
查询LMH6646供应商
LMS75ALS176A
Differential Bus Transceivers
LMS75ALS176A Differential Bus Transceivers
April 2003
General Description
The LMS75ALS176A is a differential bus/line transceiver
designed for bidirectional data communication on multipoint
bus transmission lines. It is designed for balanced transmission lines. It meets ANSI Standards TIA/EIA RS422-B, TIA/
EIA RS485-A and ITU recommendation V.11 and X.27. The
LMS75ALS176A combines a TRI-STATE
driver and differential input receiver, both of which operate
from a single 5.0V power supply. The driver and receiver
have an active high and active low enable, respectively, that
can be externally connected to function as a direction control. The driver and receiver differential inputs are internally
connected to form differential input/output (I/O) bus ports
that are designed to offer minimum loading to bus whenever
the driver is disabled or when V
wide positive and negative common mode voltage ranges,
making the device suitable for multipoint applications in
noisy environments. The LMS75ALS176A is available in a
8-Pin SOIC package. It is a drop-in socket replacement to
TI’s SN75ALS176A.
CC
™
differential line
= 0V. These ports feature
Typical Application
Features
n Bidirectional transceiver
n Meet ANSI standard RS-485-A and RS-422-B
n Low skew, 2ns
n Low supply current, 8mA (max.)
n Wide input and output voltage range
n High output drive capacity
n Thermal shutdown protection
n Open circuit fail-safe for receiver
n Receiver input sensitivity
n Receiver input hysteresis 10mV (min.)
n Single supply voltage operation, 5V
n Glitch free power-up and power-down operation
n Data rates up to 35 Mbaud
n Pin and functional compatible with TI’s SN75ALS176A
n 8-Pin SOIC
±
60mA
±
200mV
Applications
n Network hubs, bridges, and routers
n Point of sales equipment (ATM, barcode readers,…)
n Industrial programmable logic controllers
n High speed parallel and serial applications
n Multipoint applications with noisy environment
A Typical multipoint application is shown in the above figure. Terminating resistors, RT, are typically required but only located at the two ends of the cable.
Pull up and pull down resistors maybe required at the end of the bus to provide failsafe biasing. The biasing resistors provide a bias to the cable when all
drivers are in TRI-STATE, See National Application Note, AN-847 for further information.
© 2003 National Semiconductor Corporation DS200478 www.national.com
20047801

Connection Diagram
LMS75ALS176A
8-Pin SOIC
Top View
20047802
Ordering Information
Package Part Number Package Marking Transport Media NSC Drawing
8-Pin SOIC
LMS75ALS176AM
LMS75ALS176AMX 2.5k Units Tape and Reel
LMS75LS176A
Rail
Truth Table
DRIVER SECTION
RE
XHHHL
XHL LH
XLXZZ
RECEIVER SECTION
RE
LL ≥ +0.2V H
LL ≤ −0.2V L
HX X Z
L L OPEN
Note:*= Non Terminated, Open Input only
X = Irrelevant
Z = TRI-STATE
H = High level
L = Low level
DE DI A B
DE A-B RO
*
M08A
H
www.national.com 2

LMS75ALS176A
Absolute Maximum Ratings (Note 1)
If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required,
please contact the National Semiconductor Sales Office/
Distributors for availability and specifications.
Supply Voltage, V
Voltage Range at Any Bus
Terminal −7V to 12V
Input Voltage, V
Package Thermal Impedance, θ
Junction Temperature (Note 3) 150˚C
Operating Free-Air Temperature
Range, T
A
Storage Temperature Range −65˚C to 150˚C
Soldering Information
Infrared or Convection (20 sec.) 235˚C
ESD Rating (Note 4) 2KV
(Note 2) 7V
CC
(DI, DE, or RE) −0.3V to VCC+ 0.3V
IN
JA
125C/W
0˚C to 70˚C
Operating Ratings
Supply Voltage, V
Voltage at any Bus Terminal
(Separately or Common Mode)
V
or V
IN
IC
High-Level Input Voltage, V
(Note 5)
Low-Level Input Voltage, V
(Note 5)
Differential Input Voltage, V
(Note 6)
High-Level Output
Driver, I
Receiver, I
Low-Level Output
Driver, I
Receiver, I
CC
OH
OH
OL
OL
Min Nom Max
4.75 5.0 5.25 V
IH
IL
ID
2V
12−7V
0.8 V
±
12 V
−60 mA
−400 µA
60 mA
8mA
Electrical Characteristics
VCC= 5V, TA= 0˚C to 70˚C
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Units
Driver Section
V
CL
V
O
|V
OD1
|V
OD2
V
OD3
∆V
OD
V
OC
∆V
OC
I
O
I
IH
I
IL
I
OSD
I
CC
Switching Characteristics
(OD) Differential Output Delay
t
d
Input Clamp Voltage II= −18mA −1.5 V
Output Voltage IO=0 0 6 V
| Differential Output Voltage IO= 0 1.5 6 V
| Differential Output Voltage RL= 100Ω,2
R
=54Ω 1.5 1.9 5
L
Differential Output Voltage V
Change in Magnitude of
= −7V to 12 V 1.5 5 V
TEST
=54Ω or 100Ω
R
L
±
0.2 V
Differential Output Voltage
(Note 7)
Common-Mode Output
Voltage
Change in Magnitude of
RL=54Ω or 100Ω 3
=54Ω or 100Ω
R
L
±
−1
0.2 V
Differential Output Voltage
(Note 7)
Output Current Output Disabled
(Note 8)
High-Level
VIN= 2.4V 20 µA
VO= 12V 1
V
= −7V −0.8
O
mA
Input Current
Low-Level
VIN= 0.4V −400 µA
Input Current
Short-Circuit Output Current VO= −7V −250
V
= 0 −150
O
V
O=VCC
V
= 8V 250
O
Supply Current No Load Outputs
250
4.8 8 mA
mA
Enabled or
Disabled
RL=54Ω ,CL= 50pF 3 7 14 ns
Time
V
V
www.national.com3
Electrical Characteristics (Continued)
VCC= 5V, TA= 0˚C to 70˚C
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Units
t
(OD) Differential Output Transition
t
LMS75ALS176A
t
sk(p)
t
sk(lim)
t
PZH
Time
Pulse Skew, (|t
Pulse Skew RL=54Ω,CL= 50pF
Output Enable Time to High
Level
t
PZL
Output Enable Time to Low
Level
t
PHZ
Output Disable Time from
High Level
t
PLZ
Output Disable Time from
Low Level
Receiver Section
V
TH+
Positive-Going Input
Threshold Voltage
V
TH−
Negative-Going Input
Threshold Voltage
∆V
V
V
V
I
TH
CL
OH
OL
OZ
Hysteresis Voltage
(V
TH+-VTH−
)
Enable-Input Clamp Voltage II= −18mA 1.5 V
High-Level Output Voltage VID= 200mV, IOH= −400µA 2.7 V
Low-Level Output Voltage VID= −200mV, IOL= 8mA 0.45 V
High-Impedance-State Output
Current
I
IN
I
IH
Line Input Current Other Input = 0V,
High-Level Enable-Input
Current
I
IL
Low-Level Enable-Input
Current
R
I
I
IN
OSR
CC
Input Resistance 12 20 kΩ
Short-Circuit Output Current VID= 200mV, VO= 0V −15 −85 mA
Supply Current No Load Outputs
d(ODH-td(ODL
RL=54Ω,CL= 50pF 8 ns
|) RL=54Ω,CL= 50pF 0 3 ns
4ns
(Note 9)
RL= 110Ω,CL= 50pF 18 50 ns
RL= 110Ω,CL= 50pF 18 35 ns
RL= 110Ω,CL= 50pF 9 35 ns
RL= 110Ω,CL= 50pF 10 17 ns
VO= 2.7V, IO= −0.4mA 0.2 V
VO= 0.5V, IO= 8mA −0.2 V
10 mV
VO= 0.4V to 2.4V
±
20 µA
VIN= 12V 1
(Note 5)
V
= −7V −0.8
IN
VIH= 2.7V 20 µA
VIL= 0.4V −100 µA
4.8 8 mA
Enabled or
Disabled
mA
Switching Characteristics
t
PD
t
sk(p)
t
sk(lim)
Propagation Delay Time VID= −1.5V to 1.5V, CL= 15pF 8 18 30 ns
Pulse Skew (|t
PLH-tPHL
|) VID= −1.5V to 1.5V, CL= 15pF 2 ns
Pulse Skew RL=54Ω ,CL= 50pF
(Note 9)
t
PZH
Output Enable Time to High
CL= 15pF 5 35 ns
Level
t
PZL
Output Enable Time to Low
CL= 15pF 5 35 ns
Level
t
PHZ
Output Disable Time from
CL= 15pF 20 35 ns
High Level
t
PLZ
Output Disable Time from
CL= 15pF 10 17 ns
Low Level
www.national.com 4
7.5 ns

Electrical Characteristics (Continued)
Note 1: Absolute Maximum Ratings indicate limits beyond which damage to the device may occur. Operating Ratings indicate conditions for which the device is
intended to be functional, but specific performance is not guaranteed. For guaranteed specifications and the test conditions, see the Electrical Characteristics
Note 2: All voltage values, except differential I/O bus voltage, are with respect to network ground terminal.
Note 3: The maximum power dissipation is a function of T
(T
J(MAX)-TA
Note 4: ESD rating based upon human body model, 100pF discharged through 1.5kΩ.
Note 5: Voltage limits apply to DI, DE, RE pins.
Note 6: Differential input/output bus voltage is measured at the non-inverting terminal A with respect to the inverting terminal B.
Note 7: |∆V
Note 8: Applies to both power on and off (ANSI Standard RS-485 conditions). Does not apply to TIA/EIA-422-B for a combined driver and receiver combination.
Note 9: Skew limit is the maximum difference in propagation delay between any two channels of any two devices.
)/θJA. All numbers apply for packages soldered directly into a PC board.
| and |∆VOC| are changes in magnitude of VODand VOC, respectively when the input changes from high to low levels.
OD
, θJA, and TA. The maximum allowable power dissipation at any ambient temperature is PD=
J(MAX)
Typical Performance Characteristics
LMS75ALS176A
Driver High-Level Output Voltage vs.
High-Level Output Current
Driver Differential Output Voltage vs.
Output Current
20047812
Driver Low-Level Output Voltage vs.
Low-Level Output Current
20047813
Receiver High-Level Output Voltage vs. High-Level
Output Current
20047814
20047815
www.national.com5
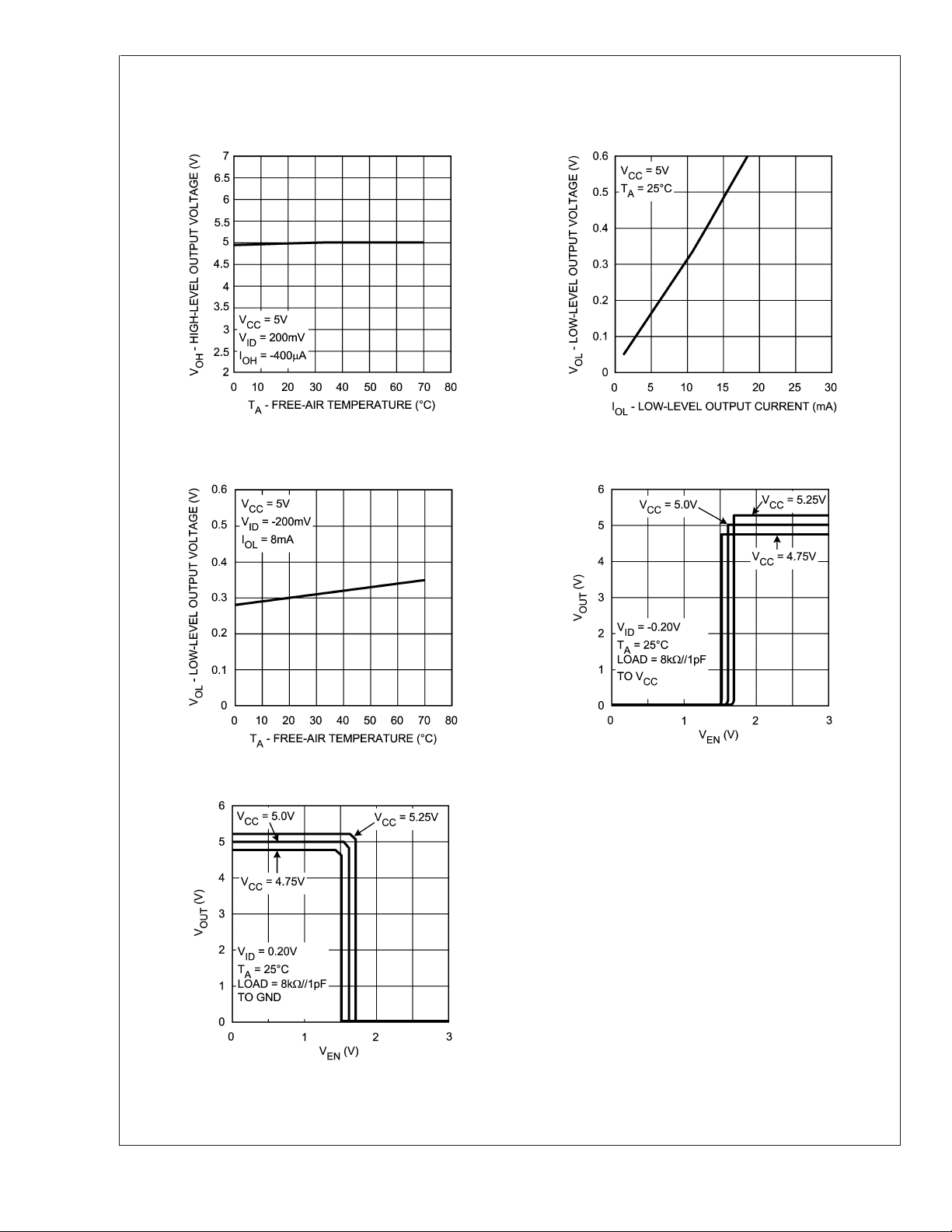
Typical Performance Characteristics (Continued)
Receiver High-Level Output Voltage vs.
LMS75ALS176A
Receiver Low-Level Output Voltage vs.
Receiver Low-Level Output Voltage vs.
Free-Air Temperature
20047816
Low-Level Output Current
20047817
Free-Air Temperature Receiver Output Voltage vs. Enable Voltage
20047818
Receiver Output Voltage vs. Enable Voltage
20047820
www.national.com 6
20047819

Parameter Measuring Information
LMS75ALS176A
20047803
FIGURE 1. Test Circuit for V
FIGURE 2. Test Circuit for V
OD2
and V
OD3
OC
20047804
20047805
FIGURE 3. Test Circuit for Driver Differential Output Delay and Transition Times
FIGURE 4. Test Circuit for Driver T
PZH
and T
PHZ
20047806
www.national.com7

Parameter Measuring Information (Continued)
LMS75ALS176A
20047807
FIGURE 5. Test Circuit for T
PZL
and T
PLZ
20047808
FIGURE 6. Test Circuit for Receiver VOHand V
FIGURE 7. Test Circuit for T
PLH
and T
PHL
OL
20047809
www.national.com 8

Parameter Measuring Information (Continued)
Test Circuit
Voltage Waveforms
LMS75ALS176A
20047810
FIGURE 8. Test Circuit for Receiver T
PZH/TPZL
and T
20047811
PHZ/TPLZ
www.national.com9

Application Information
POWER LINE NOISE FILTERING
A factor to consider in designing power and ground is noise
filtering. A noise filtering circuit is designed to prevent noise
generated by the integrated circuit (IC) as well as noise
LMS75ALS176A
entering the IC from other devices. A common filtering
method is to place by-pass capacitors (C
power and ground lines.
Placing a by-pass capacitor (C
) with the correct value at
bp
the proper location solves many power supply noise problems. Choosing the correct capacitor value is based upon
the desired noise filtering range. Since capacitors are not
) between the
bp
ideal, they may act more like inductors or resistors over a
specific frequency range. Thus, many times two by-pass
capacitors may be used to filter a wider bandwidth of noise.
It is highly recommended to place a larger capacitor, such as
10µF, between the power supply pin and ground to filter out
low frequencies and a 0.1µF to filter out high frequencies.
By pass-capacitors must be mounted as close as possible to
the IC to be effective. Long leads produce higher impedance
at higher frequencies due to stray inductance. Thus, this will
reduce the by-pass capacitor’s effectiveness. Surface
mounted chip capacitors are the best solution because they
have lower inductance.
20047821
FIGURE 9. Placement of by-pass Capacitors, C
bp
www.national.com 10

Physical Dimensions inches (millimeters) unless otherwise noted
8-Pin SOIC
NS Package Number M08A
LMS75ALS176A Differential Bus Transceivers
LIFE SUPPORT POLICY
NATIONAL’S PRODUCTS ARE NOT AUTHORIZED FOR USE AS CRITICAL COMPONENTS IN LIFE SUPPORT
DEVICES OR SYSTEMS WITHOUT THE EXPRESS WRITTEN APPROVAL OF THE PRESIDENT AND GENERAL
COUNSEL OF NATIONAL SEMICONDUCTOR CORPORATION. As used herein:
1. Life support devices or systems are devices or
systems which, (a) are intended for surgical implant
into the body, or (b) support or sustain life, and
whose failure to perform when properly used in
accordance with instructions for use provided in the
2. A critical component is any component of a life
support device or system whose failure to perform
can be reasonably expected to cause the failure of
the life support device or system, or to affect its
safety or effectiveness.
labeling, can be reasonably expected to result in a
significant injury to the user.
National Semiconductor
Americas Customer
Support Center
Email: new.feedback@nsc.com
Tel: 1-800-272-9959
www.national.com
National does not assume any responsibility for use of any circuitry described, no circuit patent licenses are implied and National reserves the right at any time without notice to change said circuitry and specifications.
National Semiconductor
Europe Customer Support Center
Fax: +49 (0) 180-530 85 86
Email: europe.support@nsc.com
Deutsch Tel: +49 (0) 69 9508 6208
English Tel: +44 (0) 870 24 0 2171
Français Tel: +33 (0) 1 41 91 8790
National Semiconductor
Asia Pacific Customer
Support Center
Email: ap.support@nsc.com
National Semiconductor
Japan Customer Support Center
Fax: 81-3-5639-7507
Email: jpn.feedback@nsc.com
Tel: 81-3-5639-7560
 Loading...
Loading...