Page 1
FieldPoint Operating Instructions
CFP-RLY-421
Eight-Channel SPST Relay Module
These operating instructions describe how to install and use the
National Instruments cFP-RLY-421 relay module. For details on
configuring and accessing the cFP-RLY-421 over a network, refer
to the user manual for the FieldPoint network module you are
using.
Features
The cFP-RLY-421 is a Compact FieldPoint relay output module
with the following features:
• Eight single-pole single-throw (SPST) relay channels
• Switching capacity 1.5 A at 35 VDC or 250 VAC
• LED relay status indicators
• Hot swappable
• –40 to 60 °C operation
• 250 V
• 2,300 V
maximum isolation voltage
rms
transient overvoltage protection
rms
Power Requirement
The cFP-RLY-421 is powered by the FieldPoint network module
through the backplane bus. The cFP-RLY-421 is a high-power
consumption module, which may limit the number of I/O modules
that you can connect to a single network module.
FieldPoint™, National Instruments™, NI™, and ni.com™ are trademarks of National Instruments Corporation.
Product and company names mentioned herein are trademarks or trade names of their respective companies.
For patents covering National Instruments products, refer to the appropriate location: Help»Patents in your software,
the
patents.txt file on your CD, or ni.com/patents.
323617A-01 May 2003
© 2003 National Instruments Corp. All rights reserved.
Page 2

Before you configure a FieldPoint system that uses a cFP-RLY-421
module, calculate the total power consumption of the I/O modules
on the FieldPoint bank. You can find the power requirement
specification in the operating instructions for each I/O module.
The maximum power the network module can supply is specified
in the network module user manual. Make sure the total power
requirement for all of the I/O modules in the bank is less than the
maximum power available from the network module.
Suppose you have a bank with a cFP-2000 network module,
four cFP-RLY-421 modules, and four cFP-DI-301 modules. The
cFP-2000 can supply up to 9 W. The cFP-RLY-421 requires 1.7 W,
and cFP-DI-301 requires 0.325 W. The four cFP-RLY-421 and four
cFP-DI-301 modules require a total of 8.1 W:
4 × 1.7 W + 4 × 0.325 W = 8.1 W
This configuration meets the 9 W power requirement.
Installing the cFP-RLY-421
The cFP-RLY-421 mounts on a Compact FieldPoint backplane
(cFP-BP-x), which provides operating power to the module.
Installing the cFP-RLY-421 onto a powered backplane does not
disrupt the operation of the bank.
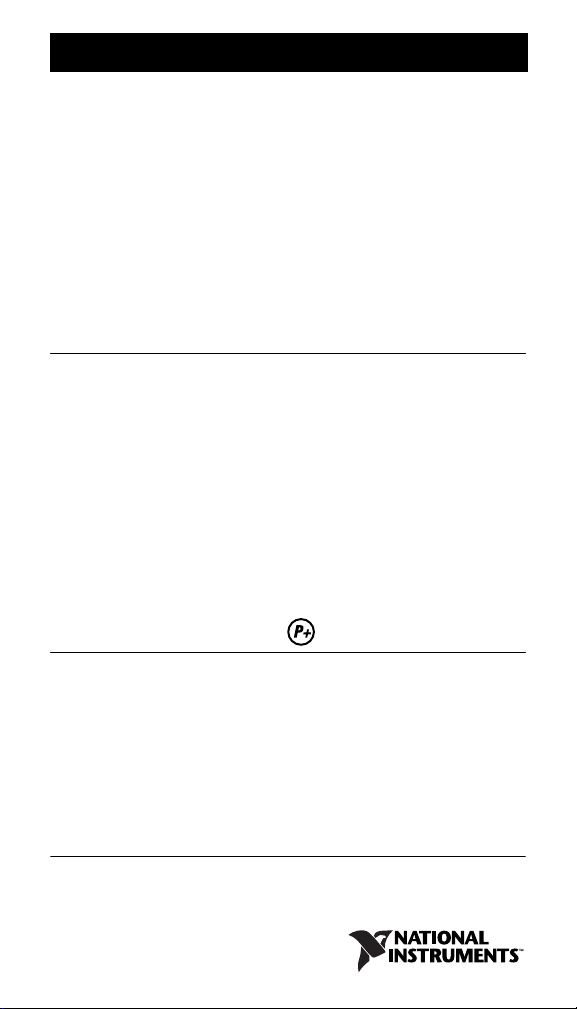
To install the cFP-RLY-421, refer to Figure 1 and complete the
following steps:
1. Align the captive screws on the cFP-RLY-421 with the holes
on the backplane. The alignment keys on the cFP-RLY-421
prevent backward insertion.
2. Press firmly to seat the cFP-RLY-421 on the backplane.
3. Using a number 2 Phillips screwdriver with a shank of at least
64 mm (2.5 in.) length, tighten the captive screws to 1.1 N ⋅ m
(10 lb ⋅ in.) of torque. The nylon coating on the screws prevents
them from loosening.
cFP-RLY-421 2 ni.com
Page 3
2 1
4
4
3
5
5
1 cFP I/O Module
2 Captive Screws
3 cFP Controller Module
Figure 1. Installing the cFP-RLY-421
4 Screw Holes
5 cFP Backplane
Wiring the cFP-RLY-421
The cFP-CB-x connector block has connections for each of the
eight cFP-RLY-421 relay channels and for an external supply to
power field devices. If you are using the cFP-RLY-421 in a
hazardous voltage application, you must use the cFP-CB-1
connector block or a suitable hazardous voltage cable. A hazardous
voltage is a voltage greater than 42.4 V
Caution Ensure that hazardous voltage wiring is
performed only by qualified personnel adhering to local
electrical standards.
Each relay channel of the cFP-RLY-421 has two terminals:
one NO (normally open) and one IC (isolated common).
© National Instruments Corp. 3 cFP-RLY-421
or 60 VDC.
peak
Page 4
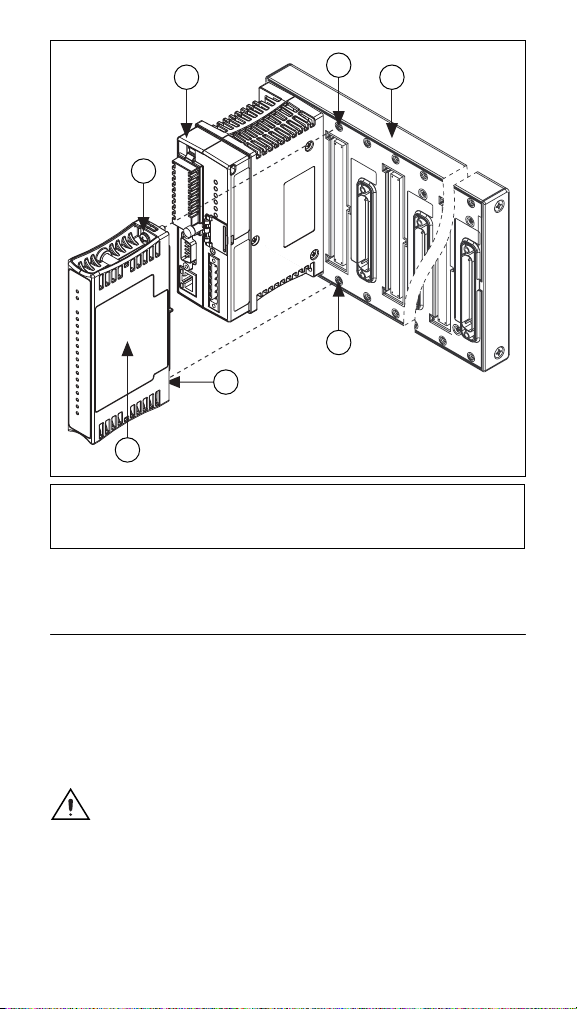
Table 1 lists the terminal assignments for the signals of each
channel.
Table 1. Terminal Assignments
Terminal Numbers
Channel
0 1 2
1 3 4
2 5 6
3 7 8
4 9 10
5 11 12
6 13 14
7 15 16
NO IC
All of the COM terminals are connected internally and all of the
V
terminals are connected internally. NI does not recommend
SUP
using them with the cFP-RLY-421.
Table 2. V
Caution Cascading power between two modules defeats
and COM Terminal Assignments
SUP
V
SUP
17 18
19 20
21 22
23 24
25 26
27 28
29 30
31 32
COM
isolation between those modules. Cascading power from
the network module defeats all isolation between
modules in the FieldPoint bank.
cFP-RLY-421 4 ni.com
Page 5
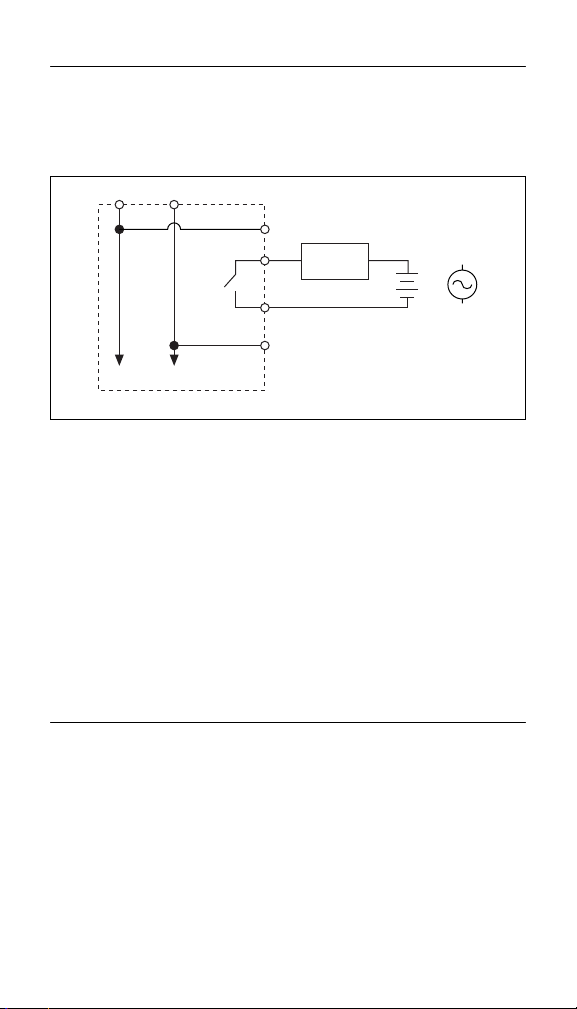
Connecting Loads to the cFP-RLY-421
Wire an external power supply to the load and IC terminal of the
individual channel as shown in Figure 2. This method of wiring
keeps the electrical connections of the cFP-RLY-421 within safe
current limits.
V C
To next channel
cFP-RLY-421
Figure 2. Connecting a Load
V
SUP
NO
IC
COM
Sourcing
Load
+
or
–
AC
The cFP-RLY-421 has eight SPST (Single-Pole-Single-Throw)
electromechanical relays. The power-up state is off (open) to
ensure safe installation. In the ON state, the NO and IC contacts
connect to form a short circuit. In the ON state, there is an effective
resistance of 100 mΩ between the NO and IC terminals, which
causes a voltage drop. For example, if the current is 1.5 A, the
voltage drop across the NO and IC terminals is 0.15 V.
The amount of current the relay can switch depends on the voltage,
the type of load, and ambient temperature. Refer to the
Specifications section for more information
.
Protecting Contacts for Inductive Loads
When inductive loads are connected to the relays, a large
counter-electromotive force may occur at relay switching time
because of the energy stored in the inductive load. These flyback
voltages can severely damage the relay contacts and greatly
shorten the life of the relay.
It is best to limit flyback voltages by installing a flyback diode
across an inductive DC load or a metal oxide varistor (MOV)
across an inductive AC load. Refer to the Guidelines for Selecting
Contact Protection Circuits section for more information.
© National Instruments Corp. 5 cFP-RLY-421
Page 6

In addition, the cFP-RLY-421 has internal protection MOVs to
prevent excessively high voltage from being applied across the
contacts. The MOVs are located between the NO and IC contacts
of each relay. However, National Instruments still recommends the
use of a protection circuit across an inductive load. The flyback
protection causes a small leakage current, which is detailed in the
Specifications section.
Guidelines for Selecting Contact Protection Circuits
Proper selection is critical, as the use of a contact-protection device
can extend contact life. When mounting the protection device,
always locate it near the immediate area of the load or contact.
Typically, you should mount a protective device within 18 in. of the
load or contact.
Typically, contact-protection circuits are provided for an overview,
but you should thoroughly examine the circuit you are planning
to use.
Diode and Zener Diode Circuit
Diagram Notes
Load
1
Use in DC applications only.
Use when diode circuit causes too long
release time.
Use zener diode with zener voltage about
equal to power supply voltage.
1
This section has been reprinted with permission from American Zettler, Inc.
cFP-RLY-421 6 ni.com
Page 7

Diode Circuit
Diagram Notes
Use in DC applications only.
Compared to RC type, circuit delays release
time (2 to 5 times values stated in catalog).
For larger voltages, use diode with reverse
breakdown 10 times circuit voltage and
forward load circuit.
Load
For smaller voltages, use reverse breakdown
voltage of 2 to 3 times power supply voltage.
CR Circuits
Diagram Notes
Load
Load
Circuit A is suitable for AC or DC
applications, but if used with AC
voltage, impedance of the load
should be smaller than the CR
circuit’s. Do not utilize for timer
loads, as leakage current can cause
faulty operations.
Circuit B is suitable for AC or DC.
If the load is a relay or solenoid,
release times lengthen. Effective
when connected to both contacts,
power supply voltage across the
load is 100 to 200 V.
Varistor Circuit
Diagram Notes
Effective for AC and DC
applications.
Circuit slightly delays release time.
Load
Effective when connected to both
contacts, power supply voltage
across the load is 100 to 200 V.
© National Instruments Corp. 7 cFP-RLY-421
Page 8

In-Rush Current
R
The type of load and its in-rush current characteristics, together
with switching frequency, can cause contact welding. For loads
with in-rush current, measure the steady state current and in-rush
current to determine the proper relay. Some typical types of loads
and the in-rush current they create are summarized in the following
chart.
Type of Load In-Rush Current
Resistive load Steady-state current
Solenoid load 10 to 20 times the steady-state current
Motor load 5 to 10 times the steady-state current
Incandescent lamp load 10 to 15 times the steady-state current
Mercury lamp load Approximately 3 times the steady-state
Sodium vapor lamp load 1 to 3 times the steady-state current
Capacitive load 20 to 40 times the steady-state current
Transforme r load 5 to 15 times the steady-state current
current
Status Indicators
Figure 3 shows the status indicator LEDs on the cFP-RLY-421.
01234567
READY
POWE
Figure 3. Status Indicators
After you insert the cFP-RLY-421 into a backplane and apply
power to the network module, the green POWER indicator lights
and the cFP-RLY-421 informs the network module of its presence.
When the network module recognizes the cFP-RLY-421, it sends
initial configuration information to the cFP-RLY-421. After the
cFP-RLY-421 receives this initial information, the green READY
indicator lights and the module is in normal operating mode.
In addition to the green POWER and READY indicators, each
channel has a numbered, green output state indicator that lights
when the channel is in the ON state.
cFP-RLY-421 8 ni.com
Page 9

Upgrading the FieldPoint Firmware
You may need to upgrade the FieldPoint firmware when you add
new I/O modules to the FieldPoint system. For information on
determining which firmware you need and how to upgrade the
firmware, go to
ni.com/info and enter fpmatrix.
Isolation and Safety Guidelines
Caution Read the following information before
attempting to connect the cFP-RLY-421 to any circuits
that may contain hazardous voltages.
This section describes the isolation of the cFP-RLY-421 and its
compliance with international safety standards. The field wiring
connections are isolated from the backplane. The isolation is
provided by the module, which has optical and galvanic isolation
barriers designed and tested to protect against transient fault
voltages of up to 2,300 V
insulation (compliant with IEC 61010-1) for working voltages of
250 V
1
. Safety standards (such as those published by UL and
rms
IEC) require the use of double insulation between hazardous
voltages and any human-accessible parts or circuits.
Never try to use any isolation product between human-accessible
parts (such as DIN rails or monitoring stations) and circuits that
can be at hazardous potentials under normal conditions, unless the
product is specifically designed for such an application, as is the
cFP-RLY-421.
Even though the cFP-RLY-421 is designed to handle applications
with hazardous potentials, follow these guidelines to ensure a safe
total system:
• The cFP-RLY-421 has a safety isolation barrier between the
I/O channels and the inter-module communication bus. There
is no isolation between channels unless otherwise noted. If any
of the channels on a module are wired at a hazardous potential,
make sure that all other devices or circuits connected to that
module are properly insulated from human contact.
. The cFP-RLY-421 provides double
rms
1
Working voltage is defined as the signal voltage plus the common-mode voltage.
Common-mode voltage is the voltage of the module with respect to ground.
© National Instruments Corp. 9 cFP-RLY-421
Page 10

•Do not share the external supply voltages (the V and C
terminals) with other devices (including other FieldPoint
devices), unless those devices are isolated from human contact.
• You must connect the protective earth (PE) ground terminal on
the cFP-BP-x backplane to the system safety ground. The
backplane PE ground terminal has the following symbol
stamped beside it: . Connect the backplane PE ground
terminal to the system safety ground using 14 AWG (1.6 mm)
wire with a ring lug. Use the 5/16 in. panhead screw shipped
with the backplane to secure the ring lug to the backplane PE
ground terminal.
• As with any hazardous voltage wiring, make sure that all
wiring and connections meet applicable electrical codes and
commonsense practices. Mount backplanes in an area,
position, or cabinet that prevents accidental or unauthorized
access to wiring that carries hazardous voltages.
• The isolation of the cFP-RLY-421 is certified as
double-insulated for working voltages of 250 V
. Do not use
rms
the cFP-RLY-421 as the only isolating barrier between human
contact and working voltages of more than 250 V
rms
.
• Operate the cFP-RLY-421 only at or below Pollution Degree 2.
Pollution Degree 2 means that only nonconductive pollution
occurs in most cases. Occasionally, however, a temporary
conductivity caused by condensation must be expected.
•Do not operate FieldPoint products in an explosive atmosphere
or where there may be flammable gases or fumes. If you need
to operate FieldPoint products in such an environment, the
FieldPoint products must be in a suitably rated enclosure.
• Operate the cFP-RLY-421 at or below Installation Category II.
Installation Category II is for measurements performed on
circuits directly connected to the low-voltage installation.
This category refers to local-level distribution, such as that
provided by a standard wall outlet.
cFP-RLY-421 10 ni.com
Page 11

Specifications
The following specifications are typical for a range of –40 to 60 °C
unless otherwise noted.
Relay Characteristics
Number of channels .......................... 8
Relay type ......................................... 1 SPST, nonlatching
Maximum switching capacity (resistive load)
–40 to 60 °C
AC........................................ 1.5 A at 250 VAC
DC........................................ 1.5 A at 0 to 35 VDC
1 A at 55 VDC
0.4 A at 120 VDC
Minimum switching load .................. 10 mA at 5 VDC
On resistance..................................... 100 mΩ
Off-state leakage (120 VDC/250 VAC)
Frequency Off-State Leakage
DC 0.12 µA
50/60 Hz 8 µA
Expected life
Mechanical ................................. 20
Electrical (at 30 cpm) .................300,000 operations at 1.5 A,
Maximum switching frequency
Mechanical ................................. 20 operations per second
Electrical..................................... 1 operation per second at
Relays operate time........................... 6 ms typical, 8 ms max
Relays release time ........................... 3 ms typical, 4 ms max
Relay bounce time ............................ 3 ms max
Contact material................................ Gold-plated silver cadmium
6
× 10
operations min
35 VDC;
100,000 operations at 1.5 A,
250 VAC
maximum load
oxide
© National Instruments Corp. 11 cFP-RLY-421
Page 12

Physical
Indicators .......................................... Green POWER and
READY indicators, 8 green
output state indicators
Weight
cFP-RLY-421 .............................. 130 g (4.5 oz)
Power Requirements
Power from network module ............1,700 mW
Isolation Voltage
Maximum isolation voltage.............. 250 V
Channel-to-channel isolation............ No isolation between
channels
Transient overvoltage........................ 2,300 V
rms
rms
Environmental
FieldPoint modules are intended for indoor use only. For outdoor
use, they must be mounted inside a sealed enclosure.
Operating temperature ...................... – 40 to 60 °C
Storage temperature.......................... –55 to 85 °C
Humidity ........................................... 10 to 90% RH,
Maximum altitude............................. 2,000 m; at higher altitudes
Pollution Degree ............................... 2
noncondensing
the isolation voltage ratings
must be lowered
Shock and Vibration
Operating vibration, random
(IEC 60068-2-64).............................. 10–500 Hz, 5 g
Operating vibration, sinusoidal
(IEC 60068-2-6)................................ 10–500 Hz, 5 g
Operating shock
(IEC 60068-2-27).............................. 50 g, 3 ms half sine,
18 shocks at 6 orientations;
30 g, 11 ms half sine,
18 shocks at 6 orientations
cFP-RLY-421 12 ni.com
rms
Page 13

Safety
This product is designed to meet the requirements of the following
standards of safety for electrical equipment for measurement,
control, and laboratory use:
• IEC 61010-1, EN 61010-1
• UL 3121-1, UL 61010C-1
• CAN/CSA C22.2 No. 1010.1
For UL, hazardous location, and other safety certifications, refer to
the product label or to
ni.com.
Electromagnetic Compatibility
CE, C-Tick, and FCC Part 15 (Class A) Compliant
Emissions.......................................... EN 55011 Class A at 10 m
FCC Part 15A above 1 GHz
Immunity........................................... EN 61326:1997 + A2:2001,
Table 1
Note For EMC compliance, you must operate this device
with shielded cabling.
CE Compliance
This product meets the essential requirements of applicable
European Directives, as amended for CE Marking, as follows:
Low-Voltage Directive (safety).........73/23/EEC
Electromagnetic Compatibility
Directive (EMC) ............................... 89/336/EEC
Note Refer to the Declaration of Conformity (DoC) for
this product for any additional regulatory compliance
information. To obtain the DoC for this product, click
Declarations of Conformity Information at
ni.com/hardref.nsf/.
© National Instruments Corp. 13 cFP-RLY-421
Page 14

Where to Go for Support
For more information about setting up the FieldPoint system, refer
to these National Instruments documents:
• FieldPoint network module user manual
• Other FieldPoint I/O module operating instructions
• FieldPoint connector block operating instructions
Go to
ni.com/support for the most current manuals, examples,
and troubleshooting information.
For telephone support in the United States, create your service
request at ni.com/ask and follow the calling instructions or dial
512 795 8248. For telephone support outside the United States,
contact your local branch office:
Australia 02 612 9672 8846, Austria 43 0 662 45 79 90 0,
Belgium 32 0 2 757 00 20, Brazil 55 11 3262 3599,
Canada (Calgary) 403 274 9391,
Canada (Montreal) 514 288 5722,
Canada (Ottawa) 613 233 5949, Canada (Québec) 514 694 8521,
Canada (Toronto) 905 785 0085,
Canada (Vancouver) 514 685 7530, China 86 21 6555 7838,
Czech Republic 420 2 2423 5774, Denmark 45 45 76 26 00,
Finland 385 0 9 725 725 11, France 33 0 1 48 14 24 24,
Germany 49 0 89 741 31 30, Greece 30 2 10 42 96 427,
India 91 80 51190000, Israel 972 0 3 6393737,
Italy 39 02 413091, Japan 81 3 5472 2970,
Korea 82 02 3451 3400, Malaysia 603 9131 0918,
Mexico 001 800 010 0793, Netherlands 31 0 348 433 466,
New Zealand 64 09 914 0488, Norway 47 0 32 27 73 00,
Poland 48 0 22 3390 150, Portugal 351 210 311 210,
Russia 7 095 238 7139, Singapore 65 6226 5886,
Slovenia 386 3 425 4200, South Africa 27 0 11 805 8197,
Spain 34 91 640 0085, Sweden 46 0 8 587 895 00,
Switzerland 41 56 200 51 51, Taiwan 886 2 2528 7227,
Thailand 662 992 7519, United Kingdom 44 0 1635 523545
cFP-RLY-421 14 ni.com
 Loading...
Loading...