Motorola MC88920DW Datasheet

SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA
Order this document
from Logic Marketing
# # "
### !
The MC88920 Clock Driver utilizes phase–locked loop technology to
lock its low skew outputs’ frequency and phase onto an input reference
clock. It is designed to provide clock distribution for CISC microprocessor
or single processor RISC systems. The RST
provide a processor reset function designed specifically for the
MC68/EC/LC030/040 microprocessor family.
The PLL allows the the high current, low skew outputs to lock onto a
single clock input and distribute it with essentially zero delay to multiple
locations on a board. The PLL also allows the MC88920 to multiply a low
frequency input clock and distribute it locally at a higher (2X) system
frequency.
• 2X_Q Output Meets All Requirements of the 20 and 25MHz 68040
Microprocessor PCLK Input Specifications
• Three Outputs (Q0–Q2) With Output–Output Skew <500ps and Six
Outputs T otal (Q0–Q2, Q3, 2X_Q,) With <1ns Skew Each Being Phase
and Frequency Locked to the SYNC Input
• The Phase Variation From Part–to–Part Between SYNC and the ‘Q’
Outputs Is Less Than 600ps (Derived From the TPD Specification,
Which Defines the Part–to–Part Skew)
• SYNC Input Frequency Range From 5MHZ to 2X_Q F
• Additional Outputs Available at 2X and ÷2 the System ‘Q’ Frequency.
Also a Q
(180° Phase Shift) Output Available.
• All Outputs Have ±36mA Drive (Equal High and Low) CMOS Levels. Can Drive Either CMOS or TTL Inputs. All Inputs Are
TTL–Level Compatible
• Test Mode Pin (PLL_EN) Provided for Low Frequency Testing
• Special Power–Down Mode With 2X_Q, Q0, and Q1 Being Reset (With MR), and Other Outputs Remain Running. 2X_Q, Q0
and Q1 Are Guaranteed to Be in Lock 3 Clock Cycles After MR
_IN/RST_OUT(LOCK) pins
/4
Max
Is Negated
LOW SKEW CMOS PLL
CLOCK DRIVER
With Power–Down/
Power–Up Feature
20
1
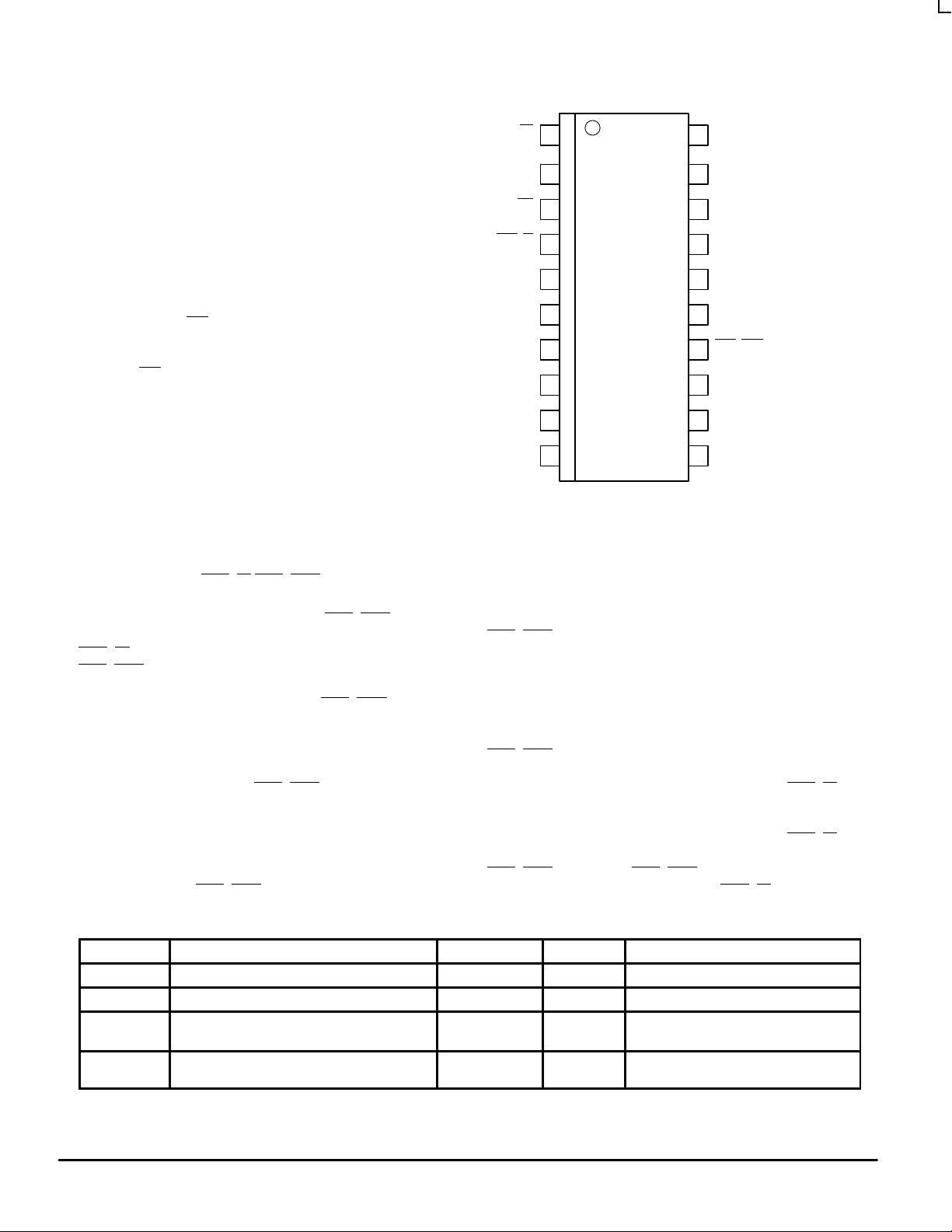
DW SUFFIX
PLASTIC SOIC PACKAGE
CASE 751D–04
Three ‘Q’ outputs (Q0–Q2) are provided with less than 500ps skew between their rising edges. The Q3
phase shift) from the ‘Q’ outputs. A 2X_Q output runs at twice the ‘Q’ output frequency. The 2X_Q output is ideal for 68040
systems which require a 2X processor clock input, and it meets the tight duty cycle spec of the 20 and 25MHz 68040. The Q/2
output runs at 1/2 the ‘Q’ frequency. This output is fed back internally, providing a fixed 2X multiplication from the ‘Q’ outputs to
the SYNC input. Since the feedback is done internally (no external feedback pin is provided) the input/output frequency
relationships are fixed.
In normal phase–locked operation the PLL_EN pin is held high. Pulling the PLL_EN pin low disables the VCO and puts the
88920 in a static ‘test mode’. In this mode there is no frequency limitation on the input clock, which is necessary for a low
frequency board test environment.
The RST
pin will be pulled actively low until phase–lock is achieved. When phase–lock occurs, the RST_OUT(LOCK) is released and a
pull–up resistor will pull the signal high. To give a processor reset signal, the RST_IN pin is toggled low, and the
RST
Description of the RST
The RST
a lock indicator. If the RST_IN pin is held high during system power–up, the RST_OUT pin will be in the low state until steady
state phase/frequency lock to the input reference is achieved. 1024 ‘Q’ output cycles after phase–lock is achieved the
RST
AC/DC specs for the characteristics of the RST
RST
8/95
Motorola, Inc. 1995
_OUT(LOCK) pin doubles as a phase–lock indicator. When the RST_IN pin is held high, the open drain RST_OUT
_OUT(LOCK) pin will stay low for 1024 cycles of the ‘Q’ output frequency after the RST_IN pin is brought back high.
_IN/RST_OUT(LOCK) Functionality
_IN and RST_OUT(LOCK) pins provide a 68030/040 processor reset function, with the RST_OUT pin also acting as
_OUT(LOCK) pin will go into a high impedance state, allowing it to be pulled high by an external pull–up resistor (see the
_OUT(LOCK) pin). If the RST_IN pin is held low during power–up, the
_OUT(LOCK) pin will remain low.
1
REV 2
output is inverted (180°
MC88920
Power–Down Mode Functionality
The MC88920 has a special feature
designed in to allow the processor clock
inputs to be reset for total processor
power–down, and then to return to
phase–locked operation very quickly when
the processor is powered–up again.
The MR
pin resets outputs 2X_Q, Q0
and Q1 only leaving the other outputs
operational for other system activity . When
MR
is negated, all outputs will be operating
normally within 3 clock cycles.
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
GNDQ3
2X_QV
Q/2MR
V
CC
Q2VCC(AN)
GNDRC1
RST
PLL_ENSYNC
Q1GND
V
CC
_OUT(LOCK)GND(AN)
CC
RST_IN
Q0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Pinout: 20–Lead Wide SOIC Package (Top View)
Description of the RST
After the system start–up is complete and the 88920 is
phase–locked to the SYNC input signal (RST
processor reset functionality can be utilized. When the
RST
_IN pin is toggled low (min. pulse width=10nS),
RST
_OUT(LOCK) will go to the low state and remain there
for 1024 cycles of the ‘Q’ output frequency (512 SYNC
cycles). During the time in which the RST
actively pulled low, all the 88920 clock outputs will continue
operating correctly and in a locked condition to the SYNC
input (clock signals to the 68030/040 family of processors
must continue while the processor is in reset). A propagation
delay after the 1024th cycle RST
the high impedance state to be pulled high by the resistor.
_IN/RST_OUT(LOCK) Functionality (continued)
phase–lock to the reference source, some constraints must
_OUT high), the
be placed on the power supply ramp rate to make sure the
RST
_OUT(LOCK) signal holds the processor in reset during
system start–up (power–up). With the recommended loop
filter values (see Figure 7) the lock time is approximately
10ms. The phase–lock loop will begin attempting to lock to a
_OUT(LOCK) is
reference source (if it is present) when VCC reaches 2V. If
the VCC ramp rate is significantly slower than 10ms, then the
PLL could lock to the reference source, causing
RST
_OUT(LOCK) to go high before the 88920 and ’030/040
processor is fully powered up, violating the processor reset
_OUT(LOCK) goes back to
specification. Therefore, if it is necessary for the RST
to be held high during power–up, the VCC ramp rate must be
less than 10mS for proper ‘030/040 reset operation.
Power Supply Ramp Rate Restriction for Correct 030/040
Processor Reset Operation During System Start–up
Because the RST_OUT(LOCK) pin is an indicator of
This ramp rate restriction can be ignored if the RST
can be held low during system start–up (which holds
RST
_OUT low). The RST_OUT(LOCK) pin will then be
pulled back high 1024 cycles after the RST
CAPACITANCE AND POWER SPECIFICATIONS
Symbol Parameter Value Typ Unit Test Conditions
C
C
PD
PD
IN
PD
1
2
Input Capacitance 4.5 pF VCC = 5.0V
Power Dissipation Capacitance 40 pF VCC = 5.0V
Power Dissipation at 33MHz With 50Ω
Thevenin Termination
Power Dissipation at 33MHz With 50Ω
Parallel Termination to GND
15mW/Output
90mW/Device
37.5mW/Output
225mW/Device
mW VCC = 5.0V
T = 25°C
mW VCC = 5.0V
T = 25°C
_IN pin
_IN pin
_IN pin goes high.
MOTOROLA TIMING SOLUTIONS
2
BR1333 — REV 5
MC88920
MAXIMUM RATINGS*
Symbol Parameter Limits Unit
VCC, AV
V
V
I
I
I
T
* Maximum Ratings are those values beyond which damage to the device may occur. Functional operation should be restricted to the
CC
in
out
in
out
CC
stg
Recommended Operating Conditions.
RECOMMENDED OPERATING CONDITIONS
Symbol Parameter Limits Unit
V
CC
V
in
V
out
T
A
ESD Static Discharge Voltage > 1500 V
DC Supply Voltage Referenced to GND –0.5 to 7.0 V
DC Input Voltage (Referenced to GND) –0.5 to VCC +0.5 V
DC Output Voltage (Referenced to GND) –0.5 to VCC +0.5 V
DC Input Current, Per Pin ±20 mA
DC Output Sink/Source Current, Per Pin ±50 mA
DC VCC or GND Current Per Output Pin ±50 mA
Storage Temperature –65 to +150 °C
Supply Voltage 5.0 ±10% V
DC Input Voltage 0 to V
DC Output Voltage 0 to V
Ambient Operating Temperature 0 to 70 °C
CC
CC
V
V
DC CHARACTERISTICS (TA = 0°C to 70°C; VCC = 5.0V ± 5%)
Symbol Parameter V
V
IH
V
IL
V
OH
V
OL
I
IN
I
CCT
I
OLD
I
OHD
I
CC
1. IOL is +12mA for the RST_OUT output.
2. The PLL_EN input pin is not guaranteed to meet this specification.
3. Maximum test duration 2.0ms, one output loaded at a time.
Minimum High Level Input Voltage 4.75
Minimum Low Level Input Voltage 4.75
Minimum High Level Output Voltage 4.75
Minimum Low Level Output Voltage 4.75
Maximum Input Leakage Current 5.25 ±1.0 µA VI = VCC, GND
Maximum ICC/Input 5.25 2.0
Minimum Dynamic3 Output Current 5.25 88 mA V
Maximum Quiescent Supply Current 5.25 750 µA VI = VCC, GND
CC
5.25
5.25
5.25
5.25
5.25 –88 mA V
Guaranteed Limits Unit Condition
2.0
2.0
0.8
0.8
4.01
4.51
0.44
0.44
2
V V
V V
V VIN = VIH or V
V VIN = VIH or V
mA VI = VCC – 2.1V
= 0.1V or
OUT
VCC – 0.1V
= 0.1V or
OUT
VCC – 0.1V
I
OH –36mA
I
OH +36mA
OLD
OHD
–36mA
+36mA
= 1.0V Max
= 3.85 Min
IL
IL
1
TIMING SOLUTIONS
BR1333 — REV 5
3 MOTOROLA
 Loading...
Loading...