Motorola MMDF3N04HDR2 Datasheet
1
Motorola TMOS Power MOSFET Transistor Device Data
Medium Power Surface Mount Products
MiniMOS devices are an advanced series of power MOSFETs
which utilize Motorola’s High Cell Density HDTMOS process. These
miniature surface mount MOSFETs feature ultra low R
DS(on)
and true
logic level performance. They are capable of withstanding high energy
in the avalanche and commutation modes and the drain–to–source
diode has a very low reverse recovery time. MiniMOS devices are
designed for use in low voltage, high speed switching applications
where power efficiency is important. Typical applications are dc–dc
converters, and power management in portable and battery powered
products such as computers, printers, cellular and cordless phones.
They can also be used for low voltage motor controls in mass storage
products such as disk drives and tape drives. The avalanche energy is
specified to eliminate the guesswork in designs where inductive loads
are switched and offer additional safety margin against unexpected
voltage transients.
• Ultra Low R
DS(on)
Provides Higher Efficiency and Extends Battery Life
• Logic Level Gate Drive — Can Be Driven by Logic ICs
• Miniature SO–8 Surface Mount Package — Saves Board Space
• Diode Is Characterized for Use In Bridge Circuits
• Diode Exhibits High Speed, With Soft Recovery
• I
DSS
Specified at Elevated Temperature
• Mounting Information for SO–8 Package Provided
• Avalanche Energy Specified
MAXIMUM RATINGS
(TJ = 25°C unless otherwise noted)
Rating
Symbol Value Unit
Drain–to–Source Voltage V
DSS
40 Vdc
Drain–to–Gate Voltage (RGS = 1.0 MΩ) V
DGR
40 Vdc
Gate–to–Source Voltage — Continuous V
GS
± 20 Vdc
Drain Current — Continuous @ TA = 25°C (1)
Drain Current — Continuous @ TA = 70°C (1)
Drain Current — Pulsed Drain Current (4)
I
D
I
D
I
DM
3.4
3.0
40
Adc
Apk
Total Power Dissipation @ TA = 25°C (1)
Linear Derating Factor (1)
P
D
2.0
16
Watts
mW/°C
Total Power Dissipation @ TA = 25°C (2)
Linear Derating Factor (2)
P
D
1.39
11.11
Watts
mW/°C
Operating and Storage Temperature Range TJ, T
stg
– 55 to 150 °C
Single Pulse Drain–to–Source Avalanche Energy — Starting TJ = 25°C
(VDD = 25 Vdc, VGS = 10 Vdc, Peak IL = 9.0 Apk, L = 4.0 mH, VDS = 40 Vdc)
E
AS
162
mJ
THERMAL RESISTANCE
Rating Symbol Typ. Max. Unit
Thermal Resistance — Junction to Ambient, PCB Mount (1)
— Junction to Ambient, PCB Mount (2)
R
θJA
R
θJA
—
—
62.5
90
°C/W
(1) When mounted on 1 inch square FR–4 or G–10 board (VGS = 10 V, @ 10 Seconds)
(2) When mounted on minimum recommended FR–4 or G–10 board (VGS = 10 V, @ Steady State)
DEVICE MARKING ORDERING INFORMATION
Device Reel Size Tape Width Quantity
D3N04H
MMDF3N04HDR2 13″ 12 mm embossed tape 2500 units
Designer’s Data for “Worst Case” Conditions — The Designer’s Data Sheet permits the design of most circuits entirely from the information presented. SOA Limit
curves — representing boundaries on device characteristics — are given to facilitate “worst case” design.
Preferred devices are Motorola recommended choices for future use and best overall value.
HDTMOS, MiniMOS, and Designer’s are trademarks of Motorola, Inc. TMOS is a registered trademark of Motorola, Inc.
Micro–8 is a registered trademark of International Rectifier. Thermal Clad is a trademark of the Berquist Company.
REV 1
SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA
Order this document
by MMDF3N04HD/D
Motorola, Inc. 1996
DUAL TMOS
POWER MOSFET
3.4 AMPERES
40 VOLTS
R
DS(on)
= 0.080 OHM
Motorola Preferred Device
D
S
G
Source–1
1
2
3
4
8
7
6
5
Top View
Gate–1
Source–2
Gate–2
Drain–1
Drain–1
Drain–2
Drain–2
CASE 751–05, Style 14
SO–8

MMDF3N04HD
2
Motorola TMOS Power MOSFET Transistor Device Data
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
(TC = 25°C unless otherwise noted)
Characteristic
Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
OFF CHARACTERISTICS
Drain–to–Source Breakdown Voltage (Cpk ≥ 2.0) (1) (3)
(VGS = 0 Vdc, ID = 0.25 mAdc)
Temperature Coefficient (Positive)
V
(BR)DSS
40
—
—
4.3
—
—
Vdc
mV/°C
Zero Gate Voltage Drain Current
(VDS = 40 Vdc, VGS = 0 Vdc)
(VDS = 40 Vdc, VGS = 0 Vdc, TJ = 125°C)
I
DSS
—
—
0.015
0.15
2.5
10
µAdc
Gate–Body Leakage Current (VGS = ± 20 Vdc, VDS = 0) I
GSS
— 0.013 500 nAdc
ON CHARACTERISTICS
(1)
Gate Threshold Voltage (Cpk ≥ 2.0) (1) (3)
(VDS = VGS, ID = 0.25 mAdc)
Threshold Temperature Coefficient (Negative)
V
GS(th)
1.0
—
2.0
4.9
3.0
—
Vdc
mV/°C
Static Drain–to–Source On–Resistance (Cpk ≥ 2.0) (1) (3)
(VGS = 10 Vdc, ID = 3.4 Adc)
(VGS = 4.5 Vdc, ID = 1.7 Adc)
R
DS(on)
—
—
55
79
80
100
mΩ
Forward Transconductance (VDS = 3.0 Vdc, ID = 1.7 Adc) (1) g
FS
2.0 4.5 — Mhos
DYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS
Input Capacitance
C
iss
— 450 900 pF
Output Capacitance
(VDS = 32 Vdc, VGS = 0 Vdc,
f = 1.0 MHz)
C
oss
— 130 230
Transfer Capacitance
f = 1.0 MHz)
C
rss
— 32 96
SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS
(2)
Turn–On Delay Time
t
d(on)
— 9.0 18 ns
Rise Time
DD
= 20 Vdc, ID = 3.4 Adc,
t
r
— 15 30
Turn–Off Delay Time
(VDD = 20 Vdc, ID = 3.4 Adc,
VGS = 10 Vdc, RG = 6 Ω) (1)
t
d(off)
— 28 56
Fall Time t
f
— 19 38
Turn–On Delay Time
t
d(on)
— 13 26 ns
Rise Time
DD
= 20 Vdc, ID = 1.7 Adc,
t
r
— 77 144
Turn–Off Delay Time
(VDD = 20 Vdc, ID = 1.7 Adc,
VGS = 4.5 Vdc, RG = 6 Ω) (1)
t
d(off)
— 17 34
Fall Time t
f
— 20 40
Q
T
— 13.9 28 nC
DS
= 40 Vdc, ID = 3.4 Adc,
Q
1
— 2.1 —
(VDS = 40 Vdc, ID = 3.4 Adc,
VGS = 10 Vdc) (1)
Q
2
— 3.7 —
Q
3
— 5.4 —
SOURCE–DRAIN DIODE CHARACTERISTICS
Forward On–Voltage
(IS = 3.4 Adc, VGS = 0 Vdc) (1)
(IS = 3.4 Adc, VGS = 0 Vdc, TJ = 125°C)
V
SD
—
—
0.87
0.8
1.5
—
Vdc
t
rr
— 27 —
(IS = 3.4 Adc, VGS = 0 Vdc,
dI
/dt = 100 A/µs) (1)
t
a
— 20 —
dIS/dt = 100 A/µs) (1)
t
b
— 7.0 —
Reverse Recovery Storage Charge Q
RR
— 0.03 — µC
(1) Pulse Test: Pulse Width ≤ 300 µs, Duty Cycle ≤ 2%.
(2) Switching characteristics are independent of operating junction temperature.
(3) Reflects typical values.
Cpk =
Max limit – Typ
3 x SIGMA
(4) Repetitive rating; pulse width limited by maximum junction temperature.
Gate Charge
Reverse Recovery Time
(V
(V
(V
ns
MMDF3N04HD
3
Motorola TMOS Power MOSFET Transistor Device Data
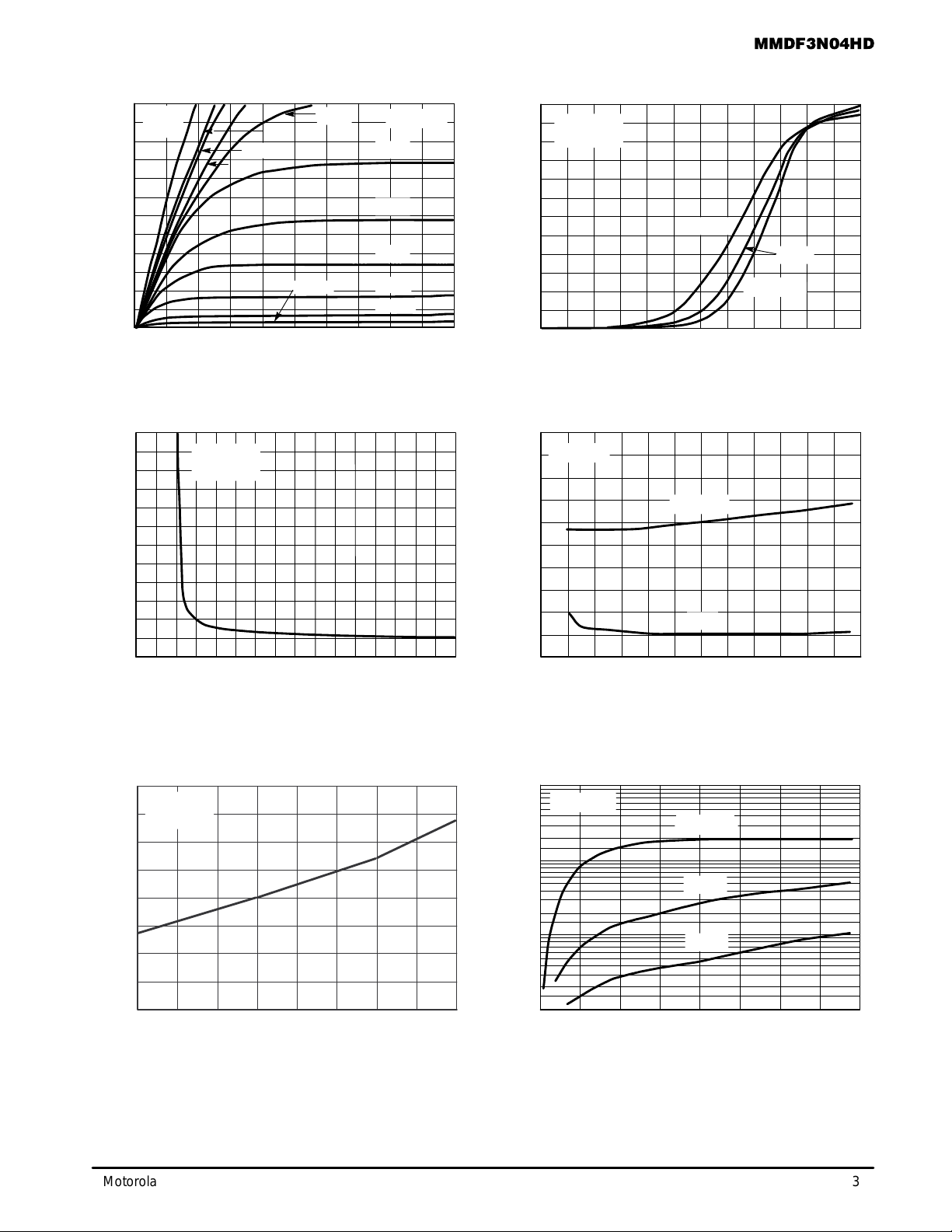
TYPICAL ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
R
DS(on)
, DRAIN–TO–SOURCE RESISTANCE (OHMS)
0
0 0.2 1.2 2
0
1
3
VDS, DRAIN–TO–SOURCE VOLTAGE (VOLTS)
Figure 1. On–Region Characteristics
I
D
, DRAIN CURRENT (AMPS)
I
D
, DRAIN CURRENT (AMPS)
VGS, GATE–TO–SOURCE VOLTAGE (VOLTS)
Figure 2. Transfer Characteristics
0.05
Figure 3. On–Resistance versus
Gate–to–Source Voltage
ID, DRAIN CURRENT (AMPS)
Figure 4. On–Resistance versus Drain Current
and Gate Voltage
Figure 5. On–Resistance Variation
with Temperature
Figure 6. Drain–to–Source Leakage Current
versus Voltage
VDS ≥ 10 V
TJ = 25
°
C
TJ = –55°C
25°C
100°C
4
2
TJ = 25°C
2
4
6
5
1
2 2.5 3 3.5 4
0.08
0 1 2 5 6
3.1 V
0.06
0.07
3
3 4
10 V
VGS = 4.5
TJ = 25°C
R
DS(on)
, DRAIN–TO–SOURCE RESISTANCE (NORMALIZED)
TJ, JUNCTION TEMPERATURE (°C)
–50 0 50 100 150
0
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
VGS = 10 V
ID = 3.4 A
1257525–25
1
5
6
2.9 V
3.3 V
3.5 V
3.7 V
4.1 V
4.5 V
VGS =
10 V
4.3 V
1.5 4.5
0.055
0.065
0.075
I
DSS
, LEAKAGE (nA)
1
100
VDS, DRAIN–TO–SOURCE VOLTAGE (VOLTS)
10
0 5 10 15 3020 25
VGS = 0 V
TJ = 125°C
100°C
0.1
35 40
25°C
R
DS(on)
, DRAIN–TO–SOURCE RESISTANCE (OHMS)
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.3
0.1
0.2
0
2 3 4 5 86 7
9 10
VGS, GATE–TO–SOURCE VOLTAGE (VOLTS)
ID = 3.4 A
TJ = 25
°
C
0.4 1.40.6 1.60.8 1.8
3.9 V
2.7 V
0.085
0.09
0.095
0.1
 Loading...
Loading...