ active from T1 state)
•
8.2 REFRESH OPERATIONS
The REFU has two priorities. Normally, it has the lowest priority, and a refresh cycle cannot be started unless the bus
is completely idle. However, if there are 7 or more pending refresh requests, it is given the highest priority, and it requests
the bus master holding the bus to relinquish it. (See 6. BAU.)
The refresh address is output on A0 to A15. Every refresh cycle the refresh address is incremented by 1 (for the V40HL)
or by 2 (for the V50HL), and the next refresh address is generated.
In a refresh cycle, a low-level signal is output on the low address pins (A16 to A19).
This refresh address is not affected by a reset. When the device is powered on, the refresh address is undefined.
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
29
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
9. TCU (TIMER/COUNTER UNIT)
The TCU incorporates 3 counters, and can be used as a timer, event counter, rate generator, etc. Functionally it is a
subset of the
9.1 FEATURES
3 × 16-bit counters
•
Six programmable count modes
•
Binary/BCD count
•
Multiple latch command
•
Choice of two input clocks: internal/external
•
9.2 TCU INTERNAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
µ
PD71054.
IORDIOWR
Read/Write Control
Register)
Note 1
TMD
(Mode
Note 2
TCU
Selection
Signal
TCLK
(External)
TCT #0
Status
Register
(8)
Status
Latch
(8) (8) (8)
CLOCK
Prescaler
Down Counter (16)
H(8) L(8)
Count
Register
Internal Data Bus
Notes 1. A0 or A1 (Set by a system I/O area register)
2. A1 or A2 (Set by a system I/O area register)
Control Logic
(16)
H(8) L(8)
TCTL0=High
TOUT0 (To INTL0)
(16)
Count
Latch
TCTL1=High
TOUT1
(External
)
TCTL2
To INTL2/SCU
SWSWSW
TCT #1 TCT #2
(External)
TOUT2
(External)
30
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00

µ
PD70208H, 70216H
10. SCU (SERIAL CONTROL UNIT)
The SCU performs control of serial communication (asynchronous). Its functions are a subset of the µPD71051 excluding
synchronous communication. Also, what was the control word register in the
command register and a mode register.
10.1 FEATURES
Dedicated baud rate generator incorporated (using internal clock)
•
Asynchronous serial communication
•
Clock rate: baud rate × 16, × 64
•
Baud rate: DC – 500 kbps
•
Character length: 7/8 bits
•
Transmit stop bits: 1/2 bits
•
Break transmission
•
Automatic break detection
•
Full-duplex double-buffer system
•
Parity addition/checking
•
Error detection: parity, overrun, framing
•
Interrupt generation maskable
•
µ
PD71051 has been divided into two: a
10.2 SCU INTERNAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
SST
Status Register
SCM
Command Register
SRB
Receive Data Buffer
STB
Transmit Data Buffer
Internal Data Bus
SMD
Mode Register
From CG
Baud Rate
Generator
RESET CLOCK
Read/Write
Control
SCU Status Control Bus
(8)
(8)
Receiver
(Including Receive Buffer)
Transmitter
(Including Transmit Buffer)
Selector
RTCLK
From TCU
(TOUT1 Output)
IORD
IOWR
Note 1
Note 2
SCU Selection Signal
SRDY (External)
R
X
D (External)
T
X
D (External)
SIMK
Interrupt Mask Register
Notes 1. A0 or A1 (Set by a system I/O area register)
2. A1 or A2 (Set by a system I/O area register)
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
Interrupt
Generation Logic
SINT (To INTL1)
31

µ
PD70208H, 70216H
11. ICU (INTERRUPT CONTROL UNIT)
The ICU arbitrates among up to 8 interrupt requests (maskable interrupts) generated inside and outside the V40HL and
V50HL, and transfers one of them to the CPU. The ICU functions comprise the functions of the V40HL and V50HL minus
those functions not required by the V40HL and V50HL.
11.1 FEATURES
8 interrupt inputs
•
µ
PD71059 cascading possible
•
Edge- or level-triggered request input
•
(input from internally connected TCU is edge-triggered only)
Interrupt requests individually maskable
•
Programmable interrupt request priority order
•
Polling operation capability
•
11.2 ICU INTERNAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
Initialize &
Command Word
IORD
IOWR
Note 1
Note 2
ICU Selection Signal
Read/Write
Control
Register Group
Interrupt
In-Service
Register
(IIS)
Internal Data Bus
Notes 1. A0 or A1 (Set by a system I/O area register)
2. A1 or A2 (Set by a system I/O area register)
Control Logic
Priority
Determination Logic
Interrupt
Mask
Register
(IMK)
Slave Control
Interrupt
Request
Register
(IRQ)
INTL0
INTL1
INTL2
INTL3
INTL4
INTL5
INTL6
INTL7
SA0
SA1
To BIU
SA2
INTAK (From CPU)
INT (To CPU)
TOUT0 (From TCU)
SINT (From SCU)
TOUT1 (From TCU)
SW
SW
INTP1
INTP2
INTP3
INTP4
INTP5
INTP6
INTP7
A8
A9
A10
External Pins
32
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00

µ
PD70208H, 70216H
12. DMAU (DMA CONTROL UNIT)
The DMAU has 4 DMA channels, and provides the functions (subset) of two LSIs, the µPD71071 and µPD71037.
12.1 FEATURES
Two operating modes (µPD71071 mode, µPD71037 mode)
•
20-bit address register
•
16-bit count register
•
Four independent DMA channels
•
Byte transfer/word transfer selectable
•
Three transfer modes (settable on an individual channel basis)
•
Single transfer mode, demand transfer mode, block transfer mode
Two bus modes (common to all channels: in µPD71037 mode, bus release mode only)
•
Bus release mode
Bus hold mode
DMA requests maskable on an individual channel basis
•
Auto initialization function
•
Transfer address increment/decrement
•
Two channel priority systems (fixed priority/rotating priority)
•
TC output at end of transfer
•
Forced termination of service by END input
•
Cascading capability
•
12.2 DMAU INTERNAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
Internal Address Bus
Internal Data Bus
Internal Control Bus
BUSRQ
BAU
BUSAK
DMARQ0DMARQ3
External
pins
DMAAK0DMAAK3
END/TC
(20)
(8)
Internal Bus
Interface
Priority Control
DMAU Address Bus (20)
Address
Registers
DMAU Data Bus
Count
Registers
Terminal Count
Address Increment/
Decrement
(20)
Current Address (20 × 4)
Base Address (20 × 4)
Base Count (16 × 4)
Current Count (16 × 4)
Count Decrementer
(16)
Control Register Group
Channel
Device Control
Status
Mode Control
Mask
Request
Note 1
Note 2
(4)
(10)
(8)
(7 × 4)
(4)
(4)
Notes 1. In µPD71071 mode
µ
2. In
PD71037 mode
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
33

µ
PD70208H, 70216H
13. STANDBY FUNCTIONS
The V40HL and V50HL have two modes, the HALT mode and STOP mode, as standby functions.
(1) HALT mode
When the HALT instruction is executed, the clock to internal CPU circuitry (excluding the HALT mode release circuit)
is stopped.
(2) STOP mode
When the HALT instruction is executed, all clocks to the CPU and internal I/Os are stopped.
STOP mode should be used when a resonator is connected to the X1 and X2 pins.
Remark Switching between HALT mode and STOP mode is performed by setting a system I/O area register.
14. RESET OPERATION
When the RESET pin is driven low and this level is held for 4 clock cycles or more from the fall of the signal, the CPU
and on-chip peripheral LSIs are reset.
When the RESET pin subsequently returns to the high level, the CPU begins an instruction prefetch from address
FFFF0H.
When the V40HL and V50HL are reset, its status is fully compatible with the V40 and V50.
Extended functions added to those of the V40 and V50 are mapped onto unused V40 and V50 registers and the reserved
area.
Table 14-1 shows the main statuses of the on-chip peripheral LSIs when a reset is performed.
Table 14-1. Main Statuses of On-Chip Peripheral LSIs After Reset
WCU
REFU
SCU
DMAU
Memory, external I/O, DMA & refresh : 3-wait insertion
Upper & lower memory blocks : set to 512 KB
Refresh cycle : set to 72 clock cycles
Refresh enabling/disabling : not affected by reset
Baud rate : x 64
Character : 7 bits
Parity : None
Stop bits : 1 bit
Break detection : None
µ
PD71071 mode
Demand mode
Auto initialization disabled
Verify transfer, byte transfer
Bus release mode
DMA enabled
Caution When a reset is performed, the SCU, TCU, ICU and DMAU cannot be used.
34
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00

15. INSTRUCTION SET
Table 15-1. Operand Type Legend
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
Identifier
reg
reg’
reg8
reg8’
reg16
reg16’
dmem
mem
mem8
mem16
mem32
imm
imm3
imm4
imm8
imm16
acc
sreg
src-table
src-block
dst-block
near-proc
far-proc
near-label
short-label
far-label
memptr16
memptr32
regptr16
pop-value
fp-op
R
Description
8/16-bit general register
(destination register in an instruction using two 8/16-bit general registers)
Source register in an instruction using two 8/16-bit general registers
8-bit general register
(destination register in an instruction using two 8-bit general registers)
Source register in an instruction using two 8-bit general registers
16-bit general register
(destination register in an instruction using two 16-bit general registers)
Source register in an instruction using two 16-bit general registers
8/16-bit memory location
8/16-bit memory location
8-bit memory location
16-bit memory location
32-bit memory location
Constant in range 0 to FFFFH
Constant in range 0 to 7
Constant in range 0 to FH
Constant in range 0 to FFH
Constant in range 0 to FFFFH
Accumulator AW or AL
Segment register
Name of 256-byte conversion translation table
Name of block addressed by register IX
Name of block addressed by register IY
Procedure in current program segment
Procedure in a different program segment
Label in current program segment
Label in range –128 to +127 bytes from end of instruction
Label in a different program segment
Word containing location offset in a different program segment to which control is to be shifted and segment
base address
Doubleword containing location offset in a different program segment to which control is to be shifted and
segment base address
General register containing location offset in a different program segment to which control is to be shifted
Number of bytes to be removed from stack (0 to 64K, normally an even number)
Immediate value which identifies external floating-point operation coprocessor operation code
Register set
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
35

Table 15-2. Operation Code Legend
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
Identifier
W
reg
reg’
mem
mod
s
X, XXX, YYY, ZZZ
Description
Byte/word specification bit (0: byte, 1: word). However, when s =1, byte data of sign extension is 16-bit
operand if W = 1.
Register field (000 to 111)
Register field (000 to 111) (source register in instruction which uses two registers)
Memory field (000 to 111)
Mode field (00 to 10)
Sign-extended specification bit (0: without sign extension, 1: with sign extension)
Data used to determine external floating-point coprocessor operation code
36
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00

AW
AH
AL
BW
CW
CL
DW
BP
SP
PC
PSW
IX
IY
PS
SS
DS0
DS1
AC
CY
P
S
Z
DIR
IE
V
BRK
MD
...
(
)
disp
ext-disp8
temp
TA
TB
TC
tmpcy
seg
offset
←
+
–
×
÷
%
∨
∨
∨
××H
××××H
Table 15-3. Operand Description Legend
Accumulator (16-bit)
Accumulator (high-order byte)
Accumulator (low-order byte)
Register BW (16-bit)
Register CW (16-bit)
Register CL (low-order byte)
Register DW (16-bit)
Base pointer (16-bit)
Stack pointer (16-bit)
Program counter (16-bit)
Program status word (16-bit)
Index register (source) (16-bit)
Index register (destination) (16-bit)
Program segment register (16-bit)
Stack segment register (16-bit)
Data segment 0 register (16-bit)
Data segment 1 register (16-bit)
Auxiliary carry flag
Carry flag
Parity flag
Sign flag
Zero flag
Direction flag
Interrupt enable flag
Overflow flag
Break flag
Mode flag
Contents of memory indicated by contents of ( )
Displacement (8/16-bit)
16 bits with 8-bit displacement sign-extended
Temporary register (8/16/32-bit)
Temporary register A (16-bit)
Temporary register B (16-bit)
Temporary register C (16-bit)
Temporary carry flag (1-bit)
Immediate segment data (16-bit)
Immediate offset data (16-bit)
Transfer direction
Addition
Subtraction
Multiplication
Division
Modulo
Logical product
Logical sum
Exclusive logical sum
Two-digit hexadecimal number
Four-digit hexadecimal number
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
DescriptionIdentifier
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
37

Table 15-4. Flag Operation Legend
Identifier Description
(Blank) No change
0 Cleared to 0
1 Set to 1
× Set or cleared depending upon result
U Undefined
R Previously saved value is restored
Table 15-5. Memory Addressing
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
mem
000
001
010
011
100
101
110
111
mod
BW + IX
BW + IY
BP + IX
BP + IY
IX
IY
DIRECT ADDRESS
BW
00
BW + IX + disp 8
BW + IY + disp 8
BP + IX + disp 8
BP + IY + disp 8
IX + disp 8
IY + disp 8
BP + disp 8
BW + disp 8
Table 15-6. 8/16-Bit General Register Selection
reg, reg’ W=0 W=1
000 AL AW
001 CL CW
010 DL DW
011 BL BW
100 AH SP
101 CH BP
110 DH IX
111 BH IY
01 10
BW + IX + disp 16
BW + IY + disp 16
BP + IX + disp 16
BP + IY + disp 16
IX + disp 16
IY + disp 16
BP + disp 16
BW + disp 16
Table 15-7. Segment Register Selection
sreg
00 DS1
01 PS
10 SS
11 DS0
38
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00

µ
PD70208H, 70216H
The instruction set is shown in tabular form on the following pages.
Clock cycle shown in table is the time required for execution of instruction by the execution unit and is based on the
following conditions.
• Prefetch time and wait time for using bus, etc. are not included.
• 0 wait is assumed for memory access. That is, the clock number of one bus cycle is four clock cycle.
• 0 wait is assumed for I/O access.
• Primitive block transfer instruction and primitive input/output instruction is included repeat prefixes.
The number of clock cycle of instruction with byte processing and word processing (with W bit) is shown as the followings.
(1) V40HL
On the left of "/" : The value corresponding to byte processing (W= 0) or word processing (W = 1) of even
address
On the right of "/": The value corresponding to word processing (W =1) of odd address
For the clock of block transfer related instruction of V40HL, see Table 15-8.
Table 15-8. Number of Clock Cycles in Block Transfer Related Instruction (V40HL)
Instruction
Byte Processing (W = 0) Word Processing (W = 1)
MOVBK 9 + 8 × rep 9 + 16 × rep
(9) (17)
CMPBK 7 + 14 × rep 7 + 22 × rep
(13) (21)
CMPM 7 + 10 × rep 7 + 14 × rep
(7) (11)
LDM 7 + 9 × rep 7 + 13 × rep
(7) (11)
STM 5 + 4 × rep 5 + 8 × rep
(5) (9)
INM 9 + 8 × rep 9 + 16 × rep
(10) (18)
OUTM 9 + 8 × rep 9 + 16 × rep
(10) (18)
Number of Clock Cycles
Remark The figures in parentheses apply to one-time processing only.
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
39

µ
PD70208H, 70216H
(2) V50HL
On the left of "/" : The value corresponding to byte processing (W= 0) or word processing (W = 1) of even
address
On the right of "/" : The value corresponding to word processing (W =1) of odd address
For the clock of block transfer related instruction of V50HL, see Table 15-9.
Table 15-9. Number of Clock Cycles in Block Transfer Related Instruction V50HL (1/2)
Number of Clock Cycles
Instruction Byte Processing Word Processing (W = 1)
(W = 0) Odd/Odd Address Odd/Even Address Even/Even Address
MOVBK 9 + 8 × rep 9 + 16 × rep 9 + 12 × rep 9 + 8 × rep
(9) (17) (13) (9)
CMPBK 7 + 14 × rep 7 + 22 × rep 7 + 18 × rep 7 + 14 × rep
(13) (21) (17) (13)
INM 9 + 8 × rep 9 + 16 × rep 9 + 12 × rep 9 + 8 × rep
(10) (18) (14) (10)
OUTM 9 + 8 × rep 9 + 16 × rep 9 + 12 × rep 9 + 8 × rep
(10) (18) (14) (10)
Remark The figures in parentheses apply to one-time processing only.
Table 15-9. Number of Clock Cycles in Block Transfer Related Instruction (V50HL) (2/2)
Number of Clock Cycles
Instruction Byte Processing Word Processing (W = 1)
(W = 0) Odd Address Even Address
CMPM 7 + 10 × rep 7 + 14 × rep 7 + 10 × rep
(7) (11) (7)
LDM 7 + 9 × rep 7 + 13 × rep 7 + 9 × rep
(7) (11) (7)
STM 5 + 4 × rep 5 + 8 × rep 5 + 4 × rep
(5) (9) (5)
Remark The figures in parentheses apply to one-time processing only.
40
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00

Instruction
Group
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
Mnemonic Operand(s) Operation
MOV
Data transfer instructions
LDEA
TRANS
XCH
reg, reg’
mem, reg
reg, mem
mem, imm
reg, imm
acc, dmem
dmem, acc
sreg, reg16
sreg, mem16
reg16, sreg
mem16, sreg
DS0, reg16,
mem32
DS1, reg16,
mem32
AH, PSW
PSW, AH
reg16, mem16
src-table
reg, reg’
mem, reg
reg, mem
AW, reg16
reg16, AW
Operation Code Flags
76543210 76543210
1000101W
1000100W
1000101W
1100011W
1011W reg
1010000W
1010001W
10001110
10001110
10001100
10001100
11000101
11000100
10011111
10011110
10001101
11010111
1000011W
1000011W
10010 reg
11 reg reg’
mod reg mem
mod reg mem
mod
000mem
110 sreg reg
mod 0 sreg mem
110 sreg reg
mod
0 sreg mem
mod reg mem
mod reg mem
mod reg mem
1 1 reg reg’
mod reg mem
Bytes
2
2-4
2-4
3-6
2-3
3
3
2
2-4
2
2-4
2-4
2-4
1
1
2-4
1
2
2-4
1
Clock Cycles
V40HL V50HL
2
2
7/11
10/14
9/13
10/14
9/13
13/21
14
12
25
25
7/11
10/14
9/13
4
4
10/14
9/13
2
2
10/14
2
2
8/12
17/25
17/25
2
2
3
3
4
4
9
9
3
3
13/21
3
3
reg ← reg’
(mem) ← reg
reg ← (mem)
(mem) ← imm
reg ← imm
If W=0: AL ← (dmem)
If W=1: AH ← (dmem + 1), AL ← (dmem)
If W=0: (dmem) ←AL
If W=1: (dmem + 1) ← AH, (dmem) ←AL
sreg ← reg16 sreg:SS, DS0, DS1
sreg ← (mem16) sreg:SS, DS0, DS1
reg16 ← sreg
(mem16) ← sreg
reg16← (mem32)
DS0 ← (mem32 + 2)
reg16 ← (mem32)
DS1 ← (mem32 + 2)
AH ← S, Z, ×, AC, ×, P, ×, CY
S, Z, ×, AC, ×, P, ×, CY← AH
reg16 ←mem16
AL← (BW + AL)
reg ↔ reg’
(mem) ↔ reg
AW ↔ reg16
AC CY V P S Z
×× ×××
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
41

42
Instruction
Group
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
Mnemonic Operand(s)
REPC
REPNC
REP
REPE
Repeat prefixes
REPZ
REPNE
REPNZ
MOVBK
CMPBK
CMPM
LDM
Primitive block transfer instructions
STM
dst-block,
src-block
src-block,
dst-block
dst-block
src-block
dst-block
Operation Code Flags
76543210
01100101
01100100
11110011
11110010
1010010W
1010011W
1010111W
1010110W
1010101W
76543210
Bytes
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Clock Cycles
V40HL V50HL
2
2
2
2
See
Table
15-8
See
Table
15-8
See
Table
15-8
See
Table
15-8
See
Table
15-8
2
2
2
2
See
Table
15-9
See
Table
15-9
See
Table
15-9
See
Table
15-9
See
Table
15-9
Operation
While CW ≠ 0, the following byte primitive block transfer
instruction is executed and CW is decremented (–1).
If there is a pending interrupt, it is serviced.
If CY ≠ 1 the loop is exited.
Same as above
If CY ≠ 0 the loop is exited.
While CW ≠ 0, the following byte primitive block transfer
instruction is executed and CW is decremented (–1).
If there is a pending interrupt, it is serviced.
If the primitive block transfer instruction is CMPBK or
CMPM and Z ≠ 1 the loop is exited.
Same as above
If Z ≠ 0 the loop is exited.
If W = 0: (IY) ← (IX)
DIR = 0 : IX ← IX + 1, IY ← IY + 1
DIR = 1 : IX ← IX – 1, IY ← IY – 1
If W = 1: (IY + 1, IY) ← (IX + 1, IX)
DIR = 0 : IX ← IX + 2, IY ← IY + 2
DIR = 1 : IX ← IX – 2, IY ← IY – 2
If W = 0: (IX) – (IY)
DIR = 0 : IX ← IX + 1, IY ← IY + 1
DIR = 1 : IX ← IX – 1, IY ← IY – 1
If W = 1: (IX + 1, IX) – (IY + 1, IY)
DIR = 0 : IX ← IX + 2, IY ← IY + 2
DIR = 1 : IX ← IX – 2, IY ← IY – 2
If W = 0: AL – (IY)
DIR = 0 : IY ← IY + 1; DIR = 1 : IY ← IY – 1
If W = 1: AW – (IY + 1, IY)
DIR = 0 : IY ← IY + 2; DIR = 1 : IY ← IY – 2
If W = 0: AL ← (IX)
DIR = 0 : IX ← IX + 1; DIR = 1 : IX ← IX – 1
If W = 1: AW ← (IX + 1, IX)
DIR = 0 : IX + 2; DIR = 1 : IX ← IX – 2
If W = 0: (IY) ← AL
DIR = 0 : IY ← IY + 1; DIR = 1 : IY ← IY – 1
If W = 1: (IY + 1, IY) ← AW
DIR = 0 : IY ← IY + 2; DIR = 1 : IY ← IY – 2
AC CY V P S Z
ЧЧЧЧЧЧ
ЧЧЧЧЧЧ
µ
PD70208H, 70216H

Instruction
Group
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
Mnemonic Operand(s)
INS
EXT
Bit field manipulation
instructions
IN
OUT
Input/output instructions
INM
OUTM
Primitive input/output
instructions
reg8, reg8’
reg8, imm4
reg8, reg8’
reg8, imm4
acc, imm8
acc, DW
imm8, acc
DW, acc
dst-block,
DW
DW,
src-block
Operation Code Flags
76543210
00001111
1 1 reg’ reg
00001111
11000 reg
00001111
1 1 reg’ reg
00001111
11000 reg
1110010W
1110110W
1110011W
1110111W
0110110W
0110111W
76543210
00110001
00111001
00110011
00111011
Bytes
3
4
3
4
2
1
2
1
1
1
Clock Cycles
V40HL V50HL
35-133
31-117/
35-133
35-133
31-117/
35-133
34-59
26-55/
34-59
34-59
26-55/
34-59
9/13
8/12
8/12
8/12
See
Table
15-9
See
Table
15-9
Note
Note
Note
Note
9/13
8/12
8/12
8/12
See
Table
15-8
See
Table
15-8
Operation
16-bit field ← AW
16-bit field ← AW
AW ← 16-bit field
AW ← 16-bit field
If W = 0: AL ← (imm8)
If W = 1: AH ← (imm8 + 1), AL ← (imm8)
If W = 0: AL ← (DW)
If W = 1: AH ← (DW + 1), AL ← (DW)
If W = 0: (imm8) ← AL
If W = 1: (imm8 + 1) ← AH, (imm8) ← AL
If W = 0: (DW) ← AL
If W = 1: (DW + 1) ← AH, (DW) ← AL
If W = 0: (IY) ← (DW)
DIR = 0 : IY ← IY + 1 ; DIR = 1 : IY ← IY – 1
If W = 1: (IY + 1, IY) ← (DW + 1, DW)
DIR = 0 : IY ← IY + 2 ; DIR = 1 : IY ← IY – 2
If W = 0: (DW) ← (IX )
DIR = 0 : IX ← IX + 1 ; DIR = 1 : IX ← IX – 1
If W = 1: (DW + 1, DW) ← (IX + 1, IX)
DIR = 0 : IX ← IX + 2 ; DIR = 1 : IX ← IX – 2
AC CY V P S Z
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
43
Note In case of IN/OUT instruction to internal DMAU, the number of word processing clock cycles applied is always that to the right of "/".

44
Instruction
Group
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
Mnemonic Operand(s) Operation
ADD
ADDC
SUB
Addition/subtraction instructions
SUBC
reg, reg’
mem, reg
reg, mem
reg, imm
mem, imm
acc, imm
reg, reg’
mem, reg
reg, mem
reg, imm
mem, imm
acc, imm
reg, reg’
mem, reg
reg, mem
reg, imm
mem, imm
acc, imm
reg, reg’
mem, reg
reg, mem
reg, imm
mem, imm
acc, imm
Operation Code Flags
76543210 76543210
0000001W
0000000W
0000001W
100000sW
100000sW
0000010W
0001001W
0001000W
0001001W
100000s W
100000sW
0001010W
0010101W
0010100W
0010101W
100000sW
100000sW
0010110W
0001101W
0001100W
0001101W
100000sW
100000sW
0001110W
1 1 reg reg’
mod reg mem
mod reg mem
11000 reg
mod
000 mem
1 1 reg reg’
mod reg mem
mod reg mem
11010 reg
mod
010
mem
1 1 reg reg’
mod reg mem
mod reg mem
11101 reg
mod
101
mem
1 1 reg reg’
mod reg mem
mod reg mem
11011 reg
mod
011 mem
Bytes
2
2-4
2-4
3-4
3-6
2-3
2
2-4
2-4
3-4
3-6
2-3
2
2-4
2-4
3-4
3-6
2-3
2
2-4
2-4
3-4
3-6
2-3
Clock Cycles
V40HL V50HL
2
13/21
10/14
4
15/23
4
2
13/21
10/14
4
15/23
4
2
13/21
10/14
4
15/23
4
2
13/21
10/14
4
15/23
4
2
13/21
10/14
4
15/23
4
2
13/21
10/14
4
15/23
4
2
13/21
10/14
4
15/23
4
2
13/21
10/14
4
15/23
4
reg ← reg + reg’
(mem) ← (mem) + reg
reg ← reg + (mem)
reg ← reg + imm
(mem) ← (mem) + imm
If W = 0: AL ← AL + imm
If W = 1: AW ← AW + imm
reg ← reg + reg’+ CY
(mem) ← (mem) + reg + CY
reg ← reg + (mem) + CY
reg ← reg + imm + CY
(mem) ← (mem) + imm + CY
If W = 0: AL ← AL + imm + CY
If W = 1: AW ← AW + imm + CY
reg ← reg – reg’
(mem) ← (mem) – reg
reg ← reg – (mem)
reg ← reg – imm
(mem) ← (mem) – imm
If W = 0: AL ← AL – imm
If W = 1: AW ← AW – imm
reg ← reg – reg’– CY
(mem) ← (mem) – reg – CY
reg ← reg – (mem) – CY
reg ← reg – imm – CY
(mem) ← (mem) – imm – CY
If W = 0: AL ← AL – imm – CY
If W = 1: AW ← AW imm– CY
AC CY V P S Z
ЧЧЧЧЧЧ
ЧЧЧЧЧЧ
ЧЧЧЧЧЧ
ЧЧЧЧЧЧ
ЧЧЧЧЧЧ
ЧЧЧЧЧЧ
ЧЧЧЧЧЧ
ЧЧЧЧЧЧ
ЧЧЧЧЧЧ
ЧЧЧЧЧЧ
ЧЧЧЧЧЧ
ЧЧЧЧЧЧ
ЧЧЧЧЧЧ
ЧЧЧЧЧЧ
ЧЧЧЧЧЧ
ЧЧЧЧЧЧ
ЧЧЧЧЧЧ
ЧЧЧЧЧЧ
ЧЧЧЧЧЧ
ЧЧЧЧЧЧ
ЧЧЧЧЧЧ
ЧЧЧЧЧЧ
ЧЧЧЧЧЧ
ЧЧЧЧЧЧ
µ
PD70208H, 70216H

Instruction
Group
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
Mnemonic Operand(s)
ADD4S
SUB4S
CMP4S
ROL4
BCD operation instructions
ROR4
INC
DEC
Increment/decre-
ment instructions
reg8
mem8
reg8
mem8
reg8
mem
reg16
reg8
mem
reg16
Operation Code Flags
76543210
00001111
00001111
00001111
00001111
11000 reg
00001111
mod
000 mem
00001111
11000 reg
00001111
mod
000 mem
11111110
1111111W
01000 reg
11111110
1111111W
01001 reg
76543210
00100000
00100010
00100110
00101000
00101000
00101010
00101010
11000 reg
mod
000 mem
11001 reg
mod
001 mem
Bytes
2
2
2
3
3-5
3
3-5
2
2-4
1
2
2-4
1
Clock Cycles
V40HL
19 × n
19 × n
19 × n
+ 7
+ 7
+ 7
13
25
17
29
2
13/21
2
2
13/21
2
V50HL
19 × n
+ 7
19 × n
+ 7
19 × n
+ 7
13
25
17
29
2
13/21
2
2
13/21
2
dst BCD string ← dst BCD string + src BCD string*
dst BCD string ← dst BCD string – src BCD string*
dst BCD string – src BCD string*
ALL
ALL Lower
ALL Lower
ALL
reg8 ← reg8 + 1
(mem) ← (mem) + 1
reg16 ← reg16 + 1
reg8 ← reg8 – 1
(mem) ← (mem) – 1
reg16 ← reg16 – 1
reg
Upper
mem
Upper
Upper
Upper
Operation
Lower
reg
mem
Lower
n: 1/2 the number of BCD digits
* The number of BCD digits is given by the CL register: a value between 1 and 254 can be set.
AC CY V P S Z
U × UUU×
U×UUU×
U×UUU×
×××××
×××××
×××××
×××××
×××××
×××××
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
45

46
Instruction
Group
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
Mnemonic Operand(s) Operation
MULU
MUL
Multiplication instructions
reg8
mem8
reg16
mem16
reg8
mem8
reg16
mem16
reg16,
(reg16’,)
imm8
reg16,
mem16,
imm8
reg16,
(reg16’,)
imm16
reg16,
mem16,
imm16
Operation Code Flags
76543210 76543210
11110110
11110110
11110111
11110111
11110110
11110110
11110111
11110111
01101011
Note
01101011
01101001
Note
01101001
1110 0 reg
mod
100 mem
1110 0 reg
mod
100 mem
1110 1 reg
mod
10 1 mem
1110 1 reg
mod
10 1 mem
1 1 reg reg’
mod reg mem
1 1 reg reg’
mod reg mem
Bytes
2
2-4
2
2-4
2
2-4
2
2-4
3
3-5
4
4-6
Clock Cycles
V40HL V50HL
21-22
21-22
26-27
26-27
29-30
29-30
38-39
34-35/
38-39
33-39
33-39
38-44
38-44
41-47
41-47
50-56
46-52/
50-56
28-34
28-34
37-43
33-39/
37-43
36-42
36-42
45-51
41-47/
45-51
AW ← AL × reg8
AH = 0: CY ← 0, V ← 0
AH ≠ 0: CY ← 1, V ← 1
AW ← AL × (mem8)
AH = 0: CY ← 0, V ← 0
AH ≠ 0: CY ← 1, V ← 1
DW, AW ← AW × reg16
DW = 0: CY ← 0, V ← 0
DW ≠ 0: CY ← 1, V ← 1
DW, AW ← AW × (mem16)
DW = 0: CY ← 0, V ← 0
DW ≠ 0: CY ←1, V ← 1
AW ←AL × reg8
AH = AL sign extension: CY ← 0, V ← 0
AH ≠ AL sign extension: CY ← 1, V ← 1
AW ← AL × (mem8)
AH = AL sign extension: CY ← 0, V ← 0
AH ≠ AL sign extension: CY ← 1, V ← 1
DW, AW ← AW × reg16
DW = AW sign extension: CY ← 0, V ← 0
DW ≠ AW sign extension: CY ← 1, V ← 1
DW, AW ← AW × (mem16)
DW = AW sign extension: CY ← 0, V ← 0
DW ≠ AW sign extension: CY ← 1, V ← 1
reg16 ← reg16’ × imm8
Product ≤ 16 bits : CY ← 0, V ← 0
Product > 16 bits : CY ← 1, V ← 1
reg16 ← (mem16) × imm8
Product ≤ 16 bits : CY ← 0, V ← 0
Product > 16 bits : CY ← 1, V ← 1
reg16 ← reg16’ × imm16
Product ≤ 16 bits : CY ← 0, V ← 0
Product > 16 bits : CY ← 1, V ← 1
reg16 ← (mem16) × imm16
Product ≤ 16 bits : CY ← 0, V ← 0
Product > 16 bits : CY ← 1, V ← 1
AC CY V P S Z
U ××UUU
U××UUU
U××UUU
U××UUU
U××UUU
U××UUU
U××UUU
U××UUU
U××UUU
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
U××UUU
U××UUU
U××UUU
Note The 2nd operand can be omitted, in which case the same register as the 1st operand is taken as being specified.

Instruction
Group
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
Mnemonic Operand(s)
DIVU
Unsigned division instructions
reg8
mem8
reg16
mem16
Operation Code Flags
76543210 76543210
11110110
11110110
11110111
11110111
11110 reg
mod
110 mem
11110 reg
mod
110 mem
Bytes
2
2-4
2
2-4
Clock Cycles
V40HL V50HL
19
24
25
34
19
24
25
30/34
Operation
temp ← AW
If temp ÷ reg8 ≤ FFH
AH ← temp%reg8, AL ←temp ÷ reg8
If temp ÷ reg8 > FFH
TA ← (001H, 000H), TC ← (003H, 002H)
SP ← SP – 2, (SP + 1, SP) ← PSW, IE ← 0, BRK ← 0
SP ← SP – 2, (SP + 1, SP) ← PS, PS ← TC
SP ← SP – 2, (SP + 1, SP) ← PC, PC ← TA
temp ← AW
If temp ÷ (mem8) ≤ FFH
AH ← temp%(mem8), AL ←temp ÷ (mem8)
If temp ÷ (mem8) > FFH
TA ← (001H, 000H), TC ← (003H, 002H)
SP ← SP – 2, (SP + 1, SP) ← PSW, IE ← 0, BRK ← 0
SP ← SP – 2, (SP + 1, SP) ← PS, PS ← TC
SP ← SP – 2, (SP + 1, SP) ← PC, PC ← TA
temp ← DW, AW
If temp ÷ reg16 ≤ FFFFH
DW ← temp%reg16, AW ←temp ÷ reg16
If temp ÷ reg16 > FFFFH
TA ← (001H, 000H), TC ← (003H, 002H)
SP ← SP – 2, (SP + 1, SP) ← PSW, IE ← 0, BRK ← 0
SP ← SP – 2, (SP + 1, SP) ← PS, PS ← TC
SP ← SP – 2, (SP + 1, SP) ← PC, PC ← TA
temp ← DW, AW
If temp ÷ (mem16) ≤ FFFFH
DW ← temp%(mem16), AW ←temp ÷ (mem16)
If temp ÷ (mem16) > FFFFH
TA ← (001H, 000H), TC ← (003H, 002H)
SP ← SP – 2, (SP + 1, SP) ← PSW, IE ← 0, BRK ← 0
SP ← SP – 2, (SP + 1, SP) ← PS, PS ← TC
SP ← SP – 2, (SP + 1, SP) ← PC, PC ← TA
AC CY V P S Z
UUUUUU
UUUUUU
UUUUUU
UUUUUU
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
47

48
Instruction
Group
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
Mnemonic Operand(s)
DIV
Signed division instructions
reg8
mem8
reg16
mem16
Operation Code Flags
76543210 76543210
11110110
11110110
11110111
11110111
11111 reg
mod
111 mem
11111 reg
mod
111 mem
Bytes
2
2-4
2
2-4
Clock Cycles
V40HL V50HL
29-34
34-39
38-43
47-52
29-34
34-39
38-43
43-48/
47-52
Operation
temp ← AW
If temp ÷ reg8 > 0 and temp ÷ reg8 ≤ 7FH
or temp ÷ reg8 < 0 and temp ÷ reg8 > 0 – 7FH –1
AH ← temp%reg8, AL ← temp ÷ reg8
If temp ÷ reg8 > 0 and temp ÷ reg8 > 7FH
or temp ÷ reg8 < 0 and temp ÷ reg8 ≤ 0 – 7FH –1
TA ← (001H, 000H), TC ← (003H, 002H)
SP ← SP – 2, (SP + 1, SP) ← PSW, IE ← 0, BRK ← 0
SP ← SP – 2, (SP + 1, SP) ← PS, PS ← TC
SP ← SP – 2, (SP + 1, SP) ← PC, PC ← TA
temp ← AW
If temp ÷ (mem8) > 0 and temp ÷ (mem8) ≤ 7FH
or temp ÷ (mem8) < 0 and temp ÷ (mem8) > 0 – 7FH –1
AH ← temp%(mem8), AL ← temp ÷(mem8)
If temp ÷ (mem8) > 0 and temp ÷ (mem8) > 7FH
or temp ÷ (mem8) < 0 and temp ÷ (mem8) ≤ 0 – 7FH –1
TA ← (001H, 000H), TC ← (003H, 002H)
SP ← SP – 2, (SP + 1, SP) ← PSW, IE ← 0, BRK ← 0
SP ← SP – 2, (SP + 1, SP) ← PS, PS ← TC
SP ← SP – 2, (SP + 1, SP) ← PC, PC ← TA
temp ← DW, AW
If temp ÷ reg16 > 0 and temp ÷ reg16 ≤ 7FFFH
or temp ÷ reg16 < 0 and temp ÷ reg16 > 0 – 7FFFH –1
DW ← temp%reg16, AW ← temp ÷ reg16
If temp ÷ reg16 > 0 and temp ÷ reg16 > 7FFFH
or temp ÷ reg16 < 0 and temp ÷ reg16 ≤ 0 – 7FFFH –1
TA ← (001H, 000H), TC ← (003H, 002H)
SP ← SP – 2, (SP + 1, SP) ← PSW, IE ← 0, BRK ← 0
SP ← SP – 2, (SP + 1, SP) ← PS, PS ← TC
SP ← SP – 2, (SP + 1, SP) ← PC, PC ← TA
temp ← DW, AW
If temp ÷ (mem16) > 0 and temp ÷ (mem16) ≤ 7FFFH
or temp ÷ (mem16) < 0 and temp ÷ (mem16) > 0 – 7FFFH
–1
DW ← temp%(mem16), AW ← temp ÷ (mem16)
If temp ÷ (mem16) > 0 and temp ÷ (mem16) > 7FFFH
or temp ÷ (mem16) < 0 and temp ÷ (mem16) ≤ 0 – 7FFFH
–1
TA ← (001H, 000H), TC ← (003H, 002H)
SP ← SP – 2, (SP + 1, SP) ← PSW, IE ← 0, BRK ← 0
AC CY V P S Z
UUUUUU
UUUUUU
UUUUUU
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
UUUUUU

Instruction
Group
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
Mnemonic Operand(s)
ADJBA
ADJ4A
ADJBS
ADJ4S
BCD adjustment instructions
CVTBD
CVTDB
CVTBW
CVTWL
Data conversion
instructions
CMP
Comparison instructions
NOT
NEG
Complement
operation
instructions
reg, reg’
mem, reg
reg, mem
reg, imm
mem, imm
acc, imm
reg
mem
reg
mem
Operation Code Flags
76543210 76543210
00110111
00100111
00111111
00101111
11010100
11010101
10011000
10011001
0011101W
0011100W
0011101W
100000sW
100000sW
0011110W
1111011W
1111011W
1111011W
1111011W
00001010
00001010
1 1 reg reg’
mod reg mem
mod reg mem
11111 reg
mod
111 mem
1 1 01 0 reg
mod
01 0 mem
1 1 01 1 reg
mod
0 1 mem
Bytes
1
1
1
1
2
2
1
1
2
2-4
2-4
3-4
3-6
2-3
2
2-4
2
2-4
Clock Cycles
V40HL V50HL
7
7
3
3
7
7
3
3
15
4-5
10/14
10/14
12/16
13/21
13/21
15
7
7
2
2
4-5
2
2
10/14
10/14
4
4
12/16
4
4
2
2
13/21
2
2
13/21
Operation
∨
If AL 0FH > 9 or AC = 1: AL ← AL + 6
AH ← AH + 1, AC ← 1, CY ← AC, AL ← AL 0FH
∨
If AL 0FH > 9 or AC = 1
AL ← AL + 6, CY ← CY ∨ AC , AC← 1
If AL > 9FH or CY = 1
AL ← AL + 60H, CY ← 1
∨
If AL 0FH > 9 or AC = 1
AL ← AL – 6, AH ← AH – 1 , AC← 1
CY ← AC, AL ← AL 0FH
∨
If AL 0FH > 9 or AC = 1
AL ← AL –6, CY ← CY ∨ AC , AC← 1
If AL > 9FH or CY = 1
AL ← AL – 60H, CY ← 1
AH ← AL ÷ 0AH, AL ← AL%0AH
AL ← AH × 0AH + AL, AH ← 0
If AL < 80H: AH ← 0, otherwise: AH ← FFH
If AW < 8000H: DW ← 0, otherwise: DW ← FFFFH
reg – reg’
(mem) – reg
reg – (mem)
reg – imm
(mem) – imm
If W = 0: AL – imm
If W = 1: AW – imm
reg ← reg
(mem) ← (mem)
reg ← reg + 1
(mem) ← (mem) + 1
∨
∨
AC CY V P S Z
××UUUU
××U×××
××UUUU
××U×××
UUU×××
UUU×××
ЧЧЧЧЧЧ
ЧЧЧЧЧЧ
ЧЧЧЧЧЧ
ЧЧЧЧЧЧ
ЧЧЧЧЧЧ
ЧЧЧЧЧЧ
ЧЧЧЧЧЧ
ЧЧЧЧЧЧ
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
49

50
Instruction
Group
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
Mnemonic Operand(s) Operation
TEST
AND
OR
Logical operation instructions
XOR
reg, reg’
mem, reg
reg, mem
reg, imm
mem, imm
acc, imm
reg, reg’
mem, reg
reg, mem
reg, imm
mem, imm
acc, imm
reg, reg’
mem, reg
reg, mem
reg, imm
mem, imm
acc, imm
reg, reg’
mem, reg
reg, mem
reg, imm
mem, imm
acc, imm
Operation Code Flags
76543210 76543210
1000010W
1000010W
1111011W
1111011W
1010100W
0010001W
0010000W
0010001W
1000000W
1000000W
0010010W
0000101W
0000100W
0000101W
1000000W
1000000W
0000110W
0011001W
0011000W
0011001W
1000000W
1000000W
0011010W
1 1 reg’ reg
mod reg mem
11000 reg
mod
000 mem
1 1 reg reg’
mod reg mem
mod reg mem
11100 reg
mod
100 mem
1 1 reg reg’
mod reg mem
mod reg mem
11001 reg
mod
001 mem
1 1 reg reg’
mod reg mem
mod reg mem
11110 reg
mod
110 mem
Bytes
2
2-4
3-4
3-6
2-3
2
2-4
2-4
3-4
3-6
2-3
2
2-4
2-4
3-4
3-6
2-3
2
2-4
2-4
3-4
3-6
2-3
Clock Cycles
V40HL V50HL
2
2
9/13
10/14
13/21
10/14
15/23
13/21
10/14
15/23
13/21
10/14
15/23
9/13
4
4
10/14
4
4
2
2
13/21
10/14
4
4
15/23
4
4
2
2
13/21
10/14
4
4
15/23
4
4
2
2
13/21
10/14
4
4
15/23
4
4
∨
reg reg’
(mem) reg
reg imm
(mem) imm
If W = 0: AL imm8
If W = 1: AW imm16
reg ← reg reg’
(mem) ← (mem) reg
reg ← reg (mem)
reg ← reg imm
(mem) ← (mem) imm
If W = 0: AL ← AL imm8
If W = 1: AW ← AW imm16
reg ← reg ∨ reg’
(mem) ← (mem) ∨ reg
reg ← reg ∨ (mem)
reg ← reg ∨ imm
(mem) ← (mem) ∨ imm
If W = 0: AL ← AL ∨ imm8
If W = 1: AW ← AW ∨ imm16
reg ← reg ∨ reg’
(mem) ← (mem) ∨ reg
reg ← reg ∨ (mem)
reg ← reg ∨ imm
(mem) ← (mem) ∨ imm
If W = 0: AL ← AL ∨ imm8
If W = 1: AW ← AW ∨ imm16
∨
∨
∨
∨
∨
∨
∨
∨
∨
∨
∨
∨
AC CY V P S Z
U0 0 ×××
U00×××
U00×××
U00×××
U00×××
U00×××
U00×××
U00×××
U00×××
U00×××
U00×××
U00×××
U00×××
U00×××
U00×××
U00×××
U00×××
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
U00×××
U00×××
U00×××
U00×××
U00×××
U00×××

Instruction
Group
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
Mnemonic Operand(s) Operation
TEST1
Bit manipulation instructions
NOT1
reg8, CL
mem8, CL
reg16, CL
mem16, CL
reg8, imm3
mem8, imm3
reg16, imm4
mem16, imm4
reg8, CL
mem8, CL
reg16, CL
mem16, CL
reg8, imm3
mem8, imm3
reg16, imm4
mem16, imm4
Operation Code Flags
76543210 76543210
00010000
0000
0001
0001
1000
1000
1001
1001
0110
0110
0111
0111
1110
1110
1111
1111
11000 reg
mod
000 mem
11000 mem
mod
000 mem
11000 reg
mod
000 mem
11000 reg
mod
000 mem
11000 reg
mod
000 mem
11000 reg
mod
000 mem
11000 reg
mod
000 mem
11000 reg
mod
000 mem
Bytes
3
3-5
3
3-5
4
4-6
4
4-6
3
3-5
3
3-5
4
4-6
4
4-6
Clock Cycles
V40HL V50HL
3
3
7
7
3
3
11
7/11
4
4
8
8
4
4
12
8/12
4
4
10
10
4
4
18
10/18
5
5
11
11
5
5
19
11/19
reg8 bit NO.CL = 0 : Z ← 1
reg8 bit NO.CL = 1 : Z ← 0
(mem8) bit NO.CL = 0 : Z← 1
(mem8) bit NO.CL = 1 : Z← 0
reg16 bit NO.CL = 0 : Z ← 1
reg16 bit NO.CL = 1 : Z ← 0
(mem16) bit NO.CL = 0 : Z← 1
(mem16) bit NO.CL = 1 : Z← 0
reg8 bit NO.imm3 = 0 : Z ← 1
reg8 bit NO.imm3 = 1 : Z ← 0
(mem8) bit NO.imm3 = 0 : Z← 1
(mem8) bit NO.imm3 = 1 : Z← 0
reg16 bit NO.imm4 = 0 : Z ← 1
reg16 bit NO.imm4 = 1 : Z ← 0
(mem16) bit NO.imm4 = 0 : Z← 1
(mem16) bit NO.imm4 = 1 : Z← 0
reg8 bit NO.CL← reg8 bit NO.CL
(mem8) bit NO.CL← (mem8) bit NO.CL
reg16 bit NO.CL← reg16 bit NO.CL
(mem16) bit NO.CL← (mem16) bit NO.CL
reg8 bit NO.imm3← reg8 bit NO.imm3
(mem8) bit NO.imm3← (mem8) bit NO.imm3
reg16 bit NO.imm4← reg16 bit NO.imm4
(mem16) bit NO.imm4← (mem16) bit NO.imm4
AC CY V P S Z
U00UU×
U00UU×
U00UU×
U00UU×
U00UU×
U00UU×
U00UU×
U00UU×
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
51
2nd byte*
NOT1 CY 11110101 1 2
3rd byte*
* 1st byte = 0FH
2
CY← CY
×

52
Instruction
Group
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
Mnemonic Operand(s) Operation
CLR1
SET1
Bit manipulation instructions
reg8, CL
mem8, CL
reg16, CL
mem16, CL
reg8, imm3
mem8, imm3
reg16, imm4
mem16, imm4
reg8, CL
mem8, CL
reg16, CL
mem16, CL
reg8, imm3
mem8, imm3
reg16, imm4
mem16, imm4
Operation Code Flags
76543210 76543210
00010010
0010
0011
0011
1010
1010
1011
1011
0100
0100
0101
0101
1100
1100
1101
1101
11000 reg
mod
000 mem
11000 mem
mod
000 mem
11000 reg
mod
000 mem
11000 reg
mod
000 mem
11000 reg
mod
000 mem
11000 reg
mod
000 mem
11000 reg
mod
000 mem
11000 reg
mod
000 mem
Bytes
3
3-5
3
3-5
4
4-6
4
4-6
3
3-5
3
3-5
4
4-6
4
4-6
Clock Cycles
V40HL V50HL
5
5
11
19
12
20
10
18
11
19
11
5
5
11/19
6
6
12
6
6
12/20
4
4
10
4
4
10/18
5
5
11
5
5
11/19
AC CY V P S Z
reg8 bit NO.CL ← 0
(mem8) bit NO.CL ← 0
reg16 bit NO.CL ← 0
(mem16) bit NO.CL ← 0
reg8 bit NO.imm3 ← 0
(mem8) bit NO.imm3 ← 0
reg16 bit NO.imm4 ← 0
(mem16) bit NO.imm4 ← 0
reg8 bit NO.CL ← 1
(mem8) bit NO.CL ← 1
reg16 bit NO.CL ← 1
(mem16) bit NO.CL ← 1
reg8 bit NO.imm3 ← 1
(mem8) bit NO.imm3 ← 1
reg16 bit NO.imm4 ← 1
(mem16) bit NO.imm4 ← 1
CLR1
SET1
CY
DIR
CY
DIR
2nd byte*
11111000
11111100
11111001
11111101
3rd byte*
* 1st byte = 0FH
1
1
1
1
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
CY ← 0
DIR ← 0
CY ← 1
DIR ← 1
0
1
µ
PD70208H, 70216H

Instruction
Group
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
Mnemonic
SHL
Shift instructions
Operand(s) Operation
reg, 1
mem, 1
reg, CL
mem, CL
reg, imm8
mem, imm8
76543210 76543210
1101000W
1101000W
1101001W
1101001W
1100000W
1100000W
Operation Code Flags
11100 reg
mod
100 mem
11100 reg
mod
100 mem
11100 reg
mod
100 mem
Bytes
2
2-4
2
2-4
3
3-5
Clock Cycles
V40HL V50HL
6
13/21
7 + n
16/24
+ n
7 + n
16/24
+ n
6
13/21
7 + n
16/24
+ n
7 + n
16/24
+ n
CY ← reg MSB, reg ← reg × 2
If reg MSB ≠ CY: V ← 1
If reg MSB = CY: V ← 0
CY ← (mem) MSB, (mem) ← (mem) × 2
If (mem) MSB ≠ CY: V ← 1
If (mem) MSB = CY: V ← 0
temp ← CL, while temp ≠0 the following operation are repeated:
CY ← reg MSB, reg ← reg × 2
temp ← temp – 1
temp ← CL, while temp ≠0 the following operation are repeated:
CY ← (mem) MSB, (mem) ← (mem) × 2
temp ← temp – 1
temp ← imm8, while temp ≠ 0 the following operations are
repeated:
CY ← reg MSB, reg← reg × 2
temp ← temp – 1
temp ← imm8, while temp ≠ 0 the following operations are
repeated:
CY ← (mem) MSB, (mem) ← (mem) × 2
temp ← temp – 1
AC CY V P S Z
U ЧЧЧЧЧ
UЧЧЧЧЧ
U×U×××
U×U×××
U×U×××
U×U×××
53
n: Number of shifts
µ
PD70208H, 70216H

54
Instruction
Group
Mnemonic
SHR
Operand(s)
reg, 1
Operation Code Flags
76543210
1101000W
76543210
11101 reg
Bytes
2
Clock Cycles
V40HL V50HL
6
6
Operation
CY ← reg LSB, reg ← reg ÷ 2
If reg MSB ≠ bit after reg MSB : V ← 1
If reg MSB = bit after reg MSB : V ← 0
AC CY V P S Z
U ЧЧЧЧЧ
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
Shift instructions
mem, 1
reg, CL
mem, CL
reg, imm8
mem, imm8
1101000W
1101001W
1101001W
1100000W
1100000W
mod
101 mem
11101 reg
mod
101 mem
11101 reg
mod
101 mem
2-4
13/21
2
7 + n
2-4
16/24
+ n
3
7 + n
3-5
16/24
+ n
n: Number of shifts
CY ← (mem) LSB, (mem) ← (mem) ÷ 2
13/21
If (mem) MSB ≠ bit after (mem) MSB : V ← 1
If (mem) MSB = bit after (mem) MSB : V ← 0
temp ← CL, while temp ≠ 0 the following operations are
7 + n
repeated:
CY ← reg LSB, reg ← reg ÷ 2
temp ← temp – 1
temp ← CL, while temp ≠ 0 the following operations are
16/24
repeated:
+ n
CY ← (mem) LSB, (mem) ← (mem) ÷ 2
temp ← temp – 1
temp ← imm8, while temp ≠ 0 the following operations are
7 + n
repeated:
CY ← reg LSB, reg ← reg ÷ 2
temp ← temp – 1
temp ← imm8, while temp ≠ 0 the following operations are
16/24
repeated:
+ n
CY ← (mem) LSB,(mem) ← (mem) ÷ 2
temp ← temp – 1
UЧЧЧЧЧ
U×U×××
U×U×××
U×U×××
U×U×××
µ
PD70208H, 70216H

Instruction
Group
Mnemonic
SHRA
Operand(s)
reg, 1
Operation Code Flags
76543210
1101000W
76543210
11111 reg
Bytes
2
Clock Cycles
V40HL V50HL
6
6
Operation
CY ← reg LSB, reg ← reg ÷ 2, V ← 0
MSB of operand is unchanged.
AC CY V P S Z
U × 0 ×××
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
mem, 1
reg, CL
mem, CL
reg, imm8
mem, imm8
1101000W
1101001W
1101001W
1100000W
1100000W
mod
111 mem
11111 reg
mod
111 mem
11111 reg
mod
111 mem
2-4
13/21
2
7 + n
2-4
16/24
+ n
3
7 + n
3-5
16/24
+ n
n: Number of shifts
13/21
7 + n
16/24
+ n
7 + n
16/24
+ n
CY ← (mem) LSB,(mem) ← (mem) ÷ 2, V ← 0
MSB of operand is unchanged.
temp ← CL, while temp ≠ 0 the following operations are
repeated:
CY ← reg LSB, reg ← reg ÷ 2
temp ← temp – 1, MSB of operand is unchanged.
temp ← CL, while temp ≠ 0 the following operations are
repeated:
CY ← (mem) LSB, (mem) ← (mem) ÷ 2
temp ← temp – 1, MSB of operand is unchanged.
temp ← imm8, while temp ≠ 0 the following operations are
repeated:
CY ← reg LSB, reg ← reg ÷ 2
temp ← temp – 1, MSB of operand is unchanged.
temp ← imm8, while temp ≠ 0 the following operations are
repeated:
CY ← (mem) LSB,(mem) ← (mem) ÷ 2
temp ← temp – 1, MSB of operand is unchanged.
U×0×××
U×U×××
U×U×××
U×U×××
U×U×××
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
55

56
Instruction
Group
Mnemonic Operand(s)
ROL
reg, 1
Operation Code Flags
76543210
1101000W
76543210
11000 reg
Bytes
2
Clock Cycles
V40HL V50HL
6
6
Operation
CY ← reg MSB, reg ← reg × 2 + CY
reg MSB ≠ CY : V ← 1
reg MSB = CY : V ← 0
AC CY V P S Z
××
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
Rotate instructions
mem, 1
reg, CL
mem, CL
reg, imm8
mem, imm8
1101000W
1101001W
1101001W
1100000W
1100000W
mod
000 mem
11000 reg
mod
000 mem
11000 reg
mod
000 mem
2-4
13/21
2
7 + n
2-4
16/24
+ n
3
7 + n
3-5
16/24
+ n
n: Number of shifts
13/21
7 + n
16/24
+ n
7 + n
16/24
+ n
CY ← (mem) MSB, (mem) ← (mem) × 2 + CY
(mem) MSB ≠ CY : V ← 1
(mem) MSB = CY : V ← 0
temp ← CL, while temp ≠ 0 the following operations are
repeated:
CY ← reg MSB, reg ← reg × 2 + CY
temp ← temp – 1
temp ← CL, while temp ≠ 0 the following operations are
repeated:
CY ← (mem) MSB, (mem) ← (mem) × 2 + CY
temp ← temp – 1
temp ← imm8, while temp ≠ 0 the following operations are
repeated:
CY ← reg MSB, reg ← reg × 2 + CY
temp ← temp – 1
temp ← imm8, while temp ≠ 0 the following operations are
repeated:
CY ← (mem) MSB, (mem) ← (mem) × 2 + CY
temp ← temp – 1
××
×U
×U
×U
×U
µ
PD70208H, 70216H

Instruction
Group
Mnemonic Operand(s)
ROR
reg, 1
Operation Code Flags
76543210
1101000W
76543210
11001 reg
Bytes
2
Clock Cycles
V40HL V50HL
6
6
Operation
CY ← reg LSB, reg← reg ÷ 2
reg MSB ← CY
reg MSB ≠ bit after reg MSB : V ← 1
reg MSB = bit after reg MSB : V ← 0
AC CY V P S Z
××
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
Rotate instructions
mem, 1
reg, CL
mem, CL
reg, imm8
mem, imm8
1101000W
1101001W
1101001W
1100000W
1100000W
mod
001 mem
11001 reg
mod
001 mem
11001 reg
mod
001 mem
2-4
13/21
2
7 + n
2-4
16/24
+ n
3
7 + n
3-5
16/24
+ n
n: Number of shifts
13/21
7 + n
16/24
+ n
7 + n
16/24
+ n
CY ← (mem) LSB, (mem) ← (mem) ÷ 2
(mem) MSB ← CY
(mem) MSB ≠ bit after (mem) MSB : V ← 1
(mem) MSB = bit after (mem) MSB : V ← 0
temp ← CL, while CL ≠ 0 the following operations are repeated:
CY ← reg LSB, reg ← reg ÷ 2
reg MSB ← CY
temp ← temp – 1
temp ← CL, while CL ≠ 0 the following operations are repeated:
CY ← (mem) LSB,(mem) ← (mem) ÷ 2
(mem) MSB ← CY
temp ← temp – 1
temp ← imm8, while CL ≠ 0 the following operations are
repeated:
CY ← reg LSB,reg ← reg ÷ 2
reg MSB ← CY
temp ← temp – 1
temp ← imm8, while CL ≠ 0 the following operations are
repeated:
CY ← (mem) LSB,(mem) ← (mem) ÷ 2
(mem) MSB ← CY
temp ← temp – 1
××
×U
×U
×U
×U
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
57

58
Instruction
Group
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
Mnemonic Operand(s)
ROLC
Rotate instructions
reg, 1
mem, 1
reg, CL
mem, CL
reg, imm8
mem, imm8
Operation Code Flags
76543210
1101000W
1101000W
1101001W
1101001W
1100000W
1100000W
76543210
11010 reg
mod
010 mem
11010 reg
mod
010 mem
11010 reg
mod
010 mem
Bytes
2
2-4
2
2-4
3
3-5
Clock Cycles
V40HL V50HL
6
13/21
7 + n
16/24
+ n
7 + n
16/24
+ n
6
13/21
7 + n
16/24
+ n
7 + n
16/24
+ n
Operation
tmpcy ← CY, CY ← reg MSB
reg ← reg × 2 + tmpcy
reg MSB ≠ CY : V ← 1
reg MSB = CY : V ← 0
tmpcy ← CY, CY ← (mem) MSB
(mem)← (mem) × 2 + tmpcy
(mem) MSB ≠ CY : V ← 1
(mem) MSB = CY : V ← 0
temp ← CL, while CL ≠ 0 the following operations are repeated:
tmpcy← CY, CY ← reg MSB
reg ← reg × 2 + tmpcy
temp ← temp – 1
temp ← CL, while CL ≠ 0 the following operations are repeated:
tmpcy ← CY, CY ← (mem) MSB
(mem) ← (mem) × 2 + tmpcy
temp ← temp – 1
temp ← imm8, while CL ≠ 0 the following operations are
repeated:
tmpcy ← CY, CY ← reg MSB
reg ← reg × 2 + tmpcy
temp ← temp – 1
temp ← imm8, while CL ≠ 0 the following operations are
repeated:
tmpcy ← CY, CY ← (mem) MSB
(mem) ← (mem) × 2 + tmpcy
temp ← temp – 1
AC CY V P S Z
××
××
×U
×U
×U
×U
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
n: Number of shifts

Instruction
Group
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
Mnemonic
RORC
Rotate instructions
Operand(s)
reg, 1
mem, 1
reg, CL
mem, CL
reg, imm8
mem, imm8
Operation Code Flags
76543210
1101000W
1101000W
1101001W
1101001W
1100000W
1100000W
76543210
11011 reg
mod
011 mem
11011 reg
mod
011 mem
11011 reg
mod
011 mem
Bytes
2
2-4
2
2-4
3
3-5
Clock Cycles
V40HL V50HL
6
13/21
7 + n
16/24
+ n
7 + n
16/24
+ n
6
13/21
7 + n
16/24
+ n
7 + n
16/24
+ n
Operation
tmpcy ← CY, CY ← reg LSB
reg ← reg ÷ 2
reg MSB ← tmpcy
reg MSB ≠ bit after reg MSB : V ← 1
reg MSB = bit after reg MSB : V ← 0
tmpcy ← CY, CY ← (mem) LSB
(mem) ← (mem) ÷ 2
(mem) MSB ← tmpcy
(mem) MSB ≠ bit after (mem) MSB : V ← 1
(mem) MSB = bit after (mem) MSB : V ← 0
temp ← CL, while CL ≠ 0 the following operations are repeated:
tmpcy ← CY, CY ← reg LSB
reg ← reg ÷ 2
reg MSB ← tmpcy
temp ← temp – 1
temp ← CL, while CL ≠ 0 the following operations are repeated:
tmpcy ← CY, CY ← (mem) LSB
(mem) ← (mem) ÷ 2
(mem) MSB ← tmpcy
temp ← temp – 1
temp ←imm8, while CL ≠ 0 the following operations are
repeated:
tmpcy ← CY, CY ← reg LSB
reg ← reg ÷ 2
reg MSB ← tmpcy
temp ← temp – 1
temp ← imm8, while CL ≠ 0 the following operations are
repeated:
tmpcy ← CY, CY ← (mem) LSB
(mem) ← (mem) ÷ 2
(mem) MSB ← tmpcy
temp ← temp – 1
AC CY V P S Z
××
××
×U
×U
×U
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
×U
59
n: Number of shifts

60
Instruction
Group
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
Mnemonic Operand(s) Operation
CALL
RET
Subroutine control instructions
near-proc
regptr16
memptr16
far-proc
memptr32
pop-value
pop-value
Operation Code Flags
76543210
11101000
11111111
11111111
10011010
11111111
11000011
11000010
11001011
11001010
76543210
11010 reg
mod
010 mem
mod
011 mem
Bytes
3
2
2-4
5
2-4
1
3
1
3
Clock Cycles
V40HL V50HL
16/20
20
14/18
18
23/31
31
21/29
29
31/47
47
15/19
19
20/24
24
21/29
29
24/32
32
AC CY V P S Z
SP ← SP – 2, (SP + 1, SP) ← PC
PC ← PC + disp
SP ← SP – 2, (SP + 1, SP) ← PC
PC ← regptr16
TA ← (memptr16)
SP ← SP – 2, (SP + 1, SP) ← PC, PC ← TA
SP ← SP – 2, (SP + 1, SP) ← PS, PS ← seg
SP ← SP – 2, (SP + 1, SP) ← PC, PC ← offset
TA ← (memptr32),TB ← (memptr32 + 2)
SP ← SP – 2, (SP + 1, SP) ← PS, PS ← TB
SP ← SP – 2, (SP + 1, SP) ← PC, PC ← TA
PC ← (SP + 1, SP)
SP ← SP + 2
PC ← (SP + 1, SP)
SP ← SP + 2, SP ← SP + pop-value
PC ← (SP + 1, SP)
PS ← (SP + 3, SP + 2)
PS ← SP + 4
PC ← (SP + 1, SP)
PS ← (SP + 3, SP + 2)
SP ← SP + 4, SP ← SP + pop-value
µ
PD70208H, 70216H

Instruction
Group
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
Mnemonic Operand(s)
PUSH
POP
Stack manipulation instructions
PREPARE
DISPOSE
mem16
reg16
sreg
PSW
R
imm8
imm16
mem16
reg16
sreg
PSW
R
imm16, imm8
Operation Code Flags
76543210
11111111
01010 reg
000
sreg
110
10011100
01100000
011010 10
0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0
10001111
01011 reg
000
sreg
111
10011101
01100001
11001000
11001001
76543210
mod
110 mem
mod
000 mem
Bytes
2-4
1
1
1
1
2
3
2-4
1
1
1
1
4
1
Clock Cycles
V40HL V50HL
15/23
23
6/10
10
6/10
10
6/10
10
33/65
65
5/9
9
6/10
10
16/24
24
8/12
12
8/12
12
8/12
12
43/75
75
10
Note 2
6/10
Note 1
Operation
SP ← SP – 2
(SP + 1, SP) ← (mem16)
SP ← SP – 2
(SP + 1, SP) ← reg16
SP ← SP – 2
(SP + 1, SP) ← sreg
SP ← SP – 2
(SP + 1, SP) ← PSW
Push registers on the stack
SP ← SP – 2
(SP + 1, SP) ← imm8, sign of extension
SP ← SP – 2
(SP + 1, SP) ← imm16
(mem16) ← (SP + 1, SP)
SP ← SP + 2
reg16← (SP + 1, SP)
SP ← SP + 2
sreg← (SP + 1, SP)
SP ← SP + 2
PSW← (SP + 1, SP)
SP ← SP + 2
Pop registers from the stack
Prepare New Stack Frame
Dispose of Stack Frame
sreg : SS, DS0, DS1
AC CY V P S Z
RRRRRR
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
61
Notes1. If imm8 = 0 16
If imm8 ≥ 1 21 + 16 (imm8 – 1)
2. If imm8 = 0 12/16
If imm8 ≥ 1 {17 + 8 (imm8 – 1)} / {21 + 16 (imm8 – 1)}

62
Instruction
Group
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
Mnemonic Operand(s)
BR
Branch instructions
near-label
short-label
regptr16
memptr16
far-label
memptr32
Operation Code Flags
76543210
11101001
11101011
11111111
11111111
11101010
11111111
76543210
11100 reg
mod
100 mem
mod
101 mem
Bytes
3
2
2
2-4
5
2-4
Clock Cycles
V40HL V50HL
13
12
11
23
15
34
13
12
11
19/23
15
26/34
Operation
AC CY V P S Z
PC ← PC+ dsip
PC ← PC+ ext-disp8
PC ← regptr16
PC ← (memptr16)
PS ← seg
PC ← offset
PS ← (memptr32 + 2)
PC ← (memptr32)
µ
PD70208H, 70216H

Instruction
Group
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
Mnemonic
BV
BNV
BC
BL
BNC
BNL
BE
BZ
BNE
BNZ
BNH
BH
BN
BP
BPE
BPO
BLT
Conditional branch instructions
BGE
BLE
BGT
DBNZNE
DBNZE
DBNZ
BCWZ
Operand(s)
short-label
short-label
short-label
short-label
short-label
short-label
short-label
short-label
short-label
short-label
short-label
short-label
short-label
short-label
short-label
short-label
short-label
short-label
short-label
short-label
Operation Code Flags
76543210
01110000
0001
0010
0011
0100
0101
0110
0111
1000
1001
1010
1011
1100
1101
1110
1111
11100000
1110 0001
1110 0010
1110 0011
76543210
Bytes
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
Clock Cycles
V40HL V50HL
14/4
14/4
14/4
14/4
14/4
14/4
14/4
14/4
14/4
14/4
14/4
14/4
14/4
14/4
14/4
14/4
14/5
14/5
13/5
13/5
Note
14/4
14/4
14/4
14/4
14/4
14/4
14/4
14/4
14/4
14/4
14/4
14/4
14/4
14/4
14/4
14/4
14/5
14/5
13/5
13/5
Operation
if V = 1 PC ← PC + ext-disp8
if V = 0 PC ← PC + ext-disp8
if CY = 1 PC ← PC + ext-disp8
if CY = 0 PC ← PC + ext-disp8
if Z = 1 PC ← PC + ext-disp8
if Z = 0 PC ← PC + ext-disp8
if CY ∨ Z = 1 PC ← PC + ext-disp8
if CY ∨ Z = 0 PC ← PC + ext-disp8
if S = 1 PC ← PC + ext-disp8
if S = 0 PC ← PC + ext-disp8
if P = 1 PC ← PC + ext-disp8
if P = 0 PC ← PC + ext-disp8
if S ∨ V = 1 PC ← PC + ext-disp8
if S ∨ V = 0 PC ← PC + ext-disp8
if (S ∨ V) ∨ Z = 1 PC ← PC + ext-disp8
if (S ∨ V) ∨ Z = 0 PC ← PC + ext-disp8
CW = CW – 1 PC ← PC + ext-disp8
if Z = 0 and CW ≠ 0
CW = CW – 1 PC ← PC + ext-disp8
if Z = 1 and CW ≠ 0
CW = CW – 1 PC ← PC + ext-disp8
if CW ≠ 0
if CW = 0 PC ← PC + ext-disp8
AC CY V P S Z
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
63
Note Condition determination: true/false

64
Instruction
Group
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
Mnemonic Operand(s)
BRK
BRKV
RETI
Interrupt instructions
BRKEM
CHKIND
3
imm8
( = 3)
imm8
reg16, mem32
Operation Code Flags
76543210
11001100
11001101
11001110
11001111
00001111
01100010
76543210
11111111
mod reg mem
Bytes
1
2
1
1
3
2-4
Clock Cycles
V40HL V50HL
38/50
50
38/50
50
Note 2
Note 1
27/39
39
38/50
50
Note 4
Note 3
Operation
TA ← (00DH, 00CH), TC ← (00FH, 00EH)
SP ← SP – 2, (SP + 1, SP) ← PSW, IE ← 0, BRK ← 0
SP ← SP – 2, (SP + 1, SP) ← PS, PS ← TC
SP ← SP – 2, (SP + 1, SP) ← PC, PC ← TA
TA ← (4 n + 1, 4n), TC ← (4n + 3, 4n + 2) n = imm8
SP ← SP – 2, (SP + 1, SP) ← PSW, IE ← 0, BRK ← 0
SP ← SP – 2, (SP + 1, SP) ← PS, PS ← TC
SP ← SP – 2, (SP + 1, SP) ← PC, PC ← TA
If V = 1
TA ← (011H, 010H), TC ← (013H, 012H)
SP ← SP – 2, (SP + 1, SP) ← PSW, IE ← 0, BRK ← 0
SP ← SP – 2, (SP + 1, SP) ← PS, PS ← TC
SP ← SP – 2, (SP + 1, SP) ← PC, PC ← TA
PC ← (SP + 1, SP), PS ← (SP + 3, SP + 2),
PSW ← (SP + 5, SP + 4), SP ← SP + 6
TA ← (4 n + 1, 4n), TC ← (4n + 3, 4n + 2) n = imm8
SP ← SP – 2, (SP + 1, SP) ← PSW, MD ← 0
MD is set to write enabled
SP ← SP – 2, (SP + 1, SP) ← PS, PS ← TC
SP ← SP – 2, (SP + 1, SP) ← PC, PC ← TA
If (mem32) > reg16 or (mem32 + 2) < reg16
TA ← (015H, 014H), TC ← (017H, 016H)
SP ← SP – 2, (SP + 1, SP) ← PSW, IE ← 0, BRK ← 0
SP ← SP – 2, (SP + 1, SP) ← PS, PS ← TC
SP ← SP – 2, (SP + 1, SP) ← PC, PC ← TA
AC CY V P S Z
RRRRRR
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
Notes 1. When V = 1: 52
When V = 0: 3
2. When V = 1: 40/52
When V = 0: 3
3. When interrupt condition is established : 72 to 75
When interrupt condition is not established : 25
4. When interrupt condition is established : (52 to 55)/(72 to 75)
When interrupt condition is not established : 17/25

Instruction
Group
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
Mnemonic Operand(s)
HALT
POLL
DI
EI
BUSLOCK
FPO1
FPO2
CPU control instructions
NOP
fp-op
fp-op, mem
fp-op
fp-op, mem
Operation Code Flags
76543210
11110100
10011011
11111010
11111011
11110000
11011
11011
0110011
0110011
10010000
XXX
XXX
76543210
11
mod YYY mem
X
11
X
mod YYY mem
YYYZ Z Z
YYYZ Z Z
Bytes
1
1
1
1
1
2
2-4
2
2-4
1
Clock Cycles
V40HL V50HL
2
2 + 5n
2
2
2
2
14
2
14
3
2
2 + 5n
2
2
2
2
10/14
2
10/14
3
Operation
AC CY V P S Z
CPU Halt
Poll and wait n: Number of times POLL pin is sampled
IE ← 0
IE ← 1
Bus Lock Prefix
No Operation
data bus ← (mem)
No Operation
data bus ← (mem)
No Operation
65
*
* DS0:, DS1:, PS:, and SS:.
Instruction
Group
Mnemonic Operand(s)
RETEM
8080
CALLN
imm8
001
sreg
110
Operation Code Flags
76543210
11101101
11101101
76543210
11111101
11101101
1
Bytes
2
3
2
Clock Cycles
V40HL V50HL
39
58
2
27/39
38/58
Segment override prefix
Operation
PC ← (SP + 1, SP), PS ← (SP + 3, SP + 2),
PSW ← (SP + 5, SP + 4), SP ← SP + 6, MD is set to write
disabled
TA ← (4n + 1, 4n), TC ← (4n + 3, 4n + 2) n = imm8
SP ← SP – 2, (SP + 1, SP) ← PSW, MD ← 1
SP ← SP – 2, (SP + 1, SP) ← PS, PS ← TC
SP ← SP – 2, (SP + 1, SP) ← PC, PC ← TA
AC CY V P S Z
RRRRRR
µ
PD70208H, 70216H

µ
PD70208H, 70216H
16. ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
Applied standard
The electrical characteristics shown below are applied to devices other than the old models conforming
to K mask.
Therefore, these characteristics are different from those conforming to the K mask. For the electrical
characteristics of the K mask, consult NEC.
“Others” in the table below means products conforming to the masks other than E, P, X, and M (but
conforming to the L, F mask).
16.1 AT 5 V OPERATION
OPERATING RANGE
E, P, X, M Mask Model Others
µ
PD70208H, 70216H-10/12/16 VDD = 5 V ±10%
µ
PD70208H, 70216H-20 — VDD = 5 V ±5%
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS (TA = 25 °C)
Parameter
Supply voltage
Input voltage
Clock input voltage
Output voltage
Operating ambient temperature
Storage temperature
Symbol Test Conditions Rating Unit
VDD
VI
VK
VO
TA
Tstg
VDD = 5 V ±10%
(µPD70208H, 70216H-10/12/16)
VDD = 5 V ±5%
(µPD70208H, 70216H-20)
–0.5 to +7.0 V
–0.5 to VDD + 0.3 V
–0.5 to VDD + 1.0 V
–0.5 to VDD + 0.3 V
–40 to +85 °C
–65 to +150 °C
Cautions 1. Do not directly connect the output pins of two or more IC products and do not directly connect
the output pins to V
DD or VCC and GND. However, open-drain pins or open-collector pins may be
connected directly. Moreover, an external circuit whose timing is designed to avoid output
collision can be connected to pins that go into a high-impedance state.
2. If even one of the above parameters exceeds the absolute maximum rating even momentarily, the
quality of the program may be degraded. Absolute maximum ratings, therefore, are the values
exceeding which the product may be physically damaged. Use the program keeping all the
parameters within these rated values.
The standards and conditions shown in DC and AC Characteristics below specify the range within
which the normal operation of the product is guaranteed.
66
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00

µ
PD70208H, 70216H
DC CHARACTERISTICS
(T
A = –40 to +85 °C, VDD = 5 V ±10% (
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
Input voltage high VIH E, P, X, M Except RESET 2.2 VDD+0.3 V
Input voltage low VIL Except RESET –0.5 +0.8 V
Clock input voltage high VKH 3.9 VDD+1.0 V
Clock input voltage low VKL –0.5 +0.6 V
Output voltage high VOH IOH = –2.5 mA 0.7 VDD V
Output voltage low VOL Except END/TC : IOL = 2.5 mA 0.4 V
Input leak current high ILIH VI = VDD 10
Input leak current low ILIL Except INTP:VI = 0 V –10
INTP input current low ILIPL INTP input:VI = 0 V –300
Output leak current high ILOH VO = VDD 10
Output leak current low ILOL VO = 0 V –10
Latch leak current high ILLH VI = 3.0 V –50 –300
Latch leak current low ILLL VI = 0.8 V 50 300
Latch inversion current (L → H) IILH 400
Latch inversion current (H → L) IILL –400
Supply current
Note
µ
PD70208H, 70216H-10/12/16), VDD = 5 V ±5% (µPD70208H, 70216H-20))
masks RESET 0.8 VDD VDD+0.3
Others Except RESET, 2.2 VDD+0.3
INTP1 to INTP7
RESET 0.8 VDD VDD+0.3
INTP1 to INTP7 2.4 VDD+0.3
RESET –0.5 0.2VDD
IOH = –100 µAVDD – 0.4
END/TC : IOL = 5.0 mA
IDD E, P, X, M On operation 5.5 fX 9.0 fX mA
masks
Others On operation 4.5 fX 6.0 fX mA
On standby (HALT) 1.5 fX 2.5 fX
On standby (STOP) 50
On standby (HALT) 1.5 fX 2.2 fX
On standby (STOP) 50
µ
A
µ
A
µ
A
µ
A
µ
A
µ
A
µ
A
µ
A
µ
A
µ
A
µ
A
Note The unit of constant values (1.5, 2.2, 2.5, 4.5, 5.5, 6.0 and 9.0) is mA/MHz.
CAPACITANCE (TA = 25 ˚C, VDD = 0 V)
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
Input capacitance CI fC = 1 MHz 10 pF
Input/output capacitance CIO 0 V other than test pin. 15 pF
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
67

AC CHARACTERISTICS
(1)µPD70208H, 70216H-10/12/16 (TA = –40 to +85 °C, V DD = 5 V ±10%) (1/3)
µ
PD70208H-10
µ
PD70216H-10
MIN. MAX. MIN. MAX. MIN. MAX.
External clock input cycle
External clock input high-level width (VKH=3.0 V)
External clock input low-level width (VKL=1.5 V)
External clock input rise time (1.5→3.0 V)
External clock input fall time (3.0→1.5 V)
Clock output cycle
Clock output high-level width (VOH=3.0 V)
Clock output low-level width (VOL=1.5 V)
Clock output rise time (1.5→3.0 V)
Clock output fall time (3.0→1.5 V)
CLKOUT delay time (vs. external clock)
Input rise time (except external clock) (0.8→2.2 V)
Input fall time (except external clock) (2.2→0.8 V)
Output rise time E, P, X, M masks
(except CLKOUT) (0.8→2.2 V)
Output fall time (except CLKOUT) (2.2→0.8 V)
RESET setup time (vs. CLKOUT↓)
RESET hold time (vs. CLKOUT↓)
RESOUT output delay time (vs. CLKOUT↓)
READY inactive setup time (vs. CLKOUT↑)
READY inactive hold time (vs. CLKOUT↑)
READY active setup time (vs. CLKOUT↑)
READY active hold time (vs. CLKOUT↑)
NMI setup time (vs. CLKOUT↑)
POLL setup time (vs. CLKOUT↑)
Data setup time (vs. CLKOUT↓)
Data hold time (vs. CLKOUT↓)
CLKOUT → address delay time
CLKOUT → address hold time
CLKOUT↓ → PS delay time
CLKOUT↓ → PS float delay time
Address setup time (vs. ASTB↓)
CLKOUT↓ → address float delay time
CLKOUT↓ → ASTB↑ delay time
Others
Note 1
Note 1
Note 2
Note 3
tCYX 50 DC 40 DC 31.25 DC ns
<1>
tXXH 19 14 12 ns
<2>
tXXL 19 14 12 ns
<3>
tXR 555ns
<4>
tXF 555ns
<5>
tCYK 100 DC 80 DC 62.5 DC ns
<6>
tKKH 0.5tCYK–5 0.5tCYK–5 0.5tCYK–5 ns
<7>
tKKL 0.5tCYK–5 0.5tCYK–5 0.5t CYK–5 ns
<8>
tKR 555ns
<9>
tKF 555ns
<10>
tDXK 40 35 20 ns
<11>
tIR 15 15 15 ns
<12>
tIF 10 10 10 ns
<13>
tOR 15 15 15 ns
<14>
10 10 10 ns
tOF 10 10 10 ns
<15>
tSRESK 20 20 20 ns
<16>
tHKRES 25 25 15 ns
<17>
tDKRES 550540530ns
<18>
tSRYLK 15 10 7 ns
<19>
tHKRYL 20 15 15 ns
<20>
tSRYHK 15 10 7 ns
<21>
tHKRYH 20 20 15 ns
<22>
tSNMIK 15 15 15 ns
<23>
tSPOLK 20 20 20 ns
<24>
tSDK 15 10 7 ns
<25>
tHKD 555ns
<26>
tDKA 550540528ns
<27>
tHKA 555ns
<28>
tDKP 550540530ns
<29>
tFKP 550540530ns
<30>
tSAST tKKL–20 tKKL–10 t KKL–10 ns
<31>
tFKA t HKA 50 tHKA 40 tHKA 30 ns
<32>
tDKSTH 40 30 25 ns
<33>
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
Output Pin Load Capacitance: CL = 100 pF
µ
µ
PD70208H-12
µ
PD70216H-12
PD70208H-16
µ
PD70216H-16
UnitSymbol Parameter
Notes 1. When reset with the minimum pulse width or when guaranteeing the RESOUT output timing.
2. Specifications also corresponding to the QS0, QS1, and BUSLOCK signals, and A16/PS0-A19/PS3, UBE,
BUFEN, BUFR/W, MRD, IORD, MWR, IOWR, and BS0-BS2 signals at HLDRQ/HLDAK timing.
3. Specifications also corresponding to the A16/PS0-A19/PS3, UBE, BUFEN, BUFR/W, MRD, IORD, MWR,
IOWR, and BS0-BS2 signals at HLDRQ/HLDAK timing.
68
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00

(1)µPD70208H, 70216H-10/12/16 (TA = –40 to +85 °C, V DD = 5 V ±10%) (2/3)
µ
PD70208H-10
µ
PD70216H-10
MIN. MAX. MIN. MAX. MIN. MAX.
tKKL–30 tKKL–20 t KKL–15 ns
CLKOUT↑ → ASTB↓ delay time
ASTB high-level width
ASTB↓ → address hold time
CLKOUT → control 1
CLKOUT → control 2
Address float → RD↓ delay time
CLKOUT↓ → RD↓ delay time
CLKOUT↓ → RD↑ delay time
RD↑ → address delay time
RD low-level width
BUFEN↑ → BUFR/W delay time (read cycle)
CLKOUT↓ → data output delay time
CLKOUT↓ → data float delay time
WR low-level width
WR↑ → BUFEN↑ or BUFR/W↓ (write cycle)
CLKOUT↑ → BS↓ delay time
CLKOUT↓ → BS↑ delay time
HLDRQ setup time (vs. CLKOUT↓)
CLKOUT↓ → HLDAK delay time
CLKOUT↑ → DMAAK delay time
CLKOUT↓ → DMAAK delay time (cascade mode)
WR low-level width DMA extended write
(DMA cycle) DMA normal write
RD↓, WR↓ delay time (vs. DMAAK↓)
DMAAK↑ delay time (vs. RD↑)
RD↑ delay time (vs. WR↑)
TC output delay time (vs. CLKOUT↑)
TC OFF delay time (vs. CLKOUT↑)
TC low-level width
TC pull-up delay time (vs. CLKOUT↑)
END setup time (vs. CLKOUT↑)
END low-level width
DMARQ setup time (vs. CLKOUT↑)
INTPn low-level width
RXD setup time (vs. SCU internal clock↓)
Note 1
Note 2
delay time
delay time
Symbol Parameter Unit
tDKSTL 45 35 30 ns
<34>
tSTST tKKL–10 t KKL–10 tKKL–10 ns
<35>
tHSTA tKKH–20 tKKH–10 t KKH–10 ns
<36>
tDKCT1 560550540ns
<37>
tDKCT2 555545535ns
<38>
tDAFRL 000ns
<39>
tDKRL 565550540ns
<40>
tDKRH 560545535ns
<41>
tDRHA t CYK–40 tCYK–20 t CYK–10 ns
<42>
tRR 2tCYK–40 2t CYK–20 2tCYK–20 ns
<43>
tDBECT tKKL–20 t KKL–10 tKKL–10 ns
<44>
tDKD 555540530ns
<45>
tFKD 555540530ns
<46>
tWW 2tCYK–40 2tCYK–20 2tCYK–20 ns
<47>
tDWCT tKKL–20 t KKL–10 tKKL–10 ns
<48>
tDKBL 555540530ns
<49>
tDKBH 555540530ns
<50>
tSHQK 15 10 7 ns
<51>
tDKHA 560550540ns
<52>
tDKHDA 555545535ns
<53>
tDKLDA 580570555ns
<54>
tWW1 2tCYK–40 2tCYK–20 2tCYK–20 ns
<55>
tWW2 t CYK–40 tCYK–20 tCYK–15 ns
<56>
tDDARW tKKH–30 tKKH–20 t KKH–15 ns
<57>
t
DRHDAH
<58>
tDWHRH 333ns
<59>
tDKTCL 55 45 35 ns
<60>
tDKTCF 55 45 35 ns
<61>
tTCTCL tCYK–15 tCYK–10 tCYK–10 ns
<62>
tDKTCH Note 3 Note 4 Note 4 ns
<63>
tSEDK 30 25 20 ns
<64>
tEDEDL 80 65 50 ns
<65>
tSDQK 30 20 15 ns
<66>
tIPIPL 80 80 80 ns
<67>
tSRX 500 500 500 ns
<68>
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
Output Pin Load Capacitance: CL = 100 pF
µ
µ
PD70208H-12
µ
PD70216H-12
PD70208H-16
µ
PD70216H-16
Notes 1. MWR and IOWR signals in DMA cycle
2. MWR and IOWR signals in CPU cycles and BUFEN, BUFR/W, INTAK and REFRQ signals.
3. tKKH + 2tCYK – 10 (Reference value when a 1.1-kΩ pull-up resistor is connected.)
4. tKKH + 2tCYK – 5 (Reference value when a 1.1-kΩ pull-up resistor is connected.)
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
69

(1)µPD70208H, 70216H-10/12/16 (TA = –40 to +85 °C, V DD = 5 V ±10%) (3/3)
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
RXD hold time (vs. SCU internal clock↓)
CLKOUT↓ → SRDY delay time
TOUT1↓ → TXD delay time
TCTL2 setup time (vs. CLKOUT↓)
TCTL2 setup time (vs. TCLK↑)
TCTL2 hold time (vs. CLKOUT↓)
TCTL2 hold time (vs. TCLK↑)
TCTL2 high-level width
TCTL2 low-level width
TOUT output delay time (vs. CLKOUT↓)
TOUT output delay time (vs. TCLK↓)
TOUT output delay time (vs. TCTL2↓)
TCLK rise time
TCLK fall time
TCLK high-level width
TCLK low-level width
TCLK cycle
Access interval
REFRQ↑ delay time (vs. MRD↑)
RESET pulse width
Note 1
Note 2
Note 3
Output Pin Load Capacitance: C
µ
PD70208H-10
µ
PD70216H-10
MIN. MAX. MIN. MAX. MIN. MAX.
tHRX 500 500 500 ns
<69>
tDKSR 100 100 100 ns
<70>
tDTX 200 200 200 ns
<71>
tSGK 40 40 40 ns
<72>
tSGTK 40 40 40 ns
<73>
tHKG 80 80 80 ns
<74>
tHTKG 40 40 40 ns
<75>
tGGH 40 40 40 ns
<76>
tGGL 40 40 40 ns
<77>
tDKTO 150 150 150 ns
<78>
tDTKTO 100 100 100 ns
<79>
tDGTO 90 90 90 ns
<80>
tTKR 25 25 25 ns
<81>
tTKF 25 25 25 ns
<82>
t
TKTKH
<83>
tTKTKL 45 40 30 ns
<84>
tCYTK 100 DC 80 DC 62.5 DC ns
<85>
tAI 2tCYK–40 2tCYK–25 2tCYK–20 ns
<86>
t
DRQHRH
<87>
tWRESL 4tCYK 4tCYK 4tCYK ns
<88>
45 40 30 ns
tKKL–30 t KKL–15 tKKL–10 ns
µ
PD70208H-12
µ
PD70216H-12
µ
PD70208H-16
µ
PD70216H-16
L = 100 pF
UnitSymbol Parameter
Notes 1. Specification to guarantee read/write recovery time for I/O device.
2. Specification to guarantee that REFRQ↑ is always later than MRD↑.
Only guaranteed when the EREF bit of the SCTL register is 0.
3. When using internal clock generator by connecting a resonator to the X1 and X2 pins, the oscillation
stabilization time must be added at power-ON. Because the oscillation stabilization time varies depending
on the characteristics of the resonator and oscillator used, evaluate the oscillation stabilization time with the
resonator and oscillator actually used.
70
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00

µ
PD70208H, 70216H
(2)µPD70208H, 70216H-20 (TA = –40 to +85 °C, VDD = 5 V ±5%) (1/3)
Output Pin Load Capacitance: CL = 100 pF
µ
PD70208H-20
µ
PD70216H-20 Unit Parameter Symbol
MIN. MAX.
External clock input cycle
External clock input high-level width (VKH=3.0 V)
External clock input low-level width (VKL=1.5 V)
External clock input rise time (1.5→3.0 V)
External clock input fall time (3.0→1.5 V)
Clock output cycle
Clock output high-level width (VOH=3.0 V)
Clock output low-level width (VOL=1.5 V)
Clock output rise time (1.5→3.0 V)
Clock output fall time (3.0→1.5 V)
CLKOUT delay time (vs. external clock)
Input rise time (except external clock) (0.8→2.2 V)
Input fall time (except external clock) (2.2→0.8 V)
Output rise time (except CLKOUT) (0.8→2.2 V)
Output fall time (except CLKOUT) (2.2→0.8 V)
RESET setup time (vs. CLKOUT↓)
RESET hold time (vs. CLKOUT↓)
RESOUT output delay time (vs. CLKOUT↓)
READY inactive setup time (vs. CLKOUT↑)
READY inactive hold time (vs. CLKOUT↑)
READY active setup time (vs. CLKOUT↑)
READY active hold time (vs. CLKOUT↑)
NMI setup time (vs. CLKOUT↑)
POLL setup time (vs. CLKOUT↑)
Data setup time (vs. CLKOUT↓)
Data hold time (vs. CLKOUT↓)
CLKOUT → address delay time
CLKOUT → address hold time
CLKOUT ↓ → PS delay time
CLKOUT ↓ → PS float delay time
Address setup time (vs. ASTB↓)
CLKOUT ↓ → address float delay time
CLKOUT ↓ → ASTB ↑ delay time
CLKOUT ↑ → ASTB ↓ delay time
ASTB high-level width
Note 1
Note 1
Note 2
Note 3
tCYX 25 DC ns
<1>
tXXH 10 ns
<2>
tXXL 10 ns
<3>
tXR 5ns
<4>
tXF 5ns
<5>
tCYK 50 DC ns
<6>
tKKH 0.5tCYK–5 ns
<7>
tKKL 0.5t CYK–5 ns
<8>
tKR 5ns
<9>
tKF 5ns
<10>
tDXK 20 ns
<11>
tIR 15 ns
<12>
tIF 10 ns
<13>
tOR 10 ns
<14>
tOF 10 ns
<15>
tSRESK 20 ns
<16>
tHKRES 10 ns
<17>
tDKRES 525ns
<18>
tSRYLK 7ns
<19>
tHKRYL 10 ns
<20>
tSRYHK 7ns
<21>
tHKRYH 10 ns
<22>
tSNMIK 10 ns
<23>
tSPOLK 20 ns
<24>
tSDK 7ns
<25>
tHKD 5ns
<26>
tDKA 525ns
<27>
tHKA 5ns
<28>
tDKP 530ns
<29>
tFKP 530ns
<30>
tSAST t KKL–10 ns
<31>
tFKA tHKA 25 ns
<32>
tDKSTH 20 ns
<33>
tDKSTL 20 ns
<34>
tSTST tKKL–10 ns
<35>
Notes 1. When reset with the minimum pulse width or when guaranteeing the RESOUT output timing.
2. Specifications also corresponding to the QS0, QS1, and BUSLOCK signals, and A16/PS0-A19/PS3, UBE,
BUFEN, BUFR/W, MRD, IORD, MWR, IOWR, and BS0-BS2 signals at HLDRQ/HLDAK timing.
3. Specifications also corresponding to the A16/PS0-A19/PS3, UBE, BUFEN, BUFR/W, MRD, IORD, MWR,
IOWR, and BS0-BS2 signals at HLDRQ/HLDAK timing.
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
71

(2)µPD70208H, 70216H-20 (TA = –40 to +85 °C, VDD = 5 V ±5%) (2/3)
ASTB ↓ → address hold time
CLKOUT → control 1
CLKOUT → control 2
Address float → RD ↓ delay time
CLKOUT ↓ → RD ↓ delay time
CLKOUT ↓ → RD ↑ delay time
RD ↑ → address delay time
RD low-level width
BUFEN ↑ → BUFR/W delay time (read cycle)
CLKOUT ↓ → data output delay time
CLKOUT ↓ → data float delay time
WR low-level width
WR ↑ → BUFEN ↑ or BUFR/W ↓ (write cycle)
CLKOUT ↑ → BS ↓ delay time
CLKOUT ↓ → BS ↑ delay time
HLDRQ setup time (vs. CLKOUT ↓)
CLKOUT ↓ → HLDAK delay time
CLKOUT ↑ → DMAAK delay time
CLKOUT ↓ → DMAAK delay time (cascade mode)
WR low-level width (DMA cycle) DMA extended write
RD ↓, WR ↓ delay time (vs. DMAAK ↓)
DMAAK ↑ delay time (vs. RD ↑)
RD ↑ delay time (vs. WR ↑)
TC output delay time (vs. CLKOUT ↑)
TC OFF delay time (vs. CLKOUT ↑)
TC low-level width
TC pull-up delay time (vs. CLKOUT ↑)
END setup time (vs. CLKOUT ↑)
END low-level width
DMARQ setup time (vs. CLKOUT ↑)
INTPn low-level width
RxD setup time (vs. SCU internal clock ↓)
RxD hold time (vs. SCU internal clock ↓)
CLKOUT ↓ → SRDY delay time
Note 1
Note 2
delay time
delay time
DMA normal write
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
Output Pin Load Capacitance: CL = 100 pF
µ
PD70208H-20
µ
PD70216H-20
MIN. MAX.
<36>
tHSTA tKKH–10 ns
<37>
tDKCT1 525ns
<38>
tDKCT2 530ns
<39>
tDAFRL 0ns
<40>
tDKRL 525ns
<41>
tDKRH 528ns
<42>
tDRHA tCYK–5 ns
<43>
tRR 2tCYK–15 ns
<44>
tDBECT tKKL–10 ns
<45>
tDKD 525ns
<46>
tFKD 525ns
<47>
tWW 2tCYK–15 ns
<48>
tDWCT tKKL–10 ns
<49>
tDKBL 530ns
<50>
tDKBH 525ns
<51>
tSHQK 7ns
<52>
tDKHA 525ns
<53>
tDKHDA 525ns
<54>
tDKLDA 545ns
<55>
tWW1 2tCYK–15 ns
<56>
tWW2 t CYK–15 ns
<57>
tDDARW tKKH–10 ns
<58>
t
DRHDAH
<59>
tDWHRH 3ns
<60>
tDKTCL 25 ns
<61>
tDKTCF 25 ns
<62>
tTCTCL tCYK–10 ns
<63>
tDKTCH
<64>
tSEDK 20 ns
<65>
tEDEDL 40 ns
<66>
tSDQK 10 ns
<67>
tIPIPL 60 ns
<68>
tSRX 500 ns
<69>
tHRX 500 ns
<70>
tDKSR 100 ns
tKKL–10 ns
Note 3
Unit Parameter Symbol
ns
Notes 1. MWR and IOWR signals in DMA cycle
2. MWR and IOWR signals in BUFEN, BUFR/W, INTAK, REFRQ, and CPU cycles
3. tKKH + 2tCYK – 5 (reference value when a 1.1-kΩ pull-up resistor is connected)
72
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00

(2)µPD70208H, 70216H-20 (TA = –40 to +85 °C, VDD = 5 V ±5%) (3/3)
TOUT1 ↓ → TxD delay time
TCTL2 setup time (vs. CLKOUT ↓)
TCTL2 setup time (vs. TCLK ↑)
TCTL2 hold time (vs. CLKOUT ↓)
TCTL2 hold time (vs. TCLK ↑)
TCTL2 high-level width
TCTL2 low-level width
TOUT output delay time (vs. CLKOUT ↓)
TOUT output delay time (vs. TCLK ↓)
TOUT output delay time (vs. TCTL2 ↓)
TCLK rise time
TCLK fall time
TCLK high-level width
TCLK low-level width
TCLK cycle
Access interval
REFRQ ↑ delay time (vs. MRD ↑)
RESET pulse width
Note 1
Note 2
Note 3
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
Output Pin Load Capacitance: CL = 100 pF
µ
PD70208H-20
µ
PD70216H-20
MIN. MAX.
tDTX 200 ns
<71>
tSGK 40 ns
<72>
tSGTK 40 ns
<73>
tHKG 80 ns
<74>
tHTKG 40 ns
<75>
tGGH 40 ns
<76>
tGGL 40 ns
<77>
tDKTO 150 ns
<78>
tDTKTO 100 ns
<79>
tDGTO 90 ns
<80>
tTKR 25 ns
<81>
tTKF 25 ns
<82>
t
TKTKH
<83>
tTKTKL 23 ns
<84>
tCYTK 50 DC ns
<85>
tAI 2tCYK–15 ns
<86>
t
DRQHRH
<87>
tWRESL 4tCYK ns
<88>
23 ns
tKKL–10 ns
Unit Parameter Symbol
Notes 1. This rating is to guarantee the read/write recovery time for the I/O device.
2. This rating is to guarantee that REFRQ ↑ is always behind MRD ↑, and guaranteed only when the EREF
bit of the STCL register is 0.
3. When using internal clock generator by connecting a resonator to the X1 and X2 pins, the oscillation
stabilization time must be added at power-ON. Because the oscillation stabilization time varies depending
on the characteristics of the resonator and oscillator used, evaluate the oscillation stabilization time with the
resonator and oscillator actually used.
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
73

RECOMMENDED OSCILLATOR
The clock input circuits (1) and (2) shown below are recommended.
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
(1) Ceramic resonator connection (T
µ
PD70208H, 70216H-20))
(
Cautions 1. The oscillator should be as close as possible to the X1 and X2 pins.
2. No other signal lines should pass through the area enclosed in dashed line.
3. For matching between V40HL, V50HL and resonator, the efficient evaluation should be carried
out.
4. The values of the oscillator constants C1 and C2 depend on the characteristics of the
resonator used. Evaluate them with the resonator actually used.
Manufacturer
Murata Mfg.
Co., Ltd.
TDK Corp.
A = –40 to +85 °C, VDD = 5 V ± 10% (
X2
C2
Product Name
Frequency
(fXX) [MHz]
40
32
25
20
32
25
20
X1
C1
CSA40.00MXZ040
CSA32.00MXZ040
CSA25.00MXZ040
CSA20.00MXZ040
FCR32.0M2G
FCR25.0M2G
FCR20.0M2G
µ
PD70208H, 70216H-10/12/16), VDD = 5 V ±5%
Recommended
Constant
C1 [pF]
3
5
5
10
5
5
10
C2 [pF]
3
5
5
10
5
5
10
(2) External clock input
X1
External Clock
X2
or
High-speed
CMOS
Inverter
X1
High-speed
CMOS
Inverter
External Clock
Caution The high-speed CMOS inverter should be as close as possible to the X1 and X2 pins.
74
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
X2
Open

16.2 AT 3 V OPERATION
OPERATING RANGE
E, P, X, M Masks Others
µ
PD70208H, 70216H-10/12/16 VDD = 3 V ±10%
µ
PD70208H, 70216H-20 — VDD = 3 V ±10%
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS (TA = 25 °C)
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
Parameter
Supply voltage
Input voltage
Clock input voltage
Output voltage
Operating ambient temperature
Storage temperature
Symbol Test Conditions Rating Unit
VDD
VI
VK
VO
TA
Tstg
VDD = 3 V ±10%
–0.5 to +7.0 V
–0.5 to VDD + 0.3 V
–0.5 to VDD + 1.0 V
–0.5 to VDD + 0.3 V
–40 to +85 °C
–65 to +150 °C
Cautions 1. Do not directly connect the output pins of two or more IC products and do not directly connect
the output pins to V
DD or VCC and GND. However, open-drain pins or open-collector pins may be
connected directly. Moreover, an external circuit whose timing is designed to avoid output
collision can be connected to pins that go into a high-impedance state.
2. If even one of the above parameters exceeds the absolute maximum rating even momentarily, the
quality of the program may be degraded. Absolute maximum ratings, therefore, are the values
exceeding which the product may be physically damaged. Use the program keeping all the
parameters within these rated values.
The standards and conditions shown in DC and AC Characteristics below specify the range within
which the normal operation of the product is guaranteed.
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
75

µ
PD70208H, 70216H
DC CHARACTERISTICS (TA = –40 to +85 °C, VDD = 3 V ±10%)
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
Input voltage high VIH Except RESET 0.7 VDD VDD+0.3 V
RESET 0.8 VDD VDD+0.3
Input voltage low VIL Except RESET –0.5 0.2 VDD V
RESET
Clock input voltage high VKH 0.8 VDD VDD+0.5 V
Clock input voltage low VKL –0.5 0.2 VDD V
Output voltage high VOH IOH = –2.5 mA 0.7 VDD V
IOH = –100 µAVDD – 0.4
Output voltage low VOL Except END/TC : IOL = 2.5 mA 0.4 V
END/TC : IOL = 5.0 mA
Input leak current high ILIH VI = VDD 10
Input leak current low ILIL VI = 0 V : Except INTP –10
INTP input current low ILIPL VI = 0 V : INTP input –300
Output leak current high ILOH VO = VDD 10
Output leak current low ILOL VO = 0 V –10
Latch leak current high ILLH VI = 3.0 V –50 –300
Latch leak current low ILLL VI = 0.8 V 50 300
Latch inversion current (L → H) IILH 400
Latch inversion current (H → L) IILL –400
Supply current
Note
IDD E, P, X, M On Operation 3.0 fX 5.5 fX mA
masks On standby (HALT) 0.9 fX 1.5 fX
On standby (STOP) 30
Others On Operation 2.5 fX 4.0 fX mA
On standby (HALT) 0.9 fX 1.5 fX
On standby (STOP) 30
µ
A
µ
A
µ
A
µ
A
µ
A
µ
A
µ
A
µ
A
µ
A
µ
A
µ
A
Note The unit of constant values (0.9, 1.5, 2.5, 3.0, 4.0 and 5.5) is mA/MHz.
CAPACITANCE (TA = 25˚C, VDD = 0 V)
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
Input capacitance CI fC = 1 MHz 10 pF
Input/output capacitance CIO 0 V other than test pin. 15 pF
76
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00

µ
PD70208H, 70216H
AC CHARACTERISTICS
(1)µPD70208H, 70216H-10/12/16 (TA = –40 to +85 °C, VDD = 3 V ±10%) (1/3)
Output Pin Load Capacitance: CL = 100 pF
µ
External clock input cycle
External clock input high-level width (VKH=0.8 VDD)
External clock input low-level width (VKL=0.2 VDD)
External clock input rise time (0.2 VDD→0.8 VDD)
External clock input fall time (0.8 VDD→0.2 VDD)
Clock output cycle
Clock output high-level width (VOH=0.7 VDD)
Clock output low-level width (VOL=0.2 VDD)
Clock output rise time (0.2 VDD→0.7 VDD)
Clock output fall time (0.7 VDD→0.2 VDD)
CLKOUT delay time (vs. external clock)
Input rise time (except external clock) (0.2 VDD→0.7 VDD)
Input fall time (except external clock) (0.7 VDD→0.2 VDD)
Output rise time (except CLKOUT) (0.2 VDD→0.7 VDD)
Output fall time (except CLKOUT) (0.7 VDD→0.2 VDD)
RESET setup time (vs. CLKOUT↓)
RESET hold time (vs. CLKOUT↓)
RESOUT output delay time (vs. CLKOUT↓)
READY inactive setup time (vs. CLKOUT↑)
READY inactive hold time (vs. CLKOUT↑)
READY active setup time (vs. CLKOUT↑)
READY active hold time (vs. CLKOUT↑)
NMI setup time (vs. CLKOUT↑)
POLL setup time (vs. CLKOUT↑)
Data setup time (vs. CLKOUT↓)
Data hold time (vs. CLKOUT↓)
CLKOUT → address delay time
CLKOUT → address hold time
CLKOUT↓ → PS delay time
CLKOUT↓ → PS float delay time
Address setup time (vs. ASTB↓)
CLKOUT↓ → address float delay time
CLKOUT↓ → ASTB↑ delay time
CLKOUT↑ → ASTB↓ delay time
ASTB high-level width
Note 1
Note 1
Note 2
Note 3
PD70208H-10
µ
PD70216H-10
MIN. MAX. MIN. MAX. MIN. MAX.
tCYX 100 DC 83 DC 62.5 DC ns
<1>
tXXH 40 30 20 ns
<2>
tXXL 40 30 20 ns
<3>
tXR 10 10 10 ns
<4>
tXF 10 10 10 ns
<5>
tCYK 200 DC 166 DC 125 DC ns
<6>
tKKH 0.5tCYK–7 0.5tCYK–7 0.5tCYK–7 ns
<7>
tKKL 0.5t CYK–7 0.5tCYK–7 0.5t CYK–7 ns
<8>
tKR 777ns
<9>
tKF 777ns
<10>
tDXK 75 65 55 ns
<11>
tIR 20 20 20 ns
<12>
tIF 12 12 12 ns
<13>
tOR 20 20 20 ns
<14>
tOF 12 12 12 ns
<15>
tSRESK 25 25 25 ns
<16>
tHKRES 35 35 35 ns
<17>
tDKRES 580570560ns
<18>
tSRYLK 20 20 15 ns
<19>
tHKRYL 30 30 25 ns
<20>
tSRYHK 20 20 15 ns
<21>
tHKRYH 30 30 25 ns
<22>
tSNMIK 15 15 15 ns
<23>
tSPOLK 20 20 20 ns
<24>
tSDK 20 20 15 ns
<25>
tHKD 555ns
<26>
tDKA 575565555ns
<27>
tHKA 555ns
<28>
tDKP 580570560ns
<29>
tFKP 580570560ns
<30>
tSAST tKKL–30 tKKL–30 t KKL–30 ns
<31>
tFKA 580570560ns
<32>
tDKSTH 565555545ns
<33>
tDKSTL 570560550ns
<34>
tSTST tKKL–10 tKKL–10 tKKL–10 ns
<35>
µ
PD70208H-12
µ
PD70216H-12 UnitSymbol Parameter
µ
PD70208H-16
µ
PD70216H-16
Notes 1. When reset with the minimum pulse width or when guaranteeing the RESOUT output timing.
2. Specifications also corresponding to the QS0, QS1, and BUSLOCK signals, and A16/PS0-A19/PS3, UBE,
BUFEN, BUFR/W, MRD, IORD, MWR, IOWR, and BS0-BS2 signals at HLDRQ/HLDAK timing.
3. Specifications also corresponding to the A16/PS0-A19/PS3, UBE, BUFEN, BUFR/W, MRD, IORD, MWR,
IOWR, and BS0-BS2 signals at HLDRQ/HLDAK timing.
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
77

(1)µPD70208H, 70216H-10/12/16 (TA = –40 to +85 °C, VDD = 3 V ±10%) (2/3)
µ
PD70208H-10
µ
PD70216H-10
MIN. MAX. MIN. MAX. MIN. MAX.
ASTB↓ → address hold time
CLKOUT → control 1
CLKOUT → control 2
Address float → RD↓ delay time
CLKOUT↓ → RD↓ delay time
CLKOUT↓ → RD↑ delay time
RD↑ → address delay time
RD low-level width
BUFEN↑ → BUFR/W delay time (read cycle)
CLKOUT↓ → data output delay time
CLKOUT↓ → data float delay time
WR low-level width
WR↑ → BUFEN↑ or BUFR/W↓ (write cycle)
CLKOUT↑ → BS↓ delay time
CLKOUT↓ → BS↑ delay time
HLDRQ setup time (vs. CLKOUT↓)
CLKOUT↓ → HLDAK delay time
CLKOUT↑ → DMAAK delay time
CLKOUT↓ → DMAAK delay time (cascade mode)
WR low-level width DMA extended write
(DMA cycle)
RD↓ WR↓ delay time (vs. DMAAK↓)
DMAAK↑ delay time (vs. RD↑)
RD↑ delay time (vs. WR↑)
TC output delay time (vs. CLKOUT↑)
TC OFF delay time (vs. CLKOUT↑)
TC low-level width
TC pull-up delay time (vs. CLKOUT↑)
END setup time (vs. CLKOUT↑)
END low-level width
DMARQ setup time (vs. CLKOUT↑)
INTPn low-level width
RXD setup time (vs. SCU internal clock↓)
RXD hold time (vs. SCU internal clock↓)
CLKOUT↓ → SRDY delay time
Note 1
Note 2
delay time
delay time
DMA normal write
tHSTA tKKH–30 t KKH–30 tKKH–20 ns
<36>
tDKCT1 590580570ns
<37>
tDKCT2 580570560ns
<38>
tDAFRL 000ns
<39>
tDKRL 595585575ns
<40>
tDKRH 590580570ns
<41>
tDRHA tCYK–70 tCYK–60 tCYK–50 ns
<42>
tRR 2tCYK–70 2tCYK–60 2tCYK–50 ns
<43>
tDBECT t KKL–30 tKKL–30 tKKL–20 ns
<44>
tDKD 580570560ns
<45>
tFKD 580570560ns
<46>
tWW 2tCYK–50 2tCYK–50 2tCYK–40 ns
<47>
tDWCT t KKL–30 tKKL–30 tKKL–20 ns
<48>
tDKBL 580570560ns
<49>
tDKBH 580570560ns
<50>
tSHQK 25 25 20 ns
<51>
tDKHA 590580570ns
<52>
tDKHDA 580570560ns
<53>
tDKLDA 5 110 5 100 5 90 ns
<54>
tWW1 2tCYK–50 2tCYK–50 2tCYK–40 ns
<55>
tWW2 t CYK–50 tCYK–50 tCYK–40 ns
<56>
tDDARW tKKH–40 t KKH–40 tKKH–30 ns
<57>
t
DRHDAH
<58>
tDWHRH 555ns
<59>
tDKTCL 580570560ns
<60>
tDKTCF 580570560ns
<61>
tTCTCL tCYK–25 tCYK–25 tCYK–15 ns
<62>
tDKTCH Note 3 Note 4 Note 4 ns
<63>
tSEDK 45 40 35 ns
<64>
tEDEDL 140 120 100 ns
<65>
tSDQK 45 40 35 ns
<66>
tIPIPL 100 100 100 ns
<67>
tSRX 1000 1000 1000 ns
<68>
tHRX 1000 1000 1000 ns
<69>
tDKSR 150 150 150 ns
<70>
tKKL–40 t KKL–40 tKKL–30 ns
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
Output Pin Load Capacitance: CL = 100 pF
µ
µ
PD70208H-12
µ
PD70216H-12
PD70208H-16
µ
PD70216H-16 Unit Parameter Symbol
Notes 1. MWR and IOWR signals in DMA cycle
2. MWR and IOWR signals in CPU cycles and BUFEN, BUFR/W, INTAK and REFRQ signals.
3. t KKH + 2tCYK – 20 (Reference value when a 1.1-kΩ pull-up resistor is connected)
4. t KKH + 2tCYK – 10 (Reference value when a 1.1-kΩ pull-up resistor is connected)
78
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00

(1)µPD70208H, 70216H-10/12/16 (TA = –40 to +85 °C, VDD = 3 V ±10%) (3/3)
µ
PD70208H-10
µ
PD70216H-10 Unit Parameter
MIN. MAX. MIN. MAX. MIN. MAX.
60 55 50 ns
tKKL–50 t KKL–40 tKKL–30 ns
TOUT1↓→ TXD delay time
TCTL2 setup time (vs. CLKOUT↓)
TCTL2 setup time (vs. TCLK↑)
TCTL2 hold time (vs. CLKOUT↓)
TCTL2 hold time (vs. TCLK↑)
TCTL2 high-level width
TCTL2 low-level width
TOUT output delay time (vs. CLKOUT↓)
TOUT output delay time (vs. TCLK↓)
TOUT output delay time (vs. TCTL2↓)
TCLK rise time
TCLK fall time
TCLK high-level width
TCLK low-level width
TCLK cycle
Access interval
REFRQ↑ delay time (vs. MRD↑)
RESET pulse width
Note 1
Note 2
Note 3
Symbol
<71>
tDTX 500 500 500 ns
<72>
tSGK 50 50 50 ns
<73>
tSGTK 50 50 50 ns
<74>
tHKG 100 100 100 ns
<75>
tHTKG 50 50 50 ns
<76>
tGGH 50 50 50 ns
<77>
tGGL 50 50 50 ns
<78>
tDKTO 200 200 200 ns
<79>
tDTKTO 150 150 150 ns
<80>
tDGTO 120 120 120 ns
<81>
tTKR 25 25 25 ns
<82>
tTKF 25 25 25 ns
<83>
t
TKTKH
<84>
tTKTKL 60 55 50 ns
<85>
tCYTK 200 DC 166 DC 125 DC ns
<86>
tAI 2tCYK–70 2tCYK–60 2tCYK–50 ns
<87>
t
DRQHRH
<88>
tWRESL 4tCYK 4tCYK 4tCYK ns
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
Output Pin Load Capacitance: CL = 100 pF
µ
PD70208H-12
µ
PD70216H-12
µ
PD70208H-16
µ
PD70216H-16
Notes 1. Specification to guarantee read/write recovery time for I/O device.
2. Specification to guarantee that REFRQ↑ is always later than MRD↑.
Only guaranteed when the EREF bit of the SCTL register is 0.
3. When using internal clock generator by connecting a resonator to the X1 and X2 pins, the oscillation
stabilization time must be added at power-ON. Because the oscillation stabilization time varies depending
on the characteristics of the resonator and oscillator used, evaluate the oscillation stabilization time with the
resonator and oscillator actually used.
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
79

(2)µPD70208H, 70216H-20 (TA = –40 to +85 °C, VDD = 3 V ±10%) (1/3)
External clock input cycle
External clock input high-level width (VKH=0.8 VDD)
External clock input low-level width (VKL=0.2 VDD)
External clock input rise time (0.2 VDD→0.8 VDD)
External clock input fall time (0.8 VDD→0.2 VDD)
Clock output cycle
Clock output high-level width (VOH=0.7 VDD)
Clock output low-level width (VOL=0.2 VDD)
Clock output rise time (0.2 VDD→0.7 VDD)
Clock output fall time (0.7 VDD→0.2 VDD)
CLKOUT delay time (vs. external clock)
Input rise time (except external clock) (0.2 VDD→0.7 VDD)
Input fall time (except external clock) (0.7 VDD→0.2 VDD)
Output rise time (except CLKOUT) (0.2 VDD→0.7 VDD)
Output fall time (except CLKOUT) (0.7 VDD→0.2 VDD)
RESET setup time (vs. CLKOUT↓)
RESET hold time (vs. CLKOUT↓)
RESOUT output delay time (vs. CLKOUT↓)
READY inactive setup time (vs. CLKOUT↑)
READY inactive hold time (vs. CLKOUT↑)
READY active setup time (vs. CLKOUT↑)
READY active hold time (vs. CLKOUT↑)
NMI setup time (vs. CLKOUT↑)
POLL setup time (vs. CLKOUT↑)
Data setup time (vs. CLKOUT↓)
Data hold time (vs. CLKOUT↓)
CLKOUT → address delay time
CLKOUT → address hold time
CLKOUT ↓ → PS delay time
CLKOUT ↓ → PS float delay time
Address setup time (vs. ASTB↓)
CLKOUT ↓ → address float delay time
CLKOUT ↓ → ASTB ↑ delay time
CLKOUT ↑ → ASTB ↓ delay time
ASTB high-level width
Note 1
Note 1
Note 2
Note 3
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
Output Pin Load Capacitance: CL = 100 pF
µ
PD70208H-20
µ
PD70216H-20 Unit Parameter Symbol
MIN. MAX.
tCYX 50 DC ns
<1>
tXXH 19 ns
<2>
tXXL 19 ns
<3>
tXR 5ns
<4>
tXF 5ns
<5>
tCYK 100 DC ns
<6>
tKKH 0.5tCYK–7 ns
<7>
tKKL 0.5tCYK –7 ns
<8>
tKR 7ns
<9>
tKF 7ns
<10>
tDXK 45 ns
<11>
tIR 15 ns
<12>
tIF 10 ns
<13>
tOR 15 ns
<14>
tOF 10 ns
<15>
tSRESK 25 ns
<16>
tHKRES 25 ns
<17>
tDKRES 550ns
<18>
tSRYLK 15 ns
<19>
tHKRYL 20 ns
<20>
tSRYHK 15 ns
<21>
tHKRYH 20 ns
<22>
tSNMIK 15 ns
<23>
tSPOLK 20 ns
<24>
tSDK 15 ns
<25>
tHKD 5ns
<26>
tDKA 550ns
<27>
tHKA 5ns
<28>
tDKP 550ns
<29>
tFKP 550ns
<30>
tSAST tKKL–20 ns
<31>
tFKA t HKA 50 ns
<32>
tDKSTH 40 ns
<33>
tDKSTL 45 ns
<34>
tSTST tKKL–10 ns
<35>
Notes 1. When reset with the minimum pulse width or when guaranteeing the RESOUT output timing.
2. Specifications also corresponding to the QS0, QS1, and BUSLOCK signals, and A16/PS0-A19/PS3, UBE,
BUFEN, BUFR/W, MRD, IORD, MWR, IOWR, and BS0-BS2 signals at HLDRQ/HLDAK timing.
3. Specifications also corresponding to the A16/PS0-A19/PS3, UBE, BUFEN, BUFR/W, MRD, IORD, MWR,
IOWR, and BS0-BS2 signals at HLDRQ/HLDAK timing.
80
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00

(2)µPD70208H, 70216H-20 (TA = –40 to +85 °C, VDD = 3 V ±10%) (2/3)
ASTB ↓ → address hold time
CLKOUT → control 1
CLKOUT → control 2
Address float → RD ↓ delay time
CLKOUT ↓ → RD ↓ delay time
CLKOUT ↓ → RD ↑ delay time
RD ↑ → address delay time
RD low-level width
BUFEN ↑ → BUFR/W delay time (read cycle)
CLKOUT ↓ → data output delay time
CLKOUT ↓ → data float delay time
WR low-level width
WR ↑ → BUFEN ↑ or BUFR/W ↓ (write cycle)
CLKOUT ↑ → BS ↓ delay time
CLKOUT ↓ → BS ↑ delay time
HLDRQ setup time (vs. CLKOUT ↓)
CLKOUT ↓ → HLDAK delay time
CLKOUT ↑ → DMAAK delay time
CLKOUT ↓ → DMAAK delay time (cascade mode)
WR low-level width (DMA cycle) DMA extended write
RD ↓, WR ↓ delay time (vs. DMAAK ↓)
DMAAK ↑ delay time (vs. RD ↑)
RD ↑ delay time (vs. WR ↑)
TC output delay time (vs. CLKOUT ↑)
TC OFF delay time (vs. CLKOUT ↑)
TC low-level width
TC pull-up delay time (vs. CLKOUT ↑)
END setup time (vs. CLKOUT ↑)
END low-level width
DMARQ setup time (vs. CLKOUT ↑)
INTPn low-level width
RxD setup time (vs. SCU internal clock ↓)
RxD hold time (vs. SCU internal clock ↓)
CLKOUT ↓ → SRDY delay time
Note 1
Note 2
delay time
delay time
DMA normal write
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
Output Pin Load Capacitance: CL = 100 pF
µ
PD70208H-20
µ
PD70216H-20 Unit Parameter Symbol
MIN. MAX.
tHSTA tKKH–20 ns
<36>
tDKCT1 560ns
<37>
tDKCT2 555ns
<38>
tDAFRL 0ns
<39>
tDKRL 565ns
<40>
tDKRH 560ns
<41>
tDRHA tCYK–40 ns
<42>
tRR 2tCYK–40 ns
<43>
tDBECT tKKL–20 ns
<44>
tDKD 555ns
<45>
tFKD 555ns
<46>
tWW 2tCYK–40 ns
<47>
tDWCT tKKL–20 ns
<48>
tDKBL 555ns
<49>
tDKBH 555ns
<50>
tSHQK 15 ns
<51>
tDKHA 560ns
<52>
tDKHDA 555ns
<53>
tDKLDA 580ns
<54>
tWW1 2tCYK–40 ns
<55>
tWW2 tCYK–40 ns
<56>
tDDARW tKKH–30 ns
<57>
t
DRHDAH
<58>
tDWHRH 3ns
<59>
tDKTCL 55 ns
<60>
tDKTCF 55 ns
<61>
tTCTCL tCYK–15 ns
<62>
tDKTCH Note 3 ns
<63>
tSEDK 30 ns
<64>
tEDEDL 80 ns
<65>
tSDQK 30 ns
<66>
tIPIPL 80 ns
<67>
tSRX 500 ns
<68>
tHRX 500 ns
<69>
tDKSR 100 ns
<70>
tKKL–30 ns
Notes 1. MWR and IOWR signals in DMA cycle
2. MWR and IOWR signals in CPU cycles and BUFEN, BUFR/W, INTAK and REFRQ signals.
3. tKKH + 2tCYK – 10 (reference value when a 1.1-kΩ pull-up resistor is connected)
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
81

(2)µPD70208H, 70216H-20 (TA = –40 to +85 °C, VDD = 3 V ±10%) (3/3)
TOUT1 ↓ → TxD delay time
TCTL2 setup time (vs. CLKOUT ↓)
TCTL2 setup time (vs. TCLK ↑)
TCTL2 hold time (vs. CLKOUT ↓)
TCTL2 hold time (vs. TCLK ↑)
TCTL2 high-level width
TCTL2 low-level width
TOUT output delay time (vs. CLKOUT ↓)
TOUT output delay time (vs. TCLK ↓)
TOUT output delay time (vs. TCTL2 ↓)
TCLK rise time
TCLK fall time
TCLK high-level width
TCLK low-level width
TCLK cycle
Access interval
REFRQ ↑ delay time (vs. MRD ↑)
RESET pulse width
Note 1
Note 2
Note 3
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
Output Pin Load Capacitance: CL = 100 pF
µ
PD70208H-20
µ
PD70216H-20
MIN. MAX.
tDTX 200 ns
<71>
tSGK 40 ns
<72>
tSGTK 40 ns
<73>
tHKG 80 ns
<74>
tHTKG 40 ns
<75>
tGGH 40 ns
<76>
tGGL 40 ns
<77>
tDKTO 150 ns
<78>
tDTKTO 100 ns
<79>
tDGTO 90 ns
<80>
tTKR 25 ns
<81>
tTKF 25 ns
<82>
t
TKTKH
<83>
tTKTKL 45 ns
<84>
tCYTK 100 DC ns
<85>
tAI 2tCYK–40 ns
<86>
t
DRQHRH
<87>
tWRESL 4tCYK ns
<88>
45 ns
tKKL–30 ns
Unit Parameter Symbol
Notes 1. This rating is to guarantee the read/write recovery time for the I/O device.
2. This rating is to guarantee that REFRQ ↑ is always behind MRD ↑, and is guaranteed only when the EREF
bit of the STCL register is 0.
3. When using internal clock generator by connecting a resonator to the X1 and X2 pins, the oscillation
stabilization time must be added at power-ON. Because the oscillation stabilization time varies depending
on the characteristics of the resonator and oscillator used, evaluate the oscillation stabilization time with the
resonator and oscillator actually used.
82
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00

RECOMMENDED OSCILLATOR
The clock input circuits (1) and (2) shown below are recommended.
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
(1) Ceramic resonator connection (T
Cautions 1. The oscillator should be as close as possible to the X1 and X2 pins.
2. No other signal lines should pass through the area enclosed in dashed line.
3. V40HL, V50HL and resonator matching requires careful evaluation.
4. The values of the oscillator constants C1 and C2 depend on the characteristics of the
resonator used. Evaluate them with the resonator actually used.
Manufacturer
Murata Mfg.
Co., Ltd.
TDK Corp.
A = –40 to +85 °C, VDD = 3 V ±10%
X2
C2
Note
Frequency
(fXX) [MHz]
20
16
12.5
10
20
16
10
X1
C1
Product Name
CSA20.00MXZ040
CSA16.00MXZ040
CSA16.00MXW0C3
CSA12.5MTZ
CSA12.5MTW
CSA10.0MTZ
CST10.0MXW
FCR20.0M2G
FCR16.0M2G
FCR10.0MC
Note
)
Recommended
Constant
C1 [pF]
10
15
–
30
–
30
–
10
15
–
C2 [pF]
10
15
–
30
–
30
–
10
15
–
Note Use the CAS20.00MXZ040 within the range of VDD = 2.9 to 3.3 V.
(2) External clock input
X1
External Clock
X2
High-speed
CMOS
Inverter
X1
or
External Clock
X2
Open
High-speed
CMOS
Inverter
Caution The high-speed CMOS inverter should be as close as possible to the X1 and X2 pins.
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
83

AC Test Input Waveform (Except X1 and X2) (at 5 V operation)
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
2.4 V
0.4 V
2.2 V
0.8 V
Test
points
AC Test Output Test Points (at 5 V operation)
2.2 V
0.8 V
Test
points
AC Test Input Waveform (Except X1 and X2) (at 3 V operation)
0.8 V
DD
0.4 V
0.7 V
0.2 V
DD
DD
Test
points
AC Test Output Waveform (at 3 V operation)
2.2 V
0.8 V
2.2 V
0.8 V
0.7 V
0.2 V
DD
DD
0.7 V
0.2 V
DD
DD
Test
points
0.7 V
0.2 V
DD
DD
Load Conditions
DUT
L
C = 100pF
Caution If the load capacitance exceeds 100 pF due to the configuration of the circuit, the load capacitance
of this device should be reduced to 100 pF or less by insertion of a buffer, etc.
84
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00

µ
PD70208H, 70216H
Clock Timing
External Clock (Input)
(X1)
CLKOUT (Output)
Reset Timing
CLKOUT (Output)
RESET (Input)
<11>
<16>
<7>
<4> <5>
<11>
<6>
<88>
<8>
<17>
<10>
Note
<1>
<2>
<3>
<9>
<16>
RESOUT (Output)
Ready Timing (1)
CLKOUT (Output)
READY (Input)
Ready Timing (2)
CLKOUT (Output)
<18>
T1 T2 T3 T4 T1
<22>
<21>
Variation Range Variation Range
T1 T2 T3 TW T4
<18>
READY (Input)
Variation Range
Note Variation range
<19>
<22>
<21>
Note
<20>
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
Variation Range
85

Read Timing
CLKOUT (Output)
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
T4 T1 T2 T3 T4
A16/PS0A19/PS3
(Output)
A8-A15 (Output): V40HL
UBE (Output): V50HL
AD0-AD7 (I/O): V40HL
AD0-AD15 (I/O): V50HL
ASTB (Output)
BUFEN (Output)
BUFR/W (Output)
<27><28>
A16-A19 PS0-PS3
<27>
<27>
<33>
<38><39>
<31>
<31>
A0-A7
(Output)
A0-A15
<35>
(Output)
<34>
<28>
:
V40HL
:
V50HL
<36>
<40><41>
<29>
<32>
<25>
D0-D7(Intput)
D0-D15(Intput)
Note
<30>
: V40HL
: V50HL
<26>
<38><38>
<38>
<44>
MRD (Output)
IORD (Output)
BS0-BS2 (Output)
<49><
Bus Status
Note High-level signal is output in case of internal access.
Remark A dashed line indicates high impedance.
Note
<43><42>
50
>
86
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00

Write Timing
CLKOUT (Output)
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
T4 T1 T2 T3 T4
A16/PS0A19/PS3
(Output)
A8-A15 (Output): V40HL
UBE (Output): V50HL
AD0-AD7 (I/O): V40HL
AD0-AD15 (I/O): V50HL
ASTB (Output)
BUFEN (Output)
BUFR/W (Output)
<27> <28>
A16-A19 PS0-PS3
<27> <29>
<31>
<27><45><46>
<33>
A0-A7 (Output)
A0-A15 (Output)
<31>
<35>
<38>
<38>
<34>
: V40HL
: V50HL
<28>
<36>
D0-D7 (Output)
D0-D15 (Output)
Note
: V40HL
: V50HL
<48>
<30>
<38>
<38>
<38><38>
MWR (Output)
IOWR (Output)
BS0-BS2 (Output)
<49>
Bus Status
Note High-level signal is output in case of internal access.
Remark A dashed line indicates high impedance.
Note
<47>
<50>
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
87

Status Timing
CLKOUT (Output)
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
T4 T1 T2 T3 T4
A16/PS0A19/PS3
(Output)
A8-A15 (Output): V40HL
UBE (Output): V50HL
AD0-AD7 (I/O): V40HL
AD0-AD15 (I/O): V50HL
ASTB (Output)
BS0-BS2 (Output)
Note 1
<27>
<27>
<27><28>
A0-A7 (Output)
A0-A15 (Output)
<33>
<49>
<27><40>
<28>
A16-A19 PS0-PS3
<31>
<31>
: V40HL
: V50HL
<36>
<35>
<34>
Bus Status
<29>
<32>
<39>
<25>
D0-D7 (Input)
D0-D15 (Input)
<50>
Note 2
<43>
<30>
<26>
: V40HL
: V50HL
<42>
<41>
QS0, QS1 (Output)
Notes 1. MRD, IORD, MWR, IOWR (all output)
2. High-level signal is output in case of internal access.
Remark A dashed line indicates high impedance.
88
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00

Interrupt Acknowledge Timing (V40HL)
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
CLKOUT (Output)
A8-A15 (Output)
AD0-AD7 (I/O)
ASTB (Output)
INTAK (Output)
BUFEN (Output)
BUFR/W (Output)
BUSLOCK (Output)
T1 T2 T3
<32>
<38>
<38>
Note 3 Note 3
<27>
T4 T1
<27>
<38>
Note 1
T2 T3 TI
Note 1
<32>
<25>
Note 2
Vector Number
<26>
µ
Notes 1. Slave address in case of interrupt from external
PD71059.
Invalid data in case of interrupt from internal ICU.
2. Data read as vector address in case of interrupt from external µPD71059.
High impedance in case of interrupt from internal ICU.
* 3. Low-level output in case of interrupt from external µPD71059.
High-level output in case of interrupt from internal ICU.
Remark A dashed line indicates high impedance.
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
89

Interrupt Acknowledge Timing (V50HL)
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
<38>
<27>
T2
Note 3
T3
TI×3T4 T1
<38>
T1
CLKOUT (Output)
AD0-AD15 (I/O)
ASTB (Output)
<38>
INTAK (Output)
BUFEN (Output)
BUFR/W (Output)
BUSLOCK (Output)
Notes 1. Slave address in case of interrupt from external µPD71059.
Invalid data in case of interrupt from internal ICU.
2. Data read as vector address in case of interrupt from external µPD71059.
High impedance in case of interrupt from internal ICU.
* 3. Low-level output in case of interrupt from external µPD71059.
High-level output in case of interrupt from internal ICU.
<27>
Note 1
T2 T3 TI
<32><32>
<25>
Note 2
Vector Number
Note 3
<26>
Remark A dashed line indicates high impedance.
90
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00

HLDRQ/HLDAK Timing (1)
CLKOUT (Output)
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
TI TI T4 T1
<51>
HLDRQ (Input)
<52>
HLDAK (Output)
<32>
Note
<32>
BS0-BS2 (Output)
<51>
<52>
<27>
Note A16/PS0 to A19/PS3, UBE, BUFEN, BUFR/W, MRD, IORD, MWR, IOWR (all output): V40HL, V50HL
A8-A15 (output): V40HL AD0-AD7 (input/output): V40HL AD0-AD15 (input/output) V50HL
Remark A dashed line indicates high impedance.
HLDRQ/HLDAK Timing (2)
<27>
TI
CLKOUT (Output)
HLDRQ (Input)
<52>
HLDAK (Output)
Note
BS0-BS2 (Output)
TI TI TI T4 T1 T2
<51>
Variation Range
<6>
or longer
<27>
Highest-Priority Refresh
Cycle or DMA Cycle
<49>
Highest-Priority Refresh
Cycle or DMA Cycle
Note A16/PS0 to A19/PS3, UBE, BUFEN, BUFR/W, MRD, IORD, MWR, IOWR (all output): V40HL, V50HL
A8-A15 (output): V40HL AD0-AD7 (input/output): V40HL AD0-AD15 (input/output) V50HL
Remark A dashed line indicates high impedance.
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
91

POLL, NMI Input Timing
BUSLOCK Output Timing
CLKOUT (Output)
POLL (Input)
NMI (Input)
<24>
<23>
Tn
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
CLKOUT (Output)
BUSLOCK (Output)
Access Interval
MRD (Output)
IORD (Output)
MWR (Output)
IOWR (Output)
<27>
<86>
<27>
<86>
<86>
<86>
92
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00

Refresh Timing (V40HL)
CLKOUT (Output)
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
T4 T1 T2 T3 T4
A16/PS0A19/PS3
(Output)
A8-A15 (Output)
AD0-AD7 (I/O)
ASTB (Output)
BUFEN (Output)
MRD (Output)
<27>
Invalid
<27>
<27>
<33> <36>
<31>
Refresh Address
<35>
<34>
<38>
<28>
<29>
<28>
<32>
<40>
Refresh Address
<39>
<43>
<41>
<38>
REFRQ (Output)
<49><50>
BS0-BS2 (Output)
BS2 = 1, BS1 = 0, BS0 = 1
Remark A dashed line indicates high impedance.
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
93

Refresh Timing (V50HL)
CLKOUT
(Output)
A16/PS0A19/PS3
(Output)
UBE
(Output)
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
T4 T1 T2 T3 T4
<27>
Invalid
<27>
<28>
<29>
AD0-AD15 (I/O)
(Output)
ASTB
BUFEN
(Output)
MRD
(Output)
REFRQ
(Output)
BS0-BS2
(Output)
<27>
<33>
<49><50>
<31>
Refresh Address
<35>
<34>
<38>
BS2 = 1, BS1 = 0, BS0 = 1
<28>
<32>
<36>
<39>
<40>
<43>
<41>
<38>
Remark A dashed line indicates high impedance.
94
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00

TCU Timing (1)
CLKOUT (Output)
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
<72>
TCTL2 (Input)
TOUTn (Output)
(n=1, 2)
Note Applies to TOUT2 output.
TCU Timing (2)
<81>
TCLK (Input)
<82>
<74>
<80>
<77>
Note
<72>
<76>
<85><83>
<74>
<78>
TCTL2 (Input)
TOUTn (Output)
(n=1, 2)
Note Applies to TOUT2 output.
<73>
<75>
Note
<84>
<77>
<76>
<73>
<75>
<79><80>
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
95

SCU Timing
RxD (Input)
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
TOUT1 (Output)
TxD (Output)
CLKOUT (Output)
SRDY (Output)
<68>
<69>
16 Cycles or 64 Cycles
16 Cycles or 64 Cycles
<71>
<70>
96
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00

DMAU Timing (1)
CLKOUT (Output)
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
T4 T1 T2 T3 T4
<49><50>
BS0-BS2 (Output)
ASTB (Output)
A16/PS0A19/PS3
(Output)
A8-A15
(Output):
UBE
(Output):
AD0-AD7 (I/O): V40HL
AD0-AD15 (I/O): V50HL
DMAAK (Output)
V40HL
V50HL
MRD (Output)
IORD (Output)
MWR (Output)
IOWR (Output)
Bus Status
<33> <36>
<35>
<34>
<27>
<27>
<27><28>
<29>
<28>
<32>
<53>
<40>
<57>
<37>
<57>
<39>
<37>
Note
<43>
<55>
<56>
<41>
<37>
<53>
<58>
<59>
Note Low-level signal is output in extended write mode.
Remark A dashed line indicates high impedance.
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
97

DMAU Timing (2)
CLKOUT (Output)
TC (Input/Output)
T1 T2 T3 T4
<60>
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
<61>
<63>
END (Input/Output)
CLKOUT (Output)
DMARQn (Input)
(n=0-3)
<64>
<65>
<62>
<66>
98
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00

DMAU Timing (3) (Cascade Mode)
In Normal Operation:
CLKOUT (Output)
DMARQ (Input)
DMAAK (Output)
When Refresh Cycle is Inserted:
<66>
T1 T4
<66>
<54>
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
<54>
CLKOUT (Output)
ICU Timing
DMARQ (Input)
DMAAK (Output)
INTPn (Input)
(n=1-7)
<67>
<54>
<54>
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
99

17. PACKAGE DRAWINGS
80 PIN PLASTIC QFP (14x20)
µ
PD70208H, 70216H
A
B
24
41
40
25
65
80
64
1
F
G
H
M
I
P
S
N
NOTE
1. Controlling dimension millimeter.
2. Each lead centerline is located within 0.15 mm (0.006 inch) of
its true position (T.P.) at maximum material condition.
L
J
CD
K
M
S
detail of lead end
S
Q
ITEM MILLIMETERS INCHES
A 23.6±0.4 0.929±0.016
B 20.0±0.2 0.795
C 14.0±0.2 0.551
D 17.6±0.4 0.693±0.016
F
1.0
G
0.8
H 0.37 0.015
I 0.15 0.006
J 0.8 (T.P.) 0.031 (T.P.)
K 1.8±0.2 0.071
L 0.8±0.2 0.031
M 0.17 0.007
N 0.10 0.004
P 2.7±0.1 0.106
Q 0.1±0.1 0.004±0.004
R5°±5° 5°±5°
S
+0.08
–0.07
+0.08
–0.07
3.0 MAX. 0.119 MAX.
R
+0.009
–0.008
+0.009
–0.008
0.039
0.031
+0.003
–0.004
+0.008
–0.009
+0.009
–0.008
+0.003
–0.004
+0.005
–0.004
P80GF-80-3B9-4
100
Data Sheet U13225EJ4V0DS00
 Loading...
Loading...