September 2007
DAC128S085
12-Bit Micro Power OCTAL Digital-to-Analog Converter
with Rail-to-Rail Outputs
DAC128S085 12-Bit Micro Power OCTAL Digital-to-Analog Converter with Rail-to-Rail Outputs
General Description
The DAC128S085 is a full-featured, general purpose OCTAL
12-bit voltage-output digital-to-analog converter (DAC) that
can operate from a single +2.7V to +5.5V supply and consumes 1.95 mW at 3V and 4.85 mW at 5V. The DAC128S085
is packaged in a 16-lead LLP package and a 16-lead TSSOP
package. The LLP package makes the DAC128S085 the
smallest OCTAL DAC in its class. The on-chip output amplifiers allow rail-to-rail output swing and the three wire serial
interface operates at clock rates up to 40 MHz over the entire
supply voltage range. Competitive devices are limited to 25
MHz clock rates at supply voltages in the 2.7V to 3.6V range.
The serial interface is compatible with standard SPI™, QSPI,
MICROWIRE and DSP interfaces. The DAC128S085 also offers daisy chain operation where an unlimited number of
DAC128S085s can be updated simultaneously using a single
serial interface.
There are two references for the DAC128S085. One reference input serves channels A through D while the other
reference serves channels E through H. Each reference can
be set independently between 0.5V and VA, providing the
widest possible output dynamic range. The DAC128S085 has
a 16-bit input shift register that controls the mode of operation,
the power-down condition, and the DAC channels' register/
output value. All eight DAC outputs can be updated simultaneously or individually.
A power-on reset circuit ensures that the DAC outputs power
up to zero volts and remain there until there is a valid write to
the device. The power-down feature of the DAC128S085 allows each DAC to be independently powered with three different termination options. With all the DAC channels
powered down, power consumption reduces to less than 0.3
µW at 3V and less than 1 µW at 5V. The low power consumption and small packages of the DAC128S085 make it an
excellent choice for use in battery operated equipment.
The DAC128S085 is one of a family of pin compatible DACs,
including the 8-bit DAC088S085 and the 10-bit DAC108S085.
All three parts are offered with the same pinout, allowing system designers to select a resolution appropriate for their
application without redesigning their printed circuit board. The
DAC128S085 operates over the extended industrial temperature range of −40°C to +125°C.
Features
Guaranteed Monotonicity
■
Low Power Operation
■
Rail-to-Rail Voltage Output
■
Daisy Chain Capability
■
Power-on Reset to 0V
■
Simultaneous Output Updating
■
Individual Channel Power Down Capability
■
Wide power supply range (+2.7V to +5.5V)
■
Dual Reference Voltages with range of 0.5V to V
■
Operating Temperature Range of −40°C to +125°C
■
Industry's Smallest Package
■
Key Specifications
Resolution 12 bits
■
INL ±8 LSB (max)
■
DNL +0.75 / −0.4 LSB (max)
■
Settling Time 8.5 µs (max)
■
Zero Code Error +15 mV (max)
■
Full-Scale Error −0.75 %FSR (max)
■
Supply Power
■
Normal 1.95 mW (3V) / 4.85 mW (5V) typ
—
■
Power Down 0.3 µW (3V) / 1 µW (5V) typ
—
Applications
Battery-Powered Instruments
■
Digital Gain and Offset Adjustment
■
Programmable Voltage & Current Sources
■
Programmable Attenuators
■
Voltage Reference for ADCs
■
Sensor Supply Voltage
■
Range Detectors
■
A
Ordering Information
Order Numbers Temperature Range Package Top Mark
DAC128S085CISQ
DAC128S085CISQX
DAC128S085CIMT
DAC128S085CIMTX
DAC128S085EB Evaluation Board - BOTH
SPI™ is a trademark of Motorola, Inc.
© 2007 National Semiconductor Corporation 300169 www.national.com
−40°C ≤ TA ≤ +125°C
−40°C ≤ TA ≤ +125°C
−40°C ≤ TA ≤ +125°C
−40°C ≤ TA ≤ +125°C
16-Lead LLP
LLP Tape-and-Reel
16-Lead TSSOP X78C
TSSOP Tape-and-Reel X78C
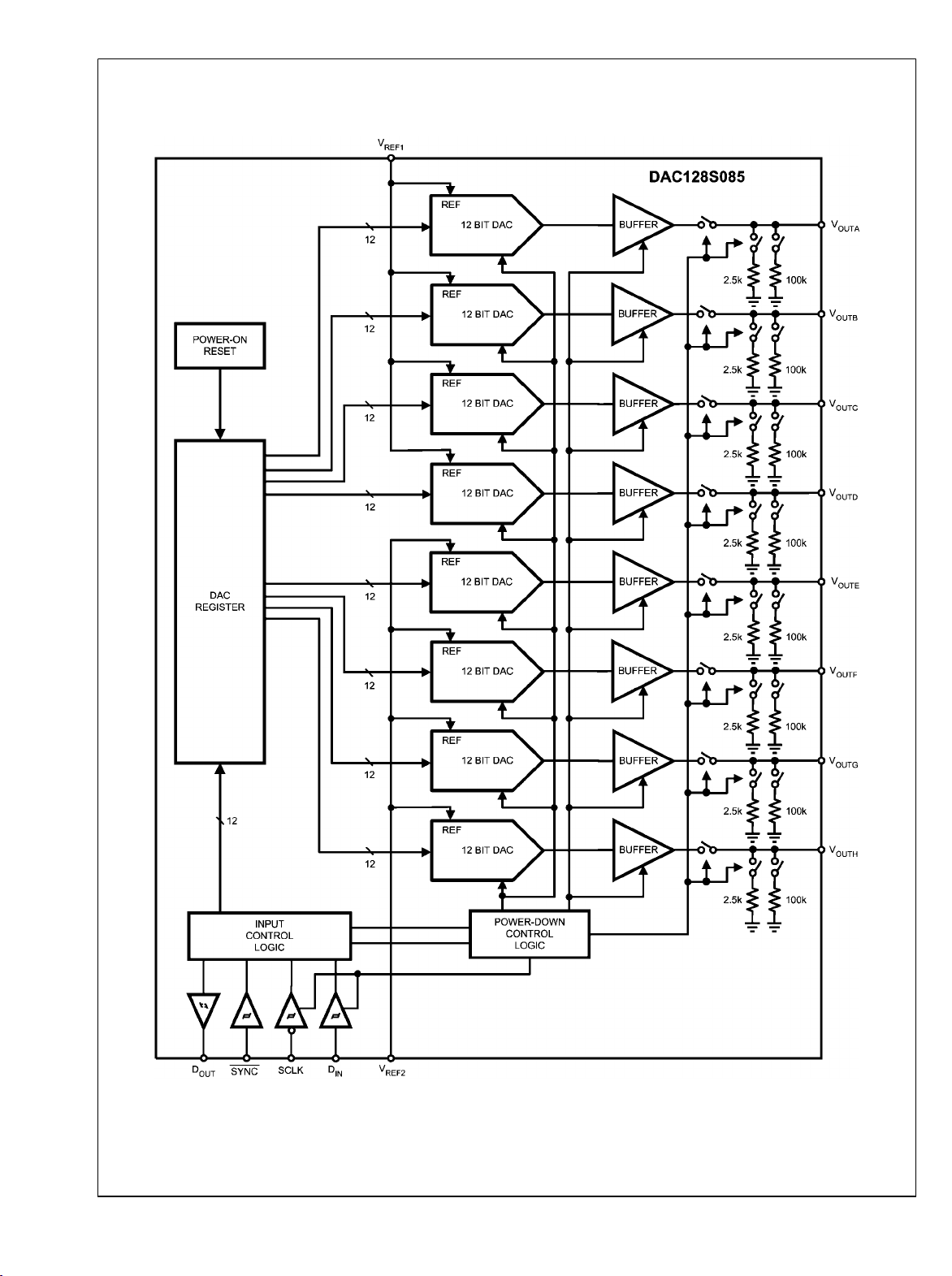
Block Diagram
DAC128S085
www.national.com 2
30016903
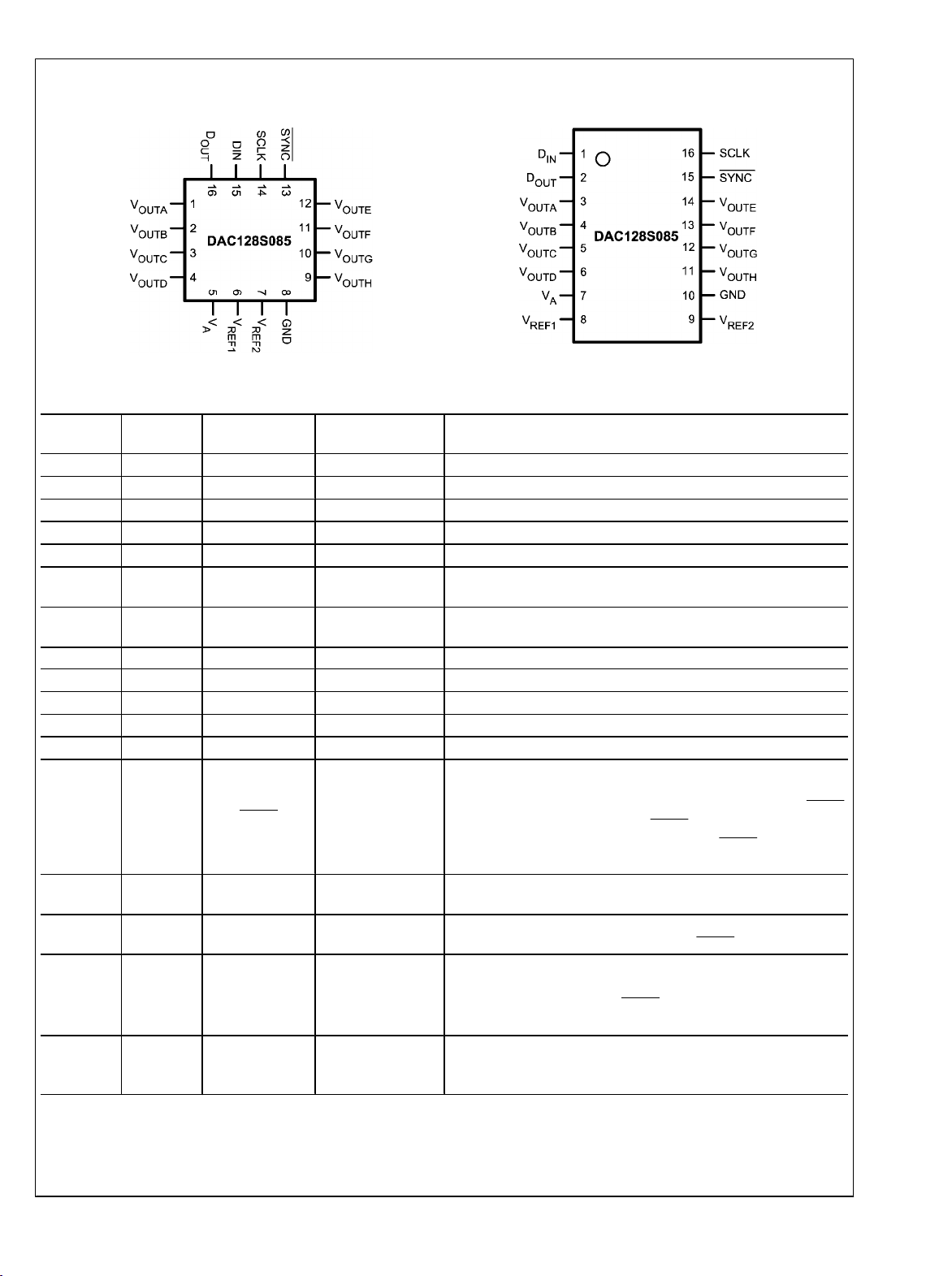
Pin Configuration
DAC128S085
30016901
Pin Descriptions
LLP
Pin No.
1 3
2 4
3 5
4 6
5 7
6 8
7 9
8 10 GND Ground Ground reference for all on-chip circuitry.
9 11
10 12
11 13
12 14
13 15 SYNC Digital Input
14 16 SCLK Digital Input
15 1
16 2
17
TSSOP
Pin No.
Symbol Type Description
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
OUTA
OUTB
OUTC
OUTD
V
A
REF1
REF2
OUTH
OUTG
OUTF
OUTE
Analog Output Channel A Analog Output Voltage.
Analog Output Channel B Analog Output Voltage.
Analog Output Channel C Analog Output Voltage.
Analog Output Channel D Analog Output Voltage.
Supply Power supply input. Must be decoupled to GND.
Analog Input
Analog Input
Unbuffered reference voltage shared by Channels A, B, C, and D.
Must be decoupled to GND.
Unbuffered reference voltage shared by Channels E, F, G, and H.
Must be decoupled to GND.
Analog Output Channel H Analog Output Voltage.
Analog Output Channel G Analog Output Voltage.
Analog Output Channel F Analog Output Voltage.
Analog Output Channel E Analog Output Voltage.
Frame Synchronization Input. When this pin goes low, data is
written into the DAC's input shift register on the falling edges of
SCLK. After the 16th falling edge of SCLK, a rising edge of SYNC
causes the DAC to be updated. If SYNC is brought high before the
15th falling edge of SCLK, the rising edge of SYNC acts as an
interrupt and the write sequence is ignored by the DAC.
Serial Clock Input. Data is clocked into the input shift register on
the falling edges of this pin.
D
IN
D
OUT
Digital Input
Digital Output
Serial Data Input. Data is clocked into the 16-bit shift register on
the falling edges of SCLK after the fall of SYNC.
Serial Data Output. D
is utilized in daisy chain operation and is
OUT
connected directly to a DIN pin on another DAC128S085. Data is
not available at D
unless SYNC remains low for more than 16
OUT
SCLK cycles.
PAD
(LLP only)
Ground
Exposed die attach pad can be connected to ground or left floating.
Soldering the pad to the PCB offers optimal thermal performance
and enhances package self-alignment during reflow.
30016902
3 www.national.com
Absolute Maximum Ratings (Notes 1, 2)
If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required,
please contact the National Semiconductor Sales Office/
Distributors for availability and specifications.
DAC128S085
Supply Voltage, V
Voltage on any Input Pin −0.3V to 6.5V
Input Current at Any Pin (Note 3) 10 mA
Package Input Current (Note 3) 30 mA
Power Consumption at TA = 25°C
ESD Susceptibility (Note 5)
Human Body Model
Machine Model
Charge Device Mode
Junction Temperature +150°C
Storage Temperature −65°C to +150°C
A
See (Note 4)
6.5V
2500V
250V
1000V
Operating Ratings (Notes 1, 2)
Operating Temperature Range
Supply Voltage, V
Reference Voltage, V
A
REF1,2
Digital Input Voltage (Note 7) 0.0V to 5.5V
Output Load 0 to 1500 pF
SCLK Frequency Up to 40 MHz
−40°C ≤ TA ≤ +125°C
Package Thermal Resistances
Package
16-Lead LLP 38°C/W
16-Lead TSSOP 130°C/W
Soldering process must comply with National
Semiconductor's Reflow Temperature Profile specifications.
θ
JA
Refer to www.national.com/packaging. (Note 6)
Electrical Characteristics
The following specifications apply for VA = +2.7V to +5.5V, V
range 48 to 4047. Boldface limits apply for T
≤ TA ≤ T
MIN
Symbol Parameter Conditions Typical
STATIC PERFORMANCE
Resolution 12 Bits (min)
Monotonicity 12 Bits (min)
INL Integral Non-Linearity ±2.0 ±8 LSB (max)
DNL Differential Non-Linearity
I
ZE Zero Code Error
FSE Full-Scale Error
OUT
I
OUT
= 0
= 0
GE Gain Error −0.2 −1.0 % FSR (max)
ZCED Zero Code Error Drift −20 µV/°C
TC GE Gain Error Tempco −1.0 ppm/°C
OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Output Voltage Range
I
High-Impedance Output
OZ
Leakage Current (Note 9)
±1 µA (max)
VA = 3V, I
ZCO Zero Code Output
VA = 3V, I
VA = 5V, I
VA = 5V, I
VA = 3V, I
FSO Full Scale Output
VA = 3V, I
VA = 5V, I
VA = 5V, I
VA = 3V, V
I
Output Short Circuit Current
OS
(source) (Note 10)
Input Code = FFFh
VA = 5V, V
Input Code = FFFh
= V
REF1
and all other limits are at TA = 25°C, unless otherwise specified.
MAX
= VA, CL = 200 pF to GND, f
REF2
= 30 MHz, input code
SCLK
Limits
(Note 8)
+0.15 +0.75 LSB (max)
−0.09 −0.4 LSB (min)
+5 +15 mV (max)
−0.1 −0.75 % FSR (max)
0
V
REF1,2
= 200 µA
OUT
= 1 mA
OUT
= 200 µA
OUT
= 1 mA
OUT
= 200 µA
OUT
= 1 mA
OUT
= 200 µA
OUT
= 1 mA
OUT
OUT
OUT
= 0V,
= 0V,
10 mV
45 mV
8 mV
34 mV
2.984 V
2.933 V
4.987 V
4.955 V
−50 mA
−60 mA
+2.7V to 5.5V
+0.5V to V
Units
(Limits)
V (min)
V (max)
A
www.national.com 4
DAC128S085
Symbol Parameter Conditions Typical
VA = 3V, V
I
OS
Output Short Circuit Current (sink)
(Note 10)
Input Code = 000h
VA = 5V, V
OUT
OUT
= 3V,
= 5V,
Input Code = 000h
TA = 105°C
TA = 125°C
RL = ∞
RL = 2kΩ
1500 pF
1500 pF
Z
I
O
C
OUT
Continuous Output Current per
channel (Note 9)
Maximum Load Capacitance
L
DC Output Impedance 8
REFERENCE INPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Input Range Minimum 0.5 2.7 V (min)
VREF1,2
Input Range Maximum
Input Impedance 30
LOGIC INPUT CHARACTERISTICS
I
V
V
C
Input Current (Note 9) ±1 µA (max)
IN
Input Low Voltage
IL
Input High Voltage
IH
Input Capacitance (Note 9) 3 pF (max)
IN
VA = 2.7V to 3.6V
VA = 4.5V to 5.5V
VA = 2.7V to 3.6V
VA = 4.5V to 5.5V
POWER REQUIREMENTS
V
Supply Voltage Minimum 2.7 V (min)
A
Supply Voltage Maximum 5.5 V (max)
VA = 2.7V
Normal Supply Current for supply
pin V
A
I
N
Normal Supply Current for V
V
REF2
REF1
f
= 30 MHz,
SCLK
output unloaded
or
f
= 30 MHz,
SCLK
output unloaded
to 3.6V
VA = 4.5V
to 5.5V
VA = 2.7V
to 3.6V
VA = 4.5V
to 5.5V
VA = 2.7V
Static Supply Current for supply pin
V
A
I
ST
Static Supply Current for V
V
REF2
REF1
f
SCLK
output unloaded
or
f
SCLK
output unloaded
= 0,
= 0,
to 3.6V
VA = 4.5V
to 5.5V
VA = 2.7V
to 3.6V
VA = 4.5V
to 5.5V
f
= 30 MHz, SYNC =
SCLK
VA and DIN = 0V after PD
Total Power Down Supply Current
I
PD
for all PD Modes
(Note 9)
mode loaded
f
= 0, SYNC = VA and
SCLK
DIN = 0V after PD mode
loaded
VA = 2.7V
to 3.6V
VA = 4.5V
to 5.5V
VA = 2.7V
to 3.6V
VA = 4.5V
to 5.5V
Limits
(Note 8)
Units
(Limits)
50 mA
70 mA
10 mA (max)
6.5 mA (max)
Ω
V
A
V (max)
kΩ
1.0 0.6 V (max)
1.1 0.8 V (max)
1.4 2.1 V (min)
2.0 2.4 V (min)
460 560 µA (max)
650 830 µA (max)
95 130 µA (max)
160 220 µA (max)
370 µA
440 µA
95 µA
160 µA
0.2 1.5 µA (max)
0.5 3.0 µA (max)
0.1 1.0 µA (max)
0.2 2.0 µA (max)
5 www.national.com
Symbol Parameter Conditions Typical
VA = 2.7V
to 3.6V
VA = 4.5V
to 5.5V
VA = 2.7V
to 3.6V
VA = 4.5V
DAC128S085
P
N
Total Power Consumption (output
unloaded)
f
= 30 MHz
SCLK
output unloaded
f
= 0
SCLK
output unloaded
to 5.5V
f
= 30 MHz, SYNC =
SCLK
VA and DIN = 0V after PD
Total Power Consumption in all PD
P
PD
Modes,
(Note 9)
mode loaded
f
= 0, SYNC = VA and
SCLK
DIN = 0V after PD mode
loaded
VA = 2.7V
to 3.6V
VA = 4.5V
to 5.5V
VA = 2.7V
to 3.6V
VA = 4.5V
to 5.5V
1.95 3.0 mW (max)
4.85 7.0 mW (max)
1.68 mW
3.80 mW
0.6 5.4 µW (max)
2.5 16.5 µW (max)
0.3 3.6 µW (max)
1 11 µW (max)
Limits
(Note 8)
A.C. and Timing Characteristics
The following specifications apply for VA = +2.7V to +5.5V, V
48 to 4047. Boldface limits apply for T
≤ TA ≤ T
MIN
and all other limits are at TA = 25°C, unless otherwise specified.
MAX
Symbol Parameter Conductions Typical
f
SCLK Frequency 40 30 MHz (max)
SCLK
Output Voltage Settling Time
t
s
(Note 9)
400h to C00h code change
RL = 2kΩ, CL = 200 pF
SR Output Slew Rate 1 V/µs
GI Glitch Impulse Code change from 800h to 7FFh 40 nV-sec
DF Digital Feedthrough 0.5 nV-sec
DC Digital Crosstalk 0.5 nV-sec
CROSS DAC-to-DAC Crosstalk 1 nV-sec
V
MBW Multiplying Bandwidth
THD+N Total Harmonic Distortion Plus Noise
= 2.5V ± 2Vpp
REF1,2
V
= 2.5V ± 0.5Vpp
REF1,2
100Hz < fIN < 20kHz
ONSD Output Noise Spectral Density DAC Code = 800h, 10kHz 40 nV/sqrt(Hz)
ON Output Noise BW = 30kHz 14 µV
VA = 3V
VA = 5V
1.0 2.5 ns (min)
1.0 2.5 ns (min)
1/f
t
t
WU
SCLK
t
CH
t
CL
t
SS
t
DS
t
DH
t
SH
SYNC
Wake-Up Time
SCLK Cycle Time 25 33 ns (min)
SCLK High time 7 10 ns (min)
SCLK Low Time 7 10 ns (min)
SYNC Set-up Time prior to SCLK
Falling Edge
Data Set-Up Time prior to SCLK
Falling Edge
Data Hold Time after SCLK Falling
Edge
SYNC Hold Time after the 16th falling
edge of SCLK
SYNC High Time 5 15 ns (min)
= VA, CL = 200 pF to GND, f
REF1,2
= 30 MHz, input code range
SCLK
Limits
(Note 8)
6 8.5 µs (max)
360 kHz
−80 dB
3 µsec
20 µsec
3 10 ns (min)
1 / f
SCLK
- 3
0 3 ns (min)
1 / f
SCLK
- 3
Units
(Limits)
Units
(Limits)
ns (max)
ns (max)
www.national.com 6
Note 1: Absolute Maximum Ratings indicate limits beyond which damage to the device may occur. Operating Ratings indicate conditions for which the device is
functional, but do not guarantee specific performance limits. For guaranteed specifications and test conditions, see the Electrical Characteristics. The guaranteed
specifications apply only for the test conditions listed. Some performance characteristics may degrade when the device is not operated under the listed test
conditions. Operation of the device beyond the maximum Operating Ratings is not recommended.
Note 2: All voltages are measured with respect to GND = 0V, unless otherwise specified.
Note 3: When the input voltage at any pin exceeds 5.5V or is less than GND, the current at that pin should be limited to 10 mA. The 30 mA maximum package
input current rating limits the number of pins that can safely exceed the power supplies with an input current of 10 mA to three.
Note 4: The absolute maximum junction temperature (TJmax) for this device is 150°C. The maximum allowable power dissipation is dictated by TJmax, the
junction-to-ambient thermal resistance (θJA), and the ambient temperature (TA), and can be calculated using the formula PDMAX = (TJmax − TA) / θJA. The values
for maximum power dissipation will be reached only when the device is operated in a severe fault condition (e.g., when input or output pins are driven beyond
the operating ratings, or the power supply polarity is reversed). Such conditions should always be avoided.
Note 5: Human body model is 100 pF capacitor discharged through a 1.5 kΩ resistor. Machine model is 220 pF discharged through 0 Ω. Charge device model
simulates a pin slowly acquiring charge (such as from a device sliding down the feeder in an automated assembler) then rapidly being discharged.
Note 6: Reflow temperature profiles are different for lead-free packages.
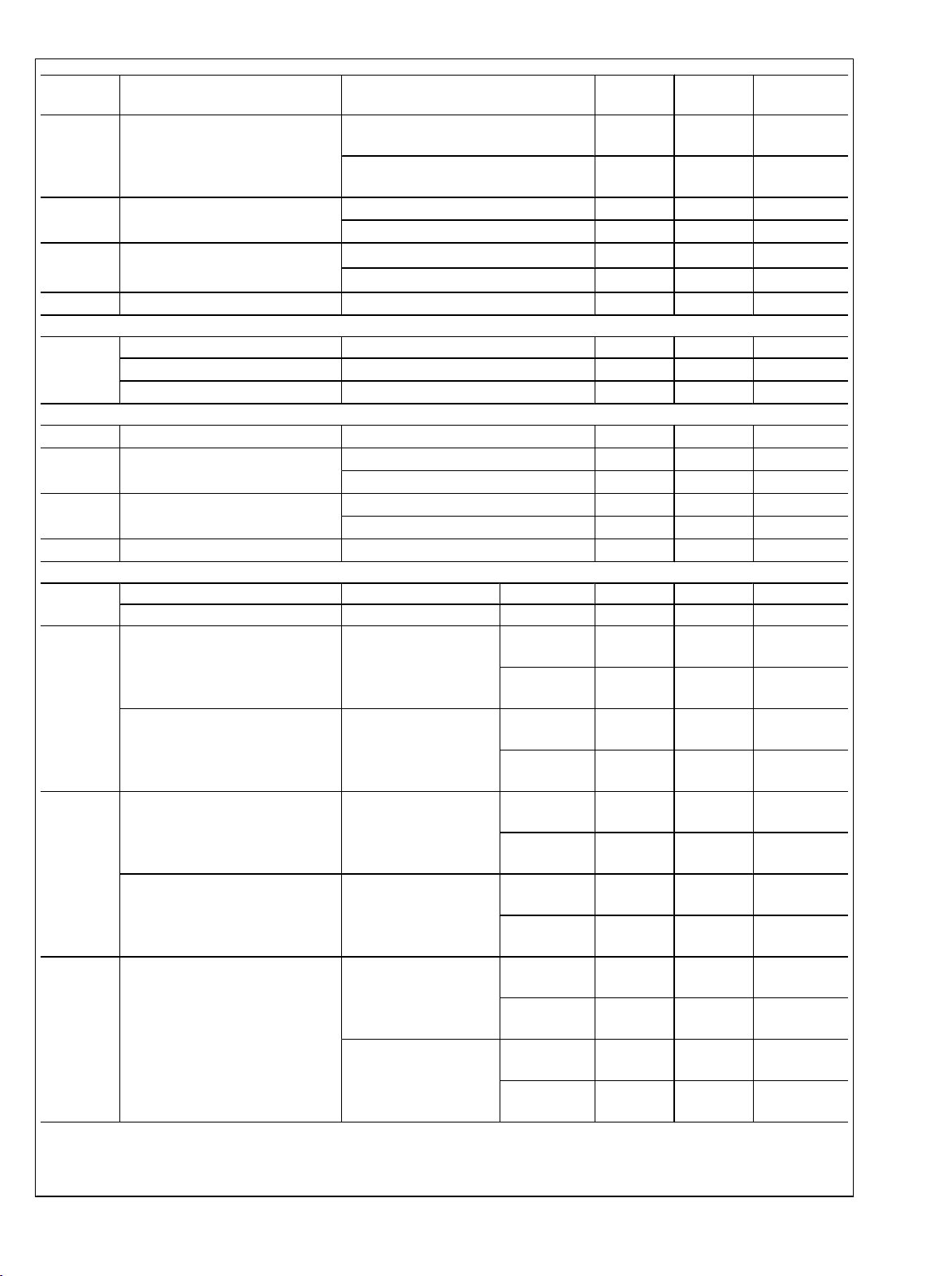
Note 7: The inputs are protected as shown below. Input voltage magnitudes up to 5.5V, regardless of VA, will not cause errors in the conversion result. For
example, if VA is 3V, the digital input pins can be driven with a 5V logic device.
30016904
Note 8: Test limits are guaranteed to National's AOQL (Average Outgoing Quality Level).
Note 9: This parameter is guaranteed by design and/or characterization and is not tested in production.
Note 10: This parameter does not represent a condition which the DAC can sustain continuously. See the continuous output current specification for the maximum
DAC output current per channel.
DAC128S085
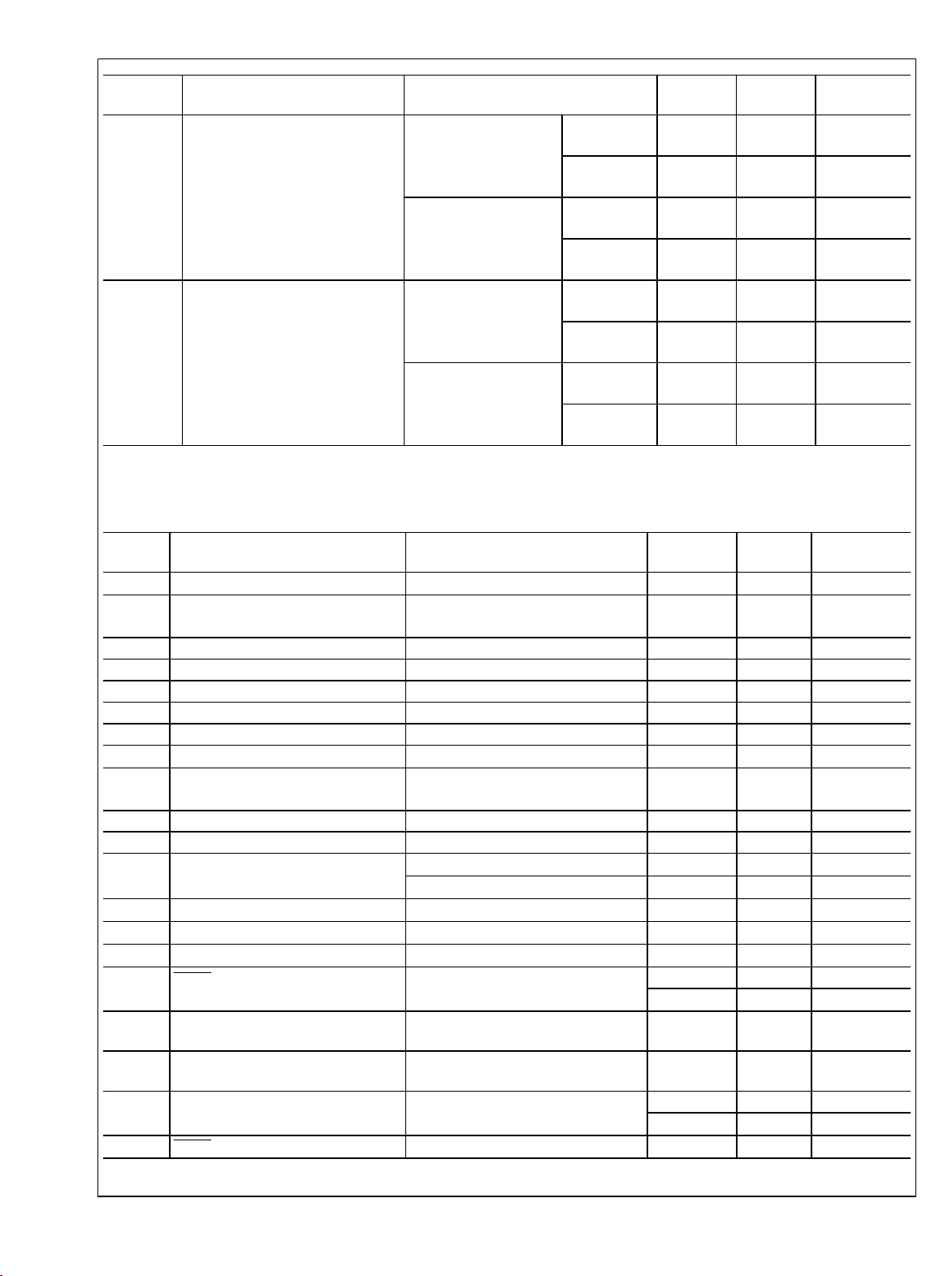
Timing Diagrams
30016906
FIGURE 1. Serial Timing Diagram
7 www.national.com
Specification Definitions
DIFFERENTIAL NON-LINEARITY (DNL) is the measure of
the maximum deviation from the ideal step size of 1 LSB,
which is V
DAC128S085
DAC-to-DAC CROSSTALK is the glitch impulse transferred
to a DAC output in response to a full-scale change in the output of another DAC.
DIGITAL CROSSTALK is the glitch impulse transferred to a
DAC output at mid-scale in response to a full-scale change in
the input register of another DAC.
DIGITAL FEEDTHROUGH is a measure of the energy injected into the analog output of the DAC from the digital inputs
when the DAC outputs are not updated. It is measured with a
full-scale code change on the data bus.
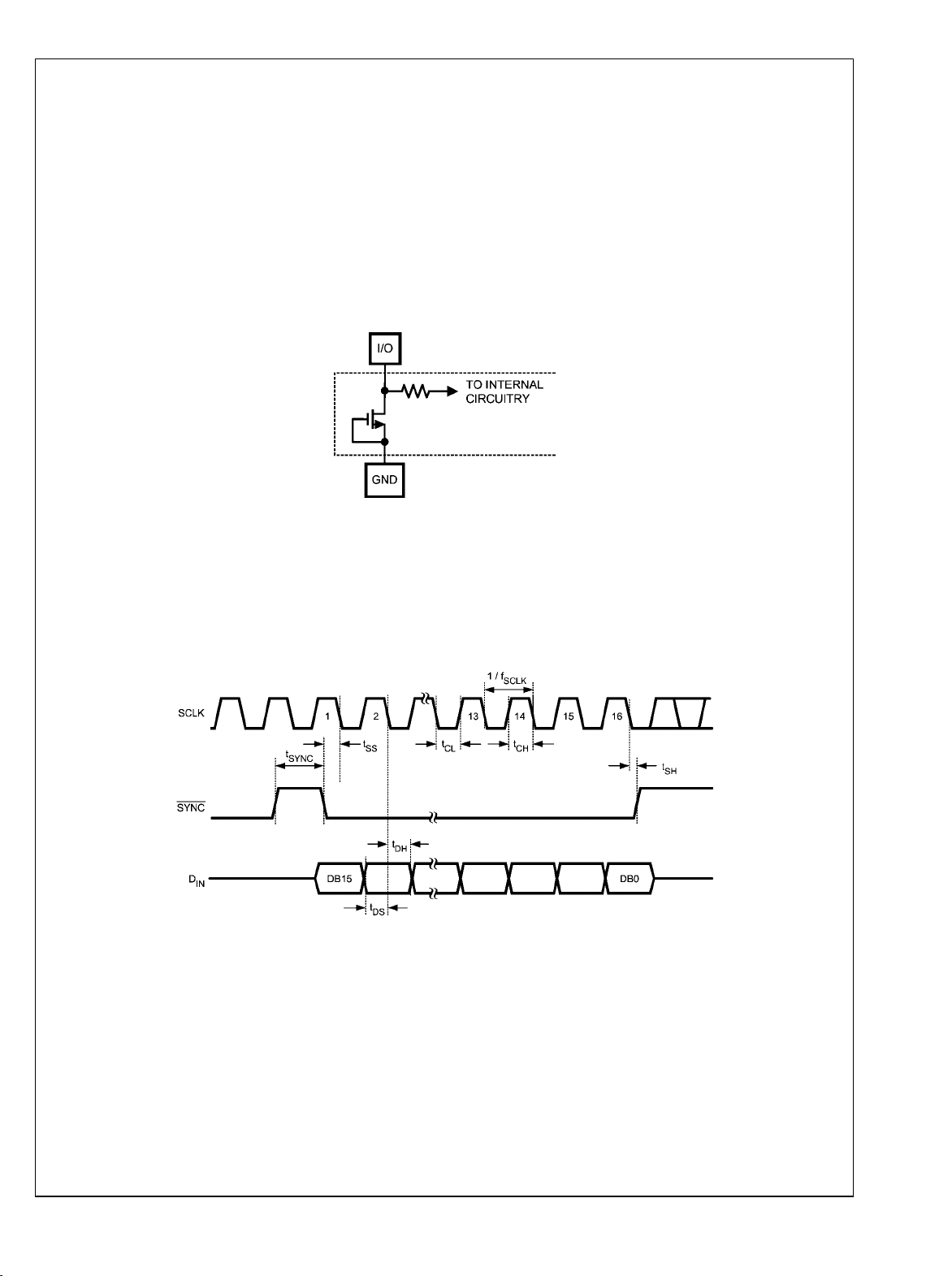
FULL-SCALE ERROR is the difference between the actual
output voltage with a full scale code (FFFh) loaded into the
DAC and the value of VA x 4095 / 4096.
GAIN ERROR is the deviation from the ideal slope of the
transfer function. It can be calculated from Zero and FullScale Errors as GE = FSE - ZE, where GE is Gain error, FSE
is Full-Scale Error and ZE is Zero Error.
GLITCH IMPULSE is the energy injected into the analog output when the input code to the DAC register changes. It is
specified as the area of the glitch in nanovolt-seconds.
INTEGRAL NON-LINEARITY (INL) is a measure of the deviation of each individual code from a straight line through the
input to output transfer function. The deviation of any given
code from this straight line is measured from the center of that
code value. The end point method is used. INL for this product
is specified over a limited range, per the Electrical Tables.
LEAST SIGNIFICANT BIT (LSB) is the bit that has the smallest value or weight of all bits in a word. This value is
/ 4096 = VA / 4096.
REF
LSB = V
REF
/ 2
n
where V
the DAC resolution in bits, which is 12 for the DAC128S085.
is the supply voltage for this product, and "n" is
REF
MAXIMUM LOAD CAPACITANCE is the maximum capacitance that can be driven by the DAC with output stability
maintained.
MONOTONICITY is the condition of being monotonic, where
the DAC has an output that never decreases when the input
code increases.
MOST SIGNIFICANT BIT (MSB) is the bit that has the largest
value or weight of all bits in a word. Its value is 1/2 of VA.
MULTIPLYING BANDWIDTH is the frequency at which the
output amplitude falls 3dB below the input sine wave on
V
with the DAC code at full-scale.
REF1,2
NOISE SPECTRAL DENSITY is the internally generated random noise. It is measured by loading the DAC to mid-scale
and measuring the noise at the output.
POWER EFFICIENCY is the ratio of the output current to the
total supply current. The output current comes from the power
supply. The difference between the supply and output currents is the power consumed by the device without a load.
SETTLING TIME is the time for the output to settle to within
1/2 LSB of the final value after the input code is updated.
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE (THD+N)
is the ratio of the harmonics plus the noise present at the output of the DACs to the rms level of an ideal sine wave applied
to V
with the DAC code at mid-scale.
REF1,2
WAKE-UP TIME is the time for the output to exit power-down
mode. This is the time from the rising edge of SYNC to when
the output voltage deviates from the power-down voltage of
0V.
ZERO CODE ERROR is the output error, or voltage, present
at the DAC output after a code of 000h has been entered.
Transfer Characteristic
30016905
FIGURE 2. Input / Output Transfer Characteristic
www.national.com 8

DAC128S085
Typical Performance Characteristics V
unless otherwise stated
INL vs Code
30016952
INL/DNL vs V
REF
= +2.7V to +5.5V, V
A
= VA, f
REF1,2
DNL vs Code
INL/DNL vs f
= 30 MHz, TA = 25°C,
SCLK
30016955
SCLK
INL/DNL vs V
30016957
A
30016922
9 www.national.com
INL/DNL vs Temperature
30016924
30016927

DAC128S085
Zero Code Error vs. V
A
Zero Code Error vs. V
REF
Zero Code Error vs. f
Full-Scale Error vs. V
SCLK
A
30016930
30016934
Zero Code Error vs. Temperature
Full-Scale Error vs. V
REF
30016931
30016936
30016937
www.national.com 10
30016932

DAC128S085
Full-Scale Error vs. f
IVA vs. V
A
SCLK
30016933
Full-Scale Error vs. Temperature
30016939
IVA vs. Temperature
I
VREF
vs. V
REF
30016944
30016925
I
vs. Temperature
VREF
30016945
30016935
11 www.national.com

DAC128S085
Settling Time
Glitch Response
Wake-Up Time
Power-On Reset
30016928
30016951
30016946
DAC-to-DAC Crosstalk
30016938
Multiplying Bandwidth
30016947
www.national.com 12
30016950

DAC128S085
1.0 Functional Description
1.1 DAC ARCHITECTURE
The DAC128S085 is fabricated on a CMOS process with an
architecture that consists of switches and resistor strings that
are followed by an output buffer. The reference voltages are
externally applied at V
V
for DAC channels E through H.
REF2
For simplicity, a single resistor string is shown in Figure 3.
This string consists of 4096 equal valued resistors with a
switch at each junction of two resistors, plus a switch to
ground. The code loaded into the DAC register determines
which switch is closed, connecting the proper node to the
amplifier. The input coding is straight binary with an ideal output voltage of:
V
OUTA,B,C,D
V
OUTE,F,G,H
where D is the decimal equivalent of the binary code that is
loaded into the DAC register. D can take on any value between 0 and 4095. This configuration guarantees that the
DAC is monotonic.
for DAC channels A through D and
REF1
= V
= V
x (D / 4096)
REF1
x (D / 4096)
REF2
30016907
1.2 OUTPUT AMPLIFIERS
The output amplifiers are rail-to-rail, providing an output voltage range of 0V to VA when the reference is VA. All amplifiers,
even rail-to-rail types, exhibit a loss of linearity as the output
approaches the supply rails (0V and VA, in this case). For this
reason, linearity is specified over less than the full output
range of the DAC. However, if the reference is less than VA,
there is only a loss in linearity in the lowest codes.
The output amplifiers are capable of driving a load of 2 kΩ in
parallel with 1500 pF to ground or to VA. The zero-code and
full-scale outputs for given load currents are available in the
Electrical Characteristics Table.
1.3 REFERENCE VOLTAGE
The DAC128S085 uses dual external references, V
V
, that are shared by channels A, B, C, D and channels
REF2
E, F, G, H respectively. The reference pins are not buffered
REF1
and
and have an input impedance of 30 kΩ. It is recommended
that V
output impedance. The reference voltage range is 0.5V to
REF1
and V
be driven by voltage sources with low
REF2
VA, providing the widest possible output dynamic range.
1.4 SERIAL INTERFACE
The three-wire interface is compatible with SPI, QSPI and
MICROWIRE, as well as most DSPs and operates at clock
rates up to 40 MHz. A valid serial frame contains 16 falling
edges of SCLK. See the Timing Diagram for information on a
write sequence.
A write sequence begins by bringing the SYNC
line low. Once
SYNC is low, the data on the DIN line is clocked into the 16bit serial input register on the falling edges of SCLK. To avoid
mis-clocking data into the shift register, it is critical that
SYNC not be brought low on a falling edge of SCLK (see
minimum and maximum setup times for SYNC in the Timing
Characteristics and Figure 5). On the 16th falling edge of
SCLK, the last data bit is clocked into the register. The write
sequence is concluded by bringing the SYNC line high. Once
SYNC
is high, the programmed function (a change in the DAC
channel address, mode of operation and/or register contents)
is executed. To avoid mis-clocking data into the shift register,
it is critical that SYNC be brought high between the 16th and
17th falling edges of SCLK (see minimum and maximum hold
times for SYNC in the Timing Characteristics and Figure 5).
FIGURE 3. DAC Resistor String
Since all eight DAC channels of the DAC128S085 can be
controlled independently, each channel consists of a DAC
register and a 12-bit DAC. Figure 4 is a simple block diagram
of an individual channel in the DAC128S085. Depending on
the mode of operation, data written into a DAC register causes
the 12-bit DAC output to be updated or an additional command is required to update the DAC output. Further description of the modes of operation can be found in the Serial
Interface description.
30016969
FIGURE 4. Single Channel Block Diagram
30016965
FIGURE 5. CS Setup and Hold Times
If SYNC is brought high before the 15th falling edge of SCLK,
the write sequence is aborted and the data that has been
shifted into the input register is discarded. If SYNC is held low
beyond the 17th falling edge of SCLK, the serial data presented at DIN will begin to be output on D
tion on this mode of operation can be found in the Daisy Chain
Section. In either case, SYNC
must be brought high for the
. More informa-
OUT
minimum specified time before the next write sequence is initiated with a falling edge of SYNC.
Since the DIN buffer draws more current when it is high, it
should be idled low between write sequences to minimize
power consumption. On the other hand, SYNC should be
13 www.national.com

idled high to avoid the activation of daisy chain operation
where D
is active.
OUT
1.5 DAISY CHAIN OPERATION
Daisy chain operation allows communication with any number
DAC128S085
of DAC128S085s using a single serial interface. As long as
the correct number of data bits are input in a write sequence
(multiple of sixteen bits), a rising edge of SYNC will properly
update all DACs in the system.
To support multiple devices in a daisy chain configuration,
SCLK and SYNC are shared across all DAC128S085s and
D
of the first DAC in the chain is connected to DIN of the
OUT
second. Figure 6 shows three DAC128S085s connected in
daisy chain fashion. Similar to a single channel write sequence, the conversion for a daisy chain operation begins on
a falling edge of SYNC and ends on a rising edge of SYNC.
A valid write sequence for n devices in a chain requires n
times 16 falling edges to shift the entire input data stream
through the chain. Daisy chain operation is guaranteed for a
maximum SCLK speed of 30MHz.
30016967
The serial data output pin, D
DAC128S085 to allow daisy-chaining of multiple
, is available on the
OUT
DAC128S085 devices in a system. In a write sequence,
D
remains low for the first fourteen falling edges of SCLK
OUT
before going high on the fifteenth falling edge. Subsequently,
the next sixteen falling edges of SCLK will output the first sixteen data bits entered into DIN. Figure 7 shows the timing of
three DAC128S085s in Figure 6. In this instance, It takes
forty-eight falling edges of SCLK followed by a rising edge of
SYNC to load all three DAC128S085s with the appropriate
register data. On the rising edge of SYNC, the programmed
function is executed in each DAC128S085 simultaneously.
FIGURE 6. Daisy Chain Configuration
FIGURE 7. Daisy Chain Timing Diagram
1.6 SERIAL INPUT REGISTER
The DAC128S085 has two modes of operation plus a few
special command operations. The two modes of operation are
Write Register Mode (WRM) and Write Through Mode
(WTM). For the rest of this document, these modes will be
referred to as WRM and WTM. The special command oper-
30016968
ations are separate from WRM and WTM because they can
be called upon regardless of the current mode of operation.
The mode of operation is controlled by the first four bits of the
control register, DB15 through DB12. See Table 1 for a detailed summary.
TABLE 1. Write Register and Write Through Modes
DB[15:12] DB[11:0] Description of Mode
1 0 0 0 X X X X X X X X X X X X WRM: The registers of each DAC Channel can be written to
without causing their outputs to change.
1 0 0 1 X X X X X X X X X X X X WTM: Writing data to a channel's register causes the DAC
output to change.
www.national.com 14

DAC128S085
When the DAC128S085 first powers up, the DAC is in WRM.
In WRM, the registers of each individual DAC channel can be
written to without causing the DAC outputs to be updated.
This is accomplished by setting DB15 to "0", specifying the
DAC register to be written to in DB[14:12], and entering the
new DAC register setting in DB[11:0] (see Table 2).The
DAC128S085 remains in WRM until the mode of operation is
changed to WTM. The mode of operation is changed from
writing data to a DAC channel's register causes the DAC's
output to be updated as well. Changing a DAC channel's register in WTM is accomplished in the same manner as it is done
in WRM. However, in WTM the DAC's register and output are
updated at the completion of the command (see Table 2).
Similarly, the DAC128S085 remains in WTM until the mode
of operation is changed to WRM by setting DB[15:12] to
"1000".
WRM to WTM by setting DB[15:12] to "1001". Once in WTM,
TABLE 2. Commands Impacted by WRM and WTM
DB15 DB[14:12] DB[11:0] Description of Mode
0 0 0 0 D11 D10 ... D1 D0 WRM: D[11:0] written to ChA's data register only
WTM: ChA's output is updated by data in D[11:0]
0 0 0 1 D11 D10 ... D1 D0 WRM: D[11:0] written to ChB's data register only
WTM: ChB's output is updated by data in D[11:0]
0 0 1 0 D11 D10 ... D1 D0 WRM: D[11:0] written to ChC's data register only
WTM: ChC's output is updated by data in D[11:0]
0 0 1 1 D11 D10 ... D1 D0 WRM: D[11:0] written to ChD's data register only
WTM: ChD's output is updated by data in D[11:0]
0 1 0 0 D11 D10 ... D1 D0 WRM: D[11:0] written to ChE's data register only
WTM: ChE's output is updated by data in D[11:0]
0 1 0 1 D11 D10 ... D1 D0 WRM: D[11:0] written to ChF's data register only
WTM: ChF's output is updated by data in D[11:0]
0 1 1 0 D11 D10 ... D1 D0 WRM: D[11:0] written to ChG's data register only
WTM: ChG's output is updated by data in D[11:0]
0 1 1 1 D11 D10 ... D1 D0 WRM: D[11:0] written to ChH's data register only
WTM: ChH's output is updated by data in D[11:0]
As mentioned previously, the special command operations
can be exercised at any time regardless of the mode of operation. There are three special command operations. The
first command is exercised by setting data bits DB[15:12] to
"1010". This allows a user to update multiple DAC outputs
simultaneously to the values currently loaded in their respective control registers. This command is valuable if the user
wants each DAC output to be at a different output voltage but
still have all the DAC outputs change to their appropriate values simultaneously (see Table 3).
The second special command allows the user to alter the DAC
output of channel A with a single write frame. This command
is exercised by setting data bits DB[15:12] to "1011" and data
bits DB[11:0] to the desired control register value. It also has
the added benefit of causing the DAC outputs of the other
channels to update to their current control register values as
well. A user may choose to exercise this command to save a
write sequence. For example, the user may wish to update
several DAC outputs simultaneously, including channel A. In
order to accomplish this task in the minimum number of write
TABLE 3. Special Command Operations
DB[15:12] DB[11:0] Description of Mode
1 0 1 0 X X X X H G F E D C B A Update Select: The DAC outputs of the channels selected with
a "1" in DB[7:0] are updated simultaneously to the values in
their respective control registers.
1 0 1 1 D11 D10 ... D1 D0 Channel A Write: Channel A's control register and DAC output
are updated to the data in DB[11:0]. The outputs of the other
seven channels are also updated according to their respective
control register values.
1 1 0 0 D11 D10 ... D1 D0 Broadcast: The data in DB[11:0] is written to all channels'
control register and DAC output simultaneously.
frames, the user would alter the control register values of all
the DAC channels except channel A while operating in WRM.
The last write frame would be used to exercise the special
command "Channel A Write Mode". In addition to updating
channel A's control register and output to a new value, all of
the other channels would be updated as well. At the end of
this sequence of write frames, the DAC128S085 would still
be operating in WRM (see Table 3).
The third special command allows the user to set all the DAC
control registers and outputs to the same level. This command is commonly referred to as "broadcast" mode since the
same data bits are being broadcast to all of the channels simultaneously. This command is exercised by setting data bits
DB[15:12] to "1100" and data bits DB[11:0] to the value that
the user wishes to broadcast to all the DAC control registers.
Once the command is exercised, each DAC output is updated
by the new control register value. This command is frequently
used to set all the DAC outputs to some known voltage such
as 0V, V
can be found in Table 3.
/2, or Full Scale. A summary of the commands
REF
15 www.national.com

1.7 POWER-ON RESET
The power-on reset circuit controls the output voltages of the
eight DACs during power-up. Upon application of power, the
DAC registers are filled with zeros and the output voltages are
set to 0V. The outputs remain at 0V until a valid write se-
DAC128S085
quence is made.
1.8 POWER-DOWN MODES
The DAC128S085 has three power-down modes where different output terminations can be selected (see Table 4). With
all channels powered down, the supply current drops to 0.1
µA at 3V and 0.2 µA at 5V. By selecting the channels to be
powered down in DB[7:0] with a "1", individual channels can
be powered down separately or multiple channels can be
powered down simultaneously. The three different output ter-
minations include high output impedance, 100k ohm to
ground, and 2.5k ohm to ground.
The output amplifiers, resistor strings, and other linear circuitry are all shut down in any of the power-down modes. The
bias generator, however, is only shut down if all the channels
are placed in power-down mode. The contents of the DAC
registers are unaffected when in power-down. Therefore,
each DAC register maintains its value prior to the
DAC128S085 being powered down unless it is changed during the write sequence which instructed it to recover from
power down. Minimum power consumption is achieved in the
power-down mode with SYNC idled high, DIN idled low, and
SCLK disabled. The time to exit power-down (Wake-Up Time)
is typically 3 µsec at 3V and 20 µsec at 5V.
TABLE 4. Power-Down Modes
DB[15:12] DB[11:8] 7 6
5
1 1 0 1 X X X X H G F E D C B A High-Z outputs
1 1 1 0 X X X X H G F E D C B A
1 1 1 1 X X X X H G F E D C B A
2.0 Applications Information
2.1 EXAMPLES PROGRAMMING THE DAC128S085
This section will present the step-by-step instructions for programming the serial input register.
2.1.1 Updating DAC Outputs Simultaneously
When the DAC128S085 is first powered on, the DAC is operating in Write Register Mode (WRM). Operating in WRM
allows the user to program the registers of multiple DAC
channels without causing the DAC outputs to be updated. As
an example, here are the steps for setting Channel A to a full
scale output, Channel B to three-quarters full scale, Channel
C to half-scale, Channel D to one-quarter full scale and having
all the DAC outputs update simultaneously.
As stated previously, the DAC128S085 powers up in WRM.
If the device was previously operating in Write Through Mode
(WTM), an extra step to set the DAC into WRM would be required. First, the DAC registers need to be programmed to the
desired values. To set Channel A to an output of full scale,
write "0FFF" to the control register. This will update the data
register for Channel A without updating the output of Channel
A. Second, set Channel B to an output of three-quarters full
scale by writing "1C00" to the control register. This will update
the data register for Channel B. Once again, the output of
Channel B and Channel A will not be updated since the DAC
is operating in WRM. Third, set Channel C to half scale by
writing "2800" to the control register. Fourth, set Channel D
to one-quarter full scale by writing "3400" to the control register. Finally, update all four DAC channels simultaneously by
writing "A00F" to the control register. This procedure allows
the user to update four channels simultaneously with five
steps.
Since Channel A was one of the DACs to be updated, one
command step could have been saved by writing to Channel
A last. This is accomplished by writing to Channel B, C, and
D first and using the the special command "Channel A Write"
4 3 2 1 0 Output Impedance
100 kΩ outputs
2.5 kΩ outputs
to update Channel A's DAC register and output. This special
command has the added benefit of updating all DAC outputs
while updating Channel A. With this sequence of commands,
the user was able to update four channels simultaneously with
four steps. A summary of this command can be found in Table
3.
2.1.2 Updating DAC Outputs Independently
If the DAC128S085 is currently operating in WRM, change
the mode of operation to WTM by writing "9XXX" to the control
register. Once the DAC is operating in WTM, any DAC channel can be updated in one step. For example, if a design
required Channel G to be set to half scale, the user can write
"6800" to the control register and Channel G's data register
and DAC output will be updated. Similarly, if Channel F's output needed to be set to full scale, "5FFF" would need to be
written to the control register. Channel A is the only channel
that has a special command that allows its DAC output to be
updated in one command regardless of the mode of operation. Setting Channel A's DAC output to full scale could be
accomplished in one step by writing "BFFF" to the control
register.
2.2 USING REFERENCES AS POWER SUPPLIES
While the simplicity of the DAC128S085 implies ease of use,
it is important to recognize that the path from the reference
input (V
ply Rejection Ratio (PSRR). Therefore, it is necessary to
provide a noise-free supply voltage to V
lize the full dynamic range of the DAC128S085, the supply
pin (VA) and V
same supply voltage. Since the DAC128S085 consumes very
) to the DAC outputs will have zero Power Sup-
REF1,2
. In order to uti-
REF1,2
can be connected together and share the
REF1,2
little power, a reference source may be used as the reference
input and/or the supply voltage. The advantages of using a
reference source over a voltage regulator are accuracy and
stability. Some low noise regulators can also be used. Listed
below are a few reference and power supply options for the
DAC128S085.
www.national.com 16

DAC128S085
2.2.1 LM4132
The LM4132, with its ±0.05% accuracy over temperature, is
a good choice as a reference source for the DAC128S085.
The 4.096V version is useful if a 0V to 4.095V output range
is desirable. Bypassing the LM4132 voltage input pin with a
4.7µF capacitor and the voltage output pin with a 4.7µF capacitor will improve stability and reduce output noise. The
LM4132 comes in a space-saving 5-pin SOT23.
30016913
FIGURE 8. The LM4132 as a power supply
2.2.2 LM4050
Available with accuracy of ±0.1%, the LM4050 shunt reference is also a good choice as a reference for the
DAC128S085. It is available in 4.096V and 5V versions and
comes in a space-saving 3-pin SOT23.
R(max) = ( VIN(min) − VZ(max) ) / ( (I
(max) + IZ(min) )
DAC
where VZ(min) and VZ(max) are the nominal LM4050 output
voltages ± the LM4050 output tolerance over temperature, I
(max) is the maximum allowable current through the LM4050,
IZ(min) is the minimum current required by the LM4050 for
proper regulation, and I
DAC128S085 supply current.
(max) is the maximum
DAC
2.2.3 LP3985
The LP3985 is a low noise, ultra low dropout voltage regulator
with a ±3% accuracy over temperature. It is a good choice for
applications that do not require a precision reference for the
DAC128S085. It comes in 3.0V, 3.3V and 5V versions, among
others, and sports a low 30 µV noise specification at low frequencies. Since low frequency noise is relatively difficult to
filter, this specification could be important for some applications. The LP3985 comes in a space-saving 5-pin SOT23 and
5-bump micro SMD packages.
30016915
Z
30016914
FIGURE 9. The LM4050 as a power supply
The minimum resistor value in the circuit of Figure 9 must be
chosen such that the maximum current through the LM4050
does not exceed its 15 mA rating. The conditions for maximum current include the input voltage at its maximum, the
LM4050 voltage at its minimum, and the DAC128S085 drawing zero current. The maximum resistor value must allow the
LM4050 to draw more than its minimum current for regulation
plus the maximum DAC128S085 current in full operation. The
conditions for minimum current include the input voltage at its
minimum, the LM4050 voltage at its maximum, the resistor
value at its maximum due to tolerance, and the DAC128S085
draws its maximum current. These conditions can be summarized as
R(min) = ( VIN(max) − VZ(min) ) /IZ(max)
and
FIGURE 10. Using the LP3985 regulator
An input capacitance of 1.0µF without any ESR requirement
is required at the LP3985 input, while a 1.0µF ceramic capacitor with an ESR requirement of 5mΩ to 500mΩ is required
at the output. Careful interpretation and understanding of the
capacitor specification is required to ensure correct device
operation.
2.2.4 LP2980
The LP2980 is an ultra low dropout regulator with a ±0.5% or
±1.0% accuracy over temperature, depending upon grade. It
is available in 3.0V, 3.3V and 5V versions, among others.
30016916
FIGURE 11. Using the LP2980 regulator
Like any low dropout regulator, the LP2980 requires an output
capacitor for loop stability. This output capacitor must be at
least 1.0µF over temperature, but values of 2.2µF or more will
provide even better performance. The ESR of this capacitor
should be within the range specified in the LP2980 data sheet.
Surface-mount solid tantalum capacitors offer a good combi-
17 www.national.com

nation of small size and low ESR. Ceramic capacitors are
attractive due to their small size but generally have ESR values that are too low for use with the LP2980. Aluminum
electrolytic capacitors are typically not a good choice due to
their large size and high ESR values at low temperatures.
DAC128S085
2.3 BIPOLAR OPERATION
The DAC128S085 is designed for single supply operation and
thus has a unipolar output. However, a bipolar output may be
achieved with the circuit in Figure 12. This circuit will provide
an output voltage range of ±5 Volts. A rail-to-rail amplifier
should be used if the amplifier supplies are limited to ±5V.
FIGURE 12. Bipolar Operation
The output voltage of this circuit for any code is found to be
VO = (VA x (D / 4096) x ((R1 + R2) / R1) - VA x R2 / R1)
where D is the input code in decimal form. With VA = 5V and
R1 = R2,
VO = (10 x D / 4096) - 5V
A list of rail-to-rail amplifiers suitable for this application are
indicated in Table 5.
TABLE 5. Some Rail-to-Rail Amplifiers
AMP PKGS
Typ V
LMP7701 SOT23-5 ±37 µV 0.79 mA
LMV841 SOT23-5 −17 µV 1.11 mA
LMC7111 SOT23-5 900 µV 25 µA
LM7301 SOT23-5 30 µV 620 µA
LM8261 SOT23-5 700 µV 1 mA
2.4 VARIABLE CURRENT SOURCE OUTPUT
The DAC128S085 is a voltage output DAC but can be easily
converted to a current output with the addition of an opamp.
In Figure 13, one of the channels of the DAC128S085 is converted to a variable current source capable of sourcing up to
40mA.
OS
Typ I
30016917
SUPPLY
30016958
FIGURE 13. Variable Current Source
The output current of this circuit (IO) for any DAC code is found
to be
IO = (V
x (D / 4096) x (R2) / (R1 x RB)
REF
where D is the input code in decimal form and R2 = RA + RB.
2.5 APPLICATION CIRCUITS
The following figures are examples of the DAC128S085 in
typical application circuits. These circuits are basic and will
generally require modification for specific circumstances.
2.5.1 Industrial Application
Figure 14 shows the DAC128S085 controlling several different circuits in an industrial setting. Channel A is shown providing the reference voltage to the ADC121S625, one of
National Semiconductor's general purpose Analog-to-Digital
Converters (ADCs). The reference for the ADC121S625 may
be set to any voltage from 0.2V to 5.5V, providing the widest
dynamic range possible. Typically, the ADC121S625 will be
monitoring a sensor and would benefit from the ADC's reference voltage being adjustable. Channel B is providing the
drive or supply voltage for a sensor. By having the sensor
supply voltage adjustable, the output of the sensor can be
optimized to the input level of the ADC monitoring it. Channel
C is defined to adjust the offset or gain of an amplifier stage
in the system. Channel D is configured with an opamp to provide an adjustable current source. Being able to convert one
of the eight channels of the DAC128S085 to a current output
eliminates the need for a separate current output DAC to be
added to the circuit. Channel E, in conjunction with an opamp,
provides a bipolar output swing for devices requiring control
voltages that are centered around ground. Channel F and G
are used to set the upper and lower limits for a range detector.
Channel H is reserved for providing voltage control or acting
as a voltage setpoint.
www.national.com 18

FIGURE 14. Industrial Application
DAC128S085
30016953
2.5.2 ADC Reference
Figure 15 shows Channel A of the DAC128S085 providing the
drive or supply voltage for a bridge sensor. By having the
sensor supply voltage adjustable, the output of the sensor can
be optimized to the input level of the ADC monitoring it. The
output of the sensor is amplified by a fixed gain amplifier stage
with a differential gain of 1 + 2 × (RF / RI). The advantage of
this amplifier configuration is the high input impedance seen
by the output of the bridge sensor. The disadvantage is the
poor common-mode rejection ratio (CMRR). The commonmode voltage (VCM) of the bridge sensor is half of Channel
A's DAC output. The VCM is amplified by a gain of 1V/V by the
amplifier stage and thus becomes the bias voltage for the input of the ADC121S705. Channel B of the DAC128S085 is
providing the reference voltage to the ADC121S705. The reference for the ADC121S705 may be set to any voltage from
1V to 5V, providing the widest dynamic range possible.
The reference voltage for Channel A and B is powered by an
external 5V power supply. Since the 5V supply is common to
the sensor supply voltage and the reference voltage of the
ADC, fluctuations in the value of the 5V supply will have a
minimal effect on the digital output code of the ADC. This type
of configuration is often referred to as a "Ratio-metric" design.
For example, an increase of 5% to the 5V supply will cause
the sensor supply voltage to increase by 5%. This causes the
gain or sensitivity of the sensor to increase by 5%. The gain
of the amplifier stage is unaffected by the change in supply
voltage. The ADC121S705 on the other hand, also experiences a 5% increase to its reference voltage. This causes the
size of the ADC's least significant bit (LSB) to increase by 5%.
As a result of the sensor's gain increasing by 5% and the LSB
size of the ADC increasing by the same 5%, there is no net
effect on the circuit's performance. It is assumed that the amplifier gain is set low enough to allow for a 5% increase in the
sensor output. Otherwise, the increase in the sensor output
level may cause the output of the amplifiers to clip.
FIGURE 15. Driving an ADC Reference
19 www.national.com
30016956

2.5.3 Programmable Attenuator
Figure 16 shows one of the channels of the DAC128S085
being used as a single-quadrant multiplier. In this configuration, an AC or DC signal can be driven into one of the reference pins. The SPI interface of the DAC can be used to
DAC128S085
digitally attenuate the signal to any level from 0dB (full scale)
to 0V. This is accomplished without adding any noticeable
level of noise to the signal. An amplifier stage is shown in
Figure 16 as a reference for applications where the input signal requires amplification. Note how the AC signal in this
application is ac-coupled to the amplifier before being amplified. A separate bias voltage is used to set the common-mode
voltage for the DAC128S085's reference input to VA / 2, allowing the largest possible input swing. The multiplying bandwidth of V
peak signal swing of 2V.
is 360kHz with a VCM of 2.5V and a peak-to-
REF1,2
FIGURE 16. Programmable Attenuator
2.6 DSP/MICROPROCESSOR INTERFACING
Interfacing the DAC128S085 to microprocessors and DSPs
is quite simple. The following guidelines are offered to hasten
the design process.
30016954
SYNC signal comes from a bit-programmable pin on the microcontroller. The example shown here uses port line P3.3.
This line is taken low when data is transmitted to the
DAC128S085. Since the 80C51/80L51 transmits 8-bit bytes,
only eight falling clock edges occur in the transmit cycle. To
load data into the DAC, the P3.3 line must be left low after the
first eight bits are transmitted. A second write cycle is initiated
to transmit the second byte of data, after which port line P3.3
is brought high. The 80C51/80L51 transmit routine must recognize that the 80C51/80L51 transmits data with the LSB first
while the DAC128S085 requires data with the MSB first.
30016910
FIGURE 18. 80C51/80L51 Interface
2.6.3 68HC11 Interface
A serial interface between the DAC128S085 and the 68HC11
microcontroller is shown in Figure 19. The SYNC line of the
DAC128S085 is driven from a port line (PC7 in the figure),
similar to the 80C51/80L51.
The 68HC11 should be configured with its CPOL bit as a zero
and its CPHA bit as a one. This configuration causes data on
the MOSI output to be valid on the falling edge of SCLK. PC7
is taken low to transmit data to the DAC. The 68HC11 transmits data in 8-bit bytes with eight falling clock edges. Data is
transmitted with the MSB first. PC7 must remain low after the
first eight bits are transferred. A second write cycle is initiated
to transmit the second byte of data to the DAC, after which
PC7 should be raised to end the write sequence.
2.6.1 ADSP-2101/ADSP2103 Interfacing
Figure 17 shows a serial interface between the DAC128S085
and the ADSP-2101/ADSP2103. The DSP should be set to
operate in the SPORT Transmit Alternate Framing Mode. It is
programmed through the SPORT control register and should
be configured for Internal Clock Operation, Active Low Framing and 16-bit Word Length. Transmission is started by writing
a word to the Tx register after the SPORT mode has been
enabled.
30016909
FIGURE 17. ADSP-2101/2103 Interface
2.6.2 80C51/80L51 Interface
A serial interface between the DAC128S085 and the
80C51/80L51 microcontroller is shown in Figure 18. The
www.national.com 20
30016911
FIGURE 19. 68HC11 Interface
2.6.4 Microwire Interface
Figure 20 shows an interface between a Microwire compatible
device and the DAC128S085. Data is clocked out on the rising
edges of the SK signal. As a result, the SK of the Microwire
device needs to be inverted before driving the SCLK of the
DAC128S085.
30016912
FIGURE 20. Microwire Interface

DAC128S085
2.7 LAYOUT, GROUNDING, AND BYPASSING
For best accuracy and minimum noise, the printed circuit
board containing the DAC128S085 should have separate
analog and digital areas. The areas are defined by the locations of the analog and digital power planes. Both of these
planes should be located in the same board layer. A single
ground plane is preferred if digital return current does not flow
through the analog ground area. Frequently a single ground
plane design will utilize a "fencing" technique to prevent the
mixing of analog and digital ground current. Separate ground
planes should only be utilized when the fencing technique is
inadequate. The separate ground planes must be connected
in one place, preferably near the DAC128S085. Special care
is required to guarantee that digital signals with fast edge
rates do not pass over split ground planes. They must always
have a continuous return path below their traces.
For best performance, the DAC128S085 power supply should
be bypassed with at least a 1µF and a 0.1µF capacitor. The
0.1µF capacitor needs to be placed right at the device supply
pin. The 1µF or larger valued capacitor can be a tantalum
capacitor while the 0.1µF capacitor needs to be a ceramic
capacitor with low ESL and low ESR. If a ceramic capacitor
with low ESL and low ESR is used for the 1µF value and it
can be placed right at the supply pin, the 0.1µF capacitor can
be eliminated. Capacitors of this nature typically span the
same frequency spectrum as the 0.1µF capacitor and thus
eliminate the need for the extra capacitor. The power supply
for the DAC128S085 should only be used for analog circuits.
It is also advisable to avoid the crossover of analog and digital
signals. This helps minimize the amount of noise from the
transitions of the digital signals from coupling onto the sensitive analog signals such as the reference pins and the DAC
outputs.
21 www.national.com

Physical Dimensions inches (millimeters) unless otherwise noted
DAC128S085
Order Numbers DAC128S085CISQ
NS Package Number SQA16A
Order Numbers DAC128S085CIMT
NS Package Number MTC16
16-Lead LLP
16-Lead TSSOP
www.national.com 22

Notes
DAC128S085
23 www.national.com

Notes
THE CONTENTS OF THIS DOCUMENT ARE PROVIDED IN CONNECTION WITH NATIONAL SEMICONDUCTOR CORPORATION
(“NATIONAL”) PRODUCTS. NATIONAL MAKES NO REPRESENTATIONS OR WARRANTIES WITH RESPECT TO THE ACCURACY
OR COMPLETENESS OF THE CONTENTS OF THIS PUBLICATION AND RESERVES THE RIGHT TO MAKE CHANGES TO
SPECIFICATIONS AND PRODUCT DESCRIPTIONS AT ANY TIME WITHOUT NOTICE. NO LICENSE, WHETHER EXPRESS,
IMPLIED, ARISING BY ESTOPPEL OR OTHERWISE, TO ANY INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS IS GRANTED BY THIS
DOCUMENT.
TESTING AND OTHER QUALITY CONTROLS ARE USED TO THE EXTENT NATIONAL DEEMS NECESSARY TO SUPPORT
NATIONAL’S PRODUCT WARRANTY. EXCEPT WHERE MANDATED BY GOVERNMENT REQUIREMENTS, TESTING OF ALL
PARAMETERS OF EACH PRODUCT IS NOT NECESSARILY PERFORMED. NATIONAL ASSUMES NO LIABILITY FOR
APPLICATIONS ASSISTANCE OR BUYER PRODUCT DESIGN. BUYERS ARE RESPONSIBLE FOR THEIR PRODUCTS AND
APPLICATIONS USING NATIONAL COMPONENTS. PRIOR TO USING OR DISTRIBUTING ANY PRODUCTS THAT INCLUDE
NATIONAL COMPONENTS, BUYERS SHOULD PROVIDE ADEQUATE DESIGN, TESTING AND OPERATING SAFEGUARDS.
EXCEPT AS PROVIDED IN NATIONAL’S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE FOR SUCH PRODUCTS, NATIONAL ASSUMES NO
LIABILITY WHATSOEVER, AND NATIONAL DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTY RELATING TO THE SALE
AND/OR USE OF NATIONAL PRODUCTS INCLUDING LIABILITY OR WARRANTIES RELATING TO FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR
PURPOSE, MERCHANTABILITY, OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY
RIGHT.
LIFE SUPPORT POLICY
NATIONAL’S PRODUCTS ARE NOT AUTHORIZED FOR USE AS CRITICAL COMPONENTS IN LIFE SUPPORT DEVICES OR
SYSTEMS WITHOUT THE EXPRESS PRIOR WRITTEN APPROVAL OF THE CHIEF EXECUTIVE OFFICER AND GENERAL
COUNSEL OF NATIONAL SEMICONDUCTOR CORPORATION. As used herein:
Life support devices or systems are devices which (a) are intended for surgical implant into the body, or (b) support or sustain life and
whose failure to perform when properly used in accordance with instructions for use provided in the labeling can be reasonably expected
to result in a significant injury to the user. A critical component is any component in a life support device or system whose failure to perform
can be reasonably expected to cause the failure of the life support device or system or to affect its safety or effectiveness.
National Semiconductor and the National Semiconductor logo are registered trademarks of National Semiconductor Corporation. All other
brand or product names may be trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective holders.
Copyright© 2007 National Semiconductor Corporation
For the most current product information visit us at www.national.com
National Semiconductor
Americas Customer
Support Center
Email:
new.feedback@nsc.com
DAC128S085 12-Bit Micro Power OCTAL Digital-to-Analog Converter with Rail-to-Rail Outputs
www.national.com
Tel: 1-800-272-9959
National Semiconductor Europe
Customer Support Center
Fax: +49 (0) 180-530-85-86
Email: europe.support@nsc.com
Deutsch Tel: +49 (0) 69 9508 6208
English Tel: +49 (0) 870 24 0 2171
Français Tel: +33 (0) 1 41 91 8790
National Semiconductor Asia
Pacific Customer Support Center
Email: ap.support@nsc.com
National Semiconductor Japan
Customer Support Center
Fax: 81-3-5639-7507
Email: jpn.feedback@nsc.com
Tel: 81-3-5639-7560
 Loading...
Loading...