Page 1

FIELDPOINT™ OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
AND SPECIFICATIONS
cFP-CB-1/2/3/4
Compact FieldPoint Connector Blocks
These operating instructions describe how to install and use the
cFP-CB-1, cFP-CB-2, cFP-CB-3, and cFP-CB-4 (referred to
inclusively in this manual as the cFP-CB-x).
Features
The cFP-CB-x Compact FieldPoint connector blocks have the
following features:
• Designed for general-purpose and hazardous-voltage
operation with all Compact FieldPoint I/O modules (cFP-CB-1
and cFP-CB-2)
• Isothermal construction minimizes temperature gradients for
use with thermocouples (cFP-CB-3)
• Mounting on a cFP-BP-x or cFP-180x Compact FieldPoint
backplane
• Up to 36 terminals
• Tie-wrap anchors for wires (cFP-CB-1 and cFP-CB-3)
• Front-panel access to terminals (cFP-CB-2 and cFP-CB-4)
• Removable front-mounted connectors (cFP-CB-2 and
cFP-CB-4)
• Spring terminals or screw terminals available
• V and C terminals for voltage supply and common connections
• –40 to 70 °C operation
Page 2
6
5
C
C
4
3
2
1
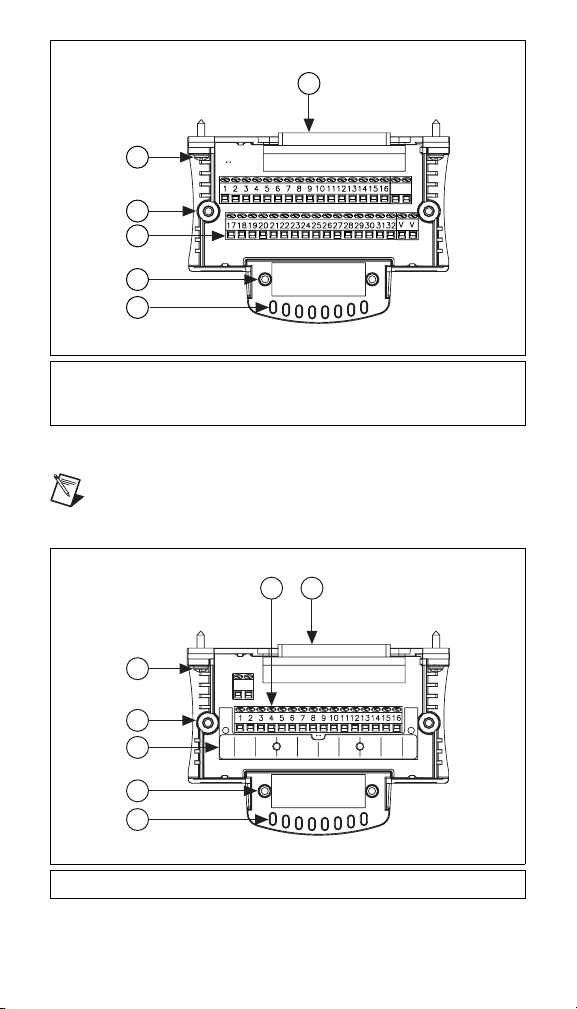
1 Tie-Wrap Anchors
2 Screw Hole for Strain-Relief Bar
3 Screw Terminals
4 Screw Hole for Top Cover
5 Mounting Screw
6 37-Pin I/O Connector
Figure 1. cFP-CB-1 Parts Locator Diagram
Earlier cFP-CB-1 connector blocks have a different
Note
screw-terminal numbering arrangement.
76
5
4
3
2
1
1 36-Pin Spring-Terminal Block 2 Mounting Screw
Figure 2. cFP-CB-2 Parts Locator Diagram
cFP-TC-120
C
C
+ –
+ –
+ –
+
–
+ –
+ –
CH 0
–+
CH 1
CH 2
CH 3
CH 4
+ –
CH 5
TERMINAL
CH 6
CH 7
ASSIGNMENTS
cFP-CB-1/2/3/4 2 ni.com
Page 3

76
5
C
C
4
+ –
3
cFP-TC-120
+ –
CH 0
CH 1
2
1
1 Tie-Wrap Anchors
2 Screw Hole for Strain-Relief Bar
3 Overlay Showing Channel
Assignments of Screw Terminals
Figure 3. cFP-CB-3 Parts Locator Diagram
5
4
3
cFP-TC-120
C
C
+ –
+ –
CH 0
CH 1
+ –
+
–
+ –
+ –
–+
CH 2
CH 3
CH 4
+ –
CH 5
TERMINAL
CH 6
CH 7
ASSIGNMENTS
4 Screw Hole for Top Cover
5 Mounting Screw
6 Screw Terminals
7 37-Pin I/O Connector
76
+ –
+
–
+ –
+ –
–+
CH 2
CH 3
CH 4
+ –
CH 5
TERMINAL
CH 6
CH 7
ASSIGNMENTS
2
1
1 20-Pin Screw-Terminal Block 2 Mounting Screw
Figure 4. cFP-CB-4 Parts Locator Diagram
© National Instruments Corp. 3 cFP-CB-1/2/3/4
Page 4

Wiring to the Connector Block
Refer to the I/O module operating instructions for information
about wiring configurations, including detailed wiring diagrams
and fuse recommendations.
Note To protect the FieldPoint system and connected
devices, install appropriate external fuses on all
terminals. Refer to the Specifications section for the
current limits of the cFP-CB-x terminals.
Note The V terminals are internally connected to each
other and the C terminals are internally connected to each
other.
Caution Ensure that hazardous voltage wiring is
performed only by qualified personnel adhering to local
electrical standards.
Wirng to the cFP-CB-1 and cFP-CB-3
1. Loosen the top cover screws and remove the cover. Refer to
Figure 5.
Figure 5. Removing the Top Cover from the cFP-CB-x
cFP-CB-1/2/3/4 4 ni.com
Page 5
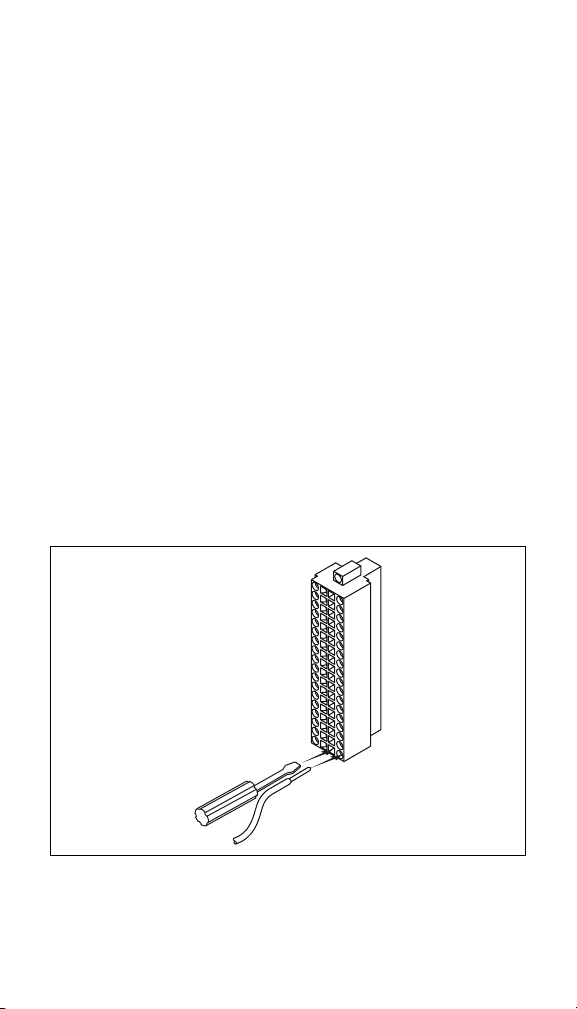
2. Verify that there are no cuts in the wire insulation that can
cause a safety hazard.
3. Strip 6 mm (0.24 in.) of insulation from the ends of the wires.
4. Insert the entire stripped ends of the wires into the appropriate
screw terminals. Do not allow any bare wire to show outside
the screw terminals.
5. Using a 1/8 in. flathead screwdriver, tighten the screw
terminals to 0.5–0.6 N ⋅ m (4.4–5.3 lb ⋅ in.) of torque.
Wiring to the cFP-CB-2
You need a flathead screwdriver with a blade smaller than
2.3 × 1.0 mm (0.09 × 0.04 in.) to connect wires to the detachable
spring-terminal connector. Complete the following steps:
1. Verify that there are no cuts in the wire insulation that can
cause a safety hazard.
2. Strip 7 mm (0.28 in.) of insulation from the ends of the wires.
3. Insert the screwdriver into a spring clamp activation slot.
4. Insert the entire stripped end of the wire into the corresponding
spring terminal. Do not allow any bare wire to show outside the
terminal.
5. Remove the screwdriver to clamp the wire into the terminal.
Figure 6.
Connecting a Wire to the Spring-Terminal Connector of the cFP-CB-2
6. When the wiring is complete, insert the connector into the
cFP-CB-2.
© National Instruments Corp. 5 cFP-CB-1/2/3/4
Page 6
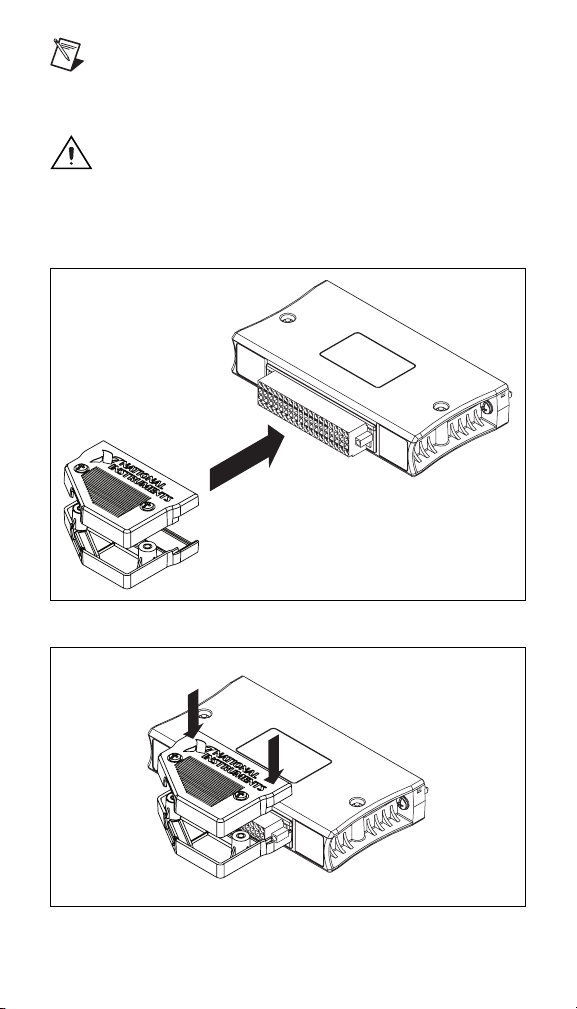
Note If your application is subject to high vibration,
National Instruments recommends installing the NI 9940
backshell on the spring-terminal connector. You can
order the NI 9940 from
Caution If your application is subject to hazardous
ni.com.
voltage, you must install the NI 9940 backshell on the
spring-terminal connector.
Figures 7, 8, and 9 show how to install the NI 9940 connector
backshell on the cFP-CB-2.
Figure 7. NI 9940 Connector Backshell and cFP-CB-2
Figure 8. Closing the NI 9940 Connector Backshell
cFP-CB-1/2/3/4 6 ni.com
Page 7

Figure 9. NI 9940 Connector Backshell Installed on cFP-CB-2
Wiring to the cFP-CB-4
You need a flathead screwdriver with a blade smaller than
2.3 × 1.0 mm (0.09 × 0.04 in.) to connect wires to the detachable
screw-terminal connector. Complete the following steps:
1. Verify that there are no cuts in the wire insulation that can
cause a safety hazard.
2. Strip 9 mm (0.35 in.) of insulation from the ends of the wires.
3. Insert the entire stripped ends of the wires into the appropriate
screw terminals. Do not allow any bare wire to show outside
the screw terminals.
4. Tighten the screw terminals to 0.22– 0.25 N ⋅ m
(1.9–2.2 lb ⋅ in.) of torque.
5. When the wiring is complete, insert the connector into the
cFP-CB-4 and tighten the screws on the ends of the connector.
© National Instruments Corp. 7 cFP-CB-1/2/3/4
Page 8

Wiring to the cFP-CB-4 for High-Vibration Environments and Hazardous-Voltage Applications
If your application is subject to high vibration or hazardous
voltage, National Instruments recommends affixing ferrules to the
ends of all signal wires. Refer to Figure 10.
Figure 10. Inserting a Wire with a Ferrule into the cFP-CB-4
cFP-CB-1/2/3/4 8 ni.com
Page 9

Installing the Strain-Relief Bar (cFP-CB-1 and cFP-CB-3 Only)
The cFP-CB-1 is shipped with two strain-relief bars, one with a
foam cushion for wires and one with grooves for jacketed cables.
The cFP-CB-3 has one foam-cushion strain relief bar. The tie-wrap
anchors on the connector block provide additional strain relief.
Figure 11 shows the two strain-relief bars.
Figure 11. cFP-CB-1 and cFP-CB-3 Strain-Relief Bars
Choose the strain-relief bar that suits your application and
complete the following steps:
1. Using a number 2 Phillips screwdriver, install the strain-relief
bar on the connector block as shown in Figure 12.
Figure 12. Installing the Strain-Relief Bar
© National Instruments Corp. 9 cFP-CB-1/2/3/4
Page 10

2. Tighten the strain-relief screws. If you are using the cushioned
strain-relief bar, make sure all the wires are secure against the
cushion and not touching metal parts of the connector block.
3. Reinstall the top cover and tighten the top cover screws.
4. Install tie wraps as shown in Figure 13.
Front View Rear View
Figure 13. Tie Wraps
cFP-CB-1/2/3/4 10 ni.com
Page 11

Installing the cFP-CB-x
To install the cFP-CB-x, refer to Figure 14 and complete the
following steps:
1. Align the captive screws on the cFP-CB-x with the holes on the
backplane. The shape of the I/O connector on the cFP-CB-x
prevents backward insertion.
2. Press firmly to seat the cFP-CB-x on the backplane.
3. Using a number 2 Phillips screwdriver with a shank of at least
64 mm (2.5 in.) length, tighten the captive screws to 1.1 N ⋅ m
(10 lb ⋅ in.) of torque. The nylon coating on the screws prevents
them from loosening.
2
3
4
1
3
1
1 Connector Block Captive Screws
2 I/O Module
Figure 14. Installing the cFP-CB-x
© National Instruments Corp. 11 cFP-CB-1/2/3/4
3 Screw Holes for Connector Block
4 Socket for Connector Block
Page 12

Thermocouple Wiring
Compact FieldPoint thermocouple input modules can measure the
temperature of the terminals on the cFP-CB-x connector block.
The modules use this measurement, called the cold junction
temperature, to compensate for the thermoelectric voltages
generated at these junctions. For the most accurate cold-junction
compensation, use the cFP-CB-3 for connecting thermocouple
signals.
Heat dissipated by adjacent modules (or other nearby heat sources)
can cause errors in thermocouple measurements by heating the
terminals to a different temperature than the sensor used to
measure the cold junction. The thermal gradient generated across
the terminals can cause the terminals of different channels to differ
in temperatures. The resulting measurement creates errors in
absolute and relative accuracy between channels. The actual
thermal gradient depends on the connector block you use and
the details of your installation. The following section provides
guidelines for minimizing thermal gradients.
Minimizing Thermal Gradients
To minimize the thermal gradient across the terminals, use the
cFP-CB-3 for connecting thermocouple signals. The cFP-CB-3 is
designed with isothermal construction to keep the terminals at the
same temperature. In addition to using the cFP-CB-3, you can
minimize thermal gradients by following these guidelines:
• Do not place power supplies or other heat sources directly
above or below the Compact FieldPoint system.
• Do not install high-power modules, such as the cFP-DO-4xx
and cFP-RLY-4xx, adjacent to the cFP-CB-3.
• Use small-gauge thermocouple wire to transfer less heat.
• Run thermocouple wires together near the connector block to
keep them at the same temperature.
• Avoid running thermocouple wires near hot or cold objects.
• Use the foam cushion strain relief to restrict air flow.
cFP-CB-1/2/3/4 12 ni.com
Page 13

Isolation and Safety Guidelines
Caution Read the following information before
attempting to connect the cFP-CB-x to any circuits that
may contain hazardous voltages.
This section describes the isolation of the cFP-CB-x and its
compliance with international safety standards. The field wiring
connections are isolated from the backplane and the inter-module
communication bus. The isolation is provided by the module,
which has optical and galvanic isolation barriers designed and
tested to protect against transient fault voltages of up to 2,300 V
The cFP-CB-x provides double insulation (compliant with
IEC 61010-1) for working voltages of 250 V
1
. Safety standards
rms
(such as those published by UL and IEC) require the use of double
insulation between hazardous voltages and any human-accessible
parts or circuits.
Never try to use any isolation product between human-accessible
parts (such as DIN rails or monitoring stations) and circuits that
can be at hazardous potentials under normal conditions, unless the
product is specifically designed for such an application as is the
cFP-CB-x.
Even though the cFP-CB-x is designed to handle applications with
hazardous potentials, follow these guidelines to ensure a safe total
system:
• If any of the channels on a module are wired at a hazardous
potential, make sure that all other devices or circuits connected
to that module are properly insulated from human contact.
•Do not share the external supply voltages (the V and C
terminals) with other devices (including other FieldPoint
devices), unless those devices are isolated from human contact.
rms
.
1
Working voltage is defined as the signal voltage plus the common-mode voltage.
Common-mode voltage is the voltage of the module with respect to ground.
© National Instruments Corp. 13 cFP-CB-1/2/3/4
Page 14

• You must connect the protective earth (PE) ground terminal on
the cFP-BP-x or cFP-180x backplane to the system safety
ground. The backplane PE ground terminal has the following
symbol stamped beside it: . Connect the backplane PE
ground terminal to the system safety ground using 14 AWG
(1.6 mm) wire with a ring lug. Use the 5/16 in. panhead screw
shipped with the backplane to secure the ring lug to the
backplane PE ground terminal.
• As with any hazardous voltage wiring, make sure that all
wiring and connections meet applicable electrical codes and
commonsense practices. Mount the backplane in an area,
position, or cabinet that prevents accidental or unauthorized
access to wiring that carries hazardous voltages.
• The isolation of the cFP-CB-x is certified as double-insulated
for working voltages of up to 250 V
rms
.
• Operate the cFP-CB-x only at or below Pollution Degree 2.
Pollution Degree 2 means that only nonconductive pollution
occurs in most cases. Occasionally, however, a temporary
conductivity caused by condensation must be expected.
•Do not operate FieldPoint products in an explosive atmosphere
or where there may be flammable gases or fumes. If you need
to operate FieldPoint products in such an environment, the
FieldPoint products must be in a suitably rated enclosure.
• Operate the cFP-CB-x at or below Measurement Category II.
Measurement Category II is for measurements performed on
circuits directly connected to the electrical distribution system.
This category refers to local-level distribution, such as that
provided by a standard wall outlet.
cFP-CB-1/2/3/4 14 ni.com
Page 15

Safety Guidelines for Hazardous Locations
The cFP-CB-x is suitable for use in Class I, Division 2, Groups A,
B, C, D, T4 hazardous locations; Class I, Zone 2, AEx nA IIC T4
and Ex nA IIC T4 hazardous locations; and nonhazardous
locations only. Follow these guidelines if you are installing the
cFP-CB-x in a potentially explosive environment. Not following
these guidelines may result in serious injury or death.
Caution Do not disconnect I/O-side wires or connectors
unless power has been switched off or the area is known
to be nonhazardous.
Caution Do not remove modules unless power has been
switched off or the area is known to be nonhazardous.
Caution Substitution of components may impair
suitability for Class I, Division 2.
Specifications
The following specifications are typical for the range –40 to 70 °C,
unless otherwise noted.
Installation
Terminal wiring
cFP-CB-1 and cFP-CB-3............ 16–26 AWG copper
cFP-CB-2.................................... 18–22 AWG copper
cFP-CB-4.................................... 16–28 AWG copper
1
Use only copper conductor wire unless you are working with a sensing device, such
as a thermocouple, that requires a different type of wire.
© National Instruments Corp. 15 cFP-CB-1/2/3/4
1
conductor wire with 6 mm
(0.24 in.) of insulation
stripped from the end
conductor with 7 mm
(0.28 in.) of insulation
stripped from the end
conductor with 9 mm
(0.35 in.) of insulation
stripped from the end
Page 16

Maximum cable diameter
for cFP-CB-1 and cFP-CB-3 ............ 8 mm (5/16 in.) with
cable-grooved strain
relief
Torque for screw terminals
cFP-CB-1 and cFP-CB-3............ 0.5 – 0.6 N ⋅ m
(4.4–5.3 lb ⋅ in.)
cFP-CB-4.................................... 0.22– 0.25 N ⋅ m
(1.9–2.2 lb ⋅ in.)
Maximum current for terminals
1
V and C terminals....................... 4 A
All other terminals...................... 2 A
Accuracy
Cold-junction accuracy ..................... 0.15 °C typ, 0.3 °C max
There is typically an additional 0.2 °C difference between the
temperature of the cold-junction sensor and that of the actual
terminals.
Physical
Weight
cFP-CB-1.................................... 201 g (7.1 oz)
cFP-CB-2.................................... 135 g (4.8 oz)
cFP-CB-3.................................... 201 g (7.1 oz)
cFP-CB-4.................................... 141 g (5.0 oz)
Isolation Voltage
Channel-to-earth ground
Continuous ................................. 250 V
Measurement Category II
Withstand.................................... 2,300 V
dielectric withstand test
Channel-to-channel isolation............Refer to I/O module
operating instructions
1
Use fast-acting fuses to limit the current through screw terminals. Some I/O module
terminals require a lower maximum current value. Refer to the I/O module operating
instructions for more information.
cFP-CB-1/2/3/4 16 ni.com
,
rms
, verified by a 2 s
rms
Page 17

Caution Improper wiring may defeat isolation barrier.
Environmental
Compact FieldPoint connector blocks are intended for indoor use
only. For outdoor use, the Compact FieldPoint system must be
mounted inside a sealed enclosure.
Operating temperature ...................... – 40 to 70 °C
Storage temperature .......................... –55 to 85 °C
Humidity ........................................... 10 to 90% RH,
noncondensing
Maximum altitude............................. 2,000 m; at higher altitudes,
the isolation voltage ratings
must be lowered
Pollution Degree ............................... 2
Shock and Vibration
Operating vibration, random
(IEC 60068-2-64).............................. 10–500 Hz, 5 g
Operating vibration, sinusoidal
(IEC 60068-2-6)................................ 10–500 Hz, 5 g
Operating shock
(IEC 60068-2-27).............................. 50 g, 3 ms half sine,
18 shocks at 6 orientations;
30 g, 11 ms half sine,
18 shocks at 6 orientations
rms
Safety
This product is designed to meet the requirements of the following
standards of safety for electrical equipment for measurement,
control, and laboratory use:
• IEC 61010-1, EN 61010-1
• UL 61010-1, CSA 61010-1
Note For UL and other safety certifications, refer to the
product label or visit
by model number or product line, and click the
appropriate link in the Certification column.
© National Instruments Corp. 17 cFP-CB-1/2/3/4
ni.com/certification, search
Page 18

Electromagnetic Compatibility
This product is designed to meet the requirements of the following
standards of EMC for electrical equipment for measurement,
control, and laboratory use:
• EN 61326 EMC requirements; Industrial Immunity
• EN 55011 Emissions; Group 1, Class A
• CE, C-Tick, ICES, and FCC Part 15 Emissions; Class A
Note For For EMC compliance, operate this device
according to product documentation.
CE Compliance
This product meets the essential requirements of applicable
European Directives, as amended for CE marking, as follows:
• 2006/95/EC; Low-Voltage Directive (safety)
• 2004/108/EC; Electromagnetic Compatibility Directive (EMC)
Note Refer to the Declaration of Conformity (DoC) for
this product for any additional regulatory compliance
information. To obtain the DoC for this product, visit
ni.com/certification, search by model number or
product line, and click the appropriate link in the
Certification column.
cFP-CB-1/2/3/4 18 ni.com
Page 19

Environmental Management
⬉ᄤֵᙃѻક∵ᶧࠊㅵ⧚ࡲ⊩ ˄Ё
˅
Ёᅶ᠋
NI is committed to designing and manufacturing products in
an environmentally responsible manner. NI recognizes that
eliminating certain hazardous substances from our products is
beneficial not only to the environment but also to NI customers.
For additional environmental information, refer to the NI and the
Environment Web page at ni.com/environment. This page
contains the environmental regulations and directives with which
NI complies, as well as other environmental information not
included in this document.
Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE)
EU Customers At the end of their life cycle, all products
must be sent to a WEEE recycling center. For more
information about WEEE recycling centers and
National Instruments WEEE initiatives, visit
ni.com/environment/weee.
RoHS
ѻકЁ䰤ࠊՓ⫼ᶤѯ᳝ᆇ⠽䋼ᣛҸ
National Instruments
National InstrumentsЁRoHS
ni.com/environment/rohs_china
about China RoHS compliance, go to
environment/rohs_china
ヺড়Ё⬉ᄤֵᙃ
DŽ݇Ѣ
(RoHS)
ড়㾘ᗻֵᙃˈ䇋ⱏᔩ
DŽ
(For information
ni.com/
.)
© National Instruments Corp. 19 cFP-CB-1/2/3/4
Page 20

Where to Go for Support
For more information about setting up the Compact FieldPoint
system, refer to these National Instruments documents:
• Compact FieldPoint controller user manual
• Compact FieldPoint I/O module operating instructions
Go to
ni.com/support for the most current manuals, examples,
and troubleshooting information.
For telephone support in the United States, create your service
request at ni.com/ask and follow the calling instructions or dial
512 795 8248. For telephone support outside the United States,
contact your local branch office:
Australia 1800 300 800, Austria 43 662 457990-0,
Belgium 32 (0) 2 757 0020, Brazil 55 11 3262 3599,
Canada 800 433 3488, China 86 21 5050 9800,
Czech Republic 420 224 235 774, Denmark 45 45 76 26 00,
Finland 358 (0) 9 725 72511, France 01 57 66 24 24,
Germany 49 89 7413130, India 91 80 41190000,
Israel 972 3 6393737, Italy 39 02 41309277, Japan 0120-527196,
Korea 82 02 3451 3400, Lebanon 961 (0) 1 33 28 28,
Malaysia 1800 887710, Mexico 01 800 010 0793,
Netherlands 31 (0) 348 433 466, New Zealand 0800 553 322,
Norway 47 (0) 66 90 76 60, Poland 48 22 3390150,
Portugal 351 210 311 210, Russia 7 495 783 6851,
Singapore 1800 226 5886, Slovenia 386 3 425 42 00,
South Africa 27 0 11 805 8197, Spain 34 91 640 0085,
Sweden 46 (0) 8 587 895 00, Switzerland 41 56 2005151,
Taiwan 886 02 2377 2222, Thailand 662 278 6777,
Turkey 90 212 279 3031, United Kingdom 44 (0) 1635 523545
National Instruments, NI, ni.com, and LabVIEW are trademarks of National Instruments Corporation. Refer to the
Terms of Use section on
product and company names mentioned herein are trademarks or trade names of their respective companies.
For patents covering National Instruments products, refer to the appropriate location: Help»Patents in your software,
the
patents.txt file on your CD, or ni.com/patents.
© 2002–2007 National Instruments Corp. All rights reserved.
373322C-01 Dec07
ni.com/legal for more information about National Instruments trademarks. Other
 Loading...
Loading...