Page 1
MINIATURE SIGNAL RELAYS
EC2 SERIES (DIP TYPE)
EE2 SERIES (SMD TYPE)
TECHNICAL DATA
Document No. 0170EMDD03VOL01E
Date Published July 2002 P
Printed in Japan
Page 2

MINIATURE SIGNAL RELAYS
EC2 SERIES (DIP TYPE)
EE2 SERIES (SMD TYPE)
TECHNICAL DATA
Page 3

No part of this document may be copied or reproduced in any form or by any means without the
prior written consent of NEC/TOKIN Corporation. NEC/TOKIN Corporation assumes no resposibility
for any errors which may appear in this document.
NEC/TOKIN Corporation does not assume any liability for infringement of patents, copyrights or
other intellectual property rights of third parties by or arising from use of a device described herein
or any other liability arising from use of such device. No license, either express, implied or
otherwise, is granted under any patents, copyrights or other intellectual property rights of NEC
/TOKIN Corporation or others.
While NEC/TOKIN Corporation has been making continuous effort to enhance the reliability of its
electronic components, the possibility of defects cannot be eliminated entirely. To minimize risks
of damage or injury to persons or property arising from a defect in an NEC/TOKIN electronic component,
customers must incorporate sufficient safety measures in its design, such as redundancy,firecontainment, and anti-failure features. NEC/TOKIN devices are classified into the following three
quality grades:
"Standard," "Special," and "Specific". The Specific quality grade applies only to devices
developed based on a customer designated "quality assurance program" for a specific
application. The recommended applications of a device depend on its quality grade, as indicated
below. Customers must check the quality grade of each device before using it in a particular
application.
Standard: Computers, office equipment, communications equipment, test and measurement
equipment, audio and visual equipment, home electronic appliances, machine tools,
personal electronic equipment and industrial robots
Special: Transportation equipment (automobiles, trains, ships, etc.), traffic control systems,
anti-disaster systems, anti-crime systems, safety equipment and medical
equipment (not specifically designed for life support)
Specific: Aircrafts, aerospace equipment, submersible repeaters, nuclear reactor control
systems, life support systems or medical equipment for life support, etc.
The quality grade of NEC/TOKIN devices is "Standard" unless otherwise specified in NEC/TOKIN’s
Data Sheets or Data Books. If customers intend to use NEC/TOKIN devices for applications other
than those specified for Standard quality grade, they should contact an NEC/TOKIN sales representative
in advance.
(Note)
(1) "NEC/TOKIN" as used in this statement means NEC/TOKIN Corporation and also includes
its majority-owned subsidiaries.
(2) "NEC/TOKIN electronic component products" means any electronic component product developed
or manufactured by or for NEC/TOKIN (as defined above).
DE0202
Page 4

CONTENTS
1. Preface ........................................................................................................................................... 1
2. Structure ........................................................................................................................................ 2
3. Basic Characteristics ................................................................................................................... 3
3.1 Switching power ..................................................................................................................................... 3
3.2 Life curve ................................................................................................................................................ 3
3.3 Maximum coil voltage ............................................................................................................................. 4
3.4 Coil temperature rise .............................................................................................................................. 4
3.5 Driving power vs. timing ......................................................................................................................... 5
3.6 Driving pulse width vs. set & reset voltages ........................................................................................... 6
3.7 Thermal characteristics .......................................................................................................................... 7
3.8 Magnetic interference ............................................................................................................................. 8
3.9 High-frequency characteristics ............................................................................................................... 9
3.10 Coil inductance ....................................................................................................................................... 10
3.10.1 Measurement by LCR meter .................................................................................................... 10
3.10.2 Measurement by coil current waveform ................................................................................... 10
3.11 Capacitance ........................................................................................................................................... 11
3.12 Resistance to surge voltage ................................................................................................................... 12
3.13 Current surge interrupt test .................................................................................................................... 13
3.14 Resistance to carrying current ................................................................................................................ 13
4. Distribution of Characteristics .................................................................................................... 14
4.1 Operate & release voltages (set & reset voltages) ................................................................................. 14
4.2 Operate & release times (set & reset times) .......................................................................................... 15
4.3 Transfer time .......................................................................................................................................... 16
4.4 Timing and details .................................................................................................................................. 17
4.5 Contact resistance.................................................................................................................................. 21
4.6 Breakdown voltage ................................................................................................................................. 22
4.7 Thermal Electromotive Force (EMF) (offset voltage between contacts) ................................................ 22
5. Test Data ....................................................................................................................................... 23
5.1 Environmental tests ................................................................................................................................ 24
5.1.1 High-temperature test ................................................................................................................. 24
5.1.2 Low-temperature test ................................................................................................................. 27
5.1.3 Moisture resistance test ............................................................................................................. 29
5.1.4 Heat shock test ........................................................................................................................... 31
5.1.5 Vibration test .............................................................................................................................. 33
5.1.6 Shock test ................................................................................................................................... 35
5.1.7 Resistance to solder heat test (only EC2 series) ....................................................................... 37
5.1.8 Resistance to reflow solder heat test (only EE2 series) ............................................................. 38
5.1.9 Terminal strength test (only EC2 series) .................................................................................... 40
- i -
Page 5

5.2 Contact life tests ..................................................................................................................................... 41
5.2.1 Non-load test A (Mechanical life test, Ta = 25˚C) ....................................................................... 41
5.2.2 Non-load test B (Mechanical life test, T
5.2.3 Resistive load test A (10 m Vdc, 10
a = 85˚C) ....................................................................... 42
µ
A, Ta = 25˚C) ................................................................... 42
5.2.4 Resistive load test B (10 Vdc, 10 mA, Ta = 85˚C) ...................................................................... 43
5.2.5 Resistive load test C (28 Vdc, 100 mA, T
5.2.6 Resistive load test D (50 Vdc, 100 mA, T
a = 85˚C) .................................................................... 43
a = 25˚C) .................................................................... 44
5.2.7 Resistive load test E (50 Vdc, 100 mA, Ta = 85˚C) .................................................................... 44
5.2.8 Inductive load test (48 Vdc, 110 mA, Ta = 25˚C) ........................................................................ 45
5.2.9 Resistive load test F (220 Vdc, 0.14 A, Ta = 25˚C) .................................................................... 45
5.2.10 Resistive load test G (125 Vdc, 0.5 A, T
5.2.11 Resistive load test H (30 Vdc, 1 A, T
a = 25˚C) ...................................................................... 46
a = 25˚C) ........................................................................... 46
- ii -
Page 6
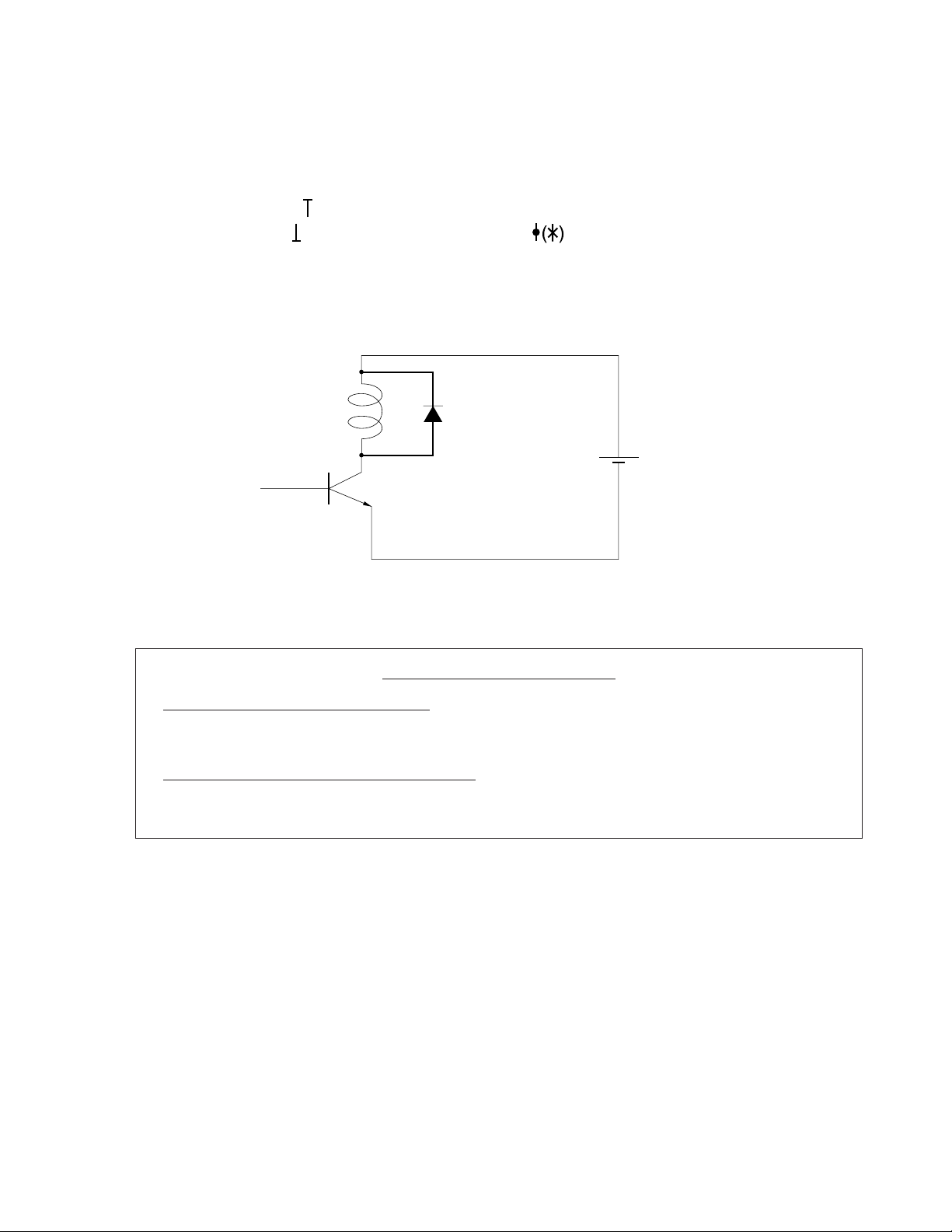
1. Preface
Miniature signal relays are used in a wide range of application fields including communication, measurement, and
factory automation. This document gives the basic characteristics and test data of NEC’s EC2 and EE2 series
miniature signal relays.
Notes 1. The symbol
shown in the graphs throughout this document indicates the maximum value of the data.
Likewise, indicates the minimum value, and indicates the mean value.
2. When a relay is driven by an IC, a protective element such as a diode may be connected in parallel
with the relay coil to protect the IC from damage caused by the counter-electromotive force (EMF) due
to the inductance of the coil. However, unless otherwise specified, the operate time and release time
(set and reset times) shown in this document are measured without such a protective element.
Relay Coil
Tr
Diode
Power Supply
For Right Use of Miniature Relays
DO NOT EXCEED MAXIMUM RATINGS.
Do not use relays under exceeding conditions such as over ambient temperature, over voltage and over
current. Incorrect use could result in abnormal heating, damage to related parts or cause burning.
READ CAUTIONS IN THE SELECTION GUIDE.
Read the cautions described in NEC/TOKIN’s “Miniature Relays” (0123EMDD03VOL01E) when you choose
relays for your application.
1
Page 7
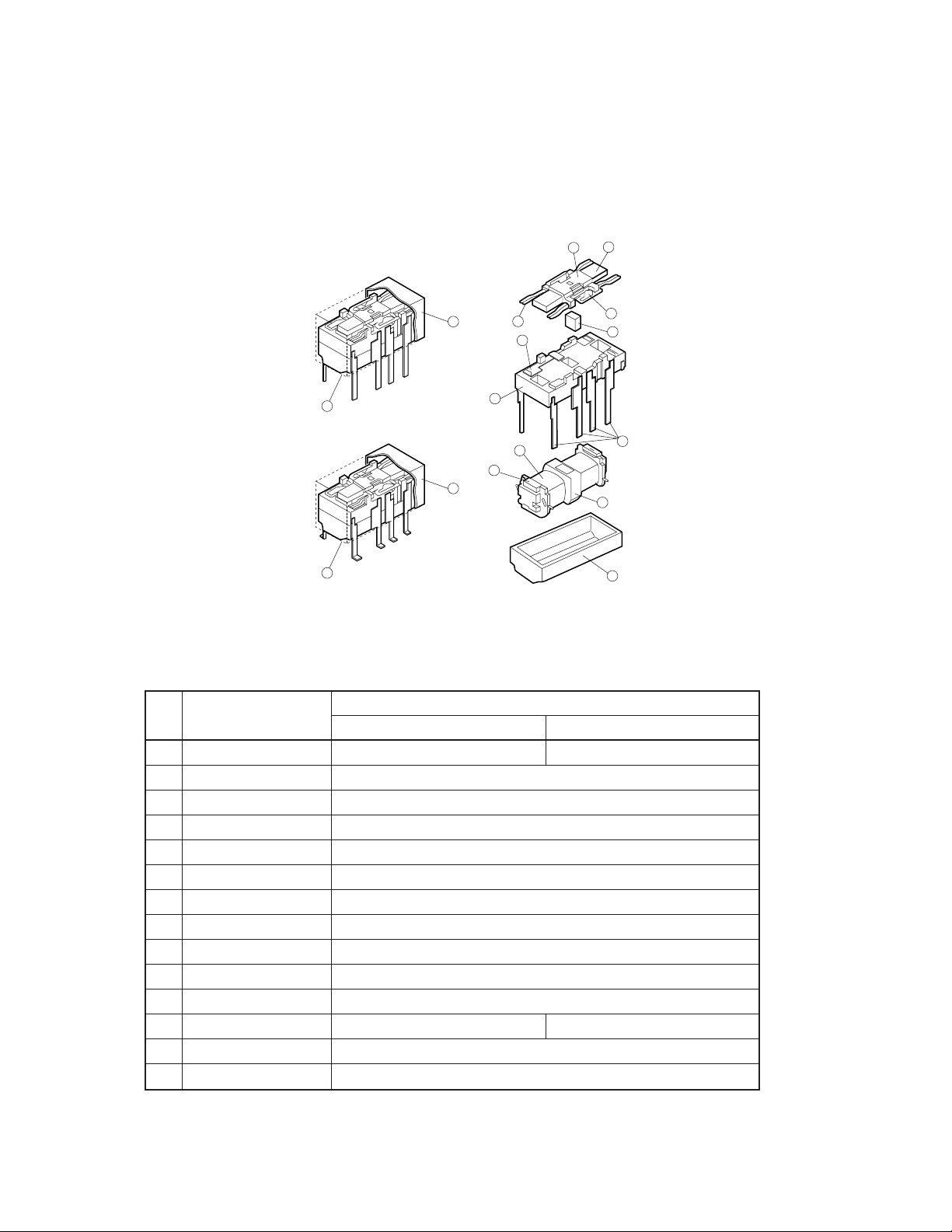
2. Structure
Figure 2.1 shows the structures of the EC2 and the EE2 series relays. EC2 series relay has a terminal configuration
called dual in-line leads (DIL), and EE2 series relay has a resistibility to solder heat, and a terminal configuration that
conforms to surface mounting. Table 2.1 lists the parts constituting relay.
EC2 series and EE2 series relays have a common structure except difference of a terminal configuration and some
parts.
11
[EC2 series]
12
10
13
7
5
3
14
[EE2 series]
14
1
1
8
9
2
4
6
Figure 2.1 Structure of the EC2/EE2 Series Relay
Table 2.1 Parts of EC2/EE2 Series Relay
No. Parts
EC2 Series EE2 Series
1 Cover Polybutylene telephthalate
2 Base Liquid crystalline polymer
3 Base pad Liquid crystalline polymer
4 Coil wire Polyurethane copper wire
5 Coil spool Polyphenylene sulfide
#
6 Core Pure iron
7 Terminal Phosphor bronze (surface is treated with preparatory solder)
8 Moving contact Au-alloy + AgNi
9 Stationary contact Au-alloy + AgNi
*
*
10 Contact spring Phosphor bronze
11 Armature Pure iron
12 Armature block mold Polyethersulfone Liquid crystallene polymer
13 Magnet Cobalt magnet
14 Sealing material Epoxy resin
Material
*
*
*
Liquid crystalline polymer
*
Note: *: Standard type
#: Conforms to UL94V-0
2
Page 8
3. Basic Characteristics
)
This section provides data necessary for designing an external circuit that uses the relay.
EC2 and EE2 series relays are designed with common specifications. So, this section shows common
characteristics of EC2 and EE2 series.
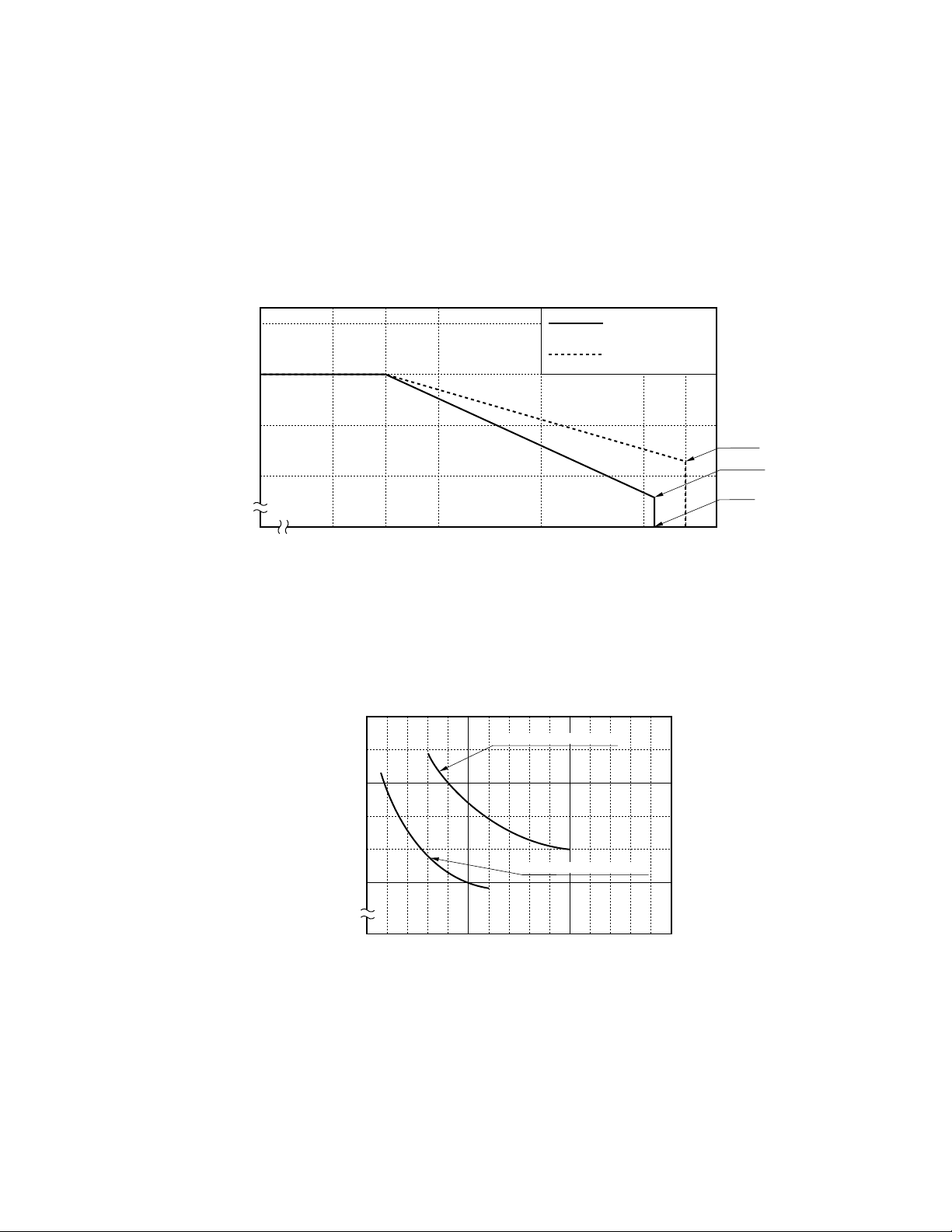
3.1 Switching power
If the contact load voltage and current of the relay are in the region enclosed by the solid and dotted lines in the
figure below, the relay can perform stable switching operation. If the relay is used at a voltage or current exceeding
this region, the life of the contacts may be significantly shortened.
2.0
1.0
0.5
Load Current (A)
0.2
20 30 50 100 200 250
Load Voltage (V
DC Resistive Load
AC Resistive Load
0.25 A
0.136 A
220 V
Figure 3.1 Switching Power
3.2 Life curve
The life expectancy of the relay can be roughly estimated from the switching voltage and current of the contact
load shown in Figure 3.2.
200
30 Vdc Resistive Load
100
50
operations)
4
20
Life (×10
10
0 0.5 1.0
Switching Current (A)
125 Vac Resistive Load
Figure 3.2 Life Curve
3
Page 9
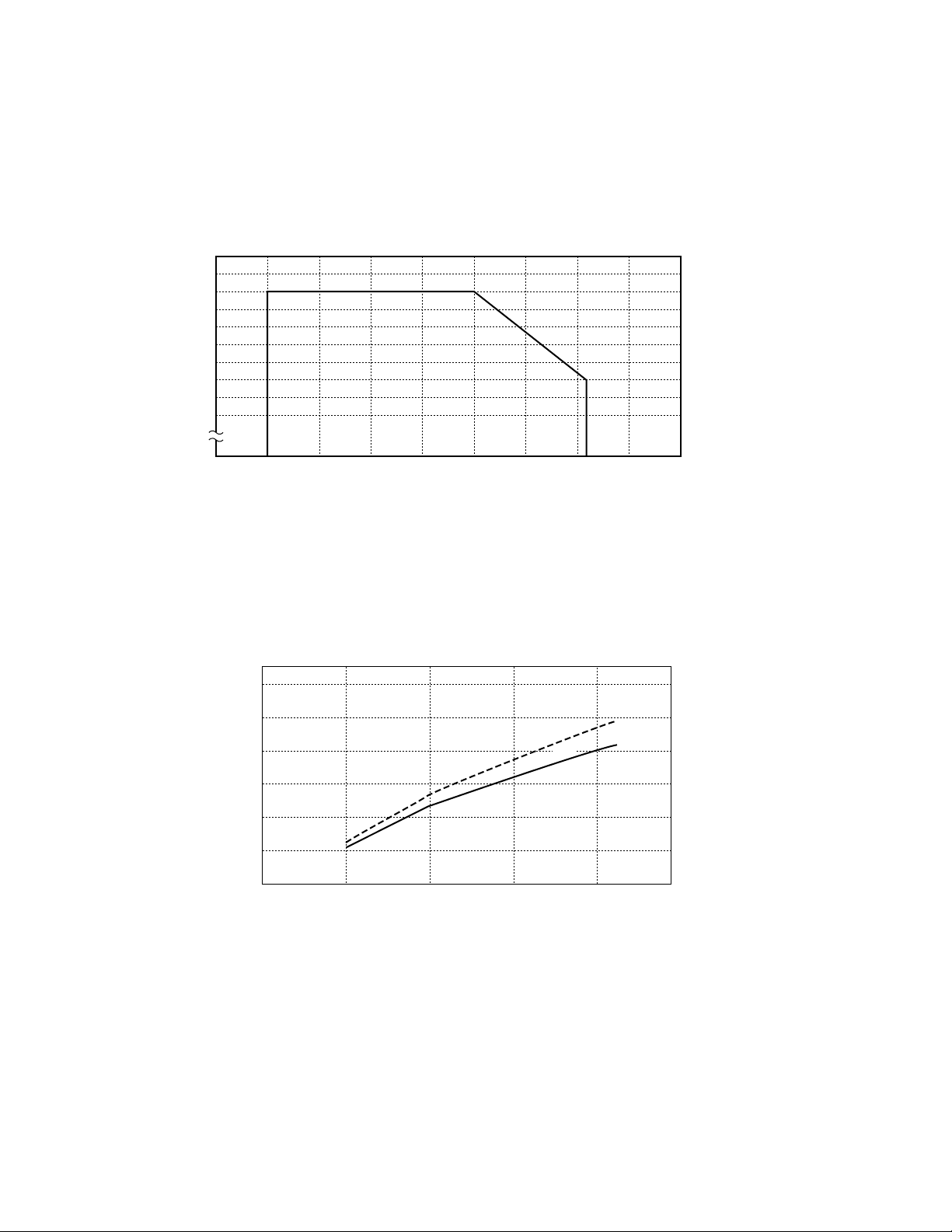
3.3 Maximum coil voltage
)
)
Figure 3.3 shows the ratio of maximum voltage that can be continuously applied to the coil of the relay to the nominal
voltage. As long as the relay is used in the enclosed region in this figure, the coil is not damaged due to burning
and the coil temperature does not rise to an abnormally high level.
(* Rated Coil Voltage: 3 to 24 Vdc)
(Rated of decrease in maximum voltage: 50%/45˚C)
150
100
Ratio of maximum applied voltage
to nominal voltage (%)
0 – 40 –200 20406080100
Ambient temperature (˚C
85˚C
Figure 3.3 Maximum Voltage Applied to Coil
3.4 Coil temperature rise
Figure 3.4 shows the relation between the rise in coil temperature and the power (product of the coil voltage and
current) dissipated by the coil. This figure shows the difference between the temperature before the power is applied
to the coil and the saturated temperature after application of power to the coil.
60
50
40
30
20
2 A
0 A
Carrying
Current
Temperature Rise (˚C)
10
0 100 200 300 400
Applied Power (mW
Figure 3.4 Coil Temperature Rise
4
Page 10
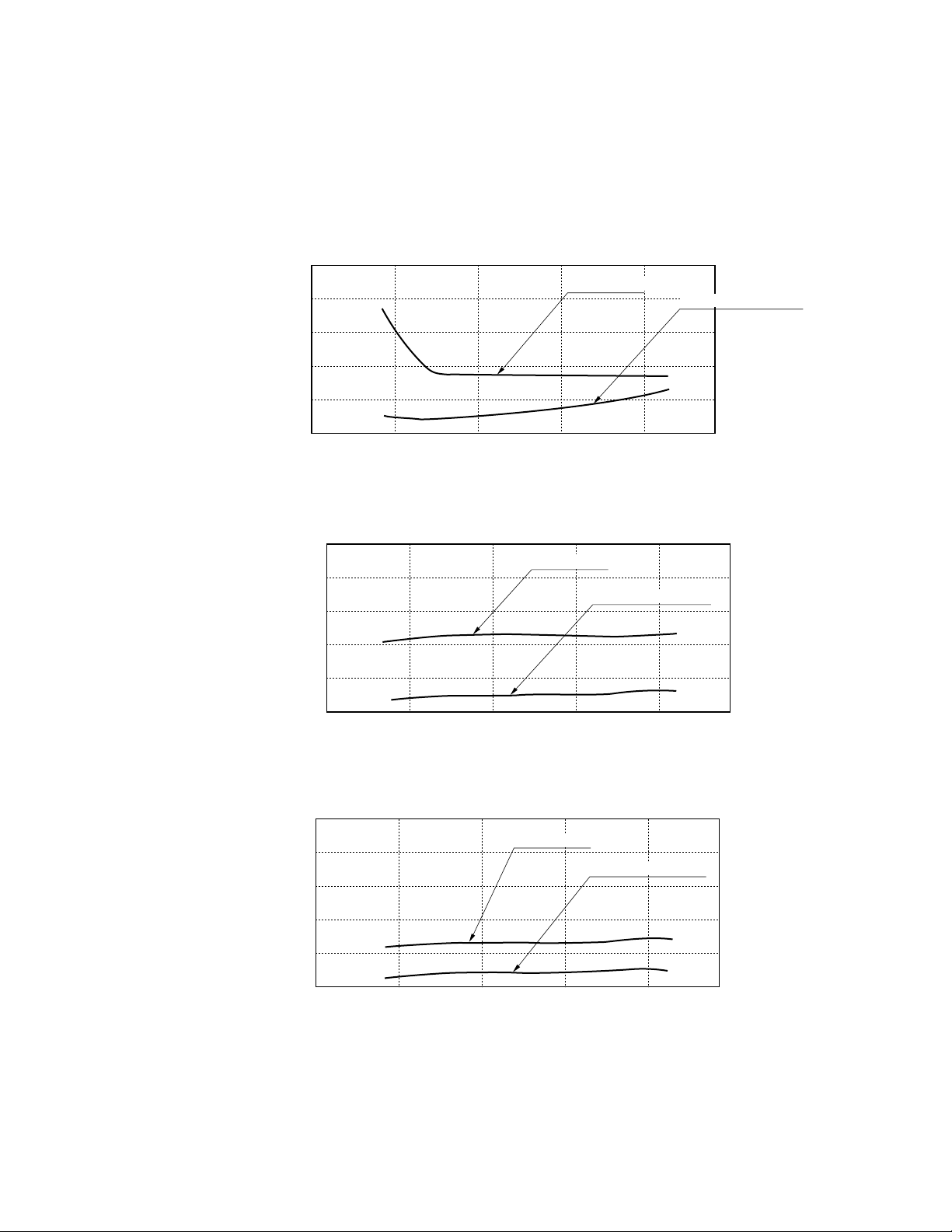
3.5 Driving power vs. timing
Figure 3.5 (1) shows the relations among the power applied to drive the relay, the operate time, and the bounce
time. Figure 3.5 (2) shows the relations among the supplied power, the release time, and the bounce time, and Figure
3.5 (3) shows the relations among the supplied power, the release time, and the bounce time when a diode is not
connected to the coil to absorb surges.
(1) Operate time
4
3
2
1
Operate Time
Operate Bounce Time (ms)
0 100 200 300 400
(2) Release time (with diode)
4
3
2
1
Release Bounce Time (ms)
(with diode)
Release Time
0 100 200 300 400
Operate time
Operate bounce time
Applied Power (mW)
Release time
Release bounce time
Applied Power (mW)
(3) Release time
4
3
2
1
Release Time
Release Bounce Time (ms)
0 100 200 300 400
Applied Power (mW)
Release time
Release bounce time
Figure 3.5 Driving Power vs. Timing
5
Page 11
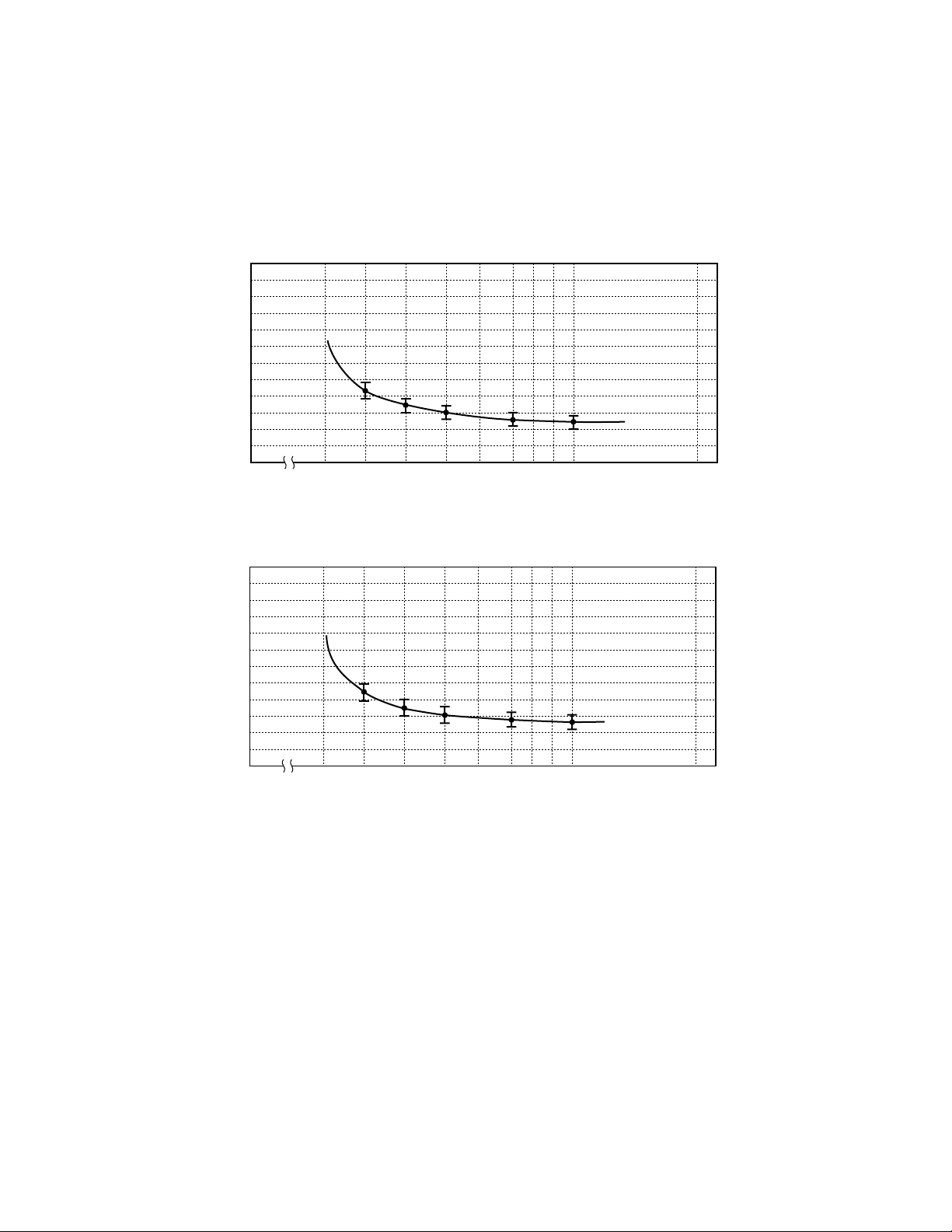
3.6 Driving pulse width vs. set & reset voltages
Because the latching type relay can be driven on a pulse voltage, it can save power. However, if the pulse width
is too narrow, the relay does not operate correctly.
Figure 3.6 shows the relations among the width of the pulse voltage applied to the coil, the set voltage, and the
reset voltage of the latching type relay.
(1) Set voltage
200
100
Ratio of set voltage to
nominal voltage (%)
0
2345678910 20
Driving Pulse Width (ms)
(2) Reset voltage
200
100
Ratio of reset voltage to
nominal voltage (%)
0
2345678910 20
Driving Pulse Width (ms)
Figure 3.6 Driving Pulse Width vs. Set & Reset Voltages
(Hints on correct use)
If the driving pulse width is too narrow, the relay cannot be driven at the nominal voltage. Hence, in actual
applications, apply a pulse with a width of 10 ms or more to the relay.
6
Page 12
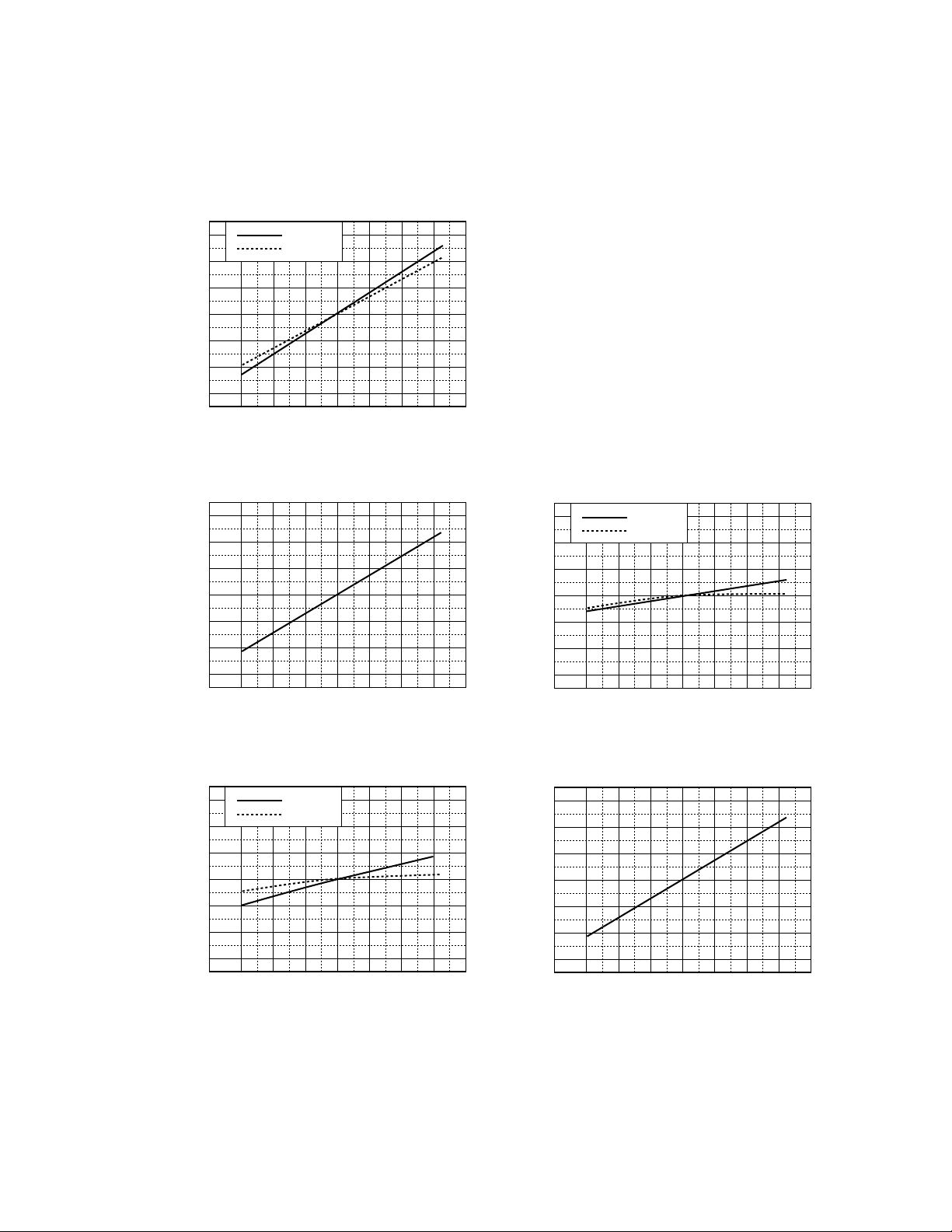
3.7 Thermal characteristics
p
p
)
p
)
p
)
p
)
The general characteristics of a relay gradually change with the ambient temperature. Figure 3.7 shows the typical
characteristics of the EC2 series relay.
(1) Operate & release voltages
130
120
110
100
90
80
70
Change in Must Operate and Must
Release Voltages (%)
– 40 –20 0 20406080100
Operate
Release
Ambient Tem
rature Ta (˚C)
(2) Contact resistance* (4) Transfer times
130
120
110
100
90
80
70
Changes in Contact Resistance (%)
– 40 –20 0 20406080100
Ambient Tem
rature Ta (˚C
130
120
110
100
90
80
Cange in Transfer Time (%)
70
– 40 –20 0 20406080100
Operate
Release
Ambient Tem
rature Ta (˚C
(3) Operate & release times (5) Coil resistance
130
120
110
100
90
80
70
Change in Must Operate and Must
Release Times (%)
– 40 –20 0 20406080100
Operate
Release
Ambient Tem
rature Ta (˚C
130
120
110
100
90
80
70
Change in Coil Resistance (%)
– 40 –20 0 20406080100
Ambient Tem
rature Ta (˚C
Figure 3.7 Temperature Characteristics
* The contact resistance includes the conductive resistance of the terminals. It is this conductive resistance
component that changes with the temperature.
7
Page 13
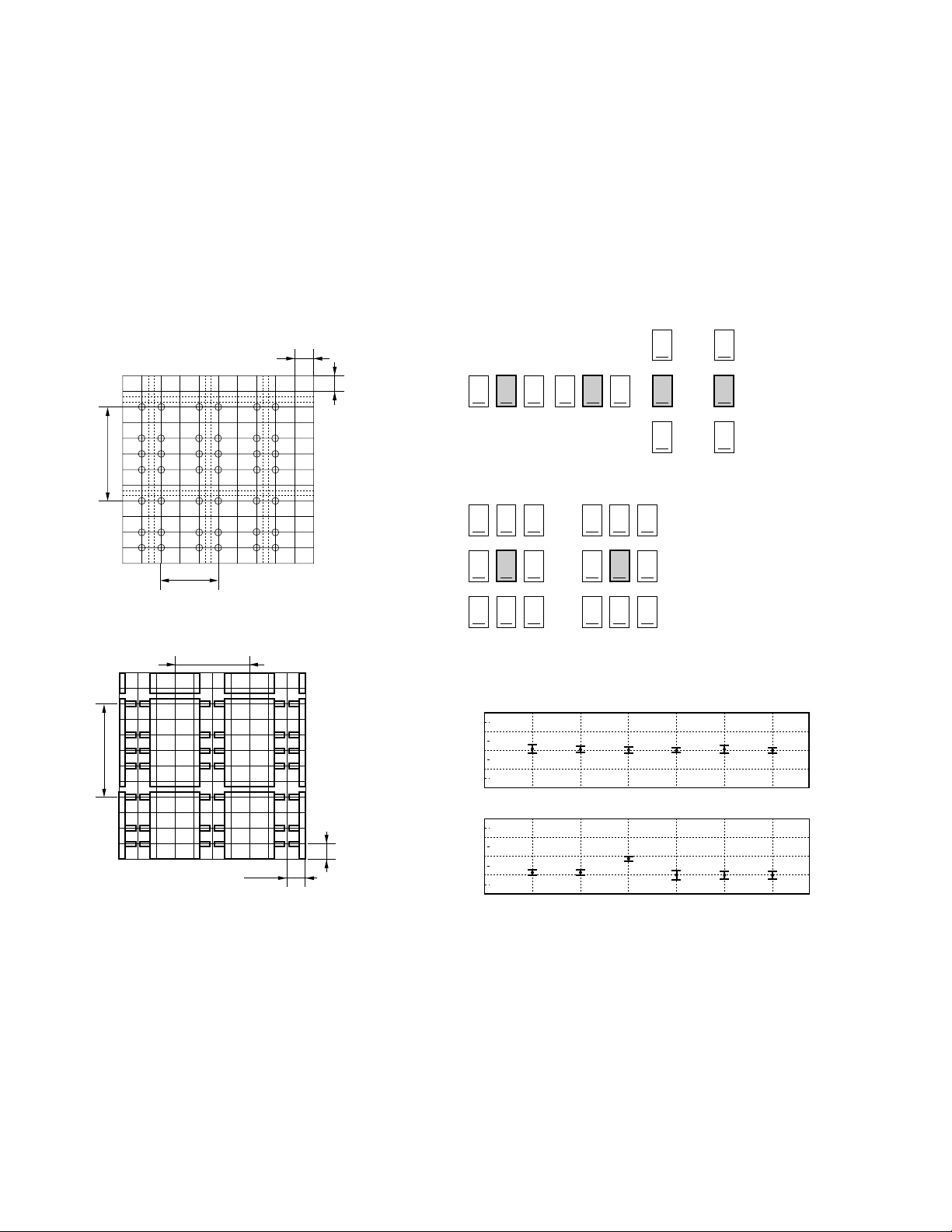
3.8 Magnetic interference
This section describes changes in the operate voltage caused by mutual magnetic interference when several relays
are closely mounted on a printed circuit board (PCB). Figure 3.8 (1) shows the distance among the relays mounted
on the PCB. As shown, the pin pitch of each relay is 2.54 mm. Figure 3.8 (2) shows the relay that is subject to
interference. In this figure, the hatched relay shown in the center of each relay arrangement is subject to interference,
and the surrounding relays influence the center relay. The condition under which the center relay suffers interference
and the surrounding relays affect the center relay differs depending on whether power is supplied to each relay. Figure
3.8 (3) shows the deviation in percent of the operate and release voltages of the center relays in Figure 3.8 (2).
(1) Mounting pitch (mm) (2) Relay arrangement
[EC2 series]
6 × 2.54
[EE2 series]
6 × 2.54
3 × 2.54
2.54
2.54
10.16
2.54
2.54
ON
ON
ON OFF OFF
OFF
Condition1 Condition2
ON
OFF
Condition3 Condition4
ON
ON
ON
OFF
OFF
OFF
Condition5 Condition6
(3) Deviation of must operate and must release voltages
+20
+10
0
–10
–20
Deviation of Must
Operate Voltage (%)
+20
+10
0
–10
–20
Deviation of Must
Release Voltage (%)
123456
123456
Condition
Condition
Figure 3.8 Magnetic Interference
8
Page 14
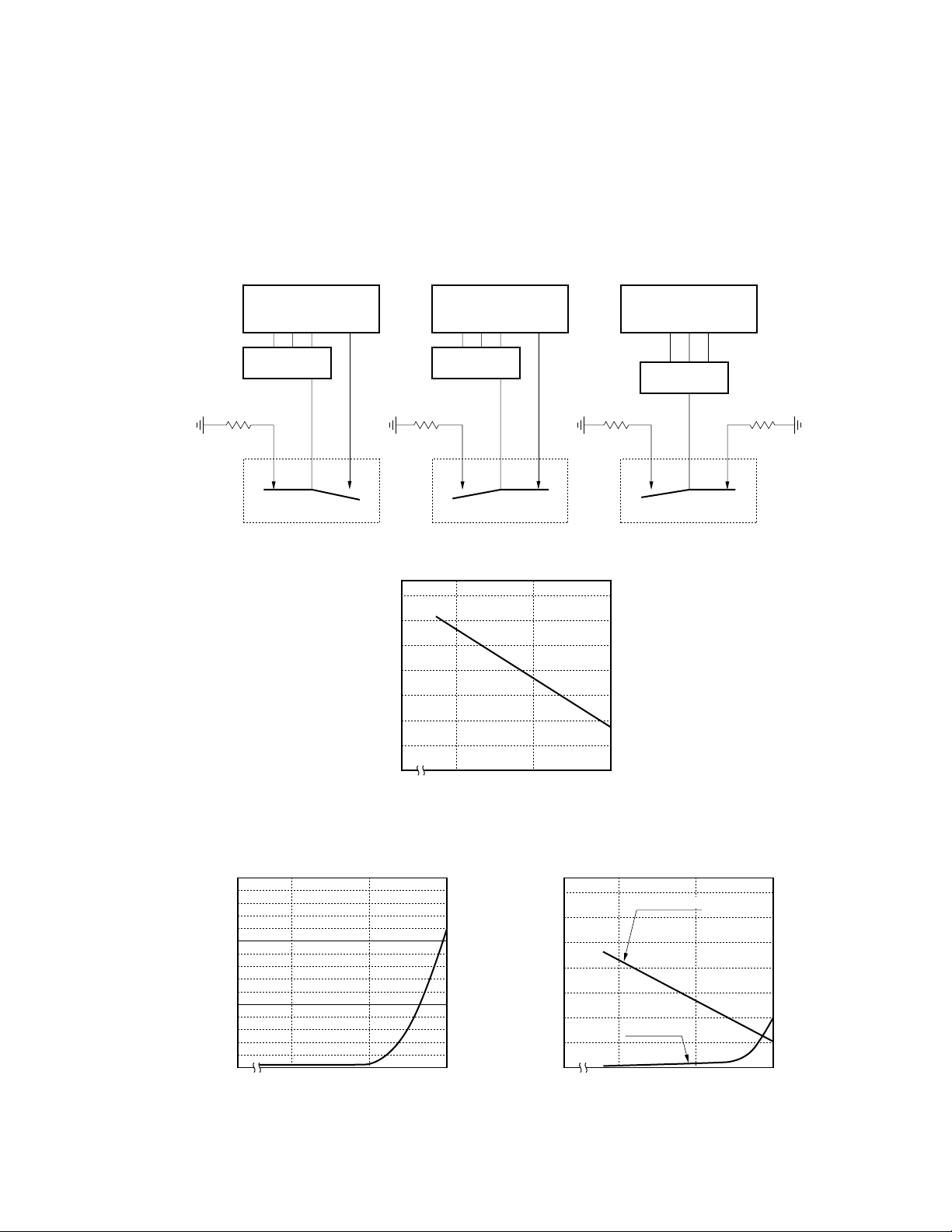
3.9 High-frequency characteristics
Figure 3.9 shows the performance of the EC2 and the EE2 series relays when a high-frequency signal is switched
by the contacts of the relay. Figure 3.9 (1) shows the test circuit. Figure 3.9 (2) shows the isolation loss of the relay.
Figure 3.9 (3) and Figure 3.9 (4) respectively show the insertion loss and return loss.
(1) Test circuit
Test equipment: HP8505A Network Analyzer (characteristic impedance: 50 Ω)
50 Ω
(2) Isolation loss
Isolation Loss
Network Analyzer
Test Set
IN
OUT
50 Ω
70
60
50
40
30
Isolation Loss (dB)
20
10
0
Insertion Loss
Network Analyzer
OUT
Test Set
IN
50 Ω
10 100 1000
Frequency (MHz)
Return Loss
Network Analyzer
IN
Bridge
OUT
50 Ω
(3) Insertion loss (4) Return loss
1.5
1.0
0.5
Insertion Loss (dB)
0
10 100 1000
Frequency (MHz)
70
60
50
40
30
Return Loss (dB)
20
10
0
Figure 3.9 High-frequency characteristics
Return Loss
V. S. W. R.
10 100 1000
Frequency (MHz)
3
2
V. S. W. R.
1
9
Page 15
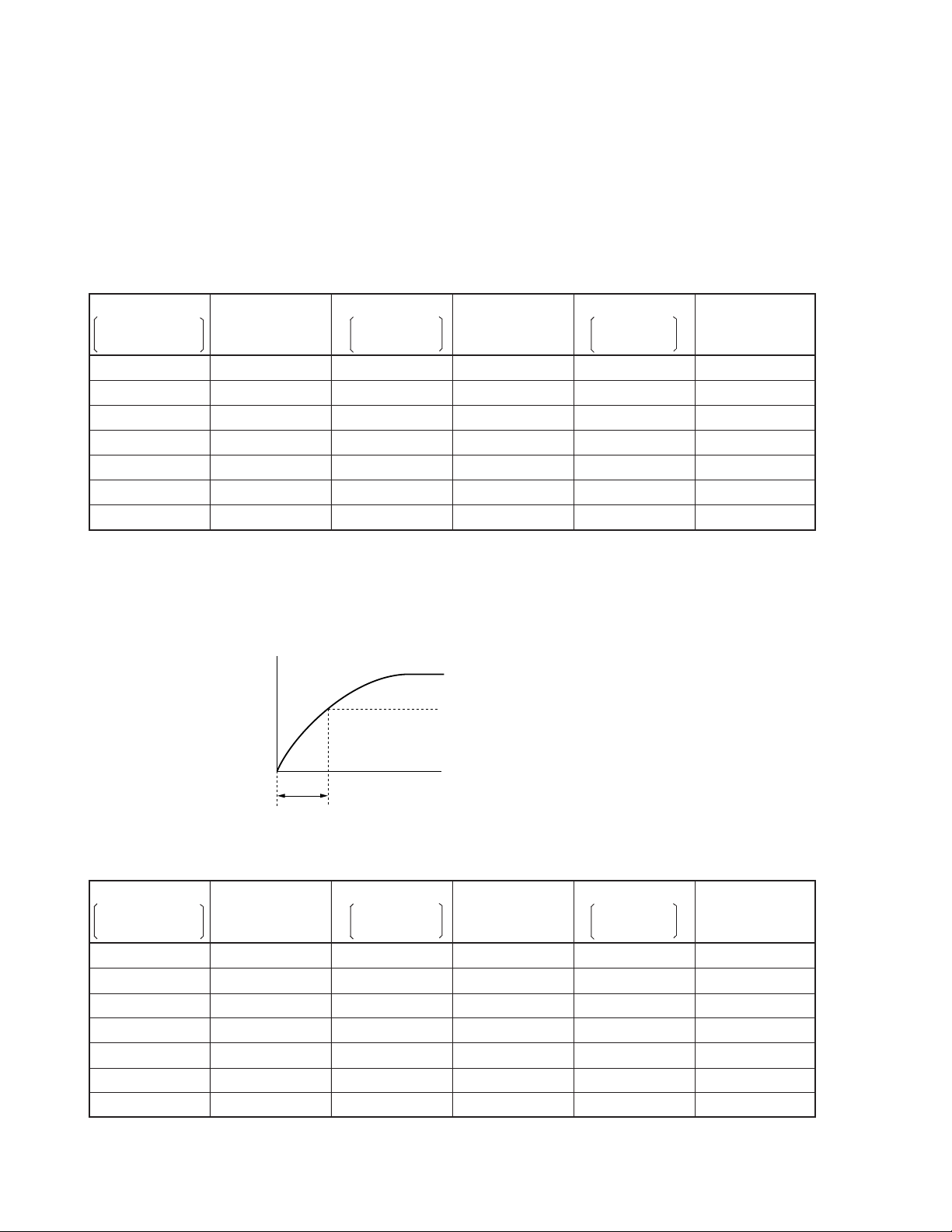
3.10 Coil inductance
The control input of a relay is the coil. The coil inductance can be measured using the following two methods.
Either method may be used based on preference.
Table 3.1.1 and 3.1.2 show the results of measurement.
3.10.1 Measurement by LCR meter
Table 3.1.1 Coil Inductance
(Unit: mH)
Part Number Part Number Part Number
Non-latching type Inductance Single coil Inductance Double coil Inductance
(Standard type) Latching type Latching type
EC2/EE2-3 30 EC2/EE2-3S 14 EC2/EE2-3T 10
EC2/EE2-4.5 48 EC2/EE2-4.5S 32 EC2/EE2-4.5T 21
EC2/EE2-5 64 EC2/EE2-5S 40 EC2/EE2-5T 26
EC2/EE2-6 83 EC2/EE2-6S 56 EC2/EE2-6T 38
EC2/EE2-9 180 EC2/EE2-9S 130 EC2/EE2-9T 78
EC2/EE2-12 340 EC2/EE2-12S 220 EC2/EE2-12T 135
EC2/EE2-24 868 EC2/EE2-24S 1450 EC2/EE2-24T 825
(Measurement frequency: 1 kHz)
3.10.2 Measurement by coil current waveform
τ
The inductance is calculated by observation of
τ
: Determined by current waveform I = Imax (1 – e
Coil Current
τ
equaling 63.2 % of max value
-t/τ
).
100 %
63.2 %
τ
= × R
L
= Coil resistance
R
= Coil current
I
Time (t)
Table 3.1.2 Coil Inductance
(Unit: mH)
Part Number Part Number Part Number
Non-latching type Inductance Single coil Inductance Double coil Inductance
(Standard type) Latching type Latching type
EC2/EE2-3 19 EC2/EE2-3S 11 EC2/EE2-3T 7
EC2/EE2-4.5 46 EC2/EE2-4.5S 27 EC2/EE2-4.5T 20
EC2/EE2-5 54 EC2/EE2-5S 34 EC2/EE2-5T 23
EC2/EE2-6 88 EC2/EE2-6S 51 EC2/EE2-6T 36
EC2/EE2-9 206 EC2/EE2-9S 120 EC2/EE2-9T 85
EC2/EE2-12 392 EC2/EE2-12S 241 EC2/EE2-12T 151
EC2/EE2-24 983 EC2/EE2-24S 1100 EC2/EE2-24T 820
10
(Applied voltage = Nominal D.C. voltage)
Page 16
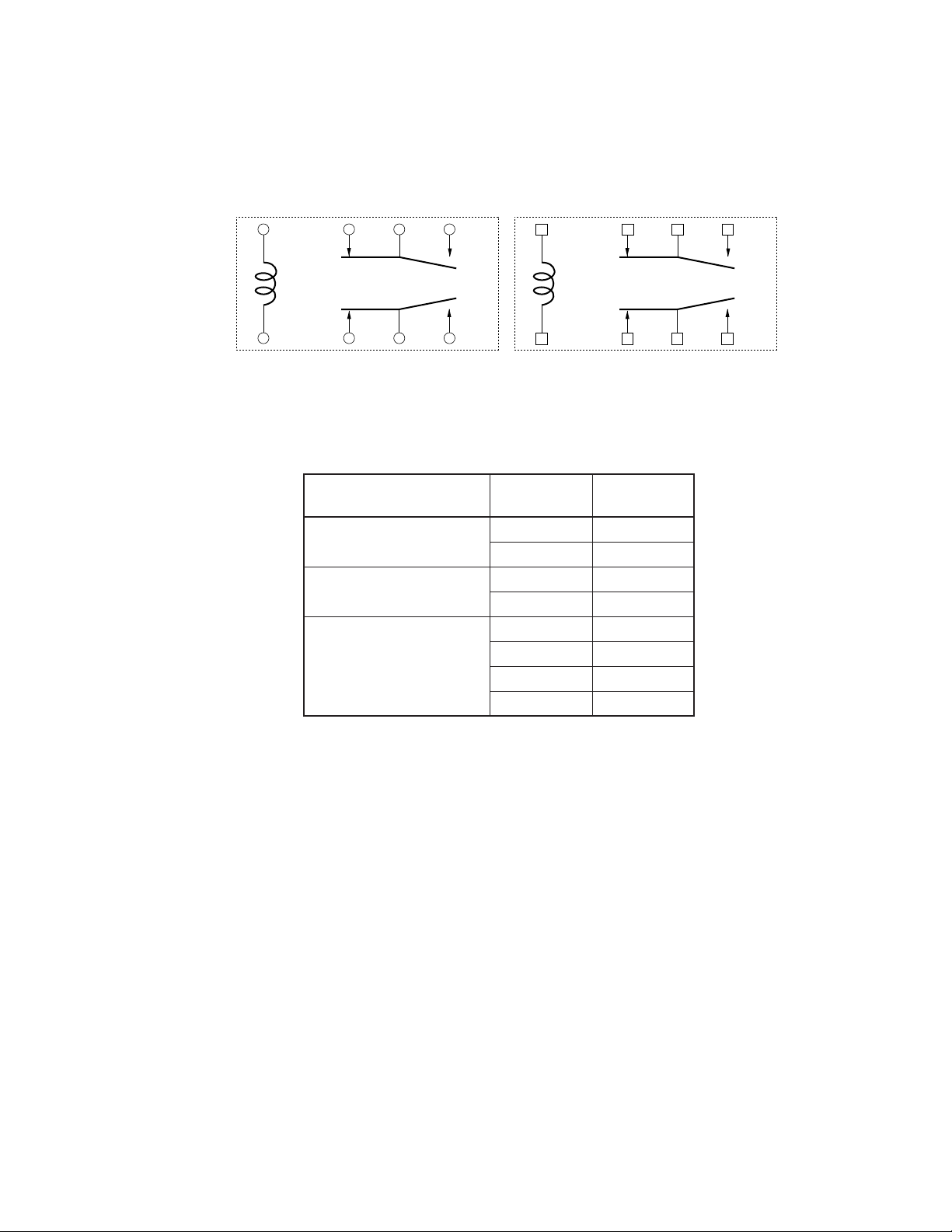
3.11 Capacitance
Table 3.2 shows the capacitance between terminals of the EC2 and the EE2 series relay.
Note that the terminals not tested are left open.
[EC2 series] [EE2 series]
1 345
1 345
12 10 9 8
Internal Connection of Relay (Bottom View)
Table 3.2 Capacitance
Parameter
Between Coil and Contact 1, 4 1.44
Between Opening Contacts 4, 5 0.56
Between Adjacent Contacts 4, 8 0.34
12 10 9 8
(Unit: pF)
Terminal
Number
9, 12 1.45
8, 9 0.57
4, 9 0.64
5, 8 0.19
5, 9 0.34
Capacitance
11
Page 17

3.12 Resistance to surge voltage
When a relay is used in a communication circuit, it may be subjected to a lightning surge via the circuit or due to
induction. A surge voltage test is conducted to measure the resistance of the EC2 and the EE2 series relays to surge
voltage.
(1) Test condition 1
The voltage waveform used for this test is specified by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Standard
Part 68.
The EC2 series relay can withstand even if the surge voltage shown in Figure 3.10 is applied (1) between opening
contacts, (2) between coil and contacts, or (3) between adjacent contacts.
MAX
. = 1500 V
V
µ
10 s
V
MAX
.
V
MAX
./2
Voltage (V)
0
µ
160 s
Time
Figure 3.10 Surge Voltage Waveform
(2) Test condition 2
The voltage waveform used for this test is specified by the Bellcore Standard. The EC2 and the EE2 series relay
can withstand even if the surge voltage shown in Figure 3.11 is applied between coil and contact.
2500
2250
1250
250
Voltage (V)
0
2 s
µ
10 s
Time
µ
12
Figure 3.11 Surge Current Waveform
Page 18

3.13 Current surge interrupt test
This test is conducted for the relay used in a communication circuit to evaluate the resistance to abnormally high
current appeared in the case of a touch between the communication circuit and an electric power line.
[Test conditions]
1. Voltage : 700 Vac (50 Hz)
2. Current : 4.2 A
3. Switching times : 4 times (At N.C. contact)
3.14 Resistance to carrying current
If an abnormally high current flows continuously through the closed contacts of the relay for a long time, meltdown
of inner mold of the relay, and large deviation of characteristics may occur.
Figure 3.12 shows the relation between the value of the carrying current at which the relay can operate normally
and time.
100
Meltdown of Inner Mold
50
<Destruction Region>
20
Large Deviation of Characteristics
10
Carrying Current (A)
5
2
10 s 20 s 30 s 40 s 50 s 1 m 2 m 5 m
Time
After Test
Figure 3.12 Resistance to Carrying Current
(Hints on correct use)
Limit the carrying current of the contacts to a maximum of 2 A to maintain the reliability of the relay.
13
Page 19

4. Distribution of Characteristics
This chapter presents the distribution data of the general characteristic values of the EC2 series relay on behalf
of the EC2 and the EE2 series relays, because they are designed with common specifications. The data shown in
this chapter are sampled from a certain production lot, and do not necessarily guarantee the characteristics of any
particular lot that is shipped. The number of samples is 40 relays for each test.
4.1 Operate & release voltages (set & reset voltages)
This section shows the distribution of the voltage at which the relay operates.
(1) Non-latching, 5-V type (EC2-5)
10
5
Number of Samples
0
2.5 3.0
Operate Voltage (V)
(2) Non-latching, 12-V type (EC2-12)
10
5
Number of Samples
0
58
Operate Voltage (V)
10467 9
10
5
Number of Samples
0
10
5
Number of Samples
0
1.0 2.0
Release Voltage (V)
32.5 4.543.5 5
Release Voltage (V)
(3) Latching of single-wound coil, 5-V type (EC2-5S)
10
5
Number of Samples
0
2.0 2.5
Set Voltage (V)
3.0 3.0
Figure 4.1 Operate & Release Voltages
14
10
5
Number of Samples
0
2.0 2.5
Reset Voltage (V)
Page 20

4.2 Operate & release times (set & reset times)
p
)
(ms)
)
)
This section shows the operate time that elapses from the time when the relay coil is energized until the relay
contacts close, and the release time that elapses from the time when the relay coil is deenergized until the closed
contacts open.
The number of samples used for each measurement is 40.
(1) Non-latching, 5-V type (EC2-5)
20
10
Number of Samples
0
O
erate Time (ms
(2) Non-latching, 12-V type (EC2-12)
20
10
Number of Samples
0
2.0 2.5 3.0
Operate Time (ms)
20
10
Number of Samples
0
20
10
Number of Samples
0
2.0 2.5 3.02.0 2.5 3.0
Release Time
2.0 2.5 3.0
Release Time (ms)
(3) Latching of single-wound coil, 5-V type (EC2-5S)
20
10
Number of Samples
0
1.5 2.0 2.5
Set Time (ms
Figure 4.2 Operate & Release Times
20
10
Number of Samples
0
1.5 2.0 2.5
Reset Time (ms
15
Page 21

4.3 Transfer time
p
)
(ms)
)
)
(ms)
(ms)
This section gives data on the transfer time, which is the total time between the breaking of one set of contacts
and the making of another. The number of samples used for each measurement of the transfer time is 40.
(1) Non-latching, 5-V type (EC2-5)
20
10
Number of Samples
0
0.5 1 1.5
O
erate Transfer Time (ms
(2) Non-latching, 12-V type (EC2-12)
20
10
Number of Samples
20
10
Number of Samples
0
Release Transfer Time
20
10
Number of Samples
10.5 1.5
0
0.5 1 1.5 0.5 1 1.5
Operate Transfer Time (ms
(3) Latching of single-wound coil, 5-V type (EC2-5S)
20
10
Number of Samples
0
Set Transfer Time
Figure 4.3 Transfer Times
16
0
Release Transfer Time (ms
20
10
Number of Samples
0
0.5 1.510.5 1.51
Reset Transfer Time
(without diode)
Page 22

4.4 Timing and details
The EC2 and the EE2 series relays have two sets of transfer contacts. This section shows the movements of each
contact, which are not included in the timing specifications, using the timing chart shown in Figure 4.4A.
Coil Voltage
Normally Open
Contact No. 1
Normally Close
Contact No. 1
Normally Open
Contact No. 2
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
TOB
Energized
Not Energized
1 THM1 TRM1
TOM
1
TTO1
TOM2 THM2 TRM2
TRB1
THB1
TTR1
Normally Close
Contact No. 2
ON
OFF
TOB2
TRB2 THB2
TTR2
TTO2
COR
COO
Figure 4.4A Timing Chart of Coil and Contacts
(Test results)
The timing specifications show the greater of the values of the two sets of contacts. The time difference between
the two contact sets, however, is almost negligible as shown in data (1) through (8) on the following pages. Practically,
therefore, the time difference can be ignored.
17
Page 23

The following charts show the distribution of timing. Twenty EC2-5’s are used as the samples.
)
)
)
)
(1) On times of make contacts at operation (TOM)
Contact #1
20
10
Number of Samples
0
2.0 2.5
TOM
1
(ms)
(2) Off times of break contacts at operation (TOB)
Contact #1
20
20
10
Number of Samples
0
2.0 2.5
20
Contact #2
TOM
2
(ms)
Contact #2
10
Number of Samples
0
1.0 1.5 2.0 1.0 1.5 2.0
TOB
1
(ms
(3) Off times of make contacts at release (TRM)
Contact #1 Contact #2
20
10
Number of Samples
0
1.0 1.5
TRM
1
(ms
10
Number of Samples
0
20
10
Number of Samples
0
TOB
2
(ms
1.0 1.5
TRM
2
(ms
18
Figure 4.4B Timing
Page 24

(4) On times of break contacts at release (TRB)
)
)
)
)
Contact #1
20
10
Number of samples
0
1.5 2.0 2.5 1.5 2.0 2.5
TRB
1
(ms)
(5) Bounce times of make contacts at operation (THM)
Contact #1
20
20
10
Number of samples
0
20
Contact #2
2
(ms)
TRB
Contact #2
10
Number of samples
0
0.5 1.0
THM1 (ms
(6) Bounce times of break contacts at release (THB)
Contact #1
20
10
Number of samples
0
0.5 1.0
1
(ms
THB
10
Number of samples
0
20
10
Number of samples
0
0.5 1.0
THM2 (ms
Contact #2
0.5 1.0
2
(ms
THB
Figure 4.4C Timing
19
Page 25

(7) Operate transfer times (TTO)
)
)
Contact #1
20
10
Number of Samples
0
1.0 1.5 1.0 1.5
TTO
1
(8) Release transfer times (TTR)
Contact #1
20
(ms)
20
10
Number of Samples
0
20
Contact #2
TTO
2
(ms)
Contact #2
10
Number of Samples
0
(9) Common open times
20
10
Number of Samples
0
10
Number of Samples
0
TTR1 (ms
At operation
20
10
1.0 1.51.0 1.5
TTR2 (ms
At release
Number of Samples
1.0 1.5 1.00.50.5 1.5
COO (ms)
0
COR (ms)
20
Figure 4.4D Timing
Page 26

4.5 Contact resistance
This section gives data on the resistance of the contacts when the contacts are closed. The number of sample
used for measurement of the contact resistance is 40 each.
(1) Non-latching, 5-V type (EC2-5)
20
10
Number of Samples
0
35 40 45
Contact Resistance (mΩ)
(N.O. Contact)
(2) Non-latching, 24-V type (EC2-24)
20
10
Number of Samples
20
10
Number of Samples
0
35 40 45
Contact Resistance (mΩ)
(N.C. Contact)
20
10
Number of Samples
0
35 40 45
Contact Resistance (mΩ)
(N.O. Contact)
(3) Latching of single-wound coil, 5-V type (EC2-5S)
20
10
Number of Samples
0
35 40 45
Contact Resistance (mΩ)
(N.O. Contact)
Figure 4.5 Contact Resistance
0
35 40 45
Contact Resistance (mΩ)
(N.C. Contact)
20
10
Number of Samples
0
35 40 45
Contact Resistance (mΩ)
(N.C. Contact)
21
Page 27

4.6 Breakdown voltage
)
)
µµ
This section gives data on the breakdown voltage between terminals of the EC2 series relay.
(Sample: EC2-5, n = 10 pcs.)
(a) Between open contacts (n = 20)
10
5
Number of Samples
0
1.0 1.5 2.0
10
5
Breakdown Voltage (kV)
(c) Between coil and contacts (n = 20)
(b) Between adjacent contacts (n = 10)
10
5
Number of Samples
0
2.0 2.5 3.0
Breakdown Voltage (kV)
Number of Samples
0
1.5 2.0 2.5
Breakdown Voltage (kV)
Figure 4.6 Breakdown Voltage
4.7 Thermal Electromotive Force (EMF) (offset voltage between contacts)
This section gives data on the thermal EMF which is a voltage that appears when the contacts are closed.
(Sample: EC2-5, number of samples = 10 pcs., number of data = 20)
(a) N.C. contact (not energized)
10
5
Number of Samples
10
5
Number of Samples
(b) N.O. contact (energized)
22
0
0.5 1.0
Thermal EMF ( V
0
0.5 1.0
Thermal EMF ( V
Figure 4.7 Thermal EMF
Page 28

5. Test Data
This chapter shows examples of the results of environmental tests (refer to 5.1 for details) and contact life tests
(refer to 5.2). The table below lists the types of tests, conditions, and data. As the sample, the EC2/EE2-5 and EC2/
EE2-5S are used for the environmental tests, and the EC2-5 is used for the contact life tests.
Table 5 Types of Tests, Conditions, and Data
Test Test Conditions Refer to Page:
Environ- High-temperature test Ambient temperature: +105˚C 24 to 26
mental Duration: 672 hours
test
Contact Non-load test A 25˚C 41
life
test
Low-temperature test Ambient temperature: –40˚C 27, 28
Duration: 672 hours
Moisture resistance test Ambient temperature: –10˚C to +65˚C 29, 30
Humidity: 95% RH, test cycles: 10
Heat shock test Ambient temperature: –55˚C/+85˚C 31, 32
Test cycles: 100
Vibration test
Shock test Waveform: Half sine wave, 75 G max. 35, 36
Resistance to solder Solder temperature: 260 ± 10˚C37
heat test Immersion time: 10 seconds
Resistance to reflow Maximum temperature: 235 ˚C 38, 39
solder heat test Refer to Figure 5.8
Terminal strength Ambient temperature: 25˚C, Tensile strength: 1.36 kg 40
Non-load test B 85˚C 42
Resistive load test A 10 mV, 10 µA, 25˚C42
Amplitude: 1.52 mm, Test time: 2 hours each in X, Y, and Z directions
Frequency: 10 Hz to 500 Hz, Peak acceleration: 20 G
6 Times each in X, Y, and Z directions, totaling 36 times
Number of times of bending: 2
33, 34
Resistive load test B 10 Vdc, 10 mA, 85˚C43
Resistive load test C 28 Vdc, 100 mA, 85˚C43
Resistive load test D 50 Vdc, 100 mA, 25˚C44
Resistive load test E 50 Vdc, 100 mA, 85˚C44
Inductive load test 48 Vdc, 110 mA, 25˚C45
Resistive load test F 220 Vdc, 0.14 A, 25˚C45
Resistive load test G 125 Vdc, 0.5 A, 25˚C46
Resistive load test H 30 Vdc, 1 A, 25˚C46
23
Page 29

5.1 Environmental tests
This section shows the results of environmental tests to be conducted to evaluate the performance of the relay
under specific storage and operating environmental conditions. No abnormality was found after all the tests had been
conducted.
* The operate and release voltages, contact resistance, operate and release times, and transfer time of the sample
before and after each test were compared, but no major change in these parameters was observed, and the sample
still satisfied the initial standard values of the parameters after the test. For details, refer to the graph for each
test.
9
* The initial standard value of the insulation resistance of 10
* The initial standard value of two breakdown voltages of 1500 Vac (between coil and contact), and of 1000 Vac
(between opening contacts, and between adjacent contacts) were satisfied for 1 minute after the test.
* After each test, no abnormality was found in the appearance. The cover of the relay was removed and the internal
mechanism was also inspected visually for dirt, deformation, and other abnormalities, but no such abnormalities
was found.
* After each test, a sealability test was conducted to examine the sealability of the relay by immersing the relay into
a fluorocarbon solution and checking to see if the internal gas of the relay leaked out. No abnormality was observed
as a result of this sealability test.
5.1.1 High-temperature test (test conditions: temperature: +105˚C, duration: 672 hours, sample: 10 pcs. each)
This test was conducted to check whether the performance of the relay is degraded after the relay has been left
at the upper-limit value of the rated ambient temperature for the specified duration.
Ω or higher was still satisfied after the test.
[EC2 series]
(1) Non-latching, 5-V type
(a) Operate & release voltages
5
4
3
2
1
0
Operate & Release Voltages (V)
Before Test
(c) Operate & release times (d) Transfer times
3
2.5
2
Operate Voltage
Release Voltage
After Test
Operate Time
Release Time
Contact Resistance (mΩ)
200
100
50
20
1.5
1
1
(b) Contact resistances
Before Test
Normally Open (N.O.) Contact
Normally Close (N.C.) Contact
After Test
At Operation
At Release
24
1.5
Operate & Release Times (ms)
0
Before Test
0.5
Transfer Time (ms)
0
After Test After Test
Before Test
Figure 5.1 (1) High-temperature Test
Page 30

(2) Latching of single-wound coil, 5-V type
(a) Set & reset voltages
5
4
3
2
1
Set & Reset Voltages (V)
0
Before Test
(c) Set & reset times (d) Transfer times
3
2.5
2
1.5
Set & Reset Times (ms)
0
Before Test
(b) Contact resistances
Set Voltage
Reset Voltage
After Test
Set Time
Reset Time
After Test After Test
200
100
50
20
Contact Resistance (mΩ)
Before Test
2
1.5
1
0.5
Transfer Time (ms)
0
Before Test
N.O. Contact
N.C. Contact
After Test
At Set
At Reset
Figure 5.1 (2) High-temperature Test
25
Page 31

[EE2 series]
(1) Non-latching, 5-V type
(a) Operate & release voltages
5
4
3
2
1
0
Operate & Release Voltages (V)
Before Test
(c) Operate & release times (d) Transfer times
3
2.5
2
1.5
Operate & Release Times (ms)
0
Before Test
(b) Contact resistances
Operate Voltage
Release Voltage
After Test
Operate Time
Release Time
After Test After Test
200
100
50
20
Contact Resistance (mΩ)
Before Test
1
1.5
1
0.5
Transfer Time (ms)
0
Before Test
Normally Open (N.O.) Contact
Normally Close (N.C.) Contact
After Test
At Operation
At Release
Figure 5.1 (3) High-temperature Test
(2) Latching of single-wound coil, 5-V type
(a) Set & reset voltages
5
4
3
2
1
Set & Reset Voltages (V)
0
Before Test
(c) Set & reset times (d) Transfer times
3
2.5
2
1.5
Set & Reset Times (ms)
0
Before Test
Set Voltage
Reset Voltage
After Test
Set Time
Reset Time
After Test After Test
Figure 5.1 (4) High-temperature Test
200
100
50
20
Contact Resistance (mΩ)
Before Test
2
1.5
1
0.5
Transfer Time (ms)
0
Before Test
(b) Contact resistances
N.O. Contact
N.C. Contact
After Test
At Set
At Reset
26
Page 32

5.1.2 Low-temperature test (test conditions: temperature: –40˚C, duration: 672 hours, sample: 10 pcs. each)
This test is conducted to check whether the performance of the relay is degraded after the relay has been left at
the lower-limit value of the rated ambient temperature for the specified duration.
[EC2 series]
(1) Non-latching, 5-V type
(a) Operate & release voltages (b) Contact resistances
5
4
3
2
1
0
Before Test
Operate & Release Voltages (V)
(c) Operate & release times (d) Transfer times
3
2.5
2
1.5
0
Operate & Release Times (ms)
Before Test
Operate Voltage
Release Voltage
Operate Time
Release Time
After Test After Test
Figure 5.2 (1) Low-temperature Test
(2) Latching of single-wound coil, 5-V type
200
100
50
20
Contact Resistance (mΩ)
Before Test
2
1.5
1
0.5
Transfer Time (ms)
0
Before Test
N.O. Contact
N.C. Contact
After TestAfter Test
At Operation
At Release
(a) Set & reset voltages (b) Contact resistances
5
4
3
2
1
Set & Reset Voltages (V)
0
Before Test
(c) Set & reset times (d) Transfer times
3
2.5
1
1.5
Set & Reset Times (ms)
0
Before Test
Set Voltage
Reset Voltage
Set Time
Reset Time
After Test After Test
200
100
50
20
Contact Resistance (mΩ)
Before Test
2
1.5
1
0.5
Transfer Time (ms)
0
Before Test
N.O. Contact
N.C. Contact
After TestAfter Test
At Operation
At Release
Figure 5.2 (2) Low-temperature Test
27
Page 33

[EE2 series]
(1) Non-latching, 5-V type
(a) Operate & release voltages (b) Contact resistances
5
4
3
2
1
0
Before Test
Operate & Release Voltages (V)
(c) Operate & release times (d) Transfer times
3
2.5
2
1.5
0
Operate & Release Times (ms)
Before Test
Operate Voltage
Release Voltage
Operate Time
Release Time
After Test After Test
Figure 5.2 (3) Low-temperature Test
(2) Latching of single-wound coil, 5-V type
200
100
50
20
Contact Resistance (mΩ)
Before Test
2
1.5
1
0.5
Transfer Time (ms)
0
Before Test
N.O. Contact
N.C. Contact
After TestAfter Test
At Operation
At Release
(a) Set & reset voltages (b) Contact resistances
5
4
3
2
1
Set & Reset Voltages (V)
0
Before Test
(c) Set & reset times (d) Transfer times
3
2.5
1
1.5
Set & Reset Times (ms)
0
Before Test
Set Voltage
Reset Voltage
Set Time
Reset Time
After Test After Test
200
100
50
20
Contact Resistance (mΩ)
Before Test
2
1.5
1
0.5
Transfer Time (ms)
0
Before Test
N.O. Contact
N.C. Contact
After TestAfter Test
At Operation
At Release
Figure 5.2 (4) Low-temperature Test
28
Page 34

5.1.3 Moisture resistance test (test conditions: temperature: –10 ˚C to 65˚C, humidity: 90 to 98% RH, test cycles:
10, sample: 10 pcs. each)
This test is conducted to check whether the performance of the relay is degraded after the relay has been left in
a highly humid atmosphere for the specified duration.
[EC2 series]
(1) Non-latching, 5-V type
(a) Operate & release voltages (b) Contact resistances
5
4
3
2
1
0
Before Test
Operate & Release Voltages (V)
(c) Operate & release times (d) Transfer times
3
2.5
2
1.5
1
0
Operate & Release Times (ms)
Before Test
Operate Voltage
Release Voltage
Operate Time
Release Time
After Test After Test
Figure 5.3 (1) Moisture Resistance Test
(2) Latching of single-wound coil, 5-V type
200
100
50
20
Contact Resistance (mΩ)
Before Test
2
1.5
1
0.5
Transfer Time (ms)
0
Before Test
N.O. Contact
N.C. Contact
After TestAfter Test
At Operation
At Release
(a) Set & reset voltages (b) Contact resistances
5
4
3
2
1
Set & Reset Voltages (V)
0
Before Test
(c) Set & reset times (d) Transfer times
3
2.5
2
1.5
Set & Reset Times (ms)
0
Before Test
Set Voltage
Reset Voltage
Set Time
Reset Time
After Test After Test
200
100
50
20
Contact Resistance (mΩ)
Before Test
2
1.5
1
0.5
Transfer Time (ms)
0
Before Test
Figure 5.3 (2) Moisture Resistance Test
N.O. Contact
N.C. Contact
After TestAfter Test
At Operation
At Release
29
Page 35

[EE2 series]
(1) Non-latching, 5-V type
(a) Operate & release voltages (b) Contact resistances
5
4
3
2
1
0
Before Test
Operate & Release Voltages (V)
(c) Operate & release times (d) Transfer times
3
2.5
2
1.5
1
0
Operate & Release Times (ms)
Before Test
Operate Voltage
Release Voltage
Operate Time
Release Time
After Test After Test
Figure 5.3 (3) Moisture Resistance Test
(2) Latching of single-wound coil, 5-V type
200
100
50
20
Contact Resistance (mΩ)
Before Test
2
1.5
1
0.5
Transfer Time (ms)
0
Before Test
N.O. Contact
N.C. Contact
After TestAfter Test
At Operation
At Release
(a) Set & reset voltages (b) Contact resistances
5
4
3
2
1
Set & Reset Voltages (V)
0
Before Test
(c) Set & reset times (d) Transfer times
3
2.5
2
1.5
Set & Reset Times (ms)
0
Before Test
Set Voltage
Reset Voltage
Set Time
Reset Time
After Test After Test
200
100
50
20
Contact Resistance (mΩ)
Before Test
2
1.5
1
0.5
Transfer Time (ms)
0
Before Test
Figure 5.3 (4) Moisture Resistance Test
N.O. Contact
N.C. Contact
After TestAfter Test
At Operation
At Release
30
Page 36

5.1.4 Heat shock test (test conditions: temperature: –55˚C to 85˚C, test cycles: 100, sample: 10 pcs, each)
This test is to check whether the performance of the relay is degraded if the ambient temperature abruptly changes.
[EC2 series]
(1) Non-latching, 5-V type
(a) Operate & release voltages (b) Contact resistances
5
4
3
2
1
0
Before Test
Operate & Release Voltages (V)
(c) Operate & release times (d) Transfer times
3
2.5
2
1.5
0
Operate & Release Times (ms)
Before Test
Operate Voltage
Release Voltage
Operate Time
Release Time
After Test After Test
Figure 5.4 (1) Heat Shock Test
(2) Latching of single-wound coil, 5-V type
200
100
50
20
Contact Resistance (mΩ)
Before Test
2
1.5
1
0.5
Transfer Time (ms)
0
Before Test
N.O. Contact
N.C. Contact
After TestAfter Test
At Operation
At Release
(a) Set & reset voltages (b) Contact resistances
5
4
3
2
1
Set & Reset Voltages (V)
0
Before Test
(c) Set & reset times (d) Transfer times
3
2.5
1
1.5
Set & Reset Times (ms)
0
Before Test
Set Voltage
Reset Voltage
Set Time
Reset Time
After Test
200
100
50
20
Contact Resistance (mΩ)
Before Test
2
1.5
1
0.5
Transfer Time (ms)
0
Before Test
Figure 5.4 (2) Heat Shock Test
N.O. Contact
N.C. Contact
After TestAfter Test
At Operation
At Release
After Test
31
Page 37

[EE2 series]
(1) Non-latching, 5-V type
(a) Operate & release voltages (b) Contact resistances
5
4
3
2
1
0
Before Test
Operate & Release Voltages (V)
(c) Operate & release times (d) Transfer times
3
2.5
2
1.5
0
Operate & Release Times (ms)
Before Test
Operate Voltage
Release Voltage
Operate Time
Release Time
After Test After Test
Figure 5.4 (3) Heat Shock Test
(2) Latching of single-wound coil, 5-V type
200
100
50
20
Contact Resistance (mΩ)
Before Test
2
1.5
1
0.5
Transfer Time (ms)
0
Before Test
N.O. Contact
N.C. Contact
After TestAfter Test
At Operation
At Release
(a) Set & reset voltages (b) Contact resistances
5
4
3
2
1
Set & Reset Voltages (V)
0
Before Test
(c) Set & reset times (d) Transfer times
3
2.5
1
1.5
Set & Reset Times (ms)
0
Before Test
Set Voltage
Reset Voltage
Set Time
Reset Time
After Test
200
100
50
20
Contact Resistance (mΩ)
Before Test
2
1.5
1
0.5
Transfer Time (ms)
0
Before Test
Figure 5.4 (4) Heat Shock Test
N.O. Contact
N.C. Contact
After TestAfter Test
At Operation
At Release
After Test
32
Page 38

5.1.5 Vibration test (test conditions: amplitude: 1.52 mm, frequency: 10 Hz to 500 Hz, 20 G peak, test time:
2 hours each in X, Y, and Z directions, totaling 6 hours, sample: 10 pcs. each)
This test is conducted to check whether the performance of the relay is degraded after vibration is continuously
applied to the relay while the relay is being transported.
[EC2 series]
(1) Non-latching, 5-V type
(a) Operate & release voltages (b) Contact resistances
5
4
3
2
1
0
Before Test
Operate & Release Voltages (V)
(c) Operate & release times (d) Transfer times
3
2.5
2
1.5
0
Operate & Release Times (ms)
Before Test
Operate Voltage
Release Voltage
(2) Latching of single-wound coil, 5-V
N.O. Contact
200
100
50
20
Contact Resistance (mΩ)
Before Test
Operate Time
Release Time
After Test After Test
2
1.5
1
0.5
Transfer Time (ms)
0
Before Test
N.C. Contact
After TestAfter Test
At Operation
At Release
Figure 5.5 (1) Vibration Test
(a) Set & reset voltages (b) Contact resistances
5
4
3
2
1
Set & Reset Voltages (V)
0
Before Test
(c) Set & reset times (d) Transfer times
2
2.5
2
1.5
Set & Reset Times (ms)
0
Before Test
Set Voltage
Reset Voltage
Set Time
Reset Time
After Test After Test
200
100
50
20
Contact Resistance (mΩ)
Before Test
1
1.5
1
0.5
Transfer Time (ms)
0
Before Test
N.O. Contact
N.C. Contact
After TestAfter Test
At Operation
At Release
Figure 5.5 (2) Vibration Test
33
Page 39

[EE2 series]
(1) Non-latching, 5-V type
(a) Operate & release voltages (b) Contact resistances
5
4
3
2
1
0
Before Test
Operate & Release Voltages (V)
(c) Operate & release times (d) Transfer times
3
2.5
2
1.5
0
Operate & Release Times (ms)
Before Test
Operate Voltage
Release Voltage
(2) Latching of single-wound coil, 5-V
N.O. Contact
200
100
50
20
Contact Resistance (mΩ)
Before Test
Operate Time
Release Time
After Test After Test
2
1.5
1
0.5
Transfer Time (ms)
0
Before Test
N.C. Contact
After TestAfter Test
At Operation
At Release
Figure 5.5 (3) Vibration Test
(a) Set & reset voltages (b) Contact resistances
5
4
3
2
1
Set & Reset Voltages (V)
0
Before Test
(c) Set & reset times (d) Transfer times
2
2.5
2
1.5
Set & Reset Times (ms)
0
Before Test
Set Voltage
Reset Voltage
Set Time
Reset Time
After Test After Test
200
100
50
20
Contact Resistance (mΩ)
Before Test
1
1.5
1
0.5
Transfer Time (ms)
0
Before Test
N.O. Contact
N.C. Contact
After TestAfter Test
At Operation
At Release
Figure 5.5 (4) Vibration Test
34
Page 40

5.1.6 Shock test (test conditions: waveform: half sine wave, peak acceleration: 75 G, 6 times each in X, Y, and
Z directions, totaling 36 times, sample: 10 pcs. each)
This test is conducted to check whether the performance of the relay is degraded after an abrupt shock is applied
to the relay while the relay is being transported.
[EC2 series]
(1) Non-latching, 5-V type
(a) Operate & release voltages (b) Contact resistances
5
4
3
2
1
0
Before Test
Operate & Release Voltages (V)
(c) Operate & release times (d) Transfer times
3
2
1
0
Operate & Release Times (ms)
Before Test
Operate Voltage
Release Voltage
Operate Time
Release Time
After Test After Test
Figure 5.6 (1) Shock Test
(2) Latching of single-wound coil, 5-V type
200
100
50
20
Contact Resistance (mΩ)
Before Test
2
1.5
1
0.5
Transfer Time (ms)
0
Before Test
N.O. Contact
N.C. Contact
After TestAfter Test
At Operation
At Release
(a) Set & reset voltages (b) Contact resistances
5
4
3
2
1
Set & Reset Voltages (V)
0
Before Test
(c) Set & reset times (d) Transfer times
3
2.5
2
1.5
Set & Reset Times (ms)
0
Before Test
Set Voltage
Reset Voltage
Set Time
Reset Time
After Test After Test
200
100
50
20
Contact Resistance (mΩ)
Before Test
1
1.5
1
0.5
Transfer Time (ms)
0
Before Test
N.O. Contact
N.C. Contact
After TestAfter Test
At Set
At Reset
Figure 5.6 (2) Shock Test
35
Page 41

[EE2 series]
(1) Non-latching, 5-V type
(a) Operate & release voltages (b) Contact resistances
5
4
3
2
1
0
Before Test
Operate & Release Voltages (V)
(c) Operate & release times (d) Transfer times
3
2
1
0
Operate & Release Times (ms)
Before Test
Operate Voltage
Release Voltage
Operate Time
Release Time
After Test After Test
Figure 5.6 (3) Shock Test
(2) Latching of single-wound coil, 5-V type
200
100
50
20
Contact Resistance (mΩ)
Before Test
2
1.5
1
0.5
Transfer Time (ms)
0
Before Test
N.O. Contact
N.C. Contact
After TestAfter Test
At Operation
At Release
(a) Set & reset voltages (b) Contact resistances
5
4
3
2
1
Set & Reset Voltages (V)
0
Before Test
(c) Set & reset times (d) Transfer times
3
2.5
2
1.5
Set & Reset Times (ms)
0
Before Test
Set Voltage
Reset Voltage
Set Time
Reset Time
After Test After Test
200
100
50
20
Contact Resistance (mΩ)
Before Test
1
1.5
1
0.5
Transfer Time (ms)
0
Before Test
N.O. Contact
N.C. Contact
After TestAfter Test
At Set
At Reset
Figure 5.6 (4) Shock Test
36
Page 42

5.1.7 Resistance to solder heat test (test conditions: solder temperature = 260 ± 10˚C, immersion time: 10
seconds, sample: 10 pcs. each)
This test is conducted to check whether the performance of the relay is degraded after the relay has been exposed
to heat when it is soldered to a printed circuit board (PCB).
[EC2 series]
(1) Non-latching, 5-V type
(a) Operate & release voltages (b) Contact resistances
5
4
3
2
1
0
Before Test
Operate & Release Voltages (V)
(c) Operate & release times
3
2.5
2
1.5
1
0
Operate & Release Times (ms)
Before Test
Operate Voltage
Release Voltage
Operate Time
Release Time
After Test After Test
Figure 5.7 (1) Resistance to Solder Heat Test
(2) Latching of single-wound coil, 5-V type
200
100
50
20
Contact Resistance (mΩ)
Before Test
(d) Transfer times
2
1.5
1
0.5
Transfer Time (ms)
0
Before Test
N.O. Contact
N.C. Contact
After TestAfter Test
At Operation
At Release
(a) Set & reset voltages (b) Contact resistances
5
4
3
2
1
Set & Reset Voltages (V)
0
Before Test
(c) Set & reset times (d) Transfer times
3
2.5
2
1.5
Set & Reset Times (ms)
0
Before Test
Figure 5.7 (2) Resistance to Solder Heat Test
Set Voltage
Reset Voltage
Set Time
Reset Time
After Test After Test
200
100
50
20
Contact Resistance (mΩ)
Before Test
2
1.5
1
0.5
Transfer Time (ms)
0
Before Test
N.O. Contact
N.C. Contact
After TestAfter Test
At Operation
At Release
37
Page 43

5.1.8 Resistance to reflow solder heat test
This test is conducted to check whether the performance of the relay is degraded after the relay has been exposed
to heat when it is soldered to a printed circuit board (PCB).
Test condition:
<1> Soldering method: IRS (Infrared Ray Soldering)
<2> PCB: Material epoxy-glass
Thickness 1.6 mm
Size 25 × 30 cm
<3> Temperature measurement point: Printed circuit board surface near the relay terminals
<4> Temperature profile: Refer to Figure 5.8
Tmax.: 235
200
175
150
Temperature (˚C)
30 sec.
200 sec.
80 sec.
Figure 5.8 Temperature Profiles
38
Page 44

[EE2 series]
(1) Non-latching, 5-V type
(a) Operate & release voltages (b) Contact resistances
5
4
3
2
1
0
Operate & Release Voltages (V)
Before Test
(c) Operate & release times (d) Transfer times
3
2
1
0
Operate & Release Times (ms)
Before Test
Operate Voltage
Release Voltage
Operate Time
Release Time
After Test After Test
Figure 5.8 (1) Resistance to Reflow Solder Heat
(2) Latching of single-wound coil, 5-V type
100
50
20
10
Contact Resistance (mΩ)
Before Test
1
0.5
Transfer Time (ms)
0
Before Test
N.O. Contact
N.C. Contact
After TestAfter Test
At Operation
At Release
(a) Set & reset voltages (b) Contact resistances
5
4
3
2
1
Set & Reset Voltages (V)
0
Before Test
(c) Set & reset times (d) Transfer times
2
1
Set & Reset Times (ms)
0
Before Test
Figure 5.8 (2) Resistance to Reflow Solder Heat
Set Voltage
Reset Voltage
Set Time
Reset Time
After Test After Test
100
50
20
10
Contact Resistance (mΩ)
Before Test
1
0.5
Transfer Time (ms)
0
Before Test
N.O. Contact
N.C. Contact
After TestAfter Test
At Set
At Reset
39
Page 45

5.1.9 Terminal strength test (test conditions: ambient temperature: 25˚C, tensile strength: 1.36 kg, number of
times of bending: 2, sample: 10 pcs. each)
The purpose of this test is to check whether the performance of the relay is degraded after an excessive force
is applied to the terminals of the relay when the relay is mounted on a PCB.
[EC2 series]
(1) Non-latching, 5-V type
(a) Operate & release voltages (b) Contact resistances
5
4
3
2
1
0
Before Test
Operate & Release Voltages (V)
(c) Operate & release times (d) Transfer times
3
2.5
2
1.5
0
Operate & Release Times (ms)
Before Test
Operate Voltage
Release Voltage
Operate Time
Release Time
After Test After Test
Figure 5.9 (1) Terminal Strength
(2) Latching of single-wound coil, 5-V type
200
100
50
20
Contact Resistance (mΩ)
Before Test
2
1.5
1
0.5
Transfer Time (ms)
0
Before Test
N. O. Contact
N. C. Contact
After TestAfter Test
At Operation
At Release
40
(a) Set & reset voltages (b) Contact resistances
5
4
3
2
1
Set & Reset Voltages (V)
0
Before Test
(c) Set & reset times (d) Transfer times
2
2.5
1
1.5
Set & Reset Times (ms)
0
Before Test
Set Voltage
Reset Voltage
Set Time
Reset Time
After Test After Test
200
100
50
20
Contact Resistance (mΩ)
Before Test
1
1.5
1
0.5
Transfer Time (ms)
0
Before Test
N.O. Contact
N.C. Contact
After TestAfter Test
At Operation
At Release
Figure 5.9 (2) Terminal Strength
Page 46

5.2 Contact life tests
p
This section shows the results of tests conducted to examine the service life of the contacts, which has a significant
influence on the life of the relay.
To test the service life of the contacts, the operate and release voltages, contact resistance, operate and release
times, and transfer time of each relay is measured each time the relay has performed the specified number of
operations under the specified conditions.
The service life of contacts of the EC2 series relay is equal to the one of the EE2 series relay, because they have
common structure.
For changes in the characteristics, refer to the graphs shown below.
5.2.1 Non-load test A (driving frequency: 50 Hz, ambient temperature: +25˚C, sample: 10 non-latching types
(rated at 5 V))
The cleanness of the contact surfaces influences the result of this test because no electric load is applied to the
relay.
(a) Operate & release voltages (b) Contact resistances
5
4
3
2
1
0
Operate & Release Voltages (V)
Number of Operations (×107 Times)
(c) Operate & release times (d) Transfer times
3
2.5
2
1.5
1
Operate & Release Times (ms)
Number of Operations (×107 Times)
Operate Voltage
Release Voltage
510Before Test
510Before Test
200
100
50
20
Contact Resistance (mΩ)
0
Number of Operations (×10
Operate Time
Release Time
2
1.5
1
0.5
Transfer Time (ms)
0
Number of O
Figure 5.10 Non-load Test A
N.O. Contact
N.C. Contact
510Before Test
510Before Test
erations (×107 Times)
7
Times)
At Operation
At Release
41
Page 47

5.2.2 Non-load test B (driving frequency: 50 Hz, ambient temperature: +85˚C, sample: 10 non-latching types
p
)
(rated at 5 V))
The conditions of this test are more stringent than those of the test in 5.2.1 because the relay is exposed to a higher
ambient temperature and consequently organic gas is more likely to be generated inside the relay housing.
(a) Operate & release voltages (b) Contact resistances
5
4
3
2
1
0
Operate & Release Voltages (V)
Number of Operations (×107 Times)
Operate Voltage
Release Voltage
510Before Test
200
100
50
20
Contact Resistance (mΩ)
0
Number of Operations (×10
(c) Operate & release times (d) Transfer times
3
2
1
0
Operate & Release Times (ms)
Number of Operations (×107 Times)
Operate Time
Release Time
510Before Test
2
1.5
1
0.5
Transfer Time (ms)
0
Number of O
N.O. Contact
N.C. Contact
510Before Test
510Before Test
erations (×107 Times
7
Times)
At Operation
At Release
Figure 5.11 Non-load Test B
µ
5.2.3 Resistive load test A (contact load: 10 mVdc, 10
A, resistive, driving frequency: 25 Hz, ambient
temperature: +25˚C, sample: 10 non-latching types (rated at 5 V))
This test is conducted with the relay under the minimum applied load condition.
(a) Operate & release voltages (b) Contact resistances
5
4
3
2
1
0
Operate & Release Voltages (V)
Number of Operations (×107 Times)
(c) Operate & release times (d) Transfer times
3
2.5
2
1.5
0
Operate & Release Times (ms)
Number of Operations (×107 Times)
Operate Voltage
Release Voltage
510Before Test
Operate Time
Release Time
510Before Test
200
100
50
20
Contact Resistance (mΩ)
0
Number of Operations (×10
2
1.5
1
0.5
Transfer Time (ms)
0
Number of Operations (×10
N.O. Contact
N.C. Contact
510Before Test
At Operation
At Release
510Before Test
7
Times)
7
Times)
42
Figure 5.12 Resistive Load Test A
Page 48

5.2.4 Resistive load test B (contact load: 10 Vdc, 10 mA, resistive, driving frequency: 2 Hz, ambient temperature:
p
)
+85˚C, sample: 10 non-latching types (rated at 5 V))
This test is conducted with a load equivalent to the signal level of an IC applied to the relay.
(a) Operate & release voltages (b) Contact resistances
5
4
3
2
1
0
Operate & Release Voltages (V)
Number of Operations (×105 Times)
Operate Voltage
Release Voltage
510Before Test
(c) Operate & release times (d) Transfer times
3
2.5
2
1.5
0
Operate & Release Times (ms)
Number of Operations (×105 Times)
510Before Test
Operate Time
Release Time
200
100
50
20
Contact Resistance (mΩ)
0
Number of Operations (×10
1
1.5
1
0.5
Transfer Time (ms)
0
Number of Operations (×10
N.O. Contact
N.C. Contact
510Before Test
At Operation
At Release
510Before Test
5
Times)
5
Times)
Figure 5.13 Resistive Load Test B
5.2.5 Resistive load test C (contact load: 28 Vdc, 100 mA, resistive, driving frequency: 2 Hz, ambient tempera-
ture: +85˚C, sample: 10 non-latching types (rated at 5 V))
This test is conducted with a load of medium level applied to the relay contacts.
(a) Operate & release voltages (b) Contact resistances
5
4
3
2
1
0
Operate & Release Voltages (V)
Number of Operations (×105 Times)
Operate Voltage
Release Voltage
25Before Test
100
50
20
10
Contact Resistance (mΩ)
0
Number of Operations (×10
(c) Operate & release times (d) Transfer times
Operate Time
3
2.5
2
1.5
0
Operate & Release Times (ms)
Number of Operations (×105 Times)
Release Time
25Before Test
1
1.5
1
0.5
Transfer Time (ms)
0
Number of O
N.O. Contact
N.C. Contact
25Before Test
25Before Test
erations (×105 Times
5
Times)
At Operation
At Release
Figure 5.14 Resistive Load Test C
43
Page 49

5.2.6 Resistive load test D (contact load: 50 Vdc, 100 mA, resistive, driving frequency: 5 Hz, ambient tempera-
p
)
ture: +25˚C, sample: 10 non-latching types (rated at 5 V))
The load conditions of this test are equivalent to the voltage and current levels of a public telephone circuit.
(a) Operate & release voltages (b) Contact resistances
5
4
3
2
1
0
Operate & Release Voltages (V)
Number of Operations (×105 Times)
Operate Voltage
Release Voltage
510Before Test
200
100
50
20
Contact Resistance (mΩ)
0
Number of Operations (×10
(c) Operate & release times (d) Transfer times
Operate Time
3
2.5
2
1.5
0
Operate & Release Times (ms)
Number of Operations (×105 Times)
Release Time
510Before Test
2
1.5
1
0.5
Transfer Time (ms)
0
Number of Operations (×10
N.O. Contact
N.C. Contact
510Before Test
At Operation
At Release
510Before Test
5
Times)
5
Times)
Figure 5.15 Resistive Load Test D
5.2.7 Resistive load test E (contact load: 50 Vdc, 100 mA, resistive, driving frequency: 5 Hz, ambient temperature:
+85˚C, sample: 10 non-latching types (rated at 5 V))
The conditions of this test are more stringent for the relay than those in 5.2.6 above because the ambient
temperature is higher.
(a) Operate & release voltages (b) Contact resistances
5
4
3
2
1
0
Operate & Release Voltages (V)
Number of Operations (×105 Times)
Operate Voltage
Release Voltage
510Before Test
(c) Operate & release times (d) Transfer times
3
2.5
1
1.5
0
Operate & Release Times (ms)
Number of Operations (×105 Times)
510Before Test
Operate Time
Release Time
200
100
50
20
Contact Resistance (mΩ)
0
Number of Operations (×10
2
1.5
1
0.5
Transfer Time (ms)
0
Number of O
N.O. Contact
N.C. Contact
510Before Test
510Before Test
erations (×105 Times
5
Times)
At Operation
At Release
44
Figure 5.16 Resistive Load Test E
Page 50

5.2.8 Inductive load test (contact load: 48 Vdc, 110 mA, inductive load by wire spring relay, driving frequency:
p
)
2 Hz, ambient temperature: +25˚C, sample: 10 non-latching types (rated at 5 V))
The conditions of this test are practical load conditions under which the relay is used to switch a public telephone
circuit.
(a) Operate & release voltages (b) Contact resistances
5
4
3
2
1
0
Operate & Release Voltages (V)
Number of Operations (×105 Times)
Operate Voltage
Release Voltage
510Before Test
(c) Operate & release times (d) Transfer times
3
2.5
2
1.5
0
Operate & Release Times (ms)
Number of Operations (×105 Times)
510Before Test
Operate Time
Release Time
200
100
50
20
Contact Resistance (mΩ)
0
Number of Operations (×10
2
1.5
1
0.5
Transfer Time (ms)
0
Number of O
N.O. Contact
N.C. Contact
510Before Test
510Before Test
erations (×105 Times
5
Times)
At Operation
At Release
Figure 5.17 Inductive Load Test
5.2.9 Resistive load test F (contact load: 220 Vdc, 0.14 A, resistive, driving frequency: 2 Hz, ambient temperature:
+25˚C, sample: 10 non-latching types (rated at 5 V))
The load conditions of this test are at the maximum switching voltage and maximum switching power with the
contacts switching a DC load.
(a) Operate & release voltages (b) Contact resistances
5
4
3
2
1
0
Operate & Release Voltages (V)
Number of Operations (×105 Times)
Operate Voltage
Release Voltage
12Before Test
(c) Operate & release times (d) Transfer times
3
2.5
2
1.5
0
Operate & Release Times (ms)
Number of Operations (×105 Times)
12Before Test
Operate Time
Release Time
200
100
50
20
Contact Resistance (mΩ)
0
Number of Operations (×10
2
1.5
1
0.5
Transfer Time (ms)
0
Number of Operations (×10
N.O. Contact
N.C. Contact
12Before Test
At Operation
At Release
12Before Test
5
Times)
5
Times)
Figure 5.18 Resistive Load Test F
45
Page 51

5.2.10 Resistive load test G (contact load: 125 Vac, 0.5 A, resistive, driving frequency: 2 Hz, ambient tempera-
p
)
p
)
ture: +25˚C, sample: 10 non-latching types (rated at 5 V))
The load conditions of this test are at the maximum switching voltage and maximum switching power with the
contacts switching an AC load.
(a) Operate & release voltages (b) Contact resistances
5
4
3
2
1
0
Operate & Release Voltages (V)
Number of Operations (×105 Times)
Operate Voltage
Release Voltage
12Before Test
200
100
50
20
Contact Resistance (mΩ)
0
Number of Operations (×10
(c) Operate & release times (d) Transfer times
Operate Time
3
2.5
2
1.5
0
Operate & Release Times (ms)
Number of Operations (×105 Times)
Release Time
12Before Test
2
1.5
1
0.5
Transfer Time (ms)
0
Number of O
N.O. Contact
N.C. Contact
12Before Test
12Before Test
erations (×105 Times
5
Times)
At Operation
At Release
Figure 5.19 Resistive Load Test G
5.2.11 Resistive load test H (contact load: 30 Vdc, 1 A, resistive, driving frequency: 2 Hz, ambient temperature:
+25˚C, sample: 10 non-latching types (rated at 5 V))
The load conditions of this test are at the maximum switching current and maximum switching power with the
contacts switching a DC load.
(a) Operate & release voltages (b) Contact resistances
5
4
3
2
1
0
Operate & Release Voltages (V)
Number of Operations (×105 Times)
Operate Voltage
Release Voltage
12Before Test
200
100
50
20
Contact Resistance (mΩ)
0
Number of Operations (×10
(c) Operate & release times (d) Transfer times
Operate Time
3
2.5
2
1.5
0
Operate & Release Times (ms)
Number of Operations (×105 Times)
Release Time
12Before Test
2
1.5
1
0.5
Transfer Time (ms)
0
Number of O
N.O. Contact
N.C. Contact
12Before Test
12Before Test
erations (×105 Times
5
Times)
At Operation
At Release
46
Figure 5.20 Resistive Load Test H
Page 52

 Loading...
Loading...