Page 1

Product Description RoboKing®
MK Part Number 091-0389
MK Form Number OM-RK
NWSA Form Number 550
RoboKing
®
Effective with Serial
Number
Voltage Rating 24VDC
Printing/Revision
Date
This manual applies
to the following torch
model numbers
41500
November 2002 E
218-XXX
16882 Armstrong Ave., Irvine, California 92606 TEL 949.863.1234 FAX 949.474.1428 www.mkproducts.com
Page 2
SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS
ELECTRIC ARC WELDING EQUIPMENT
CAUTION : READ BEFORE ATTEMPTING INSTALLATION,
OPERATION ORMAINTENANCE OF THIS EQUIPMENT
1-1 INTRODUCTION
This equipment is intended for ultimate application by commercial/industrial users and for
operation by persons trained and experienced
in the use and maintenance of welding equipment. Operation should not be undertaken without adequate training in the use of such equipment. Training is available from many public
and private schools or similar facilities.
Safe practices in the installation, operation and
maintenance of this equipment requires proper
training in the art, a careful study of the information provided with the equipment, and the use
of common sense. Rules for safe use are generally provided by suppliers of welding power
sources, compressed gas suppliers, and electrode suppliers. Careful compliance with these
rules will promote safe use of this equipment.
The following Safety Rules cover some of the
more generally found situations. READ THEM
CAREFULLY. In case of any doubt, obtain qualied help before proceeding.
1-2 GENERAL PRECAUTIONS
A. Burn Prevention
ELECTRIC ARC WELDING PRODUCES HIGH
INTENSITY HEAT AND ULTRAVIOLET RADIANT ENERGY WHICH MAY CAUSE SERIOUS
AND PERMANENT EYE DAMAGE AND WHICH
MAY DAMAGE ANY EXPOSED SKIN AREAS.
Wear helmet with safety goggles or glasses with
side shields underneath, appropriate lter lenses
or plates (protected by clear cover glass). This
is a must for welding or cutting (and chipping) to
protect the eyes from radiant energy and ying
metal. Replace cover glass when broken, pitted,
or spattered.
Medical rst aid and eye treatment. First aid
facilities and a qualied rst aid person should
be available for each shift unless medical facilities are close by for immediate treatment of ash
burns of the eyes and skin burns.
Wear protective clothing - leather (or asbestos)
gauntlet gloves, hat, and high safety-toe shoes.
Button shirt collar and pocket aps, and wear
cufess trousers to avoid entry of sparks and
slag.
Avoid oily or greasy clothing. A spark may ignite
them.
Flammable hair preparations should not be used
by persons intending to weld or cut.
Hot metal such as electrode stubs and work
pieces should never be handled without gloves.
Ear plugs should be worn when working on
overhead or in a conned space. A hard hat
should be worn when others work overhead.
B. Toxic Fume Prevention
WARNING: The use of this product may result
in exposure to chemicals known to the State of
California to cause cancer and birth defects or
other reproductive harm.
Adequate ventilation. Severe discomfort, illness
or death can result from fumes, vapors, heat, or
oxygen enrichment or depletion that welding (or
cutting) may produce. Prevent them with adequate
ventilation. NEVER ventilate with oxygen.
Lead-, cadmium-, zinc-, mercury-, beryllium-bearing
and similar materials, when welded or cut, may produce harmful concentrations of toxic fumes. Adequate local exhaust ventilation must be used, or
each person in the area, as well as the operator,
must wear an air-supplied respirator. For beryllium,
both must be used.
Metals coated with or containing materials that emit
toxic fumes should not be heated unless coating
is removed form the work surface, the area is well
ventilated, or the operator wears an air-supplied
respirator.
Work in a conned space only while it is being
ventilated and, if necessary, while wearing an airsupplied respirator.
Gas leaks in a conned space should be avoided.
Leaked gas in large quantities can change oxygen
concentration dangerously. Do not bring gas cylinders into a conned space.
Leaving conned space, shut OFF gas supply at
source to prevent possible accumulation of gases in
the space if downstream valves have been accidentally opened or left open. Check to be sure that the
space is safe before reentering it.
Vapors from chlorinated solvents can be decomposed by the heat of the arc (or ame) to form
PHOSGENE, a highly toxic gas, and other lung
and eye irritating products. The ultraviolet (radiant)
energy of the arc can also decompose trichloroethylene and perchloroethylene vapors to form phosgene. DO NOT WELD or cut where solvent vapors
can be drawn into the welding or cutting atmosphere or where the radiant energy can penetrate
to atmospheres containing even minute amounts of
trichloroethylene or perchloroethylene.
C. Fire and Explosion Prevention
Causes of re and explosion are: combustibles
reached by the arc, ame, ying sparks, hot slag, or
heated material, misuse of compressed gases and
cylinders, and short circuits.
BE AWARE THAT ying sparks or falling slag can
pass through cracks, along pipes, through windows
or doors, and through wall or oor openings, out
of sight of the goggled operator. Sparks can y
many feet.
To prevent res and explosion:
Keep equipment clean and operable, free of oil,
grease, and (in electrical parts) of metallic particles
that can cause short circuits.
If combustibles are in area, do NOT weld or cut.
Move the work if practicable, to an area free of
combustibles. Avoid paint spray rooms, dip tanks,
storage areas, ventilators. If the work cannot be
moved, move combustibles at least 35 feet away,
out of reach of sparks and heat; or protect
against ignition with suitable and snug-tting,
re-resistant covers or shields.
Walls touching combustibles on opposite sides
should not be welded on (or cut). Walls, ceilings, and oor near work should be protected by
heat-resistant covers or shields.
Fire watcher must be standing by with suitable
re extinguishing equipment during and for
some time after welding or cutting if:
1. Appreciable combustibles (including building
construction) are within 35 feet.
2. Appreciable combustibles are further than 35
feet, but can be ignited by sparks.
3. Openings (concealed or visible) in oors or
walls within 35 feet may expose combustibles
to sparks.
4. Combustibles adjacent to walls, ceilings,
roofs, or metal partitions can be ignited by radiant or conducted heat.
Hot work permit should be obtained before
operation to ensure supervisor’s approval that
adequate precautions have been taken.
After work is done, check that area is free of
sparks, glowing embers, and ames.
An empty container that held combustibles, or
that can produce ammable or toxic vapors
when heated, must never be welded on or
cut, unless container has rst been cleaned in
accordance with industry standards.
This includes: a thorough steam or caustic
cleaning (or a solvent of water washing,
depending on the combustible’s solubility), followed by purging and inerting with nitrogen or
carbon dioxide, and using protective equipment.
Water-lling just below working level may substitute for inerting.
A container with unknown contents should be
cleaned (see paragraph above). Do NOT
depend on sense of smell or sight to determine
if it is safe to weld or cut.
Hollow castings or containers must be vented
before welding or cutting. They can explode.
Explosive atmospheres. NEVER weld or cut
where the air may contain ammable dust, gas,
or liquid vapors (such as gasoline).
D. Compressed Gas Equipment
The safe handling of compressed gas equipment is detailed in numerous industry publications. The following general rules cover many
of the most common situations.
1. Pressure Regulators
Regulator relief valve is designed to protect
only the regulator from overpressure; it is not
intended to protect any downstream equipment.
Provide such protection with one or more relief
devices.
Never connect a regulator to a cylinder containing gas other than that for which the regulator
i
Page 3
was designed.
Remove faulty regulator from service immediately for repair (rst close cylinder valve). The
following symptoms indicate a faulty regulator:
Leaks - if gas leaks externally.
Excessive Creep - if delivery pressure continues
to rise with downstream valve closed.
Faulty Gauge - if gauge pointer does not move
off stop pin when pressurized, nor returns to
stop pin after pressure release.
Repair. Do NOT attempt repair. Send faulty
regulators for repair to manufacturer’s designated repair center, where special techniques
and tools are used by trained personnel.
2. Cylinders
Cylinders must be handled carefully to prevent
leaks and damage to their walls, valves, or
safety devices:
Avoid electrical circuit contact with cylinders
including third rails, electrical wires, or welding
circuits. They can produced short circuit arcs
that may lead to a serious accident. (See 1-3C)
ICC or DOT marking must be on each cylinder.
It is an assurance of safety when the cylinder is
properly handled.
Identifying gas content. Use only cylinders with
name of gas marked on them; do not rely on
color to identify gas content. Notify supplier
if unmarked. NEVER DEFACE or alter name,
number, or other markings on a cylinder. It is
illegal and hazardous.
Empties: Keep valves closed, replace caps
securely; mark MT; keep them separate from
FULLS, and return promptly.
Prohibited use. Never use a cylinder or its contents for other than its intended use, NEVER as
a support or roller.
Locate or secure cylinders so they cannot be
knocked over.
Passageways and work areas. Keep cylinders
clear of areas where they may be stuck.
Transporting cylinders. With a crane, use a
secure support such as a platform or cradle. Do
NOT lift cylinders off the ground by their valves
or caps, or by chains, slings, or magnets.
Do NOT expose cylinders to excessive heat,
sparks, slag, and ame, etc. that may cause
rupture. Do not allow contents to exceed 55
degrees C (130 degrees F.) Cool with water
spray where such exposure exists.
Protect cylinders, particularly valves from
bumps, falls, falling objects, and weather.
Replace caps securely when moving cylinders.
Stuck valve. Do NOT use a hammer or wrench
to open a cylinder valve that cannot be opened
by hand. Notify your supplier.
Mixing gases. NEVER try to mix any gases in
a cylinder.
NEVER rell any cylinder.
Cylinder ttings should never be modied or
exchanged.
3. Hose
Prohibited use. Never use hose other than that
designed for the specied gas. A general hose
identication rule is: red for fuel gas, green for
oxygen, and black for inert gases.
Use ferrules or clamps designed for the hose (not
ordinary wire or other substitute) as a binding to
connect hoses to ttings.
No copper tubing splices. Use only standard brass
ttings to splice hose.
Avoid long runs to prevent kinks and abuse. Suspend hose off ground to keep it from being run over,
stepped on, or otherwise damaged.
Coil excess hose to prevent kinks and tangles.
Protect hose from damage by sharp edges, and by
sparks, slag, and open ame.
Examine hose regularly for leaks, wear, and loose
connections. Immerse pressured hose in water;
bubbles indicate leaks
Repair leaky or worn hose by cutting area out and
splicing. Do NOT use tape.
4. Proper Connections
Clean cylinder valve outlet of impurities that
may clog orices and damage seats before connecting regulator. Except for hydrogen, crack valve
momentarily, pointing outlet away from people and
sources of ignition. Wipe with a clean, lintless
cloth.
Match regulator to cylinder. Before connecting,
check that the regulator label and cylinder marking
agree, and that the regulator inlet and cylinder
outlet match. NEVER Connect a regulator
designed for a particular gas or gases to a cylinder
containing any other gas.
Tighten connections. When assembling threaded
connections, clean and smooth seats where necessary. Tighten. If connection leaks, disassemble,
clean, and retighten, using properly tting wrench.
Adapters. Use a CGA adapter (available from your
supplier) between cylinder and regulator, if one is
required. Use two wrenches to tighten adapter
marked RIGHT and LEFT HAND threads.
Regulator outlet (or hose) connections may be
identied by right hand threads for oxygen and left
hand threads (with grooved hex on nut or shank)
for fuel gas.
5. Pressurizing Steps:
Drain regulator of residual gas through suitable vent
before opening cylinder (or manifold valve) by turning adjusting screw in (clockwise). Draining prevents excessive compression heat at high pressure
seat by allowing seat to open on pressurization.
Leave adjusting screw engaged slightly on singlestage regulators.
Stand to side of regulator while opening cylinder
valve.
Open cylinder valve slowly so that regulator pressure increases slowly. When gauge is pressurized
(gauge reaches regulator maximum) leave cylinder
valve in following position: for oxygen and inert
gases, open fully to seal stem against possible
leak; for fuel gas, open to less than one turn to
permit quick emergency shut-off.
Use pressure charts (available from your supplier)
for safe and efcient recommended pressure settings on regulators.
Check for leaks on rst pressurization and regularly
thereafter. Brush with soap solution. Bubbles indicate leaks. Clean off soapy water after test; dried
soap is combustible.
E. User Responsibilities
Follow all Safety Rules.
Remove leaky or defective equipment from service immediately for repair. Read and follow
user manual instructions.
F. Leaving Equipment Unattended
Close gas supply at source and drain gas.
G. Rope Staging-Support
Rope staging-support should not be used for
welding or cutting operation; rope may burn.
1-3 ARC WELDING
Comply with precautions in 1-1, 1-2, and this
section. Arc Welding, properly done, is a safe
process, but a careless operator invites trouble.
The equipment carries high currents at signicant voltages. The arc is very bright and hot.
Sparks y, fumes rise, ultraviolet and infrared
energy radiates, weldments are hot, and compressed gases may be used. The wise operator
avoids unnecessary risks and protects himself
and others from accidents.
A. Burn Protection
Comply with precautions in 1-2.
The welding arc is intense and visibly bright.
Its radiation can damage eyes, penetrate lightweight clothing, reect from light-colored surfaces, and burn the skin and eyes. Skin
burns resemble acute sunburn; those from gasshielded arcs are more severe and painful.
DON’T GET BURNED; COMPLY WITH PRECAUTIONS.
1. Protective Clothing
Wear long-sleeve clothing in addition to gloves,
hat, and shoes. As necessary, use additional
protective clothing such as leather jacket or
sleeves, ameproof apron, and re-resistant
leggings. Avoid outer garments of untreated
cotton.
Bare skin protection. Wear dark, substantial
clothing. Button collar to protect chest and
neck, and button pockets to prevent entry of
sparks.
2. Eye and Head Protection
Protect eyes from exposure to arc. Eyes may
be damaged by radiant energy when exposed
to the electric arc, even when not looking in the
direction of the arc. Never look at an electric arc
without protection.
Welding helmet or shield containing a lter plate
shade no. 12 or denser must be used when
welding. Place over face before striking arc.
Protect lter plate with a clear cover plate.
Cracked or broken helmet or shield should NOT
be worn; radiation can be passed through to
cause burns.
Cracked, broken, or loose lter plates must be
replaced IMMEDIATELY. Replace clear cover
plate when broken, pitted, or spattered.
Flash goggles with side shields MUST be worn
under the helmet to give some protection to the
eyes should the helmet not be lowered over the
face before an arc is struck. Looking at an arc
momentarily with unprotected eyes (particularly
a high intensity gas-shielded arc) can cause a
retinal burn that may leave a permanent dark
area in the eld of vision.
3. Protection of Nearby Personnel
Enclose the welding area. For production welding, a separate room or enclosed bay is best.
In open areas, surround the operation with low-
ii
Page 4
reective, noncombustible screens or panels.
Allow for free air circulation, particularly at oor
level.
Viewing the weld. Provide face shields for all
persons who will be looking directly at the weld.
Others working in area. See that all persons are
wearing ash goggles.
Before starting to weld, make sure that screen
aps or bay doors are closed.
B. Toxic Fume Prevention
Comply with precautions in 1-2B.
Generator engine exhaust must be vented to the
outside air. Carbon monoxide can kill.
C. Fire and Explosion Prevention
Comply with precautions in 1-2C.
Equipment’s rated capacity. Do not overload arc
welding equipment. It may overheat cables and
cause a re.
Loose cable connections may overheat or ash
and cause are.
Never strike an arc on a cylinder or other pressure vessel. It creates a brittle area that can
cause a violent rupture or lead to such a rupture
later under rough handling.
D. Compressed Gas Equipment
Comply with precautions in 1-2D.
E. Shock Prevention
Exposed electrically hot conductors or other
bare metal in the welding circuit, or in
ungrounded, electrically-HOT
equipment can fatally shock a person whose
body becomes a conductor. DO NOT STAND,
SIT, LIE, LEAN ON, OR TOUCH a wet surface
when welding without suitable protection.
To protect against shock:
Keep body and clothing dry. Never work in
damp area without adequate insulation against
electrical shock. Stay on a dry duckboard, or
rubber mat when dampness or sweat cannot be
avoided. Sweat, sea water, or moisture between
body and an electrically HOT part - or grounded
metal - reduces the body surface electrical resistance, enabling dangerous and possibly lethal
currents to ow through the body.
1. Grounding the Equipment
When installing, connect the frames of each
unit such as welding power source, control,
work table, and water circulator to the building
ground. Conductors must be adequate to carry
ground currents safely. Equipment made electrically HOT by stray currents may shock, possibly
fatally. Do NOT GROUND to electrical conduit,
or to a pipe carrying ANY gas or a ammable
liquid such as oil or fuel.
Three-phase connection. Check phase requirement of equipment before installing. If only
three-phase power is available, connect singlephase equipment to only two wires of the threephase line. Do NOT connect the equipment
ground lead to the third (live) wire, or the equipment will become electrically HOT - a dangerous
condition that can shock, possibly fatally.
Before welding, check ground for continuity. Be
sure conductors are touching bare metal of
equipment frames at connections.
If a line cord with a ground lead is provided with
the equipment for connection to a switch box,
connect the ground lead to the grounded switch
box. If a three-prong plug is added for connection
to a grounded mating receptacle, the ground lead
must be connected to the ground prong only. If the
line cord comes with a three-prong plug, connect
to a grounded mating receptacle. Never remove
the ground prong from a plug, or use a plug with a
broken ground prong.
2. Connectors
Fully insulated lock-type connectors should be used
to join welding cable lengths.
3. Cables
Frequently inspect cables for wear, cracks, and
damage. IMMEDIATELY REPLACE those with
excessively worn or damaged insulation to avoid
possibly lethal shock from bared cable. Cables with
damaged areas may be taped to give resistance
equivalent to original cable.
Keep cable dry, free of oil and grease, and protected from hot metal and sparks.
4. Terminals and Other Exposed Parts
Terminals and other exposed parts of electrical
units should have insulating covers secured before
operation.
5. Electrode Wire
Electrode wire becomes electrically HOT when the
power switch of gas metal-arc welding equipment
is ON and welding gun trigger is pressed. Keep
hands and body clear of wire and other HOT parts.
6. Safety Devices
Safety devices such as interlocks and circuit breakers should not be disconnected or shunted out.
Before installation, inspection, or service of equipment, shut OFF all power, and remove line fuses
(or lock or red-tag switches) to prevent accidental
turning ON of power. Disconnect all cables from
welding power source, and pull all 115 volts linecord plugs.
Do not open power circuit or change polarity while
welding. If, in an emergency, it must be disconnected, guard against shock burns or ash from
switch arcing.
Leaving equipment unattended. Always shut OFF,
and disconnect all power to equipment.
Power disconnect switch must be available near the
welding power source.
iii
Page 5

For selecting a quality product. We want you to take
Thank You
pride in operating this product...as much pride as we
have in bringing the product to you!
Please Examine Carton and Equipment For Damage Immediately
When this equipment is shipped, title passes to the purchaser upon receipt by the
carrier. Consequently, claims for material damaged in shipment must be made by the
purchaser against the transportation company at the time the shipment is received.
Please record your equipment identification information below for future reference. This
information can be found on your machine nameplate.
Model Name & Number _____________________
Code & Serial Number _____________________
Date of Purchase _____________________
Whenever you request replacements parts for, or information on this equipment always
supply the information you have recorded above.
Read this Owner’s Manual completely before attempting to use this equipment. Save this manual
and keep it handy for quick reference. Pay particular attention to the safety instructions we
have provided for your protection.
Printed in the U.S.A.
MK Products, Inc.
Page 6
Table of Contents
Safety ConSiderationS .................................................... i-iv
inStallation ........................................................ SeCtion a
Technical SpecificaTionS ................................................................... 1
SupporT equipmenT required .............................................................. 1
coolanT recommendaTionS ................................................................. 1
Torch lead connecTionS .................................................................. 1
operation .......................................................... SeCtion B
General ................................................................................... 2
moTor Gear Box .......................................................................... 2
drive and idler rollS ..................................................................... 2
aCCeSSorieS ......................................................... SeCtion C
drive roll KiTS ........................................................................... 4
opTional acceSSorieS ...................................................................... 4
conTacT TipS .............................................................................. 5
GaS cupS .................................................................................. 5
Torch linerS .............................................................................. 5
MaintenanCe ........................................................ SeCtion d
recommended Spare parTS liST ............................................................. 6
trouBleShooting ................................................... SeCtion e
TeSTinG The Torch ........................................................................ 7
TrouBleShooTinG Guide ................................................................... 7
appendiCeS .......................................................... SeCtion f
MK r
epair StationS
Safety WarningS
liMited Warranty
Page 7
This page intentionally blank
Page 8
Section A inStAllAtion
technicAl SpecificAtionS
Wire Capacity
.030" - .045" (0.8mm - 1.2mm) solid and hard wire
.030" - 1/16" (0.8mm - 1.6mm) aluminum and cored wire
Wire Speed
800 IPM (20mpm) Max. at rated feeder Input Voltage (120VAC / 42VAC)
Duty Cycle
Water Cooled (model 218 series) - 400 amps @ 100%
500 amp rating when used with #2 optional Power Cable
All ratings are at 25 volts max. using Argon Gas
Shipping Weight
15' (4.5m) 15 lbs. (6.8 Kg)
25' (7.6m) 19 lbs. (8.6 Kg)
Support equipment reqired
C.V. or C.C. Power SourCe of SuffiCient CaPaCity for your needS.
Regulated gas supply and hoses.
Properly sized power leads from power source to wire feeder and ground.
Water source and hose capable of providing a minimum of 1 qt(liter) / min. at
45 p.s.i. when using water cooled torches.
coolAnt recommendAtion
Use a name-brand additive which does not contain reactive sulphur or
chlorine and does not react with copper, brass, or aluminum. Here's also
mixture that works well :
Use 3 Gallons (11.4 Liters) deionized water. (NOT DISTILLED)
Use 1 Gallon (3.8 Liters) ethleyne glycol.
Use 1 tsp (5 ml) liquid glycerin per gallon (3.8 Liters) of mixture
The Coolant rate should be 1 qt (liter) / minute at 35 p.s.i.
torch leAd connectionS
Power Cable
The torch tting is screwed into the back of the torch block using a conductive
sealant. RoboKing torches use a #4 AWG power cable which is secured to
the torch in the same manner. The power cable tting on the other end
connects to the power block inside the Cobramatic feeder.
ALL ROBOKING TORCHES MUST BE WATER COOLED
Conduit
The RoboKing comes standard with a teon lined conduit. The torch end
is secured with a set screw accessable through a hole in the handle under
RoboKing Owner's Manual - Page 1
Page 9
the rear Handle nut. Spiral steel conduits are available when using hard
and cored wires.
Gas Hose
The gas hose is pushed on to the inlet tube of the front body. The gas inlet
tube is located in the top center of the torch when viewed from the rear.
Water Hose
The water hose is pushed on to the inlet tube of the front body. The Water
tube is located in the lower left of the torch when viewed from the rear.
Electric Cable
A seven conductor control cable is used on RoboKing Torch, although only
2 conductors are used. The torch end of the control cable is secured to the
back of the torch with a cable clamp and the wires are connected to the motor
through a connector. The cabinet end has a 7 pin “W” clocked Amphenol
connector. See schematic for wiring information.
Section B operAtion
GenerAl deScription
The RoboKing is designed to be used in automation processes and is unique
in its design from other torches made by MK Products. The RoboKing Torch
maintains a constant, steady, uniform feed speed, regardless of curved or
looped wire conduit. The constant push exerted by the slave motor in the
cabinet, combined with the pull of the torch motor, causes the wire to literally
oat friction-free through the wire conduit. The 24 volt DC torch motor is
controlled by the speed control in the Cobramatic II cabinet.
There is no trigger in the torch to start the arc, this is controlled by means
of an outboard control.
motor GeAr Box
A 19.5:1 24VDC motor gear box is used on this version of the RoboKing
Torch. The motor gear box attaches to the angle head with three (3) Allen
screws. The torch serial number is stamped on the angle head. There are no
spare parts for the motor gear box; it must be replaced as a whole unit.
drive And idler rollS
General
The RoboKing comes setup from the factory with the drive roll & idler
roll requested at the time of order. Other sizes of grooved drive rolls for
aluminum wire are also available (see Optional Kits). Use Knurled drive
rolls for all steel applications. One set will feed all wire diameters from .030
(0.8mm) to 1/6"(1.6mm)
Drive roll tension is accomplished by means of a pressure-adjusting screw
located on the left hand side of the torch. Proper tension is achieved when
wire does not slip when a small amount of pressure is added to the wire
as it exits the tip.
RoboKing Owner's Manual - Page 2
Page 10
----------- IMPORTANT ----------NOTE:
Over-tightening of the drive rolls will cause excessive knurling and/or deformation
of the wire. When the complete system is set-up properly, wire will feed out of the
end of the torch and fall on the ground forming a uniform circle. If it forms a spiral
or spring then there is too much tension in the system. Please refer to the Cabinet
Owners Manual for adjustment to the tension setting detailed there.
THIS IS THE NUMBER ONE CAUSE OF POOR WIRE FEED PERFORMANCE
---------------------------------------------
Drive Roll Installation/Removal
Please Note : Drive rolls have a LEFT HAND thread.
Remove the drive roll with small nose pliers by turning the drive roll clockwise.
Install new drive roll on motor shaft using left hand thread. Drive roll will
self-tighten when feeding wire.
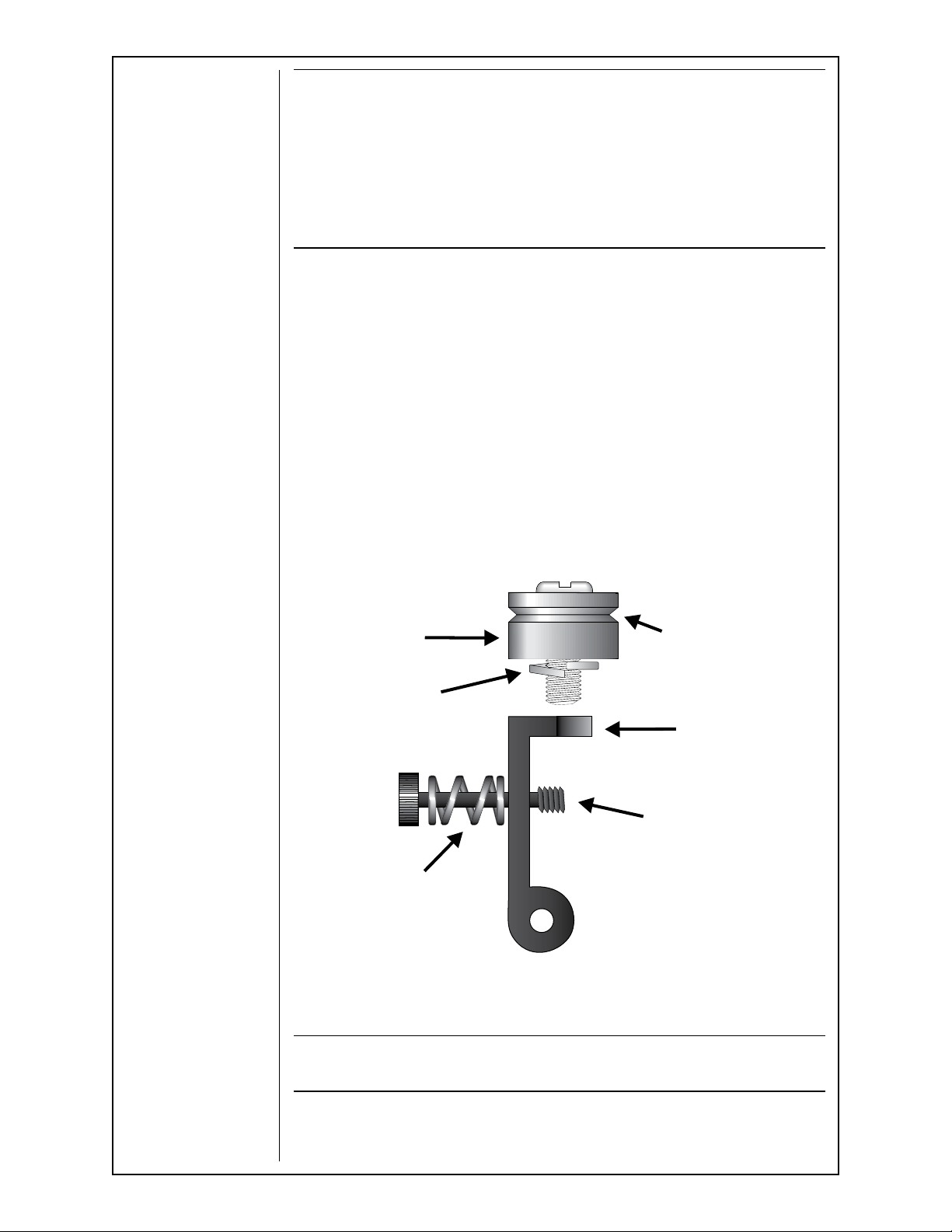
Idler Roll Installation and Removal
1. Using a slot type screwdriver, loosen idler screw, taking care not to lose
lock washer under idler roll.
2. Insert new idler roll and lock washer onto screw, insuring that idler groove
is toward top and lock washer is beneath.
3. Tighten.
IDLER
ROLL
LOCK
WASHER
SPRING
GROOVE
TOWARDS
TOP
IDLER
ARM
SCREW
Figure 2
NOTE:
Lock washer must be under idler roll or it will not turn freely.
RoboKing Owner's Manual - Page 3
Page 11

Section c AcceSSorieS
drive rollS KitS
Insulated Drive Roll Kits are used to prevent preheating of the wire which
may soften it and clog the liner. This picking up of current at the drive rolls
rather than at the contact tip is usually not a problem usless using too large
of a contact tip or excessively oxidized aluminum wire.
Insulated Groove Drive Roll Kit ......................................................005-0640
For .030" (0.8mm) dia. aluminum wire.
Includes insulated drive roll P/N 511-0150 and idler roll assy. P/N 003-1870.
Insulated Groove Drive Roll Kit ......................................................005-0641
For .035" (0.9mm) dia. aluminum wire.
Includes insulated drive roll P/N 511-0151 and idler roll assy. P/N 003-1870.
Insulated Groove Drive Roll Kit ......................................................005-0642
For .040" (1.0mm)dia. aluminum wire.
Includes insulated drive roll P/N 511-0152 and idler roll assy. P/N 003-1870.
Insulated Groove Drive Roll Kit ......................................................005-0643
For .045" (1.2mm) dia. aluminum wire.
Includes insulated drive roll P/N 511-0153 and idler roll assy. P/N 003-1870.
Insulated Groove Drive Roll Kit ......................................................005-0644
For .062" (1.6mm) dia. aluminum wire.
Includes insulated drive roll P/N 511-0154 and idler roll assy. P/N 003-1870.
Knurled Drive Roll .......................................................................... 511-0101
Idler Roll Kit .................................................................................... 005-0686
optionAl AcceSSorieS
Flat Spiral Steel Conduit Standard Conduit
for steel & cored wire. with additional protective cover.
615-0208 ............. 15 ft./4.5m 001-0774 ................ 15 ft./4.5m
615-0216 ............. 25 ft./7.6m 001-0775 ................ 25 ft./7.6m
NOTE:
The protective cover is used to help protect the conduit from burns.
Snake Skin protective boot covers are now standard on all torches. You may
order spare repleacement covers to protect the lead assy of the torch when
the factory one becomes damaged or worn. It can eaily be replaced in the
eld be means of a side zipper.
Snake Skin Cover 13ft (for 15ft leads) ......................................................................931-0110
Snake Skin Cover 23ft (for 25ft leads) ......................................................................931-0122
RoboKing Owner's Manual - Page 4
Page 12

contAct tipS
Standard Contact Tips
Wire Size Tip I.D. Arc Tip Length Part No.
.030”/0.8mm .040”/1.0mm
.035”/0.9mm .044”/1.0mm
.045”/1.2mm .053”/1.35mm
.045” or .052” .060”/1.5mm
.063”/1.6mm .075”/1.9mm
.063”/1.6mm .075”/1.9mm
.063”/1.6mm .085”/2.16mm Spray 1 5/8”/41.3mm 621-0164
Spray 1 5/8”/41.3mm 621-0158
Short 1 7/8”/47.6mm 621-0165
Spray 1 5/8”/41.3mm 621-0157
Short 1 7/8”/47.6mm 621-0166
Spray 1 5/8”/41.3mm 621-0161
Short 1 7/8”/47.6mm 621-0167
Spray 1 5/8”/41.3mm 621-0162
Short 1 7/8”/47.6mm 621-0168
Spray 1 5/8”/41.3mm 621-0163
Short 1 7/8”/47.6mm 621-0169
Spray 1 5/8”/41.3mm 621-0163
Short 1 7/8”/47.6mm 621-0169
GAS cupS
Standard Water Cooled Cup
Cup Size Cup I.D. Cup Length Part No.
No. 10 5/8”/15.9mm 3”/76.2mm 621-0065
Optional Air Cooled Cups*
Cup Size Cup I.D. Cup Length Part No.
No. 6 3/8”/9.5mm 1.43”/36.5mm 621-0170
No. 8 1/2”/12.7mm 1.43”/36.5mm 621-0159
No. 10 5/8”/15.9mm 1.43”/36.5mm 621-0160
*Requires Cup Adapter P/N 621-0101 & Cup Nut P/N 449-0193
torch linerS
Liners for Barrels
Wire Size Liner Material Application Part No.
Use genuine MK Parts
.030-.035”/0.8-0.9mm White Teon Aluminum 615-0542
.045-.062”/1.2-1.6mm White Teon Aluminum 615-0538
.030-.045”/0.8-1.2mm Steel Spiral Steel/Hard wire 615-0543
RoboKing Owner's Manual - Page 5
Page 13

Section d mAintenAnce
Maintenance of the torch will normally consist of a general cleaning of
the wire guide system, including tubes, drive rolls, and conduits at regular
intervals.
Remove spatter build-up from inside of nozzles with a hardwood stick.
The only parts on the RoboKing system that are subject to normal wear are
the conduit, contact tips, gas cups, front body liners, wire guides, drive and
idler rolls. A supply of these parts should be maintained on hand.
If repairs do become necessary, any part can easily be replaced by a
qualied shop maintenance personnel.
Your RoboKing System is designed to provide years of reliable service.
Normal wear and component failure may require occasional service.
The number of units in operation and the importance of minimal “down time”
will determine to what extent spare parts should be stocked on hand. See
the "Recommended spare parts list" for the most commonly replaced parts.
recommended SpAre pArtS
Qty. Part Number Description
1 615-0007 Conduit 15’
1 615-0008 Conduit 25’
2 511-0101 Knurled Drive Roll
2 005-0686 Idler Roll for steel
GOLD
DRIVE ROLL
511-0101
Section e trouBleShootinG
Regardless of which torch or feeder used, all MK Products’ push-pull guns
operate on the same principle. The 115 (42) VAC slave motor in the feeder
runs at a fast, constant speed, but has very low torque. It is always trying
to feed more wire than the torch motor wants, and when the motor gets all
it wants, it slows the slave motor, preventing a bird’s nest. Because of the
low torque produced by the slave motor, a brake system is used to prevent
wire overrun rather than tension. The drag adjustment in the spindle is
used simply to keep the wire slightly taut, so it will not pull off the spool while
feeding wire.
The high torque 24 VDC torch motor is controlled by a solid state speed
control. The torch motor is connected to the cabinet/control box via a control
RoboKing Owner's Manual - Page 6
IDLER ROLL KIT
005-0686
Page 14

cable and Amphenol. If this cable becomes damaged, a variety of symptoms
can occur, depending on which wire(s) break. To test, check each wire for
continuity and shorts.
teStinG the torch
See "W" clocked torch wiring diagram for infomation about pin-outs and locations.
Motor Check
Remove the torch connector from the cabinet.
Using the torch Amphenol connector, check the resistance across pins “A”
and “B” (motor leads). The resistance across the motor should be between
5-10 ohms.
If an open circuit or short exist, check the motor leads and motor
independently.
trouBleShootinG Guide
Trouble Cause Remedy
No wire feed at torch,
feeder not operating, I.e.
no slave motor or brake
solenoid.
No wire feed at torch,
feeder operating properly.
Wire feeds, but welding
wire is not energized.
Control fuse in feeder/Control box
blown.
Broken electrical cable. Check motor leads for continuity.
24VAC control fuse in feeder/
Control box blown.
Broken electrical cable. Check motor leads for continuity.
Bad speed control/PCB.
Loose or no cable connections. Check all power connections.
Contactor control cable loose or in
wrong position.
Welding power source Check power source.
Excessive spool drag pressure. Decrease spool drag pressure.
Replace fuse.
Check motor leads for shorts; then
replace fuse.
See specic cabinet/control box
owner’s manual for speed control
operation.
Check power supply owner’s
manual for locations and type of
contactor signal required, I.e.,
closing or 115VAC
Wire feeds erratically.
Wire feeds one speed
only.
Wire walks out of drive
rolls.
Dirty or worn conduit. Blow out or replace conduit.
Incorrect pressure on drive rolls.
Idler roll stuck.
Idler roll stuck.
Wrong size contact tip. See contact tip table.
Bad speed control.
Idler roll upside-down.
Rear wire guide missing. Replace wire guide.
RoboKing Owner's Manual - Page 7
Adjust pressure at both feeder &
torch.
Adjust pressure at both feeder &
torch.
Check for lock washer under idler
roll, or replace if damaged.
See specic cabinet/control box
owner’s manual for speed control
operation.
Place groove in idler roll toward
top.
Page 15

Section f AppendiceS
diAGrAmS And pArtS liStS
exploded view ........................................ 9
caBle aSSemBlieS ..................................... 10
Barrel aSSemBlieS .................................... 11
elecTrical ........................................... 12
Gear Box aSSemBly .................................. 13
RoboKing Owner's Manual - Page 8
Page 16

exploded view
RoboKing Owner's Manual - Page 9
Page 17

cABle ASSemBlieS
Water Cooled Cable Assemblies
Length Conduit
15”/4.5m 615-0007 001-2521 005-0268 001-0537 001-0529 931-0110
25”/7.6m 615-0008 001-2524 005-0269 001-0538 001-0530 931-0122
#4 Water/
Power Cable
RoboKing Owner's Manual - Page 10
Electrical
Cable
Gas Hose Water Hose Snake Skin
Page 18

BArrel ASSemBlieS
RoboKing Owner's Manual - Page 11
Page 19

electricAl
E
D
G
C
F
A
B
"W" Clocked
Amphenol Connector
Viewed from front of connector
RoboKing Owner's Manual - Page 12
Page 20

GeAr Box ASSemBly
RoboKing Owner's Manual - Page 13
Page 21

MK Warranty Repair Stations
for MK Products
Current as of 10/11/02
Please visit our website for up-to-date listing
www.mkproducts.com
ALABAMA
AIRGAS - SOUTH, INC.
Birmingham, AL
205/251-6835
KIBRO, INC.
Theodore, AL
251/653-4672
ALASKA
RNR, INC. dba
Rubey Engine & Electric
Anchorage, AK
907/336-5152
ARIZONA
PRAXAIR DISTRIBUTION, INC.
Phoenix, AZ
602/269-2151
MK Warranty Repair Stations
for MK Products
Please visit our website for up-to-date listing
DIXIE WELDING SUPPLY
Attalla, AL
256/538-6157
WELDING ENGRNG SUPPLY CO.
Prichard, AL
334/457-8681
FAIRBANKS AERO SERVICES
Fairbanks, AK
907/479-6666
ALLSTATE ELECTRIC MOTOR CO.
Phoenix, AZ
602/233-0500
Current as of 10/11/02
www.mkproducts.com
INDUSTRIAL WELDING
SERVICES
Quinton, AL
205/674-3258
WELDING MACHINE HOSPITAL
Montgomery, AL
334/832-9353
ARKANSAS
APPLIED SERVICES, INC.
Benton, AR
501/860-6464
CALIFORNIA
ADVANCED WELDER REPAIR
Commerce, CA
323/263-7383
ARC PRODUCTS
San Diego, CA
619/628-1022
CAL-WELD SUPPLY
Fresno, CA
209/445-0131
FRESNO OXYGEN
Fresno, CA
559/233-6684
PRAXAIR DISTRIBUTION
(ARC RENTS)
Signal Hill, CA
562/989-3212
RED-D-ARC, INC.
Carson, CA
310/233-3327
SWEINHART ELEC. CO., INC.
Long Beach, CA
714/521-9100
ARKANSAS WELDING IND’L
SUPPLY
Hot Springs, AR
501/321-9922
AIRGAS - WEST, INC.
Gardena, CA
310/523-9355
ARCO WELDER REPAIR
Santa Fe Springs, CA
562/921-5240
DELTA-TECH
Sun Valley, CA
818/767-4234
INDUSTRIAL WELDER REPAIR
LaPuente, CA
626/961-7643
PRAXAIR DISTRIBUTION, INC.
Bakersfield, CA
661/321-9922
SIMS-ORANGE WELDING SUPPLY
Santa Ana, CA
714/549-9393
EL DORADO WELDING &
INDUSTRIAL SUPPLY
El Dorado, AR
870/863-4088
ALL PHASE WELDER REPAIR &
CONSULTING
Sacramento, CA
916/331-0595
ARK WELDER REPAIR
Fresno, CA
559/292-4714
EMCO-EAST WELD’R REPAIR
Concord, CA
925/798-4411
NESCO WELDING SUPPLY
Fontana, CA
909/427-9670
R. J. KATES
San Diego, CA
619/565-6960
SOUTHWEST WELDER REPAIR
Fontana, CA
909/357-1661
Page 22

MK Warranty Repair Stations
for MK Products
Current as of 10/11/02
Please visit our website for up-to-date listing
www.mkproducts.com
COLORADO
AIRGAS - INTERMOUNTAIN,
INC.
Colorado Springs, CO
719/473-1947
CONNECTICUT
ABCO WELDING & INDUSTRIAL
SUPPLY CO.
Waterford, CT
800/962-0285
DELAWARE
KEEN COMPRESSED GAS
New Castle, DE
302/594-4555
FLORIDA
A & I SPECIALTIES
Lehigh Acres, FL
941/368-7435
AMVEL CORPORATION
Miami, FL
305/592-5678
HOLOX
Ocala, FL
352/351-4417
SMITTY’S WELDER SERVICE
West Palm Beach, FL
561/845-1224
TRI-TECH
Sarasota, FL
941/758-3825
GEORGIA
B&W INDUSTRIAL SERVICES
Augusta, GA
706/738-8722
HAWAII
DC ELECTRIC, INC.
Aiea, HI
808/483-8900
IDAHO
NORCO
Boise, ID
208/336-1643
MK Warranty Repair Stations
for MK Products
Please visit our website for up-to-date listing
WELDERS & EQUIP. SVC. &
TESTING
Littleton, CO
303/932-8755
TECH AIR
Milford, CT
203/783-1834
AAA GENERATOR & PUMP
Ft. Myers, FL
941/332-1136
ELECTRICAL WELDERS SERVICE
Orlando, FL
407/999-5214
J.K. CIRCUIT TECHNOLOGY
Boynton Beach, FL
561/733-7859
TRI-GAS
Miami, FL
305/592-3180
V.A. ELECTRICAL MOTORS
CENTER, INC.
Hialeah, FL
305/825-3327
Mc CULLOUGH ELEC. MOTOR SVC.
Atlanta, GA
404/688-5251
ROSSITER ELECTRIC
Idaho Falls, ID
208/529-3665
Current as of 10/11/02
www.mkproducts.com
WESTERN SLOPE WELDER
REPAIR
Grand Junction, CO
970/243-9616
ACTION WELDING SUPPLY
Jacksonville, FL
904/786-2254
HAUN SYSTEMS REPAIR, INC.
Winter Park, FL
407/681-6064
ROPER ELECTRIC MOTOR
SERVICE
Panama City, FL
850/769-6643
TRI-STATE SALES & LEASING
Lake City, FL
904/397-3340
Page 23

MK Warranty Repair Stations
for MK Products
Current as of 10/11/02
Please visit our website for up-to-date listing
www.mkproducts.com
ILLINOIS
CMS ELECTROMECHANICAL
SERVICES, INC.
Galesburg, IL
309/342-4125 – 888/9643526
RELIABLE EQUIPMENT REPAIR
Hamel, IL
618/633-5000
INDIANA
AGA GAS, INC.
Hammond, IN
219/989-9030
COX EQUIPMENT COMPANY
Indianapolis, IN
317/241-8881
MODERN SUPPLY CO., INC.
Evansville, IN
812/425-9353
IOWA
AIRGAS NORTH CENTRAL
Des Moines, IA
515/266-1111
SUPERIOR WELDING SUPPLY
Waterloo, IA
319/236-9660
KANSAS
AEROFORM CORPORATION
Coffeyville, KS
620/251-1430
KENTUCKY
GENERAL WELDING PRODUCTS
Louisville, KY
502/635-5218
LOUISIANA
RED BALL OXYGEN CO.
Shreveport, LA
318/425-3211
MK Warranty Repair Stations
for MK Products
Please visit our website for up-to-date listing
FRED ARMS ELECTRIC MOTOR
REPAIR
Stone Park, IL
708/343-6262
ROCKFORD INDUSTRIAL WELDING
SUPPLY
Rockford, IL
815/226-1900
AIRGAS - MID AMERICA, INC.
Evansville, IN
800/424-8905
EVANSVILLE ARMATURE, INC.
Evansville, IN
812/428-9034
PRAXAIR DISTRIBUTION, INC.
Speedway, IN
317/481-4550
CEDAR RAPIDS WELDING SUPPLY
Cedar Rapids, IA
319/365-1466
WRIGHT WELDING SUPPLY
Ft. Dodge, IA
515/576-0640
KANOX
Hutchinson, KS
316/665-5551
RED-D-ARC
Lexington, KY
800/245-3660
WELDERS EQUIPMENT CO.
Broussard, LA
337/837-5701
Current as of 10/11/02
www.mkproducts.com
INDUSTRIAL WELDER
REBUILDERS
Alsip, IL
708/371-5688
B & H ELECTRIC
Seymour, IN
812/522-5607
HARRISON ELECTRIC, INC.
Michigan City, IN
219/879-0444
SUTTON-GARTEN COMPANY
Indianapolis, IN
317/264-3236
ELECTRICAL ENGRG. &
EQUIPMENT
Des Moines, IA
515/266-8890
WELDING EQUIPMENT
Louisville, KY
502/636-0545
MARYLAND
CCM MECH/ELEC REPAIR
SERVICE
Owings, MD
301/855-7508
Page 24

MK Warranty Repair Stations
MK Warranty Repair Stations
for MK Products
Current as of 10/11/02
Please visit our website for up-to-date listing
www.mkproducts.com
MASSACHUSETTS
AIMTEK WELDING SUPPLY
Auburn, MA
508/832-5035
MICHIGAN
ANN ARBOR WELDING SUPPLY
CO.
Ypsilanti, MI
734/572-0444
GREAT LAKES EQUIPMENT
Clare, MI
517/386-4630
SIMPKINS ELECTRICAL SVC.
Michigan Center, MI
517/764-7766
WESAR COMPANY
Three Rivers, MI
616/483-9125
MINNESOTA
AIRGAS – NORTH CENTRAL
Albert Lea, MN
507/373-2411
OXYGEN SERVICE CO.
St. Paul, MN
612/644-7273
MISSOURI
CEE-KAY SUPPLY, INC.
St. Louis, MO
324/644-3500
MISSISSIPPI
NORDAN SMITH WELDING
SUPPLY
Hattiesburg, MS
601/545-1800
NEVADA
SIERRA WELDING SUPPLY CO.
Sparks, NV
775/359-0542
NEW HAMPSHIRE
WELDING SYSTEMS SVC.
Raymond, NH
603/895-4700
NEW JERSEY
INDUSTRIAL ELEC. SERV. CO.
Hawthorne, NJ
973/423-1212
for MK Products
Please visit our website for up-to-date listing
Current as of 10/11/02
www.mkproducts.com
APEX WELDING GASES & SUPPLY
Muskegon Heights, MI
616/722-3185
HAMILTON ELECTRIC CO.
Saginaw, MI
517/799-6291
SOUTHPARK WELDING
Marysville, MI
810/364-6521
CAPITOL CITY WELDING SUPPLY
St. Paul, MN
651/224-4843
P.G. WALKER
Springfield, MO
417/862-1745
3D SUPPLIES, INC.
Jackson, MS
601/353-3330
AUTOMATIC WELD
Midland, MI
517/496-9245
SAGINAW WELDING SUPPLY CO.
Saginaw, MI
517/793-9696
WELDING METALS, INC.
Madison Heights, MI
248/585-0480
MINNEAPOLIS OXYGEN CO.
Minneapolis, MN
612/588-8855
ROD’S SERVICE, INC.
St. Louis, MO
314/721-6000
Page 25

MK Warranty Repair Stations
MK Warranty Repair Stations
for MK Products
Current as of 10/11/02
Please visit our website for up-to-date listing
www.mkproducts.com
NEW YORK
DELO WELDING SUPPLY
Syracuse, NY
315/478-2188
JACKSON WELDING SUPPLY
Rochester, NY
585/235-2920
NORTH CAROLINA
ADAMS WELDER REPAIR &
ELECTRICAL SERVICE, INC.
Nashville, NC
252/459-1960
MACHINE & WELDING SUPPLY
CO.
Dunn, NC
910/892-4016
MACHINE AND WELDING
SUPPLY CO.
Winston-Salem, NC
336/723-9651
OHIO
AGA GASES, INC.
Lima, OH
419/228-2828
ARC EQUIPMENT COMPANY
Struthers, OH
333/750-9353
BIG RIVER ELECTRIC
Gallipolis, OH
740/446-4360
MAINTENANCE UNLTD. & TOOL
REPAIR
Cincinnati, OH
513/554-1313
RICK’S WELDER REPAIR
SERVICE
Eastlake, OH
440/269-1204
VALLEY NATIONAL GASES
Lima, OH
419/228-1008
VOLLMER ELECTRIC CO.
Columbus, OH
614/476-8800
for MK Products
Please visit our website for up-to-date listing
Current as of 10/11/02
www.mkproducts.com
DYNAMIC WELD’G & REPAIR
Bayshore, NY
631/643-1308
HOLOX LTD.
Colfax, NC
336/996-1974
MACHINE AND WELDING SUPPLY
CO.
Greenville, NC
252/752-3089
NATIONAL WELDERS SUPPLY CO.
High Point, NC
910/882-1110
ALBRIGHT WELDING SUPPLY
Wooster, OH
330/264-2021
ARC SERVICES, INC.
Toledo, OH
419/478-6204
CnD MACHINE, INC.
Canton, OH
330/478-8811
O.E. MEYER CO.
Sandusky, OH
419/621-4201
S.D. NOLD, INC.
Lisbon, OH
330/424-3134
VALLEY NATIONAL GASES
Hilliard, OH
614/771-1311
WEILER WELDING CO., INC.
Dayton, OH
937/222-8312
HAUN WELDING SUPPLY
Syracuse, NY
315/463-5241
M & L WELDER REPAIR
Asheville, NC
828/250-9353
MACHINE AND WELDING
SUPPLY CO.
Raleigh, NC
919/772-9500
NATIONAL WELDERS SUPPLY
CO.
Charlotte, NC
704/392-7317
ALL ABOUT SERVICE
Wickliffe, OH
440/516-0303
BELAIR PRODUCTS, INC.
Akron, OH
330/253-3116
ELECTRIC WELDER REPAIR
Cuyahoga Heights, OH
216/271-5600
OHIO AIR PRODUCTS
Canton, OH
330/821-2771
VALLEY NATIONAL GASES
Cincinnati, OH
513/241-5840
VALLEY NATIONAL GASES
Toledo, OH
419/241-9114
WELDINGHOUSE, INC.
Cleveland, OH
216/524-1955
Page 26

MK Warranty Repair Stations
for MK Products
Current as of 10/11/02
Please visit our website for up-to-date listing
www.mkproducts.com
OKLAHOMA
AIRGAS MID-SOUTH
Tulsa, OK
918/582-0885
OKLAHOMA WELDERS SUPPLY
Madill, OK
580/795-5561
OREGON
ARC SYSTEMS SERVICES
Central Point, OR
541/665-2676
WELDER SERVICE & REPAIR
Redmond, OR
541/548-8711
PENNSYLVANIA
ALLWELD EQUIPMENT REPAIR
Pittsburgh, PA
412/821-8460
J.A. CUNNINGHAM
EQUIPMENT, INC.
Philadelphia, PA
215/426-6650
VALLEY NATIONAL GASES
Pittsburgh, PA
412/281-1835
SOUTH CAROLINA
CAROLINA WELDER SVC.
Lake City, SC
843/687-0413
TENNESSEE
INDUSTRIAL MACHINE
REPAIRS
Rogersville, TN
423/272-8199
QUALITY WELD’G EQUIPMENT
Nashville, TN
615/726-5282
TEXAS
AIRGAS-SOUTHWEST, INC.
Austin, TX
512/835-0202
FT. WORTH WELDERS SUPPLY,
INC.
Ft. Worth, TX
817/332-8696
MK Warranty Repair Stations
for MK Products
Please visit our website for up-to-date listing
BILL’S WELDER REPAIR
Oklahoma City, OK
405/232-4799
E C COMPANY
dba ELECTRICAL CONSTRUCTION
COMPANY
Portland, OR
800/452-1511
BY DESIGN
Columbia, PA
717/681-9494
JOSEPH PINTO, JR. EQUIPMENT
CO.
E. Lansdowne, PA
610/259-4100
NEXAIR
Memphis, TN
901/523-6821
TRAMCO
Bristol, TN
423/968-4499
AIRGAS-SOUTHWEST, INC.
Houston, TX
713/462-8027
GPC SERVICES, INC.
San Angelo, TX
915/655-4545
Current as of 10/11/02
www.mkproducts.com
MUNN SUPPLY
Enid, OK
580/234-4120
INDUSTRIAL SOURCE
Eugene, OR
541/344-1438
GEOVIC WELDING SUPPLY
Milton, PA
717/742-9377
POWER SOURCE REPAIR CO.,
INC.
Collingdale, PA
610/532-6460
NATIONAL RENTAL & REPAIR
Knoxville, TN
423/584-6390
DENISON OXYGEN
Denison, TX
903/465-3369
LEKTROTECH, INC.
Greenville, TX
903/454-7146
Page 27

MK Warranty Repair Stations
for MK Products
Current as of 10/11/02
Please visit our website for up-to-date listing
www.mkproducts.com
CANADA
A&A WELDER SERVICES LTD.
Saskatoon, Saskatchewan
306/934-1601
MK Warranty Repair Stations
for MK Products
Please visit our website for up-to-date listing
ARC & GENERATOR REPAIR
Garson, Ontario
705/525-2141
Current as of 10/11/02
www.mkproducts.com
B. HARRIS WELDING SVCS.
Dartmouth, Nova Scotia
902/468-6255
BARRY HAMEL EQUIPMENT
LTD.
Coquitlam, B.C.
604/945-9313
GPR INDUSTRIES 1994 LTD.
Grande Prairie, Alberta
780/532-5900
LADEL LTD.
Quebec
819/376-6577
OZARK ELEC. MARINE LTD.
St. Johns, Newfoundland
709/726-4554
WELDERS SUPPLY
Winnipeg, Manitoba
204/772-9476
CHINA
PHT Group Company
Beijing, China
86-10-6858 8395
D-TECH WELD SERVICES
Regina, Saskatchewan
306/586-9353
HYPERDYNAMICS TECHNOLOGIES
LTD.
Pickering, Ontario
905/683-9938
LeBLANC ELECTRO-TECH, INC.
Boucherville, Quebec
450/449-5244
PEEL ENGINES
Mississauga, Ontario
905/670-1535
WELDERTECH
Calgary, Alberta
403/279-3432
ELECTRO-MÉCANIK, INC.
Sainte-Foy, Quebec
418/683-1724
INDUSTRIAL ELECTRONIC
SERVICES
Calgary, Alberta
403/279-3432
M.R.T. REPAIR CENTER, INC.
Montreal, Quebec
514/648-0800
PROMOTECH ÉLECTRIQUE, INC.
Fleurimont, Quebec
819/822-2111
WELDTEC
B.C.
604/545-3886
Page 28

MK Warranty Repair Stations
for MK Products
Current as of 10/11/02
Please visit our website for up-to-date listing
www.mkproducts.com
CANADA
A&A WELDER SERVICES LTD.
Saskatoon, Saskatchewan
306/934-1601
MK Warranty Repair Stations
for MK Products
Please visit our website for up-to-date listing
ARC & GENERATOR REPAIR
Garson, Ontario
705/525-2141
Current as of 10/11/02
www.mkproducts.com
B. HARRIS WELDING SVCS.
Dartmouth, Nova Scotia
902/468-6255
BARRY HAMEL EQUIPMENT
LTD.
Coquitlam, B.C.
604/945-9313
GPR INDUSTRIES 1994 LTD.
Grande Prairie, Alberta
780/532-5900
LADEL LTD.
Quebec
819/376-6577
OZARK ELEC. MARINE LTD.
St. Johns, Newfoundland
709/726-4554
WELDERS SUPPLY
Winnipeg, Manitoba
204/772-9476
CHINA
PHT Group Company
Beijing, China
86-10-6858 8395
D-TECH WELD SERVICES
Regina, Saskatchewan
306/586-9353
HYPERDYNAMICS TECHNOLOGIES
LTD.
Pickering, Ontario
905/683-9938
LeBLANC ELECTRO-TECH, INC.
Boucherville, Quebec
450/449-5244
PEEL ENGINES
Mississauga, Ontario
905/670-1535
WELDERTECH
Calgary, Alberta
403/279-3432
ELECTRO-MÉCANIK, INC.
Sainte-Foy, Quebec
418/683-1724
INDUSTRIAL ELECTRONIC
SERVICES
Calgary, Alberta
403/279-3432
M.R.T. REPAIR CENTER, INC.
Montreal, Quebec
514/648-0800
PROMOTECH ÉLECTRIQUE, INC.
Fleurimont, Quebec
819/822-2111
WELDTEC
B.C.
604/545-3886
Page 29

Page 30

Page 31

Page intentionally blank
Page 32

LimiTEd WarraNTy
Effective March 1, 2001
This warranty supersedes all previous MK Products warranties and is
exclusive, with no other guarantees or warranties expressed or implied.
LIMITED WARRANTY - MK Products,Inc.,Irvine,California
warrants that all new and unused equipment furnished by MK
Products is free from defect in workmanship and material as
of the time and place of delivery by MK Products. No warranty
is made by MK Products with respect to trade accessories or
other items manufactured by others. Such trade accessories
and other items are sold subject to the warranties of their
respective manufacturers, if any.
MK Products’ warranty does not apply to components having
normal useful life of less than one (1) year, such as relay
points, wire conduit, tungsten, and welding torch parts that
come in contact with the welding wire, including nozzles,
nozzle insulators, and contact tips where failure does not result
from defect in workmanship or material.
In the case of MK Products’ breach of warranty or any other
duty with respect to the quality of any goods, the exclusive
remedies therefore shall be at MK Products’ option: (1)
repair; (2) replacement; (3) where authorized in writing by
MK Products, the reasonable cost of repair or replacement
at our Irvine, California plant; or (4) payment of or credit for
the purchase price (less reasonable depreciation based upon
actual use) upon return of the goods at customer’s risk and
expense. Upon receipt of notice of apparent defect or failure,
MK Products shall instruct the claimant on the warranty claim
procedures to be followed.
As a matter of general policy only, MK Products may honor
an original user’s warranty claims on warranted equipment
in the event of failure resulting from a defect within the
following periods from the date of delivery of equipment
to the original user:
1. Torches, Weldheads & Water Recirculators ..........1 year
2. All Other Equipment ............................................... 2 years
3. Repairs ..................................................................90 days
Classication of any item into the foregoing categories shall be
at the sole discretion of MK Products. Notication of any failure
must be made in writing within 30 days of such failure.
A copy of the invoice showing the date of sale must accompany
products returned for warranty repair or replacement.
All equipment returned to MK Products for service must be
properly packaged to guard against damage from shipping.
MK Products will not be responsible for any damages resulting
from shipping.
Normal surface transportation charges (both ways) for
products returned for warranty repair or replacement will
be borne by MK Products, except for products sold to
foreign markets.
ANY EXPRESS WARRANTY NOT PROVIDED HEREIN AND
ANY IMPLIED WARRANTY, GUARANTY, OR REPRESENTATION AS TO PERFORMANCE, AND ANY REMEDY FOR
BREACH OF CONTRACT WHICH, BUT FOR THIS PROVISION, MIGHT ARISE BY IMPLICATION, OPERATION OF
LAW, CUSTOM OF TRADE, OR COURSE OF DEALING,
INCLUDING ANY IMPLIED WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY OR OF FITNESS FOR PARTICULAR PURPOSE,
WITH RESPECT TO ANY AND ALL EQUIPMENT FURNISHED
BY MK PRODUCTS, IS EXCLUDED AND DISCLAIMED
BY MK PRODUCTS.
EXCEPT AS EXPRESSLY PROVIDED BY MK PRODUCTS
IN WRITING, MK PRODUCTS ARE INTENDED FO R
ULTIMATE PURCHASE BY COMMERCIAL/INDUSTRIAL
USERS AND FOR OPERATION BY PERSONS TRAINED
AND EXPERIENCED IN THE USE AND MAINTENANCE OF
WELDING EQUIPMENT AND NOT FOR CONSUMERS OR
CONSUMER USE. MK PRODUCTS WARRANTIES DO
NOT EXTEND TO, AND NO RE-SELLER IS AUTHORIZED
TO EXTEND MK PRODUCTS’ WARRANTIES TO ANY
CONSUMER.
MK PRODUCTS, INC.
16882 ARMSTRONG AVE.
IRVINE, CA 92714
TEL (949) 863-1234
FAX (949) 474-1428
DATE : March 1, 2001
Page 33

M.K. PRODUCTS, INC.
16882 ARMSTRONG AVE.
IRVINE, CALIFORNIA 92606
TEL (949) 863-1234 FAX (949) 474-1428
www.mkproducts.com
 Loading...
Loading...