Page 1

Monarch
P
u
b
l
i
s
h
e
d
b
y
t
h
e
T
e
c
h
n
i
c
a
l
C
o
m
m
u
n
i
c
a
t
i
o
n
s
D
e
p
a
r
t
m
e
n
t
.
P
r
i
n
t
e
d
i
n
t
h
e
U
.
S
.
A
.
®
9820™/ 9830™/ 9835™
Printers
TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 ©1996 Monarch Marking Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 2

Table of Contents
CHAPTER 1 PRINTER OVERVIEW & INSTALLATION---------------------------------------------1
PRINTER FEATURES---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------1
PRINTER OPTIONS -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------1
PRINTER SPECIFICATIONS ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------1
STOCK SPECIFICATIONS---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------2
UNPACKING THE PRINTER ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------3
DOCUMENTATION ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------3
SETTING DIP SWITCHES---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------3
FUSE REPLACEMENT--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4
CONNECTING TO A HOST--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4
CHAPTER 2 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION-----------------------------------------------------------7
OVERVIEW OF MODULES --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------7
Power Transformer Assembly --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------8
Inlet Power Module -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------8
Power Transformer -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------8
Bridge Rectifier ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------8
CONTROL BOARD ASSEMBLY--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------8
Functional Description ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------8
Power Conversion --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------9
Memory----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------9
Flash Memory-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------9
DRAM Memory ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------9
SRAM Memory ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------9
Printer Control -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------9
Data Handling-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------9
Printhead Thermal Control-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------9
Print Imaging------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------9
Motion Control ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------9
Platen Drive Interface -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------9
Ribbon Drive Interface------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------9
Analog to Digital Conversion----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------9
Supply Detection & Tracking System-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------9
Operator Control Panel--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------9
Communications ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------9
RS-232 interface -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------10
Centronics IEEE-1284 Parallel Interface-----------------------------------------------------------------------------10
IEEE 1284 Bi-Directional Parallel Interface -------------------------------------------------------------------------10
Contrast Control---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------10
Hardware Power-up Settings (DIPS)-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------10
Peel Module Assembly ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------10
PRINT ASSEMBLY-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------10
Thermal Printhead------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------10
Ribbon Supply & Take-up Spools-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------10
Ribbon Transfer Rollers -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------10
Ribbon Spool Drive Motors-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------11
Supply Deflector and Bi-Cell Emitter (IR LED) ------------------------------------------------------------------------11
Ribbon Transfer Rollers -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------11
Functional Description ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------11
Ribbon Drive Operation -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------11
Printing---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------11
i
Page 3

FEED ASSEMBLY------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------11
Platen Module------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------11
24VDC Stepper Motor -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------11
Lower Supply Guide and Bi-Cell Sensor --------------------------------------------------------------------------------11
Printhead Latch----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------11
Functional Description ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------11
Printhead Locking-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------12
SUPPLY HOLDER ASSEMBLY -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------12
Functional Description ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------12
CONTROL PANEL ASSEMBLY-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------12
Functional Description ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------12
CHAPTER 3 TROUBLESHOOTING------------------------------------------------------------------- 13
PRELIMINARY CHECK -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------13
ANALYZING FAILURE DURING POWER UP ------------------------------------------------------------------------------13
EVALUATION OF A 616 ERROR (DOT SHIFTING FAILED)-----------------------------------------------------------13
EVALUATION OF A 704 ERROR (OUT OF SUPPLY)--------------------------------------------------------------------13
EVALUATION OF A 754 ERROR (OUT OF RIBBON)--------------------------------------------------------------------14
EVALUATION OF A 755 ERROR (PRINTHEAD OPEN)-----------------------------------------------------------------14
EVALUATION OF A 765 ERROR (PRINTHEAD FAILURE)-------------------------------------------------------------14
EVALUATION OF THE CONTROL BOARD ASSY. -----------------------------------------------------------------------14
EVALUATION OF COMMUNICATIONS--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------14
GENERAL TROUBLESHOOTING SUGGESTIONS-----------------------------------------------------------------------15
CHAPTER 4 DIAGNOSTICS ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- 19
POWER-UP SELF-TEST---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------19
NV RAM ByteTest----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------19
Version String Mismatch -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------19
System Restart Condition---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------19
Printhead Dot Resistance------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------19
TEST LABEL (LEVEL 1) ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------19
SERVICE DIAGNOSTICS--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------20
Accessing Diagnostic Modes--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------20
Data Dump Mode ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------20
Serial Loop Back Test-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------21
Parallel Port Test -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------21
Diagnostics Test Mode----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------21
Performing a Virgin Printer Reset-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------21
Printing a Test Label ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------21
CHAPTER 5 TESTS AND ADJUSTMENTS--------------------------------------------------------- 23
SERVICE TESTS-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------23
CN6 Power Supply------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------23
Continuity Tests ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------23
Transformer - Primary Side ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------23
Transformer - Secondary Side---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------23
Bridge Rectifier ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------23
Head Open Sensor -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------23
Displaying Machine/Service Totals---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------23
Print Contrast Adjustment------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------24
Platen Motor Gear Adjustment -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------24
Ribbon Tension Adjustment---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------24
CHECKING SUPPLY QUALITY-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------25
ii TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential
Page 4

CHAPTER 6 SERVICE PROCEDURES -------------------------------------------------------------- 27
MAINTENANCE OVERVIEW----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------27
GENERAL SAFETY TIPS --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------27
CONTROL PANEL REMOVAL--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------27
COVER HOUSING REMOVAL--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------27
POWER TRANSFORMER ASSEMBLY --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------28
Transformer Removal-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------28
Bridge Rectifier Removal ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------28
AC Inlet Removal ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------28
Control Board Assy. Removal ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------29
PRINT ASSEMBLY-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------29
Bi-Cell Emitter Removal--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------30
Upper Supply Guide Removal------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------30
Printhead Module Removal----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------30
Ribbon Spool Assembly Removal -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------30
Ribbon Roller Assembly Removal-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------30
DC Ribbon Motor Removal----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------30
Print Assembly Removal-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------31
FEED ASSEMBLY------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------31
Latch Fascia Removal----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------31
Platen Module Removal--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------31
Platen Module Replacement --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------32
Bi-Cell Sensor Removal--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------32
Lower Supply Guide Removal------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------32
Bi-Cell Sensor Replacement --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------32
Lower Supply Guide-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------33
Replacement ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------33
SUPPLY HOLDER ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------33
Supply Holder Removal --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------33
PLATEN MOTOR-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------33
Platen Motor Removal----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------33
PEEL MODULE----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------33
Peel Module Removal ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------33
Peel Motor Replacement-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------33
CHAPTER 7 USING FLASH----------------------------------------------------------------------------- 35
FLASH DOWNLOADING PROCEDURES -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------35
CHAPTER 8 SUPPLY SENSING SYSTEMS -------------------------------------------------------- 37
SUPPLY DETECTION/TRACKING SYSTEM -------------------------------------------------------------------------------37
SUPPLY DEFLECTOR/BI-CELL EMITTER (IR LED) ---------------------------------------------------------------------37
LOWER SUPPLY GUIDE/BI-CELL SENSOR-------------------------------------------------------------------------------38
SUPPLY FEEDING-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------38
SUPPLY SENSING-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------38
MECHANICAL ADJUSTMENTS ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------39
Bi-Cell Sensor Adjustment-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------39
REPLACING A SENSOR ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------40
SENSOR SETUP WITH VERSION 5.2 OR GREATER-------------------------------------------------------------------41
POWER UP SENSOR RECOGNITION ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------41
Performing a Sensor Display Test-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------42
TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential iii
Page 5

APPENDIX A PRINTER ERROR/STATUS CODES ----------------------------------------------- 43
READING AN ERROR LABEL --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------43
DATA ERRORS (001 - 499) ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------43
COMMUNICATION FAILURES (410 - 499)----------------------------------------------------------------------------------47
DATA FORMATTING FAILURES (571 - 619)-------------------------------------------------------------------------------48
MACHINE FAULTS (700 - 766) -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------48
HARD PRINTER FAULTS (900 - 910)-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------50
FLASH FAULTS (930 - 940) -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------50
FAULTS (950 - 999)----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------50
APPENDIX B CONNECTORS AND CABLES------------------------------------------------------- 51
Daughter Board Connectors---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------55
APPENDIX C CONNECTOR LOCATIONS ---------------------------------------------------------- 57
APPENDIX D MODEL 928 STACKER ---------------------------------------------------------------- 59
SPECIFICATIONS------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------59
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------59
INSTALLATION ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------59
TROUBLESHOOTING-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------60
Error Messages-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------60
Alignment --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------60
CABLES AND CONNECTORS --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------60
LUBRICATION-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------62
MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------62
REPLACE ROLLERS--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------63
Replacing Transport Assembly -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------63
Replace DC Motor ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------64
Replace Stepper Motor---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------64
Replace Stacker Sensors ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------64
Replace Power Supply----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------64
Replace Control Board----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------64
APPENDIX E 926 KNIFE ASSEMBLY ---------------------------------------------------------------- 65
KNIFE SPECIFICATIONS--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------65
TAG CUT DIMENSIONS ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------65
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------65
Functional Description ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------65
TROUBLESHOOTING-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------65
Evaluation of Error 760---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------65
VOLTAGE TESTS---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------66
LUBRICATION-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------66
MAINTENANCE OVERVIEW----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------66
GENERAL SAFETY TIPS --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------66
Blade Assembly Replacement------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------68
Drive Board Replacement -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------68
Motor Replacement--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------68
CONNECTORS AND CABLES --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------69
iv TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential
Page 6

List Of Tables
Table 1 – 1 Daughter Board DIP Switches ................................................................................................................ 4
Table 1 - 2. Exterior Rear (SW2 and SW3) DIP Switch Settings .............................................................................. 5
Table 4- 1. Diagnostics Tests.................................................................................................................................. 21
Table D- 1. Stacker Control Harness........................................................................................................................ 60
Table D- 2 Jam/Full Sensor Harness....................................................................................................................... 61
Table D- 3. Extended Motor Interface Harness........................................................................................................ 61
Table D- 4. AC Power Harness. .............................................................................................................................. 61
Table D- 5. Power Supply Connector J2.................................................................................................................. 61
Table D- 6. Power Supply Connector J1.................................................................................................................. 62
Table E- 1. Knife Drive Board Voltages................................................................................................................... 66
Table E- 2. Drive Board Connector J1..................................................................................................................... 69
Table E- 3. Drive Board Connector J2..................................................................................................................... 69
Table E- 4. Knife Drive Board Connector J3............................................................................................................ 69
Table E- 5. Drive Board Connector J4 To 928 Stacker Assembly............................................................................ 69
Table E- 6. Knife Drive Board Connector J5............................................................................................................ 69
List of Figures
Figure 1 - 1. 9830 Printer (Housing removed) ........................................................................................................... 1
Figure 1 - 2. Printer Unpacking ................................................................................................................................. 3
Figure 1 - 3. SW2/SW3 DIP Switch Location ............................................................................................................. 4
Figure 2- 1. Print Assembly ..................................................................................................................................... 10
Figure 2- 2. Feed Assembly.................................................................................................................................... 11
Figure 2- 3. Supply Holder Assembly...................................................................................................................... 12
Figure 2- 4. Control Panel Assembly....................................................................................................................... 12
Figure 4- 1. Test Labels.......................................................................................................................................... 20
Figure 4- 2. Loop Back Plug Wiring......................................................................................................................... 21
Figure 5- 1. Print Contrast Adjustment .................................................................................................................... 24
Figure 5- 2. Platen Motor Gear Adjustment............................................................................................................. 24
Figure 5- 4. Eccentric And Locking Screw............................................................................................................... 25
Figure 6 -1. Transformer Wiring Diagram................................................................................................................ 28
Figure 6 -2 Bridge Rectifier (Four Wires) ................................................................................................................ 28
Figure 6 -3 . Bridge Rectifier (Four Wires) .............................................................................................................. 28
Figure 6 -4.. Print Assembly .................................................................................................................................... 30
Figure 6 -5. BI-Cell Emitter Removal ...................................................................................................................... 30
Figure 6 -6. Print Assembly Plate & Printhead Module............................................................................................ 31
Figure 6 -7. Latch Removal..................................................................................................................................... 31
Figure 6 - 8. Bi-Cell Sensor ..................................................................................................................................... 33
Figure 8 -1. Bi-Cell Sensor Adjustment ................................................................................................................... 40
Figure 8 -2. Sensor Board....................................................................................................................................... 40
Figure B- 1. CN 1 IEEE 1284 Parallel Port............................................................................................................. 51
Figure B- 2. CN 2 Printhead Assembly ................................................................................................................ 51
Figure B- 3. CN 3 Platen Stepper Motor ............................................................................................................. 52
TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential v
Page 7

Figure B- 4. CN 4 Control Panel............................................................................................................................. 52
Figure B- 5. CN 5 Coax/Twinax Interface................................................................................................................ 52
Figure B- 6. CN 6 Transformer Output Power ....................................................................................................... 53
Figure B- 7. CN 7 RS-232 Serial Port................................................................................................................. 53
Figure B- 8. CN 8 Supply Sensor (Bi-Cell) .............................................................................................................. 53
Figure.B- 9. CN 10 Board Interface..................................................................................................................... 54
Figure B- 10. CN 11................................................................................................................................................. 55
Figure B- 11. CN 15............................................................................................................................................... 55
Figure B- 12. CN 16................................................................................................................................................ 55
Figure B- 13. CN 19 (to Daughter Board CN3) ....................................................................................................... 55
Figure B- 14. CN 3 To MotherBoard CN 19............................................................................................................ 55
Figure B- 15.. CN 10 Peel Motor............................................................................................................................ 55
Figure B- 16. CN 6 On-Demand Sensor.................................................................................................................. 55
Figure C- 1. Control Board Assy. (Mother Board)................................................................................................... 57
Figure C-2. Control Board Assy. (Daugher Board) ................................................................................................... 58
Figure D- 1. Stacker Control Board......................................................................................................................... 62
Figure D- 2. Stacker Lubrication Points................................................................................................................... 62
Figure D- 3. Model 928 Stacker Assembly. ............................................................................................................. 63
Figure D- 4. Lower Transport Rollers....................................................................................................................... 63
Figure D- 5. Upper Transport Rollers. ..................................................................................................................... 63
Figure D- 6. Power Supply/Control Board................................................................................................................ 64
Figure E -1. Knife Lubrication Points....................................................................................................................... 66
Figure E -2. Location of Connectors........................................................................................................................ 66
Figure E -3. Knife Assembly.................................................................................................................................... 67
Figure E -4. Drive Board Connector Locations. ........................................................................................................ 68
vi TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential
Page 8

Safety Summary
Warning and caution messages appear throughout this manual. They alert you to potentially safety hazards or
potential damage to equipment. The messages and there meaning are shown below.
WARNING
Calls attention to practices that could cause
Calls attention to improper practices that could
result in a potentially serious, even lethal injury.
Familiarize yourself with proper procedures before operating or repairing the equipment. Follow these precautions
for your own safety.
Personal Safety
• Treat every circuit as if it is “Live”. If in doubt,
check with a neon tester or voltmeter.
• Know how to turn off power in the work area
and how to obtain help in an emergency.
• Don’t work on equipment under power unless
it’s absolutely necessary. If you must, use
extreme caution.
• Shock. Don’t under estimate the danger of
shock. 12 mA causes hand muscles to
contract, so you cannot free yourself; 24 mA
has proven fatal.
• Tools. Use the right tools for the job. A tool
which slips can cause a short -- or a shock.
When working on live circuits, use tools with
insulated handles.
• Safety Devices. Don’t bypass safety devices,
particularly fuses. If a hot wire shorts to an
ungrounded frame, the frame itself becomes
hot and potentially dangerous.
• Electrical Fires Use Type C, BC, or ABC
extinguishers only.
minor injury or that could cause damage to
equipment.
Equipment Safety
Your body is a giant capacitor. It can store several
thousand volts of electricity. Digital equipment is
easily damaged or destroyed by this static
electricity. You don’t have to see a spark to ruin an
IC -- 50 volts is enough. To protect the equipment
from static damage, follow these guidelines:
• Ground yourself before reaching into the
equipment or touching any circuit board or
other electrical component. The Monarch Static
Ground Kit contains everything you need.
• Re-ground whenever you have walked away
and returned to the equipment. Be especially
careful around carpet. Carpet is a major
source of static buildup in the body. Even a
few steps can recharge you.
• The smaller the object, the greater the
precautions must be. A board in the machine
is better protected than one which is not
plugged in; a chip on a board is better
protected than one in your hand.
• Avoid touchings pins coming out of a chip or
the connector edge of circuit boards. These
metal parts have signal and data lines which
are connected directly to fragile circuits.
CAUTION
TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential vii
Page 9

viii TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential
Page 10
CHAPTER 1 PRINTER OVERVIEW & INSTALLATION
9820/9830/9835 printer operation is controlled online
PRINTER FEATURES
The 9820/9830/9835 printers are on-line table-top
printers that accepts Monarch Printer Control
Language II (MPCLII) data structure.
They use a 203 dpi thermal printhead for printing. The
printhead supports both thermal transfer (heat
activated ribbon) and thermal direct (heat activated
stock) printing.
via an RS-232 port, a Centronics® parallel port,
Ethernet adapter, or a CoAx/TwinAx port. Local
operation is controlled by the Control Panel and DIP
Switch settings and include Printer On/Off,
Diagnostics, On-Demand Mode , Error/Fault Condition
Indication and Clear.
PRINTER OPTIONS
These options are available for all printers:
• TwinAx /CoAx Interface
• Memory Expansion Board
• Ethernet Adapter Plug #117531-01 (10BaseT)
• Ethernet Adapter Plug #117532-02 (10Base2)
The following options are available for the 9835
printer:
• 917 Keypad (for offline batch entry)
• 926 Knife
• 928 Stacker (must be used with knife)
The 9835 printer also supports 9445 emulation,
connection for an optional keyboard, and a verifier.
Service can install the above options on-site.
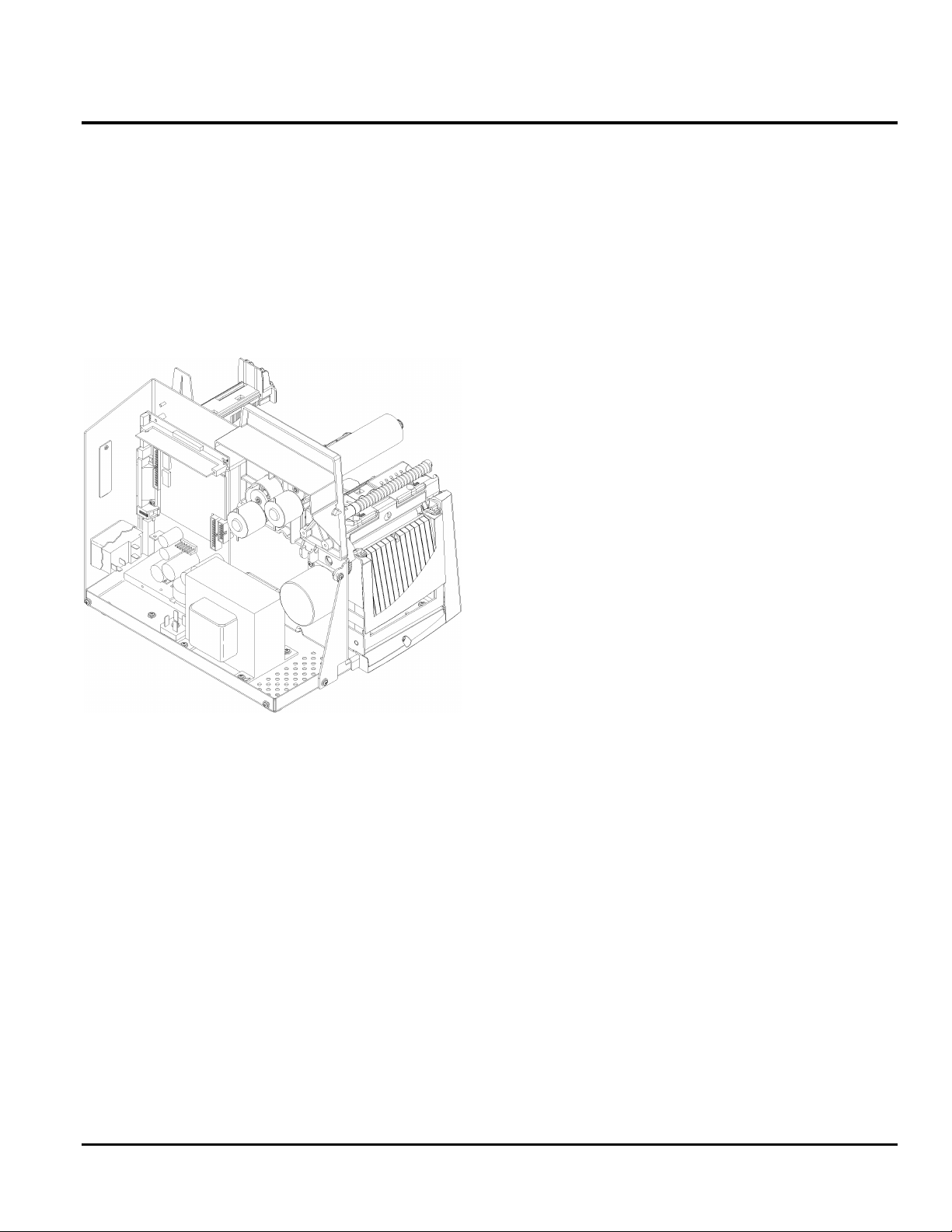
Figure 1 - 1. 9830 Printer (Housing removed)
The printers have a hinged print assembly for ease in
loading and unloading the supply. The supply spool,
lower paper guide, and ribbon spool are center
justified and can be adjusted by the user to handle
various supply widths.
The printers support fanfold or roll supply. The 9835
supports tag stock to 10 mil thickness. Standard,
smudgeless, durable, and steam resistant ribbon types
are supported by all printers. Ribbon length is 600
meters and is available in core widths of 1.3”, 1.6”,
2.16”, 3.15”, and 4.13”. Used ribbon is collected on a
take-up spool by taping the ribbon leader to an empty
core. One empty core is supplied with the printer.
The 9830/9835 models offer a Service installed tear
bar, Flash ROM programming, and an optional Peel
Module for separation of supply and backing. The
Peel Module is standard on the 9830, optional for the
9835, but not available on the 9820. The 9835
supports either a Peel Module or a knife, but not both.
NOTE: The knife and stacker attachments can be
installed by the customer or Field Service
technicians. Ethernet Adapter Plugs are
not factory installed.
PRINTER SPECIFICATIONS
Height: 12.5 inches (318 mm)
Width: 12 inches (305 mm)
Depth: 13 inches (330 mm)
Weight: 29 pounds (13 kg)
Shipping Wgt: 33 pounds (15 kg)
Power: 115 VAC, 60 Hz
July 1998 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential 1
Page 11

9820/9830/9835 Service Manual Printer Overview and Installation
Fuse, Inlet Module: 4.0 amp, 250 V Slo-Blow®
(1 required)
Fuse, Main PCB 7.0 amp, 125 V Slo-Blow
(Soldered radial leads)
Tear Bar: 9830/9835 (Service Installed)
Programming: Flash
Communications: Parallel Port; IEEE 1284
compliant or
Centronics Mode
Operating With Ribbon
Limits: 40 to 95 degrees F
(4 to 35 degrees C)
Without Ribbon
40 to 104 degrees F
(4 to 40 degrees C)
Storage 15 to 120 degrees F
Limits: (-10 to 49 degrees C)
Relative 5 to 90 % Non Condensing
Humidity:
Display: Liquid Crystal Display
3 numeric digits
Light Emitting Diodes
POWER green
SUPPLIES amber
PAUSED amber
Thermal Thin Film
Printhead: 4.15 inches (105mm) wide
832 dots
203 dots/inch (8 dots/mm)
0.0049 inch dot width,
( 0.1245 mm), center-center
Printing Thermal Transfer
Methods: Thermal Direct
Supply Types: 9820 – labels only
9830 -- labels only
9835 -- labels or tags
Ribbon Types: Roll (Non Cartridge)
Standard
Smudgeless
Durable
Steam Resistant
High Energy (9830/9835)
Ribbon Length 23,600 inches (600 m)
Ribbon Widths: 1.3 inches (33 mm)
1.6 inches (41 mm)
2.16 inches (55 mm)
3.15 inches (80 mm)
4.13 inches (105 mm)
Max Ribbon 3.6 inches (91 mm)
Roll O.D.
Ribbon Storage: 41 to 95 degrees F
(5 to 35 degrees C)
Print Speed: 2D Bar Code
2.5, 4, or 6 inches/sec
Serial Bar Code
2.5 inches/sec
Max Print Image: 4 inches wide (102 mm)
16 inches long (405 mm)
Max Print +/- 0.050 inches (1.3 mm)
Tolerance: (side to side)
Feed Method: On-Demand, Continuous, and
optional Peel Mode
STOCK SPECIFICATIONS
Ribbon: Thermal Transfer
Requirements
Stock Width: 1.2 inches (31mm)
4.25 inches (108mm) max
Version 5.2 or .75 inches (19mm) min
greater width:
Stock Length: 1 inch (25mm) min
16 inches (405mm) max
12 inches (305mm) max 9820
Version 5.2 or .75 inches (19mm) min
greater length:
Cut Length: 1.2 inches (31mm) min with
optional knife installed
Stock 0.007 inches min
Thickness: (0.18mm)
0.010 inches max
(0.25mm)
Stock Roll: Outside Diameter
9.375 inches ( 229 mm)
Inside/Core Diameter
3-4 inches (102 mm)
8100 inches (200 m) long
Stock Output: Roll or Fanfold
Stock Type: Die cut without Black Mark
Black Mark
Continuous
Coated Supplies
Version 5.2 or Die Cut Edge
greater stock type: Black Mark
Continuous
Center or Edge Aperture
2 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential July 1998
Page 12
Printer Overview and Installation 9820/9830/9835 Service Manual
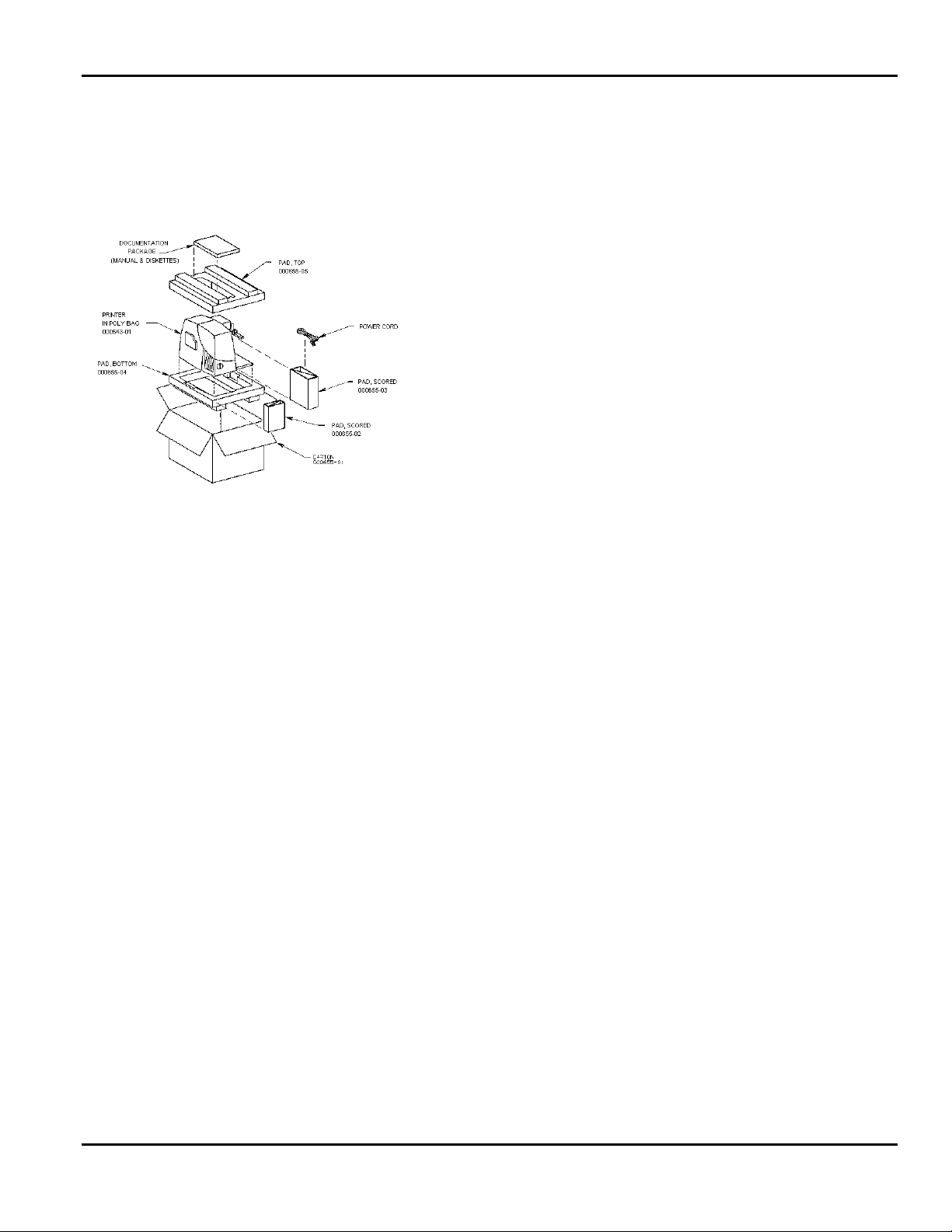
UNPACKING THE PRINTER
1. Clear a work area approximately four feet wide.
2. Open shipping carton top flaps.
3. Remove the Documentation Package. and top
pad 000655-05.
Figure 1 - 2. Printer Unpacking
4. Remove scored pad 000655-02 and scored pad
000655-03 (Figure 1-2).
5. Remove power cord from scored pad 000655-03.
NOTE: The power cord is not included with some
models.
1. Grasp printer at base by inserting hands into
cutouts in bottom pad 000655-04. Lift printer out
of box and set on solid surface.
2. Remove poly bag 000543-01.
3. Put all packing back in the carton and set carton
aside.
4. Inspect printer for damage. Report any damage
following established procedures.
5. Open printer door and remove packing tape from
the printhead assembly.
6. Remove empty four-inch core from ribbon take-up
spool.
7. Install customer’s ribbon roll.
8. Install customer’s supply stock.
DOCUMENTATION
The following Documentation Package (TC9830DP or
TC9835DP) is provided with each printer:
• quick-set Software Diskettes
• Operator’s Handbook
In addition, these documents are available on your
Service CD-ROM as Adobe Acrobat Reader files
(.pdf):
• Service Manual TC9830SM
• Programmer’s Manual TC9800PM
• TwinAx/CoAx Manual TC9800TXCX
The Operator’s Handbook (TC9830OH or TC9835OH)
can be ordered separately.
SETTING DIP SWITCHES
These printers have three sets of DIP switches. Two
sets are located on the back of the printer and
accessed from outside of the printer. They are
designated SW2 (Upper) and SW3 (Lower). The third
set is located on the Control Board Assembly daughter
board and is designated SW1. The printer is
delivered with the SW2 and SW3 DIP Switches set to
the defaults shown in Table 1-2. SW1 switch setting
are shown in Table 1-1.
NOTE: DIP switches are only read at power-up.
Turn off the printer immediately after
changing DIP switch settings.
To change the DIP switch settings:
TOOLS REQUIRED:
Small Flat Blade Screwdriver
NOTE: If software control is enabled (by setting
rear DIP switches 1 thru 3 to OFF), all rear
communications switches are ignored.
Downloaded communications settings
remain in effect until a new packet is sent
or until software control is disabled by
setting rear DIP switches 1 thru 3 to a valid
baud rate. Downloaded communications
settings remain in memory and take effect
when software control is again enabled.
DIP Switches for Version 5.2 or greater are shaded.
July 1998 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential 3
Page 13
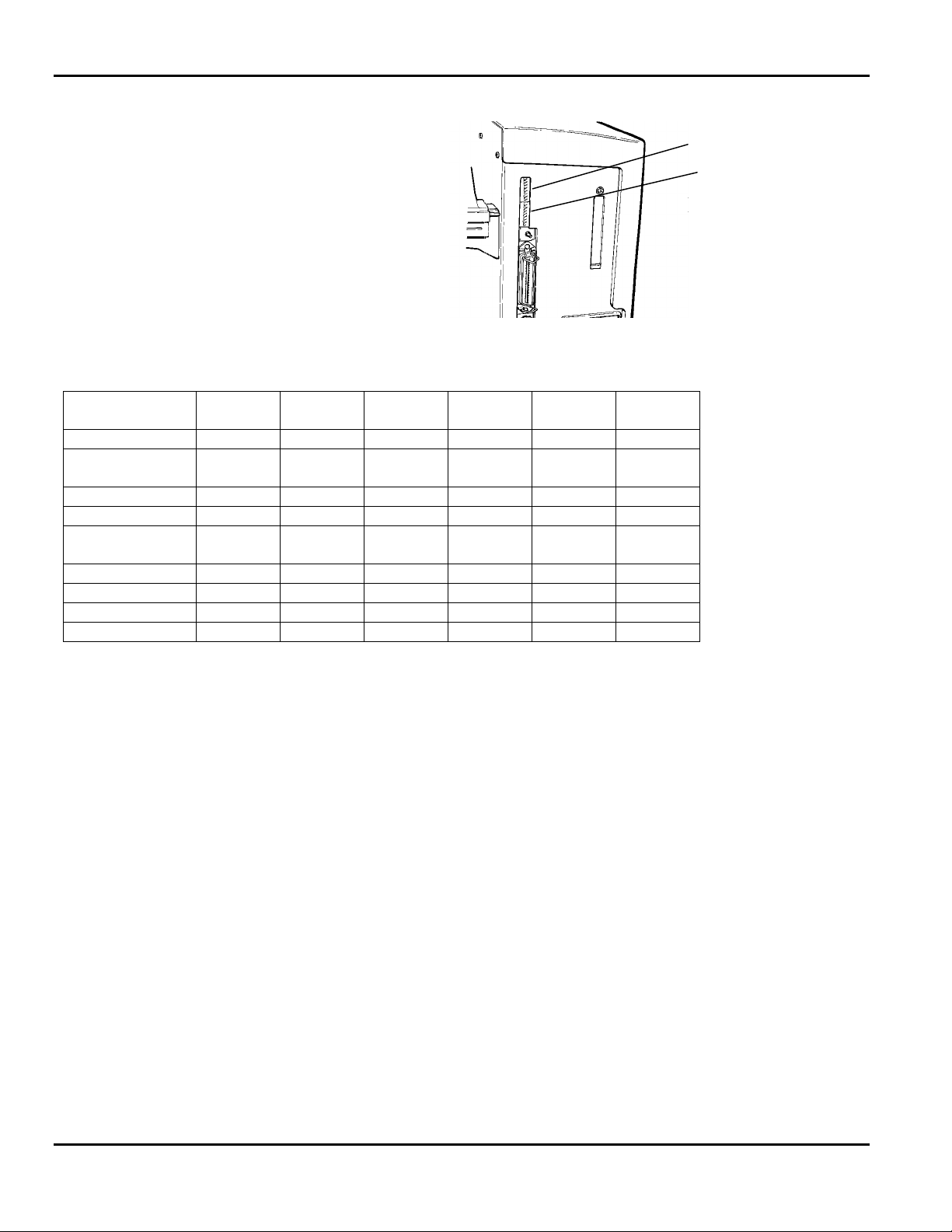
9820/9830/9835 Service Manual Printer Overview and Installation
1. Locate Upper or Lower DIP Switch block as
shown in Figure 1-3.
2. Turn printer off and change individual DIP
switches as required. Use Table 1-1 as a guide.
3. Daughter board SW1 settings are factory set.
However, when replacing the Control Board
Assembly, the new board must be set as shown
in Table 1-1.
Figure 1 - 3. SW2/SW3 DIP Switch Location
Table 1 - 1. Daughter Board DIP Switches
SW1
Model #
9820 OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF
9820 with new
sensing system
9830 No Peel OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF ON
9830 With Peel OFF ON OFF OFF OFF ON
Fox IV
printer/applicator
Paxar CL OFF ON OFF OFF ON ON
9835 With Peel ON ON OFF OFF OFF ON
9835 With Knife ON OFF OFF OFF OFF ON
9835 No Peel/Knife ON OFF OFF OFF OFF ON
ON OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF
OFF ON OFF ON OFF ON
SW2
Peel
SW3
Not used
SW4
Fox IV
SW5
Paxar CL
Upper DIP Switches
Lower DIP Switches
SW6
Memory
FUSE REPLACEMENT
Refer to the Operator’s Handbook for fuse replacement procedures.
CONNECTING TO A HOST
For instructions on connecting the printer to a host, refer to the Operator’s Handbook.
4 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential July 1998
Page 14
Printer Overview and Installation 9820/9830/9835 Service Manual
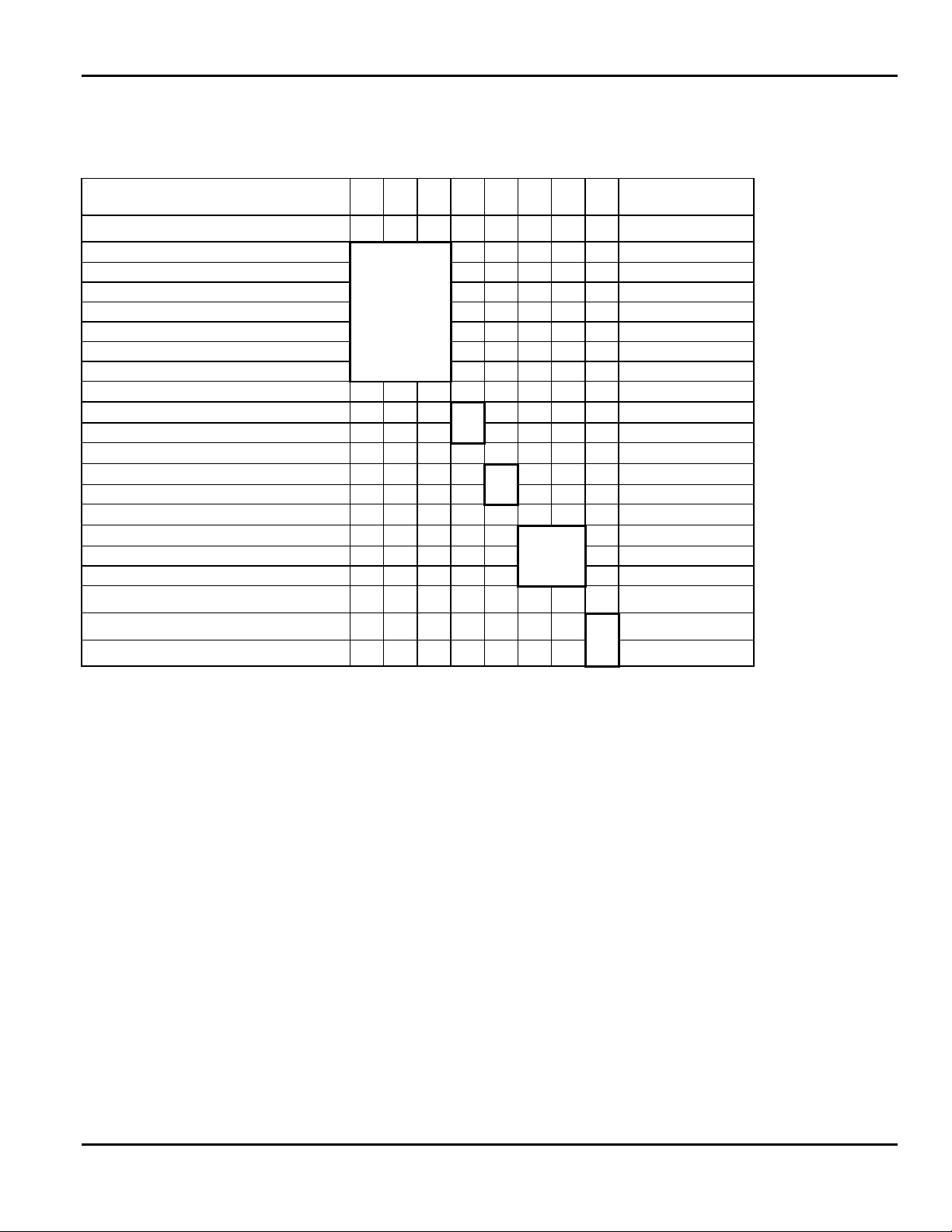
Table 1 - 2. Exterior Rear (SW2 and SW3) DIP Switch Settings
Upper DIP Switches:
SELECTION 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 DEFAULT
Baud Rate
38400 ON ON OFF
19200 ON OFF ON
9600 ON OFF OFF 9600
4800 OFF ON ON
2400 OFF ON OFF
1200 OFF OFF ON
Software Ctrl OFF OFF OFF
Data Bits
7 Data Bits ON
8 Data Bits OFF 8 Data Bits
Stop Bits
2 Stop Bits ON
ON Stop Bit OFF 1 Stop Bit
Parity
Even ON OFF
Odd OFF ON
None OFF OFF None
Parallel Port
Centronics Mode
IEEE-1284
OFF Centronics
ON
July 1998 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential 5
Page 15
9820/9830/9835 Service Manual Printer Overview and Installation
Lower DIP Switches:
SELECTION 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 DEFAULT
Flow Control
XON/XOFF ON OFF
RTS/CTS OFF ON
DTR OFF OFF DTR
Diagnostics
Normal Run Mode OFF Normal
Diagnostics Mode ON
Verifier
No Verifier
Verifier Installed
Supply Type/ Sensing
Die Cut or Edge Aperture (edge sensor) OFF OFF
Black Mark (center sensor) OFF ON Die Cut
Continuous (no sensor) ON OFF
Center Aperture (center sensor)
Ribbon
Transfer OFF Transfer
Direct ON
Feed Mode
Continuous OFF Continuous
On-Demand ON
OFF No Verifier
ON
ON ON
NOTE: DIP Switches for Version 5.2 or greater are shaded.
6 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential July 1998
Page 16
CHAPTER 2 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
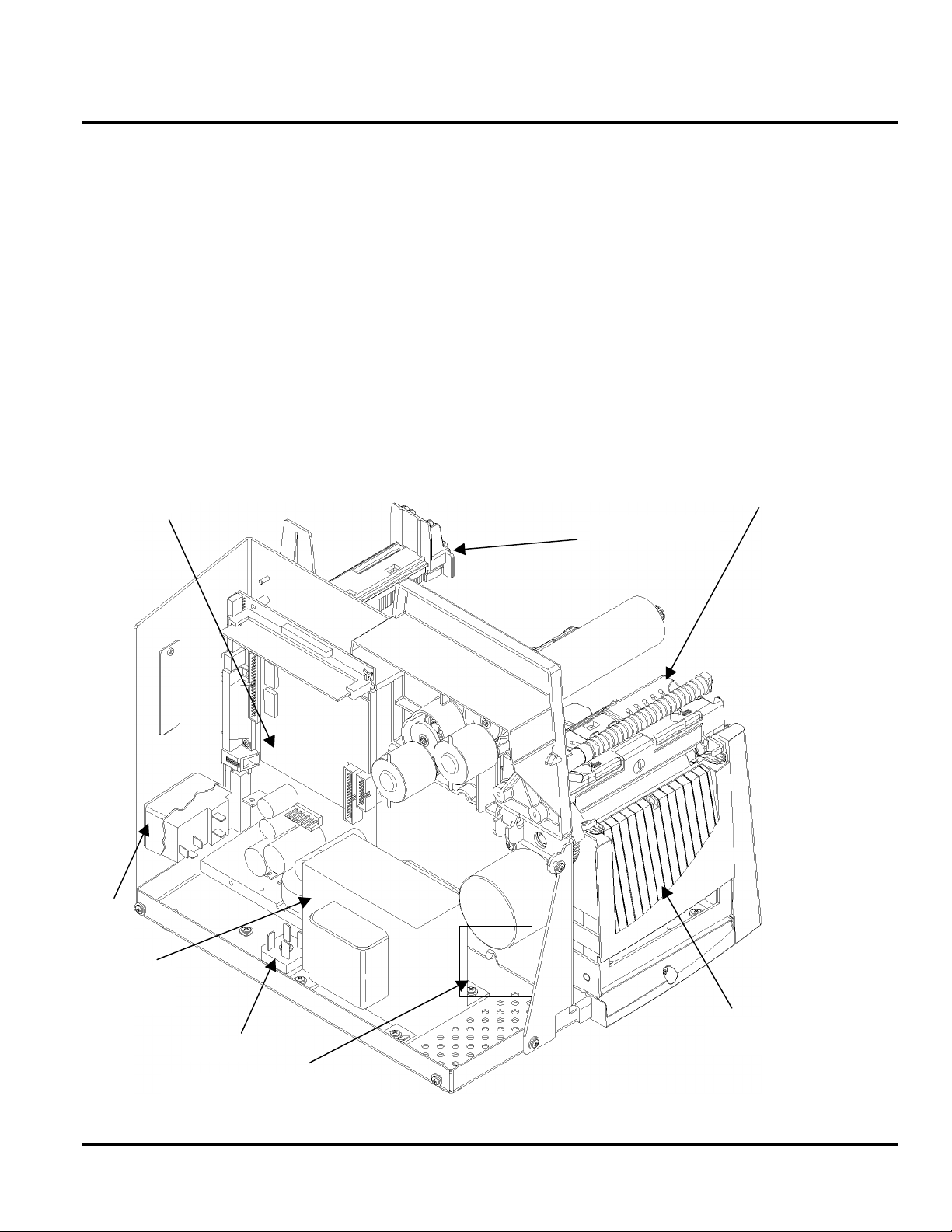
OVERVIEW OF MODULES
• Power Transformer Assembly (Power Supply and Distribution)
• Control Board Assy. (Data Handling and Control)
• Peel Module (Supply/Backing Separation)
• Print Assembly (Thermal Control and Motion Synchronization)
• Feed Assembly (Supply Alignment/Tension)
• Supply Holder Assembly (Supply Guide)
• Control Panel Assembly (Operator Interface)
Control Board
Assy.
Supply Holder Assy.
Print Assembly
AC Inlet
Module
Power
Transformer
Assy.
Rectifier
Peel Module
(inside door of 9830)
Control Panel Assembly (Mounted
to printer housing- not shown)
July 1998 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential
Page 17

9820/9830/9835 Service Manual Functional Description
Power Transformer Assembly
The power transformer assembly is located beneath
the printer’s back cover and includes three
components:
Inlet Power Module
The power module is attached to the printer’s rear
panel just in front of the Control Board Assy. Its face
plate partially extends through the rear panel to allow
users access to the power receptacle, fuse box/power
selector and the on/off switch. It has wire attachments
to ground the Power Transformer.
This module includes the following components:
• International line cord receptacle
• 4.0 Amp, 250VAC Slo-Blow fuse
Line voltage enters at the cord receptacle and passes
through a slow-blow fuse. The slow-blow fuse protects
the system from damage by power surges. Line
ground is provided to the printer via a ground harness
connected to the bottom frame.
Power Transformer
The power transformer is available in three voltages:
110V, 115V, or 220V. It is attached to the frame base
just below the print module. The transformer gets AC
line voltage from the inlet power module and converts
it to two AC output voltages. The first is sent directly
to the Control Board Assembly for futher conditioning.
The second output is sent to the bridge rectifier for
additional conversion.
The power transformer assembly outputs the required
AC and DC voltages for operation of the printer and
sends both voltages directly to the Control Board
Assy. Further conversion and/or distribution is made
by the Control Board Assy. Major functions of the
power transformer include providing power to the Inlet
Power Module, Power Transformer, and to the Bridge
Rectifier.
Bridge Rectifier
The bridge rectifier is a 1” x 1” assembly fastened to
the printer frame base left of the power transformer. It
has wire attachments to ground, the power
transformer, and the Control Board Assy.
The bridge rectifier accepts the AC from the power
transformer and converts it to DC. This voltage is
then supplied to the Control Board Assembly for
further conversion.
CONTROL BOARD
ASSEMBLY
The Control Board Assembly is located on the back
side of the printer frame wall beneath the printer’s
back cover. It consists of a mother board and a
daughter board. The two boards are replaced as a
single assembly. The board assembly is mounted on
six quick-release aluminum standoffs. Three of the
standoffs are threaded for retainer screws.
The board has three connectors (serial port, parallel
port, and bar code verifier), the print contrast control,
and three DIP switch assemblies. Two are mounted
on the long vertical side allowing for external access.
The third DIP switch is located on the daughter board.
There is a connector across the top of the board and a
hall effect sensor at the top right corner of the board to
sense a “Head Open” condition. Eight additional
connectors accept cabling to other printer assemblies.
The daughter board has a connector for cabling to the
mother board, and two connectors for functional
expansion.
Functional Description
The Control Board Assy. controls all electrical
requirements for the printer and contains interfaces for
controlling all printer functions, including Ribbon
Supply and Take-up motors, Stepper Motor, Peel
motor, Knife motor, and the Printhead. A single
microcomputing unit consisting of a 32-bit RISC
processor, 256K OTPROM (16 bits), and 256K (16
bits) of Dynamic RAM (DRAM) controls the interfaces.
Major functions of the Control Board Assy. are:
• Power Conversion
• Memory
• Printer Control
• Operator Panel Control
• Communications
• Contrast Control
• Hardware Power-up Settings (DIP Switches)
• Peel Motor Control
• On-Demand Sensor Interface
• Knife Motor
8 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential July 1998
Page 18

Functional Description 9820/9830/9835 Service Manual
Power Conversion
Power conversion interface receives AC and DC
voltage from the Power Transformer assembly.
35VAC is converted to +12VDC and -12VDC, while
the 40VDC input is converted to +25VDC and +5VDC.
Memory
Control Board Assebmly contains three types of
memory: Flash, DRAM and SRAM.
Flash Memory
Flash memory contains the necessary BOOT code
and Operating System functions for I/O routines used
for communications, the application program, fonts,
formats, and the Kernel/Library functions.
DRAM Memory
DRAM is used for variable storage, buffers, and image
memory. The base memory configuration for the
printer is 256K (16 bits).
SRAM Memory
SRAM (32K of non-volatile static RAM ) is used to
store system parameters and machine totals. All
relevant information is automatically stored in the
SRAM when the printer is turned off.
Printer Control
Control Board Assembly controls all printer functions.
It use a high performance, 32-bit, RISC based,
integrated microcontroller. The microcontroller
performs imaging and provides interfaces to printer
control operations. Major functions of the board are:
Data Handling
During operation, communication with both the RS232 port and the High Speed parallel port is
maintained. MPCL data received is transferred to
Dynamic RAM (DRAM)
Printhead Thermal Control
Printhead thermal control operation is a dynamic
closed loop servo circuit that adjusts the on/off duty
cycle in response to a continuously monitored
Printhead operating temperature and resistance.
Print Imaging
The Thermal Printhead Interface is controlled by the
microcontroller. Page image data is transferred from
Dynamic RAM to the thermal printhead as a serial
data stream.
Motion Control
Motion control sub-system controls four DC motors.
Two DC motors drive the Ribbon control, a stepper
motor controls the platen drive, and a fourth motor
drives the Peel Module.
Platen Drive Interface
Control Board Assembly controls the platen drive
motor’s torque, speed and direction through the use of
four phased 25Vdc output signals. Motor torque and
direction is controlled by changing the sequence and
pattern of the four signals. Motor speed is controlled
by increasing or decreasing the speed of the digital
pulse that make up the four phased signals.
Ribbon Drive Interface
Electronically controlled DC motors drive the ribbon
over the printhead. The motors, and associated
control software, control the tension of the ribbon web
as the ribbon spools from the supply side to the takeup side. A speed-detection method using BEMF
(Back Electromagnetic Motor Force) provides
accurate ribbon tension control.
Analog to Digital Conversion
An ML2255 A/D converter, in conjunction with the
microcontroller, monitors system functions. The A/D
converter combines an 8-Bit A/D converter, 8-channel
analog multiplexer, and a microcontroller-compatible,
8-bit parallel interface and control logic. The A/D
converter monitors various system functions and
provides information to the printers firmware to control
the supply motion, print quality, etc.
Supply Detection & Tracking System
See Chapter 8, “Supply Sensing Systems” for more
information.
Operator Control Panel
Printer Control Board uses a Peripheral Interface Unit
(PIU) to control the operator control panel interface
comprised of a three digit display, three push-button
keys and three LEDs.
An optional 917 Keypad is available for the 9835
printer (offline batch entry).
Communications
RS-232 interface and the Centronics/IEEE 1284
compliant parallel interfaces are mounted on the
Control Board Assy. Both are located on the left edge
of the board and accessed by the user at the rear of
the printer near the supply roll.
July 1998 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential 9
Page 19
9820/9830/9835 Service Manual Functional Description
RS-232 interface
This interface allows connection to devices capable of
RS-232 communications. The interface is incorporated
in the microcontroller and has DIP switches to set
communications parameters. The DIP switches can
be set manually by the user or through software
control.
Centronics IEEE-1284 Parallel Interface
This interface accommodates high data rates, up to
2M Bits/Second.
IEEE 1284 Bi-Directional Parallel Interface
An IEEE 1284 High Speed Bi-directional Parallel
interface provides parallel communications. The
microcontroller directly controls the port. The
interface allows compatibility with the Centronics
interface as well as allowing for High Speed Bidirectional communications.
NOTE: Third party LAN devices are connected
through the parallel interface to allow the
printer to interface different LAN networks.
Contrast Control
A manual contrast control, located at the edge of the
Control Board Assy., extends out of the rear cover. It
is used for fine adjustments to the print contrast
values.
Hardware Power-up Settings (DIPS)
Two 8-switch DIP switches, located on the back panel
of the printer above the contrast adjustment, control
the default power-up configuration of the printer.
Settings include the serial port settings, diagnostics,
ribbon setup, printer mode and supply type.
Peel Module Assembly
The peel module separates the supply from the
backing paper. It consists of an on-demand sensor,
rollers, and a 12Vdc motor drive. Dip SW1 (switch 2)
located on the daughter board enables and disables
the peel function.
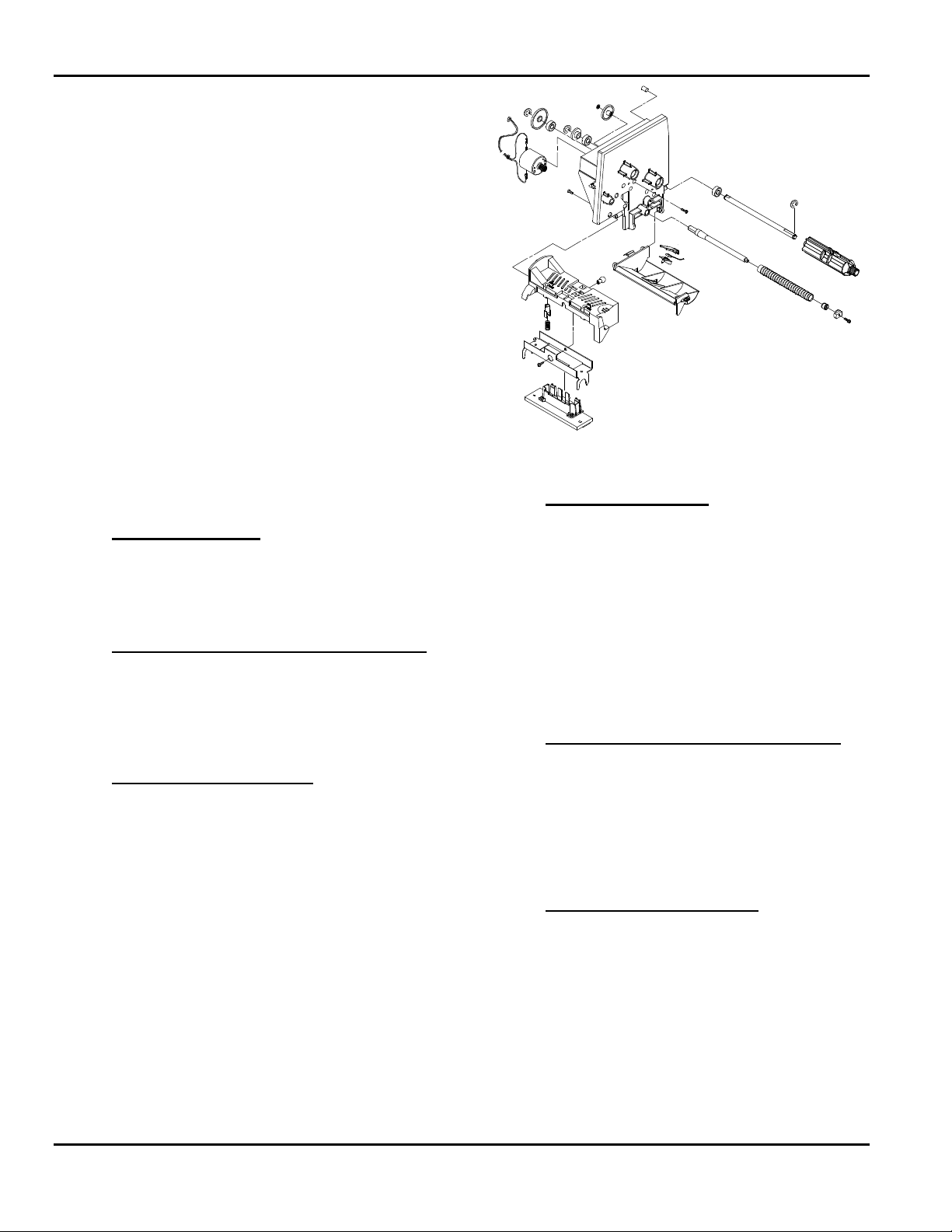
PRINT ASSEMBLY
This Print Module is a plastic casting located inside
the printer’s hood. It is attached to the mid frame by
two bearing blocks which capture studs on the module
back plate. Components of the Print Module are:
Figure 2- 1. Print Assembly
Thermal Printhead
The printhead is located at the bottom front of the
module. It is held in place by a plastic carrier which
acts as an interlock to a formed metal bracket. The
bracket is center-mounted and pivots to ensure an
even pressure on the supply. The printhead bracket
has two alignment loops which slip over the platen
roller to assure dot row to platen roller alignment. The
printhead mount also has two spring loaded
adjustment knobs to adjust printhead pressure for
wide or narrow supplies. A 30 pin ribbon cable
connects the printhead to the Control Board Assy
Ribbon Supply & Take-up Spools
The ribbon supply and ribbon take-up spools are
located on the supply side of the module. Each spool
shaft extends through the module wall and connects to
its own DC drive motor. The spools are designed to
handle a detented ribbon core so when ribbons of
various widths are installed they maintain center
justification.
Ribbon Transfer Rollers
Two ribbon transfer rollers are located on the supply
side of the module. The rollers are ribbed and
attached to metal shafts by retainer screws. One sits
at the very front of the module wall above the
printhead while the other is positioned just above the
supply deflector.
10 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential July 1998
Page 20
Functional Description 9820/9830/9835 Service Manual
Ribbon Spool Drive Motors
wo DC ribbon drive motors are mounded to the back
of the module wall. Each motor drives a ribbon spool.
The motors are connected directly to the Control
Board Assembly via separate two-wire harness.
Supply Deflector and Bi-Cell Emitter
(IR LED)
See Chapter 8, “Supply Sensing Systems” for more
information.
Ribbon Transfer Rollers
The two ribbon transfer rollers allow ribbon tension
adjustments. Each roller has an eccentric which
allows slight skew adjustments to each, which in turn
affects the ribbon tension.
Functional Description
The print module, performs ribbon drive operations,
provides mechanical ribbon tension adjustments,
performs print functions, helps maintain supplies
tracking, and houses half of the sensor assembly. It is
controlled by the Control Board Assembly.
Ribbon Drive Operation
The ribbon drive operation is made up of two ribbon
spools, two 25Vdc drive motors, and two ribbon
transfer rollers. It is controlled by the Control Board
Assy. Each drive motor sends continuous information
to the Control Board Assy. where it is used to evaluate
ribbon conditions, maintain optimum ribbon tension,
and sense the end of ribbon condition. This system
eliminates the need for ribbon sensors.
Printing
The printhead has a line array of 832 dot elements
sized to produce 203 dots per inch. Printing occurs by
sending image data to the printhead one line at a
time. Each time a line of data is received,
corresponding dots on the printhead are heated to
create an image line on the stock. Successive image
lines generated across moving stock make up the total
image. The Control Board Assy. controls all image
data sent to the printhead, and regulates the energy
level of the printhead. Energy levels are raised and
lowered to create darker or lighter print respectively.
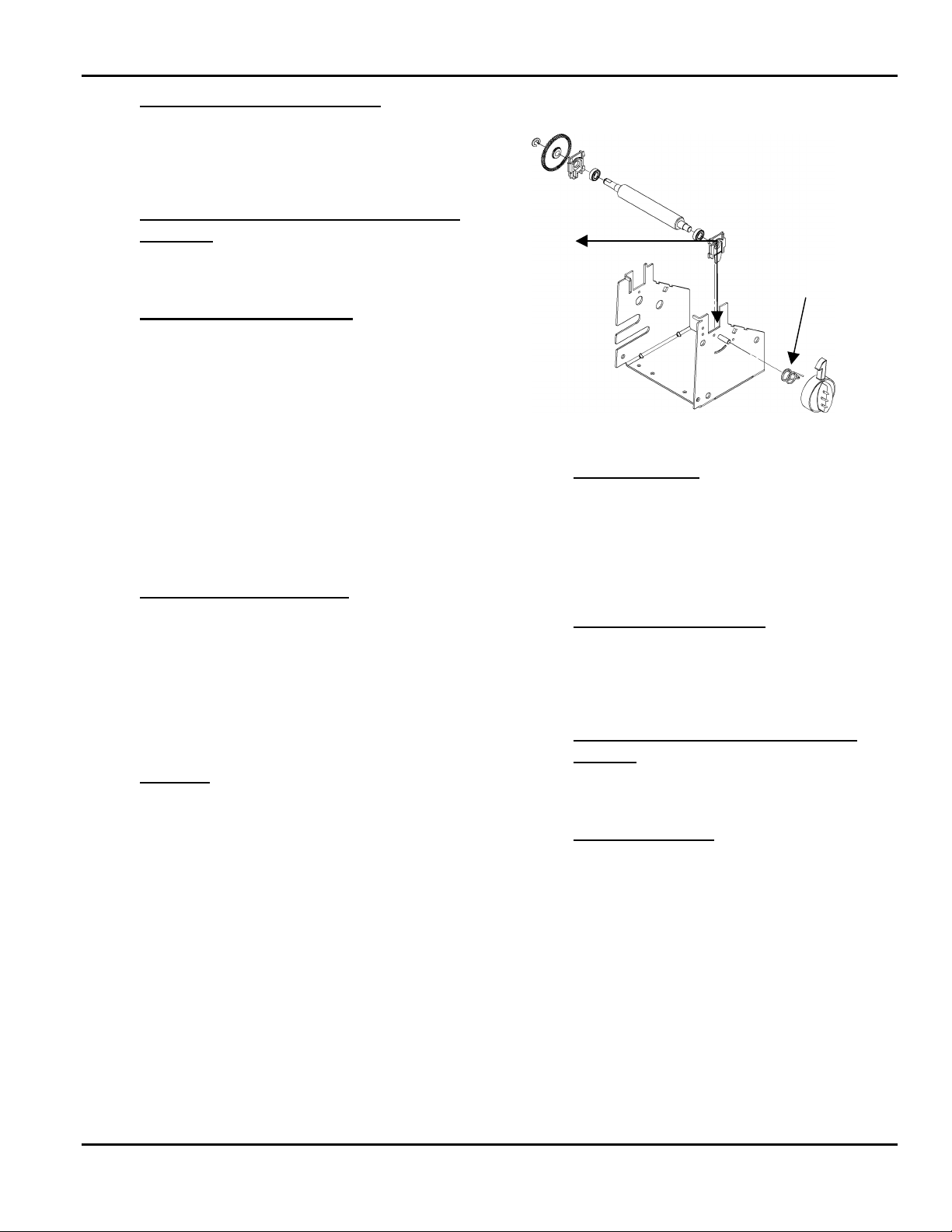
FEED ASSEMBLY
The feed module components are mounted on a metal
frame positioned beneath the Print module and
fastened to the printer base. Components of the feed
module are:
Bearing
Blocks
Spring
Latch
Figure 2- 2. Feed Assembly
Platen Module
The platen rollers are on top of the feed module frame
just beneath the printhead. It is held in place by two
bearing blocks latched on the frame sides. The inner
side of the platen roller shaft extends through the
inside wall of the feed module where a drive gear is
attached.
24VDC Stepper Motor
The stepper motor is located behind the mid-frame of
the printer. Its drive shaft and gear extends through to
the space between the printer mid-frame and the feed
module frame.
Lower Supply Guide and Bi-Cell
Sensor
See Chapter 8, “Supply Sensing Systems” for more
information.
Printhead Latch
The printhead latch is spring loaded and mounted on
the outside of the feed module frame; within the latch
fascia. It locks the printhead in position.
Functional Description
The feed module transports supply through the printer
and across the printhead. It also maintaining proper
alignment, tension, and speed. This is accomplished
by sensing the stock position while securing the
printhead down onto the platen roller. Major functions
are supply feeding and supply sensing. See Chapter
8, “Supply Sensing Systems” for more information.
July 1998 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential 11
Page 21
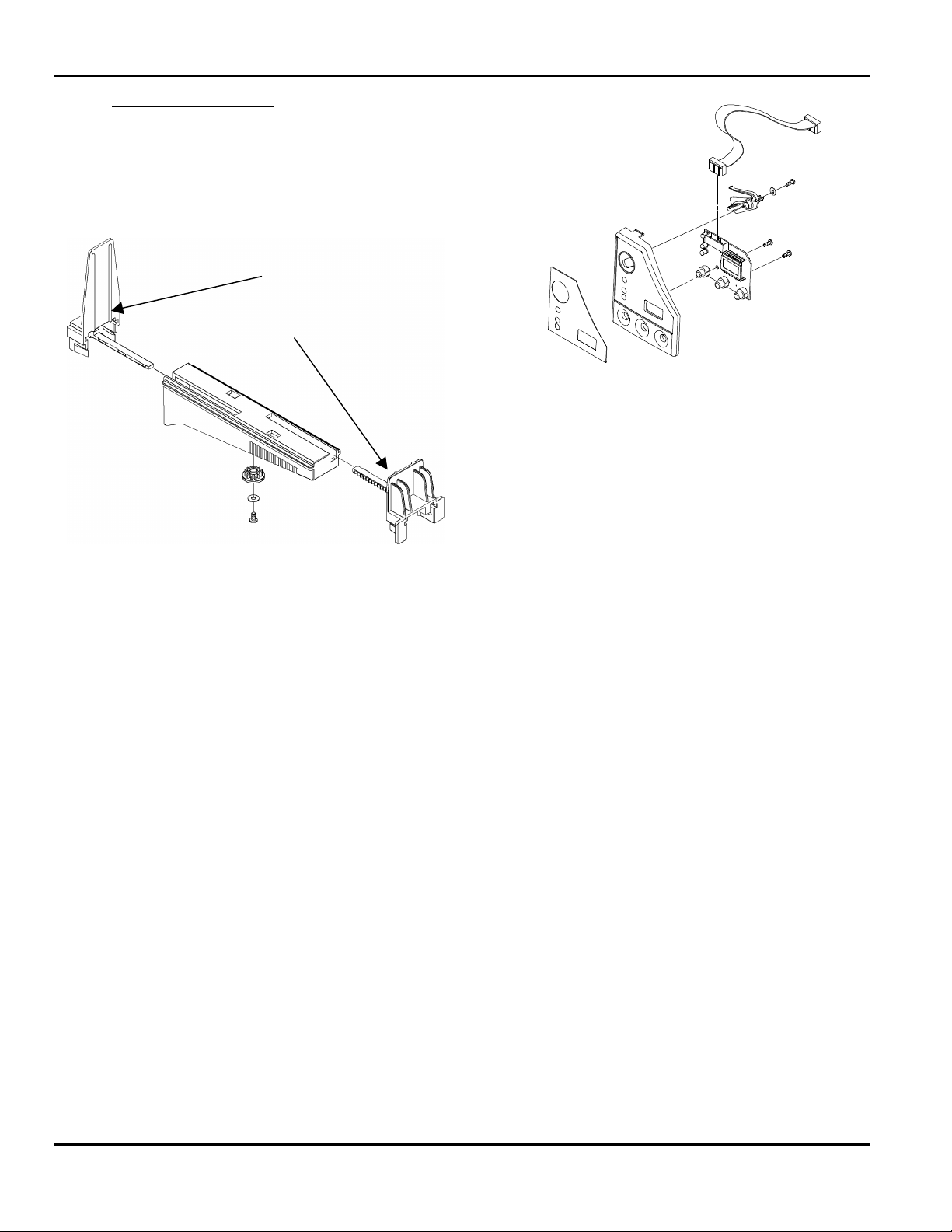
9820/9830/9835 Service Manual Functional Description
Printhead Locking
Printhead release knob is used to release the print
module from its open position.
SUPPLY HOLDER ASSEMBLY
Inner Guide
Outer Guide
Figure 2- 4. Control Panel Assembly
Functional Description
Figure 2- 3. Supply Holder Assembly
Functional Description
The supply holder module holds the supply roll in a
center-justified position to ensure optimum supply
tracking. The guides are gently pushed inward until
they center the roll and back off to the next detent
position when released.
The front guide pivots down for supply
loading/unloading. When loading fanfold supply, the
stack is placed behind the printer or under the table
and fed through the supply holder guides.
CONTROL PANEL ASSEMBLY
The Control Panel Assembly is mounted on the front
of the printer. The associated electronic components
are mounted on a circuit board behind the panel
fascia. A ground wire connects the board to the
chassis ground and a single wire harness connects it
to the Control Board Assy.
LEDs
LCD
Feed
Pause
Clear
Feed + Pause
Feed + Clear
The three LEDs indicate general printer
status and activity.
The three-character LCD identifies
specific printer conditions through the
use of numeric codes. These codes are
listed and described in Appendix A.
In Normal mode, advances a label from
the printer. In Offline mode or Online
Diagnostic mode, prints a test label.
Stops the current batch from printing.
Printing resumes when Pause is
pressed a second time.
Cancels the current batch from being
printed if pressed for only a moment.
Cancels all batches associated with the
current format if pressed and held for
two seconds. Cancels some error
codes that appear on the LCD.
In Normal mode, prints a test
label.
In Diagnostics mode, places the
printer in data dump mode. See
Chapter 4, “Diagnostics” for
more information.
12 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential July 1998
Page 22

CHAPTER 3 TROUBLESHOOTING
This chapter contains suggestions for diagnostic and repair actions.
PRELIMINARY CHECK
The following checks should be made before going further:
1. Are the DIP switches set properly to match communication values and existing supply?
See Chapter 1 for DIP Switch settings and procedures.
2. Ensure that the proper fuse has been installed. See the Operator’s Handbook.
3. Inspect printhead to ensure it is locked in place.
4. Ensure stock and ribbon are properly loaded. Refer to the Operator’s Handbook for printer loading instructions.
ANALYZING FAILURE DURING POWER UP
Each time the printer is turned on, it runs Power-up Diagnostics. These Level 0 Diagnostic Tests are described in
detail in Chapter 4. If any of the first eight tests result in a fault condition, a three digit status code is indicated on the
Control Panel LCD. As shown in Figure 4-2, if any of the following status codes are indicated, the printer will stop
operating, and remain in a “hold mode” until CLEAR is pressed:
909 Memory Failure 765 Printhead Test Failure
911 Virgin Reset
NOTE: These error codes only appear during a power-up test sequence. If a “765” status code is indicated during
the power on tests, the printer is still operational but may not be able to print all of the commanded label
images.
The Control Panel is tested during the power-up tests by blanking the three digit LCD display momentarily. This is the
final Level 0 test, and would be noticed only if a “765” status code were previously indicated.
EVALUATION OF A 616 ERROR (DOT SHIFTING FAILED)
This error occurs if at least one dot element is non-functional. Shifting the image pattern will not work. You must
replace the printhead.
EVALUATION OF A 704 ERROR (OUT OF SUPPLY)
This error occurs when the sensor is not sensing the supply. This can happen if there is a problem with the supply or
with the sensor. Perform the following procedure:
1. Verify stock is loaded and properly aligned in the supply guide.
2. Verify that DIP switches and online settings are set for proper supply type.
3. Check Bi-cell alignment using gray scale, and check operation using diagnostic procedures (be sure to check
the harness). See Sensor Tests and Bi-Cell Sensor Adjustment, in Chapter 8, for instructions.
4. Verify Emitter is operational (including the harness) by using an infrared detector probe.
July 1998 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential 13
Page 23

9820/9830/9835 Service Manual Troubleshooting
EVALUATION OF A 754 ERROR (OUT OF RIBBON)
This error occurs whenever the ribbon stops turning. This can happen if the motors are not working, the stock is
binding, the platen is sticky, or if any condition is present that prevents ribbon rotation. Perform the following
procedure:
1. Verify Ribbon Motors are turning. If they are not, check connectors to the Control Board Assy. and the
connections to the motors.
2. Verify Platen Motor is feeding. If is is not, check the connections.
EVALUATION OF A 755 ERROR (PRINTHEAD OPEN)
This error occurs if the printhead is not functioning properly. Perform the following procedure:
1. Ensure the printhead is properly latched.
2. Verify that the magnet is present and inserted properly.
3. Verify that sensor is functioning properly.
EVALUATION OF A 765 ERROR (PRINTHEAD FAILURE)
This error occurs if a dot is out of specification. This error can occur even if print quality is not visibly affected.
Operation can be continued until the problem is corrected. Perform the following procedure:
1. Check connections to the printhead.
2. Check the printhead harness.
3. Check the printhead itself and replace if necessary.
EVALUATION OF THE CONTROL BOARD ASSY.
The following status codes indicate the Control Board Assembly has a fault.
900 RAM Test Failure 905 Illegal Interrupt
901 ROM/EPROM Test Failure 906 Power Failure
902 Timer Failure 907 No Application Memory
903 Interrupt Test Failure 908 NVRAM Checksum Failure
904 No Kernel Memory 910 Warm Restart
1. To determine if this fault is permanent or temporary, turn the printer off, wait 15 seconds then turn the printer on
again. If any of these status codes are repeated, turn off the printer and replace the Control Board Assy.
2. Print a test label. See Test Label (Level 1), in Chapter 4, for instructions on printing a test label.
3. Place the printer in Data Dump mode and send data to the printer.
EVALUATION OF COMMUNICATIONS
If the printer functions properly off-line, examine communications. There are two communication paths for the
printer. The RS-232 serial path uses a 25 position connector. The IEEE-1284 parallel path consists of an external
36 position connector, CN1, and an internal 40 position connector, CN5, that is used to support the Coax/TwinAx
Interface. CN1 also supports an external Ethernet adapter.
14 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential July 1998
Page 24

Troubleshooting 9820/9830/9835 Service Manual
The external Coax/TwinAx Interface is a 15 position connector into which is plugged either a Coax adapter cable or a
TwinAx adapter cable. (All electronic activity for the serial port is limited to the Control Board Assembly. All
electronic activity through CN1 is limited to the Control Board Assy.) There is a small circuit board mounted on the
inside rear printer wall that interconnects the 15 position external connector with the internal CN5. Both CN1 and
CN5 share common PCB electronics.
1. Make sure the printer is plugged in and connected to a host with the proper cables. See Connecting to a Host,
in Chapter 1.
2. Compare host communication values to values reported on the test label. See Test Label (Level 1), in Chapter
4, for instructions on printing a test label.
3. Check printer ports using SENDFILE to send an ENQ.
GENERAL TROUBLESHOOTING SUGGESTIONS
There are a number of printer self-reporting fault detection/fault isolation avenues built into the 9820/9830/9835
printers. Three digit status codes, detailed in Appendix A, all help to pinpoint the problem. In addition, the printer
provides status information in the two test labels, in the SENDFILE service diagnostics tests, and in information
labels printed in response to a FEED command following a status code between 571 through 619.
PROBLEM SUGGESTED ACTION
Printer does not print test labels Check for status code on LCD.
Verify stock is installed correctly.
Verify ribbon is installed correctly.
Verify printer voltage measurements.
Verify printhead is installed correctly.
Verify printhead harness connection is on PCB.
Verify DIP switch settings.
Confirm supply feed operation.
Confirm ribbon feed operation.
Perform sensor display service test using SENDFILE.
Perform test label immediate command.
Replace control panel.
Replace printhead.
Replace Control Board Assy.
Printer only prints test labels Check for status code on LCD.
Verify comm DIP switch settings.
Perform serial /parallel comm test.
Perform data transfer immediate commands.
Transfer format using Windows Terminal.
July 1998 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential 15
Page 25

9820/9830/9835 Service Manual Troubleshooting
PROBLEM SUGGESTED ACTION
Partially printed data Check for status code on LCD.
Verify wide/narrow printhead adjustment.
Perform sensor display service test.
Verify ribbon installed correctly.
Confirm ribbon feed operation.
Clean printhead.
Confirm supply sensor operation.
Send a packet you know has no syntax errors.
Printing shadows or smears Check status code on LCD.
Verify wide/narrow printhead adjustment.
Perform contrast sensor display service test using SENDFILE.
Verify supply installed correctly.
Verify ribbon installed correctly.
Confirm stock feed operation.
Confirm ribbon feed operation.
Clean printhead.
Light printing Check status code on LCD.
Verify wide/narrow printhead adjustment.
Perform contrast sensor display service test using SENDFILE.
Adjust contrast.
Verify ribbon installed correctly.
Confirm ribbon feed operation.
Check platen roller surface.
Clean printhead.
Heavy printing Check status code on LCD.
Perform contrast sensor display service test using SENDFILE.
Adjust contrast.
Verify correct stock/ribbon installed correctly.
Clean printhead.
Voids in printing Check status code on LCD.
Confirm test label printhead operation.
Perform printhead sensor display service test using
SENDFILE.
Replace printhead.
Confirm fault via immediate command service test.
Confirm test label printer config parameters.
Verify communication DIP switch settings.
Send a corrected format packet.
Perform terminal data transfer tests.
Replace Control Board Assy.
16 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential July 1998
Page 26

CHAPTER 4 DIAGNOSTICS
If you have any problems using SENDFILE, refer to the Sendfile Manual on your Service CD-ROM.
The following diagnostics are resident in the
9820/9830/9835 printer’s firmware ROM:
• Power-Up Self-Test
• Test Label
• Service Diagnostics (Level 1)
Data Dump Mode
Diagnostics Test Mode
Off-line Diagnostics Tests
Loopback Test (Level 2)
Parallel Port Test (Level 3)
POWER-UP SELF-TEST
When the printer is turned on, a test sequence is
initiated. The diagnostics routine initializes the
Control Board Assembly and evaluates the Printhead.
The test sequence is:
• Non-Volatile RAM Byte Test
• Version String Mismatch
• Printhead Dot Resistance
A failure in any of the test sequences results in the
display of an error code on the 3 digit Control Panel
Display.
An error during the printhead dot test indicates that
bar code scan quality may be compromised.
However, such a failure may not be evident in text
printing.
• Different versions of software installed.
• Clearing memory with the “Reset NVRAM”
function in service diagnostics.
• Memory corrupt due to a hardware/software
error.
If the restart flag was set during these diagnostic tests,
the software re-allocates all available memory as
blocks of working storage. Then the routine performs
an integrity check on the working storage to verify that
it is accessible.
When the version string mismatch test passes, the
firmware begins the printhead dot resistance test.
Printhead Dot Resistance
The printhead resistance routine is a hardware test of
all 832 individual dots for correct resistance value. If
the test passes, the printer switches to online ready
mode. If the test detects any dots that are open or
have high resistance (>852 Ohms), error #765
appears on the LCD. Failure does not halt printer
operations.
TEST LABEL (LEVEL 1)
Test Label can be performed in Normal or Diagnostics
Test mode. When the printer finishes printing the two
test labels, it returns to the ready state.
MATERIALS REQUIRED:
NV RAM ByteTest
The Non-Volatile RAM test checks the first two bytes
of NVRAM. If the test passes, the next test begins. If
the test fails, error #909 appears on the display.
Version String Mismatch
The version string test compares the software version
in ROM to the version in RAM. If the versions match,
the current software is in RAM and the software clears
storage RAM. Then the software clears the working
storage routine. If the versions in ROM and RAM do
not match, error #911 appears on the LCD.
System Restart Condition
The three conditions that cause a system
restart are:
July 1998 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential 19
Installed supply stock, at least 1” wide X 2” long.
1. If the printer is in Normal Mode, press Feed +
Pause at the same time. If the printer is in
Diagnostics Test mode, press Feed.
Two test labels print (See Figure 4-3). If the test
fails, an error appears on the LCD. Press Clear
to reset the printer.
2. Examine the test labels for smearing, image
washout, print uniformity, contrast, missing dots,
or out of specification readings.
Page 27

9820/9830/9835 Service Manual Diagnostics
Parallel Port Timeout Test
Test Label
Virgin Reset
SENDFILE Diagnostic Tests
Test Label
Sensor Display
Service Totals
Immediate Commands
Job Request
Printer Interactive Mode
Supporting Hardware Accessories Required:
• SENDFILE and Flashloader requires a laptop
or PC connected to the printer via a serial
cable. PC should be capable of
communicating at 38.4 baud.
Figure 4- 1. Test Labels
The first test label prints firmware version and current
printer configuration in I packet format (refer to the
printer’s Packet Reference Manual ).
NOTE: Some reported settings may not be
configurable on a given printer:
A System Setup
B Supply Setup
C Print Control
D Monetary Formatting
The second label prints basic diagnostic information:
E Control Characters
F Serial Comm Settings
G Backfeed Control
M Memory Allocation
• Serial Loop Back Test requires Loop Back
Plug #114271.
Accessing Diagnostic Modes
To use the different modes available in Service
Diagnostics, you must have lower DIP switch 3 turned
on and the display reads 000.
From the 000 display, press Feed and Clear at the
same time until you see 001 (data dump mode),
002 (serial loop back test), or
003 (parallel port test). Each mode is activated by
pressing Pause.
Total Inches Printed
Current Inches
+40 VDC Value (s/b 30-47)
Dot Resist (s/b 832 Ohms)
Installed Options:
M
R
V
P
C
S
X
256K memory expansion
RS-232 option (Keypad)
Verifer
Peel
Cutter
Stacker
V5.2 sensing system
No of Bad Dots (s/b < 3)
Total RAM (Max 512K)
DIP Settings
Contrast Pot
SERVICE DIAGNOSTICS
Service Diagnostics is initiated by setting the Lower
DIP switch 3 to the ON position before powering up.
At power-up, 000 is displayed on the control panel.
Two Service Diagnostic modes are available:
• Data Dump Mode
• Diagnostics Test Mode
Off-line Diagnostics Tests
Serial Loop Back Test
Data Dump Mode
To use data dump mode:
1. Set lower DIP switch 3 to ON. The display reads
000.
2. Press Feed and Clear at the same time. The
display changes to 001 (Mode 1).
3. Press Pause to enter data dump mode. Two
blank labels feed and the display reads 111.
4. Download the data stream you want to dump (print
on a label).
5. Press Feed and Clear at the same time to exit
data dump mode. The display reads 000.
Data dump mode captures all data being sent to the
printer and holds it in a buffer. No data is acted upon
(ex: Immediate commands or Job request packets).
Once the buffer is full, a label automatically prints with
the downloaded data printed on it. You must press
Feed to print a label if the amount of data sent does
not fill the buffer to the required level.
NOTE: If you are sending data down through
SENDFILE, be sure to disable ENQ. This
20 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential July 1998
Page 28

Diagnostics 9820/9830/9835 Service Manual
applies only when you are in Data Dump
mode.
Serial Loop Back Test
This test evaluates serial port circuits on the Control
Board Assembly (nothing external to the Control
Board), so communication setting DIPs 1 through 10
do not affect this test.
TOOLS REQUIRED:
• Loop Back Plug 114271
1. Turn printer off and disconnect host serial port
connector from CN 7.
2. Install Loop Back Plug into RS-232 Serial Port
CN 7. See Figure 4-4 for plug wiring.
3. Turn the printer on and go into Diagnostics Test
Mode 2 (002). This is accomplished by pressing
the Feed or Clear key from Mode 1 (001).
4. Press PAUSE.
Jumper Pins Signal
2-3 TXD-RXD
To change the parallel port timeout:
1. Set lower DIP switch 3 to ON. The display reads
000.
2. Press Feed and Clear at the same time until the
display reads 003 (Mode 3).
3. Press Pause to enter the parallel port timeout
mode.
4. Press Clear to increase the timeout and press
Feed to decrease the timeout.
The display changes to show the amount of the
timeout.
5. Press Feed and Clear at the same time to exit
data dump mode. The display reads 000.
The amount of data the application processes from
the communication driver is 128 bytes at a time. Flow
control is now activated when there is 512 bytes left
available in the buffer and flow control is now
deactivated when there is 1024 bytes available in the
receive queue.
Diagnostics Test Mode
There are two types of Diagnostics Tests; those
performed off-line by pressing some keys and those
performed using SENDFILE. Table 4-1 lists the tests
and procedures that can be performed in Diagnostics
Test mode.
4-6 RTS/DSR
5-20 DTR-CTS
Figure 4- 2. Loop Back Plug Wiring
5. The test runs automatically once initiated, and
takes approximately two seconds.
6. If the test passes, 222 is displayed. If the test
fails (Loopback Plug not installed, installed
incorrectly, or bad Control Board Assy.
components) error #499 is displayed.
7. Press Feed and Clear to exit.
Parallel Port Test
The parallel port timeout test can be used with version
3.1 or greater firmware. When the parallel port is in
flow control, the printer continues to accept data one
character at a time until the entire receive buffer is
full. The rate that data is accepted can be set through
this diagnostic mode. The default is one character per
every 10 seconds. This value prints out on the test
label.
Table 4- 1. Diagnostics Tests
DIAGNOSTICS
TEST
Loop Back Test off-line
Virgin Printer Reset off-line
OFF-LINE
ONLINE KEYS
Pause
Feed+Clear+
Pause
Performing a Virgin Printer Reset
A Virgin Printer Reset sets the printer to its original
factory settings and erases all data in RAM. To
initiate a virgin reset, hold down Feed + Clear +
Pause for approximately two seconds, and release.
NOTE: Using “Virgin Reset Command“ in
SENDFILE requires the Service Password.
Printing a Test Label
Print a test label by pressing the Feed while in Data
Dump mode or Diagnostics Test mode. For more
information on printing a test label, see “Test Label,”
earlier in this chapter.
July 1998 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential 21
Page 29

9820/9830/9835 Service Manual Diagnostics
22 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential July 1998
Page 30

CHAPTER 5 TESTS AND ADJUSTMENTS
Bridge Rectifier
SERVICE TESTS
The following tests are described in this section:
• Voltage Tests
• Continuity Tests
• Supply Quality
NOTE: Sensor tests are described in Chapter 8,
“Supply Sensing Systems.”
CN6 Power Supply
Pin numbers are read from left to right including
empty positions.
• Transformer secondary non-rect AC output
Pin 1 & 3 = 15VAC Pin 3& 4 = 15VAC
• Transformer secondary rect DC output
Pin 5(+) & Pin 6 (Grnd) = 40VDC
Continuity Tests
WARNING
Failure to turn off and unplug printer for these test
could result in electrical shock.
Transformer - Primary Side
Should be tested at AC Inlet under the boot.
• Black & Brown = 0-2 ohms
• Black-White & Brown-White = 0-2 ohms
• Orange & Orange-White = 0-2 ohms
• All other combinations must read infinite
(open) resistance.
Transformer - Secondary Side
Ohm reading must be taken with power off.
• At CN6, all combinations of
Pins 1, 3, & 4 = 0-1 ohms
• At bridge rectifier, reading across both
Yellow wires = 0-1 ohms
• All other combinations must read infinite
(open) resistance
1. Set Ohm meter to 2000K scale.
2. Remove wires from device.
3. Black lead on Red wire terminal (labeled + on
device, at the notched corner) and leave attached
while moving red lead to other terminals of the
device should yield:
• Red lead on either yellow wire 90° from that
corner should read approx. 500 ohms.
• Red lead on black wire (diagonal from red
wire terminal) should read approx. 1000
ohms.
Switch Red lead to red wire terminal and move Black
lead to all other positions. The result should be
infinite ohms.
Head Open Sensor
Hall Effect Sensor (HALL1) is located at the top of the
board and must be within 6 mm of the magnet.
Top leg of chip (closest to the top edge of the board)
changes between +5VDC and ground in response to
the magnet in the Print Module. It should be at 0VDC
(with respect to frame ground) when head is closed. If
magnet is bent, operation may be affected.
Displaying Machine/Service Totals
This test is performed online using SENDFILE. Only
the Service Totals test sequence requires an
intermediate step to access. It requires the operator to
run Diagnostics (D) from the SENDFILE Format Page
screen, resulting in the Sensor Display format, and
then run Service Totals (S) from the Sensor Display
screen.
1. Press M for Modify Service Totals.
2. The initial Service Totals format has a temporary
prompt box in the center of the screen that
requests a password.
NOTE: If a password is not given, totals are
displayed but can not be changed.
3. To modify totals, enter the applicable number
(1,2,3,4 ).
4. Before clearing a totals number, the routine
prompts another response. Pressing Y causes a
reset to 0. Any other entry results in an abort.
July 1998 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential
23
Page 31

9820/9830/9835Service Manual Confidential Tests and Adjustments
5. Following a totals number, the routine prompts
another response. Any entry other than Y results
in an abort.
6. Press D to return to the Sensor Display screen or
press L to exit the Sensor Display test sequence.
Print Contrast Adjustment
Adjust print contrast if printing is too light or too dark.
TOOLS REQUIRED:
• Small Flat-head Screwdriver
Using a small flat-head screwdriver, turn print contrast
knob(clockwise for darker print--counterclockwise
for lighter print).
Figure 5- 1. Print Contrast Adjustment
NOTE: Adjustments may also be made via
immediate commands. Refer to the Packet
Reference Manual for information on proper
syntax.
Platen Motor Gear Adjustment
This procedure adjusts the backlash in the platen drive
gear train. It should be performed each time a Platen
Assembly or a Platen Motor Assembly is replaced.
TOOLS/MATERIALS REQUIRED:
• 6-inch Phillips Screwdriver
• Paper Shimstock (0.006” to 0.008” thick) or
Label Backing Paper Liner (folded 3 layers
thick)
1. Turn printer off and unplug power cord.
2. Raise cover and ensure printhead is latched in the
down position.
3. Remove printer housing.
Figure 5- 2. Platen Motor Gear Adjustment
4. Using the paper shimstock, check clearance
between the bearer on the platen motor gear and
the bearer on the platen gear. (See Figure 5-2)
Clearance should be between 0.006” and 0.008”.
5. If clearance is less than or greater than the
specification, perform steps 7 thru 11.
6. With printhead fully latched, loosen four Phillips
head screws holding platen motor.
7. With paper shimstock in place, move platen motor
housing to adjust for specification clearance.
8. Tighten all four screws.
9. Rotate platen by hand 360° to check for binding or
excessive backlash.
10. Repeat steps 7 thru 10 as necessary.
Ribbon Tension Adjustment
There are two Ribbon Tension Adjustments: The
Ribbon Supply Roller Eccentric, and the Ribbon Takeup Roller Eccentric.
Rotation of the supply roller eccentric provides even
tension across the width of the ribbon on the supply
side of the printhead (Typically, the factory setting for
the supply eccentric is primarily horizontal). Rotation
of the take-up roller eccentric (adjusted after the
supply eccentric) provides even tension across the
width of the ribbon on the take-up side of the
printhead.
Either adjustment moves the outside end of the ribbon
roller to change the pressure on the ribbon. The
overall result of properly adjusted eccentrics is
consistent ribbon tracking.
MATERIALS REQUIRED:
• 4” thermal transfer supply (ex: MMTP4055
900091)
• 4” ribbon
24 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential July 1998
Page 32

Tests and Adjustments Confidential 9820/9830/9835 Service Manual
l User Diag. r
Supply Quality r
l 1568 034 124 Y r
1. Ensure printer is in Normal Mode with the
printhead Wide/Narrow detents set to Wide.
2. Loosen locking screw and set eccentric at the
nominal position (vertical for take-up roller,
horizontal for supply roller). See Figure 5-3.
3. Tighten both locking screws.
Figure 5- 3. Eccentric And Locking Screw
4. Press Feed several times until the supply roller
serrations are visible across the ribbon width.
5. Turn supply eccentric clockwise until serrations
are the same across the ribbon width.
6. Hold eccentric and tighten locking screw to secure
the adjustment.
7. Press Feed several times until the serrations of
the take-up roller are visible across the ribbon
width.
8. Turn take-up eccentric clockwise until serrations
are the same across ribbon width.
9. Hold eccentric and tighten locking screw.
10. Press Feed and Pause (to get test labels) several
times and watch for ribbon wrinkle.
11. If wrinkles occur, re-check step 8 to ensure takeup roller is properly adjusted. If wrinkles occur,
repeat adjustment.
12. Re-check that printhead Wide/Narrow detents are
set to Wide (button locked down).
13. Press Feed several times and observe the
smoothness of the ribbon as it enters the
printhead platen roller area. Readjust the supply
roller eccentric as required.
14. If wrinkles occur, loosen the take-up eccentric
screw with the printer running, and rotate the
eccentric to eliminate wrinkle.
15. Hold eccentric and tighten the screw.
CHECKING SUPPLY QUALITY
The printer continuously stores data from the most
recent 16 supplies printed. This checks the reflectivity
of the sensor marks on the supply. Before you check
your supply quality, print a batch of supplies or test
labels. Use Sendfile version 2.19 to check your
supply quality. This test can also be performed using
the optional 917 Keypad.
To check your supply quality from the optional
keypad:
1. From the Diagnostics menu, press L or R until
you see
DIAGNOSTICS
2. Press E. You will be at the User Diagnostics
menu. Press L or R until you see
USER DIAG
3. Press E. If you have not printed any labels,
the message “No data! Press Enter” appears.
If you have printed labels since turning on the printer,
you will see
Len Min Max OK
The Len listing is the length of the loaded supply in
dots. The Min listing should be greater than the Max
listing when
• white is under the sensor.
• a die cut label gap is under the sensor.
The Max listing should be greater than the Min listing
when
• black is under the sensor.
• the solid black area of a die cut label is under
the sensor.
The OK listing tells whether the sense mark on the
supply passed a detection test. Press R to see the
other readings.
If you are not using a Version 5.2 sensing system and
you try to check the supply quality, the message “HW
not supported” appears.
July 1998 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential 25
Page 33

9820/9830/9835Service Manual Confidential Tests and Adjustments
26 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential July 1998
Page 34

CHAPTER 6 SERVICE PROCEDURES
MAINTENANCE OVERVIEW
This chapter describes removal and replacement
procedures for the following assemblies:
Operator Control Panel
Cover Housing
Power Transformer Assembly
Power Transformer
Bridge Rectifier
AC Inlet
Control Board Assembly
Print Assembly
Bi-Cell Emitter
Upper Supply Guide
Printhead Module
Ribbon Spool Assemblies
Ribbon Roller Assemblies
DC Ribbon Motors
Feed Assembly
Platen Module
Bi-Cell Sensor
Lower Guide Assembly
Supply Holder Assembly
Supply Holder
Supply Holder Guides
Platen Motor
Peel Module
GENERAL SAFETY TIPS
Note these general safety reminders before servicing
the printer. Additional cautions and warnings appear
in this document as they apply to specific procedures.
WARNING
NEVER perform maintenance on the printer with the
power cord connected. Doing so exposes points where
AC voltages are present. Reattach the power cord
only when test procedures indicate that power is
required.
CONTROL PANEL REMOVAL
TOOLS REQUIRED:
• Phillips Screwdriver
• Flat-head Screwdriver
1. Turn the printer off and unplug the power cord.
2. Place printer on a flat, uncluttered surface.
3. Remove Control Panel by applying light
downward pressure on the latching tab on the top
of panel fascia.
4. Remove ribbon harness assembly by grasping
the connector, applying slight force away from
the control panel circuit board.
5. Remove single line ground wire.
6. Set Control Panel aside and place the ribbon
harness and ground wire back into the printer, to
prevent snagging on Cover Housing.
7. Reassemble in reverse order.
COVER HOUSING REMOVAL
The cover housing is attached to the printer frame by
five Phillips head screws. Two screws are located near
the printer base, one is behind the Control Panel, and
two are on the supply spool frame wall.
TOOLS REQUIRED:
• Phillips screwdriver
• Flat-head Screwdriver
1. Remove two screws at printer base.
2. Remove two screws on frame wall.
3. Remove screw from under control panel.
4. Lift cover housing to clear the frame walls.
5. Reassemble in reverse order.
CAUTION
Static electricity can damage printer parts. Use a
static ground wrist strap whenever possible. If a wrist
strap is not available, ground yourself by touching
some metal before touching the printer.
July 1998 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential 27
Page 35

9820/9830/9835 Service Manual Service Procedures
POWER TRANSFORMER
ASSEMBLY
Maintenance of the Power Transformer involves
• removing/reassembling the power
transformer.
• removing/reassembling the bridge rectifier.
• removing/reassembling the AC Inlet.
TOOLS REQUIRED:
• Longnose Pliers
• Phillips Screwdriver
Transformer Removal
CAUTION
You must remove several wires from the Bridge
Rectifier, AC Inlet module, and the Control Board
Assembly power connector. It is crucial to reconnect
the wires properly when replacing the transformer.
7. Reassemble in reverse order.
Bridge Rectifier Removal
Figure 6-2 Bridge Rectifier (Four Wires)
CAUTION
The bridge rectifier has four wire connections. See
Figure 6-2. Reconnect the black and red wires
properly when replacing these wires or the printer
could be damaged (voltages vary).
1. Remove the four wires and single retainer screw
located in the center of the rectifier.
2. Remove the bridge rectifier.
3. Reassemble in reverse order.
CN6
Connection
to AC Inlet
Bridge Rectifier
Transformer
Figure 6-1. Transformer Wiring Diagram
1. Remove four bridge rectifier wires as shown in
Figure 6-1.
2. Remove power connector CN6 from the Control
Board Assembly. (See Appendix C for location of
connectors.)
3. Remove six transformer wires from the AC Inlet
module.
4. Remove four transformer base screws.
5. Lay the two grounding wires aside so they do not
snag when replacing the transformer.
6. Remove the transformer.
AC Inlet Removal
6-3 . Bridge Rectifier (Four Wires)
The AC Inlet has six wires coming from the
transformer and one ground wire. Reconnect the wires
properly when replacing this part (voltages vary).
28 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential July 1998
Page 36

Service Procedures 9820/9830/9835 Service Manual
1. Release wires from loop holder
2. Remove six wires leading to the transformer.
3. Remove flange screw fastening green wire from
the AC Inlet to the Control Board Assembly.
4. Slide AC Inlet boot back and disconnect seven
spade connectors wires.
5. Depress top and bottom retaining detents on the
AC Inlet and remove it through the back of the
printer.
6. Reassemble in reverse order.
Control Board Assy. Removal
The Control Board Assembly has eight connectors to
interface with external assemblies. A single connector
(CN5) is used with the TwinAx/CoAx interface option
as an external interface. The other seven connectors
are used with board-mounted option assemblies. The
daughter board also has three connectors which must
be disconnected for board assembly removal.
CAUTION
CN15 and CN16 are identical in appearance, but are
oriented differently. Reversing the two connectors
could damage the printer.
1. Remove the following connectors from the
Control Board:
• CN2 Printhead
• CN3 Stepper Motor
• CN4 Operator Panel
• CN6 Power
• CN8 Bi-Cell Sensor (detector)
• CN11 Bi-Cell Emitter
• CN15 Ribbon Take-Up Motor
• CN16 Ribbon Supply Motor
NOTE: CN3 is not readily accessible in its installed
position. It is removed with the board
partially lifted free.
6. Release the AC inlet retaining tabs and slide the
AC inlet out the back of the printer.
7. Remove the AC inlet’s green ground wire from
the frame to allow the module to clear the back
frame.
8. Before removing the Control Board Assembly:
• Verify the print assembly is in the closed and
latched position.
• pull the two yellow AC supply wires to the
front side of the transformer.
• reposition the parallel port latch wires inside
the frame opening.
CAUTION
• Do not bend the hall effect sensor (HALL1),
located in the upper right corner of the board.
The leaded device is fragile and can be bent
or broken easily.
• Use care not to scratch the back side of
Control Board with the stand-offs, or the board
could be damaged.
9. Remove three stand-off retainer screws located in
connectors CN1,CN7, and below CN4.
10. Carefully pull the Control Board off the stand-off
detents, while lifting it past the transformer wires
to clear the large slot in the rear frame wall.
CAUTION
There is a large metal thermal heat sink on the bottom
of the board. Snagging it on the AC inlet module boot
or transformer wires can damage the equipment.
1. Remove stepper motor connector CN3.
2. Reassemble in reverse order except before
seating the Control Board:
• Reconnect stepper motor connector CN 3.
• Feed the wire latches through the printer
frame opening.
• Reconnect the ground wire.
2. Remove wiring at connectors CN3, CN6 and
CN10 from the daughter board.
3. Move harness cables aside to allow clearance for
board removal.
4. Slide AC inlet module boot back to access
connectors.
5. Disconnect seven spade connectors at back of
inlet.
July 1998 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential 29
PRINT ASSEMBLY
Maintenance of the Print Assembly involves removing
and replacing of the following assemblies:
• bi-cell emitter, upper supply guide, and
printhead module.
• ribbon spool and ribbon roller assemblies.
Page 37

9820/9830/9835 Service Manual Service Procedures
• ribbon motors and print assembly.
Figure 6-4. Print Assembly
TOOLS/MATERIALS REQUIRED:
• Phillips Screwdriver
• Flat-head Screwdriver
• Ribbon spool intermediate gear retaining clip.
Upper Supply Guide Removal
1. Remove bi-cell emitter from the upper supply
guide.
2. Gently pry the supply guide from the pin and
remove it.
Printhead Module Removal
1. Remove the printhead ribbon cable connector at
the printhead end.
2. Remove three printhead module screws, as
shown in Figure 6-4.
3. Remove the printhead module and lay it aside to
prevent it from being damaged.
4. Carefully work the printhead cable back through
the exposed cable slot, and lay it aside.
Ribbon Spool Assembly Removal
1. Remove the C clip at the outer shaft end.
2. Slide spindle off shaft.
3. Reassemble in reverse order.
Bi-Cell Emitter Removal
Cover Tab
Figure 6-5. Bi-Cell Emitter Removal
1. Using fingers, release emitter cover from the
emitter housing. Slide the emitter out of the
housing. See Figure 6-5.
2. Remove the connector from the sensor circuit
board.
3. Carefully work the sensor harness through the
upper supply guide openings and through the
print assembly opening.
4. Lay the sensor circuit board and harness aside.
Ribbon Roller Assembly Removal
1. Remove the screw at the end of the roller shaft.
2. Slide the serrated roller and eccentric adjuster off
the end of the shaft.
3. Reassemble in reverse order.
4. Adjust ribbon tension. See Chapter 5.
DC Ribbon Motor Removal
1. Locate the two patterns of three recessed screws
on the front side of the print module casting.
2. Mark each motor so they aren’t interchanged
when reassembling.
3. Remove the three screws from each pattern while
holding the ribbon motor so it doesn’t fall.
4. Unplug the single wire from the Control Board
Assy.
30 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential July 1998
Page 38

Service Procedures 9820/9830/9835 Service Manual
Print Assembly Removal
1. Remove two screws holding pivot retainers to the
frame.
2. Lift the upper supply guide and remove the
retainer pins from the upper supply guide.
3. Remove the magnet from the tunnel housing on
the side facing the Control Board Assy. See
Figure 6-6. Save the magnet.
Magnet
Pivot Retainer
Latch Fascia Removal
1. Remove cover housing.
2. Remove snap pin from rear latch fascia by prying
gently outward with a screwdriver.
WARNING
Leave the printhead latched to hold the latch knob in
place, or it may fly off and cause harm.
Latch Knob
Spring
Figure 6-6. Print Assembly Plate & Printhead
Module.
4. Reassemble in reverse order.
5. Adjust ribbon tension. See Chapter 5.
FEED ASSEMBLY
Maintenance of the Feed Assembly involves:
• removing the latch fascia and platen module.
• replacing the platen module.
• removing the sensor and lower supply guide.
• replacing the bi-cell sensor and supply guide.
TOOLS/MATERIALS REQUIRED:
• Phillips Screwdriver
• Flat-head Screwdriver
• Ribbon spool intermediate gear retaining clip.
Figure 6-7. Latch Removal
3. With the printhead latched, remove the latch
fascia. See Figure 6-7.
4. Carefully unlatch and raise printhead.
5. Pull latch knob away from platen frame until the
stop tab disengages from the frame.
6. Rotate latch knob counterclockwise until all spring
tension is relieved.
7. Remove latch knob and spring.
8. Remove the front exit door by lightly pressing one
side, until the hinge pin clears the platen frame.
9. Reassemble in reverse order.
Platen Module Removal
1. Remove the backing paper deflector.
2. Remove the three phillips screws that hold the
feed module to the printer base.
3. Lift up on the outboard side of the platen module
to allow the platen roller gear to clear the
printhead alignment bracket.
4. Rotate the platen module counterclockwise to
make room for removal of the platen assembly.
CAUTION
The sensor harness limits platen rotation. Be careful
not to damage the harness.
July 1998 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential 31
Page 39

9820/9830/9835 Service Manual Service Procedures
5. Unlatch the bearing block latch on each side of
the platen roller by inserting a small blade
screwdriver between the latch and the platen
frame. While holding the latch out with the
screwdriver, push the bearing block up so the
latch pawl clears the hole in the platen frame.
NOTE: Remove the rivot from bearing block on
printhead latch side.
6. When both bearing blocks are unlatched, push the
platen assembly up and out of the platen frame.
CAUTION
Do not run the platen roller into the printhead or the
assemblies could be damaged.
Platen Module Replacement
1. Locate the left side of the platen frame by
locating the cable harness exit hole.
2. Turn feed assembly so the drive gear is on the
same side of platen frame as cable exit hole.
3. Position bearing blocks in the slot on each side of
frame, then push down on roller until bearing
block latches snap into place.
4. Rotate platen module clockwise to locate it in its
original position. The platen module must be
lifted up to allow the platen gear to clear the
printhead alignment bracket. Detents in the base
plate assure alignment of the platen frame.
5. Reinstall the three phillips screws and tighten.
6. Verify clearance between platen drive gear and
the stepper gear bearer, this should not have
changed for this procedure. Nominal gap for this
adjustment is factory set at .0005".
Bi-Cell Sensor Removal
1. Grasp the bi-cell sensor holder at its base,
squeeze together to release the latch tabs and lift
the back of the sensor holder upwards.
2. Release latch tabs by pulling back and up on
sensor holder.
3. Rotate sensor holder back to expose sensor
circuit board.
4. Insert the blade of a small screwdriver through
the sensor holder on the left side (about 3/8”
down from the top) and pushs the sensor board
away from the sensor housing. (apply thumb
pressure to the cover to gain leverage).
CAUTION
The recommended pushing location minimizes the
possibility for damaging the circuit card.
5. Carefully remove sensor board from sensor
holder.
NOTE: Use caution not to damage the circuit
board.
6. Unplug sensor harness from sensor circuit board
by grasping the harness by the connector.
Lower Supply Guide Removal
1. Turn printer off and unplug AC cord.
2. Remove bi-cell sensor.
3. Remove sensor harness from two retainer loops.
4. Open print module until it latches.
5. Locate locking tabs on either side of the guide
frame which lock into the platen frame.
6. With a small straight blade screwdriver, gently
pry latches in (towards the feed path) while
pushing up on guide frame until latch releases
from frame. Repeat for latch on the other side.
Bi-Cell Sensor Replacement
1. Connect sensor harness to the sensor board.
2. Insert sensor board in holder on an angle to
engage board in holder tabs.
3. Apply light pressure on the opposite side of the
board to seat board into holder.
4. Ensure sensor window is showing through the
hole in sensor holder.
5. Insert top holder tab into guide frame.
6. Pivot sensor holder assembly down and latch the
back tabs. Use your thumb to support the under
side of the guide frame.
Latch
Bi-Cell Sensor
Figure 6-8. Bi-cell Sensor
32 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential July 1998
Page 40

Service Procedures 9820/9830/9835 Service Manual
Lower Supply Guide
Replacement
1. Reinstall sensor harness through retainer loops.
2. Align guide frame with notches in platen frame.
3. Press down on guide frame until latches engage
the platen frame.
SUPPLY HOLDER
TOOLS/MATERIALS REQUIRED:
• Phillips Screwdriver
• Flat-head Screwdriver
Supply Holder Removal
1. Pull upward on supply holder and lift it away from
the frame.
2. To replace the supply holder guides:
• Remove screw from the washer and gear.
• Pull front guide up and out of frame and
replace.
• Pull back guide up and out of frame and
replace.
• Move front and back guides to the center and
install supply gear and washer with the screw.
3. Insert the supply holder into the main frame and
push downward.
PLATEN MOTOR
Disconnect the wires from the AC Inlet to gain access
to the stepper motor connector. If you have problems
removing the motor (access is difficult), you must
remove the Control Board Assy.
TOOLS REQUIRED:
Platen Motor Removal
1. Remove Control Board Assy.
2. Remove four screws from platen motor housing.
3. Reassemble in reverse order.
4. Adjust platen motor gear. See Chapter 5.
PEEL MODULE
Maintenance to the Peel Module includes replacement
of the motor and peel roller.
NOTE: The peel roller is removed in the same
manner as the platen rollers.
TOOLS REQUIRED:
• Phillips Screwdriver
• Flat-head Screwdriver
Peel Module Removal
1. Remove printer housing.
2. Unload supply.
3. Raise Printhead and retain it in the up position.
4. Disconnect Peel Motor wiring connector at
motor.
5. Remove On-Demand Sensor wiring connector at
sensor and release wiring from the door
assembly.
6. Remove supply backing exit door assembly.
7. Remove peel module paper exit chute.
8. Remove three screws attaching the peel module
to the platen module.
9. Remove Peel Module through the end of the
printer.
10. Reassemble in reverse order.
• Phillips Screwdriver, Magnetic
July 1998 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential 33
Peel Motor Replacement
1. Remove Peel Module.
2. Carefully pry peel motor gear from shaft.
3. Remove three motor mounting screws and
remove motor.
4. Reassemble in reverse order.
Page 41

34 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential July 1998
Page 42

CHAPTER 7 USING FLASH
FLASH DOWNLOADING
PROCEDURES
The following information should be used as a
guideline for programming a 9800 series printer using
DOS- Flash Download Utility.
NOTE: Close all applications to prevent any
conflicts with the communications ports on
your PC.
CAUTION
Follow these steps exactly, failure to do so will result in
an unsuccessful attempt that may require board
replacement.
1. Open the ZIPPED file (98XXVXX.zip) into a
directory called FLASH.
NOTE: The PC should be capable of
communicating at 38.4 baud.
12. Turn printer off for 10 seconds and then back on.
After printer powers up, print a test label to confirm
correct operation.
13. Test printer with SENDFILE formats or the
customer’s data stream.
2. Make sure the printer is powered down.
3. Connect Serial Cable to PC and printer. Cable
must support DTR flow control.
4. Note DIP switch settings so printer can be
returned to its original configuration.
5. Move ALL DIP switches to the ON position.
6. Turn printer on. The Operator panel will display
001 (ok to download Flash).
7. From FLASH directory type GO and press Enter.
8. The program will prompt you for COM 1 or COM 2.
Select the appropriate port.
Once you select the COM port, the application
begins transfer of data and the green LED will lite.
The download takes approximately five minutes at
38.4 baud. The below listed download status
codes will be displayed during the download
process:
• 002--Transient Programmer now erasing flash.
• 003--Transient Programmer now ready to
accept download
9. When the application is finished, it will return the
PC to the DOS prompt. (C:\Flash) Turn printer off.
10. Return DIP switches to original setting noted in
step 4.
11. Turn printer on. Display should read 909.
July 1998 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential 35
Page 43

9820/9830/9835 Service Manual Using Flash
36
TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential July 1998
Page 44

CHAPTER 8 SUPPLY SENSING SYSTEMS
Several supply sensing systems have been used for
the 9800 series printers. This chapter contains:
• Supply detection and tracking for each printer.
• A description of the supply deflector, Bi-cell
emitter, lower supply guide, and Bi-cell sensor.
• Sensor tests and adjustments for each
sensing system.
• Information about the version 5.2 sensing
system.
SUPPLY
DETECTION/TRACKING
SYSTEM
An electro-optical system, consisting of a single
infrared emitter and a bi-cell sensor, allows the printer
to support die-cut, butt-cut (black mark only), with
aperture, and non-indexed supplies. The supply
detection and tracking system detects the document
edge position and out-of-stock condition. The infrared
emitter is located above the web path and is
positioned to allow the bi-cell sensor detector to serve
as a receiver for recognizing die-cut supplies.
Version 5.2 or greater:
The software uses an adaptive threshold algorithm
that has successfully been used in the M9446 printer.
This method provides the benefit of accurately
processing apertures, die cut gaps, and black marks
even though the electronic signal response may vary
greatly between supply types. It consists of measuring
the difference between the minimum and maximum
A/D (Analog to Digital converter) values captured from
the sensor.
The amplitude of this signal range represents the
sensor response to the feature. The minimum value
captured plus half the height of the signal range
constitutes the threshold level for both the Top of Form
(TOF) and Bottom of Form (BOF). This means that on
the leading edge of the feature when the threshold
value is crossed the BOF is marked. Likewise when
the feature is departing the sensor and the trailing
edge threshold is crossed the TOF is marked.
be an average threshold value calculated from the
previous two features.
TOF/BOF Average = (BOF/TOF Threshold1 +
BOF/TOF Threshold2) / 2
SUPPLY DEFLECTOR/BICELL EMITTER (IR LED)
The supply deflector is attached to the bottom of the
print module and pivots up and down to load labels
and ribbon. The IR Emitter is mounted in the center of
the deflector, which positions it in the middle of the
paper path and above the supply sensor located in the
supply guide.
Version 5.2 or greater:
The sensing system consists of three sensing
systems: an edge justified transmissive sensor, a
center justified reflective sensor, and a center justified
transmissive sensor which contains an LED positioned
directly over the phototransistor of the reflective
sensor.
The edge justified transmissive sensor provides an
index signal when using die cut labels and edge
justified aperture tags. It is mounted on the inside
supply guide and moves with the guide depending on
the supply width. This sensor is connected with an
integral harness to the reflective sensor junction board.
The center justified overhead LED is mounted in the
upper supply guide (flapper) and the phototransistor of
the reflective sensor (located below the web) and
provides an index signal when using center justified
aperture tags. The overheard LED is connected with a
harness to the reflective sensor junction board. A wire
harness connected between the main PCB and the
reflective sensor junction board provides the path for
the power, ground, LED power, and sensor output
signals.
NOTE: The new supply guide mechanisms are not
backward compatible.
TOF/BOF Threshold = Low value + ((High Value Low Value) / 2)
The paragraph above describes how the algorithm is
developed on one feature. For V5.2 the threshold will
July 1998 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential 37
Page 45

9820/9830/9835 Service Manual Supply Sensing Systems
where they are compared to a known base-line
LOWER SUPPLY GUIDE/BICELL SENSOR
The supply guide assembly spans the feed module
frame just behind and below the platen roller. It sits
within two détentes on each frame edge to maintain
proper positioning. It is held in place by individual
plastic tabs engaging square holes on both sides of
the frame.
Two center-justifying supply guides sit on top of a
guide frame and are interlocked. A guide lock arm is
positioned on the outside guide. The Bi-Cell supply
sensor and housing are attached to the middle of the
supply guide frame so that it is lined-up with the IR
emitter in the upper supply guide. The sensor wiring
harness attaches to the sensor housing and runs
along the bottom of the guide frame and through the
feed module frame to the Control Board Assembly.
Version 5.2 or greater:
The center justified reflective sensor is mounted on the
lower supply guide support and provides an index
signal when using black mark butt cut labels and black
mark tags. The reflective sensor is surface mounted
to the reflective sensor junction PCB assembly.
NOTE: The new supply guide mechanisms are not
backward compatible.
SUPPLY FEEDING
The main components of supply feeding are the platen
roller, 25VDC stepper motor, and supply guide.
Supply guides are used to capture the supply and
maintain center-justified tracking. The supply must be
positioned between the platen and printhead to feed
properly. The printhead applies pressure to the supply
to hold it against the platen roller. As the platen roller
rotates, the supply is forced to move between it and
the printhead. The stepper motor engages the platen
drive gear (located behind the inner feed module wall)
and drives the platen roller. The function is controlled
by the Control Board Assembly.
SUPPLY SENSING
Supply sensing begins when the IR Emitter in the
supply deflector, emits an IR beam through the supply.
The Bi-Cell sensor located in the supply guide,
receives the beam and changes it into corresponding
voltage level. As the beam intensity changes, the
associated voltage output of the Bi-Cell also changes.
Voltages are reported to the Control Board Assy.
voltage. When the input characteristics match (relative
to predefined times, voltage levels, and expected
supply position), a gap or black mark is sensed.
For the 9820/9830 printers, SENDFILE provides volts
relating to the sensor’s activity as stock moves past
the sensor. Two points are of interest: high point
(must be approx. 176) and low count (must be approx.
79). Two sensor channels are used. One measures
the paper’s presence. The other detects the transition
from stock to gap and back. These transitions
produce an analog waveform which changes from
reference (typically -2.5 VDC or approx. 128 A/D
counts). These voltages are continually monitored and
adjusted by the microprocessor. Because of this
microprocessor control, no meaningful static
measurements can be made to the sensing circuitry.
Paper to Gap is a negative waveform whose active
threshold is +1.75VDC or 89 A/D counts. The
waveform must drop approx. 10 A/D counts to be
acted upon as a valid transition. Gap to Paper is a
positive +waveform whose active threshold is
+3.25VDC or 166 A/D counts.
The 9835 uses a new sensing system that is optimized
for black mark sensing while still having the ability to
detect die cut supplies. All 9835 printers contain a set
of matched components that are factory adjusted. Our
intent is to produce a sensing system that does not
require physical alignment in the field. If a sensor fails,
order a Sensor Kit (11879801). The kit contains a
matched set of components that must be installed and
configured using Sendfile Version 2.14 or later.
Version 5.2 or greater:
When a label advance command is received the
software checks to see if the supply has been
calibrated. If not Resync resets the A/D signal
measuring parameters. When the supply starts
moving forward the A/D signal value is captured. It is
matched against the highest value saved and the
lowest value saved. If the new value is larger then the
current high value or lower than the current low value it
replaces that value. In this way the differential
between minimum and maximum signal can be
determined. Sometimes this differential is referred to
as the span. This cycle is repeated for each motor
step interval while the motor is running during
calibration.
The first transition edge of software significance is the
BOF. This is defined as the leading edge of the
feature. It is based on an algorithm that on every step
checks to see if the AD count is at a value that has
passed through a calculated threshold moving from
white into the feature. Before the algorithm can be
used the signal differential must be larger then a
predefined minimum. Once this criteria has been
TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential July 199838
Page 46

Supply Sensing Systems 9820/9830/9835 Service Manual
meet, the threshold count is calculated as the sum of
half of the differential between the Low and Hi AD
counts captured plus the Low count. When a valid
BOF has been found it is saved and used as the
threshold for the TOF.
The next transition edge of importance is the TOF. It
is defined as the trailing edge of the feature. Once the
BOF has been found the software looks for a TOF. In
fact it uses the same AD threshold count calculated for
the BOF. The difference is that the TOF point is
determined as the AD count passes through the
threshold from the feature back to white.
The threshold value used for this first feature is not
saved in the averaging array because it only
represents the minimum span distance as defined by
the algorithm criteria. However, by the time the TOF
position is reached a full representation of the signal
profile has been captured and this actual profile is
what is used for BOF/TOF on the second feature.
When the second feature passes by the sensor the
valid BOT and TOF are those points that were
calculated from the first feature. The threshold points
calculated based on the signal profile captured from
this feature are saved as the second entry in the array.
For the third feature the threshold points become an
average of the first two features. Here after the array
is continually updated containing the last two threshold
values.
The calibration function is complete when the second
valid feature is found and measured. The existing
software has processed the physical aspects of the
label such as print length, feature length and TOF to
TOF distance into the tracking system. The software
can now track the label just seen by the sensor so that
it will be synchronized in correct position under the
printhead. Knowing label length provides the ability to
predict when the next feature can be expected.
Therefore, the only time the sensor will be enabled is
after calibration during the window of time when the
feature should pass by the sensor. The reason in
using a small window is to minimize detection of
extraneous pulses that may adversely affect the
accuracy of the algorithm.
MECHANICAL ADJUSTMENTS
This section describes:
• Bi-Cell Sensor Adjustment
• Print Contrast Adjustment
• Platen Motor Gear Adjustment
• Ribbon Tension Adjustment
NOTE: Field Service performs no electrical
adjustments.
Bi-Cell Sensor Adjustment
1. Turn Printer Off.
2. Load die-cut supply and turn off printer.
3. Connect laptop computer to printer’s serial port
(laptop must have SENDFILE V2.07 installed).
4. Set DIP switch 3 (bottom set) to ON (Diagnostics
Mode)
5. Set DIP switch 6 (bottom set) to OFF (Die Cut).
6. Turn printer on. Printer will feed two labels and
display 000.
7. Start SENDFILE (as follows).
8. Press M for Model number and press Enter.
9. Press Feed and Clear simultaneously on keypad
to access Diagnostics. SENDFILE will display
DIAG IDLE.
10. After SENDFILE displays IDLE, press D for
Diagnostics.
11. Remove Die Cut labels from the printer.
12. Check the emitter for operation, using an Infrared
Detector Probe.
13. Cover the Bi-Cell switch with a piece of black
electricians tape. Completely block all light.
DO NOT TOUCH THE SENSOR LENS WITH
YOUR FINGERS.
14. With all light blocked from Bi-Cell, note the
reading on SENDFILE. This is the reference
value for the sensor. Range is 2.35V to 2.55V. If
reading is out of range, replace Bi-Cell Sensor.
15. Remove electrical tape.
16. Place gray scale over sensor, glossy side down.
(HANDLE FILTER BY EDGES ONLY. SKIN
OILS CAN ALTER THE BI-CELL READING)
17. Close print module and note the Bi-Cell reading in
SENDFILE.
18. From back of Bi-Cell housing, turn adjusting
screw to obtain the reference value observed in
Step 14.
19. Open and close printhead carriage to verify
adjustment.
July 1998 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential
39
Page 47

9820/9830/9835 Service Manual Supply Sensing Systems
20. Remove gray scale and test printer with
customer’s supplies.
118718
118705
Figure 8- 1. Bi-Cell Sensor Adjustment
NOTE: A hood covers the adjusting screw on the
back of the housing.
REPLACING A SENSOR
Use these instructions for 9835 printers version 5.0 or
earlier. All of the harnesses are identified with part
numbers and must be attached to the sensor board
(118699). Follow the same cable routing that was
used for the original system.
To replace a sensor:
1. Remove the ferrite noise filter from the
old reflective object harness (118704) and install it
on the new harness (118704).
NOTE: Be sure the Reflective Object Sensor is
located in the middle of the sensor
housing (117990)
TX 7B RX 8A Ref 4.0
118704
118706
Figure 8- 2. Sensor Board
8. Press 3 followed by the 3-digit decimal value
converted using the scientific calculator. You have
now completed the sensor kit installation.
9. Exit Sendfile and take the printer out of Diagnostic
mode.
10. Test the 9835 using the customers tags or labels
to verify correct operation.
2. Locate the label that is applied to the top of the
sensor board (118699) and make note of the
Trans and REFL HEX values.
These values must be entered using Sendfile V
2.15. You must convert the HEX value to decimal
using
Microsoft Windows Scientific Calculator.
3. Once the parts have been installed you will need
to power up the printer in Diagnostic Mode. Set
SW-3 on lower
bank of switches to the “ON” position and turn on
the 9835 printer.
4. Start Sendfile and go to the Diagnostics section.
On the left side of the screen you will see a
command that says: Reset 98xx DAC values.
5. Press "R" to enter this function.
6. A pop up menu appears. This is where the
Transmissive (Trans) and Reflective (REFL)
values recorded from the board will be entered.
7. Press 2 followed by the 3-digit decimal value
converted using the scientific calculator.
TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential July 199840
Page 48

Supply Sensing Systems 9820/9830/9835 Service Manual
To set/adjust the aperture (center) sensor:
SENSOR SETUP WITH
VERSION 5.2 OR GREATER
Manufacturing sets all three sensors before a printer is
shipped. Service needs to adjust the sensor if a
sensor component fails in the field or for specific
customer supplies. Use Sendfile Version 2.21 (or
greater) to set the sensor values. The three sensors
are: aperture (center), black mark (center), and die cut
(edge).
WARNING
You must follow these steps exactly. Failure to do
so may cause the printer to lock up and not be
able to recover.
1. Set switch on bottom row, position #3 (on CPU
board) to diagnostic mode.
2. Remove any supply from printer.
3. Close the printhead.
4. Make sure printer is turned OFF.
5. Connect the correct printer voltage (115 or 230).
6. Connect the serial cable to printer and computer.
7. Start Sendfile version 2.21 (or greater).
8. Turn on printer. Press Clear if error 792 is
displayed.
9. Press D to go into diagnostics.
10. For standard 9820/9830/9835 printers, set print
contrast to 2.50 (+/- .02). For linerless 9830, set
print contrast to 1.25 (+/-.02).
11. Press X for sensor adjustments.
12. Press C to get to the screen on the right-hand
side. It should show version 5.0 at the top right
and the center should show
aperture die cut black mark. Toggle C
until you see this screen.
13. Press S, this saves the virgin settings.
14. Press D to go into diagnostics.
15. Press X for sensor adjustments.
16. Press C to get to the screen on the right-hand
side. It should show version 5.0 at the top right
and the center should show
aperture die cut black mark. Toggle C
until you see this screen.
17. Remove supplies (if any are loaded) and close
printhead.
18. Press 1 to set aperture sensor.
19. Press A to automatically set adjustment. The
ideal setting is 4.00. The acceptable range is +/-
0.10. The word “Calibrating” appears on the
screen. The process is complete when
“Calibrating” disappears.
To set/adjust the die cut (edge) sensor:
20. Load a minimum of 4-inch long die cut liner stock,
with the labels removed. Close printhead.
21. Press 2 to set the die cut sensor.
22. Press A to automatically set adjustment. The
ideal setting is 4.00. The acceptable range is +/-
0.10. The word “Calibrating” appears on the
screen. The process is complete when
“Calibrating” disappears.
To set/adjust the black mark (center) sensor:
23. Remove the liner stock from the printer.
24. Load a minimum of 4-inch long piece of tag stock
into printer. Make sure the black mark is not over
the center sensor. Close the printhead.
25. Press 3 to set the black mark sensor.
26. Press A to automatically set adjustment. The
ideal setting is 4.00. The acceptable range is +/-
0.10. The word “Calibrating” appears on the
screen. The process is complete when
“Calibrating” disappears.
27. Press S to save the adjustments.
The printer displays 909. Turn off the printer. Wait
three seconds and turn the printer back on.
POWER UP SENSOR
RECOGNITION
During power up initialization the software checks a
reserved area in flash to see if the printer has the V5.2
sensor system hardware installed. If it does then the
V5.2 sensing is activated. If not then the daughter
board is checked to see if the model switch is set to
the 9835 sensing system. If no daughter board is
installed, then the 9820/9830 sensor system control
software is enabled. For the 9820/30 and for the
M9835 the selectable modes are transmissive,
reflective, and non-index (continuous) which currently
exists in these models.
July 1998 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential
41
Page 49

9820/9830/9835 Service Manual Supply Sensing Systems
Version 5.2 or greater:
For the new V5.2 system there will be transmissive,
reflective, non-index (continuous), and center aperture.
The center transmissive sensor is intended only for
supplies that have an aperture hole located in the
middle of the web. It is referred to as the aperture
mode. The transmissive edge sensor is used for both
die cut and edge aperture supplies. The reflective
sensor is used with center web black marks.
The aperture sensing mode is enabled when the
software selects the overhead center of web LED as
the emitter and the black mark detector located
beneath the web and directly under the LED. If the
transmissive mode is selected then the edge sensor
assembly will be used. For reflective mode the black
mark sensor assembly located under the web will be
selected. Lower DIP switches 5 and 6 control the
supply type/sensing system.
Description 5 6
Die Cut or Edge Aperture Supplies (edge sensor)
Black Mark Supplies (center sensor)
Non-indexed/Continuous Supplies (no sensor)
Center Aperture supplies (center sensor)
OFF
OFF
ON
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
The software has the capability of identifying both the
Main Processor circuit board level and the sensor
system installed in a printer. The V5.2 software is
compatible with combinations of previous main
processor boards and sensor systems. It also
supports the new main processor board with V5.2 and
earlier sensor systems installed. Use Sendfile to save
(in flash) the code that identifies that the V5.2 sensor
hardware is installed.
Performing a Sensor Display Test
This test is performed online using SENDFILE with
version 5.0 or earlier printers.
1. To display Analog-to-Digital static values,
minimum and maximum A/D dynamic values, or
information on options, press D.
2. To see the min/max range of each of the A/D
channels, highlight each sensor output and press
Enter. SENDFILE displays the following
channels:
• Uni-cell
• Head Temp
• Head Volt:
• Dot Test
• Back EMF
• High Volt:
• Contrast
• Bi-cell
Version 5.2 or greater:
To perform a sensor test with version 5.2 or greater,
see “Sensor Setup With Version 5.2 or Greater” earlier
in this chapter.
TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential July 199842
Page 50

APPENDIX A PRINTER ERROR/STATUS CODES
This section contains the error/status codes used with the 9800 series printers. These same codes are called status
codes when they are displayed on the Control Panel LCD; and error codes when they are part of Diagnostics “Status
Polling” test sequences. These error/status codes are organized into Data Errors, Communications Failures, Data
Formatting Failures, Machine Faults, and Hard Printer Faults.
To clear an error/status code, press Clear. If a data formatting error (571 through 619) occurs, press Feed. The label
prints, but data may be missing.
READING AN ERROR LABEL
An error label queues and prints when you press FEED after a data error occurs. The error label contains the packet
type, field type, line number, and error number. The packet and field type return the first letter after the { or ¦. If the
letter cannot be determined, ? is returned. The line number refers to which line in the packet the error occurs. The
error number is the three-digit error code. Use this information to correct the format, batch, font, check digit, graphic,
or online configuration packet.
The first label shows an error in line 8, which is a constant text field within the format packet. The error number is
18.
The second label shows an error in line 1 of the batch packet. The error number is 101.
DATA ERRORS (001 - 499)
Error/Status Codes 001 to 499 are data errors. They indicate that incorrect data was received from the external PC,
causing the printer to ignore the entire print job. After checking the packet and correcting the problem, transmit the
print job again. The following is a list of data errors. These errors occur because data in the format, batch, check
digit, font, or graphic packet is invalid.
Code Description
001 Packet ID number must be 1 to 999.
002 Name must be 1 to 8 characters inside quotes or a printer-assigned name ("").
003 Action must be A (add) or C (clear).
004
005
006
007
Supply length is invalid.
Supply width is invalid.
Storage device must be R (volatile RAM).
Unit of measure must be E (English), M (Metric), or G (Dots).
July 1998 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential 43
Page 51

9820/9830/9835 Service Manual Printer Error/Status Codes
010
011
012
013
014
015
016
017
018
020
021
022
023
024
025
030
Field ID number is outside range 0 to 999.
Field length exceeds 2710.
Row field position is greater than maximum stock dimension.
Column field position is greater than maximum stock dimension.
Font style must be 1, 2, 3, 4, 10, 11, 15, 16, 17, 18, or 50.
Character rotation must be 0 (0 degree), 1 (90 degree), 2 (180 degree), or 3 (270 degree).
Field rotation must be 0 (0 degree), 1 (90 degree), 2 (180 degree), or 3 (270 degree).
Field restriction must be V (variable) or F (fixed).
Code page selection defined in field must be 0 (Internal), 1 (ANSI), 2 (DOS 437), or 3 (DOS 850).
Vertical magnification must be 1 to 7 or 4 to 90 points for scalable font.
Horizontal magnification must be 1 to 7 or 4 to 90 points for scalable font.
Color must be A, B, D, E, F, N, O, R, S, T, or W.
Intercharacter gap must be 0 to 99 dots.
Field justification must be B (balanced), C (centered), E (end), L (left), or R (right).
String length is outside range 0 to 2710.
Bar code height must be at least 20 (English), 51 (Metric), 40 (Dots), and within supply dimensions.
031
032
033
Human readable option must be:
default
0
no CD or NS
1
NS at bottom, no CD
5
CD at bottom, no NS
6
CD and NS at bottom
7
no text
8
Bar code type is invalid.
Bar code density is invalid.
040 Line thickness must be 0 to 99 dots.
041 Line direction must be 0, 90, 180, or 270.
042
043
044
045
End row is invalid. Line segment or box end row is defined outside of printable area.
End column is invalid. Line segment or box end column is defined outside of printable area.
Dot pattern for line or box must be "".
Line length is defined beyond maximum length.
046 Line type must be S (segment) or V (vector).
051 Imaging mode in graphic header must be 0.
101
The format referenced by batch is not in memory.
102 Print quantity is outside range 0 to 32000.
TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential July 199844
Page 52

Printer Error/Status Codes 9820/9830/9835 Service Manual
104 Batch mode must be N (new) or U (update).
105 Batch separator must be 0 (Off) or 1 (On) in the batch control field.
106 Print multiple is outside range 1 to 999.
107 Cut multiple is outside range 0 to 999. Only valid for printers with a knife.
108 Multiple part supply is outside range 1 to 5.
109
Reserved for knife usage. Only valid for printers with a knife.
200 Option number must be 1, 4, 30, 31, 42, 50, 51, 52, 60, or 61.
201 Copy length is outside range 0 to 2710.
202 Copy start position must be 1 to 2710.
203 Destination start position must be 1 to 2710.
204 Source field must be 0 to 999.
205 Copy type must be 1 (copy after rules) or 2 (copy before rules).
206 Increment/Decrement selection must be I (increment) or D (decrement).
207 Incrementing start position must be 0 to 2710.
208 Incrementing end position must be 0 to 2710.
209 The incrementing amount must be 0 to 999.
210 Security value for a PDF417 bar code must be 0 to 8. Correct and resend format to printer.
211 Narrow element value is less than 1 or greater than 99. Correct and resend format to printer.
212 Wide element value is less than 1 or greater than 99. Correct and resend format to printer.
213 Dimension must be 1 to 30 for a column or 3 to 90 for a row on a PDF417 bar code.
214 Truncation code must be S (standard) or T (truncated bar code).
215 Aspect code must be C (columns) or R (rows).
216 Option definition must be S (set) or T (template).
217 Input device must be D (Default), H (Host), K (Keyboard), N (None), or S (Scanner).
218 Pad direction must be L (from left) or R (from right).
219 Pad character is outside range 0 to 255.
220 Check digit selection must be G to generate check digit.
221 Primary or secondary price format is outside range 1 to 15.
222 Data type restriction is outside range of 1 to 6.
223
Option is not valid for field.
224 Bar code Interchar gap must be 0 to 99 dots (known as additional character gap with Option 50).
251 Power up mode must be 0 (online) or 1 (offline).
252 Language selection must be 0.
253 Batch separator code must be 0 (off) or 1 (on) in the system setup packet.
254 Slash zero selection must be 0 (standard zero) or 1 (slash zero).
255 Supply type must be 0 (black mark) , 1 (die cut), or 2 (continuous).
July 1998 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential 45
Page 53

9820/9830/9835 Service Manual Printer Error/Status Codes
256 Ribbon selection must be 0 (direct) or 1 (transfer).
257 Feed mode must be 0 (continuous) or 1 (on-demand).
258
259 Contrast adjustment must be -390 to 156 dots.
260 Print adjustment must be -99 to 99 dots.
261 Margin adjustment must be -99 to 99 dots.
262 Speed adjustment must be 25 (2.5 IPS), 40 (4.0 IPS), or 60 (6.0 IPS).
263
264 Secondary symbol selection must be 0 (none) or 1 (print secondary sign).
265 Monetary decimal places must be 0 to 3.
266 Character string length in control characters packet must be 5 (MPCL control characters) or 7
267 Baud rate selection must be 0 (1200), 1 (2400), 2 (4800), 3 (9600), 4 (19200), or 5 (38400). Resend
268 Word length selection must be 0 (7 bits), or 1 (8 bits). Resend communication settings packet or
269 Stop bits selection must be 0 (1 bit), or 1 (2 bits). Resend communication settings packet or check
270 Parity selection must be 0 (none), 1 (odd), or 2 (even). Resend communication settings packet or
Supply position is outside range.
Primary monetary symbol is invalid.
(ENQ/IMD command character).
communication settings packet or check DIP switch settings.
check DIP switch settings.
DIP switch settings.
check DIP switch settings.
271 Flow control selection must be 0 (none), 1 (DTR), 2 (CTS/RTS), or 3 (XON/XOFF). Resend
communication settings packet or check DIP switch settings.
272 Internal code page selection must be 0 (Internal), 1 (ANSI), 2 (DOS 437), or 3 (DOS 850).
273 Cut adjustment must be -99 to 99 dots.
282 RS232 Trailer string is too long. Use a maximum of 3 characters.
283 ENQ Trailer string is too long. Use a maximum of 3 characters.
284 The storage device type in memory configuration packet must be N (non-volatile RAM) or R (volatile
RAM).
285 The buffer type must be T (Transmit), R (Receive), I (Image), F (Format), or D (Downloadable Fonts).
286
287 The printhead width must be 244 to 812 dots.
288 The battery voltage must be 0 (15-volt battery) or 1 (12-volt battery).
289
290 Action must be 0 (disable) or 1 (enable) for backfeed control packet.
291 Dispense position must be 50 to 200 dots.
292 Backfeed distance must be 10 to 200 dots.
310 Check digit scheme number must be 1 to 10.
The buffer size is invalid.
The printer address specified in communication settings packet must use exactly six characters.
311 Modulus must be 2 to 11.
314 Check digit algorithm must be D (sum of digits) or P (sum of products).
TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential July 199846
Page 54

Printer Error/Status Codes 9820/9830/9835 Service Manual
325 Duplicating direction must be 0 (insert after) or 1 (insert before) in duplicate fields for graphics.
327 Amount of row adjustment must be 0 to 999 dots in duplicate fields for graphics.
328 Duplicate count must be 0 to 999.
340 Bitmap line encoding must be H (hex) or R (run length).
350 Font selector must be 1 to 9999.
351 Font data length must be 68 to 16384.
352
380 Job request is outside range 0 to 4.
400 The character immediately following { is invalid.
402
403
404
405
409
Insufficient font memory is available for downloaded font.
Field separator is not in expected location.
Field separator was not found.
The number or string that is currently being processed is too long.
Too many fields exist in format. You cannot have more than 1000 fields in format. Lines, boxes, and
constant text fields count as fields.
The printer memory is full. Delete unnecessary formats or graphics from memory. If you are using a
graphic file that is very large, consider using another mapping method (such as run length encoding) to
reduce required memory.
COMMUNICATION FAILURES (410 - 499)
Errors 410 to 414 are usually caused by a hardware failure, by an incorrect SETUP option, or by the host
PC ignoring flow control (XON/XOFF, CTS/RTS, or DTR). The serial communication settings are:
Baud rate 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200, 38400
Word length 7 or 8
Stop bits 1 or 2
Parity Odd, Even, None
Flow control None, XON/XOFF, CTS/RTS, DTR
Code Description
410
411
412
413
414
415
July 1998 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential 47
Parity on printer doesn’t match parity on host. Check parity setting under SETUP options.
Framing error. The printer cannot communicate with host. Make sure host is turned on,
communication cables are connected correctly, port settings are correct, and communications are
active. Check baud rate, word length, and stop bits to make sure they match those at host. Do not
toggle between Microsoft® Windows® and MS-DOS, while using COPY command, or you will receive
a framing error. Exit Windows before using COPY command. Re-transmit data.
There is a problem with flow control between printer and host. Make sure printer and host flow control
settings match (both are DTR or both are XON/XOFF).
Online receive queue is full. Check your printer's XON/XOFF or DTR SETUP values to be sure there
isn't a flow control problem.
The internal keyboard buffer is full or you need a new keypad.
The buffer size you defined exceeds total available in your machine.
Page 55

9820/9830/9835 Service Manual Printer Error/Status Codes
427
428 Batch name is invalid or graphic not found. Press Clear and try to continue.
429
430
433
497
499
Format name is invalid. Valid name is 1 - 8 characters inside quotes or "" for a printer-assigned name.
Press Clear and try to continue.
A field number appears more than once in a format.
The format uses a graphic file that cannot be found.
The batch references a field number that doesn’t exist in format.
An error occurred during loop back test on parallel port.
An error occurred during loop back test on serial port.
DATA FORMATTING FAILURES (571 - 619)
Formatting errors indicate that a field will print incorrectly. After you have checked the data stream and
corrected the data, retransmit the batch. The batch will still print, but the field, font, bar code, or density
may be incomplete, missing, or contain incorrect data.
Code Description
571
572
UPC/EAN data length is invalid. The bar code data length in batch doesn’t fit format.
A field (copy, padded, or incrementing) length is invalid. The field length in batch doesn’t fit format or
field contains blanks. Or, fixed length field doesn’t contain specified number of characters.
573
574
575
611
612
613
614 Field is off tag or there is an invalid character in packet. Make sure you did not enter O for Ø.
615
616
618 Magnification must be 1 to 7, or 4 to 90 for the scalable font.
619
Price field length is invalid. The price field length in batch doesn’t fit format or field contains blanks.
No CD scheme or room for CD. The CD scheme in batch doesn’t fit format or field contains blanks.
The graphic included in your format could not be found.
Font, bar code or density is invalid. The font, bar code or density in batch doesn’t fit format.
The data in this line of batch is either missing or doesn’t match format.
Reference point off tag.
Bar code width is greater than 16 inches or number of keywords for your PDF417 bar code exceeds
928. Decrease density or shorten amount of data to print bar code.
Dot shifting failed. A bad dot falls on a bar code that cannot be shifted.
The JIS (16-bit) code for Kanji is invalid.
MACHINE FAULTS (700 - 766)
Errors 700 to 766 occur when there is a problem with the printer.
Code Description
703
704
750
751
The printer sensed a calibration of different-sized black marks. Make sure correct supply is loaded.
Printer has not sensed a supply mark within specified number of inches or out of supplies.
Printhead is overheated. Turn off printer to let printhead cool.
Printer did not sense a mark when expected.
TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential July 199848
Page 56

Printer Error/Status Codes 9820/9830/9835 Service Manual
752
753
754
755
756
757 Load supplies. The calibrated supply length differs by + or - .25 inches from format. Press Feed.
NOTE: For errors 751-753, check supply tracking, supply marks, black mark sensor position, supply roll for
Printer sensed a mark in wrong place.
Printer sensed a mark that is too long.
The printer is either out of ribbon or ribbon is jammed.
Printhead is open. Close printhead before continuing.
The printer is out of supplies. Load supplies.
binding. Then press Clear. If error continues to appear, change supply.
Code Description
758
759
760
761
762
Either on-demand sensor is broken, supply is not seen, or continuous unit set to on-demand mode.
Adjust sensor so it is over a white area on supply, or set unit to continuous mode. This error may
occur if you remove a label too quickly in on-demand mode. The printer does not recalibrate after this
error.
Knife is not moving.
Knife jam.
Stacker is full or jammed. Empty stacker before continuing. The printer does not recalibrate after this
error.
Low battery. Recharge battery.
763 Waiting to dispense label. Press Feed.
764
765
768
770
771
790 Printer busy. Press Clear. Resend packets. If problem continues call Technical Support.
791
792
793
Verifier failure. Check verifier by referring to your verifier's manual. The printer does not recalibrate
after this error.
Printhead failure. You need a new printhead.
Printhead is not present. Make sure the printhead is connected and closed.
Print motor not ready. Call Technical Support
Format specified by application not found. Reload application and format. If problem continues call
Technical Support.
Printer has an error pending. Turn printer off. Wait 15 second and turn printer on. Resend packets.
If problem continues call Technical Support.
Check daughter board switches or configuration. Reset sensor kit or values.
Printer job queue is full. Turn printer off. Wait 15 seconds and turn printer on. Resend packets. If
problem continues call Technical Support.
July 1998 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential 49
Page 57

9820/9830/9835 Service Manual Printer Error/Status Codes
HARD PRINTER FAULTS (900 - 910)
Errors 900 to 910 are hard printer faults. If a 900 series error is displayed, turn the printer off, then cycle on again. If
the error occurs again, the Main PCB has probably failed and needs to be replaced.
Errors 905, 906, and 907 can occur at any time the printer is powered. The other 900 series errors are only indicated
at Level 0, initial power-up test.
Code Description
900
901
902
903
905
906
907
908
909
910
911
RAM test failure.
ROM/EPROM checksum failure.
Software timer failure.
Software interrupt failure.
Illegal interrupt.
Non-maskable interrupt.
Low RAM error.
Non Volatile RAM checksum failure.
RAM corrupted.
Warm restart.
Version string mismatch.
FLASH FAULTS (930 - 940)
Errors 930 - 940 are errors that may occur during the loading of flash memory.
Code Description
930
931
932
933
934
935
936
937
938
938
940
Error occurred erasing FLASH.
Error occurred writing FLASH.
Error occurred writing RAM.
Communications parity error.
Communications framing error.
Communications buffer overran.
Invalid record type specified.
Invalid ASCII hex data in record.
Invalid checksum.
Invalid record count recorded.
Illegal FLASH address being programmed.
FAULTS (950 - 999)
Errors 950 - 999 indicate circuit board failure. Call Technical Support.
TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential July 199850
Page 58

APPENDIX B CONNECTORS AND CABLES
This appendix contains charts of the pinouts for the Control Board Assembly connectors
1 F PP STROBE bar 1 2 LC PD00
3 LC PD01 4 LC PD02
5 LC PD03 6 LC PD04
7 LC PD05 8 LC PD06
9 LC PD07 10 F MC ACK bar
11 F MC BUSY 12 F MC PERROR
13 F MC SELECT 14 F MC AUTOFD bar
15 N/C 16 CHASSIS GROUND
17 EMI GROUND 18 N/C
19 CHASSIS GROUND 20 CHASSIS GROUND
21 CHASSIS GROUND 22 CHASSIS GROUND
23 CHASSIS GROUND 24 CHASSIS GROUND
25 CHASSIS GROUND 26 CHASSIS GROUND
27 CHASSIS GROUND 28 CHASSIS GROUND
29 CHASSIS GROUND 30 CHASSIS GROUND
31 F MC INIT bar 32 F MC FAULT bar
33 N/C 34 N/C
35 N/C 35 36 F MC SELIN bar
Figure B- 1. CN 1 IEEE 1284 Parallel Port
1 CHASSIS GROUND 1 2 VTPH
3 CHASSIS GROUND 4 VTPH
5 CHASSIS GROUND 6 VTPH
7 CHASSIS GROUND 8 VTPH
9 CHASSIS GROUND 10 VTPH
11 BANK ENABLE OUTPUT 12 CHASSIS GROUND
13 VDAT bar 14 CHASSIS GROUND
15 LATCH bar 16 CHASSIS GROUND
17 TPHCLK 18 CHASSIS GROUND
19 TPH STB B bar 20 TPH STB A bar
21 TPH STB B bar 22 TPH STB A bar
23 TPH STB B bar 24 TPH STB A bar
25 TPH STB A bar 26 N/C
27 V TM 28 VREF
29 + 5 VDC 29 30 + 5 VDC
Figure B- 2. CN 2 Printhead Assembly
July 1998 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential 51
Page 59

9820/9830/9835ervice Manual Connectors and Cables
1 + 25 VDC
2 SM PH A
3 SM PH A bar
4 + 25 VDC
5 SM PH B
6 SM PH B bar
Figure B- 3. CN 3 Platen Stepper Motor
1 LED 1 1 2 + 5 VDC
3 CHASSIS GROUND 4 DISPLAY CLK
5 CHASSIS GROUND 6 DISPLAY LATCH
7 CHASSIS GROUND 8 DISPLAY DATA
9 KEY 1 A 10 CHASSIS GROUND
11 KEY 2 A 12 CHASSIS GROUND
13 KEY 3 A 14 CHASSIS GROUND
15 LED 2 16 LED 3
Figure B- 4. CN 4 Control Panel
1 F PP STROBE bar 1 2 CHASSIS GROUND
3 LC PD00 4 CHASSIS GROUND
5 LC PD01 6 CHASSIS GROUND
7 LC PD02 8 CHASSIS GROUND
9 LC PD03 10 CHASSIS GROUND
11 LC PD04 12 CHASSIS GROUND
13 LC PD05 14 CHASSIS GROUND
15 LC PD06 16 CHASSIS GROUND
17 LC PD07 18 CHASSIS GROUND
19 N/C 20 CHASSIS GROUND
21 F MC BUSY 22 CHASSIS GROUND
23 F MC PERROR 24 CHASSIS GROUND
25 F MC SELECT 26 F MC INIT bar
27 N/C 28 N/C
29 N/C 30 N/C
31 N/C 32 N/C
33 N/C 34 N/C
35 + 5 VDC 36 CHASSIS GROUND
37 N/C 38 N/C
39 N/C 39 40 N/C
Figure B- 5. CN 5 Coax/Twinax Interface
TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential July 199852
Page 60

Connectors and Cables 9830/9835 Service Manual
1 15 VAC - 1
2 N/C
3 CHASSIS GROUND
4 15 VAC - 2
5 + 40 VDC
6 CHASSIS GROUND
Figure B- 6. CN 6 Transformer Output Power
1 CHASSIS GROUND 1
3 RXD bar 2 TXD bar
5 CTS 4 RTS
7 CHASSIS GROUND 6 DSR
9 N/C 8 N/C
11 N/C 10 N/C
13 N/C 12 N/C
15 N/C 14 N/C
17 N/C 16 N/C
19 N/C 18 N/C
21 N/C 20 DTR
23 N/C 22 N/C
25 N/C 25 24 N/C
Figure B- 7. CN 7 RS-232 Serial Port
1 BIPOLAR SIGNAL
2 BP GUARD (GROUND)
3 UNIPOLAR SIGNAL
4 UP GUARD (GROUND)
5 + 12 VDC
6 12 V RTN (GROUND)
7 - 12 VDC
Figure B- 8. CN 8 Supply Sensor (Bi-Cell)
July 1998 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential 53
Page 61

9820/9830/9835ervice Manual Connectors and Cables
1 BOARD GROUND 1 2 VCC
3 N/C 4 ROMOE bar
5 RSWE bar 6 RSWE bar
7 BOARD GROUND 8 MC D16
9 MC D17 10 MC D18
11 MC D19 12 MC D20
13 MC D21 14 MC D22
15 MC D23 16 MC D24
17 MC D25 18 MC D26
19 MC D27 20 MC D28
21 ROMCS1 bar 22 ROMCS1 bar
23 ROMCS1 bar 24 ROMCS1 bar
25 BOARD GROUND 26 MC D29
27 MC D30 28 MC D31
29 RSWE bar 30 N/C
31 N/C 32 N/C
33 MC A21 34 MC A20
35 MC A19 36 MC A18
37 MC A17 38 MC A16
39 MCB A15 39 40 MCB A14
41 MCB A13 41 42 MCB A12
43 MCB A11 44 MCB A10
45 MCB A09 46 MCB A08
47 MCB A07 48 MCB A06
49 MCB A05 50 MCB A04
51 MCB A03 52 MCB A02
53 RSWE bar 54 BOARD GROUND
55 MC D15 56 MC D14
57 MC D13 58 MC D12
59 MC D11 60 MC D10
61 MC D09 62 MC D08
63 MC D07 64 MC D06
65 MC D05 66 MC D04
67 MC D03 68 MC D02
69 MC D01 70 MC D00
71 N/C 72 VCC
73 N/C 74 N/C
75 N/C 76 N/C
77 N/C 78 N/C
79 N/C 79 80 BOARD GROUND
Figure.B- 9. CN 10 Board Interface
TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential July 199854
Page 62

Connectors and Cables 9830/9835 Service Manual
1 TDX ANODE
2 TDX COMM
Figure B- 10. CN 11
GND
Two-wire harness connect red wire to TP5 (+25 volts)
Figure B- 11. CN 14
1 RT_MTR_1
2 RT_MTR2
Figure B- 12. CN 15
1 RS_MTR_1
2 RS_MTR2
Figure B- 13. CN 16
1 +12V
2 GND
3 -12v
4 GND
5 _NO_RAT( +25V)
6 GND
Daughter Board Connectors
1 +12V
2 GND
3 -12v
4 GND
5 _NO_RAT( +25V)
6 GND
Figure B- 15. CN 3 To MotherBoard CN 19
1 PEEL_MFTR_1
2 PEEL_MFTR_2
Figure B- 16. CN 10 Peel Motor
1 _OD_A
2 OD_K
3 +12V
4 OD_E
5 GND
6 N/C
Figure B- 17. CN 6 On-Demand Sensor
Figure B- 14. CN 19 (to Daughter Board CN3)
July 1998 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential 55
Page 63

9820/9830/9835ervice Manual Connectors and Cables
56 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential July 1998
Page 64

APPENDIX C CONNECTOR LOCATIONS
Legend:
CN1 IEEE 1284 Parallel Port
CN2 Printhead Assy
CN3 Platen Stepper Motor
CN4 Control Panel
CN5 Coax/Twinax
CN6 Transformer Output Power
CN7 RS-232 Serial Port
CN8 Index Sensor Receiver Assy
CN9 Not Used
CN14 Top pin for knife motor
Figure C- 1. Control Board Assy. (Mother Board)
CN10 Index Sensor Connector Assy (2-wire pigtail) from
CN8
CN11 Index Sensor Emitter Assy
CN12 Daughter Board Connector
CN13 Daughter Board Connector
CN14 DRAM Expansion (Not Shown)
CN15 Ribbon Take Up Motor
CN16 Ribbon Supply Motor
CN17-CN18 Engineering Use (Not Shown)
CN19 Daughter Board Connector
CN20 Engineering Use
July 1998 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential 57
Page 65

9820/9830/9835 Service Manual Connector Locations
Auxillary keypad connects to CN9
5-wire knife harness
4-wire knife harness
Legend:
CN3 Mother Board CN19
CN4 Cutter Option
CN5 Stacker Option
CN6 On-Demand Sensor
Figure C-2. Control Board Assy. (Daugher Board)
CN7 Reserved
CN8 Reserved
CN9 Reserved
CN10 Peel Motor
SW1 See Chapter 1 for settings
58
TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential July 1998
Page 66

APPENDIX D MODEL 928 STACKER
The 928 Stacker only works with a 9835 printer with a 926 Knife attached.
SPECIFICATIONS
Height: 14.4 inches (366 mm)
Base Width: 25.6 inches (650 mm)
Tag Bed: 29.6 inches (752 mm)
Depth: 7.9 inches (201 mm)
Weight: 18 pounds (8.2 kg)
Shipping Weight: 30 pounds (13.6 kg)
Power: 115 VAC, 60 Hz,
100 VAC, 50/60 Hz,
230 VAC, 50 Hz
Capacity: Up to 1,500 tags with tag
thickness of 0.010 inches (.25 mm) thick
Operating Limits: Thermal Transfer:
40 to 95 degrees F
(4 to 35 degrees C)
Direct:
40 to 104 degrees F
(4 to 40 degrees C)
Storage Limits: 15 to 120 degrees F
(-9 to 49 degrees C)
Relative Humidity:
(Operating and 5 to 90 percent non Storage):
condensing
Speed: Up to 6.0 inches
(152 mm)
Minimum Stackable Tag Sizes:
Width Length
Printed widthwise: 1.63 inches 1.2 inches
(41 mm) (30 mm)
Printed Lengthwise: 1.2 inches 1.57 inches
(30 mm) (40 mm)
Header Length: 3.66 inches (93 mm)
NOTE: Supply roll must be wound printed side in.
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
The 928 Stacker consists of the following modules:
• Upper Transport Assembly
• Upper Drive Shaft Assembly
• Lower Transport Assembly
• Stepper Motor
• D C Motor
• Stacker Full/Jam Sensors
• Power Supply
• Control Board
The Model 928 Stacker is attached to a 9835 Printer
which has the Model 926 Knife Assembly installed.
The printer and knife attaches to tabs on the stacker
mounting plate.
A wiring harness carries electronic signals and 12 Vdc
from the knife to the stacker. Additional electrical
power required by the stacker is provided by an onboard power supply. The power supply converts 115
VAC to 24 Vdc for the DC motor.
The Control Board contains the necessary circurity to
provide control of the motors and sensors, and has a
daughter board to provide power to the stepper motor.
The DC motor drives the Lower Transport Assembly
through a series of pulleys and gears. The Lower
Transport Assembly and Upper Transport Assembly
move cut tags from the knife to the stacker belt.
A stepper motor drives the stacker belt. As the
stacker belt revolves, the accumulating tags move
with the belt toward the end of the stacker tray. Belt
movement is automatically stopped when the tags
reach the end of the stacker tray and the Stacker full
sensor sends a stop signal to the printer. Belt
movement can also be stopped by turning the printer
off.
The purpose of the Stacker Full Sensor is to detect
when the stacker tray has been filled with tags and to
signal the Stacker Control Board to stop operations.
INSTALLATION
1. Unpack stacker from shipping carton. Retain
carton.
July 1998 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential 59
Page 67

9820/9830/9835 Service Manual Model 928 Stacker
2. Turn printer off.
3. Lift the knife/printer slightly and slide the knife on
to the stacker mounting plate tabs.
4. Attach stacker AC power cable to stacker and AC
power outlet.
5. Attach knife-to-stacker cable.
6. Adjust cutter as necessary. Refer to Operating
Instructions TC0928OI.
CAUTION
To avoid damage to the motor, the stacker rollers and
front of knife must not be in direct contact.
NOTE: When installing, make sure the stacker is
properly aligned with the knife. The stacker
tray should angle down and away from the
926. Align the stacker by lowering the
stacker’s feet, turn them in to lower and out
to raise the stacker. Lock the legs in place
by tightening the locking nut provided.
TROUBLESHOOTING
1. Check AC inlet fuse and power switch.
2. Ensure the stacker-to-knife harness is properly
connected.
3. Inspect stacker drive belts for proper adjustment.
4. Check all wiring harness connector for proper
connection.
Error Messages
Error Message 761 is shown on the printer display if a
stacker fault or jam is detected.
Stacker Full: Empty the tray. Press Clear to
clear the error and resume printing.
Stacker Jam: Clear the jam. Press Clear to clear
the error and resume printing.
If the jam is not inside the stacker, check inside the
knife or printer.
Alignment
The stacker’s bed must slant slightly down (away from
the knife). Raise or lower the stacker’s feet by turning
them. Tighten leg nuts to lock into place. For
additional alignments, refer to the Operating
Instructions, TC0928OI.
CABLES AND CONNECTORS
The following tables provide pinouts for stacker connectors. Connector locations are shown in Figure D-1.
Table D- 1. Stacker Control Harness.
Knife Connector Pin Signal Control Board CN1 Pin
1 STKR_ENABLE 1
2 STKR_PRESENT 3
3 GND 5
4 +12Vdc 7
5 GND 9
6 STKR_ERROR 10
7 N/C
8 N/C
9 +12Vdc 2
10 GND 4
11 6
12 8
13 10
14 N/C
15 N/C
60 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential July 1998
Page 68

Model 928 Stacker 9820/9830/9835 Service Manual
Table D- 2 Jam/Full Sensor Harness.
Control Board CN3 Pin Full Sensor (S1) Pin Jam Sensor (S2) Pin
1 2
2 2
3 N/C
4 KEY
5 1
6 3
7 3
8 1
9 4
10 4
Table D- 3. Extended Motor Interface Harness.
(Soldered to Control Board Connector CN4)
Extender Connector Pin Signal Stepper Motor Connector Pin
1 1
2 2
3 +24 Vdc 3
4 +24 Vdc 4
5 5
6 6
Table D- 4. AC Power Harness.
Power Supply Connector J1 Signal Power Switch (SW1)
Pin Terminal
1 GND
2 N/C
3 115 VAC 1
4 N/C
5 N/C
Table D- 5. Power Supply Connector J2.
Connector J2 Pin Signal/Pin Control Board Connector CN2 Pin
1 (Orange) 4
2 N/C
3 N/C
4 (Brown) 5
5 (Green/Yellow) GND
6-13 N/C
July 1998 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential 61
Page 69

9820/9830/9835 Service Manual Model 928 Stacker
Table D- 6. Power Supply Connector J1
Connector J1 Pin Color To
1 GND
2 N/C
3 Black On/Off Switch
4 N/C
5 White AC Inlet
Bearings
Figure D- 1. Stacker Control Board.
LUBRICATION
The stacker should be lubricated whenever the idler
shafts are replaced.
NOTE: Do not get lubricant on stacker rollers or
belts; performance could be adversely
affected.
1. Turn stacker and printer off.
2. Remove stacker from knife assembly.
3. Remove the stacker rear and side covers.
4. Apply silicon lubricant to the two bearing on the
rear frame and two bearings on the front frame.
See Figure D-2.
5. Replace the stacker covers.
6. Reattach stacker to knife.
7. Turn on printer and stacker and test for correct
operation.
Figure D- 2. Stacker Lubrication Points.
MAINTENANCE
PROCEDURES
Use the illustrations provided and the Stacker
Illustrated Parts Breakdown for assistance in
performing maintenance. Maintenance procedures for
the stacker are described below.
Note the following general safety reminders before
servicing the stacker. Additional Warnings and
Cautions are provided where appropriate as they
apply to specific procedures.
WARNING
Never perform maintenance on the stacker with the
power cord connected. Doing so exposes points
where AC voltages are present. Reattach power cord
only when test procedures indicate that power is
required.
CAUTION
Static electricity can damage stacker parts. Use a
static ground wrist strap.
62 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential July 1998
Page 70

Model 928 Stacker 9820/9830/9835 Service Manual
Cover
1. Unplug stacker power and stacker-to-knife cable.
Rear Frame
Front Frame
Full Sensor
2. Remove side, rear, and back covers as necessary
to access rollers being replaced.
3. From front main frame side, remove E-ring
Rear Cover
holding the shaft containing the rollers being
replaced.
4. Withdraw the shaft from the rear frame side.
5. Remove rollers from the shaft while withdrawing
the shaft from the frame.
Electronics
Jam Sensor
6. Reassemble in reverse order.
If replacing serrated rollers, make sure teeth face up
(toward end of stacker bed).
Back Cover
Stacker-to-Knife Cable
Side Cover
Replacing Transport Assembly
1. Disconnect the power.
Figure D- 3. Model 928 Stacker Assembly.
2. Remove the upper transport lockshaft or (BAIL)
and set aside.
REPLACE ROLLERS
E Clips
3. Remove transport covers (118480 / 118479 /
118532).
4. Remove aluminum support plate (110590) to
acess the lower drive shaft pulley and spur gear.
5. Loosen the set screws from the lower drive shaft
pulley (110594) and spur gear (098330).
6. Remove aluminum pulley (098367) to allow lower
exit drive shaft’s spur gear clearance for removal.
7. Remove the pulley and spur gear.
8. Remove the lower drive shaft pulley (110594) and
white spur gear (098330).
9. Remove the remaining four white spur gears
(098330).
10. Remove the four black idler gears (098373) and
keep the attaching screws and nylon washers.
Figure D- 4. Lower Transport Rollers.
11. Remove the E-Ring from the gear train side of the
rear main frame (118475) on the upper exit drive
shaft (098320).
12. Pull out the old drive shaft from the front main
frame (118476, operator side of 928).
13. Turn the 928 upside down and remove the front
mounting plate (118467) to allow access to the
front main frame (118476) mounting screws.
14. Remove the two front main frame screws.
15. Turn the stacker upright and remove all of the Erings and screws holding the front main frame
(118476) attaching assemblies.
16. Disconnect the spring from the tamper plate to
Figure D- 5. Upper Transport Rollers.
allow the front main frame (118476) to be
July 1998 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential 63
Page 71

9820/9830/9835 Service Manual Model 928 Stacker
removed from the stacker. Be careful not to lose
the spring.
17. Slide the front main frame off the tamper plate
shaft and gently pull it clear of the stacker.
18. The old lower transport assembly should now be
held in place by the four remaining plastite screws
on the rear main frame (118475).
19. Remove 4 screws holding the assembly in place,
and remove the lower transport assembly.
20. Install the replacement kit.
21. Reassemble in reverse order.
Replace DC Motor
1. Unplug stacker power and stacker-to-knife cable.
2. Remove rear, back, and side covers.
3. Disconnect motor wiring harness at motor
terminals 1 and 2.
4. Remove four motor mounting screws, belt, and
motor assembly.
5. Reassemble in reverse order.
Replace Stepper Motor
1. Unplug stacker power and stacker-to-knife cable.
2. Remove rear, back, and side covers.
3. Loosen set screws and remove belt speed
adjustment knob.
4. Remove belt adjustment potentiometer mounting
nut and washer.
5. Remove four screws and electronics cover.
6. Disconnect motor wiring harness at control board
connector P1.
7. Remove four motor mounting screws, belt, and
motor assembly.
8. Reassemble in reverse order.
Replace Stacker Sensors
The stacker full and stacker jam sensors share the
same wiring harness, so replace as an assembly.
1. Unplug stacker power and stacker-to-knife cable.
2. Remove screw attaching stacker full sensor to
stacker bed.
3. Remove 2 clips holding sensor wiring harness to
the stacker bed.
4. Thread sensor cable through frame to control
board.
5. Loosen set screws and remove belt speed
adjustment knob.
6. Remove 4 retaining screws and electronics cover.
7. Remove 4 screws holding control board to
standoffs.
8. Slide sensor out of transport mounting and thread
sensor cable through frame back to control board.
9. Move control board back to expose sensor wiring
harness connector.
10. Disconnect wire harness from control board
connector CN3 and remove sensor.
11. Reassemble in reverse order.
Replace Power Supply
1. Unplug stacker power and stacker-to-knife cable.
2. Loosen set screws and remove belt speed
adjustment knob.
3. Remove belt adjustment potentiometer mounting
nut and washer.
4. Remove 4 retaining screws and electronics cover.
5. Remove four power supply mounting screws.
6. Tilt power supply up to disconnect wiring harness
at connectors J1 and J2.
7. Remove power supply.
8. Reassemble in reverse order.
Replace Control Board
1. Unplug stacker power and stacker-to-knife cable.
2. Loosen set screws and remove belt speed
adjustment knob.
3. Remove belt adjustment potentiometer mounting
nut and washer.
4. Remove 4 retaining screws and electronics cover.
5. Disconnect harness connectors at control board
connectors J1, J2, and J3.
6. Remove the four screws holding the control board
to the standoffs.
7. Disconnect power supply harness at control board
connector CN1.
8. Remove control
board.
9. Reassemble in
reverse order.
Figure D- 6. Power Supply/Control Board.
64 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential July 1998
Page 72

APPENDIX E 926 KNIFE ASSEMBLY
The 926 Knife only works with a 9835 printer.
Board at connectors CN4 and CN5. A separate
KNIFE SPECIFICATIONS
Height: 8.5 inches (216mm)
Width: 9.3 inches (236mm)
Depth: 7.6 inches (193mm)
Weight: 9.0 pounds (4.1 Kg)
Shipping Wgt: 9.5 pounds (4.3 Kg)
Power: Input Voltage; 24.0 Vdc. (From
9835 Printer).
Output Voltage: 12.0 Vdc and +5Vdc to Stacker
Assembly
Operating Limits: 40 to 104 degrees F
(4 to 40 degrees C)
Storage Limits: 15 to 120 degrees F
(-10 to 49 degrees C)
Relative Humidity: 5 to 90 percent non condensing
Speed: Up to 6.0 inches (152mm) per
second
TAG CUT DIMENSIONS
Width: 1.2 to 4.0 inches (30 mm to 102 mm)
Lengths: 1.2 to 16 inches (31 mm to 406 mm)
Thickness: 0.007 inch to 0.010 inch (0.18 mm to
0.25 mm)
NOTE: Supply roll must be wound printed side in.
Labels should not be cut.
harness carries power to the knife from printer control
board connector CN11. The knife drive board also
has a connector to attach cabling to the 928 Stacker
Assembly.
Functional Description
The Knife Assembly is controlled by the Feature
Board installed in the 9835 Printer. All power to the
knife is provided by the printer via cabling from the
printer control board. The rotary knife has a helical
blade positioned below the supply path and is
activated by the knife solenoid.
The knife is driven by a DC motor controlled via
software by the printer. When the knife is enabled (by
software) the motor is turned on and a solenoid,
located on the Blade Assembly, is energized, and the
knife blade completes one rotation, producing a cut
tag. (The motor runs constantly as long as there is
power to the knife.)
The Knife Assembly also has circuitry to provide 12
Vdc power and necessary control signals to the
attached 928 Stacker Assembly. The functionality of
the stacker is explained in Appendix D.
TROUBLESHOOTING
Drive Board circuits generate two error codes to assist
in the detection of knife failures. Error 759 indicates
that the knife is not moving and Error 760 indicates a
knife jam.
The following paragraphs contain suggestions for
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
The 926 Knife Assembly consists of the following
modules:
• Blade Assembly
• Drive Board
• DC Drive Motor
• Solenoid
The Knife Assembly is attached to the front of the
9835 Printer beneath the print module. It is fastened
to the printer base with three fasteners and has two
wiring harnesses that connect to the 9835 Feature
July 1998 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential 65
troubleshooting the two conditions. Voltage tests are
also included to further isolate a knife failure.
Evaluation of Error 760
The printer software reports an Error 760 when a
knife jam is detected. The following checks are
suggested to correct the problem:
1. Turn printer off.
2. Check supply path for jammed tags, or obstruction
in path.
Page 73

9820/9830/9835 Service Manual Model 926 Knife
3. Check Blade Assembly alignment and ensure
assembly mounting screws are tight.
4. Verify supply type; cutter only cuts tags. Labels
should not be cut.
5. Check to ensure tags being used do not exceed
0.010 inch (0.25 mm) thickness.
VOLTAGE TESTS
Before replacing the Drive Board, check for the static
voltages shown in Table E-1 to determine if the board
has failed. If all voltages are correct, troubleshoot the
9835 printer control board. See Chapter 3.
1. If 25Vdc is not detected at J3 pin 1, the printer is
not providing power to the knife drive board.
Troubleshoot the printer.
2. If 25Vdc is detected at J3, pin 1, but not at both
pins of J1 and J2, replace Knife Drive Board.
3. If 25Vdc is detected at J1 but not at J2, replace
solenoid.
4. If 25Vdc is at J2 but not J1, replace knife drive
motor.
Table E- 1. Knife Drive Board Voltages.
NOTE: Lubricate with multi-purpose grease using a
long cotton swab. Do not over lubricate.
Do not get grease on knife blade or
performance could be affected.
1. Turn printer off.
NOTE: The knife unit has two cam surfaces that
should lubricated with multi-purpose grease.
2. Using a long cotton swab,
lubricate the knife cams.
3. Turn printer on and test for correct
operation.
Cam hidden
from view
Figure E-1. Knife Lubrication Points.
Cam
MAINTENANCE OVERVIEW
Connector Voltage
J1 25v on both pins
J2 25v on both pins
J3 25v on pin 1 only
J5
Connector Pin Voltage
1
2 5v
3 5v
4
5
6 5v
7 5v
8 5v
9
LUBRICATION
To prevent excessive wear, the knife should be
lubricated every 100,000 cuts. (Approximately, every
10 rolls of 1.2” supply.) A Knife Lubrication Kit (Part
Number 118782) is available.
This section describes removal and replacement
procedures for the knife assembly. See Figure E-2 for
printer-to-knife connector locations. See Figure E-3 to
identify parts and assist in performance of
maintenance procedures. Figure E-4 shows the
location of connectors on the drive board.
GENERAL SAFETY TIPS
Observe these general safety precautions before
servicing the knife. Additional Warnings and Cautions
appear in this document as they apply to specific
procedures.
Knife Assembly
Connectors
9835 Printer
Figure E-2. Location of Connectors.
66 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential July 1998
Page 74

Model 926 Knife 9820/9830/9835 Service Manual
Blade
Assembly
Connector J4
(To 928 Stacker)
Solenoid
Knife Assembly
Mounting Screws (3)
Drive Board
Cover
Mounting
Screws (3)
Motor Mounting
Screws (2)
Pulley Set Screw
Allen Head Cap
Screws
Drive Motor
Drive Belt
Cover
Figure E-3. Knife Assembly.
July 1998 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential 67
Page 75

9820/9830/9835 Service Manual Model 926 Knife
J1
J2
J3
To Motor
To Solenoid
To Printer Control Board
Figure E-4. Drive Board Connector Locations.
Blade Assembly Replacement
1. Turn printer off.
2. Remove 928 Stacker Assembly. See Appendix D.
3. Remove three cover screws to gain access to the
Blade Assembly.
4. Note the position of the Blade Assembly in
relation to its mounting frame. This relationship is
critical to provide a straight cut from left edge to
right edge of tag.
5. Using an Allen wrench, remove two cap screws
that attach the knife unit to its mounting frame.
6. Disconnect solenoid at connector J2 on Drive
Board.
7. Remove the Knife Blade Assembly.
8. Reassemble in reverse order.
NOTE: Carefully align the edge of the knife
assembly to the mounting frame. There
should be almost no variation side to side
on a cut tag (0.030 +/- 0.020). The
mounting hole closest to the operator panel
is slotted for this adjustment.
9. Adjust Blade Assembly. When a straight cut
across the tag has been achieved, lock down all
adjustments.
10. Run 50 - 100 tags to verify proper cut operation.
11. Replace the knife cover.
12. Attach the Stacker Assembly, see Appendix D.
13. Turn printer on and test for correct operation.
J4
J5
To 928 Stacker
To Printer Daughter Board
Drive Board Replacement
Replace the Drive Board using the following
procedure:
1. Turn printer off.
2. Remove the Stacker Assembly, see Appendix D.
3. Remove three cover screws to gain access to the
Drive Board.
4. Note the positions of all wiring harness
connections.
5. Disconnect each harness from the Drive Board.
6. Lift the Drive Board off its standoffs.
7. Reassemble in reverse order.
8. Attach the 928 Stacker Assembly and test for
correct operation.
Motor Replacement
1. Turn printer off.
2. Remove 928 Stacker Assembly. See Appendix D.
3. Remove three cover screws to gain access to the
motor.
4. Remove two motor mounting screws and remove
motor.
5. Remove knife motor wiring at motor connector.
6. Loosen the pulley set screw and remove pulley.
Make sure set screw is on flat of shaft.
7. Reassemble in reverse order.
68 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential July 1998
Page 76

Model 926 Knife 9820/9830/9835 Service Manual
8. Adjust belt tension.
9. Squeeze halfway between pulleys. When
distance from outside of one side of belt to outside
of opposite side is approximately 1.0”, tighten
screws on motor.
10. Turn printer on and test for correct operation.
11. Replace the knife cover.
12. Attach the Stacker Assembly to the Knife
Assembly, see Appendix D.
CONNECTORS AND CABLES
The following tables provide pinouts for the Knife
Assembly cables and connectors.
Table E- 2. Drive Board Connector J1.
To Motor
Terminal
1 25 Vdc 2
2 25 Vdc 2
Table E- 3. Drive Board Connector J2.
Signal Pin
Table E- 5. Drive Board Connector J4 To 928 Stacker
Assembly.
Pin Signal Pin
1 STKR_PRESENT 1
2 STKR_ERROR 2
3 STKR_ENABLE 3
4 +12Vdc 4
5 GND 5
6 GND 6
N/A 7
N/A 8
N/A 9
N/A 10
N/A 11
N/A 12
N/A 13
N/A 14
To Motor
Solenoid
Terminal
1 25 Vdc 1
2 GND 2
Table E- 4. Knife Drive Board Connector J3.
From
Printer
CN11 Pin Signal Pin
1 12Vdc 1
Signal Pin
12Vdc 2
N/A 15
Table E- 6. Knife Drive Board Connector J5.
From Printer
Daughter Board
CN5 PIN 5 GROUND 1
CN5 PIN 1 STKR_PRESENT 2
CN5 PIN 2 STKR_ERROR 3
CN5 PIN 3 STKR_ENABLE 4
CN4 PIN 6 GROUND 5
CN4 PIN 1 CUT_PRESENT 6
CN4 PIN 3 CUT_ENABLE 7
CN4 Pin 2 CUT_ERROR 8
CN5 PIN 5 CUT_CONTROL 9
Signal Pin
Julyl 1998 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential 69
Page 77

9820/9830/9835 Service Manual Model 926 Knife
70 TC9830SM Rev. B 7/98 Confidential July 1998
 Loading...
Loading...