Page 1

Draft for Regulatory Approva l
Supplement to the Canopy System Release 8 User Guide
PMP 400 Series Networks
PTP 200 Series Bridges
Issue 3
January 2009
Page 2

PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series Canopy User Guide Supplement
Issue 3, January 2009 Page 2 of 45
Notices
See important safety notice on exposure distance in Section 6.3 on page 40.
See important regulatory and legal notices in Section 2 on page 6.
Trademarks, Product Names, and Service Names
MOTOROLA, the stylized M Logo, Canopy, and all other trademarks indicated as such herein are
registered trademarks of Motorola, Inc. ® Reg. US Pat & Tm. Office. MOTOwi4 is a trademark of
Motorola, Inc. All other product or service names are the property of their respective owners.
© 2009 Motorola, Inc. All rights reserved
http://www.motorola.com/canopy
Page 3

PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series Canopy User Guide Supplement
Issue 3, January 2009 Page 3 of 45
Table of Contents
1 Introduction ............................................................................................................... 4
2 Product Description .................................................................................................. 6
3 Planning ................................................................................................................... 13
4 Configuring.............................................................................................................. 17
5 Installation ............................................................................................................... 29
6 Regulatory and Legal Notices ............................................................................... 36
List of Tables
Table 1: Products and Model Numbers ........................................................................... 6
Table 2: Performance Details........................................................................................ 12
Table 3: 5.4 GHz Channel Center Frequencies, by Region ........................................... 13
Table 4: 4.9 GHz Channel Center Frequencies............................................................. 13
Table 5: Control Slot Settings........................................................................................ 20
Table 6: Release 8.4 Operation based on Region Code ............................................... 21
Table 7: US FCC IDs and Industry Canada Certification Numbers and Covered
Configurations ........................................................................................................ 37
Table 8: Disclosure Table ............................................................................................. 40
Table 9: Exposure Separation Distances ...................................................................... 40
Table 10: Calculated Exposure Distances and Power Compliance Margins .................. 41
List of Figures
Figure 1: Radio (with or without integrated antenna) 7
Figure 2: PMP 54400 AP with connectorized radio and antenna 7
Figure 3: PMP 49400 AP with connectorized radio and antenna 8
Figure 4: LOS, nLOS, and NLOS 9
Figure 5: Dynamic Rate Adapt on AP "Configuration => General" page 18
Figure 6: Region Code on AP “Configuration => General” page 24
Figure 7: Configured Region Code on SM Configuration => General page 25
Figure 8: Active Region Code on SM Home => General Status page 25
Figure 9: Ground lug highlighted on AP 34
Page 4

PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series Canopy User Guide Supplement
Issue 3, January 2009 Page 4 of 45
1 Introduction
This guide provides product description, planning, configuration, and installation information
specific to the PMP 400 Series networks and PTP 200 Series bridges. It should be used along
with the Canopy System Release 8 User Guide, which covers general information, including all
network features, RF control features, and GUI (Graphical User Interface) features common
across PMP 100, 200 and 400 Series networks and PTP 100 and 200 Series bridges. The
Canopy System Release 8 User Guide is available from the “User Guides” section of the Canopy
Document Library, http://motorola.canopywireless.com/support/library/?region=1&cat=8.
This guide assumes that the reader has general RF (Radio Frequency) and Internet Protocol (IP)
knowledge and background.
This issue, Issue 2, is consistent with features provided by Canopy Release 8.4.3. Separate
Release Notes for Canopy Software Release 8.4.3 are available and include open issues and
other notes.
1.1 ABBREVIATIONS
The following abbreviations may be used in these notes:
1X
1X operation, with typical max aggregate (up and down)
throughput of 7 Mbps (2 Mbps for 900 MHz)
2X
2X operation, with typical max aggregate (up and down)
throughput of 14 Mbps (4 Mbps for 900 MHz)
3X
3X operation, with typical max aggregate (up and down)
throughput of over 20 Mbps
AP
Access Point Module
BH
Backhaul Module, either timing master or timing slave
BHM
Backhaul Module – timing master
BHS
Backhaul Module – timing slave
CMM
Cluster Management Module
CNUT
Canopy Network Updater Tool
DFS
Dynamic Frequency Selection for radar avoidance
EIRP
Equivalent Isotropically Radiated Power
ETSI
European Telecommunications Standards Institute
FSK
Frequency Shift Keying
MIB
Management Information Base for SNMP
OFDM
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing
PtP
Point-to-Point (Backhauls)
PtMP
Point-to-Multi-Point (AP to SMs)
QAM
Quadrature Amplitude Modulation
QPSK
Quadrature Phase Shift Keying
RF
Radio Frequency
SM
Subscriber Module
1.2 DOCUMENT CHANGE HISTORY
Issue 1
First Issue
Issue 2
Significant changes for:
Page 5
PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series Canopy User Guide Supplement
Issue 3, January 2009 Page 5 of 45
• PTP 200 Series bridges (BHs)
• Products using AES encryption
• Release 8.4.3 features
Issue 3
Added PMP 49400 APs and SMs (4.9 GHz public safety
band)
1.3 FEEDBACK ON DOCUMENTATION
Is this document accurate, complete, and clear? How can it be improved? Please send your
feedback on Canopy documentation to technical-documentation@canopywireless.com.
1.4 TECHNICAL SUPPORT
Tip! Don’t clear the Event Log after you encounter issues – it may be useful to Technical
Support if you need to escalate the issue.
Here is the escalation path for resolution of a problem:
1. Check documentation:
This document
Canopy System Release 8 User’s Guide, available at
http://motorola.canopywireless.com/support/library/
2. Consider checking the Canopy Community Forum at
http://motorola.canopywireless.com/support/community.
3. Consider checking the Canopy Knowledge Base at
http://motorola.canopywireless.com/support/knowledge/
4. Escalate the problem to your Canopy supplier or reseller.
5. Escalate the problem to Canopy Technical Support or other designated Tier 3
technical support:
Worldwide Canopy Technical Support
email: technical-support@canopywireless.com
1-888-605-2552 or +1 217 824 9742
Canopy Technical Support, Europe
email: essc@motorola.com
+44 (0)1793 564680
Calls are logged 24 x 7, cases are worked Mon-Fri 09:00 - 17:00 GMT
When you send e-mail or call, please include, as appropriate, software release on each
module, IP addresses, MAC addresses, and features enabled, like NAT, VLAN, high
priority channel, or CIR. You may be asked to run the Support Tool on CNUT or Prizm to
provide a complete network picture.
Page 6
PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series Canopy User Guide Supplement
Issue 3, January 2009 Page 6 of 45
2 Product Description
PMP 400 Series networks and PTP 200 Series bridges add OFDM-based (Orthogonal Frequency
Division Multiplexing) products to the Canopy family.
• SMs are available with either an integrated antenna or an external N-type connector
on a short length of coaxial cable for connecting to a connectorized antenna.
• APs are always connectorized, and sold either with a connectorized antenna as a kit,
or with no antenna.
• BHs are available with either an integrated antenna or an external N-type connector
on a short length of coaxial cable for connecting to a connectorized antenna.
PMP 400 Series networks are available in multiple bands:
• PMP 54400 APs and SMs provide connectivity in the unlicensed 5.4 GHz band.
• PMP 49400 APs and SMs provide connectivity in the licensed 4.9 GHz band
allocated to public safety services. State and local governmental entities are eligible
to hold 4.9 GHz licenses.
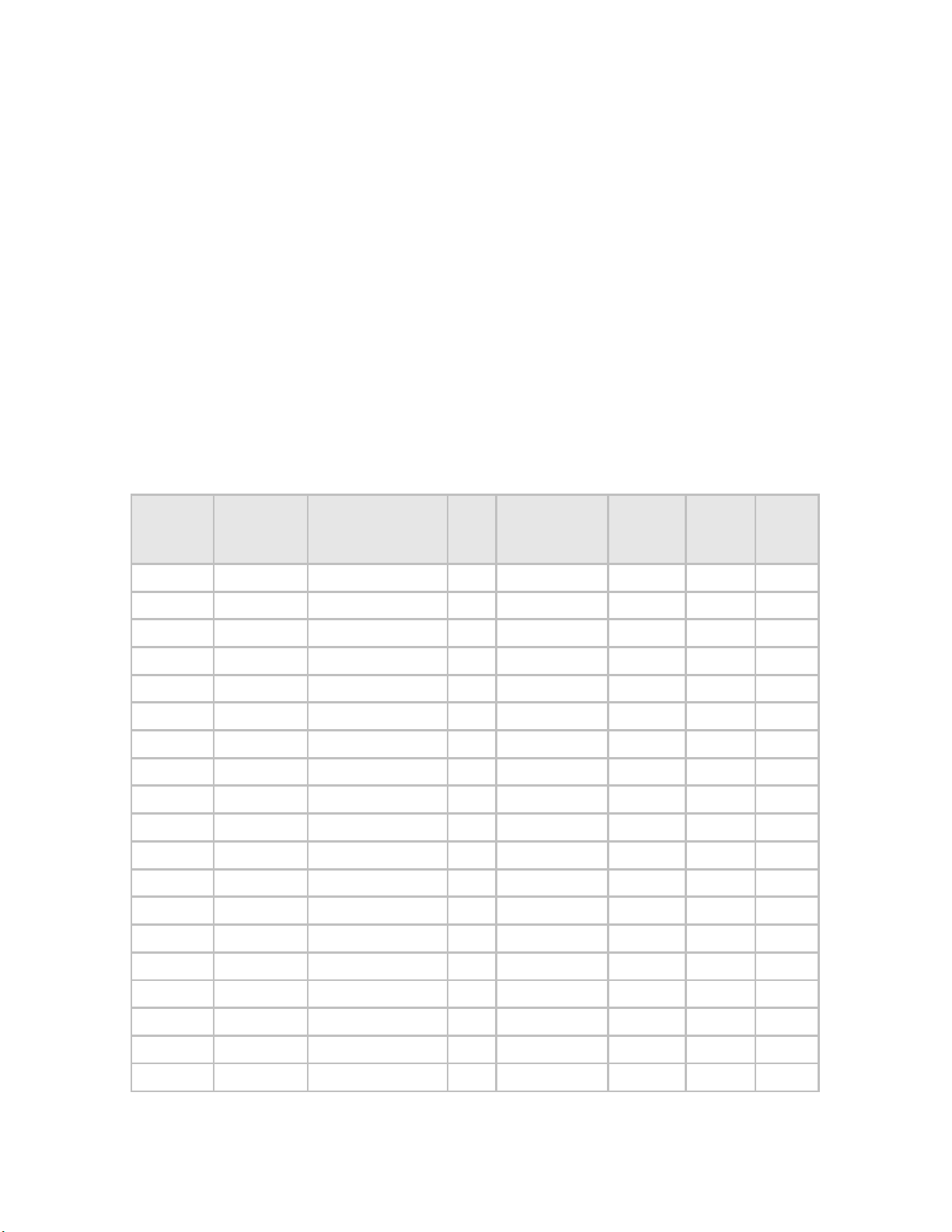
Table 1 shows the Motorola PMP 400 Series and PTP 200 Series products available.
Table 1: Products and Model Numbers
Model
Number
Name
Module
DES
or
AES
Antenna Type
Antenna
included
?
Picture
Specs
5440SM
PMP 54400
5.4 GHz OFDM SM
DES
Integrated
Yes
Figure 1
2.7.2
5441SM
PMP 54400
5.4 GHz OFDM SM
AES
Integrated
Yes
Figure 1
2.7.2
5440SMC
PMP 54400
5.4 GHz OFDM SM
DES
Connectorized
No
Figure 1
2.7.3
5441SMC
PMP 54400
5.4 GHz OFDM SM
AES
Connectorized
No
Figure 1
2.7.3
5440AP
PMP 54400
5.4 GHz OFDM AP
DES
Connectorized
Yes
Figure 2
2.7.4
5441AP
PMP 54400
5.4 GHz OFDM AP
AES
Connectorized
Yes
Figure 2
2.7.4
5440APC
PMP 54400
5.4 GHz OFDM AP
DES
Connectorized
No
Figure 1
2.7.3
5441APC
PMP 54400
5.4 GHz OFDM AP
AES
Connectorized
No
Figure 1
2.7.3
5440BH
PTP 54200
5.4 GHz OFDM BH
DES
Integrated
Yes
Figure 1
2.7.2
5441BH
PTP 54200
5.4 GHz OFDM BH
AES
Integrated
Yes
Figure 1
2.7.2
5440BHC
PTP 54200
5.4 GHz OFDM BH
DES
Connectorized
No
Figure 1
2.7.3
5441BHC
PTP 54200
5.4 GHz OFDM BH
AES
Connectorized
No
Figure 1
2.7.3
4940SM
PMP 49400
4.9 GHz OFDM SM
DES
Integrated
Yes
Figure 1
2.7.2
4941SM
PMP 49400
4.9 GHz OFDM SM
AES
Integrated
Yes
Figure 1
2.7.2
4940SMC
PMP 49400
4.9 GHz OFDM SM
DES
Connectorized
No
Figure 1
2.7.3
4941SMC
PMP 49400
4.9 GHz OFDM SM
AES
Connectorized
No
Figure 1
2.7.3
4940AP
PMP 49400
4.9 GHz OFDM AP
DES
Connectorized
Yes
Figure 3
2.7.4
4941AP
PMP 49400
4.9 GHz OFDM AP
AES
Connectorized
Yes
Figure 3
2.7.4
4940APC
PMP 49400
4.9 GHz OFDM AP
DES
Connectorized
No
Figure 1
2.7.3
Page 7

PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series Canopy User Guide Supplement
Issue 3, January 2009 Page 7 of 45
Model
Number
Name
Module
DES
or
AES
Antenna Type
Antenna
included
?
Picture
Specs
4941APC
PMP 49400
4.9 GHz OFDM AP
AES
Connectorized
No
Figure 1
2.7.3
Figure 1: Radio (with or without integrated antenna)
Figure 2: PMP 54400 AP with connectorized radio and antenna
Page 8

PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series Canopy User Guide Supplement
Issue 3, January 2009 Page 8 of 45
Figure 3: PMP 49400 AP with connectorized radio and antenna
A Canopy CMMmicro or CMM4 provides synchronization and power to the PMP 400 Series APs
and PTP 200 Series BHMs. A 600SSC surge suppressor, a successor to the 300SS and 600SSB
surge suppressors, provides over-voltage and over-current protection to APs, SMs, and BHs in
various configurations.
2.1 TECHNOLOGY AND BENEFITS
These radios automatically select QPSK (Quadrature Phase Shift Keying), 16-QAM (Quadrature
Amplitude Modulation), or 64-QAM based on RF environment to provide 1X, 2X, and 3X
operation, respectively. This provides 3 speeds and a throughput of over 20 Mbps aggregate
(sum of up plus down) compared to FSK Canopy products with 2 speeds and a throughput of up
to 14 Mbps.
The OFDM radios feature lower receive sensitivity, FEC (Forward Error Correction), and higher
antenna gain, all of which combine to provide longer range within regulatory-specified EIRP
(Equivalent Isotropic Radiated Power).
Details on performance are listed in Table 2 on page 12.
The PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series radios use an OFDM physical layer with 10 MHz channels and
256 sub-carriers. Due to the different carrier and modulation schemes between these OFDM
radios and FSK Canopy radios, the two do not interoperate over the air. For example, an OFDM
SM cannot connect to an FSK AP.
Page 9

PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series Canopy User Guide Supplement
Issue 3, January 2009 Page 9 of 45
2.1.1 NLOS and nLOS Benefits and Limitations
The use of OFDM technology will help in many cases of NLOS (Non Line-of-Sight) and nLOS
near Line-of-Sight (nLOS) links. LOS (Line-of-Sight ) means the installer can see the AP from the
SM and the first Fresnel zone is clear. An example of nLOS is when the installer can see the AP
from the SM, but a portion of the first Fresnel is blocked. An example of NLOS is when the
installer cannot see the AP from the SM, and a portion or even much of the first Fresnel is
blocked, but subsequent Fresnel zones are open. Figure 4 shows examples of such links.
Figure 4: LOS, nLOS, and NLOS
Whereas multi-pathing degrades a link in some technologies, like FSK, OFDM can often use
multi-pathing to advantage to overcome nLOS and NLOS, especially in cases where the Fresnel
zone is only partially blocked by buildings, “urban canyons”, or foliage. OFDM tends to help
especially when obstacles are near the middle of the link, and less so when the obstacles are
very near the SM, AP, or BH.
However, attenuation through walls and trees is substantial for any use of the 5.4 GHz or 4.9 GHz
frequency bands. Even with OFDM, these products should not be expected to penetrate walls or
extensive trees and foliage.
2.2 APPLICATIONS
Applications for the PMP 54400 and PTP 54200 Series systems include
• High throughput enterprise applications
• NLOS/nLOS video surveillance in metro areas
• Extend networks into urban areas
• Extend networks into areas with foliage
Applications for the PMP 49400 Series systems include
• High throughput licensed network for government applications
• Municipal network - NLOS/nLOS video surveillance in metro areas
• Disaster relief network
• Data service network - extend licensed networks into areas with foliage
Page 10

PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series Canopy User Guide Supplement
Issue 3, January 2009 Page 10 of 45
2.3 CONFIGURATION OPTIONS – RF, IP, DFS
These systems use the Canopy Media Access Controller (MAC) layer. Settings like Downlink
Data %, Range, and Control Slots are similar to Canopy FSK radios. An AP can communicate to
over 200 SMs, similar to a Canopy FSK AP.
The GUI (Graphical User Interface) is almost identical to Canopy’s, with a few additions to
support OFDM-specific features.
Network features like High Priority using DiffServ, MIR, CIR, NAT, DHCP and VLAN are available
for the PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series OFDM radios, and are configured in the same way as they
are for the PMP 100 and 200 Series and PTP 100 Series radios.
In the 5.4 GHz band, DFS (Dynamic Frequency Selection) is provided for regulatory compliant
operation, and is activated using the “Region Code” feature. Two alternate frequencies can be
configured to provide service in the unlikely case a module detects radar and triggers DFS, the
same as standard Canopy. “External Antenna Gain” may need to be configured consistent with
any antennas used, to avoid making the system overly sensitive to radar detection. “Whitening,” a
technique used to avoid self-interference on Canopy FSK radios is not offered as an option on the
PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series radios, as whitening is not a technology applicable to an OFDM
signal.
2.4 RELEASE MAPPING TO PRODUCTS
Releases run on the various products as follows:
• Release 9.0 or Release 8.2.x runs on Canopy FSK radios (PMP 100 and 200 and
PTP 100 Series radios).
• Release 8.4.x runs on PMP 54400 and PTP 54200 Series OFDM radios.
• “Release 8.3” is not planned to be used for release numbering.
• Release 9.3.1 runs on PMP 49400 Series OFDM radios
2.5 POWER AND GROUNDING
The PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series radios use a 30 VDC nominal power system, instead of the 24
VDC nominal power system used previously in standard Canopy. A new 30 VDC power supply is
available for the CMMmicro, and a new 30 VDC nominal (specified and labeled as 29.5 VDC)
power supply is available for the SM.
The new 30 VDC power supplies can also be used for standard Canopy, and are replacing the 24
VDC power supplies in the Canopy product line.
The PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series radios have slightly higher power use than Canopy FSK
radios, and the higher voltage is needed to carry the higher wattage on cable runs approaching
the 100 meter (328 ft) maximum length. CMMmicro 24 VDC power supplies and the latest version
of SM 24 VDC power supplies can power PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series radios for shorter runs.
Earlier versions of SM 24 VDC power supplies, especially the earlier heavier transformers,
cannot. The best practice is to use 30 VDC power supplies with PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series
radios, and avoid potential issues and cable-length-specific engineering.
Due to the full metallic connection to the tower or support structure through the AP’s antenna or a
connectorized BH’s antenna, grounding of the AP or BH and a 600SSC surge suppressor within 3
ft (1 m) of the AP or BH is strongly recommended to suppress overvoltages and overcurrents,
such as those caused by near-miss lightning. APs and BHs provide a grounding lug for grounding
to the tower or support structure. A pole mount kit is available for the 600SSC, and provides a
grounding lug that can be used for terminating grounding straps from both the 600SSC and the
AP.
Page 11

PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series Canopy User Guide Supplement
Issue 3, January 2009 Page 11 of 45
2.6 ADMINISTRATION SYSTEMS
Standard Canopy administration systems are used to support the PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series
products, with the only requirement being that the administration systems must be at the
appropriate release level:
• Prizm 3.1 is the element management system for PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series
products. In addition to managing and monitoring Canopy modules, Prizm 3.1 can be
used to update them.
• CNUT 3.1 (Canopy Network Update Tool) is the stand-alone update tool for PMP 400
and PTP 200 Series products for operators not using Prizm.
2.7 TECHNICAL DETAILS, SPECIFICATIONS, PERFORMANCE
PMP 400 and PTP 200 systems consist of radios and antennas available in various
combinations. The following sections list technical details for the radio and for each form factor.
2.7.1 Radio specifications (common to all form factors)
• APs and BHs have settable Transmit Output Power.
• SMs have Auto TPC (Transmit Power Control), set by the AP to provide power
leveling for close-in SMs
• 5.4 GHz radios have a range of -30 to 10 dBm, and a default of 10 dBm.
• 4.9 GHz radios have a range of -30 to 18 dBm, and a default of 18 dBm.
• 12.5 W DC power
2.7.2 Radio with integrated antenna – form factor specifications
• Radio with an integrated, internal antenna
• 18° x 18° 3 dB beam
• 17 dBi gain for antenna at 5.4 GHz. 17 dBi antenna gain plus 10 dBm transmit power
gives the regulatory maximum 27 dBm EIRP.
• 16 dBi gain for antenna at 4.9 GHz. 16 dBi antenna gain plus 18 dBm transmit power
gives 34 dBm EIRP.
• 2.8 lb, 13.25 x 8.25 x 3.75 in (hwd) (~1.3 kg, 34 x 21 x 9.5 cm)
2.7.3 Connectorized radio – form factor specifications
• Connectorized radio only (antenna to be provided by operator) – N-type connector
• 2.8 lb, 13.25 x 8.25 x 3.75 in (hwd) (~1.3 kg, 34 x 21 x 9.5 cm)
2.7.4 Kitted connectorized radio specifications (antenna included) – form factor
specifications
• Connectorized radio and connectorized antenna kitted together – N-type connector
• 90° sectors
• Antenna optimized for system coverage vs system self-interference for 90° sectors (3
dB beam pattern of 60° azimuth by 5° elevation, with near-in null fill)
• 18 dBi gain for antenna at 5.4 GHz. 18 dBi antenna gain minus 1 dB cable loss plus
10 dBm transmit power gives the regulatory max 27 dBm EIRP.
• 17 dBi gain for antenna at 4.9 GHz. 17 dBi antenna gain minus 1 dB cable loss plus
18 dBm transmit power gives 34 dBm EIRP.
• 13 lb, 28 x 8.25 x 11 in (hwd) (~6 kg, 71 x 21 x 28 cm)
Page 12
PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series Canopy User Guide Supplement
Issue 3, January 2009 Page 12 of 45
2.7.5 System technical details
• Standard Canopy temperature range of -40° C to +55° C
• Latency of 5-7 msec roundtrip
• Products available with either DES or AES encryption
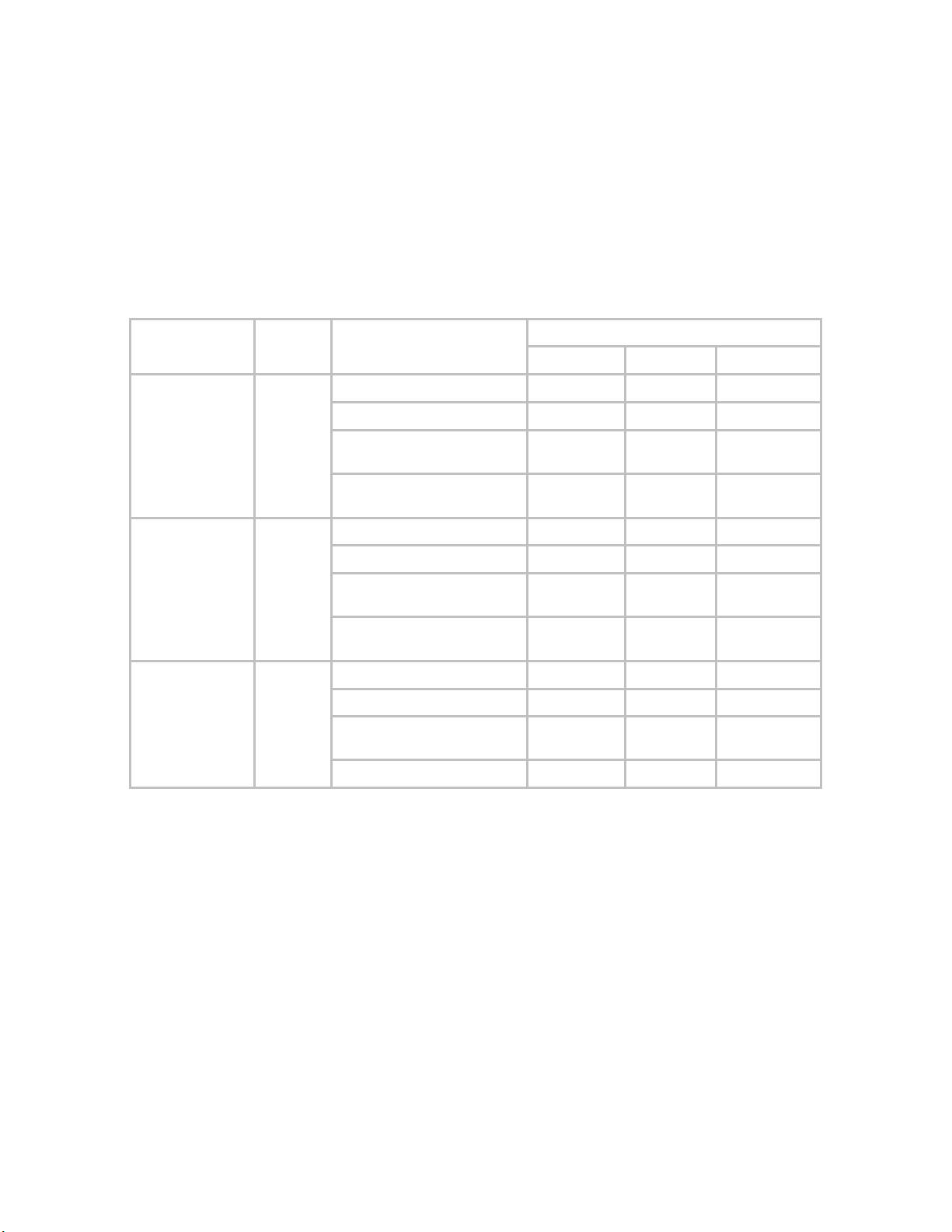
Table 2 shows performance details for the PMP 54400, PTP 54200, and PMP 49400 systems,
with the standard Canopy PMP 54200 5.4 GHz FSK details shown for comparison.
Table 2: Performance Details
Performance Details
Product
Channel
Width
Parameters
1X
2X
3X
Modulation
QPSK
16 QAM
64 QAM
Typical Maximum Range
5 mi/8 km
2.5 mi/4 km
1.25 mi/2 km
Typical Maximum Aggregate
(up+down) Throughput
7 Mbps
14 Mbps
21 Mbps
PMP 54400
and
PTP 54200
(5.4 GHz OFDM)
10 MHz
Nominal Receive Sensitivity
(including FEC)
-89 dBm
-78 dBm
-70 dBm
Modulation
QPSK
16 QAM
64 QAM
Typical Maximum Range
15 mi/24 km
4 mi/6.5 km
1.7 mi/2.7 km
Typical Maximum Aggregate
(up+down) Throughput
7 Mbps
14 Mbps
21 Mbps
PMP 49400
(4.9 GHz OFDM)
10 MHz
Nominal Receive Sensitivity
(including FEC)
-89 dBm
-78 dBm
-70 dBm
Modulation
2-level FSK
4-level FSK
none
Typical Maximum Range
2 mi/3.2 km
1 mi/1.6 km
none
Typical Maximum Aggregate
(up+down) Throughput
7 Mbps
14 Mbps
none
PMP 54200
(5.4 GHz FSK)
(for comparison)
20 MHz
Nominal Receive Sensitivity
-86 dBm
-70 dBm
none
.
Page 13
PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series Canopy User Guide Supplement
Issue 3, January 2009 Page 13 of 45
3 Planning
PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series systems use a 10 MHz channel size configurable on 5 MHz
centers. This channel size, along with some different characteristics due to the use OFDM carrier
technology and QPSK, 16 QAM, or 64 QAM modulation, supports somewhat different channel
planning than for standard Canopy. (For reference, PMP 100/200 Series uses 20 MHz channels
configurable on 5 MHz centers, single carrier technology, and 2-level and 4-level FSK
modulation.)
3.1 TOWER CHANNEL PLANNING
For a single cluster of 4 APs on a tower, 2-channel re-use with channels on 10 MHz channel
center spacing gives good performance. In channel design parlance, this can be stated as ABAB
channel planning, with no guard band needed between A and B. A typical arrangement might be
to use radios configured for 5480 MHz aimed north and south, and radios configured for 5490
MHz aimed east and west.
(For reference, standard Canopy uses 2-channel re-use with clusters of 6 APs on a tower with
channel center spacing of either 25 MHz for Advantage APs or 20 MHz for non-Advantage APs.
This is ABCABC channel planning, with 5 MHz guard band between the 20 MHz channels for
Advantage APs and no guard band needed for non-Advantage.)
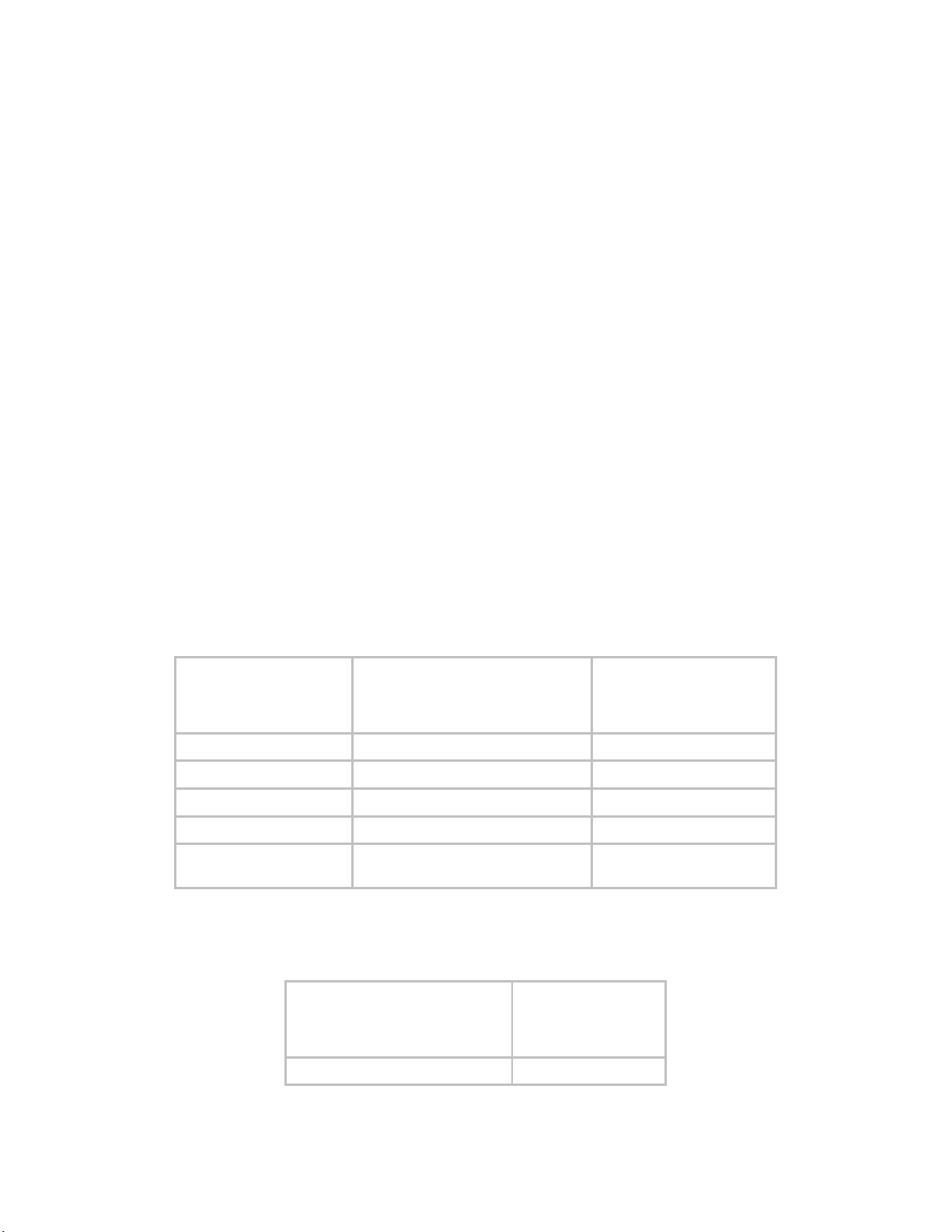
Available 5.4 GHz channel center frequencies for each region are shown in Table 3. These vary
by region due to
• different band edge RF specifications (for example, between Canada/US and
Europe)
• requirements in Europe and Canada to not impinge on the frequencies between 5600
and 5650 MHz, which are frequencies on which some weather radar operate
Table 3: 5.4 GHz Channel Center Frequencies, by Region
Region
Range of Center Frequencies
Available (MHz)
(on 5 MHz centers within this
range, inclusive)
Maximum number of
non-overlapping
channels
US
5480 - 5710
24
Canada
5480 – 5595, 5655 - 5710
18
Europe
5475 - 5595, 5655 - 5715
20
US FSK (for comparison)
5495 - 5705
11
Canada FSK (for
comparison)
5495 - 5575, 5675 - 5705
7
Available 4.9 GHz channel center frequencies are shown in Table 4.
Table 4: 4.9 GHz Channel Center Frequencies
Range of Center Frequencies
Available (MHz)
(on 5 MHz centers within this
range, inclusive)
Maximum number of
non-overlapping
channels
4945 - 4985
5
Page 14

PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series Canopy User Guide Supplement
Issue 3, January 2009 Page 14 of 45
The best practice for channel planning for APs is to conduct extensive site RF surveys before
choosing channels. For those with the equipment and expertise, use commercial and industrial
spectrum analysis equipment. The PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series APs and SMs do not provide a
spectrum analyzer in the first release (planned for a subsequent release), but standard 5.4 GHz
FSK SMs can be used to give useful information on the RF environment in the planned PMP 400
and PTP 200 Series AP deployment location.
3.2 DOWNTILT
The standard AP antenna produces a 3 db beam elevation (up and down) of 5°, with near-in null
fill that allows good coverage of close-in SMs that otherwise would be affected by the narrow
pattern. This is a narrower pattern than operators may be used to with standard Canopy’s 60° 3
dB beam, and may require downtilt on the antenna. The standard antenna has provision for
measured downtilt. The operator should estimate downtilt based on antenna height above the
service area and using one of the many radio analysis and mapping tools or on-line calculation
tools for calculating downtilt.
3.3 WEATHER RADAR
Spectrum between 5600 and 5650 MHz (sometimes called the “weather notch”) is used by some
weather radar and is not allowed for use by regulations in some regions, including Canada and,
for new equipment, Europe. When the Canopy module is set to one of those regions (configured
on the “Configuration => General” page of the module), it will not allow configuration of the
appropriate frequencies, as shown in Table 3. Even in regions where use of the spectrum
between 5600 and 5650 MHz is allowed, such as the US, the best practice is to not use these
channels if there are any other usable channels available. Only use the channels in this “weather
notch” after performing long-term site surveys (minimum of a week) to ascertain the spectrum is
clear and that there don’t appear to be any weather radar in the area that will cause interference
to your Canopy system.
3.4 RANGE AND THROUGHPUT PLANNING
PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series modules provide up to 21 Mbps aggregate throughput at distances
of 1.25 mi (~1 km) (1.7 mi for 4.9 GHz systems) in RF environments with clear line-of-sight and
low background interference levels. Additional performance details are shown in Table 2 on page
12. RF environments with occluded Fresnel zones or higher background interference levels may
give lower, but still very good, performance, depending on the specifics of the environment.
Similar to standard Canopy, at any given instant, any radios operating at 1X or 2X take more “air
time” to transmit a given amount of data than if they were running at 3X. Similar to standard
Canopy, PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series modules may see reduced total throughput when
handling traffic with a high percentage of small packets.
The effect of this, again similar to standard Canopy, is that at any given instant total throughput
depends on
• Mix of links running at 3X, 2X, and 1X
• Mix of packet sizes
3.5 SPECTRUM ANALYZER
A spectrum analyzer is available on the SM at Tools => Spectrum Analyzer. The spectrum
analyzer is also available on an AP by temporarily converting it to an SM by setting the Device
Type to SM on the AP’s Configuration => General page. The spectrum analyzer works like the
spectrum analyzer in classic FSK SMs.
Spectrum analyzer uses include
Page 15

PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series Canopy User Guide Supplement
Issue 3, January 2009 Page 15 of 45
• Showing relative power levels across the band, to aid in selecting channels and
performing RF planning.
• Troubleshooting to finding the frequency, relative power level, and location of
interferers by rotating a single SM, or triangulating from multiple SMs in a
geographical area.
The OFDM spectrum analyzer, the FSK spectrum analyzer, and the FSK Receive Power Level
are all measuring and displaying peak power levels. The OFDM Receive Power Level is
measuring and displaying the average power level. In addition, an OFDM SM measures power
across 10-MHz channels while an FSK SM measures power across 20-MHz channels.
Due to all this, the reported Receive Power Level on an OFDM SM can be 10 to 15 dB lower
than the value shown for that channel on the spectrum analyzer. For example, for an OFDM AP
transmitting on 5540 MHz, the OFDM SM might show a Receive Power Level of -70 dBm while
the OFDM and FSK spectrum analyzers show power levels of -54 and -51 dBm at 5540 MHz.
The built-in spectrum analyzer can be very useful as a tool for troubleshooting and RF planning,
but doesn’t duplicate the accuracy and programmability of a dedicated, high-end spectrum
analyzer, which may be needed in some cases.
3.6 COLLOCATION OF 5.4 GHZ OFDM WITH STANDARD 5.4 GHZ
CANOPY FSK
When locating 5.4 GHz PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series OFDM APs near 5.4 GHz standard
Canopy FSK APs (especially on the same tower, but also in the same geographical area), the
following practices should be followed to avoid interference between the two systems:
• Plan spacing between OFDM and FSK channels to provide 25 MHz center spacing,
which gives a 10 MHz guard band between the 10 MHz OFDM channel and the 20
MHz FSK channel.
• Coordinate Downlink Data %, Range, and Control Slot settings using both the
OFDM and the FSK frame calculators
The following paragraphs give more details on these recommended practices.
3.6.1 Channel Spacing
Center spacing of 25 MHz between collocated FSK and OFDM APs provides a 10 MHz guard
band between the 20 MHz and 10 MHz channels, which has proven useful and needed in field
testing. Alternatively, in cases where channel planning is severely restricted and the 10 MHz
guard band (25 MHz spacing) is not possible, using vertical separation of 5 feet or more between
the OFDM and FSK APs may allow collocation with no guard band (15 MHz spacing) in some
deployments.
3.6.2 Frame Calculations and Configuration Settings
Interference between collocated Canopy systems can be avoided by following two practices:
1. Use a CMM. This synchronizes frame start, so that all collocated APs begin
transmitting at the same time each 2.5 millisecond frame.
2. Use the frame calculators in each module, OFDM and FSK (the frame calculators are
different, as frame details are different) to select Downlink Data %, Range, and
Control Slots for each system that produce “Rec SEQ Start” values that are within
300 bit times. This ensures that all collocated APs end transmission each frame
before any collocated AP begins to receive.
Page 16

PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series Canopy User Guide Supplement
Issue 3, January 2009 Page 16 of 45
When collocating only Canopy OFDM APs together, or collocating only Canopy hardwarescheduled FSK APs together, the simple practice of setting the Downlink Data %, Range, and
Control Slots the same on all APs ensures they won’t interfere with each other. (These
parameters are set on the “Configuration => Radio” page of the AP.) However, due to the
different “physical” layer between Canopy OFDM and Canopy FSK, this doesn’t necessarily work
when collocating OFDM and FSK together.
You will need to use frame calculators on both the OFDM and FSK modules, as they are different
frame calculators. For the same Downlink Data %, Range, and Control Slots, the frame
calculators give different results. Use of the frame calculators is similar to the previous use when
collocating software-scheduled and hardware-scheduled APs.
Procedure 1: Finding collocation values using Frame Calculators
1. Using the “Tools => Frame Calculator” on an OFDM module, enter the desired
Downlink Data %, Range, and Control Slot settings, click Calculate, and observe the
“Rec SEQ Start” value.
2. Using the “Tools => Frame Calculator” on an FSK module, enter the desired
Downlink Data %, Range, and Control Slot settings, click Calculate, and observe the
“Rec SEQ Start” value.
3. Iterate, usually adjusting the FSK Downlink Data % and the OFDM Downlink Data %
values by a few percent each time, until the “Rec SEQ Start” times of all collocated
modules are within 300 bit times of each other.
4. Configure the OFDM modules using the resulting OFDM values, and the FSK
modules using the resulting FSK values.
=========================== end of procedure ======================
Page 17

PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series Canopy User Guide Supplement
Issue 3, January 2009 Page 17 of 45
4 Configuring
Most Canopy Series 400 configuration items are identical or very similar to configuration items in
standard FSK Canopy modules. This section discusses those that are new or changed and also
remarks on some that remain unchanged.
4.1 LINK OPERATION – 1X/2X/3X
PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series products offer three levels or speeds of operation – 1X, 2X, and 3X
- instead of the two levels offered by standard Canopy. 3X supports a typical maximum aggregate
(sum of up and down) throughput of up to 21 Mbps.. If received power is less due to distance
between the AP/BHM and the SM/BHS or due to obstructions, or interference affects the RF
environment, the Canopy system will automatically and dynamically adjust links to the best
operation level. Distance, rates and other information associated with the operation levels are
shown in Table 2 on page 12.
Similar to standard Canopy, the system chooses its operation rate dynamically, based on
Canopy’s internal ARQ (Automatic Repeat reQuest) error control method. With ARQ, every data
slot of every frame sent over the air (expect downlink broadcast) is expected to be acknowledged
by the receiver, and if acknowledgement is not received, the data is resent. The sending unit
monitors these resends, and adjusts the operation rate accordingly. A normal system may have
links that move from 3X to 2X and back (or 1X) as the RF environment changes, or links.
Furthermore, the links operate independently, and it is normal, for example, for the downlink to
run at 3X while the uplink RF environment only supports 2X.
The default is for both AP/BHM and SM/BHS to be enabled for 3X operation. An operator may
“lock down” a link to 2X and 1X operation, or to only 1 X operation, using the Dynamic Rate Adapt
parameter on the SM’s “Configuration => General” page as shown in Figure 3 on page 15 . This
parameter locks down both uplink and downlink operation. An operator may lock down an entire
sector to 2X and 1X operation, or to only 1 X operation, using the Dynamic Rate Adapt parameter
on the AP’s “Configuration => General” page. This parameter locks down uplink and downlink of
all links in the sector, and overrides any SM 1X/2X/3X settings. That is, if an individual link is set
for 3X operation at the SM, but the sector is set for 1X operation at the AP, that link (and all links
in the sector) will be locked down to 1X operation.
Page 18

PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series Canopy User Guide Supplement
Issue 3, January 2009 Page 18 of 45
Figure 5: Dynamic Rate Adapt on AP "Configuration => General" page
In most cases, an operator is well-served to leave the setting at 1X/2X/3X and let the system
automatically and dynamically choose the best rate for each link. Cases when it may be useful to
lock down a link to 1X include
• Some aiming and alignment efforts, although usually aiming and alignment and link
optimization work well with 3X operation allowed. If you are having trouble aiming a
link or getting it to register, locking the link down to 2X or 1X may help in some cases.
• If the link is suspected to be oscillating between operation rates to the detriment of
throughput. Usually, even if the link is moving rapidly between operation rates,
overall link throughput and sector capacity are highest if the link is left at 3X and the
link can choose its own rate dynamically.
• General link troubleshooting
Note that it is useful for as many links as possible to run at 3X to provide as much capacity as
possible for the sector. In particular, just because you want to limit throughput to an individual
subscriber does not mean you should set that link to 1X operation. Use MIR (Maximum
Information Rate) settings to cap the SM’s bandwidth use, but let the link run at as high an
operation rate as the RF environment will allow. This ensures that when transmitting data the link
uses as little “air time” as possible, leaving more “air time” for other SMs.
4.2 TRANSMITTER OUTPUT POWER (AND NO JITTER)
The AP/BHM’s Transmitter Output Power is configured on the AP/BHM’s “Configuration =>
Radio” page. For 5.4 GHz radios, Transmitter Output Power is settable in a range from –30 dBm
to 12 dBm, with a factory default setting of 10 dBm. For 4.9 GHz radios, Transmitter Output
Power is settable in a range from -30 dBm to 18 dBm, with a factory default setting of 18 dBm.
In most regulatory regions, including the US, Canada, and Europe, PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series
modules operating in the 5.4 GHz band are limited to 27 dBm EIRP (Equivalent Isotropic
Page 19

PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series Canopy User Guide Supplement
Issue 3, January 2009 Page 19 of 45
Radiated Power). This is different than the 30 dBm EIRP allowed for Canopy FSK modules
operating in the 5.4 GHz band because the regulations are for spectral power density and with
half the channel size (10 MHz vs 20 MHz), PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series radios are allowed half
the power (27 dBm vs 30 dBm).
To meet 27 dBm EIRP with the connectorized 18 dBi antenna (with 1 dB of cable loss) that
comes with the 5440AP or 5441AP, or the integrated 17 dBi antenna that comes with a 5440BH
or 5441BH, the maximum setting allowed is 10 dBm (the default) since 27-17=10.
If a connectorized AP or BHM has been purchased and the operator has provided the antenna,
the Transmitter Output Power must be configured based on that antenna and consistent with
local or regional regulations. For example, if a 5440APC is being used with a 12 dBi antenna,
then the maximum setting allowed to meet 27 dBm EIRP is the full 15 dBm of which the radio is
capable, since 27-12=15.
IMPORTANT!
It is the responsibility of the operator and professional installer to ensure
Transmitter Output Power is set within regulatory limits for their country
or region. These must be set or confirmed on initial configuration and
after a module is reset to factory defaults, and should be confirmed after
the software on a module is upgraded.
In most cases, the operator will want to set the AP’s Transmitter Output Power to the maximum
allowed so as to have the greatest overall range and the greatest range for 3X operation. It may
be useful to reduce Transmitter Output Power when Canopy systems are located close together,
with good coverage given because of their proximity and full power isn’t needed, or in cases
where an operator is trying to reduce interference from the Canopy system to other systems.
Each SM’s Transmitter Output Power is automatically set by the AP, not by the operator. The
AP’s Auto-TPC (Transmit Power Control) sets each SM’s Transmitter Output Power to the lesser
of
• 10 dBm for a 5.4 GHz radio, the maximum allowed on the SM since it has an
integrated 17 dBi antenna and a regulatory maximum EIRP of 27 dBm (27-17=10)
• 18 dBm for a 4.9 GHz radio
• a power level so that the received power at the AP from that SM is not greater than
60 dBm.
PMP 400 Series networks use Auto-TPC because OFDM technology is more sensitive to large
differences in power levels from SMs operating at various distances from the AP than the single
carrier technology used in Canopy FSK.
PTP 200 Series networks do not use Auto-TPC – the operator sets Transmitter Output Power on
the “Configuration => Radio” page of both the BHM and the BHS.
PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series modules display the typical Canopy “Receive Power Level” but
due to the different modulation technique no “jitter” is calculated or displayed.
4.3 DOWNLINK DATA %, RANGE, AND CONTROL SLOTS
The Downlink Data % parameter on the AP’s and BHM’s “Configuration => General” page can be
set in 1% increments between 10% and 90%. (Standard Canopy can be set between 1% and
99%, although internal calculations don’t result in that extreme of slot assignment between uplink
and downlink.) The default is 75%, the same as standard Canopy.
Page 20

PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series Canopy User Guide Supplement
Issue 3, January 2009 Page 20 of 45
The default Range, set on the AP’s “Configuration => General” page, is 5 miles, but can be set in
1 mile increments between 1 and 10 miles. The BHM performs its own ranging and so no range
need be set for it.
If the Range is set to greater than 5 miles, then the Downlink Data % can be a maximum of 85%,
else some close-in SMs won’t register due to details of the Canopy scheduler. For example, a
Range of 6 miles and a Downlink Data % of 90% is not allowed. Operationally,
• if the Downlink Data % is set to greater than 85% and the user enters a range greater
than 5 miles, the module will reset the Downlink Data % to 85%
• if the range is set to greater than 5 miles and the user enters a Downlink Data % of
greater than 85%, the module will reset the Downlink Data % to 85%.
Suggested Control Slot settings as a function of number of SMs in the sector are shown in Table
5. Generally all APs in a cluster should use the same number of control slots so as to keep the
frame structures, and thereby the send and receive timing, the same.
Table 5: Control Slot Settings
Number of SMs that
Register to the AP
Number of Control
Slots Recommended
1 to 10
01
11 to 50
1
51 to 150
2
151 to 200
3
Note 1: Any sector with the Hi Priority Channel enabled on any SM should be
configured with at least 1 Control Slot on the AP.
In some cases, operators may find that sectors with high levels of small packet requests, such as
might be seen in a sector handling several VoIP streams, benefit overall from slightly higher
Control Slot settings. If different sectors require different numbers of Control Slots, the operator
should use the Frame Calculator to find a combination of settings that put “Rec SEQ Start” times
within 300 bit times. See section 3.6.2 on page 15 for details.
Control Slots are reserved for SMs’ bandwidth requests and never handle data. A higher number
of control slots gives higher probability that an SM’s bandwidth request will be heard when the
system is heavily loaded, but with the tradeoff that sector capacity is reduced by about 100 kbps
for each Control Slot configured, so there will be less capacity to handle the request.
Uplink Data Slots are used first for data, but if not needed for data in a given frame can be used
by the SMs for bandwidth requests. So, even with zero control slots configured, the SMs can still
make bandwidth requests, using any unused data slots.
BHMs do not have settings for control slots, as there is no contention on the one-to-one link.
Downlink Data %, Range, and Control Slots should be set consistent with the results of any
collocation planning done using OFDM and FSK frame calculators in section 3.6.2 on page 15.
4.4 DFS AND REGULATORY PARAMETERS FOR 5.4 GHZ RADIOS
Dynamic Frequency Selection (DFS) is a requirement in several countries and regions for 5 GHz
unlicensed systems to detect radar systems and avoid co-channel operation. DFS and other
Page 21

PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series Canopy User Guide Supplement
Issue 3, January 2009 Page 21 of 45
regulatory requirements drive the settings for the following parameters, as discussed in this
section:
• Region Code
• Primary Frequency
• Alternate 1 and Alternate 2 Frequencies
• External Antenna Gain
On the AP, the “Home => DFS Status” page shows current DFS status of all three frequencies
and a DFS log of past DFS events. Note, unlike standard Canopy, the PMP 400 and PTP 200
Series AP, SM, and BH do not offer “Whitening”, as the OFDM technology obviates the need for
it.
4.4.1 Background and Operation
The modules use region-specific DFS based on the “Region Code” selected on the module’s
“Configuration => General” page. By directing installers and technicians to set the Region Code
correctly, the operator gains confidence the module is operating according to national or regional
regulations, without having to deal with the details for each region.
Available “Region Codes” include Other, United States, Canada, Europe, Brazil, Russia, and
Australia. Operators in regions or countries not listed and with requirements aligned with one of
the listed countries should set the Region Code to that country. Operators in regions or countries
with no requirements for DFS should use the “Other” Region Code.
New APs and BHMs from the factory will show a Region Code of “None”, and will not transmit
until the Region Code is set to a value other than “None”.
Canada and, for new equipment, Europe, have requirements to avoid certain frequencies used by
some weather radar. To meet this requirement, modules set to a Region Code of Canada or
Europe will display the center channel frequencies shown in Table 3 on page 13 on the AP’s and
BHM’s Carrier Frequency pop-up and on the SM’s and BHS’s Frequency Scan Selection List.
Table 6 shows the details of DFS operation and channels available for each Region Code,
including whether DFS is active on the AP/BHM, SM/BHS, which DFS regulation apply, and any
channel restrictions..
Table 6: Release 8.4 Operation based on Region Code
5.4 GHz
Region Code1
AP
SM
Center Channel
Frequencies Available
2
(MHz)
United States
FCC/IC DFS3
No effect
5480 - 5710
Canada
FCC/IC DFS
No effect
5480 – 5595, 5655 - 5710
Europe
ETSI DFS4
ETSI DFS
5475 - 5595, 5655 - 5715
Brazil
ETSI DFS
No effect
5475 - 5715
Australia
FCC/IC DFS
No effect
5480 – 5595, 5655 - 5710
Russia
NA
NA
5480 - 5710
Other
No effect
No effect
5480 - 5710
1. In all cases, set the Region Code to the region you are in, and the
Page 22

PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series Canopy User Guide Supplement
Issue 3, January 2009 Page 22 of 45
5.4 GHz
Region Code1
AP
SM
Center Channel
Frequencies Available
2
(MHz)
equipment will provide DFS consistent with that regions’s regulations.
For countries or regions not listed, use a Region Code that provides DFS
functionality and channels consistent with your country’s regulatory
requirements.
2. In some countries and regions, 5600 MHz to 5650 MHz is “notched” out to
meet requirements to not transmit in weather radar frequencies.
3. FCC/IC indicates compliance with FCC Report and Order 03-287 and
Industry Canada requirements.
4. ETSI DFS indicates compliance with ETSI EN 301 893 v1.3.1
After an AP or BHM with DFS boots, it performs a channel availability check on its main carrier
frequency for 1 minute, monitoring for the radar signature, without transmitting. If no radar
signature is detected during this minute, the module then proceeds to normal beacon transmit
mode. If it does detect a radar signature, the frequency is marked for a 30 minute non-occupancy
period, and the module moves to its 1st alternate carrier frequency. It continues this behavior
through its 2nd alternate carrier frequency if needed, then will wait until the first frequency ends its
30 minute non-occupancy period. If while in operation, the AP or BHM detects the radar
signature, it mark its current carrier frequency for a 30 minute non-occupancy period, and move
to trying the next-in-line carrier frequency.
Since an SM or BHS only transmits if it is receiving beacon from an AP or BHS, the SMs or BHSs
in the sector are also not transmitting when the AP or BHM is not transmitting.
The FCC and IC require DFS only on APs and BHMs. Europe applies the ETSI specificiation to
both APs/BHMs and SMs/BHSs, while Brazil applies it only to APs and BHMs. In the ETSI case,
when an SM or BHS boots, it scans to see if an AP is present (if it can detect a Canopy beacon).
If an AP or BHM is found, the SM performs a channel availability check on that frequency for 1
minute, monitoring for the radar signature, without transmitting.
• If no radar pulse is detected during this 1 minute, the SM or BHS proceeds through
normal steps to register to an AP or BHM.
• If the SM or BHS does detect radar, it locks out that frequency for 30 minutes and
continues scanning other frequencies in its scan list.
Note, after an SM or BHS with DFS has seen a radar signature on a frequency and locked out
that frequency, it may connect to a different AP or BHM if color codes, AP/BHM transmitting
frequencies, and SM/BHS scanned frequencies support that connection.
To simplify operation and ensure compliance, an SM or BHS takes on the DFS type of the AP it is
registering to. For example, when an SM in Europe registers to an AP with the Region Code set
to “Europe”, that SM will use ETSI DFS, no matter what its Region Code is set to, even if its
Region Code is set to “None”. Note, the operator should still configure the Region Code in the SM
correctly, as future releases may use the Region Code for additional region-specific options.
For all modules running DFS, the module displays its DFS state on its Home => General Status
page as one of the following:
• Checking Channel Availability Remaining time n seconds, where n
counts down from 60 to 1.
Page 23

PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series Canopy User Guide Supplement
Issue 3, January 2009 Page 23 of 45
• Normal Transmit
• Radar Detected Stop Transmitting for n minutes, where n counts down
from 30 to 1.
• Idle, only for SM or BHS, indicates module is scanning, but has not detected a
beacon from an AP or BHM. Once it detects beacon, the SM or BHS begins a
Channel Availability Check on that frequency.
4.4.2 Setting DFS and Regulatory Parameters
Setting the Region Code
All modules display a Region Code pop-up on the :Configuration => General” page, as shown in
Figure 6.
On new modules from the factory, or after resetting to factory defaults, the operator should set
this Region Code consistent with their country or region. For countries or regions not listed in the
Region Code pop-up, set the Region Code consistent with your country’s regulatory
requirements. (For example, several countries in South America follow the same DFS regulations
as Brazil, so in those countries the Region Code should be set to “Brazil”.)
IMPORTANT!
Operators under regulatory requirements for DFS must ensure the new
Canopy parameter “Region Code” is set correctly. This applies to initial
configuration, after a module is reset to factory defaults, or after a
module is upgraded.
An AP or BHM will not transmit if the Region Code is configured to “None”.
IMPORTANT!
On APs or BHMs received from the factory, with Region Code set to
“None”, the operator must set the Region Code before the module will
transmit. The same is true of APs and BHMS which have been reset to
factory defaults.
Page 24

PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series Canopy User Guide Supplement
Issue 3, January 2009 Page 24 of 45
Figure 6: Region Code on AP “Configuration => General” page
An SM or BHS has both a configurable Region Code and, once it registers to an AP or BHM, an
active Region Code. After an SM/BHS registers to an AP/BHM, it uses the Region of the AP/BHM
to determine its DFS behavior and displays the AP’s or BHM’s Region Code on its Home =>
General Status page, as shown in Figure 8.
The two Region Codes should be the same in normal operation, but will not be the same if, for
example, as shown in Figure 7 and Figure 8, an SM configured with a Region Code of “None” has
registered to an AP with a Region Code of Europe.
Page 25

PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series Canopy User Guide Supplement
Issue 3, January 2009 Page 25 of 45
Figure 7: Configured Region Code on SM Configuration => General page
Figure 8: Active Region Code on SM Home => General Status page
The AP or BHM always operates under its manually configured Region Code (the one on the
Configuration => General page), and so does not show a Region Code on its Home => General
Status page.
Under normal operations, APs and BHMs operating with DFS (see Table 6) will experience an
additional minute after power-up or reboot before they will register any SMs or BHSs. SMs and
BHSs operating with DFS (see Table 6) will experience an additional minute after they reboot
before they will register to an AP or BHM.
Page 26

PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series Canopy User Guide Supplement
Issue 3, January 2009 Page 26 of 45
It takes two reboots to set the parameters described below on a module starting from factory
defaults. Set the Region Code as described above, “Save Changes”, and “Reboot”. If the module
then invokes DFS (based on the Region Code and frequency band as shown in Table 6), the
Radio Frequency Carriers and External Antenna Gain parameters will be displayed. Set them as
described below, “Save Changes”, and “Reboot” again.
IMPORTANT!
Set the Region Code, “Save Changes”, and “Reboot” to see the contextsensitive DFS parameters. Unlike with many context-sensitive
parameters, these do not appear in the GUI with only a “Save Changes”.
Setting Radio Frequencies
APs and BHMs running DFS include an option for setting up to two alternate frequencies on the
“Configuration => Radio” page, in addition to the primary frequency. These alternate frequencies
are used in the unlikely event radar is detected and the main frequency is locked out due to DFS
detection. If these are left at “None”, no backup frequencies will be used in the case of DFS
detection, and the AP or BHM will lock itself out from any transmission for 30 minutes.
If radar is detected on the main frequency, either at startup or during operation, a Channel
Availability Check will be performed on the 1st alternate frequency before it is then used for
transmission. If radar is detected on the 1st alternate frequency, either during Channel Availability
Check or during operation, a Channel Availability Check will be performed on the 2nd alternate
frequency before it is then used for transmission. If radar is detected on the 2nd alternate
frequency, either during Channel Availability Check or during operation, the radio will cease
transmission unless or until the primary channel clears its 30 minute lock-out.
The alternate frequencies configured in the AP or BHM must be included in the SM’s or BHS’s
Frequency Scan List, or the SMs/BHSs can’t follow their AP/BHM if it switches to a new channel.
Additional frequencies may checked in the Frequency Scan List depending on local practices, for
example if an operator wants to configure an SM to only register on certain frequencies to drive a
known SM to AP mapping, or configure an SM to register on many frequencies so that it may find
another AP to register to if its usual AP isn’t available.
Note, use site surveys and RF planning to choose alternate frequencies useful for each sector,
and consider testing on the alternate frequencies to ensure compatibility with the sector’s RF
environment.
4.5 NET ANTENNA GAIN FIELD
An AP, SM, or BH needs to know the gain of its antenna to perform DFS and Auto-TPC
(Automatic Transmit Power Control) (SM only) consistent with regional or national regulations.
The GUI includes a Net Antenna Gain field to support this.
Key points about the Net Antenna Gain field include:
• Net Antenna Gain is defined as the gain of the antenna minus the loss in the coaxial
cable and connectors.
• The Net Antenna Gain is set on the Configuration -> Radio page of each module
(AP, SM, BHM, or BHS)
• The default on a new unit, or when the unit is reset to factory defaults, is 17 dB for
5.4 GHz radios and 16 dB for 4. 9 GHz radios..
• The range is 0 to 35 dB.
Page 27

PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series Canopy User Guide Supplement
Issue 3, January 2009 Page 27 of 45
• A 5.4 GHz SM or BH with an integrated antenna has a Net Antenna Gain of 17 dB.
• The antenna sold with the connectorized 5.4 GHz AP has a gain of 18 dB and cable
loss of approximately 1 dB, giving a Net Antenna Gain of 17 dB.
• A 4.9 GHz SM or BH with an integrated antenna has a Net Antenna Gain of 16 dB.
• The antenna sold with the connectorized 4.9 GHz AP has a gain of 17 dB and cable
loss of approximately 1 dB, giving a Net Antenna Gain of 16 dB.
• Any radio using DFS will use the Net Antenna Gain to appropriately adjust sensitivity
to radar signals. The use of DFS is determined by the Region Code setting on the
Configuration => Home page.
• The Auto-TPC used by the PMP 400 Series system takes into account the Net
Antenna Gain so as not to exceed national or regional EIRP limits.
Procedure for setting the Net Antenna Gain
1. If using a BH or SM with an integrated antenna, or a connectorized AP with the
connectorized antenna sold with it, leave the Net Antenna Gain on the Configuration
=> Radio page set to the factory default of 17 dB for 5.4 GHz radios or 16 dB for 4.9
GHz radios.
2. If using another antenna, set the Net Antenna Gain to the gain of the antenna minus
the loss in coaxial cable and connectors.
Important! Ensure the Net Antenna Gain is set correctly. Setting it low or high can lead to
either a system overly sensitive to DFS events or a system not transmitting at its full legal power.
4.6 NETWORK CONTROL PARAMETERS
Network control parameters are configured the same as they are in standard Canopy. These
include, High Priority/DiffServ, NAT, DHCP, VLAN, MIR, and CIR. MIR and CIR are configured
the same way as in standard Canopy, but the operator may (or may not) want to take advantage
of the higher MIR possible to provide greater bandwidth to a given SM.
4.7 FORWARD ERROR CORRECTION
PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series radios use FEC (Forward Error Correction) to extend the range of
the modules. They use Reed-Solomon error correction optimized at 3/4 coding. The coding rate is
not settable by the operator.
4.8 CYCLIC PREFIX (CONFIGURABLE ONLY ON BH)
OFDM technology uses a cyclic prefix, where a portion of the end of a symbol (slot) is repeated at
the beginning of the symbol (slot) to allow multi-pathing to settle before receiving the desired
data. A 1/4 cyclic prefix means that for every 4 bits of throughput data transmitted, an additional
bit is used, A 1/8 cyclic prefix means that for every 8 bit of throughput data transmitted, an
additional bit is used.
PMP 400 Series networks use a cyclic prefix of 1/4 that is not configurable by the user.
PTP 200 Series modules (OFDM BHs) are settable for either 1/8 or 1/4 cyclic prefix. The use of
1/8 cyclic prefix provides about 11% higher maximum throughput, and is recommended in most
cases.
• The Cyclic Prefix is set on the Configuration => Radio page of the BHM.
• The default on a new unit, or when the unit is reset to factory defaults, is 1/4 Cyclic
Prefix.
Page 28

PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series Canopy User Guide Supplement
Issue 3, January 2009 Page 28 of 45
• In most deployments, 1/8 Cyclic Prefix will provide a high quality, higher throughput
link. In cases with severe multi-pathing or obstructions, 1/4 Cyclic Prefix may give
better overall results.
Procedure for setting the Cyclic Prefix
3. Set the Cyclic Prefix on the Configuration => Radio page of both the BHM and the
BHS to 1/8 before deployment.
Important! The Cyclic Prefix must be set the same on both the BHM and the BHS. If they
don’t match, the BHS will not register to the BHM.
4. During installation use Link Tests to confirm link quality per standard installation and
alignment procedures.
5. If a Link Test shows low throughput or efficiency, consider changing the Cyclic Prefix
to 1/4 on both the BHM and the BHS along with other standard installation
troubleshooting procedures such as re-aiming, off-axis aiming, changing location,
raising or lowering the height of the radio, adjusting Transmission Power up or
down, or identifying and mitigating sources of interference.
Page 29

PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series Canopy User Guide Supplement
Issue 3, January 2009 Page 29 of 45
5 Installation
WARNING!
Installing an AP or a BH usually involves height and electricity and
exposure to RF (Radio Frequency) energy. To avoid personal injury,
know and follow applicable national and local safety regulations and
industry best practices, and follow the specific guidelines in this
document, including Exposure Separation Distances in section 6.3 on
page 40.
5.1 INSTALLING AN AP WITH ITS KITTED ANTENNA
This section addresses installation aspects specific to the PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series AP.
General communications equipment, infrastructure, and facilities site design should be performed
in line with Motorola’s “Standards and Guidelines for Communications Sites” (also known as the
R56 manual), available from
http://www.motorola-wls.com/Dynamic/Course_Description.asp?number=ANT001-CD&CourseKe
y=125
The AP ships either as a kit consisting of a connectorized antenna and a connectorized radio, or
just the connectorized radio, with the antenna provided by the operator. These instructions focus
on the former case, but are also generally applicable to the latter case for APs, SMs, or BHs
where the antenna is purchased separately by the operator.
A short coaxial cable from the radio terminates in a male N connector. The antenna has a
chassis-mounted female N connector. The antenna includes tower mount brackets with
adjustable down-tilt.
Installing an AP typically consists of 4 phases:
1. Configuring the AP in a depot or at the job site using the information and decisions
from section 3, Planning, and section 4, Configuring
2. Assembling the AP (radio and antenna and brackets) and physically installing it using
Procedure 2 for 5.4 GHz APs or Procedure 3 for 4.9 GHz APs, along with physically
installing a CMMmicro or CMM4 and backhauls, if any.
3. Cabling the AP to the CMMmicro or CMM4, and grounding it to Protective Earth – PE
using Procedure 4. This phase can also include cabling to backhauls, or running
terrestrial feeds.
4. Confirming operation, using SMs on the ground.
Local practices and choices of installation options will dictate the actual processes used. For
example, installing on a building requires somewhat different procedures.. Also, operators may
use their own procedures to attach one or more APs to a pipe mount while on the ground, and
then lift the assembled unit up a tower for final attachment. These generalized procedures will not
be applicable in every case, but should give good insight into the steps necessary.
Page 30

PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series Canopy User Guide Supplement
Issue 3, January 2009 Page 30 of 45
Procedure 2: Assembling a 5.4 GHz AP, and attaching to tower
1. Perform a parts check to ensure all
parts are present.
2. Assemble the upper bracket, per the
diagram that comes with the
antenna.
3. Connect the radio to the antenna by
sliding it into the captive space.
Secure the radio to the antenna
using the two bolts provided.
4. Assemble the lower bracket on the
antenna assembly.
Although it may seem intuitive to
attach both brackets to the tower or
pole and then hang the antenna, it
usually works better to have the
bottom bracket already attached to
the antenna before climbing.
5. Weatherproof the connector using
standard practices, with waterproof
wrap.
Page 31

PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series Canopy User Guide Supplement
Issue 3, January 2009 Page 31 of 45
6. Use standard work and
safety practices for
tower climbing, and
connect the upper
bracket to a pole,
mounting fixture, or the
tower.
7. Hang the antenna assembly
on the upper bracket
8. Connect the lower bracket
to the pole or tower, using
the quick-connect system
provided
9. The quick-connect system allows
easy attachment and detachment
and adjustment without any lose
parts.
Page 32

PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series Canopy User Guide Supplement
Issue 3, January 2009 Page 32 of 45
10. Adjust downtilt as desired, per
previous calculations done during
Planning. If any doubts, confirm
downtilt after the radio is operational
using SMs in the field at selected
test locations.
=========================== end of procedure ======================
Procedure 3: Assembling a 4.9 GHz AP, and attaching to tower
1. Perform a parts check to
ensure all parts are present.
2. Assemble unit per the
instructions that come with the
kit.
Page 33

PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series Canopy User Guide Supplement
Issue 3, January 2009 Page 33 of 45
3. Connect the radio to the
antenna by sliding it into the
captive space. Secure the
radio to the antenna using the
two bolts provided.
4. Weatherproof the connector
using standard practices, with
waterproof wrap.
5. Use standard work and safety
practices for tower climbing,
and connect the upper
assembly to a pole, mounting
fixture, or the tower.
6. Adjust downtilt as desired, per
previous calculations done
during Planning. If any doubts,
confirm downtilt after the radio
is operational using SMs in the
field at selected test locations.
=========================== end of procedure ======================
Procedure 4: Cabling and Grounding/Earthing the AP
1. Standard Canopy installation practices apply, including using shielded Ethernet cable
for all infrastructure cabling, using drip loops, providing extra cable for future use at
any termination, and ensuring the tower or structure is fully grounded (Protective
Earth – PE).
2. Use dielectric grease on all connections and in all RJ-45 Ethernet connectors.
(Dielectric grease is generally available in the trade, and is specially formulated so as
to be uniformly non-conducting.) The best practice is to use enough grease to fill the
RJ-45 female connector, and then insert the RJ-45 male connector and push the
grease further into the Canopy unit and around the RJ-45 connector. Excess grease
Page 34

PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series Canopy User Guide Supplement
Issue 3, January 2009 Page 34 of 45
can be wiped over the connector area to provide some resistance to water ingress
around the connector.
3. Use a 600SSC surge suppressor within 3 ft (~1 m) of the AP, and ground it to known
good ground (Protective Earth - PE) on the tower or support structure with a 10 AWG
ground strap.
A pole mount kit is available for mounting the 600SSC to the tower or mast. The
mount includes a termination point for the ground strap from the 600SSC.
4. Run a 10 AWG ground strap from the grounding lug on the AP (see Figure 9) to
known good ground (Protective Earth - PE) to complete the grounding and protection
of the AP. The termination point on the 600SSC pole mount kit may be used for this.
=========================== end of procedure ======================
Figure 9: Ground lug highlighted on AP
Unlike standard Canopy APs, the PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series AP have metal-to-metal contact
from the tower or support structure, through the antenna, through the coax cable, to the radio.
Due to this, to provide the best protection from near lightning hits, it is strongly recommended to
install surge suppression at the AP.
The 600SSC surge suppressor replaces earlier surge suppressors, and supports up to three
600SSCs on an Ethernet link in series, for example, a 600SSC within 3 ft (~1 m) of an AP,
another 600SSC where the Ethernet cable enters a telecommunications hut, and the equivalent
of a 600SSC built into each of the 8 ports on a CMM4. A pole mount kit, Model No. SGHN5169A,
is available to facilitiate mounting the 600SSC close (within 3 ft or 1 m) of the AP.
The CMMmicro uses a different protection scheme and and up to 3 600SSCs can be used in-line
on Ethernet links terminated to the CMMmicro.
Page 35

PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series Canopy User Guide Supplement
Issue 3, January 2009 Page 35 of 45
5.2 INSTALLING AN SM OR BH WITH AN INTEGRATED ANTEANNA
Installing an SM or BH with an integrated antenna is very similar to installing standard Canopy
SMs as described in the Canopy System Release 8 User Guide, with the differences outlined
below.
Use an SMMB2 SM mounting bracket, not an SMMB1 typically used with standard Canopy SMs.
The PMP 400 Series SM or the PTP 200 Series BH is heavier and has a higher wind load than a
classic Canopy module, and so the stronger SMMB2 is required. The SMMB2 is the mounting
arm used with Canopy 900 MHz integrated APs and SMs, and used with reflectors.
Use dielectric grease on all connections and in all RJ-45 Ethernet connectors. (Dielectric grease
is generally available in the trade, and is specially formulated so as to be uniformly nonconducting.) The best practice is to use enough grease to fill the RJ-45 female connector, and
then insert the RJ-45 male connector and push the grease further into the Canopy unit and
around the RJ-45 connector. Excess grease can be wiped over the connector area to provide
some resistance to water ingress around the connector.
The PMP 400 SM and PTP 200 BH have a ground/Protective Earth lug, just like the AP. Although
not as critical as in the case of the AP (where there is metal-to-metal connectivity through the
coax and antenna to ground), the lug can be used to ground the SM for additional protection.
Similarly, a 600SSC can be used within 3 ft (~1 m) of the SM or BH to provide additional
protection. Especially for a BH, or in cases where the SM is mounted high and is more exposed,
or in known difficult areas for lightning, consider using these two techniques to increase the
radio’s resistance to lightning.
PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series modules do not display a jitter value. Use “Received Power Level”
for aiming and then use Link Tests to confirm, similar to standard Canopy practice.
Be mindful when using the “Receive Power Level” that it is a relative, not absolute, value. The
"Receive Power Level" on a module is useful during installation to aid in aiming, where relative
values over a short period of time are of interest. However, the displayed “Receive Power Level”
is not designed to be highly accurate over time. Even if the actual received power is not varying,
the displayed "Receive Power Level" will vary with board-level temperature and may vary from
module to module. Know the limitations and use caution and judgment for any other use of
“Receive Power Levels”, including monitoring a link over time. deciding if the link is within
operating margins. deciding if a link is serviceable (link tests give a much better indication), or
comparing the link to other links.
The alignment headset will play a tone that varies in pitch (received power level), but not volume
(jitter), since PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series modules don’t calculate a jitter.
Page 36

PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series Canopy User Guide Supplement
Issue 3, January 2009 Page 36 of 45
6 Regulatory and Legal Notices
6.1 IMPORTANT NOTE ON MODIFICATIONS
Intentional or unintentional changes or modifications to the equipment must not be made unless
under the express consent of the party responsible for compliance. Any such modifications could
void the user’s authority to operate the equipment and will void the manufacturer’s warranty.
6.2 NATIONAL AND REGIONAL REGULATORY NOTICES
6.2.1 U.S. Federal Communication Commission (FCC) Notification
This device complies with Part 15 of the US FCC Rules and Regulations. Operation is subject to
the following two conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) This
device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired
operation.
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device,
pursuant to Part 15 of the US FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable
protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates,
uses, and can radiate radio-frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with
these instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. If this equipment
does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by
turning the equipment on and off, the user is encouraged to correct the interference by one or
more of the following measures:
• Increase the separation between the affected equipment and the unit;
• Connect the affected equipment to a power outlet on a different circuit from that
which the receiver is connected to;
• Consult the dealer and/or experienced radio/TV technician for help.
The 4.9 GHz band is a licensed band allocated to public safety services. State and local
governmental entities are eligible to hold 4.9 GHz licenses. For additional information, refer to
FCC regulations.
FCC IDs and the specific configurations covered are listed in Table 7.
Page 37

PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series Canopy User Guide Supplement
Issue 3, January 2009 Page 37 of 45
Table 7: US FCC IDs and Industry Canada Certification Numbers and Covered Configurations
FCC ID
Industry
Canada Cert
Number
Frequencies
Module
Families
Antenna
Maximum
Transmitter
Output Power
5440 AP
18 dBi connectorized
PCTEL Model
8514724E01 antenna
(60° x 5° -3 dB beam
width) with 1 dB
connector cable loss
10 dBm
ABZ89FT7629
---
10 MHz channels,
centered on 54805710 in 5 MHz
increments (within
the 5470-5725 MHz
U-NII band)
5440 SM
5440 BH
17 dBi integrated
antenna (18° x 18° -3
dB beam width)
10 dBm
5440 AP
18 dBi connectorized
PCTEL Model
8514724E01 antenna
(60° x 5° -3 dB beam
width) with 1 dB
connector cable loss
10 dBm
---
109W-5440
10 MHz channels,
centered on 54805595 and 56555710 MHz in 5 MHz
increments (within
the 5470-5725 MHz
U-NII band with
5600-5650 MHz
excluded)
5440 SM
5440 BH
17 dBi integrated
antenna (18° x 18° -3
dB beam width)
10 dBm
5440 AP
17 dBi connectorized
PCTEL Model AP
85010066001
antenna (60° x 5° -3
dB beam width) with
1 dB cable loss
18 dBm
ABZ89FT7631
109W-4940
10 MHz channels,
centered on 49454985 in 5 MHz
increments (within
the 4940-4990 MHz
public safety
licensed band)
5440 SM
16 dBi integrated
antenna (18° x 18° -3
dB beam width)
18 dBm
6.2.2 Industry Canada (IC) Notification
This device complies with RSS-210 of Industry Canada. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) This device must accept
any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
Users should be cautioned to take note that in Canada high power radars are allocated as
primary users (meaning they have priority) of 5650 – 5850 MHz and these radars could cause
interference and/or damage to license-exempt local area networks (LELAN).
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device,
pursuant to RSS-210 of Industry Canada. These limits are designed to provide reasonable
protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates,
uses, and can radiate radio-frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with
these instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. If this equipment
does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by
turning the equipment on and off, the user is encouraged to correct the interference by one or
more of the following measures:
• Increase the separation between the affected equipment and the unit;
• Connect the affected equipment to a power outlet on a different circuit from that
which the receiver is connected to;
Page 38

PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series Canopy User Guide Supplement
Issue 3, January 2009 Page 38 of 45
• Consult the dealer and/or experienced radio/TV technician for help.
To reduce potential radio interference to other users, the antenna type and its gain should be
chosen so its Equivalent Isotropic Radiated Power (EIRP) is not more than that permitted for
successful communication.
The 4.9 GHz band is a licensed band allocated to public safety services. State and local
governmental entities are eligible to hold 4.9 GHz licenses. For additional information, refer to
Industry Canada regulations.
Industry Canada Certification Numbers and the specific configurations covered are listed in Table
7.
This device has been designed to operate with the antennas listed in Table 7 and having a
maximum gain as shown in Table 7. Antennas not included in Table 7 or having a gain greater than
as shown in Table 7 are strictly prohibited from use with this device. Required antenna impedance
is 50 ohms.
6.2.3 Regulatory Requirements for CEPT Member States (www.cept.org)
When operated in accordance with the instructions for use, Motorola Canopy Wireless equipment
operating in the 5.4 GHz bands is compliant with CEPT Recommendation 70-03 Annex 3 for
Wideband Data Transmission and HIPERLANs. For compliant operation in the 5.4 GHz band, the
transmit power (EIRP) from the integrated antenna or a connectorized antenna shall be no more
than 0.5 W (27 dBm).
For EU member states, RLAN equipment in the 5.4GHz bands is exempt from individual licensing
under Commission Recommendation 2003/203/EC. Contact the appropriate national
administrations for details on the conditions of use for the bands in question and any exceptions
that might apply. Also see www.ero.dk for further information.
10 MHz channels are used, centered on 5475 to 5595 and 5655 to 5715 in 5 MHz increments.
This is within the 5470 to 5725 MHz U-NII band with 5600 to 5650 MHz excluded.
Motorola Canopy Radio equipment operating in the 5470 to 5725 MHz band are categorized as
“Class 1” devices within the EU in accordance with ECC DEC(04)08 and are “CE” marked
to show compliance with the European Radio & Telecommunications Terminal Equipment
(R&TTE) directive 1999/5/EC. The relevant Declaration of Conformity can be found at
http://motorola.canopywireless.com/doc.php.
A European Commission decision, implemented by Member States on 31 October 2005, makes
the frequency band 5470-5725 MHz available in all EU Member States for wireless access
systems. Under this decision, the designation of Canopy 5.4GHz products become “Class 1
devices” and these do not require notification under article 6, section 4 of the R&TTE Directive.
Consequently, these 5.4GHz products are only marked with the symbol and may be used in
any member state.
For further details, see
http://europa.eu.int/information_society/policy/radio_spectrum/ref_documents/index_en.htm
6.2.4 Equipment Disposal
Waste (Disposal)
of Electronic
and Electric
Equipment
Page 39

PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series Canopy User Guide Supplement
Issue 3, January 2009 Page 39 of 45
Please do not dispose of Electronic and Electric Equipment or Electronic and Electric Accessories
with your household waste. In some countries or regions, collection systems have been set up to
handle waste of electrical and electronic equipment. In European Union countries, please contact
your local equipment supplier representative or service center for information about the waste
collection system in your country.
6.2.5 EU Declaration of Conformity for RoHS Compliance
Motorola hereby declares that these Motorola products are in compliance with the essential
requirements and other relevant provisions of Directive 2002/95/EC, Restriction of the use of
certain Hazardous Substances (RoHS) in electrical and electronic equipment.
The relevant Declaration of Conformity can be found at http://www.canopywireless.com/doc.php.
6.2.6 Luxembourg Notification
5.4GHz products can only be used for mobile services.
6.2.7 Czech Republic Notification
5.4 GHz products can be operated in accordance with the Czech General License
No. GL-30/R/2000.
6.2.8 Greece Notification
The outdoor use of 5470-5725MHz is under license of EETT but is being harmonized according
to the CEPT Decision ECC/DEC/(04) 08, of 9th July. End users are advised to contact the EETT
to determine the latest position and obtain any appropriate licenses.
6.2.9 Brazil Notification
Brazil regulatory authorities have not approved these devices for operation in Brazil. Until
they are approved, they are not available for sale in Brazil, and the information in this
section is provisional and preliminary.
For compliant operation in the 5.4 GHz band, the Equivalent Isotropic Radiated Power from the
integrated antenna or connectorized anteanna shall not exceed 27 dBm (0.5 W).
The operator is responsible for enabling the DFS feature on any Canopy 5.4 GHz radio by setting
the Region Code to “Brazil”, including after the module is reset to factory defaults.
Important Note: This equipment operates as a secondary application, so it has no rights against
harmful interference, even if generated by similar equipment, and cannot cause harmful
interference on systems operating as primary applications.
6.2.10 Labeling and Disclosure Table for China
The People’s Republic of China requires that Motorola’s products comply with China
Management Methods (CMM) environmental regulations. (China Management Methods refers to
the regulation Management Methods for Controlling Pollution by Electronic Information Products.)
Two items are used to demonstrate compliance; the label and the disclosure table.
The label is placed in a customer visible position on the product.
• Logo 1 means that the product contains no substances in excess of the maximum
concentration value for materials identified in the China Management Methods
regulation.
• Logo 2 means that the product may contain substances in excess of the maximum
concentration value for materials identified in the China Management Methods
regulation, and has an Environmental Friendly Use Period (EFUP) in years, fifty
years in the example shown.
Page 40

PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series Canopy User Guide Supplement
Issue 3, January 2009 Page 40 of 45
Logo 1
Logo 2
The Environmental Friendly Use Period (EFUP) is the period (in years) during which the Toxic
and Hazardous Substances (T&HS) contained in the Electronic Information Product (EIP) will not
leak or mutate causing environmental pollution or bodily injury from the use of the EIP. The EFUP
indicated by the Logo 2 label applies to a product and all its parts. Certain field-replaceable parts,
such as battery modules, can have a different EFUP and are marked separately.
The Disclosure Table (see Table 8) is intended only to communicate compliance with China
requirements; it is not intended to communicate compliance with EU RoHS or any other
environmental requirements.
Table 8: Disclosure Table
有毒有害物质或元素
部件名称
铅
(Pb)
汞
(Hg) 镉 (Cd)
六价铬
(Cr6+)
多溴联苯
(PBB)
多溴二苯醚
(PBDE)
金属部件
× ○ × × ○
○
电路模块
× ○ × × ○
○
电缆及电缆组件
× ○ × × ○
○
塑料和聚合物部件
○ ○ ○ ○ ○
×
○: 表示该有毒有害物质在该部件所有均质材料中的含量均在S J/T11363-2006 标准规定的限量要求以下。
×: 表示该有毒有害物质至少在该部件的某一均质材料中的含量超出SJ/T11363-2006 标准规定的限量要求。
6.3 EXPOSURE SEPARATION DISTANCES
To protect from overexposure to RF energy, install Canopy radios so as to provide and maintain
the minimum separation distances from all persons shown in Table 9.
Table 9: Exposure Separation Distances
Module Type
Separation Distance from Persons
PMP 400 AP or SM or PTP 200 BH
At least 20 cm (approx 8 in)
Canopy Module (for comparison)
At least 20 cm (approx 8 in)
Section 6.3.1 and Table 10 give details and discussion of the associated calculations.
Page 41

PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series Canopy User Guide Supplement
Issue 3, January 2009 Page 41 of 45
6.3.1 Details of Exposure Separation Distances Calculations and Power
Compliance Margins
Limits and guidelines for RF exposure come from:
• US FCC limits for the general population. See the FCC web site at
http://www.fcc.gov, and the policies, guidelines, and requirements in Part 1 of Title 47
of the Code of Federal Regulations, as well as the guidelines and suggestions for
evaluating compliance in FCC OET Bulletin 65.
• Health Canada limits for the general population. See Safety Code 6 on the Health
Canada web site at
http://www.hc-sc.gc.ca/ewh-semt/pubs/radiation/99ehd-dhm237/index_e.html.
• ICNIRP (International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection) guidelines
for the general public. See the ICNIRP web site at http://www.icnirp.de/ and
Guidelines for Limiting Exposure to Time-Varying Electric, Magnetic, and
Electromagnetic Fields.
The applicable power density exposure limits from the documents referenced above are
• 10 W/m2 for RF energy in the 5.4-GHz frequency bands.
Peak power density in the far field of a radio frequency point source is calculated as follows:
S =
P " G
4#d
2
where
S = power density in W/m2
P = RMS transmit power capability of the radio, in W
G = total Tx gain as a factor, converted from dB
d = distance from point source, in m
Rearranging terms to solve for distance yields
d =
P " G
4#S
Table 10 shows calculated minimum separation distances d, recommended distances and
resulting power compliance margins for each frequency band and antenna combination.
Table 10: Calculated Exposure Distances and Power Compliance Margins
Variable
Frequency
Band
Antenna
P G S
d
(calcu-
lated)
Recommended
Separation
Distance
Power
Compliance
Margin
Integrated,
17 dBi
0.05 W
(10 dBm)
50
(17 dB)
10
W/m2
6 cm
20 cm
(8 in)
10
5.4 GHz
Connectori
zed, 17 dBi
0.05 W
(10 dBm)
50
(17 dB)
10
W/m2
6 cm
20 cm
(8 in)
10
Integrated,
16 dBi
0.063 W
(18 dBm)
40
(16 dB)
10
W/m2
14 cm
20 cm
(8 in)
2
4.9 GHz
Connectori
zed, 16 dBi
0.063 W
(18 dBm)
40
(16 dB)
10
W/m2
14 cm
20 cm
(8 in)
2
Page 42

PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series Canopy User Guide Supplement
Issue 3, January 2009 Page 42 of 45
The “Recommended Distances” are chosen to give significant compliance margin in all cases.
They are also chosen so that an OFDM module has the same exposure distance as a Canopy
module, to simplify communicating and heeding exposure distances in the field.
These are conservative distances:
• They are along the beam direction (the direction of greatest energy). Exposure to the
sides and back of the module will be significantly less.
• They meet sustained exposure limits for the general population (not just short term
occupational exposure limits), with considerable margin.
• The calculated compliance distance d is overestimated because the far-field equation
models the antenna as a point source and neglects the physical dimension of the
antenna.
6.4 LEGAL NOTICES
6.4.1 Software License Terms and Conditions
ONLY OPEN THE PACKAGE, OR USE THE SOFTWARE AND RELATED PRODUCT IF YOU
ACCEPT THE TERMS OF THIS LICENSE. BY BREAKING THE SEAL ON THIS DISK KIT /
CDROM, OR IF YOU USE THE SOFTWARE OR RELATED PRODUCT, YOU ACCEPT THE
TERMS OF THIS LICENSE AGREEMENT. IF YOU DO NOT AGREE TO THESE TERMS, DO
NOT USE THE SOFTWARE OR RELATED PRODUCT; INSTEAD, RETURN THE SOFTWARE
TO PLACE OF PURCHASE FOR A FULL REFUND. THE FOLLOWING AGREEMENT IS A
LEGAL AGREEMENT BETWEEN YOU (EITHER AN INDIVIDUAL OR ENTITY), AND
MOTOROLA, INC. (FOR ITSELF AND ITS LICENSORS). THE RIGHT TO USE THIS
PRODUCT IS LICENSED ONLY ON THE CONDITION THAT YOU AGREE TO THE
FOLLOWING TERMS.
Now, therefore, in consideration of the promises and mutual obligations contained herein, and for
other good and valuable consideration, the receipt and sufficiency of which are hereby mutually
acknowledged, you and Motorola agree as follows:
Grant of License. Subject to the following terms and conditions, Motorola, Inc., grants to you a
personal, revocable, non-assignable, non-transferable, non-exclusive and limited license to use
on a single piece of equipment only one copy of the software contained on this disk (which may
have been pre-loaded on the equipment)(Software). You may make two copies of the Software,
but only for backup, archival, or disaster recovery purposes. On any copy you make of the
Software, you must reproduce and include the copyright and other proprietary rights notice
contained on the copy we have furnished you of the Software.
Ownership. Motorola (or its supplier) retains all title, ownership and intellectual property rights to
the Software and any copies,
including translations, compilations, derivative works (including images) partial copies and
portions of updated works. The Software is Motorola’s (or its supplier's) confidential proprietary
information. This Software License Agreement does not convey to you any interest in or to the
Software, but only a limited right of use. You agree not to disclose it or make it available to
anyone without Motorola’s written authorization. You will exercise no less than reasonable care to
protect the Software from unauthorized disclosure. You agree not to disassemble, decompile or
reverse engineer, or create derivative works of the Software, except and only to the extent that
such activity is expressly permitted by applicable law.
Termination. This License is effective until terminated. This License will terminate immediately
without notice from Motorola or judicial resolution if you fail to comply with any provision of this
License. Upon such termination you must destroy the Software, all accompanying written
Page 43

PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series Canopy User Guide Supplement
Issue 3, January 2009 Page 43 of 45
materials and all copies thereof, and the sections entitled Limited Warranty, Limitation of
Remedies and Damages, and General will survive any termination.
Limited Warranty. Motorola warrants for a period of ninety (90) days from Motorola’s or its
customer’s shipment of the Software to you that (i) the disk(s) on which the Software is recorded
will be free from defects in materials and workmanship under normal use and (ii) the Software,
under normal use, will perform substantially in accordance with Motorola’s published
specifications for that release level of the Software. The written materials are provided "AS IS"
and without warranty of any kind. Motorola's entire liability and your sole and exclusive remedy
for any breach of the foregoing limited warranty will be, at Motorola's option, replacement of the
disk(s), provision of downloadable patch or replacement code, or refund of the unused portion of
your bargained for contractual benefit up to the amount paid for this Software License.
THIS LIMITED WARRANTY IS THE ONLY WARRANTY PROVIDED BY MOTOROLA, AND
MOTOROLA AND ITS LICENSORS EXPRESSLY DISCLAIM ALL OTHER WARRANTIES,
EITHER EXPRESS OF IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO IMPLIED WARRANTIES
OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND
NONINFRINGEMENT. MOTOROLA DOES NOT WARRANT THAT THE OPERATION OF THE
SOFTWARE WILL BE UNINTERRUPTED OR ERROR-FREE, OR THAT DEFECTS IN THE
SOFTWARE WILL BE CORRECTED. NO ORAL OR WRITTEN REPRESENTATIONS MADE
BY MOTOROLA OR AN AGENT THEREOF SHALL CREATE A WARRANTY OR IN ANY WAY
INCREASE THE SCOPE OF THIS WARRANTY. MOTOROLA DOES NOT WARRANT ANY
SOFTWARE THAT HAS BEEN OPERATED IN EXCESS OF SPECIFICATIONS, DAMAGED,
MISUSED, NEGLECTED, OR IMPROPERLY INSTALLED. BECAUSE SOME JURISDICTIONS
DO NOT ALLOW THE EXCLUSION OR LIMITATION OF IMPLIED WARRANTIES, THE ABOVE
LIMITATIONS MAY NOT APPLY TO YOU.
Limitation of Remedies and Damages. Regardless of whether any remedy set forth herein fails
of its essential purpose, IN NO EVENT SHALL MOTOROLA OR ANY OF THE LICENSORS,
DIRECTORS, OFFICERS, EMPLOYEES OR AFFILIATES OF THE FOREGOING BE LIABLE TO
YOU FOR ANY CONSEQUENTIAL, INCIDENTAL, INDIRECT, SPECIAL OR SIMILAR
DAMAGES WHATSOEVER (including, without limitation, damages for loss of business profits,
business interruption, loss of business information and the like), whether foreseeable or
unforeseeable, arising out of the use or inability to use the Software or accompanying written
materials, regardless of the basis of the claim and even if Motorola or a Motorola representative
has been advised of the possibility of such damage. Motorola's liability to you for direct damages
for any cause whatsoever, regardless of the basis of the form of the action, will be limited to the
price paid for the Software that caused the damages. THIS LIMITATION WILL NOT APPLY IN
CASE OF PERSONAL INJURY ONLY WHERE AND TO THE EXTENT THAT APPLICABLE
LAW REQUIRES SUCH LIABILITY. BECAUSE SOME JURISDICTIONS DO NOT ALLOW THE
EXCLUSION OR LIMITATION OF LIABILITY FOR CONSEQUENTIAL OR INCIDENTAL
DAMAGES, THE ABOVE LIMITATION MAY NOT APPLY TO YOU.
Maintenance and Support. Motorola shall not be responsible for maintenance or support of the
software. By accepting the license granted under this agreement, you agree that Motorola will be
under no obligation to provide any support, maintenance or service in connection with the
Software or any application developed by you. Any maintenance and support of the Related
Product will be provided under the terms of the agreement for the Related Product.
Transfer. In the case of software designed to operate on Motorola equipment, you may not
transfer the Software to another party except: (1) if you are an end-user, when you are
transferring the Software together with the Motorola equipment on which it operates; or 2) if you
are a Motorola licensed distributor, when you are transferring the Software either together with
such Motorola equipment or are transferring the Software as a licensed duly paid for upgrade,
update, patch, new release, enhancement or replacement of a prior version of the Software. If
you are a Motorola licensed distributor, when you are transferring the Software as permitted
herein, you agree to transfer the Software with a license agreement having terms and conditions
Page 44

PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series Canopy User Guide Supplement
Issue 3, January 2009 Page 44 of 45
no less restrictive than those contained herein. You may transfer all other Software, not
otherwise having an agreed restriction on transfer, to another party. However, all such transfers
of Software are strictly subject to the conditions precedent that the other party agrees to accept
the terms and conditions of this License, and you destroy any copy of the Software you do not
transfer to that party. You may not sublicense or otherwise transfer, rent or lease the Software
without our written consent. You may not transfer the Software in violation of any laws,
regulations, export controls or economic sanctions imposed by the US Government.
Right to Audit. Motorola shall have the right to audit annually, upon reasonable advance notice
and during normal business hours, your records and accounts to determine compliance with the
terms of this Agreement.
Export Controls. You specifically acknowledge that the software may be subject to United
States and other country export control laws. You shall comply strictly with all requirements of all
applicable export control laws and regulations with respect to all such software and materials.
US Government Users. If you are a US Government user, then the Software is provided with
"RESTRICTED RIGHTS" as set forth in subparagraphs (c)(1) and (2) of the Commercial
Computer Software-Restricted Rights clause at FAR 52 227-19 or subparagraph (c)(1)(ii) of the
Rights in Technical Data and Computer Software clause at DFARS 252.227-7013, as applicable.
Disputes. You and Motorola hereby agree that any dispute, controversy or claim, except for any
dispute, controversy or claim involving intellectual property, prior to initiation of any formal legal
process, will be submitted for non-binding mediation, prior to initiation of any formal legal process.
Cost of mediation will be shared equally. Nothing in this Section will prevent either party from
resorting to judicial proceedings, if (i) good faith efforts to resolve the dispute under these
procedures have been unsuccessful, (ii) the dispute, claim or controversy involves intellectual
property, or (iii) interim relief from a court is necessary to prevent serious and irreparable injury to
that party or to others.
General. Illinois law governs this license. The terms of this license are supplemental to any
written agreement executed by both parties regarding this subject and the Software Motorola is to
license you under it, and supersedes all previous oral or written communications between us
regarding the subject except for such executed agreement. It may not be modified or waived
except in writing and signed by an officer or other authorized representative of each party. If any
provision is held invalid, all other provisions shall remain valid, unless such invalidity would
frustrate the purpose of our agreement. The failure of either party to enforce any rights granted
hereunder or to take action against the other party in the event of any breach hereunder shall not
be deemed a waiver by that party as to subsequent enforcement of rights or subsequent action in
the event of future breaches.
6.4.2 Hardware Warranty in US
Motorola US offers a warranty covering a period of 1 year from the date of purchase by the
customer. If a product is found defective during the warranty period, Motorola will repair or
replace the product with the same or a similar model, which may be a reconditioned unit, without
charge for parts or labor.
6.5 LIMIT OF LIABILITY
IN NO EVENT SHALL MOTOROLA BE LIABLE TO YOU OR ANY OTHER PARTY FOR ANY
DIRECT, INDIRECT, GENERAL, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, EXEMPLARY OR
OTHER DAMAGE ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THE PRODUCT
(INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, DAMAGES FOR LOSS OF BUSINESS PROFITS,
BUSINESS INTERRUPTION, LOSS OF BUSINESS INFORMATION OR ANY OTHER
PECUNIARY LOSS, OR FROM ANY BREACH OF WARRANTY, EVEN IF MOTOROLA HAS
BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES. (Some states do not allow the
exclusion or limitation of incidental or consequential damages, so the above exclusion or
Page 45

PMP 400 and PTP 200 Series Canopy User Guide Supplement
Issue 3, January 2009 Page 45 of 45
limitation may not apply to you.) IN NO CASE SHALL MOTOROLA’S LIABILITY EXCEED THE
AMOUNT YOU PAID FOR THE PRODUCT.
 Loading...
Loading...