Page 1

Weld Control
Selector Guide
Product: Weld Control
Selector Guide
Manual: 091-0458
Revision: Oct 2003 Rev E
The Most Comprehensive Guide to
Connecting Prince® XL Spool Guns &
Cobramatic® Wire Feed Systems
to Welding Power Supplies
Page 2
SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS
ELECTRIC ARC WELDING EQUIPMENT
CAUTION : READ BEFORE ATTEMPTING INSTALLATION, OPERATION OR
MAINTENANCE OF THIS EQUIPMENT
1-1 INTRODUCTION
This equipment is intended for ultimate
application by commercial/industrial users
and for operation by persons trained and
experienced in the use and maintenance of
welding equipment. Operation should not
be undertaken without adequate training
in the use of such equipment. Training
is available from many public and private
schools or similar facilities.
Safe practices in the installation, operation
and maintenance of this equipment requires
proper training in the art, a careful study of
the information provided with the equipment,
and the use of common sense. Rules for
safe use are generally provided by suppliers
of welding power sources, compressed gas
suppliers, and electrode suppliers. Careful
compliance with these rules will promote
safe use of this equipment.
The following Safety Rules cover some of
the more generally found situations. READ
THEM CAREFULLY. In case of any doubt,
obtain qualied help before proceeding.
1-2 GENERAL PRECAUTIONS
A. Burn Prevention
ELECTRIC ARC WELDING PRODUCES
H I G H I N T E NS I T Y H E AT AN D
ULTR AV I O L E T RADIAN T EN E R G Y
WHICH MAY CAUSE SERIOUS AND
PERM A N E N T EY E DAMA G E AN D
WHICH MAY DAMAGE ANY EXPOSED
SKIN AREAS.
Wear helmet with safety goggles or glasses
with side shields underneath, appropriate
lter lenses or plates (protected by clear
cover glass). This is a must for welding
or cutting (and chipping) to protect the
eyes from radiant energy and ying metal.
Replace cover glass when broken, pitted,
or spattered.
Medical rst aid and eye treatment. First
aid facilities and a qualied rst aid person
should be available for each shift unless
medical facilities are close by for immediate
treatment of ash burns of the eyes and skin
burns.
Wear protective clothing - leather (or
asbestos) gauntlet gloves, hat, and high
safety-toe shoes. Button shirt collar and
pocket aps, and wear cufess trousers to
avoid entry of sparks and slag.
Avoid oily or greasy clothing. A spark may
ignite them.
Flammable hair preparations should not be
used by persons intending to weld or cut.
Hot metal such as electrode stubs and
work pieces should never be handled
without gloves.
Ear plugs should be worn when working on
overhead or in a conned space. A hard hat
should be worn when others work overhead.
B. Toxic Fume Prevention
WARNING: The use of this product may result
in exposure to chemicals known to the State
of California to cause cancer and birth defects
or other reproductive harm.
Adequate ventilation. Severe discomfort,
illness or death can result from fumes, vapors,
heat, or oxygen enrichment or depletion that
welding (or cutting) may produce. Prevent
them with adequate ventilation. NEVER
ventilate with oxygen.
Lead-, cadmium-, zinc-, mercury-, berylliumbearing and similar materials, when welded
or cut, may produce harmful concentrations
of toxic fumes. Adequate local exhaust
ventilation must be used, or each person in
the area, as well as the operator, must wear
an air-supplied respirator. For beryllium, both
must be used.
Metals coated with or containing materials that
emit toxic fumes should not be heated unless
coating is removed form the work surface, the
area is well ventilated, or the operator wears
an air-supplied respirator.
Work in a conned space only while it is being
ventilated and, if necessary, while wearing an
air-supplied respirator.
Gas leaks in a conned space should be
avoided. Leaked gas in large quantities can
change oxygen concentration dangerously.
Do not bring gas cylinders into a conned
space.
Leaving conned space, shut OFF gas supply
at source to prevent possible accumulation of
gases in the space if downstream valves
have been accidentally opened or left open.
Check to be sure that the space is safe before
reentering it.
Vapors from chlorinated solvents can be
decomposed by the heat of the arc (or ame)
to form PHOSGENE, a highly toxic gas,
and other lung and eye irritating products.
The ultraviolet (radiant) energy of the arc
can also decompose trichloroethylene and
perchloroethylene vapors to form phosgene.
DO NOT WELD or cut where solvent vapors
can be drawn into the welding or cutting
atmosphere or where the radiant energy
can penetrate to atmospheres containing
even minute amounts of trichloroethylene or
perchloroethylene.
C. Fire and Explosion Prevention
Causes of re and explosion are: combustibles
reached by the arc, ame, ying sparks, hot
slag, or heated material, misuse of compressed
gases and cylinders, and short circuits.
BE AWARE THAT ying sparks or falling
slag can pass through cracks, along pipes,
through windows or doors, and through wall
or oor openings, out of sight of the goggled
operator. Sparks can y many feet.
To prevent res and explosion:
Keep equipment clean and operable, free
of oil, grease, and (in electrical parts) of
metallic particles that can cause short
circuits.
If combustibles are in area, do NOT weld
or cut. Move the work if practicable, to
an area free of combustibles. Avoid paint
spray rooms, dip tanks, storage areas,
ventilators. If the work cannot be moved,
move combustibles at least 35 feet away,
out of reach of sparks and heat; or protect
against ignition with suitable and snug-
tting, re-resistant covers or shields.
Walls touching combustibles on opposite
sides should not be welded on (or cut).
Walls, ceilings, and oor near work should
be protected by heat-resistant covers or
shields.
Fire watcher must be standing by with
suit able fi re exti nguis hing eq uipme nt
during and for some time after welding or
cutting if:
1. Appreciable combustibles (including
building construction) are within 35 feet.
2. Appreciable combustibles are further
than 35 feet, but can be ignited by sparks.
3. Openings (conce aled or visible) in
oors or walls within 35 feet may expose
combustibles to sparks.
4. Combustibles adjacent to walls, ceilings,
roofs, or metal partitions can be ignited by
radiant or conducted heat.
Hot work permit should be obtained before
operation to ensure supervisor’s approval
that adequate precautions have been
taken.
After work is done, check that area is free of
sparks, glowing embers, and ames.
An empty container that held combustibles,
or that can produce ammable or toxic
vapors when hea ted, must n ever be
welded on or cut, unless container has rst
been cleaned in accordance with industry
standards.
This includes: a thorough steam or caustic
cleaning (or a solvent of water washing,
depending on the combustible’s solubility),
followed by p urging and inerting with
nitrogen or carbon dioxide, and using
protective equipment.
Water-lling just below working level may
substitute for inerting.
Weld Control Selector Guide - Page i
Page 3
SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS
- Continued -
A container with unknown contents should
be cleaned (see paragraph above). Do
NOT depend on sense of smell or sight to
determine if it is safe to weld or cut.
Hollow castings or containers must be
vented before welding or cutting. They
can explode.
Explosive atmospheres. NEVER weld or cut
where the air may contain ammable dust,
gas, or liquid vapors (such as gasoline).
D. Compressed Gas Equipment
The safe handling of compressed gas
equipment is detailed in numerous industry
pu bli cat ions . Th e fo llo win g gener al
rules cover many of the most common
situations.
1. Pressure Regulators
Regulator relief valve is designed to protect
only the regulator from overpressure; it is
not intended to protect any downstream
equipment. Provide such protection with
one or more relief devices.
Never connect a regulator to a cylinder
containing gas other than that for which the
regulator was designed.
Rem ove faulty regulator f rom service
immediately for repair (rst close cylinder
valve). The following symptoms indicate a
faulty regulator:
Leaks - if gas leaks externally.
Excessive Creep - if delivery pressure
continues to rise with downstream valve
closed.
Faulty Gauge - if gauge pointer does not
move off stop pin when pressurized, nor
returns to stop pin after pressure release.
Repair. Do NOT attempt repair. Send faulty
regulators for repair to manufacturer’s
designated repair center, where special
techniques and tools are used by trained
personnel.
2. Cylinders
Cylinders must be handled carefully to
prevent leaks and damage to their walls,
valves, or safety devices:
Avoid electrical circuit contact with cylinders
including third rails, electrical wires, or
welding circuits. They can produced short
circuit arcs that may lead to a serious
accident. (See 1-3C)
ICC or DOT marking must be on each
cylinder. It is an assurance of safety when
the cylinder is properly handled.
Identifying gas content. Use only cylinders
with name of gas marked on them; do not
rely on color to identify gas content. Notify
supplier if unmarked. NEVER DEFACE or
alter name, number, or other markings on a
cylinder. It is illegal and hazardous.
Empties: Keep valves closed, replace caps
securely; mark MT; keep them separate
from FULLS, and return promptly.
Prohibited use. Never use a cylinder or its
contents for other than its intended use,
NEVER as a support or roller.
Locate or secure cylinders so they cannot be
knocked over.
Passageways and work areas. Keep cylinders
clear of areas where they may be stuck.
Transporting cylinders. With a crane, use
a secure support such as a platform or
cradle. Do NOT lift cylinders off the ground
by their valves or caps, or by chains, slings,
or magnets.
Do NOT expose cylinders to excessive heat,
sparks, slag, and ame, etc. that may cause
rupture. Do not allow contents to exceed 55
degrees C (130 degrees F.) Cool with water
spray where such exposure exists.
Protect cylinders, particularly valves from
bumps, falls, falling objects, and weather.
Re p l a c e c aps secu r e l y w h en movin g
cylinders.
Stuck valve. Do NOT use a hammer or wrench
to open a cylinder valve that cannot be opened
by hand. Notify your supplier.
Mixing gases. NEVER try to mix any gases
in a cylinder.
NEVER rell any cylinder.
Cylinder ttings should never be modied or
exchanged.
3. Hose
Prohibited use. Never use hose other than that
designed for the specied gas. A general hose
identication rule is: red for fuel gas, green for
oxygen, and black for inert gases.
Use ferrules or clamps designed for the hose
(not ordinary wire or other substitute) as a
binding to connect hoses to ttings.
No copper tubing splices. Use only standard
brass ttings to splice hose.
Avoid long runs to prevent kinks and abuse.
Suspend hose off ground to keep it from being
run over, stepped on, or otherwise damaged.
Coil ex ce ss h ose to prevent kinks and
tangles.
Protect hose from damage by sharp edges,
and by sparks, slag, and open ame.
Examine hose regularly for leaks, wear, and
loose connections. Immerse pressured hose
in water; bubbles indicate leaks
Repair leaky or worn hose by cutting area out
and splicing. Do NOT use tape.
4. Proper Connections
Clean cylinder valve outlet of impurities that
may clog orices and damage seats before
connecting regulator. Except for hydrogen,
crack valve momentarily, pointing outlet away
from people and sources of ignition. Wipe with
a clean, lintless cloth.
Match regulator to cylinder. Before connecting,
check that the regulator label and cylinder
marking agree, and that the regulator inlet and
cylinder outlet match. NEVER Connect a
regulator designed for a particular gas or
gases to a cylinder containing any other
gas.
Tighten connections. When assembling
threaded connections, clean and smooth
seats whe re n ec es sa ry. Ti gh te n. If
connection leaks, disassemble, clean, and
retighten, using properly tting wrench.
Adapters. Use a CGA adapter (available
from your supplier) between cylinder and
regulator, if one is required. Use two
wrenches to tighten adapter marked RIGHT
and LEFT HAND threads.
Regulator outlet (or hose) connections
may be identied by right hand threads for
oxygen and left hand threads (with grooved
hex on nut or shank) for fuel gas.
5. Pressurizing Steps:
Drain regulator of residual gas through
suitable vent before opening cylinder (or
manifold valve) by turning adjusting screw
in (clockwise). Draining prevents excessive
compression heat at high pressure seat by
allowing seat to open on pressurization.
Leave adjusting screw engaged slightly on
single-stage regulators.
Stand to side of regulator while opening
cylinder valve.
Open cylinder valve slowly so that regulator
pressure increases slowly. When gauge is
pre ssurized (gauge reaches regu lator
maximum) leave cylinder valve in following
position: for oxygen and inert gases, open
fully to seal stem against possible leak; for
fuel gas, open to less than one turn to permit
quick emergency shut-off.
Use pressure charts (available from your
supplier) for safe and efcient recommended
pressure settings on regulators.
Check for leaks on rst pressurization
and regularly thereafter. Brush with soap
solution. Bubbles indicate leaks. Clean
off soapy water after test; dried soap is
combustible.
E. User Responsibilities
Follow all Safety Rules.
Remove leaky or defective equipment from
service immediately for repair. Read and
follow user manual instructions.
F. Leaving Equipment Unattended
Close gas supply at source and drain gas.
G. Rope Staging-Support
Rope staging-support should not be used
for welding or cutting operation; rope may
burn.
1-3 ARC WELDING
Comply with precautions in 1-1, 1-2, and
this section. Arc Welding, properly done,
is a safe process, but a careless operator
invites trouble. The equipment carries high
currents at signicant voltages. The arc is
Weld Control Selector Guide - Page ii
Page 4
SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS
- Continued -
very bright and hot. Sparks y, fumes rise,
ultraviolet and infrared energy radiates,
weldments are hot, and compressed gases
may be used. The wise operator avoids
unnecessary risks and protects himself
and others from accidents.
A. Burn Protection
Comply with precautions in 1-2.
The welding arc is intense and visibly
bright. Its radiation can damage eyes,
penetrate lightweight clothing, reect from
light-colored surfaces, and burn the skin and
eyes. Skin burns resemble acute sunburn;
those from gas-shielded arcs are more
severe and painful. DON’T GET BURNED;
COMPLY WITH PRECAUTIONS.
1. Protective Clothing
Wear long-sleeve clothing in addition to
gloves, hat, and shoes. As necessary,
use additional protective clothing such
as leather jacket or sleeves, ameproof
apron, and re-resistant leggings. Avoid
outer garments of untreated cotton.
Bare skin protection. Wear dark, substantial
clothing. Button collar to protect chest and
neck, and button pockets to prevent entry
of sparks.
2. Eye and Head Protection
Protect eyes from exposure to arc. Eyes
may be damaged by radiant energy when
exposed to the electric arc, even when not
looking in the direction of the arc. Never look
at an electric arc without protection.
Welding helmet or shield containing a lter
plate shade no. 12 or denser must be used
when welding. Place over face before
striking arc.
Protect lter plate with a clear cover plate.
Cracked or broken helmet or shield should
NOT be worn; radiation can be passed
through to cause burns.
Cracked, broken, or loose filter plates
must be replaced IMMEDIATELY. Replace
clear cover plate when broken, pitted, or
spattered.
Flash goggles with side shields MUST
be worn under the helmet to give some
protection to the eyes should the helmet
not be lowered over the face before an arc
is struck. Looking at an arc momentarily
with unprotected eyes (particularly a high
intensity gas-shielded arc) can cause a
retinal burn that may leave a permanent
dark area in the eld of vision.
3. Protection of Nearby Personnel
Enclose the welding area. For production
welding, a separate room or enclosed bay is
best. In open areas, surround the operation
with low-reective, noncombustible screens
or panels. Allow for free air circulation,
particularly at oor level.
Viewing the weld. Provide face shields for
all persons who will be looking directly at
the weld.
Others working in area. See that all persons
are wearing ash goggles.
Before starting to weld, make sure that screen
aps or bay doors are closed.
B. Toxic Fume Prevention
Comply with precautions in 1-2B.
Generator engine exhaust must be vented to
the outside air. Carbon monoxide can kill.
C. Fire and Explosion Prevention
Comply with precautions in 1-2C.
Equipment’s rated capacity. Do not overload
arc welding equipment. It may overheat cables
and cause a re.
Loose cable connections may overheat or
ash and cause are.
Never strike an arc on a cylinder or other
pressure vessel. It creates a brittle area that
can cause a violent rupture or lead to such a
rupture later under rough handling.
D. Compressed Gas Equipment
Comply with precautions in 1-2D.
E. Shock Prevention
Expo sed elec trica lly hot co ndu ctors or
other bare metal in the welding circuit, or in
ungrounded, electrically-HOT equipment can
fatally shock a person whose body becomes a
conductor. DO NOT STAND, SIT, LIE, LEAN
ON, OR TOUCH a wet surface when welding
without suitable protection.
To protect against shock:
Keep body and clothing dry. Never work in
damp area without adequate insulation against
electrical shock. Stay on a dry duckboard, or
rubber mat when dampness or sweat cannot
be avoided. Sweat, sea water, or moisture
between body and an electrically HOT part or grounded metal - reduces the body surface
electrical resistance, enabling dangerous
and possibly lethal currents to ow through
the body.
1. Grounding the Equipment
When installing, connect the frames of each
unit such as welding power source, control,
work table, and water circulator to the building
ground. Conductors must be adequate to carry
ground currents safely. Equipment made
electrically HOT by stray currents may shock,
possibly fatally. Do NOT GROUND to electrical
conduit, or to a pipe carrying ANY gas or a
ammable liquid such as oil or fuel.
Three-ph ase conn ect ion . C hec k p has e
requirement of equipment before installing. If
only three-phase power is available, connect
single-phase equipment to only two wires of
the three-phase line. Do NOT connect the
equipment ground lead to the third (live) wire,
or the equipment will become electrically
HOT - a dangerous condition that can shock,
possibly fatally.
Before welding, check ground for continuity.
Be sure conductors are touching bare metal
of equipment frames at connections.
If a line cord with a ground lead is provided
with the equipment for connection to a
switch box, connect the ground lead to
the grounded switch box. If a three-prong
plug is added for connection to a grounded
mating receptacle, the ground lead must be
connected to the ground prong only. If the
line cord comes with a three-prong plug,
connect to a grounded mating receptacle.
Never remove the ground prong from a plug,
or use a plug with a broken ground prong.
2. Connectors
Fully insulated lock-type connectors should
be used to join welding cable lengths.
3. Cables
Frequently inspect cables for wear, cracks,
and damage. IMMEDIATELY REPLACE
those with excessively worn or damaged
insulation to avoid possibly lethal shock
from bared cable. Cables with damaged
areas may be taped to give resistance
equivalent to original cable.
Keep cable dry, free of oil and grease, and
protected from hot metal and sparks.
4. Terminals and Other Exposed Parts
Terminals and other exposed parts of
electrical units should have insulating
covers secured before operation.
5. Electrode Wire
Electrode wire becomes electrically HOT
when the power switch of gas metal-arc
welding equipment is ON and welding gun
trigger is pressed. Keep hands and body
clear of wire and other HOT parts.
6. Safety Devices
Safety devices such as interlocks and circuit
breakers should not be disconnected or
shunted out.
Before installation, inspection, or service of
equipment, shut OFF all power, and remove
line fuses (or lock or red-tag switches) to
prevent accidental turning ON of power.
Disconnect all cables from welding power
source, and pull all 115 volts line-cord
plugs.
Do not open power circuit or change polarity
while welding. If, in an emergency, it must
be disconnected, guard against shock burns
or ash from switch arcing.
Leaving equipment unattended. Always
shut OFF, and disconnect all power to
equipment.
Power disconnect switch must be available
near the welding power source.
Weld Control Selector Guide - Page iii
Page 5
ABOUT THIS GUIDE
This Weld Control Selector Guide is designed to aid in selection and installation of various weld controls and
Cobramatic feeders. The most popular power supplies from various manufacturers are covered, however,
many others are not. The power supplies not covered in this guide can also be hooked up to Cobramatic
feeders by modifying the connections. Spool-guns may also be hooked up by using a WC-1 control box.
The exception to this is "synergic" type of power supplies. There are two types of "synergic" units. If the
controls for the power supply are on the power supply, then a Cobramatic II feeder may be adaptable. If
the controls for the power supply are incorporated into that manufacturers wire feeder, then it becomes
difcult to hook up a different type of feeder.
When working with voltages present in this product and
CAUTION :
At the time of its printing the information in this guide was accurate according to the information provided
by the various manufacturers. Due to model variations, modications and other unknowns, this information
may not be accurate in all cases. Refer to the power supply owner's manual if there are any questions
or doubts about proper hook-up. Upon using this guide the user accepts full responsibility of the
consequences that may occur during hook-up. All work should only be attempted by a qualied service
technician with the proper tools and knowledge of electronics.
others, always obser ve warning and caution signs. Ser vice
must only be perfor med by qualied service personnel.
DISCLAIMER
WHY DO I NEED A WELD CONTROL?
The weld control provides the electronics needed to operate the spool gun, as well as, provide the contactor
signal to activate the power supply. In a GMAW (MIG) system the wire is not electrically hot until the weldor
activates the trigger. The weld control then sends the contactor signal to energize the power supply.
There are two types of contactor signals that various power supply manufacturers use. The rst is a "Closing
Contact" signal. With this type of signal the weld control simply touches the two contactor leads together
(providing continuity to the power supply). The second type of signal is the "115VAC" signal. With this
type of signal the weld control sends 115 volts AC to the power supply. If you were to touch the contactor
leads in this position, you would get a SHOCK when the trigger is activated. All GTAW (TIG) machines use
a closing contact signal because it would be unsafe to put a 115VAC contactor signal in a foot control.
WHICH WELD CONTROL?
The WC-1 can be used on all power supplies, although it may not be the most economical or most feasible
approach. Where possible, a dedicated weld control has been developed to simplify installation and lower
cost. These controls interface to a particular power supply or a group of power supplies from a certain
manufacturer.
HOW TO USE THIS GUIDE
1. Using the charts on pages 1 thru 5, locate the power supply you wish to connect to.
2. The next column over will indicate which control is needed for the Prince XL Spool-gun. Sometimes, an
optional control is available. This will be indicated in the third column. The fourth column will list any
special notes. Note: For Cobramatic feeders a weld control is not needed, however, if a contactor
box is listed it should be used.
3. Check the notes column for important information.
4. Check the hook-up instructions column for the section, then go to that section.
5. The Posa Start on the Cobramatic feeders can be used with all CV/CC power supplies by simply
connecting the single black lead extending from the back of the unit to work ground (-).
6. Reference the Appendix for connection information to many utility type welders.
Weld Control Selector Guide - Page iv
Page 6
Table of Contents
Power Supply Listing 1
Airco 7
Esab 9
Hobart 12
Lincoln 14
Miller 18
Powcon 21
Panasonic 23
Thermal Dynamics 24
Appendix 25
Warranty
Weld Control Selector Guide - Page v
Page 7
This page intentionally blank.
Weld Control Selector Guide - Page vi
Page 8
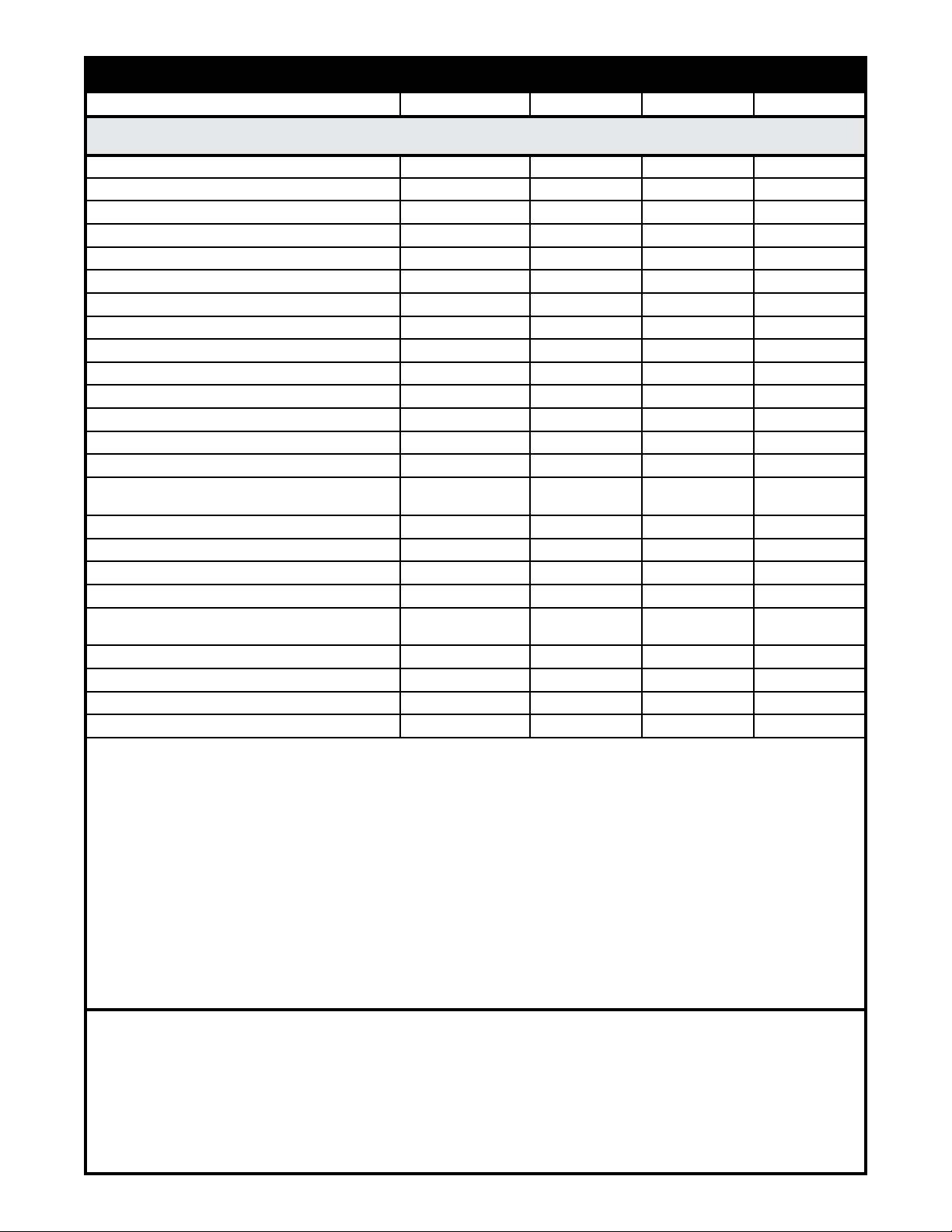
Weld Control Selector Guide
Power Supply Control Required Optional Notes* Section
Miller Electric
Millermatic 35, Spoolmate 200 I M-5
Millermatic 200, Regency 250, 300, 350 A 1, 6, 7 M-1, 3, 5
Millermatic 250, Vintage C M-6
Millermatic 250-X, 251 D M-5, 6
CP-200, 250TS, 300, 302, MC-300VS A 1,6, 7 M-1, 2, 3
Shopmaster 300 A 7 M-1, 3
All Delta Welds, Pulstar 450, IntelliWeld 650 A 1, 6, 7 M-1, 3, 5
Arc Pak 350 A 1, 6, 7 M-1, 3
XMT-200, 300, 304 (Optima Excluded) A 6, 7, 8 M-1, 3
XMT-300CC & CC/TIG I 2, 7, 8 M-4
Maxtron 300, 400 A 6, 7, 8 M-1, 3
All Maxstars (except 140 & 200) I 2 M-4
Dimension 400 A 1, 6, 7 M-1, 2, 3
MP30E, MP45E, MP65E, 300MT I M-2
All Gold Star SS, 320/330 A/BP
All Syncro Waves, 300ST Aircrafter
Dialarc HF I J (Rec.) 2 M-8
Legend AEAD-200LE I J (Rec.) 2, 3, 5 M-8
Bobcat 225G, 225NT I J (Rec.) M-8
Trailblazer 250, 251, Air Pak A 1, 6, 7 M-1, 3
Big 30A, 40G/D, 50D
with CV-3 installed
Big Blue 251D, 400D I J (Rec.) 2 M-8
Trailblazer 44G/D I 2 M-8
Trailblazer 55G/D A 1, 6, 7 M-1, 3
Invision 354, 456MP A 8 M-1, 3
I 2 M-4, 7
I
A
J (Rec.)
---
2
6, 7
M-4, 8
M-1, 3
WELD CONTROLS AVAILABLE
A P/N 005-0261 PA-M1 Spool Gun Control F P/N 005-0624 MigMaster 251 Kit
B P/N 005-0264 PA-G1 Spool Gun Control I P/N 001-3062 WC-1 Control
C P/N 005-0205 MillerMatic Module J P/N 001-3066 MK200 Contactor
D P/N 005-0629 MillerMatic 250/250-X Intfc Cbl K P/N 005-0617 Gunslinger 260 Intfc Cbl
E P/N 005-0206 MigMaster 250 Module L P/N 005-0676 PA-L1 Spool Gun Control
Weld Control Selector Guide - Page 1
Page 9

Weld Control Selector Guide
Power Supply Control Required Optional Notes* Section
Lincoln Electric
SP-150, 200 I L-1
SP-250 I B L-2
Wirematic 250, 255 I B L-3
PowerMig 255, 455 I 9 L-7
DC-250, 400, 600, Pulse Power 500 I L-4
R3S-250, 325, 400 I L-4, 5
CV-200, 250, 300, 400 I, L 7 L-6
Invertec V300-PRO, V350-PRO (Fac. & Adv.)
Invertec V350-PRO (Contractor)
TIG 250/300, Squarewave 300/350 I 2 L-8
Weldanpower 225/250 I J (Rec.) 2 L-9
G7, G8000, Ranger 8 (Red-D-Arc ZR-8 & ZR-10) I J (Rec.) L-9
G9, D-10 PRO, Classic w/CV Tap I L-4
Ranger 9, 10, 10-XL, 250, 275, 305 I, L 7, 10 L-6
Commander 300, 500, Vantage 500 I, L 7, 10 L-6
PowerWave 450, 450-ONE --- 8 L-10
L
I
I
J (Rec.)
7, 8
8
L-6
L-9
ESAB (Includes L-Tec & Linde)
L-Tec 225 I E-1
MigMaster 250 E E-2
MigMaster 251 F 8 E-3
MigMaster 300 I 8 E-4
ESAB 352CV, 452CV I 8 E-6
ESAB 251CV 8 E-7
MultiMaster 260 8, 12 E-7
Most V, VI, SVI Units I 8 E-5, 6
L-Tec 300, 400, 450, 650 I E-5, 6
UCC-301, 305, 306 I 2 E-8
HeliArc 250, 306, 301, 401 I 2, 8 E-8
L-Tec 250 Stick I J (Rec.) 2 M-8
ESAB Pulse Arc II-400, 500 I A-3
WELD CONTROLS AVAILABLE
A P/N 005-0261 PA-M1 Spool Gun Control F P/N 005-0624 MigMaster 251 Kit
B P/N 005-0264 PA-G1 Spool Gun Control I P/N 001-3062 WC-1 Control
C P/N 005-0205 MillerMatic Module J P/N 001-3066 MK200 Contactor
D P/N 005-0629 MillerMatic 250/250-X Intfc Cbl K P/N 005-0617 Gunslinger 260 Intfc Cbl
E P/N 005-0206 MigMaster 250 Module L P/N 005-0676 PA-L1 Spool Gun Control
Weld Control Selector Guide - Page 2
Page 10
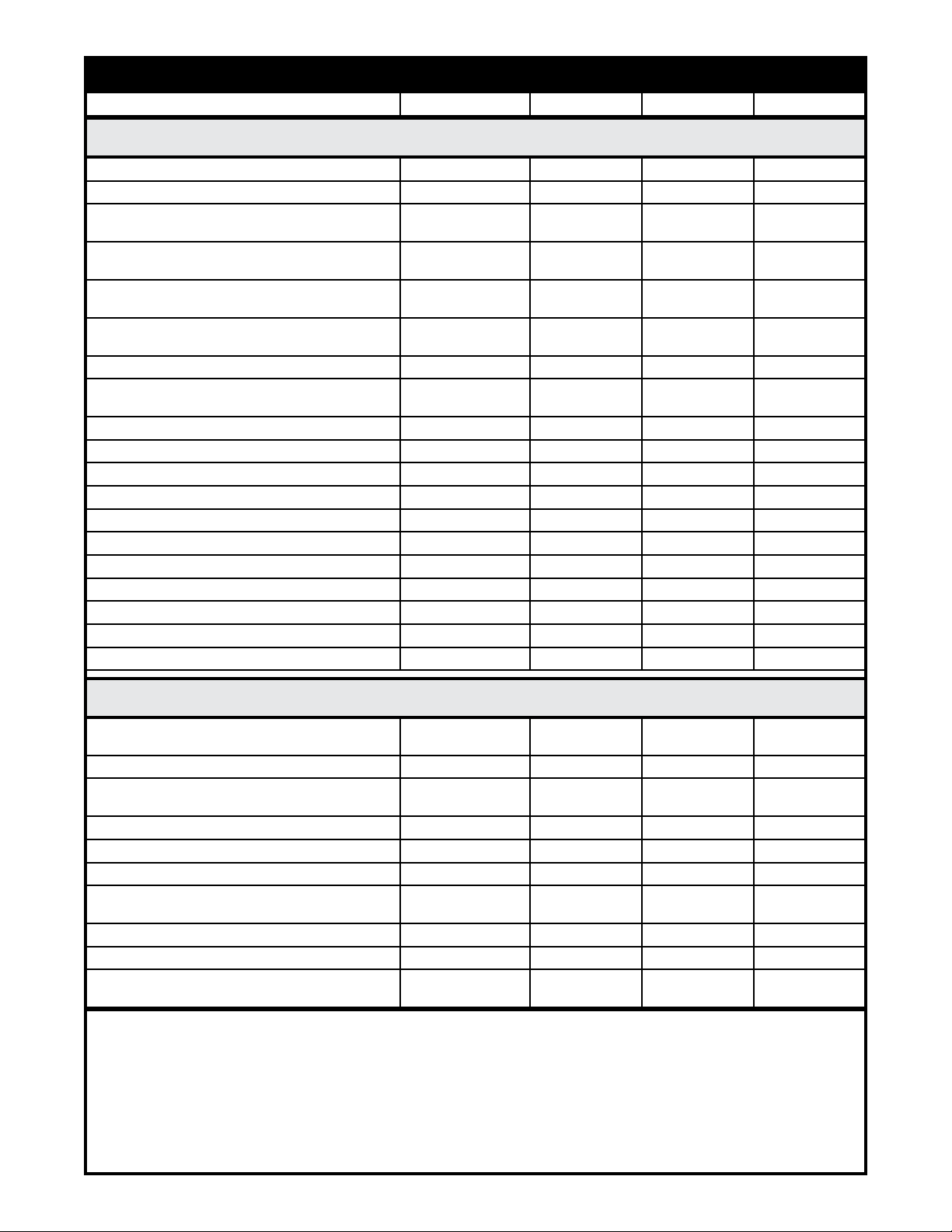
Weld Control Selector Guide
Power Supply Control Required Optional Notes* Section
Hobart (Includes ThermalArc)
BetaMig 200 B H-1
BetaMig 250, 251 I H-2
BetaMig 2510, IronMan 250 C
Mega Mig RC/RBS, Fabstar I
Hobart Excel Arc CV, CV/CC I
Fabricator 210, 300LF I 11
Fabricator 250 I T-2
Mega Flex RCC/RVS I
CyberTig, CyberWave I 2 H-4
Porta-Tig/Stick I 2 H-4
TR-250 I J (Rec.) 2 M-8
TR-250HF I 2 H-4
TigWave 250, 350 I 2 H-4
Champion/Titan Combo I H-4
Champion Fabshop I 2 H-4
Champion 16, 16D, 18 I J (Rec.) 2 H-4
Mega Arc Engine Driven I J (Rec.) 2, 5 M-8
Hobart DCC 353P I H-3
Titan 7000, 8000 AC/DC I J (Rec.) 2 M-8
H-2
M-6
H-3
HT-1,2
H-3
HT-1,2
T-2
M-1
H-3
HT-1
Thermal Dynamics (Includes ThermalArc)
300GMS, 400SMT, 400SMT-W A 6
Fabricator 210, 250 P/N 005-0689 11
Fabricator 310LF I
Fabricator 2620, 4030 I HT-1, 2
Viking 210, 250GM I P/N 003-1623 T-1
Excel Arc CV, CV/CC; Arc Master 351, 501 I HT-1, 2
PowerMaster I
Predator, Explorer (w/o Contactor) I J (Rec.) T-3
Exciter, Hog I J (Rec.) T-3
Predator, Explorer, Hercules, T-Bird (w/contactor) A, I
WELD CONTROLS AVAILABLE
A P/N 005-0261 PA-M1 Spool Gun Control F P/N 005-0624 MigMaster 251 Kit
B P/N 005-0264 PA-G1 Spool Gun Control I P/N 001-3062 WC-1 Control
C P/N 005-0205 MillerMatic Module J P/N 001-3066 MK200 Contactor
D P/N 005-0629 MillerMatic 250/250-X Intfc Cbl K P/N 005-0617 Gunslinger 260 Intfc Cbl
E P/N 005-0206 MigMaster 250 Module L P/N 005-0676 PA-L1 Spool Gun Control
T-2
M-3
T-2
M-1
HT-1, 2
M-3
HT-1
M-1
Weld Control Selector Guide - Page 3
Page 11
Weld Control Selector Guide
Power Supply Control Required Optional Notes* Section
Powcon
200SM B 6 P-2
300SM I P-1
300T, 300SS I 2 P-4
400SS I 2 P-5
400SM, 400SMT, 630SMP B 1, 6 P-3
500SM, 500SM AC/DC B 6 P-3
500MP I P-1
Plasma +, 225SMC (Single Phase) B 6 P-2
Plasma +, 225SMC (Three Phase) I P-1
Panasonic
Gunslinger 260 K PA-1
Airco
Dip-Pak 200, 225, 250 B 6 A-1
Dip-Cor 300 I A-2
CV-200, 250, 300, 450, 600 I A-3
PA-3A, PulseArc 350, 400, 500 I 4 A-3
Pulse Arc II400, 500 I A-3
Phase Arc 350, 550, 650 I A-3
AC/DC Heli-Welders I 2 A-4
AC/DC Square Waves I 2 A-4
WELD CONTROLS AVAILABLE
A P/N 005-0261 PA-M1 Spool Gun Control F P/N 005-0624 MigMaster 251 Kit
B P/N 005-0264 PA-G1 Spool Gun Control I P/N 001-3062 WC-1 Control
C P/N 005-0205 MillerMatic Module J P/N 001-3066 MK200 Contactor
D P/N 005-0629 MillerMatic 250/250-X Intfc Cbl K P/N 005-0617 Gunslinger 260 Intfc Cbl
E P/N 005-0206 MigMaster 250 Module L P/N 005-0676 PA-L1 Spool Gun Control
Weld Control Selector Guide - Page 4
Page 12
Weld Control Selector Guide
Notes:
1. Miller power supply must have 14 pin Amphenol or the WC-1 must be used. See WC-1
hookup, section M-2.
2. Constant current (CC) power supplies can only be used in spray transfer mode with
ALUMINUM and CORED wire only.
3. These power supplies put out less than 24VAC to the spool gun therefore maximum speed will
not be obtained. This means 3/64 diameter wire should be used when welding materials thicker
than 1/4.
4. Must be used in the non "synergic" mode.
5. Contactor box not needed if power supply has optional remote control facilities (panel).
6. WC-1 Weld Control can also be used.
7. An adapter cable with Amphenol already attached can be used with the power supply and
WC–1 or Cobramatic combination.
8. Many of the newer power supplies, especially the inverter style units now use a Dinse style
connector for the weld power out. This means the lug on the power cable of the Spool-gun
must be cut-off and replaced by a male Dinse connector (MK P/N: 153-0755).
9. MK does not make a weld control for the Lincoln PowerMig 255. Since Lincoln makes their
own control for a Prince XL Spool-gun, they furnish the control module with the Spool-gun.
However the WC-1 or the MK Cobramatic Cabinet may be used with that unit (See L-7 ).
10. At this time, the Lincoln Commander 300 and 500 does not have 42VAC volts at the 14-Pin
connector. An optional kit (P/N: K1597-1) must be obtained from Lincoln in order to use the
Prince® XL spool gun with the PA-L1. Units with a date code of November 2001 have 42VAC.
11. If the Fabricator 210 has a 4 digit specication number (xxxx), then the 14-Pin Control will
work. If the 4 digit specication has an "A" at the end (xxxxA), then a WC-1 Control must be
used. (See H-2)
12. To use an MK 003-1341 Adapter, the Multimaster 260 requires the optional ESAB spool gun
control module. Units after S/N 0558001793 come standard with the Spool Gun Module.
13. The Classic Series engine driven welder is a CC type power supply. To properly operate this
unit while welding aluminum, the CV tap is required. However, because 42VAC is unavailable
a WC-1 Weld Control must be used.
WELD CONTROLS AVAILABLE
A P/N 005-0261 PA-M1 Spool Gun Control F P/N 005-0624 MigMaster 251 Kit
B P/N 005-0264 PA-G1 Spool Gun Control I P/N 001-3062 WC-1 Control
C P/N 005-0205 MillerMatic Module J P/N 001-3066 MK200 Contactor
D P/N 005-0629 MillerMatic 250/250-X Intfc Cbl K P/N 005-0617 Gunslinger 260 Intfc Cbl
E P/N 005-0206 MigMaster 250 Module L P/N 005-0676 PA-L1 Spool Gun Control
Weld Control Selector Guide - Page 5
Page 13

This page intentionally blank.
Weld Control Selector Guide - Page 6
Page 14
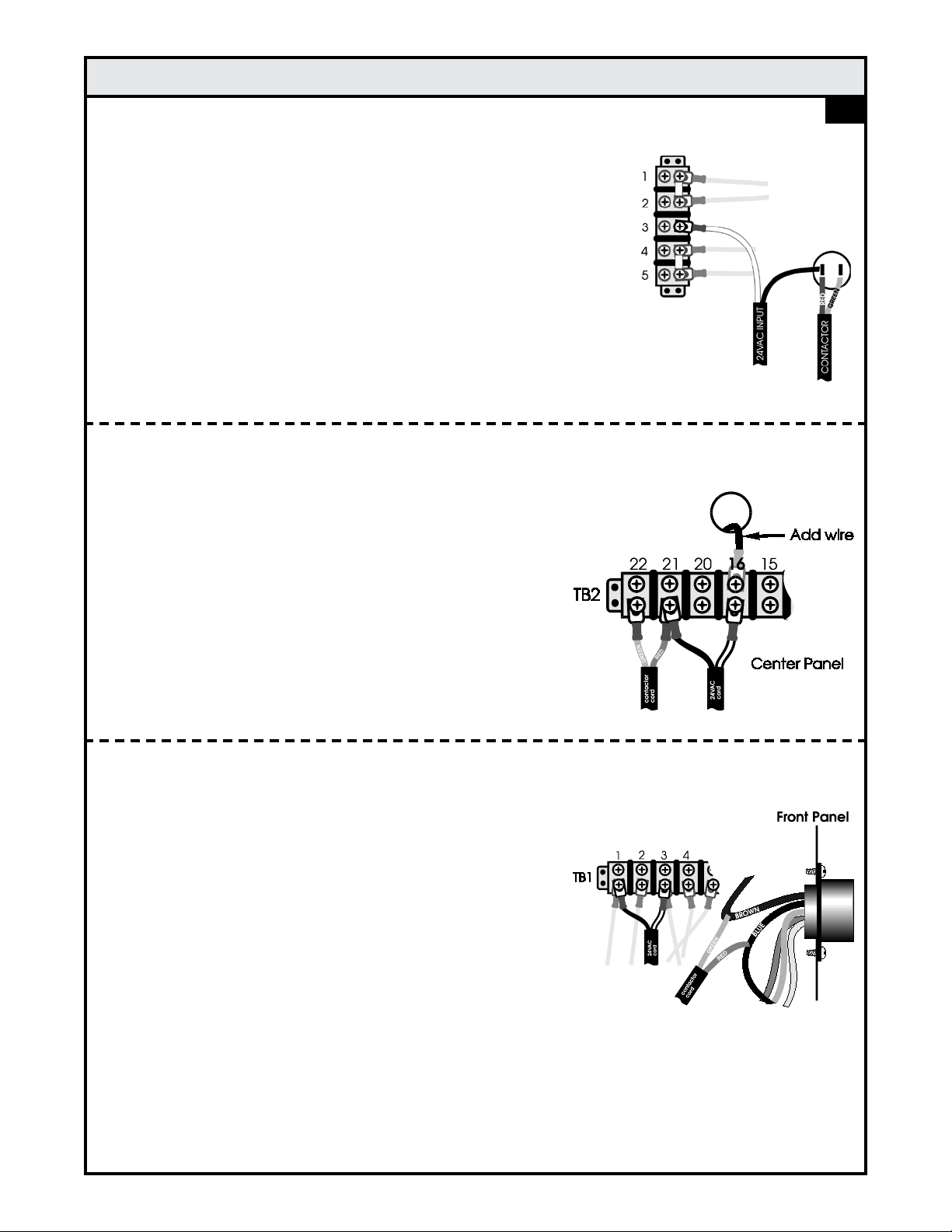
Airco
The PA-G1 Control (P/N 005-0264) is connected to the Dip-Pak 200 as follows:
1. Connect the red and green contactor leads extending from the
Control to the spade connectors located next to the wire feed
motor; red to wire to the left spade and green wire to the right
spade.
2. Connect the black wire extending from the Control to the left
spade along with the red and the white wire to #3 on the
terminal strip located above the wire feed motor.
3. Set the unit on "MANUAL" and adjust the voltage using the "UP
& DOWN" push-button.
4. Place Wire Feed/Midget Switch to "MIDGET" position.
Note: The feeder inside this unit will also be turned on, so disengage
the spring tension on drive roll.
The PA-G1 Control (P/N 005-0264) is connected to the Dip-Pak 225 as follows:
1. Remove the left panel and locate pin 1 of terminal strip
(where all blue wires converse). Add a wire from pin 1
and route it through the access hole on the center panel
into the left side. Connect the added wire to terminal strip
TB 2 #16 located above the wire feed motor.
2. Connect the green contactor lead extending from the
Control to TB2 #22 and the red contactor lead to TB2
#21.
3. Connect the black wire extending from the Control to TB2
#21 and the white wire to TB2 #16.
Note: The feeder inside this unit will also be turned on, so
disengage the spring tension on drive roll.
A-1
The PA-G1 Control (P/N 005-0264) is connected to the Dip-Pak 250 as follows:
1. Remove the left panel. Splice the red and green
contactor leads extending from the Control to the brown
and blue wires extending from the front panel amphenol;
red to wire to blue and green wire to brown.
2. Locate TB-1 (an 8 position terminal strip inside unit).
Connect the black wire extending from the Control to
TB1 #1 and white wire to #3.
3. Set the switch inside the Dip-Pak wire feed compartment
to "Spoolgun"
4. Connect the spoolgun power lug to the front connector or
to the bolt next to the wire feed motor.
Note: Splice and fork connectors are included in Control kit.
THE WC-1 OR COBRAMATIC CAN ALSO BE CONNECTED TO THESE UNITS BY SIMPLY
CONNECTING THE CONTACTOR AND PLUGGING THE UNIT INTO A STANDARD WALL OUTLET.
(Both the WC-1 or Cobramatic Contactor will be in CLOSING CONTACTS position, see Appendix for
contactor information.)
Weld Control Selector Guide - Page 7
Page 15

Airco
A-2
The WC-1 Weld Control or the Cobramatic Cabinet can be connected to the Dip-Cor 300 as follows:
1. Connect the black and white contactor leads extending from the WC-1 or Cobramatic to the
spade connectors located on the center panel below the wire feed motor. Place the contactor in
the CLOSING CONTACTS position (see Appendix for contactor information).
2. Plug the 115VAC plug extending from the WC-1 or Cobramatic into a standard wall outlet.
3. Tape off WC-1 red and green leads and turn off Posa Start switch as Posa Start is not used.
Note: The feeder inside these units will also be turned on, so disengage the spring tension
on the drive roll.
A-3
Airco CV power supplies use a two-prong twist lock for the contactor. Some units have a standard wall
outlet 115VAC plug.
1. To hook-up the WC-1 or Cobramatic to these units connect the black and white
contactor leads extending from the WC-1 or Cobramatic to the two-prong twist
lock plug (black to hot & white to neutral). Change the contactor to the 115VAC
position (see Appendix for contactor information).
2. Plug the 115VAC plug extending from the WC-1 or Cobramatic into a standard
wall outlet.
3. Tape off WC-1 red and green leads and turn off Posa Start switch as Posa Start
is not used.
4. If the power supply has a Remote/Standard contactor switch set it to "REMOTE".
Two Prong Plug
Miller 039-635
Hubbel 7101
Note: On Pulse Arc series machines:
1. Place remote pendant Wire Speed switch in "MANUAL".
2. Use Voltage Trim for voltage control.
3. Use spoolgun wire speed knob to adjust wire speed.
A-4
The WC-1 Weld Control or the Cobramatic Cabinet can be connected to Airco CC power supplies as
follows:
Airco has used a variety of contactor plugs over the years. (On some older units, a 6-Pin Cinch-Jones
plug was popular. The WC-1 or Cobramatic contactor leads would go to pins 1 and 3.)
All TIG machines use CLOSING CONTACTS!
1. Connect the black and white contactor leads extending from the WC-1 OR Cobramatic to the
remote foot control receptacle. Using the owner's manual or the foot control nd out which leads
go to the switch inside the foot control; this is where the contactor leads will be connected on the
front panel receptacle. Place the WC-1 or Cobramatic in the CLOSING CONTACTS position (see
Appendix for contactor information).
2. Plug the 115VAC plug extending from the WC-1 or Cobramatic into a standard wall outlet.
3. *Connect the red and green leads from the WC-1 to the power supply positive (+) and negative
(-) terminals of the power supply; red to positive (+) and green to negative (-).
4. If the power supply has a Remote/Standard contactor switch set it to "REMOTE".
5. Set the amperage control to "panel" and the process switch to "TIG".
6. Place polarity switch to DC Reverse Polarity (electrode positive).
Required Plug
Check the owner's manual for the
correct plug part number. The plug
will be found on the end of the foot
control cable.
*See Appendix for Cobramatic Posa Start information.
CAUTION: MAKE SURE THAT THE HIGH FREQUENCY IS
TURNED OFF OR DAMAGE TO THE WC-1 OR
COBRAMATIC WILL OCCUR.
Weld Control Selector Guide - Page 8
Page 16

ESAB (Includes L-Tec & Linde)
The older L-Tec 225 is connected as follows:
1. Install 1/4 (.250) wide female spade connectors to the Black and White contactor wires extending
from the WC-1 Weld Control or the Cobramatic Cabinet to the male spade connectors located on
the inside wall of the welder by the wire feeder. First remove the existing trigger leads from the L-
Tec torch. Place the WC-1 or Cobramatic in the CLOSING CONTACTS position (see Appendix for
contactor information).
2. Plug the 115VAC plug extending from the WC-1 or Cobramatic into a standard wall outlet.
Note: The feeder inside this unit will also be activated so disengage the spring tension on
the drive roll.
The 005-0206 Kit will interface a Prince XL Spool-gun to a Migmaster 250. It plugs directly into the
amphenol on the front of the unit and includes everything needed to interface to that power supply.
A Cobramatic system may be used on this unit and would be interfaced as
follows:
1. Plug the 115VAC plug from the Cobramatic Cabinet into a standard
wall outlet.
2. Connect the black and white contactor leads from the Cobramatic
Cabinet to the 8-Pin (Spool-gun) plug on the Migmaster 250:
the black wire to Pin A and the white wire to Pin B. Put the
Cobramatic in CLOSING CONTACTS Position (see Appendix for
contactor information).
E-1
E-2
8-Pin Amphenol
Note - The power cable to the Cobramatic hooks to bolt holding an
existing cable just in front of the MM-250's wire feed motor. Place the
Switch (Std/Spool-gun) in Spool-gun position.
Socket 153-0922
Cord Clamp 411-0191
Rubber Boot 301-0054
E-3
The 005-0624 Kit will interface a Prince XL Spool-gun to a Migmaster 251. It replaces a blank
panel on the front of the machine and includes everything needed to interface to this welder.
A Cobramatic system may be used on this unit and would interface as follows:
1. Plug the 115VAC plug from the Cobramatic Cabinet into a standard wall outlet
2. Install 1/4 (.250) wide female spade connectors to the Black and White contactor wires extending
from the Cobramatic Cabinet to the male spade connectors located on the inside wall of the
welder by the wire feeder. First remove the existing trigger leads from the Migmaster torch. Place
the Cobramatic in the CLOSING CONTACTS position (see Appendix for contactor information).
3. Place the power cable lug from the Cobramatic Cabinet on the positive ( + ) terminal of the
Migmaster 251 located by the wire feeder inside the welder.
E-4
The WC-1 Weld Control of the Cobramatic Cabinet may be connected to the Migmaster 300 as follows:
1. Plug the 115VAC plug from the WC-1 Weld Control of the Cobra
Cabinet into a standard wall outlet.
2. Connect the Black and White contactor leads from the WC-1 or
Cobramatic to the 8-Pin plug on the Migmaster 300. The black
wire to Pin A and the white wire to Pin B. Put the WC-1 or
Cobramatic into CLOSING CONTACTS position (see Appendix for
contactor information).
3. A male Dinse style connector is required on this machine. Cut the
lug off of the power cable on the Prince XL Spool-gun and replace
with the Dinse connector.
8-Pin Amphenol
Socket 153-0922
Cord Clamp 411-0191
Rubber Boot 301-0054
DInse Connector
Male Plug 153-0755
Weld Control Selector Guide - Page 9
Page 17

ESAB (Includes L-Tec & Linde)
E-5
The older Linde CV machines are connected as follows:
1. Connect the black and white contactor leads extending from the WC-1 Weld Control or the
Cobramatic Cabinet to the 6-Pin metal Pyle-National plug; black to pin 3 and white to pin 5.
Place WC-1 or Cobramatic in the 115VAC CONTACTOR position (See Appendix for changing
contactor).
2. Plug the 115VAC plug extending from the WC-1 or Cobramatic into a standard wall outlet or
cut off the plug and wire the black wire to pin 1, the white wire to pin 2 and the
green wire to pin 4.
3. Tape off WC-1 red and green leads and turn off Posa Start switch as
Posa Start is not used.
Pyle National “Triploc”
Male Plug AP-610
Housing APD-2004
E-6
The newer ESAB/Linde/L-Tec CV machines are connected as follows:
1. Connect the black and white contactor leads extending from the WC-1 Weld Control or
Cobramatic Cabinet to the 7-Pin plastic AMP plug; black to pin 1 and white to pin 3. Place WC-
1 or Cobramatic in the CLOSING CONTACTS position (see Appendix for contactor information).
2. Plug the 115VAC plug extending from the WC-1 or Cobramatic into a standard wall outlet or
cut off the plug and wire the black wire to pin 1, the white wire to pin 2 and the green
wire to pin 4.
3. Tape off WC-1 red and green leads and turn off Posa Start switch
as Posa Start is not used.
7-Pin Amp Connector
L-Tec P/N AMP P/N
7-Pin Plug 674655 206226-1
Cord Clamp 674568 206138-1
Pins (4 req.) 674564 66255-1
Some ESAB/L-TEC CV/CC machines have 19 pin (J1) amphenols and are connected as follows:
1. Connect the black and white contactor leads extending from the
WC-1 or the Cobramatic to the 19 pin amphenol plug; black to pin
A and white to pin C. Place WC-1 or Cobramatic in the CLOSING
CONTACTS position (see Appendix for contactor information). Pins
U & V can also be used for contactor.
2. Plug the 115VAC plug extending from the WC-1 or Cobramatic into a
standard wall outlet or cut off the plug and wire the black wire to pin
A, the white wire to pin B and the green wire to pin D.
A
M
L
K
N
P
V
J
R
H
F
G
C
A
L
B
B
U
C
T
D
S
E
The MultiPower 460 units do not supply 115VAC at the 19-Pin.
3. Tape off WC-1 red and green leads and turn off Posa Start switch as Posa Start is not used. On
the Cobramatic System hook up the Posa-Start lead to the Power Supplies ARC GROUND and
use PosaStart when welding aluminum only.
19-Pin Amphenol
MK P/N’s Amphenol P/N’s
Complete 8' cable with 19P Amphenol attached.
Easily connects to SVI 450 (115VAC on 19-Pin).
P/N 005-0614
19-Pin Plug 153-0314 3106A22-14P
Cord Clamp 411-0035 3057-1012
Rubber Boot 301-0026 MS3420-12
Note: Use in CV-Mig mode and be
sure that nothing is plugged
into J2 (8-Pin).
r
o
t
c
a
t
n
o
C
d
r
o
C
K
E
IT
H
W
B
L
A
C
K
115VAC
E
T
I
Leads
H
W
N
E
E
GR
Weld Control Selector Guide - Page 10
Page 18

ESAB (Includes L-Tec & Linde)
E-5
The Prince XL Spool-gun may be hooked up to the ESAB 251cv Power Supply using the welders built-
in speed control module. This is accomplished by using a MK adapter pigtail (P/N 003-1341) which will
plug directly into the ESAB power supply's 8-Pin amphenol on the front of the machine.
The lug on the Prince XL's power cable will have to be cut off and replaced by a male Dinse connector
(MK P/N: 153-0755). There's a switch on the front upper panel that has to be in the Spool-gun position.
If the Multimaster 260 has ESAB's optional spool gun module already installed, then the 003-1341 MK
adapter pigtail will work.
A Cobramatic system may be connected to this power supply. Use the instructions found in section E-2
for the Cobramatic system. However, the switch on the upper panel of the welder will have to be in the
Spool-gun position.
Do not attempt to hook up the Cobramatic system using the 19-Pin Amphenol on this unit.
E-5
The WC-1 Weld Control or the Cobramatic Cabinet can be connected to All L-Tec/Linde TIG/CC)
machines as follows: Note - Various contactor plugs have been used over the years.
1. Connect the black and white contactor leads extending from the WC-1 Weld Control or the
Cobramatic Cabinet to the remote foot control receptacle on the unit. Using the owner's manual
or the foot control nd out which leads go to the switch inside the foot control; this is where the
contactor leads will be connected on the receptacle.
2. Place WC-1 or Cobramatic in CLOSING CONTACTS position (see Appendix for contactor
information).
3. Plug the 115VAC plug extending from the WC-1 or Cobramatic into a standard wall outlet.
4. *Connect the red and green leads from the WC-1 to the power supply positive (+) and negative
(-) terminals of the power supply; red to positive (+) and green to negative (-).
5. Place the Weld Control Switch to "INERT GAS or TIG" and the Remote Switch to "PANEL".
6. Set the Polarity Switch to "DC REVERSE POLARITY" (electrode positive).
7. Set the Soft Start to "OFF" and the High Frequency Switch to "OFF".
8. The Posa Start must be used. See WC-1 or Cobramatic owner's manual for Posa Start
information.
Required Plug
Check the owner's manual
for the correct plug part
number. The plug will be
found on the end of the foot
control cable.
*See Appendix for Posa Start information.
CAUTION: MAKE SURE THAT THE HIGH FREQUENCY IS
TURNED OFF OR DAMAGE TO THE WC-1 OR
COBRAMATIC WILL OCCUR.
Weld Control Selector Guide - Page 11
Page 19

Hobart (Includes ThermalArc)
H-1
The Prince XL Spool-gun may be hooked up to the BetaMig 200 or the BetaMig LF by using the PA-G1
Control (P/N 005-0264) as follows:
1. Open the left side of BetaMig.
2. Splice the red and green contactor leads extending from the Control to the spade connectors
below the wire feed motor on the deck (trigger connection).
3. Remove the right side panel of BetaMig and locate the small control transformer next to the input
voltage taps. The transformer is marked 110/110 on one side and 24/24 on the other.
4. Splice the black wire extending from the Control to one side of the Spade 24 and the white wire
to the other Spade 24.
A WC-1 Weld Control or Cobramatic System may be hooked up to these units as follows:
1. Plug the WC-1 or Cobramatic Cabinet 115VAC plug into a standard wall outlet.
2. Install 1/4 (.250) wide female spade connectors to the black and white contactor leads from the
Cobramatic Cabinet. Inside the Wire Feeder portion of the BetaMig console, remove the torch
trigger leads from the spade connector and plug on the ones from the Cobramatic contactor
leads.
Note: The feeder inside these units will also be turned on,
so disengage the spring tension on drive roll.
H-2
The BetaMig 2510 Kit (P/N 005-0205) is the same kit for the Millermatic 250 and plugs directly into
the front panel on the front of the unit. It includes everything needed to interface to this power supply.
However, the printing on the kit identies it as a Millermatic 250 kit.
A WC-1 Weld Control or Cobramatic System may be hooked up to any of the BetaMig systems above.
In each case, the 115VAC plug from the Cobramatic Cabinet must go to a standard wall outlet.
On the BetaMig 250, female spade connectors have to be installed on the WC-1 or Cobramatic
Cabinet's contactor leads (CLOSING CONTACTS position) and installed like that listed in H-1 .
On the BetaMig 251 and BetaMig 2510, splice the WC-1 or Cobramatic Cabinet's contactor leads
(CLOSING CONTACTS position) to the trigger leads coming from the back of the Hobart's torch
connection to the welder.
Note: In all three cases, the feeder inside these unit will also be turned on, so disengage the spring
tension on the drive roll.
H-3
The WC-1 Weld Control and the Cobramatic Cabinet is connected to Hobart CV and CV/CC power
supplies as follows:
The contactor is always found on pins "A" and "B" regardless of the type of amphenol.
Most of the Hobart CV power supplies use a 5-Pin amphenol.
1. Connect the black and white contactor leads from the WC-1 or Cobramatic to pins
A & B of the 5-Pin amphenol; black to "A" and white to "B". Place the contactor
in the CLOSING CONTACTS position (see Appendix for contactor information).
2. Plug the 115VAC plug extending from the WC-1 or Cobramatic into a standard wall outlet.
3. Tape off WC-1 red and green leads and turn off Posa Start switch as Posa Start is not used.
4. If the power supply has a Remote/Standard contactor switch set it to "REMOTE".
5-Pin Amphenol
Plug 3106A18-20P
Cord Clamp 3057-1010
Boots
MS3420-10
MS3420-8
Note: If unit is a CV/CC power supply use in the CV
mode. If hooking up a Cobramatic Cabinet, it is
recommended to hook up and use the PosaStart
feature.
C
E
D
Weld Control Selector Guide - Page 12
Page 20

Hobart (Includes ThermalArc)
H-4
The WC-1 Weld Control or the Cobramatic Cabinet can be connected to Hobart CC power supplies as
follows (The contactor is always found on pins "A" and "B" regardless of the type of amphenol):
All TIG machines use CLOSING CONTACTS!
1. Connect the black and white contactor leads from the WC1 or Cobramatic to pins A & B of the remote amphenol: black
to "A" and white to "B". Place the contactor in the CLOSING
CONTACTS position (see Appendix for contactor information).
2. Plug the 115VAC plug from the WC-1 or Cobramatic into a standard
wall outlet.
3. Connect the red and green leads from the WC-1 to the power
supply positive (+) and negative (-) terminals of the power supply;
red to positive (+) and green to negative (-).
4. If the power supply has a Remote/Standard contactor switch set
it to "REMOTE". Set the amperage control to "panel" and the
process switch to "TIG".
5. Place polarity switch to DC Reverse Polarity (electrode positive).
CAUTION: MAKE SURE THAT THE HIGH FREQUENCY IS TURNED OFF OR DAMAGE TO THE
WC-1 OR COBRAMATIC WILL OCCUR.
Note: The TR-250 HF uses a 10 pin amphenol and you must jumper pins D & E together.
5-Pin Amphenol
Plug 3106A18-20P
Cord Clamp 3057-1010
Boots
10-Pin Amphenol
Plug 3106A18-19P
Cord Clamp 3057-1010
Boots
MS3420-10
MS3420-8
MS3420-10
MS3420-8
HT-1
Since Hobart was divided up and sold to several different companies; the type of interfacing plug might
be different depending on the age of the machines. At one time Hobart put both a 5-Pin and a 19-Pin
Amphenol on their units. Then they went strictly to a 5-Pin Amphenol. As other companies came into
the picture, some introduced the Miller version of a 14-P Amphenol. Then on some models, both a 5-Pin
and a 14-Pin were used. To add to the confusion, some later models have both a 14-Pin and a 19-Pin
Amphenol (The Fabstar is a good example of this). The one constant seems that all of these amphenols
used CLOSING CONTACTS to pins A and B. Check each particular machine to see what type of
amphenol is used. If there are any questions, refer to the machine's Owners Manual and/or check for
voltages with a V-O-M. (Volt-Ohmmeter)
HT-2
A WC-1 Weld Control or the Cobramatic Cabinet may be connected to any Thermal-Hobart CV type
power supply that has a nineteen (19) pin amphenol.
1. Connect the black and white contactor leads from the WC-1 or Cobramatic Cabinet to pins A
& B of the 19-Pin Amphenol; black to “A” and white to “B”. Place the contactor in CLOSING
CONTACTS position (see Appendix for contactor information).
2. Plug the 115VAC plug from the WC-1 or Cobramatic Cabinet into a standard
wall outlet or cut off the plug and wire the cord to the 19-Pin Amphenol;
black to pin “E”, white to pin “F”, and green to pin “G”.
3. With the WC-1, the Posa-start switch will be in the “OFF” Position and
the Red and Green leads will not be used.
4. If the power supply has a Remote/Standard contactor switch, set it to
“Remote.”
19-Pin Amphenol
19-Pin 153-0314
Cord Clamp 411-0035
Rubber Boot 301-0026
P/N 005-0630
Complete 8' cable with
19P Amphenol attached.
Note: Thermal furnishes 24VAC to pins “D” and “R”. This means a spool-gun may be used with a 005-0264 PA-G1 Control on
the Thermal-Arc units. Wire a 19-Pin amphenol to PA-G1 Control as follows: the black wire to pin “D”, the white wire to
pin “R”, the red wire to pin “A” and the green wire to pin “B”. (If there are any questions if voltages are or are not
available, check the amphenol on the welder with a V-O-M. (Volt-Ohmmeter)
Weld Control Selector Guide - Page 13
Page 21

Lincoln Electric
L-1
The SP-150 & 200 are interfaced using the WC-1 Weld Control or the Cobramatic Cabinet as follows:
1. Connect the black and white contactor leads extending from the WC-1 or
Cobramatic to the 4-Pin plug located below the wire feed motor. Place the
contactor in the CLOSING CONTACTS position (see Appendix for contactor
information).
2. Plug the 115VAC plug extending from the WC-1 or Cobramatic into a
standard wall outlet (in some cases 115VAC can be found at the fan motor).
3. Tape off WC-1 red and green leads and turn off Posa Start switch as Posa
Start is not used.
Four Pin Plug
Cinch-Jones P/N P-304
Lincoln P/N T-10662-1
L-2
The WC-1 Weld Control or the Cobramatic Cabinet can be connected to the SP-250 as follows:
1. Remove the left side panel of SP-250.
2. Splice the black and white contactor leads from the WC-1 or
Cobramatic to the J5 plug located below the wire feed motor;
black to # 325 and white to # 324. Place the contactor in the
CLOSING CONTACTS position (see Appendix for contactor
information).
3. Plug the 115VAC plug from the WC-1 or Cobramatic into a
standard wall outlet.
4. Tape off WC-1 red and green leads and turn off Posa Start switch
as Posa Start is not used.
5. Set the unit on "MANUAL" and adjust the voltage using the "UP &
DOWN" push-button.
Splice Connectors
MK P/N 153-0818
3M P/N 558 (2 req'd)
The PA-G1 Control (P/N 005-0264) can also be connected to the SP-250 as follows:
1. Remove the left side panel of SP-250
2. Splice the red and green contactor leads extending from the
Control to the J5 plug located below the wire feed motor; red to
wire # 325 and green to # 324. The trigger plug on the SP-250
front panel can also be used.
3. Remove the right side panel of the SP-250 and locate red wires
# 202 and # 203 going to plug # J6 on the main P.C. board.
4. Splice the black wire extending from the Control to wire # 202 and
the white wire to # 203.
5. Set the unit on "MANUAL" and adjust the voltage using the "UP &
DOWN" push-button.
Splice Connectors
MK P/N 153-0818
3M P/N 558 (4 req'd)
Note: The feeder inside the SP-250 will also be
turned on so disengage the spring tension on
the drive roll.
Notes: 1. Proper operation of the PA-G1 kit is
dependant upon the correct input voltage
value.
2. Four of the 153-0818 splice connectors are
included in the PA-G1 Control kit.
Weld Control Selector Guide - Page 14
Page 22

Lincoln Electric
The Wirematic 250 and Wirematic 255 are interfaced using the WC-1 Weld Control or the Cobramatic
Cabinet as follows:
1. Connect the black and white contactor leads from the WC-1 or Cobramatic
to the two solid pins on the 4-Pin Amp plug (trigger plug). Place the
contactor in the CLOSING CONTACTS position (see Appendix for contactor
information).
2. Plug the 115VAC plug from the unit into a standard wall outlet.
3. Tape off WC-1 red and green leads and turn off Posa Start switch as Posa
Start is not used.
4. Adjust the "VOLTAGE" knob as needed and ignore the "WIRE FEED" knob.
Back
side of
plug
L-3
4-Pin Amp
MK P/N’s AMP P/N’s
Socket 153-0998 206429-1
Cord Clamp 153-0946 206062-3
Pins (2 req.) 153-0958 66099-2/-3
The PA-G1 Control (P/N 005-0264) can also be connected to the Wirematic 250 as follows:
1. Remove the left side panel of the Wirematic 250.
2. Splice the red and green contactor leads extending from the
Control to the J5 plug located below the wire feed motor; red to
wire # 325 and green to # 324.
3. Remove the right side panel of the Wirematic 250 and locate red
wires # 202 and # 203 going to plug # J3 on the main P.C. board.
4. Splice the black wire extending from the Control to wire # 202 and
the white wire to # 203.
5. Adjust the "VOLTAGE" control as necessary and ignore the "WIRE
FEED" knob on the Wirematic front panel.
Notes: 1. Proper operation of the PA-G1 kit is dependant upon the correct input voltage value.
2. The feeder inside this unit will also be turned ON, so disengage the spring tension on the
drive roll.
3. Four of the 153-0818 splice connectors are included in the PA-G1 Control kit.
Note: The feeder inside the Wirematic unit
will also be turned on, so disengage
the spring tension on the drive roll.
The PA-G1 Control (P/N 005-0264) can also be connected to the SP255 as follows:
1. Remove the hinged lid and right side panel of the SP255.
2. Locate Plug J3 on the main PC Board (lower center). Find the red wires # 202 (goes to plug J3
- pin 1) and # 203 (goes to J3 - pin 3).
3. Splice the black wire extending from the Control to the red wire # 202 and the white wire to the
red wire # 203.
4. Locate trigger lead plug J13. It is a connector plug coming through the center divider of SP255.
It can be found just forward of the upper left side of the main PC Board. There'll be a 6-Pin plug
and just below it a 4-Pin plug. The 4-Pin plug is J13. Splice the red to wire #325 PIN #2 and the
green to wire #324 PIN #4.
5. Replace the right side panel and hinged lid.
6. The easiest way to mount the PA-G1 Control is on the side of the unit and to bring the wires from
the Control through the louvres on the front of the unit.
7. Adjust the "VOLTAGE" control as necessary and ignore the "WIRE FEED" knob on the Wirematic
front panel.
Notes: 1. Proper operation of the PA-G1 kit is dependant upon the correct input voltage value.
2. The feeder inside this unit will also be turned ON, so disengage the spring tension on the
drive roll.
3. Four of the 153-0818 splice connectors are included in the PA-G1 Control kit.
Weld Control Selector Guide - Page 15
Page 23

Lincoln Electric
L-4
For all Lincoln CV power supplies except the R3S-325 the following applies. See section L-5 for the
R3S-325.
1. Connect the black and white contactor leads from the WC-1 or
Cobramatic to the terminal strip on the Lincoln power supply;
black to 2 & white to 4. Place WC-1 or Cobramatic in CLOSING
CONTACTS position (see Appendix for contactor information).
2. Plug the 115VAC plug from the WC-1 or Cobramatic into a
standard wall outlet or cut off the plug and wire black to 31, white
to 32 and green to ground lug.
3. Tape off WC-1 red and green leads and turn off Posa Start switch
as Posa Start is not used.
Note: Some Lincoln gas drives use slightly different numbering on the terminal strip. However, 2 & 4
are still the contactor and 31 & 32 are still the 115VAC. If using a gas drive in CC mode red and
green Posa Start leads must be connected. (see section L-8, 9 ).
L-5
For the Lincoln R3S-325 the following applies.
1. Connect the black and white contactor leads extending from the
WC-1 or Cobramatic to the terminal strip on the R3S-325; black
to 32 & white to 4. Place the unit in CLOSING CONTACTS
position (see Appendix for contactor information).
2. Plug the 115VAC plug extending from the WC-1 or Cobramatic
into a standard wall outlet or cut off the plug and wire black to
32, white to 31 and green to ground lug.
3. Tape off WC-1 red and green leads and turn off Posa Start
switch as Posa Start is not used.
L-6
The PA-L1 Control (P/N 005-0676) comes equipped with a 14 Pin (X-clocked) amphenol connector and
simply plugs into any Lincoln CV-type welder that has a 14 Pin (X) socket. This unit operates on 42
volts and is for "CV" only. If the welder has a remote voltage control, it should be set on "Panel". The
contactor switch should be on "Remote". Most of the newer Lincoln shop machines now use a dinse
style connector (MK P/N 153-0755) which would have to replace the lug on the power cable of the
Prince XL spool gun.
New Lincoln power supplies use a 14-Pin (X clocked) amphenol similar to the Miller machines, however,
the pins are clocked differently than the Miller (S clocked) amphenol.
1. Connect the black and white contactor leads from the WC-1 or
Cobramatic to the 14-Pin amphenol; black to D & white to pin C.
Place unit in CLOSING CONTACTS position (see Appendix for
contactor information).
2. Plug the 115VAC plug from the WC-1 or Cobramatic into a
standard wall outlet or cut off the plug and wire black to J, white
to A and green to pin B.
3. Tape off WC-1 red and green leads and turn off Posa Start
switch as Posa Start is not used.
Note: If unit does not have a 14-Pin see section L-4 .
P/N 005-0608
Complete 8' cable with 14P
(X clocked) Amphenol attached.
P/N 005-0659
Complete 25' cable with 14P
(X clocked) Amphenol attached.
14-Pin
Amphenol
Socket 153-1161 S-12020-32
Cord Clamp 411-0035 S-12024-2
Rubber Boot 301-0021 ---
MK P/N’s LE P/N’s
CONTACTOR
LEADS
115VAC
OUTPUT
Weld Control Selector Guide - Page 16
Page 24

Lincoln Electric
A Cobramatic Cabinet and Torch can be used in conjunction with the Lincoln PowerMig 255: If a user
already has a Prince Spool-gun with a WC-1 Control, The WC-1 would be hooked up the same.
1. Since there's no 115VAC easily available on the PowerMig 255, Plug the 115VAC plug from
the WC-1 or Cobramatic into a standard wall plug.
2. Connect the black and white contactor leads from the WC-1 or Cobramatic Cabinet to the
two solid pins on the 4-Pin (Same Plug as listed in L-3 ) Plug located inside the door of the
PowerMig 255. Place the contactor in the CLOSING CONTACTS position (see Appendix for
contactor information).
Note: The feeder inside the PowerMig 255 will also be turned on, so disengage the spring tension on
the drive roll assembly.
L-7
The WC-1 Weld Control or the Cobramatic Cabinet can be connected to All Lincoln TIG machines as
follows: Lincoln has used three types of contactor plugs over the years. The very old machines used a
two-prong plug; then came a 5-Pin amphenol, followed by a 6-Pin amphenol.
1. If the power supply has a two-prong twist lock, connect the black and white contactor leads from
the WC-1 or Cobramatic to the two-prong plug (color code not important). If the power supply has
either the 5-Pin or the 6-Pin amphenol the black and white contactor leads usually go to pins D
and E; black to D & white to pin E (consult unit owners manual).
2. Place unit in CLOSING CONTACTS position (see Appendix for contactor information).
3. Plug the 115VAC plug from the WC-1 or Cobramatic into a standard wall outlet.
4. *Connect the red and green leads from the WC-1 to the power supply positive (+) and negative
(-) terminals of the power supply; red to positive (+) and green to negative (-).
5. Place the Weld Control Switch to "INERT GAS or TIG" and the Remote Switch to "PANEL".
6. Set the Polarity Switch to "DC REVERSE POLARITY" (electrode positive).
7. Set the Soft Start to "OFF" and the High Frequency Switch to "OFF".
*See Appendix for Posa Start information.
Required Plug
Check the owner's manual for the
correct plug part number. The plug
will be found on the end of the foot
control cable.
The WC-1 Weld Control or the Cobramatic Cabinet can be connected to Lincoln CC power
supplies that do not have contactors (stick machines) as follows:
CAUTION: MAKE SURE THAT THE HIGH FREQUENCY
Lincoln 6-Pin Amphenol S-12020-27
MK Cord Clamp 411-0191
IS TURNED OFF OR DAMAGE TO THE WC-1
OR COBRAMATIC WILL OCCUR.
L-8
L-9
With both the WC-1 or the Cobramatic, a Contactor box is recommended:
1. Connect the WC-1 or Cobramatic to the contactor box as shown in the Appendix.
2. Connect the spool gun power lug to the contactor box "TORCH" side and the positive (+) lead
from the power supply to the "+ WELD POWER" side.
2. Plug the 115VAC plug from the WC-1 or Cobramatic into a standard wall outlet.
3. *Connect the red and green leads from the WC-1 to the power supply positive (+) and negative
(-) terminals of the power supply; red to positive (+) and green to negative (-).
4. Place polarity switch to DC Reverse Polarity (electrode positive).
5. The Posa Start must be used. See WC-1 or Cobramatic owner's manual for Posa Start
information.
*See Appendix for Cobramatic Posa Start information.
The PowerWave 450 Kit (P/N 005-0254) connects directly to the 120VAC Cobramatic Wire Feed
Cabinets, 150-003 and 150-004.
The PowerWave 450 Kit (P/N 005-0315) connects directly to the 42VAC Cobramatic Wire Feed Cabinets
150-203 and 150-204.
The PowerWave 450 Kit (P/N 005-0322) connects directly to the Lincoln Cobramatic Wire Feed Cabinets
K1587-1.
Weld Control Selector Guide - Page 17
L-10
Page 25

Miller Electric
M-1
The PA-M1 Control (P/N 005-0261) comes equipped with a 14-Pin amphenol and simply plugs into the
Miller power supply. If the unit is a CV/CC power supply operate in the "CV" mode; have the remote
voltage selector on "panel" and the contactor selector on "14- Pin". Note - On the XMT series machines,
a Dinse style connector (MK P/N 153-0755) would have to replace the lug on the power cable of the
spool-gun.
M-2
Older style Miller CV power supplies without 14-Pin amphenols used a two prong twist lock for the
contactor and a three prong twist lock supplied an auxiliary 115VAC. Some units also had a standard
wall outlet 115VAC plug which can be used instead of the three prong plug.
1. To hook-up the WC-1 Weld Control or the Cobramatic cabinet to these units connect the black
and white contactor leads from the unit to the two prong twist lock plug (black to hot & white
to neutral). Change WC-1 or Cobramatic contactor to 115VAC (see Appendix for contactor
information).
2. Plug the 115VAC plug from the unit into a standard wall outlet or cut off the plug and wire it to the
three prong twist lock; green to pin with tang, black to hot and white to neutral pin.
3. Tape off WC-1 red and green leads and turn off Posa Start switch as Posa Start is not used.
4. If the power supply has a Remote/Standard contactor switch set it to "REMOTE".
Two Prong Three Prong
Miller 039-635 039-687
Hubbel
7101, 7224 & 3223
or 9768
4770 or 4773
M-3
The WC-1 Weld Control or the Cobramatic Cabinet can also be connected to Miller CV power supplies
with a 14-Pin amphenol as follows:
1. Connect the black and white contactor leads from
the WC-1 or Cobramatic to pins A & B of the 14 pin
amphenol; black to "A" and white to "B". Place the
contactor in the CLOSING CONTACTS position (see
Appendix for contactor information).
2. Plug the 115VAC plug from the unit into a standard
wall outlet or cut off the plug and wire it to the 14-Pin
amphenol; black to pin "I", white to pin "G" and green
to pin "K".
3. Tape off WC-1 red and green leads and turn off Posa Start switch as Posa Start is not used.
4. If the power supply has a Remote/Standard contactor switch set it to "REMOTE".
Note: Some Miller amphenols do not have pins A & B. If this is the case do the following for the
contactor hook-up. Everything else is unchanged.
1. Connect the black contactor lead to pin "J" and cut off the white contactor lead (not used).
Place the contactor in the 115VAC contactor position.
P/N 005-0658
Complete 25' cable
with 14-Pin (S clocked)
amphenol attached.
P/N 005-0316
Complete 8' cable
with 14-Pin (S clocked)
amphenol attached.
14-Pin
Amphenol
Socket 153-0325 094-481
Cord Clamp 411-0035 108-852
Rubber Boot 301-0021 ---
MK P/N’s
MILLER
P/N’s
Weld Control Selector Guide - Page 18
Page 26

Miller Electric
M-4
The WC-1 Control Box or a Cobramatic system can also be connected to Miller CC power supplies with
14-Pin amphenols as follows:
1. Connect the black and white contactor leads from the WC-1 or
Cobramatic to pins A & B of the 14-Pin amphenol; black to "A"
and white to "B". Place the contactor in CLOSING CONTACTS
position (see Appendix for contactor information).
2. Plug the 115VAC plug from the WC-1 or Cobramatic into a
standard wall outlet.
3. *Connect the red and green leads from the WC-1 to the power
supply positive (+) and negative (-) terminals of the power supply;
red to positive (+) and green to negative (-).
4. If the power supply has a Remote/Standard contactor switch set it to "REMOTE" (14-Pin).
5. Set the amperage control to "panel" and the process switch to "TIG".
6. Place polarity switch to DC Reverse Polarity (electrode positive).
7. The Posa Start must be used. See WC-1 or Cobramatic owner's manual for Posa Start
information.
*See Appendix for Posa Start information.
14-Pin
Amphenol
Socket 153-0325 094-481
Cord Clamp 411-0035 108-852
Rubber Boot 301-0021 ---
MK P/N’s
MILLER
P/N’s
CAUTION: MAKE SURE THAT THE HIGH
FREQUENCY IS TURNED OFF
OR DAMAGE TO THE WC-1 OR
COBRAMATIC WILL OCCUR.
M-5
Older style MM35, MM200 and Spoolmate 200 units without 14-Pin amphenols have either 4-Pin plastic
AMP plugs (trigger plug) and/or a 4-Pin Amphenol plug in the lower right hand corner.
Some newer Miller power supplies, such as the MM250-X & MM251 use this same receptacle (AMP
style) for the trigger on their push type guns.
1. Connect the black and white contactor leads from the WC-1 or Cobramatic to pins B & D of the
4-Pin Amphenol; black to "B" and white to "D".
The AMP plug only has two pins installed so place the contactor leads on those two pins (color
code not important). Place the contactor in CLOSING CONTACTS (see Appendix for contactor
information).
2. There is no 115VAC available on these units so plug the WC-1 or Cobramatic into a wall outlet.
3. Tape off WC-1 red and green leads and turn off Posa Start switch as Posa Start is not used.
Note: The feeder inside these units will also be turned on when using the trigger plug, so disengage
the spring tension on drive roll. The 4 pin amphenol plug does not turn on the feeder.
4-Pin Amphenol Amphenol P/N’s Miller P/N’s
Socket 3106A18-4P 073-329
Cord Clamp 3057-1010 073-331
Rubber Boot
4-Pin AMP MK P/N’s AMP P/N’s Miller P/N’s
Socket 153-0998 206429-1 079-878
Cord Clamp 153-0946 206062-3 048-834
Pins (2 req.) 153-0958 66099-2/-3 ---
Weld Control Selector Guide - Page 19
MS3420-10
MS3420-8
---
Page 27

Miller Electric
M-6
The Vintage/Millermatic 250/Hobart Beta-Mig 2510 kit P/N 005-0205 includes everything needed to
attach to these power supplies.
1. The blank panel on the front of the unit is removed and the Spool Gun Control is put in its place.
Both the push gun and the spool gun may be hooked-up at the same time.
2. For spool gun operation set the desired voltage on the Millermatic 250 front panel and set the
wire speed on the bottom of the spool gun.
3. For push gun operation set both voltage and wire speed on the Millermatic 250 front panel.
Kit P/N 005-0629, for both the MM250-X & MM251, is an adapter pigtail that goes between the Prince
XL Spool-gun and the power supply. The control module inside the power supplies are used for WFS.
The spool-gun power cable goes to the positive (+) terminal inside the wire feeder door on the welder.
M-7
The WC-1 Weld Control or the Cobramatic Cabinet can be connected to Miller CC power supplies
without 14-Pin amphenols as follows: Miller has used two types of contactor plugs over the years. In
the 1970's a male two prong "twist lock" plug was used. In the early 1980's they changed to a 5 pin
amphenol plug. All TIG machines use closing contacts!
1. For power supplies with the two prong plug, connect the black and white contactor leads from
the WC-1 or Cobramatic to the two prong plug. For power supplies with 5-Pin amphenols connect
the black and white contactor leads to pins A & B of the 5-Pin amphenol; black to "A" and
white to "B". Place unit in CLOSING CONTACTS (see Appendix for contactor information).
2. Plug the 115VAC plug from the WC-1 or Cobramatic into a standard wall outlet.
3. *Connect the red and green leads extending from the WC-1 to the power supply positive (+) and
negative (-) terminals of the power supply; red to positive (+) and green to negative (-).
4. If the power supply has a Remote/Standard contactor switch set it to "REMOTE".
5. Set the amperage control to "panel" and the process switch to "TIG".
6. Place polarity switch to DC Reverse Polarity (electrode
positive).
7. The Posa Start must be used. See WC-1 or Cobramatic
owner's manual for Posa Start information.
*See Appendix for Posa Start information.
E
D
C
Two Prong Plug
Miller P/N 039-618
Hubbel P/N 7102
5-Pin Amphenol
Miller P/N 039-273
Cord Clamp 039-685
CAUTION: MAKE SURE THAT THE HIGH
FREQUENCY IS TURNED OFF
OR DAMAGE TO THE WC-1 OR
COBRAMATIC WILL OCCUR.
M-8
The WC-1 Weld Control of the Cobramatic Cabinet can be connected to CC power supplies that do not
have contactors (stick machines) as follows. With Both the WC-1 Weld Control or Cobramatic Cabinet
the Contactor box is recommended:
1. Connect the WC-1 or Cobramatic to the contactor box as shown in the Appendix.
2. Connect the spool gun power lug to the contactor box "TORCH" side and the positive (+) lead
from the power supply to the "+ WELD POWER" side.
3. Plug the 115VAC plug from the WC-1 or Cobramatic into a standard wall outlet.
4. *Connect the red and green leads from the WC-1 to the power supply positive (+) and negative
(-) terminals of the power supply; red to positive (+) and green to negative (-).
5. Place polarity switch to DC Reverse Polarity (electrode positive).
6. The Posa Start must be used. See WC-1 or Cobramatic owner's manual for Posa Start
information.
Note: These instructions are for use with all manufacturers of CC stick machines.
Weld Control Selector Guide - Page 20
Page 28

Powcon
The WC-1 Weld Control or the Cobramatic Cabinet is connected to Powcon power supplies as follows:
1. Connect the black and white contactor leads extending from the WC-1 or Cobramatic
to pins 8 & 9 of the 14-Pin AMP plug; black to 8 and white to 9. Place the contactor
in the CLOSING CONTACTS position (see Appendix for contactor information).
2. Plug the 115VAC plug extending from the WC-1 or Cobramatic into a standard wall
outlet or cut off the plug and wire it to the 14 pin; black to pin 1, white to pin 2
and green to pin 3.
3. Add a jumper between pins 10 and 14.
4. Tape off WC-1 red and green leads and turn off Posa Start switch as
Posa Start is not used.
Note: Use in Mig or CV position.
14-Pin AMP Powcon P/N’s AMP P/N’s
Plug 250011-001 206044-1
Cord Clamp 206070-1
Pins (7 req.) --- 66099-2/-3
The PA-G1 Control (P/N 005-0264) is connected to Powcon power supplies as follows:
1. Connect the red and green contactor leads from the Control to pins 8 & 9 of the
14 pin AMP plug; red to 8 and green to pin 9. Place the contactor in the
CLOSING CONTACTS position (see Appendix for contactor information).
2. Connect the black wire from the Control to pin 4 and the white wire to pin 5.
3. Add a jumper between pins 10 and 14.
Note: Use in GMAW (CV) position.
P-1
P-2
14-Pin AMP Powcon P/N’s AMP P/N’s
Plug 250011-001 206044-1
Cord Clamp 206070-1
Pins (7 req.) --- 66099-2/-3
The PA-G1 Control (P/N 005-0264) is connected to Powcon power supplies as follows:
1. Connect the red and green contactor leads from the Control to pins B & E of the 17 pin amphenol
plug; red to B and green to E. Place the contactor in the CLOSING CONTACTS position (see
Appendix for contactor information).
2. Connect the black wire from the Control to pin S and the white wire to pin J.
3. Add a jumper between pins P and T.
Note: Use in GMAW (CV) position.
17-Pin
Amphenol
Plug & Pins 930014-101 3106A20-29PW
Cord Clamp 930014-301 3057-1012
Boot 930014-405 MS3420-12
Powcon
P/N’s
Amphenol
P/N’s
P-3
Note: Newer Powcon units use a 14-Pin similar to Miller. See section
M-3 or use the 14-Pin Control - P/N 005-0261.
Weld Control Selector Guide - Page 21
Page 29

Powcon
P-4
The WC-1 Weld Control or the Cobramatic Cabinet is connected to Powcon power supplies as follows:
1. Connect the black and white contactor leads extending from the WC-1 or Cobramatic to pins 8 &
9 of the 14-Pin AMP plug; black to 8 and white to 9. Place the contactor
in the CLOSING CONTACTS position (see Appendix for contactor
information).
2. Plug the 115VAC plug extending from the WC-1 or Cobramatic into
a standard wall outlet.
3. Add a jumper between pins 10 and 14.
4. *Connect the red and green leads extending from the WC-1 to
the power supply positive (+) and negative (-) terminals of the
power supply; red to positive (+) and green to negative (-).
5. Place the Weld Process Switch to "SMAW" (stick) position.
6. The Posa Start must be used; see WC-1 or Cobramatic
owner's manual for Posa Start operation.
*See Appendix for Posa Start information.
14-Pin AMP Powcon P/N’s AMP P/N’s
Plug 250011-001 206044-1
Cord Clamp 206070-1
Pins (7 req.) --- 66099-2/-3
P-5
The WC-1 Weld Control or the Cobramatic Cabinet is connected to Powcon power supplies as follows:
1. Connect the black and white contactor leads from the WC-1 or
the Cobramatic to pins B & E of the 17-Pin amphenol plug;
black to B and white to E. Place the contactor in the
CLOSING CONTACTS position (see Appendix for contactor
information).
2. Plug the 115VAC plug from the WC-1 or the Cobramatic into
a standard wall outlet.
3. *Connect the red and green leads extending from the WC-1
to the power supply positive (+) and negative (-) terminals of
the power supply; red to positive (+) and green to negative
(-).
4. Jumper pins T and P together.
5. Place the Weld Process Switch to "SMAW" (stick) position.
6. The Posa Start must be used; see WC-1/Cobramatic owner's manual for Posa Start operation.
*See below for Cobramatic Posa Start information.
17-Pin
Amphenol
Plug & Pins 930014-101 3106A20-29PW
Cord Clamp 930014-301 3057-1012
Boot 930014-405 MS3420-12
Powcon
P/N’s
Amphenol
P/N’s
Note: Newer Powcon units use a 14-Pin similar to Miller. Use section
M-3 or use 14-Pin Control - P/N 005-0261
Weld Control Selector Guide - Page 22
Page 30

Panasonic
PA-1
The Gunslinger 260 kit (P/N 005-0617) plugs directly into the amphenol on the front of the unit.
The lug on the power cable of the Prince XL Spool-gun will be hooked up to the positive (+) terminal of
the welder. It is inside the door housing the unit's wire feeder, just under the feeder.
A Cobramatic Cabinet may be hooked up to the Gunslinger 260 as follows:
1. Plug the 115VAC plug extending from the Cobramatic Cabinet into a standard wall outlet.
2. Connect the black and white contactor leads of the Cobramatic Cabinet to pins 1 and of the
Spool-gun plug on the front of the Gunslinger 260. Place the contactor on the Cobramatic in the
CLOSING CONTACTS position (see Appendix for contactor information).
3. Even though you're operating a Cobramatic push-pull system instead of a spool-gun, the
Gunslinger 260 must have the Mode Plug inserted into the Spool-gun location. The power cable
to the Cobramatic would be hooked up to positive (+) terminal which is just under the units wire
feeder inside the door.
4-Pin AMP MK P/N’s AMP P/N’s
Socket 153-0998 206429-1
Cord Clamp 153-0946 206062-3
Pins (2 req.) 153-0958 66099-2/-3
Weld Control Selector Guide - Page 23
Page 31

Thermal Dynamics (Includes ThermalArc)
T-1
The WC-1 or Cobramatic can be connected to the Thermal Viking 210/250-GM power supplies as
follows:
1. Connect the black and white contactor leads from the WC-1 or
Cobramatic to the spade style terminal inside the door above the wire
feed motor of the Viking unit. The contactor leads will replace the
existing wires going to the two spades on the right side. Place the
contactor in CLOSING CONTACTS position (see Appendix for contactor
information).
2. Plug the 115VAC plug from the WC-1 or Cobramatic cabinet into a
standard wall outlet.
3. Tape off the WC-1 red and green leads and turn off the Posa Start switch as the Posa Start will
not be used.
A Prince XL Spool-gun may be connected to the Viking 210/250-GM power supplies without the use of a
control module by using a MK 003-1623 Panel mount kit with 4 female (.25) Forked Tongue connectors.
(See the NOTE below - No WFS at the Prince XL Torch).
1. Punch 1" hole in the front panel approximately 2" below meter cutoff hole.
2. Cut off the blue, green and white (or yellow if there's no white
wire) wires from the back side of the 003-1623 panel mount. Crimp
the female spade connectors to the brown, orange, black and red
wires.
3. Mount the 003-1623 amphenol in the 1" hole. Inside the hinged left
door there's a terminal strip with four male spades. Remove the
existing wires and fasten the wires from the amphenol as shown
below:
NOTE: With this hook-up, the WFS (Wire Feed Speed) Potentiometer on the Prince® Spool
gun is unoperative. WFS will be controlled by the control on the front of the welder.
T-2
A Prince XL Spool-gun may be hooked up to the Thermal-Arc 300GMS, Fabricator 210 or 300-LF Welder
with a MK 005-0261 Miller style 14-Pin PA-M1 Control (See section M-1 ). Note - Cut off the lug on
the Spool-gun power cable and install a male Dinse style connector (MK P/N 153-0755). Exception
- Fabricator 210 that has a specication with an "A" at the end (See Note 11).
A Cobramatic system may be hooked up to this same power supply. The instructions in section M-3
would apply. A Dinse style (MK P/N 153-0755) connector would be needed on the power cable from the
welder to the Cobramatic Cabinet.
Note: A prince XL Spool Gun can be connected to the Fabricator 250 using a WC-1 only.
T-3
A Prince XL Spool gun may be hooked up to many of the Thermal-Arc engine driven welders. The
Exciter and Hog units are CC only and need a WC-1 Control Box that is CC Posa-start Ready and
connected with a contactor box as shown in the Appendix. The Predator and the Explorer units are CC/
CV and normally come without a contactor. Then a WC-1 and a Contactor box is needed.
Weld Control Selector Guide - Page 24
Page 32

Appendix
PosaStart Connections 27
Contactor Output Conguration 28
MK200 Contactor Box Connections 29
WC-1 & Spool Gun Connections 30
Spool Gun Controls 31
Utility Style Welders 32
Cobramatic Connectivity 33
Prince XL Spool Gun Connectivity 34
Weld Control Selector Guide - Page 25
Page 33

This page intentionally blank.
Weld Control Selector Guide - Page 26
Page 34

POSASTART CONNECTIONS
The Cobramatic and Cobra II Wire Feeders each have, a single black 14 ga. wire with an
alligator clip, extending from the back connected to the main board. This is the voltage sensing lead for the PosaStart circuit. In order for PosaStart to properly work, this lead must be
connected to the welding GROUND.
Typically, most power supplies will accept
the PosaStart lead connected to either the
work GROUND lug on their front panel or the
GROUND clamp.
However, some newer types of inverters must
have this PosaStart lead connected directly to
the GROUND lug.
Newer Cobramatic units have a CC/CV conguration switch on the main board. Consult the
owners manual in order to properly congure
this switch.
PosaStart Conguration
Switch on Cobramatic
Main Board
SW1
Weld Control Selector Guide - Page 27
Page 35

CONTACTOR OUTPUT CONFIGURATION
Contactor Selection
There are two types of contactor signals that various power supply manufacturers use. A "Closing Contact
or Contactor" and a “115VAC Contactor” signal. Once the power supply contactor is closed, the welding
leads become electrically live and are referred to as being “live” or “hot”.
For the Closing Contactor type, the weld control simply touches the two contactor leads together (providing
a continuity signal to the power supply) like a light switch. ALL Cobramatic wire feeders and Weld Controls
are shipped in this conguration (Figure A). Since no voltage is applied to the leads in tis conguration, it
is safe to handle and there is no risk of personal injury from electrocution.
COBRAMATIC / WC-1
MAIN BOARD
J6
1 43
2
CLOSING
CONTACTS
CONNECTION
For the 115VAC Contactor type, the weld control must send 115VAC into the power supply to close the
contactor. In order to obtain this conguration from a Cobramatic wire feeder or Weld Control, the internal
wiring or each must be modied as shown (Figure B).
WHITE
BLACK
Figure A
1 43
J5
2
COBRAMATIC / WC-1
MAIN BOARD
J6
2
1 43
J5
21 43
BLACK
WHITE
Figure B
If a 115VAC signal is required, remove the four screws from both sides of control box, and remove
cover. For Cobramatic open left door. Locate white and black wire on #3 and #4 of terminal strip J6.
Move white wire to #3 and black wire to #4 of terminal strip J5. The unit will now supply 115VAC on
the black (hot) and white (neutral) wires.
WARNING: Disconnect the WC-1 & Cobramatic from all power sources before changing contactor.
Weld Control Selector Guide - Page 28
115 VAC
CONTACTOR
CONNECTION
Page 36

MK200 CONTACTOR BOX CONNECTIONS
1. Remove the existing black
and white contactor cord
from WC-1 or Cobramatic.
2. Connect the leads extending
from the contactor box to
the WC-1/ Cobramatic main
board as shown below.
115VAC
INPUT
WHITE
GREEN
BLACK
COBRAMATIC / WC-1
WC-1 & COBRAMATIC
MAIN BOARD
GREEN
BLACK
J5
3 41 2
WHITE
115VAC
CONTACTOR
OUTPUT
CAUTION:
Weld Control Selector Guide - Page 29
When working with voltages present in this Product and others,
always observe warning and caution signs. Service must only
be performed by qualied service personnel.
Page 37

WC-1 & SPOOLGUN HOOK-UP
GROUND
Cylinder or Manifold
Shielding Gas Supply
CV or CC Power Supply
CONTACTOR LEADS
POSASTART
SENSING LEADS
GreenRed
CABLE
ELECTRICAL
M.K. P/N 753-3377
COUPLER - AW-430-RH
POWER CABLE
Weld Control Box
Weld Control Selector Guide - Page 30
GAS HOSE
NOTE: The Posa Start feature permits the WC-1 to be used in
combination with any Constant Current DC power source with
an open circuit voltage in excess of 55 volts.
Page 38

SPOOL GUN CONTROLS
FOR POWER SUPPLIES THAT SUPPLY AN AUXILIARY 26 VAC
The PA-G1 is designed to hook-up to CV power supplies that supply an
auxiliary 26 VAC @ 1.7 amps and uses a closing contact signal. The unit is
supplied with bare wires that must be connected to the power supply. Some
examples of power supplies that can be hooked-up are:
PA-G1
P/N 005-0264
PA-M1
P/N 005-0261
Lincoln SP-250, 255 & Wirematic 250 & 255
Beta-Mig 200 & Beta-Mig LF
Airco Dip-Pak 200, 225 & 250
FOR POWER SUPPLIES WITH 14 PIN AMPHENOLS
The PA-M1 connects directly to Miller power supplies (24V system) that are
classied with 14-Pin amphenols as type 6 or 9 and to Thermal Arc units,
such as:
Miller Welders
Millermatic 200 Deltawelds
Shopmaster CO Series, Regency's
XMT's & Maxtron Trailblazer 250, 251, 280, All engine-driven
welders with a CV-tap and a 14 pin amphenol.
Thermal-Arc Welders
Thermal-Arc 300GMS CC/CV, 400GMS
Fabricator 210, 250, 300 LF
The PA-L1 connects directly to Lincoln Electric power supplies (42V system) with
14-Pin (X-clocked) amphenol connectors, such as:
PA-L1
P/N 005-0676
Panasonic Gunslinger 260
P/N 005-0617
Lincoln Electric
Ranger 9, 10, 250, 275, 304 CV Series
Commander 300, 500 (See Note 10) Vantage 500
Invertec V300-Pro, V350-Pro (Fac. or Adv.)
ESAB (L-TEC) MIGMASTER 250
P/N 005-0206
MillerMatic250X/251
P/N 005-0629
Fabricator Series
P/N 005-0689
MILLER VINTAGE, MILLERMATIC 250, HOBART BETAMIG 2510
or IronMan 250
P/N 005-0205
This easy to install, plug in module ts the Millermatic 250, Miller Vintage machine,
or Hobart Betamig 2510. It and a Prince Spool Gun are all that is needed to get
your customer up and running.
Weld Control Selector Guide - Page 31
Page 39

UTILITY STYLE WELDERS
There are many other welders made by companies like CK Systematics, Century
Manufacturing, and some foreign manufactured machines that are capable of
welding aluminum, utilizing the Cobramatic system or Prince XL Spool Guns.
These units can usually be broken down into two categories.
1. A utility MIG welder with the wire feeder built into the unit.
These units need to be in 200 to 275 amp range and operate
from 208/230/460 Volts
2. A CC/CV Power supply capable of accepting a wire feeder.
(These units are usually 3-Phase).
Units in the second category usually have some sort of connector for the wire
feeder that needs to be identied by model and pin conguration. Then an
adapter pigtail may be made that will interconnect with these units.
Units in the rst category are a little more difcult. There’s usually no internal
or external hookup for a secondary wire feed system; 115VAC must be derived
from a secondary source (i.e. extension cord from a wall outlet) to run the
Cobramatic system or a Prince XL Spool Gun with a WC-1 Control Box. What
becomes difcult is “How to trigger the contactor?”
If the trigger leads from the units are accessible, then the contactor leads from
the Cobra Cabinet or the WC-1 Control Box may be spliced to these leads
(Cobra or WC-1 must be in “Closing Contacts” mode). However, this will also
trigger the units internal welder, so care must be taken to loosen the idler roll
on the unit’s internal wire feeder so that it does not feed wire while welding with
the Cobramatic Cabinet or Spool Gun.
Sometimes the most difcult thing to locate is the source of welding current.
There has to be a cable going to the unit’s internal wire feeder. A connection
can usually be made to one of the ends of this cable to the Spool Gun.
A Cobramatic Cabinet or a WC-1 Control for the Prince XL Spool Gun may be
hooked up to many other MIG welders beside those listed on the previous pages.
In some cases, the size and output of many of the smaller units, especially
those that operate on 115VAC only, do not lend themselves to an efcient arc.
Examples of these are the Lincoln SP125, the Millermatic 130XP, and the Hobart
Handler. These units only deliver 18-19 Open Circuit Volts (max). Since welding
on 1/8" thick aluminum requires 100 to 120 amps at 20 to 21 volts, the welds
are marginal at best.
Weld Control Selector Guide - Page 32
Page 40

COBRAMATIC CONNECTIVITY
Cobramatic
“Sho w Us Your C olor s”
®
19 & 14 Pin
14 Pin
®
Prince XL
Pistol Grip
Python
Advanced Gooseneck
®
CobraMAX™
Gooseneck Torch
V350PRO
120VAC Output
14 Pin
XMT 304
120VAC Output
Weld Control Selector Guide - Page 33
SVI 450i
120VAC Output
19 Pin
Ultra Flex™ 350
120VAC Output
Page 41

PRINCE XL SPOOL GUN CONNECTIVITY
Prince XL Spool Gun
®
PowerMIG 300
Gunslinger 260
MillerMatic 251
Fabricator 250
Direct Connect
Interface Cable
005-0617
Interface Cable
005-0629
Interface Cable
005-0689
MultiMaster 260
Interface Cable
005-0206
PA-L1
005-0676
V350PRO
PA-M-1
005-0261
Ultra Flex™ 350XMT 304
Weld Control Selector Guide - Page 34
PA-M-1
005-0261
Interface Cable
005-0206
Migmaster 250
Page 42

Page 43

Page 44

3 YEAR
LIMITED WARRANTY
Effective February 1, 2003
This warranty supersedes all previous MK Products warranties and is
exclusive, with no other guarantees or warranties expressed or implied.
LIMITED WARRANTY - MK Products, Inc., Irvine, California
warrants that all new and unused equipment furnished by MK
Products is free from defects in workmanship and material as
of the time and place of delivery by MK Products. No warranty
is made by MK Products with respect to trade accessories or
other items manufactured by others. Such trade accessories and
other items are sold subject to the warranties of their respective
manufacturers, if any.
MK Products’ warranty does not apply to components having
normal useful life of less than one (1) year, such as relay points,
wire conduit, tungsten, and welding torch parts that come in
contact with the welding wire, including gas cups, gas cup insulators, and contact tips where failure does not result from defect
in workmanship or material.
MK Products’ shall, exclusively remedy the limited warranty or
any duties with respect to the quality of goods, based upon the
following options:
(1) repair
(2) replacement
(3) where authorized in writing by MK Products, the reasonable
cost of repair or replacement at our Irvine, California plant; or
(4) payment of or credit for the purchase price (less reasonable
depreciation based upon actual use) upon return of the goods at
customer’s risk and expense. Upon receipt of notice of apparent
defect or failure, MK Products shall instruct the claimant on the
warranty claim procedures to be followed.
As a matter of general policy only, MK Products may honor an
original user’s warranty claims on warranted equipment in the
event of failure resulting from a defect within the following periods
from the date of delivery of equipment to the original user:
1. Torches, Weldheads & Water Recirculators .....1 year
2. All Other Equipment ....................................... 3 years
3. Repairs ..........................................................90 days
Classication of any item into the foregoing categories shall be
at the sole discretion of MK Products. Notication of any failure
must be made in writing within 30 days of such failure.
A copy of the invoice showing the date of sale must accompany
products returned for warranty repair or replacement.
All equipment returned to MK Products for service must be
properly packaged to guard against damage from shipping.
MK Products will not be responsible for any damages resulting from shipping.
Normal surface transportation charges (both ways) for
products returned for warranty repair or replacement will
be borne by MK Products, except for products sold to foreign markets.
ANY EXPRESS WARRANTY NOT PROVIDED HEREIN AND
ANY IMPLIED WARRANTY, GUARANTY, OR REPRESENTATION
AS TO PERFORMANCE, AND ANY REMEDY FOR BREACH OF
CONTRACT WHICH, BUT FOR THIS PROVISION, MIGHT
ARISE BY IMPLICATION, OPERATION OF LAW, CUSTOM OF
TRADE, OR COURSE OF DEALING, INCLUDING ANY IMPLIED
WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY OR OF FITNESS FOR
PARTICULAR PURPOSE, WITH RESPECT TO ANY AND ALL
EQUIPMENT FURNISHED BY MK PRODUCTS, IS EXCLUDED
AND DISCLAIMED BY MK PRODUCTS.
EXCEPT AS EXPRESSLY PROVIDED BY MK PRODUCTS IN
WRITING, MK PRODUCTS ARE INTENDED FOR ULTIMATE
PURCHASE BY COMMERCIAL/INDUSTRIAL USERS AND FOR
OPERATION BY PERSONS TRAINED AND EXPERIENCED IN
THE USE AND MAINTENANCE OF WELDING EQUIPMENT AND
NOT FOR CONSUMERS OR CONSUMER USE. MK PRODUCTS
WARRANTIES DO NOT EXTEND TO, AND NO RE-SELLER IS
AUTHORIZED TO EXTEND MK PRODUCTS’ WARRANTIES TO
ANY CONSUMER.
US E O F O T HER THAN
CONSUMABLES, PARTS, AND ACCESSORIES MAY INVALIDATE
YOUR PRODUCT WARRANTY.
GENUINE
M K P R O D U CTS’
16882 Armstrong Ave.
Irvine, CA 92606
Tel (949)863-1234
Fax (949)474-1428
www.mkproducts.com
DATE: February 1, 2003
Page 45

www.mkproducts.com
16882 Armstrong Ave.
Irvine, California 92606
TEL (949) 863-1234 FAX (949) 474-1428
 Loading...
Loading...