Page 1

OPERATION MANUAL
MODEL MLT25 SERIES
DEDICATED LIGHT TOWER
Revision #0 (11/28/12)
To find the latest revision of this
publication, visit our website at:
www.multiquip.com
THIS MANUAL MUST ACCOMPANY THE EQUIPMENT AT ALL TIMES.
PN 49808
Page 2

PROPOSITION 65 WARNING
Diesel engine exhaust and some of
PAGE 2 — MLT25 SERIES LIGHT TOWER • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (11/28/12)
Page 3
REPORTING SAFETY DEFECTS
If you believe that your vehicle has a defect that could cause a crash or could cause
injury or death, you should immediately inform the National Highway Traffic Safety
Administration (NHTSA) in addition to notifying Multiquip at 1-800-421-1244.
If NHTSA receives similar complaints, it may open an investigation, and if it finds
that a safety defect exists in a group of vehicles, it may order a recall and remedy
campaign. However, NHTSA cannot become involved in individual problems
between you, your dealer, or Multiquip.
To contact NHTSA, you may either call the Vehicle Safety Hotline toll-free at 1-888327-4236 (TTY: 1-800-424-9153), go to http://www.nhtsa.dot.gov; or write to:
Administrator
NHTSA
1200 New Jersey Avenue S.E.
Washington, DC 20590
You can also obtain information about motor vehicle safety from
http://www.safecar.gov.
MLT25 SERIES LIGHT TOWER • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (11/28/12) — PAGE 3
Page 4

MLT25 Series Light Tower
Proposition 65 Warning ........................................... 2
Reporting Safety Defects ......................................... 3
Table Of Contents .................................................... 4
Safety Information ............................................5-110
Specifications ........................................................ 11
Dimensions ............................................................ 12
General Information ............................................... 13
Components ..................................................... 14-15
Inspection ......................................................... 16-17
Operation .......................................................... 18-21
Maintenance ..................................................... 22-23
Maintenance — Trailers .................................... 24-26
Safety Guidelines — Trailers ............................ 27-41
Troubleshooting ................................................ 42-44
Electronic Components Locator ............................ 45
Wiring Diagram ................................................. 46-48
TABLE OF CONTENTS
NOTICE
Specifications are subject to change without notice.
PAGE 4 — MLT25 SERIES LIGHT TOWER • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (11/28/12)
Page 5
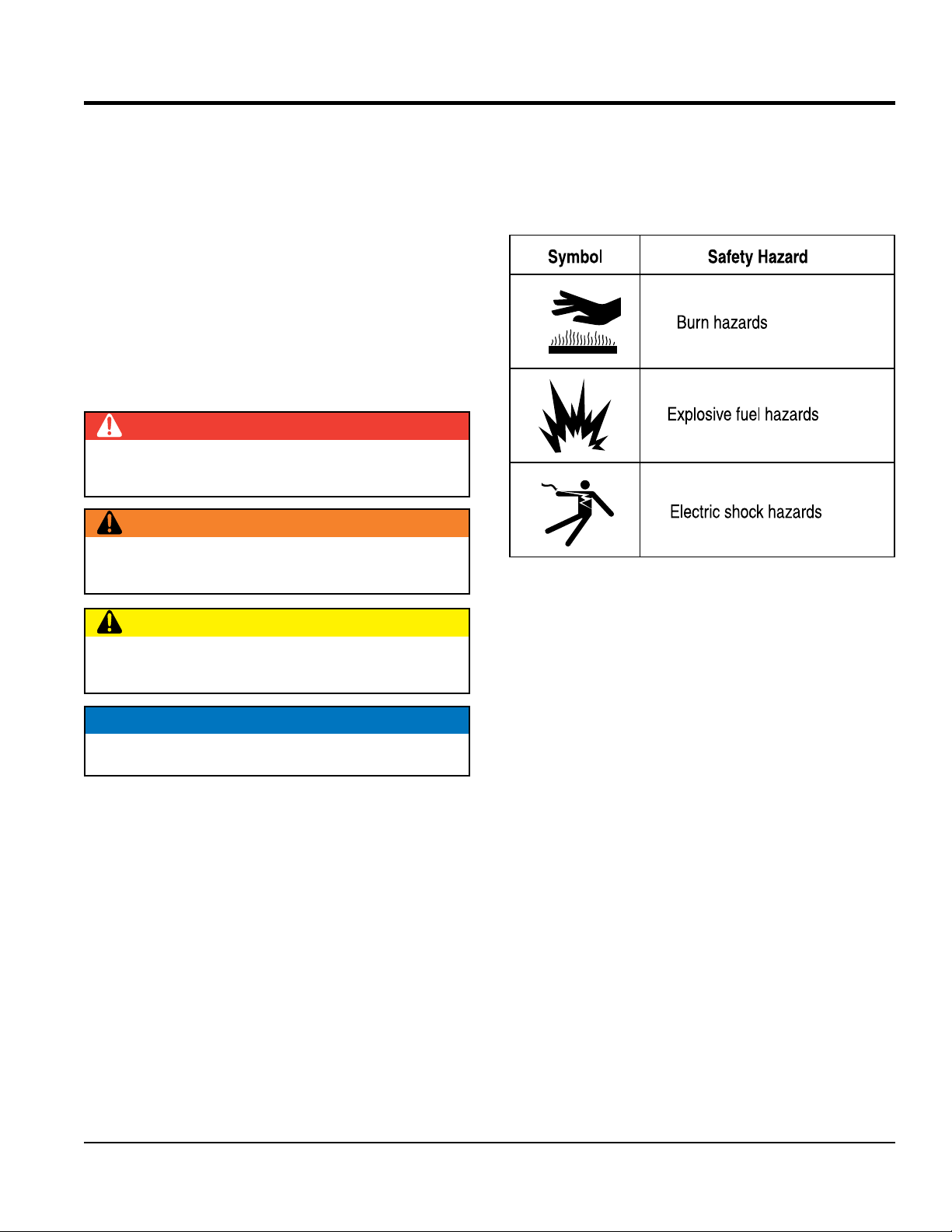
SAFETY INFORMATION
Do not operate or service the equipment before reading the
SAFETY SYMBOLS
entire manual. Safety precautions should be followed at all
times when operating this equipment. Failure to read and
understand the safety messages and operating instructions
could result in injury to yourself and others.
SAFETY MESSAGES
The four safety messages shown below will inform you
about potential hazards that could injure you or others. The
safety messages specifi cally address the level of exposure
to the operator and are preceded by one of four words:
DANGER, WARNING, CAUTION or NOTICE.
SAFETY SYMBOLS
DANGER
Indicates a hazardous situation which, if not avoided,
WILL result in DEATH or SERIOUS INJURY.
WARNING
Indicates a hazardous situation which, if not avoided,
COULD result in DEATH or SERIOUS INJURY.
Potential hazards associated with the operation of this
equipment will be referenced with hazard symbols which
may appear throughout this manual in conjunction with
safety messages.
CAUTION
Indicates a hazardous situation which, if not avoided,
COULD result in MINOR or MODERATE INJURY.
NOTICE
Addresses practices not related to personal injury.
MLT25 SERIES LIGHT TOWER • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (11/28/12) — PAGE 5
Page 6

GENERAL SAFETY
NOTICE
This equipment should only be operated by trained and
Whenever necessary, replace nameplate, operation and
accident due to equipment modifi cations. Unauthorized
recommended by Multiquip for this equipment. Damage
Also, know the phone
fi re
SAFETY INFORMATION
CAUTION
NEVER operate this equipment without proper protective
clothing, shatterproof glasses, respiratory protection,
hearing protection, steel-toed boots and other protective
devices required by the job or city and state regulations.
NEVER operate this equipment when not
feeling well due to fatigue, illness or when
under medication.
NEVER operate this equipment under the infl uence of
drugs or alcohol.
ALWAYS check the equipment for loosened threads or
bolts before starting.
DO NOT use the equipment for any purpose other than
its intended purposes or applications.
qualifi ed personnel 18 years of age and older.
safety decals when they become diffi cult read.
Manufacturer does not assume responsibility for any
equipment modifi cation will void all warranties.
NEVER use accessories or attachments that are not
to the equipment and/or injury to user may result.
ALWAYS know the location of the nearest
fi re extinguisher.
ALWAYS know the location of the nearest
fi rst aid kit.
ALWAYS know the location of the nearest phone or
keep a phone on the job site.
numbers of the nearest ambulance, doctor and
department. This information will be invaluable in the
case of an emergency.
PAGE 6 — MLT25 SERIES LIGHT TOWER • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (11/28/12)
Page 7

LIGHT TOWER SAFETY
NOTICE
keep the immediate area surrounding the light
keep the machine in proper running condition.
store equipment properly when it is not being
used. Equipment should be stored in a clean, dry location
out of the reach of children and unauthorized personnel.
use
Always shut down the engine and turn off circuit breakers
allow a suffi cient amount of time for the lamp to
before touching or changing. The possibility exists of
use force when installing the lamp. Excessive force
leave any grease or oil residue on lamp surface
install and remove
SAFETY INFORMATION
DANGER
NEVER operate the equipment in an explosive
atmosphere or near combustible materials. An
explosion or fi re could result causing severe
bodily harm or even death.
WARNING
NEVER disconnect any emergency or safety devices.
These devices are int ended for operator safet y.
Disconnection of these devices can cause severe injury,
bodily harm or even death. Disconnection of any of these
devices will void all warranties.
CAUTION
NEVER lubricate components or attempt service on a
running machine.
ALWAYS ensure light tower is on level ground before use
so that it cannot slide or shift around, endangering workers.
Always keep immediate area free of bystanders.
ALWAYS make sure trailer is leveled with all outriggers
extended before raising tower. Outriggers must remain
extended while tower is up.
ALWAYS keep area behind trailer clear of people while
raising and lowering mast.
NEVER remove safety pin or pull mast locking pin while
tower is in a raised position!
CHECK the mast and winch cables for wear. If any
problem occurs when lowering or raising the tower, STOP
immediately! Contact a trained technician for assistance.
ALWAYS
tower clean, neat, and free of debris.
ALWAYS
Fix damage to machine and replace any broken parts
immediately.
ALWAYS
To prevent the light tower from overturning, NEVER
in winds that exceed 65 mph (105 kph).
LAMP SAFETY
WARNING
NEVER attempt to replace lamp with the power on.
when changing the lamp.
ALWAYS
cool
severe burns.
CAUTION
NEVER
could cause the lamp to break, causing bodily harm.
NOTICE
NEVER
when replacing or removing lamp. This can create hot
spots, reducing the service life of the lamp.
ALWAYS make sure lamp surface is clean and dry.
NEVER pivot or retract mast while unit is operating.
NEVER use the light tower mast as a crane. DO NOT
lift anything with the mast.
NEVER attach anything to the light tower mast unless it
is an authorized Multiquip component.
ALWAYS lower the light tower when not in use, or if high
winds or electrical storms are expected.
MLT25 SERIES LIGHT TOWER • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (11/28/12) — PAGE 7
ALWAYS replace with MQ recommended type lamp.
ALWAYS have a trained technician
a fl oodlight, or replace any damaged fi xture wiring.
Page 8

TOWING SAFETY
CAUTION
Avoid sudden stops and starts. This can cause skidding,
Trailer should be adjusted to a level position at all times
rolling
underneath the trailer’s bumper
Use the trailer’s swivel jack to adjust the trailer height to
SAFETY INFORMATION
or jack-knifi ng. Smooth, gradual starts and stops will
improve towing.
Check with your local county or state safety
towing regulations, in addition to meeting
Depar tment of Transpor tation (DOT)
Safety Towing Regulations, before towing
your light tower.
In order to reduce the possibility of an accident while
transporting the light tower on public roads, ALWAYS
make sure the trailer that supports the light tower and
the towing vehicle are mechanically sound and in good
operating condition.
ALWAYS shutdown engine before transporting.
Make sure the hitch and coupling of the towing vehicle
are rated equal to, or greater than the trailer “gross
vehicle weight rating.”
ALWAYS inspect the hitch and coupling for wear. NEVER
tow a trailer with defective hitches, couplings, chains, etc.
Check the tire air pressure on both towing vehicle and
trailer. Trailer tires should be infl ated to 50 psi cold.
Also check the tire tread wear on both vehicles.
Avoid sharp turns to prevent rolling.
when towing.
Raise and lock trailer wheel stand in up position when
towing.
Place chock blocks underneath wheel to prevent
while parked.
Place support blocks
to prevent tipping while parked.
a level position while parked.
ALWAYS make sure the trailer is equipped with a safety
chain.
ALWAYS properly attach trailer’s safety chains to towing
vehicle.
ALWAYS make sure the vehicle and trailer directional,
backup, brake and trailer lights are connected and
working properly.
DOT Requirements include the following:
• Connect and test electric brake operation.
• Secure portable power cables in cable tray with tie
wraps.
The maximum speed for highway towing is 55 MPH unless
posted otherwise. Recommended off-road towing is not to
exceed 15 MPH or less depending on type of terrain.
PAGE 8 — MLT25 SERIES LIGHT TOWER • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (11/28/12)
Page 9
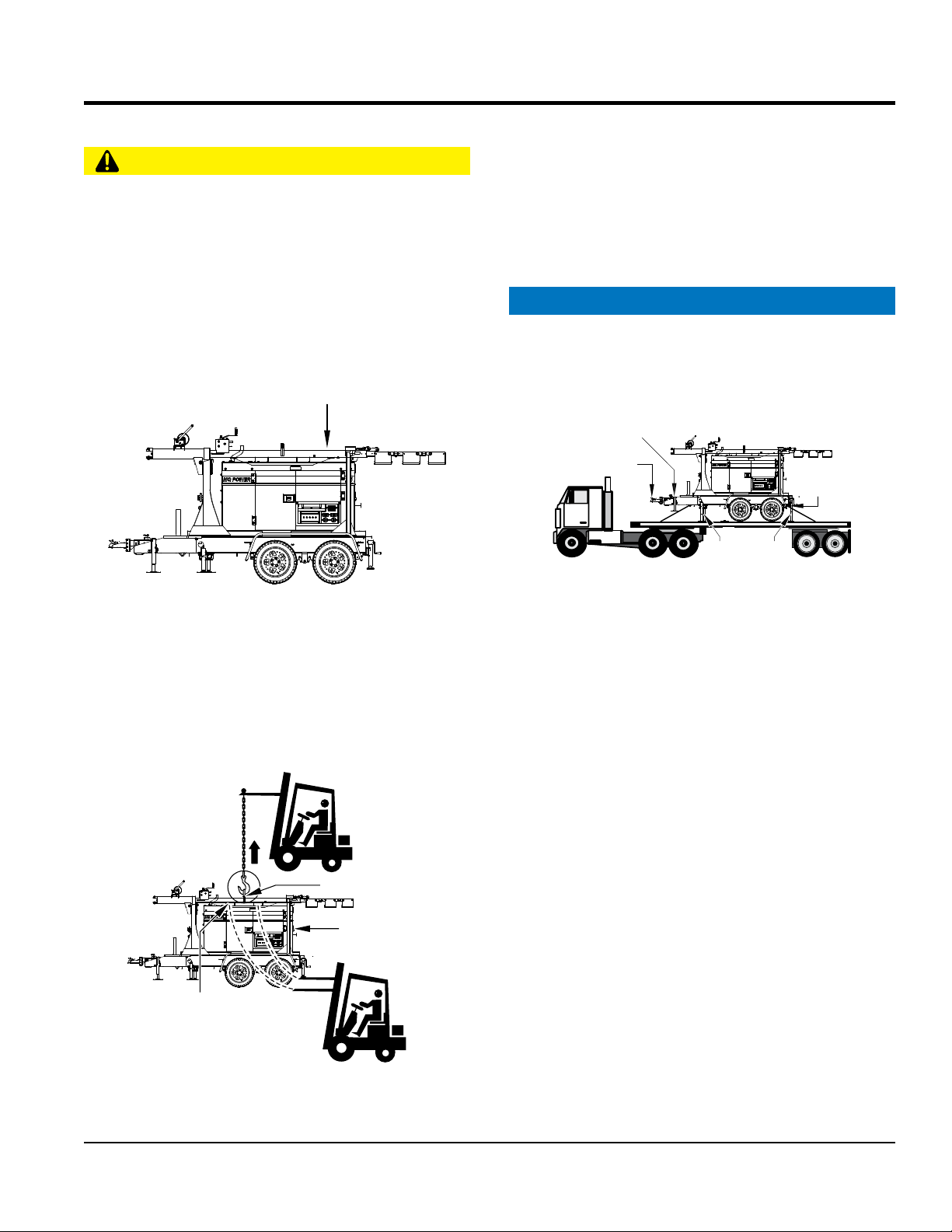
TRANSPORTING SAFETY
CAUTION
STOWED
If lifting through pockets, make sure forks of forklift are
Never allow any person or animal to stand underneath the
jackstand of light tower is retracted and in the horizontal
position so that the foot does not make contact with the
Make sure that the two side (left and right) and two rear
jackstands are in the vertical postion, slightly extended,
Straps and chains should be routed through the transport
secure the unit by running a strap or chain over
FRONT
Before lifting, make sure that light tower parts are not
damaged and screws are not loosened or lost.
ALWAYS make sure crane or lifting device has been
properly secured to lifting hook of the equipment.
NEVER lift the equipment while engine is running.
SAFETY INFORMATION
inserted in pockets as far as possible before lifting.
equipment while lifting.
DO NOT lift equipment to unnecessary heights.
Loading and Tie-Down on Flatbed Truck
NOTICE
Make sure the tower is in the stowed position before
lifting.
POSITION
ALWAYS Make sure rear mast lock is secure before
lifting.
Use adequate lifting cable (wire or rope) of suffi cient
strength.
Use one point suspension hook and lift straight upwards.
When loading onto fl atbed truck, make sure that front
deck fl oor.
JACKSTAND
RETRACTED
TONGUE
SIDE
JACK
STAND
(2)
REAR
JACK
STAND
(2)
TRANSPORT
TIE-DOWN
POINT
so that each foot makes contact with the deck fl oor.
tie-down points located beneath each corner of the
cabinet to allow even application of forece to the front
and rear of the machine.
DO NOT
the tongue of the light tower. This may cause severe
damage to the unit.
FORKLIFT
POCKETS
(2)
LIFTING BALE
LIGHT TOWER
MLT25 SERIES LIGHT TOWER • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (11/28/12) — PAGE 9
Page 10
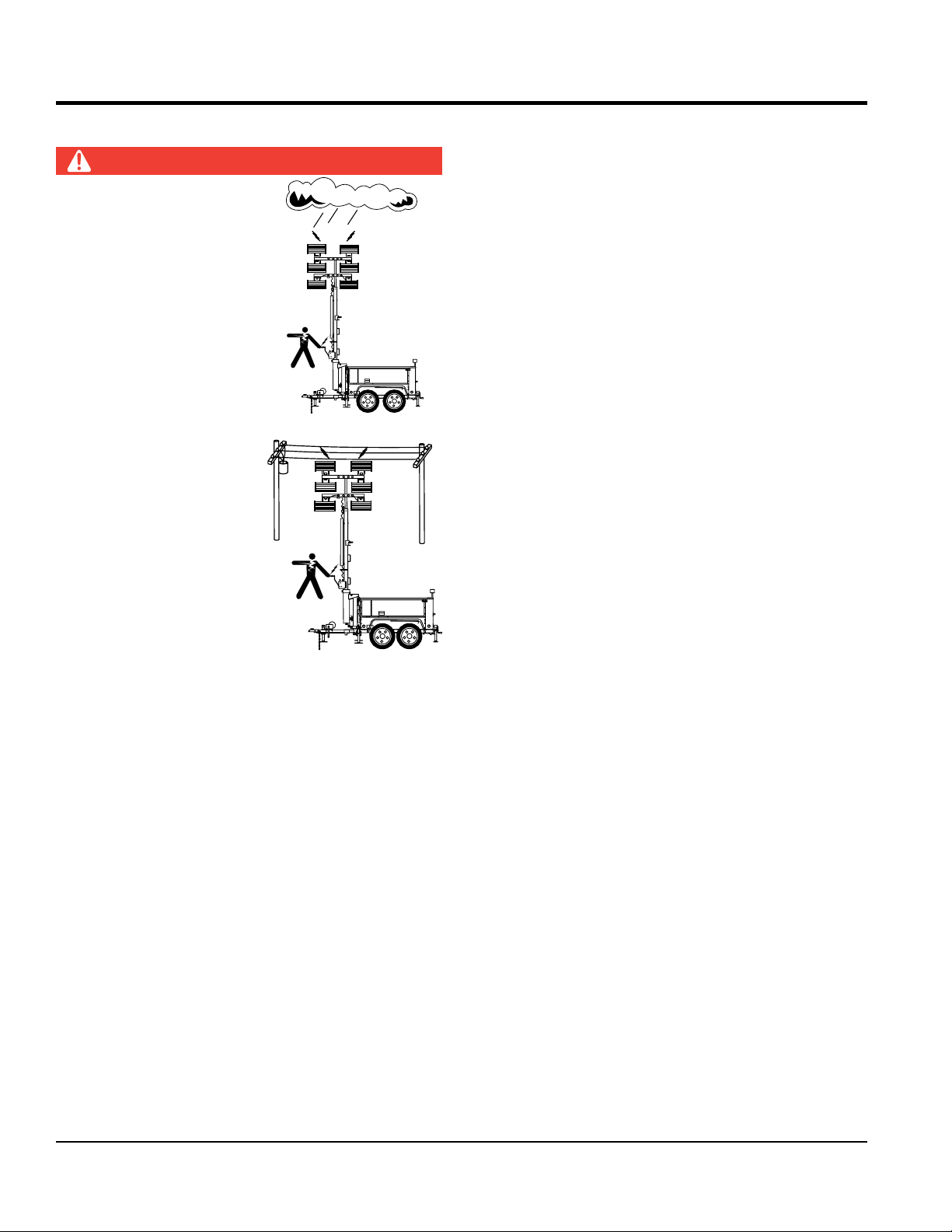
ELECTRICAL SAFETY
DANGER
.
NEVER operate light tower
or han dle any elec trical
equipment while standing in
water, while barefoot, while
hands are wet or in the rain.
A dangerous el ectrical
shock could occur, causing
severe bodily harm or
even death.
ALWAYS make sure the
area above the light tower is
open and clear of overhead
powe r lin e s a n d ot h er
ob s truction s. The tower
extends in excess of 30
feet (9 meters). Contact
w i t h ov e r h e a d p o w e r
lines or other obstructions
could result in equipment
damage, electrical shock,
electrocution and even
death.
SAFETY INFORMATION
Similar to boom equipment, light tower may become
energized with high voltage. DO NOT operate the light
tower within a radial distance of 17 feet from high voltage
power lines. If light tower becomes energized with high
voltage, contact with the equipment could result in
electrocution.
PAGE 10 — MLT25 SERIES LIGHT TOWER • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (11/28/12)
Page 11
Light Tower Specifications
SPECIFICATIONS
Table 1. MLT25 Series Specifications
Weight (with genset/trailer)
Lamps Six 1,000-Watt Metal Halide
Lumens 660,000
Light Color Bright White
Trailer Specifications
Trailer Model TRLR75XF
Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR) 7,000 lb (3,175 kg.)
Gross Axle Weight Rating (GAWR) (ea.) 3,500 lb (1,587 kg)
Tire Size ST205/75D15 LR-C
Tire Load Rating (ea.) 1,820 lb (825 kg)
Wheel Bolt Pattern 5-Lug on 4.5 in
Fuel Tank Capacity 100 gal (378 L)
Generator/Engine Specifications
Refer to Accompanying DCA25SSIU3 Operation and Parts
Manual (Part No. 49810) for generator/engine specifications.
With Fuel - 4,450 lb. (2,018 kg.)
Without Fuel - 3,740 lb. (1,696 kg.)
MLT25 SERIES LIGHT TOWER • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (11/28/12) — PAGE 11
Page 12
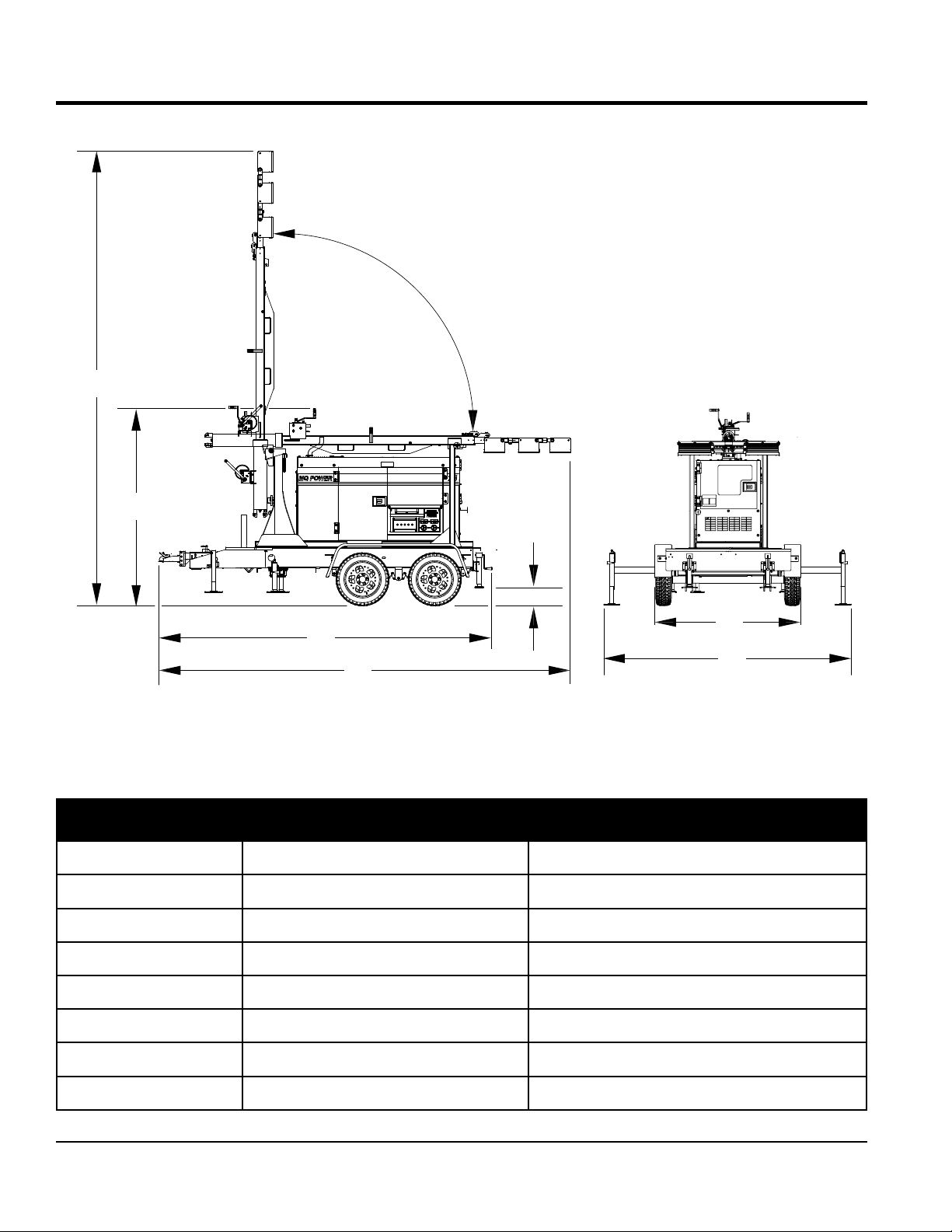
DEPLOYED
POSITION
DIMENSIONS
C
D
B
A
Figure 1. Dimensions
Table 2. Dimensions
STOWED
POSITION
E
F
G
Reference Letter Description Dimension
A Length (Mast Stowed Position) 170 in. (431 cm.)
B Length (Mast Deployed Position) 101 in. (256 cm.)
C Max. Height (Mast Deployed Position) 31.5 ft. (9.6 m)
D Height (Mast Stowed Position) 74 in. (187 cm.)
E Ground Clearance (From Axle) 8 in. (20 cm.)
F Width (Tow Ready) 51 in. (129 cm.)
G Width (Outriggers Deployed) 109 in. (276 cm.)
PAGE 12 — MLT25 SERIES LIGHT TOWER • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (11/28/12)
Page 13

GENERAL INFORMATION
The Multiquip MLT25 Series Light Tower is a dedicated
general pur pose light tower engineered to provide
dependable lighting for a wide range of applications. This
includes lighting for construction sites, industrial locations,
special events, and emergency conditions.
METAL HALIDE LAMPS
The lighting system of the MLT25 Series Light Tower is
comprised of 6 metal halide, 1000-watt lamps. These lamps
provide maximum illumination with typical lighting coverage
of 5 to 7 acres. The lamps are controlled by individual circuit
breakers for versatility.
ENGINE
The MLT25 Series Light Tower is powered by a diesel
engine that is equipped with automatic shutdowns for
low oil pressure, high coolant temperature, and alternator
charge failure.
STABILITY
The light tower can be raised vertically in excess of 31.5
feet (9.6 meters) by means of a manual winch. The tower
tensioning system is designed to provide the necessary
tension to safely control the pivot of the tower. The light
tower has a wind stability of up to 65 mph with outriggers
and jackstands fully deployed.
PANEL LIGHT
A panel light automatically illuminates the control panel and
all functions when the engine access door is opened. This
feature is convenient for night deployment.
TRAILER DESIGN
The trailer design of the MLT25 Series light tower
withstands the rigors of the jobsite in addition to providing
smooth highway towing.
MLT25 SERIES LIGHT TOWER • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (11/28/12) — PAGE 13
Page 14
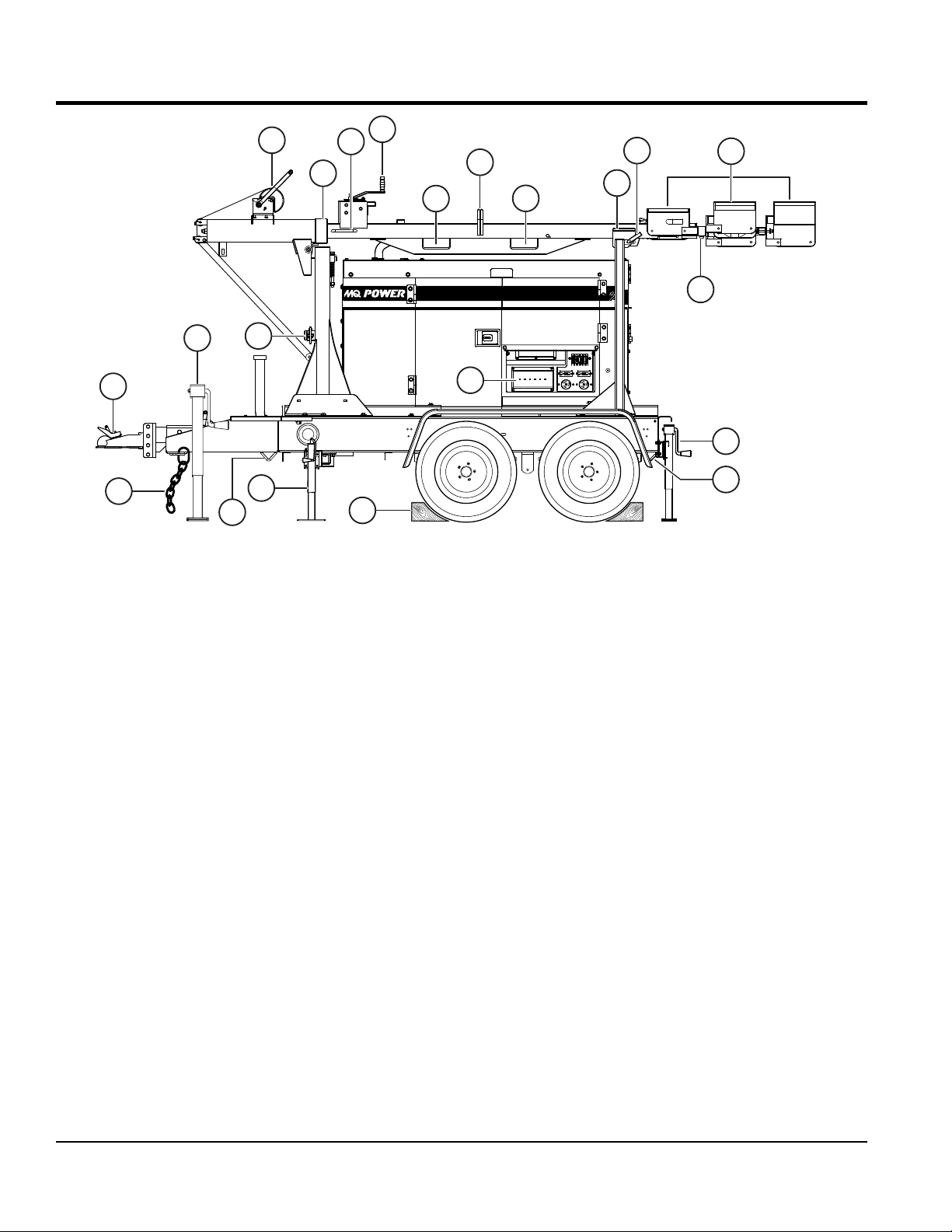
COMPONENTS
15
14
13
16
1
17
12
18
Figure 2. Major Components (Control Panel Side)
2
3
4
5
19
11
5
9
6
8
7
10
18
Figure 2 and Figure 3 show the location of the controls and
components for the MLT25 Series light tower. The function
of each control is described below.
1. Mast Rotation Locking Knob — Unscrew this knob
to release mast for rotation. Tighten this knob to lock
mast after it is set to the desired position.
2. Mast Extension Winch — Use this winch to extend
the mast to the desired height. Maximum height is
approximately 31.5 feet (9.6 meters).
3. Mast Rotation Handles — Grip these handles to rotate
mast to desired position.
4. Lifting Bale — Light tower can be lifted using this lifting
bale. The lifting bale is balanced for a fully configured
light tower. Removal of any components will unbalance
the lifting bale.
5. Forklift Pockets — Light tower can be lifted using
these forklift pockets. Insert the forks of the forklift as
far possible into the pockets.
6. Mast Cradle Support — When towing of the light
tower is required, place the tower mast into the cradle
support. Make sure cradle lock/release pin has been
inserted and mast is locked.
7. T-Bar — Allows the lamps to be mounted vertically or
horizontally.
8. Lamps — Six 1000-watt metal-halide bulbs with a
110,000 lumens capacity each. Light coverage is
typically between 5 to 7 acres.
9. Cradle Lock/Release Pin — Locks mast in cradle
support and releases mast when removed.
10. Rear Jackstands — There are two jackstands located
at the rear of the trailer. Use these jackstands to level
and support the light tower.
11. Chock Blocks — Place these blocks (not included
as part of the light tower package) under each trailer
wheel to prevent rolling.
12. Outrigger Jacks — Use these 2 outrigger jacks to
level and support the light tower. For more stability, the
outriggers can be deployed.
PAGE 14 — MLT25 SERIES LIGHT TOWER • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (11/28/12)
Page 15
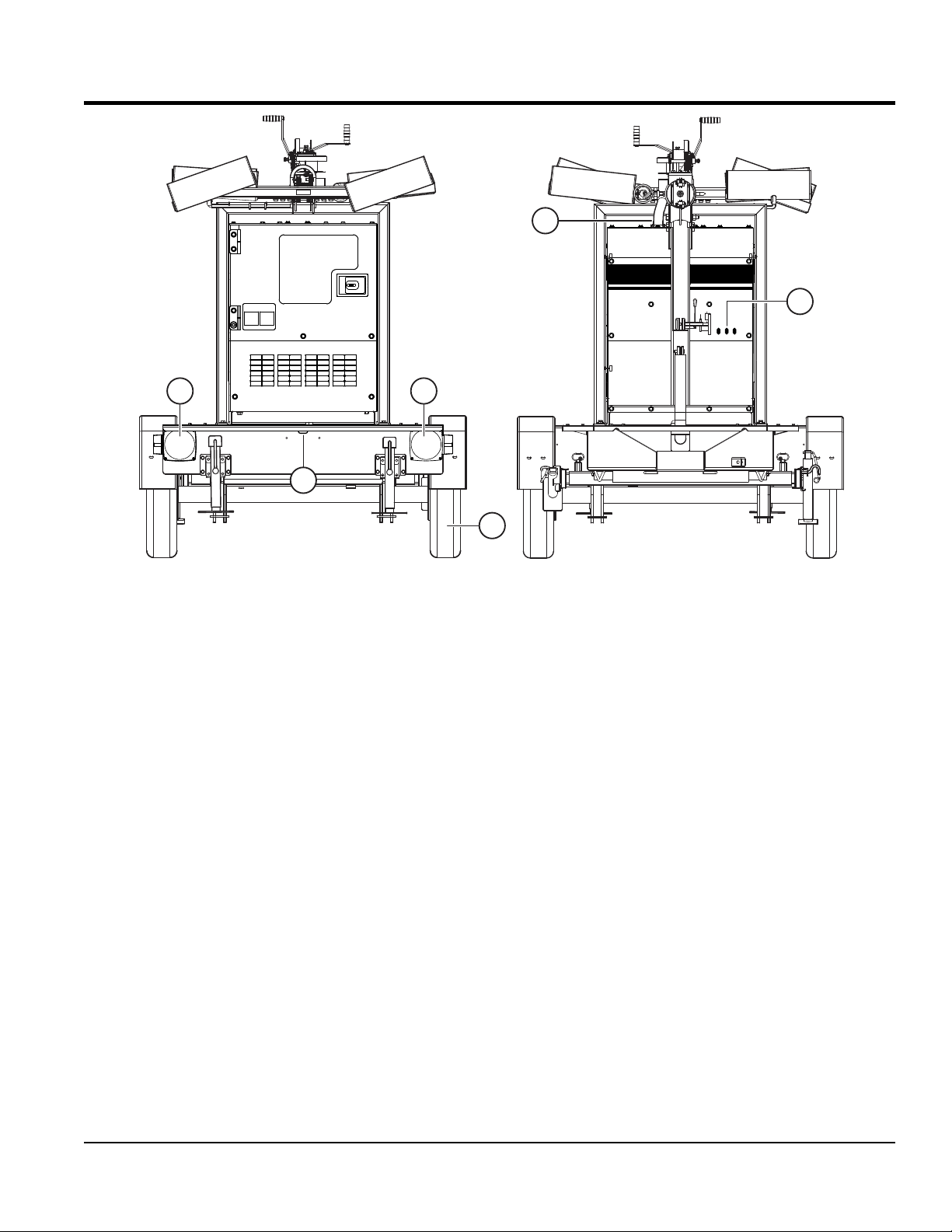
COMPONENTS
22
2121
20
23
REAR VIEW FRONT VIEW
24
Figure 3. Major Components (Front/Rear)
13. Tongue Jackstand — Use this jackstand to support
the tongue when attaching the light tower to a towing
vehicle.
14. Safety Chain — Always attach safety chain to the
towing vehicle. Never tow the light tower with the safety
chain unattached.
15. Ball Hitch Coupler — Attach this coupler to the
towing vehicle. Use only the specified ball diameter
as indicated on your coupler. Use of any other ball
diameter will create an extremely dangerous condition
which can result in separation of the coupler and ball
or ball failure.
16. Vertical Mast Winch — Use this winch to raise the
mast to the vertical position.
17. Mast Lock/Release Pin — Pull this pin to start placing
the tower mast in the vertical position. When tower
mast has reached full vertical position, insert pin to
keep mast from falling.
18. Tie-Down Points — Used to tie down light tower with
strap or chains to allow even application of force to
the front and rear of the equipment during transport.
19. Fuse Block Assembly — Contains the fuses that
protect the lamp circuit breakers.
20. License Light — This light illuminates the license plate.
Whenever towing of the light tower is required, make
sure this light is operational.
21. Brake Lights — Before towing the light tower, make
sure that these lights are operational and are working
correctly. Never tow the light tower if these lights are
inoperative.
22. Engine Exhaust Pipe — Directs engine exhaust to
the rear of the light tower. NEVER block this exhaust
pipe with obstructions. ALWAYS place the generator
in an area free of obstructions.
23. Tires — This light tower uses ST205/75D15 LR-C size
tire. Replace with only recommended tire size. Never
tow light tower with bad or worn tires.
24. Circuit Breakers, 3-Pole, 15 A — Turn the lamps on
and off.
MLT25 SERIES LIGHT TOWER • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (11/28/12) — PAGE 15
Page 16

BEFORE STARTING
FRONT
1. Read all safety instructions at the beginning of
manual.
2. Clean the light tower, removing dirt and dust, particularly
the engine cooling air inlet and air cleaner.
3. Check the air filter for dirt and dust. If air filter is dirty,
replace air filter with a new one as required.
4. Check all fastening nuts and bolts for tightness.
WARNING
INSPECTION
DANGER
ALWAYS make sure the area above
light tower is open and clear of
overhead power lines and other
obstructions. The tower extends
in excess of 3 0 ft. (9 me ters).
Contact with overhead power lines
or other obstructions could result in
equipment damage, serious injury
or death!
The engine's exhaust contains harmful
emissions. ALWAYS ventilate the exhaust
when operating inside tunnels, excavations
or buildings. Direct exhaust away from
nearby personnel.
Before starting the engine, make sure of the following:
The electrical load is disconnected and the main circuit
breaker and all lamp circuit breakers are switched to the
OFF position.
CAUTION
NEVER start the engine with any circuit breakers in
the ON position.
Light tower is placed on secure level ground with chock
blocks underneath each wheel to prevent the light tower
from rolling.
Outriggers have been fully extended to prevent the trailer
from tipping.
Light tower trailer support stands have been positioned
properly and the trailer is level.
Lamps have been adjusted to desired position.
Lamp power cables have been plugged into the
appropriate receptacles (J1-J6) on the T-Bar assembly.
Follow instructions below to correctly install the power
cable plugs.
a. Locate the 6 key-lock, 3-pin, female connectors on
the T-bar. See Figure 4.
REAR
LAMP 1
LAMP 4
LAMP 2
LAMP 5
LAMP 3
LAMP 6
MAST RAISED
FEMALE CONNECTORS
J4
J5
J6
T-BAR
J1
J2
J3
Chocked blocks have been positioned under each wheel
to prevent trailer from rolling.
Light tower trailer frame has been grounded correctly.
Lamps do not interfere with any overhead obstructions.
PAGE 16 — MLT25 SERIES LIGHT TOWER • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (11/28/12)
LOCKING NUT
(MALE CONNECTOR)
Figure 4. T-Bar and Cable Connectors
Page 17

b. Locate the key slot A on each female connector
as shown in Figure 5.
MALE CONNECTOR
FEMALE CONNECTOR
INSPECTION
KEY SLOT A
KEY TAB B
Figure 5. Female and Male Connector
c. On the corresponding male connector, locate the
key tab B as shown in Figure 5.
d. Align the key tab B on the male connector with
the key slot A on the female connector and press
together until seated.
e. Secure the connector by screwing the knurled
locking nut of the male connector to the threaded
portion of the female connector to ensure good
contact between the two connectors.
MLT25 SERIES LIGHT TOWER • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (11/28/12) — PAGE 17
Page 18

STARTING THE ENGINE
NOTICE
Refer to the accompanying DCA25SSIU3 generator
operation and parts manual (Part Number 49810) for
information on how to start the engine.
MAST OPERATION
DANGER
ALWAYS make sure the area above
light tower is open and clear of
overhead power lines and other
obstructions. The tower extends
in excess of 30 feet (9 meters).
Contact with overhead power lines
or other obstructions could result in
equipment damage, serious injury
or death!
DANGER
DO NOT stand behind
the t r ail e r whi l e th e
mast is being raised or
lowered. Serious injury
could result if the mast
falls down.
Outriggers and Support Stands
OPERATION
PULL PIN TO
RELEASE
OUTRIGGER
PULL OUTRIGGER
TO EXTEND
OUTRIGGER
JACKSTAND
Figure 6. Deploying Outriggers
2. As soon as the pin clears the travel position hole,
release it and continue sliding out the outrigger. The
pin must snap into the outrigger locking hole in the
extended position.
3. After extending all outriggers, rotate all trailer jack
stands into the foot down position, then turn the crank
handle on the jackstands clockwise to lower it and level
the light tower.
4. Check behind the light tower and make sure all
personnel and objects are clear of the mast.
ROTATE
JACKSTAND
TO PLACE
IN SUPPORT
POSITION
See Figure 6 for location of components.
1. Make sure both outriggers are extended. To extend the
outriggers, pull the locking pin on the outrigger and hold
while sliding out the outrigger assembly.
PAGE 18 — MLT25 SERIES LIGHT TOWER • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (11/28/12)
Deploying the Mast to Vertical Position
Refer to Figure 7 for the location of components:
1. To release the mast from the mast cradle support, pull
the retaining pin out of the cradle lock/release pin. Pull
the cradle lock/release pin. This will unlock the mast
from the horizontal position.
2. Remove the mast lock/release pin before raising tower
to the vertical position.
3. To place the mast in the vertical position, turn the
vertical mast winch hand lever clockwise until the mast
is pointing upwards at 90 degrees.
4. Once the mast is in the vertical position, insert the
mast lock/release pin to prevent the mast from falling.
Page 19

MAST ROTATION
HANDLE (2)
OPERATION
MAST
CRADLE SUPPORT
CRADLE
LOCK/RELEASE
LEVER
MAST
ROTATION
LOCKING
KNOB
MAST LOCK
HANDLE
MAST LOCK/RELEASE PIN
Figure 7. Raising the Mast
MLT25 SERIES LIGHT TOWER • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (11/28/12) — PAGE 19
Page 20

OPERATION
CB1
CB2 CB3
Raising the Mast
Once the tower mast has been locked into its vertical
position, the mast can now be raised. The tower allows the
lamps to be extended upwards in excess of 30 feet.
Refer to Figure 7 for location of components.
1. Turn the mast extension winch clockwise and observe
that the mast begins to extend upwards.
2. Continue turning the winch in the clockwise direction
until the desired height has been reached.
3. Release the winch. This winch is of the self-locking
type. The tension on the cable will keep the mast in
place.
Lowering the Mast
1. Turn the mast extension winch counterclockwise, and
observe that the mast begins to lower.
2. Continue turning the winch counterclockwise until the
mast has been fully retracted (slack in the cable).
Stowing the Mast to Horizontal Position
1. With the mast in the deployed position (vertical),
unscrew the mast rotation locking knob to release the
mast for rotation.
2. Grip the mast rotation handles and rotate the mast until
the lamps are facing the desired direction.
3. When the lamps are facing the desired direction,
tighten the mast rotation lock knob to lock the mast
in place.
TURNING ON THE LAMPS
Three lamp circuit breakers (15 amps each) are located
on the front of the light tower to turn the lamps on and off.
The lamps can be turned on with the voltage selector
in three different positions. See Table 3 for the different
settings.
Voltage
Selector
Switch
Setting
Table 3. Lamp Settings
Voltage
Regulator
Setting
Circuit
Breaker
(ON)
Lamps
(ON)
Refer to Figure 7 for the location of components:
1. Remove the mast lock/release pin to allow the mast
section to be lowered to the horizontal position. Pull
out the mast lock handle to unlatch.
2. Turn the vertical mast winch counterclockwise and
observe that mast begins to approach the horizontal
position. The mast lock handle can now be released.
3. Continue turning the vertical mast winch in the
counterclockwise direction. As the mast approaches
the mast cradle support, pull the retaining pin and
then the cradle lock/release pin to allow the mast to
rest in the cradle.
4. Once the mast is resting in the mast cradle support,
inser t the cradle lock/release pin and secure with
retaining pin to keep mast in place.
Rotating the Mast
To change the direction that the lamps are facing, the mast
can be rotated.
CB1 1 & 3
1 PHASE
240/120
3 PHASE
240/139
3 PHASE
480/277
1. Before turning on the lamps, make sure that main circuit
breaker on the generator control panel and the circuit
breakers shown in Figure 8 are all in the off position.
ON
OFF
240V
208V
480 V
CB2 4 & 6
CB3 2 & 5
CB1 1, 2, & 3
CB2 4, 5, & 6
CB3 N/A
Refer to Figure 7 for the location of components.
PAGE 20 — MLT25 SERIES LIGHT TOWER • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (11/28/12)
Figure 8. Lamp Circuit Breakers
Page 21

2. Move the Voltage Selector (Figure 9) to the desired
FRONT
position.
OPERATION
3 PHASE
240/139
3 PHASE
480/277
PRESS TO LOCK
1 PHASE
240/120
Figure 9. Voltage Selector Positions
3. Adjust the Voltage Regulator Knob to the corresponding
voltage noted in Table 3. Check the AC voltmeter for
the correct reading. See Figure 10.
INCREASE
DECREASE
REAR
LAMP 1
LAMP 4
LAMP 2
LAMP 5
LAMP 3
LAMP 6
MAST RAISED
Figure 11. Lamp Orientation
5. When the lamps turn on, check the AC voltmeter
reading and adjust the Voltage Regulator knob, if
necessary, to correct the voltage.
AC Voltmeter
Voltage Regulator
Figure 10. Voltage Regulator Knob and AC
Voltmeter
4. Switch the appropriate circuit breakers to the ON
position for the lamps (Figure 11) that you want to
turn on (in the selected Voltage Selector setting), as
detailed in Table 3.
6. If any of the lamps do not turn on as they should, refer
to the troubleshooting section of this manual.
7. Close all cabinet doors after desired lights are on.
NOTICE
NEVER operate the light tower with the engine
compartment doors open. Operation with the doors
open may cause insufficient cooling to the unit, and
damage may result.
MLT25 SERIES LIGHT TOWER • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (11/28/12) — PAGE 21
Page 22

MAINTENANCE
GENERAL INSPECTION
Prior to each use, the light tower should be cleaned and
inspected. Check for loose, missing, or damaged nuts, bolts
or other fasteners.
GENERATOR/ENGINE MAINTENANCE
Refer to the accompanying DCA25SSIU3 Operator and
Parts Manual (Part Number 49810) for information on how
to maintain the generator and engine.
CHECK CABLE WEAR
The wire rope (cable) that raises and extends the mast is
a very important part of the light tower. There is one cable/
hand winch system, located on the tongue of the trailer, that
raises and extends the light tower mast. There is a second
cable/hand winch system located on the mast that serves to
raise and lower the two extendable sections of the mast.
DANGER
Wire rope (cable) will fail if it is worn, frayed, misused,
crushed, kinked or damaged in any way. Always check
the cables and pulleys for any abnormalities before use.
SERVICING THE MAST RAISE/LOWER CABLE
SYSTEM
To replace any components in the mast raise/lower cable
system, use the following steps (See Figure 12):
HAND WINCH
CABLE
MAST
PULLEY
CABLE SHEAVE
Do not use it if there is even the slightest cause for
concern and replace any damaged cables or pulleys
immediately.
Figure 12. Mast Raise/Lower Cable System
1. Lower the mast to the horizontal resting position.
2. Inspect the cable clamps, pulleys, and other components
for worn or damaged parts.
3. Disconnect the cable from the ball socket pin and
remove from the mast pulley and cable sheave. Detach
the cable from the hand winch as necessary.
4. Replace the pulley and the cable as needed.
5. Rethread the cable through the pulley and reattach the
cable to the ball socket pin.
6. Raise and lower the mast several times to verify correct
operation.
PAGE 22 — MLT25 SERIES LIGHT TOWER • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (11/28/12)
Page 23

MAINTENANCE
SERVICING THE MAST EXTE N S ION CABLE
SYSTEM
To replace the cable in the mast extension cable system,
use the following steps (See Figure 13):
CENTER
MAST
PULLEY
UPPER
MAST
LOWER
MAST
PULLEY
CENTER
MAST
Figure 13. Mast Extension Cable System
1. Lower the mast to the horizontal resting position.
2. Inspect the cable clamps, pulleys, and other components
for worn or damaged parts. If either of the cables on
the mast needs to be replaced, they should both be
replaced at the same time.
LOWER
MAST
SHACKLE
ROUTE TO
HAND WINCH
LOWER
MAST
4. There are two pulleys in the mast raise/lower cable
system. They should be removed and replaced if worn
or damaged. Worn or damaged pulleys can cause
premature cable failure.
5. Reassemble the mast extension cable system by
connecting the cable to the bottom of the upper mast
and sliding the upper mast into the opening of the
center mast. Connect the second cable to the bottom
of the center mast and slide the center mast into the
opening of the lower mast, observing proper lifting
techniques.
6. Route the upper mast cable through the center mast
pulley and connect the free end of the cable to the
lower mast ankle shackle. Route the center mast
cable through the lower mast pulley and connect the
free end of the cable to the hand winch at the bottom
of the lower mast.
7. Raise, extend, retract and lower the mast several times
to verify correct operation.
3. Disassemble the mast by disconnecting the cables
from the mast and sliding the sections apart. The lower
cable can be disconnected from the winch.
WARNING
The mast sections are heavy and awkward to handle.
Use proper lifting devices and procedures when
servicing the mast and its components.
MLT25 SERIES LIGHT TOWER • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (11/28/12) — PAGE 23
Page 24

MAINTENANCE — TRAILERS
The following trailer maintenance guidelines are intended
to assist the operator in preventive maintenance.
TRAILER BRAKES
Properly functioning brake shoes and drums are essential
to ensure safety. The brakes should be inspected the first
200 miles of operation. This will allow the brake shoes and
drums to seat properly. After the first 200 mile interval,
inspect the brakes every 3,000 miles. If driving over rough
terrain, inspect the brakes more frequently.
HYDRAULIC BRAKES
If your trailer has hydraulic brakes, they function the same
way the surge brakes do on your tow vehicle. The hydraulic
braking system must be inspected at least as often as the
brakes on the tow vehicle, but no less than once per year.
This inspection includes an assessment of the condition
and proper operation of the wheel cylinders, brake shoes,
brake drums and hubs.
MANUALLY ADJUSTING THE BRAKES
6. Replace the adjusting-hole cover.
7. Repeat the above procedure on all brakes.
8. Lower the trailer to the ground.
Check the fluid level in the master cylinder reservoir at least
every three months. If you tow your trailer an average of
1,000 miles per month in a hot and dry environment, you
must check the brake fluid level once a month. The brake
fluid reservoir is located on the tongue of the trailer. Always
fill with clean, uncontaminated DOT 4 brake fluid.
Figure 14 below displays the major hydraulic brake
components that will require inspection and maintenance.
Please inspect these components as required using steps
1 through 6 as referenced in the “Manually Adjusting The
Brakes” section on this page. See Table 4 for Hydraulic
Brake Troubleshooting.
Most axles are fitted with a brake mechanism that will adjust
the brakes during a hard stop. However, some braking
systems are not automatically adjusted by hard stopping.
These brakes require manual adjustment. The following
steps apply to adjust most manually adjustable brakes.
1. Jack up the trailer and secure it on adequate capacity
jackstands.
2. Be sure the wheel and brake drum rotate freely.
3. Remove the adjusting-hole cover from the adjusting
slot on the bottom of the brake backing plate.
4. With a screwdriver or standard adjusting tool, rotate the
starwheel of the adjuster assembly to expand the brake
shoes. Adjust the brake shoes out until the pressure
of the linings against the drum makes the wheel very
difficult to turn. Note: Your trailer maybe equipped with
drop spindle axles. See axle manual for your axle type.
You will need a modified adjusting tool for adjusting
the brakes in these axles. With drop spindle axles, a
modified adjusting tool with about an 80 degree angle
should be used.
Figure 14. Hydraulic Brake Components
HYDRAULIC BRAKE ACTUATOR
The hydraulic brake actuator (Figure 15) is the mechanism
that activates the trailer’s brake system. This actuator
changes fluid power into mechanical power. Therefore, the
fluid level must be checked frequently to assure that the
brakes function properly.
HYDRAULIC
BRAKE FLUID
RESERVOIR
5. Rotate the starwheel in the opposite direction until the
wheel turns freely with a slight drag.
PAGE 24 — MLT25 SERIES LIGHT TOWER • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (11/28/12)
Figure 15. Hydraulic Brake Actuator
Page 25

WARNING
Failure to maintain proper fluid level in the actuator
may result in loss of braking action which could cause
severe property damage, injury or death.
Periodically check the actuator mounting fasteners for
damage or loosening. Inspect the actuator for worn or
damaged parts. As you are towing your trailer, be aware
of any changes in braking quality. This could be an early
warning of brake or actuator malfunction and requires
immediate attention. Consult a certified brake specialist to
make necessary adjustment or repairs.
Table 4. Hydraulic Brake Troubleshooting
Symptom Possible Cause Solution
No Brakes Brake line broken or kinked? Repair or replace.
Brake lining glazed? Reburnish or replace.
Trailer overloaded? Correct weight.
Weak Brakes or
Brakes Pull to
One Side
Locking Brakes
Noisy Brakes
Dragging
Brakes
Brake drums scored or
grooved?
Tire pressure correct? Inflate all tires equally.
Tires unmatched on the
same axle?
Brake components loose,
bent or broken?
Brake drums out-of-round? Replace.
System lubricated? Lubricate.
Brake components correct? Replace and correct.
Brake lining thickness
incorrect or not adjusted
correctly?
Enough brake fluid or correct
fluid?
Machine or replace.
Match tires.
Replace components.
Install new shoes and
linings.
Replace rubber parts
fill with dot 4 fluid.
MAINTENANCE — TRAILERS
Figure 16. Adjustable Channel
Wheel Bearings
Wheel bearings (Figure 17) must be inspected and
lubricated once a year or 12,000 miles to insure safe
operation of your trailer.
If trailer wheel bearings are immersed in water, they must
be replaced.
DANGER
If trailer wheels are under water for a long period of
time, wheel bearings may fail. If this is the case, service
wheel bearings immediately.
The possibility exists of the wheels falling off causing
equipment damage and severe bodily harm even death!
If the trailer has not been used for an extended amount
of time, have the bearings inspected and packed more
frequently, at least every six months and prior to use.
ADJUSTABLE CHANNEL
Your trailer may be equipped with an adjustable channel
(Figure 16) that allows the coupler to be raised or lowered
to a desired height. Periodically check the channel bolts
for damage or loosening.
NOTICE
When replacing channel mounting hardware (nuts, bolts
and washers), never substitute substandard hardware.
Pay close attention to bolt length and grade. ALWAYS
use manufacturer's recommended parts when replacing
channel mounting hardware.
MLT25 SERIES LIGHT TOWER • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (11/28/12) — PAGE 25
Follow the steps below to disassemble the wheel hub and
service the wheel bearings. See Figure 17.
BEARING
OIL
SEAL
BEARING
CUP
Figure 17. Wheel Hub Components
LUG
NUT
WHEEL
HUB
SPINDLE
WASHER
BEARING
CUP
BEARING
COTTER
PIN
DUST
CAP
SPINDLE
NUT
Page 26

MAINTENANCE — TRAILERS
After removing the dust cap, cotter pin, spindle nut and
spindle washer, remove the hub to inspect the bearings
for wear and damage.
Replace bearings that have flat spots on rollers, broken
roller cages, rust or pitting. Always replace bearings
and cups in sets. The inner and outer bearings are to
be replaced at the same time.
Replace seals that have nicks, tears or wear.
Lubricate the bear ings wit h a high quality EP-2
automotive wheel bearing grease.
WHEEL HUB ADJUSTMENT
Every time the wheel hub is removed and the bearings are
reassembled, follow the steps below to check the wheel
bearings for free running and adjust.
Turn the hub slowly, by hand, while tightening the spindle
nut until you can no longer turn the hub by hand.
Loosen the spindle nut just until you are able to turn it
(the spindle nut) by hand. Do not turn the hub while the
spindle nut is loose.
DANGER
Improper weld repair will lead to early failure of the
trailer structure and can cause serious injury or death.
DO NOT repair cracked or broken welds unless you
have a certified welder perform the repair. If not, have
the welds repaired by your dealer.
WARNING
If the trailer is involved in an accident, have it inspected
immediately by qualified personnel. In addition, the
trailer should be inspected annually for signs of wear
or deformations.
LEAF SUSPENSION
The leaf suspension springs and associated components
(Figure 18) should be visually inspected every 6,000 miles
for signs of excessive wear, elongation of bolt holes, and
loosening of fasteners. Replace all damaged par ts
(suspension) immediately.
Install a new cotter pin through the spindle nut and axle.
Check the adjustments. Both the hub and the spindle nut
should be able to move freely (the spindle nut motion
will be limited by the cotter pin).
DANGER
NEVER crawl under the trailer unless it is on firm
and level ground and resting on properly placed and
secured jackstands.
The possibility exists of the trailer falling thus causing
equipment damage and severe bodily harm even death!
DANGER
When performing trailer inspection and maintenance
activities, you must jack up the trailer using jacks and
jackstands.
When jacking and using jackstands, place them so
as to clear wiring, brake lines, and suspension parts
(i.e., springs, torsion bars). Place jacks and jackstands
inside of the perimeter strip on the supporting structure
to which the axles are attached.
Figure 18. Leaf Suspension Components
DANGER
Worn or broken suspension parts can cause loss of
control, damage to equipment and severe bodily injury,
even death!
Check suspension regularly.
PAGE 26 — MLT25 SERIES LIGHT TOWER • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (11/28/12)
Page 27

SAFETY GUIDELINES — TRAILERS
The following guidelines are intended to assist the operator
Shift your automatic transmission into a lower gear for
use lower gears for climbing and descending
ride the brakes while descending grades, they
Slow down for bumps in the road. Take your foot off the
curve and power through the curve. This way, the towing
swaying. Continued pulling of the trailer, and even slight
trucks and buses. Continued pulling of the trailer provides
a stabilizing force to correct swaying. DO NOT apply the
Use lower gear when driving down steep or long grades.
in the operation and handling of a trailer.
Safety precautions should be followed at all times when
operating a trailer. Failure to read, understand and follow
the safety guidelines could result in injury to yourself and
others. Loss of control of the trailer or tow vehicle can result
in death or serious injury.
COMMON CAUSES FOR LOSS OF TRAILER
Driving too fast for the conditions (maximum speed when
towing a trailer is 55 mph).
Overloading the trailer or loading the trailer unevenly.
Trailer improperly coupled to the hitch.
No braking on trailer.
Not maintaining proper tire pressure.
Not keeping lug nuts tight.
Not properly maintaining the trailer structure.
Ensure machine is towed level to tow vehicle.
TRAILER TOWING GUIDELINES
Recheck the load tiedowns to make sure the load will
not shift during towing.
city driving.
ALWAYS
grades.
DO NOT
may get so hot that they stop working. Then you will
potentially have a runaway tow vehicle and trailer.
To conserve fuel, don’t use full throttle to climb a hill.
Instead, build speed on the approach.
brake when crossing the bump.
DO NOT brake while in a curve unless absolutely
necessary. Instead, slow down before you enter the
vehicle remains in charge.
DO NOT apply the brakes to correct extreme trailer
acceleration, will provide a stabilizing force.
Anticipate the trailer “swaying.” Swaying is the trailer
reaction to the air pressure wave caused by passing
brakes to correct trailer swaying.
Before towing, check coupling, safety chain, safety
brake, tires, wheels and lights.
Check the lug nuts or bolts for tightness.
Check coupler tightness after towing 50 miles.
Use your mirrors to verify that you have room to change
lanes or pull into traffi c.
Use your turn signals well in advance. Allow plenty of
stopping space for your trailer and tow vehicle.
Allow plenty of stopping space for your trailer and tow
vehicle.
DO NOT drive so fast that the trailer begins to sway
due to speed.
Allow plenty of room for passing. A rule of thumb is that
the passing distance with a trailer is 4 times the passing
distance without the trailer.
Use the engine and transmission as a brake. Do not
ride the brakes, as they can overheat and become
ineffective.
Be aware of your trailer height, especially when
approaching roofed areas and around trees.
Make regular stops, about once each hour. Confi rm
that:
• Coupler is secure to the hitch and is locked.
• Electrical connectors are secure.
• There is appropriate slack in the safety chains.
• There is appropriate slack in the breakaway switch
pullpin cable.
• Tires are not visibly low on pressure.
MLT25 SERIES LIGHT TOWER • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (11/28/12) — PAGE 27
Page 28

DRIVING CONDITIONS
When towing a trailer, you will have decreased acceleration,
for the use of your trailer. Again, be sure your hitch and tow
Use of a hitch with a load rating less than the load rating
the load rating of the trailer can result in loss of control,
increased stopping distance, and increased turning radius
(which means you must make wider turns to keep from
hitting curbs, vehicles, and anything else that is on the
inside corner). In addition, you will need a longer distance
to pass, due to slower acceleration and increased length.
Be alert for slippery conditions. You are more likely to be
affected by slippery road surfaces when driving a tow
vehicle with a trailer, than driving a tow vehicle without
a trailer.
Check rearview mirrors frequently to observe the trailer
and traffi c.
NEVER drive faster than what is safe.
WARNING
Driving too fast for severe road conditions can result in
loss of control and cause death or serious injury.
Decrease your speed as road, weather, and lighting
conditions deteriorate.
Always check for local trailer tow speed limits in your
area.
WARNING
Do not transport people on the trailer. The transport of
people puts their lives at risk and may be illegal.
COUPLING TO THE TOW VEHICLE
SAFETY GUIDELINES — TRAILERS
vehicle are rated for the Gross Vehicle Weight Rating of
your trailer.
WARNING
Proper selection and condition of the coupler and hitch
are essential to safely towing your trailer. A loss of
coupling may result in death or serious injury.
• Be sure the hitch load rating is equal to or greater
than the load rating of the coupler.
• Be sure the hitch size matches the coupler size.
• Observe the hitch for wear, corrosion and cracks
before coupling. Replace worn, corroded or cracked
hitch components before coupling the trailer to the
tow vehicle.
• Be sure the hitch components are tight before
coupling the trailer to the tow vehicle.
WARNING
An improperly coupled trailer can result in death or
serious injury.
DO NOT move the trailer until:
• The coupler is secured and locked to hitch.
• The safety chains are secured to the tow vehicle.
• The trailer jack(s) are fully retracted.
DO NOT tow the trailer on the road until:
• Tires and wheels are checked.
• The trailer brakes are checked.
Follow all of the safety precautions and instructions in
this manual to ensure safety of persons, equipment, and
satisfactory life of the trailer. Always use an adequate tow
vehicle and hitch. If the vehicle or hitch is not properly
selected and matched to the Gross Vehicle Weight Rating
(GVWR) of your trailer, you can cause an accident that
could lead to death or serious injury.
If you already have a tow vehicle, know your vehicle tow
rating and make certain the trailer’s rated capacity is less
than or equal to the tow vehicle’s rated towing capacity. If
you already have (or plan to buy) a trailer, make certain
that the tow rating of the tow vehicle is equal to or greater
than that of the trailer.
The trailer VIN tag contains the critical safetyinformation
PAGE 28 — MLT25 SERIES LIGHT TOWER • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (11/28/12)
• The breakaway switch is connected to the tow
vehicle.
• The load is secured to the trailer.
• The trailer lights are connected and checked.
WARNING
of the trailer can result in loss of control and may lead
to death or serious injury.
Use of a tow vehicle with a towing capacity less than
and may lead to death or serious injury.
Be sure your hitch and tow vehicle are rated for the
Gross Vehicle Weight Rating of your trailer.
Page 29

SAFETY GUIDELINES — TRAILERS
INOPERABLE BRAKES, LIGHTS OR MIRRORS
Drive slowly at fi rst, 5 mph or so, and turn the wheel to
get the feel of how the tow vehicle and trailer combination
different combinations of trailer brake and tow vehicle brake.
Note the effect that the trailer brakes have when they are
the only brakes used. When properly adjusted, the trailer
with a trailer attached. Take it slow. Before backing up, get
out of the tow vehicle and look behind the trailer to make
Some drivers place their hands at the bottom of the steering
wheel, and while the tow vehicle is in reverse, “think” of the
hands as being on the top of the wheel. When the hands
turn the tow vehicle to the left when moving forward), the
rear of the trailer moves to the right. Conversely, rotating
the steering wheel clockwise with your hands at the bottom
of the wheel will move the rear of the trailer to the left while
If you are towing a bumper hitch rig, be careful not to allow
the trailer to turn too much because it will hit the rear of the
tow vehicle. To straighten the rig, either pull forward or turn
Number (VIN) Tag which is typically located on the left front
Be sure that the brakes and all of the lights on your trailer
are functioning properly before towing your trailer. Check
the trailer taillights by turning on your tow vehicle headlights.
Check the trailer brake lights by having someone step on
the tow vehicle brake pedal while you look at trailer lights.
Do the same thing to check the turn signal lights. See Trailer
Wiring Diagram section in this manual.
Standard mirrors usually do not provide adequate visibility
for viewing traffi c to the sides and rear of a towed trailer.
You must provide mirrors that allow you to safely observe
approaching traffi c.
WARNING
Improper electrical connection between the tow vehicle
and the trailer will result in inoperable lights and can
lead to collision.
Before each tow, check that the tail lights, brake lights
and turn signals work.
TRAILER TOWING TIPS
Driving a vehicle with a trailer in tow is vastly different
from driving the same vehicle without a trailer in tow.
Acceleration, maneuverability and braking are all diminished
with a trailer in tow.
It takes longer to get up to speed, you need more room to
turn and pass, and more distance to stop when towing a
trailer. You will need to spend time adjusting to the different
feel and maneuverability of the tow vehicle with a loaded
trailer.
Because of the signifi cant differences in all aspects of
maneuverability when towing a trailer, the hazards and risks
of injury are also much greater than when driving without
a trailer. You are responsible for keeping your vehicle and
trailer in control, and for all the damage that is caused if
you lose control of your vehicle and trailer.
responds. Next, make some right and left hand turns.
Watch in your side mirrors to see how the trailer follows
the tow vehicle. Turning with a trailer attached requires
more room.
Stop the rig a few times from speeds no greater than
10 mph. If your trailer is equipped with brakes, try using
brakes will come on just before the tow vehicle brakes.
It will take practice to learn how to back up a tow vehicle
sure that there are no obstacles.
move to the right (counterclockwise, as you would do to
backing up.
the steering wheel in the opposite direction.
TRAILER VIN TAG
Figure A below is a sample of the Vehicle Identifi cation
of the trailer. See Figure B for location.
As you did when learning to drive an automobile, fi nd
an open area with little or no traffi c for your fi rst practice
trailering. Of course, before you start towing the trailer, you
must follow all of the instructions for inspection, testing,
loading and coupling. Also, before you start towing, adjust
the mirrors so you can see the trailer as well as the area
to the rear of it.
MLT25 SERIES LIGHT TOWER • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (11/28/12) — PAGE 29
Figure A. Vehicle VIN Tag
Page 30

VIN TAG
To determine the “empty” or “net” weight of your trailer,
weigh it on an axle scale. To fi nd the weight of the trailer
trailer weight will be transferred from the trailer to the tow
vehicle axles, and an axle scale weighs all axles, including
The towing hitch attached to your tow vehicle must have a
capacity equal to or greater than the load rating of the trailer
you intend to tow. The hitch capacity must also be matched
to the tow vehicle capacity. Your vehicle dealer can provide
For trailers equipped with electric brakes, the electric brake
controller is part of the tow vehicle and is essential in the
controller is not the same as the safety breakaway brake
law regulations determine the size of the mirrors. However,
A Heavy Duty Flasher is an electrical component that may
be required when your trailer turn signal lights are attached
SAFETY GUIDELINES — TRAILERS
using an axle scale, you must know the axle weights of
your tow vehicle without the trailer coupled. Some of the
the tow vehicle axles.
VIN TAG
Figure B. VIN Tag Location
The trailer VIN Tag contains the following critical safety
information for the use of your trailer.
GAWR: The maximum gross weight that an axle cansupport.
It is the lowest of axle, wheel, or tire rating.
Usually, the tire or wheel rating is lower than the axle rating,
and determines GAWR.
GVWR: The maximum allowable gross weight of the trailer
and its contents. The gross weight of the trailer includes
the weight of the trailer and all of the items within it. GVWR
is sometimes referred to as GTWR (Gross Trailer Weight
Rating), or MGTW (Maximum Gross Trailer Weight). GVWR,
GTWR and MGTW are all the same rating.
The sum total of the GAWR for all trailer axles may be less
than the GVWR for the trailer, because some of the trailer
load is to be carried by the tow vehicle, rather than by the
trailer axle(s). The total weight of the cargo and trailer must
not exceed the GVWR, and the load on an axle must not
exceed its GAWR.
PSIC: The tire pressure (psi) measured when cold.
TOW VEHICLE
and install the proper hitch on your tow vehicle.
SUSPENSION SYSTEM
Sway bars, shock absorbers, heavy duty springs, heavy
duty tires and other suspension components may be
required to suffi ciently tow the trailer and pump.
BRAKE CONTROLLER
operation of the electric brakes on the trailer. The brake
system that may be equipped on the trailer.
SIDE VIEW MIRRORS
The size of the trailer that is being towed and your state
some states prohibit extended mirrors on a tow vehicle,
except while a trailer is actually being towed. In this
situation, detachable extended mirrors are necessary.
Check with your dealer or the appropriate state agency
for mirror requirements.
VIN: The Vehicle Identifi cation Number.
EMPTY WEIGHT: Some information that comes with the
trailer (such as the Manufacturer’s Statement of Origin)
is not a reliable source for “empty” or “net” weight. The
shipping documents list average or standard weights and
your trailer may be equipped with options.
PAGE 30 — MLT25 SERIES LIGHT TOWER • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (11/28/12)
HEAVY DUTY FLASHER
to the tow vehicle fl asher circuit.
ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
An Electrical Connector connects the light and brake
systems on the trailer to the light and brake controls on
the towing vehicle.
Page 31

SAFETY GUIDELINES — TRAILERS
EMERGENCY FLARES AND TRIANGLE REFLECTORS
BALL HITCH COUPLER
system of coupling a trailer to a tow vehicle is sometimes
A ball hitch trailer may be fi tted with a tongue jack that can
raise and lower the coupler. The tongue jack is mounted to
the A-frame (front or tongue) part of the trailer. By rotating
Before each tow, coat the ball with a thin layer of automotive
bearing grease to reduce wear and ensure proper operation.
the proper action to prevent possible failure of the ball and
coupler system. All bent or broken coupler parts must be
The coupler handle lever must be able to rotate freely and
motor oil. Keep the ball socket and latch mechanism clean.
Dirt or contamination can prevent proper operation of the
The load rating of the coupler and the necessary ball size
are listed on the trailer tongue. You must provide a hitch and
ball for your tow vehicle where the load rating of the hitch
Also, the ball size must be the same as the coupler size. If
the hitch ball is too small, too large, is underrated, is loose
It is wise to carry these warning devices even if you are
not towing a trailer. It is particularly important to have these
when towing a trailer because the hazard fl ashers of your
towing vehicle will not operate for as long a period of time
when the battery is running both the trailer lights and tow
vehicle lights.
SAFETY CHAINS
If the coupler connection comes loose, the safety chains
can keep the trailer attached to the tow vehicle. With
properly rigged safety chains, it is possible to keep the
tongue of the trailer from digging into the road pavement,
even if the coupler-to-hitch connection comes apart.
TRAILER LIGHTING AND BRAKING CONNECTOR
A device that connects electrical power from the tow vehicle
to the trailer. Electricity is used to turn on brake lights,
running lights, and turn signals as required. In addition, if
your trailer has a separate braking system, the electrical
connector will also supply power to the brakes from the
tow vehicle.
A ball hitch coupler (Figure C) connects to a ball that is
located on or under the rear bumper of tow vehicle. This
referred to as “bumper pull.”
the jack handle clockwise, the jack will extend and raise
the tongue of the trailer.
Figure C. Ball Hitch Coupler
BREAKAWAY SYSTEM
If the trailer coupler connection comes loose, the breakaway
system can actuate emergency hydraulic brakes depending
on the type of actuator on the trailer. The breakaway cable
must be rigged to the tow vehicle with appropriate slack
that will activate the system if the coupler connection
comes loose.
JACKSTAND
A device on the trailer that is used to raise and lower the
coupler. The jack is sometimes called the “landing gear” or
the “tongue jack”.
COUPLER TYPES
Two types of coupler used wit the trailer are discussed
below.
Ball Hitch Coupler
Pintel Eye Coupler
Check the locking device that secures the coupler to the
ball for proper operation.
If you see or feel evidence of wear, such as fl at spots,
deformations, pitting or corrosion, on the ball or coupler,
immediately have your dealer inspect them to determine
replaced before towing the trailer.
automatically snap into the latched position. Oil the pivot
points, sliding surfaces, and spring ends with SAE 30W
latching mechanism.
and ball is equal to or greater than that of your trailer.
MLT25 SERIES LIGHT TOWER • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (11/28/12) — PAGE 31
Page 32

SAFETY GUIDELINES — TRAILERS
or is worn, the trailer can come loose from the tow vehicle
the trailer tongue. Wood or concrete blocks may also
Coupling the Trailer to the Tow Vehicle (Ball Coupler)
Lubricate the hitch ball and the inside of the coupler with
Using the jackstand at the front of trailer (tongue), turn
the jackstand crank handle to raise the trailer. If the ball
Open the coupler locking mechanism. Ball couplers have
a locking mechanism with an internal moving piece and
Lower the trailer (Figure D) until the coupler fully engages
Engage the coupler locking mechanism. In the engaged
Be sure the coupler is all the way on the hitch ball and
the locking mechanism is engaged. A properly engaged
locking mechanism will allow the coupler to raise the rear
of the tow vehicle. Using the trailer jackstand, verify that
you can raise the rear of the tow vehicle by 1 inch after
Lower the trailer so that its entire tongue weight is held
Raise the jackstand to a height where it will not interfere
and may cause death or serious injury.
THE TOW VEHICLE, HITCH AND BALL MUST HAVE A
RATED TOWING CAPACITY EQUAL TO OR GREATER
THAN THE TRAILER Gross Vehicle Weight Rating
(GVWR). IT IS ESSENTIAL THAT THE HITCH BALL BE
OF THE SAME SIZE AS THE COUPLER.
The ball size and load rating (capacity) are marked on the
ball. Hitch capacity is marked on the hitch.
WARNING
Coupler-to-hitch mismatch can result in uncoupling,
leading to death or serious injury.
Be sure the LOAD RATING of the hitch ball is equal or
greater than the load rating of the coupler.
Be sure the SIZE of the hitch ball matches the size of
the ball coupler.
WARNING
A worn, cracked or corroded hitch ball can fail while
towing and may result in death or serious injury.
Before coupling trailer, inspect the hitch ball for wear,
corrosion and cracks.
Replace worn or damaged hitch ball.
be used.
a thin layer of automotive bearing grease.
Slowly back up the tow vehicle so that the hitch ball is
near or aligned under the coupler.
coupler does not line up with the hitch ball, adjust the
position of the tow vehicle.
an outside handle. In the open position, the coupler is
able to drop fully onto the hitch ball.
the hitch ball.
2-INCH
TRAILER
COUPLER
TOW
VEHICLE
2-INCH
BALL
WARNING
A loose hitchball nut can result in uncoupling, leading
to death or serious injury.
Be sure the hitch ball is tight to the hitch before coupling
the trailer.
Rock the ball to make sure it is tightened to the hitch,
and visually check that the hitch ball nut is solid against
the lock washer and hitch frame.
Wipe the inside and outside of the coupler. Clean and
visually inspect it for cracks and deformations. Feel the
inside of the coupler for worn spots and pits.
Be sure the coupler is secured tightly to the tongue of the
trailer. All coupler fasteners must be visibly solid against
the trailer frame.
The bottom surface of the coupler must be above the top
of the hitch ball. Use the tongue jackstand to support
PAGE 32 — MLT25 SERIES LIGHT TOWER • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (11/28/12)
Figure D. Ball Hitch Coupling Mechanism
position, the locking mechanism securely holds the
coupler to the hitch ball.
Insert a pin or lock through the hole in the locking
mechanism.
the coupler is locked to the hitch.
by the hitch.
with the road.
Page 33

NOTICE
Breakaway Brake System
working breakaway brake system (Figure F) will apply the
hydraulic brakes on the trailer. The safety chains will keep
the tow vehicle attached and as the brakes are applied at
system is not working, DO NOT tow the trailer. Have
SAFETY GUIDELINES — TRAILERS
Overloading can damage the tongue jack. DO NOT
use the tongue jack to raise the tow vehicle more than
one inch.
If the coupler cannot be secured to the hitch ball, do not
tow the trailer. Call your dealer for assistance. Lower the
trailer so that its entire tongue weight is held by the hitch and
continue retracting the jack to its fully retracted position.
Attaching Safety Chain
Visually inspect the safety chains and hooks for wear or
damage. Replace worn or damaged safety chains and
hooks before towing.
Attach the safety chains so that they:
• Cross underneath the coupler. See Figure E.
TOW
VEHICLE
TRAILER
TONGUE
IMPORTANT!
SAFETY CHAIN
MASTER LINK
Figure E. Attaching Safety Chain (Ball Hitch)
CROSS BOTH
SAFETY CHAINS
• Loop around a frame member of the tow vehicle or holes
provided in the hitch system (DO NOT attach them to
an interchangeable part of the hitch assembly).
• Have enough slack to permit tight turns, but not be
close to the road surface, so if the trailer uncouples, the
safety chains can hold the tongue up above the road
.
WARNING
Improper rigging of the safety chains can result in
loss of control of the trailer and tow vehicle, leading
to death or serious injury, if the trailer uncouples from
the tow vehicle.
• Fasten chains to frame of tow vehicle. DO NOT fasten
chains to any part of the hitch unless the hitch has
holes or loops specifi cally for that purpose.
• Cross chains underneath hitch and coupler with
enough slack to permit turning and to hold tongue
up, if the trailer comes loose.
If the coupler or hitch fails, a properly connected and
the trailer’s axles, the trailer/tow vehicle combination will
come to a controlled stop.
Connect Cable to
Tow Vehicle
Breakaway Lever
Hydraulic Actuator
Figure F. Breakaway Brake System
Breakaway Cable Surge Brake System
The breakaway brake system includes a brake cable
connected to the tow vehicle on one end and to the
emergency brake lever located on the hydraulic actuator
on the other end.
WARNING
• An ineffective breakaway brake system can result in
a runaway trailer, leading to death or serious injury,
if the coupler or ball hitch fails.
• Connect the breakaway cable to the tow vehicle and
NOT to the hitch, ball or support.
• Before towing the trailer, test the function of the
breakaway brake system. If the breakaway brake
it serviced or repaired.
NOTICE
DO NOT tow the trailer with the breakaway brake
system ON because the brakes will overheat which
can result in permanent brake failure.
NOTICE
Replace the breakaway brake battery (if equipped) at
intervals specifi ed by manufacturer.
MLT25 SERIES LIGHT TOWER • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (11/28/12) — PAGE 33
Page 34

Connecting Trailer Lights
Connect the trailer lights to the tow vehicle’s electrical
PINTLE HITCH COUPLER
A pintle eye coupler (Figure G) connects to a pintle-hook
hitch that is located on or under the rear bumper of the tow
vehicle. This system of coupling a trailer to a tow vehicle is
A pintle hitch trailer may be fi tted with a tongue jackstand
mounted to the A-frame (front or tongue) part of the trailer.
By rotating the jack handle clockwise, the jack will extend
hitch size are listed on the trailer tongue. You must provide
a pintle hitch and pintle coupler for your tow vehicle, where
the load rating of the pintle hitch and pintle coupler is equal
coupler size. If the hitch is too small, too large, underrated,
Before each tow, check the locking device that secures the
Lightly oil the pivot points and sliding surfaces with SAE30W
motor oil to prevent rust and help ensure proper operation
determine the proper action to prevent possible failure of
system using the electric connectors at the front of the
trailer (tongue). Refer to the wiring diagram shown in the
trailer wiring diagram section of this manual. Before towing
the trailer check for the following:
Running lights (turn on tow vehicle headlights).
Brake Lights (step on tow vehicle brake pedal).
Backup Lights (place tow vehicle gear shift in reverse).
Turn Signals (activate tow vehicle directional signal
lever).
WARNING
Improper electrical connection between the tow vehicle
and the trailer will result in inoperable lights and electric
brakes, and can lead to collision.
SAFETY GUIDELINES — TRAILERS
sometimes referred to as a “lunette eye, tow ring or G.I.
hitch.”
Figure G. Pintle Hitch Coupler
Before each tow:
• Check that the taillights, brake lights and turn signals
work.
• Check that the electric brakes work by operating the
brake controller inside the tow vehicle.
Uncoupling the Ball Hitch
Follow these steps to uncouple ball hitch from tow
vehicle:
Block trailer tires to prevent the trailer from rolling, before
jacking the trailer up.
Disconnect the electrical connector.
Disconnect the breakaway brake switch cable. Promptly
replace the pullpin in the switchbox.
Before extending jackstand, make certain the ground
surface below the jackstand foot will support the tongue
load.
Rotate the jackstand handle (or crank) clockwise. This
will slowly extend the jack and transfer the weight of the
trailer tongue to the jack.
that can raise and lower the coupler. The tongue jack is
and raise the tongue of the trailer.
The load rating of the coupler and the necessary pintle
to or greater than that of your trailer.
Also, the pintle hitch size must be the same as the pintle
loose or worn, the trailer can come loose from the tow
vehicle, and may cause death or serious injury.
Pintle Coupler and Pintle Hook
coupler to the pintle hook assembly.
The pintle hook lever must be able to operate freely and
automatically snap into place into the latched position.
of the latching mechanism.
If you see or feel evidence of wear, such as fl at spots,
PAGE 34 — MLT25 SERIES LIGHT TOWER • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (11/28/12)
deformations, pitting or corrosion, on the pintle hook or
coupler, immediately have your dealer inspect them to
Page 35

SAFETY GUIDELINES — TRAILERS
the ball andcoupler system. All bent or broken coupler parts
Using the jackstand at the front of trailer (tongue), turn
the jackstand crank handle to raise the trailer. If the pintle
eye coupler does not line up with the pintle hitch hook,
Place the hook inside the eye coupler. CLOSE the pintle
trailer jack, test to see that you can raise the rear of the
Lower the trailer so that its entire tongue weight is held
Raise the jackstand to a height where it will not interfere
A defective pintle hitch not properly fastened can result
must be replaced before towing the trailer.
THE TOW VEHICLE, PINTLE HITCH AND PINTLE
COUPLER MUST HAVE A RATED TOWING CAPACITY
EQUAL TO OR GREATER THAN THE TRAILER Gross
Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR).
IT IS ESSENTIAL THAT THE PINTLE HITCH BE OF THE
SAME SIZE AS THE PINTLE COUPLER.
The coupler size and load rating (capacity) are marked on
the coupler. Hitch capacity is marked on the hitch.
WARNING
Coupler-to-hitch mismatch can result in uncoupling,
leading to death or serious injury.
Be sure the LOAD RATING of the pintle hitch hook is
equal or greater than the load rating of the pintle eye
coupler.
Be sure the SIZE of the pintle hitch hook matches the
size of the pintle eye coupler.
WARNING
WARNING
in uncoupling, leading to death or serious injury.
Be sure the pintle hook is securly tighten to the tow
vehicle before coupling the trailer.
Coupling Trailer to Tow Vehicle (Pintle Coupler)
Slowly back up the tow vehicle so that the pintle
hitch hook is near or aligned under the pintle eye ring
coupler.
adjust the position of the tow vehicle.
OPEN the pintle hook locking mechanism (Figure H).
hook mechanism.
TOW
VEHICLE
PINTLE
HOOK
TRAILER
TONGUE
A worn, cracked or corroded pintle hitch hook can
fail while towing, and may result in death or serious
injury.
Before coupling trailer, inspect the pintle hitch hook for
wear, corrosion and cracks.
Replace worn or damaged pintle hitch hook.
Rock the pintle eye coupler to make sure it is secured
tightly to the hitch.
Wipe the inside and outside of the pintle coupler. Clean
and inspect it visually for cracks and deformations. Feel
the inside of the coupler for worn spots and pits.
Be sure the coupler is secured tightly to the tongue of the
trailer. All coupler fasteners must be visibly solid against
the trailer frame.
Raise the bottom surface of the coupler to be above the
top of the pintle hitch hook. Use the tongue jackstand
to support the trailer tongue. Wood or concrete blocks
may also be used.
SAFETY CHAIN
MASTER LINK
PINTLE
RING “EYE”
SAFETY
CHAIN
Figure H. Attaching Safety Chain (Pintle Hitch)
IMPORTANT!
CROSS BOTH
SAFETY CHAINS
Insert a pin or lock through the hole in the locking
mechanism.
Be sure the pintle hook is inserted completely through
the eye ring and the locking mechanism is engaged.
A properly engaged locking mechanism will allow the
coupler to raise the rear of the tow vehicle. Using the
tow vehicle by1-inch after the coupler is locked to the
hitch.
by the hitch.
with the road.
MLT25 SERIES LIGHT TOWER • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (11/28/12) — PAGE 35
Page 36

TIRE SAFETY
Unsafe Tires, Lug Nuts or Wheels
Lug nuts are also prone to loosen after first being
have been remounted), check to make sure they are tight
Failure to perform this check can result in a wheel parting
Determining the load limits of a trailer includes more than
located on the forward half of the left (road) side of the unit.
This certifi cation/VIN label will indicate the trailer’s Gross
Gross Axle Weight Rating (GAWR). This is the most a the
Improper lug nut torque can cause a wheel parting from
Be sure tires are infl ated to pressure indicated on side
Trailer tires and wheels are more likely to fail than car tires
and wheels because they carry a heavier load. Therefore,
it is essential to inspect the trailer tires before each tow.
If a tire has a bald spot, bulge, cuts, is showing any cords,
or is cracked, replace the tire before towing. If a tire has
uneven tread wear, take the trailer to a dealer service
center for diagnosis.
Uneven tread wear can be caused by tire imbalance, axle
misalignment or incorrect infl ation.
Tires with too little tread will not provide adequate tracking
on wet roadways and can result in loss of control, leading
to death or serious injury.
Improper tire pressure causes an unstable trailer and
can result in a tire blowout and loss of control. Therefore,
before each tow you must also check the tire pressure. Tire
pressure must be checked when tires are cold.
Allow 3 hours cool-down after driving as much as 1 mile at
40 mph before checking tire pressure. Trailer tires will be
infl ated to higher pressures than passenger vehicle tires.
Since trailer wheels and lug nuts (or bolts) are subjected
to greater side loads than automobile wheels, they are
more prone to loosen. Before each tow, check to make
sure they are tight.
SAFETY GUIDELINES — TRAILERS
assembled. When driving a new trailer (or after wheels
after the fi rst 10, 25 and 50 miles of driving and before
each tow thereafter.
from the trailer and a crash, leading to death or serious
injury.
WARNING
Lug nuts are prone to loosen after initial installation,
which can lead to death or serious injury.
Check lug nuts for tightness on a new trailer or when
wheel(s) have been remounted after the fi rst 10, 25
and 50 miles of driving.
WARNING
the trailer, leading to death or serious injury.
Be sure lug nuts are tight before each tow.
WARNING
Improper tire pressure can result in a blowout and loss
of control, which can lead to death or serious injury.
wall before towing trailer.
The proper tightness (torque) for lug nuts is listed in the
lug nut tightening section of this manual. Use a torque
wrench to tighten the lug nuts. If you do not have a torque
wrench, use a lug wrench (from your tow vehicle) and
tighten the nuts as much as you can. Then have a service
garage or trailer dealer tighten the lug nuts to the proper
torque.
WARNING
Metal creep between the wheel rim and lug nuts will
cause rim to loosen and could result in a wheel coming
off, leading to death or serious injury.
Tighten lug nuts before each tow.
PAGE 36 — MLT25 SERIES LIGHT TOWER • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (11/28/12)
Determining Load Limit of Trailer
understanding the load limits of the tires alone. On all
trailers there is a Federal certifi cation/VIN label that is
Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR). This is the most weight
the fully loaded trailer can weigh. It will also provide the
axle can weigh.
Page 37

There is a vehicle placard (Figure I) located in the same
location as the certifi cation label described above. This
Determining Load Limit of Tow Vehicle
Locate the statement, “The combined weight of occupants
and cargo should never exceed XXX lbs.,” on your vehicle’s
Subtract the combined weight of the driver and passengers
The resulting fi gure equals the available amount of cargo
equals 1400 lbs. and there will be fi ve 150 lb. passengers
in your vehicle, the amount of available cargo and luggage
exceed the available cargo and luggage capacity calculated
If your vehicle will be towing a trailer, load from your trailer
will be transferred to your vehicle. Consult the tow vehicle’s
manual to determine how this weight transfer reduces the
pressure, observing tire and vehicle load limits (not carrying
more weight in your vehicle than your tires or vehicle can
safely handle), avoiding road hazards and inspecting tires
tread separation or blowout and fl at tires. These actions,
Help protect you and others from avoidable breakdowns
placard provides tire and loading information. In addition,
this placard will show a statement regarding maximum
cargo capacity.
The weight of cargo should never exceed XXX kg. Or XXX lbs
TIRE
FRONT
REAR
SPARE
TIRE AND LOADING INFORMATION
SIZE
COLD TIRE PRESSURE
SEE OWNER’S
MANUAL FOR
ADDITIONAL
INFORMATION
SAFETY GUIDELINES — TRAILERS
Step 1.
.
placard.
Step 2.
Determine the combined wei ght of the driver and
passengers who will be riding in your vehicle.
Step 3.
Figure I. Trailer Tire Placard
If additional work items (hoses, tools, clamps etc.) are
going to be added to the trailer, be sure they are distributed
evenly to prevent overloading front to back and side to side.
Heavy items should be placed low and as close to the axle
positions as reasonable. Too many items on one side may
overload a tire.
Excessive loads and/or underinfl ation cause tire overloading
and, as a result, abnormal tire fl exing occurs. This situation
can generate an excessive amount of heat within the tire.
Excessive heat may lead to tire failure. It is the air pressure
that enables a tire to support the load, so proper infl ation
is critical. The proper air pressure may be found on the
certifi cation/VIN label and/or on the Tire and Loading
Information placard. This value should never exceed the
maximum cold infl ation pressure stamped on the tire.
Perform the following steps to determine the load limit of
your trailer.
Step 1.
Locate the statement, “The weight of cargo should never
exceed XXX kg or XXX lbs.,” on your vehicle’s Tire and
Loading Information placard (Figure I). This value equals
the available amount of equipment load capacity.
Step 2.
Determine the weight of the equipment being loaded
on the tow vehicle. That weight may not safely exceed
the available equipment load capacity. The trailer’s Tire
Information Placard is attached adjacent to or near the
trailer’s VIN (Certifi cation) label at the left front of the trailer
(See Figure I).
from XXX kilograms or XXX pounds.
Step 4.
and luggage capacity. For example, if the “XXX” amount
capacity is 650 lbs. (1400-750 (5 x 150) = 650 lbs.).
Step 5.
Determine the combined weight of luggage and cargo
being loaded on the vehicle. That weight may not safely
in Step 4.
available cargo and luggage capacity of your vehicle.
Studies of tire safety show that maintaining proper tire
for cuts, slashes and other irregularities are the most
important things you can do to avoid tire failure, such as
along with other care and maintenance activities, can
also:
Improve vehicle handling.
and accidents.
Improve fuel economy.
Increase the tire life.
MLT25 SERIES LIGHT TOWER • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (11/28/12) — PAGE 37
Page 38

SAFETY GUIDELINES — TRAILERS
Use the information contained in this section to make tire
M+S: The “M+S” or “M/S” indicates that the tire has
which a tire is designed to be driven for extended periods
of time. The ratings range from 99 miles per hour (mph) to
186 mph. These ratings are listed in Table A. Note: You may
not fi nd this information on all tires because it is not required
: This begins with the
code where it was manufactured, and the last four numbers
represent the week and year the tire was built. For example,
the numbers 3197 means the 31st week of 1997. The other
numbers are marketing codes used at the manufacturer’s
discretion. This information is used to contact consumers
: The number of
plies indicates the number of layers of rubber-coated fabric
in the tire. In general, the greater the number of plies, the
must indicate the materials in the tire, which include steel,
maximum load in kilograms and pounds that can be carried
: This number
is the greatest amount of air pressure that should ever be
safety a regular part of your vehicle maintenance routine.
Recognize that the time you spend is minimal compared
with the inconvenience and safety consequences of a fl at
tire or other tire failure.
TIRE FUNDAMENTALS
Federal law requires tire manufacturers to place standardized
information on the sidewall of all tires (Figure J). This
information identifies and describes the fundamental
characteristics of the tire and also provides a tire
identifi cation number for safety standard certifi cation and
in case of a recall.
Figure J. Standard Tire Sidewall Information
P: The “P” indicates the tire is for passenger vehicles.
Next number: This three-digit number gives the width in
millimeters of the tire from sidewall edge to sidewall edge.
In general, the larger the number, the wider the tire.
Next number: This two-digit number, known as the aspect
ratio, gives the tire’s ratio of height to width. Numbers of
70 or lower indicate a short sidewall for improved steering
response and better overall handling on dry pavement.
P: The “R” stands for radial. Radial ply construction of tires
has been the industry standard for the past 20 years.
Next number: This two-digit number is the wheel or rim
diameter in inches. If you change your wheel size, you
will have to purchase new tires to match the new wheel
diameter.
Next number: This two- or three-digit number is the tire’s
load index. It is a measurement of how much weight each
tire can support. You may fi nd this information in your
owner’s manual. If not, contact a local tire dealer. Note:
You may not fi nd this information on all tires because it is
not required by law.
some mud and snow capability. Most radial tires have
these markings; hence, they have some mud and snow
capability.
Speed Rating: The speed rating denotes the speed at
by law.
Letter Rating Speed Rating
Table A. Speed Rating
Q 99 mph
R 106 mph
S 112 mph
T 118 mph
U 124 mph
H 130 mph
V 149 mph
W 168* mph
Y 186* mph
U.S. DOT Tire Identifi cation Number
letters “DOT” and indicates that the tire meets all federal
standards. The next two numbers or letters are the plant
if a tire defect requires a recall.
Tire Ply Composition and Materials Used
more weight a tire can support. Tire manufacturers also
nylon, polyester, and others.
Maximum Load Rating: This number indicates the
by the tire.
Maximum Permissible Infl ation Pressure
put in the tire under normal driving conditions.
PAGE 38 — MLT25 SERIES LIGHT TOWER • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (11/28/12)
Page 39

SAFETY GUIDELINES — TRAILERS
Uniform Tire Quality Grading Standards (UTQGS)
Load Range: This information identifi es the tire’s load-
Check tire infl ation pressure weekly during use to insure
check tire pressure on tow vehicle and trailer
overload tow vehicle. Check the tire information
The proper repair of a punctured tire requires a plug for the
hole and a patch for the area inside the tire that surrounds
from the rim to be properly inspected before being plugged
visible. Check infl ation pressure weekly during use to insure
the maximum tire life and tread wear. A bubble, cut or bulge
in a side wall can result in a tire blowout. Inspect both side
walls of each tire for any bubble, cut or bulge; and replace
Treadwear Number: This number indicates the tire’s wear
rate. The higher the treadwear number is, the longer it
should take for the tread to wear down. For example, a tire
graded 400 should last twice as long as a tire graded 200.
Traction Letter: This letter indicates a tire’s ability to stop
on wet pavement. A higher graded tire should allow you
to stop your car on wet roads in a shorter distance than a
tire with a lower grade. Traction is graded from highest to
lowest as “AA”,”A”, “B”, and “C”.
Tem perat ure Lette r: This lett er ind icate s a tire’s
resistance to heat. The temperature grade is for a tire that
is infl ated properly and not overloaded. Excessive speed,
underinfl ation or excessive loading, either separately or
in combination, can cause heat build-up and possible tire
failure. From highest to lowest, a tire’s resistance to heat
is graded as “A”, “B”, or “C”.
Refer to Figure K for additional tire information for light
trucks.
carrying capabilities and its infl ation limits.
Tire Safety Tips
Slow down if you have to go over a pothole or other
object in the road.
DO NOT run over curbs or other foreign objects in the
roadway, and try not to strike the curb when parking.
the maximum tire life and tread wear.
DO NOT bleed air from tires when they are hot.
Inspect tires for uneven wear patterns on the tread,
cracks, foreign objects, or other signs of wear or
trauma.
Remove bits of glass and foreign objects wedged in
the tread.
Make sure your tire valves have valve caps.
ALWAYS
before towing. Check tire pressure at least once a
month.
Figure K. UTQGS Tire Information
Tires for light trucks have other markings besides those
found on the sidewalls of passenger tires.
LT: The “LT” indicates the tire is for light trucks or trailers.
ST: An “ST” is an indication the tire is for trailer use only.
Max. Load Dual kg (lbs) at kPa (psi) Cold: This information
indicates the maximum load and tire pressure when the tire
is used as a dual, that is, when four tires are put on each
rear axle (a total of six or more tires on the vehicle).
Max. Load Single kg (lbs) at kPa (psi) Cold: This
information indicates the maximum load and tire pressure
when the tire is used as a single.
MLT25 SERIES LIGHT TOWER • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (11/28/12) — PAGE 39
DO NOT
and loading placard for safe allowable tire loading
conditions.
Tire Repair
the puncture hole. Punctures through the tread can be
repaired if they are not too large, but punctures to the
sidewall should not be repaired. Tires must be removed
and patched.
Replacing Worn or Damaged Tires
Replace the tire before towing the trailer if the tire treads
have less than 1/16 inch depth or the telltale bands are
a damaged tire before towing the trailer.
Page 40

safety guidelines — tRaileRs
Table B below will help pinpoint the causes and solutions
It is extremely important to apply and maintain proper wheel
fasteners matched to the cone angle of the wheel. Proper
Tighten each lug nut in 3 separate passes as defi ned
Check to see if the lug nuts are tight after the fi rst 10,
Over-tightening lug nuts will result in breaking the studs
of tire wear problems.
Table B. Tire Wear Troubleshooting
Wear Pattern Cause Solution
Center Wear Over infl ation.
Edge Wear Under infl ation.
Side Wear
Toe Wear Incorrect toe-in. Align wheels.
Cupping Out-of-balance.
Flat Spots
Loss of camber
or overloading.
Wheel lockup and
tire skidding.
Adjust pressure to particular
load per tire manufacturer.
Adjust pressure to particular
load per tire manufacturer.
Make sure load does not
exceed axle rating.
Align wheels.
Check bearing adjustment
and balance tires.
Avoid sudden stops when
possible and adjust brakes.
WARNING
ALWAYS wear safety glasse s when
removing or installing force fi tted parts. DO
NOT attempt to repair or modify a wheel.
DO NOT install an inner-tube to correct a
leak through through the rim. If the rim is
cracked, the air pressure in the inner tube may cause
pieces of the rim to explode (break off) with great force
and cause serious eye or bodily injury.
Wheel Rims
NOTICE
NEVER use an pneumatic air gun to tighten wheel
lug nuts.
or permanently deforming the mounting stud holes in
the wheels.
WARNING
Lug nuts are prone to loosen after initial installation,
which can lead to death or serious injury. Check all
wheel lug nuts periodically.
Lug Nut Torque Requirements
mounting torque on the trailer. Be sure to use only the
procedure for attachment of the wheels is as follows:
1. Start all wheel lug nuts by hand.
2. Torque all lug nuts in sequence. See Figure L. DO
NOT torque the wheel lug nuts all the way down.
by Table C.
3.
25 and 50 miles of driving and before each tow
thereafter
If the trailer has been struck, or impacted, on or near the
wheels, or if the trailer has struck a curb, inspect the rims for
damage (i.e. being out of round); and replace any damaged
wheel. Inspect the wheels for damage every year, even if
no obvious impact has occurred.
Wheels, Bearings and Lug Nuts
A loose, worn or damaged wheel bearing is the most
common cause of brakes that grab.
To check wheel bearings, jack trailer and check wheels
for side-to-side looseness. If the wheels are loose, or spin
with a wobble, the bearings must be serviced or replaced.
Check infl ation pressure weekly during use to insure the
maximum tire life and tread wear. Most trailer axles are
built with sealed bearings that are not serviceable. Sealed
bearings must be replaced as complete units.
PAGE 40 — MLT25 SERIES LIGHT TOWER • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (11/28/12)
Figure L. Wheel Lug Nuts Tightening Sequence
Page 41

Table C. Tire Torque Requirements
Replace any broken or burned-out lamps as necessary.
Check the wire harness for cuts, fraying or other damage.
Improper operating taillights, stoplights and turn signals
Figure M. Trailer to Tow Vehicle Wiring Diagram
Wheel Size
12" 20-25 35-40 50-65
13" 20-25 35-40 50-65
14" 20-25 50-60 90-120
15" 20-25 50-60 90-120
16" 20-25 50-60 90-120
First Pass
FT-LBS
Second Pass
FT-LBS
safety guidelines — tRaileRs
Third Pass
FT-LBS
If it needs replacing, contact your dealer.
WARNING
can cause collisions.
Check all lights before each tow.
Lights and Signals
Before each tow, check the trailer taillights, stoplights, turn
signals and any clearance lights for proper operation.
MLT25 SERIES LIGHT TOWER • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (11/28/12) — PAGE 41
Page 42

TROUBLESHOOTING
Table 5. Lamp Troubleshooting
Symptom Possible Cause Solution
Lamp will not start.
Lamp Burned Out?
Lamp Loose in Socket?
Lamp Plugs Not Tight? Check plug and receptacle. Tighten if loose.
Defective Ballast?
Low Voltage?
Improper Ballast?
Test the lamp in a fixture which is operating properly.
Replace if necessary.
Inspect lamp base to see if there is arcing at center
contact button. Tighten lamp snugly. Check socket for
damage. Replace if defective.
Interchange ballast plugs in generator enclosure.
If lamp starts, replace ballast. Check ballast wiring
against diagram. Check for swollen capacitor, charred
wiring, core and coil or other signs of excessive heat.
Check line voltage at ballast input. Voltage should
be within 10% of nameplate rating when operating
at normal load. Increase supply voltage or remove
external load.
Proper HID lamps will perform erratically or fail to
start on an improper ballast. The ballast nameplate
data must agree with the line voltage and lamp used.
Improper ballast causes lamp failure. Note: Mercury
lamps of the same wattage will operate properly on
Metal Halide ballasts.
Lamp flickers and goes
out intermittent or
cycling.
Operating position should agree with the lamp tech.
A BU-HOR lamp can be operated base up vertical to
Improper Lamp Operating
Position (Metal Halide only)?
Lamp has been Operating: Cool
Down Time Insufficient?
Improper Ballast?
New Lamp?
Defective Lamp? Replace lamp.
and including the horizontal and a BD can be operated
base down vertical to, approaching, but not including
the horizontal. A lamp operated beyond the specified
position may not start.
HID lamps (High Pressure Sodium, Metal Halide,
Mercury Vapor) require from 4 to 8 minutes cool-down
time before restarting. Switch off breaker and allow
lamp to cool.
Improper ballasting can cause flickering or erratic
operation. In the start-up period the lamp may ignite,
start to warm up and then extinguish (cycle).
Under certain conditions new lamps may "cycle".
Usually after 3 tries to start at 30 to 60 second
intervals, lamps will stabilize and operate satisfactorily.
PAGE 42 — MLT25 SERIES LIGHT TOWER • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (11/28/12)
Page 43

Symptom Possible Cause Solution
Lamp starts slowly
(ARC does not strike
when switch is first
turned on)
Table 5. Lamp Troubleshooting (continued)
Defective Lamp?
TROUBLESHOOTING
Lamp may glow for extended period of time. Replace after
checking voltage and ballast.
Circuit breaker trips on
lamp start-up
Lamp light output low
Lamp colors different.
Short Circuit or Ground? Check wiring against diagram. Check for shorts or ground.
Normal Lamp
Depreciation?
Dirty Lamp or Fixture? Clean lamp and fixture.
Defective Ballast?
Wrong Voltage?
Improper Ballast? Check ballast nameplate against lamp data.
Normal Lamp
Depreciation?
Dirty Fixture?
Replace Lamp.
Interchange ballast plugs in generator enclosure. If lamp
returns to normal light output, replace ballast. Check for
swollen capacitor, charred wiring, core and coil, or other signs
of excessive heat.
Check voltage at ballast input. Voltage should be within 10%
of nameplate rating. Check wiring connections for voltage
loss. Check socket contact point.
Lamp output and brightness decreases and color changes
slightly as lamps age. Spot replacement with new lamps
may cause noticeable differences in lamp colors. Group
replacement minimizes color differences.
Dirty fixtures will cause lamps to appear different in color.
Clean fixture.
ARC tube discolored or
swollen.
Short lamp life.
MLT25 SERIES LIGHT TOWER • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (11/28/12) — PAGE 43
Wrong Lamp?
Over Voltage from Power
Supply?
Improper Ballast?
Lamp Damaged?
Improper Ballast?
Check data on lamps which appear different in color. Replace
with correct color lamp.
Check voltage at ballast. Check for current or voltage surges.
Check for shorted capacitors and replace if defective.
Lamp operated on ballast designed for higher wattage lamp.
Check ballast nameplate against lamp data.
Check for outer bulb cracks. If air enters outer bulb, arc tube
may continue to burn for 100 hours before failure. Check for
bulb cracks where glass meets the base due to tightening
Lamp too firmly in socket or scoring of glass where socket
inadvertently touches the lamp bulb. Look for broken arc tube
or loose metal parts. Replace lamp. (Bulb leads will cause
oxidation of metal parts.)
Ballast nameplate data should agree with lamp line voltage
and lamp use. If improper ballast is used, the lamp life will be
shortened. A mismatch may also cause the ballast to fail.
Page 44

TROUBLESHOOTING
LAMP TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE
Use the following procedure and wiring diagrams on the
next pages to determine which of the four lamps is not
functioning:
Connections
1. Make sure that lamp #1 power cable is plugged into
the J1 connector on the T-Bar assembly.
2. Make sure that lamp #2 power cable is plugged into
the J2 connector on the T-Bar assembly.
3. Make sure that lamp #3 power cable is plugged into
the J3 connector on the T-Bar assembly.
4. Make sure that lamp #4 power cable is plugged into
the J4 connector on the T-Bar assembly.
5. Make sure that lamp #5 power cable is plugged into
the J5 connector on the T-Bar assembly.
6. Make sure that lamp #6 power cable is plugged into
the J6 connector on the T-Bar assembly.
Starting
1. Start the generator and verify that there are no
abnormal sounds.
2. Turn CB1 thru CB3 circuit breakers, depending on what
voltage is selected, (see Table 3) to the ON position.
8. Connect the positive lead of the voltmeter to the output
side of the circuit breaker where the lamp was originally
OFF and observe that 120 VAC is present. Make sure
circuit breaker is ON.
9. If no output voltage is present, the circuit breaker is
defective and needs to be replaced.
10. If the correct output voltage is present then it can be
assumed that the generator is working correctly and
the correct voltage (120 VAC) is being supplied to the
ballast. Then it can be assumed that the ballast for that
lamp is defective. Replace ballast.
Ballast Removal
1. Remove the power cable from the generator, and make
sure that no voltage is being supplied to the ballast
compartment.
2. Remove the four screws securing the ballast cover,
and remove cover.
3. Make sure to discharge the ballast capacitor.
4. Remove the defective ballast, taking care to guard
against electrical shock when coming in contact with
the ballast and capacitor. The capacitor is known to
store an electrical charge, that when discharged could
result in a harmful shock. Make sure to discharge
capacitor.
3. Wait a few minutes and determine which lamp is not
igniting.
4. If one of the lamps is OFF, disconnect its power cable
and plug it into a receptacle that is known to be working.
DO NOT unplug a power cable from the T-Bar while
power is being supplied by the generator. Always turn
the circuit breaker OFF before unplugging a power
cable.
5. If the lamp still does not ignite after plugging it into a
working receptacle (120 VAC present), then the lamp
is defective and has to be replaced.
6. If the lamp ignites after plugging it into a working
receptacle, continue with step 7.
7. With the voltmeter set to the AC position, connect the
negative lead of the AC voltmeter to any (neutral) white
wire on the junction terminal block. This block connects
all the neutral wires (white) in the system.
PAGE 44 — MLT25 SERIES LIGHT TOWER • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (11/28/12)
Page 45

LAMP 1
LAMP 2
LAMP 3
ELECTRONIC COMPONENTS LOCATOR
Y
Z
D1
J6
C1
J5
B1
J4
A1
J3
J2
J1
H
F
I
G
D
B
E
C
A
F1
G1
I1
H1
J
K
S
T
N
K1
J1
M
U
L1
N1
M1
L
O
V
W
Q
X
E1
P
R
MLT25 SERIES LIGHT TOWER • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (11/28/12) — PAGE 45
Page 46

OUTPUT TERMINAL PANEL
REAR CONNECTIONS
GROUND CONNECTION
BE USED
MUST
ATALL TIMES
WIRING DIAGRAM (SHEET 1)
BLACK RED
U
V
L1 L2 L3
BLUE
WHITE
O
W
NEU. GND.
3-POLE FUSE
15 AMP
15 AMP
15 AMP
3-POLE FUSE
15 AMP
GREEN
HOLDER
F1
F2
F3
HOLDER
F4
A
B
C
D
F1
BLK 14AWG
RED 14 AWG
BLUE 14 AWG
BRN 14AWG
GREEN 10 AWG
3-POLE, 15 AMP
CIRCUIT BREAKER ( )CB1
3-POLE, 15 AMP
CIRCUIT BREAKER ( )CB2
GRAY/RED 14 AWG
GROUND
STUD
TO SMART RELAY (Q1-1)
J
BLK/WHT 14 AWG
K1-NC
R4
RED/WHT 14 AWG RED/YEL 14 AWG
1
BLUE/WHT 14 AWG
GRAY/BLUE 14 AWG
R3
1
K1-NO
2
K
BRN/WHT 14AWG
SEE SHEET 2
AM
K2-NO
A
L1
T1
K4-NO
L1
L1
T1
T1
K2-NO
L2
T2
K4-NO
L2
T2
TO VOLTAGE
TRANSDUCER
AC INPUT PIN 1 (L3.)
SEE SHEET 2
K2-NO
L3
T3
K4-NO
L3
T3
A
B
B
C
D
E
F
K1-NC
R6
R5
7
K1-NO
8
SPARE
F5
15 AMP
F6
15 AMP
3-POLE FUSE
3-POLE FUSE
HOLDER
HOLDER
F7
15 AMP
15 AMP
F8
15 AMP
15 AMP
F9
E
F
G
H
ORG 14 AWG
YEL 14 AWG
BLK 14 AWG
SINGLE PHASE
MODE ONLY
PINK 14 AWG
3-POLE, 15 AMP
CIRCUIT BREAKER ( )CB3
ORG/WHT 14 AWG
YEL/WHT 14 AWG
L
PURPLE/WHT 14 AWG
PINK/WHT 14 AWG
I
PAGE 46 — MLT25 SERIES LIGHT TOWER • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (11/28/12)
K3-NO
L1
K5-NO
L1
K3-NO
L2
K5-NO
L2
K3-NO
L3
K5-NO
L3
A
T1
T1
T2
T2
T3
T3
G
B
H
I
J
K
L
Page 47

T-BAR ASSEMBLY
P/N 49796
WIRING DIAGRAM (SHEET 1)
WHT
J1
J1
(LAMP 1)
(LAMP 1)
BLK
WHT
Y Z
GRN
J2
(LAMP 2)
RED
WHT
GRN GRN GRN
(LAMP 3)
BLUE
J3
WHT
J4
(LAMP 4)
YEL
J5
(LAMP 5)
WHT
ORG PURPLE
(LAMP 6)
A1 B1 C1 D1
GRN
GRN
J6
AM
AA
BB
C
D
E
F
BLK/YEL 16 AWG
BLK 16 AWG
BALLAST ASSEMBLY
BLK/YEL 16 AWG
BLK 16 AWG
BLK/YEL 16 AWG
BLK 16 AWG
120V IN
277V IN
P/N 29614
120V IN
277V IN
120V IN
277V IN
BALLAST #1
(LAMP 1)
NEU.
G
BALLAST #2
NEU.
BALLAST #3
YEL
NEU.
M
OUTPUT
RED 16 AWG
N
OUTPUT
RED 16 AWG
O
OUTPUT
RED 16 AWG
C1
24µF@480V
CAPACITOR
S
R1
2
C2
24µF@480V
CAPACITOR
T
C3
24µF@480V
CAPACITOR
U
BLK
RED
BLUE
16 AWG
10-WIRE COIL CORD
P/N 49609
VOLTAGE
SELECTOR
SWITCH
POSITION
1Ø
240/120V
3Ø
240/139V
OR
3Ø
480/277V
NEUTRAL BUS
WHT 14 AWG
WHT 14 AWG
WHT 14 AWG
LAMP SETTINGS
E1
CB
(ON)
CB1 1 & 3
CB2 4 & 6
CB3 2 & 5
CB1 1, 2 & 3
CB2 4, 5 & 6
CB3 N/A
VOLTAGE REG.
ADJ. SETTING
240V
208V
480V
TB1
LAMPS
(ON)
1, 2 & 3
G
H
I
J
K
BL
BLK/YEL 16 AWG
BLK 16 AWG
BLK/YEL 16 AWG
BLK 16 AWG
BLK/YEL 16 AWG
BLK 16 AWG
120V IN
277V IN
120V IN
277V IN
120V IN
277V IN
NOTES:
1
WIRE COLOR CODE IS BASE COLOR/STRIPE
MLT25 SERIES LIGHT TOWER • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (11/28/12) — PAGE 47
BALLAST #4
NEU.
BALLAST #5
NEU.
BALLAST #6
NEU.
P
OUTPUT
RED 16 AWG
Q
OUTPUT
RED 16 AWG
R
OUTPUT
RED 16 AWG
C4
24µF@480V
CAPACITOR
V
YEL 16 AWG
C5
24µF@480V
CAPACITOR
W
ORG 16 AWG
C6
24µF@480V
CAPACITOR
X
PURPLE 16 AWG
RESISTOR IS INTERNALLY
2
INSTALLED WITHIN THE CAPACITOR.
YEL 16 AWG
YEL 16 AWG
YEL 16 AWG
YEL 16 AWG
YEL 16 AWG
YEL 16 AWG
WHITE 10 AWG
Page 48

TO CB1 L2
Q1
1 2Q21 2Q31 2Q41 2
WHT 16 AWG
RED/GRAY
16 AWG
RED/BLUE
16 AWG
WHT 16 AWG
NOTES:
1
K1 CONTACTOR (ABB) AF09Z-22-00-20
RED 16 AWG
GRAY/BLUE 16 AWG
BLK16 AWG
RED 16 AWG
RED 16 AWG
RED 16 AWG
NO
3Ø 277V
1Ø 120V 3Ø 120V
3Ø 120V 3Ø 277V
ESC
ESC
DEC
SmartRelay
FL1E-H12RCE
OUTPUT 4X RELAY /10A
X 9
10 11
BLK/ORG 16 AWG
RED/PINK 16 AWG
AC IN (NEU)
0-10 VDC OUT
GND. (-DC)
+12VDC
12/24 VDC
INPUT 8x DC
I1, I2 = A I3, AI4 (0..10V)
I7, I8 = A I1, AI2 (0..10V)
SHIELD
BRN/BLUE 18 AWG
BRN/YEL 18 AWG
1
2
2
K2-K5 CONTACTORS (ABB) AF09Z-40-00-20
3
PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC CONTROLLER
FOR REPLACEMENT CONTACT MQ PARTS DEPT.
3
RED 16 AWG
4
WIRE COLOR CODE IS BASE COLOR/STRIPE
4
AC INPUT (L3)
SEE SHEET 1
TO CB1 L3
SEE SHEET 1
GRAY/RED 16 AWG
L+ M I1 I2 I3 I4 I5 I6 I7 I8
WIRING DIAGRAM (SHEET 2)
3Ø PRESENT
WHT 16 AWG
WHT 16 AWG
TRANSDUCER
5
6
7
8
9
K6
8
AC VOLTAGE
GRAY/BLUE 16 AWG
13
12
K6
RED 18 AWG
4
3
2
1
14
GRAY 16 AWG
NEUTRAL BUS
E1
TB1
OIL PRESSURE
GAUGE TERMINAL “G”
(GROUND)
OIL PRESSURE
GAUGE TERMINAL “I”
(IGNITION)
A1 A2
1 R3 R5
K1
1 R4 R6
7
K3
8
K2
A1 A2
L1 L2 L3 L4
T1 T2 T3 T4
K4
A1 A2
L1 L2 L3 L4
T1 T2 T3 T4
A1 A2
L1 L2 L3 L4
T1 T2 T3 T4
K5
A1 A2
L1 L2 L3 L4
T1 T2 T3 T4
PAGE 48 — MLT25 SERIES LIGHT TOWER • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (11/28/12)
Page 49

NOTES
MLT25 SERIES LIGHT TOWER • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (11/28/12) — PAGE 49
Page 50

OPERATION MANUAL
HERE’S HOW TO GET HELP
© COPYRIGHT 2012, MULTIQUIP INC.
Multiquip Inc
of their respective owners and used with permission.
This manual
The information and specifications included in this publication were in effect at the time of approval for printing. Illustrations, descriptions, references and technical data contained in
this manual are for guidance only and may not be considered as binding. Multiquip Inc. reserves the right to discontinue or change specifications, design or the information published
in this publication at any time without notice and without incurring any obligations.
PLEASE HAVE THE MODEL AND SERIAL
NUMBER ON-HAND WHEN CALLING
United StateS
Multiquip Corporate Office MQ Parts Department
18910 Wilmington Ave.
Carson, CA 90746
Contact: mq@multiquip.com
Service Department Warranty Department
800-421-1244
310-537-3700
Technical Assistance
800-478-1244 Fax: 310-943-2238
Tel. (800) 421-1244
Fax (310) 537-3927
Fax: 310-537-4259 800-421-1244
800-427-1244
310-537-3700
310-537-3700
Fax: 800-672-7877
Fax: 310-637-3284
Fax: 310-943-2249
mexico United Kingdom
MQ Cipsa Multiquip (UK) Limited Head Office
Carr. Fed. Mexico-Puebla KM 126.5
Momoxpan, Cholula, Puebla 72760 Mexico
Contact: pmastretta@cipsa.com.mx
Tel: (52) 222-225-9900
Fax: (52) 222-285-0420
Unit 2, Northpoint Industrial Estate,
Globe Lane,
Dukinfield, Cheshire SK16 4UJ
Contact: sales@multiquip.co.uk
Canada
Multiquip
4110 Industriel Boul.
Laval, Quebec, Canada H7L 6V3
Contact: jmartin@multiquip.com
Tel: (450) 625-2244
Tel: (877) 963-4411
Fax: (450) 625-8664
Tel: 0161 339 2223
Fax: 0161 339 3226
, the MQ logo are registered trademarks of Multiquip Inc. and may not be used, reproduced, or altered without written per mission. All other trademarks are the property
MUST accompany the equipment at all times. This manual is considered a permanent part of the equipment and should remain with the unit if resold.
Your Local Dealer is:
 Loading...
Loading...