Page 1

User Guide
SBG900
Wireless Cable
Modem Gateway
Page 2

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
WARNING: TO PREVENT FIRE OR SHOCK HAZARD, DO NOT EXPOSE THIS PRODUCT TO RAIN OR
MOISTURE. THE UNIT MUST NOT BE EXPOSED TO DRIPPING OR SPLASHING. DO NOT PLACE OBJECTS
FILLED WITH LIQUIDS, SUCH AS VASES, ON THE UNIT.
CAUTION: TO ENSURE REGULATORY AND SAFETY COMPLIANCE, USE ONLY THE PROVIDED POWER
AND INTERFACE CABLES. DO NOT CONNECT THE PLUG INTO AN EXTENSION CORD, RECEPTACLE, OR
OTHER OUTLET UNLESS THE PLUG CAN BE FULLY INSERTED WITH NO PART OF THE BLADES
EXPOSED.
CAUTION: DO NOT OPEN THE UNIT. DO NOT PERFORM ANY SERVICING OTHER THAN THAT CONTAINED
IN THE INSTALLATION AND TROUBLESHOOTING INSTRUCTIONS. REFER ALL SERVICING TO QUALIFIED
SERVICE PERSONNEL.
CAUTION: CHANGES AND MODIFICATIONS NOT EXPRESSLY APPROVED BY MOTOROLA FOR
COMPLIANCE COULD VOID USER’S AUTHORITY TO OPERATE THE EQUIPMENT.
CAUTION: Exposure to Radio Frequency Radiation. To comply with the FCC RF exposure compliance
requirements, the separation distance between the antenna and any person’s body (including hands, wrists, feet
and ankles) must be at least 8 inches (20 cm).
This device complies with part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) This
device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received, including
interference that may cause undesired operation.
Note: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to
part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference
in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not
installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications.
However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does
cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off
and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
This device must be installed and used in strict accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions as described in
the user documentation that comes with the product.
Postpone cable modem installation until there is no risk of thunderstorm or lightning activity in the area.
Do not overload outlets or extension cords, as this can result in a risk of fire or electric shock. Overloaded AC
outlets, extension cords, frayed power cords, damaged or cracked wire insulation, and broken plugs are
dangerous. They may result in a shock or fire hazard.
Route power supply cords so that they are not likely to be walked on or pinched by items placed upon or against
them. Pay particular attention to cords where they are attached to plugs and convenience receptacles, and
examine the point where they exit from the product.
Place this equipment in a location that is close enough to an electrical outlet to accommodate the length of the
power cord.
Place this equipment on a stable surface.
Home
X
ExitPrint
ii
SBG900 User Guide
Page 3

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Be sure that the outside cable system is grounded, so as to provide some protection against voltage surges and
built-up static charges. Article 820-20 of the NEC (Section 54, Part I of the Canadian Electrical Code) provides
guidelines for proper grounding and, in particular, specifies the CATV cable ground shall be connected in the
grounding system of the building, as close to the point of cable entry as practical.
When using this device, basic safety precautions should always be followed to reduce the risk of fire, electric
shock and injury to persons, including the following
:
• Read all of the instructions {listed here and/or in the user manual} before you operate this equipment. Give
particular attention to all safety precautions. Retain the instructions for future reference.
• Comply with all warning and caution statements in the instructions. Observe all warning and caution symbols
that are affixed to this equipment.
• Comply with all instructions that accompany this equipment.
•
Avoid using this product during an electrical storm.
added protection for this product during a lightning storm, or when it is left unattended and unused for long
periods of time, unplug it from the wall outlet, and disconnect the cable system. This will prevent damage to
the product due to lightning and power surges.
There may be a risk of electric shock from lightning. For
• Avoid damaging the cable modem with static by touching the coaxial cable when it is attached to the earth
grounded coaxial cable TV wall outlet.
• Always first touch the coaxial cable connector on the cable modem when disconnecting or re-connecting USB
or Ethernet cable from the cable modem or the user’s PC.
• Operate this product only from the type of power source indicated on the product’s marking label. If you are
not sure of the type of power supplied to your home, consult your dealer or local power company.
• Upon completion of any service or repairs to this product, ask the service technician to perform safety checks
to determine that the product is in safe operating condition.
It is recommended that the customer install an AC surge protector in the AC outlet to which this device is
connected. This is to avoid damaging the equipment by local lightning strikes and other electrical surges.
Different types of cord sets may be used for connections to the main supply circuit. Use only a main line cord that
complies with all applicable product safety requirements of the country of use.
Installation of this product must be in accordance with national wiring codes.
Place unit to allow for easy access when disconnecting the power cord/adapter of the device from the AC wall
outlet.
Wipe the unit with a clean, dry cloth. Never use cleaning fluid or similar chemicals. Do not spray cleaners directly
on the unit or use forced air to remove dust.
This product was qualified under test conditions that included the use of the supplied cables between system
components. To be in compliance with regulations, the user must use these cables and install them properly.
Connect the unit to a grounding type AC wall outlet using the power adapter supplied with the unit.
Do not cover the device, or block the airflow to the device with any other objects. Keep the device away from
excessive heat and humidity and keep the device free from vibration and dust.
Installation must at all times conform to local regulations.
Home
X
ExitPrint
iii
SBG900 User Guide
Page 4

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
This product is provided with a separate
Regulatory, Safety, Software License, and Warranty Information
card. If
one is not provided with this product, please ask your service provider or point-of-purchase representative, as the
case may be.
• THIS PRODUCT IS IN COMPLIANCE WITH ONE OR MORE OF THE STANDARDS LISTED ON THE
REGULATORY, SAFETY, SOFTWARE LICENSE, AND WARRANTY INFORMATION
STANDARDS APPLY TO ALL MODELS.
CARD. NOT ALL
• NO WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND ARE PROVIDED BY MOTOROLA WITH RESPECT TO THIS PRODUCT,
EXCEPT AS STATED ON THE
INFORMATION
CARD. MOTOROLA’S WARRANTIES DO NOT APPLY TO PRODUCT THAT HAS BEEN
REFURBISHED OR REISSUED BY YOUR SERVICE PROVIDER.
REGULATORY, SAFETY, SOFTWARE LICENSE, AND WARRANTY
Copyright © 2003 b y Motorola, Inc.
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced in any form or by any means or used to make any derivative work (such as
translation, transformation or adaptation) without written permission from Motorola, Inc.
Motorola reserves the right to revise this publication and to make changes in content from time to time without obligation on the part of Motorola
to provide notification of such revision or change. Motorola provides this guide without warranty of any kind, either implied or expressed,
including, but not limited to, the implied warranties of merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose. Motorola may make improvements or
changes in the product(s) described in this manual at any time.
MOTOROLA and the Stylized M Logo are registered in the US Patent & Trademark Office. Microsoft, Windows, Windows Me, and Windows NT are
registered trademarks and
Microsoft Corporation.
Corporation. Linux is a registered trademark of Linus Torvalds. Acrobat Reader is a registered trademark of Adobe Systems, Inc. Netscape and
Navigator are registered trademarks of
States and other countries. All other
Home
Windows XP is a trademark of
Macintosh and AppleTalk are registered trademarks
Netscape Communications Corporation
product or service names are the property of their respective owners. © Motorola, Inc. 2003.
X
ExitPrint
Microsoft Corporation. Microsoft Windows screen shots are used by permission of
iv
of Apple Computer, Inc. Iomega is a registered trademark of Iomega
. UNIX is a registered trademark of the Open Group in the United
SBG900 User Guide
Page 5

Contents
Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Easy Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Network Connection Types . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Powerful Features in a Single Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Sample LAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Optional Accessories . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Front Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Rear Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Label on the Bottom of the SBG900 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
SBG900 LAN Choices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Wireless LAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Wired Ethernet LAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
USB Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Firewall . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
DMZ . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Port Triggering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Wireless Security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Port Forwarding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Virtual Private Networks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Related Documentation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Installation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Before You Begin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Signing Up for Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Computer System Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Connecting the SBG900 to the Cable System . . . . . . . 18
Cabling the LAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Obtaining an IP Address for Ethernet . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Obtaining an IP Address in Windows 98,
Windows 98 SE, or Windows Me . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Obtaining an IP Address in Windows 2000 or
Windows XP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Obtaining an IP Address on Macintosh or UNIX
Systems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Connecting a PC to the USB Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Basic Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Starting the SBG900 Setup Program . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Changing the Default Password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Enabling Remote Access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Getting Help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Setting the Firewall Policy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Firewall > POLICY — advanced Page . . . . . . . . . . 29
Firewall > ALERT — basic Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Firewall > ALERT — email Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Firewall > LOGS Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Gaming Configuration Guidelines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Configuring the Firewall for Gaming . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Configuring Port Triggers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Configuring a Gaming DMZ Host
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Configuring the Gateway . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Gateway > STATUS Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Gateway > WAN Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Gateway > LAN — nat config Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Gateway > LAN — dhcp server config Page . . . . . . . . 42
Gateway > LAN — dhcp leases Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Gateway > PORT FORWARDING — status Page . . . 44
Gateway > PORT FORWARDING — config Page . . . 45
Gateway > PORT TRIGGERS — predefined Page . . 46
Gateway > PORT TRIGGERS — custom Page . . . . . 48
Gateway > LOG Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Configuring TCP/IP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Configuring TCP/IP in Windows 95, Windows 98, or
Windows Me . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Configuring TCP/IP in Windows 2000 . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Configuring TCP/IP in Windows XP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Verifying the IP Address in Windows 95, Windows 98, or
Windows Me . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Verifying the IP Address in Windows 2000 or Windows XP . 62
Setting Up the Wireless LAN . . . . . . . . . . 64
Configuring the Wireless Network Name on the SBG900 .65
Configuring WEP on the SBG900 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Configuring a MAC Access Control List on the SBG900 . .68
Configuring the Wireless Clients . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Configuring a Wireless Client with a Network
Name (ESSID) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Configuring a Wireless Client for WEP . . . . . . . . . . 69
Wireless Pages in the SBG900 Setup Program . . . . . 70
Wireless > STATUS Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Wireless > NETWORK Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
Wireless > SECURITY — basic Page . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Wireless > SECURITY — advanced Page . . . . . . . 75
Wireless > STATISTICS page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Home
X
ExitPrint
v
SBG900 User Guide
Page 6

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Setting Up a USB Driver. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Setting Up a USB Driver in Windows 98 . . . . . . . . . . .79
Setting Up a USB Driver in Windows 2000 . . . . . . . . .83
Setting Up a USB Driver in Windows Me . . . . . . . . . . .86
Setting Up a USB Driver in Windows XP . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Removing the USB Driver from Windows 98 or
Windows Me . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .88
Removing the USB Driver from Windows 2000 . . . . . . 91
Removing the USB Driver from Windows XP . . . . . . . .94
Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
Front-Panel Lights and Error Conditions . . . . . . . . . . .99
Contact Us . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
Frequently-Asked Questions. . . . . . . . . 101
Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
Cable Modem . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .104
Glossary. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Software License . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
Home
X
ExitPrint
vi
SBG900 User Guide
Page 7

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Overview
Thank you for purchasing a Motorola® SURFboard® Wireless Cable Modem Gateway SBG900 for your home,
home office, or small business/enterprise. Applications where the SURFboard Gateway (SBG) is especially useful
include:
• Households having multiple computers requiring connection to the Internet and each other
• Small businesses or home offices requiring fast, affordable, and secure Internet access
• Internet gamers desiring easier setup for:
®
— Programs such as DirectX
— Sites such as MSN Games by Zone.com or Battle.net
• Video conferencing
7 or DirectX® 8
®
The features and physical appearance of your SBG900 may differ slightly from the picture.
Home
X
ExitPrint
1
SBG900 User Guide
Page 8

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Home networking enables you to access and move information between two or more computers in your home or
business. Your home network connects to the cable TV system and enables you to connect to the Internet or other
networks connected to the Internet. The SBG900 acts as the
and the Internet. It directs (routes) computer data to the Internet and between your computers. A SURFboard
cable modem in the SBG passes information between your home network computers and the Internet. An
SBG900:
central connection point
between your computers
• Combines a SURFboard cable modem, IEEE 802.11g wireless access point, Ethernet 10/100Base-T
connection, and an advanced firewall into one compact product
• Eliminates the need for four or five separate products, enabling you to maximize the potential of your existing
resources
• Enables you to create a custom network sharing a single broadband connection, files, and other peripherals
like scanners, with or without wires
• Offers enhanced network security for wired and wireless users
• Provides easy setup
• Enables cable operators to add future value-added services
This product is subject to change. Not all features described in this guide are available on all SBG900 models.
For the most recent documentation, visit the Product Documentation page on the Motorola Broadband website
http://broadband.motorola.com/.
Easy Setup
It is much easier to configure a local area network (LAN) using an SBG900 than it is using typical networking
equipment:
• The Installation Assistant application on the
enables easy connection to the cable network.
Motorola SURFboard Wireless Cable Modem Gateway
CD-ROM
• For basic operation, most default settings require no modification.
• The Setup Program provides a graphical user interface (GUI) for easy configuration of necessary wireless,
Ethernet, router, DHCP, and security settings. For a list of issues, see “Basic Configuration”.
Network Connection Types
The SBG900 provides different network connection types for your computers to exchange data. The connection
between your computers and the SBG900 may be with a wireless or a wired connection or a combination of the
two. Your network can use one or any combination of all the following network connections:
• Ethernet local area network (LAN)
• Wireless LAN (IEEE 802.11g that also supports IEEE 802.11b devices)
• Universal Serial Bus (USB)
Home
X
ExitPrint
2
SBG900 User Guide
Page 9

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Powerful Features in a Single Unit
An SBG900 combines high-speed Internet access, networking, and computer security for a home or small-office
LAN. An SBG900 provides:
• An integrated high-speed SURFboard cable modem for continuous broadband access to the Internet and
other online services, with much faster data transfer than traditional dial-up or ISDN modems
• A single broadband connection for up to 253 computers to surf the web; all computers on the LAN
communicate as if they were connected to the same physical network
• An IEEE 802.11g wireless access point to enable laptop users to remain connected while moving around the
home or small office or to connect desktop computers without installing network wiring. Depending on
distance, wireless connection speeds can match that of Ethernet.
• A USB connection for a single PC
• A dual-purpose 10/100Base-T Ethernet uplink port supporting half- or full-duplex connections and Auto-MDIX
• Routing for a wireless LAN or a wired Ethernet LAN connected using a hub or switch
• A built-in DHCP server to easily configure a combined wired and/or wireless Class C private LAN
• An advanced firewall supporting stateful-inspection, intrusion detection, DMZ, denial-of-service attack
prevention, and Network Address Translation (NAT)
• Virtual private network (VPN) pass-through operation supporting IPSec, PPTP, or L2TP to securely connect
remote computers over the Internet
• Port Forwarding to configure ports to run applications having special network requirements
Home
X
ExitPrint
3
SBG900 User Guide
Page 10

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
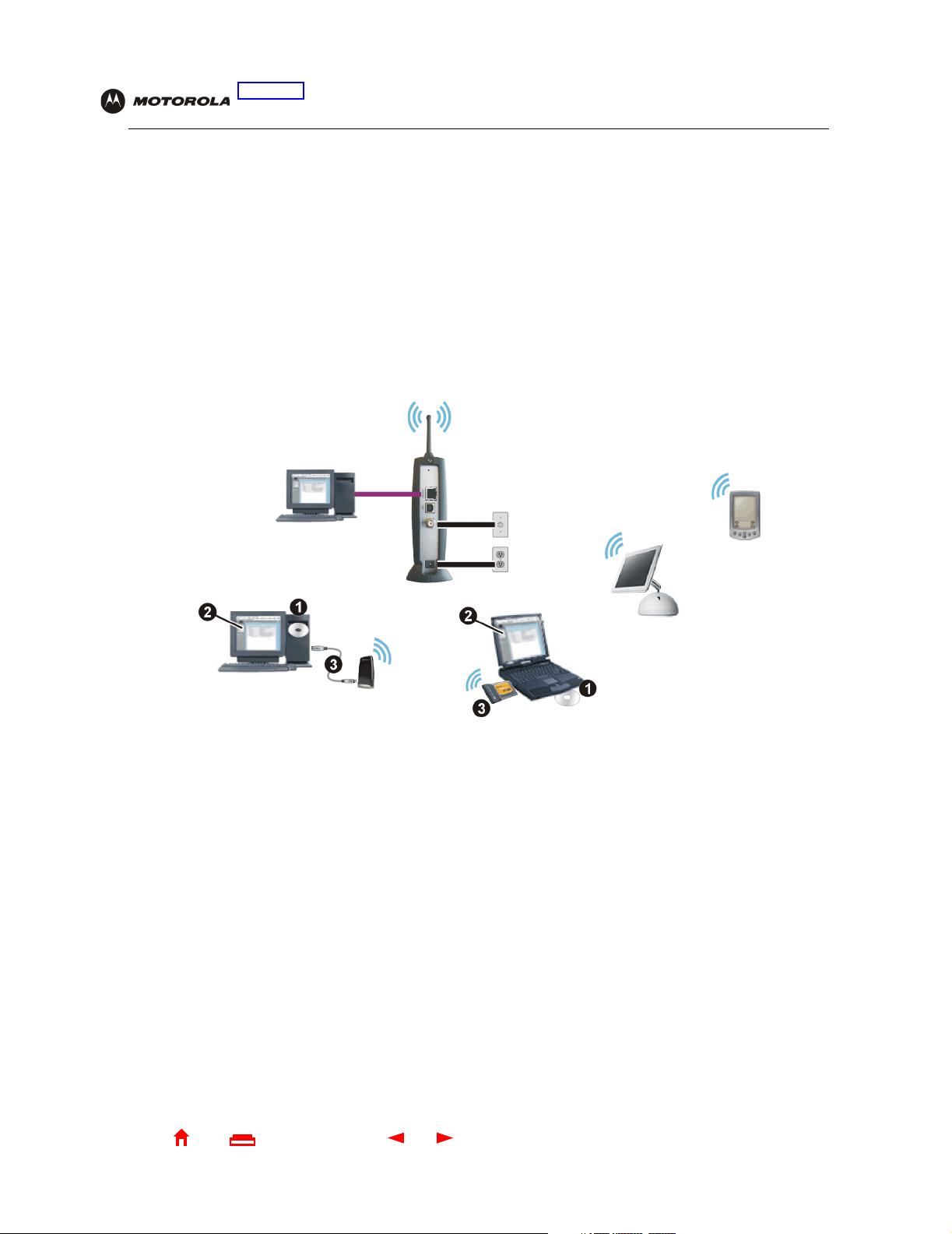
Sample LAN
The sample LAN shown in the figure contains the following devices, all protected by the SBG900 firewall:
• A PDA connected through the wireless connection
• One desktop Macintosh on a wireless connection
• One desktop PC on a wireless connection using a Motorola USB Adapter
• A laptop PC on a wireless connection connected using a Motorola PC Card
• One computer connected directly to Ethernet port one
• Three computers connected to Ethernet port two using a hub or switch
• One PC connected to the USB port
Sample SBG900 hybrid network
Internet
Ethernet
Hub or switch
USB
SBG900
High-speed HFC
cable network
PCC11b
Wireless Card
Firewall
Wireless
USB to Ethernet
Wireless Adapter
Home
X
ExitPrint
4
SBG900 User Guide
Page 11

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Optional Accessories
While any IEEE 802.11g or IEEE 802.11b compliant client product will work with the SBG900, Motorola has
wireless adapters available for use with the SBG900.
You can use the Motorola PCC11b wireless card or the USB11b wireless adapter, which comply with the
IEEE 802.11b wireless standard, to connect a PC to the wireless LAN:
USB11b Wireless
Adapter
PCC11b Wireless Card A credit-card sized adapter that connects a laptop to the wireless LAN. You can roam in, or
Connects a desktop, laptop, printer, or other peripheral device to the wireless LAN. It has a
built-in antenna and a six feet (two meter) long cable that connects to the PC USB port.
Its light indicates:
• Off — Not connected to a USB port or not receiving power from the PC
• Yellow — Not installed or initializing
• Green — Installed and operational
• Flashing Green — Receiving data from another wireless LAN device
• Flashing Yellow — Transmitting data to another wireless LAN device
around, the home or small office and remain connected. It fits in a
standard slot on the laptop supporting 3.3 Volt PC card. The PCC11b has also has a
built-in antenna.
PCMCIA Type II
Motorola USB11b Wireless Adapter (left) and PCC11b Wireless Card
For installation instructions, see the documentation provided with each product.
Home
X
ExitPrint
5
SBG900 User Guide
Page 12

Front Panel
Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
The front panel provides indicator lights.
The model number on your SBG may be different than in some
illustrations and screen images.
1
2
3
4
5
6
Key Light Flashing On
1 POWER None The power supply is working properly
2
RECEIVE Scanning for a receive (downstream)
channel connection
SEND Scanning for a send (upstream) channel
3
connection
ONLINE Scanning for a network connection The startup process is complete and the SBG900
4
5
PC/ACTIVITY Transmitting or receiving data A computer or other device is connected to the
6
WIRELESS Wireless activity Wireless feature is functioning normally
The downstream channel is connected
The upstream channel is connected
is online
USB or Ethernet port
Home
X
ExitPrint
6
SBG900 User Guide
Page 13

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Rear Panel
The rear panel provides cabling connectors, status lights, and the power receptacle:
1
2
3
4
5
Key Item Description
1
2 Use the
3 For Windows
4 The
5 The +12
•
If you experience a problem, you can push this recessed button to restart the SBG900 (see
“Troubleshooting”). To reset all values to their defaults, hold down the button for more than five
seconds
appropriate communications channels.
Ethernet-equipped computer, hub, bridge, or switch.
SBG900 USB port to a Macintosh or UNIX computer.
. Resetting may take 5 to 30 minutes because the SBG900 must find and lock on the
ETHERNET port to connect an Ethernet LAN cable with RJ-45 connectors to an
CABLE port provides a connection to the coaxial cable outlet.
VDC power connector to the external power supply.
only
, use the USB port for Connecting a PC to the USB Port. You cannot connect the
Home
X
ExitPrint
7
SBG900 User Guide
Page 14

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Label on the Bottom of the SBG900
To receive data service, you need to provide the MAC address marked HFC MAC ID
provider
:
HFC MAC ID
SBG900 LAN Choices
The SBG900 enables connection of up to 253 client computers on a combination of:
• Wireless LAN
• Wired Ethernet LAN
• USB Connection
to your cable service
Each computer needs appropriate network adapter hardware and driver software. The clients on the Ethernet,
wireless, or USB interfaces can share:
• Internet access with a single cable service provider account, subject to cable provider terms and conditions
• Files, printers, storage devices, multi-user software applications, games, and video conferencing
Wireless and wired network connections use Windows networking to share files and peripheral devices such as
printers, CD-ROM drives, floppy disk drives, and Iomega
®
Zip Drives.
Home
X
ExitPrint
8
SBG900 User Guide
Page 15
Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Wireless LAN
Wireless communication occurs over radio waves rather than a wire. Like a cordless telephone, a wireless LAN
uses radio signals instead of wires to exchange data. A wireless network eliminates the need for expensive and
intrusive wiring to connect computers throughout the home or office. Mobile users can remain connected to the
network even when carrying their laptop to different locations in the home or office.
Each computer on a wireless LAN requires an adapter described in “Optional Accessories”:
Laptop PCs Use a Motorola PCC11b Wireless Card in the PCMCIA slot.
Desktop PCs Use a Motorola USB11b Wireless Adapter to connect the USB port.
Sample wireless network connections
To set up the SBG900, on a computer wired to the SBG900 over Ethernet or USB, perform the procedures in
“Setting Up the Wireless LAN
To set up each wireless client (station):
1 Insert the
PCC11b and USB11b Wireless Adapter
”. Do not attempt to configure the SBG900 over a wireless connection.
CD-ROM in the CD-ROM drive on the client.
2 Install the device software from the CD.
3 Connect the Motorola PCC11b wireless card or USB11b wireless adapter following the instructions supplied
with the card or adapter.
Home
X
ExitPrint
9
SBG900 User Guide
Page 16
Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
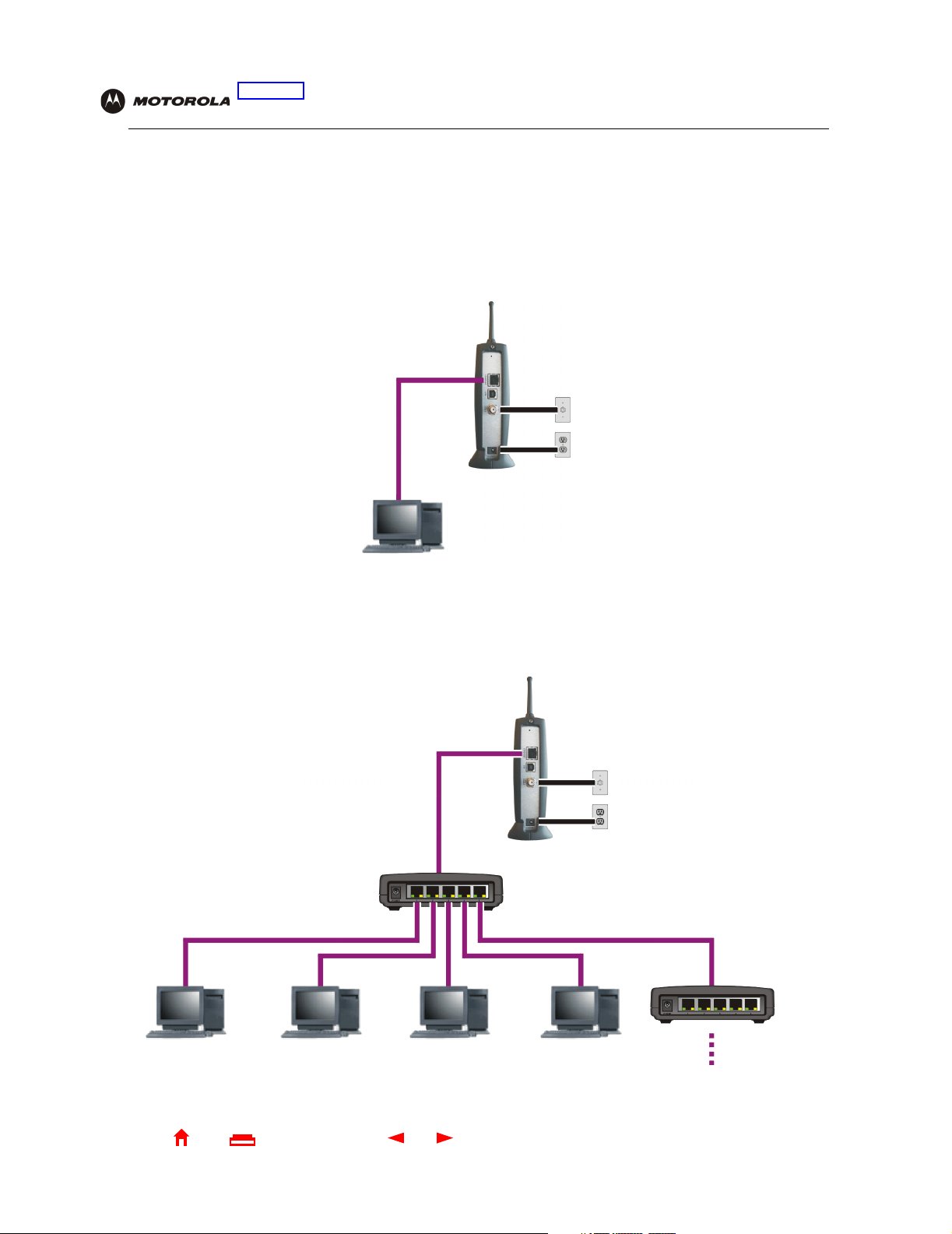
Wired Ethernet LAN
Each computer on the 10/100Base-T Ethernet LAN requires an Ethernet network interface card (NIC) and driver
software installed. Because the SBG900 Ethernet port supports auto-MDIX, you can use straight-through or
cross-over cable to connect a hub, switch, or computer. Use category 5 cabling for all Ethernet connections.
The physical wiring arrangement has no connection to the logical network allocation of IP addresses.
Sample Ethernet to computer connection
Coaxial
cable
Category 5 Ethernet cable
A wired Ethernet LAN with more than one computer requires one or more hubs or switches. You can connect a
hub or switch to the Ethernet port on the SBG900.
The following illustration is an example of an Ethernet LAN you can set up using the SBG900. Cable the LAN in an
appropriate manner for the site. A complete discussion of Ethernet cabling is beyond the scope of this document.
Sample Ethernet connection to hubs or switches
Home
Add additional hubs or switches
for further expansion
X
ExitPrint
10
SBG900 User Guide
Page 17

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
USB Connection
You can connect a single PC running Windows®98, Windows XP™, Windows Me®, or Windows®2000 to the
SBG900 USB V1.1 port. For cabling instructions, see “Connecting a PC to the USB Port”.
Caution!
Before plugging in the USB cable, be sure the Motorola SURFboard Wireless Cable Modem Gateway
CD-ROM is inserted in the PC CD-ROM drive.
Sample USB connection
Home
X
ExitPrint
11
SBG900 User Guide
Page 18
Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Security
The SBG900 provides:
• A firewall to protect the SBG900 LAN from undesired attacks over the Internet
• Security measures to prevent eavesdropping of wireless data
Network Address Translation (NAT) provides some security because the IP addresses of SBG900 LAN computers
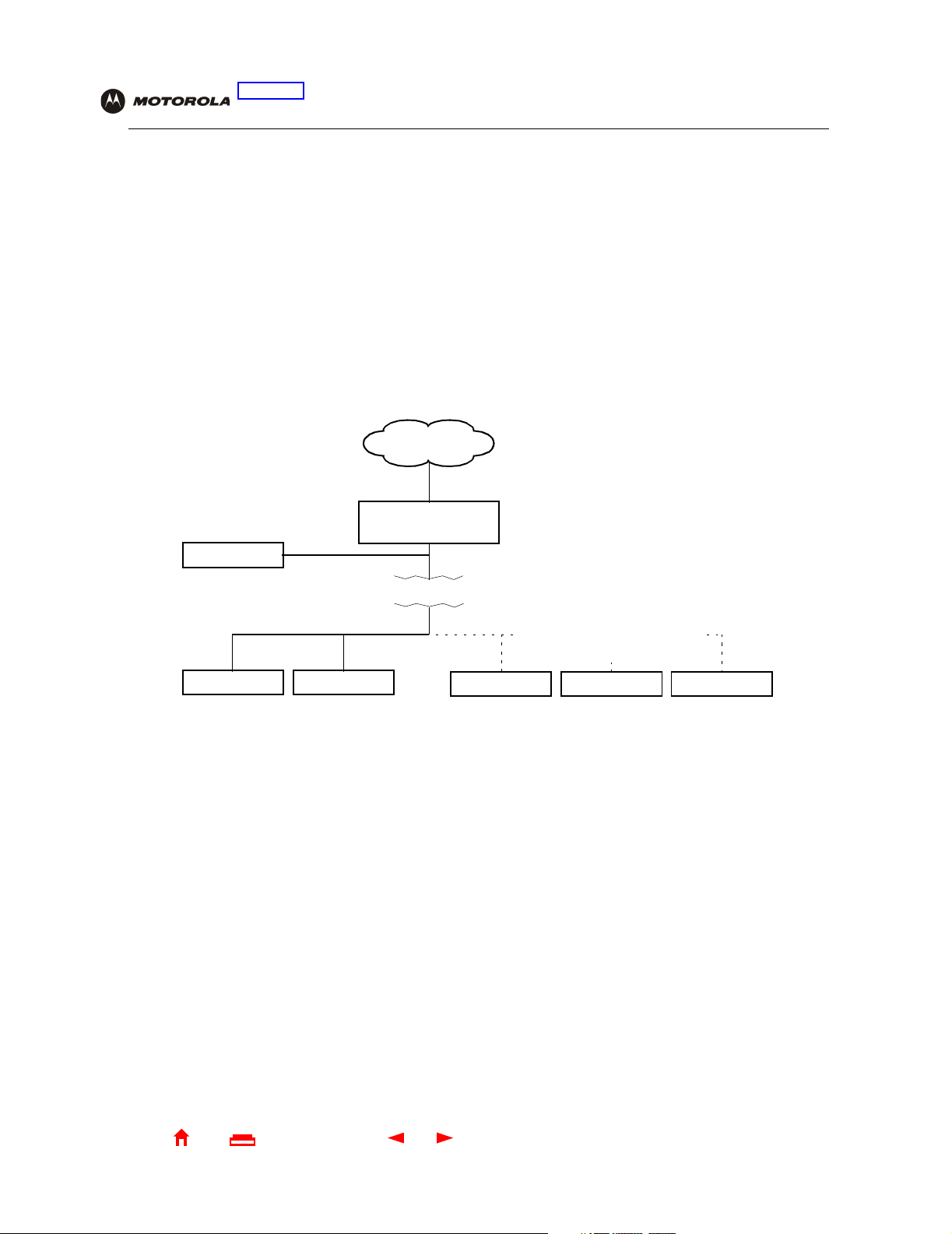
are not visible on the Internet.
The logical network diagram does not necessarily correspond to the network cabling. A full discussion of network
security is beyond the scope of this document.
SBG900 security measures shown in a logical network diagram
Internet
SBG900
DMZ computer
Firewall
ComputerComputer
Wired Ethernet LAN Wireless LAN
Wireless Security:
WEP shared key encryption
MAC access control list
Disable ESSID Broadcast
LaptopComputer PDA
Firewall
The SBG900 firewall protects the SBG900 LAN from undesired attacks and other intrusions from the Internet. It
provides an advanced integrated stateful-inspection firewall supporting intrusion detection, session tracking, and
denial-of-service attack prevention. The firewall:
• Maintains state data for every TCP/IP session on the OSI network and transport layers
• Monitors all incoming and outgoing packets, applies the firewall policy to each one, and screens for improper
packets and intrusion attempts
• Provides comprehensive logging for all:
— User authentications
— Rejected internal and external connection requests
— Session creation and termination
— Outside attacks (intrusion detection)
You can configure the firewall filters to set rules for port usage. For information about choosing a predefined
firewall policy template, see “Setting the Firewall Policy”.
Home
X
ExitPrint
12
SBG900 User Guide
Page 19

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
DMZ
A de-militarized zone (DMZ) is one or more computers logically located outside the firewall between an SBG900
LAN and the Internet. A DMZ prevents direct access by outside users to private data.
For example, you can set up a web server on a DMZ computer to enable outside users to access your website
without exposing confidential data on your network.
A DMZ can also be useful to play interactive games that may have a problem running through a firewall. You can
leave a computer used for gaming
information, see Gaming Configuration Guidelines.
only
exposed to the Internet while protecting the rest of your network. For more
Port Triggering
When you run a PC application that accesses the Internet, it typically initiates communications with a computer on
the Internet. In some applications, especially gaming, the computer on the Internet also initiates communications
with your PC. Because NAT does not normally allow these incoming connections to occur, the SBG900 supports
port triggering.
The SBG900 is preconfigured with port triggering for common applications. You can also configure additional port
triggers if needed on the Gateway > PORT TRIGGERS — custom Page.
Wireless Security
Because wireless LAN signals are transmitted using radio signals, it may be possible for your neighbor or
someone else you do not want accessing your wireless LAN. You need to limit access to only the intended
persons. To prevent unauthorized eavesdropping of data transmitted over the wireless LAN, you must enable
wireless security.
The default SBG900 settings provide no security for transmitted data.
The SBG900 enables you to use the following wireless security measures:
• Restrict access to computers having the same unique network name as the SBG900
• Encrypt data transmitted over the wireless interface by configuring a Wired Equivalency Privacy (WEP) key
on the SBG900 and wireless LAN clients (stations)
• Define a MAC access control list to restrict wireless LAN access to clients based on the MAC address.
If you disable ESSID broadcasting to enable closed network operation, the SBG900 does not transmit the network
name (ESSID). This provides additional protection because only wireless stations configured with your network
name can communicate with the SBG900. Closed network operation is an enhancement of the IEEE 802.11b
standard.
For information about configuring a wireless security, see “Setting Up the Wireless LAN”.
Home
X
ExitPrint
13
SBG900 User Guide
Page 20

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Port Forwarding
Port forwarding is the configuration of SBG logical data ports for applications having special network
requirements.
The SBG900 opens logical data ports when a computer on its LAN sends data, such as e-mail messages or web
data, to the Internet. A logical data port is different from a physical port, such as an Ethernet port. Data from a
protocol must go through certain data ports. Here are the data ports used by some protocols:
Protocol Port
FTP 20, 21
HTTP 80
NTP 123
Secure Shell 22
SMTP e-mail 25
Teln et 23
Some applications, such as games and videoconferencing, require multiple data ports. If you enable NAT, this can
cause problems because NAT assumes that data sent through one port will return to the same port. You may need
to configure port forwarding to run applications with special requirements.
To configure port forwarding, you must specify an inbound (source) port or range of ports. The inbound port opens
only when data is sent to the inbound port and closes again after a specified time elapses with no data sent to it.
You can configure up to 32 port forwarding entries using the Gateway > PORT FORWARDING — config Page.
Virtual Private Net work s
The SBG900 allows multiple tunnel VPN pass-through operation to securely connect remote computers over the
Internet through the SBG900. The SBG900:
• Is compatible with Point to Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) and Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP)
• Is fully interoperable with any IPSec client or gateway and ANX certified IPSec stacks
Relate d Documentation
The following documents also provide information you can use with the SBG900:
•
SURFboard Wireless Cable Modem Gateway Quick Start Guide
•
PCC11b Wireless Card Quick Start Guide and on-line help on the PCC11b and USB11b Wireless Adapter
CD-ROM
•
USB11b Wireless Adapter Quick Start Guide and on-line help on the PCC11b and USB11b Wireless Adapter
CD-ROM
For the most recent documentation, visit the Product Documentation page on the Motorola Broadband website
http://broadband.motorola.com.
Home
X
ExitPrint
14
SBG900 User Guide
Page 21

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Installation
The following subsections provide information about installing the SBG900 hardware:
• Before You Begin
• Precautions
• Signing Up for Service
• Computer System Requirements
• Connecting the SBG900 to the Cable System
• Cabling the LAN
• Obtaining an IP Address for Ethernet
• Connecting a PC to the USB Port
For information about wireless LAN setup, see “Setting Up the Wireless LAN”.
Before You Begin
Before you begin the installation, check that you received the following items with your SBG900:
Item Description
Power adapter
cord
10/100Base-T
Ethernet cable
USB cable Connects to the USB port
Motorola SURFboard
Wireless Cable Modem
Gateway
You will need 75-ohm coaxial cable with F-type connectors to connect the SBG900 to the nearest cable outlet. If a
TV is connected to the cable outlet, you may need a 5 to 900 MHz RF splitter and two additional coaxial cables to
use both the TV and the SBG900.
Determine the connection types you will make to the SBG900. Check that you have the required cables, adapters,
and adapter software. You may need:
Wireless LAN W
Wired Ethernet LAN Ethernet cables and network interface cards (NICs) with accompanying installation software
CD-ROM
ireless adapter and driver software for each computer having a wireless connection (see
“Optional Accessories”)
To connect more than one computer to the SBG900, one or more Ethernet hubs or switches
Connects the SBG 900 to the external AC power supply
Connects to the Ethernet port
Contains this
User Guide
and USB drivers
USB A USB cable and the
containing the software for USB installation
Coaxial cable, RF splitters, hubs, and switches are available at consumer electronic stores.
Home
X
ExitPrint
Motorola SURFboard Wireless Cable Modem Gateway
15
SBG900 User Guide
CD-ROM
Page 22

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Precautions
Postpone SBG900 installation until there is no risk of thunderstorm or lightning activity in the area. SBG900.
To avoid damaging the SBG900 or computers with static electricity:
Before you connect or
disconnect the USB or
Ethernet cables,
touch the coaxial cable
connector on the
always
SBG900.
Always make the wall
connection first.
• To avoid potential shock, always unplug the power cord from the wall outlet or other power source before
disconnecting it from the SBG900 rear panel.
• To prevent overheating the SBG900, do not block the ventilation holes on the sides of the unit.
• Do not open the unit. Refer all service to your cable service provider.
• Wipe the unit with a clean, dry cloth. Never use cleaning fluid or similar chemicals. Do not spray cleaners
directly on the unit or use forced air to remove dust.
Signing Up for Service
You must sign up with a cable service provider to access the Internet and other online services.
To activate your service, call your local cable service provider.
You need to provide the MAC address marked HFC MAC ID printed on the
you printed this document, you can record it here:
Label on the Bottom of the SBG900. If
00 : ______ : ______ : ______ : ______ : ______
You should ask your cable service provider the following questions:
• Do you have any special system requirements?
• When can I begin to use my SBG900?
• Are there any files I need to download after I am connected?
• Do I need a user name or password to access the Internet or use e-mail?
Home
X
ExitPrint
16
SBG900 User Guide
Page 23

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Computer System Requirements
You can connect Microsoft Windows, Macintosh, UNIX, or Linux computers equipped as follows to the
SBG900 LAN:
•
One
of the following:
Ethernet 10Base-T or 10/100Base-T Ethernet adapter with proper NIC driver software installed
Wireless
Any IEEE 802.11g or IEEE 802.11b device
For information about the Motorola PCC11b Wireless Card (
USB11b Wireless Adapter, see “Optional Accessories
”.
PCMCIA type II 3.3 V slot) or
• PC with Pentium class or better processor
• Windows
or Linux operating system with operating system CD-ROM available
®
98, Windows® 98 SE, Windows Me®, Windows® 2000, Windows XPTM, Windows NT®, Macintosh,
• Minimum 16 MB RAM recommended
• 10 MB available hard disk space
You can use any web browser such as Microsoft® Internet Explorer or Netscape Navigator® with the SBG900.
You can use the USB connection with any PC running Windows 98, Windows 2000, Windows Me, or Windows XP
that has a USB interface. The USB connection requires special USB driver software that is supplied on the
Motorola SURFboard Wireless Cable Modem Gateway
Downloads page http://broadband.motorola.com/noflash/usb_drivers.asp on the Motorola Broadband website.
CD-ROM. You can upgrade your USB drivers from the
Home
X
ExitPrint
17
SBG900 User Guide
Page 24

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Connecting the SBG900 to the Cable System
1 Be sure the computer is on and the SBG900 is unplugged.
2 Connect one end of the coaxial cable to the cable outlet or splitter.
3 Connect the other end of the coaxial cable to the cable connector on the SBG900.
Hand-tighten the connectors to avoid damaging them.
4 Insert the
Motorola SURFboard Wireless Cable Modem Gateway
CD-ROM into the CD-ROM drive.
5 Plug the power cord into the power connector on the SBG900.
6 Connect the external power supply.
7 Plug the power cord into the electrical outlet.
not in use. The first time you plug in the SBG900, allow 5 to 30 minutes to find and lock on the appropriate
communications channels.
Step 3
This turns the SBG900 on. You do not need to unplug it when
Step 2
Steps 5 to 7
8 Check that the lights on the front panel cycle through this sequence:
POWER Turns on when AC power is connected to the SBG900. Indicates that the power supply is working
properly.
RECEIVE Flashes while scanning for the receive channel. Changes to solid green when the receive channel is
locked.
SEND Flashes while scanning for the send channel. Changes to solid green when the send channel is
locked.
ONLINE Flashes during SBG900 registration and configuration. Changes to solid green when the SBG900 is
registered.
PC/ACTIVITY Flashes when the SBG900 is transmitting or receiving data.
Cabling the LAN
After connecting to the cable system, you can connect your wired Ethernet LAN. Some samples are shown in
“Wired Ethernet LAN”. On each networked computer, you must install proper drivers for the Ethernet NIC.
Detailed information about network cabling is beyond the scope of this document.
Home
X
ExitPrint
18
SBG900 User Guide
Page 25
Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Obtaining an IP Address for Ethernet
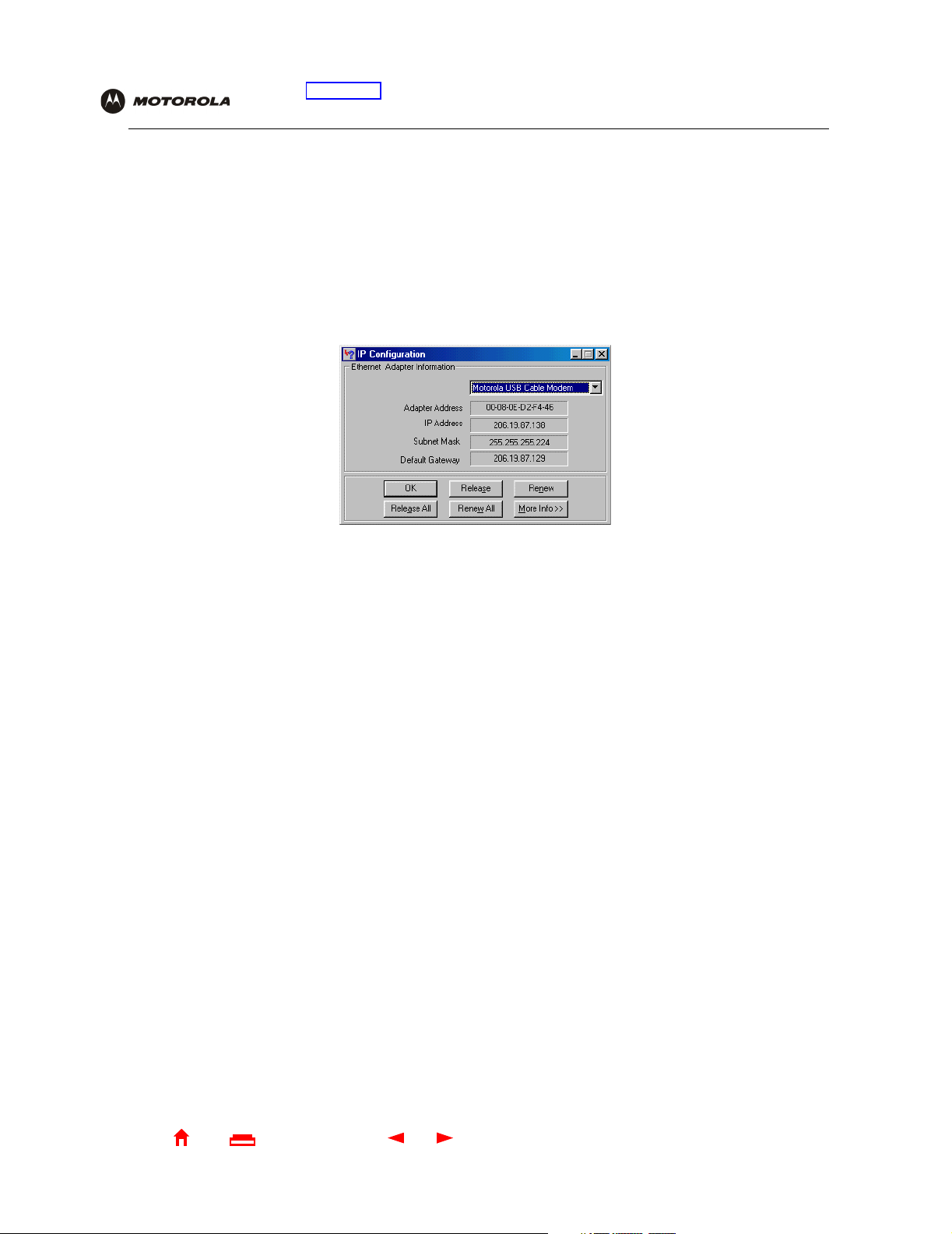
Obtaining an IP Address in Windows 98, Windows 98 SE, or Windows Me
You must do the following on each Ethernet client PC running Windows 98, Windows 98 SE, or Windows Me:
1 On the Windows Desktop, click Start.
2 Select Run. The Run window is displayed.
3 Type winipcfg.exe and click OK. The IP Configuration window is displayed:
4 Click the Renew button to obtain an IP address for the PC from the DHCP server on the SBG900.
Obtaining an IP Address in Windows 2000 or WindowsXP
You must do the following on each Ethernet client PC running Windows 2000 or Windows XP:
1 On the Windows Desktop, click Start.
2 Select Run. The Run window is displayed.
3 Type cmd and click OK to display a command prompt window.
4 Type ipconfig /renew and press ENTER to obtain an IP address for the PC from the DHCP server on the
SBG900.
5 Type exit and press ENTER to return to Windows.
Obtaining an IP Address on Macintosh or UNIX Systems
Follow the instructions in your user manual.
Home
X
ExitPrint
19
SBG900 User Guide
Page 26
Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Connecting a PC to the USB Port
You can connect a single PC running Windows 98, Windows XP, Windows Me, or Windows 2000 to the SBG900
USB port.
Caution!
Before plugging in the USB cable, be sure the Motorola SURFboard Wireless Cable Modem Gateway
CD-ROM is inserted in the PC CD-ROM drive.
To connect a PC to the USB port:
1 Insert the
Motorola SURFboard Wireless Cable Modem Gateway
CD-ROM in the CD-ROM drive.
2 Connect the USB cable to the USB port on the SBG900.
3 Connect the other end to the USB port on the computer.
4 Install the USB driver following the appropriate procedure for “Setting Up a USB Driver”.
Home
X
ExitPrint
20
SBG900 User Guide
Page 27
Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Basic Configuration
The following sections provide information about basic SBG900 configuration:
• Starting the SBG900 Setup Program
• Changing the Default Password
• Getting Help
• Setting the Firewall Policy
• Gaming Configuration Guidelines
For more advanced configuration information, see “Configuring TCP/IP”, “Setting Up the Wireless LAN”, or
“Setting Up a USB Driver”.
For normal operation, you do not need to change most default settings.
summarize the issues you must be aware of:
Caution!
To prevent unauthorized configuration, change the default password
configure the SBG900. See “Changing the Default Password”.
Firewalls are not foolproof. Choose the most secure firewall policy you can. See “Setting the Firewall
Policy”.
For a wireless LAN only, be sure you follow the instructions in “Setting Up the Wireless LAN”.
The following caution statements
immediately
when you first
Home
X
ExitPrint
21
SBG900 User Guide
Page 28

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Starting the SBG900 Setu p Pr ogram
1 On a computer wired to the SBG900 over Ethernet or USB, open a web browser.
the SBG900 over a wireless connection.
Do not attempt to configure
2 In the Address or Location field, type http://192.168.100.1 and press ENTER to display the Login window:
3 In the User ID field, type the
User Name;
4 In the Password field, type the
Home
X
ExitPrint
Password
the default is “admin” (this field is case sensitive).
; the default is “motorola” (this field is case sensitive).
22
SBG900 User Guide
Page 29
Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
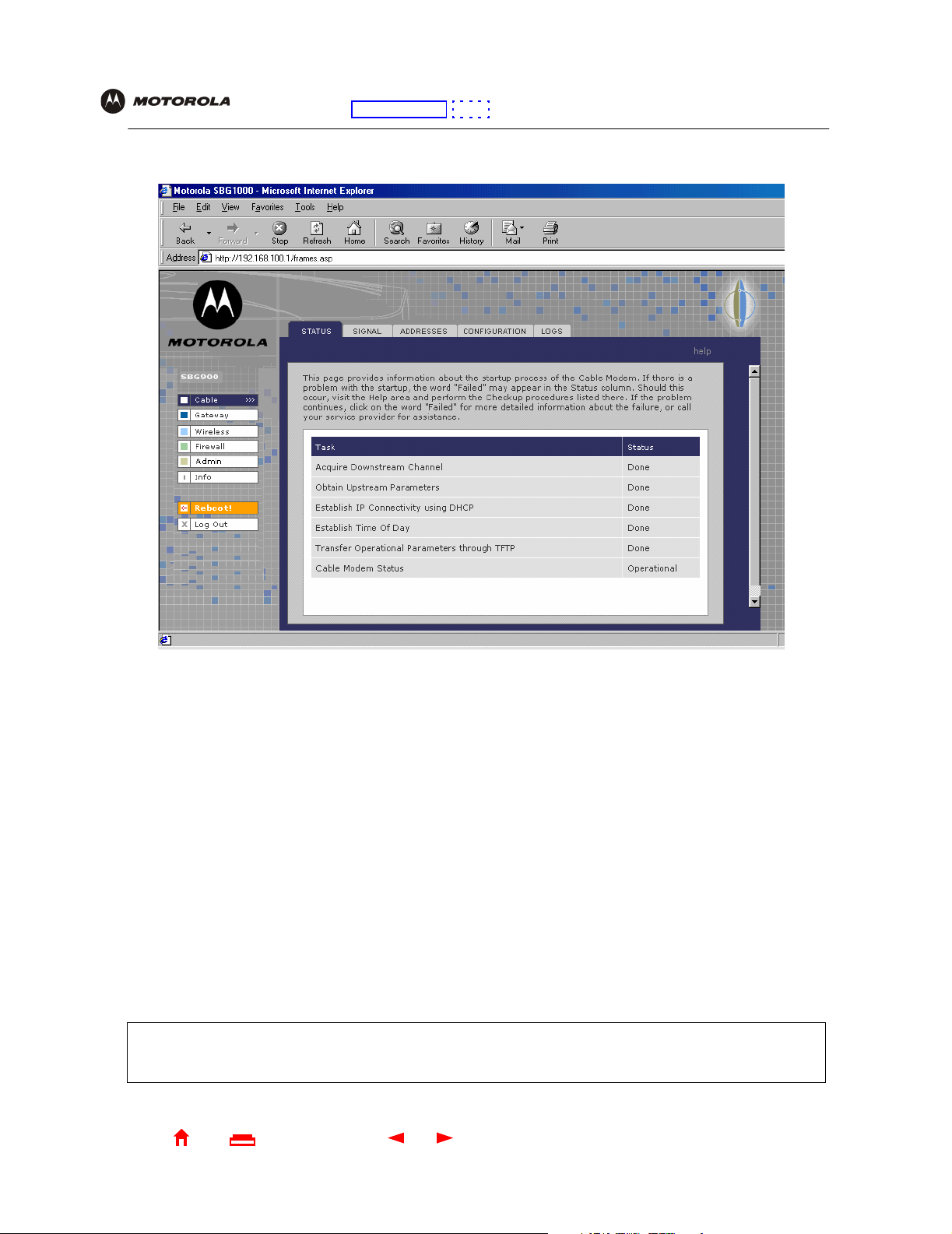
5 Click Log In to display the SBG900 user configuration and status windows:
Click To Perform
Cable Configure and monitor the cable system connection.
Gateway Configure and monitor the gateway preferences (see Configuring the Gateway).
Wireless Configure and monitor the wireless interface (see “Setting Up the Wireless LAN”).
Firewall Configure and monitor the firewall (see “Setting the Firewall Policy”).
Admin Changing the Default Password.
Info Display information about the
Reboot Restart the SBG900. It is the same as pressing the reset button on the rear panel for less than five
seconds.
Log Out Log out of the SBG900.
If you have difficulty starting the SBG900 Setup Program, see “Troubleshooting” for information.
Router is a configuration option that may appear on your window but may not be supported.
For some settings, after you edit the field and click Apply, you are warned that you must reboot for your change
to take effect. Rebooting takes 10 to 15 seconds. After rebooting, you must log-in again.
SBG900 Setup Program.
Home
X
ExitPrint
23
SBG900 User Guide
Page 30
Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
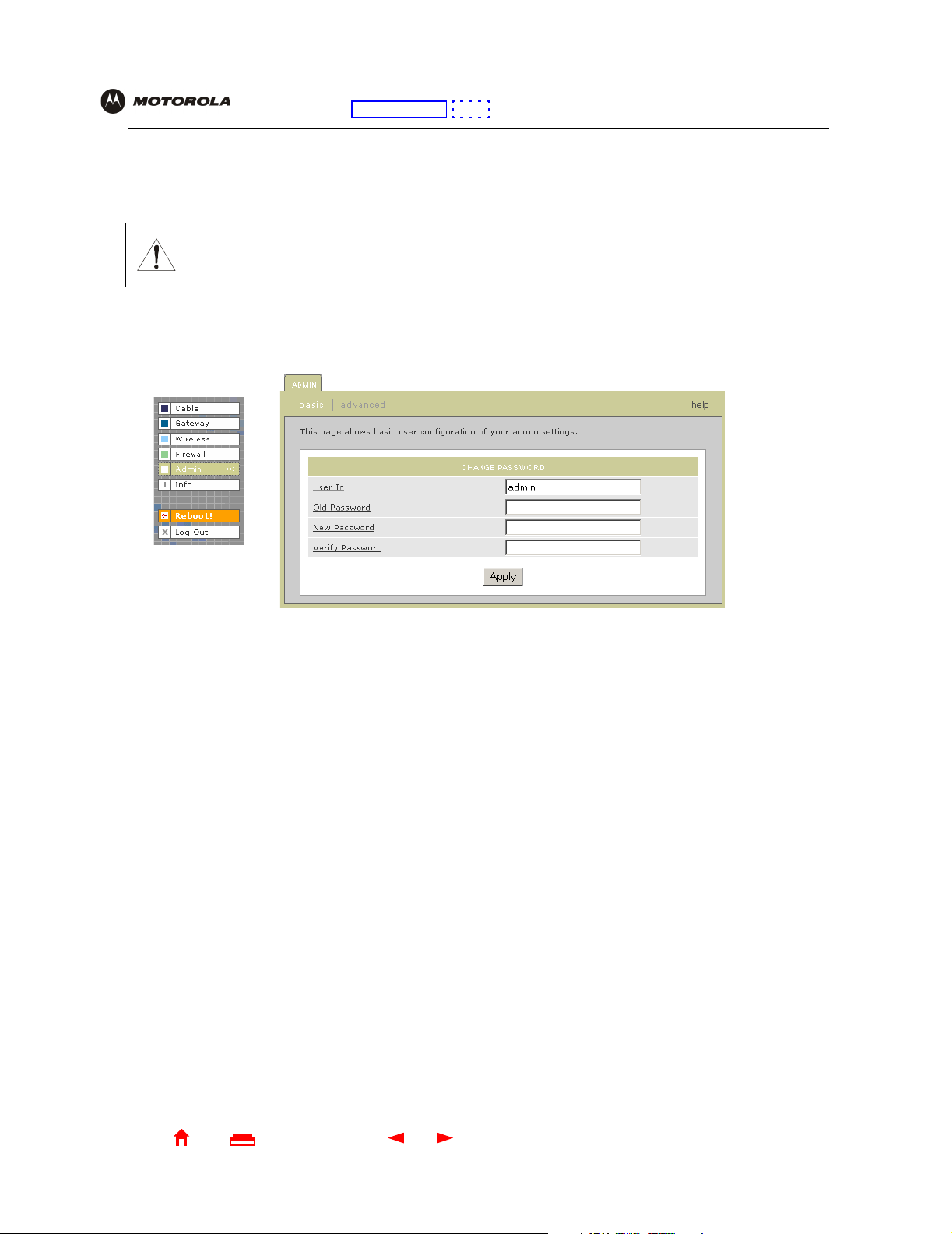
Changing the Default Password
Caution!
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
To prevent unauthorized configuration, change the default password
configure the Motorola SURFboard Wireless Cable Modem Gateway.
To change the default password:
immediately
1 On the SBG900 Setup Program screen, click Admin to display the ADMIN — basic page:
2 In the Old Password field, type the old
sensitive).
password
. The default password is “motorola” (this field is case
when you first
3 In the New Password field, type the new
4 In the Verify Password field, type the new
5 Click Apply to apply your changes.
Home
X
ExitPrint
password
password
24
.
again.
SBG900 User Guide
Page 31

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Enabling Remote Access
Enabling remote access permits you to access the SBG900 from the Internet. You must know the userid,
password, and public IP address assigned to your SBG900 to obtain access to the configuration pages from the
Internet. Remote access is provided using a Web browser on the remote client, and connecting to the Web server
on the SBG900.
To access the SBG900 remotely:
1 On the SBG900 Setup Program screen, click Admin to display the ADMIN — basic page.
2 Click advanced to display the ADMIN — advanced page.
3 Click the box next to Enable remote access to enable it.
4 Click Apply to apply your change.
Home
X
ExitPrint
25
SBG900 User Guide
Page 32

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Getting Help
To get help on any underlined item or field, click the text. For example, if you click a field or the help button on the
ADMIN — basic page, the following help is displayed:
This button also displays
help for the window.
You can scroll to browse the help or click another item to display help for that item.
Home
X
ExitPrint
26
SBG900 User Guide
Page 33

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Setting the Firewall Poli cy
The SBG900 firewall protects the SBG900 LAN from undesired attacks and other intrusions from the Internet. This
section describes using the Firewall > POLICY — basic page to
templates provided with the SBG900.
Caution!
Firewalls are not foolproof. Choose the most secure firewall policy you can. To enable easy network
setup, the default firewall policy is None, which provides no security.
To select a predefined policy for all packets processed by the SBG900 firewall:
1 On the SBG900 Setup Program left panel, click Firewall.
2 Click POLICY.
3 Click basic to display the predefined firewall policy templates:
choose one of the predefined firewall policy
Home
X
ExitPrint
27
SBG900 User Guide
Page 34

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
4 Select the most secure firewall policy you can:
High The safest predefined firewall policy template, providing the highest security.
setting.
Medium A predefined firewall policy template providing a common configuration having modest risk.
Low A predefined firewall policy template providing minimum security, with a higher risk of intrusions.
Custom You may need to create a custom firewall policy on the Firewall > POLICY — advanced Page
create a custom policy unless you have the necessary expertise and the need to do so.
None Disables the firewall. To enable easy network setup, it is the default.
High, Medium, or Low to improve your security.
After you set up your network, use
Motorola recommends this
. Do not
5 Click Apply to apply your changes.
After you edit some fields and click Apply, you are warned that you must reboot for your change to take effect.
Rebooting takes 10 to 15 seconds. After rebooting, you must log-in again.
If you have the need, you can:
• View the rules for the High, Medium, or Low predefined policy templates or create a custom policy on the
Firewall > POLICY — advanced Page
• Configure a firewall alert on Firewall > ALERT — basic Page and Firewall > ALERT — email Page
• View the firewall logs on the Firewall > LOGS Page
For information about how the firewall can affect gaming, see “Gaming Configuration Guidelines”.
The predefined policies provide outbound Internet access for computers on the SBG900 LAN. The SBG900
firewall uses stateful inspection to allow inbound responses when there already is an outbound session running
corresponding to the data flow. For example, if you use a web browser, outbound HTTP connections are permitted
on port 80. Inbound responses from the Internet are allowed because an outbound session is established.
When required, you can configure the SBG900 firewall to allow inbound packets without first establishing an
outbound session. You also need to configure a port forwarding entry on the
Gateway > PORT FORWARDING — config Page or a DMZ client on the Gateway > LAN — nat config Page.
Home
X
ExitPrint
28
SBG900 User Guide
Page 35

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Firewall > POLICY — advanced Page
Do not create a custom firewall policy unless you have the necessary expertise and the need to do so.
select one of the predefined policy templates as described in “Setting the Firewall Policy”.
To create a custom firewall policy, first select Custom and click Apply on the Firewall > POLICY — basic Page.
Then use this page to configure a custom firewall policy:
Instead,
To base the custom policy on a predefined firewall policy template, choose High, Medium, or Low in the Policy
Temp la te field and click Apply Policy Template.
Home
X
ExitPrint
29
SBG900 User Guide
Page 36

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
.
Firewall > POLICY — advanced page fields
Field Description
NEW FILTER ENTRY Section of the advanced policy window where you can construct a custom firewall
Port ID The name of the protocol being filtered.
Enable Check this box to enable firewall policy filtering for the port.
Allowed Protocol The allowed protocols.
Port Range (From:To) Sets the port range, which must contain all ports required by the protocol.
Protocol Number The protocol number of the IP packets to allow.
Allow Inbound Filters inbound data from the Internet on the specified ports.
Allow Outbound Filters outbound data to the Internet on the specified ports. Stateful inspection ensures
appropriate responses for outbound sessions.
Add Click to add the new filter. It is displayed on the FIREWALL POLICY table.
FIREWALL POLICY Table Lists the firewall policies.
Enable Check this box to enable firewall policy filtering for the port.
Delete Select the Delete box to delete the filter.
Apply Click to apply your changes.
FIREWALL POLICY
TEMPLATE
Apply Policy Template Click to apply the selected predefined firewall policy template and cancel any customizations.
Enables you to select a predefined firewall policy template on which to base your custom
template — High, Medium, or Low.
Home
X
ExitPrint
30
SBG900 User Guide
Page 37

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Firewall > ALERT — basic Page
You can use this page to set the alert mechanism for firewall intrusion detection events.
Firewall > ALERT — basic page fields
Field or Button Description
Intrusion Detection Check Email to be alerted through SMTP e-mail. An SMTP server that does not require any
authentication such as a user name or password must be present to receive the e-mail.
Apply Click to apply your changes.
Home
X
ExitPrint
31
SBG900 User Guide
Page 38

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Firewall > ALERT — email Page
You can use this page to configure the e-mail alert parameters:
Firewall > ALERT — email page fields
Field or Button Description
E-mail Server IP Address Sets the e-mail server IP address in dotted-decimal format.
E-mail Server Port Sets the e-mail server port number.
E-mail Sender Sets the sender e-mail address.
E-mail Recipient List Sets the list of e-mail addresses that receive alerts from the
Apply Click to apply your changes.
SBG900 firewall.
Home
X
ExitPrint
32
SBG900 User Guide
Page 39

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Firewall > LOGS Page
You can use this page to set which firewall events are logged.
Firewall > LOGS page fields
Field or Button Description
Enable Session Log Check this box to log session events.
Enable Blocking Log Check this box to log blocking events.
Enable Intrusion Log Check this box to log intrusions.
Apply Click to apply your changes.
Home
X
ExitPrint
33
SBG900 User Guide
Page 40

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Firewall > LOGS
Option Description
Session Log The Session Log shows data sessions that have occurred and tracked by the Firewall. To
enable logging of sessions, the Enable Session Log option must be selected in the Firewall
Logs Config Page. A firewall policy must be in effect for session events to be generated. If the
firewall policy is set to None then no new session entry will be generated.
The log entries correspond to data sessions that have occurred in the device that are
authorized by the normal firewall filters. Usually, this log shows the history of normal data
traffic. Though a session may be terminated early by the firewall due to policy or session
change, or if the session is later determined by the firewall to be an intrusion attack.
Blocking Log The Blocking Log shows firewall blocking events. To enable logging of blocking events, the
Enable Blocking Log option must be selected in the Firewall Logs Config Page. A firewall
policy must be in effect for blocking events to be generated. If the firewall policy is set to None
then no new blocking entry will be generated.
The log entries correspond to firewall blocking events that occur when unauthorized inbound
or outbound data packets are detected. Unauthorized data packets are those that use
protocols and/or ports that are not explicitly allowed by the current firewall policy. In addition,
data packets that are determined to be invalid due to session time-outs or reassembly
time-outs are also blocked.
Intrusion Log The Intrusion Log shows the intrusions attempts that have occurred and stopped by the
firewall. To enable logging of intrusion events, the Enable Intrusion Log option must be
selected in the Firewall Logs Config Page. A firewall policy must be in effect for intrusion
events to be generated. If the firewall policy is set to None then no new intrusion entry will be
generated.
The log entries correspond to intrusion attacks that have been detected and stopped by the
firewall. The firewall is capable of detecting several well-known intrusion tactics that is used to
attack a network device. This log is a history of those intrusion events.
Blacklist The Blacklist Log shows the IP addresses that have been determined by the firewall to have
breached the firewall policy of the SBG. A firewall policy must be in effect for blacklist entries
to be generated. If the firewall policy is set to None then no new blacklist entry will be
generated.
Once an IP address has been blacklisted, the firewall will block all traffic to and from that IP
address for 24 hours or when the SBG is rebooted. The user can manually clear the blacklist
by pressing the Clear button on the Blacklist Page. Clearing the blacklist table also allows
normal traffic to flow between the SBG and the formerly blacklisted entries
Home
X
ExitPrint
34
SBG900 User Guide
Page 41

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Gaming Configurati on Guide lines
The following subsections provide information about configuring the SBG900 firewall and DMZ for gaming.
Configuring the Firewall for Gaming
By default, the SBG900 firewall is disabled. If, as recommended, you enable the firewall, refer to the game’s
documentation to ensure that the necessary ports are open for use by that game.
The pre-defined SBG firewall policies affect X-Box Live
Low XBox Live data can pass through the firewall. No user action is required.
Medium or high To enable X-Box Live traffic to pass, you must configure:
• Choose Custom on the Firewall > POLICY — basic Page
• UDP 88:88 and UDP/TCP 3074:3074 on the Firewall > POLICY — advanced Page
Configuring Port Triggers
Because the SBG has pre-defined port triggers for games using any of the following applications, no user action is
required to enable them:
• DirectX 7 and DirectX 8
TM
as follows:
• MSN Games by Zone.com
• Battle.net
For a list of games supported by Battle.net, visit http://www.battle.net.
You may need to create custom port triggers to enable other games to operate properly. If you set custom port
triggers and enable the firewall, you must customize the firewall to allow traffic through those ports. To create
custom port triggers, use the Gateway > PORT TRIGGERS — custom Page.
®
Home
X
ExitPrint
35
SBG900 User Guide
Page 42

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuring a Gaming DMZ Host
Caution!
The gaming DMZ host is not protected by the firewall. It is open to communication or hacking from any
computer on the Internet.
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Consider carefully before configuring a device to be in the DMZ.
Some games and game devices require
one
of:
• The use of random ports
• The forwarding of unsolicited traffic
For example, to connect a PlayStation
the ports required vary from game to game. For these games, we recommend configuring the gaming computer or
device as a gaming DMZ device.
To configure a gaming DMZ device, on the Gateway > LAN — dhcp leases Page:
1 Reserve a private IP address for the computer or game device MAC address.
2 Designate the device as a DMZ device.
You can reserve IP addresses for multiple devices, but only one can be designated as the gaming DMZ at once.
®
2 for PS2® on-line gaming, designate it as the gaming DMZ host because
Home
X
ExitPrint
36
SBG900 User Guide
Page 43

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Configuring the Gateway
This section describes the Gateway configuration pages in the SBG900 Setup Program:
• Gateway > STATUS Page
• Gateway > WAN Page
• Gateway > LAN — nat config Page
• Gateway > LAN — dhcp server config Page
• Gateway > LAN — dhcp leases Page
• Gateway > PORT FORWARDING — status Page
• Gateway > PORT FORWARDING — config Page
• Gateway > PORT TRIGGERS — predefined Page
• Gateway > PORT TRIGGERS — custom Page
• Gateway > LOG Page
After you edit some fields and click Apply, you are warned that you must reboot for your change to take effect.
Rebooting takes 10 to 15 seconds. After rebooting, you must log-in again.
Home
X
ExitPrint
37
SBG900 User Guide
Page 44

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
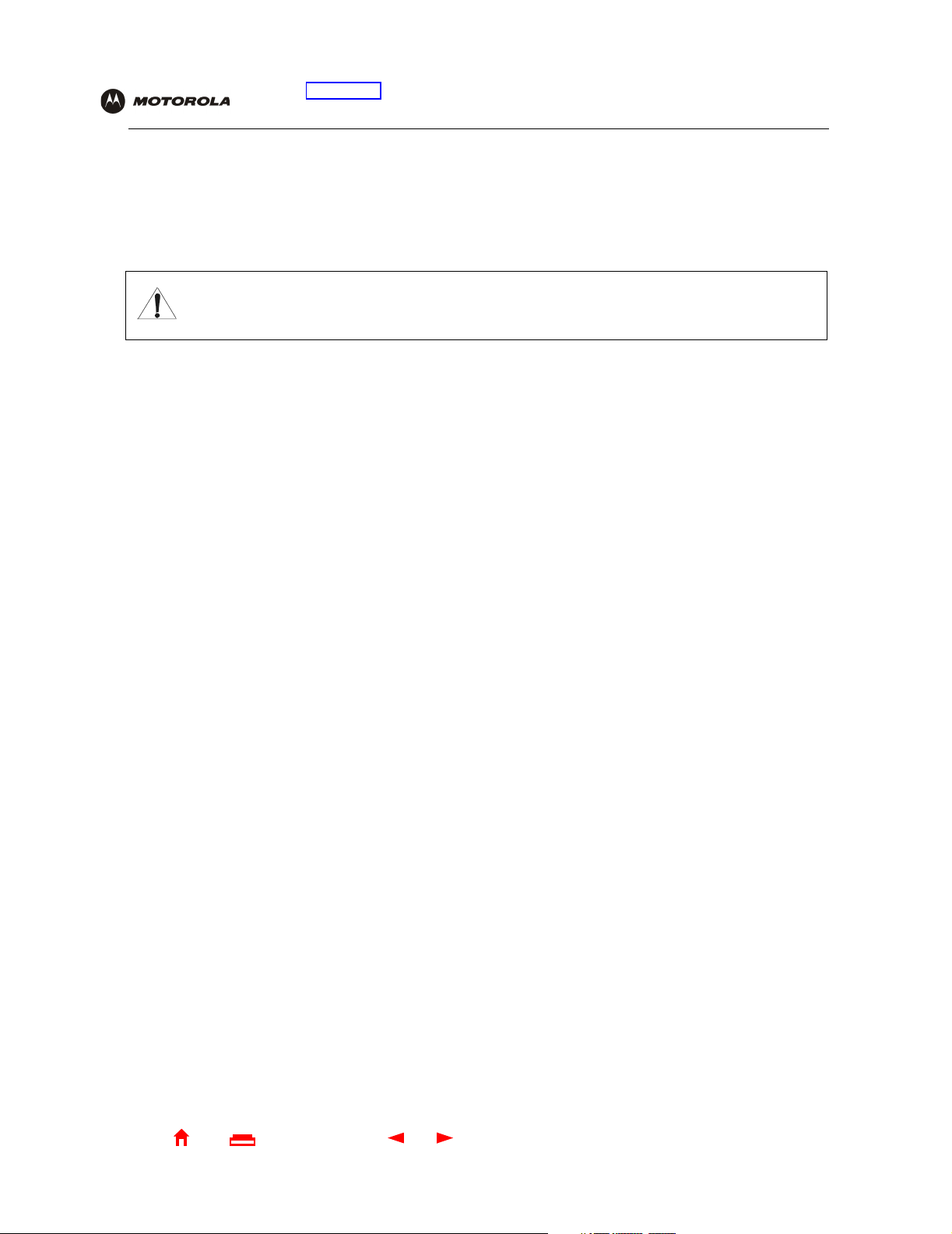
Gateway > STATUS Page
This page displays the gateway status information:
These fields display settings that are set on the other Gateway pages. For field descriptions, see the following
subsections that describe the fields on each tab.
Home
X
ExitPrint
38
SBG900 User Guide
Page 45

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Gateway > WAN Page
Use this page to configure the external (public) wide area network (WAN) interface:
Gateway > WAN page fields
Field Description
Host Name If the cable service provider requires a hostname to access to their network, type the
they provided in this field. The default is None.
Enable DHCP Client Enabling the DHCP client causes the wireless gateway to automatically obtain the public IP
address, subnet mask, domain name, and DNS server(s). Most commonly, the DHCP client is
enabled if the cable service provider automatically assigns a public IP address from their
DHCP server. Enable DHCP Client is on by default.
Disable DHCP Client If the cable service provider does not automatically assign a public IP address using DHCP,
they must provide a static IP address. Select Disable DHCP Client. When you disable the
DHCP client, you must type the static IP address, subnet mask, DNS server(s), and domain
name (if necessary) in the fields provided. Disable DHCP Client is off by default.
Static IP Address If Disable DHCP Client is on, type the static IP address provided by the cable service provider
in dotted-decimal format. The default is None.
Static IP Subnet Mask If Disable DHCP Client is on, type the subnet mask associated with the static IP address in
dotted-decimal format. The default is None.
WAN Default Gateway When using a statically assigned IP address from your ISP, enter the default gateway the SBG
should be using to communicate with on the WAN.
hostname
Home
X
ExitPrint
39
SBG900 User Guide
Page 46

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Gateway > WAN page fields (continued)
Field Description
DNS IP Address 1
DNS IP Address 2
DNS IP Address 3
TCP Session Wait
Timeout
UDP Session Wait
Timeout
ICMP Session Wait
Timeout
Apply Click to apply your changes.
The cable service provider DNS server provides name-to-IP address resolution. If the cable
service provider does not automatically assign DNS addresses from their DHCP server, they
must provide at least one DNS server IP address to enter in these fields in dotted-decimal
format. The default is None.
Sets the maximum time in seconds to wait before assuming a TCP session has timed out. The
default is 24 hours.
Sets the maximum time in seconds to wait before assuming a UDP session has timed out. The
default is 300 seconds (5 minutes).
Sets the maximum time in seconds to wait before assuming an ICMP session has timed out.
The default is 300 seconds (5 minutes).
Home
X
ExitPrint
40
SBG900 User Guide
Page 47

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Gateway > LAN — nat config Page
Use this page to enable NAT and add clients to the CURRENT NAT PASSTHROUGH list:
Gateway > LAN — nat config page fields
Field or Button Description
LAN
Enable NAT If enabled, the single HFC IP Address (public IP address) assigned by the cable service
provider is mapped to many private IP addresses on the
Apply Click to apply your changes. You must reboot the SBG900.
NEW NAT
PASSTHROUGH
MAC Address Type the passthrough client MAC address. The format is 16 hexadecimal numerals.
Bypass Firewall
(True DMZ)
Add Click to add the MAC address to the CURRENT NAT PASSTHROUGH list.
CURRENT NAT
PASSTHROUGH
Delete Click to delete the selected MAC address from the NAT passthrough list.
Specifies up to 32 computers as passthrough clients not subject to NAT, using their MAC
addresses.
Check this box to set the NAT passthrough computer as a DMZ client.
extreme caution because a DMZ client is completely open to Internet hackers.
Lists the computers on the LAN that are configured for NAT passthrough.
SBG900 LAN.
Use this setting with
Home
X
ExitPrint
41
SBG900 User Guide
Page 48

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Gateway > LAN — dhcp server config Page
Only experienced network administrators should use this page to perform advanced DHCP server configuration:
CAUTION!
Do not modify these settings unless you are an experienced network administrator with strong
knowledge of IP addressing, subnetting, and DHCP.
Gateway > LAN — dhcp server config page fields
Field Description
LAN IP Address Enter the IP address of the SBG900 for your private LAN. The default is 192.168.0.1.
LAN IP Subnet Mask The subnet mask in dotted-decimal format. The default is 255.255.255.0.
Starting IP Address Enter the starting IP address to be assigned by the
dotted-decimal format. The default is 192.168.0.2.
# of DHCP Users Sets the number of clients for the
are 253 possible client addresses. The default is 253.
DHCP Server Lease Time Sets the time in seconds that the
default is 3600 seconds (60 minutes).
Domain Name Sets the domain name for the SBG900 LAN. The default is None.
Time To Live Sets the TTL (hop limit) for outbound packets. The default is 64.
Interface Maximum
Transmission Unit
Sets the SBG900 LAN MTU in bytes. The minimum is 68 bytes. The default is 1500 bytes.
SBG900 DHCP server to assign a private IP address. There
SBG900 DHCP server leases an IP address to a client. The
SBG900 DHCP server to clients in
Apply Click to apply your changes. You must reboot the
Home
X
ExitPrint
42
SBG900.
SBG900 User Guide
Page 49

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Gateway > LAN — dhcp leases Page
Use this page to configure DHCP leases:
Gateway > LAN — dhcp leases page fields
Field Description
GAMING DMZ
Enable Gaming DMZ Check this box to designate the selected computer or gaming device as the gaming DMZ
host. For more information, see “Configuring a Gaming DMZ Host”. This can be useful if you
have difficulties running certain applications; typically gaming applications.
(Gaming) DMZ Host The gaming DMZ host is a computer with a reserved IP address designated as the default
DMZ host. Only one gaming DMZ host can be active at once.
The gaming DMZ host is not protected by the firewall. It is open to communication or hacking
Home
from any computer on the Internet.
the DMZ.
The benefit of using a gaming DMZ host instead of a NAT passthrough host is that a gaming
DMZ host does not require a public IP address as does a NAT passthrough host. If the
application requires a public IP address, configure the computer for NAT passthrough on the
Gateway > LAN — nat config Page.
X
ExitPrint
43
Consider carefully before configuring a computer to be in
SBG900 User Guide
Page 50

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Gateway > LAN — dhcp leases page fields (continued)
Field Description
RESERVE NEW IP
ADDRESS
MAC Address Type the MAC address of the DHCP client for which a reserved IP address is required. The
IP Address Sets the host portion of the reserved IP address for the LAN client having the specified MAC
Host Name If your ISP requires a hostname to access their network, enter the hostname provided to you
Add Click Add to reserve a new IP address.
CURRENTLY RESERVED
IP ADDRESSES
MAC Address Displays the client MAC address.
IP Address Displays its reserved IP address
Host Name Displays its host name.
Method Displays dynamic and static lease status. Add or delete dynamic or static lease status in this
Delete Click this box to remove the reserved IP address for the client.
Delete Click this button to remove the reserved IP addresses for clients designated by the Delete
You can reserve up to 32 IP addresses assigned by the SBG900 DHCP server for specific
LAN clients. For example, to ensure that they always receive the same private IP address,
you can reserve IP addresses for a private FTP server or gaming DMZ device.
format is 16 hexadecimal numerals.
address. When the LAN client requests an IP address, the SBG900 DHCP server assigns the
client this IP address.
in the Host Name field.
Displays all DHCP clients having reserved IP addresses.
field.
box.
Gatewa y > PORT FORWARDING — sta tus Page
Use this page to display the configured port forwarding entries on the SBG900 LAN. The fields are the same as on
the Gateway > PORT FORWARDING — config Page:
Home
X
ExitPrint
44
SBG900 User Guide
Page 51

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Gateway > PORT FORWARDING — config Page
Use this page to configure up to 32 virtual servers:
Gateway > PORT FORWARDING — config page fields
Field Description
ADD NEW PORT
FORWARDING ENTRY
Tem pla te If you select Custom, you must set the Name, Port Start, Port End, and LAN IP Address.
Name Type a unique identifier for the custom virtual server. The typical practice is to use the
Port Start Sets the LAN internal interface port or the start of a port range. Inbound Internet connection
Port End If a range of ports is required, sets the end of the port range.
LAN IP Address Sets the private LAN IP address for the port forwarding page. An Internet user must know the
Enable Check this box to enable the port forwarding entries to be accessed through NAT.
Add Click to add the virtual server to the PORT FORWARDING list.
PORT FORWARDING Displays the configured custom virtual servers.
You can configure up to 32 virtual servers.
If you select a predefined template such as HTTP or FTP, the Name, Port Start, Port End
values are provided. You only need to enter LAN IP Address and change default values only
if necessary.
protocol as a unique identifier (for example “ftp”).
requests are statically mapped to this port.
public IP address to access any port forwarding entry you define on the private LAN.
Home
X
ExitPrint
45
SBG900 User Guide
Page 52

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Gateway > PORT TRIGGERS — predefined Page
When you run a PC application that accesses the Internet, it communicates with a computer on the Internet. In
some applications, especially gaming, the computer on the Internet also communicates with your PC. Because
NAT does not normally allow these incoming connections, the SBG900 supports port triggering.
The SBG900 is preconfigured with port triggering for common applications. You can also configure additional port
triggers if needed. Configuring port triggers for an application requires:
• The application transport protocol — TCP or UDP
• The application port number
You can use the default values for the remaining parameters.
Only one PC at a time connected to the SBG900 can use an application requiring port triggering. Use this page to
view predefined port triggers:
Home
X
ExitPrint
46
SBG900 User Guide
Page 53

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Gateway > PORT TRIGGERS — predefined page fields
Field Description
Name Displays the unique name for the port triggers. This is typically the protocol name.
Enable Select the Enable check box to activate the port triggers for the predefined application.
Protocol Displays the transport protocol for the port trigger — TCP or UDP.
Port Range Displays the port range (From/To) for the port trigger.
Session Chaining Displays the session chaining selection for the port trigger — Disable, TCP, or TCP/UDP.
Session Interval Displays the session interval set for the port trigger.
Address Replace Displays the address replacement method for the port trigger.
Multi Host Displays the multi host selection for the port trigger.
Home
X
ExitPrint
47
SBG900 User Guide
Page 54

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Gateway > PORT TRIGGERS — custom Page
Use this page to create a custom port trigger:
Gateway > PORT TRIGGERS — custom page fields
Field Description
ADD NEW SPECIAL
APPLICATION
Name Enter the unique name for the port trigger. This is typically the protocol.
Enable Check this box to enable the custom port trigger.
Protocol Sets the transport protocol for the port trigger — TCP or UDP.
Port Range
(From:To)
Session Chaining Enable session chaining if the application needs to open one or more ports in different ranges to
Session Interval Sets the session interval for the application:
Address Replace Sets the address replacement method for the application.
Multi Host Check if appropriate for the application.
Add Click to add the port trigger to the PORT TRIGGERS TABLE.
Sets the port range for the port trigger. Type the start of the range in the left field and the end in
the right field.
operate properly. The options are Disable, TCP, or TCP/UDP.
• If the port triggers detect traffic on the Port Range within the Session Interval, it is considered
to be related to the initial session.
• If the port triggers detect traffic on the Port Range after the Session Interval expires, it is
considered to be a new and unique session.
Home
X
ExitPrint
48
SBG900 User Guide
Page 55

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Gateway > PORT TRIGGERS — custom page fields
Field Description
PORT TRIGGERS TABLE Lists all port triggers you defined and their parameters.
Priority Port Select the port to have a priority status.
Gateway > LOG Page
Use this page to view detailed information about the gateway:
Gateway > LOG page fields
Field Description
Time The date and time in the format yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss (hours hh are 00 to 23).
Priority Indicates the importance of the message.
Code Code associated with this message.
Message Describes the event.
Home
X
ExitPrint
49
SBG900 User Guide
Page 56

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Configuring TCP/IP
You must be sure all client computers are configured for TCP/IP (a protocol for communication between
one
computers). Perform
• Configuring TCP/IP in Windows 95, Windows 98, or Windows Me
• Configuring TCP/IP in Windows 2000
• Configuring TCP/IP in Windows XP
• Follow the instructions in your Macintosh or UNIX user manual
After configuring TCP/IP, perform
• Verifying the IP Address in Windows 95, Windows 98, or Windows Me
• Verifying the IP Address in Windows 2000 or Windows XP
• Follow the instructions in your Macintosh or UNIX user manual
of:
one
of the following to verify the IP address:
Home
X
ExitPrint
50
SBG900 User Guide
Page 57

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Configuring TCP/IP in Windows 95, Windows 98, or Windows Me
1 On the Windows Desktop, click Start.
2 Select Settings and then Control Panel from the pop-up menus to display the Control Panel window.
3 Double-click the Network icon to display the Network window:
Although your SBG model number may be different than in the images in this guide, the procedure is
the same.
4 Select the Configuration tab.
5 Verify that TCP/IP is installed for the adapter used to connect to the SBG900. If TCP/IP is installed, skip to
step 10. If TCP/IP is not installed for the adapter, continue with step 6.
6 Select the adapter to use for the SBG900 connection and click Add. The Select Network Component Type
window is displayed:
7 Click Protocol and click the Add button.
Home
X
ExitPrint
51
SBG900 User Guide
Page 58

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
8 Click Microsoft in the Manufacturers section and click TCP/IP in the Network Protocol section of Select
Network Protocol window:
9 Click OK.
10 Click TCP/IP on the Network window. If there is more than one TCP/IP entry, choose the one for the Ethernet
card or USB port connected to the SBG900.
11 Click Properties. The TCP/IP Properties window is displayed:
12 Click the IP Address tab.
13 Click Obtain an IP address automatically.
14 Click OK to accept the TCP/IP settings.
15 Click OK to close the Network window.
16 Click OK when prompted to restart the computer and click OK again.
When you complete TCP/IP configuration, go to “Verifying the IP Address in Windows 95, Windows 98, or
Windows Me”.
Home
X
ExitPrint
52
SBG900 User Guide
Page 59

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Configuring TCP/IP in Windows 2000
1 On the Windows Desktop, click Start.
2 Select Settings and then Control Panel from the pop-up menus to display the Control Panel window:
3 Double-click the Network and Dial-up Connections icon to display the Network and Dial-up Connections
window:
Home
X
ExitPrint
53
SBG900 User Guide
Page 60

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
4 Click Local Area Connection
Connection
number
Status window is displayed:
number
. The value of
number
varies from system to system. The Local Area
5 Click Properties. Information similar to the following window is displayed:
6 If Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) is in the list of components, TCP/IP is installed. You can skip to step 10.
If Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) is not in the list, click Install. The Select Network Component Type window is
displayed:
Home
X
ExitPrint
54
SBG900 User Guide
Page 61

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
7 Click Protocol on the Select Network Component Type window and click Add. The Select Network Protocol
window is displayed:
8 Click Internet Protocol (TCP/IP).
9 Click OK. The Local Area Connection
number
Properties window is re-displayed.
10 Be sure the box next to Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) is checked.
Home
X
ExitPrint
55
SBG900 User Guide
Page 62

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
11 Click Properties. The Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties window is displayed:
12 Be sure Obtain IP address automatically and Obtain DNS server address automatically are selected.
13 Click OK to accept the TCP/IP settings.
14 Click OK to close the Local Area Connection
number
Properties window.
15 Click OK when prompted to restart the computer and click OK again.
When you complete the TCP/IP configuration, go to “Verifying the IP Address in Windows 2000 or Windows XP”.
Home
X
ExitPrint
56
SBG900 User Guide
Page 63

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Configuring TCP/IP in Windows XP
1 On the Windows desktop, click Start to display the Start window:
2 Click Control Panel to display the Control Panel window. The display varies, depending on the Windows XP
view options. If the display is a Category view as shown below, continue with step 3. Otherwise, skip to
step 5.
Home
X
ExitPrint
57
SBG900 User Guide
Page 64

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
3 Click Network and Internet Connections to display the Network and Internet Connections window:
4 Click Network Connections to display the LAN or High-speed Internet connections. Skip to step 7.
5 If a classic view similar to below is displayed:
6 Click Network Connections to display the LAN or High-speed Internet connections.
Home
X
ExitPrint
58
SBG900 User Guide
Page 65

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
7 Right-click on the network connection. If more than one connection is displayed, be sure to select the one for
your network interface:
8 Select Properties from the pop-up menu to display the Local Area Connection Properties window:
9 On the Local Area Connection Properties window, be sure Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) is checked. If it is not
selected, check it.
Home
X
ExitPrint
59
SBG900 User Guide
Page 66

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
10 Select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) and click Properties to display the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties
window:
11 Verify that the settings are correct, as shown above.
12 Click OK to close the TCP/IP Properties window.
13 Click OK to close the Local Area Connection Properties window.
When you complete the TCP/IP configuration, go to “Verifying the IP Address in Windows 2000 or Windows XP”.
Home
X
ExitPrint
60
SBG900 User Guide
Page 67

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Verifying the IP Address in Windows 95, Windows 98, or Windows Me
To check the IP address:
1 On the Windows Desktop, click Start.
2 Select Run. The Run window is displayed.
3 Type winipcfg.exe and click OK. The IP Configuration window is displayed. The Ethernet Adapter
Information field will vary depending on the system, as shown in the following examples:
The values for Adapter Address, IP Address, Subnet Mask, and Default Gateway on the PC will be different
than in the image.
In Windows 98, if “Autoconfiguration” is displayed before the IP Address as in the following image, call your
service provider.
4 Select the adapter name — the Ethernet card or USB device.
5 Click Renew.
6 Click OK after the system displays an IP address.
If after performing this procedure the computer cannot access the Internet, call your cable service provider for
help.
Home
X
ExitPrint
61
SBG900 User Guide
Page 68

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Verifying the IP Address in Windows 2 000 or Windows XP
To check the IP address:
1 On the Windows Desktop, click Start.
2 Select Run. The Run window is displayed.
3 Type cmd and click OK to display a command prompt window.
4 Type ipconfig and press ENTER to display the IP configuration. A display similar to the following indicates a
normal configuration:
If an Autoconfiguration IP Address is displayed as in the following window, there is an incorrect connection
between the PC and the SBG900 or there are cable network problems. Check the cable connections and
determine if you can view cable-TV channels on your television:
After verifying the cable connections and proper cable-TV operation, renew the IP address.
Home
X
ExitPrint
62
SBG900 User Guide
Page 69

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
To renew the IP address:
1 Type ipconfig /renew and press ENTER. If a valid IP address is displayed as shown, Internet access should
be available.
2 Type exit and press ENTER to return to Windows.
If after performing this procedure the computer cannot access the Internet, call your cable service provider
for help.
Home
X
ExitPrint
63
SBG900 User Guide
Page 70

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Setting Up the Wireless LAN
You can use the SBG900 as an access point for a wireless LAN without changing its default settings.
Caution!
The default SBG900 settings provide no wireless security. After your wireless LAN is operational,
be sure to enable security as described in “Setting Up the Wireless LAN” in the SBG900 User
Guide.
To enable security for your SBG900 wireless LAN, you can do the following on the SBG900:
To
Configure an Extended
Service Set Identifier (ESSID)
and enable closed network
operation
Enable Wired Equivalent
Privacy (WEP) encryption and
configure a WEP key
Restrict access to computers
with known MAC addresses
Perform on the
SBG900
Configuring the Wireless
Network Name on the
SBG900
Configuring WEP on the
SBG900
Configuring a MAC
Access Control List on
the SBG900
Advantages Disadvantages
Provides a unique name to
distinguish from other
nearby wireless LANs.
Encrypts wireless data You must configure the
No configuration on client
required
No code that can be
broken.
You must configure the
ESSID on each client
computer.
Does not encrypt wireless
data
WEP key on each client
computer.
You must input each client
MAC address on the
SBG900
Does not encrypt wireless
data
Connect at least one computer to the SBG900 Ethernet or USB port to use for performing configuration. Do not
attempt to configure the SBG900 over a wireless connection.
You need to configure each wireless client station to access the SBG900 LAN as described in “Configuring the
Wireless Clients
”
.
Caution!
Never provide the ESSID or WEP key to anyone who is not authorized to use your wireless LAN.
For descriptions of all wireless configuration fields, see “Wireless Pages in the SBG900 Setup Program”.
Another common-sense step to improve wireless security is to place wireless components away from windows.
This decreases the signal strength outside the intended area.
Home
X
ExitPrint
64
SBG900 User Guide
Page 71

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Configuring the Wireless Network Name on the SBG900
If you check Disable ESSID Broadcast on the SBG900 Wireless > SECURITY — advanced Page, you must
configure the same network name (ESSID) on all wireless LAN clients (stations). Never provide the ESSID to
anyone who is not authorized to use your wireless LAN.
To configure the ESSID:
1 Start the SBG900 Setup Program as described in “Starting the SBG900 Setup Program”.
2 On the left frame, click Wireless.
3 Click the NETWORK tab to display:
4 In the ESSID field, type a unique
32 characters. The default is “Motorola.”
name
. It can be any alphanumeric, case-sensitive string up to
Do not use the default ESSID.
5 Click Save Changes to save your changes.
6 To restrict wireless LAN access to clients configured with the same Network Name (ESSID) as the SBG900,
click the SECURITY tab.
Home
X
ExitPrint
65
SBG900 User Guide
Page 72

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
7 Click advanced to display the Wireless > SECURITY — advanced Page
:
8 Check Disable ESSID Broadcast to restrict wireless LAN access to clients configured with the same
Network Name (ESSID) as the SBG900.
9 Click Apply to save your changes.
Home
X
ExitPrint
66
SBG900 User Guide
Page 73

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuring WEP on the SBG900
Caution!
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
The default settings provide no security for wireless data.
sure to enable Shared Key Authentication and Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) encryption. You must
configure the same WEP key on the SBG900 access point and all wireless clients (stations).
After the wireless LAN is operational, be
provide the WEP key to anyone who is not authorized to use the wireless LAN.
To enable WEP and set the key on the SBG900:
1 On the SBG900 Setup Program left frame, click Wireless.
2 Click the SECURITY tab to display the Wireless > SECURITY — basic page:
Never
3 Set the following:
Authentication Sets whether shared key authentication is enabled to provide data privacy on the wireless LAN:
• Open System — Any wireless LAN client can transmit data to any other client without
authentication.
• Shared Key — All data transmitted over the wireless LAN is encrypted. The SBG900
and transfers data to and from all clients having shared key authentication enabled and an identical
WEP key.
Encryption Use a WEP key length that is compatible with your wireless client adapters. Choose
• Enable 64-Bit — Use only if you have wireless clients that do not support 128-bit encryption
• Enable 128-Bit — The recommended setting for stronger encryption; supported by the Motorola
PCC11b wireless card, USB11b wireless adapter, and most current wireless adapters
• Disable WEP — Recommended during network setup
Key 1 to Key 4 Sets the active WEP key. You can enter up to four 64-bit or 128-bit WEP
non-case-sensitive hexadecimal characters 0 to 9 and A to F. Only
• For 64-bit encryption, set the 10-character long key under Enable 64-Bit.
• For 128-bit encryption, set the 26-character long key under Enable 128-Bit.
For optimal security, we recommend changing the WEP keys frequently. Never provide the WEP key
to anyone who is not authorized to use your wireless LAN.
Open authentication provides no security for transmitted data.
only
keys
containing the
one
key can be active:
It is the default.
4 If necessary, click Reset Wireless Defaults to reset the wireless defaults.
5 Click Save Changes to save your changes.
Home
X
ExitPrint
67
SBG900 User Guide
authenticates
one
of:
Page 74

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Configuring a MAC Access Control List on the SBG900
You can restrict wireless access to one to 32 wireless clients, based on the client MAC address.
To configure a MAC access control list:
1 On the SBG900 Setup Program left frame, click Wireless.
2 Click the SECURITY tab.
3 Click advanced to display the Wireless > SECURITY — advanced Page:
4 To restrict wireless access to systems in the MAC access control list, check Allow Only Listed Stations
Access and click Apply.
5 To add a wireless client, type its MAC address in the format
click Add Station.
You can add up to 32 wireless clients to the MAC access control list.
Home
X
ExitPrint
68
xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx
SBG900 User Guide
in the New Station field and
Page 75

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Configuring the Wireless Clients
For each wireless client computer (station), install the wireless adapter — such as a Motorola PCC11b wireless
card or Motorola USB11b wireless adapter — following the instructions supplied with the adapter.
Configure the card or adapter to obtain an IP address automatically. The Motorola PCC11b wireless card and
Motorola USB11b wireless adapter are supplied with a client configuration program called Wireless Client
Manager, which is installed in the Windows Startup group.
If Wireless Client Manager is running, the icon is displayed on the Windows task bar. Double-click the icon to
launch the utility.
After you correctly set the network name and WEP key on the client computer to match the SBG900, you should
be able to use the computer to surf the Internet.
Configuring a Wireless Client with a Network Name (ESSID)
To distinguish it from other nearby wireless LANs, you can identify your wireless LAN with a unique network name
(also known as a network identifier or ESSID). When prompted for the network identifier, network name, or ESSID,
name
type the
information, see “Configuring the Wireless Network Name on the SBG900”.
After you specify the network name, many wireless cards or adapters automatically scan for an access point
as the SBG900 and the proper channel and data rate. If your card requires you to manually start scanning for an
access point, do so following the instructions in the documentation supplied with the card.
set in the ESSID field on the Wireless > NETWORK Page in the SBG900 Setup Program. For more
such
Never provide the ESSID to anyone who is not authorized to use your wireless LAN.
Configuring a Wireless Client for WEP
If shared key Authentication is enabled and a WEP key is set on the SBG900 as described in “Configuring WEP
on the SBG900”, you must enter the same WEP key on the wireless client. The SBG900 cannot authenticate a
client if:
• Shared key Authentication is enabled on the SBG900 but not on the client
• The client WEP key does not match the SBG900 WEP key
Caution!
If shared key authentication is not enabled and no WEP key is set, there is no encryption for wireless
You must configure the same WEP key on the SBG900 and all wireless clients.
data.
the WEP key to anyone who is not authorized to use your wireless LAN.
Never provide
Home
X
ExitPrint
69
SBG900 User Guide
Page 76

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Wireless Pages in the SBG900 Setup Program
Use the Wireless pages to control and monitor the wireless interface:
• Wireless > STATUS Page
• Wireless > NETWORK Page
• Wireless > SECURITY — basic Page
• Wireless > SECURITY — advanced Page
• Wireless > STATISTICS page
After you edit some fields and click Apply, you are warned that you must reboot for your change to take effect.
Rebooting takes 10 to 15 seconds. After rebooting, you must log-in again.
Home
X
ExitPrint
70
SBG900 User Guide
Page 77

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Wireless > STATUS Page
You can use this display-only page to
• View the wireless interface status
• Help perform Troubleshooting for wireless network problems
Wireless > STATUS Page Fields
Regulatory Domain Indicates the country the SBG900 is manufactured for. The list of channels depends on the
country’s standards for operation of wireless devices. Depending on the domain set at the
factory, USA FCC, Europe, Spain, France, Japan, or some other country name is displayed.
ESSID Displays the ESSID set on the Wireless > NETWORK Page. For more information, see
“Configuring the Wireless Network Name on the SBG900”.
who is not authorized to use your wireless LAN.
Channel Displays the radio channel for the access point. If you encounter interference, you can set a
different channel on the Wireless > NETWORK Page.
RTS Threshold Displays the Request to Send Threshold set on the Wireless > NETWORK Page.
Frag Threshold Displays the Fragmentation Threshold set on the Wireless > NETWORK Page.
MAC Address Displays the
WEP Enabled Displays the type of Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) that is enabled. For more information, see
“Configuring WEP on the SBG900”.
MAC Access Control Displays the MAC Access Control setting set on the Wireless > SECURITY — advanced Page:
• Allow Listed — Only clients in the MAC access control list can access the wireless LAN.
• Allow Any Station Access — Any wireless client can access the wireless LAN.
MAC Access Control List Displays the MAC addresses of wireless clients having access. The list is set on the Wireless >
SECURITY — advanced Page.
SBG900 MAC address.
Never provide the ESSID to anyone
Home
X
ExitPrint
71
SBG900 User Guide
Page 78

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Wireless > NETWORK Page
Use this page for:
• Configuring the Wireless Network Name on the SBG900
• Configuring other wireless LAN settings
You can use the SBG900 to operate a wireless LAN without changing its default settings.
Wireless > NETWORK page fields
Field Description
WIRELESS
Enable Wireless
Interface
ESSID Sets a unique network name for the SBG900 wireless LAN to distinguish between multiple
Channel Sets the wireless radio channel. You can change the channel if you encounter interference on
Home
Check this box to enable the wireless interface.
wireless LANs in the vicinity.
SECURITY — advanced Page, all clients on the wireless LAN must have the same ESSID
(network name) as the SBG900.
32 characters. The default is “Motorola.”
provide the ESSID to anyone who is not authorized to use your wireless LAN.
the default channel. The default is 1 (one), except in countries where the first channel
permitted for wireless operation is not one.
X
ExitPrint
If you check Disable ESSID Broadcast on the Wireless >
It can be any alphanumeric, case-sensitive string up to
We strongly recommend not using the default. Never
72
SBG900 User Guide
Page 79

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Wireless > NETWORK page fields (continued)
Field Description
Operating Mode Sets how the SBG900 communicates with wireless clients (stations):
• 11b/11g Standard — Enables all IEEE 802.11b and IEEE 802.11g clients to work with the
SBG900.
• 11g Enhanced — Choose this option only if all IEEE 802.11g clients on the network support
the performance-enhancing features of the IEEE 11g Enhanced mode. It is not supported by
all IEEE 802.11g stations.
ADVANCED SETUP
We recommend using this default setting in most cases because it is more flexible.
Transmit Power Sets the transmit power on the
mW. The default is 32 mW. Transmit power control is an optional IEEE 802.11b feature.
RTS Threshold The Request To Send Threshold sets the packet size at which the access point issues an RTS
before sending the packet. A low RTS can help when many clients are associated with the
SBG900 wireless access point — 1, 2, 5, 10, 25, 50, or 100
SBG900 or when the clients are far apart and can detect the SBG900 but not each other. It
can be 0 to 2347 bytes. The default is 2347.
Fragmentation
Threshold
Beacon Period Sets the time between beacon frames sent by the SBG900 for wireless network
DTIM Period The delivery traffic indication message (DTIM) period is the number of Beacon Periods that
Sets the size at which packets are fragmented (sent as several packets instead of as one
packet). A low Fragmentation Threshold can help when communication is poor or when there
is a significant interference. It can be 256 to 2346 bytes. The default is 2346.
synchronization. It can be from 1 to 999 ms. The default is 100 ms.
elapse before a wireless client operating in power save mode “listens” for buffered broadcast
or multicast messages from the SBG900. It can be from 1 to 99999. The default is 3.
Home
X
ExitPrint
73
SBG900 User Guide
Page 80

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Wireless > SECURITY — basic Page
Use this page to configure basic Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) settings.
Caution!
The default Authentication setting Disable WEP provides no security for transmitted data.
For information about using this page, see “Configuring WEP on the SBG900”.
Home
X
ExitPrint
74
SBG900 User Guide
Page 81

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Wireless > SECURITY — advanced Page
Use this page to configure advanced wireless security settings.
Wireless > Security — ADVANCED page fields
Field or Button Description
Disable ESSID Broadcast If checked, only wireless clients (stations) having the same Network Name (ESSID) as the
SBG900 can communicate with the SBG900. Closed network operation is a SBG900
enhancement to IEEE 802.11b. The default is unchecked (off).
MAC ACCESS CONTROL
LIST
Allow Any Station
Access
Allow Only Listed
Stations Access
Apply Click to apply your change.
Listed Stations Lists the wireless clients in the MAC access control list having access if Allow Only Listed
Delete To delete a wireless client from the MAC access control list, select its Delete check box
Home
You can restrict wireless access to one to 32 wireless clients, based on the client MAC
address.
If checked, any wireless client can access the SBG900 wireless LAN.
If checked, only wireless clients in the MAC access control list can access the SBG900
wireless LAN.
Stations Access is checked.
and click the Delete button.
X
ExitPrint
75
SBG900 User Guide
Page 82

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Wireless > Security — ADVANCED page fields (continued)
Field or Button Description
ADD NEW STATION
New Station Type the MAC address of the wireless client to add to the MAC access control list. Use
the format
Add Station Click to add the New Station to the MAC access control list.
xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx
. The MAC access control list can contain one to 32 clients.
Wireless > STATISTICS page
Use this page to display wireless statistics.
Wireless > STATISTICS page fields
Field or Button Description
Transmitted
Fragment Count
Multicast
Transmitted
Fragment Count
Failed Count The number of MSDUs not transmitted successfully because the number of transmit attempts
Retry Count The number of successfully transmitted MSDUs after one or more retransmissions.
Home
The number of acknowledged MAC protocol data units (MPDUs) with an address in the
address 1 field or an MPDU with a multicast address in the address 1 field of type data or
management.
The number of transmitted fragments when the multicast bit is set in the destination MAC
address of a successfully transmitted MAC service data unit (MSDU). When operating as a
STA in an ESS, where these frames are directed to the AP, this implies having received an
acknowledgment to all associated MPDUs.
exceeded the IEEE 802.11b short or long retry limit.
X
ExitPrint
76
SBG900 User Guide
Page 83

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Wireless > STATISTICS page fields (continued)
Field or Button Description
Multiple Retry Count The number of successfully transmitted MSDUs after more than one retransmission.
Frame Duplicate
Count
Request To Send
Success Count
Request To Send
Failure Count
Acknowledge Failed
Count
Received Fragment
Count
Multicast Received
Fragment Count
Frame Check
Sequence Error
Count
Transmitted Frame
Count
WEP Undecryptable
Count
Refresh Click to collect new data.
The number of frames received where the Sequence Control field indicated the frame was a
duplicate.
The number of CTS messages received in response to RTS messages.
The number of CTS messages not received in response to RTS messages.
The number of acknowledgment messages not received when expected from a data
message transmission.
The number of successfully received MPDUs of type Data or Management.
The number of MSDUs received when the multicast bit was set in the destination MAC
address.
The number of FCS errors detected in a received MPDU.
The number of successfully transmitted MSDUs.
This number of frames received with the WEP subfield of the Frame Control field set to one
and the WEP On key value mapped to the client MAC address. This indicates that the frame
should not have been encrypted or was discarded due to the receiving client not having WEP
enabled.
Home
X
ExitPrint
77
SBG900 User Guide
Page 84

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Setting Up a USB Driver
The following subsections describe setting up a USB driver if you connect a PC to the USB port on the SBG900.
Perform one of the following procedures based on your Windows version:
• Setting Up a USB Driver in Windows 98
• Setting Up a USB Driver in Windows 2000
• Setting Up a USB Driver in Windows Me
• Setting Up a USB Driver in Windows XP
The SBG900 USB driver does not support Macintosh or UNIX computers. For those systems, you can connect
only
through Ethernet
Caution!
Be sure the Motorola SURFboard Wireless Cable Modem Gateway CD-ROM is inserted in the
CD-ROM drive before you plug in the USB cable.
If you have a problem setting up the USB driver, remove it by performing
.
one
of the following procedures:
• Removing the USB Driver from Windows 98 or Windows Me
• Removing the USB Driver from Windows 2000
• Removing the USB Driver from Windows XP
Home
X
ExitPrint
78
SBG900 User Guide
Page 85

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Setting Up a USB Dr iv er in Window s 98
1
Insert the Motorola SURFboard Wireless Cable Modem Gateway CD-ROM in the CD-ROM drive.
contains the USB drivers and must be inserted and read by the PC
PC.
2 Connect the USB cable as shown in USB Connection.
A few seconds after you complete the USB connection, the Add New Hardware Wizard window is displayed:
This CD
before you connect the SBG900 to the
3 Click Next. The following window is displayed:
4 Be sure “Search for the best driver for your device” is selected.
Home
X
ExitPrint
79
SBG900 User Guide
Page 86

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
5 Click Next. The following window is displayed:
Be sure “CD-ROM drive” is the only box checked.
6 Click Next. The message “Please wait while Windows searches for a new driver for this device” is displayed.
If the computer successfully locates the driver, you can skip to step 9.
If the computer does not locate the driver, the previous window is displayed again.
7 Select Specify a location and type the location of the CD-ROM drive:
To load the driver successfully, you may need to click Browse to manually select the NetMotCM.sys file on
the CD-ROM.
Home
X
ExitPrint
80
SBG900 User Guide
Page 87

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
8 Click Next. The following window is displayed:
9 Select The updated driver... and click Next. If the following window is not displayed, verify that the
SURFboard Wireless Cable Modem Gateway
cannot find the correct driver file, click Cancel to cancel the installation and perform the procedure for
“Removing the USB Driver from Windows 98 or Windows Me”. Then repeat this procedure.
Although your SBG model number may be different than in the images in this guide,
the procedure is the same.
CD-ROM is properly inserted in the CD-ROM drive. If you still
10 After the window shown under step 9 is displayed, click Next.
If a window with the message
drive
letter
(for example, “D:”) and click OK.
Copying Files...
displays and asks for the CD-ROM drive, type the CD-ROM
Motorola
If an Insert Disk window similar to the one below is displayed, Windows 98 system files are needed to
complete the installation. To install the files, insert your Windows 98 CD-ROM in the CD-ROM drive and
click OK.
Home
X
ExitPrint
81
SBG900 User Guide
Page 88

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
After all the necessary files are loaded, the following window is displayed to confirm a successful installation:
11 Click Finish. The Systems Settings Change window is displayed:
12 Click Yes to restart the computer.
When you finish setting up the USB driver, you can continue with “Configuring TCP/IP”.
If you have difficulties setting up the USB driver, perform “Removing the USB Driver from Windows 98 or
Windows Me” and repeat this procedure. If that does not correct the problem, see the
License, and Warranty Information
service.
card provided with the SBG900 for information about obtaining warranty
Regulatory, Safety, Software
Home
X
ExitPrint
82
SBG900 User Guide
Page 89

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Settin g Up a US B Dr iver in Windo ws 2000
1
Insert the Motorola SURFboard Wireless Cable Modem Gateway CD-ROM in the CD-ROM drive.
contains the USB drivers and must be inserted and read by the PC
PC.
2 Connect the USB cable as shown in USB Connection.
A few seconds after you complete the USB connection, the Found New Hardware window is displayed:
This CD
before you connect the SBG900 to the
3 Click Next. The following window is displayed:
Although your SBG model number may be different than in the images in this guide, the procedure is
the same.
Be sure “Search for a suitable driver for my device” is selected.
Home
X
ExitPrint
83
SBG900 User Guide
Page 90

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
4 Click Next. The following window is displayed:
Be sure “CD-ROM drives” is the only box checked.
5 Click Next. The following window is displayed:
6 Click Next.
If the Insert Disk window is displayed, be sure the
CD-ROM is in the CD-ROM drive and follow steps 7 to 12. Otherwise, you can skip to step 13.
Home
X
ExitPrint
84
Motorola SURFboard Wireless Cable Modem Gateway
SBG900 User Guide
Page 91

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
7 On the Insert Disk window, click OK. The Files Needed window is displayed:
8 If necessary, select the CD-ROM drive in the Copy files from list.
9 Click Browse.
10 Locate the NetMotCM.sys file in the CD-ROM root directory.
11 Double-click the NetMotCM.sys file. The Files Needed window is displayed.
12 Click OK. The Found New Hardware Wizard window is displayed:
13 Click Finish to complete the installation.
When you finish setting up the USB driver, you can continue with “Configuring TCP/IP”.
If you have any difficulties setting up the USB driver, perform “Removing the USB Driver from Windows 2000” and
repeat this procedure.
Home
X
ExitPrint
85
SBG900 User Guide
Page 92

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Setting Up a USB Dr iv er in Windo ws Me
1
Insert the Motorola SURFboard Wireless Cable Modem Gateway CD-ROM in the CD-ROM drive.
contains the USB drivers and must be inserted and read by the PC
PC.
2 Connect the USB cable as shown in USB Connection.
A few seconds after you complete the USB connection, the Add New Hardware Wizard window is displayed:
This CD
before you connect the SBG900 to the
3 Click Next. Windows automatically searches for the correct USB drivers and installs them. If the installation is
successful, the following window is displayed:
Although your SBG model number may be different than in the images in this guide,
the procedure is the same.
4 If the window above is displayed, click Finish. Otherwise, be sure the
Modem Gateway
When you finish setting up the USB driver, you can continue with “Configuring TCP/IP”.
CD-ROM is correctly inserted in the CD-ROM drive.
Motorola SURFboard Wireless Cable
Home
X
ExitPrint
86
SBG900 User Guide
Page 93

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Setting Up a USB Dr iv er in Windo ws XP
1
Insert the Motorola SURFboard Wireless Cable Modem Gateway CD-ROM in the CD-ROM drive.
contains the USB drivers and must be inserted and read by the PC
PC.
2 Connect the USB cable as shown in USB Connection.
A few seconds after you complete the USB connection, the Found New Hardware Wizard window is
displayed:
This CD
before you connect the SBG900 to the
3 Be sure “Install the software automatically” is selected.
4 Click Next. Windows automatically searches for the correct USB drivers and installs them. If the installation is
successful, the following window is displayed:
Although your SBG model number may be different than in the images in this guide, the procedure
is the same.
Home
X
ExitPrint
87
SBG900 User Guide
Page 94

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
5 Click Finish to complete the installation. Otherwise, be sure the
Gateway
When you finish setting up the USB driver, you can continue with “Configuring TCP/IP”.
CD-ROM is correctly inserted in the CD-ROM drive.
Motorola SURFboard Wireless Cable Modem
Removing the USB Driver from Windows 98 or Windows Me
1 On the Windows Desktop, right-click
• In Windows 98, the Network Neighborhood icon
• In Windows ME, the My Network Places icon
The Network window is displayed:
one
of:
Although your SBG model number may be different than in the images in this guide, the procedure is
the same.
2 Click the Motorola SURFboard SBG900 USB Gateway.
Home
X
ExitPrint
88
SBG900 User Guide
Page 95

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
3 Click Remove. The Network window no longer displays Motorola SURFboard SBG900 USB Gateway
list:
4 Click OK. The System Settings Change window is displayed:
in the
5
Disconnect the USB cable from the PC or SBG900.
6 Click Yes to restart the computer.
7 Insert the
short time, a window with language choices is displayed.
Motorola SURFboard Wireless Cable Modem Gateway
CD-ROM in the CD-ROM drive. After a
8 Press the Esc key on the keyboard to exit the start-up screens.
9 To start Windows Explorer, click Start and select Run to display the Run window.
10 Type explorer and click OK.
Home
X
ExitPrint
89
SBG900 User Guide
Page 96

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
The Exploring window is displayed.
variations between Windows versions and you can configure Windows Explorer as you like.
Windows Explorer may appear different than in the image. There are
11 Double-click the Motorola SBG900 CD-ROM drive (D: in the image above).
12 Double-click remove or remove.exe to run the Remove utility from the
Modem Gateway
CD-ROM. The SURFboard Cable Modem USB Driver Removal window is displayed:
Motorola SURFboard Wireless Cable
13 Click Remove Driver.
After you remove the USB driver, re-install it on the computer. Perform
• Setting Up a USB Driver in Windows 98
• Setting Up a USB Driver in Windows Me
If you continue to have problems, contact your cable service provider.
Home
X
ExitPrint
90
one
of:
SBG900 User Guide
Page 97

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Removing the USB Driver from Windows 2000
1 On the Windows desktop, click Start.
2 Click Settings.
3 Click Control Panel to display the Control Panel window:
4 Double-click System to display the System Properties window.
5 Click the Hardware tab:
Home
X
ExitPrint
91
SBG900 User Guide
Page 98

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
6 Click Device Manager to display the Device Manager window:
Although your SBG model number may be different than in the images in this guide, the procedure is
the same.
7 Double-click Network Adapters.
8 Click the Motorola SURFboard SBG900 USB Gateway. The Uninstall icon displays on the window near the
top.
9 Click the Uninstall icon. The following window is displayed:
10 Click OK.
11 Close the Device Manager window.
12 Close the Control Panel window.
13 Insert the
Motorola SURFboard Wireless Cable Modem Gateway
CD-ROM in the CD-ROM drive.
14 Press the Esc key on the keyboard to exit the start-up screens.
15 To start Windows Explorer, click Start and select Run to display the Run window.
Home
X
ExitPrint
92
SBG900 User Guide
Page 99

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
16 On the Run window, type explorer and click OK to display Windows Explorer:
Windows Explorer may appear different than in the image. There are variations between Windows versions
and you can configure Windows Explorer as you like.
17 Double-click My Computer.
18 Double-click the Motorola SBG900 CD icon (D: in the image).
19 Double-click remove or remove.exe to run the Remove utility from the
Modem Gateway
20
Be sure the USB cable is disconnected.
CD-ROM. The SURFboard Cable Modem USB Driver Removal window is displayed:
Motorola SURFboard Wireless Cable
21 Click Remove Driver.
Informational messages similar to the ones shown are displayed on the SURFboard Cable Modem USB
Driver Removal window.
After you remove the USB driver, re-install it following “Setting Up a USB Driver in Windows 2000”. If you continue
to have problems, contact your cable service provider.
Home
X
ExitPrint
93
SBG900 User Guide
Page 100

Overview Installation Troubleshooting Contact FAQ Specifications Glossary License
Configuration: Basic Gateway TCP/IP Wireless USB
Removing the USB Driver from Windows XP
1 On the Windows desktop, click Start to display the Start window:
2 Click Control Panel to display the Control Panel window. The display varies, depending on the Windows XP
view options:
Home
X
ExitPrint
94
SBG900 User Guide
 Loading...
Loading...