Motorola MC88PL117FN Datasheet

SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA
#
"% $ $
"!
The MC88PL117 utilizes proven phase–locked loop clock driver
technology to create a large fan–out, multiple frequency and phase, low
skew clock driver. The 88PL117 provides the clock frequencies
necessary to drive systems using the PowerPC 601 microprocessor
and the Pentium microprocessor (see applications section for details).
A total of 14 high current, matched impedance outputs are available in 8
programmable output frequency and phase configurations. Output
frequencies are referenced to a system frequency , Q, and are available at
2X, 1X, and 1/2X the Q frequency. Four programmable input frequency
multiplication ratios can be programmed to provide outputs at 1X, 2X, and
4X the system frequency Q. Details on the programmable configurations
can be found in the applications section of this data sheet.
CMOS PLL
CLOCK DRIVER
• Clock Driver for PowerPC 601 and Pentium Microprocessors
• 14 programmable outputs
• Maximum output–to–output skew of 500ps for a single frequency
• Maximum output–to–output skew of 500ps for multiple frequencies
• f
of 2X_Q = 120MHz
MAX
• One output with programmable phase capability
• ±36mA DC current outputs drive 50Ω transmission lines
• A lock indicator output (LOCK) goes high when steady–state
phase–lock is achieved
52–LEAD PLASTIC LEADLESS
FN SUFFIX
CHIP CARRIER (PLCC)
CASE 778–02
• OE/MR 3–state control
• Dedicated feedback output
• Two selectable clock inputs
• PLL enable pin for testability
• Dynamic Switch Between SYNC Inputs
One output (QFEED) is dedicated for feedback. It is located physically close to the FEEDBACK input pin to minimize the
feedback line length. External delay (increased wire length) or logic can be inserted in the feedback path if necessary. Proper
termination of the feedback line is necessary for any line length over one inch.
One output is provided with up to eight selectable 1/8 or 1/4 period (45° or 90°) delay increments. Three control pins, ∅2, ∅1
and ∅0, program the eight increments; the increment/phase shift positions are shown in Table 3. in the applications section.
All outputs can be 3–stated (high impedance) during board–level testing with the OE/MR
will not be 3–stated, which allows the 88PL1 17 to remain in a phase–locked condition. Correct phase and frequency coherency
will be guaranteed one to two cycles after bringing the OE/MR
input signal directly into the internal clock distribution network to provide low frequency testability. Two selectable SYNC inputs
(SYNC0 and SYNC1) are provided for clock redundancy or ease of testability . The device is guaranteed to lock to the new SYNC
input when the REF_SEL input is switched dynamically.
A phase–lock indicator output (LOCK) stays low when the part is out of lock (start–up, etc.) and goes high when steady–state
phase–lock is achieved. The lock indicator circuitry works reliably for VCO frequencies down to 55MHz. For VCO frequencies
less than 55MHz, no guarantees are offered for the lock indicator output.
The MC88PL1 17 VCO is capable of operating at frequencies higher than the output divider and feedback structures are able
to follow. When the VCO is in the mode described above, it is referred to as “runaway” and the device will not lock. The condition
usually occurs at power–up. To avoid runaway, it is recommended that the device be fully powered before a sync signal is
applied.
pin high. The PLL_EN pin disables the PLL and gates the SYNC
pin; the QFEED and LOCK outputs
PowerPC is a trademark of International Business Machines Corporation.
1/97
Motorola, Inc. 1997
1
REV 4
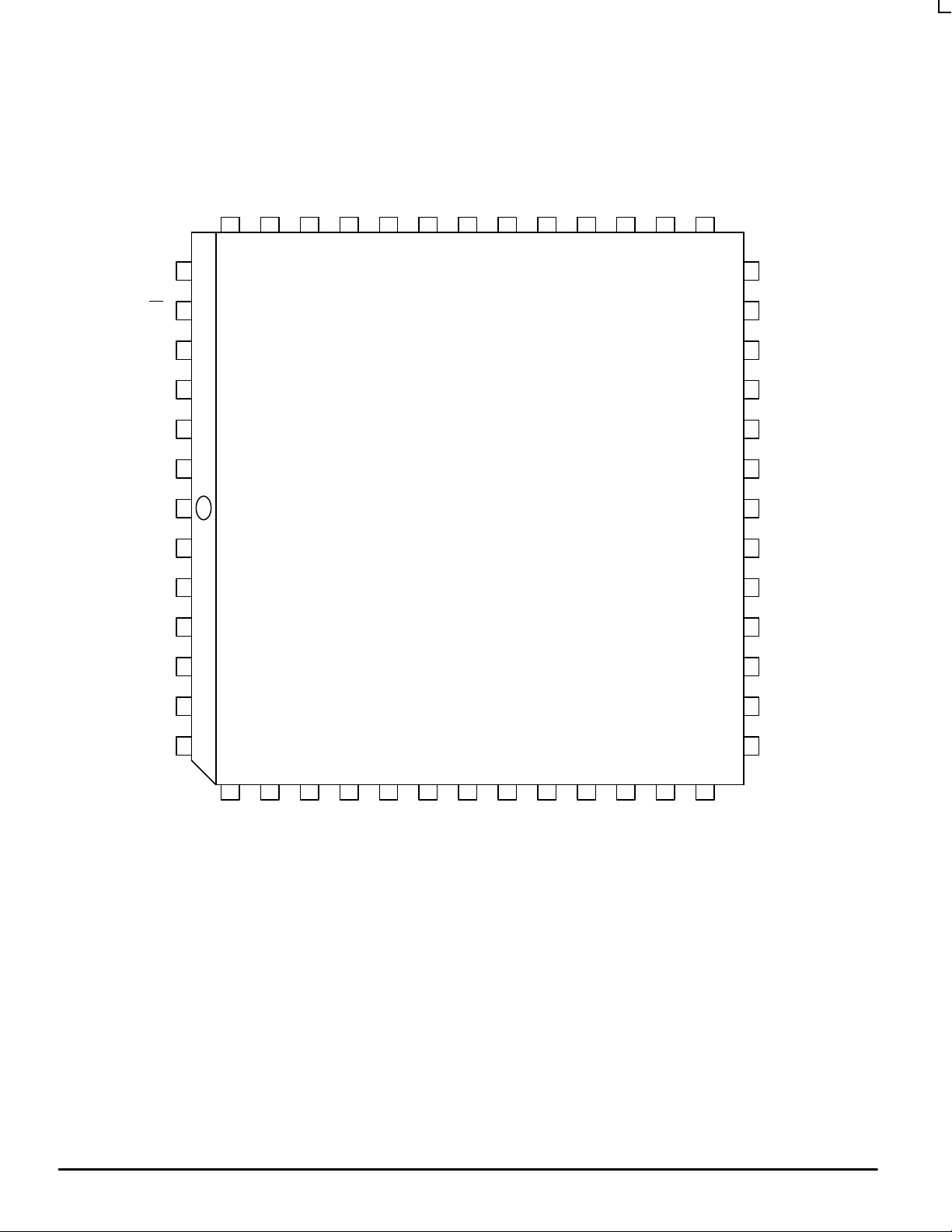
MC88PL117
LOCK
OE/MR
Q0
V
CC
Q1
GND
Q2
V
CC
Q3
GND
QFEED46V
47
48
49
50
51
52
1
2
3
4
FEEDBACK44GND43AV
CC
45
FIL41AGND40GND39Q1338V
CC
42
MC88PL117
Q1236REF_SEL35SYNC1
CC
37
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
SYNC0
DV
DD
DGND
Q
∅
Q11
V
CC
Q10
GND
Q9
V
CC
OPT0
OPT1
OPT2
5
6
7
8
MULT09MULT110GND11Q412V
13Q514
CC
GND15Q616V
CC
Pinout: 52–Lead PLCC (Top View)
17Q718
∅
019∅
120∅
23
22
21
2
Q8
GND
PLL_EN
MOTOROLA TIMING SOLUTIONS
2
BR1333 — Rev 6

MC88PL117
SYNC0
SYNC1
REF_SEL
FEEDBACK
PLL_EN
OPT2
OPT1
OPT0
0
1
POWER–ON
RESET
LOCK INDICAT OR
PFD
OUTPUT
FREQUENCY
AND PHASE
CONTROL
LOGIC
CIRCUITRY
CH
PUMP
10
EXTERNAL
FILTER PIN
LOCK
VCO
Disable
DQ
R
Q0
MULT1
MULT0
∅
2
∅
1
∅
0
OE/MR
FEEDBACK
LOGIC
PHASE DELAY
LOGIC
MC88PL117 Block Diagram (Logical Representation)
DQ
R
DQ
R
DQ
R
Q13
QFEED
Q
∅
TIMING SOLUTIONS
BR1333 — Rev 6
3 MOTOROLA
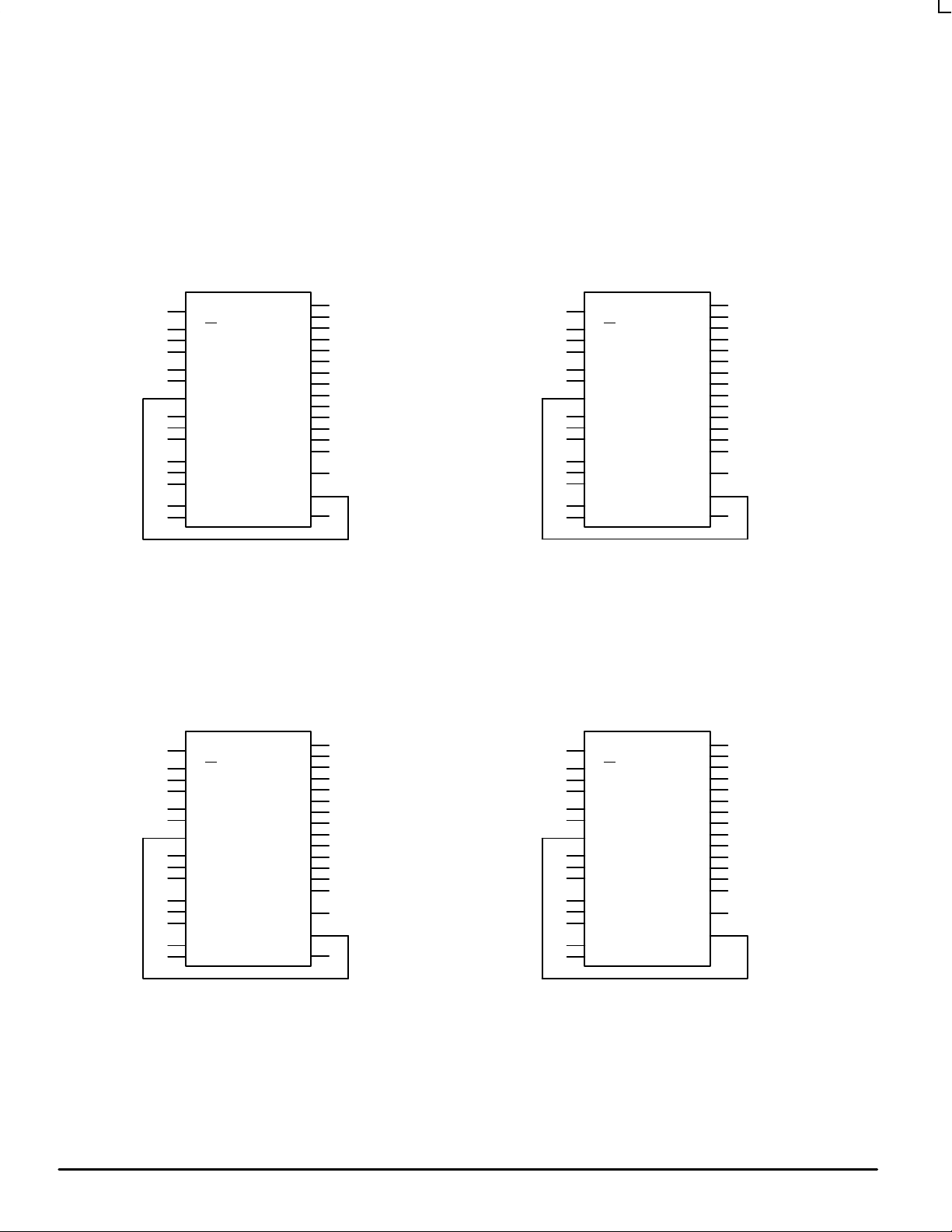
MC88PL117
Explanation of Programmable Frequency Configurations
The MC88PL117 has six different output frequency
configurations. Figures 1 to 6 graphically depict these output
configurations. There are also three feedback frequency
options, which yields a total of 18 unique input–to–output
frequency configurations. All configurations use ‘Q’ as the
system frequency frame of reference. Therefore all output
and feedback frequencies are referenced as a multiple of Q.
Figures 1 to 6 also indicate the input levels of OPT0, OPT1,
and OPT2 for each of the eight output configurations. The
input levels of MUL T0 and MULT1 are varied in these figures
to represent the different feedback (multiplication)
frequencies. The frequency of the phase shift output, Q∅, is
also indicated in the figures. Tables 1. and 2. lists all 18
input/output frequency configurations. Table 3. gives the Q∅
phase shift increments.
H
Q/2 In (40MHz)
L
H
L
MC88PL117
FIL
OE/MR
PLL_ENH
REF_SELL
SYNC0
SYNC1
FEEDBACK
OPT2L
OPT1L
OPT0L
∅
2
∅
1
∅
0
MULT1L
MULT0H
QFEED
LOCK
Q0
Q1
Q2
Q3
Q4
Q5
Q6
Q7
Q8
Q9
Q10
Q11
Q12
Q13
Q
∅
2X_Q (120MHz)
2X_Q (120MHz)
Q (60MHz)
Q (60MHz)
Q (60MHz)
Q (60MHz)
Q (60MHz)
Q (60MHz)
Q (60MHz)
Q (60MHz)
Q (60MHz)
Q (60MHz)
Q (60MHz)
Q (60MHz)
°
Phase Shift at 60MHz
0
Figure 1. Output Frequency Configuration 1
(OPT0 = L, OPT1 = L, OPT2 = L
Q/2 Input Frequency , MULT0 = H, MULT1 = L)
H
Q/2 In (30MHz)
L
H
L
MC88PL117
FIL
PLL_ENH
REF_SELL
SYNC0
SYNC1
FEEDBACK
OPT2L
OPT1H
OPT0L
∅
2
∅
1
∅
0
MULT1L
MULT0H
QFEED
LOCK
Q0
Q1
Q2
Q3
Q4
Q5
Q6
Q7
Q8
Q9
Q10
Q11
Q12
Q13
Q
∅
2X_Q (120MHz)
2X_Q (120MHz)
2X_Q (120MHz)
2X_Q (120MHz)
Q (60MHz)
Q (60MHz)
Q (60MHz)
Q (60MHz)
Q (60MHz)
Q (60MHz)
Q (60MHz)
Q (60MHz)
Q (60MHz)
Q (60MHz)
0° Phase Shift at 60MHz
H
Q/4 In (20MHz)
H
H
H
MC88PL117
FIL
OE/MR
PLL_ENH
REF_SELL
SYNC0
SYNC1
FEEDBACK
OPT2L
OPT1L
OPT0H
∅
2
∅
1
∅
0
MULT1L
MULT0L
QFEED
LOCK
Q0
Q1
Q2
Q3
Q4
Q5
Q6
Q7
Q8
Q9
Q10
Q11
Q12
Q13
Q
∅
2X_Q (120MHz)
2X_Q (120MHz)
Q (60MHz)
Q (60MHz)
Q (60MHz)
Q (60MHz)
Q/2 (30MHz)
Q/2 (30MHz)
Q/2 (30MHz)
Q/2 (30MHz)
Q/2 (30MHz)
Q/2 (30MHz)
Q/2 (30MHz)
Q/2 (30MHz)
0
°
Phase Shift at 30MHz
Figure 2. Output Frequency Configuration 2
(OPT0 = H, OPT1 = L, OPT2 = L
Q/4 Input Frequency , MULT0 = L, MULT1 = L)
H
Q/2 In (30MHz)
L
H
L
MC88PL117
FIL
OE/MROE/MR
PLL_ENH
REF_SELL
SYNC0
SYNC1
FEEDBACK
OPT2L
OPT1H
OPT0H
∅
2
∅
1
∅
0
MULT1L
MULT0H
QFEED
LOCK
Q0
Q1
Q2
Q3
Q4
Q5
Q6
Q7
Q8
Q9
Q10
Q11
Q12
Q13
Q
∅
Q (60MHz)
Q (60MHz)
Q (60MHz)
Q (60MHz)
Q (60MHz)
Q (60MHz)
Q (60MHz)
Q (60MHz)
Q (60MHz)
Q (60MHz)
Q (60MHz)
Q (60MHz)
Q (60MHz)
Q (60MHz)
°
Phase Shift at 60MHz
0
Figure 3. Output Frequency Configuration 3
(OPT0 = L, OPT1 = H, OPT2 = L
Q/2 Input Frequency , MULT0 = H, MULT1 = L)
MOTOROLA TIMING SOLUTIONS
4
Figure 4. Output Frequency Configuration 4
(OPT0 = H, OPT1 = H, OPT2 = L
Q/2 Input Frequency , MULT0 = H, MULT1 = L)
BR1333 — Rev 6
 Loading...
Loading...