Page 1
STARLINE
®
SG 2000
Telecommunications Optical Node
Installation and Operation Manual
4
2
6
IN
7
Page 2
Caution
Caution
CautionCaution
These servicing instructions are for use by qualified personnel only. To reduce the risk of electrical shock, do not perform any servicing other than that
contained in the Installation and Troubles hoot ing I ns t ruct ions unless you a r e qua lified t o do s o. Refer all servicing to qualified service personnel.
Special Symbols that Might Appear on the Equipment
Special Symbols that Might Appear on the Equipment
Special Symbols that Might Appear on the EquipmentSpecial Symbols that Might Appear on the Equipment
This is a class 1 product that contains a class IIIb laser and is intended for operation in a closed environment with fiber
attached. Do not look into the optical connector of the transmitter with power applied. Laser output is invisible, and eye
damage result. Do not defeat safety features that prevent looking into optical connector.
This product contains a class IIIb laser and is intended for operation in a closed environment with fiber attached. Do not look
into the optical connector of the transmitter with power applied. Laser output is invisible, and eye damage can result. Do not
defeat safety features that prevent looking into optical connector.
This symbol indicates that dangerous voltage levels are present within the equipment. These volt a ges ar e not insula t ed a nd
may be of sufficient strength to cause serious bodily injury when touched. The symbol may also appear on schematics.
The exclamation point, within an equilateral triangle, is intended to alert the user to the presence of important installation,
servicing, and operating instructions in t he document s a c co mpa nying t he equip ment .
For continued protection against fire, replace all fuses only with fuses having the same electrical ratings marked at the
location of the fuse.
Copyright © 2001 by Motorola Inc.
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced in any form or by any means or used to make any derivative work (such as translation,
transformation or adaptation) without written permission from Motorola, Inc.
Motorola, Inc. reserves the right to revise this publication and to make changes in content from time to time without obligation on the part Motorola, Inc.
to provide notification of such revision or change. Motorola Inc. provides this guide without warranty of any kind, either implied or expressed, including,
but not limited, to the implied warranties of merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose. Motorola, Inc. may make improvements or changes in
the product(s) described in this manual at any time.
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
MOTOROLA, the stylized M logo, and STARLINE are registered trademarks, and LIFELINE is a trademark of Motorola, Inc.
All other product or service names are the property of their respective owners.
Page 3

Contents
Section 1
Introduction
Using this Manual ..........................................................................................................................................1-3
Related Documentation ..................................................................................................................................1-3
Document Conventions ..................................................................................................................................1-4
If You Need Help...........................................................................................................................................1-4
Calling for Repairs .........................................................................................................................................1-5
Section 2
Overview
Housing ........................................................................................................................................................2-1
Mounting Holes ......................................................................................................................................2-1
Port Locations................................................................................................................. .......................2-2
Gaskets.................................................................................................................................................2-3
Power Supply................................................................................................................................................2-4
Network Monitoring ........................................................................................................................................2-5
Configuration ................................................................................................................................................2-5
Forward Path.................................................................................................................................................2-7
SG2-LR Receiver ................................................................................................................................... 2-9
Analog Return Path ..................................................................................................................................... 2-10
Analog Return Transmitt ers ..................................................................................................................2-10
Digital Return Path ......................................................................................................................................2-12
DS-SG2-DRT/A .................................................................................................................................... 2-12
DS-SG2-DRT-2X/A ............................................................................................................................... 2-13
Level Control.................................................................................................................. .............................2-14
Options and Accessories.............................................................................................................................. 2-14
Gain Selection...................................................................................................................................... 2-16
Tilt Selection ........................................................................................................................................2-18
Section 3
Bench Setup
Powering the Node ........................................................................................................................................3-3
Power Supply Settings.......................................................................................................... .........................3-5
Single Power Supply o r Commonly Po wered Redunda nt Supplie s.............................................................3-7
Individually Powered Supplies ................................................................................................................. 3-7
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 4

ii Contents
Quick Checks - Functional Testi ng.................................................................................................................3-8
Forward Path ......................................................................................................................................... 3-8
Manual Gain Control .......................................................................................................................3-9
Thermal Control, Model TCU ...........................................................................................................3-9
Automatic Level Control, Model ADU................................................................................................ 3-9
Analog Return Path .............................................................................................................................. 3-10
Digital Return Path...............................................................................................................................3-10
Forward Path Padding .................................................................................................................................3-11
Launch Amplifier Outpu t Stage Paddi ng........................................................................................................3-14
Link Performance ........................................................................................................................................ 3-15
Installing the DS-SG2-DRRB Bo ard Option ...................................................................................................3-1 8
Installing the Status Monito r Option .............................................................................................................. 3-2 2
SG 2000 Activation Worksh eet.....................................................................................................................3-23
Section 4
Installation
Splicing Fiber................................................................................................................................................ 4-1
Strand Wire Mounting....................................................................................................................................4-3
Coaxial Cables................................................................................................................. .............................4-5
Fiber Cables ................................................................................................................................................. 4-5
Section 5
Operation
Forward Path RF Configurati on......................................................................................................................5-1
Single Receiver Mode.............................................................................................................................5-1
Redundant Receiver M ode ......................................................................................................................5-2
Broadband/Narrowcast Mode ..................................................................................................................5-2
AB Override Functionali ty.......................................................................................................................5-3
B Override......................................................................................................................................5-3
A Override......................................................................................................................................5-4
Status Monitor/Manual Co ntrol Operation .........................................................................................5-4
Analog Return Path RF Configuration.............................................................................................................5-5
Digital Return Path RF Configu ration .............................................................................................................. 5-7
SG 2000 Optical Modules ..............................................................................................................................5-9
Installing SG 2000 Optical Modules......................................................................................................... 5-9
Removing SG 2000 Optic al Modules ....................................................................................................... 5-9
Cleaning the Optical Connector................................................................................................. ............5-10
SG2-LR Optical Receiv er.............................................................................................................................5-1 0
Wavelength Selection Jumpe r......................................................................................................................5-13
SG2-IFPT Optical Transmitt er......................................................................................................................5-14
SG2-FPT Optical Trans mitter.......................................................................................................................5-15
SG2-DFBT Optical Transmitt er .....................................................................................................................5-16
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 5

Contents iii
SG2-DFBT/3 Optical Trans mitter..................................................................................................................5-18
SG2-EIFPT Optical Transmitt er....................................................................................................................5-19
DS-SG2-DRT/A Digital Return T ransmitter....................................................................................................5-20
DS-SG2-DRT-2X/A Digi tal Return T ransmitter............................................................................................... 5-22
SG2-PS Power Supply..........................................................................................................................5-25
Status Monitoring ........................................................................................................................................ 5-26
Manual Control Board..................................................................................................................................5-27
Ingress Control............................................................................................................................................ 5-29
Appendix A
Specifications
Appendix B
Torque Specifications
Abbreviations and Acronyms
Figures
Figure 1-1 SG 2000 — closed ............................................................................................ 1-1
Figure 1-2 SG 2000 — open..............................................................................................1-2
Figure 2-1 SG 2000 housing dimensions - front and side view............................................. 2-1
Figure 2-2 Port locations...................................................................................................2-2
Figure 2-3 Housing gaskets............................................................................................... 2-3
Figure 2-4 SG2-PS2 power supply.....................................................................................2-4
Figure 2-5 Configuration notation....................................................................................... 2-6
Figure 2-6 Signal flow diagram .......................................................................................... 2-7
Figure 2-7 SG2-LR receiver functional diagram ..................................................................2-9
Figure 2-8 SG2 transmitter block diagram ........................................................................ 2-11
Figure 2-9 Optical input versus 750 MHz gain...................................................................2-16
Figure 2-10 Optical input versus 870 MHz gain................................................................. 2-17
Figure 2-11 Relative level dB versus 750 MHz slope 77 channels...................................... 2-18
Figure 2-12 Relative level dB versus 870 MHz slope 94 channels...................................... 2-19
Figure 2-13 Relative level dB versus 870 MHz slope 110 channels....................................2-20
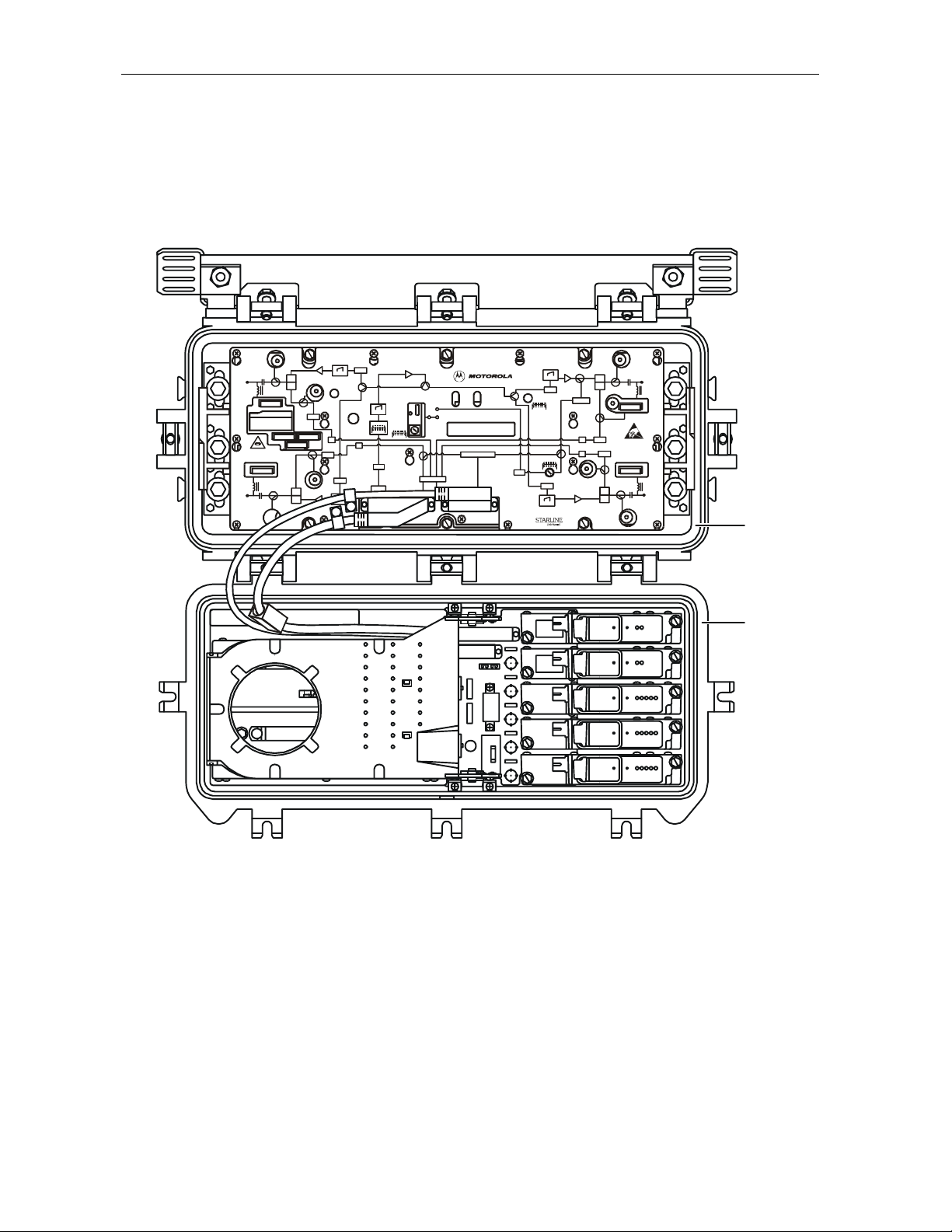
Figure 3-1 SG 2000 lid showing major components.............................................................3-1
Figure 3-2 SG 2000 RF chassis.........................................................................................3-2
Figure 3-3 Fuse configuration............................................................................................ 3-3
Figure 3-4 Fuse locations.................................................................................................. 3-5
Figure 3-5 SG2-PS2 power supply.....................................................................................3-6
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 6

iv Contents
Figure 3-6 JP1 common-powered single or redundant power configuration .......................... 3-7
Figure 3-7 JP1 split-powered redundant power supply configuration ................................... 3-7
Figure 3-8 SG2-75 low-gain output-stage pad-effects chart .............................................. 3-14
Figure 3-9 SG2-87 low-gain output-stage pad-effects chart .............................................. 3-15
Figure 3-10 SG2-* link c/n performance, 77 channels....................................................... 3-16
Figure 3-11 SG2-* link c/n performance, 110 channels ..................................................... 3-17
Figure 3-12 DS-SG2-DRRB board ................................................................................... 3-18
Figure 3-13 DS-SG2-DRRB board installed...................................................................... 3-19
Figure 3-14 Location of JXPs on E-pack.......................................................................... 3-20
Figure 3-15 SG2 lid configured with the DS-SG2-DRRB board .......................................... 3-21
Figure 4-1 Service cable connection and compression fitting .............................................. 4-1
Figure 4-2 Mounting bracket-front view.............................................................................. 4-3
Figure 4-3 Mounting bracket-rear and side views............................................................... 4-4
Figure 4-4 Center conductor length................................................................................... 4-5
Figure 4-5 Housing lid and fiber spool tray......................................................................... 4-6
Figure 4-6 Fiber spool tray................................................................................................ 4-6
Figure 5-1 Single receiver................................................................................................. 5-1
Figure 5-2 Redundant receiver .......................................................................................... 5-2
Figure 5-3 Broadband/narrowcast...................................................................................... 5-2
Figure 5-4 B override........................................................................................................ 5-3
Figure 5-5 A override........................................................................................................ 5-4
Figure 5-6 Status monitor/MCB operation .......................................................................... 5-4
Figure 5-7 Redundant return.............................................................................................5-5
Figure 5-8 Split return....................................................................................................... 5-5
Figure 5-9 RF chassis and location of the SG2-RPM/C or SG2-RPM/S board...................... 5-6
Figure 5-10 DS-SG2-DRT/A redundant return .................................................................... 5-7
Figure 5-11 DS-SG2-DRT-2X/A split return........................................................................ 5-8
Figure 5-12 DS-SG2-DRT-2X/A redundant return...............................................................5-8
Figure 5-13 SG2-LR ....................................................................................................... 5-10
Figure 5-14 Test-point voltage versus optical power......................................................... 5-12
Figure 5-15 Wavelength selection jumper........................................................................ 5-13
Figure 5-16 SG2-IFPT .................................................................................................... 5-14
Figure 5-17 SG2-FPT ..................................................................................................... 5-15
Figure 5-18 SG2-DFBT................................................................................................... 5-16
Figure 5-19 SG2-DFBT/3 ................................................................................................ 5-18
Figure 5-20 SG2-EIFPT .................................................................................................. 5-19
Figure 5-21 DS-SG2-DRT/A............................................................................................ 5-20
Figure 5-22 DS-SG2-DRT/A............................................................................................ 5-20
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 7

Contents v
Figure 5-23 DS-SG2-DRT-2X/A........................................................................................5-22
Figure 5-24 DS-SG2-DRT-2X/A........................................................................................5-22
Figure 5-25 DS-SG2-DRT-2X/A cable connector ...............................................................5-24
Figure 5-26 DS-SG2-DRT-2X/A installed in SG 2000 ........................................................5-24
Figure 5-27 DS-SG2-DRT-2X/A second RF input cable connection ....................................5-25
Figure 5-28 SG2-PS power supply................................................................................... 5-25
Figure 5-29 MCB board ................................................................................................... 5-28
Tables
Table 2-1 Analog return transmitters................................................................................2-10
Table 2-2 Digital return transmitters .................................................................................2-12
Table 2-3 Options and accessories..................................................................................2-14
Table 3-1 AC fuses ........................................................................................................... 3-4
Table 3-2 SG 2000 pad chart-standard gain ..................................................................... 3-12
Table 3-3 SG 2000 pad chart-high gain ............................................................................3-13
Table 3-4 Common problems...........................................................................................3-22
Table 5-1 SG2-LR features ..............................................................................................5-11
Table 5-2 SG2-LR minimum output levels.........................................................................5-11
Table 5-3 SG2-IFPT features ...........................................................................................5-14
Table 5-4 SG2-FPT features ............................................................................................5-15
Table 5-5 SG2-DFBT features.......................................................................................... 5-16
Table 5-6 SG2-DFBT/3 features.......................................................................................5-18
Table 5-7 SG2-EIFPT features.........................................................................................5-19
Table 5-8 DS-SG2-DRT/A features................................................................................... 5-21
Table 5-9 DS-SG2-DRT-2X/A features .............................................................................5-23
Table 5-10 Reporting and control provisions..................................................................... 5-26
Table 5-11 MCB user-interface settings............................................................................ 5-27
Table A-1 SG 2000 optical characteristics ......................................................................... A-1
Table A-2 Station RF characteristics................................................................................. A-1
Table A-3 SG 2000 General characteristics ....................................................................... A-2
Table A-4 SG2-LR specifications ...................................................................................... A-2
Table A-5 SG2-IFPT RF specifications.............................................................................. A-3
Table A-6 SG2-FPT RF specifications............................................................................... A-3
Table A-7 SG2-DFBT RF specifications............................................................................. A-4
Table A-8 SG2-DFBT/3 RF specifications .......................................................................... A-4
Table A-9 SG2-EIFPT RF specifications ............................................................................ A-5
Table A-10 SG2-DRT/A RF specifications ......................................................................... A-5
Table A-11 SG2-DRT-2X/A RF specifications .................................................................... A-6
Table A-12 Optical output power vs. wavelength for DS-SG2-DRT*/A transmitters .............. A-6
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 8

vi Contents
Table A-13 Current requirements ......................................................................................A-7
Table A-14 SG2-75 performance, with 77 channels............................................................ A-8
Table A-15 SG2-87 performance, with 94 channels............................................................ A-8
Table A-16 SG2-87 performance, with 110 channels.......................................................... A-8
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 9

Section 1
Introduction
Motorola’s SG 2000 telecommunications optical node performs light wave-to-RF and RF-to-light
wave signal conversions in an optical transmission link. This product is designed to support a wide
variety of advanced hybrid-fiber/coaxial network topologies.
As broadband communication systems continue to evolve, the demand increases for optical links that
carry the signal further into the transport system. These systems require additional features and
functionality such as digital compression and alternate access at significantly lower costs. Fully
configured, the SG 2000 supports these next-generation telecommunication networks. It also
supports a variety of single and two-way broadband network applications such as broadcast video,
interactive video, telephony, and data.
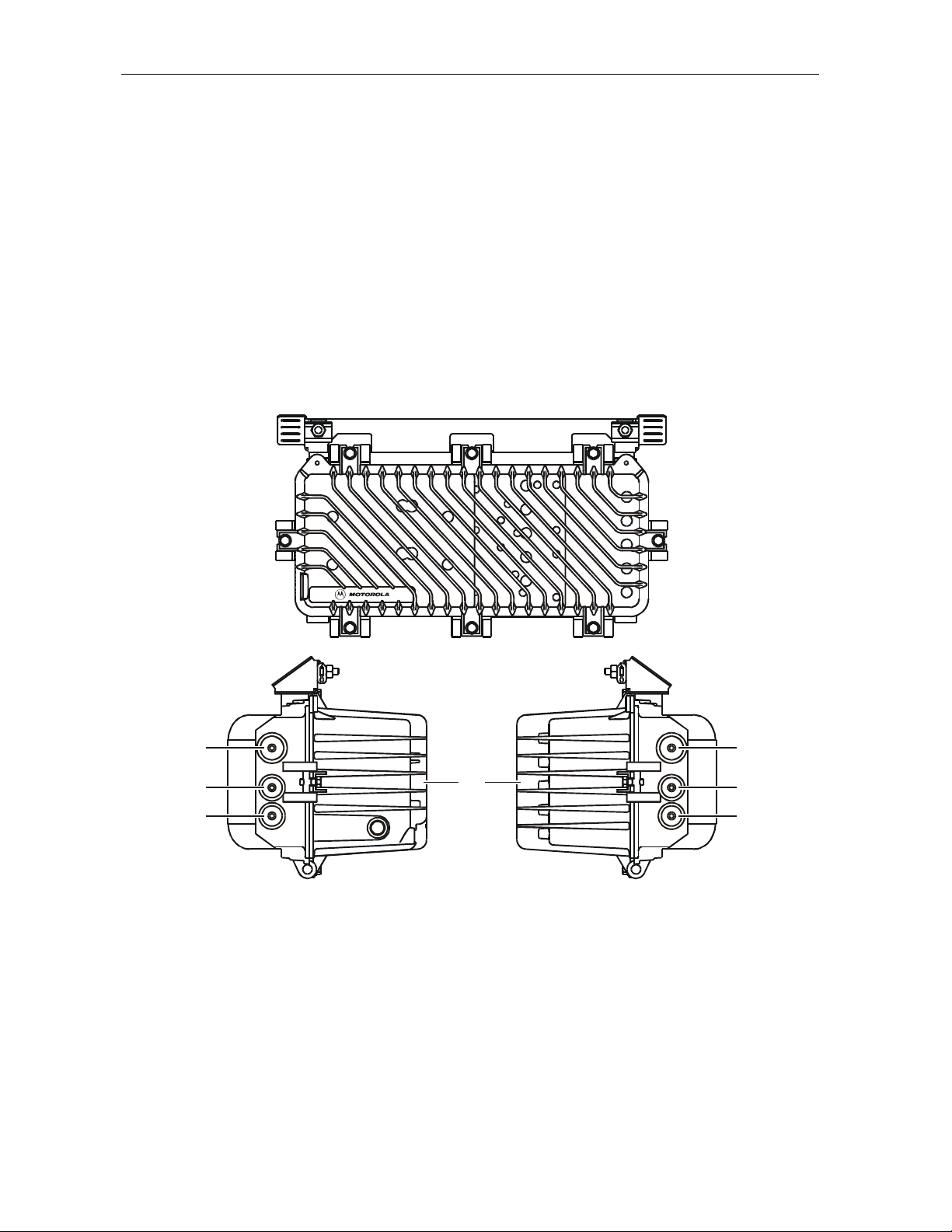
Figure 1-1 illustrates a closed SG 2000 telecommunications optical node:
Figure 1-1
SG 2000 — closed
6
7 8
3
2
1
4
5
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 10
1-2 Introduction
A
A
Figure 1-2 illustrates an open SG 2000 telecommunications optical node:
Figure 1-2
SG 2000 — open
H
L
JXP 2
JXP 4
L
H
SSEMBLED IN MEXICO
-20dB
-20dB
CAUTION:
CONTAINS PARTS
ND ASSEM B LI E S
SUSCEPTIBLE TO
DAMAGE BY
ELECTROSTATIC
DISCHARGE (ESD)
-20dB
-20dB
REFER TO
MANUA L F OR
FUSE VALUES
-20dB
H
L
JXP 1
L
H
PORT 1 PORT 2
FTEC
PORT 3
JXP 1
FWD EQ
ON
-20dB
+24 V DC
IS
IS
JXP 3
JXP 3
-20dB
FWD EQ
MDR
VARILOSSE R
RCVR
INPUT
ADU
ON
OFF
MAN
SG2-
FRB
STATUS MO NI TOR
RPM/*
SG 2000
Optical Node
FWD EQ
JXP 2
TCU
JXPADU
IS
IS
ADU
ADU
FWD EQ
-20dB
JXP 4
PORT 4
Base
Lid
Features include:
! 52 through 870 MHz forward passband, 5 through 40 MHz return standard (other splits are
available, see Appendix A, “Specifications”)
! Optical receivers - up to three
! Optical transmitters - up to two
! Four independent RF outputs
! Ingress switching capability through manual or headend control
! Redundant powering capability
! 15 A power passing
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 11

Introduction 1-3
! Optional LIFELINE
! User-friendly fiber management
! 60/90 volt powering
! Digital return redundancy capability
! Modular plug-in diplex filters and equalizers
! Custom configuration for unique system requirements
™
status monitoring
Using this Manual
The following sections provide information and instructions to install, configure, and operate the
SG 2000:
Section 1 Introduction provides a brief description of the product, identifies the information
Section 2 Overv iew describes the SG 2000 node and includes details regarding your options
Section 3 Bench Setup provides full configuration, set-up of options, and bench testing
Section 4 Installation provides instructions for installing the SG 2000 in a distribution
contained in this manual, and gives the help line telephone number and repair
return information.
and their functions.
procedures that are recommended before installation.
system.
Section 5 Operation provides information governing the use of various options and
applications required by your system.
Appendix A Specifications provides technical specifications for the SG 2000 node and major
options.
Appendix B Torque Specifications provides the appropriate torque specifications for the
screws, clamps, connectors, and bolts used in the SG 2000.
Abbreviations
and Acronyms
The Abbreviations and Acronyms list contains the full spelling of the short forms
used in this manual.
Related Documentation
Although these documents provide information that may be of interest to you, they are not required
to install or operate the SG 2000.
# LL-CU LIFELINE Control Unit Installation and Operation Manual
# LIFELINE for Windows Site Preparation Guide
# LIFELINE for Windows Software Operations Manual
# Return Path Level Selection, Setup, and Alignment Procedure Reference Guide
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 12

1-4 Introduction
Document Conventions
Before you begin to use the SG 2000, familiarize yourself with the stylistic conventions used in this
manual:
Bold type
SMALL CAPS
*
(Asterisk)
Italic type
Indicates text that you must type exactly as it appears or indicates a default value
Denotes silk screening on the equipment, typically representing front and rear-
panel controls, I/O connections and indicators (LEDs).
Indicates that there are several versions of the same model number and the
information applies to all models. When the information applies to a specific model,
the complete model number is given.
Denotes a displayed variable, a variable that you must type, or is used for
emphasis
If You Need Help
If you need assistance while working with the SG 2000, contact the Motorola Technical Response
Center (TRC):
# Inside the U.S.: 1-888-944-HELP (1-888-944-4357 )
# Outside the U.S.: 215-323-0044
# Online: http://www.motorola.com/broadband
Support, then click Web Support.
The TRC is open from 8:00 a.m. to 7:00 p.m. Eastern Time, Monday through Friday and 10 AM to
6 PM Eastern Time, Saturday. When the TRC is closed, emergency service only is available on a
call-back basis. Web Support offers a searchable solutions database, technical documentation, and
low priority issue creation/tracking 24 hours per day, 7 days per week.
, click HTML/Modem Version, click Customer
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 13

Introduction 1-5
Calling for Repairs
If repair is necessary, call the Motorola Repair Facility at 1-800-642-0442 for a Return for Service
Authorization (RSA) number before sending the unit. The RSA number must be prominently
displayed on all equipment cartons. The Repair Facility is open from 7 AM to 4 PM Pacific Time,
Monday through Friday.
When calling from outside the United States, use the appropriate international access code and then
call 526-314-1000, extension 3194, to contact the Repair Facility.
When shipping equipment for repair, follow these steps:
1 Pack the unit securely.
2 Enclose a note describing the exact problem.
3 Enclose a copy of the invoice that verifies the warranty status.
4 Ship the unit PREPAID to the following add ress:
Motorola BCS
c/o Exel
Attn: RSA #___________
6908 East Century Park Dr.
Tucson, AZ 85706
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 14
Section 2
Overview
Designed to be flexible, you can configure the SG 2000 with up to three optical receivers, four
independent high-level RF outputs, and two return-path optical transmitters. Multiple receiver and
transmitter combinations are available to satisfy split-band or redundancy requirements. The forward
passband is extended to 870 MHz to increase channel capacity and support advanced interactive
services and global applications.
Housing
The aluminum housing protects the electronics from weather damage and dissipates internally
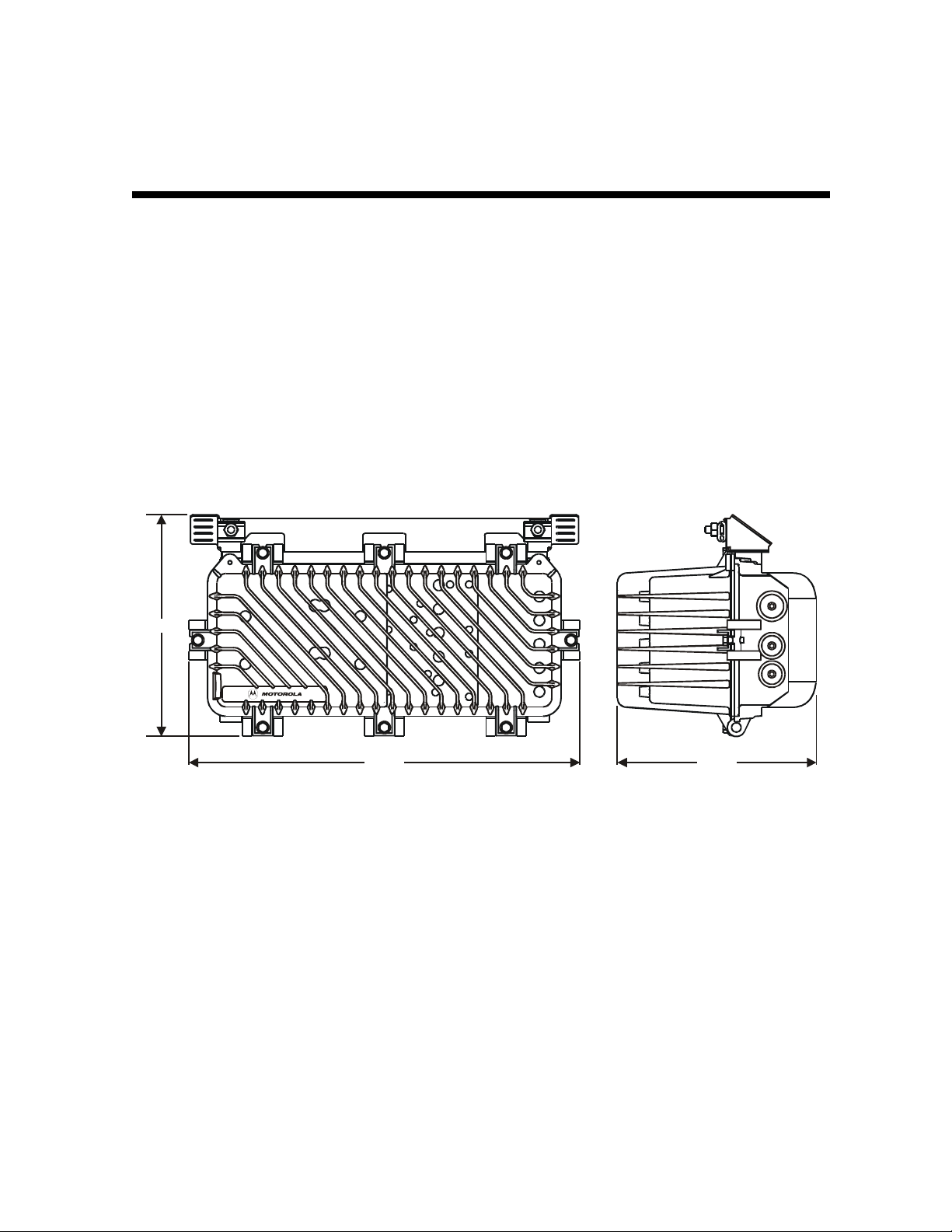
generated heat. Figure 2-1 illustrates the housing dimensions of the SG 2000 optical node:
Figure 2-1
SG 2000 housing di mensions - front and s ide view
12.25
6
7 8
3
2
1
21.60 10.99
4
5
34 OUT
For strand mounting, the optional bracket must be used. If the node is configured for strand
mounting, the bracket is installed on the node at the factory. The bracket provides two clamps,
located 16-7/8 inches apart, that secure the strand with 5/16 × 20 stainless steel bolts.
Coaxial cable connections to the housing are made using conventional 5/8 inch × 24 threads per inch,
stinger-type connectors.
Mounting Holes
Two threaded holes are located on the horizontal centerline on the back of the housing. These
5/16 × 18 × ¾ holes are separated by 11 inches center-to-center and can be used for pedestal or
surface mounting.
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 15
2-2 Overview
Port Locations
The five housing ports, shown in Figure 2-2, provide connection for coaxial cables. Note that the
housing ports are not labeled the same as the ports on the RF chassis. Side-by-side connector fittings
are limited to .750 inches at ports 1 and 2 and/or ports 3 and 4. These ports are protected by factory
inserted threaded plugs or plastic cap plugs which are discarded when the cable connectors are
installed. Port 2 is used only for connection to an external 60 Vac or 90 Vac power supply. Port 4 is
unused.
Figure 2-2 illustrates a front and end view of the housing and port locations:
Figure 2-2
Port locatio ns
6
7 8
3
2
1
4
5
Port 1 Port 2
AC port Unused
Port 3 Port 4
12IN
Lid
34 OUT
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 16
Overview 2-3
A
A
Gaskets
Each housing is equipped with a woven-wire gasket and a silicone-rubber weather gasket between
the housing base and lid as shown in Figure 2-3:
Figure 2-3
Housing ga skets
Weather ga ske t
(silicone rubber)
H
L
JXP 2
JXP 4
L
H
SSEMBLED IN MEXICO
-20dB
-20dB
CAUTION:
CONTAINS PARTS
ND ASSEMBLIES
SUSCEPTIBLE TO
DAMAGE B Y
ELECTROSTATIC
DISCHAR GE (E SD)
-20dB
-20dB
REFER TO
MANUAL FO R
FUSE VALUES
-20dB
H
L
JXP 1
L
H
PORT 1 PORT 2
FTEC
PORT 3
JXP 1
FWD EQ
ON
-20dB
+24 V DC
IS
IS
JXP 3
JXP 3
-20dB
FWD EQ
MDR
VARILOSSE R
RCVR
INPUT
ADU
ON
OFF
MAN
SG2-
FRB
STATUS MO NI TOR
RPM/*
SG 2000
Optical Node
FWD EQ
JXP 2
TCU
JXPADU
IS
IS
ADU
ADU
FWD EQ
-20dB
JXP 4
PORT 4
RF gasket
(woven wire)
The gaskets provide efficient ground continuity, RF shielding and weather protection. Both gaskets
must be in place and in good condition to ensure proper operation and protection of the node. The
silicone rubber gasket should be lightly covered with silicone grease each time the node is opened.
Replace the gasket if it is damaged or deformed.
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 17
2-4 Overview
Power Supply
The SG 2000 power supply (SG2-PS2) is located in the housing lid to optimize heat transfer and to
balance the thermal load between the base and the lid . F or high rel iab il ity or redun dancy
applications, two power supplies can be used. An umbilical cord connects the SG2-PS2 to the lid
motherboard (LIDB).
A flexible power-distribution design enables you to power the node from any of the four RF ports.
Using fuses and shunts you can configure the node to distribute power to the remaining active ports.
You can also power the node locally through the ac only port (port 2) while a second cable-plant
power supply loops through the other two main RF ports.
The power supply includes a heavy-duty, gas discharge tube surge protector located on the amplifier
module. You can replace this surge protector with the optional FTEC surge protector. The FTEC
triggers at approximately 230 V and presents a short circuit to the line during periods of over
voltage. After the ac input voltage returns to normal, the FTEC returns to its open-circuit state. This
provides the node with a level of protection against surge currents on the ac line. The same protector
is used for both supplies unless the split ac-feed option is implemented; then, the secondary or
redundant power supply is protected by a conventional heavy-duty gas discharge tube.
The 20-ampere fuses are installed at the factory to provide power passing to additional amplifiers.
Section 3, “Bench Setup,” discusses fusing options that are also diagrammed in Figure 3-1.
Figure 3-2 illustrates the location of the fuses.
The SG 2000 optical node can be powered from either 60 Vac or 90 Vac system power supplies. The
unit is shipped from the factory set for 60 Vac powering. For systems equipped with 90 Vac
powering, the suitcase jumper on the dc power supply can be repositioned to optimize the supply
start-up voltage for the higher input range. Section 3, “Bench Setup” provides a description of this
procedure.
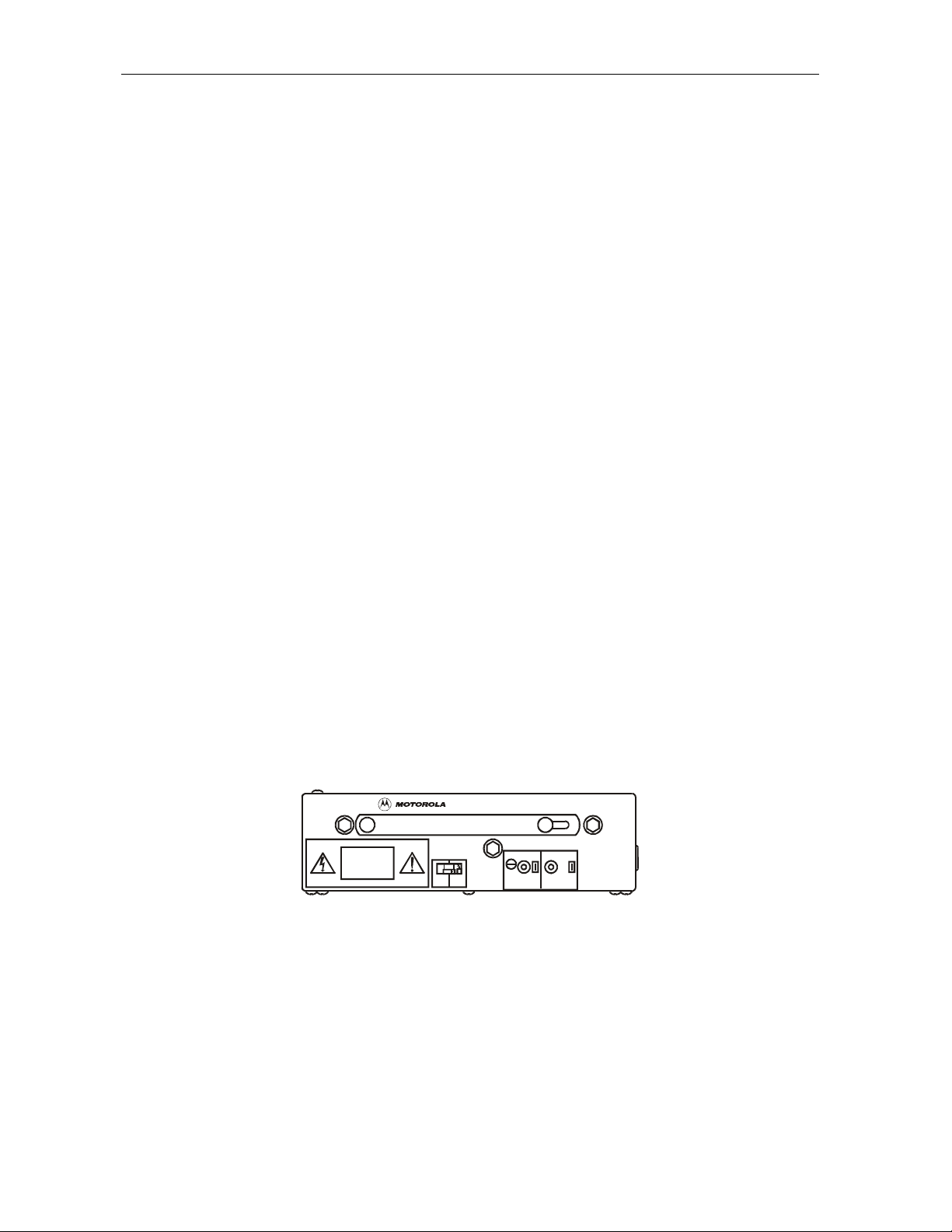
Figure 2-4 illustrates the SG2-PS2 power supply:
Figure 2-4
SG2-PS2 power supply
SG2-PS2
NO USER SERVICEABLE PARTS INSIDE
CAUTION
VOLTAGES IN EXCESS OF
300 VOLTS ARE PRESENT
UNDER COVER AND MAY
BE PRESENT AFTER POW ER
IS REMOVED
SEE INSTALLAT ION MANUAL FOR SERVICE
LO HI
ASSEMBLED IN MEXICO
24V 5V
ADJ
TEST
POINT
TEST
POINT
The optional SG2-PS power supply is required to support DS-SG2-DRT-2X/A transmitters in a
redundant configuration. The SG2-PS2 and SG2-PS power supplies are interchangeable.
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 18

Overview 2-5
Network Monitoring
The optional LIFELINE Status Monitoring System (LL-SG2) enables you to monitor the SG 2000
from a headend or a remote location. The transponder consists of a plug-in module mounted on the
main RF board. If you do not employ status monitoring and use redundant receivers and/or
transmitters, a manual control board (MCB) occupies the same position on the main RF board.
The entire LIFELINE system includes:
LL-CU control units
Are connected to the system at the headend and interrogate each
SG 2000 field transponder with FM outbound and inbound
transmissions. A variety of outbound and inbound frequencies can be
selected depending on the configuration of the system. The control unit
reports this information to the status monitor computer.
Status Monitor
Computer and
Software
LL-SG2-* Field
Installed
Transponders
Includes an IBM
unit (CU) through an RS-232 link. LIFELINE software enables the
operator to view measurements taken by the transponders.
Installed in individual field components, this unit interfaces with the CU at
the headend. It reports such parameters as: forward amplifier dc current
draw, ac and dc voltage, temperature, automatic drive unit (ADU-*) drive
-compatible computer that is connected to the control
voltage, management and control of RF ingress switching, and tamper
status.
Configuration
To accommodate unique system criteria, the SG 2000 is shipped as a configured product. Hundreds
of variations are available with configurations designed to address numerous system requirements
that include:
! Varying RF output configurations
! Forward bandwidth to 750 MHz or 870 MHz
! Forward slope options L, M, H, and U
! Band splits S, J, A, K, E, and M
! Silicon or GaAs technology
! Forward and return path redundancy
# High and low gain options
# Network monitoring
# RF output level control - thermal or automatic
# Multiple return options
Optional hardware features include:
! Analog and digital return transmitter options
! Service cable
# Surge protection
# Chromate or epoxy housing finish
# SC/APC or FC/APC optical connectors
# Ingress switching
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 19

2-6 Overview
You can order the SG 2000 in a number of configurations to suit system requirements. The shipped
configuration is noted in a label on the lower portion of the RF chassis cover.
Figure 2-5 illustrates a sample model using the configuration notation:
Figure 2-5
Configuration notation
Return Path Configurations (Analog Return)Key
No Transmitter
SG2-DFBT/*
Dual SG2-DFBT/* w/split return
Dual SG2-DFBT/* w/redundancy
E
F
N
D
Return Path Configurations (Digital Return) ***
DS-SG2-DRT/A-1310-DFB/SC w/redundancy
DS-SG2-DRT/A-1550-DFB/SC w/redundancy
DS-SG2-DRT/A-1510c-DFB/SC w/redundancy
DS-SG2-DRT/A-1530c-DFB/SC w/redundancy
23242526272829
Key
SG2-DFBT3/* (2mw)
I
DS-SG2-DRT/A-1550c-DFB/SC w/redundancy
SG2-FPT/*
Dual SG2-FPT/* w/split return
Dual SG2-FPT/* w/redundancy
SG2-EIFPT/*
Dual SG2-EIFP T/* w/split return
Dual SG2-DFBT3/* w/split return
Dual SG2-DFBT3/* w/redundancy
J
K
M
O
DS-SG2-DRT/A-1570c-DFB/SC w/redundancy
DS-SG2-DR T-2x /A-1470c-DF B/SC w/ s pl it return
DS-SG2-DR T-2x /A-1490c-DF B/SC w/ s pl it return
DS-SG2-DRT-2x/A-1590c-DFB/SC w/split return
30
31323334353637383940414243
Dual SG2-EIFPT/* w/redundancy
T
R
S
P
DS-SG2-DRT-2x/A-1610c-DFB/SC w/split return
DS-SG2-DRT/A-1470c-DFB/SC
DS-SG2-DRT/A-1490c-DFB/SC
DS-SG2-DRT/A-1590c-DFB/SC
DS-SG2-DRT/A-1610c-DFB/SC
Finish
Key
DS-SG2-DRT-2x/A-1470 c -DF B/ SC w/r e dun dancy split return
Mounting
None
Chromate
Pedestal
Strand
N
C
X
Y
Key
Ingress switch
None
Ingress switches
N
S
Key
Status Monitoring
None
AMC/Frequency agile
TollG/Frequency agile
J
N
H
NLT
SC/APC
S
MN MCB w/SIC
Power Supply
Single
Dual
Redundant w/SIC
SDR*
Key
Service Cable
6 FiberSer Cable
None
C
N
Key
FC/APC
Surge Protection
F
Surge Arre sto r
FTEC BTA Crowbar
F
N
Key
Forward Receivers
Freq
Vendor
DS-SG2-DRT-2x/A-1490 c -DF B/ SC w/r e dun dancy split return
DS-SG2-DRT-2x/A-1590 c -DF B/ SC w/r e dun dancy split return
DS-SG2-DRT-2x/A-1610 c -DF B/ SC w/r e dun dancy split return
DS-SG2-DRT/A-1470c-DFB/SC w/redundancy
DS-SG2-DRT/A-1490c-DFB/SC w/redundancy
DS-SG2-DRT/A-1570c-DFB/SC w/redundancy
DS-SG2-DRT/A-1610c-DFB/SC w/redundancy
44
Connectorization **
Key
Control
TCU
ADU 499.25/S
ADU 439.25/S
ADU 549.00/S
ADU 403.25/S
ADU 445.25/S
ADU 325.25/S
SG2-LR Single
Dual SG2-LR One Narrowcast/One Broadcast
Dual SG2-LR/Dual Receivers w/Redundancy
Dual SG2-LR/Narrowcast w/Redundancy/One Broadcast
None
Return Path Configurations (Digital Return) ***
DS-SG2-DRT-2x/A-1310-FP/SC w/split return
DS-SG2-DRT -2 x / A-1 3 10-DFB/SC w/split return
DS-SG2-DRT -2 x / A-1 5 50-DFB/SC w/split return
1
2345678
Key
Bandpass Split
5-40 MHz/52-870 MHz
5-55 MHz/70-870 MHz
5-65 MHz/85-870 MHz
SJAKE
Key
I
T
A
DEH
Key
DS-SG2-DRT-2x/A-1510c-DFB/SC w/split return
DS-SG2-DRT-2x/A-1530c-DFB/SC w/split return
DS-SG2-DRT-2x/A-1550c-DFB/SC w/split return
DS-SG2-DRT-2x/A-1570c-DFB/SC w/split return
DS-SG2-DRT/A-1310-FP/SC
DS-SG2-DRT/A-1310-DFB/SC
DS-SG2-DRT/A-1550-DFB/SC
DS-SG2-DRT/A-1510c-DFB/SC
DS-SG2-DRT/A-1530c-DFB/SC
DS-SG2-DRT/A-1550c-DFB/SC
DS-SG2-DRT/A-1570c-DFB/SC
DS-SG2-DRT-2x/A-1310-FP/SC w/redundancy split return
DS-SG2-DRT-2x/A-1310-DFB/SC w/redundancy split return
DS-SG2-DRT-2x/A-1550-DFB/SC w/redundancy split return
DS-SG2-DRT-2x/A-1510c-DFB/SC w/redundancy split return
DS-SG2-DRT-2x/A-1530c-DFB/SC w/redundancy split return
DS-SG2-DRT-2x/A-1550c-DFB/SC w/redundancy split return
DS-SG2-DRT-2x/A-1570c-DFB/SC w/redundancy split return
Bandpass
Key
DS-SG2-DRT/A-1310-FP/SC w/redundancy
Low/2 8 dB S ilicon
High/34 dB Silicon
Low/2 8 dB GaAs
Gain/Hybrid Technology
Key
RF Configurations
2 Bridger
Key
3 Bridger
BCD
750 MHz
870 MHz
75
SG2 87 S S D P T N S A 11 N S N N N N X
87
High/34 dB GaAs
S
T
P
R
4 Bridger
1 Trunk; 2 Bridger
2 Trunk; 2 Bridger
2 Trunk; 1 Bridger
F
E
G
9
10111213141516171819202122
5-42 MHz/54-870 MHz
5-30 MHz/47-870 MHz
5-80 MHz/108-870 MHz
M
Tilt
6 dB
Key
10 dB
8 dB
12.5 dB
14 dB
L
BASHU
16 dB
J
ABCDN
Key
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 20
Overview 2-7
A
A
A
A
A
A
Refer to the current Motorola catalog for option and feature availability.
Forward Path
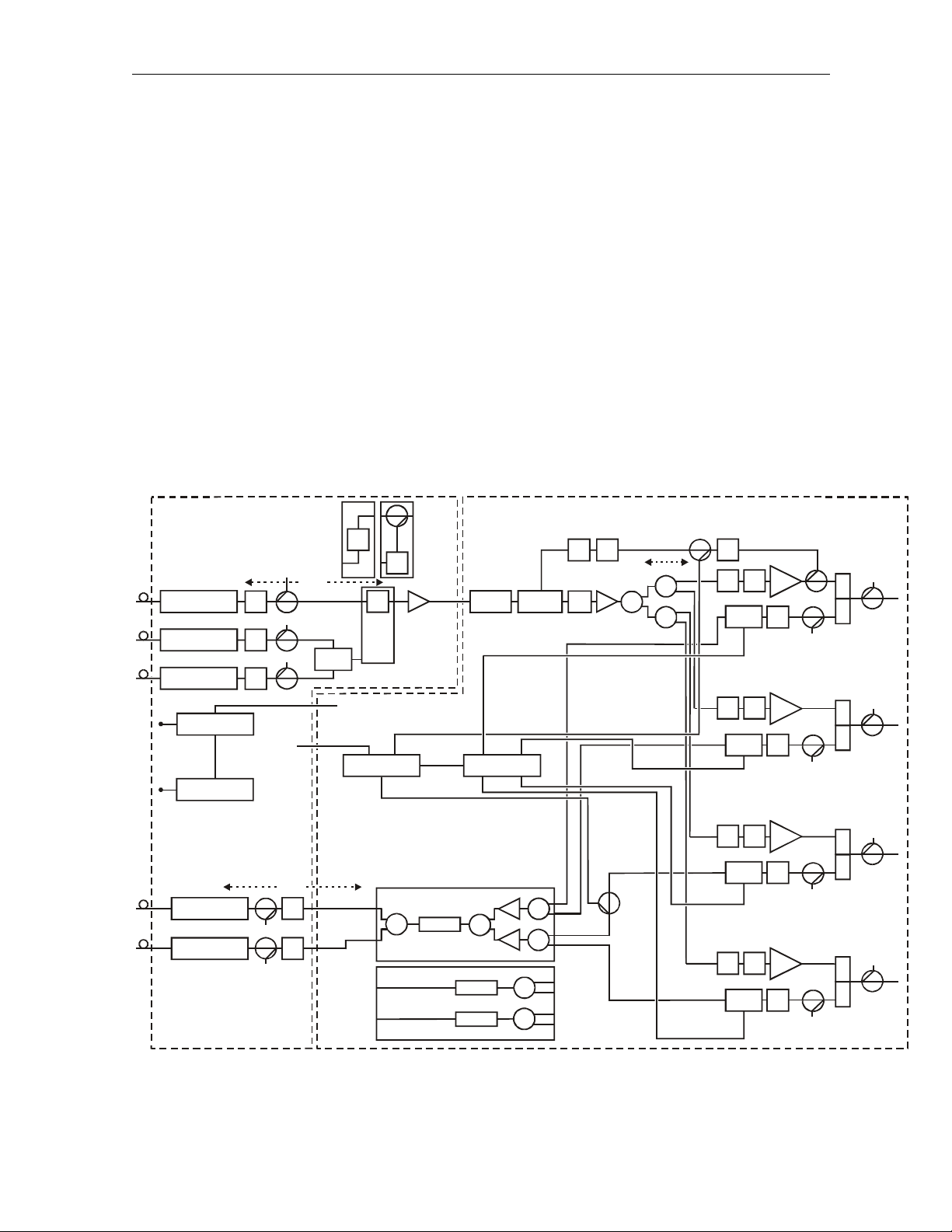
The multiple receiver functionality of the platform accommodates split-band and/or redundancy
applications. A typical split-band configuration has analog signals in the 52 MHz through 550 MHz
band feeding one receiver (C location in Figure 2-6). Digital transmissions or narrowcast signals are
carried between 450/550 MHz and 870 MHz on another fiber and processed by the second receiver
(A location). You can use the optional third receiver (B location) as a back up in the event that the
narrowcast receiver loses optical signal input. Automatic path switchover occurs through either the
optional status monitoring or manual control-board modules.
Figure 2-6 provides a diagram of the signal flow-path through the SG 2000:
Figure 2-6
Signal flow diagram
SG2 lid
Receiver C
Receiver B
Receiver A
Power supply
Power supply
Optical transmitter
Optical transmitter
JXP
JXP
JXP
Data lines
TP
TP
SG2-ABJ/P
forward
A/B
jumper
TP
TP
TP
-1.0
JXP
*
JXP
**
-1.5
Switch
JXP
JXP
+24 VDC
+5 VDC
ACV
Status monitor
SG2-FBS
forward
band
split
HP
filter
+15 Lo
+21.5 Hi
SG2-FJB/P
forward
jumper
board
-3.5 -3.5
SG2-RPLPF
SG2 RF chassis
SG2-RPM/C
-2.0
LP filter
SG2-RPM/S
LP filter
LP filter
SG2-RPLPF
-2.0 -1.5
AttenuatorSG2-FRB
-2.0
@ Min atten
Ingress control
-3.5+8.5
-3.5
-2.0
All forward and return path test points (TP) are -20dB
5dB
*
With second transmitter pad = 5dB; withou t second transmitter pad = 15dB
**
POT
DU JXP
MDR
+ 18.5
mplifier
Splitter
-0.5
-8.0
Splitter
Splitter
-1.0
EQ
JXP
Ingress
-2.0
EQ
JXP
Ingress
EQ
JXP
Ingress
JXP EQ
Ingress
mplifier
+18.5
JXP
mplifier
JXP
mplifier
JXP
mplifier
JXP
-0.5
TP
TP
TP
TP
-1.0
-1.0
Diplex
filter
H
L
-0.5
Diplex
filter
H
L
Diplex
filter
H
L
Diplex
filter
H
L
TP
-0.5
TP
TP
TP
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 21

2-8 Overview
To assess fiber link status, the optical-power monitor circuit is active at all times (even when the
receiver is disabled). An integrated optical bulkhead connector and module link status indicators
enhance fiber management and reduce troubleshooting time. The receiver module is fully compatible
with the status monitor transponder for remote monitoring of key module and link performance
parameters.
Several plug-in boards are available to configure the SG 2000 lid board for single, redundant, or
narrowcast receiver arrangements. A low-noise pre-amplifier hybrid amplifies the signal to a level
suitable for connection to the RF chassis.
An SG2-FRB flatness board, at the input to the RF chassis, compensates for hybrid and accessory
response signatures. A variable attenuator circuit enables fine adjustment of the output level, and is
driven either by the standard thermal control unit (TCU) or optional ADU pilot automatic gain
control (AGC) module to compensate for tempera tur e and input lev el var ia tion s.
The MDR-*/* circuit board provides a fixed linear equalizer for either 750 MHz or 870 MHz. This
equalizer comes in numerous values to support various levels of output tilt. The MDR board also
compensates for the low frequency roll-off inherent in plug-in diplexers.
A driver-hybrid amplifies the signal to a sufficiently high level to feed up to four power-doubling
output stages. These output hybrids can be either conventional silicon or premium gallium arsenide
types for even higher station output at low distortion. Plug-in facilities are available ahead of each
output stage for individual equalizer boards. These can be installed to customize the tilt for the
various ports. At one output, a minus 16 dB directional coupler provides signal to the optional ADU
and status-monitor modules. This signal is used only when either or both of these options is installed.
It is not necessary to terminate the coupler output when neither option is present.
Minus 20 dB directional test points are available at various points in the signal paths of the node.
Because these test points are 75-ohm source impedance, special test probes are not required.
Model JXP-* attenuator pads are used for adjusting signal levels within the signal path. The unit is
shipped with JXP-ZX versions installed.
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 22
Overview 2-9
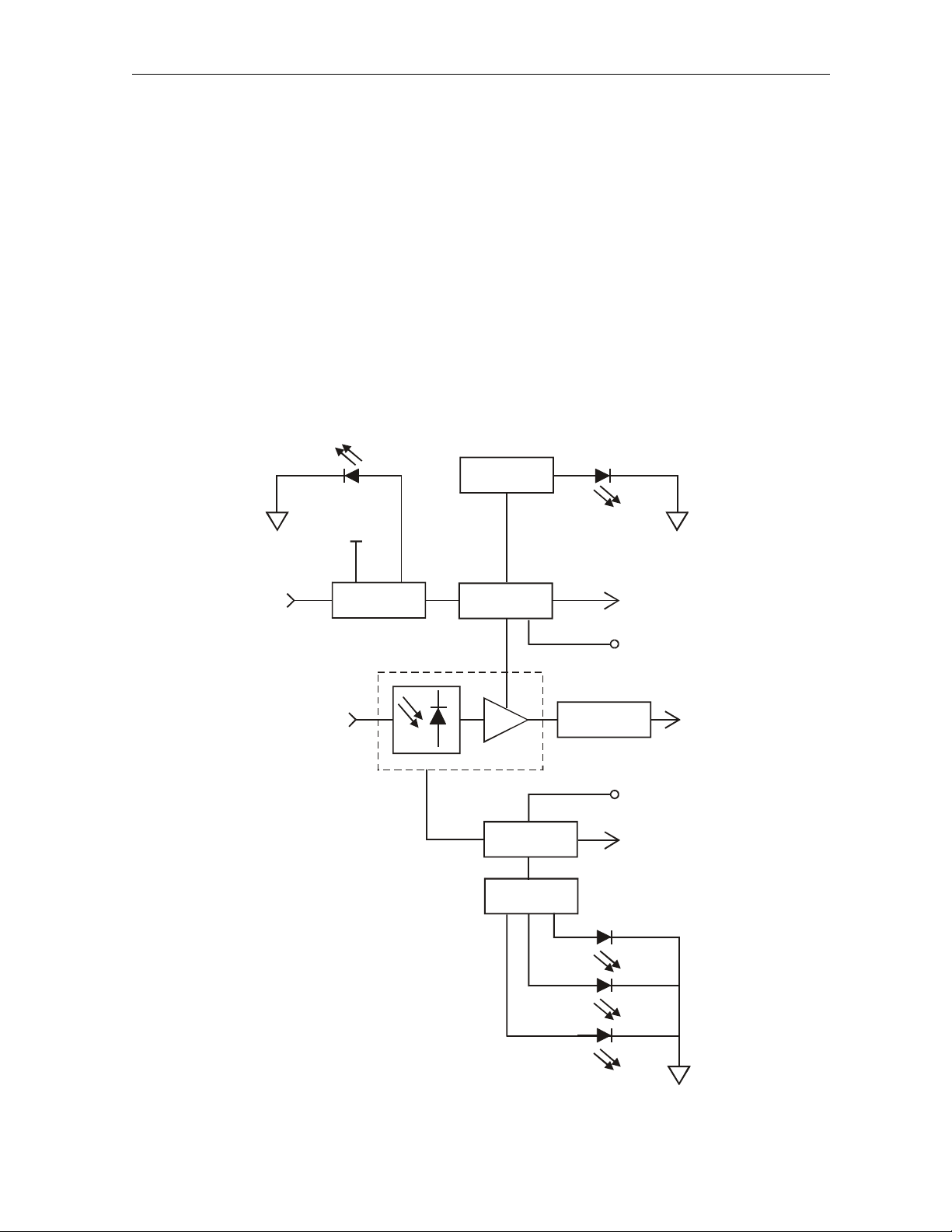
SG2-LR Receiver
The receiver module (SG2-LR) is designed specifically for high performance in the SG 2000. The
SG2-LR receiver uses an integrated optical-hybrid photo-detector for improved RF performance over
the entire 40 MHz through 870 MHz passband. It is enabled and disabled in response to a signal
from the status monitor transponder or manual control board (MCB). This provides excellent
isolation, improved reliability, and reduced power consumption when the receiver is used in
redundant applications.
Figure 2-7 illustrates a functional block diagram of the SG2-LR receiver:
Figure 2-7
SG2-LR receiver function al diagram
Module
enabled
Threshold
comparators
Module
enable
Optical
input
+24V
Module enable
logic
Optical receiver hybrid
Hybrid current
monitor
Optical power
monitor
Threshold
comparators
Module
fault
Matching
network
Hybrid current
sense signal
(10V/A)
Hybrid current
test point
(1.0 V/A)
RF
output
Optical power
test point
(1 V/mW)
Optical power
sense signal
(1 V/mW)
Low
Normal
High
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 23

2-10 Overview
Analog Return Path
Similar to the multiple optical receivers, the dual return-path optical transmitters also have
split-return or redundant functionality. In split-return applications two of the four RF return signals
are fed to one optical transmitter while the remaining two return signals are fed to the second
transmitter.
Signal levels are adjusted in each return path using model JXP-* attenuator pads. Units are shipped
with a JXP-5 (5 dB) attenuator pad at the input position of each installed transmitter. If only one
transmitter is in the unit, there will be a 15 dB pad at the second transmitter input position to serve as
a termination. Ingress switching is also an available option. If ingress switches are not used, JXP-2
pads are installed.
When configured for redundancy, both return lasers are active and transmit the combined RF return
signals simultaneously. Or, they can be activated independently using the status monitor transponder
or the MCB. In the event of path failure, return path redundancy is accomplished at the headend or
the receive site by switching to the alternate or active return fiber.
Analog Return Transmitters
Five optical analog return transmitters are available to meet the needs of most return applications.
Table 2-1 identifies and describes the five analog return transmitters:
Table 2-1
Analog return transmitters
Model Description
SG2-IFPT/*
SG2-FPT/*
SG2-DFBT/*
SG2-DFBT/3
SG2-EIFPT/*
Uses an isolated, uncooled, Fabry-Perot laser operating at 400 µW. It carries a
full 35 MHz of digital data or up to two video channels.
Uses a non-isolated, uncooled, Fabry-Perot laser operating at 400 µW. It carries a
full 35 MHz of digital data or up to two video channels.
Uses an uncooled, isolated DFB laser operating at 1 mW for improved link
performance. It carries a full 35 MHz of digital data or up to two video channels.
Uses an uncooled, isolated DFB laser operating at 2 mW for improved link
performance. It carries a full 35 MHz of digital data or up to two video channels.
Uses an uncooled, enhanced, and isolated Fabry-Perot laser operating at 1 mW
for improved link performance. It carries a full 35 MHz of digital data or up to two
video channels.
The transmitters include thermal compensation circuitry to minimize the change in received optical
and RF signal level at the headend as the node temperature varies. To reduce power consumption and
enhance reliability, the transmitters can be enabled and disabled in response to a signal from the
status monitor transponder or the MCB. An integrated optical bulkhead connector and module status
indicators enhance fiber management and reduce troubleshooting time. For remote monitoring of key
module performance parameters, the return modules are fully compatible with the status-monitor
transponder.
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 24

Overview 2-11
Figure 2-8 illustrates a functional block diagram of the SG2 transmitter:
Figure 2-8
SG2 transm itter block d iagram
Hybrid
current
test
RF
input
Thermal
compensation
Optical
power
test
JXP
factory calibration
only
Laser
bias
control
Laser
diode
module
Fiber
output
Laser
current
test
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 25

2-12 Overview
Digital Return Path
The digital return transmitter series (DS-SG2-DRT*) converts a broadband analog RF return-path
signal into digital optical signals with 10-bit resolution.
The transmitters used for digital return applications are divided into two families: DS-SG2-DRT/A
and DS-SG2-DRT-2X/A.
Seven digital return transmitters per family are available to meet the needs of most digital return
applications.
Table 2-2 identifies the fourteen opti cal dig it al re turn transmitters:
Table 2-2
Digital return transmitters
DS-SG2-DRT/A DS-SG2-DRT-2X/A
DS-SG2-DRT/A-1310 FP DS-SG2-DRT-2X
DS-SG2-DRT/A-1310 DFB DS-SG2-DRT-2X/A-1310 D FB
DS-SG2-DRT/A-1470 DFB DS-SG2-DRT-2X/A-1470 D FB
(1)
/A-1310 FP
DS-SG2-DRT/A-1490 DFB DS-SG2-DRT-2X/A-1490 D FB
DS-SG2-DRT/A-1550 DFB DS-SG2-DRT-2X/A-1550 D FB
DS-SG2-DRT/A-1510c
DS-SG2-DRT/A-1530c DFB DS-SG2-DRT-2X/A-1530c DFB
DS-SG2-DRT/A-1550c DFB DS-SG2-DRT-2X/A-1550c DFB
DS-SG2-DRT/A-1570c DFB DS-SG2-DRT-2X/A-1570c DFB
DS-SG2-DRT/A-1590 DFB DS-SG2-DRT-2X/A-1590 D FB
DS-SG2-DRT/A-1610 DFB DS-SG2-DRT-2X/A-1610 D FB
(1) 2X in the model number denotes time division multiplexing (TDM)
(2) c in the model number denotes coarse wave division multiplexing (CWDM)
(2)
DFB DS-SG2-DRT-2X/A-1510c DFB
To prepare for an anticipated increa se in retu rn tra ff ic, provisi oning fo r CWDM is buil t into the
transmitters. The CWD M optio n con sis ts of las ers at predef ined wavelengths. This option is
available to support multiplexing in the optical domain, using eight-wavelength wave division
multiplexing (WDM) in the DS-SG2-DRT/A-15XX DFB and DS-SG2-DRT-2X/A-15XX DFB
windows.
DS-SG2-DRT/A
The DS-SG2-DRT/A digitizes a single analog 5-42 MHz return path signal to produce a 1.6 Gbps
data stream. This data stream is then routed to a digital laser for transmission to a corresponding
digital return receiver. The node can be configured with one or two DS-SG2-DRT/A transmitters,
with dual transmitters providing redundancy. In conjunction with these transmitters, the node must
also be configured with the SG2 Return Path Module/Combined (SG2-RPM/C). The return signals
from all four ports are combined and fed to the optical transmitters.
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 26

Overview 2-13
When configured for redundancy , both return transm it t ers are normally active and transmit th e
combined RF return signal simultaneously. In the event of path failure, continuity of service is
accomplished at the headend or the receiver site by switching to the alternate or active return fiber.
Signal levels are adjusted in each return path using Model JXP-* attenuator pads. Units are shipped
with a JXP-5 (5 dB) attenuator pad at the input position of each installed transmitter. If only one
transmitter is installed, there will be a 15 dB pad at the second transmitter input position to serve as a
termination.
DS-SG2-DRT-2X/A
The DS-SG2-DRT-2X/A has two separate RF inputs. The transmitter digitizes these two independent
analog 5-42 MHz return-path signals to produce two 1.25 Gbps data streams. These two data streams
are then multiplexed to create a single 2.5 Gbps data stream that is then routed to a digital laser for
transmission to a corresponding digital return receiver. In conjunction with these transmitters, the
node must also be configured with the SG2 Return Path Module/Split (SG2-RPM/S). Return signals
from two of the four node ports are fed to one RF input of the transmitter while the remaining two
return signals are fed to the second RF input. The signal paths for both inputs are explained in more
detail in Section 5, “Operation”.
Signal levels are adjusted in each return path using Model JXP-* attenuator pads. The transmitter
gets one of its RF signals automatically when the unit is plugged into its appropriate slot. The second
RF signal comes through a special adapter from the adjacent connector, which is normally available
for installing a redundant transmitter. Therefore, the units are shipped with two JXP-5 attenuator
pads at the input positions.
Ingress control switching is an available option with any return transmitter configuration. If ingress
switches are not used, JXP-2 pads are installed in each ingress switch position on the main RF board.
The node can be configured with one or two DS-SG2-DRT-2X/A transmitters, with dual transmitters
providing redundancy. The redundancy configuration is explained in more detail in Section 5,
“Operation”.
Section 5, “Operation,” also provides detailed information and block diagrams for each series of
digital transmitters.
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 27

2-14 Overview
Level Control
The gain of hybrid IC amplifiers varies with temperature. In addition, changes in system channel
loading and/or splices in the fiber link can change the level of the received signal.
The standard TCU board compensates for anticipated hybrid gain changes by sensing housing
temperature and signaling needed changes to the RF attenuator.
The ADU board, an optional plug-in module, monitors the amplitude of a selected pilot frequency.
The pilot frequency is an available analog television channel not scrambled by the sync suppression
method. Any changes in amplitude are fed back to the RF attenuator that makes appropriate
corrections.
The input to the ADU contains a JXP-* pad. The factory-installed value of this pad is 6 dB (JXP-6)
for bridger level outputs and 0 dB (JXP-ZX) for trunk level outputs. Under normal conditions, it
should not be changed.
Options and Accessories
Table 2-3 provides a list of options and accessories for the SG 2000:
Table 2-3
Options and accessories
Model Description Function
ADU-*
TCU
JXP-*A
JXP-ZX
FTEC
LL-SG2
Automatic drive
unit
Thermal control
unit
Fixed
attenuator
0 dB attenuator This attenuator is used in place of JXP-*A pads when no
Crowbar
overvoltage
protection
LIFELINE
module
This option automatically adjusts gain by monitoring changes
in the level of the selected pilot carrier. E ither an ADU or T CU
must be installed.
The TCU controls amplifier gain for changes in hybrid gain at
the sensed temperature.
Attenuator pads are used to adjust amplifier levels and are
available in 1 dB steps from 1 through 24 dB. The appropriate
value must be installed.
attenuation is needed.
The FTEC is an electronic crowbar/surge protector that can be
used to replace the existing 230-volt gas discharge surge
protector.
This module enables the system operator to monitor the SG2
from a remote location. See Section 5, “Operation” for
parameters monitored. Several frequencies are available. See
the product catalog for additional information.
GFAL
F/JXP
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Test probe This probe is used to evaluate node performance.
Injection probe This probe is used to inject a signal for test purposes.
Page 28

Overview 2-15
Model Description Function
SG2-MCB
SG2-SB/*
SG2-PS
SG2-PS2
SG2-
SERCAB/*
SG2-FE-
*/750
SG2-FE*/870
SG2-IS
SG2-LR
DS-SG2-DRRB
Manual control
board
This board locally controls the ingress switch and
receiver/transmitter A/B redundant switching if the node is not
equipped with status monitoring.
Strand bracket Bracket for hanging a strand mounted node.
Power supply
Provides the +24 V and +5 V dc supply to the station. It has an
extended voltage range and is power-factor corrected.
Power supply
Provides the +24 V and +5 V dc supply to the station.
Service cable A 6-fiber service cable that is available with SC/APC or
FC/APC connectors.
Forward
equalizers
Used to increase output tilt at one or more ports in a 750 MHz
system. They are available in 1 dB increments from 2 dB
through 6 dB.
Forward
equalizers
Used to increase output tilt at one or more ports in an 870
MHz system. They are available in 1 dB increments from 2 dB
through 6 dB.
Ingress switch This switch enables the operator to troubleshoot without
shutting down the return path. It requires the use of either the
LL-SG2/* or the SG2-MCB.
Lightwave
receiver
Digital return
redundancy
board
This receiver converts the received optical signal to
broadband RF.
This board provides the redundant input to a
DS-SG2-DRT/A-2X digital return transmitter. One DRRB is
used for each -2X transmitter.
SG2-*
DS-SG2-DRT*
Analog return
transmitters
Digital return
transmitters
Table 2-1 identifies and describes the five optical analog
return-path transmitters.
Table 2-2 identifies all models of the optical digital return-path
transmitters. Section 5, “Operation,” provides detailed
information and block diagrams for each series of digital
transmitters.
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 29
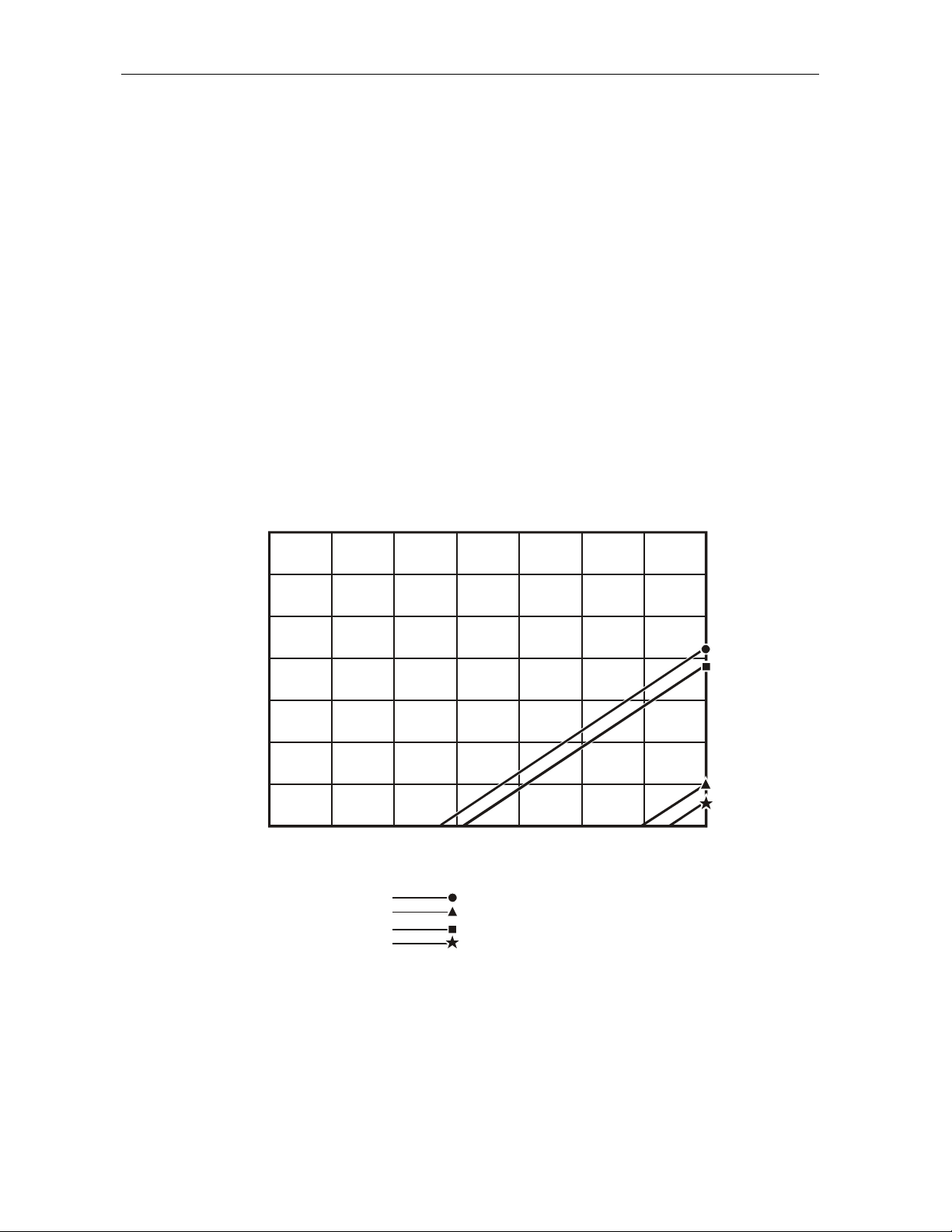
2-16 Overview
O
B
Gain Selection
Figures 2-9 through 2-13 illustrate SG 2000 gain and tilt selection charts based on frequency and
channel load options.
To use the gain option selection charts, Figures 2-9 and 2-10, first find the point on the left hand axis
that corresponds to the expected optical input power at the node. Move across this horizontal line to
the right until it intersects a vertical line corresponding to the desired RF output level.
If this intersection is above and to the left of the diagonal “lo gain limit” line for the channel loading
under consideration, the low-gain option will give optimum performance with minimum padding. If
the intersection lies between the “lo gain limit” and “hi gain limit” lines, then choose the high-gain
option. Operation at a combination of input and output levels below and to the right of the “hi gain
limit” line is not possible.
Figure 2-9 illustrates the gain option selection chart for 750 MHz:
Figure 2-9
Optical inp ut versus 750 MHz gain
2
1
0
m)
-1
-2
ptical input (d
-3
-4
-5
38 40
Lo gain limit, 94 ch
Hi gain limit, 94 ch
Lo gain limit, 77 ch
Hi gain limit, 77 ch
750 MHz Gain Selection
42
Bridger output level (dBmV), 750 MHz equivalent
(Trunk output level is 10 dB lower)
44 46 48 50 52
Figure 2-9 gives the output level at 750 MHz. For a system loaded with analog channels to
550 MHz, the actual level at 550 MHz is 3.5 dB lower with the standard overall tilt of 12.5 dB. For
the low tilt of 10 dB, the reduction at 550 MHz is 3.0 dB. For the high tilt of 14 dB, the 550 MHz
level is 4.0 dB lower than at 750 MHz.
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 30
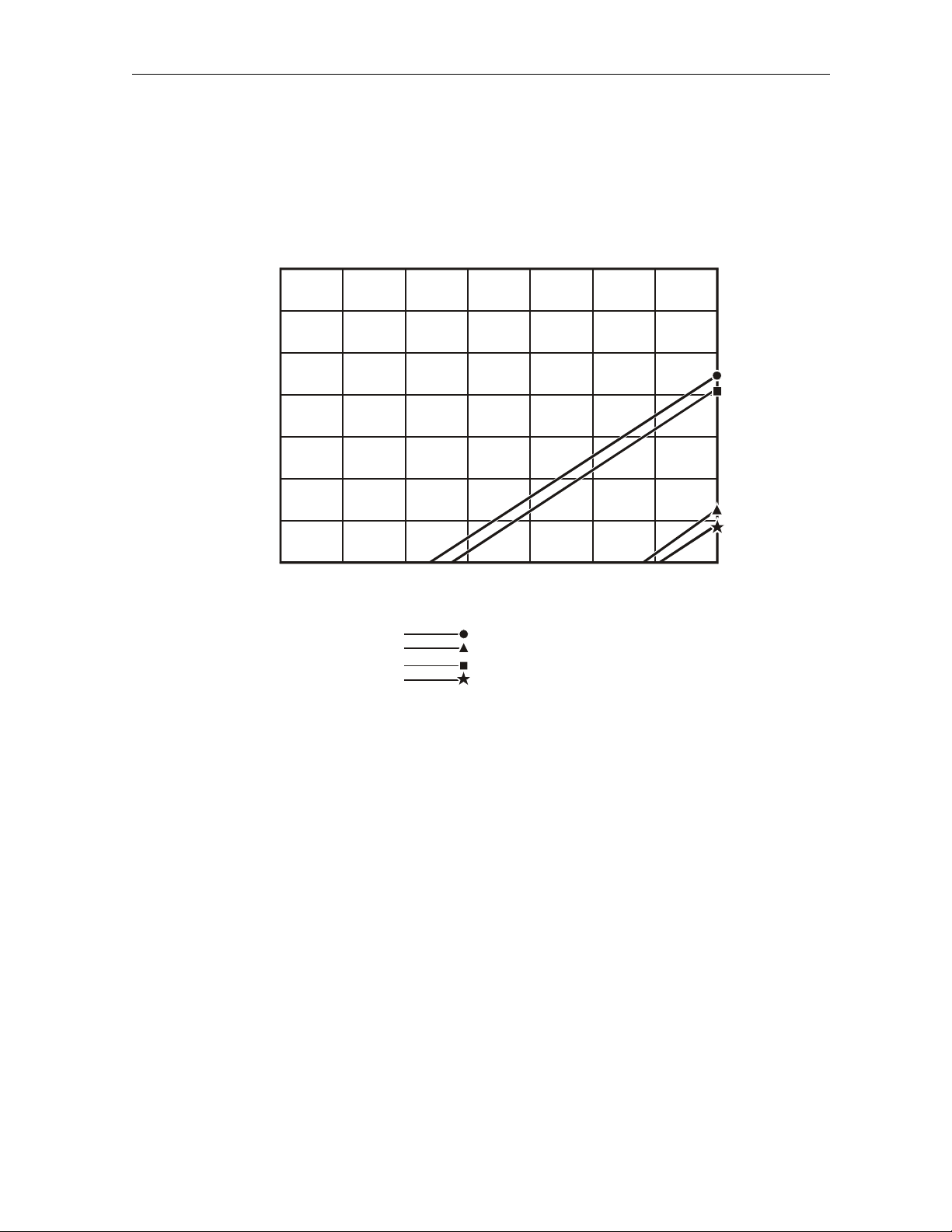
Overview 2-17
O
B
Figure 2-10 illustrates the gain option selection chart for 870 MHz:
Figure 2-10
Optical inp ut versus 870 MHz gain
2
1
0
m)
-1
-2
ptical input (d
-3
-4
-5
38 40
Lo gain limit, 110 ch
Hi gain limit, 110 ch
Lo gain limit, 94 ch
Hi gain limit, 94 ch
870 MHz Gain Selection
42
Bridger output level (dBmV), 870 MHz equivalent
(Trunk output level is 10 dB lower)
44 46 48 50 52
Figure 2-10 gives the output level at 870 MHz. For a system loaded with analog channels to
750 MHz, the actual level at 750 MHz is 1.7 dB lower with the standard overall tilt of 11.5 dB. For
the low tilt of 9.0 dB, the reduction at 750 MHz is 13 dB. For the high tilt of 14 dB, the 750 MHz
level is 2.1 dB lower than at 870 MHz.
For a system loaded with analog channels to 650 MHz, the actual level at 650 MHz is 3.1 dB lower
than the given 870 MHz level with the standard overall tilt of 11.5 dB. For the low tilt of 9.0 dB, the
reduction at 650 MHz is 2.4 dB. For the high tilt of 14 dB, the 650 MHz level is 3.8 dB lower than at
870 MHz.
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 31

2-18 Overview
R
B
Tilt Selection
To use the tilt selection charts, first determine the system operating bandwidth, either 750 MHz or
870 MHz. Next, determine the desired system channel load either 77, 94, or 110 channels. Use the
corresponding bandwidth and channel loading chart to determine the preferred tilt, either low,
standard, or high.
Figure 2-11 illustrates the tilt select ion cha rt for 750 M Hz bandwidth and 77-chan nel load:
Figure 2-11
Relative level dB versus 750 MHz slope 77 channels
SG2 750 MHz Slope Chart
77 Analog Channel s, 200 MH z Digital
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
elative level, d
3
2
1
0
-1
-2
-3
50
Low
Standar d
High
150 250 350 450 550 650 750
Frequency, MHz
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 32

Overview 2-19
R
B
Figure 2-12 illustrates the tilt select ion cha rt for 870 M Hz bandwidth and 94-chan nel load :
Figure 2-12
Relative level dB versus 870 MHz slope 94 channels
SG2 870 MHz Slope Chart
94 Analog Channel s, 220 MH z Digital
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
elative level, d
1
0
-1
-2
-3
-4
50
High
Standar d
Low
150 250 350 450 550 650 750
Frequency, MHz
870
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 33

2-20 Overview
R
B
Figure 2-13 illustrates the tilt select ion cha rt for 870 M Hz bandwidth and 110-cha nnel load :
Figure 2-13
Relative level dB versus 870 MHz slope 110 channels
SG2 870 MHz Slope Chart
110 Analog Channels, 120 MHz Digital
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
elative level, d
3
2
1
0
-1
-2
-3
50 150 250 350 450 550 650 750 870
Frequency, MHz
High
Standar d
Low
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 34

Section 3
Bench Setup
Before you install the SG 2000 you must set it up to meet the power and configuration requirements
for the node location. Bench set-up and quick check procedures are recommended to ensure proper
functioning of all components and simplify field installation. The last two pages of this section
provide an SG 2000 activation worksheet for you to record all pertinent setup information.
To facilitate on-line replacement, “hot-plugging” — inserting and removing optical modules and
power supplies — on SG 2000s equipped with redundant supplies, is possible with the node powered
and operational.
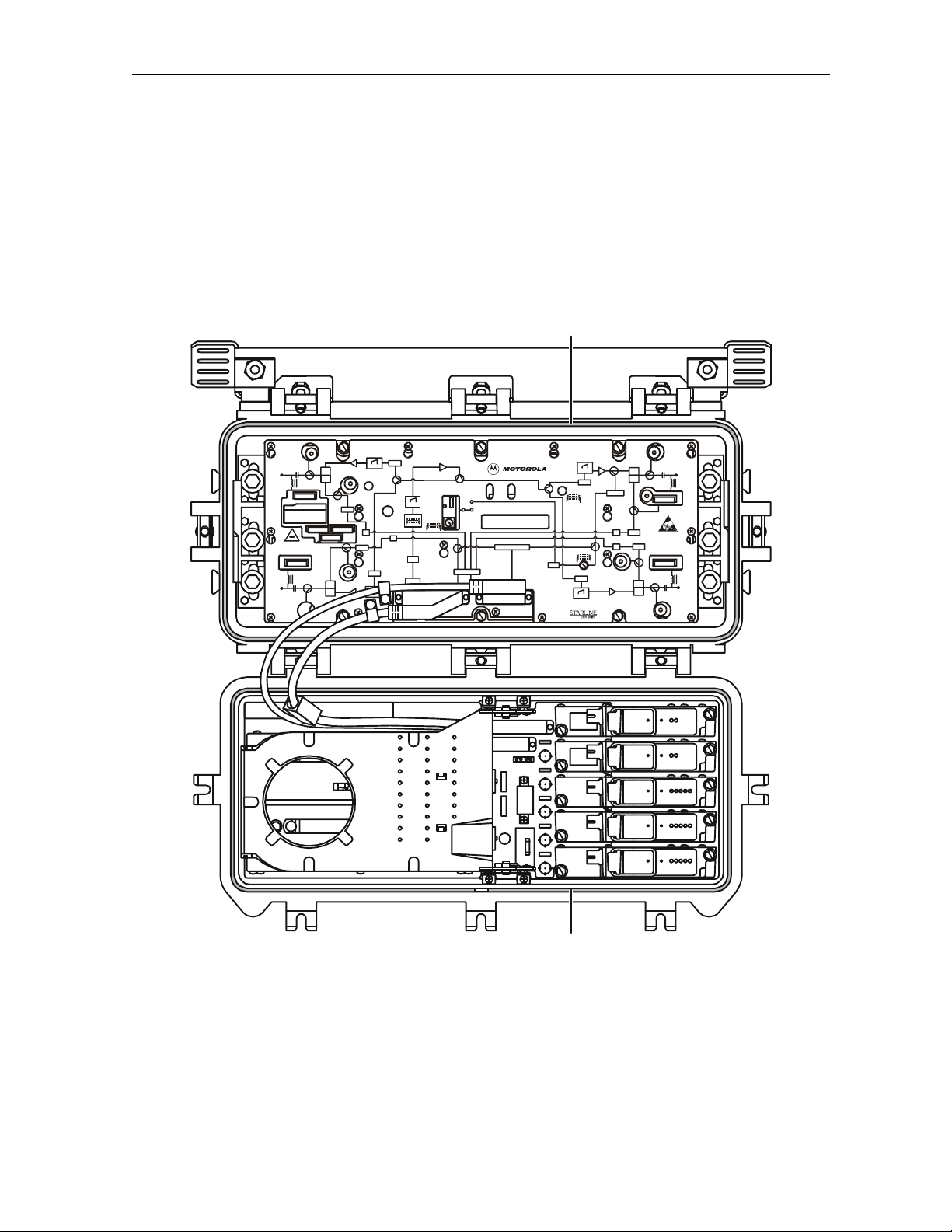
Figure 3-1 illustrates the upper-half housing or lid of the SG 2000 and identifies the location of all
major components:
Figure 3-1
SG 2000 lid showing major components
Pad - optical transmitter B
Test point - optical transmitter B
Pad - optical transmitter A
JP1
Test point - optical transmitter A
Power
supply 2
Power
supply 1
JP2
Optical
transmitter B
Optical
transmitter A
Optical
receiver C
Optical
receiver B
Optical
receiver A
Pad - optical receiver C
Test point - optical receiver C
Pad - optical receiver B
Test point - optical receiver B
Pad - optical receiver A
Test point - optical receiver A
SG 2000 Installation and Operation Manual
Page 35

3-2 Bench Setup
Figure 3-2 illustrates the RF chassis with the cover removed indicating the location of major
components:
Figure 3-2
SG 2000 RF chassis
Drive unit selector (AUTO/MAN)
Gain control (MAN ADJ)
Driver hybrid
MDR board
Forward pad
SG2-FE*
Output hybrid port 1
Ingress switch or JXP2A
Return pad
Diplex filter
Status monitor or MCB
ADU or TCU
Forward pad
SG2-FE*
Output hybrid port 2
SM & ADU pad
Ingress switches or JXP2A's
Diplex filter
Return pad
Diplex filter
Ingress switch or JXP2A
Output hybrid port 3
Forward pad
SG2-FE*
Flatness board
SG 2000 Installation and Operation Manual
Return pads
Diplex filter
Output hybrid port 4
ADU level control (ADU ADJ)
SG2-FE*
Forward pad
Optics to RF
cable interfaces
Page 36

Bench Setup 3-3
y
Powering the Node
You can conveniently power the SG 2000 by applying 60 Vac or 90 Vac to housing port 2. This port
is not used for RF purposes. All ports are rated at 15 amperes maximum and are fused with common,
blade-type 20-ampere automotive f uses. The 10-ampere fuse protects the dc power supply wiring
and can also be used to disconnect ac power from the power supply.
In addition to providing overcurrent protection, fuse locations also determine the paths for ac
bypassing through the housing.
Figure 3-3 diagrams fuse configurations for ac and dc powering:
Figure 3-3
Fuse configuration
Housing
Port 2
IN
Port 1
AC port
Port 3Port 1
F3
20 Amp
F2
20 Amp
F4
10 Amp
F1
20 Amp
SG2-PIC SG2-SIC
RF chassis
JP1
DC power
Pos 2
supply 1
SG2 lid assembly
Pos 1
F7
Jumper
F5
20 Amp
F6
20 Amp
DC power
suppl
Port 2
Unused
OUT
Port 4
Port 4 Port 3
2
SG 2000 Installation and Operation Manual
Page 37

3-4 Bench Setup
Table 3-1 identifies and describes the ac fuse options:
Table 3-1
AC fuses
Fuse Function Rating Type
F1
F2
F3
F4
F5
F6
F7
This fuse delivers ac power to all ports. It is always required
except when power from the ac input (port 2) must be
20 A,
32 Vdc
blocked at this location.
This fuse passes ac power to/from port 1. 20 A,
32 Vdc
This fuse passes ac to/from port
IN.20A,
32 Vdc
This fuse is always required for the dc power supply. 10 A,
32 Vdc
This fuse passes ac to/from port
OUT.20A,
32 Vdc
This fuse passes ac to/from port 3. 20 A,
32 Vdc
This jumper ties two sections of the ac power bus together
Jumper Auto,
thus delivering ac power to both sides of the node. It should
be removed only when dual power supplies are fed from
separate ac sources.
Auto,
plug-in, fast
blow
Auto,
plug-in, fast
blow
Auto,
plug-in, fast
blow
Auto,
plug-in, fast
blow
Auto,
plug-in, fast
blow
Auto,
plug-in, fast
blow
plug-in,
shunt
F8
The 5V circuit includes Fuse F8 which protects the lid and
RF board under short-circuit conditions in conjunction with
redundant power supplies.
F9
The 24V circuit includes Fuse F9 that protects the lid and
RF board under short-circuit conditions in conjunction with
redundant power supplies.
CAUTION!
Voltages up to 90 Vac are accessible. To avoid shock hazard, confirm that no power is
applied to the node before removing cover or replacing fuses.
SG 2000 Installation and Operation Manual
5A,32Vdc Auto,
plug-in, fast
blow
10 A,
32 Vdc
Auto,
plug-in, fast
blow
Page 38

Bench Setup 3-5
Figure 3-4 illustrates the RF chassis cover and lid showing the location of the fuses:
Figure 3-4
Fuse locations
F1 F4
F3
F7
H
L
JXP 2
JXP 4
L
H
ASSEMBLEDIN MEXIC O
-20dB
-20dB
CAUTION:
CONTAINSPARTS
ANDASSEMBLIES
SUSCEPTIBLETO
DAMAGE B Y
ELECTROSTATIC
DISCHARGE( ESD)
-20dB
-20dB
REFERTO
MANUA L FO R
FUSE VALU ES
-20dB
H
L
JXP 1
L
H
PORT1 PORT 2
FTEC
PORT3
JXP 1
FWDEQ
ON
-20dB
+24 V DC
IS
IS
JXP 3
JXP 3
-20dB
FWDEQ
MDR
VARILOSSE R
RCVR
INPUT
ADU
ON
OFF
MAN
SG2-
FRB
STATUS M ONI TOR
RPM/*
SG 20 00
Optical Node
FWDEQ
JXP 2
TCU
JXP ADU
IS
IS
ADU
ADU
FWDEQ
-20dB
JXP 4
F5
F6F2
PORT4
F8 F9
The dc power supply 24 V circuit includes fuse (F9) rated at 10 A; the 5 V circuit includes (F8)
which is rated at 5 A.
Power Supply Settings
You can power the SG 2000 from either 60 Vac or 90 Vac system supplies. The unit is shipped from
the factory set for 60 Vac (
(Figure 3-5) on the dc power supply to the 90 Vac (
voltage for the higher input range. This applies to the SG2-PS2 or the optional SG2-PS.
LO). If your system uses 90 Vac powering, reposition the suitcase jumper
HI) position to optimize the supply turn-on
SG 2000 Installation and Operation Manual
Page 39

3-6 Bench Setup
Note that no damage results if the jumper is not changed. In a 90 Vac system, changing the jumper
ensures that the dc supply does not turn on until the proper i nput voltage level is reached. This
prevents excessive loading of the cable plant power supply during t urn-on after a power-off situation.
Figure 3-5 illustrates the location of the
LO-HI jumper:
Figure 3-5
SG2-PS2 power supply
SG2-PS2
NO USER SERVICEABLE PARTSINSIDE
CAUTION
VOLTAGESIN EXCESS OF
300 VOLTSARE PRESENT
UNDERCOVERANDMAY
BEPR ESENTA FTER POWER
ISR EMOVED
SEE INSTALLATION MANUALFOR SERVICE
LO HI
ASSEMBLEDINMEXICO
24V 5V
ADJ
TEST
POINT
TEST
POINT
A second, optional dc power supply located in the lid of the SG 2000, offers full redundancy. Both
power supplies are on-line continuously and share the current load. In the event one supply fails, the
other assumes the entire load with no disruption of service. Each dc supply can deliver 4.3 A at
+24 V and 0.69 A at +5 V. Test points are provided for 24 Vdc and 5 Vdc supplies. Green LEDs—
two on each power supply and one on the RF chassis—indicate the overall health of the nodes dc
power bus. The power supply is factory calibrated for 24 V and should not need output voltage
adjustment. Power supply adjustment R51 is available but should be used only by qualified
personnel. When dual supplies are used, the supply with the lower output voltage sets the output
voltage of both supplies. Adjusting R51 on the other supply appears to have no visible effect.
However, if the “leading” supply fails, the misadjusted supply undergoes a sudden, large voltage
change. Figure 3-5 illustrates the location of R51 (
ADJ).
The ac input from the feederline to the power supply must be between 44 V and 90 Vrms with a line
frequency of 50 Hz or 60 Hz. The wave shape of the input voltage must be quasi-squarewave. The
power supply features a self-protection attribute that shuts it down for instantaneous line voltages
between 112-142 Vrms. A precision output regulator protects against overcurrent and short circuits,
thus providing a precise output voltage.
By selectively positioning a jumper (JP1) on the SG 2000 lid motherboard (LIDB), the power supply
can be configured to conform to different power requirements. Figure 3-1 illustrates the location of
jumper JP1 and Figure 3-3 illustrates the schematic.
The following subsections explain the powering options.
SG 2000 Installation and Operation Manual
Page 40

Bench Setup 3-7
Single Power Supply or Commonly Powered Redundant Supplies
To activate a single power supply or commonly powered redundant supplies, place jumper JP1
(illustrated in Figure 3-1) on the SG2-LIDB in the vertical position (strand-mount installation).
Figure 3-6 illustrates this position. Power supplies #1 and #2 are both connected to the primary ac
power feed.
Figure 3-6
JP1 common-powered single or redundant power configuration
Secondary AC
JP1
Power supply #2
Power supply #1
Primary AC
Individually Powered Supplies
To activate split ac powering of the node, place jumper JP1 on the SG2-LIDB in the horizontal
position (strand-mount installation). Figure 3-7 illustrates this position. Fuse jumper F7 must also be
removed. The primary ac power feed now connects to power supply #l and an independent
secondary ac source is connected to power supply #2. This configuration implies that the primary ac
power source originates from port
from port
OUT or port 3. For this configuration the optional interconnect cable (SG2-SIC) must be
installed between the lid board and the RF chassis.
Figure 3-7
JP1 split-powered redundant power supply configuration
Secondary AC
Primary AC
Other power configurations are possible, but not recommended.
CAUTION!
IN, port 1 or port 2. The secondary ac power source originates
JP1
Power supply #2
Power supply #1
Take extreme care so that you do not directly connect primary and secondary power
sources when implementing other configurations.
SG 2000 Installation and Operation Manual
Page 41

3-8 Bench Setup
Quick Checks - Functional Testing
It is recommended that you perform the procedures presented in the following subsections before
you place the SG 2000 in service.
Forward Path
Figure 3-1 illustrates the location of the forward-path receiver modules.
To set up the forward-path receivers:
1 Confirm the receiver configuration required. For a single receiver configuration use position C.
For redundant receivers use optical receiver A and B positions. Redundancy options are
discussedinSection5,“Operation.”
2 Test the optical power input level using an optical power meter. Figure 5-10 illustrates the
optical power test point on the top panel of the SG2-LR receiver module. The scaled voltage
present at this test point is 1.0 V/mW. For 0 dBm (1.0 mW) input, the receiver output is
approximately a flat 25 dBmV per channel for 77 channels. Other output levels are presented in
Table 5-2.
3 Verify that the green LED (ON), located on the top panel of the receiver, is illuminated to
confirmenable status.
4 Verify that the green LED (NORM), also located on the top panel of the r eceiver, is illuminated to
confirm that the optical power is within the recommended operating range. See Section 5,
“Operation” for other LED functions.
5 Select a JXP-* pad from Table 3-2 or Table 3-3. Insert it to the left of the receiver at the receiver
pad facility. The test point and pad location for receiver C is located adjacent to the receiver as
illustrated in Figure 3-1.
6 Check all four outputs at the amplifier test points located in the four corners of the RF chassis
cover as illustrated in Figure 3-4. These test points have 20 dB loss. Therefore, for example, if
the output is 44 dBmV, the test point should read 24 dBmV.
If all ports are operated at the same level, use port 2 to set the output level.
If all ports are not the same and port 2 is used as a “trunk” output and operated at a lower level,
then use port 3 to set the output level.
Port
1
2
3
4
Output (dBmV)
_____
_____
_____
_____
7 Determine how much excess output is present at the reference port. Excess _____ dBmV.
8 Insert a pad of the value determined by the excess in Step 7 into the JX P location on the lid
board immediately f ollowing the hybrid.
SG 2000 Installation and Operation Manual
Page 42

Bench Setup 3-9
9
Remeasure the output level. It should be within 1 dB of the preferred level. If necessary, adjust
the manual gain control. Check the remaining ports and add JX P pads to bring the outputs to the
correct level.
10 Set the gain reserves using one of the following gain control options. Adjust the selected gain
control option using the procedure presented in the appropriate subsection below.
S Manual control only — there is no compensation for changes in amplifier gain due to input
level or temperature fluctuations.
T Thermal control — the standard thermal control unit (TCU) is installed at the factory and
compensates for gain changes due to temperature fluctuations only.
T Automatic level control — the optional ADU drive unit holds output levels constant despite
fluctuations in temperature or input level. The ADU is available as a factory-installed option.
You can also install an ADU in place of the standard TCU in the field.
Manual Gain Control
1 Connect a signal level meter to the FORWARD TEST POINT and tune it to a channel near 750 MHz.
2 Position the drive selector horizontally. Figure 3-2 illustrates the location of the AUTO/MAN drive
selector.
3 Turn the gain control (MAN ADJ) to maximum (fully clockwise) and then turn it
counterclockwise to reduce the output by 4 dB. If the output level is greater than required,
change the pad at the receiver output location to obtain the desired level. To calculate the correct
pad value, subtract the desired level from the measured level and increase the pad by that
amount. Note: Do not install a pad larger than 15 dB at the receiver output. If more attenuation is
needed, put the remaining amount at the interstage pad location.
Thermal Control, Model TCU
1 Perform steps 1 through 3 under Manual Gain Control.
2 Position the drive unit selector vertically.
3 Turn the level control potentiometer on the TCU to the preferred output level.
Automatic Level Control, Model ADU
The system must contain a non-scrambled analog channel at the ADU pilot frequency.
1 Perform steps 1 through 3 under Manual Gain Control.
2 Position the drive unit selector vertically.
3 Turn the ADU ADJ control on the main board to the preferred output level.
SG 2000 Installation and Operation Manual
Page 43

3-10 Bench Setup
Analog Retu rn Path
Figure 3-1 illustrates the location of the return-path transmitter modules.
To set up analog return-path transmitters:
1 Confirm the transmitter configuration required. For a single transmitter, use the optical
transmitter A position. The redundant transmitter uses the optical transmitter B position.
Redundancy options are discussed in Section 5, “Operation.”
2 For each return-path transmitter, measure the optical power level at the test point provided on the
top panel of the transmitter as illustrated in Figure 5-12. The scaled voltage present at this t est
point is 1.0 V/mW.
3 Verify that the green LED (ON), located on the top panel of the transmitter, is illuminated to
confirmenable status. Refer to Section 5, “Operation,” for
4 Review return-path system levels. The unit is configured to drive the laser to the recommended
FAULT LED functions.
level (+15 dBmV) when the total combined power at all ports is approximately +28 dBmV.
Digital Return Path
To set up digital return-path transmitters:
1 Confirm the transmitter configuration required. For a single transmitter, use the optical
transmitter A position. The redundant transmitter uses the optical transmitter B position.
Redundancy options are discussed in Section 5, “Operation.”
2 Verify that the green LED (ON), located on the top panel of the transmitter, is illuminated. Refer
to Section 5, “Operation,” for
3 Review return-path system levels. The unit is configured to drive the laser to the recommended
FAULT LED functions.
level (+15 dBmV) when the total combined power at all ports is approximately +28 dBmV.
Two models of return path modules are available with analog and digital transmitters:
T With the SG 2000 return path module/combined (SG2-RPM/C), the total combined power at
all four ports totals approximately +28 dBmV.
T With the SG 2000 return path module/split (SG2-RPM/S), the total combined power at each
pair of ports is approximately +28 dBmV.
For more specific i nformation regarding return path setup procedures, refer to the supplemental
document Return Path Level Selection, Setup, and Alignment Procedure.
SG 2000 Installation and Operation Manual
Page 44

Bench Setup 3-11
Forward Path Padding
The pad values, presented in Table 3-2 or Table 3-3, serve as a starting-point reference f or typical
installations. While this chart i s prepared specifically for 77 channel loading and the low-gain option,
the difference for 110 channel loading is approximately 1 to 2 dB less.
It may be necessary to select a JXP value 1 dB or 2 dB lower for the receiver output (amplifier input)
pad t han shown in Tables 3-2 or 3 -3. This may be required to balance the four outputs for level,
which can only be done with the output stage pads. If the optical levels are high, the transmitter’s
optical modulation index (OMI) is higher than specified, or if the target output is low, the output pad
may already be a non-zero value as indicated in Tables 3-2 or 3-3. To ensure that the target output
level is reached on the lowest-level output branch, select input pads of at least 1 dB value for the
output pad.
Pads values shown are minimum values expected. If more padding is needed, increase the receiver
pads to a maximum of 15 dB and place the rest of the required attenuation at the interstage pad
facility.
SG 2000 Installation and Operation Manual
Page 45

3-12 Bench Setup
Table 3-2
SG 2000 pad chart-standard gain
Input Output dBmV
dBm/mW 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52
2.0/1.6
1.5/1.4
1.0/1.3
0.5/1.1
0.0/1.0
–0.5/0.9
–1.0/0.8
–1.5/0.7
–2.0/0.6
–2.5/0.6
–3.0/0.5
–3.5/0.5
–4.0/0.4
Receiver JXPs
Common JXP
Output JXPs
Receiver JXPs
Common JXP
Output JXPs
Receiver JXPs
Common JXP
Output JXPs
Receiver JXPs
Common JXP
Output JXPs
Receiver JXPs
Common JXP
Output JXPs
Receiver JXPs
Common JXP
Output JXPs
Receiver JXPs
Common JXP
Output JXPs
Receiver JXPs
Common JXP
Output JXPs
Receiver JXPs
Common JXP
Output JXPs
Receiver JXPs
Common JXP
Output JXPs
Receiver JXPs
Common JXP
Output JXPs
Receiver JXPs
Common JXP
Output JXPs
Receiver JXPs
Common JXP
Output JXPs
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
0
0
0
0
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
11
11
11
11
11
11
11
10
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
3
3
3
3
3
3
10
10
10
10
6
5
4
3
3
9
6
3
8
6
3
7
6
3
6
6
3
5
6
3
4
6
3
3
6
3
2
6
3
1
6
3
0
6
3
9
9
5
4
3
3
8
8
5
4
3
3
7
7
5
4
3
3
6
6
5
4
3
3
5
5
5
4
3
3
4
4
5
4
3
3
3
3
5
4
3
3
2
2
5
4
3
3
1
1
5
4
3
3
0
0
5
4
10
3
2
3
3
9
9
3
2
3
3
8
8
3
2
3
3
7
7
3
2
3
3
6
6
3
2
3
3
5
5
3
2
3
3
4
4
4
2
3
3
3
3
3
2
3
3
3
2
3
2
3
3
1
1
3
2
3
3
0
0
3
2
3
10
10
1
0
3
3
9
9
1
0
3
3
8
8
1
0
3
3
7
7
1
0
3
3
6
6
1
0
3
3
5
5
1
0
3
3
4
4
1
0
3
3
3
3
1
0
3
3
2
2
1
0
3
3
1
1
1
0
3
3
0
0
1
0
9
0
0
3
3
9
8
0
0
3
3
8
7
0
0
3
3
7
6
0
0
3
3
6
5
0
0
3
3
5
4
0
0
3
3
4
3
0
0
3
3
3
2
0
0
3
3
2
1
0
0
3
3
1
0
0
0
3
2
0
0
0
0
2
1
0
0
0
0
3
8
7
0
0
3
3
7
6
0
0
3
3
6
5
0
0
3
3
5
4
0
0
3
3
4
3
0
0
3
3
3
2
0
0
3
3
2
1
0
0
3
3
1
0
0
0
3
2
0
0
0
0
2
1
0
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
6
0
0
3
3
6
5
0
0
3
3
5
4
0
0
3
3
4
3
0
0
3
3
3
2
0
0
3
3
2
2
0
0
3
3
1
0
0
0
3
2
0
0
0
0
2
1
0
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
3
5
4
0
0
3
3
4
3
0
0
3
3
3
2
0
0
3
3
2
1
0
0
3
3
1
0
0
0
3
2
0
0
0
0
2
1
0
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
Output is the equivalent at the highest frequency.
Reserve gain set for 4 dB.
Figure 3-1 illustrates the receiver and interstage pad facilities that are located on the lid motherboard. Output pad facilities are located on the
main RF board.
SG 2000 Installation and Operation Manual
Page 46

Bench Setup 3-13
Table 3-3
SG 2000 pad chart-high gain
Input Output dBmV
dBm/mW 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52
2.0/1.6
1.5/1.4
1.0/1.3
0.5/1.1
0.0/1.0
–0.5/0.9
–1.0/0.8
–1.5/0.7
–2.0/0.6
–2.5/0.6
–3.0/0.5
–3.5/0.5
–4.0/0.4
Receiver JXPs
Common JXP
Output JXPs
Receiver JXPs
Common JXP
Output JXPs
Receiver JXPs
Common JXP
Output JXPs
Receiver JXPs
Common JXP
Output JXPs
Receiver JXPs
Common JXP
Output JXPs
Receiver JXPs
Common JXP
Output JXPs
Receiver JXPs
Common JXP
Output JXPs
Receiver JXPs
Common JXP
Output JXPs
Receiver JXPs
Common JXP
Output JXPs
Receiver JXPs
Common JXP
Output JXPs
Receiver JXPs
Common JXP
Output JXPs
Receiver JXPs
Common JXP
Output JXPs
Receiver JXPs
Common JXP
Output JXPs
NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR
NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR39
NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR39
NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR39
NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR39
NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR39
NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR39
NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR39
NR NR NR NR NR NR NR39
3
3
3
3
3
9
9
9
6
5
3
3
8
8
6
5
3
3
7
7
6
5
3
3
6
6
6
5
9
4
3
3
3
8
8
4
3
3
3
7
7
4
3
3
3
6
6
4
3
3
9
9
2
1
3
3
8
8
2
1
3
3
7
7
2
1
3
3
6
6
2
1
0
3
3
9
8
0
0
3
3
8
7
0
0
3
3
7
6
0
0
3
3
6
5
0
0
0
3
8
0
0
3
3
8
7
0
0
3
3
7
6
0
0
3
3
6
5
0
0
3
3
5
4
0
0
3
3
4
3
0
0
0
3
8
0
0
3
3
8
7
0
0
3
3
7
6
0
0
3
3
6
5
0
0
3
3
5
4
0
0
3
3
4
3
0
0
3
3
3
2
0
0
3
3
2
1
0
0
0
3
8
0
0
3
3
8
7
0
0
3
3
7
6
0
0
3
3
6
5
0
0
3
3
5
4
0
0
3
3
4
3
0
0
3
3
3
2
0
0
3
3
2
1
0
0
3
3
1
0
0
0
3
2
0
0
0
0
0
3
8
0
3
7
0
3
6
0
3
5
0
3
4
0
3
3
0
3
2
0
3
1
0
3
0
0
2
0
0
1
0
0
NR = not recommended.
Output is the equivalent at the highest frequency.
Reservegainsetfor4dB.
Figure 3-1 illustrates the receiver and interstage pad facilities that are located on the lid motherboard. Output pad facilities are located on the main RF board.
SG 2000 Installation and Operation Manual
Page 47

3-14 Bench Setup
Launch Amplifier Output Stage Padding
By definition the launch amplifier is everything between the optical receiver RF output and the node
output connector. The launch amplifier output-stage pad-effects charts show the tradeoff, over a
range of output levels, between composite triple beat (CTB) and carrier-to-noise ratio ( c/n) when
pads are inserted ahead of the individual output hybrids. It is assumed that the output of the link is
constant, so that the same amount of attenuation is removed from the pad facility at the receiver
output. The four pairs of curves, illustrated in Figures 3-8 and 3-9, are for pad values of 0, 3, 6, and
10 dB. An overall tilt of 12.5 dB is assumed for the 750 MHz model and 11.5 dB for the 870 MHz
model.
Figure 3-8
SG2-75 low-gain output-stage pad-effects chart
85.00
80.00
75.00
70.00
65.00
CNR, dB
60.00
55.00
50.00
45.00
38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50
Output Level (Highest Analog), dBmV - 12.5 dB Tilt
-85.00
-80.00
-75.00
-70.00
-65.00
-60.00
-55.00
-50.00
-45.00
CNR-10
CNR-6
CNR-3
CNR-0
CTB-0
CTB-3
CTB-6
CTB-10
SG 2000 Installation and Operation Manual
Page 48

Figure 3-9
SG2-87 low-gain output-stage pad-effects chart
Bench Setup 3-15
80.00
75.00
70.00
65.00
60.00
CNR, dB
55.00
50.00
45.00
40.00
38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50
Output Level (Highest Analog), dBmV - 11.5 dB Tilt
-80.00
-75.00
-70.00
-65.00
-60.00
-55.00
-50.00
-45.00
-40.00
CTB, dBc
CNR-10
CNR-6
CNR-3
CNR-0
CTB-0
CTB-3
CTB-6
CTB-10
Link Performance
The SG 2000-* link performance charts are meant as a guide to assist you when working with
varying link parameters. The link is defined as beginning at the transmitter RF input and ending at
the RF output j ack on the SG2-LR optical receiver. These charts show the effects of changes in fiber
loss and receiver optical power input on c/n, CTB, and composite second order (CSO).
The particular curve along which incident optical power should be equated to c/n is determined by
the fiber loss budget in the system. This must only include fiber loss; no connector or splitting losses
should be included in this number. Because these curves require knowing only the fiber loss and the
received optical power, transmitter power is not a factor. The transmitter is assumed to have a
relative intensity noise (RIN) of –158 dB/Hz.
Figures 3-10 and 3-11 illustrate the distortion curves and show the changes in CTB and CSO that can
be expected at higher optical inputs. These charts assume transmitter CTB of –66 dBc and CSO of
–62 dBc for 77 channel loading. For 110-channel loading, the transmitter assumptions are –64 dBc
CTB and –61 dBc CSO.
SG 2000 Installation and Operation Manual
Page 49

3-16 Bench Setup
Figure 3-10
SG2-* link c/n performance, 77 channels
57
56
55
54
53
52
C/n, dB
51
50
49
48
47
-6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 1 2
Received optical power, dBm
Lf = fiber loss budget
-66
-65.5
-65
-64.5
-64
-63.5
-63
-62.5
-62
-61.5
-61
Distortion, dBc
Lf=2dB
Lf=3dB
Lf=4dB
Lf=5dB
Lf=6dB
Lf=7dB
Lf=8dB
Lf=9dB
Lf=10dB
Lf=11dB
Lf=12dB
Lf=13dB
Lf=14dB
CTB
CSO
SG 2000 Installation and Operation Manual
Page 50

Figure 3-11
SG2-* link c/n performance, 110 channels
Bench Setup 3-17
55
54
53
52
51
50
C/n, dB
49
48
47
46
45
-6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 1 2
Received optical power, dBm
Lf = fiber loss budget
-65
-64.5
-64
-63.5
-63
-62.5
-62
-61.5
-61
-60.5
-60
Distortion, dBc
Lf=2dB
Lf=3dB
Lf=4dB
Lf=5dB
Lf=6dB
Lf=7dB
Lf=8dB
Lf=9dB
Lf=10dB
Lf=11dB
Lf=12dB
Lf=13dB
Lf=14dB
CTB
CSO
SG 2000 Installation and Operation Manual
Page 51

3-18 Bench Setup
Installing the DS-SG2-DRRB Board Option
The SG2 Digital Return Redundancy Board (DS-SG2-DRRB) is a fixed plug-in that only provides
the capability for RF redundancy to the input of the (DS-SG2-DRT-2X/A). This boards offers full
digital return path redundancy when installed in the SG2 fiber optic node.
Figure 3-12 illustrates the DS-SG2-DRRB board:
Figure 3-12
DS-SG2-DRRB board
The DS-SG2-DRRB board enables a reliable high-speed digital return path while utilizing a
minimum number of components. It contains two independent RF splitters, each providing a single
input and dual outputs for RF path A and RF path B in the SG2 lid board. The board can be installed
as a factory enhancement or field upgrade.
This optional kit does not have the capability of being controlled.
To install the DS-SG2-DRRB board:
1 Open the housing.
2 RemovetheJXPpadsfromP1andP2onthelidboard.
3 Grasp the push-handles provided on the DS-SG2-DRRB board (shaded in Figure 3-13) and
installitinthelidboardatP1andP2.
SG 2000 Installation and Operation Manual
Page 52

Figure 3-13
DS-SG2-DRRB board installed
Bench Setup 3-19
SG2-DRT-2X/A
(”B” location)
SG2-DRT-2X/A
(”A” location)
Push handle
DS-SG2-DRRB board
Push handle
4 Insert the MCX connector terminating cable J1 into RF INPUT B on DS-SG2-DRT-2X/A in the
transmitter A location.
5 Insert the MCX connector terminating cable J2 into RF INPUT B on DS-SG2-DRT-2X/A in the
transmitter B location.
6 Remove the existing 0 dB jumpers and install 1 dB JXPs in the four return-path JXP locations on
the E-pack as illustrated in Figure 3-14.
SG 2000 Installation and Operation Manual
Page 53

3-20 Bench Setup
P
Figure 3-14
Location of JXPs on E-pack
Replace 0 dB JXP
with1dBJXP
Replace 0 dB JXP
with1dBJX
SG 2000 Installation and Operation Manual
Page 54

Bench Setup 3-21
Figure 3-15 illustrates a complete SG2 lid with the DS-SG2-DRRB board (shaded gray) installed:
Figure 3-15
SG2 lid configured with the DS-SG2-DRRB board
DS-SG2-DRRB board
DigitalTransmitter
RF
INPUT
B
J1
J2
RF
INPUT
B
SG2000
INPUT
DANGER
INPUT
DANGER
STATUS DS-SG2-DRT-2X/A
A
SG2000
STATUS DS-SG2-DRT-2X/A
A
1310DFB
DigitalTransmitter
1310DFB
INPUT
B
INPUT
B
When signals are applied to port in and port 1, they are routed directly to the transmittersthrough the
D-type connectors on the lid board.
When signals are fed from port out and port 3, they are routed to the transmitters from the cables on
the DS-SG2-DRRB-SR board.
SG 2000 Installation and Operation Manual
Page 55

3-22 Bench Setup
Installing the Status Monitor Option
The model LL-SG2-*/* transponder is available as part of the LIFELINE s tatus-monitoring system.
The LL-SG2-*/* transponder continuously monitors node parameters, executes commands, and
reports to the polling computer when interrogated. Section 2, “Overview,” provides additional
information regarding status-monitoring functions.
Detailed instructions for installing the LL-SG2-*/* transponder are provided in the Transponder for
SG-2000 LL-SG2-*/* Installation Sheet, packaged with the t ransponder. Following physical
installation, the transponder must be added to the software system and the alarm parameters must be
configured. To complete these tasks, refer to the LIFELINE for Windows Software Operations
Manual.
If your nodes transponder was installed at the factory, it was tested and calibrated using special
automatic test fixtures. It cannot be repaired, calibrated, or aligned in the field.
If a problem is suspected, the LED visible on t op of the transponder is useful in troubleshooting.
During normal operations, it indicates the following:
T The LED illuminates when the module is powered up
T A flashing LED indicates two-way communication with the LL-CU control unit
T A dark LED indicates loss of communication or power
Table 3-4 lists some common problems and possible solutions:
Table 3-4
Common problems
Fault/Indication Check/Suggested Action
LED is off
LED is lit but not flashing
Spurious tamper alarms are
occurring
Check the input power to the receiver.
Check the amplifier fuses and circuit breakers.
This indicates that there is no communication with the control
system.
Check for proper installation of the control system.
Verify that the RF levels are correct and that there are no
interfering signals.
Check for a malfunctioning photo-optic diode.
If problems persist, call for help or return the unit for repair using the instructions provided in the
documents associated with the LL-SG2-*/* transponder.
SG 2000 Installation and Operation Manual
Page 56

Bench Setup 3-23
SG 2000 Activation Worksheet
This worksheet is provided as a convenient reference to log pertinent information associated with
setting up the SG 2000 node.
Configurator
number
Technician
Node number
Node location
Date
Temperature
Channel load
Power requirements
Power source
Port 1
Port 2
Port 3
Port 4
Output levels
Port 1
Port 2
Port 3
Port 4
ADU frequency
Received optical
power
SG2-LR output level
JXP values
Receiver output
pad
Interstage pad
Port 1 pad
Port 2 pad
Port 3 pad
Port 4 pad
Gain reserve
AC powering
AC input power is provided to which port? _____
Is more than one power source used to power the station? _____ yes _____ no
Does the node have an FTEC surge suppressor? _____yes _____ no
Is a second gas-tube surge suppressor required? _____ yes _____ no
Does the node contain one or two power packs? _____
Are fuses removed from output ports that do not require ac power? _____ yes _____no
___/____-____-____-____-_
_______________
_______________
_______________
_______________
_______________
_______________
Voltage
_____ _____
_____ _____
_____ _____
_____ _____
_____ _____
Low Frequency
Level _____
Level _____
Level _____
Level _____
_____
_____ Vdc
_____
_____ dB
_____ dB
_____ dB
_____ dB
_____ dB
_____ dB
_____ dB
Input/Output
_____ _____
_____ _____
_____ _____
_____ _____
_____ _____
High Frequency
Level _____
Level _____
Level _____
Level _____
SG 2000 Installation and Operation Manual
Page 57

3-24 Bench Setup
DC powering
Is the suitcase jumper on the power pack(s) in the correct position? _____60 V (lo) _____90 V (hi)
Is the round, green LED on the main board illuminated? _____ yes _____ no
Are the two rectangular green LEDs on each power pack illuminated? _____ 24 Vdc _____ 5 Vdc
Voltage reading at 24 Vdc test point? _____ Vdc
Voltage reading at 5 Vdc test point? _____ Vdc
SG 2000 Installation and Operation Manual
Page 58

Section 4
Installation
Installation consists of splicing the six-fiber service cable to the transportation fiber, installing the
housing and electronics on the messenger strand, applying power, and placing the unit in service.
To avoid excess weight and the possibility of damage during installation, the housing is normally
mounted prior to inclusion of the electronic components. It is assumed that the node components
have been removed, configured, and tested on the bench and only minimal alignment may be
required following field installation.
Splicing Fiber
The six-fiber service cable can be spliced to the transportation cable at any time during the node
installation. Splicing does not need to coincide with the installation of the housing.
Fusion splicing is recommended because it has low insertion loss and is the most reliable method. A
technician experienced in splicing fiber should do the splicing.
To perform fusion splicing:
1 Obtain the 50-foot, six-fiber service cable with the compression fitting from the node package.
Figure 4-1 illustrates this cable:
Figure 4-1
Service cable connection and compression fitting
39.8” ± 1.5”
Water
seal nut
2 Splice each fiber according to procedures recommended by the manufacturer of the splicing
Compression
nut
Main
body
Service
cable
Heat
shrink
SC/APC
connectors
equipment being used. A blue-coded fiber is suggested for the forward signal distribution and a
brown-coded fiber is recommended for the return pat h. Clean lin ess in the work area is essent ia l.
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 59

4-2 Installation
Assemble the splice enclosure following the instructions furnished with the enclosure.
3
CAUTION!
It is important that the connections at the headend be duplicated. If they are different
from the above recommendations, follow the scheme used for the headend
connections.
4 Complete the splicing and installation of the splice enclosure. Suspend the extra cable from the
messenger using locally accepted methods. Commonly used methods include suspending it from
the messenger along its entire length, and/or fashioning a figure eight coil and suspending it from
the messenger.
If you intend to install the housing at a later time, protect the end of the service cable with the
compression fitting and the fiber connectors from dirt and moisture.
DANGER!
To avoid possible injury to personnel or damage to the equipment, remove 60/90 volt
ac power from the system before you install the node.
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 60

Installation 4-3
Strand Wire Mounting
Two strand clamps and bolt assemblies are located on a bracket attached to the top of the housing for
normal horizontal mounting below the strand. Figures 4-2 and 4-3 illustrate the front, rear, and side
views of an installed bracket:
Figure 4-2
Mounting bracket-front vi ew
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 61

4-4 Installation
Figure 4-3
Mounting bracket-rear and side views
6
7 8
3
12IN
To mount the housing to the strand wire:
2
1
4
5
34 OUT
1 Attach the bracket to the housing using the two 5/16 × 18 bolts.
2 Loosen the 3/8 × 16 strand clamp bolt located on each mounting bracket.
3 Engage the strand in the housing strand clamps. Do not tighten the hex-head bolts at this time.
This enables the clamps to slide along the strand wire until the housing is finally positioned with
respect to the cables.
4 Re-install all modules and electronic components that were removed before the housing was
installed.
Connections to the housing are made using standard KS-type housing port entry connectors. Pin-type
connectors with a nominal center conductor diameter of 0.067 inches are required. Measuring from
the seating plane of the connector, the center conductor pin length must be 1.50 inches minimum and
1.65 inches maximum.
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 62

Installation 4-5
Figure 4-4 illustrates the dimensions of the center conductor:
Figure 4-4
Center conductor length
1.65"Max.
1.50" Min.
There are no surge protectors over the center seizure screws and none should be installed. Adding surge
protectors degrades the return loss of the housing port.
Coaxial Cables
To install coaxial cable s in the base:
1 Loosen, but do not remove, the three bolts on top of the housing and the bolt on each side of the
housing. Rotate these bolts away from the cover.
2 Swing the housing lid away from the lower housing base.
3 Remove the protective port cap(s) in the base and verify that the seizure screw within either the
trunk or feeder port is loosened to accept the center pin of the cable connector.
4 Secure the cable end in the cable connector as described in the instruction sheet for the
connector.
5 Insert the center conductor fully until it enters the seizure mechanism. Tighten the terminal
screw onto the cable connector and torque to 12 in-lbs (1 ft-lb).
6 Repeat steps 3 through 5 for all other cable connections required.
7 Protect all cable connections with heat-shrink tape or tubing.
8 Lash the cables to the strand where they approach it and secure the cable lashing wire to the
strand with commercial clamps.
9 Verify that port plugs on any unused ports are firmly seated and torqued to 5 ft-lbs.
Fiber Cables
To install fiber cables in th e lid:
1 Remove the protective port plug from the side of the housing lid and carefully pass the
connector ends of the fiber service cable through this port. It is necessary to insert one
connector at a time. Be careful not to bend the fiber any more than is necessary.
2 Thread the compression fitting into the port. The compression nut and rubber grommet must be
sufficiently loose to enable the fitting to be turned without turning the fiber cable at the same
time. Torque the main body of the fitting to 60 to 72 in-lbs (5 to 6 ft-lbs).
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 63

4-6 Installation
Carefully dress the excess fiber into the ramp of the fiber spool tray. Wrap the fiber around the
3
spooling cylinder one to two times depending on the length of the fiber. The diameter of the
spool tray is matched to the bend radius of the fiber. Also ensure that the fiber is routed under the
retaining flanges and through the pegs of the fiber tray for proper routing to the optics modules.
Figures 4-5 and 4-6 illustrate the housing lid and fiber spool tray:
Figure 4-5
Housing lid and fiber spool tray
Figure 4-6
Fiber spool tray
Fiber routed to optics modules
through fiber tray pegs
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 64

Installation 4-7
Connect each fiber by removing the protective boot from the fiber connector, cleaning the
4
connector with pure isopropyl alcohol (99%) using a lint-free wipe, and drying it with filtered
compressed air. After cleaning the fiber, insert it into the appropriate receiver or transmitter
module.
5 Position the fiber service cable in the compression fitting to provide some slack in the fibers
inside the housing. Tighten the compression nut until it bottoms out. Finally, tighten the water
seal nut until there is no gap between it and the compression nut.
6 Close the housing and use a torque wrench to sequentially and progressively tighten the housing
bolts to a final torque of 12 ft-lbs. in the sequence stamped on the housing lid as illustrated in
Figure 1-1.
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 65

P
A
Section 5
Operation
This section provides information concerning the use of various options and applications required by
your system. It may be helpful to refer to Figures 3-1 and 3-2 that illustrate the major components in
the SG 2000 lid and RF chassis.
Forward Path RF Configuration
You can configure the SG2-lid motherboard (LIDB) using three different forward path RF options.
Single Receive r Mode
If you are using a single optical receiver module (SG2-LR) it must be installed in position C. An
SG2-FJB/P jumper board must also be plugged into the LIDB. Figure 3-1 illustrates the location of
this jumper board.
The SG2-LIDB distributes an RF signal from the primary receiver (C) to the RF chassis as illustrated
in Figure 5-1:
Figure 5-1
Single receiver
Optical
rece iv e r C
Optical
rece iv e r B
Optical
receiver A
SG2-FJB/
JXP JXP
JXP
Relay
JXP
RF chassis
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 66

5-2 Operation
P
A
A
Redundant Receiver Mode
Operation in the redundant mode requires the insta llat i on of two optical rec eiv er s, one in position A
and the other in position B. An SG2-ABJ/P jumper board must be plugged into the lid motherboard.
Figure 3-1 illustrates the location of this jumper board.
The SG2-LIDB distributes an RF signal from receiver A or B to the RF chassis as illustrated in
Figure 5-2:
Figure 5-2
Redundant receiver
SG2-ABJ/
Optical
rece iv e r C
Optical
rece iv e r B
Optical
receiver A
JXP
JXP
JXP
Relay
JXP
RF chassis
Broadband/Narrowcast Mode
For broadband/narrowcast operation, the broadcast optical receiver must be installed in position C
and the narrowcast receiver in position A. If redundancy is required for the narrowcast channel,
install the backup receiver in position B. An SG2-FBS split-band combiner board must also be
plugged into the lid motherboard as illustrated in Figure 3-1.
The SG2-LIDB distributes a broadband signal from receiver C to the RF chassis. It also distributes a
narrowcast signal from receiver A or B to the RF chassis as illustrated in Figure 5-3:
Figure 5-3
Broadband/narrowcast
SG2-FBS
Optical
rece iv e r C
Secondary
Primary
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Optical
rece iv e r B
Optical
receiver A
JXP
HPF
JXP
Relay
JXP
RF chassis
Page 67

Operation 5-3
AB Override Functionality
The AB override switch (jumper JP2, illustrated in Figure 3-1) can be operated in three different
positions. The positions are B override, A override, and status monitor/MCB:
B Override
The SG2-LIDB overrides the status monitor or manual control board signal and activates receiver B,
as illustrated in Figure 5-4:
Figure 5-4
B override
+5V
JP2
Stat us mon itor
signal
Receiver enable
logic
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 68

5-4 Operation
A Override
The SG2-LIDB overrides the status monitor or manual control board signal and activates receiver A
as illustrated in Figure 5-5:
Figure 5-5
A override
+5V
JP2
Stat us mon itor
signal
Receiver enable
logic
Status Monitor/Manua l Control Operation
The SG2-LIDB enables the status monitor or manual control board to activate receiver A or receiver
B as illustrated in Figure 5-6:
Figure 5-6
Status monitor/MCB operation
+5V
JP2
Stat us mon itor
signal
Receiver enable
logic
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 69

Operation 5-5
Analog Return Path RF Configuration
If you are using a single optical transmitter, it must be installed in the optical transmitter A position
as illustrated in Figure 3-1. A JXP-15A (15 dB) pad must also be installed in the pad facility at the B
transmitter location to terminate the signal from the return-path-module combiner board
(SG2-RPM/C).
For single return applications, the SG2-LIDB distributes an individual RF signal from the RF chassis
to transmitter A. Installing an optional second transmitter (B) provides return redundancy as
illustrated in Figure 5-7. Installing a redundant B transmitter also requires that you change the pad at
that location to a JXP-5A.
Figure 5-7
Redundant return
Status
monitor
Ingress
JXP
TP
H
L
TP
Optional
transmitter
A
Optional
transmitter
B
TP
TP
JXP
JXP
LID
BASE
SG2-RPM/C
SG2-RPLPF
LP filter
Bulkhe ad connect or
for dc power
Alternatively, a second transmitter can be used to double the available return bandwidth by having
each transmitter carry the return signals from only two ports. This is illustrated in Figure 5-8. It
requires that the SG2-RPM/C (located on the bottom side of the RF chassis) be changed to a
return-path-module split board (SG2-RPM/S) as illustrated in Figure 5-9:
Figure 5-8
Split return
Optional
transmitter
A
Optional
transmitter
B
LID
TP
JXP
JXP
TP
BASE
SG2-RPM/S
SG2-RPLPF
LP filter
LP filter
Status
monitor
Ingress
JXP
TP
H
L
TP
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 70

5-6 Operation
For upgrading to split return operation, with DS-SG2-DRT-2X/A transmitters installed in positions
A and B, the SG2-RPM/C board must be replaced with an SG2-RPM/S board. The main RF chassis
must be removed to perform this exchange. Figure 5-9 illustrates the inside bottom view of the RF
chassis, the location of the SG2-RPM/C board, and the removal sequence:
Figure 5-9
RF chassis and location of the SG2-RPM/C or SG2-RPM/S board
Cover
SG2-RPM/C
Power connector
RF chassis
1 Remove any fuses at F1, F2, F3, F5, or F6 to prevent arcing of the housing connectors.
2 Remove the six 5/16-inch hex-head screws that secure the RF chassis to the housing. Remove
the housing.
3 Remove the six ¼-inch hex-head screws that secure the rear cover. Remove the cover.
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 71

Operation 5-7
Remove the eight screws that secure the SG2-RPM/C board to the chassis. Remove the
4
SG2-RPM/C board. To assist in removing the SG2-RPM/C board, the handle is cantilevered so
that pulling up on the handle extracts the board from the chassis.
5 Remove the 5-pin power connector that provided dc power to the SG2-RPM/C board.
6 Install the SG2-RPM/S board by reversing the above procedure. Do not re-install the 5-pin
power connector as the SG2-RPM/s does not require nor accept it.
Digital Return Path RF Configuration
If you are using a single DS-SG2-DRT/A transmitter, it must be installed in the optical transmitter A
position as illustrated in Figure 3-1. A JXP-5A (5 dB) pad is installed in the pad facility at the A
transmitter location. A JXP-15A (15 dB) pad must also be installed in the pad facility at the B
transmitter location to terminate the signal from the return-path-module combiner board
(SG2-RPM/C).
For single return applications, the SG2-LIDB distributes an individual RF signal from the RF chassis
to transmitter A. Installing an optional second transmitter (B) provides return redundancy as
illustrated in Figure 5-10. Installing a redundant B transmitter also requires that you change the pad
at that location to a JXP-5A.
Figure 5-10
DS-SG2-DRT/A redundant return
Optional
transmitter
A
Transmitter
B
LID
TP
JXP
JXP
TP
BASE
SG2-RPM/C
SG2-RPLPF
LP filter
Bulkhe ad connect or
for dc power
Status
monitor
Ingress
JXP
TP
H
L
TP
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 72

5-8 Operation
If you are using a single DS-SG2-DRT-2X/A transmitter, it must be installed in the optical
transmitter A position. A JXP-5A (5 dB) pad must be installed in the pad facility at the input of both
the A and B transmitter locations. With this transmitter, the SG2 is configured with the return path
module/split (SG2-RPM/S). Return signals from two of the four node ports are fed to one RF input
of the transmitter while the remaining two return signals are fed to the second RF input as illustrated
in Figure 5-11:
Figure 5-11
DS-SG2-DRT-2X/A split return
Optional
transmitter
B
LID
TP
JXP
JXP
TP
BASE
SG2-RPM/S
SG2-RPLPF
LP filter
LP filter
Status
monitor
Ingress
JXP
TP
H
L
TP
Using a DS-SG2-DRT-2X/A transmitter in conjunction with an optional second transmitter (B)
provides return redundancy as illustrated in Figure 5-12. Installing a redundant B transmitter requires
you to remove the JXPs that are installed before the input to the transmitter and replace it with a
special adapter in order to route the signal s prope rly .
Figure 5-12
DS-SG2-DRT-2X/A redundant return
LID
TP
Optional
transmitter
A
Transmitter
B
TP
BASE
SG2-RPM/S
SG2-RPLPF
LP filter
LP filter
Status
monitor
Ingress
JXP
TP
H
L
TP
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 73

Operation 5-9
SG 2000 Optical Modules
The optical modules available for the SG 2000 include:
! SG2-LR — forward path optical receiver
! SG2-EIFPT — isolated Fabry-Perot return transmitter
! SG2-IFPT — isolated Fabry-Perot return transmitter
! SG2-FPT — non-isolated Fabry-Perot return transmitter
! SG2-DFBT and SG2-DFBT/3 — isolated DFB return transmitters
! DS-SG2-DRT/A and DS-SG2-DRT-2X/A — digital return transmitters
Designed specifically for use in the SG 2000 node platform, the modules combine high performance
and easy maintenance.
Installing SG 2000 Optical Modules
The design of the SG 2000 optical modules enable you to install them while the node is in service.
To install an optical module:
1 Determine the proper slot for the module by referring to the Forward Path RF Configuration or
the Return Path RF Configuration information in the beginning of this section. Position the
module in the appropriate slot and press gently on the casting until it is fully seated. Tighten the
two mounting bolts to secure the module in the SG 2000 lid.
2 Remove the dust covers from the service cable connector and the module’s optical connector.
3 Carefully clean the optical connector using a suitable optical cleaning kit.
4 Connect the service cable to the module’s optical connector.
5 If necessary, check the optical power levels. Check and align the RF levels in accordance with
system requirements and procedures.
Removing SG 2000 Optical Modules
The SG 2000 optical modules design enables you to remove them while the node is in service.
CAUTION!
The module surfaces may be hot. Allocate sufficient time for the module to cool before
handling.
To remove an optical module:
1 Disconnect the service cable from the optical connector assembly on the module. Place dust
covers on the service cable connector and the modules opti ca l-connector assembly.
2 Loosen the two mounting bolts that secure the optical module in the SG 2000 lid.
3 Pull the module from the SG 2000 lid using the wire handle on top of the module.
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 74

5-10 Operation
Cleaning the Optic al Connector
The design of the SG 2000 optical module connector enables you to clean it easily without removing
the module from the node.
To clean the connector:
1 If necessary, disconnect the service cable from the modules’ optical-connector assembly. Place a
dust cover on the service cable connector.
2 Lift the metal tab to release the optical-connector assembly and pull it out of the module.
CAUTION!
Do not pull the optical connector out more than two inches from the casting wall. If you
pull the connector out too far, you must disassemble the module and respool the fiber.
3 Remove the bulkhead adapter from the internal optical connector.
4 Carefully clean the optical connector and bulkhead adapter using a suitable optical connector
cleaning kit. If an optical connector cleaning kit is not available, clean the connector using pure
isopropyl alcohol (99%) and a lint-free wipe. Dry it with filtered compressed air. You can also
clean the bulkhead adapter using filtered compressed air.
5 Re-assemble the bulkhead adapter to the internal optical connector. Ensure that you install the
internal optical connector in the end of the bulkhead adapter bearing the metal tangs.
6 Snap the optical connector assembly back into the module.
7 If necessary, clean and reconnect the service cable.
SG2-LR Optical Receiver
The SG2-LR is a line of forward-path optical receivers used in the SG 2000 node platform. It is
designed to be used in conjunction with an AM-Blazer, AM-OMNI-LM*, MegaStar, or other similar
optical transmitter.
Figure 5-13 illustrates the SG2-LR:
Figure 5-13
SG2-LR
SG2000
SG2-LR
ASSEMBLED
IN MEX ICO
Opti cal Rec eive r
OPTICAL
POWER
(1 V/mW)
HYBRID
CURRENT
(1 V/A)
OPTICAL
POWER
L
F
O
N
H
O
A
N
O
I
W
U
R
G
L
M
H
T
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 75

Operation 5-11
Tables 5-1 and 5-2 provide additional information on the user-related features and output levels of
the SG2-LR:
Table 5-1
SG2-LR features
Feature Description
Optical power test point
This test point enables monitoring of the optical power level
at the input to the module. The nominal scale factor is
1.0 V/mW.
Hybrid current test point
This test point enables monitoring the current drawn by the
amplifier section of the integrated optical receiver hybrid. The
nominal scale factor is 1.0 V/A. The hybrid current test-point
voltage is between 0.150 V and 0.350 V (h ybrid cur ren t of
150 mA through 350 mA) when the module is enabled under
normal operating conditions.
Receiver enable
A green LED that provides visual indication of the receiver’s
enable status.
Fault indicator
A red LED that illuminates when the module is enabled but
the hybrid current is outside the normal operating range.
Optical power status
A green LED that is ON (
within the recommended operating range (refer to Table A-4).
Two red LEDs indicate that the optical po wer is abov e (
or below (
Table 5-2
SG2-LR minimum output lev els
Optical input
level(dBm/mW)
3.2/2.1
3.0/2.0
2.8/1.9
2.6/1.8
2.3/1.7
2.0/1.6
1.8/1.5
1.5/1.4
1.0/1.3
0.8/1.2
0.5/1.1
0.0/1.0
–0.5/0.9
–1.0/0.8
–1.5/0.7
TP Volts
Output (dBmV)
(1 mW=1 V)
2.1 32 30 Low level alarm
2.0 31 30 Low level alarm
1.9 31 29 Low level alarm
1.8 30 29 Low level alarm
1.7 30 28 Low level alarm
1.6 29 28 Normal
1.5 29 27 Normal
1.4 28 26 Normal
1.3 27 25 Normal
1.2 27 25 Normal
1.1 26 24 Normal
1.0
0.9 24 22 Normal
0.8 23 21 Normal
0.7 22 20 Normal
NORM) when the optical power is
LOW) the recommended optical input power range.
Output (dBmV)
77 channels
25 23 Optimum
110 channels
Comments
HIGH)
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 76

5-12 Operation
5
Optical input
level(dBm/mW)
–2.0/0.6
–2.5/0.6
–3.0/0.5
–3.5/0.5
–4.0/0.4
–5.2/0.3
Typical output levels are approximately 2 dB greater than the minimum levels.
Optical modulation index (OMI) for 77 channels (per channel): 0.0403.
OMI for 110 channels (per channel): 0.0337.
Optical transmitter wavelength is 1310 nm.
Bold type indicates default values.
TP Volts
(1 mW=1 V)
0.6 21 19 Normal
0.6 20 18 Normal
0.5 19 17 Normal
0.5 18 16 Normal
0.4 17 16 Normal
0.3 15 13 High level alarm
Output (dBmV)
77 channels
Output (dBmV)
110 channels
Comments
Figure 5-14 illustrates the relationship between test-point voltage (Vdc) and optical power (dBm):
Figure 5-14
Test-point voltage v ersus optical power
4
3
2
1
0
-1
-2
-3
Optical power (dBm)
-4
-5
-6
1.75 2.00 2.25 2.50 2.75
Test point DC Voltage (Vdc)
1 Volt = 1 Mw optical power
10 Log x Voltage (DC) = optical power (dBm)
10
3.000.25 0.50 0.75 1.00 1.25 1.50
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 77

Operation 5-13
Wavelength Selection Jumper
The SG2-LR can be used with either 1310 nm or 1550 nm transmitters. An internal wavelength
selection jumper optimizes the optical power test point and optical power status indicator calibration
for the system wavelength. Note that the jumper has no effect on the optical-to-RF performance
(gain, flatness, slope) of the module.
The wavelength selection jumper is factory-set and provides optimum calibration in a 1310 nm
system.
If you need to reset the jumper:
1 If necessary, remove the SG2-LR from the node.
2 Remove the five screws securing the sheet metal cover to the module casting and remove the
cover. Note the position of the optical connector assembly so that you can replace it in the same
position when you re-assemble the module.
3 Carefully lift the fiber coiling tray until the wavelength selection jumper is visible. To avoid
damaging the fiber, do not lift the tray any more than is necessary to expose the wavelength
selection jumper.
4 Position the jumper block on the appropriate pins for the desired wavelength. Figure 5-15
illustrates the circui t board wh ich is labe led to fac ilit at e this step :
Figure 5-15
Wavelength selection ju mper
Wave leng th selection jumper
(shown in 1310 nm position)
1550
1310
5 Replace the fiber tray in the module taking care not to pinch the fiber between the coiling tray
and the circuit board or casting. Position the optical connector assembly in its original position.
6 Replace the sheet metal cover, being careful not to pinch the fiber. Install the five screws to
secure the cover. Torque the screws to 10-12 in-lbs.
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 78

5-14 Operation
A
To verify the position of the optical connector assembly, lift the metal tab and attempt to remove
7
the optical connector assembly from the module casting. The connector assembly should slide
out easily. If not, remove the sheet metal cover and verify the position of the optical connector
assembly. Release the metal tab and snap the optical connector assembly back into place.
CAUTION!
Do not pull the optical connector out more than two inches from the casting wall. If you
pull the connector out too far, you must disassemble the module and respool the fiber.
8 If necessary, re-install the SG2-LR in the node.
SG2-IFPT Optical Transmitter
The SG2-IFPT is an isolated Fabry-Perot return-path optical transmitter designed for use in the
SG 2000 node platform. It has a nominal optical output power of 0.4 mW and can be used in
conjunction with an AM-RPR, AM-OMNI-RPR/2, or other similar return path optical receiver.
Figure 5-16 illustrates the SG2-IFPT:
Figure 5-16
SG2-IFPT
SG2000
Opti cal Tran smit ter
SG2-IFPT
F
O
LASER
OPTICAL
POWER
(1 V/mW)
CURRENT
(1 V/A)
N
U
ASSEMBLED
L
IN MEX ICO
T
Table 5-3 provides information on the user-rela ted fe at ures of the SG2-I FPT:
Table 5-3
SG2-IFPT features
Feature Description
Optical power test point
Laser current test point
This test point enables monitoring of the optical output level of the
module. The nominal scale factor is 1.0 V/mW. The optical power
test point voltage is between 0.375 V and 0.425 V (optical power of
0.375 mW through 0.425 mW) when the module is enabled under
normal operating conditions. Note that the optical power test point
does not track changes in optical power due to the laser tracking
error.
This test point enables monitoring of the current drawn by the laser
diode. The nominal scale factor is 1.0 V/A. The laser current test
point voltage is between 4 mV through 90 mV (laser current of
4 mA through 90 mA) when the module is enabled under normal
operating conditions. The laser current is expected to vary widely
with changes in temperature, but should always remain between
the limits.
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 79

Operation 5-15
Feature Description
Transmitter enable
A green LED that provides visual indication of the transmitter’s
enable status.
Fault indicator
A single red LED that lights when the hybrid current is outside the
normal operating range, the laser output power is below normal
limits, or the laser current is above normal limits. Because the laser
output requires a short period of time to stabilize, it is acceptable
for the fault indicator to illuminate during the stabilization interval
(approximately 2 seconds). Note that the module must be enabled
for the fault indicator to function.
SG2-FPT Optical Transmitter
The SG2-FPT is a non-isolated Fabry-Perot return-path optical transmitter designed for use in the SG
2000 node platform. It has a nominal optical output power of 0.4 mW and can be used in conjunction
with an AM-RPR, AM-OMNI-RPR/2, or other similar return path optical receiver. Figure 5-17
illustrates the SG2-FPT:
Figure 5-17
SG2-FPT
SG2000
Opti cal Tran smit ter
SG2-FPT
F
O
LASER
OPTICAL
POWER
(1 V/mW)
CURRENT
(1 V/A)
A
N
U
ASSEMBLED
L
IN MEX ICO
T
Table 5-4 provides information on the user-rela ted fe at ures of the SG2-FPT:
Table 5-4
SG2-FPT features
Feature Description
Optical power test point
Laser current test point
This test point enables monitoring of the optical output level of the
module. The nominal scale factor is 1.0 V/mW. The optical power
test point voltage is between 0.375 V and 0.425 V (optical power of
0.375 mW through 0.425 mW) when the module is enabled under
normal operating conditions. Note that the optical power test point
does not track changes in optical power due to the laser tracking
error.
This test point enables monitoring of the current drawn by the laser
diode. The nominal scale factor is 1.0 V/A. The laser current test
point voltage is between 4 mV through 90 mV (laser current of
4 mA through 90 mA) when the module is enabled under normal
operating conditions. The laser current is expected to vary widely
with changes in temperature, but should always remain between
the limits.
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 80

5-16 Operation
A
Feature Description
Transmitter enable
A green LED that provides visual indication of the transmitter’s
enable status.
Fault indicator
A single red LED that lights when the hybrid current is outside the
normal operating range, the laser output power is below normal
limits, or the laser current is above normal limits. Because the laser
output requires a short period of time to stabilize, it is acceptable
for the fault indicator to illuminate during the stabilization interval
(approximately 2 seconds). Note that the module must be enabled
for the fault indicator to function.
SG2-DFBT Optical Transmitter
The SG2-DFBT is an isolated distributed feedback (DFB) return path optical transmitter used in the
SG 2000 node platform. It has a nominal optical output power of 1.0 mW and is used in conjunction
with an AM-RPR, AM-OMNI-RPR/2, or other similar return-path optical receiver.
Figure 5-18 illustrates the SG2-DFBT:
Figure 5-18
SG2-DFBT
SG2000
Opti cal Tran smit ter
SG2-DFBT
O
F
LASER
OPTICAL
POWER
(1 V/mW)
CURRENT
(1 V/A)
N
U
ASSEMBLED
L
IN MEX ICO
T
Table 5-5 provides information on the user-rela ted fe atures of the SG2- DFBT:
Table 5-5
SG2-DFBT f eatures
Feature Description
Optical power test point
Laser current test point
This test point enables monitoring of the optical output level of the
module. The nominal scale factor is 1.0 V/mW. The optical power
test-point voltage is betwee n 0.945 V thr oug h 1.055 V (optic a l
power of 0.945 mW through 1.055 mW) when the module is
enabled under normal operating conditions. Note that the optical
power test point does not track changes in optical power due to the
laser tracking error.
This test point enables monitoring of the current drawn by the laser
diode. The nominal scale factor is 1.0 V/A. The laser current test
point voltage is between 5 mV through 110 mV (laser current of
5 mA through 110 mA) when the module is enabled under normal
operating conditions. The laser current is expected to vary widely
with changes in temperature, but should always remain between
the limits.
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 81

Operation 5-17
Feature Description
Transmitter enable
Fault indicator
A green LED that provides visual indication of the transmitter’s
enable status.
A single red LED that lights if the hybrid current is outside the
normal operating range, the laser output power is below normal
limits, or the laser current is above normal limits. Because the laser
output requires a short period of time to stabilize, it is acceptable
for the fault indicator to illuminate during the stabilization interval
(approximately 2 seconds). Note that the module must be enabled
for the fault indicator to function.
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 82

5-18 Operation
A
SG2-DFBT/3 Optical Transmitter
The SG2-DFBT/3 is an isolated distributed feedback (DFB) return path optical transmitter used in
the SG 2000 node platform. It has a nominal optical output power of 2.0 mW and is used in
conjunction with an AM-RPR, AM-OMNI-RPR/2, or other similar return-path optical receiver.
Figure 5-19 illustrates the SG2-DFBT/3:
Figure 5-19
SG2-DFBT /3
SG2000
Opti cal Tran smit ter
SG2-DFBT/3
F
O
LASER
OPTICAL
POWER
(1 V/mW)
Table 5-6 provides information on the user-rela ted fe atures of the SG2- DFBT/3:
Table 5-6
SG2-DFBT/3 features
CURRENT
(1 V/A)
N
U
ASSEMBLED
L
IN MEX ICO
T
Feature Description
Optical power test point
Laser current test point
Transmitter enable
Fault indicator
This test point enables monitoring of the optical output level of the
module. The nominal scale factor is 1.0 V/mW. The optical power
test-point voltage is betwee n 0.945 V thr oug h 1.055 V (optic a l
power of 0.945 mW through 1.055 mW) when the module is
enabled under normal operating conditions. Note that the optical
power test point does not track changes in optical power due to the
laser tracking error.
This test point enables monitoring of the current drawn by the laser
diode. The nominal scale factor is 1.0 V/A. The laser current test
point voltage is between 5 mV through 110 mV (laser current of
5 mA through 110 mA) when the module is enabled under normal
operating conditions. The laser current is expected to vary widely
with changes in temperature, but should always remain between
the limits.
A green LED that provides visual indication of the transmitter’s
enable status.
A single red LED that lights if the hybrid current is outside the
normal operating range, the laser output power is below normal
limits, or the laser current is above normal limits. Because the laser
output requires a short period of time to stabilize, it is acceptable
for the fault indicator to illuminate during the stabilization interval
(approximately 2 seconds). Note that the module must be enabled
for the fault indicator to function.
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 83

Operation 5-19
SG2-EIFPT Optical Transmitter
The SG2-EIFPT is an enhanced, isolated, Fabry-Perot return-path optical transmitter designed for
use in the SG 2000 node platform. It has a nominal optical output power of 1 mW and can be used in
conjunction with an AM-RPR, AM-OMNI-RPR/2, or other similar return path optical receiver.
Figure 5-20 illustrates the SG2-EIFPT:
Figure 5-20
SG2-EIFPT
SG2000
RF
RF
INPUT
(-20 dB)
Table 5-7 provides information on the user-rela ted fe at ures of the SG2-EI FPT:
Table 5-7
SG2-EIFPT features
Opti cal Tran smit ter
OPTICAL
POWER
(1 V/mW)
LASER
CURRENT
(1 V/A)
SG2-EIFPT
F
O
A
N
U
ASSEMBLED
L
IN MEX ICO
T
Feature Description
Optical power test point
Laser current test point
Transmitter enable
Fault indicator
This test point enables monitoring of the optical output level of the
module. The nominal scale factor is 1.0 V/mW. The optical power
test point voltage is between 0.945 V and 1.055 V (optical power of
0.945 mW through 1.055 mW) when the module is enabled under
normal operating conditions. Note that the optical power test point
does not track changes in optical power due to the laser tracking
error.
This test point enables monitoring of the current drawn by the laser
diode. The nominal scale factor is 1.0 V/A. The laser current test
point voltage is between 4 mV through 90 mV (laser current of
4 mA through 90 mA) when the module is enabled under normal
operating conditions. The laser current is expected to vary widely
with changes in temperature, but should always remain between
the limits.
A green LED that provides visual indication of the transmitter’s
enable status.
A single red LED that lights when the hybrid current is outside the
normal operating range, the laser output power is below normal
limits, or the laser current is above normal limits. Because the laser
output requires a short period of time to stabilize, it is acceptable
for the fault indicator to illuminate during the stabilization interval
(approximately 2 seconds). Note that the module must be enabled
for the fault indicator to function.
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 84

5-20 Operation
A
DS-SG2-DRT/A Digital Return Transmitter
The DS-SG2-DRT/A is an SG2 return tr ansmitter that digitizes a sing le analog 5 MHz-42 MHz
return-path signal to produce a 1.6 Gbps data stream. This data stream is then routed to a digital laser
for transmission to a corresponding digital return receiver.
The transmitter can be configured with a digital laser wavelength that is applicable to the required
link length. An automatic power control (APC) system regulates the optical output power from the
laser. User-accessible input level-control adjustments enable you to adjust the transmitter +2 to
−13 dB from an input level of 15 dBmV. All transmitter status-monitor information is available at
the digital return receiver.
To facilitate easy upgrades, the DS-SG2-DRT/A fits the same footprint and has the same set-up
levels as the analog return transmitters.
Figure 5-21 illustrates a block diagram of the DS-SG2-DRT/A:
Figure 5-21
DS-SG2-DRT/A
RF TP
Return
band RF
5-42 MHz
Transmit
signal
processing
logic
CATV
gain block
Anti-
aliasing
LPF
RF
XFMR
XO
A/D
converter
Figure 5-22 illustrates the DS-SG2-DRT/A and attached cable:
Figure 5-22
DS-SG2-DRT/A
Digital Transmitter
SG2000
INPUT
STATUS
DANGER
A
DS-SG2-DRT/A
1310 DFB
Serializer
XO
Serial bit
stream
@1.6 Gbps
Optical transmitter module
Optical
TP
lightwave to
Digital
SG2 output
Test
Point
You can gain access to test point A through the transmitter test cable MCX-F (DS-SG2-DRT-TC,
P/N 476803-001).
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 85

Operation 5-21
Table 5-8 provides information on the user-related features of the DS-SG2-DRT/A transmitters:
Table 5-8
DS-SG2-DRT/A featu res
Feature Description
Test point A
Input A
Increment attenuator
setting
Decrement attenuator
setting
Change increment/
decrement direction
Restore factory default
setting
This test point enables monitoring of the RF level at the input to
the A/D. It measures −20 dB from the A/D input level.
The transmitter has a digitally controlled attenuator that adjusts
for varying input levels. Th is push- butt on is an input le ve l- contr ol
adjustment that provides +2 to −13 dB of adjustment from an
input level of 15 dBmV.
Short press (0.1 to 1.5 seconds). The status LED indication is
green with a short OFF blink (0.25 sec.) when the button is
released. A short red blink occurs if the increment attempts to go
past the maximum.
Short press (0.1 to 1.5 seconds). The status LED indication is
green with a short yellow blink (0.25 sec.) when the button is
released. A short red blink occurs if the decrement attempts to
go past the minimum.
Medium press (1.5 to 5.0 seconds). The status LED is OFF after
1.5 seconds when in the increment direction, and yellow when in
the decrement direction. The LED is restored to its green or
alarm state when the button is released. No increment or
decrement occurs.
Long press (5.0 seconds or longer). The status LED flashes
green and yellow rapidly until the button is released. After five
seconds of flashing, the factory defaults are restored.
Status
Alarms
No alarm
Over temperature (> ++++85°C)
Low ++++24 Vdc (< ++++18 Vdc)
Low ++++5 Vdc (< ++++4.5 Vdc)
Low ++++2.5 Vdc (< ++++2.2 Vdc)
Laser bias/optical power
out of spec.
This tri-color LED is green if all parameters are within
specification. A series of red flashes indicate an alarm condition.
The number of red flashes indicate the parameter that is outside
the specification.
Status LED indication:
Steady green
Long red, one red flash (repeating)
Long red, two red flashes (repeating)
Long red, three red flashes (repeating)
Long red, five red flashes (repeating)
Long red, six red flashes (repeating)
It is recommended that you restore the factory default sett ing s before you set up the node levels. This
procedure places the transmitter input level 2 dB below maximum.
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 86

5-22 Operation
A
DS-SG2-DRT-2X/A Digital Return Transmitter
The DS-SG2-DRT-2X/A is an SG2 return transmitter that digitizes two independent analog
5 MHz-42 MHz return-path signals to produce two 1.25 Gbps data streams. These two data streams
are then multiplexed to create a 2.5 Gbps data stream. This data stream is then routed to a digital
laser for transmission to a corresponding digital return receiver.
The transmitter can be configured with a digital laser wavelength that is applicable to the required
link length. An APC system regulates the optical output power from the laser. Two user-accessible
input level-control adjustments enable you to independently adjust the transmitter input levels +2 to
−13 dB from an input level of 15 dBmV. All transmitter status-monitor information is available at
the digital return receiver.
To facilitate easy upgrades, the DS-SG2-DRT-2X/A fits the same footprint and has the same set-up
levels as the analog return transmitters.
Figure 5-23 illustrates a block diagram of the DS-SG2-DRT-2X/A:
Figure 5-23
DS-SG2-DRT-2X/ A
Return
band RF
5-42 MHz
Return
band RF
5-42 MHz
CATV
gain block
CATV
gain block
Anti-
aliasing
LPF
Anti-
aliasing
LPF
RF
XFMR
XO
RF
XFMR
A/D
converter
A/D
converter
Transmit
signal
processing
logic
Serializer
XO
Figure 5-24 illustrates the DS-SG2-DRT-2X/A and attached cable:
Figure 5-24
DS-SG2-DRT-2X/ A
Digital Transmitter
SG2000
INPUT
DANGER
STA TUS DS-SG2-DRT-2X/A
A
1310 DFB
INPUT
INPUT
RF
B
@2.5 Gbps
B
Serial bit
stream
Digital
lightwave to
SG2 o u t put
Optical transmitter mo dul e
Test
Point
Test
Point
B
You can gain access to test point A through the transmitter test cable MCX-F (DS-SG2-DRT-TC,
P/N 476803-001).
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 87

Operation 5-23
Table 5-9 provides information on the user-rela ted feat ures of the DS- SG2- DRT- 2X/A:
Table 5-9
DS-SG2-DRT-2X/ A features
Feature Description
Test point A and B
Input A and B
Increment attenuator
setting
Decrement attenuator
setting
Change increment/
decrement direction
Restore factory default
setting
These test points enable monitoring of the RF level at the input to
the A/D. It measures −20 dB from the A/D input level.
The transmitter has a digitally controlled attenuator that adjusts for
varying input levels. These push-buttons are input level-control
adjustments that provide +2 to −13 dB of adjustment from an input
level of 15 dBmV. No action is taken if both buttons are pressed.
Short press (0.1 to 1.5 seconds). The status LED indication is
green with a short OFF blink (0.25 sec.) when the button is
released. A short red blink occurs if the increment attempts to go
past the maximum.
Short press (0.1 to 1.5 seconds). The status LED indication is
green with a short yellow blink (0.25 sec.) when the button is
released. A short red blink occurs if the decrement attempts to go
past the minimum.
Medium press (1.5 to 5.0 seconds). The status LED is OFF after
1.5 seconds when in the increment direction, and yellow when in
the decrement direction. The LED is restored to its green or alarm
state when the button is released. No increment or decrement
occurs.
Long press (5.0 seconds or longer). The status LED flashes green
and yellow rapidly until the button is released. After five seconds of
flashing, the factory defaults are restored.
Status
Alarms
No alarm
Over temperature (> ++++85°C)
Low ++++24 Vdc (< ++++18 Vdc)
Low ++++5 Vdc (< ++++4.5 Vdc)
Low ++++2.5 Vdc (< ++++2.2 Vdc)
Laser bias/optical power
out of spec.
RF input B
This tri-color LED is green if all parameters are within specification.
A series of red flashes indicate an alarm condition. The number of
red flashes indicate the parameter that is outside the specification.
Status LED indication:
Steady green
Long red, one red flash (repeating)
Long red, two red flashes (repeating)
Long red, three red flashes (repeating)
Long red, five red flashes (repeating)
Long red, six red flashes (repeating)
This input is the second RF return signal that is obtained from the
adjacent transmitter connector through a provided cable. The cable
is illustrated in Figure 5-27.
It is recommended that you restore the factory default sett ing s before you set up the node levels. This
procedure places the transmitter input level 2 dB below maximum.
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 88

5-24 Operation
Figure 5-25 illustrates the DS-SG2-DRT-2X/A cable connector:
Figure 5-25
DS-SG2-DRT-2X/A cable connector
Figure 5-26 illustrates the DS-SG2-DRT-2X/A installed in the SG 2000 with completed fiber
connections:
Figure 5-26
DS-SG2-DRT-2X/A installed in SG 2000
Digital Transmit ter
RF
INPUT
B
SG2000
INPUT
INPUT
STATUS DS-S G2-DRT-2X/A
DANGER
A
B
1310 DFB
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 89

Operation 5-25
Figure 5-27 provides greater detail of the DS-SG2-DRT-2X/A second RF input cable connection to
the LIDB. This cable connects the other half of the split return to the DS-SG2-DRT-2X/A.
Figure 5-27
DS-SG2-DRT-2X/A second RF input cable connection
Transmitter to node
service cable
Second RF
input cable
SG2-PS Power Supply
The DS-SG2-DRT-2X/A requires the SG2-PS power supply rather than the SG2-PS2 power supply.
The SG2-PS provides the power required to support dual DS-SG2-DRT-2X/A transmitters in a
redundant configuration.
Figure 5-28 illustrates the SG2-PS power supply:
Figure 5-28
SG2-PS power supply
SG2-PS
NO USER SERVICEABLE
PARTS INSIDE
SEE INSTALLATION MANUAL FOR SERVICE
CAUTION
VOLTAGES IN EXCESS OF 250 VOLTS ARE
PRESENT UNDER COVER AND MAY BE
PRESENT AFTER POWER IS REMOVED
LOHI
ASSEMBLED IN MEXICO
24V
ADJ
TEST
POINT
POINT
5V
TEST
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 90

5-26 Operation
Status Monitoring
Table 5-10 identifies and describes the status monitor provisions built into the SG 2000 platform:
Table 5-10
Reporting and control provisions
Parameter Description
Power supply voltage
Power supply
presence
ac volts
dc current at RF
chassis
dc current at optical
receiver
Laser current
Receiver optical
power
Transmitter optical
power
AGC drive level
RF level
Converts the +24 V and +5 V outputs from power supply #1 and #2 to a
scaled dc voltage that is referenced to ground.
A digital indication that is used to detect the presence of power supply
#1 and #2.
Measures the ac voltage provided to the dc power supplies.
Measures the dc current that the forward hybrid draws from the
+24 Vdc supply.
Measures the dc current that optical receiver A, B, or C is drawing from
the +24 Vdc supply.
Measures the dc laser bias current for optical transmitter A or B. This is
not implemented in the digital return transmitter. The status monitor
signals are returned to the digital return receiver as part of the data
stream.
Measures the optical power received by the A, B or C optical receiver.
Measures the optical power emitted by the A or B optical transmitter.
This is not implemented in the digital return transmitter. The status
monitor signals are returned to the digital return receiver as part of the
data stream.
A scaled voltage that represents the dc level within the AGC drive loop.
Measures the RF power level that is coupled to provide an exit sample
at the RF port.
Ingress control switch
Optical receiver A/B
select
Optical transmitter
enable
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Places a dc voltage on ingress control switches #1, #2, #3, and #4 to
control their attenuation.
A digital control that facilitates the status monitors ability to control the
selection of optical receiver A or B.
A digital control that enables/disables optical transmitter A or B. This is
not implemented in the digital return transmitter. The status monitor
signals are returned to the digital return receiver as part of the data
stream.
Page 91

Operation 5-27
Manual Control Board
The SG 2000 manual control board (SG2-MCB) serves to locally control redundancy functions and
ingress switch operation if a status monitor is not installed. Figure 3-2 illustrates the MCB board
mounted on the main RF board in place of the status monitor. Inputs to the MCB are the received
optical power signals from both the A and B receivers, scaled at 1 V/mW.
The MCB board contains two 3-gang, dual-in-line-package (DIP) switches and five screwdriver
adjustable potentiometers. Table 5-11 provides descriptions and functions of these user-interface
settings:
Table 5-11
MCB user-interface settings
Description Function
Switch S1-1
Switch S1-2
Switch S1-3
Switch S2-1
Switch S2-2
Determines whether the primary/redundant reset state occurs at
1.0 dB more than the defined optical level threshold. This hysteresis or “gap”
0.5 dB or
prevents the automatic switch-over function from “hunting” or switching
back and forth if the received optical power remains close to the switching
threshold. The factory setting is 1.0 dB.
Enables selection of either normal (
operation. In the
NORM position, switchover between the primary and
NORM) or manual override (OVER)
secondary optical paths is automatically controlled by the received optical
power of the primary receiver. In the
performed manually using switch S1-3. The factory setting is
Selects either receiver A (
receiver when S1-2 is in the
RXA) or receiver B (RXB) as the primary optical
NORM position. With S1-2 in the OVER position,
S1-3 manually enables either receiver. The factory setting is
OVER position, the selection is
NORM.
RXA.
Selects standard slaving or cross slaving of the transmitters to the
receivers. Set in the standard slaving (
in the
NORM position, transmitter A follows the enable/disable status of
STD_SLV ) position, with switch S1-2
receiver A, and transmitter B that of receiver B. Setting S2-1 to cross
slaving (
CRS_SLV) causes transmitter B to be on when receiver A is
enabled and transmitter A to be on when receiver B is enabled. The factory
setting is
Controls the status of return transmitter A. If S1-2 is in the
S2-2 either enables transmitter A (
(
TXA_DIS). If S1-2 is in the NORM position, then S2-2 enables slaving of the
transmitter status to the corresponding receiver (
slaving function enabling the transmitter to be on continuously (
The factory setting is
STD_SLV.
OVER position,
TXA_EN) or disables transmitter A
TXA_DIS) or overrides the
TXA_EN).
TXA_DIS.
Switch S2-3
Alarm potentiometer
Performs the same function for transmitter B as S2-2 performs for
transmitter A. The factory setting is
(
ALRM) sets the received optical power threshold at which automatic
TXB_DIS.
switchover from the primary to the secondary path occurs. It can be set for
any power level up to 2.5 mW (+4 dBm). The factory setting is 0.25 V
(-3 dBm).
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 92

5-28 Operation
A
A
Description Function
Alarm test point
(
ALRM TP) provides access for measuring the cross-over optical level
threshold.
3 dB test point
(3 dB
TP) is used to measure the optical power of the primary receiver.
Measurements at this test point are 3 dB less than the actual value.
Potentiometers ICS1
through ICS4
Control the attenuation of the ingress control switches (ICS) when they are
installed in the return paths of the RF output ports. The factory setting is for
minimum attenuation, however, they can be set for a maximum attenuation
of approximately 40 dB. The following list indicates the potentiometer and
its corresponding housing port:
ICS1 housing port IN RF chassis port 1
ICS2 housing port OUT RF chassis port 2
ICS3 housing port 1 RF chassis port 3
ICS4 housing port 3 RF chassis port 4
Figure 5-29 illustrates the MCB board, switches, potentiometers, and test points:
Figure 5-29
MCB board
ICS4
ICS3
ICS2
LRM
ICS1
S2
S1
3 dB TP
LRM TP
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 93

Operation 5-29
Ingress Control
The SG 2000 platform incorporates electronic ingress control switching enabling operators to choose
one of three options for troubleshooting noise sources. A maximum of four switches, (one ingress
switch per RF port) can populate the RF amplifier. Figure 3-2 illustrates their location on the RF
chassis.
Ingress switches are controlled in one of two ways: (1) remotely — through the optional on-board
LL-SG2 transponder in communication with the status monitoring system or; (2) locally — using the
manual control board (MCB).
The three states of the switch and their functions include:
State Description
Off
–6 dB
On
Effectively isolates the contaminated leg by adding a minimum of 40 dB attenuation.
Typically initiated at the headen d, it pro v ides –6 dB ad dit ion al atte nuat io n to the retur n
signal. This is useful in diagnosing noise presence without interfering with normal
service.
Completes the return path without alteration to the return signal.
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
Page 94

Appendix A
Specifications
Specifications for the SG 2000 are valid over the given bandpass and operating temperature range
listed in this section. The current catalog m ay contain additio nal in formation not provided below.
Table A-1 lists the optical characteristics for the SG 2000 node:
Table A-1
SG 2000 optical characteristics
Parameter Specification
Optical wavelength
Received optical power
minimum (low gain)
minimum (high gain)
maximum
Optical input return loss
Equivalent input noise
current
1310 ±20 nm through 1550 ±30 nm
–2 dBm (47 dBmV)
–4 dBm (47 dBmV)
+2 dBm (continuous)
40 dB minimum
1/2
8 pa/Hz
Table A-2 lists the station RF characteristics for the SG 2000 node:
Table A-2
Station RF ch aracteristics
Parameter Specification
Forward passband frequency
Return passband, each port
Upconverted return output
Splits
S
J
A
K
E
M
47 MHz through 870 MHz (dependent upon split)
5 MHz through 65 MHz (dependent upon split); 200 MHz
capable
50 MHz through 400 MHz
40/52 MHz
55/70 MHz
65/85 MHz
42/54 MHz
30/47 MHz
80/108 MHz
Return loss
Minimum full gain
RF amplifier (low gain)
RF amplifier (high gain)
Gain control range
Operational gain
RF amplifier (low gain)
RF amplifier (high gain)
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
16 dB
32 dB
38 dB
8 dB
28 dB
34 dB
Page 95

A-2 Specifications
Parameter Specification
Flatness over passband
Operational tilt (standard)
±0.75 dB, all ports
750 MHz:10 dB ±1 dB (low),12.5 dB ±1 dB (standard),
14 dB ±1 dB (high)
870 MHz: 9 dB ±1 dB (low), 11.5 dB ±1 dB (standard),
14 dB ±1 dB (high) (plug-in equalizers available)
Table A-3 lists the general characteristics for the SG 2000 node:
Table A-3
SG 2000 General characteristics
Parameter Specifications
AC input voltage
AC bypass current
Hum modulation
Operating temperature
Housing dimensions
Weight
44 Vac through 110 Vac quasi-squarewave
15 A
–70 dB @ 15 A bypass current
–40
°C through +60°C (–40°F through +140°F)
21.6”(L)
× 10.6”(W) × 11.0”(D), (without bracket)
Minimum 36 lbs./maximum 42 lbs. (without bracket)
Table A-4 lists the general specifications for the SG2-LR optical receiver:
Table A-4
SG2-LR specifications
Parameter Specification
Optical input power
range-recommended
Optical input
power-maximum
recommended
1
Optical input return loss
RF passband
Gain at 40 MHz
2
Flatness
Tilt
Equivalent noise input
current
1
Absolute maximum optical input power that can be applied to the optical input connector.
2
Relative to an ideal photodetector terminated in a 75-ohm impedance.
–4.0 dBm to +2.0 dBm
3dBm
40 dB minimum
40 MHz through 870 MHz
19.5 dB minimum
1.25 dB P-V maximum
–0.5 dB to +2.0 dB maximum
8pA/Hz
1/2
maximum
SG 2000 Installation and Operation Manual
Page 96

Specifications A-3
Table A-5 lists the RF performance specifications for the SG2-IFPT laser transmitter:
Table A-5
SG2-IFPT RF specifications
Parameter Specification
Nominal RF input impedance
RF passband
Flatness (peak to valley)
RF input return loss
Recommended total input
power
Carrier to noise ratio 9 dB link,
35 MHz BW
75-ohms
5 MHz to 65 MHz
1.00 dB maximum
18 dB minimum
+15 dBmV
40 dB minimum, +25±5°C and 36.5 dB minimum from –40°C
to +60°C.
Table A-6 lists the RF performance specifications for the SG2-FPT laser transmitter:
Table A-6
SG2-FPT R F specificati ons
Parameter Specification
Nominal RF input impedance
RF passband
Flatness (peak to valley)
RF input return loss
75-ohms
5 MHz through 65 MHz
1.00 dB maximum
18 dB minimum
Recommended total input
power
Carrier to noise ratio 9 dB link,
35 MHz BW
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
+15 dBmV
35 dB minimum
Page 97

A-4 Specifications
Table A-7 lists the RF performance specifications for the SG2-DFBT laser transmitter:
Table A-7
SG2-DFBT R F specificatio ns
Parameter Specification
Nominal RF input impedance
RF passband
Flatness (peak to valley)
RF input return loss
Recommended total input
power
Carrier to noise ratio 9 dB link,
35 MHz BW
75-ohms
5 MHz through 200 MHz
1.00 dB maximum
18 dB minimum
+15 dBmV
41 dB minimum
Table A-8 lists the RF performance specifications for the SG2-DFBT/3 laser transmitter:
Table A-8
SG2-DFBT/3 RF specifications
Parameter Specification
Nominal RF input impedance
RF passband
Flatness (peak to valley)
RF input return loss
75-ohms
5 MHz through 200 MHz
1.00 dB maximum
18 dB minimum
Recommended total input
power
Carrier to noise ratio 9 dB link,
35 MHz BW
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
+15 dBmV
46.5 dB minimum
Page 98

Specifications A-5
Table A-9 lists the RF performance specifications for the SG2-EIFPT laser transmitter:
Table A-9
SG2-EIFPT RF specification s
Parameter Specification
Nominal RF input impedance
RF input passband
Flatness (peak to valley)
RF input return loss
Recommended total input
power
Optical output power
Carrier to noise ratio 9 dB link,
35 MHz BW
75-ohms
5 MHz through 65 MHz
1.00 dB maximum
18 dB minimum
+15 dBmV
1 mW (1 dBm), nominal
36.5
Table A-10 lists the RF performance specifications for the SG2-DRT/A digital return transmitter:
Table A-10
SG2-DRT/A RF specifications
Parameter Specification
Nominal RF input impedance
RF passband
Flatness (peak to valley)
75-ohms
5 MHz through 42 MHz
±0.5 dB maximum
RF input return loss
Recommended total input
power
Noise power ratio (NPR)
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
18 dB minimum
+15 dBmV
40 dB with a minimum of 11 dB of input range from the RF
input of the transmitter to the electrical output of the receiver
Page 99

A-6 Specifications
Table A-11 lists the RF performance specifications for the SG2-DRT-2X/A digital return transmitter:
Table A-11
SG2-DRT- 2X/A RF specificati ons
Parameter Specification
Nominal RF input
impedance
RF passband
Flatness (peak to
valley)
RF input return loss
Recommended total
input power
Noise power ratio
75-ohms
5 MHz through 42 MHz
±0.5 dB maximum
18 dB minimum
+15 dBmV
40 dB with a minimum of 11 dB of input range from the RF input of the
transmitter to the electrical output of the receiver
Table A-12 lists the minimum optical output power ratings for each available wavelength and
transmitter model. These values are applicable for the DS-SG2-DRT/A and DS-SG2-DRT-2X/A:
Table A-12
Optical output power v s. wavelength for DS-SG2-DRT */A transmitters
Minimum Optical
Output Power
Model
(dBm)
–7
-001, DS-SG2-DRT*/A-1310-FP-SC
–2
–3
–3
–3
–3
–3
–3
–3
–3
–3
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
-002, DS-SG2-DRT*/A-1310-DFB-SC
-008, DS-SG2-DRT*/A-1470-DFB-SC
-009, DS-SG2-DRT*/A-1490-DFB-SC
-003, DS-SG2-DRT*/A-1550-DFB-SC
-004, DS-SG2-DRT*/A-1510c-DFB-SC
-005, DS-SG2-DRT*/A-1530c-DFB-SC
-006, DS-SG2-DRT*/A-1550c-DFB-SC
-007, DS-SG2-DRT*/A-1570c-DFB-SC
-010, DS-SG2-DRT*/A-1590-DFB-SC
-011, DS-SG2-DRT*/A-1610-DFB-SC
(avg. power w/randomized data patt er n
in all cases)
Page 100

Specifications A-7
Table A-13 lists the current requirements for various options and the two platforms available in the
SG 2000:
Table A-13
Current req uirements
Option Watts ac
power
Basic- platform (one-way,
Amp s
@90V
Amp s
@60V
single receiver: Note 1)
Silicon
Module D, F
Module C, E, G
Module B
Gallium Arsenide (GaAs)
Module D, F
Module C, E, G
Module B
Add for:
Additional receiver-split
82.48
69.36
56.24
92.72
77.04
61.36
1.22
1.03
0.83
1.37
1.14
0.91
1.83
1.54
1.25
2.06
1.71
1.36
8.96 0.13 0.20 0.23 0.27
band
Additional receiver,
0.64 0.01 0.01 0.02 0.02
redundant
Analog return
9.84 0.15 0.22 0.25 0.30
transmitters
Digital return
transmitters
DS-SG2-DRT/A
DS-SG2-DRT-2X/A
4.17
8.33
0.08
0.17
0.12
0.23
Amp s
@52V
2.11
1.78
1.44
2.38
1.98
1.57
0.12
0.25
Amp s
@44V
2.50
2.10
1.70
2.81
2.33
1.86
0.14
0.27
Reduction for split return
Each ingress switch
ADU
MCB
Status monitor
Note 1: Module letters denote the following:
Module B - two bridger level outputs
Module C - Three bridger level outputs
Module D - Four bridger level outputs
Module E - One trunk level, two bridger level outputs
Module F - Two trunk level, two bridger level outputs
Module G - Two trunk level, one bridger level output
SG 2000 Instal lation and Opera tion Manual
(3.52) (0.05) (0.08) (0.09) (0.11)
1.96 0.03 0.04 0.05 0.06
2.24 0.03 0.05 0.06 0.07
1.81 0.03 0.04 0.05 0.05
3.41 0.05 0.08 0.09 0.10
 Loading...
Loading...