Page 1

Symbol MiniScan MSXX07 Series
Integration Guide
Page 2

Page 3

Symbol MiniScan MSXX07 Series
Integration Guide
72E-67135-04
Revision A
May 2008
Page 4

ii Symbol MiniScan MSXX07 Series Integration Guide
© 2008 by Motorola, Inc. All rights reserved.
No part of this publication may be reproduced or used in any form, or by any electrical or mechanical means,
without permission in writing from Motorola. This includes electronic or mechanical means, such as
photocopying, recording, or information storage and retrieval systems. The material in this manual is subject to
change without notice.
The software is provided strictly on an “as i s” basis. All sof twar e, including firmware, furnished to the user is on
a licensed basis. Motorola grants to the user a non-transferab le and non-exclusive license to use each
software or firmware program delivered hereunder (licensed program). Except as noted below, such license
may not be assigned, sublicensed, or otherwise transferred by the user without prior written consent of
Motorola. No right to copy a licensed program in whole or in part is granted, except as permitted unde r
copyright law. The user shall not modify, merge, or incorporate any form or portion of a licensed program with
other program material, create a derivative work from a licensed program, or use a licensed program in a
network without written permission from Motorola. The user agrees to maintain Motorola’s copyright notice on
the licensed programs delivered hereunder, and to include the same on any authorized copies it makes, in
whole or in part. The user agrees not to deco mpile, disassemble, decode, or reverse engineer any licensed
program delivered to the user or any portion thereof.
Motorola reserves the right to make changes to any software or product to improve reliability, function, or
design.
Motorola does not assume any product liability arising out of, or in connection with, the application or use of
any product, circuit, or application described herein.
No license is granted, either expressly or by implication, estoppel, or otherwise under any Motorola, Inc.,
intellectual property rights. An implied license only exists for equipment, circuits, and subsystems contained in
Motorola products.
MOTOROLA and the Stylized M Logo and Symbol and the Symbol logo are registered in the US Patent &
Trademark Office. Bluetooth is a registered trademark of Bluetooth SIG. Microsoft, Windows and ActiveSync
are either registered trademarks or trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. All other product or service names
are the property of their respective owners.
Motorola, Inc.
One Motorola Plaza
Holtsville, New York 11742-1300
http://www.symbol.com
Patents
This product is covered by one or more of the patents listed on the website: http://www.symbol.com/patents.
Warranty
For the complete Motorola hardware product warranty statement, go to: http://www.symbol.com/warranty.
Page 5

Revision History
Changes to the original manual are listed below:
Change Date Description
-01 Rev A 2/2004 Initial release.
-02 Rev A 6/2004 Added Embedded Application information.
-03 Rev A 3/2007 Updated service information and specifications; change RSS code type references
-04 Rev A 5/2008 Updated connection drawing, added connecting via USB information, updated
iii
to GS1 DataBar
operating temperature for MS2207 and MS22 07VHD, removed Host T rigger option,
removed parameter numbers/hex values, added new UPC/EAN supplemental
options and Bookland ISBN format option, updated parameter defaults, updated
troubleshooting.
Page 6

iv Symbol MiniScan MSXX07 Series Integration Guide
Page 7

Table of Contents
About This Guide
Introduction.................................................................................................................... xiii
Chapter Descriptions..................................................................................................... xiii
Notational Conventions.................................................................................................. xiv
Related Documents....................................................................................................... xv
Service Information........................................................................................................ xv
Chapter 1: Getting Started
Introduction ................................................................................................................... 1-1
Symbol MSXX07 Series Features .......................................................................... 1-2
Typical Applications ...................................................................................................... 1-2
Block Diagram .............................................................................................................. 1-3
Miniscan Block Diagram Descriptions ..................................................................... 1-3
Chapter 2: Installation
Introduction ................................................................................................................... 2-1
Unpacking ..................................................................................................................... 2-1
Mounting ....................................................................................................................... 2-1
Symbol MS1207FZY/MS1207WA/MS2207/MS2207VHD Mounting Dimensions ... 2-2
Symbol MS3207 Mounting Dimensions .................................................................. 2-2
Mounting the Scanner on the Optional Stand ......................................................... 2-3
Mounting the Scanner on the Optional Mounting Bracket ...................................... 2-4
Connecting the MiniScan .............................................................................................. 2-6
Connecting the Symbol MSXX07 via USB .............................................................. 2-7
Location and Positioning ............................................................................................... 2-7
Using the MiniScan as an Embedded Scanner ...................................................... 2-7
Conveyor Applications ............................................................................................ 2-10
Embedded Applications Requiring a Window ......................................................... 2-12
Accessories .................................................................................................................. 2-15
Application Notes .......................................................................................................... 2-16
TTL RS-232 ............................................................................................................ 2-16
USB Warning - Potential Host Side Issues ............................................................. 2-16
Page 8

vi Symbol MiniScan MSXX07 Series Integration Guide
Chapter 3: Scanning
Introduction ................................................................................................................... 3-1
MiniScan Scan Patterns ............................................................................................... 3-1
Symbol MS1207FZY and MS1207WA Scan Pattern .............................................. 3-1
Symbol MS2207 and MS2207VHD Scan Patterns ................................................. 3-2
Symbol MS3207 Scan Patterns .............................................................................. 3-3
Scan Angle Selection .................................................................................................... 3-4
Operation in Blink Mode .......................................................................................... 3-4
Scanning Tips ............................................................................................................... 3-5
Scan the Entire Symbol .......................................................................................... 3-5
Position at an Angle ................................................................................................ 3-5
Trigger Options ............................................................................................................. 3-5
Continuous (Default) ............................................................................................... 3-5
Level Trigger ........................................................................................................... 3-6
Pulse Trigger ........................................................................................................... 3-6
Blink ........................................................................................................................ 3-6
Beeper and LED Definitions ......................................................................................... 3-7
Chapter 4: Symbol MS1207FZY Specifications
Introduction ................................................................................................................... 4-1
Symbol MS1207FZY Electrical Interface ...................................................................... 4-2
Symbol MS1207FZY Mechanical Drawings ................................................................. 4-3
Symbol MS1207FZY Technical Specifications ............................................................. 4-5
Symbol MS1207FZY Decode Zone .............................................................................. 4-7
Usable Scan Length ................................................................................................ 4-8
Chapter 5: Symbol MS1207WA Specifications
Introduction ................................................................................................................... 5-1
Symbol MS1207WA Electrical Interface ....................................................................... 5-2
Symbol MS1207WA Mechanical Drawings .................................................................. 5-3
Symbol MS1207WA Technical Specifications .............................................................. 5-5
Symbol MS1207WA Decode Zone ............................................................................... 5-7
Usable Scan Length ................................................................................................ 5-8
Chapter 6: Symbol MS2207 Specifications
Introduction ................................................................................................................... 6-1
Symbol MS2207 Electrical Interface ............................................................................. 6-2
Symbol MS2207 Mechanical Drawings ........................................................................ 6-3
Symbol MS2207 Technical Specifications .................................................................... 6-5
Symbol MS2207 Decode Zones ................................................................................... 6-8
Symbol MS2207 1D Decode Zone ......................................................................... 6-8
Symbol MS2207 1D Decode Distances .................................................................. 6-9
Symbol MS2207 2D Decode Zone ......................................................................... 6-10
Symbol MS2207 2D Decode Distances .................................................................. 6-11
Usable Scan Length ................................................................................................ 6-11
Page 9

Chapter 7: Symbol MS2207VHD Specifications
Introduction ................................................................................................................... 7-1
Symbol MS2207VHD Electrical Interface ..................................................................... 7-2
Symbol MS2207VHD Mechanical Drawings ................................................................. 7-3
Symbol MS2207VHD Technical Specifications ............................................................ 7-5
Symbol MS2207VHD Decode Zones ........................................................................... 7-8
Symbol MS2207VHD 1D Decode Zone .................................................................. 7-8
Symbol MS2207VHD 1D Decode Distances .......................................................... 7-9
Symbol MS2207VHD 2D Decode Zone .................................................................. 7-10
Symbol MS2207VHD 2D Decode Distances .......................................................... 7-11
Usable Scan Length ................................................................................................ 7-11
Chapter 8: Symbol MS3207 Specifications
Introduction ................................................................................................................... 8-1
Symbol MS3207 Electrical Interface ............................................................................. 8-2
Symbol MS3207 Mechanical Drawings ........................................................................ 8-4
Symbol MS3207 Technical Specifications .................................................................... 8-6
Symbol MS3207 Decode Zones ................................................................................... 8-9
Symbol MS3207 Omnidirectional Decode Distances ............................................. 8-9
Symbol MS3207 2D Slab/Raster Decode Distances .............................................. 8-11
Usable Scan Length ................................................................................................ 8-12
Table of Contents vii
Chapter 9: Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Introduction ................................................................................................................... 9-1
Maintenance ................................................................................................................. 9-1
Troubleshooting ............................................................................................................ 9-2
Chapter 10: Parameter Menus
Introduction ................................................................................................................... 10-1
Operational Parameters ................................................................................................ 10-1
Default Table ................................................................................................................ 10-2
Set Default Parameter .................................................................................................. 10-7
Scanning Options ......................................................................................................... 10-8
Beeper Volume ....................................................................................................... 10-8
Beeper Tone ........................................................................................................... 10-9
Beeper Frequency Adjustment ............................................................................... 10-9
Laser On Time ........................................................................................................ 10-10
Scan Angle .............................................................................................................. 10-10
Power Mode ............................................................................................................ 10-11
Trigger Mode ........................................................................................................... 10-11
Scanning Mode ...................................................................................................... 10-12
Aiming Mode ........................................................................................................... 10-13
Programmable Raster Height and Raster Expansion Speed ................................. 10-14
Timeout Between Decodes ..................................................................................... 10-15
Beep After Good Decode ........................................................................................ 10-16
Transmit “No Read” Message ................................................................................. 10-16
Parameter Scanning ............................................................................................... 10-17
Page 10

viii Symbol MiniScan MSXX07 Series Integration Guide
Linear Code Type Security Level ............................................................................ 10-18
Bi-directional Redundancy ...................................................................................... 10-19
UPC/EAN ...................................................................................................................... 10-20
Enable/Disable UPC-A ............................................................................................ 10-20
Enable/Disable UPC-E ............................................................................................ 10-20
Enable/Disable UPC-E1 .......................................................................................... 10-21
Enable/Disable EAN-8 ............................................................................................ 10-21
Enable/Disable EAN-13 .......................................................................................... 10-22
Enable/Disable Bookland EAN ............................................................................... 10-22
UPC/EAN Coupon Code ......................................................................................... 10-23
Decode UPC/EAN Supplementals .......................................................................... 10-24
User-Programmable Supplementals ....................................................................... 10-28
Decode UPC/EAN Supplemental Redundancy ...................................................... 10-28
Transmit UPC-A Check Digit .................................................................................. 10-29
Transmit UPC-E Check Digit .................................................................................. 10-29
Transmit UPC-E1 Check Digit ................................................................................ 10-30
UPC-A Preamble .................................................................................................... 10-31
UPC-E Preamble .................................................................................................... 10-32
UPC-E1 Preamble .................................................................................................. 10-33
Convert UPC-E to UPC-A ....................................................................................... 10-34
Convert UPC-E1 to UPC-A ..................................................................................... 10-34
EAN Zero Extend .................................................................................................... 10-35
Bookland ISBN Format ........................................................................................... 10-36
UPC/EAN Security Level ........................................................................................ 10-37
Linear UPC/EAN Decode ........................................................................................ 10-38
UPC Half Block Stitching ........................................................................................ 10-38
Code 128 ...................................................................................................................... 10-39
Enable/Disable Code 128 ....................................................................................... 10-39
Enable/Disable UCC/EAN-128 ............................................................................... 10-39
Enable/Disable ISBT 128 ........................................................................................ 10-40
Lengths for Code 128 ............................................................................................. 10-40
Code 128 Decode Performance ............................................................................. 10-41
Code 128 Decode Performance Level .................................................................... 10-42
Code 39 ........................................................................................................................ 10-43
Enable/Disable Code 39 ......................................................................................... 10-43
Enable/Disable Trioptic Code 39 ............................................................................ 10-43
Convert Code 39 to Code 32 .................................................................................. 10-44
Code 32 Prefix ........................................................................................................ 10-44
Set Lengths for Code 39 ......................................................................................... 10-45
Code 39 Check Digit Verification ............................................................................ 10-46
Transmit Code 39 Check Digit ................................................................................ 10-46
Enable/Disable Code 39 Full ASCII ........................................................................ 10-47
Code 39 Decode Performance ............................................................................... 10-48
Code 39 Decode Performance Level ...................................................................... 10-49
Code 93 ........................................................................................................................ 10-50
Enable/Disable Code 93 ......................................................................................... 10-50
Set Lengths for Code 93 ......................................................................................... 10-51
Code 11 ........................................................................................................................ 10-52
Enable/Disable Code 11 ......................................................................................... 10-52
Set Lengths for Code 11 ......................................................................................... 10-53
Page 11

Table of Contents ix
Code 11 Check Digit Verification ............................................................................ 10-54
Transmit Code 11 Check Digit ................................................................................ 10-55
Interleaved 2 of 5 .......................................................................................................... 10-56
Enable/Disable Interleaved 2 of 5 ........................................................................... 10-56
Set Lengths for Interleaved 2 of 5 ........................................................................... 10-57
I 2 of 5 Check Digit Verification ............................................................................... 10-58
Transmit I 2 of 5 Check Digit ................................................................................... 10-59
Convert I 2 of 5 to EAN-13 ...................................................................................... 10-59
Discrete 2 of 5 ............................................................................................................... 10-60
Enable/Disable Discrete 2 of 5 ................................................................................ 10-60
Set Lengths for Discrete 2 of 5 ............................................................................... 10-61
Codabar ........................................................................................................................ 10-62
Enable/Disable Codabar ......................................................................................... 10-62
Set Lengths for Codabar ......................................................................................... 10-63
CLSI Editing ............................................................................................................ 10-64
NOTIS Editing ......................................................................................................... 10-64
MSI Plessey .................................................................................................................. 10-65
Enable/Disable MSI Plessey ................................................................................... 10-65
Set Lengths for MSI Plessey ................................................................................... 10-66
MSI Plessey Check Digits ....................................................................................... 10-67
Transmit MSI Plessey Check Digit .......................................................................... 10-67
MSI Plessey Check Digit Algorithm ........................................................................ 10-68
PDF417/MicroPDF417 ................................................................................................. 10-69
Enable/Disable PDF417 .......................................................................................... 10-69
Enable/Disable MicroPDF417 ................................................................................. 10-69
MicroPDF Performance .......................................................................................... 10-70
Code 128 Emulation ............................................................................................... 10-71
GS1 DataBar ................................................................................................................ 10-72
GS1 DataBar-14 ..................................................................................................... 10-72
GS1 DataBar Limited .............................................................................................. 10-72
GS1 DataBar Expanded ......................................................................................... 10-73
Convert GS1 DataBar to UPC/EAN ....................................................................... 10-73
Composite .................................................................................................................... 10-74
Composite CC-C ..................................................................................................... 10-74
Composite CC-A/B .................................................................................................. 10-74
Composite TLC-39 .................................................................................................. 10-75
UPC Composite Mode ............................................................................................ 10-76
Data Options ................................................................................................................. 10-77
Transmit Code ID Character ................................................................................... 10-77
Prefix/Suffix Values ................................................................................................. 10-79
Scan Data Transmission Format ............................................................................ 10-80
Event Reporting ............................................................................................................ 10-82
Decode Event ......................................................................................................... 10-83
Boot Up Event ......................................................................................................... 10-83
Parameter Event ..................................................................................................... 10-84
Macro PDF Features ................................................................................................... 10-85
Transmit Symbols in Codeword Format .................................................................. 10-85
Transmit Unknown Codewords ............................................................................... 10-86
Escape Characters ................................................................................................. 10-86
Delete Character Set ECIs ...................................................................................... 10-87
Page 12

x Symbol MiniScan MSXX07 Series Integration Guide
ECI Decoder ........................................................................................................... 10-87
Transmit Macro PDF User-Selected Fields ................................................................. 10-88
Transmit File Name ................................................................................................. 10-88
Transmit Block Count .............................................................................................. 10-89
Transmit Time Stamp .............................................................................................. 10-89
Transmit Sender ..................................................................................................... 10-90
Transmit Addressee ................................................................................................ 10-90
Transmit Checksum ................................................................................................ 10-91
Transmit File Size ................................................................................................... 10-91
Transmit Macro PDF Control Header ..................................................................... 10-92
Last Blocker Marker ................................................................................................ 10-92
Numeric Bar Codes ...................................................................................................... 10-93
Cancel ..................................................................................................................... 10-95
Chapter 11: RS-232 Interface
Introduction ................................................................................................................... 11-1
RS-232 Default Parameters .......................................................................................... 11-2
RS-232 Host Parameters .............................................................................................. 11-3
RS-232 Host Types ................................................................................................. 11-5
Baud Rate ............................................................................................................... 11-7
Parity ....................................................................................................................... 11-8
Stop Bit Select ........................................................................................................ 11-9
Data Bits ................................................................................................................. 11-9
Check Receive Errors ............................................................................................. 11-10
Hardware Handshaking .......................................................................................... 11-10
Software Handshaking ............................................................................................ 11-12
Host Serial Response Time-out .............................................................................. 11-14
RTS Line State ........................................................................................................ 11-15
Beep on <BEL> ....................................................................................................... 11-15
Intercharacter Delay ................................................................................................ 11-16
Nixdorf Beep/LED Options ...................................................................................... 11-17
Ignore Unknown Characters ................................................................................... 11-17
Chapter 12: USB Interface
Introduction ................................................................................................................... 12-1
Connecting a USB Interface ......................................................................................... 12-1
USB Default Parameters ......................................................................................... 12-2
USB Host Parameters .................................................................................................. 12-3
USB Device Type .................................................................................................... 12-3
USB Country Keyboard Types (Country Codes) .................................................... 12-4
USB Keystroke Delay ............................................................................................. 12-7
USB CAPS Lock Override ...................................................................................... 12-8
USB Ignore Unknown Characters ........................................................................... 12-9
Emulate Keypad ...................................................................................................... 12-9
USB Keyboard FN 1 Substitution ............................................................................ 12-10
Function Key Mapping ............................................................................................ 12-10
Simulated Caps Lock .............................................................................................. 12-11
Convert Case .......................................................................................................... 12-11
Page 13

Chapter 13: Advanced Data Formatting
Introduction ................................................................................................................... 13-1
Rules: Criteria Linked to Actions ................................................................................... 13-1
Using ADF Bar Codes .................................................................................................. 13-2
ADF Bar Code Menu Example ..................................................................................... 13-2
Rule 1: The Code 128 Scanning Rule .................................................................... 13-3
Rule 2: The UPC Scanning Rule ............................................................................ 13-3
Alternate Rule Sets ................................................................................................. 13-3
Rules Hierarchy (in Bar Codes) .............................................................................. 13-4
Default Rules .......................................................................................................... 13-5
ADF Bar Codes ............................................................................................................. 13-6
Special Commands ....................................................................................................... 13-8
Pause Duration ....................................................................................................... 13-8
Begin New Rule ...................................................................................................... 13-8
Save Rule ............................................................................................................... 13-8
Erase ....................................................................................................................... 13-9
Quit Entering Rules ................................................................................................. 13-9
Disable Rule Set ..................................................................................................... 13-10
Criteria .......................................................................................................................... 13-11
Code Types ............................................................................................................. 13-11
Code Lengths .......................................................................................................... 13-16
Message Containing A Specific Data String ........................................................... 13-20
Actions .......................................................................................................................... 13-25
Send Data ............................................................................................................... 13-25
Setup Field(s) .......................................................................................................... 13-28
Modify Data ............................................................................................................. 13-33
Pad Data with Spaces ............................................................................................. 13-35
Pad Data with Zeros ............................................................................................... 13-39
Beeps ...................................................................................................................... 13-44
Send Keystroke (Control Characters and Keyboard Characters) ........................... 13-44
Send Right Control Key .......................................................................................... 13-80
Send Graphic User Interface (GUI) Characters ...................................................... 13-81
Turn On/Off Rule Sets ............................................................................................ 13-86
Alphanumeric Keyboard ............................................................................................... 13-88
Table of Contents xi
Chapter 14: Mounting Template
Introduction ................................................................................................................... 14-1
Symbol MS1207FZY/MS1207WA/MS2207/MS2207VHD Mounting Template ...... 14-1
Symbol MS3207 Mounting Template ...................................................................... 14-2
Appendix A: ASCII Character Sets
RS-232 ASCII Character Set ........................................................................................ A-1
USB ASCII Character Set ............................................................................................. A-6
Index
Tell Us What You Think...
Page 14

xii Symbol MiniScan MSXX07 Series Integration Guide
Page 15

About This Guide
Introduction
The Symbol MiniScan MSXX07 Series Integration Guide provides general instructions for mounting, setting up,
and programming the following MiniScan models:
•
MS1207FZY
•
MS1207WA
•
MS2207
•
MS2207VHD
•
MS3207.
NOTE It is recommended that an opto-mechanical engineer perform an opto-mechanical analysis prior to
integration.
Chapter Descriptions
Topics covered in this guide are as follows:
•
Chapter 1, Getting Started provides an overview of the MiniScan scanners and features, and provides a
block diagram of the scanner.
•
Chapter 2, Installation describes how to mount and install the MiniScan scanner.
•
Chapter 3, Scanning provides information on scan patterns, scanning, triggering options, and beeper and
LED definitions.
•
Chapter 4, Symbol MS1207FZY Specifications provides the technical and scanning specifications for the
Symbol MS1207FZY scanner.
•
Chapter 5, Symbol MS1207WA Specifications provides th e technical and scanning specifications for the
Symbol MS1207WA scanner.
•
Chapter 6, Symbol MS2207 Specifications provides the technical and scanning specifications for the Symbol
MS2207 scanner.
Page 16

xiv Symbol MiniScan MSXX07 Series Integration Guide
•
Chapter 7, Symbol MS2207VHD Specifications provides the technical and scanning specifications for the
Symbol MS2207VHD scanner.
•
Chapter 8, Symbol MS3207 Specifications provides the technical and scanning specifications for the Symbol
MS3207 scanner.
•
Chapter 9, Maintenance and Troubleshooting provides information on maintaining and troubleshooting the
MiniScan scanners.
•
Chapter 10, Parameter Menus describes the programmable parameters and provides bar codes for
programming.
•
Chapter 11, RS-232 Interface describes how to set up the scanner for RS-232 operation.
•
Chapter 12, USB Interface describes how to set up the scanner for USB operation.
•
Chapter 13, Advanced Data Formatting (ADF) describes how to customize scanned data befo re transmitting
to the host.
•
Chapter 14, Mounting Te mplate provides mounting templates for the MiniScan scanners.
•
Appendix A, ASCII Character Sets provides prefix and suffix values to assign for ASCII character data
transmission.
Notational Conventions
The following conventions are used in this document:
•
Italics are used to highlight chapters and sections in this and related documents.
•
bullets (•) indicate:
• Action items
• Lists of alternatives
• Lists of required steps that are not necessarily sequential
•
Sequential lists (e.g., those that describe step-by-s te p pr oc ed ur e s) ap pe a r as nu m be re d lists.
NOTE This symbol indicates something of special interest or importance to the reader. Failure to read the note
will not result in physical harm to the reader, equipment or data.
CAUTION This symbol indicates that if this information is ignored, the possiblity of data or material damage may
occur.
WARNING! This symbol indicates that if this information is ignored the possibility that serious personal
injury may occur.
Page 17

Related Documents
The following document provides more information for MiniScan Series scanners.
• MiniSca n Family of Scanners Quick Reference Guide, p/n 72-58809-xx
For the latest version of this guide and all guides, go to: http://www.symbol.com/manuals.
Service Information
If you have a problem with your equipment, contact Motorola Enterprise Mobility Support for your region. Contact
information is available at: http://www.symbol.com/contactsupport
When contacting Enterprise Mobility Support, please have the following information available:
•
Serial number of the unit
•
Model number or product name
•
Software type and version number.
About This Guide xv
.
Motorola responds to calls by E-mail, telephone or fax within the time limits set forth in support agreements.
If your problem cannot be solved by Motorola Enterprise Mobility Support, you may need to return your equipment
for servicing and will be given specific directions. Motorola is not responsible for any damages incurred during
shipment if the approved shipping container is not used. Shipping the units improperly can possibly void the
warranty.
If you purchased your Enterprise Mobility business product from a Motorola business partner, contact that business
partner for support.
Page 18

xvi Symbol MiniScan MSXX07 Series Integration Guide
Page 19

Chapter 1 Getting Started
CAUTION Use of controls, adjustments or procedures other than those specified here can result in hazardous
laser light exposure.
Introduction
The MiniScan family of industrial fixed-mount scanners is specifically designed for stand-alone applications, and
OEM applications such as kiosks.
Figure 1-1
Symbol MSXX07 Series scanners provide easy and flexible integration of bar code scanning into a host device,
and include the following models:
•
•
MiniScan Family of Scanners
The Symbol MS1207FZY offers fuzzy logic for premium scanning performance on all types of 1D bar codes
including poorly printed and low contrast symbols. The MS1207FZY features a compact design for superior
performance and durability in a form factor that easily integrates into OEM devices for embedded
applications such as medical instruments, diagnostic equipment, vending machines, and gaming. As a
fixed-mount scanner, the MS1207FZY is ideal for applications requiring unattended scanni ng such as
manufacturing, warehouse and shipping, conveyor belts, library and document tracking systems.
The Symbol MS1207WA Wide Angle Scanner features a broad 60o scan angle to accommodate large 1D
bar codes within extremely close range. This scanner is ideal for high-volume, near-contact scanning
applications such as kiosks, ATMs, assembly lines, warehouse and shipping.
Page 20

1 - 2 Symbol MiniScan MSXX07 Series Integration Guide
•
The Symbol MS2207 and MS2207VHD offer a "smart" raster pattern optimized for 2D applications and
poorly printed 1D bar codes. The high scan rate ensures fast and reliable data on all 1D symbols, and 2D
codes such as PDF417, MicroPDF, GS1 DataBar and composite codes. These scann e rs ar e pe rf ec t for
automated data entry applications that require high-speed scanning, performance, and small size, such as
conveyor belts, manufacturing and warehouse, gas pumps, and security/ID verification.
•
The Symbol MS3207 features a high-speed omnidirectio nal scan p atter n that makes it easy and intuitive for
consumers to scan bar codes at the point of activity. The omnidirectional scan pattern reads bar codes
quickly and accurately, minimizing the need for precise positioning of linear 1D bar codes. The MS3207
provides an easy and cost-effective way to enhance existing OEM devices with high-performance 1D and 2D
scanning, making it the ideal solution for applications that require fast, accurate scanning such as kiosks,
ATMs, listening stations, lottery machines, and vending machines.
Symbol MSXX07 Series Features
•
Stand-alone or OEM applications
•
Quick and easy integration for OEM devices
•
Excellent scanning performance on all types of bar codes
(MS1207FZY and MS1207WA support 1D bar codes only)
•
Rugged IP54 sealed housing with integrated beeper
•
Multi-interface (USB, Synapse, TTL RS-232)
•
Easy programming and configuration
•
Flexible mounting options
•
LEDs and an integrated beeper indicating scanner power status and successful decodes.
Typical Applications
MiniScan is the perfect solution for the following applications:
Fixed Mount Standalone Applications
•
Manufacturing / warehouse
•
Conveyer belts
•
Security / ID verification
•
POS
•
Library tracking
•
Document control.
OEM Applications
•
Kiosks / ATMs
•
Music listening stations
•
Security / ID verification
•
Lottery terminals / gaming.
Page 21
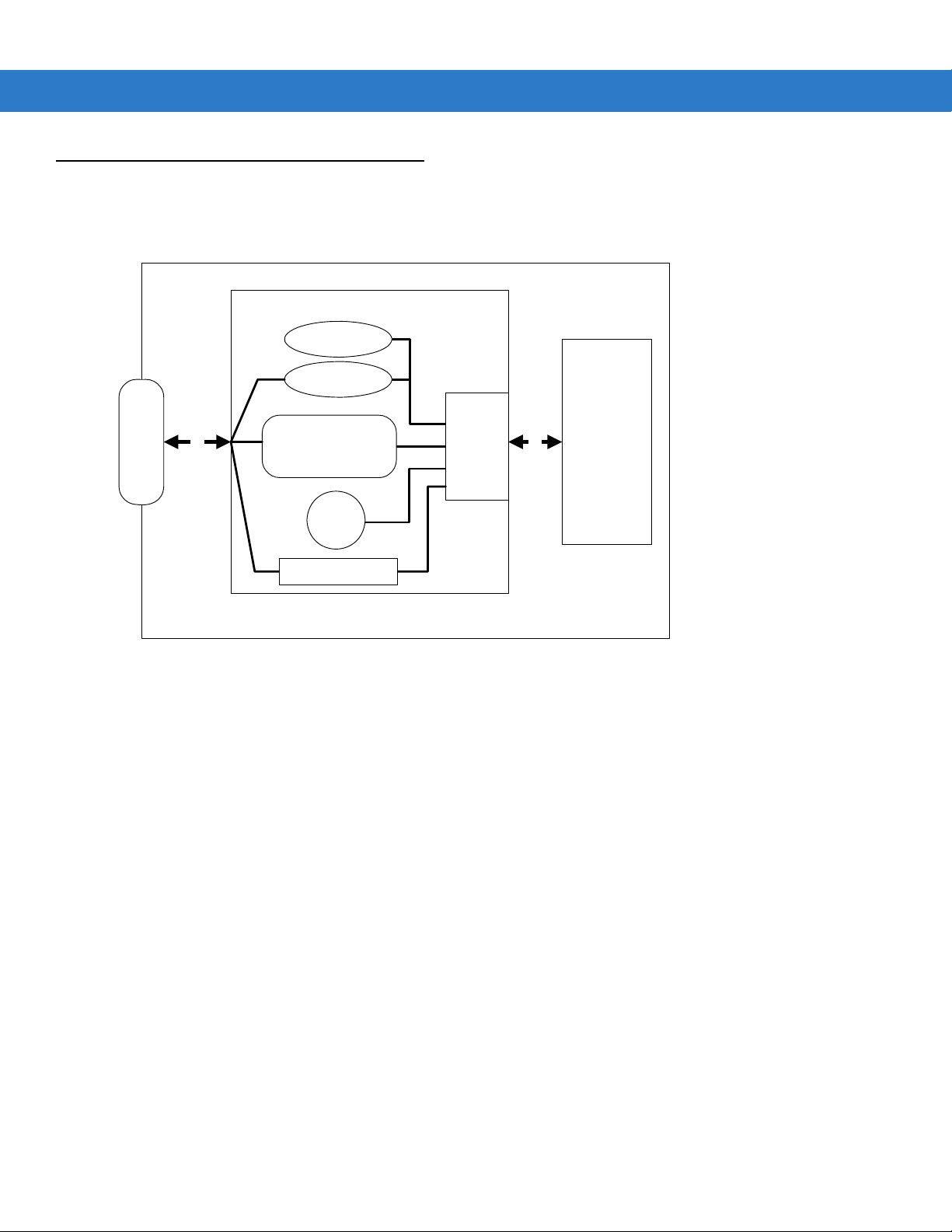
Block Diagram
The MiniScan block diagram illustrates the functional relationship of the MiniScan components. Following is a
detailed description of each component in the block diagram.
Getting Started 1 - 3
Interface Board
Beeper
External Beeper
Decoded
Scan
Engine
DB9
Figure 1-2
flex flex
Interface Circuit
TTL-RS232, Synapse, USB
Red/
Green
LED
External Trigger
Interface
MiniScan Block Diagram
Miniscan Block Diagram Descriptions
Decoded Scan Engine - The scan engine emits a beam of laser light that reflects off the bar code. Black bars
absorb light, white spaces reflect light. The scan engine collects the reflected light and processes the signal
through several analog filters. The filtered signal is digitized into a Digitized Barcode Pattern (DBP). The decoder
micro-controller analyzes timing information to decode and transmit the data contained in the bar code.
Interface Board - The interface board adapts the scan engine's interface into usable signals and data for the
intended host. It also contains a beeper and red/green LED for audio/visual feedback, and p rovides for an external
trigger and external beeper.
The interface board converts the scan engine's data to Synapse, USB, or TTL level RS-232. A separate host
adapter cable (p/n 25-62186-xx) converts the TTL level RS-232 output to standard RS-232 levels. All interface
types are auto-detected based on the host cable attached.
DB9 - The DB9 connector provides a sealed outlet for the various interface signals used between a MiniScan
scanner and the host. It also maintains pin compatibility with the previous generation LS1220 MiniScan host
cables.
Page 22

1 - 4 Symbol MiniScan MSXX07 Series Integration Guide
Page 23

Chapter 2 Installation
Introduction
This chapter provides information on unpacking, mounting, and installing the MiniScan.
Unpacking
Remove the MiniScan from its packing and inspect for damage. If the scanner is damaged, contact Motorola
Enterprise Mobility Support. See page xv for contact information.
KEEP THE PACKING. It is the approved shipping container and should be used if the equipment needs to be
returned for servicing.
Mounting
There are three mounting holes (threaded inser ts) on the bottom of the chassis.
The following figures provide mounting dimensions for the MiniScan scanner housings. For a mounting template,
see Mounting Template on page 14-1.
NOTE Use only non-magnetic M3x.5 screws with a maximum length of 3.6M to mount the MiniScan scanner
chassis.
Page 24

2 - 2 Symbol MiniScan MSXX07 Series Integration Guide
Symbol MS1207FZY/MS1207WA/MS2207/MS2207VHD Mounting Dimensions
Threaded Inserts
Note:
Dimensions are in
inches [mm].
Figure 2-1
Symbol MS1207FZY/MS1207WA/MS2207/MS2207VHD Mounting Dimensions
Symbol MS3207 Mounting Dimensions
Note:
Dimensions are in
inches [mm].
Threaded Inserts
Figure 2-2
Symbol MS3207 Mounting Dimensions
Page 25
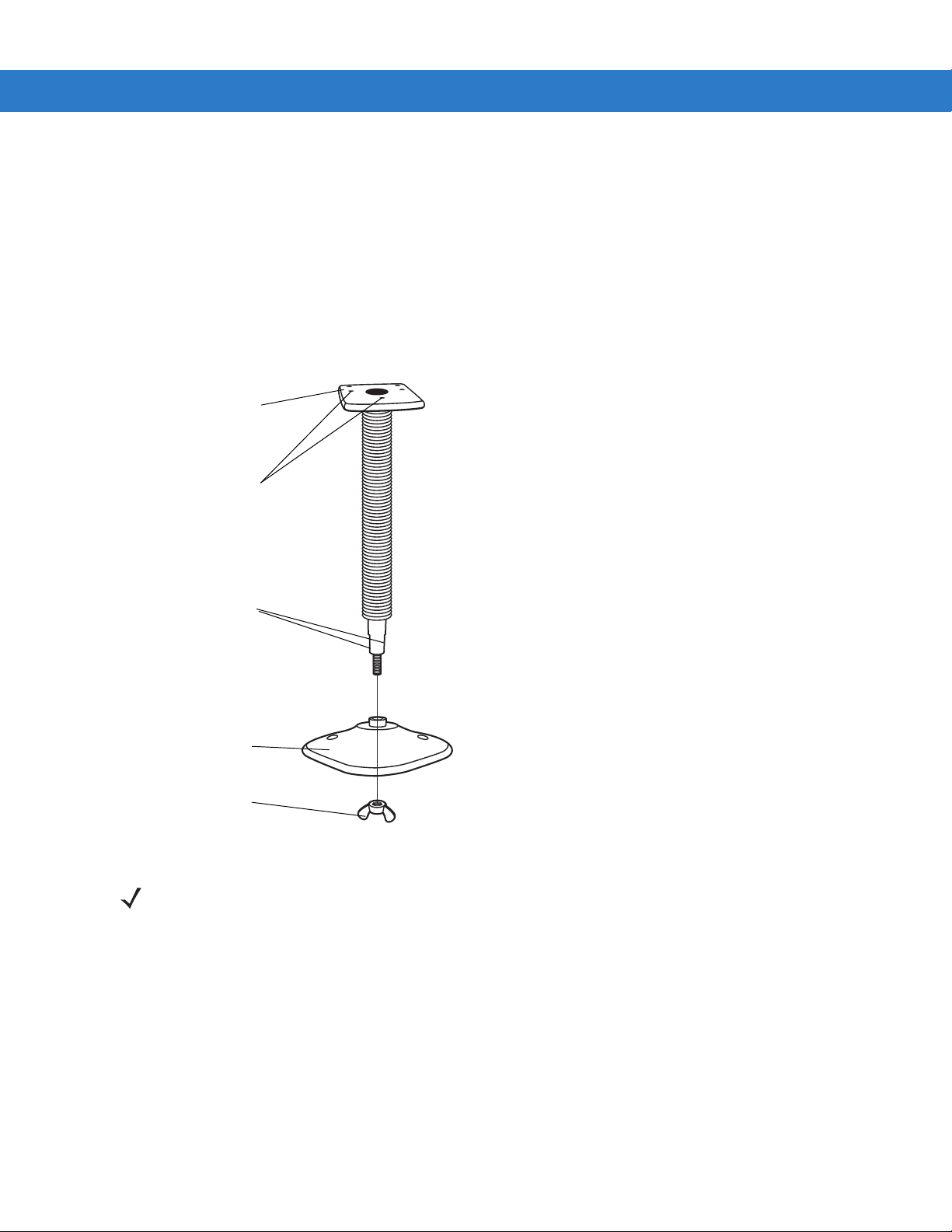
Installation 2 - 3
Mounting the Scanner on the Optional Stand
To mount the scanner on the optional stand:
1. Place the bottom of the scanner on the stand’s sca nner mount, aligning the scanner’s center threaded insert
(beneath the scan window) with the center mounting hole on the front of the stand. The two rear threaded
inserts on the bottom of the scanner align with the proper mounting holes on the stand.
2. Secure the scanner to the stand using the three screws provided with the stand.
Assembling the Stand
Scanner mount
Mounting holes
Flat areas
Stand base
Wingnut
1. Unscrew the wingnut from the bottom
of the one-piece scanner mount.
2. Fit the bottom of the neck piece into
the opening on the top of the stand
base.
3. Tighten the wingnut underneath the
base to secure the cup and neck piece
(see the note below).
4. Bend the neck to the desired position
for scanning.
Figure 2-3
Assembling the Stand
NOTE Before tightening the wingnut under the base, ensure that the flat areas on the flexible neck fit securely in
the grooves in the base.
Mounting the Stand (optional)
You can attach the base of the scanner’s stand to a fl at surface using two screws or double-sided tape (not
provided).
Screw Mount
1. Position the assembled base on a flat surface.
2. Screw one #10 wood screw into each screw-mount hole until the base of the stand is secure.
Page 26
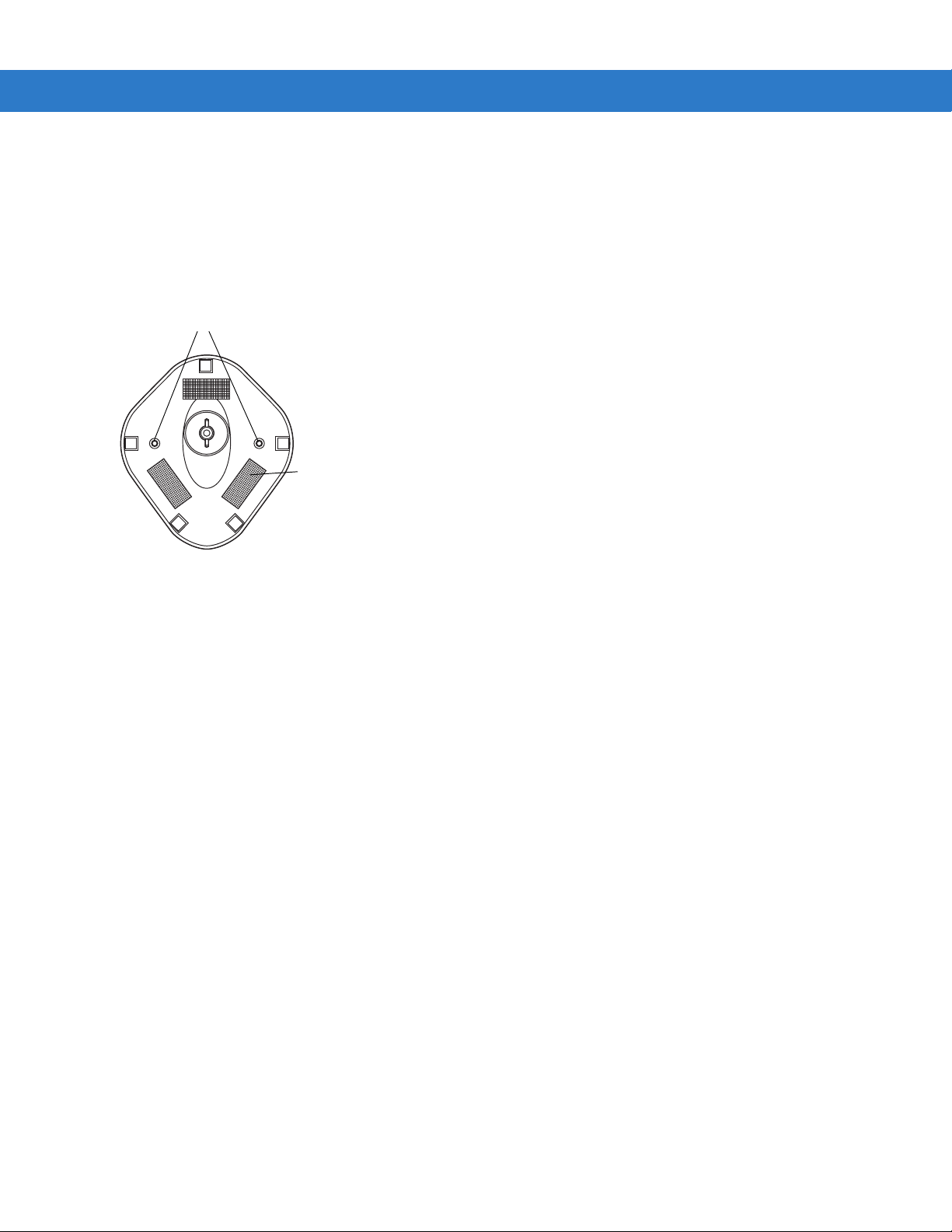
2 - 4 Symbol MiniScan MSXX07 Series Integration Guide
Tape Mount
1. Peel the paper liner off one side of each piece of tape and place the sticky surface over each of the three
rectangular tape areas.
2. Peel the paper liner off the exposed sides of each piece of tape and press the stand on a flat surface until it is
secure.
Two screw-mount holes
Double-sided tape
areas (3 places)
(dimensions = 1” x 2”)
Figure 2-4
Mounting the Stand
Mounting the Scanner on the Optional Mounting Bracket
The optional mounting bracket kit consists of a scanner bracket, a moun ting br acket, and the h ardware re qui red to
mount the scanner. The bracket kit accommodates adjustable angles for optimal positioning of the scanner.
To mount the MiniScan scanner on the bracket, first secure the scanner to the scanner bracket, then attach the
mounting bracket to the wall (see Figure 2-5 on page 2-5):
1. Tilt the scanner bracket forward to access the center scanner mounting hole on the bracket.
2. Place the bottom of the scanner on the scanner br acket, aligning the scanner’s center threaded insert (b eneath
the scan window) with the center mounting hole on the scanner bracket.
3. Insert one of the screws provided through the mounting hole and into the scanner’s center threaded insert.
For the Symbol MS1207FZY, MS1207WA, MS2207, and MS2207VHD, use a #0 Phillips screwdriver; for the
Symbol MS3207, use a #1 Phillips screwdriver.
4. Tilt the scanner bracket in the opposite direction to access the rear scanner mounting holes (which ar e aligned
with the rear inserts on the bottom of the scanner), then insert the remaining two screws provided through the
two rear mounting holes and into the scanner’s threaded inserts.
5. Secure the mounting bracket to a flat surface by inserting 1/8” or smaller fasten ers through the surfac e and into
the bracket’s mounting holes. There are four mounting holes on the bottom of the mounting bracket for
horizontal mounting, and six holes on the side for vertical mounting.
Page 27

Vertical
Mounting Holes
Installation 2 - 5
Scanner
Mounting Holes
Horizontal
Mounting Holes
Figure 2-5
Mounting Bracket
Scanner Bracket
Mounting the Scanner and Bracket
Page 28
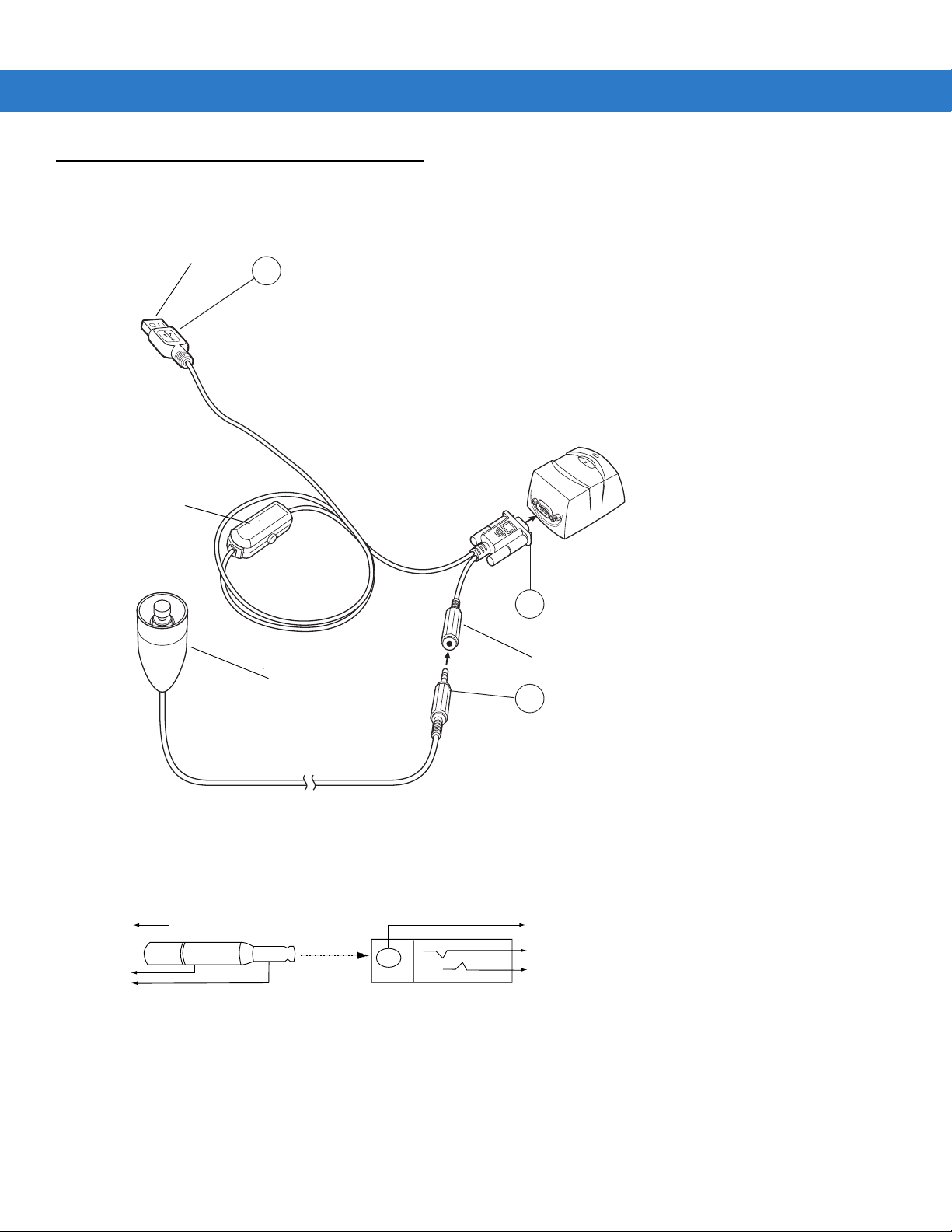
2 - 6 Symbol MiniScan MSXX07 Series Integration Guide
1
2
2
3
3
Connecting the MiniScan
To connect the MiniScan to the host, connect the scanner cables in the order shown in Figure 2-6.
To Host
3
Beeper
(Optional)
5
Trigger or Photo
Sensor (Optional)
4
1
Trigger Jack (Optional)
See Figure 2-7
2
Figure 2-6
1
Figure 2-7
Typical Connection Diagram
Male jack shown for reference
Note: Due to many variations of
jack and socket styles, identify
terminals as shown before
soldering leads.
Trigger Jack Connector Pins
Insertion
Direction
1 - Ground (Sleeve)
1 - Ground (Sleeve)
2 - Vcc (Middle Contact)
2 - Battery (Middle Contact)
3 - Trigger (Tip)
3 - Trigger (Tip)
Page 29

Connecting the Symbol MSXX07 via USB
Using a PC running Microsoft Windows:
1. Connect the USB cable to the USB port on the host.
2. Connect the other end of the USB cable to the scanner as indicated on the cable. The scanner powers up and
beeps.
3. On the host, open a word processing program such as Microsoft Word.
4. Present a bar code to the scanner . A beep indicates a decode, and the data appears on the host screen.
Location and Positioning
CAUTION The location and positioning guidelines provided do not consider unique application characteristics.
Motorola recommends that an opto-mechanical engineer perform an opto-mechanical analysis prior
to integration.
Installation 2 - 7
NOTE Integrate the scanner in an environment no more extreme than the product’s specification, where the
scanner will not exceed its temperature range. For instance, do not mount the scanner onto or next to a
large heat source. When placing the scanner with another device, ensure there is proper convection or
venting for heat. Follow these suggestions to ensure product longevity, warranty, and overall satisfaction
with the scanner.
Using the MiniScan as an Embedded Scanner
You can mount the MiniScan read symbols that are automatically presented, or that are presented in a
pre-determined location. In these applications, MinScan positioning with respect to the symbol is critical. Failure to
properly position the MiniScan can result in unsatisfactory scanning performance. A thermal analysis is also
recommended.
Two methods of positioning the scanner are provided:
•
Use the Calculating the Usable Scan Length Method on page 2-8 with consistently good quality symbols.
This provides a mathematical solution to find the usable scan length.
•
The Testing the Usable Scan Length Method on page 2-9 uses real situation testing to adjust the usable sca n
length to fit the application conditions.
Page 30

2 - 8 Symbol MiniScan MSXX07 Series Integration Guide
r
e
Calculating the Usable Scan Length Method
Calculate usable scan length as follows (see Figure 2-8 on page 2-8):
L = 1.8 x (D+d+B) x Tan (A/2)
Table 2-1
Calculation Constants
Constants B A
MS1207FZY (Default Mode) 1.17 42°
MS1207FZY (Alternate Mode) 1.17 30°
MS1207WA 1.17 60°
MS2207 1.53 34°
MS2207VHD 1.53 34°
MS3207 1.93 34°
where:
D = Distance (in inches) from the front edge of the host housing to the bar code.
d = The host housing’s internal optical path from the edge of the housing to the front of the MiniScan scanner.
B = Internal optical path from the scan mirror to the front edge of the MiniScan scanner.
A = Scan angle in degrees.
NOTE Usable scan length determined by this formula, or 90% of scan line at any working distance. This formula
is based on good quality symbols in the center of the working range and length of bar code.
MiniScan
Figure 2-8
Host System
A
B
d D
Usable Scan Length Diagram
Ba
Cod
1/2 L
L
1/2 L
Page 31

Installation 2 - 9
Testing the Usable Scan Length Method
Due to the variety of symbol sizes, densities, print quality, etc., there is no simple way to calculate the ideal symbol
distance. To op tim ize per fo rm a nc e, us e th e Testing The Usable Scan Length positioning method:
1. Measure the maximum and minimum distances at which the symbols can be read.
2. Check the near and far range on several symbols. If they are not reasonably consistent there ma y be a printing
quality problem that can degrade the performance of the system. Motorola can provide advice on how to
improve the installation.
NOTE Poor quality symbols (from bad printing, wear, or damage) may not decode well when placed in the center
of the depth of field (especially higher density codes). The scan beam has a minimum width in the central
area, and when the scanner tries to read all symbol imperfections in this area it may not decode. After a
preliminary spot is determined using good quality symbols, test several reduced quality symbols and
adjust the spot for the best overall symbol position.
3. Locate the scanner so the symbol is near the middle of the near/far range.
4. Center the symbol (left to right) in the scan line whenever possible.
5. Position the symbol so that the scan line is as near as possible to perpendicular to the bars and spaces in the
symbol.
6. Avoid specular reflection (glare ) off th e symbol by tilting the top or bottom of the symbol away from the scanner .
The exact angle is not critical, but it must be large enough so that if a mirror were inserted in the symbol
location, the reflected scan line would miss the front surface of the scanner. For the maximum allowable angles
refer to the Skew, Pitch and Roll ang les listed in each MiniScan Technical Specifications table.
7. If placing an additional window between the scanner and the symbol, determine the optimum symbol location
using a representative window in the desired window position.
8. Give the scanner time to dwell on the symbol for several scans. When first enabled, the MiniScan may take two
or three scans before it reaches maximum pe rforman ce . Enable the MiniScan before presenting the symbol, if
possible.
Page 32

2 - 10 Symbol MiniScan MSXX07 Series Integration Guide
Conveyor Applications
Conveyor applications require setting the conveyor velocity to optimize the scanner’s ability to read symbols. Also
consider the orientation of the symbol with respect to the conveyor direction. Figure 2-9 on page 2-10 illustrates the
relationship of the conveyor velocity with respect to a symbol positioned perpendicular to the conveyor direction
and Figure 2-10 on page 2-11 illustrates the relationship of the conveyor velocity with respect to a symbol
positioned parallel to the conveyor direction.
Symbol is Perpendicular to Conveyor Movement
With the symbol bars perpendicular to the conveyor belt direction (Picket Fence presentation) the relationship is:
V = (R x (F-W)) / N
where:
V = Velocity of the conveyor (inches/second)
R = Scan Rate (see technical specifications)
F = 80% of width of scan beam
W = Symbol Width (inches)
N = Number of scans over symbol (minimum of 10 scans)
F=Field Width
W=Symbol Width
Direction of Conveyor Perpendicular to Symbol
Scan Beam
Figure 2-9
Symbol Perpendicular To Conveyor Movement
Example
R = 640 scans per second
F = 80% of 6 in.
W = 4 in.
N = 10
V = (640 x ((0.8 x 6) - 4))) / 10 = 51.2 in./sec
Page 33

Installation 2 - 11
Symbol is Parallel to Conveyor Movement
With the symbol bars parallel to the conveyor belt direction (ladder presentation) the relationship is:
V = (R x H) / N
where:
V = Velocity of the conveyor (inches/second)
R = Scan Rate of scanner (see technical specifications)
H = Symbol height
N = Number of scans over symbol (minimum of 10 scans)
H=Symbol Height
Scan Beam
Direction of Conveyor Parallel to Symbol
Figure 2-10
Symbol Parallel To Conveyor Movement
Example
Use the previous formula to calculate the number of scans fo r a specific bar code, scanner, and conveyor speed; a
minimum of 10 scans per symbol is recommended.
R = 640 scans/sec
H = 60 mil
N = 10 scans
V = (640 x .060) / 10 = 3.84 in./sec
Page 34

2 - 12 Symbol MiniScan MSXX07 Series Integration Guide
Embedded Applications Requiring a Window
Use the following guidelines for applications that require a window in front of the MiniScan.
NOTE Motorola does not recommend placing an exit window in front of the MiniScan; however, the following
information is provided for applications that require such a window.
Window Material
Many window materials that look perfectly clear can contain stresses and distortions that can reduce scanner
performance. For this reason, Motorola highly recommends only optical glass or cell-cast acrylic with an
anti-reflection coating. Following is a description of acrylic, and CR-39, another popular window material.
Table 2-2 on page 2-13 outlines the suggested window properties.
CAUTION Consult an opto-mechanical engineer to recommend an appropriate window material and to
determine if coatings are appropriate for the specific application.
NOTE Do not use polycarbonate material.
Acrylic
When fabricated by cell-casting, acrylic has very good optical quality and low initial cost. However, protect the
surface from the environment as acrylic is susce pt ible to attack by chemicals, mechanical stresses, and UV light.
Acrylic has reasonably good impact resistance and can be ultrasonically welded.
CR-39
CR-39 is a thermal-setting plastic produced by the cell-casting process, and is commonly used in plastic eye
glasses lenses. CR-39 has excellent chemical and environmental resistance, including good surface hardness.
Typica lly it does not require hard- coating , but can be hard coated for severe environments. CR-39 has reasonably
good impact resistance and cannot be ultrasonically welded.
Chemically Tempered Float Glass
Glass is a hard material which provides excellent scratch and abrasion resistance. However, unannealed glass is
brittle. Increasing flexibility strength with minimal optical distortion requires chemical tempering. Glass cannot be
ultrasonically welded and is difficult to cut into odd shapes.
Page 35

Installation 2 - 13
Table 2-2
Material Red cell-cast acrylic.
Spectral Transmission 85% minimum from 640 to 690 nanometers.
Thickness 0.059 ± 0.005
Wavefront Distortion (transmission) 0.2 wavelengths peak-to-valley maximum over any 0.08 in. diameter
Clear Aperture To extend to within 0.04 in. of the edges all around.
Surface Quality 60-20 scratch/dig
Coating Both sides to be anti-reflection coated to provide 0.5% max reflectivity
Suggested Window Properties
Property Description
within the clear aperture.
(each side) from 640 to 690 nanometers at nominal window tilt angle.
Coatings must comply with the hardness adherence requirements of
MIL-M-13508.
Window Coatings
Table 2-3 on page 2-14 lists some exit window manufacturers and anti-reflection coaters.
Anti-Reflection Coatings
Apply an anti-reflection coating to the inside and/or out side of the window to significantly reduce the amount of light
reflected off the window, back into the scan engine. The coating can also improve the range of accept able window
positions and minimize performance degradation due to signal loss as the light pa sses through the window. Using
anti-reflection coatings on both the inside and outside of the window is high ly recommended.
Polysiloxane Coating
Polysiloxane type coatings are applied to plastic surfaces to improve the surface resistance to both scratch and
abrasion. They are usually applied by dipping, then air-drying in an oven with filtered hot air.
Page 36

2 - 14 Symbol MiniScan MSXX07 Series Integration Guide
Table 2-3
Evaporated Coatings, Inc.
2365 Maryland Road
Willow Grove, PA 19090
(215) 659-3080
Fosta-Tek Optics, Inc.
320 Hamilton Street
Leominster, MA 01453
(978) 534-6511
Glasflex Corporation
4 Sterling Road
Sterling, NJ 07980
(908) 647-4100
Optical Polymers Int. (OPI)
110 West Main Street
Milford, CT 06460
(203)-882-9093
Window Manufacturers and Coaters
Company Discipline Specifics
Anti-reflection coater Acrylic window supplier
Anti-reflection coater
Cell-caster, hard coater, laser
cutter
Cell-caster Acrylic exit window manufacturer
CR-39 cell-caster, coater, laser
cutter
CR39 exit window manufacturer
CR39 exit window manufacturer
Polycast
70 Carlisle Place
Stamford, CT 06902
800-243-9002
TSP
2009 Glen Parkway
Batavia, OH 45103
800-277-9778
acrylic cell-caster, hard coater,
laser cutter
acrylic cell-caster, coater, laser
cutter
Acrylic exit window manufacturer
Acrylic exit window manufacturer
Embedded Window Angle and Position
If a window is placed between the MiniScan and the item to scan, observe the following guidelines:
•
Window Clear Opening - Make the clear opening of the window large enough so that the entire scan beam
passes through the window. Cutting off any part of the beam can result in internal reflections and degrade
decode range performance. Ensure that window placement relative to the MiniScan accounts for tolerances
on all parts involved in that assembly.
•
Window Angle - Angle the window at least 2o more than the tilt of the window on the scanner (see Table
2-4). Further tilting the window is acceptable and decreases the possibility of a secondary reflection from that
window degrading the scanner's performan ce.
•
Optical Working Range - Adding a window can reduce the working range of the scanner since there is a
signal loss when passing through window material. To minimize this reduction, use a special coating
described in Window Coatings on page 2-13. To understand the difference, test the scanner in the desired
orientation and see if the difference affects scanner performance.
Page 37

Installation 2 - 15
Table 2-4
MS1207FZY, MS2207,
MS2207VHD, MS2207WA
MS3207
Accessories
The following accessories are available for the MiniScan scanner, and can be found in Symbol’s Solution Builder
(ordering guide).
•
For power connection
• 110V power supply kit, US, p/n KT-14001-001R (replaces p/n 50-14000-008/008R)
• 220V power supply, Europe, p/n 50-14000-009
• 100V power supply, Asia, p/n 50-14000-010
Secondary Window Angles
MiniScan Model
• 264V Universal power supply (also order cables below), p/n 50-14001-001
• DC line cord (power supply to scanner), p/n 50-16002-009
• AC line cord (wall outlet to power supply), p/n 23844-00-00
MiniScan Exit Window Angle
from Vertical
o
30
o
35
Minimum Secondary Window
Angle from Vertical
o
32
o
37
•
RS-232
• TTL RS-232 to True RS-232 conversion cable, p/n 25-62186-XX
• Female DB9 with straight connector to RS-232 host (female DB9), with trigger jack and no beeper,
p/n 25-13227-XX
• Female DB9 with straight connector to RS-232 host (female DB9), with trigger jack and beeper,
p/n 25-13228-XX
• Female DB9 with straight connector to RS-232 host (female DB9), p/n 25-58918-XX
• Female DB9 with right angle connector to RS-232 host (female DB9), p/n 25-58919-XX
• Female DB9 with straight connector to RS-232 host (female DB9), with trigger jack and no hardware
handshaking, p/n 25-63736-XX
•
USB
• Female DB9 with straight connector with trigger jack and beeper to USB (Type A connector),
p/n 25-58925-XX
• Female DB9 with right angle connector to USB host (Type A connector), p/n 25-58923-XX
• Female DB9 straight to USB, p/n 25-58926-XX
•
Synapse Adapter
• Female DB9 with straight connector to Synapse Adapter Cable (6 ft. straight), p/n 25-58921-XX
Page 38

2 - 16 Symbol MiniScan MSXX07 Series Integration Guide
•
Cable Adapters
• Female 25 pin D, TxD on pin 2, p/n 50-12100-378
• Female 25 pin D, TxD on pin 3, p/n 50-12100-377
• Male 25 pin D, TxD on pin 2, p/n 50-12100-380
• Male 25 pin D, TxD on pin 3, p/n 50-12100-379
•
Optional Accessories
• Push button trigger cable, p/n 25-04950-01R
• Photo sensor trigger cable, p/n 25-13176-01R (retroreflective, IR 850 nm, 7 foot range)
• Fixed-mount stand, p/n 20-60136-01R
• Mounting bracket, p/n KT-65578-01R
Application Notes
TTL RS-232
Standard RS-232 voltage levels typically range between +12V and -12V to ensure adequate noise rejection over
long distances. Devices which support TTL level RS-232 signaling typically drive signals between 0V and +5V.
Extensive testing has shown that TTL levels are interpreted correctly by the majority of st andard RS-232 host s over
cable distances of six feet or less, even in extreme conditions.
Multi-interface Miniscan products fall into the TTL RS-232 device categor y. All standard RS-232 cables available
from Motorola for the Miniscan family measure six feet or less, and should not present a problem. If a particular
host does not support TTL levels, a separate conversion cable is available (25-62186-xx) which contains
electronics to adapt the TTL levels of a multi-interface Miniscan into standard RS-232 levels.
USB Warning - Potential Host Side Issues
The Universal Serial Bus provides a smart plug-and-play interface for easy integration. In USB communication, the
root hub located on the host controls all traffic. USB hosts in general react poorly in certain harsh environments
compared to traditional host interfaces such as RS-232. These environments include areas with high ESD le vels or
situations in which the system is subject to Electrical Fast Transients (EFT).
Typical symptoms of these environments are:
•
Frequent scanner resets
•
Scanner occasionally loses power (due to host initiated shutdown)
•
Occasional host lockups.
Because multi-interface Miniscan products are often exposed to these environments due to the nature of scanner
placement, they have been safeguarded as much as possible to prevent physical damag e. Despite design
precautions, testing shows that some USB hosts cannot tolerate these environments. In this case, try placing a
self-powered USB hub close to the host, between the scanner and host, as a buffer to the host against the harsh
environment. This may not be a valid solution in all cases.
Page 39

Chapter 3 Scanning
Introduction
This chapter provides information on scan patterns, sca nning, triggering options, and beeper and LED definitions.
MiniScan Scan Patterns
Symbol MS1207FZY and MS1207WA Scan Pattern
Symbol MS1207FZY and MS1207WA scanners emit a single scan line to quickly decode 1D bar codes.
Figure 3-1
Single Scan Line Scan Pattern
Page 40

3 - 2 Symbol MiniScan MSXX07 Series Integration Guide
Symbol MS2207 and MS2207VHD Scan Patterns
The Symbol MS2207 and MS2207VHD generate different scan patterns (Smart Raster and High Density Single
Scan Line) based on the software command received at the interface. Use the raster pattern to read 1D bar codes
and PDF417 symbols.
NOTE The Symbol MS2207 and MS2207VHD also support omnidirectional and semi-omn idirectional scan
patterns, but are not optimized for these patterns.
Smart Raster Scan Pattern
The Symbol MS2207 and MS2207VHD can create a single line which opens vertically to read PDF417 symbols
using the Smart Raster feature. This feature autodetects the type of bar code b eing scanned and adju sts it s pa ttern
accordingly, providing optimal performance on 1D, PDF417, GS1 DataBar, and Composite codes.
Stage 1: “Slab” Raster Pattern
Stage 2: Open Raster Pattern
Figure 3-2
Raster Scan Pattern
High Density Single Scan Line Scan Pattern
The High Density single scan line appears as a "mini" raster and scans multiple areas of 1D codes to swiftly and
accurately capture data on poorly printed and damaged bar codes.
Figure 3-3
High Density Single Scan Line Scan Pattern
Page 41

Scanning 3 - 3
Symbol MS3207 Scan Patterns
The Symbol MS3207 generates four scan patterns based on the software command received at the interface.
These patterns are Smart Raster, Semi-omnidirectional, Omnidirectional, and High Density Single Scan Line. Use
the raster pattern to read 1D bar codes and PDF417 symbols. The omnidirectional pattern reads 1D bar codes in
an omnidirectional manner.
Smart Raster Scan Pattern
The Symbol MS3207 can create a single line which opens vertically to read PDF417 symbols using the Smart
Raster feature. This feature autodetects the type of bar code being scanned and adjusts its pattern accordingly,
providing optimal performance on 1D, PDF417, GS1 DataBar, and Composite codes.
Stage 1: “Slab” Raster Pattern
Stage 2: Open Raster Pattern
Figure 3-4
Raster Scan Pattern
Semi-omnidirectional Scan Pattern
The semi-omnidirectional pattern is an alternative to the full omnidirectional pattern that scans highly truncated 1D
and GS1 DataBar codes. Present bar codes horizontally with no more than a 20
Figure 3-5
Semi-omnidirectional Scan Pattern
o
tilt.
Page 42

3 - 4 Symbol MiniScan MSXX07 Series Integration Guide
Omnidirectional Scan Pattern
The high-speed rotating omnidirectional scan pattern provides aggressive performance on 1D bar codes because
there are no “holes” in the pattern. This ensures fast throughput at the point of activity and the ability to read 1D
symbols in 360
o
of rotation, eliminating the need to orient the bar code in the field of view.
Figure 3-6
Omnidirectional Scan Pattern
High Density Single Scan Line Scan Pattern
The High Density single scan line appears as a "mini" raster and scans multiple areas of 1D codes to swiftly and
accurately capture data on poorly printed and damaged bar codes.
Figure 3-7
High Density Single Scan Line Scan Pattern
Scan Angle Selection
The Symbol MS1207FZY scanner supports two scan angles (see Table 4-2 on page 4-5 for these angles). To set
the scan angle, scan a parameter bar code (see Scan Angle on page 10-10). Once the parameter bar code is
scanned, that scan angle setting is retained.
Operation in Blink Mode
The scan angle during Blink Mode is determined by the scan angle system parameter.
Page 43

Scanning Tips
When scanning, make sure the symbol is within the scanning range. See Calculating the Usable Scan Length
Method on page 2-8. Align the bar code with the scan beam. The gr een decode LED light s to indicate a successful
decode.
Scan the Entire Symbol
•
The scan beam must cross every bar and space on the symbol.
•
The larger the symbol, the farther away the scanner should be positioned.
•
Position the scanner closer for symbols with bars that are close together.
Scanning 3 - 5
Position at an Angle
Do not position the scanner exactly perpendicular to the bar code. In this position, light can bounce back into the
scanner's exit window and prevent a successful decode.
Trigger Options
Continuous (Default)
The laser is enabled continuously and deco de processing is continuou sly active. You can configure the scanner to
scan and transmit a bar code, and then not decode the same bar code or any bar code fo r a set period of time. See
Timeout Between Decodes on page 10-15 to customize the application to the rate at which bar codes are
presented.
RIGHT
012345
WRONG
012345
Continuous
NOTE This option is not recommended during scanner programming via bar code menus.
Page 44

3 - 6 Symbol MiniScan MSXX07 Series Integration Guide
Level Trigger
Activating the trigger line enables the laser and begins decode processing. Decode processing continues until a
good decode occurs, the trigger is released, or the Laser On Time expires. The laser is disabled once decode
processing completes. The next decode attempt does not occur until the trigger line is released and then
reactivated.
Pulse Trigger
Activating the trigger line enables the laser and begins decode processing. Decode processing continues
regardless of the trigger line until a good decode occurs, or until the Laser On Time expires. The laser is disabled
once decode processing completes. The next decode attempt does not occur until the trigger line is released and
then reactivated.
Level
Pulse
Blink
NOTE Only the Symbol MS1207FZY and MS1207WA support this option.
The laser blinks at a 25% duty cycle (reduced to 10% after 30 seconds of inactivity), until a bar code is presented.
When a bar code is presented, the laser remains on until either the bar code is decoded or removed, or the session
timeout expires. Once the bar code is decoded, the scanner does not decode it again until the bar code is
removed.
Blink
Page 45

Beeper and LED Definitions
Table 3-1 provides standard beeper definitions, and Tab le 3-2 provides LED definitions.
Scanning 3 - 7
Table 3-1
Standard Use
1 Beep - short high tone A bar code symbol was decoded (if decode beeper is enabled).
1 Beep - long high tone Thermal shutdown.
3 Beeps - short high tone
(Symbol MS2207/2207VHD/3207 only)
Parameter Menu Scanning
2 Beeps- short high tone Correct entry scanned or correct menu sequence performed.
1 Beep- hi/lo/hi/lo tone Successful program exit with change in the parameter setting.
2 Beeps - lo/hi tone Input error, incorrect bar code, or Cancel scanned, wrong entry,
Communication
4 Beeps - short high tone Communication error.
Standard Beeper Definitions
Beeper Sequence Indication
Power-on or reset. Occurs immediately after the scanner is turned on,
indicating that the system software is working properly. If three beeps
occur during normal operation, it is due to a reset and any work in
progress is lost. If this occurs often, contact Motorola Enterprise
Mobility Support.
incorrect bar code programming sequence; remain in program mode.
4 Beeps - hi/hi/hi/lo Receive error.
3 Beeps - lo/hi/lo ADF transmit error.
Table 3-2
Red Scanner is on.
Green A bar code was successfully decoded.
LED Definitions
LED Indication
Page 46

3 - 8 Symbol MiniScan MSXX07 Series Integration Guide
Page 47

Chapter 4 Symbol MS1207FZY Specifications
Introduction
This chapter provides the technical specifications for the Symbol MS1207FZY scanner.
Page 48

4 - 2 Symbol MiniScan MSXX07 Series Integration Guide
Symbol MS1207FZY Electrical Interface
Figure 4-1
Table 4-1 lists the pin functions of the Symbol MS1207FZY interface.
Table 4-1
Pin No. Pin Name Ty p e* Function
1 Trigger I Signals scanner to begin scanning session.
2 TXD O Serial data transmit output. Drives the serial data receive input on the
3 RXD I Serial data receive input. Driven by the serial dat a transmit output on the
4 Not used
5 Ground Power supply ground input and signal ground reference.
6 Power I 5.0 VDC ± 10%
7 CTS I Clear-to-send handshaking input line, used only in conjunction with the
8 RTS O Request-to-send handshaking output line, used only in conjunction with
MiniScan Connector
Symbol MS1207FZY Electrical Interface
device communicating with the scanner.
device communicating with the scanner.
RTS line. Optionally used by another device to signal the scanner to
begin transmitting data.
the CTS line. Optionally used by the scanner to signal another device
that data is available to send.
9 Beeper/Download I/O During normal operation this signal functions as an external beeper
drive line. This signal can sink 50 mA of current to drive an external
beeper, an d is normally pulled up. This signal i s also used to begin Flash
Download operation when grounded externally during power up.
*I = Input O = Output
Page 49

Symbol MS1207FZY Mechanical Drawings
Symbol MS1207FZY Specifications 4 - 3
Notes:
Unless otherwise specified:
• Dimensions are in inches,
dimensions in [ ] are mm.
• User mounting tolerances
are not included.
Figure 4-2
Symbol MS1207FZY Mechanical Drawing
Page 50

4 - 4 Symbol MiniScan MSXX07 Series Integration Guide
Notes:
Unless otherwise specified:
• Dimensions are in inches,
dimensions in [ ] are mm.
• User mounting tolerances
are not included.
Figure 4-3
Symbol MS1207FZY Mechanical Drawing
Page 51

Symbol MS1207FZY Technical Specifications
Table 4-2 provides the Symbol MS1207FZY technical specifications.
Symbol MS1207FZY Specifications 4 - 5
Table 4-2
Power Requirements
Laser Power 1.0 mW ± 0.12 mW,
Scan Rate 36 (± 5) scans/sec (bidirectional)
Print Contrast Minimum 25% absolute dark/light reflectance measured at 650 nm.
Scan Angle Default (Wide): 42° ± 2°
Scan Pattern Single scan line
Skew Tolerance ± 50° from normal (see
Pitch Angle ± 65° from normal (see
Roll ± 20° from vertical (see
Symbol MS1207FZY Technical Specifications @ 23°C
Item Description
Input Voltage
Scanning Current
Standby Current
V
Noise Level
cc
5.0 VDC ±10%
160 mA ±40 mA
20 mA ±5 mA typical
200 mV peak-to-peak max.
λ
= 650 nm nominal
Alternate (Narrow): 30° ± 2°
Figure 4-4 on page 4-6
Figure 4-4 on page 4-6
Figure 4-4 on page 4-6
)
)
)
Decode Depth of Field See
Ambient Light Immunity
Sunlight
Artificial Light
Drop Multiple 30” drops
Vibration Unpowered scanner withstands a random vibration along each of the X,
ESD ± 20kV air discharge
Sealing IP54
Operating Temperature -4° to 122°F (-20° to 50°C)
Storage Temperature -40° to 158°F (-40° to 70°C)
Humidity 5% to 95% non-condensing
Note: Environmental and/or tolerance parameters are not cumulative.
Figure 4-5 on page 4-7
8,000 ft. candles (86,112 lux)
450 ft. candles (4,844 lux)
Y and Z axes for a period of one hour per axis, defined as follows:
20 to 80 Hz Ramp up to 0.04 G^2/Hz at the rate of 3dB/octave.
80 to 350 Hz 0.04 G^2/Hz
350 to 2000 Hz Ramp down at the rate of 3 dB/octave.
± 8kV indirect discharge
Page 52

4 - 6 Symbol MiniScan MSXX07 Series Integration Guide
Table 4-2
Symbol MS1207FZY Technical Specifications @ 23°C (Continued)
Item Description
Laser Class CDRH Class II, IEC Class 2
Height 1.60 in. (4.06 cm)
Width 2.28 in. (5.79 cm)
Depth 2.94 in. (7.47 cm)
Weight 4.45 oz. (126 gm)
Note: Environmental and/or tolerance parameters are not cumulative.
Skew Pitch
+ 50° from normal
Skew
20 mil
Symbol
Angle
+ 65° from normal
20 mil
Symbol
Pitch
Angle
Scan Beam
15.0 in. (381 mm)
Roll
Roll
Angle
20 mil
Symbol
Scan Beam
Scan Beam
15.0 in. (381 mm)
+ 20° from normal
Note: Tolerances are
reduced at extreme ends
of the working range.
15.0 in. (381 mm)
Figure 4-4
Skew, Pitch and Roll
Page 53

Symbol MS1207FZY Decode Zone
The scanner has a selectable scan angle of eith er 30° or 42°. Figure 4-5 sh ows the 42° symbol decodes. The figures
shown are typical values. Table 4-3 on page 4-8 lists the typical and guaranteed distances for the 42° scan angle
for selected bar code densities. The minimum element width (or “symbol density”) is the width in mils of the
narrowest element (bar or space) in the symbol. The maximum usable length of a symbol at any give n range
appears below. To calculate this distance, see Calculating the Usable Scan Length Method on page 2-8.
Note: Typical performance at 68˚F (20˚C)
on high quality symbols.
MS-120XFZY
5 mil
7.00
3.25
7.5 mil
3.00
2.20
1.00
2.20
4.00
12.50
mil
13
UPC
100%
20 mil * (80% MRD)
20 mil * (25%MRD)
25.75
34.00
27.25
40 mil *
55 mil *
66.75
Symbol MS1207FZY Specifications 4 - 7
in
cm
35
88.9
30
76.2
25
63.5
20
50.8
W
38.1
i
d
25.4
t
h
12.7
o
0
f
12.7
F
i
25.4
e
l
38.1
d
50.8
63.5
76.2
88.9
75.00
15
10
5
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
0
In.
0
cm
Figure 4-5
12.7
5
25.4
38.1
50.8
63.5
76.2
88.9
101.6
114.3
127.0
139.7
152.4
165.1
60
55
50
45
40
35
30
25
20
15
10
177.8
75
190.5
70
65
Depth of Field
*Minimum distance determined by symbol length and scan angle
Symbol MS1207FZY Typical Decode Zone (42o Scan Angle)
Page 54

4 - 8 Symbol MiniScan MSXX07 Series Integration Guide
Table 4-3
Symbol MS1207FZY Decode Distances (42o Scan Angle)
Symbol Density/
p/n / Bar Code Type/
W-N Ratio
5.0 mil
64-17453-01
Code 39; 2.5:1
7.5 mil
64-17452-01
Code 39; 2.5:1
13 mil
64-05303-01
100% UPC
20 mil
60-01429-01
Code 39; 2.2:1
20 mil
60-02710-01
Code 39; 2.2:1
Bar Code Content/
Contrast
ABCDEFGH
80% MRD
ABCDEF
80% MRD
012345678905
80% MRD
123
80% MRD
123
25% MRD
Typical Working Ranges
1
3
Guaranteed Working
Ranges
3
Near Far Near Far
3.25 in.
8.26 cm
3.00 in.
7.62 cm
2.20 in.
5.59 cm
1.00 in.
2.54 cm
7.00 in.
17.78 cm
12.50 in.
31.75 cm
25.75 in.
65.41 cm
34.00 in.
86.36 cm
4.75 in.
12.07 cm
4.75 in.
12.07 cm
5.25 in.
13.34 cm
9.00 in.
cm
Note 2 19.00 in.
48.26 cm
Note 2
24.00 in.
60.96 cm
22.86
(Note 2)
1.00 in.
2.54 cm
27.25 in.
69.22 cm
Note 2
22.00 in.
55.88 cm
(Note 2)
40 mil
64-17457-01
Code 39; 2.2:1
55 mil
64-17458-01
Code 39; 2.2:1
AB
80% MRD
CD
80% MRD
2.20 in.
5.59 cm
(Note 2)
4.00 in.
10.16 cm
(Note 2)
66.75 in.
169.55 cm
75.00 in.
190.50 cm
Note 2 49.00 in.
124.46 cm
Note 2 55.00 in.
139.70 cm
Notes:
1. Contrast measured as Mean Reflective Difference (MRD) at 650 nm.
2. Near ranges on lower densities largely depend on the width of the bar code and the scan angle.
3. Working range specifications: Photographic quality symbols, pitch = 10°, skew = 0°, roll = 0°,
ambient light < 150 ft. candles, and temperature = 23 °C.
Usable Scan Length
The decode zone is a function of various symbol characteristics including density, print contrast, wide-to-narrow
ratio, and edge accuracy. Consider the width of the scan line at any given distance when designing a system.
Calculating the Usable Scan Length Method on page 2-8 describes how to calculate the usable scan length. The
scan angle is provided in Table 4-2 on page 4-5.
Page 55

Chapter 5 Symbol MS1207WA Specifications
Introduction
This chapter provides the technical specifications for the Symbol MS1207WA scanner.
Page 56

5 - 2 Symbol MiniScan MSXX07 Series Integration Guide
Symbol MS1207WA Electrical Interface
Figure 5-1
Table 5-1 lists the pin functions of the Symbol MS1207WA.
Table 5-1
Pin No. Pin Name Type* Function
1 Trigger I Signals scanner to begin scanning session.
2 TXD O Serial data transmit output. Drives the serial data receive input on the
3 RXD/D+ I/O RS-232 Mode: Serial data receive input. Driven by the serial data
4 SYN_CLK I/O Synapse Mode: Synapse Clock line. Signal used as a clock by a
5 Ground Power supply ground input and signal ground reference.
6 Power 5.0 VDC ± 10%
7 CTS/D- I/O RS-232 Mode: Clear-to-send handshaking input line, used only in
MiniScan Connector
Symbol MS1207WA Electrical Interface
device communicating with the scanner.
transmit output on the device communicating with the scanner.
USB Mode: D+ signal. During USB operation this s ignal is pulled up b y
a 1.5k Ohm resistor to begin USB enumeration. In this mode it is a
differential bi-directional signal.
Synapse host. Pin is shorted to RTS/SYN_DAT in USB cables to allow
auto-detection of USB mode via signal loopback.
conjunction with the RTS line. Optionally used by another device to
signal the scanner to begin transmitting data.
USB Mode: D- signal. During USB operation this signal works in
conjunction with the D+ signal as a differential bi-directional signal.
8 RTS/SYN_DAT I/O RS-232 Mode: Request-to-send handshaking output line, used only in
conjunction with the CTS line. Optionally used by the scanner to signa l
another device that data is available to send.
Synapse Mode: Synapse Data l ine. Used to transmit data to and from a
Synapse host.
9 Beeper/Download I/O During normal operation this signal functions as an external beeper
drive line. This signal can sink 50mA of current to drive an external
beeper, and is normally pulled up. This signal is also used to begin
Flash Download operation when grounded externally during power up.
*I = Input O = Output
Page 57

Symbol MS1207WA Mechanical Drawings
Symbol MS1207WA Specifications 5 - 3
Notes:
Unless otherwise specified:
• Dimensions are in inches,
dimensions in [ ] are mm.
• User mounting tolerances
are not included.
Figure 5-2
Symbol MS1207WA Mechanical Drawing
Page 58

5 - 4 Symbol MiniScan MSXX07 Series Integration Guide
Notes:
Unless otherwise specified:
• Dimensions are in inches,
dimensions in [ ] are mm.
• User mounting tolerances
are not included.
Figure 5-3
Symbol MS1207WA Mechanical Drawing
Page 59

Symbol MS1207WA Technical Specifications
Table 5-2 provides the Symbol MS1207WA technical specifications.
Symbol MS1207WA Specifications 5 - 5
Table 5-2
Power Requirements
Laser Power 0.48 mW ± 0.05 mW,
Scan Rate 36 (± 5) scans/sec (bidirectional)
Print Contrast Minimum 20% absolute dark/light reflectance measured at 670 nm.
Scan Angle 60° ± 2°
Scan Pattern Single scan line
Skew Tolerance ± 65° from normal (see
Pitch Angle ± 55° from normal (see
Roll ± 20° from vertical (see
Decode Depth of Field See
Symbol MS1207WA Technical Specifications @ 23°C
Item Description
Input Voltage
Scanning Current
Standby Current
V
Noise Level
cc
5.0 VDC ± 10%
110 mA ± 30mA
40 mA ± 5 mA typical
200 mV peak-to-peak max.
λ
Figure 5-5 on page 5-7
= 670 nm nominal
Figure 5-4 on page 5-6
Figure 5-4 on page 5-6
Figure 5-4 on page 5-6
)
)
)
Ambient Light Immunity
Sunlight
Artificial Light
Drop Multiple 30” drops
Vibration Withstands a sinusoidal vibration of 1 G along each of the 3 mutually perpendicular
ESD ± 20kV air discharge
Sealing IP54
Operating Temperature 32° to 104°F (0° to 40°C)
Storage Temperature -40° to 140°F (-40° to 60°C)
Humidity 5% to 95% non-condensing
Laser Class CDRH Class II, IEC Class 2
Height 1.60 in. (4.06 cm)
Note: Environmental and/or tolerance parameters are not cumulative.
8,000 ft. candles (86,112 lux)
450 ft. candles (4,844 lux)
axes for a period of 1 hr per axis, over a frequency range of 5 Hz to 2000Hz.
± 8kV indirect discharge
Page 60

5 - 6 Symbol MiniScan MSXX07 Series Integration Guide
Table 5-2
Symbol MS1207WA Technical Specifications @ 23°C (Continued)
Item Description
Width 2.28 in. (5.79 cm)
Depth 2.94 in. (7.47 cm)
Weight 4.45 oz. (126 gm)
Note: Environmental and/or tolerance parameters are not cumulative.
Skew Pitch
+ 65° from normal
Skew
Angle
Scan Beam
Scan Beam
20 mil
Symbol
+ 55° from normal
20 mil
Symbol
Pitch
Angle
Figure 5-4
8.0 in. (203 mm)
Skew, Pitch and Roll
Roll
Roll
Angle
20 mil
Symbol
Scan Beam
8.0 in. (203 mm)
+ 20° from normal
Note: Tolerances are
reduced at extreme ends
of the working range.
8.0 in. (203 mm)
Page 61

Symbol MS1207WA Decode Zone
Figure 5-5 shows the Symbol MS1207WA Wide Angle decode symbols. Typical values appear. Table 5-3 on page
5-8 lists the typical and guaranteed distances for selected bar code densities. The minimum element width (or
“symbol density”) is the width in mils of the narrowest element (bar or space) in the symbol. The maximum usable
length of a symbol at any given range is shown below. To calculate this distance, see Calculating the Usable Scan
Length Method on page 2-8.
Note: Typical performance at 73.4˚F (23˚C)
on high quality symbols.
In. cm
12.4
6
Symbol MS1207WA Specifications 5 - 7
31.6
W
i
d
15.2
t
h
MS-1207WA
In.
cm
*Minimum distance determined by symbol length and scan angle
Figure 5-5
5 mil
1
0.6
*
0
0
7.5 mil
4
100% UPC
20 mil
5
12.7
7.2
40 mil
10
25.4
11
55 mil
38.12050.8
15
19
15
63.5
Depth of Field
Symbol MS1207WA Decode Zone (Typical)
24
25
0
6
12.4
0
15.2
31.6
o
f
F
i
e
l
d
Page 62

5 - 8 Symbol MiniScan MSXX07 Series Integration Guide
Table 5-3
p/n / Bar Code Type/
5 mil
64-17453-01
Code 39; 2.5:1
7.5 mil
64-17452-01
Code 39; 2.5:1
13 mil
64-05303-01
100% UPC
20 mil
60-01429-01
Code 39; 2.2:1
40 mil
64-17457-01
Code 39; 2.2:1
. Symbol MS1207WA Decode Distances
Symbol Density/
W-N Ratio
Bar Code Content/
Contrast
ABCDEFGH
80% MRD
ABCDEF
80% MRD
1234567890
80% MRD
123
80% MRD
AB
80% MRD
Typical Working Ranges
1
Near Far Near Far
1.0 in.
2.54 cm
0.6 in.
1.52 cm7.2 in.
0.6 in.
1.52 cm
Note 2
Note 2
4.0 in.
10.16 cm
8.29 cm
11.0 in.
27.94 cm
15.0 in.
38.10 cm
19.0 in.
48.26 cm
Guaranteed Working
Ranges
1.2 in.
3.05 cm
0.9 in.
2.29 cm6.0 in.
0.9 in.
2.29 cm
Note 2
Note 2
3.0 in.
7.62 cm
15.24 cm
9.0 in.
22.86 cm
13.0 in.
33.02 cm
17.0 in.
3.18 cm
55 mil
64-17458-01
Code 39; 2.2:1
1. Contrast measured as Mean Reflective Difference (MRD) at 670 nm.
2. Near ranges on lower densities (not specified) largely depend on the width of the bar code and
the scan angle.
3. Working range specifications at ambient temperature 23 °C.
CD
80% MRD
Note 2
24.0 in.
60.96 cm
Note 2
22.0 in.
55.88 cm
Usable Scan Length
The decode zone is a function of various symbol characteristics including density, print contrast, wide-to-narrow
ratio, and edge acuity. Consider width of decode zone at any given distance when designing a system.
Calculating the Usable Scan Length Method on page 2-8 describes how to calculate the usable scan length. The
scan angle is provided in Table 5-2 on page 5-5.
Page 63

Chapter 6 Symbol MS2207 Specifications
Introduction
This chapter provides the technical specifications for the Symbol MS2207 scanner.
Page 64

6 - 2 Symbol MiniScan MSXX07 Series Integration Guide
Symbol MS2207 Electrical Interface
Figure 6-1
Table 6-1 lists the pin functions of the Symbol MS2207 interface.
Table 6-1
Pin No. Pin Name Type* Function
1 Trigger I Signals scanner to begin scanning session.
2 TXD O Serial data transmit output. Drives the serial data receive input on
3 RXD/D+ I/O RS232 Mode: Serial data receive input. Driven by the serial data
4 SYN_CLK I/O Synapse Mode: Synapse Clock line. Signal used as a clock by a
5 Ground Power supply ground input and signal ground reference.
6 Power 5.0 VDC ± 10%
7 CTS/D- I/O RS232 Mode: Clear-to-send handshaking input line, used only in
MiniScan Connector
Symbol MS2207 Electrical Interface
the device communicating with the scanner.
transmit output on the device communicating with the scanner.
USB Mode: D+ signal. During USB operation this signal i s pulled up
by a 1.5k Ohm resistor to begin USB enumeration. In this mode it is
a differential bi-directional signal.
Synapse host. Pin is shorted to RTS/SYN_DAT in USB cables to
allow autodetection of USB mode via signal loopback.
conjunction with the RTS line. Optionally used by another device to
signal the scanner to begin transmitting data.
USB Mode: D- signal. During USB operation this signal works in
conjunction with the D+ signal as a differential bi-directional signal.
8 RTS/SYN_DAT I/O RS232 Mode: Request-to-send handshaking output line, used only
in conjunction with the CTS line. Optionally used by the scanner to
signal another device that data is available to send.
USB Mode: Synapse Data line. Signal is used to transmit data to
and from a Synapse host.
9 Beeper/Download I/O During normal operation this signal functions as an external beeper
drive line. This signal can sink 50mA of current to drive an external
beeper, and is normally pulled up. This signal is also used to begin
Flash Download operation when grounded externally during power
up.
*I = Input O = Output
Page 65

Symbol MS2207 Mechanical Drawings
Symbol MS2207 Specifications 6 - 3
Notes:
Unless otherwise specified:
• Dimensions are in inches,
dimensions in [ ] are mm.
• User mounting tolerances
are not included.
Figure 6-2
Symbol MS2207 Mechanical Drawing
Page 66

6 - 4 Symbol MiniScan MSXX07 Series Integration Guide
Notes:
Unless otherwise specified:
• Dimensions are in inches,
dimensions in [ ] are mm.
• User mounting tolerances
are not included.
Figure 6-3
Symbol MS2207 Mechanical Drawing
Page 67

Symbol MS2207 Technical Specifications
Table 6-2 provides the Symbol MS2207 technical specifications
Symbol MS2207 Specifications 6 - 5
Table 6-2
Symbol MS2207 Technical Specifications @ 23°C
Item Description
Power Requirements
Input Voltage
Scanning Current
Standby Current
V
Noise Level
cc
Laser Power 0.95 mW ± 0.1 mW,
5.0 VDC ± 10%
250 ± 30 mA typical
45 ± 5 mA typical
200 mV peak-to-peak max.
λ
= 650 nm nominal
Scan Rate 640 scans/sec.
Scan Frequency: Horizontal 320 Hz ± 5 Hz
Scan Frequency: Vertical 282 Hz ± 5 Hz
Frame Rate 24 frames/sec. 12 Hz ±1 Hz (vertical)
Print Contrast Minimum 35% absolute dark/light reflectance differential
o
Scan Angle
Horizontal: 34
Verti cal: 34o ±1.5
±1.5
o
o
Scan Pattern Smart raster, high density single scan line
Start Time 0.065 sec. to 75% of steady state horizontal amplitude
Skew Tolerance
Pitch Angle
Roll
Decode Depth of Field See
Beam Deviation
(offset from the nominal)
o
± 15
from plane parallel to symbol (see
o
from normal (see
± 30
o
± 4
from (for scanning benchmark label, assuming 3:1 codeword aspect ratio)
(see
Figure 6-4 on page 6-7
Figure 6-4 on page 6-7
)
Figure 6-4 on page 6-7
)
Figure 6-5 on page 6-8
Horizontal: ±3.0
Verti cal: ±3.0
Horizontal tilt: ± 2
o
o
o
Ambient Light Immunity
Sunlight
Artificial Light
8,000 ft. candles (86,112 lux)
450 ft. candles (4,844 lux)
Drop Multiple 30” drops
)
Page 68

6 - 6 Symbol MiniScan MSXX07 Series Integration Guide
Table 6-2
Vibration Unpowered scanner withstands a random vibration along each of the X, Y and
ESD ± 20kV air discharge
Sealing IP54
Operating Temperature -22° to 122°F (-30° to 50°C)
Storage Temperature -40° to 158°F (-40° to 70°C)
Humidity 5% to 95% non-condensing
Laser Class CDRH Class II, IEC Class 2
Height 1.60 in. (4.06 cm)
Width 2.28 in. (5.79 cm)
Depth 2.94 in. (7.47 cm)
Symbol MS2207 Technical Specifications @ 23°C (Continued)
Item Description
Z axes for a period of one hour per axis, defined as follows:
20 to 80 Hz Ramp up to 0.04 G^2/Hz at the rate of 3dB/octave.
80 to 350 Hz 0.04 G^2/Hz
350 to 2000 Hz Ramp down at the rate of 3 dB/octave.
± 8kV indirect discharge
Weight 4.73 oz. (134 gm)
Page 69

Symbol MS2207 Specifications 6 - 7
Skew Pitch
+ 49° from normal
15 mil
Symbol
Skew
Angle
+ 55° from normal
15 mil
Symbol
Pitch
Angle
Scan Beam
10 in. (254 mm)
Roll
Roll
Angle
15 mil
Symbol
Scan Beam
Scan Beam
10 in. (254 mm)
+ 20° from normal
Note: Tolerances are
reduced at extreme ends
of the working range.
10 in. (254 mm)
Figure 6-4
Skew, Pitch and Roll
Page 70

6 - 8 Symbol MiniScan MSXX07 Series Integration Guide
Symbol MS2207 Decode Zones
The decode zone is a function of various symbol characteristics including density, print contrast, wide to narrow
ratio and edge acurity. T ypical values appear. Table 6-3 on page 6-9 and Table 6-4 on page 6-11 list the typical and
guaranteed distances for selected bar code densities. The minimum element width (or “symbol density”) is the
width in mils of the narrowest element (bar or sp ace) in the symbo l. The maximum usable len gth of a symbol at any
given range appears below. To calculate this distance, see Calculating the Usable Scan Length Method on page
2-8.
Symbol MS2207 1D Decode Zone
Note: Typical performance at 68˚F (20˚C)
on high quality symbols in normal room light.
Vcc = 5V
MS 220X
6 mil
2.0
1.5
13 mil Minimum Element Width
*
5.25
7.5 mil
7.0
20 mil Minimum Element Width
40 mil Minimum Element Width
55 mil Minimum Element Width
14.0
19.0
24.0
31.0
In. cm
10
7.5
5
2.5
0
2.5
5
7.5
10
25.4
15.2
10.1
5.1
0
5.1
10.1
15.2
25.4
W
i
d
t
h
o
f
F
i
e
l
d
In.
cm
Figure 6-5
0
0 12.7 25.4 38.1 50.8
5
10 15 20
Depth of Field
* Minimum distance determined by symbol length and scan angle.
Symbol MS2207 1D Decode Distances
25
63.5
30
76.2
35
88.9
Page 71

Symbol MS2207 1D Decode Distances
Symbol MS2207 Specifications 6 - 9
Table 6-3
Symbol MS2207 1D Decode Distances
Symbol Density/
p/n / Bar Code Type
6.0 mil
60-01755-01
Code 39
7.5 mil
64-17452-01
Code 39
13 mil
64-05303-01
100% UPC
20 mil
64-17456-01
Code 39
40 mil
64-17457-01
Code 39
Bar Code Content/
Contrast
1
123
80% MRD
ABCDEF
80% MRD
012345678905
80% MRD
123
80% MRD
AB
80% MRD
Guaranteed Working
Typical Working Ranges
3
Ranges
Near Far Near Far
2.0 in.
5.08 cm
1.5 in.
3.81 cm
Note 2 14.0 in.
5.25 in.
13.34 cm
7.0 in.
17.78 cm
2.75 in.
7.00 cm
2.25 in.
5.72 cm
N/A 10.5 in.
35.56 cm
Note 2 19.0 in.
N/A 14.0 in.
48.26 cm
Note 2 24.0 in.
N/A 18.0 in.
60.96 cm
3
4.0 in.
10.16 cm
5.0 in.
12.7 cm
26.67 cm
35.56 cm
45.72 cm
55 mil
60-01601-01
A
80% MRD
Note 2 31.0 in.
78.74 cm
Note 2 25.0 in.
63.50 cm
Code 39
Notes:
1. Contrast measured as Mean Reflective Difference (MRD) at 650 nm.
2. Near ranges on lower densities largely depend on the width of the bar code and the scan
angle.
3. Working range specifications: Photographic quality symbols, pitch = 10°, skew = 0°,
roll = 0°, ambient light < 150 ft. candles, and temperature = 23 °C.
Page 72

6 - 10 Symbol MiniScan MSXX07 Series Integration Guide
Symbol MS2207 2D Decode Zone
Note: Typical performance at 68˚F (20˚C) on high quality symbols
in normal room light. Y-module dimension = 3X.
Vcc = 5V
MS 220X
1.5
6.6 mil
10 mil Minimum Element Width, 35%
3.5
10 mil Minimum Element Width, 80%
3.5
5.6
6.0
8.0
9.0
15 mil Minimum Element Width
15.0
In. cm
5
12.7
2.5
6.35
0
0
2.556.35
12.7
W
i
d
t
h
o
f
F
i
e
l
d
In.
cm
Figure 6-6
NOTE Not optimized for omnidirectional mode.
5.1
2
4
10.1
6
15.2820.3
0
0
10 12
25.4 30.5
14
35.6
Depth of Field
Symbol MS2207 2D Slab/Raster Decode Distances
16
40.6
Page 73

Symbol MS2207 2D Decode Distances
Symbol MS2207 Specifications 6 - 11
Table 6-4
p/n / Bar Code Type
Symbol MS2207 2D Slab/Raster Decode Distances
Symbol Density/
Bar Code Content/
Contrast
1
Typical Working Ranges
3
Guaranteed Working
Ranges
Near Far Near Far
6.6 mil
64-14035-01
ABCDEF
80% MRD
1.5 in.
3.81 cm
6.00 in.
15.24 cm
Note 2 4.75 in.
PDF417
10 mil
64-14937-01
012345678905
35% MRD
3.5 in.
8.89 cm
8.0 in.
20.32 cm
Note 2 5.0 in.
PDF417
10 mil
64-14037-01
80% MRD 3.5 in.
8.89 cm
9.0 in.
22.86 cm
Note 2 7.5 in.
PDF417
15 mil
64-14038-01
80% MRD 5.6 in.
14.22 cm
15.0 in.
38.10 cm
Note 2 13.0 in.
PDF417
Notes:
1. Contrast measured as Mean Reflective Difference (MRD) at 650 nm.
2. Near ranges on lower densities largely depend on the width of the bar code and the scan angle.
3. Working range specifications: Photographic quality symbols, pitch = 10°, skew = 0°, roll = 0°,
ambient light < 150 ft. candles, and temperature = 23 °C.
3
12.07 cm
12.7 cm
19.05 cm
33.02 cm
NOTE Not optimized for omnidirectional mode.
Usable Scan Length
The decode zone is a function of various symbol characteristics including density, print contrast, wide-to-narrow
ratio, and edge acuity. Consider width of decode zone at any given distance when designing a system.
Calculating the Usable Scan Length Method on page 2-8 describes how to calculate the usable scan length.
Page 74

6 - 12 Symbol MiniScan MSXX07 Series Integration Guide
Page 75

Chapter 7 Symbol MS2207VHD
Specifications
Introduction
This chapter provides the technical specifications for the Symbol MS2207VHD scanner.
Page 76

7 - 2 Symbol MiniScan MSXX07 Series Integration Guide
Symbol MS2207VHD Electrical Interface
Figure 7-1
Table 7-1 lists the pin functions of the Symbol MS2207VHD.
Table 7-1
Pin No. Pin Name Ty p e* Function
1 Trigger I Signals scanner to begin scanning session.
2 TXD O Serial data transmit output. Drives the serial data receive input on th e
3 RXD I Serial data receive input. Driven by the serial data transmit output on
4 Not used
5 Ground Power supply ground input and signal ground reference.
6 Power I 5.0 VDC ± 10%
7 CTS I Clear-to-send handshaking input line, used only in conjunction with
8 RTS O Request-to-send handshaking output line, used only in conjunction
MiniScan Connector
Symbol MS2207VHD Electrical Interface
device communicating with the scanner.
the device communicating with the scanner.
the RTS line. Optionally used by another device to signal the scanner
to begin transmitting data.
with the CTS line. Optionally used by the scanner to signal another
device that data is available to send.
9 Beeper/Download I/O During normal operation this signal functions as an external beeper
drive line. This signal can sink 50mA of current to drive an external
beeper, and is normally pulled up. This signal is also used to begin
Flash Download operation when grounded externally during power
up.
*I = Input O = Output
Page 77

Symbol MS2207VHD Mechanical Drawings
Symbol MS2207VHD Specifications 7 - 3
Notes:
Unless otherwise specified:
• Dimensions are in inches,
dimensions in [ ] are mm.
• User mounting tolerances
are not included.
Figure 7-2
Symbol MS2207VHD Mechanical Drawing
Page 78

7 - 4 Symbol MiniScan MSXX07 Series Integration Guide
Notes:
Unless otherwise specified:
• Dimensions are in inches,
dimensions in [ ] are mm.
• User mounting tolerances
are not included.
Figure 7-3
Symbol MS2207VHD Mechanical Drawing
Page 79

Symbol MS2207VHD Technical Specifications
Table 7-2 provides the Symbol MS2207VHD technical specifications.
Symbol MS2207VHD Specifications 7 - 5
Table 7-2
Symbol MS2207VHD Technical Specifications @ 23°C
Item Description
Power Requirements
Input Voltage
Scanning Current
Standby Current
V
Noise Level
cc
Laser Power 0.7 mW ± 0.1 mW,
5.0 VDC ± 10%
250 ± 30 mA typical
25 ± 5 mA typical
200 mV peak-to-peak max.
λ
= 650 nm nominal
Scan Rate 640 scans/sec.
Scan Frequency: Horizontal 320 Hz ± 5 Hz
Scan Frequency: Vertical 282 Hz ± 5 Hz
Frame Rate 24 frames/sec. 12 Hz ±1 Hz (vertical)
Print Contrast Minimum 35% absolute dark/light reflectance differential
Scan Angle
Horizontal: 34
Vertical: 12.5o ±3
o ±3o
o
Scan Pattern Smart raster, high density single scan line
Start Time 0.065 sec. to 75% of steady state horizontal amplitude
Skew Tolerance
Pitch Angle
Roll
Decode Depth of Field See
Beam Deviation
(offset from the nominal)
Additional Post Shock Beam
Deviation (2000G Shock)
o
± 15
from plane parallel to symbol (see
o
from normal (see
± 30
o
± 4
(for scanning benchmark label, assuming 3:1 codeword aspect ratio)
(see
Figure 7-4 on page 7-7
Figure 7-5 on page 7-8
Horizontal: ±3.0
Verti cal: ±3.0
o
o
Horizontal tilt: ± 2
o
o
max
Horizontal: ±3.0
Verti cal: ±6.0
Figure 7-4 on page 7-7
)
and
o
max
Figure 7-6 on page 7-10
Figure 7-4 on page 7-7
)
Ambient Light Immunity
Sunlight
Artificial Light
8,000 ft. candles (86,112 lux)
450 ft. candles (4,844 lux)
Drop Multiple 30” drops
)
Page 80

7 - 6 Symbol MiniScan MSXX07 Series Integration Guide
Table 7-2
Vibration Unpowered scanner withstands a random vibration along each of the X, Y and
ESD ± 20kV air discharge
Sealing IP54
Operating Temperature -22° to 122°F (-30° to 50°C)
Storage Temperature -40° to 158°F (-40° to 70°C)
Humidity 5% to 95% non-condensing
Laser Class CDRH Class II, IEC Class 2
Height 1.60 in. (4.06 cm)
Width 2.28 in. (5.79 cm)
Depth 2.94 in. (7.47 cm)
Symbol MS2207VHD Technical Specifications @ 23°C (Continued)
Item Description
Z axes for a period of one hour per axis, defined as follows:
20 to 80 Hz Ramp up to 0.04 G^2/Hz at the rate of 3dB/octave.
80 to 350 Hz 0.04 G^2/Hz
350 to 2000 Hz Ramp down at the rate of 3 dB/octave.
± 8kV indirect discharge
Weight 4.73 oz. (134 gm)
Page 81

Symbol MS2207VHD Specifications 7 - 7
Skew Pitch
+ 15° from normal
10 mil
Symbol
Skew
Angle
+ 30° from normal
10 mil
Symbol
Pitch
Angle
Scan Beam
4 in. (102 mm)
Roll
Roll
Angle
10 mil
Symbol
Scan Beam
Scan Beam
4 in. (102 mm)
+ 4° from normal
Note: Tolerances are
reduced at extreme ends
of the working range.
4 in. (102 mm)
Figure 7-4
Skew, Pitch and Roll
Page 82

7 - 8 Symbol MiniScan MSXX07 Series Integration Guide
Symbol MS2207VHD Decode Zones
The decode zone is a function of various symbol characteristics including density, print contrast, wide to narrow
ratio and edge acurity. T ypical values appear. Table 7-3 on page 7-9 and Table 7-4 on page 7-11 list the typical and
guaranteed distances for selected bar code densities. The minimum element width (or “symbol density”) is the
width in mils of the narrowest element (bar or sp ace) in the symbo l. The maximum usable len gth of a symbol at any
given range appears below. To calculate this distance, see Calculating the Usable Scan Length Method on page
2-8.
Symbol MS2207VHD 1D Decode Zone
Note: Typical performance at 68˚F (20˚C)
on high quality symbols in normal room light.
Vcc = 5V
MS 220XVHD
4 mil
5 mil
6 mil
7.5 mil
3.4
4.1
4.75
5.25
55 mil
2.0
1.75
1.5
*
15.0
In. cm
10
7.5
5
2.5
0
2.5
5
7.5
10
25.4
15.2
10.1
5.1
0
5.1
10.1
15.2
25.4
W
i
d
t
h
o
f
F
i
e
l
d
In.
cm
Figure 7-5
0
0 12.7 25.4 38.1 50.8
2.5
5 7.5 10
12.5
63.5
15
76.2
Depth of Field
* Minimum distance determined by symbol length and scan angle.
Symbol MS2207VHD 1D Slab/Raster Decode Distances
Page 83

Symbol MS2207VHD 1D Decode Distances
Symbol MS2207VHD Specifications 7 - 9
Table 7-3
Symbol MS2207VHD 1D Decode Distances
Symbol Density/
p/n / Bar Code Type
4 mil
64-15660-01
Code 39
5 mil
64-18779-01
Code 39
6 mil
64-01755-01
Code 39
7.5 mil
63-04191-01
Code 39
55 mil
60-01601-01
Code 39
Bar Code Content/
Contrast
STI4026
80% MRD
STI5025
80% MRD
123
80% MRD
STI30F4
80% MRD
A
80% MRD
Guaranteed Working
Typical Working Ranges
1
3
Ranges
3
Near Far Near Far
2.0 in.
5.08 cm
1.75 in.
4.45 cm
1.75 in.
4.45 cm
1.50 in.
3.81 cm
Note 2 15.0 in.
3.4 in.
8.64 cm
4.1 in.
10.41 cm
4.75 in.
12.07 cm
5.25 in.
13.34 cm
38.10 cm
2.75 in.
7.00 cm
2.25 in.
5.72 cm
2.25 in.
5.72 cm
2.00 in.
5.08 cm
2.8 in.
7.11 cm
3.5 in.
8.89 cm
4.0 in.
10.16 cm
4.75 in.
12.07 cm
Note 2 12.5 in.
31.75 cm
Notes:
1. Contrast measured as Mean Reflective Difference (MRD) at 650 nm.
2. Near ranges on lower densities largely depend on the width of the bar code and the scan angle.
3. Working range specifications: Photographic quality symbols, pitch = 10°, skew = 0°,, roll = 0°,
ambient light < 150 ft. candles, and temperature = 23 °C.
Page 84

7 - 10 Symbol MiniScan MSXX07 Series Integration Guide
Symbol MS2207VHD 2D Decode Zone
Note: Typical performance at 68˚F (20˚C) on high quality symbols
in normal room light. Y-module dimension = 3X.
Vcc = 5V
In. cm
2.5
1.25
6.35
3.18
W
i
d
t
h
MS 220XVHD
In.
cm
Figure 7-6
NOTE Not optimized for omnidirectional mode.
0
4.0 mil
1.90
1.50
0
0
1
5.1
2
5.1
3.00
6.6 mil
3.00
10 mil, 35% MRD
3
15.2410.1
4.75
5.75
56
25.4 15.2
1.25
2.5
Depth of Field
Symbol MS2207VHD 2D Slab/Raster Decode Distances
0
3.18
6.35
o
f
F
i
e
l
d
Page 85

Symbol MS2207VHD 2D Decode Distances
Symbol MS2207VHD Specifications 7 - 11
Table 7-4
p/n / Bar Code Type
Symbol MS2207VHD 2D Slab/Raster Decode Distances
Symbol Density/
Bar Code Content/
Contrast
1
Typical Working Ranges
Guaranteed Working
3
Ranges
3
Near Far Near Far
4 mil
64-17025-01
123
80% MRD
1.90 in.
4.83 cm
3.00 in.
7.62 cm
2.20 in.
5.59 cm
2.70 in.
6.89 cm
PDF417
6.6 mil
64-14035-01
ABCDEF
80% MRD
1.50 in.
3.81 cm
4.75 in.
12.07 cm
2.00 in.
5.08 cm
4.50 in.
11.43 cm
PDF417
10 mil
64-14937-01
012345678905
80% MRD
3.00 in.
7.62 cm
5.75 in.
14.61 cm
4.25 in.
10.80 cm
5.00 in.
12.72 cm
PDF417
Notes:
1. Contrast measured as Mean Reflective Difference (MRD) at 650 nm.
2. Near ranges on lower densities largely depend on the width of the bar code and the scan angle.
3. Working range specifications: Photographic quality symbols, pitch = 10°, skew = 0°,
roll = 0°, ambient light < 150 ft. candles, and temperature = 23 °C.
NOTE Not optimized for omnidirectional mode.
Usable Scan Length
The decode zone is a function of various symbol characteristics including density, print contrast, wide-to-narrow
ratio, and edge acuity. Consider width of decode zone at any given distance when designing a system.
Calculating the Usable Scan Length Method on page 2-8 describes how to calculate the usable scan length. The
scan angle is provided in the Usable Scan Length Diagram on page 2-8.
Page 86

7 - 12 Symbol MiniScan MSXX07 Series Integration Guide
Page 87

Chapter 8 Symbol MS3207 Specifications
Introduction
This chapter provides the technical specifications for the Symbol MS3207 scanner.
Page 88

8 - 2 Symbol MiniScan MSXX07 Series Integration Guide
Symbol MS3207 Electrical Interface
This section describes the pin functions of the Symbol MS3207 interface.
Figure 8-1
Table 8-1
Pin No. Pin Name Type* Function
1 Trigger I Signals to scanner to begin scanning session.
2 TXD O Serial data transmit output. Drives the serial data receive input on the
3 RXD/D+ I/O RS-232 Mode: Serial data receive input. Driven by the serial data
4 SYN_CLK I/O Synapse Mode: Synapse Clock line. Signal used as a clock by a
5 Ground Power supply ground input and signal ground reference.
6 Power 5.0 VDC ± 10%
Symbol MS3207 Connector
Symbol MS3207 Electrical Interface
device communicating with the scanner.
transmit output on the device communicating with the scanner.
USB Mode: D+ signal. During USB operation this signal is pulled up by
a 1.5k Ohm resistor to begin USB enumeration. In this mode it is a
differential bi-directional signal.
Synapse host. Pin is shorted to RTS/SYN_DAT in USB cables to allow
for auto-detection of USB mode via signal loopback.
*I = Input O = Output
Page 89

Symbol MS3207 Specifications 8 - 3
Table 8-1
Pin No. Pin Name Type* Function
7 CTS/D- I/O RS-232 Mode: Clear-to-send handshaking input line, used only in
8 RTS/SYN_DAT I/O RS-232 Mode: Request-to-send handshaking output line, used only in
9 Beeper/Download I/O During normal operation this signal functions as an external beeper
*I = Input O = Output
Symbol MS3207 Electrical Interface (Continued)
conjunction with the RTS line. Optionally used by another device to
signal the scanner to begin transmitting data.
USB Mode: D- signal. During USB operation this signal works in
conjunction with the D+ signal as a differential bi-directional signal.
conjunction with the CTS line. Optionally used by the scanner to signal
another device that data is available to send.
Synapse Mode: Synapse Data line. Signal is used to transmit data to
and from a Synapse host.
drive line. This signal can sink 50mA of current to drive an external
beeper, and is normally pulled up. This signal is also used to begin
Flash Download operation when grounded externally during power up.
Page 90

8 - 4 Symbol MiniScan MSXX07 Series Integration Guide
Symbol MS3207 Mechanical Drawings
Notes:
Unless otherwise specified:
• Dimensions are in inches,
dimensions in [ ] are mm.
• User mounting tolerances
are not included.
Figure 8-2
Symbol MS3207 Mechanical Drawing
Page 91

Symbol MS3207 Specifications 8 - 5
Notes:
Unless otherwise specified:
• Dimensions are in inches,
dimensions in [ ] are mm.
• User mounting tolerances
are not included.
Figure 8-3
Symbol MS3207 Mechanical Drawing
Page 92

8 - 6 Symbol MiniScan MSXX07 Series Integration Guide
Symbol MS3207 Technical Specifications
Table 8-2
Symbol MS3207 Technical Specifications @ 23°C
Item Description
Power Requirements
Input Voltage
Scanning Current
Standby Current
V
Noise Level
cc
+5.0 VDC ± 10%
250 ± 30 mA typical
45 ± 10 mA typical
200 mV peak-to-peak max.
Laser Power 0.7 mW typical, 0.8 mW maximum @ 650 nm
Scan Rate 640 scans/second
Scan Frequency: Horizontal 320 Hz ± 5 Hz
Scan Frequency: Vertical 282 Hz ± 5 Hz
Frame Rate 24 frames/sec. 12 Hz ±1 Hz (vertical)
Print Contrast Minimum 35% absolute dark/light reflectance differential (PDF);
35% absolute dark/light reflectance differential (1-D)
o
Scan Angle
Horizontal: 34
Vertical: 34o ±1.5
±1.5
o
o
Scan Pattern Omnidirectional, semi-omnidirectional, smart raster, high density
single scan line
Start Time 0.065 sec. to 75% of steady state horizontal amplitude
Skew Tolerance
Pitch Angle
Roll
o
± 15
from normal (see
o
± 30
from normal (see
o
from vertical (see
± 4
Figure 8-4 on page 8-8
Figure 8-4 on page 8-8
Figure 8-4 on page 8-8
)
)
)
(For scanning benchmark label, assuming 3:1 codeword aspect
ratio). Note that this is dependent on the decoder.
Decode Depth of Field See
Beam Deviation
(offset from the nominal)
Additional Post Shock Beam
Deviation (2000G Shock)
Figure 8-5 on page 8-9
Horizontal: ±3.0
Vertical: ±3.0
o
o
Horizontal tilt: ± 2
o
o
max
Horizontal: ±3.0
Vertical: ±6.0
o
max
and
Figure 8-6 on page 8-11
Ambient Light Immunity
Sunlight
Artificial Light
8,000 ft. candles (86,112 lux)
450 ft. candles (4,844 lux)
Page 93

Symbol MS3207 Specifications 8 - 7
Table 8-2
Drop 30 inch drop
Vibration Unpowered scanner withstands a random vibration along each of
ESD ± 20kV air discharge
Sealing IP54
Operating Temperature -22°F to 122°F (-30°C to 50°C)
Storage Temperature -40°F to 158°F (-40°C to 70°C)
Humidity 5% to 95% non-condensing
Laser Class CDRH Class II, IEC Class 2
Symbol MS3207 Technical Specifications @ 23°C (Continued)
Item Description
the X, Y and Z axes for a period of one hour per axis, defined as
follows:
20 to 80 Hz Ramp up to 0.04 G^2/Hz at the rate of 3dB/
octave.
80 to 350 Hz 0.04 G^2/Hz
350 to 2000 Hz Ramp down at the rate of 3 dB/octave.
± 8kV indirect discharge
Height 1.98 in. (5.03 cm)
Width 2.41 in. (6.12 cm)
Depth 3.60 in. (9.14 cm)
Weight 4.97 oz. (142 g)
Page 94

8 - 8 Symbol MiniScan MSXX07 Series Integration Guide
Skew Pitch
+ 15° from normal
Skew
20 mil
Symbol
Angle
+ 30° from normal
20 mil
Symbol
Pitch
Angle
Scan Beam
7.0 in. (177.8 mm)
Roll
Roll
Angle
20 mil
Symbol
Scan Beam
Scan Beam
7.0 in. (177.8 mm)
+4° from normal
Note: Tolerances are
reduced at extreme ends
of the working range.
7.0 in. (177.8 mm)
Figure 8-4
Skew, Pitch and Roll
Page 95

Symbol MS3207 Decode Zones
i
d
t
h
o
f
F
i
e
l
d
The decode zone is a function of various symbol characteristics including density, print contrast, wide to narrow
ratio and edge acuity . Typical values appear. Table 8-3 on page 8-10 and Table 8-4 on page 8-12 list the typical and
guaranteed distances for selected bar code densities. The minimum element width (or “symbol density”) is the
width in mils of the narrowest element (bar or sp ace) in the symbo l. The maximum usable len gth of a symbol at any
given range appears below. To calculate this distance, see Calculating the Usable Scan Length Method on page
2-8.
Symbol MS3207 Omnidirectional Decode Distances
Note: Typical performance at 68˚F (20˚C)
on high quality symbols in normal room light.
Vcc = 5V
in.
5
2.5
cm
12.7
6.35
Symbol MS3207 Specifications 8 - 9
W
.25
1.00
6 mil
.25
1.00
1.5
1.75
3.25
80% UPC
6.5
100% UPC
20 mil
Depth of Field
0
In.
cm
0 12.7 25.4 38.1 50.8
2.5
5 7.5 10
Depth of Field
* Minimum distance determined by symbol length and scan angle.
Figure 8-5
Symbol MS3207 Omnidirectional Decode Zone (Typical)
12.5
63.5
12.5
12.5
0
0
6.35
2.5
12.7
5
Page 96

8 - 10 Symbol MiniScan MSXX07 Series Integration Guide
Table 8-3
Symbol Density/
p/n / Bar Code Type
Symbol MS3207 Omnidirectional Decode Distances
Bar Code Content/
Contrast
1
Typical Working Ranges
Guaranteed Working
3
Ranges
3
Near Far Near Far
6.0 mil
60-01755-01
123
80% MRD
0.25 in.
0.64 cm
3.25 in.
8.3 cm
0.75 in.
1.9 cm
2.25 in.
5.7 cm
Code 39
64-06629-01
80% UPC
13 mil
64-05303-01
0080015
85% MRD
012345678905
80% MRD
1.0 in.
2.5 cm
1.5 in.
3.8 cm
6.5 in.
16.5 cm
12.5 in.
31.2 cm
1.5 in.
3.8 cm
4.5 in.
11.4 cm
Note 2 9.5 in.
24.1 cm
100% UPC
20 mil 1D
60-02710-03
123
80% MRD
1.75 in.
4.4 cm
12.5 in.
31.8 cm
Note 2 10.0 in.
25.4 cm
LC 35%
Notes:
1. Contrast measured as Mean Reflective Difference (MRD) at 650 nm.
2. Near ranges on largely depend on the width of the bar code and the scan angle.
3. Working range specifications: Photographic quality symbols, pitch = 15°, skew = 0°, roll = 0°,
ambient light < 150 ft. candles, and temperature = 23 °C, Vcc = 5V.
4. Measured from the front of the scanner.
Page 97

Symbol MS3207 2D Slab/Raster Decode Distances
i
d
t
h
o
f
F
i
e
l
d
Symbol MS3207 Specifications 8 - 11
Note: Typical performance at 68˚F (20˚C)
on high quality symbols in normal room light.
Vcc = 5V
6.6 mil PDF 417
1.0
3.5
1.0
0
In.
cm
0 12.7 25.4 38.1 50.8
5.25
10 mil PDF 417
6.5
5
9.5
15 mil PDF 417
55 mil 1D
10 15 20
Depth of Field
* Minimum distance determined by symbol length and scan angle.
25
63.5
14.0
30
76.2
32.0
In. cm
11
10
7.5
5
2.5
0
2.5
5
7.5
10
11
35
88.9
27.9
25.4
15.2
10.1
5.1
0
5.1
10.1
15.2
25.4
27.9
W
Figure 8-6
Symbol MS3207 2D Slab/Raster Decode Zone
Page 98

8 - 12 Symbol MiniScan MSXX07 Series Integration Guide
Table 8-4
Symbol Density/
p/n / Bar Code Type
Symbol MS3207 2D Slab/Raster Decode Distances
Bar Code Content/
Contrast
1
Typical Working Ranges
Guaranteed Working
3
Ranges
Near Far Near Far
6.6 mil
64-14035-01
123
80% MRD
1.0 in.
2.54 cm
5.25 in.
13.34 cm
1.5 in.
3.8 cm
3.75 in.
9.5 cm
2D
10 mil
64-14037-01
ABCDEF
80% MRD
3.5 in.
8.89 cm
9.5 in.
24.13 cm
5.0 in.
12.7 cm
7.5 in.
9.5 cm
2D
15 mil
64-14038-01
012345678905
80% MRD
6.5 in.
16.51 cm
14.0 in.
35.6 cm
Note 2 11.0 in.
24.1 cm
2D
55 mil
64-17458-01
CD
80% MRD
1.0 in.
2.54 cm
32 in.
81.3 cm
Note 2 22.0 in.
55.9 cm
1D
Notes:
1. Contrast measured as Mean Reflective Difference (MRD) at 650 nm.
2. Near ranges on largely depend on the width of the bar code and the scan angle.
3. Working range specifications: Photographic quality symbols, pitch = 15º, skew = 0º, roll = 0º,
ambient light < 150 ft. candles, and temperature = 23 °C, Vcc = 5V.
4. Measured from the front of the scanner.
3
Usable Scan Length
The decode zone is a function of various symbol characteristics including density, print contrast, wide-to-narrow
ratio, and edge acuity. Width of decode zone at any given distance must be considered when designing a system.
Calculating the Usable Scan Length Method on page 2-8 provides a detailed description of how to calculate the
usable scan length. The scan angle is provided in Table 8-2 on page 8-6.
Page 99

Chapter 9 Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Introduction
The chapter provides information on maintenance and troubleshooting.
Maintenance
Cleaning the exit window is the only maintenance required. Do not allow any abrasive material to touch the
window. Clean the scan window with a damp cloth and, if necessary, a non-ammonia based detergent.
Page 100

9 - 2 Symbol MiniScan MSXX07 Series Integration Guide
Troubleshooting
Table 9-1
No red LED or nothing
happens during a scan
attempt.
Scanner cannot read the
bar code.
Laser activates, followed
by a beep sequence.
Troubleshooting
Problem Possible Cause Possible Solutions
No power to the scanner. Check the system power.
Confirm that the correct host interface cable is used.
Connect the power supply.
Re-connect loose cables.
Interface/power cables are
loose.
Scanner is not programmed
for the correct bar code type.
Incorrect communication
parameters.
Bar code symbol is
unreadable.
Inappropriately hot
environment.
Beeper is configured. See
Re-connect loose cables.
Make sure the scanner is programmed to read the
type of bar code to be scanned.
Scan other bar code(s) and bar code types.
Set the correct communication parameters (baud rate,
parity, stop bits, etc.)
Check the symbol to make sure it is not defaced. Try
scanning similar symbols of the same code type.
Remove the scanner from the hot environment, and
allow it to cool down.
Table 3-1 on page 3-7
descriptions.
for beeper indication
Scanner does not
function.
NOTE If after performing these checks the symbol still does not scan, contact the distributor or Motorola
Enterprise Mobility Support. See page xv for contact information.
Accidentally scanned
Trigger
from
page 3-5
or
Pulse Trigger
Trigger Options on
.
Level
Cycle power to the scanner. As the laser briefly
appears after power up, scan the
code from
Connect an interface cable which has an external
trigger jack, a push button trigger cable, and a power
supply to the scanner . You can purchase these cables
from Motorola, or make a similar one using the
scanner’s pinouts as a reference. See the specifi cation
chapter for your MiniScan model for pinouts.
Using a momentary switch, short the scanner’s trigger
line to ground to activate the laser, then scan the
Continuous
Trigger Options on page 3-5
option of the
Trigger Mode
Continuous
.
parameter.
bar
 Loading...
Loading...