Page 1

OPERATION MANUAL
SERIES
MODEL LS300P
CONCRETE PUMP
(Perkins 404D-22TA DIESEL ENGINE)
Revision #0 (06/09/14)
To find the latest revision of this
publication, visit our website at:
www.multiquip.com
THIS MANUAL MUST ACCOMPANY THE EQUIPMENT AT ALL TIMES.
Page 2

PROPOSITION 65 WARNING
Diesel engine exhaust and some of its
constituents are known to the State of
Californiato cause cancer,birth
defects and other reproductive harm.
Dust created by power sanding,
sawing, grinding, drilling and other
construction activities also contain
chemicals known to cause cancer.
Some examples ofthesechemicals are:
Lead from lead-based paints
Crystalline silica from bricks
Cement and other masonryproducts
Arsenic and chromium from chemically
treated lumber
Your risk from these exposures varies,
depending on how often youdo this
type of work. To reduce your exposure
to these chemicals: work in a
well-ventilated area, and work with
approved safety equipment, suchas
dust masks that are specially designed
to filter out microscopic particles.
ALWAYS
PAGE 2 — MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14)
Page 3

Grinding/cutting/drilling of masonry, concrete, metal and
other materials with silica in their composition may give
off dust or mists containing crystalline silica. Silica is a
basic component of sand, quartz, brick clay, granite and
numerous other minerals and rocks. Repeated and/or
substantial inhalation of airborne crystalline silica can
cause serious or fatal respiratory diseases, including
silicosis.In addition, California and some other
authorities have listed respirable crystalline silica as a
substance known to cause cancer. When cutting such
materials, always follow the respiratory precautions
mentioned above.
WARNING
Grinding/cutting/drilling of masonry, concrete, metal and
other materials can generate dust, mists and fumes
containing chemicals known to cause serious or fatal
injury or illness, such as respiratory disease, cancer,
birth defects or other reproductive harm. If you are
unfamiliar with the risks associated with the particular
process and/or material being cut or the composition of
the tool being used, review the material safety data
sheet and/or consult your employer, the material
manufacturer/supplier, governmental agencies such as
OSHA and NIOSH and other sources on hazardous
materials. California and some other authorities, for
instance, have published lists of substances known to
cause cancer, reproductive toxicity,or other harmful
effects.
Control dust, mist and fumes at the source where
possible. In this regard use good work practices and
follow the recommendations of the manufacturers or
suppliers, OSHA/NIOSH, and occupational and trade
associations.Water should be used for dust
suppression when wet cutting is feasible. When the
hazards from inhalation of dust, mists and fumes cannot
be eliminated, the operator and any bystanders should
always wear a respirator approved by NIOSH/MSHA for
the materials being used.
WARNING
SILICOSIS WARNING RESPIRATORY HAZARDS
SILICOSIS/RESPIRATORY WARNINGS
MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14) — PAGE 3
Page 4

LS300P Concrete Pump
Proposition 65 Warning ........................................... 2
Silicosis/Respiratory Warnings ................................ 3
Table Of Contents .................................................... 4
Parts Ordering Procedures ...................................... 5
Safety Information .............................................. 6-11
Specifications ........................................................ 12
Dimensions ............................................................ 13
Important Hand Signals ......................................... 14
General Information .......................................... 15-21
Pump Components ........................................... 22-25
Digital Control Panel Components ................... 26-27
Engine Components .............................................. 28
Inspection ......................................................... 29-31
Setup ..................................................................... 32
Operation .......................................................... 33-38
Maintenance ..................................................... 39-51
Trailer Maintenance .......................................... 52-54
Trailer Guidelines .............................................. 55-69
Appendix — Concrete Mix Information ............. 70-72
Troubleshooting (Pump) ................................... 74-75
Troubleshooting (Engine) ....................................... 76
Troubleshooting (Hydraulic Brakes) ....................... 77
Troubleshooting (Electrical) .............................. 78-79
Control Box Component Locator ........................... 80
Wiring Diagram Control Box (Internal) ................... 81
Hopper Vibrator Locator (Option) .......................... 82
Wiring Diagram Hopper Vibrator (Option) .............. 83
Hydraulic System Locator Diagram ....................... 84
Hydraulic System Diagram .................................... 85
Wiring Diagram Locator 1 (External Control Box) . 86
Wiring Diagram 1 (External Control Box) .............. 87
Wiring Diagram Locator 2 (External Control Box) . 88
Wiring Diagram 2 (External Control Box) .............. 89
TABLE OF CONTENTS
NOTICE
Specifications are subject to change without notice.
PAGE 4 — MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14)
Page 5

PARTS ORDERING PROCEDURES
www.multiquip.com
Ordering parts has never been easier!
If you have an MQ Account, to obtain a Username
parts@multiquip.
To obtain an MQ Account, contact your
Effective:
, 2006
Choose from three easy options:
January 1
st
Best Deal!
Order via Internet (Dealers Only):
Order parts on-line using Multiquip’s SmartEquip website!
■ View Parts Diagrams
■ Order Parts
■ Print Specifi cation Information
Goto www.multiquip.com and click on
Order Parts
to log in and save!
Order via Fax (Dealers Only):
All customers are welcome to order parts via Fax.
Domestic (US) Customers dial:
1-800-6-PARTS-7 (800-672-7877)
Order via Phone:
Non-Dealer Customers:
Contact your local Multiquip Dealer for
parts or call 800-427-1244 for help in
locating a dealer near you.
and Password, E-mail us at:
com.
District Sales Manager for more information.
Use the internet and qualify for a 5% Discount
on Standard orders for all orders which include
complete part numbers.*
Fax your order in and qualify for a 2% Discount
on Standard orders for all orders which include
complete part numbers.*
Domestic (US) Dealers Call:
1-800-427-1244
International Customers should contact
their local Multiquip Representatives for
Parts Ordering information.
Note: Discounts Are Subject To Change
Note: Discounts Are Subject To Change
When ordering parts, please supply:
❒ Dealer Account Number
❒ Dealer Name and Address
❒ Shipping Address (if different than billing address)
❒ Return Fax Number
❒ Applicable Model Number
❒ Quantity, Part Number and Description of Each Part
NOTICE
All orders are treated as Standard Orders and will
ship the same day if received prior to 3PM PST.
WE ACCEPT ALL MAJOR CREDIT CARDS!
MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14) — PAGE 5
❒ Specify Preferred Method of Shipment:
✓ UPS/Fed Ex ✓ DHL
■ Priority One ✓ Tr uck
■ Ground
■ Next Day
■ Second/Third Day
Page 6
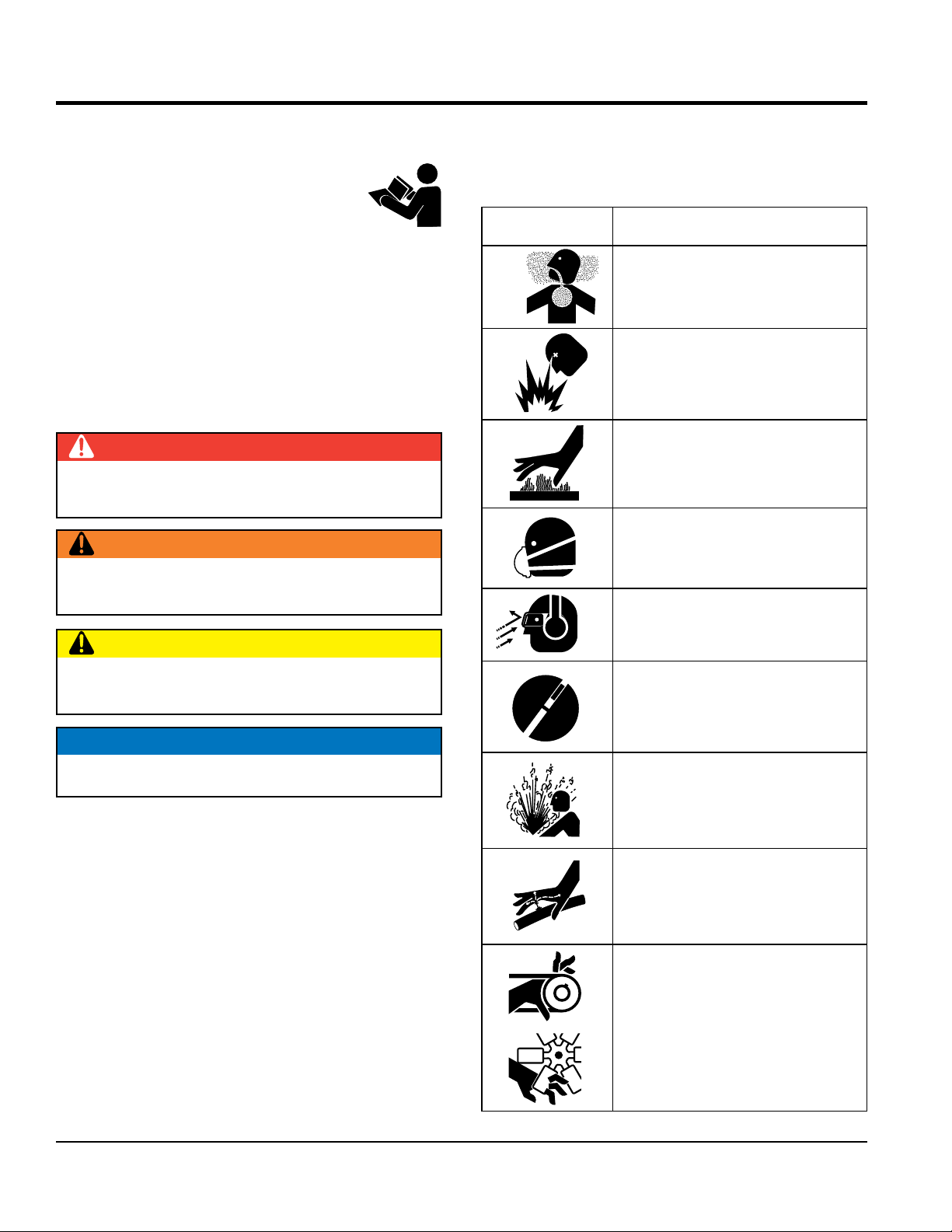
SAFETY INFORMATION
Do not operate or service the equipment before reading
the entire manual. Safety precautions should be followed
at all times when operating this equipment.
Failure to read and understand the safety
messages and operating instructions could
result in injury to yourself and others.
SAFETY MESSAGES
The four safety messages shown below will inform you
about potential hazards that could injure you or others. The
safety messages specifi cally address the level of exposure
to the operator and are preceded by one of four words:
DANGER, WARNING, CAUTION
SAFETY SYMBOLS
Potential hazards associated with the operation of this
equipment will be referenced with hazard symbols which
may appear throughout this manual in conjunction with
safety messages.
DANGER
Indicates a hazardous situation which, if not avoided,
WILL result in DEATH or SERIOUS INJURY.
WARNING
Indicates a hazardous situation which, if not avoided,
COULD result in DEATH or SERIOUS INJURY.
CAUTION
Indicates a hazardous situation which, if not avoided,
COULD result in MINOR or MODERATE INJURY.
or NOTICE.
Symbol Safety Hazard
Lethal Exhaust Gas Hazards
Explosive Fuel Hazards
Burn Hazards
Respiratory Hazards
Eye and Hearing Hazards
OFF
Accidental Starting Hazards
NOTICE
Addresses practices not related to personal injury.
PAGE 6 — MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14)
Pressure Hazards
Hydraulic Fluid Hazards
Rotating Parts Hazards
Page 7
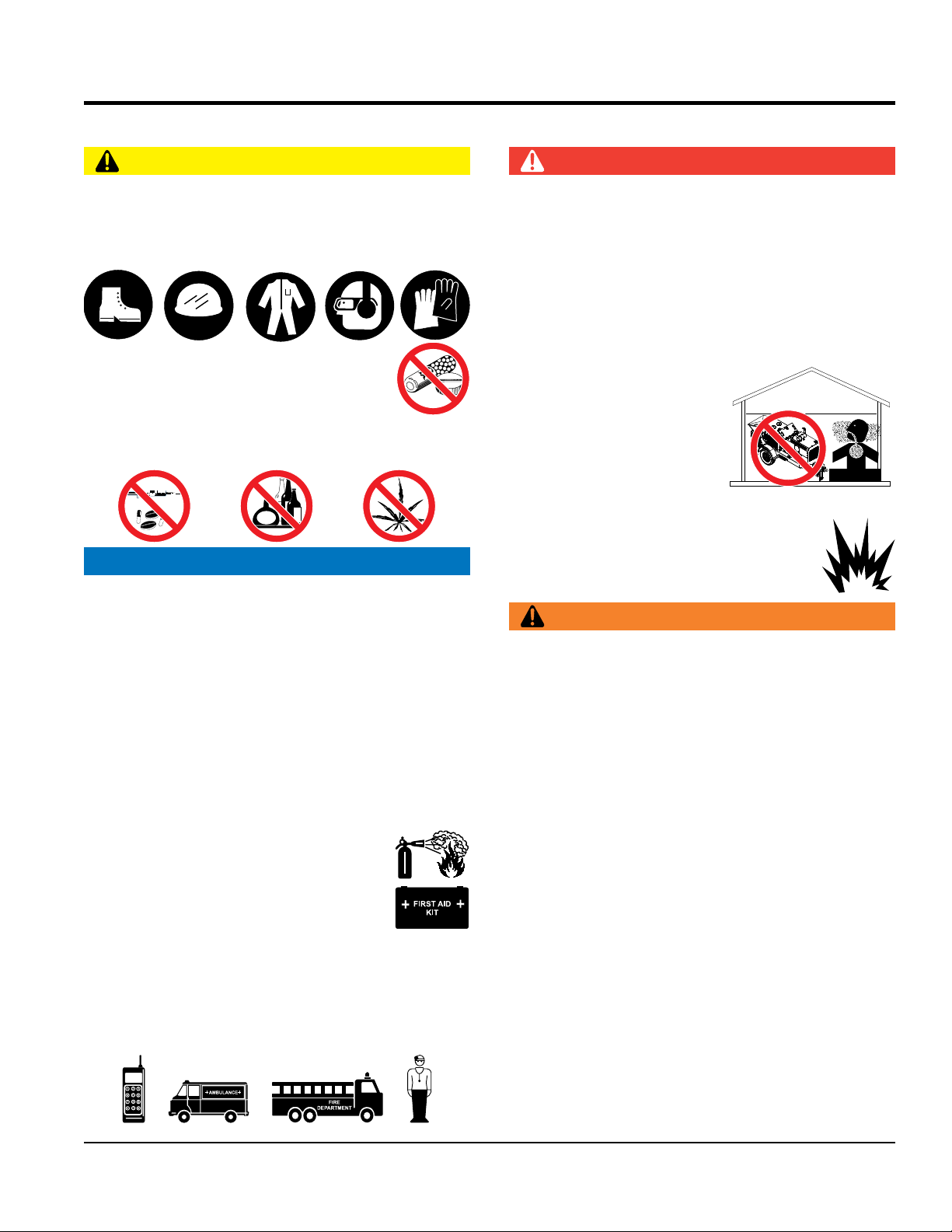
SAFETY INFORMATION
GENERAL SAFETY
PUMP SAFETY
pump volatile, explosive, fl ammable or low fl ash
The engine fuel exhaust gases contain poisonous carbon
monoxide. This gas is colorless and odorless, and can
The engine of this equipment requires an adequate free
operate this equipment in any
pump corrosive chemicals or water containing
toxic substances. These fl uids could create serious
health and environmental hazards. Contact local
operate the pump with closed discharge hose.
The liquid could reach boiling temperatures, build
emergency or safety devices.
These devices are intended for operator safety.
Disconnection of these devices can cause severe injury,
bodily harm or even death. Disconnection of any of these
CAUTION
NEVER operate this equipment without proper protective
clothing, shatterproof glasses, respiratory protection,
hearing protection, steel-toed boots and other protective
devices required by the job or city and state regulations.
NEVER operate this equipment when not
feeling well due to fatigue, illness or when
under medication.
NEVER operate this equipment under the infl uence of
drugs or alcohol.
NOTICE
This equipment should only be operated by trained and
qualifi ed personnel 18 years of age and older.
DANGER
NEVER
point fl uids. These fl uids could ignite or explode.
cause death if inhaled.
fl ow of cooling air. NEVER
enclosed or narrow area
where free fl ow of the air is
restricted. If the air fl ow is
restricted it will cause injury
to people and property and
serious damage to the
equipment or engine.
NEVER operate the equipment in an explosive
atmosphere or near combustible materials. An
explosion or fi re could result causing severe
bodily harm or even death.
WARNING
DANGEROUS
GAS FUMES
Whenever necessary, replace nameplate, operation and
safety decals when they become diffi cult read.
Manufacturer does not assume responsibility for any
accident due to equipment modifi cations. Unauthorized
equipment modifi cation will void all warranties.
NEVER use accessories or attachments that are not
recommended by Multiquip for this equipment. Damage
to the equipment and/or injury to user may result.
ALWAYS know the location of the nearest
fi re extinguisher.
ALWAYS know the location of the nearest
fi rst aid kit.
ALWAYS know the location of the nearest phone or keep
a phone on the job site. Also, know the phone numbers
of the nearest ambulance, doctor and fi re department.
This information will be invaluable in the case of an
emergency.
NEVER
authorities for assistance.
NEVER
pressure, and cause the casing to rupture or explode.
NEVER disconnect any
devices will void all warranties.
MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14) — PAGE 7
Page 8
CAUTION
NEVER lubricate components or attempt service on a
Refer to the Perkins Engine Owner's Manual for engine
technical questions or information recommended by
Multiquip for this equipment. Damage to the equipment
remove the ignition key when leaving the pump
block the wheels on the unit when using on
use properly rated hoses and clamps — 1500
allow the pump a proper amount of time to
Fix damage to machine and replace any broken parts
store equipment properly when it is not being
used. Equipment should be stored in a clean, dry location
out of the reach of children and unauthorized personnel.
place hands or fingers inside engine
operate the engine with heat shields or
running machine.
NEVER block or restrict flow from discharge hose.
Remove kinks from discharge line before starting pump.
Operation with a blocked discharge line can cause water
inside pump to overheat.
DO NOT operate this equipment unless the hopper grate,
guards and safety devices are attached and in place.
CAUTION must be exercised while servicing this
equipment. Rotating and moving parts can cause injury
if contacted.
Keep hands out of the hopper when the engine is
running.
NOTICE
In winter drain water from the lubrication box to prevent
freezing.
ALWAYS be sure the operator is familiar with proper
safety precautions and operation techniques before
using pump.
Keep all inexperienced and unauthorized people away
from the equipment at all times.
Before start-up, check the hopper and remove all foreign
matter and debris.
DO NOT use worn or damaged hose couplings, inspect
all hoses and couplings for wear. Replace any worn or
defective hose or couplings immediately.
Unauthorized equipment modifications will void all
warranties.
Check all fasteners periodically for tightness. Also check
towing tongue bolt, lock nut and wheel lug nuts for wear.
Test the pump's emergency stop switch. The purpose
of this test is to shut down the engine in the event of an
emergency.
SAFETY INFORMATION
and or injury to user may result.
ALWAYS
unattended.
ALWAYS
a slope.
ALWAYS
PSI or higher.
ALWAYS
cool before servicing.
ALWAYS keep the machine in proper running condition.
ALWAYS ensure pump is on level ground before use.
immediately.
ALWAYS
ENGINE SAFETY
WARNING
DO NOT
compartment when engine is running.
NEVER
guards removed.
DO NOT remove the engine oil drain plug
while the engine is hot. Hot oil will gush
out of the oil tank and severely scald any
persons in the general area of the pump.
CAUTION
NEVER touch the hot exhaust manifold,
muffl er or cylinder. Allow these parts to cool
before servicing equipment.
PAGE 8 — MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14)
Page 9
NOTICE
FUEL SAFETY
BATTERY SAFETY
drop the battery. There is a possibility that the
keep the battery charged. If the battery is not
charge battery if frozen. Battery can explode.
When frozen, warm the battery to at least 61°F (16°C).
recharge the battery in a well-ventilated
environment to avoid the risk of a dangerous concentration
If the battery liquid (dilute sulfuric acid) comes into
, rinse eyes immediately with plenty
of water and contact the nearest doctor or hospital to
NEGATIVE battery terminal
keep battery cables in good working condition.
SAFETY INFORMATION
NEVER run engine without an air fi lter or with a dirty air
fi lter. Severe engine damage may occur. Service air fi lter
frequently to prevent engine malfunction.
NEVER tamper with the factory settings
of the engine or engine governor. Damage
to the engine or equipment can result
if operating in speed ranges above the
maximum allowable.
DO NOT start the engine near spilled fuel or combustible
fl uids. Fuel is extremely fl ammable and its vapors can
cause an explosion if ignited.
ALWAYS refuel in a well-ventilated area, away from
sparks and open fl ames.
ALWAYS use extreme caution when working with
fl ammable liquids.
DO NOT fi ll the fuel tank while the engine is running
or hot.
DO NOT overfi ll tank, since spilled fuel could ignite if it
comes into contact with hot engine parts or sparks from
the ignition system.
Store fuel in appropriate containers, in well-ventilated
areas and away from sparks and fl ames.
NEVER use fuel as a cleaning agent.
DO NOT smoke around or near the
equipment. Fire or explosion could result
from fuel vapors or if fuel is spilled on a
hot engine.
DANGER
DANGER
DO NOT
battery will explode.
DO NOT expose the battery to open fl ames,
sparks, cigarettes, etc. The battery contains
combustible gases and liquids. If these
gases and liquids come into contact with a
fl ame or spark, an explosion could occur.
WARNING
ALWAYS wear safety glasses when
handling the battery to avoid eye irritation.
The battery contains acids that can cause
injury to the eyes and skin.
Use well-insulated gloves when picking up
the battery.
ALWAYS
charged, combustible gas will build up.
DO NOT
ALWAYS
of combustible gases.
If the battery liquid (dilute sulfuric acid)
comes into contact with clothing or skin,
rinse skin or clothing immediately with
plenty of water.
contact with eyes
seek medical attention.
MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14) — PAGE 9
CAUTION
ALWAYS disconnect the
before performing service on the equipment.
ALWAYS
Repair or replace all worn cables.
Page 10

TRANSPORTING SAFETY
CAUTION
TOWING SAFETY
Check the tire air pressure on both towing vehicle and
Trailer tires should be infl ated to 80 psi cold.
safety
attach trailer’s safety chains to towing
make sure the vehicle and trailer directional,
backup, brake and trailer lights are connected and
unless
posted otherwise. Recommended off-road towing is not
Avoid sudden stops and starts. This can cause skidding,
or jack-knifi ng. Smooth, gradual starts and stops will
Trailer should be adjusted to a level position at all times
Raise and lock trailer wheel stand in up position when
rolling
underneath the trailer’s bumper
Use the trailer’s swivel jack to adjust the trailer height to
SAFETY INFORMATION
trailer.
Also check the tire tread wear on both vehicles.
NEVER allow any person or animal to stand underneath
the equipment while lifting.
NOTICE
Before lifting, make sure that the equipment parts are not
damaged and screws are not loose or missing.
ALWAYS make sure forklift forks are inserted into pockets
(if applicable) as far as possible when lifting the pump.
ALWAYS shutdown engine before transporting.
NEVER lift the equipment while the engine is running.
Tighten fuel tank cap securel to prevent fuel from spilling.
Use one point suspension hook and lift straight upwards.
DO NOT lift machine to unnecessary heights.
ALWAYS tie down equipment during transport by
securing the equipment with straps, rope or chains.
CAUTION
Check with your local county or state safety
towing regulations, in addition to meeting
Department of Transportation (DOT)
Safety Towing Regulations, before towing
your generator.
In order to reduce the possibility of an accident while
transporting the generator on public roads, ALWAYS
make sure the trailer that supports the pump and the
towing vehicle are mechanically sound and in good
operating condition.
ALWAYS shutdown engine before transporting
Make sure the hitch and coupling of the towing vehicle
are rated equal to, or greater than the trailer “gross
vehicle weight rating.”
ALWAYS inspect the hitch and coupling for wear. NEVER
tow a trailer with defective hitches, couplings, chains, etc.
ALWAYS make sure the trailer is equipped with a
chain.
ALWAYS properly
vehicle.
ALWAYS
working properly.
DOT Requirements include the following:
• Connect and test electric brake operation.
• Secure portable power cables in cable tray with tie
wraps.
The maximum speed for highway towing is 55 MPH
to exceed 15 MPH or less depending on type of terrain.
improve towing.
Avoid sharp turns to prevent rolling.
when towing.
towing.
Place chock blocks underneath wheel to prevent
while parked.
Place support blocks
to prevent tipping while parked.
a level position while parked.
PAGE 10 — MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14)
Page 11

ENVIRONMENTAL SAFETY/DECOMMISSIONING
Decommissioning is a controlled process used to safely
retire a piece of equipment that is no longer serviceable.
If the equipment poses an unacceptable and unrepairable
safety risk due to wear or damage or is no longer cost
effective to maintain (beyond life-cycle reliability) and is to
be decommissioned (demolition and dismantlement),be
sure to follow rules below.
EMISSIONS INFORMATION
The diesel engine used in this equipment has been
designed to reduce harmful levels of carbon monoxide
(CO), hydrocarbons (HC) and nitrogen oxides (NOx)
This engine has been certifi ed to meet US EPA Evaporative
Attempting to modify or make adjustments to the engine
emission system by unauthorized personnel without proper
training could damage the equipment or create an unsafe
Additionally, modifying the fuel system may adversely affect
evaporative emissions, resulting in fi nes or other penalties.
The emission control label is an integral part of the emission
If a replacement emission label is needed, please contact
SAFETY INFORMATION
NOTICE
DO NOT pour waste or oil directly onto the ground, down
a drain or into any water source.
Contact your country's Department of
Public Works or recycling agency in your
area and arrange for proper disposal of
any electrical components, waste or oil
associated with this equipment.
When the life cycle of this equipment is over, remove
battery and bring to appropriate facility for lead
reclamation. Use safety precautions when handling
batteries that contain sulfuric acid.
When the life cycle of this equipment is over, it is
recommended that the trowel frame and all other metal
parts be sent to a recycling center.
Metal recycling involves the collection of metal from
discarded products and its transformation into raw
materials to use in manufacturing a new product.
Recyclers and manufacturers alike promote the process
of recycling metal. Using a metal recycling center
promotes energy cost savings.
NOTICE
contained in diesel exhaust emissions.
emissions requirements in the installed confi guration.
condition.
Emission Control Label
system and is strictly controlled by regulations.
The label must remain with the engine for its entire life.
your authorized Perkins Engine Distributor.
MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14) — PAGE 11
Page 12
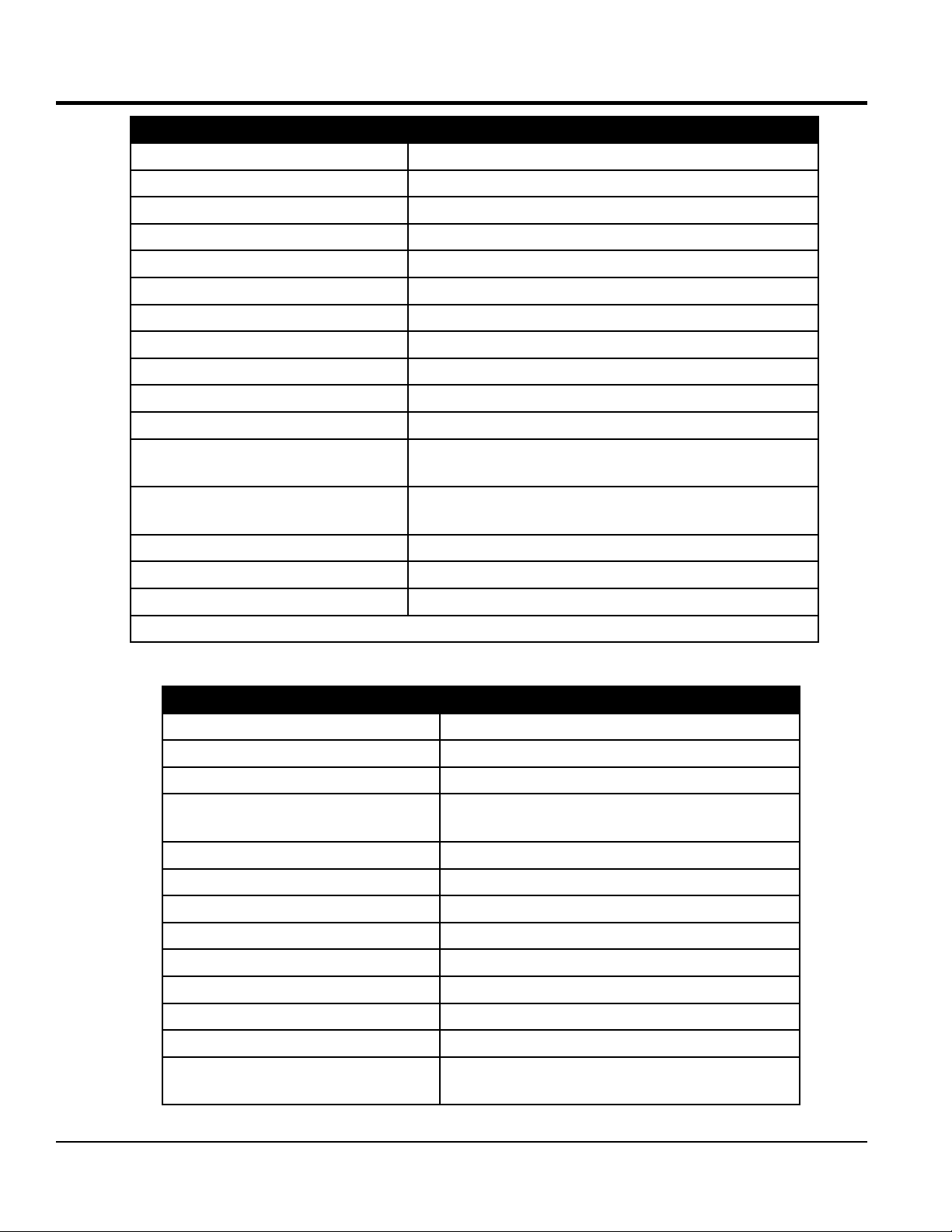
SPECIFICATIONS
Table 1. Pump Specifications
Model LS300P
Pumping Rate Up to 30 cu. yds. per hour*
Pumping Method Reciprocating Piston
Maximum Aggregate Size 1-1/2 in. minus (38 mm)
Vertical Pumping Height Up to Excess of 200 ft. (60.9 m)
Piston Face Pressure 800 PSI (55.16 bar)
Horizontal Pumping Distance 800 ft. (243m)*
Cylinder Lubrication Box Capacity 2 Gallons (7.6 Liters)
Hydraulic Fluid Capacity 33 Gallons (125 Liters)
Fuel Tank Capacity 16 Gallons (61 Liters)
Hopper Capacity 10 cu. ft.
Material Hose
Engine Model
Weight (with fluids) 3,750 lbs. (1,701 kg)
Tire Size ST 225/75 R15
Options Wireless Remote Control, Hopper Screen Vibrator
* Volume output will vary depending on mix design, slump, line size used and job site conditions
Table 2. Engine Specifications
Model Perkins Turbo Diesel 404D-22TA
Type 4 stroke, Water-Cooled Diesel
No. of Cylinders 4
Bore x Stroke
Rated Output 64.2 HP@ 2400 rpm
Displacement 135.2 cu. in. (2.2 L)
3 in., 4 in., 5 in. dia.
(76.2mm, 101.6 mm, 127 mm)
Perkins Turbo
Diesel 404D-22TA
3.31 in. x 3.94 in.
(84 mm x 100 mm)
Starting Electric 12VDC
Lube Oil Capacity 9.4 qt. (8.9 liters)
Coolant Capacity/With Radiator 3.8 qt. (3.8 liters)
Fuel Type #2 Diesel Fuel
Battery 12V BCI Group 27
Weight Dry 1,250 lbs. (567 kg)
Dimensions LxWxH in. (mm)
PAGE 12 — MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14)
50 x 28.9 x 37.9
(1,269 x 734 x 964)
Page 13
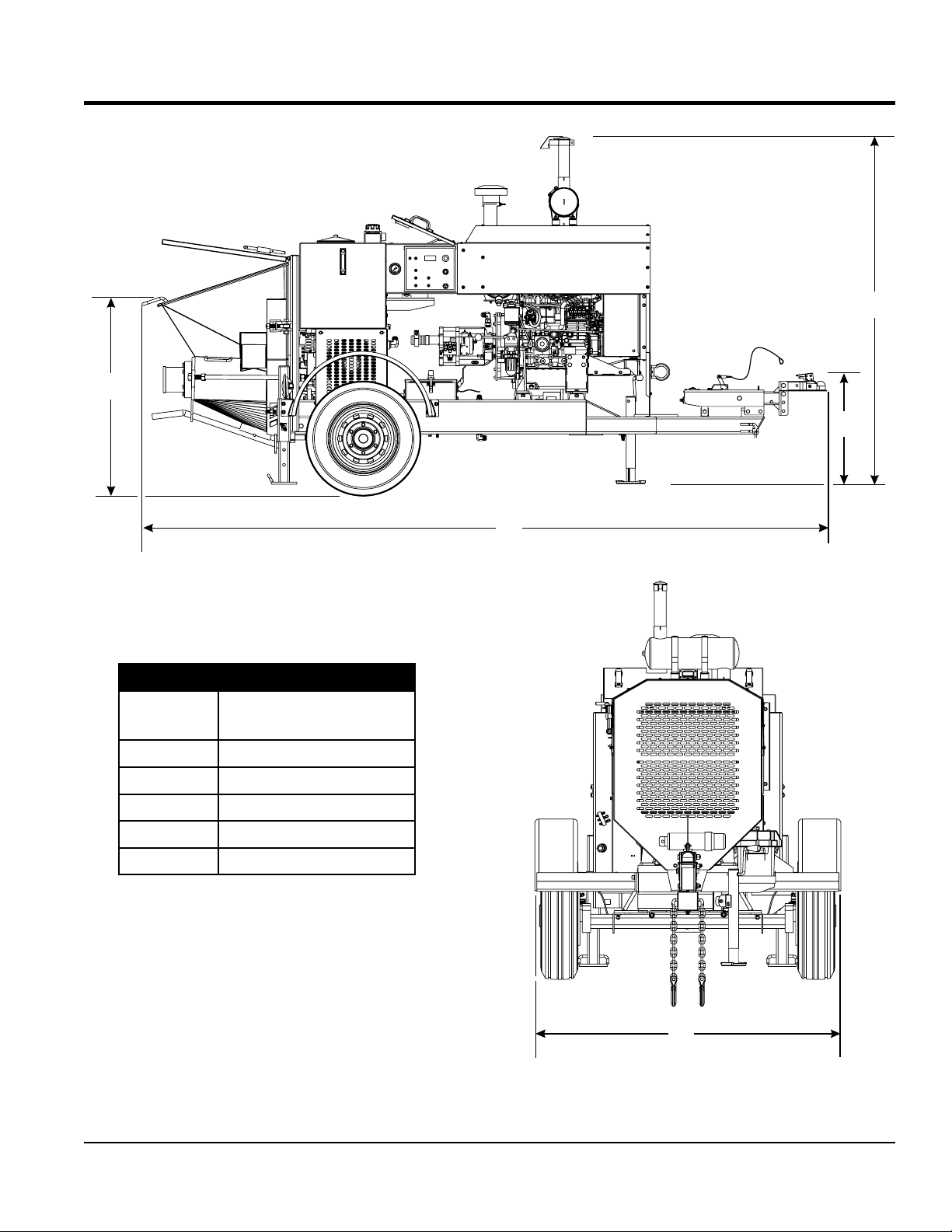
B
DIMENSIONS
C
D
A
Table 3. Pump Dimensions
Reference
Letter
A 158 (4,013.2)
B 44 (1,117.6)
C 81 (2,057.4)
D 21.5 (546.1)
E 63.5 (1,612.9)
Dimensions in. (mm)
E
Figure 1. Dimensions
MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14) — PAGE 13
Page 14
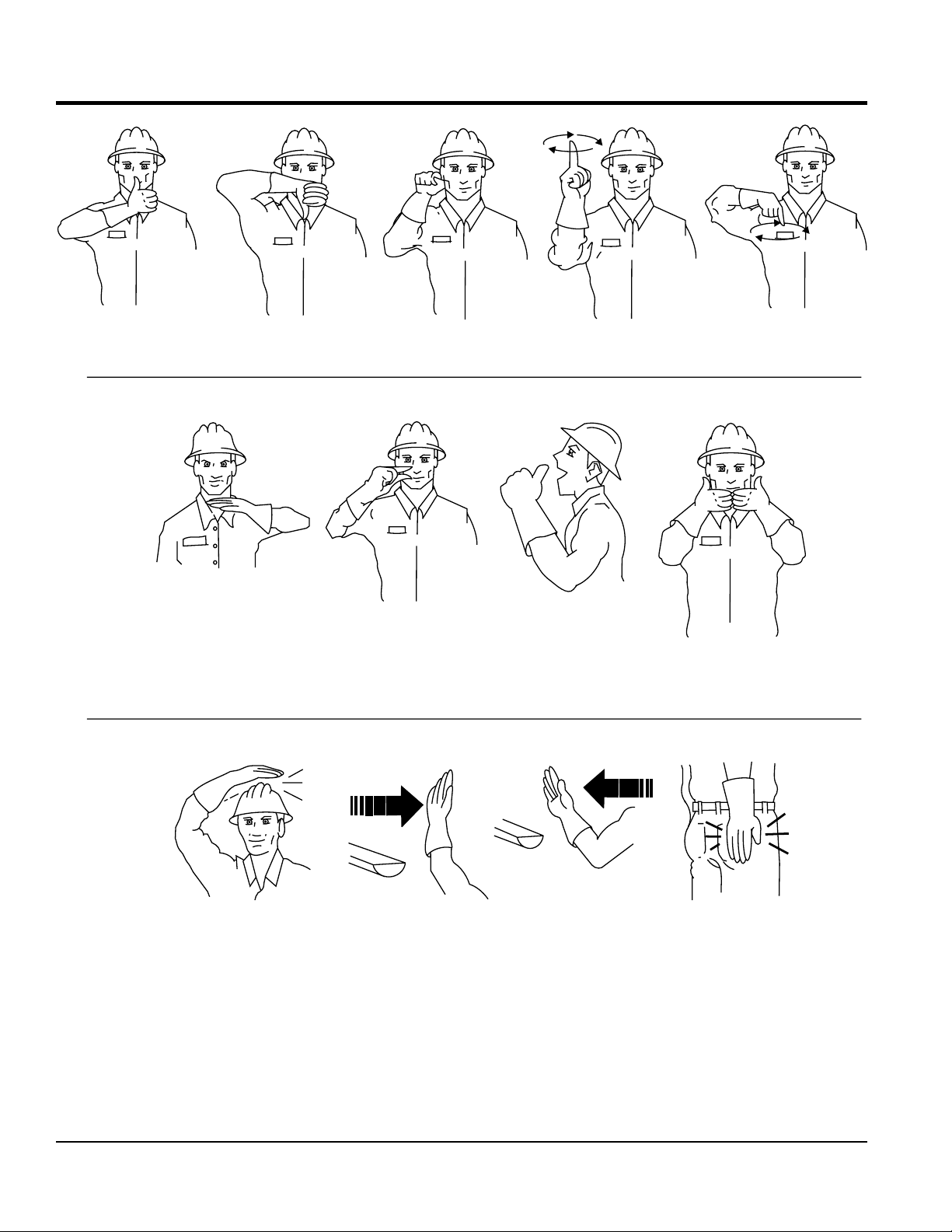
IMPORTANT HAND SIGNALS
CHUTE UP CHUTE DOWN
STOP PUMP LITTLE BIT
STOP START PUMP
SPEED UP
ADD WATER
4-GALLONS
SLOW PUMP
DOWN
ALL DONE
CLEAN-UP
DRIVE IN BACK UP
Figure 2. Operation Hand Signals
PULL FORWARD
BACK IN
PAGE 14 — MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14)
Page 15

GENERAL INFORMATION
CONCRETE MIX DESIGN
Mix design is most important to achieve maximum
pumpability. Pumpability is affected by, among other
factors, the type and gradation of aggregate used. Natural
aggregates make a more workable mix and pump more
readily than crushed aggregates. A blend of natural and
crushed aggregates will produce a workable mix. The
type and gradation of aggregates is equally important
for workability as the size and percentage of coarse
aggregates in the mix.
The term “aggregates” describes all of the solid materials,
from the largest rock to the smallest grain of sand,
contained in the concrete mix.
Concrete mixes with a consistency as dry as one-inch
slump and as wet as ten-inch slump have been pumped;
but for maximum efficiency from the pump, a slump ranging
from two to six inches will produce a more workable mix
than one that contains more or less water.
The principle of concrete pumping is based on selflubrication. As it moves through the transfer line, the
concrete takes the shape of a plastic cylinder. It is forced
through the transfer line on a film of mortar that is selftroweled to the service of the transfer line around its full
periphery by the slug of concrete itself.
A slump rating should be used with discretion; it is not
always a real indication of the pumpability of the mix. The
concrete may be workable in the sense that it will readily
flow into place, but the same mix may not respond to
pressure.
Overly wet mixes tend to separate. In addition to affecting
the strength and quality of the concrete, the delivery
system will not tolerate separation. Overly dry mixes are
similarly unsatisfactory if they lack plasticity and tend to be
crumbly. To be properly pumped, the mix must be able to
continuously coat the inside of the line with a lubricating
seal of mortar.
3. By getting a rock pocket, such as mixer tailings, into the
pump valve. This rock pocket will have an insufficient
coating of mortar and the mix will not be plastic enough
to allow the valve to operate or the mix to move in the
line.
4. Through excessive bleeding. If the mix is short or fines,
but the sand is otherwise fairly well graded, bleeding
will not normally create any problems as long as the
pump continues operation. But, if the pump is shut
down, bleeding can result in a loss of lubrication and
blocked erratic flow.
The above are bad concrete practices, regardless of how
the mix is to be placed. But, these points do show that
special mixes are not always needed, within limits, for
pumping concrete. Good aggregate gradation is most
important to pump concrete the maximum distance.
The use of admixtures can have a beneficial effect on
pumpability. Most of the dispersing agents will fatten,
retard bleeding, and increase workability. Thus, the average
concrete can be pumped for appreciably longer distances.
Air entraining agents will also improve workability, although
they cannot be used as a substitute for good gradation of
the aggregate.
Pumping will not appreciably affect the final air content of
the mix. High-early cement tends to give a more readily
pumpable mix with superior water retaining qualities.
However, if delays are likely to occur, extra care must be
exercised due to the faster setting time over regular cement.
The Mayco LS300P will pump a wide variety of concrete
pump mixes. But, there are guidelines that must be followed.
Use this information in conjunction with the Operation
section of this manual.
There are four ways in which this seal can be lost:
1. By pumping excessively wet mixes which do not have
enough cohesion to hold together.
2. By pumping harsh undersanded concrete with poorly
graded aggregates which can jam together when the
pressure becomes too great for the insufficient amount
of sand to hold the aggregates apart.
MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14) — PAGE 15
Page 16
GENERAL INFORMATION
REGIONAL DIFFERENCES
Concrete is made by mixing locally available rock and sand
with cement and water. For this reason there are great
differences in the pumpability of concrete from one region
of the country to another.
It is impossible to define a specific mix for each region that
the concrete pump be will working in. Therefore, the mixes
listed in Appendix - Concrete Mix Information will provide
a basic guideline for establishing the proper mix design
for your area.
Use this information to specify your requirements to your
local ready-mix batch plant, contractor and civil engineer.
It may take minor adjustments to make a mix pumpable,
so you should explain your needs.
The elements that have to be controlled and consistently
maintained by the batch plant are:
1. The sizing and mix percentage of rocks, gap graded
from the largest down through the smallest sizes.
2. Sand with a sieve analysis that has the proper
percentage of fines, ASTM C33 spec.
3. Sufficient cement to produce the required design
strength of the concrete and provide the lubricating
binder to pump the concrete through the delivery
system.
Use a minimum of:
In addition, this Mayco Concrete Pump can be used to
pump a large aggregate hard rock as follows:
Pea rock (1/2" minus) pump with mixes being as low as
30% rock and 70% sand. (reference maintenance for
recommendations on cleaning the pump.)
Shortening pea rock when used with an air compressor
and nozzle.
“Mud Jacking”, high pressure grouting.
PUMPING INFORMATION
Remixtures
Remixtures that are designed into the concrete mix by
the redi-mix company or an architectural engineering
company. This section lists common admixtures and a brief
explanation of their functions:
1. Pozzolith 300 — Or the equivalent acts as a water
retarder and a lubricant. On a lean mix, long pushes,
stiff mixes, and vertical pushes, Pozzolith 300R helps
pumpability.
2. MBVR — Air entraining, acts as a lubricant.
3. Calcium Chloride — Commonly referred to as C.C.,
is used as an accelerator. When pumping a load with
calcium chloride, it is recommended that you wash out
if the waiting time between delivery trucks becomes
too long.
500 lbs. of cement/cu yd for 2500 p.s.i. concrete after
28 days.
530 lbs. of cement/cu yd for 3000 p.s.i. concrete after
28 days.
600 lbs. of cement/cu yd for 4000 p.s.i. concrete after
28 days.
4. Admixture pump-aid if necessary.
5. The proper amount of water to make a workable slump
and plasticize the mix.
PAGE 16 — MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14)
4. Super Plasticizers — Acts as an accelerator. The
concrete will look very wet after the super plasticizer
is added, but will begin to set up very fast. Wash out
immediately if you do not have a truck waiting. Super
plasticizers are used mainly on commercial jobs.
5. Red Label — Acts as a water retarder and an
accelerator. Red label will be used mainly on
commercial jobs.
6. Fly Ash — Is used to help increase the strength of the
concrete and decrease the cement content per yard.
This is one of the most common admixtures used.
NOTICE
All admixtures will be shown on the redi-mix concrete
ticket. Before starting the pumping job, ask the driver of
the redi-mix truck to see the concrete ticket and note the
admixtures that exist and take the proper action.
Page 17
GENERAL INFORMATION
Downhill Pumping
Downhill pumping can be a difficult procedure on some
jobs. The slurry procedure would be the same as explained
Priming The Pump With Slurry Mixture section of this
manual. It is suggested that a sponge approximately 2”x 4”x
6” in size be placed in the hose before the start of pumping.
Wet the sponge before placing it in the hose to keep the
slurry from running too far ahead of the concrete, which
will reduce the possibility of separation. When the pump is
stopped, the material can flow slowly down, due to gravity,
and cause the hose to collapse.
When pumping is resumed, you can expect blockage at
the point of hose collapse. To prevent this from happening,
the hose can be “kinked off” at the discharge end when the
pump is stopped to prevent the gravity flow of the material
in the hose.
The use of stiffer mixes when pumping downhill will
decrease gravity flow of the material in the hose and
will assure a smoother operation between the cam roller
bearing and cam plate. As with any job, make sure that
the hose and the couplings are in good workable shape.
Vertical Pumping
When pumping vertically up the side of a building, above
40 feet, we would recommend the installation of steel pipe
securely fastened at intervals as necessary to support the
pipe. Ninety degree, long radius pipe sweeps should be
installed at the top and bottom of the steel line.
NOTICE
It is strongly recommended that steel pipe be used on all
vertical pumping for safety and convenience.
Hose Pulsation
A slight pulsation of the hose will always be noticeable near
the pump. Excessive pulsation of the hose near the pump is
normally due to higher than average line pressures caused
by stiff, harsh mixes, or extremely long pumping distances.
The use of 2 -1/2” I.D. hose in these extreme cases reduces
line pressures or the addition of slight amounts of water
to the mix, if permissible, will permit easier pumping. The
use of certain pumping admixtures may help.
If excessive pulsation exists in the hose, it is advisable to
use burlap or some means of wear protection under the
hose at points where the hose may wear through the outer
cover; e.g. over forms, steel or sharp curbs.
Snap-Joint Couplings
When using Snap-Joint couplings with gaskets to join hose,
see that they are washed clean after each job. Keeping the
hose ends clean (heavy duty) is very important for the best
job setup. A thin coat of grease on the rubber gasket or
dipping both coupling and gasket in water before coupling
the hose will make for easier installation.
Use a 25 ft. hose, or short section, off the pump; and for the
balance of the horizontal distance to the vertical line, use
steel pipe. This type of installation has been satisfactory on
many jobs being pumped in excess of 100 feet high. Line
pressures are always less using steel pipe as compared
to hose.
When pumping vertically, using all hose, it is recommended
not to go higher than 50 feet with hose. The hose should be
tied off at intervals of 10 feet, if possible. Special attention
should be given when tieing the hose off at the top as
the hose will have a tendency to stretch when filled with
concrete. This will increase the possibility of a blockage at
the point where the hose is tied off. To avoid this, a long
radius of 90° elbow is recommended. The suggested place
to tie off is on the hose, under the clamp.
MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14) — PAGE 17
Page 18

GENERAL INFORMATION
Fill the hopper with water after making sure that all sand and
rock have been removed from manifold. Operate pump at
full throttle and the 3/8" diameter hole restriction will create
sufficient back pressure to make thorough inspection of all
moving parts.
The Effects Of Heat And Excessive Time On
Concrete:
Hot concrete, commonly referred to as a hot load, is
concrete that has been in the redi-mix truck in excess of 2
to 3 hours. On a hot day, this amount of time is even less.
A brief explanation of why heat and time affect concrete:
Concrete starts setting by drying up through a chemical
reaction. The catalyst to this reaction is heat. When
pumping a hot load, it is important to remember that when
you have to stop pumping for any reason, add water to the
concrete in the hopper and hand mix and move concrete in
the hose every 5 minutes. If the shut down time becomes
too long, wash out immediately.
If it is necessary to wait 1/2 hour or more for another load
of concrete, to prevent setting of the mix in the system, it
is advisable to consider the following factors (A through D)
affecting the concrete:
3. If it is necessary to wait 10 minutes or more for another
load of concrete, it is wise to start the pump and pump
6 or 8 strokes every 5 minutes to prevent setting of the
mix in the system. If waiting time is excessive, it would
be wise to wash out the pump and hoses and start over
when the new truck arrives.
4. When pumping stiff mixes and there is waiting time
between redi-mix trucks, it is advisable to add some
water to the last hopper of material and “hand mix” to
ensure an easier start with the following load.
5. When the pumping job requires a stiffer mix, the
following method is suggested for starting: Take a water
hose with a nozzle on it and apply water with a fine
spray to the concrete as it comes down the redi-mix
chute into the pump hopper after the slurry procedure
is completed and you are ready to start pumping.
6. Using this procedure will make it easier to pump
through the clean hose.
NOTICE
Once the concrete has reached the end of the hose,
DO NOT apply any more water in this manner as this
procedure is used for starting only.
How old is the concrete?
Is there an accelerator, calcium chloride, red label, etc.,
in the concrete?
The temperature of the day, 80, 90, degrees?
How much system you have out and how stiff was the
mix you were pumping?
Preventing Mix Set-Up After Pump Shutdown
When the pump is stopped for any reason during a pour;
e.g., moving hose, waiting for redi-mix truck, the following
suggestions are offered:
1. Leave the hopper full of concrete at the time of
shutdown. It is important not to let the redi-mix driver
wash too much water into the hopper, as this could
cause separation of the concrete in the hopper.
2. If the shutdown period exceeds 2 to 3 minutes, turn
off the engine so the vibration does not separate the
mix in the hopper which can cause a blockage in the
manifold when the pump is started.
7. Hose sizing is very important: We strongly recommend
on harsh mixes, vertical pushes, stiff concrete,
shotcrete, long pushes, that a 2-1/2” line be used as
far as possible. The advantages of using the 2-1/2” line
are improved pumpability, less pumping pressure and
less wear on the pump.
8. Following the pump operation, proper wash out of all
materials or “build-up” within the pump manifold and
hoses will prevent problems when starting the next job.
9. A thorough inspection of the drive components and
greasing of all bearings after each job will ensure
adequate lubrication and service to the pump which
is normally operating in wet, gritty conditions.
NOTICE
Over-greasing any bearing on your Mayco pump will not
damage the bearing.
PAGE 18 — MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14)
Page 19
GENERAL INFORMATION
Clearing The System After Mix Set Up
If, for any reason, the mix should set up in the system, the
following procedure is suggested:
1. Disconnect the hose from the pump and wash the
pump out immediately.
WARNING
Hose Line Pressure
When disconnecting hoses, use extreme CAUTION.
The hose is under pressure. Hose could whip and cause
severe bodily harm.
2. Reconnect the hose and fill the hopper with water.
3. Reconnect the hose and fill the hopper with water. DO
NOT try to push all the concrete out of all of the hose
lines at one time.
4. For example: If you had 200 ft. of system out, you
would disconnect each hose. Clean it out by pushing
water through the first hose connected the pump, then
continue progressing through all the hoses, until all the
system is clean.
If a blockage occurs in a hose, walk the hose until you find
the point of trouble. The hose will be soft immediately past
the blockage. To clear the blockage:
1. Disconnect the hose at the first coupling past the
blockage. Be careful when disconnecting hose. Hose
is under pressure. Hose could whip and cause severe
bodily harm.
2. Elevate the hose at that point with the blockage area
hanging down.
3. Using a hammer, you can pound the downstream edge
of the packed area until it is free to flow. Shake all of
the sand and gravel out to the end of the hose.
4. Before reconnecting the hose, start the pump and
run a small amount of concrete out to the end of the
hose. This will assure that all of the separation is out
of the hose.
NOTICE
Damaged hoses with internal restrictions can cause
blockages.
Clearing Shuttle Tube Blockage
5. If waiting time is excessive, it would be wise to wash
out the pump and hoses and start over when the new
truck arrives. This can be avoided by being observant
to the pump and system, also taking into consideration
the above actors (A through D) affecting the mix.
Clearing Concrete Blockage
NOTICE
If you repeatedly pull the throttle all the way out and try
to force your pump to push through blockages due to
separation of material in the hose or manifold, you will
soon have breakdowns and costly repairs which are not
covered under warranty.
If a blockage occurs, find where it is and clear it before
further pumping. DO NOT increase the engine speed to
clear the blockage. Increasing the engine speed will only
compound the problem.
The shuttle tube is plugged if volume at the discharge end
of the hose stops and the hydraulic oil pressure gauge
reads 3200 psi or more.
To clear a plug in the shuttle tube, great care must be taken
as a dangerous condition will exist from pressure build-up
inside the shuttle tube. With the shuttle valve, the concrete
can be pumped in reverse. Use the following procedures
to clear the shuttle tubes.
WARNING
Joint Clamps
DO NOT open any of the delivery system joint clamps
during operation. The clamps are under pressure. The
clamps, if opened during operation could allow high
pressure material to escape and cause severe bodily
harm.
MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14) — PAGE 19
Page 20
GENERAL INFORMATION
Reverse Pumping Procedure
1. Switch the pump into reverse. With pump speed at a
medium-slow (approx. 12 strokes per min.) try to pull
the “pack” back into the hopper with 5 or 6 reverse
strokes.
2. Remix the concrete in the hopper.
3. Switch the pump into forward. If it is still plugged, repeat
“Reversing” procedure three times.
4. If concrete still does not move, proceed to the Shuttle
Tube Inspection Procedure.
Shuttle Tube Inspection Procedure
1. Stop the pump. Turn off the engine.
2. The senior or most experienced operator must warn all
others to stand at least 20 feet away from the machine
and turn their heads to face away from the pump.
3. The operator will position himself beside the reducing
elbow at the pump outlet. Wearing safety glasses, slip
the end of a pry bar (24" length of reinforcing steel rod)
under the latch of the hose clamp and flip it up.
4. Carefully knock the end of the hose away from the
reducer.
5. Chip the concrete out of the reducer with the pry bar.
6. Remove the reducer. From the discharge end, chip
the concrete out of the shuttle tube with the pry-bar.
If concrete cannot be loosened from the outlet of the
shuttle tube, remove the clean-out plug on the bottom
of the hopper to discharge the concrete.
7. Chip the blockage out with the pry-bar.
8. Flush the shuttle tube with water.
9. Before resuming operation of the pump, perform the
“Reverse” Pumping Procedure to relieve pressure on
the shuttle tubes.
WARNING
Transporting
It will be necessary at times to move your pump from
one job site location to another. Before moving the
pump, make sure to pump the remaining concrete out
of the hopper.
Moving the pump with a full hopper of concrete can
cause severe damage or breakage of the axle and
axle springs, excess strain and pressure on the hub
and bearing assembly.
NOTICE
Leaking manifold seals or hose coupling gaskets which
leak water can cause separation and subsequent jamming
at that point.
PAGE 20 — MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14)
Page 21
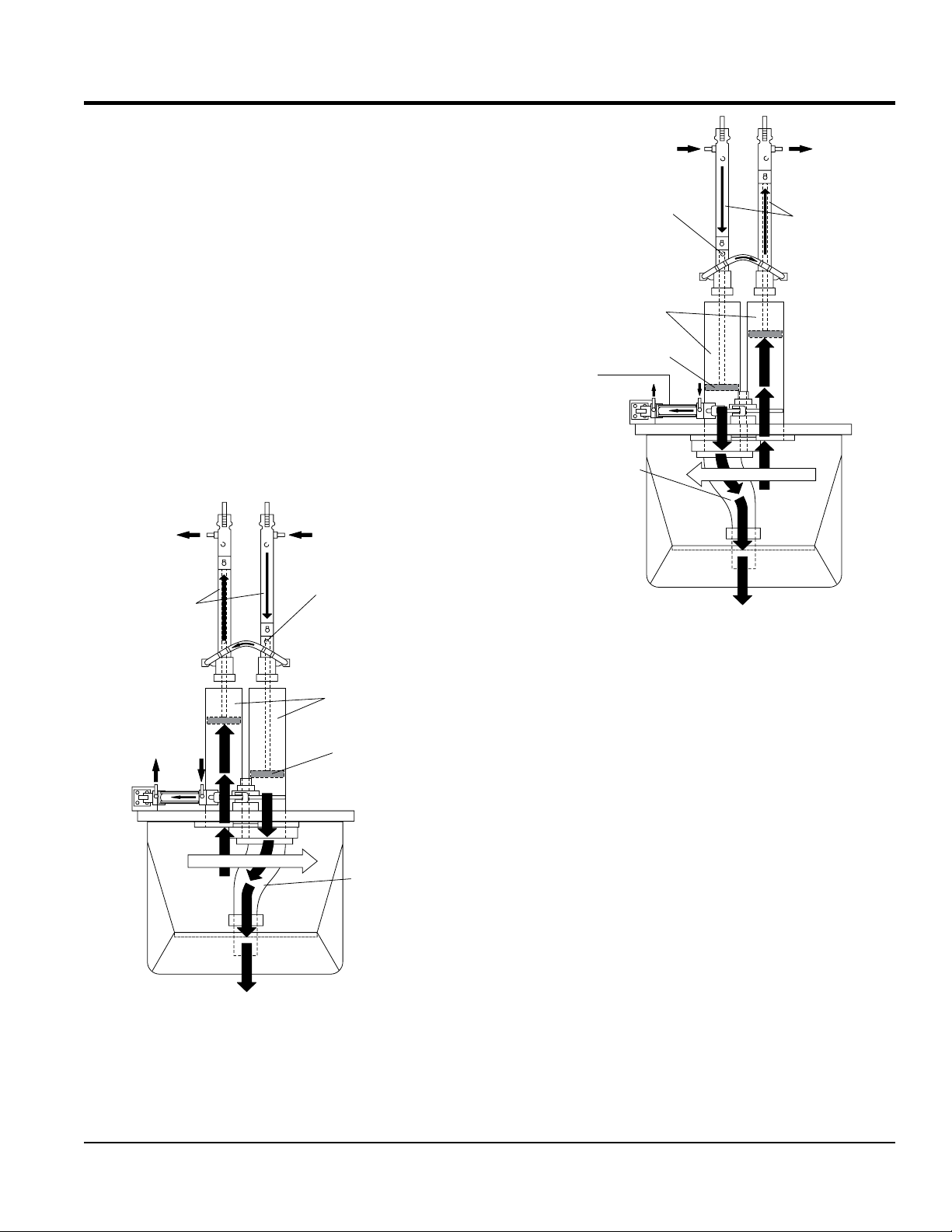
The following is a brief explanation of how the concrete
TUBE
ANK
cylinders, hydraulic cylinders, shuttle tube, valves and
hopper work in sequence to pump concrete.
GENERAL INFORMATION
HIGH PRESSURE
OIL FROM PUMP
TO T
The hydraulic pressure is generated by a variable volume,
pressure compensated, axial piston pump that is driven by
a diesel engine. The rod sides of the drive cylinders are
hydraulically connected together creating a “slave circuit,”
which allows hydraulic oil to transfer from one piston to
the other.
The two part cycling sequence is initiated by an electrical
signal generated by two proximity switches activated by
the drive cylinder. The proximity switches are normally
open, magnetically sensing the movement of the main
drive cylinder. As the drive cylinder piston head passes the
proximity switch, an electrical signal is sent to the solenoid
operated pilot valve which in turn directs pilot oil to the four
valves controlling the drive cylinder and the shuttle cylinder.
TO TANK
HYDRAULIC
CYLINDERS
SLAVE
OIL
A
B
SHUTTLE TUBE MOTION
HIGH PRESSURE
OIL FROM PUMP
PROXIMITY
SWITCH
CONCRETE
CYLINDERS
PISTON
CUP
SHUTTLE
CONCRETE
CYLINDERS
HYDRAULIC
SHUTTLE
CYLINDER
SHUTTLE TUBE
PROXIMITY
SWITCH
PISTON
CUP
SLAVE
OIL
A
SHUTTLE TUBE MOTION
B
B
HYDRAULIC
CYLINDERS
Figure 4. Pumping Cycle 2
In the first cycle (Figure 3), hydraulic pressure is applied
to cylinder (B), causing the hydraulic piston, which is
connected to the concrete piston and piston cup, to
discharge concrete into the delivery line.
As one cylinder is discharging concrete, the hydraulic
oil from the rod side (B) of the drive cylinders is being
transferred through the slave circuit causing the opposite
cylinder (A) to move back on the suction stroke, filling the
cylinder with concrete.
The shuttle tube is sequenced to pivot to each concrete
cylinder as the drive cylinders stroke to push concrete. As
the second cycling sequence begins (Figure 4), the shuttle
tube pivots to the opposite cylinder (A).
The hydraulic piston passes under the proximity switch
and sends pressure to the piston, causing it to stroke
Figure 3. Pumping Cycle 1
and discharge concrete into the delivery line. Hydraulic
oil is transferred through the slave circuit to cylinder (B),
causing it to start a suction stroke, refilling it with concrete.
The pumping sequence then repeats for the duration of
the operation.
MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14) — PAGE 21
Page 22

Table 4.
1
2
15
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
11
13
12
10
14
2
2
PUMP COMPONENTS
Figure 5. Pump Components 1
PAGE 22 — MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14)
Page 23

PUMP COMPONENTS
Figure 5 and 6 illustrates the location of the major
components for the LS300P Concrete Pump. The function
of each component is described below:
1. Tires — This trailer uses two ST205-750 x15E type
tires. Tire inflation pressure is the most important factor
in tire life. Pressure should be checked to 50 psi cold
before operation. DO NOT bleed air from tires when
they are hot. Check inflation pressure weekly during
use to insure the maximum tire life and tread wear.
2. Zerk Grease Fittings — Top fitting lubricates shuttle
cylinder top, center position lubricates nun plate and
bottom position lubricates shuttle cylinder bottom.
3. Hydraulic Oil Sight Glass — Use to determine the
amount of hydraulic oil remaining in tank. The sight
glass also contains a temperature gauge for monitoring
the temperature of the hydraulic oil.
4. Hydraulic Oil Tank/Cap — Remove cap to add
hydraulic fluid. Fill with Shell Oil Tellus 68 or Mobil Oil
DFE26 if level is low.
5. Hydraulic Oil Filter — This in-tank return hydraulic
filter with a 10 micron cleanable filter is designed to
remove all particles large enough to cause wear and
job break down. Under normal conditions, clean every
6 months.
6. Air Filter — Prevents dirt and other debris from
entering the fuel system. Release the latches on the
side of the air filter cover to gain access to filter element.
NOTICE
Operating the engine without an air filter, with a damaged
air filter, or a filter in need of replacement will allow dirt to
enter the engine, causing rapid engine wear
7. Muffler — Used to reduce noise and emissions.
NEVER touch the muffler while it is hot! Serious burns
can result. NEVER operate the engine with the muffler
removed.
8. Radiator — Fill only with recommended coolant.
Radiator coolant capacity is 4.5 gallons (17 liters).
9. Documentation Box — Contains engine and pump
operation, parts and maintenance information.
10. Breakaway Switch/Cable — Used in conjunction with
the hydraulic actuator. Connect to tow vehicle.
11. Tow Hitch Coupler — Requires a 2-inch ball hitch or
a 3-inch pintle. Capable of towing 6,000 lbs.
12. Safety Chains — This pump uses 5/16-inch thick,
72 inches long zinc-plated safety chains. ALWAYS
connect safety chains when towing. ALWAYS cross
chains when connecting to tow vehicle.
13. Hydraulic Actuator — This actuator will be activated
in the event of a breakaway. The breakaway cable must
be rigged to the tow vehicle with appropriate slack
that will activate the system if the coupler connection
comes loose.
14. Lubrication Box — This box is empty when shipped
from the factory. Please fill with 3 gallons (11.35 liters)
of SAE 30 motor oil for first time use. Also check the
dual clean-out point on bottom of lubrication box for a
secure tight fit.
15. Heat Exchanger — Reduces temperature of the
hydraulic oil. The exchanger draws oil from the
hydraulic system into the heat exchanger before
allowing it to flow back into the reservoir.
MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14) — PAGE 23
Page 24

PUMP COMPONENTS (CONTINUED)
Table 5.
19
16
30
17
18
29
27
26
28
20
25
24
21
22
23
31
32
33
34
38
37
35
36
Figure 6. Pump Components 2
PAGE 24 — MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14)
Page 25

PUMP COMPONENTS (CONTINUED)
16. Hopper/Hood — Lift hood to fill. Concrete from a Redi-
Mix truck is poured into this hopper. The hopper can
hold 10 cu. ft of concrete. NEVER put hands or any
other parts of you body into the hopper.
17. Hydraulic Oil Reservoir Access Cover — Remove
this cover to gain access to the hydraulic oil tank for
maintenance/cleaning.
18. Fuel Cap — Remove this cap to add fuel. Fill with No. 2
diesel fuel. DO NOT top off fuel. Wipe up any spilled
fuel immediately.
19. Manifold Access Door — Release latch and lift door
to access the hydraulic manifold block.
20. Control Box — Contains the electrical components
required to run the pump. See Control Box Components
section for component callouts.
21. Oil Filter — Prevents dirt and other debris from entering
the engine. Service the oil filter as recommended in the
maintenance section of this manual.
22. Engine Throttle Lever — Controls the speed of
the engine. For load conditions (pumping concrete)
ALWAYS run the engine at full speed.
23. Fuel Water Separator Filter — Prevents sediments,
water and other debris from entering the fuel system.
Service the fuel filter as recommended in the
maintenance of this manual.
24. In-Line Fuel Filter — Replace or clean fuel filter as
specified in the maintenance section of this manual.
25. Hydraulic Pump — This unit incorporates an axial
variable displacement hydraulic piston pump.
28. Rear Running Lights — ALWAYS check and make
sure both the right and left running lights are functioning
correctly before towing the pump
29. Pump End Jack Stand — Use this jack stand to
support the rear end of the pump. NEVER deploy on unlevel ground and always check for firmness of ground.
30. Hopper Discharge Outlet — Connect hoses or steel
pipes to the discharge sleeve for pouring concrete.
31. Radio Control Antenna — Mounting location for radio
control antenna. Works in conjunction with hand-held
radio remote (option).
32. Hydraulic Oil Reservoir — Holds 33 gallons (125
liters) of hydraulic oil.
33. Hydraulic Manifold Block — Manifold block
that controls the flow of hydraulic pressure to the
components required to control the pump.
34. Fuel Line Guard/Fuel Gauge — Protects the fuel line
from damage. The fuel line (tube) also serves as a fuel
gauge. To determine when fuel is low visually read the
level of fuel shown on the fuel line.
35. Fuel Tank — Holds 16 gallons (61 liters) of diesel fuel.
36. Shuttle Cylinder/Guard — Under pressure, the
shuttle cylinder shears concrete passing from the
concrete cylinder to the delivery line during the cycle
phase. ALWAYS keep hands clear from shuttle cylinder
during operation.
37. Battery — This unit uses a +12 VDC type battery.
ALWAYS use gloves and eye protection when handling
the battery.
26. Pumping Pressure Gauge — Used to monitor
pressure in the concrete cylinders and shuttle tube.
27. Stroke Volume Control Knob — Turns CW/CCW to
increase or decrease the number of strokes per minute
of the pump.
MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14) — PAGE 25
38. Tow End Jack Stand — Use this jack stand to level
and support the tow end of the pump.
Page 26
DIGITAL CONTROL PANEL COMPONENTS
2
1
SCROLL
11
0
5
7
0
0
5
0
PUMPING
PRESSURE
0
0
0
1
1
2
5
0
10
1
5
0
0
2
0
0
0
FORWARD
AUTOMATIC
FLOW
DIRECTION
Figure 7. Pump Digital Control Panel Components
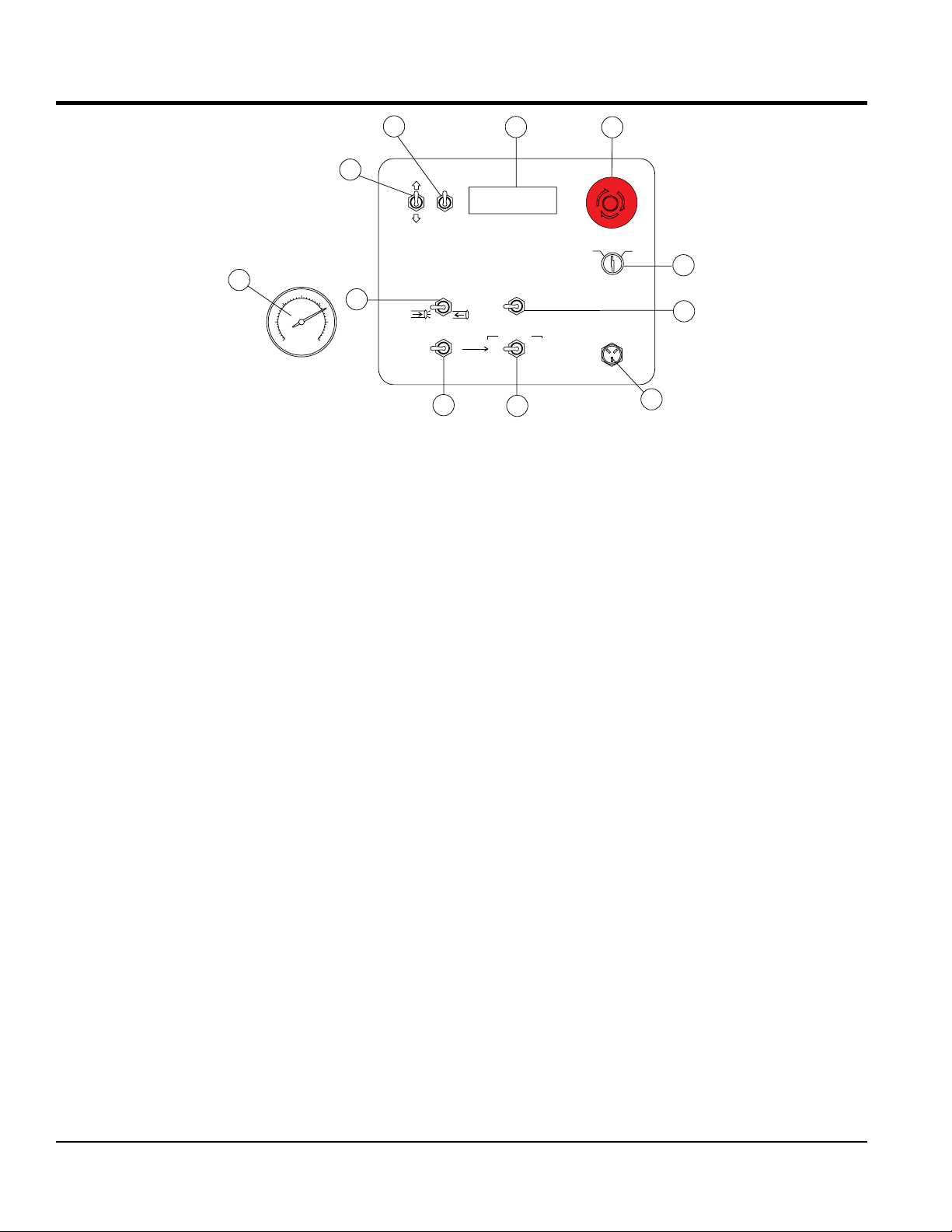
Figure 7 displays the components associated with the
digital control panel. A brief description of each component
is described below
1. Scroll Switch — Allows the operator to scroll the
various readout screens.
2. Reset Switch — Allows the operator to reset the
stroke counter.
3
RESET
SET
CONTROL
REMOTE
LOCAL
REVERSE
JOG
9
JOG“A”
CENTER
OFF
CYLINDER STROKE
8
JOG“B”
4
n
c
e
y
g
r
S
e
t
o
m
p
E
ON
OFF
IGNITION
START
5
6
REMOTE
7
8. Manual Cylinder Jogging Switch — This 2-position
switch allows the operator to manually jog the cylinders
to assist in clearing material line packs and is used to
test pumping pressure (See Initial Start-up Procedure
section of this manual for testing procedure).
The leftmost position jogs Cylinder (A) and the
rightmost position jogs Cylinder (B).
3. Digital Readout Screen — Displays and monitors the
various functions of the machine.
4. Emergency Stop Button — Press emergency stop
button to stop pump in an emergency. Turn knob
counterclockwise to disengage the stop button.
5. Ignition Switch — Insert the ignition key here to start
the engine. Turn the key clockwise to the ON position,
then continue turning clockwise to the START position
and release. To stop the engine turn the key fully
counterclockwise to the STOP position.
6. Pumping Control Switch — This 3-position switch
controls the pumping of the pump. The rightmost
position (REMOTE) is for use with the remote control
unit, the leftmost position (LOCAL) is for normal
pumping operation, and the centermost position
(CENTER OFF) prevents pumping.
7. Remote Cable Connector — Insert the remote control
input cable into this connector.
9. Cylinder Stroke Control Switch — This 2-position
switch controls the pumping function. The leftmost
position (AUTOMATIC) sets the pump to automatic
cycling. Set the switch to this position for normal pump
operation.
The rightmost position (JOG) changes the pump from
automatic to manual cycling. This allows the cylinders
to be manually cycled using the Manual Cylinder
Jogging Switch.
10. Direction Control Switch — This 2-position switch
controls the direction of flow for any mix in the pump.
The leftmost position sets the pumping direction to
forward and the rightmost position sets the pumping
direction to reverse.
11. Main Pressure Gauge — This gauge monitors
the system pressure while pumping material. The
maximum pressure rating is 3100 PSI ± 50.
PAGE 26 — MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14)
Page 27
DIGITAL CONTROL PANEL COMPONENTS
INDICATES
ELECTRIC
D OFF
INDICA
OF
ENGINE
BEEN
NO.
INDICA
RUNNING
COUNT
NO.
READ
NUMBER
INFORMATION
INDICATES
SWING A
CIRCUIT IS OFF
INDICATES
MAIN A
CIRCUIT IS OFF
INDICATES
MAIN B
CIRCUIT IS OFF
SWING A OFF
SWING B OFF
MAIN A OFF
MAIN B OFF
5
INDICATES
SWING B
CIRCUIT IS OFF
INDICATES
PROXIMITY A
CIRCUIT IS OFF
INDICATES
PROXIMITY B
CIRCUIT IS ON
INDICATES
FUEL SOLENOID
CIRCUIT IS OFF
PROX A OFF
PROX BON
FUEL SOL OFF
6
THE
INSTRUCTION
MESSAGE
INDICA
FUEL
IS
IINSTRUCTION
OR
PRIMARY SCREEN
Screen 1
Indicates the various modes of the switch settings. Monitors
engine RPM - Idle speed 900, High speed 2350. Battery
charge indicator - Normal charge 13+ volts. Indicates
electrical malfunction - Refer to Troubleshooting section.
STATUS OF PUMP
(ONOR OFF)
INDICATES
BATTERY
CHARGE
LS 300 OFF
0000 ENG RPM
BATTERY 12.5 V
LOW OIL PSI
1
INDICATES
ENGINE RPM
INDICATES
SECONDARY SCREENS
Screen 2
Displays the status of the shuttle cylinder proximity switches.
INDICATES PROX
C OFF
3
2
INDICATES
OF HOURS
PUMP HAS
BEEN USED
INDICATES
CODE
4
MESSAGE OR
PROXCOFF
PROXDOFF
INDICATES PROX
Screen 3
Displays the number of hours the engine and pump
have been used and the number of faults the pump has
registered. All three indicators can be reset to zero by the
RESET switch on the control panel.
TES NO.
HOURS
HAS
USED
MESSAGE OR
INSTRUCTION
E HRS: 00000.0
PMP HRS: 00000.0
FAULTS: 00000000
RESET TO CLEAR
Screen 4
Displays the number of strokes the main hydraulic cylinders
have gone through. This indicator can be reset to zero by
the RESET switch on the control panel.
TES A
OF
OF STROKES
EVEN
ONLY
MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14) — PAGE 27
STROKE CTR: 0000
PRESS RESET TO
ZERO STROKE CTR
Screen 5
Displays the ON/OFF electrical signal status of the various
12 volt solenoids (Swing A circuit, Main A circuit, Main B
circuit).
Screen 6
Displays the ON/OFF electrical signal status for the
Proximity Switch A, Proximity Switch B, Engine Fuel
Solenoid, and Unloader Solenoid.
Screen 7
Displays the number of times the main hydraulic cylinders
stroke and the yards per hour output. This indicator can
be reset to zero by the RESET switch on the control panel
INDICATES
THROTTLE
IS ON
INDICATES THE
NO. OF YARDS
PER HOUR
THROTTLE ON
STROKES: 20
STROKES/MIN 8.2
YDS/HR 10.7
INDICATES
NUMBER OF
7
STROKES
INDICATES THE
NO. OF STROKES
PER MINUTE
Screen 8
Displays the electrical status of the engine fuel solenoid. To
test the 12-Volt solenoid status, activate with the RESET
switch on the control panel.
8
OR
TES THE
SOLENOID
OFF
TO TEST FUEL
SOL PRESS RESET
FUEL SOL OFF
Screen 9
Displays the communication status of the (optional) radio
remote control. To activate a new remote control connection,
use the reset switch on the control panel.
INDICATES
THAT RADIO
9
REMOTE IS ON
MESSAGE
RADIO ADDRESS
COMMUNICATING
PRESS RESET TO
LEARN A NEW ONE
Page 28

ENGINE COMPONENTS
Figure 8. Perkins 404D-22TA Diesel Engine Components
The engine (Figure 8) must be checked for proper
lubrication and filled with fuel prior to operation. Refer to the
manufacturer's engine manual for instructions and details
of operation and servicing.
1. Fuel Shutoff Solenoid — When activated shuts off
fuel supply to injectors.
2. Fuel Injectors — Nozzle through which fuel is sprayed
into a combustion chamber.
3. Water Pump — Circulates coolant flow through engine
block.
4. Lower Oil Filler Port/Cap — Remove this cap to add
engine oil to the crankcase.
5. Engine Throttle Lever — Controls the speed of
the engine. For load conditions (pumping concrete)
ALWAYS run the engine at full speed.
6. Dip Stick — Remove dipstick to determine if the engine
oil level is low. If low add oil as specified in Table 4.
7. Engine Oil Cooler — Keeps engine oil cool.
8. Oil Filter — Prevents dirt and other debris from entering
the engine. Service the oil filter as recommended in the
maintenance section of this manual.
9. Fuel Injection Pump — Provides equal fuel flow to
injectors.
10. Transfer Pump — Boost the fuel pressure slightly
before the fuel is transferred into the main pump.
11. Main Fuel Filter — Prevents dirt and other debris
from entering the fuel system. Service the fuel filter
as recommended in the maintenance section of this
manual.
12. Front/Rear Lifting Eye — When lifting of the engine
is required attach a strap or chain of adequate lifting
capacity to these lifting points.
13. Turbocharger — Provides pressurized intake air to the
cylinder by means of a turbine energized by exhaust
gas that rotates the blower.
14. Starter/Solenoid — This engine uses a 12VDC, 2.7kW
(3.7 HP) starter motor with solenoid.
15. Alternator — Provides power to the electrical system.
Replace with only manufacturers recommended
replacement parts.
16. Crankcase Drain Plug — Remove this plug to drain
engine oil from the engine crankcase. For best results
drain engine oil when oil is warm.
17. V-Belt — Driven by the engine crankshaft during
operation, drives the water pump/fan as well as the
alternator.
18. Coolant Temperature Switch — When activated
indicates high coolant temperature.
19. Fan Blades — To provide adequate cooling always
remove dirt and debris from fan blades to provide
adequate cooling.
20. Upper Oil Filler Port/Cap — Remove this cap to add
engine oil to the crankcase. Fill with recommended
type of oil as specified in the maintenance section of
this manual.
PAGE 28 — MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14)
Page 29

INSPECTION
WARNING
NEVER operate the pump in a confined
area or enclosed area structure that
does not provide ample free flow of air.
ALWAYS wear approved eye and
hearing protection before operating
the pump.
NEVER operate the pumps's engine
with the engine hood removed. The
possibility exists of hands, long hair,
and clothing becoming entangled with
the V-belt, causing injury and bodily
harm.
NEVER place hands or feet inside
the hopper. ALWAYS make while the
engine is running. ALWAYS shut down
the engine before performing any kind
of maintenance service on the pump.
DANGER
Diesel fuel is extremely flammable, and
its vapors can cause an explosion if
ignited. DO NOT start the engine near
spilled fuel or combustible fluids. DO
NOT fill the fuel tank while the engine
is running or hot.
DO NOT overfill tank, since spilled fuel could ignite if it
comes into contact with hot engine parts or sparks from
the ignition system. Store fuel in approved containers, in
well-ventilated areas and away from sparks and flames.
NEVER use fuel as a cleaning agent.
Fuel Check
1. Check the fuel gauge (Figure 9) built into the fuel tank
cap to determine if the pump's engine fuel is low.
NOTICE
Reference Figures 5, 6, and 7 for the location of any control
or component referenced in this section.
Before Starting
1. Read safety instructions at the
beginning of manual.
2. Clean the entire pump, removing dirt
and dust, particularly the engine
cooling air inlet, and heat exchanger.
3. Check the air filter for dirt and dust. If air filter is dirty,
replace air filter with a new one as required.
4. Check fastening nuts and bolts for tightness.
Fuel Safety
DANGER
Handle fuel safely. Motor fuels are highly flammable
and can be dangerous if mishandled. DO NOT smoke
while refueling. DO NOT attempt to refuel the pump if
the engine is hot or running.
Figure 9. Fuel Cap Gauge
2. If fuel is low, remove fuel filler cap and fill with #2 diesel
fuel (Figure 10).
DIESEL
FUEL
Figure 10. Adding Diesel Fuel
MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14) — PAGE 29
Page 30

TURE
INSPECTION
Engine Oil Check
1. Make sure pump/engine is placed on level ground.
2. Remove the engine oil dipstick from its holder (Figure 11).
DIPSTICK
Figure 11. Engine Oil Dipstick Location
3. Verify that engine oil level (Figure 12) is maintained
between the two notches on the dipstick.
Table 6. Oil Selection Chart
F
122
104
86
68
50
-14
-4
-22
-40
50
40
30
20
10
-10
-20
-30
-40
C
032
5W/30
OIL: SAE
5W/40
10W
10W/30
10W/40
15W/40
20W/20
40
30
Hydraulic Oil Check
1. Determine if the hydraulic oil level is low by observing
the level of the oil in the hydraulic oil sight glass
(Figure 13).
Figure 12. Engine Oil Level (Dipstick)
4. If the pump's engine oil is low, fill engine crankcase with
lubricating oil through filler hole, but DO NOT overfill.
5. The oil listed in Table 6 is recommended to ensure
better engine performance. Use class CD or higher
grade motor oil.
NORMAL OIL LEVEL
HYDRAULIC OIL TEMPERA
MINIMUM OIL LEVEL
Figure 13. Hydraulic Oil Sight Glass
PAGE 30 — MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14)
Page 31

2. If the hydraulic oil level is low, remove the hydraulic oil
CAP
TOP
tank cap just above the oil level sight glass (Figure 14)
and add the correct amount of hydraulic oil to bring the
hydraulic oil level to a normal safe operating level. Use
Shell oil Tellus 68 or Mobil oil DFE26.
FILLER
HOLE
Figure 14. Adding Hydraulic Oil (Filler Hole)
3. Check the oil level in the lubrication box (Figure 15).
If low, fill with up to 3 gallons of SAE #30 motor oil
(Figure 14). The oil level must be checked daily. The
lubrication box should be serviced as described in the
maintenance section.
INSPECTION
COVER
BOX
LUBRICATION
Figure 15. Filling the Lubrication Box
MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14) — PAGE 31
Page 32

SETUP
Location of Pump
1. Place the pump in the best location on the site to pump
concrete efficiently.
2. Lay down the hose in the shortest distance possible.
Rear Stabilizer Jacks
WARNING
NEVER place feet under jack while operating.
ALWAYS retract rear stabilizer jacks prior to towing.
ALWAYS retract rear stabilizer jacks prior to servicing
to relieve load (working pressure).
To reduce excessive vibration and rocking of the pump, set
the rear stabilizers as follows:
1. Locate both the left and right rear stabilizer jacks
(Figure 16).
REAR STABILIZER JACKS
3. Position both rear stabilizers jacks on firm (not loose)
level ground (Figure 18).
INCORRECT CORRECT
Figure 18. Rear Stabilizer Stand Deployment
4. Align the hole on the stabilizer jack with the hole on
the frame body and insert handle tee bolt.
5. Insert the cotter pin into handle tee bolt eye to lock the
stabilizer jack.
Figure 16. Locating Rear Stabilizer Jacks
2. Remove the cotter pin (Figure 17) from the handle tee
bolt eye, and then pull the handle tee to release the
stabilizer jack.
ADJUSTMENT
TUBE
COTTER
PIN
HANDLE
T-BOLT
Figure 17. Rear Stabilizer Jack
BOLT
EYE
PAGE 32 — MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14)
Page 33

OPERATION
JOG
REMOTE
FOR
REVERSE
Starting Procedure
WARNING
DO NOT attempt to operate this concrete pump until
the Safety, General Information and Inspection sections
have been read and understood.
1. Locate the emergency stop switch (Figure 19) on
the digital control panel. Turn the emergency stop
switch clockwise and release (open). This will allow
the engine to start.
n
c
e
y
g
r
e
m
E
Figure 19. Emergency Stop Switch
NOTICE
If the emergency stop switch is in the closed position
(STOP), engine will not start. To start the engine, make
sure the emergency stop switch is in the OPEN position
(fully extended).
2. Place the cylinder stroke control switch in the
AUTOMATIC position (Figure 20).
S
t
o
p
4. Place the direction control switch to the FORWARD
position (Figure 22).
WARD
Figure 22. Direction Control Switch
(FORWARD)
5. To start the engine, insert the ignition key (Figure 23)
into the ignition switch and turn the key to the ON
position.
ON
OFF
IGNITION
Figure 23. Ignition Switch
START
6. When the ignition key is in the ON position, the digital
readout screen (primary) will cycle through 3 displays
as shown in Figure 24.
LS 300 OFF
0000 ENG RPM
BATTERY 12.5 V
LOWOIL PSI
1
AUTOMATIC
Figure 20. Cylinder Stroke Control Switch
(Automatic)
3. Place the pumping control switch in the CENTER
OFF position (Figure 21) for normal pumping operation.
LOCAL
CENTER
OFF
Figure 21. Pumping Control Switch (OFF)
MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14) — PAGE 33
LS 300 OFF
0000 ENG RPM
BATTERY 12.5 V
LOW RPM FAULT
LS 300 OFF
0000 ENG RPM
BATTERY 12.5 V
END OF MESSAGE
Figure 24. Primary Screen (Ignition Key ON)
1
1
7. Turn the key to the START position and listen for the
engine to start. In warm weather let engine warm up
for 5 minutes. In cold weather, let engine warm up for
10 minutes.
Page 34

REVERSE
REMOTE
DECREASEINCREASE
OPERATION
Hose Lubrication
Before pumping, it is necessary to lubricate the hose.
This procedure prevents separation and blockages in the
hose. Inspect the lines at all times to prevent problems.
Before concrete is discharged into the hopper, it is
suggested that 3 to 4 gallons of water be sprayed into the
hopper, followed by approximately 5 gallons of a creamy
cement and water slurry (1/2 bag of cement to 5 gallons
of water).
NOTICE
Getting the concrete to flow through the hose at the start
of the pumping cycle can be one of the most critical
operations of the pour.
Priming The Pump With Slurry Mixture
It is CRITICAL to the successful operation of a concrete
pump that the manifold and all delivery hoses, pipes and
elbows are coated with a film of lubrication BEFORE you
attempt to pump concrete.
Failure to properly prepare the pump and system will result
in a “dry pack” of concrete, blocking the shuttle valve tube
or delivery line.
1. Connect the entire delivery system to the pump. Pour
5 gallons of water and a bag of raw cement into the
hopper.
2. Place the direction control switch to the REVERSE
position (Figure 25). This will mix the water and cement
into slurry.
6. Keep the slurry flowing until most of it is pumped out.
However, make sure that some slurry is left on the
hopper when concrete is first discharged from the
ready-mix truck.
Pumping
WARNING
Safety glasses and hearing protection
MUST be worn at all times when
operating the pump. Failure to follow
safety guidelines can result in serious
injury.
NOTICE
A well-planned location of the pump and routing of the
hose before starting a pour may save subsequent moves
throughout the job.
1. Place the pumping control switch in the LOCAL
position (Figure 26) for normal pumping operation.
LOCAL
CENTER
OFF
Figure 26. Pumping Control Switch (Local)
2. Holding the volume control switch (Figure 27) to the
right will increase pumping volume to approximately 10
strokes per minute. Holding the volume control switch
to the left will decrease pumping volume.
FORWARD
Figure 25. Direction Control Switch (REVERSE)
3. Mix the slurry to the consistency of a smooth batter.
4. Position the first ready-mix truck at the hopper. Check
the concrete. DO NOT discharge concrete into hopper
at this time.
5. Place the direction control switch in the FORWARD
position. This will start the flow of the slurry to the hoses.
PAGE 34 — MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14)
VOLUME CONTROL
CCW
Figure 27. Volume Control Switch
CW
Page 35

L
OPERATION
3. A thumping sound (cylinder stroke) should be heard.
The thumping sound represents the number of strokes
per minute (volume) of the pump.
4. Scroll through the digital readout screen with the
scroll switch to go to screen 7 (Figure 28). This screen
will show the volume in strokes per minute.
THROTTLE ON
7
STROKES: 100
STROKES/MIN 10.0
YDS/HR 0.0
Figure 28. Strokes Per Minute Display
5. Let the pump cycle until the hydraulic oil temperature
(Figure 29) is approximately 50° to 60° F.
CAUTION
HOSE/LINE BLOCKAGE
If hoses or lines are blocked for any reason, or if the
lines are kinked when starting up or during the pumping
cycle, the pump pressure could straighten out the kink
or force out the blockage. This rapid surge of material
could cause the lines to whip or move in a manner that
could cause injury to personnel.
7. It is important that once the slurry procedure is
completed, and concrete is flowing through the hose,
DO NOT stop the pour until all the slurry is pumped
out and the concrete has reached the end of the hose.
The only time to stop the pump during the priming
procedure is if a blockage occurs.
8. If it is necessary to replace or add a section of delivery
system, after the initial lubrication procedure, wet the
inside area of the hose, pipe or elbow with 5 gallons of
water per 25 foot length, before adding it to the system.
HYDRAULIC OI
TEMPERATURE
Figure 29. Hydraulic Oil Temperature Gauge
6. Rotate the Volume Control Knob (Figure 27) to the right
to increase the volume to 25-30 strokes per minute.
Place pump control switch in the center “OFF” position.
Slowly discharge the concrete from the ready-mix truck
into the hopper and completely fill it.
Place pump control switch in the local “ON” pumping
position. Keep the pump running continuously until
concrete is discharging at the end of the delivery
system. If the pumping operation suddenly stops with
no concrete discharging from the hose, a blockage
may have occurred. Immediately place the switch in the
“OFF” position. Refer to Clearing Concrete Blockage
Section.
NOTICE
When pumping long distance or pumping stiff mixes, you
can expect a drop in volume compared to shorter lines
and wetter mixes due to the change in valve efficiency
or cavitation.
MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14) — PAGE 35
Page 36

OX
ANEL
ELECTRONIC
ELECTRONIC
KNOCK-OUT
HOL
OPERATION
Remote Control (Optional)
The LS300P Concrete Pump has a remote control feature
that allows the pump to be remotely controlled. If desired,
the pump can be operated via a receiver/transmitter (radio)
or a hardwire method, which utilizes a 25-ft. extension cable.
Contact MQ Sales Department to order remote control.
Radio Remote Control
Installation of the Radio Remote Control Assembly
1. Remove the two screws (Figure 30) on the digital
control panel that secure the front panel to the control
box.
SCROLL
RESET
SET
VOLUME
R
G
E
E
M
N
E
C
Y
S
T
O
P
INCREASE
FLOW
DIRECTION
WARD
REVERSE
CONTROL
OFF
LOCAL
TIC
ON
REMOTE
JOG
CENTER
START
OFF
CYLINDER STROKE
IGNITION
JOG
“A”
JOG
“B”
REMOTE
REMOVE 2 SCREWS
DECREASE
FOR
AUT
OMA
Figure 30. Removing The Control Box
CONTROLB
3. Install the wireless remote module (Figure 32) with the
2 screws and nuts provided inside the control panel.
Connect the 3-wire connector from the wireless remote
module to the electronic control unit.
AND NUTS
CONTROL
UNIT
E
CONNECTOR
Figure 32. Installing Remote Control Module
4. Reinstall the control panel and tighten the 2 retaining
screws.
5. On the top of the unit, to the right of the control box
(Figure 33), hammer out the knock-out hole and install
the remote antenna.
ANTENNA
2. Tilt and slowly pull out the control panel and place on
top (Figure 31) of control box to gain access inside
the box.
FRONT P
CONTROL
UNIT
Figure 31. Pulling Out Control Panel
PAGE 36 — MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14)
E
ANTENNA
CONNECTOR
CABLE
REAR OF
CONTROLBOX
CONTROLBOX
CONNECTOR
Figure 33. Antenna Installation
6. Connect the antenna cable to the connector on the
rear (Figure 33) of the control box.
Page 37

REMOTE
OFF
LED
BA
OPERATION
Radio Remote Control Buttons Operation
Before the remote control hand-held module can be used,
the pumping control switch on the control box must be
placed in the REMOTE position (Figure 34).
LOCAL
CENTER
Figure 34. Pumping Control Switch (Remote)
Remote pumping operation can be performed by the handheld radio remote control module (Figure 35).
E-STOP
PUMP
REV
ON
OFF
PUMP
ON/OFF
POWER
PUMP ON/OFF – Starts and stops the forward pumping.
PUMP REV – momentarily pumps in reverse direction.
VOLUME (+) – used to increase the pumping volume.
VOLUME (-) – used to decrease the pumping volume.
Radio Remote Control Programming
Before starting operation of the hand-held radio remote
control, go to Screen 9 of the digital readout screen:
Screen 9
RADIO ADDRESS
NO RADIO
PRESS RESET TO
LEARN A NEW ONE
1. Press the ON/OFF button on the radio (wireless)
remote control to turn on the power. Hold down the
RESET switch. The display will now show.
Screen 9
9
TTERY LED
VOLUME VOLUME
NOTE: OLDER MODELS
MAY INDICATE
INSTEAD OF
FLOW
VOLUME
Figure 35. Radio Remote Control
The buttons on the hand-held remote control module have
the following functions:
ON/OFF – Turns the power on or off. When power is on
the power LED lights red. If the battery LED turns red,
9V battery needs to be replaced.
E-STOP – Turns off the pump completely in an
emergency.
RADIO ADDRESS
9
NOW SCANNING
FOR NEW
TRANSMITTER
2. After 5 seconds, the display will show:
Screen 9
RADIO ADDRESS
9
COMMUNICATING
PRESS RESET TO
LEARN A NEW ONE
3. The hand-held remote control module is now ready
for use.
MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14) — PAGE 37
Page 38

Remote Control Cable Operation (25 ft.)
The remote control cable (Figure 36) has the following
controls:
Pump ON/OFF – Starts and stops the forward pumping.
Pump REV – Starts pumping in reverse direction.
Connect the remote control cable (Figure 36) to the
receptacle labeled remote located on front of the digital
panel.
REMOTE CONTROL CABLE UNIT
25 FT. CABLE
PUMP REV
PUMP ON/OFF
TO CONTROL BOX
CONNECTOR
OPERATION
Figure 36. Remote Control Cable
Before the remote control cable can be used the pumping
volume rate must be set.
1. Start the pump as outlined in the pumping section of
this manual.
2. Place the pumping control switch in the LOCAL
position.
3. Using the momentary volume control switch, adjust
the pumping rate (volume) to the desired strokes per
minute.
4. Once the desired pumping rate has been achieved,
place the pumping control switch in the REMOTE
position.
PAGE 38 — MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14)
Page 39

MAINTENANCE
Engine
Pump
Trailer
Table 7. Inspection/Maintenance
Check Engine Fluid Levels X
Check Air Cleaner X
Check Battery Acid Level X
Check Fan Belt Condition X
Check for Leaks X
Check for Loosening of Parts X
Replace Engine Oil and Filter
Clean Air Filter X
Check Fuel Filter/Water Separator Bowl X
Clean Unit, Inside and Outside X
Change Fuel Filter X
Clean Radiator and Check Coolant Protection Level
Replace Air Filter Element
Check all Hoses and Clamps
Clean Inside of Fuel Tank X
1
2
3
4
Check Battery
Visually Check for Oil Leaks X
10 Hrs
DAILY
250 Hrs 500 Hrs
X
X
X
X
1000
Hrs
X
OTHER
Hydraulic Oil Level X
Lubrication Box X
Replace Hydraulic Oil
X
Clean Hydraulic Filters
Grease Shuttle Axle Crank
X
2 Hrs.
Grease Shuttle Cylinder Monthly
Check System Pressure
X
Check Hardware for Tightness Weekly
Check Cutting Wear Ring Weekly
Check Brake Lights
Check Tire Conditions
Inspect Safety Devices / Decals
X
X
X
Check Wheel Bearings 6-Months
Inspect Brake Lining 6-Months
*1 Replace engine oil and filter at 100 hours, first time only.
*2 Add “Supplemental Coolant Additives (SCA’S)” to recharge the engine coolant.
*3 Replace primary air filter element when restriction indicator shows a vacuum of 625 mm (25 in. H20).
*4 If blowby hose needs to be replaced, ensure that the slope of the blowby hose is at least a 1/2 inch per foot,
with no sags or dips that could collect moisture and/or oil.
MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14) — PAGE 39
Page 40

RESET
MAINTENANCE
GENERAL INSPECTION
Prior to each use, the pump should be cleaned and
inspected for deficiencies. Check for loose, missing or
damaged nuts, bolts or other fasteners. Also check for
fuel, oil, and coolant leaks. Use Table 7 as a general
maintenance guideline Engine Side (Refer to the Engine
Instruction Manual)
CAUTION
Certain maintenance operations or machine
adjustments require specialized knowledge and skill.
Attempting to perform maintenance operations or
adjustments without the proper knowledge, skills or
training could result in equipment damage or injury to
personnel. If in doubt, consult your dealer.
WARNING
Accidental starts can cause severe injury
or death.
CAUTION
ALWAYS allow the engine to cool
before servicing. NEVER attempt any
maintenance work on a hot engine.
Air Cleaner with Dust Indicator
NOTICE
The air filter should not be changed until the indicator
reads “RED”. Dispose of old air filter. It may not be
cleaned or reused.
This indicator (Figure 37) is attached to the air cleaner.
When the air cleaner element is clogged, air intake
restriction becomes greater and the dust indicator signal
shows RED meaning the element needs changing or
service. After changing the air element, press the dust
indicator button to reset the indicator.
PUSH CENTER TO
WARNING
ALWAYS place the ON/OFF switch in the
OFF position.
Disconnect and ground spark plug leads
and disconnect negative battery cable
from battery before servicing.
Some maintenance operations may
require the engine to be run. Ensure
that the maintenance area is well
ventilated. Exhaust contains poisonous
carbon monoxide gas that can cause
unconsciousness and may result in
DEATH
RESET
AIR FILTER INDICATOR
5 KPA
Figure 37. Air Cleaner Service Indicator
PAGE 40 — MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14)
Page 41

MAINTENANCE
N
INNER
ELEMENT
(OPTION)
EVACUATOR
VALV E
ARROW
MARK
(CASE)
BLOW COMPRESSED
MAIN
Air Cleaner (250 Hours)
This Perkins diesel engine is equipped with a replaceable,
high-density paper air cleaner element (Figure 38).This air
cleaner may have an inner element (option) that is used as
a backup filter should the main element becomes damaged.
CAUTION
Wear protective equipment such as
approved safety glasses or face shields
and dust masks or respirators when
cleaning air filters with compressed air.
MAIN PAPER
AIR CLEANER
AIR CLEANER
CASE
ELEMENT
ARROW
MARK
(DUST PAN)
DUST PA
5. To clean the main element (paper air filter) as referenced
in (Figure 39), tap the filter element several times on
a hard surface to remove dirt, or blow compressed air
(not to exceed 30 psi (207 kPa, 2.1 kgf/cm2) through
the filter element from the inside out.
PAPER AIR FILTER
ELEMENT
AIR FROM THE
INSIDE OUT
Figure 39. Cleaning Paper Air Filter Element
NOTICE
LATCH
Figure 38. Air Cleaner
1. Release the latches located on either side of the air
cleaner dust pan, and remove the dust pan.
2. Remove the air cleaner element.
3. Check the air cleaner daily or before starting the engine
4. Check for and correct heavy buildup of dirt and debris
along with loose or damaged components.
NOTICE
Operating the engine with loose or damaged air cleaner
components could allow unfiltered air into the engine
causing premature wear and failure.
DO NOT use excessive air pressure or the paper air
filter element will be damaged and will need to be
replaced.
6. Replace the element if it is damaged or excessively
dirty.
7. Clean the inside of the dust pan.
8. Reinstall the element or if equipped, the precleaner
over the paper air cleaner element.
9. Reinstall the air cleaner dust pan and secure the
latches.
NOTICE
DO NOT run the engine with the air cleaner removed
or without an element.
MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14) — PAGE 41
Page 42

(ADD OIL)
DO NOT OVERFILL
MAINTENANCE
Checking Engine Oil (Daily)
1. When checking or adding oil, place the machine so
the engine is level.
2. Pull the engine oil dipstick from its holder.
3. Determine if engine oil is low. Oil level should be
between the upper land lower limit (Figure 40) on the
dipstick.
UPPER
LIMIT
LOWER
LIMIT
Figure 40. Dipstick Engine Oil Level
4. If oil level is low, add correct amount of engine oil to
bring oil level to a normal safe level (See Recommended
Viscosity Grades, Table 8).
5. Allow enough time for any added oil to make its way
to the oil pan before rechecking.
F
DIPSTICK
L
Changing Engine Oil And Filter
Change the engine oil and filter after the first 50 hours of
use, then every 6 months or 250 hours. Refer to Table 8
for recommended oil viscosity.
1. Prepare a waste oil collector to drain the oil into.
2. Remove the oil filler cap while draining the oil to
allow the engine to drain easily.
OIL
FILTER
DRAIN
PLUG
Figure 41. Oil Service Components
OIL
F
122
104
86
68
50
-14
-4
-22
-40
Table 8. Oil Selection Chart
5W/40
10W
OIL: SAE
10W/30
50
40
30
20
10
-10
-20
-30
-40
C
032
5W/30
10W/40
15W/40
30
20W/20
40
3. Remove the drain plug (Figure 41) to drain the oil.
4. After oil is sufficiently drained, securely tighten the
drain plug.
5. Using a filter wrench, turn the oil filter counterclockwise
to remove.
6. Clean sealing surface on engine where filter mounts.
7. Coat the seal of the new oil filter with clean engine oil.
Install new filter first by hand until it contacts the engine
sealing surface. Tighten it another 3/4 turn using the
filter wrench.
8. Fill engine crankcase with high quality detergent oil
classified "For Service CF, or CF-4". Fill to the upper
limit of dipstick. DO NOT overfill. Crankcase oil capacity
with oil filter replacement is 1.5 gals (7 liters).
9. Run the engine briefly for several minutes. Watch for
oil leakage. Shut the engine down and allow it to sit
for several minutes. Top off the oil to the upper limit on
the dipstick.
PAGE 42 — MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14)
Page 43

MAINTENANCE
SEAL
10. Be sure to coat the seal (Figure 42) of the new oil filter
with clean engine oil.
OIL
FILTER
Figure 42. Oil Filter/Seal
Radiator/Cooling System
COOLANT (ANTIFREEZE/SUMMER COOLANT/
WATER)
PERKINS recommends antifreeze/summer coolant for use in
their engines, which can be purchased in concentrate (and
mixed with 50% demineralized water) or pre-diluted. See the
PERKINS Engine Owner’s Manual for further details.
Radiator Maintenance
1. Check radiator for leaks that would indicate corrosion
or damage.
2. Check coolant level daily. Top off as necessary. Always
use recommended coolant/antifreeze. Use the mixing
ratios specified by the coolant/antifreeze manufacturer
or (Table 9). Replace coolant/antifreeze at least once
a year.
3. Check radiator hoses for fatigue or cracking. Replace
any defective hoses immediately.
4. Check radiator cap seal and replace as necessary.
5. Blow off dirt and dust from fins and radiator with 28
psi (193 kPa) or less of compressed air (Table 9). Be
careful not to damage the fins with the compressed air.
COOLING
FINS
RADIATOR
CAP
WARNING
If adding coolant/antifreeze mix to the
radiator, DO NOT remove the radiator cap
until the unit has completely cooled. The
possibility of hot! coolant exists which can
cause severe burns.
Day-to-day addition of coolant is done via the radiator.
When adding coolant to the radiator, DO NOT remove the
radiator cap until the unit has completely cooled. Coolant
capacity is 4.5 gallons (17 liters).
Operation in Freezing Weather
When operating in freezing weather, be certain the proper
amount of antifreeze Table 9 has been added.
Table 9. Anti-Freeze Operating Temperatures
Vol %
Anti-
Freeze
Freezing Point Boiling Point
°C °F °C °F
COMPRESSED AIR
PRESSURE WASHER
Figure 43. Radiator Cleaning
OR
NOTICE
NEVER use high-pressure water or compressed air at
greater than 28 psi (193 kPa) or a wire brush to clean
the radiator fins. Radiator fins damage easily.
6. If there is a large amount of contamination on the fins,
use detergent to clean and rinse thoroughly with tap
water.
50 -37 -34 108 226
MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14) — PAGE 43
Page 44

MAINTENANCE
WEAR
Fuel Filter
1. Replace the secondary fuel filter (Figure 44) every 800
hours. Refer to your engine manual for specific details
to perform this operation.
CUP
DRAIN
Figure 44. Fuel Filter
Fuel/Water Separator Primary Filter
1. Inspect the fuel filter water separator daily. If the fuel
filter/water separator (Figure 45) has collected a
significant amount of water and sediment at the bottom
of the cup, it should be drained off.
In-Line Fuel Filter
Replace the engine in-line fuel filter (Figure 46) every year or
300 hours.
Figure 46. In-Line Fuel Filter
Oil And Fuel Lines
1. Check the oil and fuel lines and connections regularly
for leaks or damage. Repair or replace as necessary.
2. Replace the oil and fuel lines every two years to
maintain the line's performance and flexibility.
V-BELT
Visually examine the V-belt (Figure 47) and determine if it
is full of tiny cracks, frayed, has pieces of rubber missing,
is peeling or otherwise damaged.
Also, examine the belt and determine if it is oil soaked or
"glazed " (hard shiny appearance on the sides of the belt).
Either of these two conditions can cause the belt to run hot,
which can weaken it and increase the danger of it breaking.
CUP
DRAIN
SEDIMENT
Figure 45. Fuel Water Separator
2. To remove water and sediment from the cup, place
any fuel valves to the OFF position and unscrew the
cup from the base.
3. Pour the contents of the cup into a safety container.
Rinse cup with a mild detergent and reattach cup to
base.
4. Return fuel valves to the ON position.
PAGE 44 — MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14)
If the V-belt exhibits any of the above wear conditions
replace the V-belt immediately.
OIL SOAKED
GLAZED
CRACKS
SIDEWALL
Figure 47. Drive Belt Inspection
CORD FAILURE
WORN BACK
COVER
BROKEN
MISSING RUBBER
Page 45

MAINTENANCE
VENT
Battery Maintenance
DANGER
Use all safety precautions specified by the battery
manufacturer when working with the battery.
Flammable, explosive gas. (produces
hydrogen gas while charging or during
operation). Keep area around battery well
ventilated and keep from any fire source.
Battery electrolyte contains corrosive, toxic
chemical. (dilute sulfuric acid). Avoid
contact with eyes and skin.
Shock or Fire due to electric shortcircuit. Disconnect battery cables before
inspecting electrical system and never
"spark" battery terminals to test for charge.
Mishandling of the battery shortens the service life of the
battery and adds to maintenance cost. When handling the
battery do the following:
Be careful not to let the battery electrolyte come in
contact with your body or clothing.
ALWAYS wear eye protection and rubber gloves, since
the battery contains sulfuric acid which burns skin and
eats through clothing.
CAUTION
Battery Safety
Wear safety glasses or face mask, protective clothes,
and rubber gloves when working with battery.
If the pump will not be in operation for a long period
of time, store in cool dry place and check the battery
charge level every month to maintain the performance
of the battery.
Check the battery regularly and make sure that each
electrolyte level is to the bottom of the vent well
(Figure 48). If necessary add only distilled water in
a well-ventilated area. Never operate or recharge
without sufficient fluid in the battery.
BATTERY ELECTROLYTE
WELL
TOO
LOW
Figure 48. Battery Electrolyte Levels
LEVEL
NORMAL
TOO
HIGH
Cleaning The Pump And Delivery System
DANGER
AMPUTATION HAZARD
During routine
maintenance or
removing material
blockage, you will be
required to put your
hand in the concrete
cylinders or near the
shuttle tube. You are at extreme risk of injury or
AMPUTATION if the engine is running or if pressure
is in the hydraulic system.
ALWAYS check the battery terminals periodically to
ensure that they are in good condition.
Use wire brush or sand paper to clean the battery
terminals.
ALWAYS check battery for cracks or any other damage.
If white pattern appears inside the battery or paste has
accumulated at the bottom, replace the battery.
NEVER attempt to charge a battery that is frozen. The
battery can explode unless first allowed to thaw.
MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14) — PAGE 45
Prior to performing any maintenance on the pump,
follow described lock out-tag out procedures. Stop the
engine by turning off the ignition switch and remove
the starter key.
Place a DO NOT OPERATE tag over the switch and
disconnect the battery. The pressure reading on the
pressure gauge MUST read zero.
Page 46

MAINTENANCE
Cleaning the pump is a very important operation as it
determines how the machine will pump the next time it is
used.
NOTICE
NEVER use muriatic acid to clean the pump. Acid will
dissolve the chrome finish on material cylinder bore and
main hydraulic cylinder rods.
At the end of every pour, or because of long delays during
a pour, the pump and delivery system must be thoroughly
cleaned by removing all concrete material.
1. Following the clearing concrete blockage operating
procedure, ensure that there is no blockage in the
hose and line or in the shuttle tube. If a blockage
exists, clear it.
2. Pump concrete until the opening of the concrete
cylinder intake in the hopper is visible.
3. Stop the pump.
4. Carefully disconnect the first hose joint at the shuttle
tube discharge elbow.
5. Add water to the hopper. Pump and flush clean the
entire hopper, shuttle tube and discharge elbow with
water.
Hydraulic Oil System Maintenance
This Mayco pump is equipped with an in-tank return
hydraulic filter with a 10 micron cleanable filter. The element
has been designed to remove all particles large enough to
cause wear and job break down. Under normal conditions,
we recommend replacement every 6 months.
The most important factor to keep in mind is the effect of
cold weather on the hydraulic oil. The viscosity (thickness)
of the hydraulic oil will be much heavier.
ALWAYS run machine until oil temperature reaches a
minimum of 50°F. before pumping. Damage to the main
piston pump will occur if the machine is cycled too fast
before the oil temperature reaches the minimum of
50°F. Cycle the machine at 6-8 strokes per minute at
approximately 1/3 throttle.
In areas where the weather normally remains under 50°F.,
use Shell Oil Tellus 46 (or the equivalent). The above steps
must be followed or severe damage to the main axial piston
pump can occur.
1. When changing the hydraulic oil or topping off the
reservoir (capacity 50 gal/189 liters), use only the
following type hydraulic oil:
Shell Oil Tellius 46
6. Scoop out 12 inches of concrete from the inboard end
of the delivery hose. “Cork screw” a 6" x 6" x 8" sponge
into the end of the first hose section. Reconnect the
hose to the discharge elbow.
7. Fill hopper with water. Pump until sponge and clean
water come out the discharge end of the hose and
line system.
8. When the pump has been used to pump aggregate
concrete or mixes with high fines content (60% or more
sand) there will be a tendency for hardened concrete
to build up on the inside surface of the shuttle tube.
Therefore, at the end of every such pour, after the pump
and system have been cleaned and the engine shut
off, remove all remaining concrete.
9. Use only a 2½" diameter clean-out hook when backpumping into redi-mix truck. Use a safety chain to
secure the clean-out hook to some solid part of the
mixer truck to prevent hook from jumping off of the
drum. Run the pump at 6 strokes per minute maximum
speed.
Mobil DFE 26
Texaco Rand HDC
NOTICE
DO NOT mix oil brands! This may impair quality.
2. The following components should be greased daily,
hourly if necessary:
Main Hydraulic Cylinders (2 grease fittings)
Swing Axle Bushing (1 grease fitting)
Shuttle Cylinder (2 grease fittings top and bottom)
Discharge Nipple (3 grease fittings)
Outtriggers Option (2 grease fittings)
PAGE 46 — MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14)
Page 47

CYLINDER
NUN PLA
MAINTENANCE
DRAIN
SHUTTLE
TOP
SHUTTLE
CYLINDER
BOTTOM
GREASE
POINT
CYLINDER
“B”
TE
GREASE
POINT
DISCHARGE
NIPPLE
GREASE
POINTS
SWING AXLE
BUSHING
CYLINDER
GREASE
POINTS (3)
“A”
WARNING
ALWAYS follow lock out-tag out procedures before
checking lubrication level, Stop the engine and remove
the engine starter key. The possibility exists of severe
bodily harm when hands are placed inside.
1. The lubrication level should be checked everyday prior
to pumping and maintained at a height of 5 inches or
about ½ the concrete cylinder height. We recommend
using a 30-weight motor oil.
2. As the rubber piston cups naturally wear, fine cement
particles will accumulate in the box. Once the concrete
paste reaches a height of about ½ inch from the bottom
of the box, drain and clean the lubrication box.
Cleaning the Lubrication Box
1. Remove the top cover and the drain plug (Figure 50)
located at the bottom of the box and fully drain the
inside of the box.
2. Once the box is drained, start the engine and stroke
the cylinder (keep hands out of box) ten to fifteen times.
AXLE
CRANK
SHUTTLE
CYLINDER
Figure 49. Lubrication Points
NOTICE
When lubricating the above components, use Lithium
Based EP, Texaco Multitak 20 or Lubriplate ED-2 type
grease.
Cylinder Lubrication Box
NOTICE
When using the pump during freezing conditions,
completely drain the lubrication box and cover the hopper
after pumping. Frozen liquid will restrict the piston travel
and cause severe damage to the pump.
3. While stroking, spray water inside of the box to
thoroughly clean out all contamination (Figure 50).
4. When the box is clean replace drain plug, add new
lubrication and install the top cover.
W
A
T
E
R
Figure 50. Cleaning the Lubrication Box
TOP
COVER
PLUG
MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14) — PAGE 47
Page 48

MAINTENANCE
Wear Plate and Cutting Ring
Due to the abrasive nature of concrete, it is normal for the
cutting ring to wear on its sides as it shears through the
concrete inside the hopper. The metal-to-metal friction and
the abrasiveness of the concrete will cause extreme wear
and reduce sealing capability between the cutting ring and
wear plate.
If the two components do not properly seat against each
other, slurry will pump into the hopper rather than out the
discharge line. See Figure 51. This condition can easily
be observed.
1. The sudden change of the level of concrete inside the
hopper during each pumping stroke.
2. Concrete slurry squirting into the air from the hopper
(volcano effect).
3. When the output volume at the end of the delivery line
decreases in pressure.
4. Unusual frequent material packs in the Shuttle tube.
It is important that the wear components (Figure 51) be
inspected weekly for proper sealing. Failure to inspect
will eventually cause severe damage to the nun-plate and
material cylinders. Visually inspect wear plate and cutting
ring to ensure surfaces are sealed against each other.
If a deep groove or a wide space has developed on the
sealing surfaces, it is time for replacement. Due to the
motion of the shuttle tube, the cutting ring experiences
a quicker rate of wear as opposed to the wear plate. The
wear ring typically requires replacement two times per wear
plate (2 to 1). When replacing the wear ring, also replace
the rubber energizer ring.
Changing the Concrete Cylinder Piston Cups
The urethane piston cups will occasionally require
replacement depending on the following factors.
The fluid level and cleanliness of the lubrication box.
The size and type of aggregate.
The type of concrete being pumped.
It is time to replace the cups when increasingly large
particles of sand and cement pass into the lubrication box.
DO NOT allow the cups to become so worn that they begin
to pass lubrication into the material cylinders.
If the liquid level of the lubrication box becomes to low, the
rubber cups will severely deform due to excessive heat.
Whenever replacement is due, both cylinder cups should
be replaced.
DANGER
RUBBER
ENERGIZER
SHUTTLE TUBE
(INSIDE HOPPER)
GOOD SEAL LEAKING
Figure 51. Wear Plate and Cutting Ring
CUTTING
RING
WEAR
PLATE
AMPUTATION HAZARD
During routine
maintenance or
removing material
blockage, you will be
required to put your
hand in the concrete
cylinders or near the
shuttle tube. You are at extreme risk of injury or
AMPUTATION if the engine is running or if pressure
is in the hydraulic system.
Prior to performing any maintenance on the pump,
follow described lock out-tag out procedures. Stop the
engine by turning off the ignition switch and remove
the starter key.
Place a DO NOT OPERATE tag over the switch and
disconnect the battery. The pressure reading on the
pressure gauge MUST read zero.
PAGE 48 — MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14)
Page 49

MAINTENANCE
Cylinder Cup Replacement Procedure
1. Remove the two hydraulic hoses connected to the
remix motor. Plug the ports with fittings (not provided)
to prevent hydraulic hose leakage.
2. Remove the hopper discharge nipple and loosen sleeve
seal. Inspect and replace if wear is excessive.
3. Remove the two tie rod nuts and the four eyebolt nuts
securing the hopper to the pump frame.
4. Using an approved lifting device, remove the hopper
using extreme care not to damage the hopper seal.
5. Start the engine and turn on the pressure test switch.
Cycle pump in reverse until hydraulic system obtains
maximum pressure, then turn pump and engine
off.
6. Remove ignition key and disconnect battery. Think
safety! Check the hydraulic gauges on panel and make
sure accumulator pressure reads zero. One piston
should be in the fully discharged position at the end
of the concrete cylinder.
7. Remove the three 3/8 – 16 x 3” bolts from the piston.
Remove the front faceplate.
8. Install two the 3/8’ 16x3” bolts back into the piston – do
not tighten. Use the two bolts as leverage to remove
the rubber piston cup and rear components.
13. Insert one 3/8” 16x3” bolt into the open bolt hole,
remove the alignment studs one at a time and install
the remaining 3/8” 16x3” bolts.
NOTICE
Before installing 3/8” bolts, coat the back of bolt heads
with silicon sealant. Torque all three bolts equal at 55 ft.
lbs. each.
Wear Plate And Cutting Ring Replacement
Due to the swinging motion of the nun-plate and the
abrasive nature of concrete, it is normal for the cutting
ring to wear on the side that shears through the concrete
inside the hopper.
If the wear ring and wear plate do not fully seat against each
other the concrete slurry will pump into the hopper. This
condition can be easily observed by the sudden change of
the level of concrete inside the hopper during each stroke.
1. Remove the two hydraulic hoses connected to the
remix motor. Plug the ports with fittings (not provided)
to prevent hydraulic hose leakage.
2. Remove the hopper discharge nipple and loosen sleeve
seal. Inspect and replace if wear is excessive.
3. Remove the two tie rod nuts and the four eyebolt nuts
securing the hopper to the pump frame.
9. Obtain two 3/8 16x7” full thread studs (these studs will
be used to assist in assembly alignment) insert the
two studs into the piston adapter. Coat the concrete
cylinder with grease.
10. Install the “O” Ring around the oiler plate. Install the
plate into the concrete cylinder utilizing the studs for
alignment.
NOTICE
Felt ring must be saturated with 30 wt. oil prior to
installation.
11. Install the felt holder over the oiler plate. Install felt ring
into felt holder. Install the bronze ring.
12. Using silicon sealant place a small bead of sealant
material on the front of the rubber piston cup and the
rear of the face plate. Install over alignment studs and
into concrete cylinders.
MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14) — PAGE 49
4. Using an approved lifting device, remove the hopper
using extreme care not to damage the hopper seal.
5. Remove the four 1/2” 1-1/4” bolts that hold the shuttle
tube to the nun-plate and remove shuttle tube.
6. Using two small pry bars remove the rubber energizer
ring, steel insert ring and wear ring.
NOTICE
The energizer ring and wear ring will normally have
concrete contamination holding them in position. It will
be required to chip some of the concrete loose to better
expose the energizer ring.
7. Clean out all concrete build up in and around the nunplate area with a wire brush.
8. Inspect the wear components for indications of wear.
The wear plate has two wear surfaces.
Page 50

JOG
CYLINDER STROKE
MAINTENANCE
Wear Plate Installation
1. Install the two cylinder o-rings.
2. Using silicon sealant, coat the circumference of the
concrete cylinders, the back of the wear plate and
around the five bolt holes. Next, install the wear plate
and the five bolts. The bolts must all be equally snugged
and tightened to 100 foot pounds each.
Wear Ring Installation
1. Install the wear ring into the nun plate.
2. Install the steel insert ring inside of the rubber energizer
ring.
3. Install the energizer ring assembly into the nun plate.
4. After installing the above mentioned components
the machine can be reassembled by reversing steps
1 through 5 of the Wear Plate and Cutting Ring
Replacement Procedure.
Heat Exchanger Cooling Fan
2. Place and hold the manual cylinder jogging switch
(Figure 53) to either JOG “A” or JOG “B” position to
test the pressure of that cylinder.
JOG
“A”
Figure 53. Manual Cylinder Jogging Switch
JOG
“B”
3. The pumping pressure gauge (Figure 54) should
read approximately 3100 ~ 3200 PSI.
2000 3000
1000
0
4000
5000
This section is intended to make sure the cooling fan is
working properly. Under normal conditions the fan should
be running any time the engine is turned on.
NOTICE
If the hydraulic oil temperature exceeds 170° F (77° C),
shut down the pump. DO NOT continue to operate the
pump. Failure to shut down the pump will result in severe
damage to the pump.
Pressure Test
1. To determine the pressure of the hydraulic system,
set the cylinder stroke control switch (Figure 52) to
the JOG position.
AUTOMATIC
CENTER
OFF
PUMPING
PRESSURE
Figure 54. Pumping Pressure Gauge
Figure 52. Cylinder Stroke
Control Switch (JOG)
PAGE 50 — MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14)
Page 51

Long Term Storage (Pump)
Remove the battery.
Drain the fuel tank completely. Treat with a fuel stabilizer
if necessary.
Clean exterior with a cloth soaked in clean oil.
Store unit covered with plastic sheet in moisture and
dust-free location out of direct sunlight.
CAUTION
NEVER store the pump with fuel in the tank for any
extended period of time. ALWAYS clean up spilled
fuel immediately.
Long Term Storage (Trailer)
1. Check brake system for proper fluid level in master
cylinder and bleed all lines.
MAINTENANCE
2. Lubricate all links and pivots to prevent any rusting.
3. Remove wheel and drum assemblies and spray a good
anti-corrosion compound (CRC formula 5-56) under
rubber boot on forward end of brake wheel cylinder.
Avoid spraying drum and brake lining.
4. Grease all bearings and reinstall wheel and drum
assemblies.
5. Make sure breakaway cable is fully released.
6. After extended storage, refer to the Maintenance Steps
listed above to insure that the trailer is ready for towing.
MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14) — PAGE 51
Page 52

TRAILER MAINTENANCE
HYDRAULIC
BRAKE
The following trailer maintenance guidelines are intended
to assist the operator in preventive maintenance.
TRAILER BRAKES
Properly functioning brake shoes and drums are essential
to ensure safety. The brakes should be inspected the first
200 miles of operation. This will allow the brake shoes and
drums to seat properly. After the first 200 mile interval,
inspect the brakes every 3,000 miles. If driving over rough
terrain, inspect the brakes more frequently.
HYDRAULIC BRAKES
If your trailer has hydraulic brakes, they function the same
way the surge brakes do on your tow vehicle. The hydraulic
braking system must be inspected at least as often as the
brakes on the tow vehicle, but no less than once per year.
This inspection includes an assessment of the condition
and proper operation of the wheel cylinders, brake shoes,
brake drums and hubs.
MANUALLY ADJUSTING THE BRAKES
7. Repeat the above procedure on all brakes.
8. Lower the trailer to the ground.
Check the fluid level in the master cylinder reservoir at least
every three months. If you tow your trailer an average of
1,000 miles per month in a hot and dry environment, you
must check the brake fluid level once a month. The brake
fluid reservoir is located on the tongue of the trailer. Always
fill with clean, uncontaminated DOT 4 brake fluid.
Figure 55 below displays the major hydraulic brake
components that will require inspection and maintenance.
Please inspect these components as required using steps
1 through 6 as referenced in the “Manually Adjusting The
Brakes” section on this page. See Table 10 for Hydraulic
Brake Troubleshooting.
Most axles are fitted with a brake mechanism that will adjust
the brakes during a hard stop. However, some braking
systems are not automatically adjusted by hard stopping.
These brakes require manual adjustment. The following
steps apply to adjust most manually adjustable brakes.
1. Jack up the trailer and secure it on adequate capacity
jackstands.
2. Be sure the wheel and brake drum rotate freely.
3. Remove the adjusting-hole cover from the adjusting
slot on the bottom of the brake backing plate.
4. With a screwdriver or standard adjusting tool, rotate the
starwheel of the adjuster assembly to expand the brake
shoes. Adjust the brake shoes out until the pressure
of the linings against the drum makes the wheel very
difficult to turn. Note: Your trailer maybe equipped with
drop spindle axles. See axle manual for your axle type.
You will need a modified adjusting tool for adjusting
the brakes in these axles. With drop spindle axles, a
modified adjusting tool with about an 80 degree angle
should be used.
Figure 55. Hydraulic Brake Components
HYDRAULIC BRAKE ACTUATOR
The hydraulic brake actuator (Figure 56) is the mechanism
that activates the trailer’s brake system. This actuator
changes fluid power into mechanical power. Therefore, the
fluid level must be checked frequently to assure that the
brakes function properly.
FLUID
RESERVOIR
5. Rotate the starwheel in the opposite direction until the
6. Replace the adjusting-hole cover.
wheel turns freely with a slight drag.
Figure 56. Hydraulic Brake Actuator
PAGE 52 — MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14)
Page 53

WARNING
2" or 2-5/16" BALL
NYLOC
BEARING
SEAL
NUT
DUST
Failure to maintain proper fluid level in the actuator
may result in loss of braking action which could cause
severe property damage, injury or death.
Periodically check the actuator mounting fasteners for
damage or loosening. Inspect the actuator for worn or
damaged parts. As you are towing your trailer, be aware
of any changes in braking quality. This could be an early
warning of brake or actuator malfunction and requires
immediate attention. Consult a certified brake specialist to
make necessary adjustment or repairs
TRAILER MAINTENANCE
ADJUSTABLE
CHANNEL
5/8" X 11" X 5"
BOLT
ADJUSTABLE
5/8"
NYLOC
COUPLER
5/8" FLAT
WASHER
NUT
5/8" X 11" X 5"
BOLT
3" PINTLE EYE
RING
Figure 57. Adjustable Channel
CHANNEL
5/8" FLAT
WASHER
5/8"
NUT
Table 10. Hydraulic Brake Troubleshooting
Symptom Possible Cause Solution
No Brakes Brake line broken or kinked? Repair or replace.
Brake lining glazed? Reburnish or replace.
Trailer overloaded? Correct weight.
Weak Brakes or
Brakes Pull to
One Side
Locking Brakes
Noisy Brakes
Dragging
Brakes
Brake drums scored or
grooved?
Tire pressure correct? Inflate all tires equally.
Tires unmatched on the
same axle?
Brake components loose,
bent or broken?
Brake drums out-of-round? Replace.
System lubricated? Lubricate.
Brake components correct? Replace and correct.
Brake lining thickness
incorrect or not adjusted
correctly?
Enough brake fluid or correct
fluid?
Machine or replace.
Match tires.
Replace components.
Install new shoes and
linings.
Replace rubber parts
fill with dot 4 fluid.
ADJUSTABLE CHANNEL
Your trailer may be equipped with an adjustable channel
(Figure 57) that allows the coupler to be raised or lowered
to a desired height. Periodically check the channel bolts
for damage or loosening.
NOTICE
When replacing channel mounting hardware (nuts,
bolts and washers), NEVER substitute substandard
hardware. Pay close attention to bolt length and grade.
ALWAYS use manufacturer's recommended parts
when replacing channel mounting hardware.
Wheel Bearings
Wheel bearings (Figure 57) must be inspected and
lubricated once a year or 12,000 miles to insure safe
operation of your trailer.
If trailer wheel bearings are immersed in water, they must
be replaced.
DANGER
If trailer wheels are under water for a long period of
time, wheel bearings may fail. If this is the case, service
wheel bearings immediately.
The possibility exists of the wheels falling off causing
equipment damage and severe bodily harm even death!
If the trailer has not been used for an extended amount
of time, have the bearings inspected and packed more
frequently, at least every six months and prior to use.
Follow the steps below to disassemble the wheel hub and
service the wheel bearings. See Figure 58.
WHEEL
HUB
OIL
BEARING
BEARING
CUP
LUG
NUT
SPINDLE
WASHER
CUP
Figure 58. Wheel Hub Components
COTTER
PIN
BEARING
CAP
SPINDLE
MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14) — PAGE 53
Page 54

TRAILER MAINTENANCE
5/8”-18 X 2”
GRADE C
After removing the dust cap, cotter pin, spindle nut and
spindle washer, remove the hub to inspect the bearings
for wear and damage.
Replace bearings that have flat spots on rollers, broken
roller cages, rust or pitting. Always replace bearings
and cups in sets. The inner and outer bearings are to
be replaced at the same time.
Replace seals that have nicks, tears or wear.
Lubricate the bearings with a high quality EP-2
automotive wheel bearing grease.
WHEEL HUB ADJUSTMENT
Every time the wheel hub is removed and the bearings are
reassembled, follow the steps below to check the wheel
bearings for free running and adjust.
Turn the hub slowly, by hand, while tightening the spindle
nut until you can no longer turn the hub by hand.
Loosen the spindle nut just until you are able to turn it
(the spindle nut) by hand. Do not turn the hub while the
spindle nut is loose.
Install a new cotter pin through the spindle nut and axle.
Check the adjustments. Both the hub and the spindle nut
should be able to move freely (the spindle nut motion
will be limited by the cotter pin).
DANGER
Improper weld repair will lead to early failure of the
trailer structure and can cause serious injury or death.
DO NOT repair cracked or broken welds unless you
have a certified welder perform the repair. If not, have
the welds repaired by your dealer.
WARNING
If the trailer is involved in an accident, have it inspected
immediately by qualified personnel. In addition, the
trailer should be inspected annually for signs of wear
or deformations.
TORSION SUSPENSION
The mounting bracket and associated components
(Figure 59) should be visually inspected every 6,000
miles for signs of excessive wear, elongation of bolt
holes, and loosening of fasteners. Replace all damaged
parts immediately.
MOUNTING
BOLT
MOUNTING
BRACKET
DANGER
NEVER crawl under the trailer unless it is on firm
and level ground and resting on properly placed and
secured jackstands.
The possibility exists of the trailer falling thus causing
equipment damage and severe bodily harm even death!
DANGER
When performing trailer inspection and maintenance
activities, you must jack up the trailer using jacks and
jackstands.
When jacking and using jackstands, place them so
as to clear wiring, brake lines, and suspension parts
(i.e., springs, torsion bars). Place jacks and jackstands
inside of the perimeter strip on the supporting structure
to which the axles are attached.
SPINDLE
TORSION
ARM
Figure 59. Torsion Suspension Components
TORSION
BAR
NYLOC NUT
AXLE
TUBE
5/8”-18
DANGER
Worn or broken suspension parts can cause loss of
control, damage to equipment and severe bodily injury,
even death!
Check suspension regularly.
PAGE 54 — MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14)
Page 55

TRAILER GUIDELINES
The following guidelines are intended to assist the operator
Shift your automatic transmission into a lower gear for
use lower gears for climbing and descending
ride the brakes while descending grades, they
may get so hot that they stop working. Then you will
To conserve fuel, don’t use full throttle to climb a hill.
Slow down for bumps in the road. Take your foot off the
brake while in a curve unless absolutely
necessary. Instead, slow down before you enter the
curve and power through the curve. This way, the towing
apply the brakes to correct extreme trailer
swaying. Continued pulling of the trailer, and even slight
Anticipate the trailer “swaying.” Swaying is the trailer
reaction to the air pressure wave caused by passing
trucks and buses. Continued pulling of the trailer provides
a stabilizing force to correct swaying. DO NOT apply the
Use lower gear when driving down steep or long grades.
Use the engine and transmission as a brake. Do not
ride the brakes, as they can overheat and become
Be aware of your trailer height, especially when
Make regular stops, about once each hour. Confi rm
There is appropriate slack in the breakaway switch
in the operation and handling of a trailer.
Safety precautions should be followed at all times when
operating a trailer. Failure to read, understand and follow
the safety guidelines could result in injury to yourself and
others. Loss of control of the trailer or tow vehicle can result
in death or serious injury.
COMMON CAUSES FOR LOSS OF TRAILER
Driving too fast for the conditions (maximum speed when
towing a trailer is 55 mph).
Overloading the trailer or loading the trailer unevenly.
Trailer improperly coupled to the hitch.
No braking on trailer.
Not maintaining proper tire pressure.
Not keeping lug nuts tight.
Not properly maintaining the trailer structure.
Ensure machine is towed level to tow vehicle.
city driving.
ALWAYS
grades.
DO NOT
potentially have a runaway tow vehicle and trailer.
Instead, build speed on the approach.
brake when crossing the bump.
DO NOT
vehicle remains in charge.
DO NOT
acceleration, will provide a stabilizing force.
TRAILER TOWING GUIDELINES
Recheck the load tiedowns to make sure the load will
not shift during towing.
Before towing, check coupling, safety chain, safety
brake, tires, wheels and lights.
Check the lug nuts or bolts for tightness.
Check coupler tightness after towing 50 miles.
Use your mirrors to verify that you have room to change
lanes or pull into traffi c.
Use your turn signals well in advance. Allow plenty of
stopping space for your trailer and tow vehicle.
Allow plenty of stopping space for your trailer and tow
vehicle.
DO NOT drive so fast that the trailer begins to sway
due to speed.
Allow plenty of room for passing. A rule of thumb is that
the passing distance with a trailer is 4 times the passing
distance without the trailer.
brakes to correct trailer swaying.
ineffective.
approaching roofed areas and around trees.
that:
• Coupler is secure to the hitch and is locked.
• Electrical connectors are secure.
• There is appropriate slack in the safety chains.
•
pullpin cable.
• Tires are not visibly low on pressure.
MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14) — PAGE 55
Page 56

DRIVING CONDITIONS
When towing a trailer, you will have decreased acceleration,
increased stopping distance, and increased turning radius
(which means you must make wider turns to keep from
hitting curbs, vehicles, and anything else that is on the
inside corner). In addition, you will need a longer distance
to pass, due to slower acceleration and increased length.
COUPLING TO THE TOW VEHICLE
Follow all of the safety precautions and instructions in
this manual to ensure safety of persons, equipment, and
satisfactory life of the trailer. Always use an adequate tow
vehicle and hitch. If the vehicle or hitch is not properly
selected and matched to the Gross Vehicle Weight Rating
(GVWR) of your trailer, you can cause an accident that
could lead to death or serious injury.
If you already have a tow vehicle, know your vehicle tow
rating and make certain the trailer’s rated capacity is less
than or equal to the tow vehicle’s rated towing capacity. If
you already have (or plan to buy) a trailer, make certain
that the tow rating of the tow vehicle is equal to or greater
than that of the trailer.
The trailer VIN tag contains the critical safetyinformation
for the use of your trailer. Again, be sure your hitch and tow
vehicle are rated for the Gross Vehicle Weight Rating of
your trailer.
WARNING
TRAILER GUIDELINES
Be alert for slippery conditions. You are more likely to be
affected by slippery road surfaces when driving a tow
vehicle with a trailer, than driving a tow vehicle without
a trailer.
Check rearview mirrors frequently to observe the trailer
and traffi c.
NEVER drive faster than what is safe.
WARNING
Driving too fast for severe road conditions can result in
loss of control and cause death or serious injury.
Decrease your speed as road, weather, and lighting
conditions deteriorate.
Always check for local trailer tow speed limits in your
area.
WARNING
Do not transport people on the trailer. The transport of
people puts their lives at risk and may be illegal.
Proper selection and condition of the coupler and hitch
are essential to safely towing your trailer. A loss of
coupling may result in death or serious injury.
• Be sure the hitch load rating is equal to or greater
than the load rating of the coupler.
• Be sure the hitch size matches the coupler size.
• Observe the hitch for wear, corrosion and cracks
before coupling. Replace worn, corroded or cracked
hitch components before coupling the trailer to the
tow vehicle.
• Be sure the hitch components are tight before
coupling the trailer to the tow vehicle.
WARNING
An improperly coupled trailer can result in death or
serious injury.
DO NOT move the trailer until:
• The coupler is secured and locked to hitch.
• The safety chains are secured to the tow vehicle.
• The trailer jack(s) are fully retracted.
DO NOT tow the trailer on the road until:
• Tires and wheels are checked.
PAGE 56 — MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14)
• The trailer brakes are checked.
• The breakaway switch is connected to the tow
vehicle.
• The load is secured to the trailer.
• The trailer lights are connected and checked.
WARNING
Use of a hitch with a load rating less than the load rating
of the trailer can result in loss of control and may lead
to death or serious injury.
Use of a tow vehicle with a towing capacity less than
the load rating of the trailer can result in loss of control,
and may lead to death or serious injury.
Be sure your hitch and tow vehicle are rated for the
Gross Vehicle Weight Rating of your trailer.
Page 57

INOPERABLE BRAKES, LIGHTS OR MIRRORS
Be sure that the brakes and all of the lights on your trailer
are functioning properly before towing your trailer. Check
the trailer taillights by turning on your tow vehicle headlights.
Check the trailer brake lights by having someone step on
the tow vehicle brake pedal while you look at trailer lights.
Do the same thing to check the turn signal lights. See Trailer
Wiring Diagram section in this manual.
Standard mirrors usually do not provide adequate visibility
for viewing traffi c to the sides and rear of a towed trailer.
You must provide mirrors that allow you to safely observe
approaching traffi c.
TRAILER TOWING TIPS
Driving a vehicle with a trailer in tow is vastly different
from driving the same vehicle without a trailer in tow.
Acceleration, maneuverability and braking are all diminished
with a trailer in tow.
It takes longer to get up to speed, you need more room to
turn and pass, and more distance to stop when towing a
trailer. You will need to spend time adjusting to the different
feel and maneuverability of the tow vehicle with a loaded
trailer.
Because of the signifi cant differences in all aspects of
maneuverability when towing a trailer, the hazards and risks
of injury are also much greater than when driving without
a trailer. You are responsible for keeping your vehicle and
trailer in control, and for all the damage that is caused if
you lose control of your vehicle and trailer.
As you did when learning to drive an automobile, fi nd
an open area with little or no traffi c for your fi rst practice
trailering. Of course, before you start towing the trailer, you
must follow all of the instructions for inspection, testing,
loading and coupling. Also, before you start towing, adjust
the mirrors so you can see the trailer as well as the area
to the rear of it.
Drive slowly at fi rst, 5 mph or so, and turn the wheel to
get the feel of how the tow vehicle and trailer combination
responds. Next, make some right and left hand turns.
Watch in your side mirrors to see how the trailer follows
the tow vehicle. Turning with a trailer attached requires
Stop the rig a few times from speeds no greater than
10 mph. If your trailer is equipped with brakes, try using
different combinations of trailer brake and tow vehicle brake.
Note the effect that the trailer brakes have when they are
the only brakes used. When properly adjusted, the trailer
It will take practice to learn how to back up a tow vehicle
with a trailer attached. Take it slow. Before backing up, get
out of the tow vehicle and look behind the trailer to make
Some drivers place their hands at the bottom of the steering
wheel, and while the tow vehicle is in reverse, “think” of the
hands as being on the top of the wheel. When the hands
move to the right (counterclockwise, as you would do to
turn the tow vehicle to the left when moving forward), the
rear of the trailer moves to the right. Conversely, rotating
the steering wheel clockwise with your hands at the bottom
of the wheel will move the rear of the trailer to the left while
If you are towing a bumper hitch rig, be careful not to allow
the trailer to turn too much because it will hit the rear of the
tow vehicle. To straighten the rig, either pull forward or turn
Figure A below is a sample of the Vehicle Identifi cation
Number (VIN) Tag which is typically located on the left front
TRAILER GUIDELINES
WARNING
Improper electrical connection between the tow vehicle
and the trailer will result in inoperable lights and can
lead to collision.
Before each tow, check that the tail lights, brake lights
and turn signals work.
more room.
brakes will come on just before the tow vehicle brakes.
sure that there are no obstacles.
backing up.
the steering wheel in the opposite direction.
TRAILER VIN TAG
of the trailer. See Figure B for location.
MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14) — PAGE 57
Figure A. Vehicle VIN Tag
Page 58

The trailer VIN Tag contains the following critical safety
information for the use of your trailer.
GAWR
It is the lowest of axle, wheel, or tire rating.
Usually, the tire or wheel rating is lower than the axle rating,
and determines GAWR.
GVWR
and its contents. The gross weight of the trailer includes
the weight of the trailer and all of the items within it. GVWR
is sometimes referred to as GTWR (Gross Trailer Weight
Rating), or MGTW (Maximum Gross Trailer Weight). GVWR,
GTWR and MGTW are all the same rating.
The sum total of the GAWR for all trailer axles may be less
than the GVWR for the trailer, because some of the trailer
load is to be carried by the tow vehicle, rather than by the
trailer axle(s). The total weight of the cargo and trailer must
not exceed the GVWR, and the load on an axle must not
exceed its GAWR.
PSIC
VIN
EMPTY WEIGHT
trailer (such as the Manufacturer’s Statement of Origin)
is not a reliable source for “empty” or “net” weight. The
shipping documents list average or standard weights and
your trailer may be equipped with options.
VIN
TAG
To determine the “empty” or “net” weight of your trailer,
weigh it on an axle scale. To fi nd the weight of the trailer
using an axle scale, you must know the axle weights of
your tow vehicle without the trailer coupled. Some of the
trailer weight will be transferred from the trailer to the tow
vehicle axles, and an axle scale weighs all axles, including
The towing hitch attached to your tow vehicle must have a
capacity equal to or greater than the load rating of the trailer
you intend to tow. The hitch capacity must also be matched
to the tow vehicle capacity. Your vehicle dealer can provide
Sway bars, shock absorbers, heavy duty springs, heavy
duty tires and other suspension components may be
For trailers equipped with electric brakes, the electric brake
controller is part of the tow vehicle and is essential in the
operation of the electric brakes on the trailer. The brake
controller is not the same as the safety breakaway brake
The size of the trailer that is being towed and your state
law regulations determine the size of the mirrors. However,
some states prohibit extended mirrors on a tow vehicle,
except while a trailer is actually being towed. In this
situation, detachable extended mirrors are necessary.
Check with your dealer or the appropriate state agency
A Heavy Duty Flasher is an electrical component that may
be required when your trailer turn signal lights are attached
An Electrical Connector connects the light and brake
systems on the trailer to the light and brake controls on
VIN TAG
TRAILER GUIDELINES
the tow vehicle axles.
TOW VEHICLE
Figure B. VIN Tag Location
: The maximum gross weight that an axle cansupport.
: The maximum allowable gross weight of the trailer
: The tire pressure (psi) measured when cold.
: The Vehicle Identifi cation Number.
: Some information that comes with the
and install the proper hitch on your tow vehicle.
SUSPENSION SYSTEM
required to suffi ciently tow the trailer and pump.
BRAKE CONTROLLER
system that may be equipped on the trailer.
SIDE VIEW MIRRORS
for mirror requirements.
HEAVY DUTY FLASHER
to the tow vehicle fl asher circuit.
ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
the towing vehicle.
PAGE 58 — MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14)
Page 59

EMERGENCY FLARES AND TRIANGLE REFLECTORS
It is wise to carry these warning devices even if you are
not towing a trailer. It is particularly important to have these
when towing a trailer because the hazard fl ashers of your
towing vehicle will not operate for as long a period of time
when the battery is running both the trailer lights and tow
vehicle lights.
SAFETY CHAINS
If the coupler connection comes loose, the safety chains
can keep the trailer attached to the tow vehicle. With
properly rigged safety chains, it is possible to keep the
tongue of the trailer from digging into the road pavement,
even if the coupler-to-hitch connection comes apart.
TRAILER LIGHTING AND BRAKING CONNECTOR
A device that connects electrical power from the tow vehicle
to the trailer. Electricity is used to turn on brake lights,
running lights, and turn signals as required. In addition, if
your trailer has a separate braking system, the electrical
connector will also supply power to the brakes from the
tow vehicle.
BREAKAWAY SYSTEM
If the trailer coupler connection comes loose, the breakaway
system can actuate emergency hydraulic brakes depending
on the type of actuator on the trailer. The breakaway cable
must be rigged to the tow vehicle with appropriate slack
that will activate the system if the coupler connection
comes loose.
JACKSTAND
A device on the trailer that is used to raise and lower the
coupler. The jack is sometimes called the “landing gear” or
the “tongue jack”.
COUPLER TYPES
Two types of coupler used wit the trailer are discussed
below.
BALL HITCH COUPLER
A ball hitch coupler (Figure C) connects to a ball that is
located on or under the rear bumper of tow vehicle. This
system of coupling a trailer to a tow vehicle is sometimes
A ball hitch trailer may be fi tted with a tongue jack that can
raise and lower the coupler. The tongue jack is mounted to
the A-frame (front or tongue) part of the trailer. By rotating
the jack handle clockwise, the jack will extend and raise
Before each tow, coat the ball with a thin layer of automotive
bearing grease to reduce wear and ensure proper operation.
Check the locking device that secures the coupler to the
If you see or feel evidence of wear, such as fl at spots,
deformations, pitting or corrosion, on the ball or coupler,
immediately have your dealer inspect them to determine
the proper action to prevent possible failure of the ball and
coupler system. All bent or broken coupler parts must be
The coupler handle lever must be able to rotate freely and
automatically snap into the latched position. Oil the pivot
points, sliding surfaces, and spring ends with SAE 30W
motor oil. Keep the ball socket and latch mechanism clean.
Dirt or contamination can prevent proper operation of the
The load rating of the coupler and the necessary ball size
are listed on the trailer tongue. You must provide a hitch and
ball for your tow vehicle where the load rating of the hitch
Also, the ball size must be the same as the coupler size. If
the hitch ball is too small, too large, is underrated, is loose
TRAILER GUIDELINES
referred to as “bumper pull.”
the tongue of the trailer.
Figure C. Ball Hitch Coupler
ball for proper operation.
replaced before towing the trailer.
Ball Hitch Coupler
Pintel Eye Coupler
MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14) — PAGE 59
latching mechanism.
and ball is equal to or greater than that of your trailer.
Page 60

or is worn, the trailer can come loose from the tow vehicle
and may cause death or serious injury.
THE TOW VEHICLE, HITCH AND BALL MUST HAVE A
RATED TOWING CAPACITY EQUAL TO OR GREATER
THAN THE TRAILER
(GVWR)
OF THE SAME SIZE AS THE COUPLER.
The ball size and load rating (capacity) are marked on the
ball. Hitch capacity is marked on the hitch.
the trailer tongue. Wood or concrete blocks may also
be used.
Coupling the Trailer to the Tow Vehicle (Ball Coupler)
Lubricate the hitch ball and the inside of the coupler with
Slowly back up the tow vehicle so that the hitch ball is
Using the jackstand at the front of trailer (tongue), turn
the jackstand crank handle to raise the trailer. If the ball
coupler does not line up with the hitch ball, adjust the
Open the coupler locking mechanism. Ball couplers have
a locking mechanism with an internal moving piece and
an outside handle. In the open position, the coupler is
Lower the trailer (Figure D) until the coupler fully engages
Engage the coupler locking mechanism. In the engaged
position, the locking mechanism securely holds the
Insert a pin or lock through the hole in the locking
Be sure the coupler is all the way on the hitch ball and
the locking mechanism is engaged. A properly engaged
locking mechanism will allow the coupler to raise the rear
of the tow vehicle. Using the trailer jackstand, verify that
you can raise the rear of the tow vehicle by 1 inch after
Lower the trailer so that its entire tongue weight is held
Raise the jackstand to a height where it will not interfere
2-INCH
TRAILER GUIDELINES
. IT IS ESSENTIAL THAT THE HITCH BALL BE
Gross Vehicle Weight Rating
WARNING
Coupler-to-hitch mismatch can result in uncoupling,
leading to death or serious injury.
Be sure the LOAD RATING of the hitch ball is equal or
greater than the load rating of the coupler.
Be sure the SIZE of the hitch ball matches the size of
the ball coupler.
WARNING
A worn, cracked or corroded hitch ball can fail while
towing and may result in death or serious injury.
Before coupling trailer, inspect the hitch ball for wear,
corrosion and cracks.
Replace worn or damaged hitch ball.
a thin layer of automotive bearing grease.
near or aligned under the coupler.
position of the tow vehicle.
able to drop fully onto the hitch ball.
the hitch ball.
TRAILER
COUPLER
TOW
VEHICLE
2-INCH
BALL
WARNING
A loose hitchball nut can result in uncoupling, leading
to death or serious injury.
Be sure the hitch ball is tight to the hitch before coupling
the trailer.
Rock the ball to make sure it is tightened to the hitch,
and visually check that the hitch ball nut is solid against
the lock washer and hitch frame.
Wipe the inside and outside of the coupler. Clean and
visually inspect it for cracks and deformations. Feel the
inside of the coupler for worn spots and pits.
Be sure the coupler is secured tightly to the tongue of the
trailer. All coupler fasteners must be visibly solid against
the trailer frame.
The bottom surface of the coupler must be above the top
of the hitch ball. Use the tongue jackstand to support
PAGE 60 — MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14)
Figure D. Ball Hitch Coupling Mechanism
coupler to the hitch ball.
mechanism.
the coupler is locked to the hitch.
by the hitch.
with the road.
Page 61

If the coupler cannot be secured to the hitch ball, do not
tow the trailer. Call your dealer for assistance. Lower the
trailer so that its entire tongue weight is held by the hitch and
continue retracting the jack to its fully retracted position.
Attaching Safety Chain
Visually inspect the safety chains and hooks for wear or
damage. Replace worn or damaged safety chains and
hooks before towing.
Attach the safety chains so that they:
.
NOTICE
SAFETY CHAINS
TOW
Breakaway Brake System
If the coupler or hitch fails, a properly connected and
working breakaway brake system (Figure F) will apply the
hydraulic brakes on the trailer. The safety chains will keep
the tow vehicle attached and as the brakes are applied at
the trailer’s axles, the trailer/tow vehicle combination will
The breakaway brake system includes a brake cable
connected to the tow vehicle on one end and to the
emergency brake lever located on the hydraulic actuator
Connect Cable
to
Actuator
Overloading can damage the tongue jack. DO NOT
use the tongue jack to raise the tow vehicle more than
one inch.
TRAILER GUIDELINES
• Cross underneath the coupler. See Figure E.
VEHICLE
TRAILER
TONGUE
IMPORTANT!
SAFETY CHAIN
MASTER LINK
CROSS BOTH
Figure E. Attaching Safety Chain (Ball Hitch)
• Loop around a frame member of the tow vehicle or holes
provided in the hitch system (DO NOT attach them to
an interchangeable part of the hitch assembly).
• Have enough slack to permit tight turns, but not be
close to the road surface, so if the trailer uncouples, the
safety chains can hold the tongue up above the road
WARNING
Improper rigging of the safety chains can result in
loss of control of the trailer and tow vehicle, leading
to death or serious injury, if the trailer uncouples from
the tow vehicle.
• Fasten chains to frame of tow vehicle. DO NOT fasten
chains to any part of the hitch unless the hitch has
holes or loops specifi cally for that purpose.
• Cross chains underneath hitch and coupler with
enough slack to permit turning and to hold tongue
up, if the trailer comes loose.
come to a controlled stop.
TowVehicle
Hydraulic Actuator
Figure F. Breakaway Brake System
Breakaway Lever
Connect Cable
to TowVehicle
Breakaway Switch
Electric
Breakaway Cable Surge Brake System
on the other end.
WARNING
• An ineffective breakaway brake system can result in
a runaway trailer, leading to death or serious injury,
if the coupler or ball hitch fails.
• Connect the breakaway cable to the tow vehicle and
NOT to the hitch, ball or support.
• Before towing the trailer, test the function of the
breakaway brake system. If the breakaway brake
system is not working, DO NOT tow the trailer. Have
it serviced or repaired.
NOTICE
DO NOT tow the trailer with the breakaway brake
system ON because the brakes will overheat which
can result in permanent brake failure.
NOTICE
Replace the breakaway brake battery (if equipped) at
intervals specifi ed by manufacturer.
MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14) — PAGE 61
Page 62

Connecting Trailer Lights
Connect the trailer lights to the tow vehicle’s electrical
system using the electric connectors at the front of the
trailer (tongue). Refer to the wiring diagram shown in the
trailer wiring diagram section of this manual. Before towing
the trailer check for the following:
Uncoupling the Ball Hitch
Follow these steps to uncouple ball hitch from tow
vehicle:
PINTLE HITCH COUPLER
A pintle eye coupler (Figure G) connects to a pintle-hook
hitch that is located on or under the rear bumper of the tow
vehicle. This system of coupling a trailer to a tow vehicle is
sometimes referred to as a “lunette eye, tow ring or G.I.
A pintle hitch trailer may be fi tted with a tongue jackstand
that can raise and lower the coupler. The tongue jack is
mounted to the A-frame (front or tongue) part of the trailer.
By rotating the jack handle clockwise, the jack will extend
The load rating of the coupler and the necessary pintle
hitch size are listed on the trailer tongue. You must provide
a pintle hitch and pintle coupler for your tow vehicle, where
the load rating of the pintle hitch and pintle coupler is equal
Also, the pintle hitch size must be the same as the pintle
coupler size. If the hitch is too small, too large, underrated,
loose or worn, the trailer can come loose from the tow
Before each tow, check the locking device that secures the
The pintle hook lever must be able to operate freely and
automatically snap into place into the latched position.
Lightly oil the pivot points and sliding surfaces with SAE30W
motor oil to prevent rust and help ensure proper operation
If you see or feel evidence of wear, such as fl at spots,
deformations, pitting or corrosion, on the pintle hook or
coupler, immediately have your dealer inspect them to
determine the proper action to prevent possible failure of
TRAILER GUIDELINES
Running lights (turn on tow vehicle headlights).
Brake Lights (step on tow vehicle brake pedal).
Backup Lights (place tow vehicle gear shift in reverse).
Turn Signals (activate tow vehicle directional signal
lever).
WARNING
Improper electrical connection between the tow vehicle
and the trailer will result in inoperable lights and electric
brakes, and can lead to collision.
Before each tow:
• Check that the taillights, brake lights and turn signals
work.
• Check that the electric brakes work by operating the
brake controller inside the tow vehicle.
hitch.”
Figure G. Pintle Hitch Coupler
and raise the tongue of the trailer.
Block trailer tires to prevent the trailer from rolling, before
jacking the trailer up.
Disconnect the electrical connector.
Disconnect the breakaway brake switch cable. Promptly
replace the pullpin in the switchbox.
Before extending jackstand, make certain the ground
surface below the jackstand foot will support the tongue
load.
Rotate the jackstand handle (or crank) clockwise. This
will slowly extend the jack and transfer the weight of the
trailer tongue to the jack.
PAGE 62 — MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14)
to or greater than that of your trailer.
vehicle, and may cause death or serious injury.
Pintle Coupler and Pintle Hook
coupler to the pintle hook assembly.
of the latching mechanism.
Page 63

the ball andcoupler system. All bent or broken coupler parts
must be replaced before towing the trailer.
THE TOW VEHICLE, PINTLE HITCH AND PINTLE
COUPLER MUST HAVE A RATED TOWING CAPACITY
EQUAL TO OR GREATER THAN THE TRAILER
Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR)
IT IS ESSENTIAL THAT THE PINTLE HITCH BE OF THE
SAME SIZE AS THE PINTLE COUPLER.
The coupler size and load rating (capacity) are marked on
the coupler. Hitch capacity is marked on the hitch.
Slowly back up the tow vehicle so that the pintle
hitch hook is near or aligned under the pintle eye ring
Using the jackstand at the front of trailer (tongue), turn
the jackstand crank handle to raise the trailer. If the pintle
eye coupler does not line up with the pintle hitch hook,
OPEN the pintle hook locking mechanism (Figure H).
Place the hook inside the eye coupler. CLOSE the pintle
Insert a pin or lock through the hole in the locking
Be sure the pintle hook is inserted completely through
the eye ring and the locking mechanism is engaged.
A properly engaged locking mechanism will allow the
coupler to raise the rear of the tow vehicle. Using the
trailer jack, test to see that you can raise the rear of the
tow vehicle by1-inch after the coupler is locked to the
Lower the trailer so that its entire tongue weight is held
Raise the jackstand to a height where it will not interfere
TRAILER
SAFETY CHAINS
TRAILER GUIDELINES
WARNING
A defective pintle hitch not properly fastened can result
in uncoupling, leading to death or serious injury.
.
WARNING
Coupler-to-hitch mismatch can result in uncoupling,
leading to death or serious injury.
Be sure the LOAD RATING of the pintle hitch hook is
equal or greater than the load rating of the pintle eye
coupler.
Be sure the SIZE of the pintle hitch hook matches the
size of the pintle eye coupler.
WARNING
A worn, cracked or corroded pintle hitch hook can fail
while towing, and may result in death or serious injury.
Before coupling trailer, inspect the pintle hitch hook for
wear, corrosion and cracks.
Replace worn or damaged pintle hitch hook.
Gross
Be sure the pintle hook is securly tighten to the tow
vehicle before coupling the trailer.
Coupling Trailer to Tow Vehicle (Pintle Coupler)
coupler.
adjust the position of the tow vehicle.
hook mechanism.
TONGUE
PINTLE
RING “EYE”
TOW
VEHICLE
SAFETY
CHAIN
PINTLE
HOOK
IMPORTANT!
CROSS BOTH
SAFETY CHAIN
MASTER LINK
Rock the pintle eye coupler to make sure it is secured
tightly to the hitch.
Wipe the inside and outside of the pintle coupler. Clean
and inspect it visually for cracks and deformations. Feel
the inside of the coupler for worn spots and pits.
Be sure the coupler is secured tightly to the tongue of the
trailer. All coupler fasteners must be visibly solid against
the trailer frame.
Raise the bottom surface of the coupler to be above the
top of the pintle hitch hook. Use the tongue jackstand
to support the trailer tongue. Wood or concrete blocks
may also be used.
MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14) — PAGE 63
Figure H. Attaching Safety Chain (Pintle Hitch)
mechanism.
hitch.
by the hitch.
with the road.
Page 64

TIRE SAFETY
Unsafe Tires, Lug Nuts or Wheels
Trailer tires and wheels are more likely to fail than car tires
and wheels because they carry a heavier load. Therefore,
it is essential to inspect the trailer tires before each tow.
If a tire has a bald spot, bulge, cuts, is showing any cords,
or is cracked, replace the tire before towing. If a tire has
uneven tread wear, take the trailer to a dealer service
center for diagnosis.
Uneven tread wear can be caused by tire imbalance, axle
misalignment or incorrect infl ation.
Tires with too little tread will not provide adequate tracking
on wet roadways and can result in loss of control, leading
to death or serious injury.
Improper tire pressure causes an unstable trailer and
can result in a tire blowout and loss of control. Therefore,
before each tow you must also check the tire pressure. Tire
pressure must be checked when tires are cold.
Allow 3 hours cool-down after driving as much as 1 mile at
40 mph before checking tire pressure. Trailer tires will be
infl ated to higher pressures than passenger vehicle tires.
Since trailer wheels and lug nuts (or bolts) are subjected
to greater side loads than automobile wheels, they are
more prone to loosen. Before each tow, check to make
sure they are tight.
The proper tightness (torque) for lug nuts is listed in the
lug nut tightening section of this manual. Use a torque
wrench to tighten the lug nuts. If you do not have a torque
wrench, use a lug wrench (from your tow vehicle) and
tighten the nuts as much as you can. Then have a service
garage or trailer dealer tighten the lug nuts to the proper
torque.
Lug nuts are also prone to loosen after first being
assembled. When driving a new trailer (or after wheels
have been remounted), check to make sure they are tight
after the fi rst 10, 25 and 50 miles of driving and before
Failure to perform this check can result in a wheel parting
from the trailer and a crash, leading to death or serious
Determining the load limits of a trailer includes more than
understanding the load limits of the tires alone. On all
trailers there is a Federal certifi cation/VIN label that is
located on the forward half of the left (road) side of the unit.
This certifi cation/VIN label will indicate the trailer’s Gross
Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR). This is the most weight
the fully loaded trailer can weigh. It will also provide the
Gross Axle Weight Rating (GAWR). This is the most a the
wheel(s) have been remounted after the fi rst 10, 25
TRAILER GUIDELINES
each tow thereafter.
injury.
WARNING
Lug nuts are prone to loosen after initial installation,
which can lead to death or serious injury.
Check lug nuts for tightness on a new trailer or when
and 50 miles of driving.
WARNING
Metal creep between the wheel rim and lug nuts will
cause rim to loosen and could result in a wheel coming
off, leading to death or serious injury.
Tighten lug nuts before each tow.
WARNING
Improper lug nut torque can cause a wheel parting from
the trailer, leading to death or serious injury.
Be sure lug nuts are tight before each tow.
WARNING
Improper tire pressure can result in a blowout and loss
of control, which can lead to death or serious injury.
Be sure tires are infl ated to pressure indicated on side
wall before towing trailer.
Determining Load Limit of Trailer
axle can weigh.
PAGE 64 — MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14)
Page 65

There is a vehicle placard (Figure I) located in the same
location as the certifi cation label described above. This
placard provides tire and loading information. In addition,
this placard will show a statement regarding maximum
cargo capacity.
If additional work items (hoses, tools, clamps etc.) are
going to be added to the trailer, be sure they are distributed
evenly to prevent overloading front to back and side to side.
Heavy items should be placed low and as close to the axle
positions as reasonable. Too many items on one side may
overload a tire.
Excessive loads and/or underinfl ation cause tire overloading
and, as a result, abnormal tire fl exing occurs. This situation
can generate an excessive amount of heat within the tire.
Excessive heat may lead to tire failure. It is the air pressure
that enables a tire to support the load, so proper infl ation
is critical. The proper air pressure may be found on the
certifi cation/VIN label and/or on the Tire and Loading
Information placard. This value should never exceed the
maximum cold infl ation pressure stamped on the tire.
Perform the following steps to determine the load limit of
your trailer.
Step 1.
Locate the statement, “The weight of cargo should never
exceed XXX kg or XXX lbs.,” on your vehicle’s Tire and
Loading Information placard (Figure I). This value equals
the available amount of equipment load capacity.
Step 2.
Determine the weight of the equipment being loaded
on the tow vehicle. That weight may not safely exceed
the available equipment load capacity. The trailer’s Tire
Information Placard is attached adjacent to or near the
trailer’s VIN (Certifi cation) label at the left front of the trailer
(See Figure I).
Determining Load Limit of Tow Vehicle
Step 1.
Locate the statement, “The combined weight of occupants
and cargo should never exceed XXX lbs.,” on your vehicle’s
Determine the combined weight of the driver and
Subtract the combined weight of the driver and passengers
The resulting fi gure equals the available amount of cargo
and luggage capacity. For example, if the “XXX” amount
equals 1400 lbs. and there will be fi ve 150 lb. passengers
in your vehicle, the amount of available cargo and luggage
Determine the combined weight of luggage and cargo
being loaded on the vehicle. That weight may not safely
exceed the available cargo and luggage capacity calculated
If your vehicle will be towing a trailer, load from your trailer
will be transferred to your vehicle. Consult the tow vehicle’s
manual to determine how this weight transfer reduces the
Studies of tire safety show that maintaining proper tire
pressure, observing tire and vehicle load limits (not carrying
more weight in your vehicle than your tires or vehicle can
safely handle), avoiding road hazards and inspecting tires
for cuts, slashes and other irregularities are the most
important things you can do to avoid tire failure, such as
tread separation or blowout and fl at tires. These actions,
along with other care and maintenance activities, can
Help protect you and others from avoidable breakdowns
TRAILER GUIDELINES
The weight of cargo should never exceed XXX kg. Or XXX lbs
TIRE
FRONT
REAR
SPARE
TIRE AND LOADING INFORMATION
SIZE
COLD TIRE PRESSURE
Figure I. Trailer Tire Placard
SEE OWNER’S
MANUAL FOR
ADDITIONAL
INFORMATION
MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14) — PAGE 65
.
placard.
Step 2.
passengers who will be riding in your vehicle.
Step 3.
from XXX kilograms or XXX pounds.
Step 4.
capacity is 650 lbs. (1400-750 (5 x 150) = 650 lbs.).
Step 5.
in Step 4.
available cargo and luggage capacity of your vehicle.
also:
Improve vehicle handling.
and accidents.
Improve fuel economy.
Increase the tire life.
Page 66

Use the information contained in this section to make tire
safety a regular part of your vehicle maintenance routine.
Recognize that the time you spend is minimal compared
with the inconvenience and safety consequences of a fl at
tire or other tire failure.
TIRE FUNDAMENTALS
Federal law requires tire manufacturers to place standardized
information on the sidewall of all tires (Figure J). This
information identifies and describes the fundamental
characteristics of the tire and also provides a tire
identifi cation number for safety standard certifi cation and
in case of a recall.
P
Next number
millimeters of the tire from sidewall edge to sidewall edge.
In general, the larger the number, the wider the tire.
Next number
ratio, gives the tire’s ratio of height to width. Numbers of
70 or lower indicate a short sidewall for improved steering
response and better overall handling on dry pavement.
P
has been the industry standard for the past 20 years.
Next number
diameter in inches. If you change your wheel size, you
will have to purchase new tires to match the new wheel
diameter.
Next number
load index. It is a measurement of how much weight each
tire can support. You may fi nd this information in your
owner’s manual. If not, contact a local tire dealer.
You may not fi nd this information on all tires because it is
not required by law.
M+S: The “M+S” or “M/S” indicates that the tire has
some mud and snow capability. Most radial tires have
these markings; hence, they have some mud and snow
capability.
: The speed rating denotes the speed at
which a tire is designed to be driven for extended periods
of time. The ratings range from 99 miles per hour (mph) to
186 mph. These ratings are listed in Table A. Note: You may
not fi nd this information on all tires because it is not required
: This begins with the
letters “DOT” and indicates that the tire meets all federal
standards. The next two numbers or letters are the plant
code where it was manufactured, and the last four numbers
represent the week and year the tire was built. For example,
the numbers 3197 means the 31st week of 1997. The other
numbers are marketing codes used at the manufacturer’s
discretion. This information is used to contact consumers
: The number of
plies indicates the number of layers of rubber-coated fabric
in the tire. In general, the greater the number of plies, the
more weight a tire can support. Tire manufacturers also
must indicate the materials in the tire, which include steel,
: This number indicates the
maximum load in kilograms and pounds that can be carried
: This number
is the greatest amount of air pressure that should ever be
TRAILER GUIDELINES
Figure J. Standard Tire Sidewall Information
: The “P” indicates the tire is for passenger vehicles.
Speed Rating
by law.
Letter Rating Speed Rating
Table A. Speed Rating
Q 99 mph
R 106 mph
S 112 mph
T 118 mph
U 124 mph
H 130 mph
V 149 mph
W 168* mph
Y 186* mph
U.S. DOT Tire Identifi cation Number
: This three-digit number gives the width in
: This two-digit number, known as the aspect
: The “R” stands for radial. Radial ply construction of tires
: This two-digit number is the wheel or rim
: This two- or three-digit number is the tire’s
PAGE 66 — MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14)
if a tire defect requires a recall.
Tire Ply Composition and Materials Used
nylon, polyester, and others.
Maximum Load Rating
by the tire.
Maximum Permissible Infl ation Pressure
Note:
put in the tire under normal driving conditions.
Page 67

Uniform Tire Quality Grading Standards (UTQGS)
Treadwear Number
rate. The higher the treadwear number is, the longer it
should take for the tread to wear down. For example, a tire
graded 400 should last twice as long as a tire graded 200.
Traction Letter:
on wet pavement. A higher graded tire should allow you
to stop your car on wet roads in a shorter distance than a
tire with a lower grade. Traction is graded from highest to
lowest as “AA”,”A”, “B”, and “C”.
Temperature Letter:
resistance to heat. The temperature grade is for a tire that
is infl ated properly and not overloaded. Excessive speed,
underinfl ation or excessive loading, either separately or
in combination, can cause heat build-up and possible tire
failure. From highest to lowest, a tire’s resistance to heat
is graded as “A”, “B”, or “C”.
Refer to Figure K for additional tire information for light
trucks.
Tires for light trucks have other markings besides those
found on the sidewalls of passenger tires.
LT
ST
Max. Load Dual
indicates the maximum load and tire pressure when the tire
is used as a dual, that is, when four tires are put on each
rear axle (a total of six or more tires on the vehicle).
Max. Load Single
information indicates the maximum load and tire pressure
when the tire is used as a single.
Load Range: This information identifi es the tire’s load-
Slow down if you have to go over a pothole or other
run over curbs or other foreign objects in the
Check tire infl ation pressure weekly during use to insure
Inspect tires for uneven wear patterns on the tread,
cracks, foreign objects, or other signs of wear or
Remove bits of glass and foreign objects wedged in
check tire pressure on tow vehicle and trailer
before towing. Check tire pressure at least once a
overload tow vehicle. Check the tire information
and loading placard for safe allowable tire loading
The proper repair of a punctured tire requires a plug for the
hole and a patch for the area inside the tire that surrounds
the puncture hole. Punctures through the tread can be
repaired if they are not too large, but punctures to the
sidewall should not be repaired. Tires must be removed
from the rim to be properly inspected before being plugged
Replace the tire before towing the trailer if the tire treads
have less than 1/16 inch depth or the telltale bands are
visible. Check infl ation pressure weekly during use to insure
the maximum tire life and tread wear. A bubble, cut or bulge
in a side wall can result in a tire blowout. Inspect both side
walls of each tire for any bubble, cut or bulge; and replace
TRAILER GUIDELINES
: This number indicates the tire’s wear
This letter indicates a tire’s ability to stop
This letter indicates a tire’s
carrying capabilities and its infl ation limits.
Tire Safety Tips
object in the road.
DO NOT
roadway, and try not to strike the curb when parking.
the maximum tire life and tread wear.
DO NOT bleed air from tires when they are hot.
trauma.
the tread.
Make sure your tire valves have valve caps.
ALWAYS
month.
DO NOT
conditions.
Tire Repair
Figure K. UTQGS Tire Information
: The “LT” indicates the tire is for light trucks or trailers.
: An “ST” is an indication the tire is for trailer use only.
kg (lbs) at kPa (psi) Cold: This information
kg (lbs) at kPa (psi) Cold: This
MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14) — PAGE 67
and patched.
Replacing Worn or Damaged Tires
a damaged tire before towing the trailer.
Page 68

Table B below will help pinpoint the causes and solutions
of tire wear problems.
Wheel Rims
If the trailer has been struck, or impacted, on or near the
wheels, or if the trailer has struck a curb, inspect the rims for
damage (i.e. being out of round); and replace any damaged
wheel. Inspect the wheels for damage every year, even if
no obvious impact has occurred.
Wheels, Bearings and Lug Nuts
A loose, worn or damaged wheel bearing is the most
common cause of brakes that grab.
To check wheel bearings, jack trailer and check wheels
for side-to-side looseness. If the wheels are loose, or spin
with a wobble, the bearings must be serviced or replaced.
Check infl ation pressure weekly during use to insure the
maximum tire life and tread wear. Most trailer axles are
built with sealed bearings that are not serviceable. Sealed
bearings must be replaced as complete units.
It is extremely important to apply and maintain proper wheel
mounting torque on the trailer. Be sure to use only the
fasteners matched to the cone angle of the wheel. Proper
Torque all lug nuts in sequence. See Figure L. DO
NOT torque the wheel lug nuts all the way down.
Tighten each lug nut in 3 separate passes as defi ned
Check to see if the lug nuts are tight after the fi rst 10,
25 and 50 miles of driving and before each tow
Wheel Lug Nuts Tightening Sequence
NOTICE
TRAILER GUIDELINES
Table B. Tire Wear Troubleshooting
Wear Pattern Cause Solution
Center Wear Over infl ation.
Adjust pressure to particular
load per tire manufacturer.
Edge Wear Under infl ation.
Side Wear
Toe Wear Incorrect toe-in. Align wheels.
Cupping Out-of-balance.
Flat Spots
Loss of camber
or overloading.
Wheel lockup and
tire skidding.
Adjust pressure to particular
load per tire manufacturer.
Make sure load does not
exceed axle rating.
Align wheels.
Check bearing adjustment
and balance tires.
Avoid sudden stops when
possible and adjust brakes.
WARNING
ALWAYS wear safety glasses when
removing or installing force fi tted parts. DO
NOT attempt to repair or modify a wheel.
DO NOT install an inner-tube to correct a
leak through through the rim. If the rim is
cracked, the air pressure in the inner tube may cause
pieces of the rim to explode (break off) with great force
and cause serious eye or bodily injury.
NEVER use an pneumatic air gun to tighten wheel
lug nuts.
Over-tightening lug nuts will result in breaking the studs
or permanently deforming the mounting stud holes in
the wheels.
WARNING
Lug nuts are prone to loosen after initial installation,
which can lead to death or serious injury. Check all
wheel lug nuts periodically.
Lug Nut Torque Requirements
procedure for attachment of the wheels is as follows:
1. Start all wheel lug nuts by hand.
2.
by Table C.
3.
thereafter
PAGE 68 — MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14)
Figure L.
Page 69

Lights and Signals
Before each tow, check the trailer taillights, stoplights, turn
signals and any clearance lights for proper operation.
Table C. Tire Torque Requirements
Replace any broken or burned-out lamps as necessary.
Check the wire harness for cuts, fraying or other damage.
Figure M. Trailer to Tow Vehicle Wiring Diagram
Wheel Size
12" 20-25 35-40 50-65
13" 20-25 35-40 50-65
14" 20-25 50-60 90-120
15" 20-25 50-60 90-120
16" 20-25 50-60 90-120
First Pass
FT-LBS
Second Pass
FT-LBS
TRAILER GUIDELINES
Third Pass
FT-LBS
If it needs replacing, contact your dealer.
WARNING
Improper operating taillights, stoplights and turn signals
can cause collisions.
Check all lights before each tow.
MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14) — PAGE 69
Page 70

APPENDIX — CONCRETE MIX INFORMATION
CONCRETE MIX INFORMATION
The following information has been extracted from actual testing laboratory reports. The purpose of this printing is only
to help create a better understanding of the importance of uniform gradation and proportioning of materials which affect
pumpability of concrete mixes. These weights and proportions illustrate that when the sieve analysis is ideal, the sand/
rock ratio can be adjusted (65% sand 35% rock) and pumpability should be excellent.
EXAMPLE #1 (A California Test Lab. Report)
JOB: Building Foundations (Water Project)
Sacks per cu./yd. 6.5 designed for 2,500 lbs. in 28 days
Gallons per sack 7.1
Washed Sand-#200 wash 1.3
Organic matter OK
Specifi c gravity (SSD) Sand-2.58; Pea Gravel-2.60
SIEVE ANALYSIS-PERCENT PASSING
Material 1.5” 1” 3/4” 3/8” #4 #8 #16 #30 #50 #100 #200
W.C. Sand 100 99.7 79.1 60.4 36.5 14.3 4.0 1.1
Pea Gravel 100 3.0
% Comb. 100 66 51 39 23 9 3 1.0
DESIGN FOR ONE YARD OF CONCRETE (SATURATED & SURFACE DRY):
Absolute volume of aggregate in one cu. yard: 17.78 cu. ft.
Specifi c gravity of aggregates in one cu. yard: 2.58
Weight of aggregates in one cu. yard batch: 2850 lbs.
W.C. Sand 65 1800 2.58 11.56
PEA GRAVEL 35 1000 2.60 6.22
WATER 46 gal. 1
CEMENT 6.5 sk. 611
TOTAL 27.00
ADMIXTURE: None
SLUMP 4”
REMARKS This mix is designed for pumping
NOTE: Due to the availability of well-graded sand as shown in the above sieve analysis,
this mix pumped very successfully.
% BATCH SPEC. GRAVITY ABS. VOL.
PAGE 70 — MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14)
Page 71

APPENDIX — CONCRETE MIX INFORMATION
A.S.T.M. STANDARD SPECIFICATION FOR GRADING AGGREGATE
MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14) — PAGE 71
Page 72

SLUMP TEST PROCEDURE
1.
To obtain a representative sample (concrete), take
2.
3.
4.
5.
PIECE
Remove the excess concrete (Figure Q) from the top
Slump Test (Removing Excess Concrete)
Lift the cone vertically (Figure R) with a slow even
jar the concrete or tilt the cone during
this process. Invert the withdrawn cone, and place it
Lay a straight edge (Figure S) across the top of the
slumped cone. Measure the amount of slump in inches
from the bottom of the straight edge to the top of the
slumped concrete at a point over the original center
of the base. The slump operation must be complete in
a maximum elapsed time of 1-½ minutes. Discard the
Figure S. Slump Test (Measurement)
several samples at three or more regular intervals
throughout the discharge of the mixer or truck. DO NOT
take samples at the beginning or end of the discharge.
Dampen the inside of the cone and place it on a smooth,
moist, non-absorbent, level surface large enough to
accommodate both the slumped concrete and the
slump cone. Stand on the “foot pieces” throughout the
test procedure to hold the cone fi rmly in place.
Fill the cone 1/3 full by volume (Figure N) and rod 25
times with a 1/2” dia x 24” lg. bullet-pointed steel rod.
(This is a specifi c requirement which will produce nonstandard results unless followed exactly.) Distribute
rodding evenly over the entire cross section of the
sample.
BULLET POINTED
STEEL ROD
APPENDIX — CONCRETE MIX INFORMATION
BULLET POINTED
STEEL ROD
1/2 DIAMETER
24 INCHES LONG
Figure P. Slump Test (Full-Overfl ow)
6.
of the cone, using the tamping rod as a screed.
Figure Q.
1/3 FULL
FOOT
PIECE
1/2 DIAMETER
24 INCHES LONG
1/3 FULL
FOOT
Figure N. Slump Test (1/3 Full)
Fill cone another 1/3 (Figure O) which will make the
cone 2/3 full by volume. Rod this second layer 25 times
with the rod penetrating into, but not through, the fi rst
layer. Distribute rodding evenly over the entire cross
section of the layer.
2/3 FULL
Figure O. Slump Test (2/3 Full)
Fill cone to overfl owing (Figure P). Rod this layer 25 times
with rod penetrating into, but not through, the second
layer. Distribute rodding evenly over the entire cross
section of this layer.
7.
motion. DO NOT
next to, but not touching the slumped concrete.
Figure R. Slump Test (Cone Invert)
8.
concrete. DO NOT use it in another test.
PAGE 72 — MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14)
Page 73

NOTES
MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14) — PAGE 73
Page 74

TROUBLESHOOTING (PUMP)
Troubleshooting (Pump)
Symptom Possible Problem Solution
Main Hydraulic Cylinder will
not cycle
Shuttle Cylinder slow to
complete stroke
Concrete slurry in
lubrication box
Material cylinder piston
cups squeal
Incorrect System Operating Pressure
Incorrect Engine RPM setting
Contaminated Main Relief Valve
Obstructed Material Cylinders
Improper Flow Control setting Fully open Flow Control Valve
Incorrect Engine RPM setting
Incorrect Main Hydraulic
System Operating Pressure
Hopper Discharge Nipple Seal
improperly lubricated
Worn or defective urethane cups or
worn material cylinder
Low on lubrication Check oil level
Check the pump pressure gage. Verify it is
approx. 3100 — 3200 PSI
Verify the engine's high RPM speed is set to
2550
Check the manifold for a contaminated Relief
Valve
Check for obstructions (dried material) inside
the cylinders
Verify the engine's high RPM speed is set to
2550
Check the pump pressure gage. Verify it is
approx. 3200 PSI
Check the Hopper Discharge Nipple Seal for
seizing and lack of lubricant
Replace
Battery voltage falls below
12VDC on digital display,
causing engine not to start
Blown out Fuse Check the fuse
Dead battery Check the charge on the battery
Wiring connection inside Control Box
Check the wiring connections and verify power
is reaching ignition switch
PAGE 74 — MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14)
Page 75

TROUBLESHOOTING (PUMP)
Troubleshooting (Pump — Continued)
Symptom Possible Problem Solution
Insuffi cient oil Check oil level and for closed suction strainer
Main Hydraulic Pump Noisy
Engine bogs down
Machine does not deliver
volume and pressure
Hydraulic fl uid gets hot
Air in system
Excessive pump wear Repair or replace
Excessive engine speed Check for correct engine RPM
Low engine speed Check engine RPM
Main relief cartridge set to low Adjust relief cartridge
Engine overloaded when pumping
Low engine speed Check engine RPM
Volume control set to low Adjust control to full open setting
Main hydraulic pressure too low
Cooling fan
Contaminated cooler fi ns Clean cooler fi ns
Return fi lter element closed Replace fi lter
Main relief cartridge contaminated or
set too low
Check for aeration reservoir
Vacuum leak in suction line
Decrease volume control on main pump
Material hose pack
Check for proper pressure or for contaminated
relief cartridge
Check fan electrical connection or for burnt fan
motor.
Fan rotating in wrong direction
Replace or set to proper pressure
Cylinders not completely
extended (short stroke)
Hydraulic oil level too low Fill to proper level
Excessive amount of hydraulic on
cylinder rod side
Hydraulic cylinder piston head seal
leaking
Inspect cylinder. Check values for
contamination or faulty spring
Replace seals
MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14) — PAGE 75
Page 76

Symptom Possible Problem Solution
Engine will not start or start is delayed,
although engine can be turned over.
At low temperatures engine will not start.
Engine fi res but stops soon as starter is
switched off.
Engine stops by itself during normal
operation.
Low engine power, output and speed.
TROUBLESHOOTING (ENGINE)
Troubleshooting (Diesel Engine)
No Fuel reaching injection pump? Add fuel. Check entire fuel system.
Defective fuel pump? Replace fuel pump.
Fuel fi lter clogged? Replace fuel fi lter and clean tank.
Faulty fuel supply line? Replace or repair fuel line.
Compression too low?
Fuel pump not working correctly? Repair or replace fuel pump.
Oil pressure too low? Check engine oil pressure.
Low starting temperature limit exceeded?
Defective battery? Charge or replace battery.
Air or water mixed in fuel system?
Engine oil too thick?
Defective battery? Replace battery.
Fuel fi lter blocked? Replace fuel fi lter.
Fuel supply blocked? Check the entire fuel system.
Defective fuel pump? Replace fuel pump.
Fuel tank empty? Add fuel.
Fuel fi lter blocked? Replace fuel fi lter.
Defective fuel pump? Replace fuel pump.
Mechanical oil pressure shutdown sensor
stops the engine due to low oil?
Fuel tank empty? Replace fuel fi lter.
Fuel fi lter clogged? Replace fuel fi lter.
Fuel tank venting is inadequate? Ensure that tank is adequately vented.
Leaks at pipe unions?
Speed control lever does not remain in
selected position?
Engine oil level too full? Correct engine oil level.
Injection pump wear?
Check piston, cylinder and valves. Adjust or
repair per engine repair manual.
Comply with cold starting instructions and
proper oil viscosity.
Check carefully for loosened fuel line
coupling, loose cap nut, etc.
Refi ll engine crankcase with correct type of
oil for winter environment.
Add oil. Replace low oil shutdown sensor if
necessary.
Check threaded pipe unions tape and tighten
unions a required.
See engine manual for corrective action.
Use No. 2-D diesel fuel only. Check the fuel
injection pump element and delivery valve
assembly and replace as necessary.
PAGE 76 — MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14)
Page 77

TROUBLESHOOTING (HYDRAULIC BRAKES)
Troubleshooting (Hydraulic Brakes )
Symptom Possible Problem Solution
No brakes Is the brake line broken or kinked? Repair or replace.
Is the brake lining glazed? Reburnish or replace
Is the trailer overloaded? Correct weight.
Weak brakes or brakes pull to one side
Locking brakes
Noisy brakes
Dragging brakes
Brakes squeak, chatter or chuck
Brakes overheat, fail to operate, pull to
the side, or function poorly
Are the brake drums scored or
grooved?
Is the tire pressure correct?
Are the tires unmatched on the
same axle?
Are the brake components loose,
bent or broken?
Are the brake drums out-of-round? Replace.
Is the brake system lubricated? Lubricate.
Are the correct brake components
installed?
Is the brake lining thickness correct
or innstalled incorrectly?
Is there enough brake fl uid or
correct fl uid?
Overheated wheel bearing
Low brake fl uid Fill and bleed brake system.
Siezed acutator master cylinder Replace/Rebuild master cylinder.
Brake shoe noise
Leaking wheel cylinder
Low brake fl uid level
Brake actuator frame damage Replace complete actuator unit.
Brake line being pinched Replace brake line.
Seized actuator Replace or rebuild actuator.
Broken return spring Replace spring.
Brakes improperly adjusted Check adjustment.
Break-away cable system partially
activated
Check machine or replace.
Infl ate all tires equally per manufacturer
guidelines.
Match tires.
Replace components.
Replace and correct.
Install new shoes and linings.
Fill with DOT 4 fl uid.
Replace wheel bearing and pack with
grease.
Inspect drums. Adjust shoes or replace if
necessary.
Check and replace wheel cylinder and
bleed brake system.
Fill with dot approved brake fl uid and bleed
brake system.
Break-away cable might be pulled.
Determine cause and correct. Pry up on
cable until indicator bead touches or rests
against cable spring stop. This will fully
release the frame brakes and prevent drag.
MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14) — PAGE 77
Page 78

TROUBLESHOOTING (ELECTRICAL)
Troubleshooting (Electrical)
Malfunction Reading (Screen 1) Possible Problem Solution
Measure solenoid coil resistance. It should read 6
ohms. Replace burnt solenoid.
Measure solenoid coil resistance. It should read 6
ohms. Replace shorted solenoid.
Correct connection.
Measure solenoid coil resistance. It should read 6
ohms. Replace burnt solenoid.
Measure solenoid coil resistance. It should read 6
ohms. Replace shorted solenoid.
Correct connection.
Measure solenoid coil resistance. It should read 6
ohms. Replace burnt solenoid.
Measure solenoid coil resistance. It should read 6
ohms. Replace shorted solenoid.
Correct connection.
Measure solenoid coil resistance. It should read 6
ohms. Replace burnt solenoid.
Measure solenoid coil resistance. It should read 6
ohms. Replace shorted solenoid.
Correct connection.
• Misaligned hopper
• Discharge nipple seizing
• Hopper outlet requires lubrication
• Misaligned hopper
• Discharge nipple seizing
• Hopper outlet requires lubrication
Main A OPEN
Main A SHORTED
Main B OPEN
Main B SHORTED
Swing OPEN
Swing SHORTED
Fuel solenoid open
Fuel solenoid shorted
Proximity switch C
Proximity switch D
Burnt 12 V cycling solenoid.
Wire connection broken. Replace broken wire.
The 12-volt cycling solenoid is shorted
directly to ground.
Wire connection is shorted directly to the
ground.
Burnt 12 V cycling solenoid.
Wire connection broken. Replace broken wire.
The 12-volt cycling solenoid is shorted
directly to ground.
Wire connection is shorted directly to the
ground.
Burnt 12 V cycling solenoid.
Wire connection broken. Replace broken wire.
The 12-volt cycling solenoid is shorted
directly to ground.
Wire connection is shorted directly to the
ground.
Burnt 12 V cycling solenoid.
Wire connection broken. Replace broken wire.
The 12-volt cycling solenoid is shorted
directly to ground.
Wire connection is shorted directly to the
ground.
Digital Control Box not sending signal. Check screen #5 for operational status.
Shuttle cylinder short stroking not
energizing proximity sensor.
Digital Control Box not sending signal. Check screen #5 for operational status.
Shuttle cylinder short stroking not
energizing proximity sensor.
PAGE 78 — MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14)
Page 79

TROUBLESHOOTING (ELECTRICAL)
Troubleshooting (Electrical - Continued)
Malfunction Reading (Screen 1) Possible Problem Solution
Fuel solenoid open
Fuel solenoid shorted
Coolant temperature Engine over heating. Refer to Engine Troubleshooting.
Proximity switch A
Proximity switch B
Alternator Failure
Burnt 12-volt solenoid. Replace burnt solenoid.
Wire connection broken. Replace broken wire.
The 12-volt solenoid is shorted directly
to ground.
Wire connection is shorted directly to the
ground.
Switch not energizing.
Defective proximity switch. Replace switch.
Wire connection broken. Replace broken wire.
Wire connection is directly shorted to
ground.
Switch not energizing. Improper contact clearance.
Defective proximity switch. Replace switch.
Wire connection broken. Replace broken wire.
Wire connection is directly shorted to
ground.
Defective alternator. Replace alternator. Check V-belt
Engine blower cooling fan V-belt is
broken requiring replacement.
Replace shorted solenoid.
Correct connection.
Check for contact clearance. Should be between
0.050 in. (1.27mm) and 0.065 in. (1.651 mm)
Correct connection.
Correct connection.
Replace V-belt.
MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14) — PAGE 79
Page 80

CONTROL BOX COMPONENT LOCATOR
SCROLL
A
F
FORWARD
H
AUTOMATIC
RESET
SET
FLOW
DIRECTION
B
C
DIGITAL DISPLAY READOUT MODULE
CONTROL
G
REVERSE
JOG
LOCAL
CYLINDER STROKE
JOG “A”
CENTER
OFF
I
REMOTE
JOG “B”
OFF
E
e
m
E
D
n
c
e
g
r
ON
IGNITION
J
REMOTE
y
S
t
o
p
START
PAGE 80 — MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14)
Page 81

WIRING DIAGRAM CONTROL BOX (INTERNAL)
RED (IGNITION +12VDC)
BLUE (UNLOADER SOLENOID)
RED (FUEL SOLENOID)
RED/BLACK
RED
RED
NC 1
NC 1
222
BLK
D
J4
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
E-STOP
34 56 78
12
NC 1
DIGITAL READOUT
MODULE
C
+12VDC OUT
12
BLACK
RED
ORANGE
GRAY
GND
+12VDC IN
34 56 78
J1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
BROWN
PURPLE
2
RESET/SET
BLACK
RED
WHITE
BLUE
YELLOW
GREEN
BROWN
BLACK
CONTROLLER
BLACK POTTED
BOX
RED
WHITE
BLACK
RADIO
REMOTE
CONTROL
CONNECTOR
J2J3
1
1
2
3
3
SCROLL
B
A
YELLOW (REV)
RED/BLK
RED
RED
(LOCAL)
CONTROL
2
1
G
GRN
3
(REMOTE)
BLUE
(FWD)
F
FLOW
DIRECTION
WHITE
RED
50A
15/54
IGNITION
E
SWITCH
CONNECTOR
J
REMOTE
BLACK
BLUE
(JOG A)
GRN/YEL
12 3
CYLINDER
STROKE
BLK
(JOG B)
I
ORANGE
RED
WHITE
H
AUTOMATIC/JOG
12 3
MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14) — PAGE 81
Page 82

CONTRO
A
HOPPER VIBRATOR LOCATOR (OPTION)
C
E
D
G
B
LBOX
HOPPER
F
H
PAGE 82 — MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14)
Page 83

12 AWG BRN
CONTROL BOX INTERIOR
(+12VDC INPUT)
12 AWG RED
(+12VDC)
WIRING DIAGRAM HOPPER VIBRATOR (OPTION)
DIGITAL READOUT
J1-7
EMERGENCY STOP
MODULE
J3-4
E-STOP
RED/WHT
1
1
1
SWITCH
B
CONTROLLER
BLACK
POTTED
BOX
C
+12VDC POWER OUT
FUEL SOLENOID
(SHUT-DOWN)
+12VDC
2
2
2
J1-10
FUEL
SOLONOID
+12VDC OUTPUT
A
J1-9
VIBRATOR RELAY
85
RELAY
+12VDC RED
86
11
22
REMOTE
RECEPTACLE
P/N EM26789
K1
D
RED
RED
12VDC
ORANGE
CHASSIS
GND.
DIODE 1 AMP
P/N EM98002
F
25 FT. CORD
P/N EM26788
MODEL EMDC400
VIBRATOR
BATTERY
FUSE
HOLDER
30 AMP
FUSE
E
VIBRATOR
2
H
30/51
G
ON/OFF
(SW1)
1
CHASSIS
GND.
RELAY
K1-1
87
NO
2
1
POWER
INPUT
RELAYK1
(REAR VIEW)
FUSE HOLDER
P/N EM98066
CONNECT TO
RED 10 AWG.
CHASSIS GND
85
30/51
RELAY KIT
P/N 515799
86
87
30A
FUSE NOT
INCLUDED
W/KIT
NOTES:
1
FOR COMPLETE VIBRATOR KIT ORDER P/N EMDC400K.
2
INCLUDES SWITCH.
MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14) — PAGE 83
Page 84

HYDRAULIC SYSTEM LOCATOR DIAGRAM
B
A
C
E
K
I
33
H
J
G
D
F
PAGE 84 — MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14)
Page 85

NON-OPERATOR SIDE
HYDRAULIC SYSTEM DIAGRAM
E
PORTB
H
K
MAIN
3100~3200
PSI
OPERATOR SIDE
B1
A1
SWING
41
GPM
D
D1
PRECHARGE TO 500 PSI
B
MAIN
GA
M
I
J
C
A
ACC
SWING
F
B2
A2
P2
T2
G
MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14) — PAGE 85
Page 86

WIRING DIAGRAM LOCATOR 1 (EXTERNAL CONTROL BOX)
B
A1
A
G
H
I
D
C
E
J
K
PAGE 86 — MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14)
Page 87

WIRING DIAGRAM 1 (EXTERNAL CONTROL BOX)
BATTERY
STARTER
SOLENOID
H
MAIN
SOLENOID B
MAIN
SOLENOID A
MANIFOLD
DEUTZ 10-PIN
ENGINE
CONNECTOR
YELLOW
YELLOW
WHITE
YELLOW
WHITE
J1
J2
J3
J4
J5
CONTROL
BOX REAR
VIEW
OIL PRESSURE
SWITCH
FUEL SOLENOID
(SHUT-DOWN)
10 AWG RED
1
2
CIRCUIT ACTIVE = +12VDC
CIRCUIT OFF = GND
GND
EMERGENCY
STOP
SWITCH
DIGITAL READOUT
MODULE
12
34 56 78
12
34 56 78
J4
GND
+12VDC IN
+12VDC OUT
J2J3
E-STOP
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
8765
4321
J1
8765
4321
J2
LOW BATTERY
J1
GND
14 AWG BLACK
SEE SHEET 2
12 AWG RED
(+12VDC)
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
F
G
H
I
J
A1
D
E
B
C
1N4001
A
WIRING CONNECTIONS TO J1 AND J2
RECEPTACLES ON DIGITAL CONTROLBOX (LS300P)
K
MAIN
SOLENOID
SWING A
MAIN
SOLENOID
SWING B
E-STOP
2
2
2
17
IGNITION
SWITCH
30
58
1
1
1
19
15/54
50A
+12VDC OUTPUT
FUEL SOLONOID
YELLOW
WHITE
10 AWG RED
12 AWG RED
J1
8765
4321
J2
8765
4321
INSIDE
CONTROL
P1 P1
BOX
1
2
3
J1 MALE
INTERFACE
CONNECTOR
(YELLOW)
OUTSIDE
CONTROL
4
5
6
7
8
OUTSIDE
INSIDE
CONTROL
CONTROL
BOX
BOX
BOX
4
3
2
1
8
7
6
5
A
FUSE
HOLDER
30 AMP
FUSE
F
12 AWG RED
10 AWG BLK
14 AWG PINK/BLK (STARTER SOLENOID)
16 AWG GREEN
16 AWG YELLOW
16 AWG ORANGE
14 AWG RED
14 AWG BLACK (GND.)
ALTERNATOR
W
D
BRN
+12VDC POWER IN
ENGINE CRANK
LOW OIL INPUT
+12VDC POWER OUT
FUEL SOLENOID
(SHUT-DOWN)
CONTROLLER
BLACK
POTTED
BOX
TACH INPUT
SHUTTLE C
CYL A
CYL B
THROTTLE
GROUND
BLK
RED
GRN
BLK
J2 MALE
INTERFACE
CONNECTOR
P2
(WHITE)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
OUTSIDE
INSIDE
CONTROL
CONTROL
BOX
BOX
P2
14 AWG RED
4
14 AWG BRN
3
14 AWG RED
2
14 AWG GRAY
1
14 AWG RED
8
14 AWG YEL
7
6
5
MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14) — PAGE 87
Page 88

WIRING DIAGRAM LOCATOR 2 (EXTERNAL CONTROL BOX)
T
P
M
S
R
33
Q
N
O
PAGE 88 — MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14)
Page 89

WIRING DIAGRAM 2 (EXTERNAL CONTROL BOX)
A
J3
8765
4321
J4
8765
4321
J5
8765
4321
INSIDE
CONTROL
J3 MALE
BOX
INTERFACE
CONNECTOR
(YELLOW)
P3 P3
A
CONTROL
BOX REAR
VIEW
J1
J2
J3
J4
J5
YELLOW
WHITE
YELLOW
WHITE
YELLOW
YELLOW
WHITE
YELLOW
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
INSIDE
CONTROL
A A
BOX
ENG SOL POWER 35A 1 SEC
OVER TEMP
PROX A
PROX B
PROX C
PROX D
POWER
GROUND
TIMER
NOT USED
FLOW A 12VDC
NOT USED
FLOW B 12VDC
NOT USED
BROKEN FAN BELT
SHUTTLE D
+12VDC OUT
P4 P4
1
2
3
4
12VDC
5
GND.
6
BLUE
7
GND.
8
INSIDE
A
17
IGNITION
SWITCH
15/54
30
50A
19
58
CONTROL
BOX
J4 MALE
INTERFACE
CONNECTOR
(WHITE)
12VDC
WIRING CONNECTIONS TO J3, J4 AND J5
RECEPTACLES ON DIGITAL CONTROLBOX (LS300P)
J3
8765
4321
J4
8765
4321
J5
8765
4321
OUTSIDE
CONTROL
OUTSIDE
CONTROL
BOX
CONTROLLER
OUTSIDE
CONTROL
BOX
BOX
4
3
2
1
8
7
6
5
B
B
BLACK
POTTED
BOX
4
3
2
1
8
7
6
5
AA
NOT USED
SIGNAL
SIGNAL
SIGNAL
SIGNAL
SIGNAL
+12 VDC
GND.
A
HEAT EXCHANGER
“COOLING FAN”
14 AWG BLK
GND.
85
85
16 AWG WHITE
16 AWG BLUE
16 AWG BROWN
16 AWG GREEN
16 AWG BLUE
16 AWG BROWN
16 AWG YELLOW
16 AWG BLUE
16 AWG BROWN
16 AWG
DARK
BLUE
Z
16 AWG GREEN
16 AWG BLUE
16 AWG BROWN
P
30
K1
COMMON
S
+12 VDC
14 AWG RED
K1
86
K2
86
P5 P5
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
INSIDE
OUTSIDE
CONTROL
A
CONTROL
BOX
BOX
J5 MALE
INTERFACE
CONNECTOR
(YELLOW)
B
MAIN CYLINDER
SHUTTLE CYLINDER
CB1
50 AMP
PREHEAT
K1 NC
87A
K1 NO
87
R
T
CB2
50 AMP
FAN POWER
30
K2
COMMON
14 AWG RED
4
14 AWG WHT
3
2
1
8
7
6
5
A
A
C
TO STARTER
SOLENOID
+12VDC
GLOW
PLUGS
K2 NC
87A
K2 NO
87
PROXIMITY
SWITCH “B”
INDICATOR“RED” ACTIVE
BETWEEN GND. 800 mV
PROXIMITY
SWITCH “A”
PROXIMITY
SWITCH “D”
PROXIMITY
SWITCH “C”
Q
ENGINE
TEMP. SWITCH
2
TO STARTER
SOLENOID
+12VDC
16 AWG RED
M
1
16 AWG
DARK
BLUE
Z
L
N
O
MAYCO LS300P CONCRETE PUMP • OPERATION MANUAL — REV. #0 (06/09/14) — PAGE 89
Page 90

OPERATION MANUAL
HERE’S HOW TO GET HELP
© COPYRIGHT 2014, MULTIQUIP INC.
Multiquip Inc
are registered trademarks of Multiquip Inc. and may not be used, reproduced, or altered without written permission. All other trademarks
are the property of their respective owners and used with permission.
This manual
The information and specifi cations included in this publication were in effect at the time of approval for printing. Illustrations, descriptions, references and technical data contained in
this manual are for guidance only and may not be considered as binding. Multiquip Inc. reserves the right to discontinue or change specifi cations, design or the information published
in this publication at any time without notice and without incurring any obligations.
PLEASE HAVE THE MODEL AND SERIAL
NUMBER ON-HAND WHEN CALLING
United StateS
Multiquip Corporate Office MQ Parts Department
18910 Wilmington Ave.
Carson, CA 90746
Contact: mq@multiquip.com
Service Department Warranty Department
800-421-1244
310-537-3700
Technical Assistance
800-478-1244 Fax: 310-943-2238
Canada
Multiquip Multiquip (UK) Limited Head Office
4110 Industriel Boul.
Laval, Quebec, Canada H7L 6V3
Contact: jmartin@multiquip.com
Tel. (800) 421-1244
Fax (310) 537-3927
Fax: 310-537-4259 800-421-1244
Tel: (450) 625-2244
Tel: (877) 963-4411
Fax: (450) 625-8664
800-427-1244
310-537-3700
310-537-3700
United Kingdom
Unit 2, Northpoint Industrial Estate,
Globe Lane,
Dukinfield, Cheshire SK16 4UJ
Contact: sales@multiquip.co.uk
Fax: 800-672-7877
Fax: 310-637-3284
Fax: 310-943-2249
Tel: 0161 339 2223
Fax: 0161 339 3226
, the MQ logo and the Mayco logo
MUST accompany the equipment at all times. This manual is considered a permanent part of the equipment and should remain with the unit if resold.
Your Local Dealer is:
 Loading...
Loading...