Page 1

January 2011
Pub. No. 99240-36160
The operator and supervisor are requested to read this Oper-
ation and Maintenance Manual carefully before operating the
engine or conducting inspection and maintenance.
Never operate the engine or conduct maintenance work with-
out completely understanding this manual.
OPERATION &
MAINTENANCE MANUAL
1
Page 2

Page 3

i
FOREWORD
This operation and maintenance manual contains detailed operation, inspection
and maintenance information for engines from Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
Please be forewarned that there are contents which are overlapping between the
chapters.
Please read this manual thoroughly before proceeding with operation, inspection,
and maintenance work for correct use and servicing.
Failure to follow directions in this manual may result in serious accidents.
Please observe the contents of the controls which are applied in the countries or
areas when using the engines from Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
Page 4
ii
FOREWORD
LIMITED WARRANTY
If Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. examines the returned parts and any failure at manufacturing is found, Mitsubi-
shi Heavy Industries, Ltd. shall repair or exchange the parts.
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.'s warranty is limited to the compensation work of repair or replacement of parts.
The warranty coverage is effective for the original purchaser only. Those to whom ownership is later transferred are
not provided with the warranty. However the warranty coverage is effective for the ultimate purchaser and each sub-
sequent purchaser for emission-related parts.
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. makes no warranties, either expressed or implied,
except as provided in this manual, including, but not limited to, warranties as to market-
ability, merchantability, fitness for a particular purpose or use, or against infringement of
any patent.
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. will not be liable for any damages or consequential
damages, including, but not limited to, damages or other costs resulting from any abuse,
misuse, misapplication of the engine and devices supplied from us.
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. will not be liable for any damages or personal injuries
resulting from any modification, without our written permission, of the engine and
devices supplied from us.
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. will not be liable for any damages or production losses
caused by the use of fuel, engine oil and/or long life coolant (LLC) that we are not recom-
mended.
The owner of the engine is responsible for the performance of the required maintenance
listed in this operation manual.
When performing the maintenance, follow the service manual published by Mitsubishi
Heavy Industries, Ltd.
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. may deny the warranty coverage if the engine or part
has failed due to inadequate or improper maintenance.
Page 5
iii
FOREWORD
EMISSION WARRANTY
Warranty &overage
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. warrants to the first owner and each subsequent purchaser of a new non-road die-
sel engine that the emission control system of your engine:
is designed, built and equipped so as to conform at the time of sales with all applicable regulation of the U.S. Envi-
ronmental Protection Agency. If the vehicle in which the engine is installed is registered in the state of California, a
separate California emission regulation also applies.
is free from the defects in material and workmanship which will cause the engine to fail to meet these regulations
within the warranty period.
Warranty 3eriod
Then its warranty period is 5 years or 3000 hours, whichever comes first.
However, if your engine warranty period is longer than the emission warranty period, the emission warranty period
extends to same as the engine warranty period.
Below warranty period shall begin on the date the engine is delivered to the first owner.
Warranted 3arts
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. warrants the parts which will increase the emission of pollutants when they
become defective.
The followings are examples.
Inlet/Exhaust manifold
Crankcase ventilation system
Fuel system
Limited :arranty
It conforms to "LIMITED WARRANTY" (page ii).
The following warranty applies to the engines that are approved of the emission regulation of the U.S. Environ-
mental Protection Agency.
Page 6

iv
FOREWORD
CALIFORNIA EMISSION CONTROL WARRANTY STATE-
MENT YOU WARRANTY RIGHTS AND OBLIGATIONS
The California Air Resources Board (CARB) and Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. are pleased to explain the
emission control system warranty on you 2011 or later engine. In California, new heavy-duty off-road engines
must be designed, built, and equipped to meet the State's stringent anti-smog standards. Mitsubishi Heavy
Industries, Ltd. must warrant the emission control system on your engine for the periods of time listed below
provided there has been no abuse, neglect or improper maint
enance of your engine.
Your emission control system may include parts such as the fuel-injection system and the air induction system. Also
included may be hoses, belts, connectors and other emission-related assemblies.
Where a warrantable condition exists, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. will repair your heavy-duty off-road engine
at no cost to you including diagnosis, parts, and labor.
Manufacurer's warranty coverage:
The 2011 and later h
eavy-duty off-road engines are warranted for the warranty period. If any emission-related part
on your engine is defective, the part will be repaired or replaced by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
Owner's warranty responsiblities
As the heavy-duty off-road engine owner, you are responsible for the performance of the required maintenance
listed in your owner's manual. Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. recommends that you retain all receipts covering
maintenance on your heavy-duty off-road engine, but Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. can not deny warranty sole-
ly for the lack of receipts
or for your failure to ensure the performance of all scheduled maintenance.
As the heavy-duty off-road engine owner, you should however be aware that Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. may
deny you warranty coverage if your heavy-duty off-road engine or a part has failed due to abuse, neglect, improper
maintenance or unapproved modifications.
Your engine is designed to operate on diesel fuel only. Use of any other fuel may result in your engine no longer
operating in compliance with California's emissions requirements.
You are responsible for initiating the warranty process. The Air Rexources Board suggests that you present your
heavy-duty off-road engine to a Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. dealer or distributor dealer as soon as problem
exists. The warranty repairs will be completed by the dealer or distributor as expeditiously as possible.
If you have any questions regarding your warranty rights and responsibilities, you should contact Mitsubishi
Engine North America at 1-630-268-0750.
The following warranty applies to the engines that are approved of the emission regulation of the California Air
Resources Board (CARB).
Page 7

v
FOREWORD
Warranty coverage
(a) The warranty period shall begin on the date the engine or equipment is delivered to an ultimate purchaser.
(b) Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. warrants to the ultimate purchaser and each subsequent purchaser of the en-
gine registered in the state of California that the engine is:
(1) Designed, built and equipped so as to conform with all applicable regulations adopted by the Air Resources
Board.
(2) Free from defects in materials and workmanship which cause the failure of a warranted part to be identical
in all material respects to the parts as described in Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.'s application for certifi-
cation for a period of 5 years or 3,000 hours of operation, whichever occurs first. In the absence of a device
to measure hours of use, the engine shall be warranted for a period of 5 years. For all engines rated less
than 19 kW, and for constant-speed engines rated under 37 kW with rated speeds higher than or equal to
3,000 min
-1
, the period of 2 years or 1,500 hours of operation, whichever occurs first, shall apply. In the ab-
sence of a device to measure hours of use, the engine shall be warranted for a period of 2 years.
(c) The warranty on emission-related parts shall be interpreted as follows:
(1) Any warranted part which is not scheduled for replacement as required maintenance in the written instruc-
tions required by Subsection (e) shall be warranted for the warranty period defined in Subsection (b) (2). If
any such part fails during the period of warranty coverage, it shall be repaired or replaced by Mitsubishi
Heavy Industries, Ltd. according to Subsection (4) below. Any such part repaired or replaced under the war-
ranty shall be warranted for the remaining warranty period.
(2) Any warranted part which is scheduled only for regular inspection in the written instructions required by Sub-
section (e) shall be warranted for the warranty period defined in Subsection (b) (2). A statement in such writ-
ten instructions to the effect of "repair or replace as necessary" shall not reduce the period of warranty
coverage. Any such part repaired or replaced under the warranty shall be warranted for the remaining war-
ranty period.
(3) Any warranted part which is scheduled for replacement as required maintenance in the written instructions
required in Subsection (e) shall be warranted for the period of time prior to the first scheduled replacement
point for that part. If the part fails prior to the first scheduled replacement, the part shall be repaired or re-
placed by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. according to Subsection (4) below. Any such part repaired or
replaced under warranty shall be warranted for the remainder of the period prior to the first scheduled re-
placement point for the part.
(4) Repair or replacement of any warranted part under the warranty provisions shall be performed at no charge
to the owner at a warranty station.
(5) Notwithstanding the provisions of Subsection (4) above, warranty services or repairs shall be provided at all
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. distribution centers that are franchised to service the subject engines.
(6) The owner shall not be charged for diagnostic labor that leads to the determination that a warranted part is
in fact defective, provided that such diagnostic work is performed at a warranty station.
(7) Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. shall be liable for damages to other engine components proximately caused
by failure under warranty of any warranted part.
(8) Throughout the engine's warranty period defined in Subsection (b) (2), Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. shall
maintain a supply of warranted parts sufficient to meet the expected demand for such parts.
(9)
Any replacement part, as defined in Section 1900(b)(13), Title 13, may be used in the performance of any
maintenance or repairs and must be provided without charge to the owner. It is not necessary for replace-
ment parts to be the same brand or by the same manufacturer as the original part sold with the engine.
Such use shall not reduce the warranty obligations of the engine manufacturer.
Page 8

vi
FOREWORD
(10) Add-on or modified parts, as defined in Section 1900(b)(1) and (b)(10), Title 13, that are not exempted by
the Air Resources Board may not be used. The use of any non-exempted add-on or modified parts shall be
grounds for disallowing a warranty claim made in accordance with this article. The engine manufacturer
shall not be liable under this article to warrant failures of warranted parts caused by the use of a non-
exempted add-on or modified part.
(11) The Air Resources Board may request and, in such case, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. shall provide,
any documents which describe that Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.'s warranty procedures or policies.
(d) Warranted parts list.
(1) Fuel metering system
(A) Fuel injection system.
(B) Air/fuel ratio feedback and control system.
(C) Cold start enrichment system.
(2) Air induction system
(A) Controlled hot air intake system.
(B) Intake manifold.
(C) Heat riser valve and assembly.
(D) Turbocharger/supercharger systems.
(E) Charged air cooling systems.
(3) Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) system
(A) EGR valve body, and carburetor spacer if applicable.
(B) EGR rate feedback and control system.
(4) Air injection system
(A) Air pump or pulse valve.
(B) Valves affecting distribution of flow.
(C) Distribution manifold.
(5) Catalyst or thermal reactor system
(A) Catalytic converter.
(B) Thermal reactor.
(C) Exhaust manifold.
(6) Particulate controls
(A) Traps, filters, precipitators, and any other devices used to capture particulate emissions.
(B) Regenerators, oxidizers, fuel additive devices, and any other device used to regenerate or aid in the
regeneration of the particulate control device.
(C) Control device enclosures and manifolding.
(D) Smoke puff limiters.
(7) Advances oxides of nitrogen (NOx) controls
(A) NOx absorbers.
(B) Lean NOx catalysts.
(C) Selective catalyst reduction.
(D) Reductant (urea/fuel) containers/dispensing systems.
(8) Positive crankcase ventilation (PCV) system
(A) PCV valve.
(B) Oil filler cap
Page 9

vii
FOREWORD
(9) Miscellaneous items used in above systems
(A) Vacuum, temperature, and time sensitive valves and switches.
(B) Electronic control units, sensors, solenoids, and wiring harnesses.
(C) Hoses, belts, connectors, assemblies, clamps, fittings, tubing, sealing gaskets or devices, and mount-
ing hardware.
(D) Pulleys, belts and idlers.
(E) Emission control information labels.
(F) Any other part with the primary purpose of reducing emissions or that can increase emission during fail-
ure without significantly degrading engine performance.
(e) Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. shall furnish with each new engine written instructions for the maintenance and
use of the engine by the owner.
Limited warranty
Refer to "LIMITED WARRANTY" (Page ii).
Page 10

viii
FOREWORD
IMPORTANT INFORMATION
To avoid the potential hazard, accident prevention
activities must be planned methodically and con-
ducted continually by considering all aspect of
engine operation, maintenance and inspection. All
related personnel, including managers and supervi-
sors, should actively participate, recognize their roles
and organize themselves and their work to ensure a
safe environment.
The foremost safety objective is to prevent accidents
which may result in injury or death, or equipment
damage.
Always observe laws or regulations of the local or
federal/national government.
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. cannot foresee all
potential dangers of the engine, potential danger
resulting from human error and other causes, or dan-
ger caused by a specific environment in which the
engine is used. Since there are many actions that
cannot be performed or must not be performed, it is
impossible to indicate every caution in this manual or
on warning labels. As such, it is extremely important
to follow directions in this manual and also to take
general safety measures when operating, maintain-
ing and inspecting the engine.
When the engine is used by individuals whose native
language is not English, the customer is requested to
provide thorough safety guidance to the operators.
Also add safety, caution and operating signs that
describe the original warning label statements in the
native language of the operators.
The engine must be operated, maintained and
inspected only by qualified persons who have thor-
ough knowledge of engines and their dangers and
who also have received risk avoidance training.
To prevent an accident, do not attempt to carry out
any operation other than those described in this man-
ual, and do not use the engine for any unapproved
purpose.
When the ownership of the engine is transferred, be
sure to provide this manual with the engine to the
new owner. Also inform Mitsubishi Heavy Industries,
Ltd. of the name and address of the new owner of the
engine.
This manual is copyrighted and all rights are
reserved. No part of this manual, including illustra-
tions and technical references, may be photocopied,
translated, or reproduced in any electronic medium
or machine readable form without prior written con-
sent from Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
The contents in this manual are subject to change at
any time without notice for improvement of the
engine.
Pictures or illustrations of the product in this manual
may differ from those of product you have. Please
note that, depending on specifications, items
described in this manual may differ from those on
your engine in shape, or may not be installed on your
engine.
Please contact a dealer of Mitsubishi Heavy Indus-
tries, Ltd. if you need more information or if you have
any questions.
If you lost or damaged this manual, obtain a new
copy at a dealer of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
as soon as possible.
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. recommends the
engine owner to install an hour meter on the engine
due to monitor correct running intervals and to per-
form the maintenance at the appropriate timing.
Page 11

ix
FOREWORD
WARNING INDICATION
The following means are used to call the attention of the operators and maintenance personnel to potential dangers
of the engine.
Warning statements in the manual
Warning labels affixed on the engine
Warning 6tatements
The warning statements in this manual describe potential danger in operating, inspecting or maintaining the engine,
using the following five classifications to indicate the degree of potential hazard.
Failure to follow these directions could lead to serious accidents which could result in personal injury, or death in
the worst case.
Understand the directions well, and handle engines with following directions.
Indicates an immediately hazardous situation which, if not avoided, will result in death or
serious injury.
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result in death or
serious injury.
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, may result in minor or
moderate injury.
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, may result in property
damage.
Note: Indicates important information or information which is useful for engine operation.
Page 12

x
FOREWORD
U1,76 2)0($685(0(17
Measurements are based on the International System of Units (SI), and they are converted to the metric system
units in this manual using the following conversion rates.
Pressure :1 MPa = 10.197 kgf/cm
2
Torque:1 N•m = 0.10197 kgf•m
Force:1 N = 0.10197 kgf
Horsepower:1 kW = 1.341 HP = 1.3596 PS
Meter of mercury:1 kPa = 0.75 cmHg
Meter of water:1 kPa = 10.197 cmH
2O (cmAq)
Rotation speed:1 min
-1
= 1 rpm
Kinetic viscosity:1 mm
2
/s = 1 cSt
ABBREVIATIONS, STANDARD AND OTHERS
API = American Petroleum Institute
ASTM = American Society for Testing and Materials
ISO = International Organization for Standardization
JIS = Japanese Industrial Standards
LLC = Long Life Coolant
MIL = Military Specifications and Standards
MSDS = Material Safety Data Sheet
SAE = Society of Automotive Engineers
Page 13

CONTENTS-1
CONTENTS
Chapter 1
BASIC SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Fire and Explosions.............................1-1
Keep Flames Away .......................................... 1-1
Always Swich the Water Heater ON
(Emergency generator with water heater)........ 1-1
Keep Engine Surrounding Area Tidy and Clean1-1
Ventilation of Engine Room.............................. 1-1
Do Not Open Side Cover Until Engine Cools... 1-1
Care for Fuel, Oil and Exhaust Gas Leakage .. 1-1
Use Explosion-proof Lighting Apparatus.......... 1-1
Prevent Electrical Wires From Short-circuiting. 1-1
Keep Fire Extinguishers and a First-aid Kit
Handy............................................................... 1-1
Stay Clear of All Rotating and Moving
Parts ....................................................1-2
Install Protective Covers Around Rotating Parts1-2
Check Work Area for Safety............................. 1-2
Stay Clear of Moving Parts While Engine is
Running............................................................ 1-2
Lockout and Tagout ......................................... 1-2
Keep Engine Stopped During Servicing........... 1-2
Always Restore Engine Turning Tools After Use1-2
Be Careful of Exhaust Fume Poisoning1-3
Operate Engine in a Well-ventilated Area........ 1-3
Protect Ears From Noise .....................1-3
Wear Ear Plugs ................................................ 1-3
Be Careful of Falling Down..................1-3
Lift Engine Carefully......................................... 1-3
Do Not Climb Onto the Engine......................... 1-3
Always Prepare Stable Scaffold....................... 1-3
Be Careful of Burns .............................1-4
Do Not Touch the Engine During or Immediately
After Operation................................................. 1-4
Refill Coolant Only After the Coolant Temperature
Dropped ........................................................... 1-4
Be careful of burns when changing oil ............. 1-4
Never Remove Heat Shields............................ 1-4
Be Careful of Opening and Closing Radiator
Cap .................................................................. 1-4
Do Not Touch High Pressure Injection Fuel..... 1-4
Be Careful When Handling Fuel, Engine
Oil or LLC ............................................1-5
Use Only Specified Fuel, Engine Oil and LLC . 1-5
Handle LLC Carefully ....................................... 1-5
Proper Disposal of Waste Oil, LLC and Coolant1-5
When Abnormality Occurs...................1-5
Do Not Add Coolant Immediately After a Sudden
Stop Due to Overheating.................................. 1-5
Stop Operation Immediately If You Notice Any
Unusual Symptoms .......................................... 1-5
Avoid Immediate Restart After Abnormal Stop. 1-5
Avoid Continuous Engine Operation at Low Oil
Pressure........................................................... 1-5
If Belt Breaks, Stop Engine Immediately .......... 1-5
Battery................................................. 1-6
Handle the Battery Correctly ............................ 1-6
Other Cautions.................................... 1-7
Never Modify Engine........................................ 1-7
Observe Safety Rules at Work Site.................. 1-7
Work Clothing and Protective Gear.................. 1-7
Never Break Seals ........................................... 1-7
Perform All Specified Pre-operation Inspections
and Periodic Inspections .................................. 1-7
Break-in the Engine.......................................... 1-7
Warm-up the Engine Before Use ..................... 1-7
Never Operate the Engine in an Overloaded
Condition .......................................................... 1-7
Conduct Cooling Operation Before Stopping the
Engine .............................................................. 1-8
Do Not Operate Engine Continuously Under Low
Load ................................................................. 1-8
Protection of the Engine Against Water Entry.. 1-8
Conduct Proper Maintenance of Air Cleaner....1-8
Use of Tools Optimum for Each Work.............. 1-8
Avoidance of Prolonged Time of Starter
Operation ......................................................... 1-8
Do Not Turn Off the Battery Switch During
Operation ......................................................... 1-8
Cautionary Instructions for Transporting the
Engine .............................................................. 1-8
Warning Labels ................................... 1-9
Maintenance of Warning Labels....................... 1-9
Chapter 2
NAME OF PARTS
Engine External Diagrams .................. 2-1
Left Side ........................................................... 2-1
Right Side......................................................... 2-1
Equipment and Instrument.................. 2-2
Start and Stop Instrument ................................ 2-2
Instruments ...................................................... 2-3
Engine Protection Devices.................. 2-4
Oil Pressure Switch.......................................... 2-4
Thermo Switch ................................................. 2-4
Page 14

CONTENTS
CONTENTS-2
Oil Filter Alarm Switch...................................... 2-4
Revolution Detection Pickup ............................ 2-5
Air Cleaner Indicator ........................................ 2-5
Using Turning Gear .............................2-6
Chapter 3
OPERATION
Operational Environment.....................3-1
Preparation for Operating New or
Overhauled Engine..............................3-1
Preparation of Fuel System.............................. 3-1
Preparation of Lubrication System ................... 3-4
Preparation of Cooling System ........................ 3-5
Preparation of Electrical System ...................... 3-6
Test Operation ................................................. 3-7
Normal Engine Operation....................3-8
Preparations for Operation ..................3-8
Engine External - Inspect................................. 3-8
Fuel Tank Oil Level - Check............................. 3-9
Fuel Control Link - Check................................. 3-9
Engine Oil Level - Check.................................. 3-9
Coolant Level - Check.................................... 3-10
Air Cleaner - Check for Clogging ................... 3-10
Air Tank - Drain Water ................................... 3-10
Air Tank Air Pressure - Check........................ 3-11
Temperature of Damper - Check ................... 3-11
Start...................................................3-12
Warming-up Operation ......................3-12
Checking Engine Oil Pressure ....................... 3-12
External Inspection During Warm-up ............. 3-12
Run....................................................3-13
Cautions During Operation............................. 3-13
Inspection During Operation .......................... 3-13
Stop ...................................................3-14
Emergency Stop............................................. 3-14
Inspection After Stopping ............................... 3-14
Chapter 4
FUEL
Recommended Fuel ............................4-1
Handling Fuel ......................................4-1
Fuel Specification ................................4-2
Chapter 5
ENGINE OIL
Recommended Engine Oil .................. 5-1
Engine Oil Grade ................................ 5-1
Engine Oil Specification ...................... 5-2
Selection of Oil Viscosity..................... 5-3
Handling Engine Oil ............................ 5-3
Service Limits of Engine Oil ................ 5-4
Definition of Properties of Engine Oil .. 5-5
Kinetic Viscosity ............................................... 5-5
Base Number ................................................... 5-5
Acid Number .................................................... 5-5
Water Content .................................................. 5-5
Flash Point ....................................................... 5-5
Insoluble........................................................... 5-5
Engine Oil Analysis Service ................ 5-6
Chapter 6
COOLANT
Recommended Water for Coolant ...... 6-1
Long Life Coolant (LLC)...................... 6-1
Genuine LLC....................................... 6-1
Other Brand LLCs ............................... 6-2
Standard for Other Brand LLC ............ 6-2
General Demands of LLC ................................ 6-2
LLC Specification ............................................. 6-3
Maintenance of LLC............................ 6-6
Replacement Intervals of LLC .......................... 6-6
LLC Concentration ........................................... 6-6
Importance of LLC .............................. 6-7
Characteristics of LLC Additive and
Important Notes .................................. 6-7
Examples of Abnormalities Caused by LLC
(Amine Type) ...................................... 6-7
Pitting of Iron Parts........................................... 6-7
Corrosion of Aluminum Parts ........................... 6-7
Pitting and Clogging of the Heat Exchange Equip-
ment ................................................................. 6-7
Chapter 7
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULE
How to Use the Maintenance Schedule7-1
General Definition of Engine ............... 7-2
Page 15

CONTENTS-3
CONTENTS
Periodic Maintenance Chart for Regular
Use Engine..........................................7-3
Periodic Maintenance Chart for Emergency
Engine .................................................7-5
Periodic Maintenance Chart for General
Purpose Engine...................................7-9
Chapter 8
PERIODIC INSPECTION AND
MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES
Basic Engine........................................8-1
Engine External - Inspect................................. 8-1
Belt and Belt Tension - Inspect and Adjust ...... 8-2
Damper - Inspect.............................................. 8-4
Fuel System.........................................8-6
Fuel System - Inspect ...................................... 8-6
Fuel Tank - Clean............................................. 8-6
Fuel Tank - Drain Water................................... 8-6
Water Separator - Drain Water ........................ 8-7
Water Separator Element - Replace ................ 8-7
Gauze Filter - Clean ......................................... 8-8
Fuel Filter - Replace......................................... 8-9
Fuel Control Link Ball Joint - Inspect.............. 8-10
Fuel Pipe - Inspect ......................................... 8-11
Lubricating System............................8-12
Engine Oil, Oil Filter and Bypass Oil Filter
- Replace........................................................ 8-12
Engine Oil for Mixing of Fuel and Water
- Inspect ......................................................... 8-14
Governor Oil Filter - Change .......................... 8-15
Oil Pipe - Inspect............................................ 8-15
Cooling System .................................8-16
Coolant - Change ........................................... 8-16
Radiator Fins - Check and Clean ................... 8-18
Inlet and Exhaust Systems................8-19
Turbocharger - Inspect................................... 8-19
Exhaust Muffler - Drain Water........................ 8-19
Air Cleaner - Check for Clogging ................... 8-20
Air Cleaner Element - Clean, Check and
Replace.......................................................... 8-21
Electrical System...............................8-23
Starter - Inspect.............................................. 8-24
Alternator - Inspect......................................... 8-24
Air Starter System .............................8-25
Air Strainer - Drain Water and Clean ............. 8-25
Air Tank - Drain Water ................................... 8-25
Air Tank - Inspect Safety Valve Operation ..... 8-26
Chapter 9
LONG-TERM STORAGE
Storing the Engine in an Inoperable
Condition for 3 Months or More .......... 9-1
Preparation for Storage.................................... 9-1
Maintenance During Storage ........................... 9-1
Using the Engine After Storage........................ 9-2
Storing the Engine in an Operable
Condition for 3 Months or More .......... 9-2
Operating the Engine for Maintenance ............ 9-2
Chapter 10
TRANSPORTATION
Lifting the Engine .............................. 10-1
Chapter 11
TROUBLESHOOTING
General Precautions ......................... 11-1
Contact a Dealer of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries,
Ltd. for Repair Service ................................... 11-1
Considerations Before Work .......................... 11-1
Cautions Against Contamination .................... 11-1
Cautions Regarding Parts Handling ............... 11-1
Safety Work.................................................... 11-1
Case of Problems, and Conceivable
Causes and Remedies...................... 11-2
The Starter Does Not Crank or Cranks Slowly,
Resulting in Start Failure................................ 11-2
The Starter Cranks, but the Engine Does Not
Start................................................................ 11-3
Output Decrease ............................................ 11-4
Exhaust Smoke is White or Blue .................... 11-5
Exhaust Smoke is Black or Charcoal ............. 11-6
Fuel Consumption is High .............................. 11-7
Engine Oil Consumption is High .................... 11-8
Overheating.................................................... 11-9
Low Engine Oil Pressure................................ 11-9
When Fuel has Run Out ................. 11-10
Chapter 12
MAIN SPECIFICATIONS
Main Specifications ........................... 12-1
Page 16

CONTENTS
CONTENTS-4
List of illustrations
Fig. 1-1 Warning labels...................................... 1-9
Fig. 2-1 Engine Left Side View ......................... 2-1
Fig. 2-2 Engine Right Side View ....................... 2-1
Fig. 2-3 Start Switch and Stop Switch .............. 2-2
Fig. 2-4 Manual Stop Lever .............................. 2-2
Fig. 2-5 Stop Solenoid ...................................... 2-2
Fig. 2-6 Oil Pressure Unit ................................. 2-3
Fig. 2-7 Thermo Unit ......................................... 2-3
Fig. 2-8 Revolution Detection Pickup ............... 2-3
Fig. 2-9 Oil Pressure Switch ............................. 2-4
Fig. 2-10 Thermo Switch .................................... 2-4
Fig. 2-11 Oil Filter Alarm Switch ......................... 2-4
Fig. 2-12 Revolution Detection Pickup ............... 2-5
Fig. 2-13 Air Cleaner Indicator ............................ 2-5
Fig. 2-14 Manual Turning Gear Position
(While Engine is Running) ................... 2-6
Fig. 2-15 Manual Turning Gear Position
(When Pushing Shaft in) ..................... 2-6
Fig. 2-16 Turning Gear Position
(When Turning Shaft) .......................... 2-6
Fig. 3-1 Priming Pump - Handle ........................ 3-2
Fig. 3-2 Fuel Filter - Bleed Air............................ 3-2
Fig. 3-3 Fuel Injection Pump - Bleed Air ........... 3-2
Fig. 3-4 Priming Pump Tightening Method ....... 3-3
Fig. 3-5 Priming Pump Head Packing .............. 3-3
Fig. 3-6 Oil Filler and Oil Level Gauge .............. 3-4
Fig. 3-7 Pouring Engine Oil on Valve Mechanisms
and Chamber ....................................... 3-4
Fig. 3-8 Radiator Cap ........................................ 3-5
Fig. 3-9 Coolant Drain Cock (Engine)................ 3-5
Fig. 3-10 Coolant Drain Cock (Water Pump) ....... 3-5
Fig. 3-11 Battery Electrolyte Level - Inspect ....... 3-6
Fig. 3-12 Valves for open/closed position
- Check ................................................ 3-8
Fig. 3-13 Fuel Control Link - Check .................... 3-9
Fig. 3-14 Oil Filler and Oil Level Gauge .............. 3-9
Fig. 3-15 Air Cleaner - Check for Clogging ....... 3-10
Fig. 3-16 Air Tank - Drain Water........................ 3-11
Fig. 3-17 Starting Air Tank Air Pressure
- Check ............................................... 3-11
Fig. 3-18 Thermo label of damper ......................3-12
Fig. 3-19 Manual Stop Lever .............................3-15
Fig. 5-1 Engine Oil Grade...................................5-1
Fig. 5-2 Selection of Oil Viscosity.......................5-3
Fig. 6-1 GLASSY - LLC ......................................6-1
Fig. 8-1 Belt and Belt Tension - Inspect and
Adjust ....................................................8-2
Fig. 8-2 Damper - Check Visually.......................8-4
Fig. 8-3 Damper Temperature Management ......8-5
Fig. 8-4 Fuel Tank - Drain Water ........................8-6
Fig. 8-5 Water Separator - Drain Water..............8-7
Fig. 8-6 Water Separator Element - Replace .....8-7
Fig. 8-7 Gauze Filter - Clean ..............................8-8
Fig. 8-8 Fuel Filter - Replace ..............................8-9
Fig. 8-9 Fuel Filter ..............................................8-9
Fig. 8-10 Ball Joints For Looseness - Inspect ....8-10
Fig. 8-11 Fuel Control Link - Remove.................8-10
Fig. 8-12 High Pressure Fuel Injection Pipe and
Clamp Seat - Inspect and Replace .....8-11
Fig. 8-13 Low Pressure Fuel Pipe and Clip
- Inspect ..............................................8-11
Fig. 8-14 Oil Filler and Oil Level Gauge .............8-13
Fig. 8-15 Oil Filter and Bypass Oil Filter
- Replace.............................................8-14
Fig. 8-16 Oil Filter...............................................8-14
Fig. 8-17 Governor oil filter - Drain .....................8-15
Fig. 8-18 Governor oil filter - Change .................8-15
Fig. 8-19 Oil Pipe and Clip - Inspect and
Replace ...............................................8-15
Fig. 8-20 Radiator Cap .......................................8-16
Fig. 8-21 Coolant Drain Cock (Engine)...............8-16
Fig. 8-22 Coolant Drain Cock (Water Pump) ......8-17
Fig. 8-23 Radiator fins - Clean ...........................8-18
Fig. 8-24 Turbocharger - Inspect .......................8-19
Fig. 8-25 Draining Water From the Exhaust
Muffler .................................................8-19
Fig. 8-26 Air Cleaner - Check for Clogging ........8-20
Fig. 8-27 Air Cleaner Element - Remove............8-21
Fig. 8-28 Air Cleaner Element - Clean and
Check ..................................................8-21
Fig. 8-29 Air Cleaner - Check for Clogging ........8-22
Page 17

CONTENTS-5
CONTENTS
Fig. 8-30 Battery Electrolyte Level - Inspect ..... 8-23
Fig. 8-31 Specific Gravity of Battery Electrolyte
- Check ............................................... 8-23
Fig. 8-32 Starter - Inspect.................................. 8-24
Fig. 8-33 Alternator - Inspect............................. 8-24
Fig. 8-34 Air Strainer - Drain Water and Clean . 8-25
Fig. 8-35 Air tank - Drain water.......................... 8-25
Fig. 10-1 Hanger................................................ 10-1
Fig. 10-2 Engine's center of gravity
(standard specification) ...................... 10-1
List of tables
Table 3-1 Inspection During Operation..................3-14
Table 4-1 Recommended Fuel ................................4-1
Table 4-2 Recommended Limit and Use Limit of
Fuel Property ...........................................4-2
Table 5-1 Table of Recommended Limit of Engine
Oil Properties...........................................5-2
Table 5-2 Table of engine oil properties ..................5-4
Table 6-1 Water Quality Standards .........................6-1
Table 6-2 LLC Specification.....................................6-3
Table 6-3 Recommended LLC Concentration .........6-6
Table 7-1 Periodic Maintenance Chart for
Regular Use Engine ................................7-3
Table 7-2 Periodic Maintenance Chart for
Emergency Engine ..................................7-5
Table 7-3 Periodic Maintenance Chart for
General Purpose Engine .........................7-9
Table 8-1 Ribbed Belt Tension Force......................8-3
Table 8-2 Damper Temperature Management ........8-4
Table 8-3 Thermo Label for Temperature
Management............................................8-5
Table 8-4 Specific gravity of electrolyte.................8-23
Table 9-1 Recommended Rust-preventive Oil and
Corrosion Inhibitor ...................................9-1
Table 11-1 The Starter Does Not Crank or Cranks
Slowly, Resulting in Start Failure...........11-2
Table 11-2 The Starter Cranks, but the Engine
Does Not Start.......................................11-3
Table 11-3 Output decrease....................................11-4
Table 11-4 Exhaust Smoke is White or Blue ...........11-5
Table 11-5 Exhaust Smoke is Black or Charcoal ....11-6
Table 11-6 Fuel Consumption is High .....................11-7
Table 11-7 Engine oil Consumption is High.............11-8
Table 11-8 Overheating...........................................11-9
Table 11-9 Low Engine Oil Pressure.......................11-9
Table 12-1 Main Specifications................................12-1
Page 18

Page 19

1-1
Chapter 1 BASIC SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Fire and Explosions
Keep Flames Away
Do not use flames near the engine (in
the engine room). Fuel gas vapor or
other gas can catch fire and produce
dangerous situations.
Wipe off spilled fuel, oil and LLC
immediately and thoroughly. Spilled fuel, oil and LLC
may ignite and cause a fire.
Store fuel and engine oil in a well-ventilated area.
Make sure that the caps of fuel and engine oil contain-
ers are tightly closed.
Always Swich the Water Heater
ON
(Emergency generator with
water heater)
Always swich the water heater ON (automatic mode)
through a whole year.
If the switch is not ON (automatic mode), each cylin-
der varies considerably in combustion at the starting
up the engine. Unburned fuel may explode in the
exhaust pipe.
Keep Engine Surrounding Area
Tidy and Clean
Do not leave combustible or explosive materials, such
as fuel, engine oil and LLC, near the engine. Such
substances can cause fire or explosion.
Remove dust, dirt and other foreign materials accu-
mulated on the engine and surrounding parts thor-
oughly. Such materials can cause fire or the engine to
overheat. In particular, clean the top surface of the
battery thoroughly. Dust can cause a short-circuit.
Ventilation of Engine Room
Always provide adequate ventilation in the engine
room. Insufficient air in the room can cause an
increase in the engine temperature and a decrease in
the output power and performance. It is highly recom-
mended to calculate the required amount of air supply
to the engine and install an adequate ventilation sys-
tem before installing the engine.
Do Not Open Side Cover Until
Engine Cools
Do not attempt to open the side cover of the crank-
case before the engine cools down. Wait at least 10
minutes after stopping the engine.
Opening the cover when the engine is hot allows fresh
air to flow into the crankcase, which can cause oil mist
to ignite and explode.
Care for Fuel, Oil and Exhaust
Gas Leakage
If any fuel, oil or exhaust gas leaks are found, immedi-
ately stop the engine and take corrective measures to
stop leakage.
Such leakages, if left uncorrected, can cause fuel or
engine oil to reach hot engine surfaces or hot exhaust
gas to contact flammable materials, possibly leading
to personal injury and/or damage to equipment.
Use Explosion-proof Lighting
Apparatus
When inspecting fuel, engine oil, coolant, battery elec-
trolyte, etc., use a flameproof light. An ordinary light-
ing apparatus may ignite gas and cause it to explode.
Prevent Electrical Wires From
Short-circuiting
Avoid inspecting or servicing the electrical system with
the ground cable connected to the battery. Otherwise,
a fire could result from short-circuiting. Be sure to dis-
connect the battery cable from the negative (-) termi-
nal before beginning with the work procedure.
Short-circuits, possibly resulting in fire, may be
caused by a loose terminal or damaged cable/wire.
Inspect the terminals, cables and wires, and repair or
replace the faulty parts before beginning with the ser-
vice procedure.
Keep Fire Extinguishers and a
First-aid Kit Handy
Keep fire extinguishers handy, and
become familiar with their usage.
Keep a first-aid kit at the designated
place where it is easily accessible by
anyone at any time.
Establish response procedures to follow in the event
of fire or accident. Provide an emergency evacuation
route and contact points and means of communication
in case of emergency.
Page 20

1-2
Chapter 1 BASIC SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Stay Clear of All Rotating and Moving Parts
Install Protective Covers
Around Rotating Parts
Make sure the protective covers of
the engine are correctly installed.
Repair any damaged or loose covers.
Never remove the covers such as
damper cover, camshaft cover, or
rocker cover that enclose the revolving parts during
operation.
When the engine is coupled to driven equipment, be
sure to provide protective covers over the parts such
as the connecting belts and couplings that are
exposed.
Never remove protective covers.
Check Work Area for Safety
Before starting the engine, make sure no one is near
the engine and tools are not left on or near the engine.
Verbally notify persons within the immediate area
when starting the engine.
When the starter device is posted with a sign that pro-
hibits startup operation, do not operate the engine.
Stay Clear of Moving Parts
While Engine is Running
Stay away from rotating or sliding
parts of the engine while the engine is
running. Put objects, which might be
easily caught by rotating parts, away
from rotating parts.
If any part of the clothing or outfitting is caught by a
rotating part, serious bodily injuries could result.
Lockout and Tagout
Be sure to lockout and tagout before starting inspec-
tion and maintenance.
Lockout and tagout are effective methods of cutting off
machines and equipment from energy sources.
To accomplish the lockout/tagout, remove the starter
switch key, set the battery switch to OFF and attach a
"Do Not Run" or similar caution tag to the starter
switch.
The starter switch key must be kept by the person
who performs inspection and maintenance during the
work.
In the case of pneumatic starting type, close the main
valve of the air tank and post a tag saying "Do Not
Open the Valve" or the like.
Keep Engine Stopped During
Servicing
Be sure to stop the engine before proceeding to
inspection and service procedure. Never attempt to
make adjustments on the engine parts while the
engine is running.
Rotating parts such as belt can entangle your body
and cause serious injuries.
Always Restore Engine Turning Tools After Use
Be sure to remove all turning tools used during main-
tenance and inspection work. Remember also that the
manual turning gear shaft must be pulled out before
starting the engine.
Starting the engine with the turning tools inserted or
with the turning gear in engagement can lead to not
only engine damage but also personal injuries.
Page 21

1-3
Chapter 1 BASIC SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Be Careful of Exhaust
Fume Poisoning
Operate Engine in a Well-ventilated Area
Check the exhaust pipes and where
the pipes joint together for gas leaks.
Exhaust gas from the engine contains
carbon monoxide and other harmful
substances. Operating the engine in
an poorly-ventilated area can produce gas poisoning.
Protect Ears From Noise
Wear Ear Plugs
Always wear ear plugs when entering
the machine room (engine room).
Combustion sound and mechanical
noise generated by the engine can
cause hearing problems.
Be Careful of Falling
Down
Lift Engine Carefully
To lift the engine, use slings capable
of supporting the weight of the
engine.
Attach the wire rope to the hangers
provided on the engine using a cor-
rect sling.
During lifting process, keep the engine in a well-bal-
anced position by taking the center of gravity of the
engine into consideration.
The hangers equipped with the engine are designed
for lifting the engine only. When mounting generator
on the engine, use the special hanger of common bed.
Hangers of engine cannot be used. When mounting
marine gear on the engine, be sure not to apply the
load on the hangers of engine only.
Keep the angle formed by slings attached to hangers
within 60°. If the angle exceeds this limit, excessive
load could be imposed on the hangers and this could
damage the hangers and result in a serious accident.
If the wire rope contacts the engine directly, place a
cloth or other soft padding to avoid damage to the
engine and wire rope.
Do Not Climb Onto the Engine
Do not climb onto the engine, nor step on any engine
parts located on the lateral sides.
To work on parts located on the upper section of
engine, use a ladder, stool, etc., that was firmly
secured.
Climbing on the engine may not only damage engine
parts but also cause falling down from the engine and
result in personal injuries.
Always Prepare Stable Scaffold
When working on the upper part of
the engine and other hard-to-reach
places, use a stable work platform.
Standing on a decrepit stool or parts
box may result in personal injury.
Do not place any unnecessary objects on a work plat-
form.
Page 22

1-4
Chapter 1 BASIC SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Be Careful of Burns
Do Not Touch the Engine During or Immediately After Operation
To avoid burns, do not touch the
engine during or immediately after
operation.
A hot engine can cause burns.
To conduct maintenance and inspec-
tion work, wait until the engine has cooled sufficiently
by checking the temperature gauge.
Refill Coolant Only After the
Coolant Temperature Dropped
When adding coolant, check that the coolant tempera-
ture lowers sufficiently with temperature gauge. Add-
ing coolant immediately after the engine stops may
result in burns.
Be careful of burns when
changing oil
Wear gloves when draining oil or changing oil filters. If
hot oil or parts touch your skin, it may cause burns.
Never Remove Heat Shields
The inlet and exhaust system, which becomes
extremely hot while the engine is operating, is pro-
vided with various heat shields. Do not remove these
heat shields. If any of these heat shields have been
removed owing to unavoidable circumstances during
the work, be sure to restore them after the work is
completed.
Be Careful of Opening and
Closing Radiator Cap
Never open the radiator cap while the engine is run-
ning or immediately after the engine is stopped. To
open the cap, stop the engine and allow the coolant
temperature to lower sufficiently.
To open the radiator cap, open slowly to discharge the
pressure inside the tank. Also to avoid a risk of getting
scalded by steam, wear thick rubber gloves or wrap a
cloth around the cap.
When closing the radiator cap, be sure to tighten
securely.
The coolant is hot while engine is running and immedi-
ately after the engine stops. If the cap is opened when
the coolant is at operating temperature, steam and hot
coolant may blow out and result in burns.
Do Not Touch High Pressure
Injection Fuel
If fuel leaks or sprays out from the high pressure injec-
tion pipe, do not touch the fuel.
Fuel in the fuel injection pipes is under high pressure
and if the fuel contact your skin, it goes into deep tis-
sues and may result gangrene.
Page 23

1-5
Chapter 1 BASIC SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Be Careful When Handling
Fuel, Engine Oil or LLC
Use Only Specified Fuel,
Engine Oil and LLC
Use fuel, oil and LLC specified in this manual, and
handle them carefully.
Use of any other fuel gas, oil or LLC than the specified
ones, or improper handling may cause various engine
problems and malfunctions.
Obtain the MSDS issued by the oil and LLC suppliers,
and follow the directions in the MSDSs for proper han-
dling.
Handle LLC Carefully
When handling LLC, always wear rubber gloves and a
protective face mask. If LLC or cooling water contain-
ing LLC comes into contact with your skin or eyes, or if
it is swallowed, you would suffer from inflammation,
irritation or poisoning.
Should LLC be accidentally swallowed, induce vomit-
ing immediately and seek medical attention. Should
LLC enter your eyes, flush them immediately with
plenty of water and seek medical attention. If LLC
splashes onto your skin or clothing, wash it away
immediately with plenty of water.
Keep flames away from LLC. LLC is highly flammable
and can easily catch a fire if exposed to a flame.
Proper Disposal of Waste Oil,
LLC and Coolant
Do not discharge waste engine oil, LLC and coolant
into sewerage, river, lake or other similar places. Such
a way of disposal is strictly prohibited by laws and reg-
ulations.
Dispose of waste oil, LLC and coolant and other envi-
ronmentally hazardous waste in accordance with the
applicable law and regulations.
When Abnormality Occurs
Do Not Add Coolant Immediately After a Sudden Stop Due
to Overheating
If the engine stops suddenly or if you have no choice
but stop the engine suddenly due to overheating, do
not add coolant immediately.
Adding water while the engine is hot can damage
parts such as cylinder heads due to a sudden drop of
temperature. Add coolant gradually after the engine
has completely cooled.
Stop Operation Immediately If
You Notice Any Unusual Symptoms
Stop the operation immediately if you notice any
unusual noise, odor or vibration during operation. In
case of emergency, press the emergency stop button
to stop the engine. Contact your local dealer if the
cause of problem cannot be located after stopping the
generator. Continuous operation neglecting an
unusual symptom could cause serious or fatal acci-
dent.
Avoid Immediate Restart After
Abnormal Stop
If the engine stops abnormally, do not restart the
engine immediately. If the engine stops with an alarm,
check and remedy the cause of the problem before
restarting. Sustained use of the engine without any
remedy could result in serious engine problems.
Avoid Continuous Engine Operation at Low Oil Pressure
If an abnormal engine oil pressure drop is indicated,
stop the engine immediately, and inspect the lubrica-
tion system to locate the cause. Continuous engine
operation with low oil pressure could cause bearings
and other parts to seize.
If Belt Breaks, Stop Engine
Immediately
If the belt breaks, stop the engine immediately and
replace the belt. Sustained use of the engine without
any remedy could cause defective charge and cooling
failure, and result in serious engine problems.
Page 24
1-6
Chapter 1 BASIC SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Battery
Handle the Battery Correctly
Never use flames or allow sparks to
generate near the battery. The bat-
tery releases flammable hydrogen
gas and oxygen gas. Any flames or
sparks in the vicinity could cause an
explosion.
Do not use the battery when the battery electrolyte
level is below the "LOWER LEVEL" mark. Sustained
use of the battery could result in an explosion.
Do not short the battery terminals with a tool or other
metal object.
When removing battery, always remove the plug from
the negative (-) terminal first. When connecting bat-
tery, always connect the plug to the positive (+) termi-
nal first.
Remove all plugs, then charge the battery in a well
ventilated area.
Make sure the cable clamps are securely installed on
the battery terminals. A loose cable clamp can cause
sparks that may result in an explosion.
Before servicing electrical components or conducting
electric welding, set the battery switch to [Open/OFF]
position or remove the plug from the negative (-) ter-
minal to cut off the electrical current.
Battery electrolyte contains dilute sulfuric acid. Care-
less handling of the battery can cause the loss of sight
and/or skin burns. Also, do not swallow the battery
electrolyte.
Wear protective goggles and rubber gloves when
working with the battery (e.g. adding water, charging
battery).
If battery electrolyte is spilled onto the skin or clothing,
immediately wash it away with lots of water. Use soap
to thoroughly clean.
The battery electrolyte can cause the loss of sight if
splashing into the eyes. If it gets into the eyes, imme-
diately flush it away with plenty of clean water, and
seek immediate medical attention.
If you accidentally swallow battery electrolyte, gargle
with plenty of water and then drink lots of water, and
seek immediate medical attention.
Page 25

1-7
Chapter 1 BASIC SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Other Cautions
Never Modify Engine
Unauthorized modification of the engine will void our
warranty.
Modification of the engine may not only cause engine
damage but also produce personal injuries.
If there is a need to modify the engine, contact a
dealer of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
Observe Safety Rules at Work
Site
Observe the safety rules established at your work-
place when operating and maintaining the engine.
Do not operate the engine if you are not feeling well,
and inform your supervisor of your condition. Opera-
tion of the engine with reduced awareness may cause
improper operation that could result in accidents.
When working in a team for two or more people, use
specified hand signals to communicate among work-
ers.
Work Clothing and Protective
Gear
Wear a hardhat, face shield, safety shoes, dust mask,
gloves, ear plugs and other protective gear as
needed. When handling compressed air, wear safety
goggles, a hardhat, gloves and other necessary pro-
tective gear. Working without wearing proper protec-
tive gear could result in serious injuries.
Never Break Seals
To ensure proper engine operation, the fuel control
links are sealed to prevent accidental change of the
injection volume and rotation speed settings. If the
seal is tampered, no guarantee will be provided. If the
seal is tampered, the defects shown below can occur.
Rapid wear of sliding and rotating parts
Engine damage such as seizing of engine parts
Considerably increased consumption of fuel and lu-
bricating oil
Degradation of engine performance due to improper
balance between fuel injection volume and governor
operation or overrunning of the engine which could re-
sult in a serious accident.
Perform All Specified Pre-operation Inspections and Periodic
Inspections
Conduct the pre-operation inspections and periodic
inspections as described in this manual.
Failure to conduct the specified inspections may
cause various engine problems, damage to parts, and
serious accidents.
Break-in the Engine
To break-in new engines or overhauled engines, oper-
ate the engine at a speed lower than the rated speed
in a light load condition during the first 50 hours of
operation.
Operating new engines or overhauled engines in a
severe condition during the break-in period shortens
the service life of the engine.
Warm-up the Engine Before
Use
After starting the engine, run the engine at a low idling
speed for 5 to 10 minutes for warming-up. Start the
work after this operation is completed. Warm-up oper-
ation circulates the lubricant around the engine, and
thereby, individual engine parts are well lubricated
before they are subjected to heavy loads.
Warm-up operation circulates lubricant oil around the
engine and contributes to a longer service life and
economical operation.
Do not conduct warm-up operation for prolonged
period of time. Prolonged warm-up operation causes
carbon build-up in the cylinders that leads to incom-
plete combustion.
Never Operate the Engine in an
Overloaded Condition
If the engine shows an overloaded condition such as
black exhaust smoke, reduce the load immediately to
operate the engine at an appropriate output and load.
Overloading causes not only high fuel consumption
but also excessive carbon deposits inside the engine.
Carbon deposits cause various problems and will
shorten the service life of the engine.
Page 26

1-8
Chapter 1 BASIC SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Conduct Cooling Operation
Before Stopping the Engine
Before stopping the engine, idle the engine in low gear
for 5 to 6 minutes to cool down.
Stopping the engine immediately after high-load oper-
ation will cause engine parts to heat up and shorten
the service life of the engine.
During cooling operation, check the engine for abnor-
malities.
Do Not Operate Engine Continuously Under Low Load
When operating the engine with less than 30 % of
rated load, limit each operation to an hour. Prolonged
warm-up operation causes carbon build-up in the cyl-
inders that leads to incomplete combustion. Operate
the engine with a 30 % of rated load or more for over 5
minutes to prevent carbon build-up after one hour
continuous operation is conducted.
Protection of the Engine
Against Water Entry
Do not allow rainwater, etc. to enter the engine
through the air inlet or exhaust openings.
Do not wash the engine while it is operating. Cleaning
fluid (water) can be sucked into the engine.
Starting the engine with water inside the combustion
chambers can cause the water hammer action which
may result in internal engine damage and serious
accidents.
Conduct Proper Maintenance of
Air Cleaner
Maintain the engine with air cleaner according to the
following instructions.
Never service the air cleaner while the engine is run-
ning. The turbocharger may suck particles of foreign
materials into the engine and could result in serious
accidents.
Remove the air cleaner slowly to prevent foreign ma-
terials accumulated on the element from falling off. Af-
ter removing the air cleaner, immediately cover the air
inlet with plastic sheet or similar means to prevent for-
eign materials from entering the engine.
Use of Tools Optimum for Each
Work
Always keep in mind to select most appropriate tools
for the work to be performed and use them correctly. If
tools are damaged, replace them with new tools.
Avoidance of Prolonged Time
of Starter Operation
Do not use the starter for more than 10 seconds at a
time. If the engine does not start, wait for at least 1
minute before cranking again.
Continuous operation of the starter will drain the bat-
tery power and cause the starter to seize.
Do Not Turn Off the Battery
Switch During Operation
Do not turn off the battery switch during operation.
If the battery switch is turned OFF when the engine is
running, not only various meters will stop working but
also the alternator may have its diode and transistor
deteriorated.
Cautionary Instructions for
Transporting the Engine
When transporting the engine on a truck, consider the
engine weight, width and height to ensure safety.
Abide by road traffic law, road vehicles act, vehicle
restriction ordinance and other pertinent laws.
Page 27

1-9
Chapter 1 BASIC SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Warning Labels
Maintenance of Warning Labels
Make sure all warning/caution labels are legible.
Clean or replace the warning/caution labels when the description and/or illustration are not clear to read.
For cleaning the warning/caution labels, use a cloth, water and soap. Do not use cleaning solvents, gasoline or
other chemicals to prevent the letters from getting blurred or the adhesion from being weakened.
Replace damaged or fractured labels with new ones.
If any engine part on which a warning label is attached is replaced with a new one, attach a new identical warning
label to the new part.
To obtain new warning labels, contact a dealer of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
Fig. 1-1 Warning labels
Page 28

Page 29
2-1
Chapter 2 NAME OF PARTS
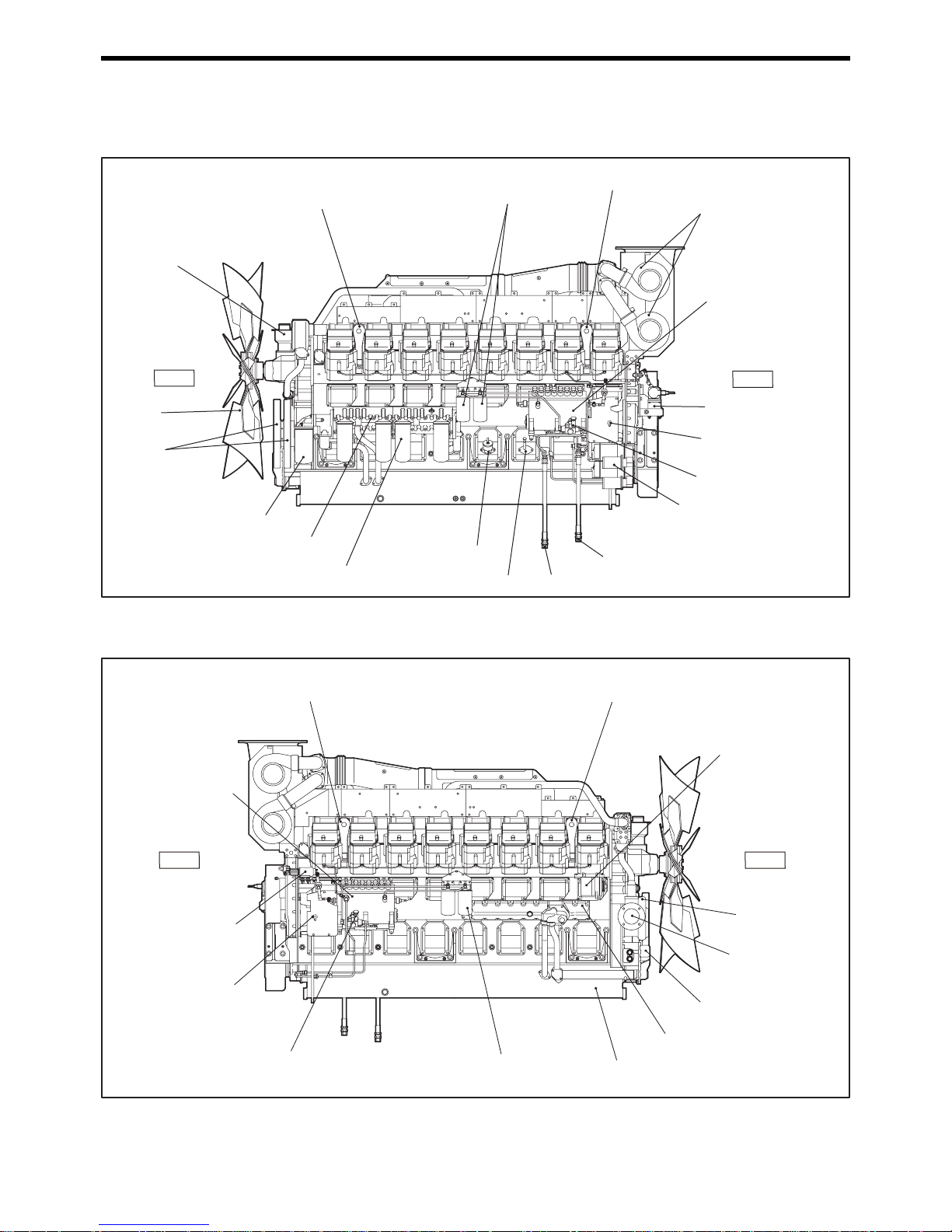
Engine External Diagrams
Left Side
Fig. 2-1 Engine Left Side View
Right Side
Fig. 2-2 Engine Right Side View
Turbocharger
Fuel injection pump
Coolant drain cock
Fuel feed pump
Starter
Fuel return port
Fuel inlet
Oil filler
Oil level gauge
Oil cooler
Bypass oil filter
Damper
Fan
Breather
Fuel filter
Rear hanger
Rear
Front
Front hanger
Oil filter
Governor actuator
Alternator
Water pump
Cooling water
inlet
Oil pump
Oil cooler
Oil pan
Fuel filter
Fuel feed pump
Cooling water
drain cock
Fuel injection
pump
Rear hanger
Front hanger
Rear
Front
Stop solenoid
Page 30
2-2
Chapter 2 NAME OF PARTS
Equipment and Instrument
The installed equipment and shapes differ on the engine type.
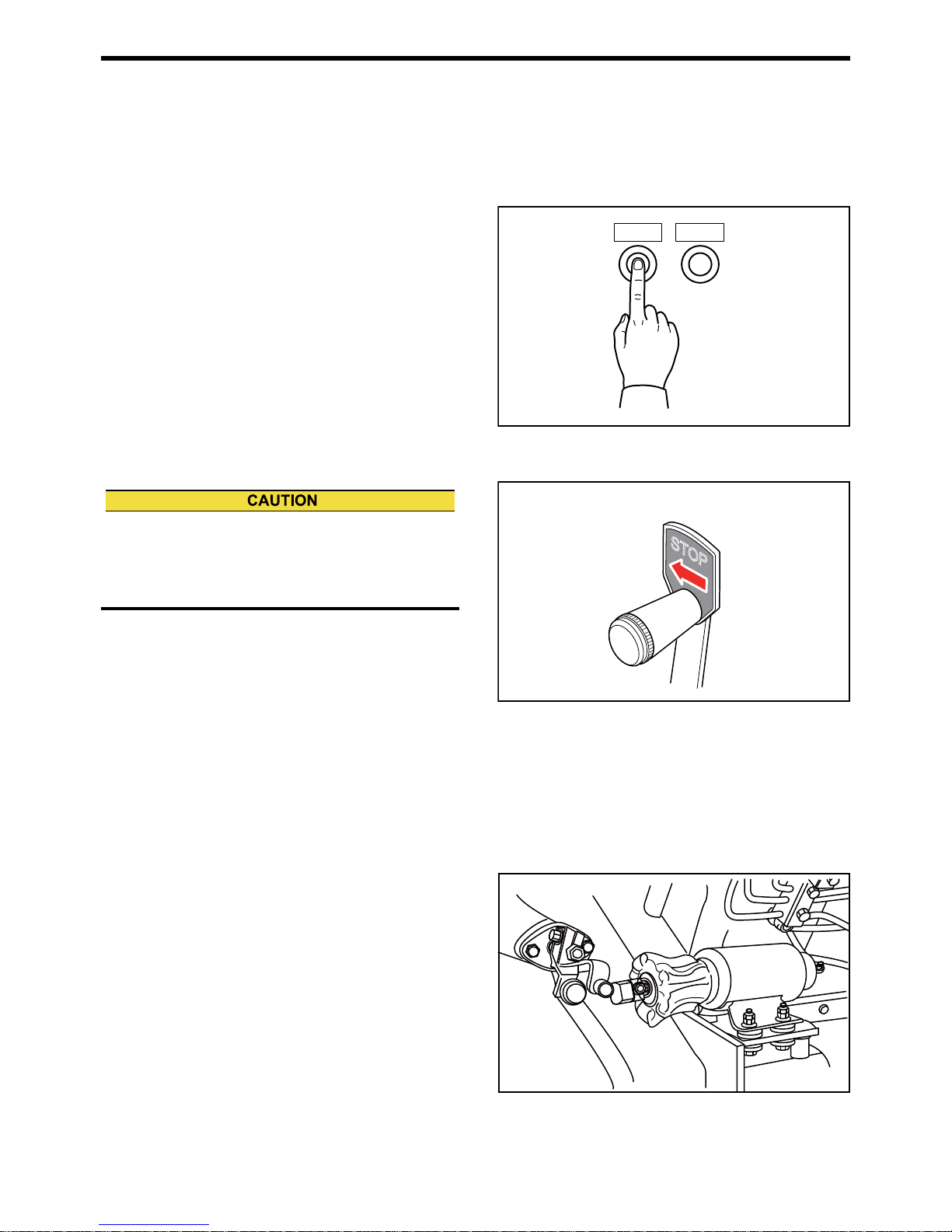
Start and Stop Instrument
Start Switch
When the start switch on the operation panel is
pressed, starting system operates to crank the engine.
Stop Switch
When the stop switch on the operation panel is
pressed, the shutdown cylinder operates and moves
the control shaft of the fuel injection pump to the noinjection position to shut down the engine operation.
Fig. 2-3 Start Switch and Stop Switch
Manual Stop Lever
Use the manual stop lever to shut down the engine in
the event of an emergency. If the st arter switch fails to
stop engine operation, use the manual stop lever.
When the manual stop lever, which is located in the
fuel control link, is moved in the "STOP" direction, the
engine stops.
If the engine continues to operate even after the manual stop lever is moved in the "STOP" direction, cut off
the fuel supply to stop the engine.
Fig. 2-4 Manual Stop Lever
Stop Solenoid
The stop solenoid operates for normal shutdown of
engine operation. The stop solenoid moves the rack of
fuel injection pump to cut the fuel, and consequently
stops the engine. Two types of stop solenoids are
available.
RUN OFF type
Not energized while the engine is running. Energized
by a stop signal to stop the engine.
RUN ON type
Energized while the engine is running, and de-energized by stop signal to stop the engine.
Fig. 2-5 Stop Solenoid
STOPSTART
(Example)
When stopping the engine with manual stop lever,
keep the manual stop lever at the stop position until
the engine completely stops. If release the lever, the
engine may restart.
STOP
Page 31

2-3
Chapter 2 NAME OF PARTS
Instruments
This section describes about devices which transmit signals to necessary instruments of the engine operation.
Read carefully and understand functions of each device.
Oil Pressure Unit
Indicate the oil pressure.
Fig. 2-6 Oil Pressure Unit
Thermo Unit
Always detect the coolant temperature of engine.
Fig. 2-7 Thermo Unit
Revolution Detection Pickup
It is installed in the timing gear case, and always
detect engine speed.
Fig. 2-8 Revolution Detection Pickup
Oil pressure unit
Thermo unit
Page 32

2-4
Chapter 2 NAME OF PARTS
Engine Protection Devices
The engine protection devices activate an alarm when an abnormality occurs in the engine in order to protect the
engine and prevent serious problems and accidents. When a protection device is activated, stop the engine, exam-
ine the cause of the abnormality, and take corrective measures. If the cause of the problem is unknown, contact a
dealer of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. Protection devices installed on the engine and their types (setting values)
and shapes vary depending on the engine specifications.
Oil Pressure Switch
The oil pressure switch generates an alarm when the
engine oil pressure becomes low and reaches the
specified pressure.
Fig. 2-9 Oil Pressure Switch
Thermo Switch
The oil pressure switch generates an alarm when the
engine coolant temperature becomes high and
reaches the specified temperature.
Fig. 2-10 Thermo Switch
Oil Filter Alarm Switch
The oil filter alarm switch generates an alarm to stop
the engine when oil filters become clogged, the differ-
ence in pressure between inlet and outlet of oil and
reaches the specified value.
Fig. 2-11 Oil Filter Alarm Switch
Oil pressure
switch
Thermo switch
Oil filter alarm switch
Page 33

2-5
Chapter 2 NAME OF PARTS
Revolution Detection Pickup
The overrun detection pickup generates an alarm
when the engine speed becomes high and reaches
the specified engine speed.
Fig. 2-12 Revolution Detection Pickup
Air Cleaner Indicator
If the element is clogged, the intake air is decreased
and the red signal mark will be displayed. The signal
indicates only, and does not generate an alarm,
Therefore, the periodic visually inspection is needed.
Press the reset button on the top of air cleaner indica-
tor and restore the signal after cleaned the air cleaner
indicator or replaced with a new one.
Fig. 2-13 Air Cleaner Indicator
Reset button
Signal
(red)
Page 34

2-6
Chapter 2 NAME OF PARTS
Using Turning Gear
1. Loosen the two bolts, and remove the plate from
the shaft groove.
Fig. 2-14 Manual Turning Gear Position
(While Engine is Running)
2. Push in the shaft fully to engage it with the ring
gear.
Fig. 2-15 Manual Turning Gear Position
(When Pushing Shaft in)
3. Using a socket wrench and a ratchet handle, turn
the shaft.
4. After turning, pull out the shaft, insert the plate in
the shaft groove, and tighten the bolts.
Fig. 2-16 Turning Gear Position (When Turning Shaft)
Before starting the engine, make sure that the manual turning gear is pulled out in the original position. Starting the
engine with the turning gear pushed in not only damages the ring gear but also may result in personal injury.
Bolt
Bolt
Plate
Shaft
Make sure the plate is securely installed in the shaft
groove.
Socket
Ratchet handle
Page 35

3-1
Chapter 3 OPERATION
Operational Environment
Preparation for Operating New or Overhauled Engine
Before proceeding with operation of a new overhauled engine, conduct the inspections described in this section.
For second operation onward, follow the instructions described in the "Normal Engine Operation" (3-8).
Preparation of Fuel System
1. Make sure the insides of the fuel tank and fuel supply pipes to the engine are thoroughly clean.
2. Check the drain valve and air inlet valve is closed at the time.
3. Fill fuel tank with fuel.
4. Remove the fuel feed pipe and drain plug from the fuel inlet of engine, and check the discharged fuel for foreign
materials such as dust.
5. Reinstall the drain plug and the fuel feed pipe.
6. Close the drain valve to fill the fuel.
7. Refill fuel tank until fuel level gauge indicates "FULL" level line, after checking the contact of float switch.
Check that the following contents are performed before the engine is operated. Failure to do so may cause various
problems and will shorten the service life of the engine.
Prevent from spreading water (especially, seawater or rainwater) and entering foreign materials to the air inlet
opening.
Prevent from entering foreign materials to the rotating parts.
Prevent from attaching water and dust to the electrical system.
Use the engine at 5 to 40 °C [41 to 104 °F].
Keep the coolant temperature properly by switching ON the water heater (automatic mode). (Emergency generator
with water heater)
When handling fuel, make sure there are no open flames or other fire hazards near the engine.
Wipe off any spilled fuel completely. Spilled fuel can ignite and cause a fire.
Do not remove the strainer during fuel tank filling.
For fuel to be used, refer to "FUEL" (4-1).
Page 36

3-2
Chapter 3 OPERATION
Fuel System - Bleed Air
While feeding fuel with priming pump, bleed air from
the location closest to the fuel tank that are the water
separator, fuel filter, then the fuel injection pump.
Lock the priming pump according to "Priming Pump
Tightening Method".
Fig. 3-1 Priming Pump - Handle
Fuel Filter - Bleed Air
1. Loosen the air vent plug of the fuel filter about 1.5
turns.
2. Move the priming pump up and down, then feed fu-
el.
3. When the fuel from the air vent plug becomes free
from air bubbles, stop priming and tighten the air
vent plug to the specified torque.
Fig. 3-2 Fuel Filter - Bleed Air
Fuel Injection Pump - Bleed Air
1. Loosen the air vent plug on the fuel injection pump
by rotating about 1.5 turns.
2. Move the priming pump up and down until the fuel
flow from the air vent plug is free from air bubbles.
Push and turn the priming pump clockwise to lock
in the original position when the fuel flows is free
from bubbles.
3. Tighten the air vent plug on the fuel injection pump.
Fig. 3-3 Fuel Injection Pump - Bleed Air
When fuel overflow from the air vent plug, wipe thor-
oughly. Spilled fuel causes fire hazard.
After bleeding, lock the priming pump securely. If the
cap is not locked tightly, the priming pump can be
damaged, causing a fuel leak that could lead to a
fire.
[Unlock] [Priming] [Lock]
Turn left
Move up
and down
Hold and
turn right
If air vent plugs, the thread portion of the bracket, or
sealing washers are damaged, replace them with
new ones.
Air vent plug
Tightening torque
8.8 ± 1 N·m
{0.9 ± 0.1 kgf·m}
[6.4 ± 0.7 lbf·ft]
Priming pump
Air vent plug
15 ± 2 N·m
{1.5 ± 0.2 kgf·m}
[11.0 ± 1.4 lbf·ft]
Page 37

3-3
Chapter 3 OPERATION
Priming Pump Tightening Method
1. Gently tighten the priming pump cap by hand until
the tightening force suddenly increases.
2. Use a wrench or another appropriate tool to tighten
the priming pump 90±10°.
3. Check the mounting position of head packing.
Note: If the head packing has abnormality such as de-
formation or scratches, consult a dealer of Mit-
subishi Heavy Industries, Ltd., as the priming
pump needs to be changed.
Fig. 3-4 Priming Pump Tightening Method
Fig. 3-5 Priming Pump Head Packing
Never fail to tighten the priming pump to the speci-
fied angle. If the priming pump is not firmly tightened,
internal thread will be worn due to engine vibration,
resulting in sudden ejection of the cap to cause fuel
flow-out. Or if the priming pump is excessively tight-
ened, the head of the priming pump can be dam-
aged.
Position where
hand-tightening
becomes suddenly
heavy
90
±10°
Priming pump
Head can be damaged
if the cap is excessively
tightened.
(120° or more)
°
Head packing
Page 38

3-4
Chapter 3 OPERATION
Preparation of Lubrication System
Engine Oil - Refill
1. Remove the cap from the oil filler.
2. Fill the engine oil pan with specified engine oil to
the specified level.
Note: For engine oil, refer to "ENGINE OIL" (5-1). For
engine oil capacity, refer to "MAIN SPECIFICA-
TIONS" (12-1).
3. Remove the rocker cover, and pour engine oil to
the valve mechanism and camshaft oil bath. Pour
engine oil to camshaft oil bath from cylinder head
side.
Oil capacity per cylinder: 0.8 L [0.21 U.S. gal.]
4. Reinstall the rocker covers.
5. Check the oil level in the oil pan.
6. Pull out the oil level gauge and wipe it clean with a
waste cloth.
7. Insert the oil level gauge fully into the oil level
gauge guide and then pull it out again.
8. The proper oil level is between the high and low
marks on the oil level gauge.
If the engine oil goes over the high marks on the oil
level gauge, open the engine oil drain valve to drain
oil.
If the engine oil is low, refill the specified engine oil.
9. Check the oil pan and other area for oil leaks. Re-
pair the oil leakage if any.
10. While pulling the stop lever, rotate the crankshaft
for approx. 10 seconds to turn on the starter. Stop
the operation for 1 minute, then, repeat the opera-
tion two or three times. Circulate engine oil to each
engine parts.
Note: Prepare for the cooling system.
11. Start the engine and run the engine in a no load
condition at low idling speed for 5 to 10 minutes.
12. Check the oil level with the oil level gauge again,
and add oil to the specified level after leaving the
engine stopped for 30 minutes or more.
For details, refer to "Test Operation" (3-7).
Fig. 3-6 Oil Filler and Oil Level Gauge
Fig. 3-7 Pouring Engine Oil on Valve Mechanisms and
Chamber
Refilling engine oil must be specified level. If the
refilling oil goes over the high marks on the oil level
gauge, engine oil may blow out. And also, the engine
component parts are adversely affected by increas-
ing in oil temperature.
H
L
Oil filler
Oil level gauge
Oil level gauge
High
Low
Improper
Improper
Proper
Camshaft
oil bath
Page 39

3-5
Chapter 3 OPERATION
Preparation of Cooling System
Radiator Cap - Open/Close
Note: If the specification of radiator differs from the
contents of this opera tion manual, follow the
manufacturer's operation manual.
Fig. 3-8 Radiator Cap
Coolant - Refill
1. Close the coolant drain cock of engine and water
pump securely.
2. Open the coolant filler and add a mixture of water
and coolant having the specified concentration.
Note: (a) Determine the quantities of LLC based on the
coolant capacity and the LLC concentration
chart.
For the coolant, refer to "COOLANT" (6-1) .
For the coolant capacit y, refer to "MAIN
SPECIFICATIONS" (12-1).
(b) For absolute air bleeding, loosen the air vent
plug on the upper section of thermostat.
3. Check the heat exchange equipment and other
parts for coolant leaks. Repair leakage if found.
4. When coolant reaches the full level, close the cool-
ant filler securely.
5. While pulling the manual stop lever, rotate the
crankshaft for approx. 10 seconds using the start-
er.Stop the operation for approx. 1 minute, then, re-
peat the operation two or three times to bleed the
cooling system.
Note: Prepare for the engine oil system.
6. Check the level of coolant.
Fig. 3-9 Coolant Drain Cock (Engine)
Fig. 3-10 Coolant Drain Cock (Water Pump)
When using the engine with radiator cooling system,
remove the radiator cap only after the engine has
cooled to the room temperature. Place a waste cloth
over the cap, and loosen the cap about a half-turn or
stand the lever to the upright position to release inter-
nal pressure. Opening the radiator cap of coolant
expansion tank while the engine is hot causes steam
and hot coolant to blow out and can result in skin
burns.
Turn the cap about
half a turn
Stand the lever to
the upright position
Always use the coolant having the same concentra-
tion.
Coolant
drain cocks
Left side
Right side
The coolant drain cocks located in the crankcase
respectively (behind the each fuel injection pump
accessory drive unit).
Coolant
drain cock
Page 40

3-6
Chapter 3 OPERATION
Preparation of Electrical System
Battery - Check
Note: If the specification of battery differs from the c ontents of this operation manual, follow the manufacturer's op-
eration manual.
Battery Electrolyte Level - Inspect
Battery electrolyte evaporates during use and the
electrolyte level gradually decreases. The proper elec-
trolyte surface level is between the LOWER LEVEL
and UPPER LEVEL lines.
For the battery without level lines, the proper electro-
lyte surface level is about 10 to 15 mm [0.39 to 0.59
in.] above the top of the plates.
If the electrolyte level is low, remove the caps and add
distilled water to the proper level.
Note: When adding distilled water, add little by little.
Fig. 3-11 Battery Electrolyte Level - Inspect
If battery electrolyte is spilled on your skin or clothes, flush immediately with plenty of water. If battery electrolyte
get into your eyes, flush them immediately with plenty of water and then get medical attention.
Do not use open flames or other fire hazards near the battery. When handling the battery, be careful of sparks gen-
erated by accidental shorting.
UPPER LEVEL
LOWER LEVEL
10 to 15 mm
[0.39 to 0.59 in.]
Proper
Page 41

3-7
Chapter 3 OPERATION
Test Operation
To conduct a test operation, follow the procedures below.
Before starting the engine, switch the water heater ON (automatic mode) and keep the coolant temperature prop-
erly. (Emergency generator with water heater)
Note: For engine operation, refer to "Normal Engine Operation" (3-8).
Starting and Stopping
1. Start the engine.
2. Operate the engine at low idling speed under no load for 5 to 10 minutes for a warm-up operation.
3. Stop the engine.
Inspection
1. Leave the engine be stopped for about 30 minutes.
2. During this period, check the engine and surrounding area for leaks of fuel, engine oil or coolant.
3. At 30 minutes after the engine stop, check the oil level with the oil level gauge. The proper oil level is between
the high and low marks on the oil level gauge.
4. If the engine oil goes over the high marks on the oil level gauge, open the engine oil drain valve to drain oil. If the
engine oil is low, refill the specified engine oil.
5. Open the coolant filler cap and check the coolant level.
6. If the coolant level is low, add coolant to the specified level.
Always switch the water heater ON (automatic mode) through a whole year.
If the switch is not ON (automatic mode), each cylinder varies considerably in combustion at the starting up the
engine. Unburned fuel may explode in the exhaust pipe. (Emergency generator with water heater)
Always use the coolant having the same concentration.
Page 42

3-8
Chapter 3 OPERATION
Normal Engine Operation
This section of the manual covers the procedures for the engine operation in normal condition.
Preparations for Operation
Always conduct the following inspection before starting the engine.
Engine External - Inspect
Inspect the engine exterior as described below.
1. Make sure there is no combustible material near
the engine or battery. Also, check to make sure that
the engine and battery are clean. If combustible
materials or dust are found near the engine or bat-
tery, remove them.
2. Check the whole engine for leaks of fuel, engine oil
or coolant. If leaks are found, repair the leak, or
contact a dealer of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries,
Ltd.
3. Visually check bolts and nuts for looseness.
4. Check the electrical wiring including the starters
and alternator.
5. Check that valves, plugs or cocks are properly po-
sitioned.
Fuel feed valve: Open
Coolant drain cock (plug): Closed
Engine oil drain plug: Closed
Air supply valve (air tank): Open
Fig. 3-12 Valves for open/closed position - Check
Should an engine abnormality be observed during operation, stop the engine and correct the problem, or contact a
dealer of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
Be sure to keep combustible materials away from the engine, especially from the hot engine parts such as exhaust
manifolds, or the battery. Check for fuel and oil leaks. Remove dust from the top surface of the battery. A fire can
be caused by combustible materials placed near hot engine parts. If any abnormality is found, be sure to repair it
or contact your local dealer.
Page 43

3-9
Chapter 3 OPERATION
Fuel Tank Oil Level - Check
Check that fuel is contained to the specified level in the fuel tank.
If the fuel level is low, refill the tank to the "FULL" level line.
Note: If the specification of fuel tank differs from the contents of this operation manual, follow the manufacturer's op-
eration manual.
Fuel Control Link - Check
Check fuel control link for smooth movement.
Push the manual stop lever to the fuel increase direc-
tion, check the movement of the rack cancel spring.
Then relax your grip on the lever little by little, check
that the manual stop lever returns to the no fuel injec-
tion position smoothly.
Also check ball joint for looseness and play.
Fig. 3-13 Fuel Control Link - Check
Engine Oil Level - Check
1. Pull out the oil level gauge and wipe oil off the oil
level gauge using a clean waste cloth.
2. Insert the oil level gauge fully into the oil level
gauge guide and then pull it out again.
3. The proper oil level is between the high and low
marks on the oil level gauge. If the engine oil goes
over the high marks on the oil level gauge, open
the engine oil drain valve to drain oil. If the engine
oil is low, refill the specified engine oil.
4. Install the oil filler cap after adding engine oil.
5. Check the oil pan and other area for oil leaks.
Fig. 3-14 Oil Filler and Oil Level Gauge
When working around fuel, make sure there are no open flames, heaters or other fire hazards.
Wipe off any spilled fuel completely. Spilled fuel can ignite and cause a fire.
Do not remove the strainer when filling the fuel tank.
If the engine has a float switch and the fuel level is higher the "LOW" level line, the float switch failure may occur.
Inspect and repair the float switch.
For fuel to be used, refer to "FUEL" (4-1).
Manual stop
Lever
Rack cancel
spring
Ball joint
Refilling engine oil must be specified level. If the
refilling oil goes over the high marks on the oil level
gauge, engine oil may blow out.
Always use the same engine oil as the first.
H
L
Oil filler
Oil level gauge
Oil level gauge
High
Low
Improper
Improper
Proper
Page 44

3-10
Chapter 3 OPERATION
Coolant Level - Check
If the coolant level is low, add coolant to the specified level.
Note: Determine the quantities of LLC based on the coolant capacity and the LLC concentration chart.
For the coolant, refer to "COOLANT" (6-1). For the coolant capacity, refer to "MAIN SPECIFICATIONS" (12-1).
Air Cleaner - Check for Clogging
1. Check the air cleaner indicator for the element
clogging.
2. If the element is clogged, the red signal mark will
be displayed.
3. Immediately clean or replace the air cleaner ele-
ment when the signal turns red.
4. After checking, press the bottom on top of the indi-
cator to re-set the alarm signal.
Note: (a) For cleaning of the air cleaner element, refer
to "Air Cleaner Element - Clean, Check and
Replace" (8-21).
(b) If the specification of air cleaner differs from
the contents of this operation manual, follow
the manufacturer's operation manual.
Fig. 3-15 Air Cleaner - Check for Clogging
Air Tank - Drain Water
1. Open the drain valve slowly, and check that water
in the tank is drained from drain pipe.
2. After water is drained and the air is discharged in
the tank, tighten the drain valve firmly.
3. Loosen the drain handle on the bottom of drain
separator. Check that water in the drain separator
is discharged from the drain pipe.
4. Close the drain handle after draining water firmly.
Note: If the s pecification of air tank differs from the
contents of this opera tion manual, follow the
manufacturer's operation manual.
Fig. 3-16 Air Tank - Drain Water
Always use the coolant having the same concentration.
Reset button
Signal
(red)
There are 2 places for draining water in the air tank:
drain valve on the top of air tank, and drain handle
on the bottom of drain separator.
Drain valve
Drain
separator
Drain
handle
Drain
pipe
Page 45

3-11
Chapter 3 OPERATION
Air Tank Air Pressure - Check
1. Check the air pressure gauge to see if the air pres-
sure in the air tank conforms to the standard.
2. Open the air pressure gauge valve.
3. Check air pressure in the air tank with air pressure
gauge.
Specified value:
For air direct starting: 2.94 MPa {30 kgf/cm
2
} [427
psi]
For air motor: 0.98 MPa {10 kgf/cm
2
} [142 psi]
4. Close the air pressure gauge valve.
Note: If the s pecification of air tank differs from the
contents of this opera tion manual, follow the
manufacturer's operation manual.
Fig. 3-17 Starting Air Tank Air Pressure - Check
Temperature of Damper - Check
Damper temperature management by thermo label
It is recommended to use the thermo label for temper-
ature management of the damper. Check the thermo
label before starting engine.
1. Check the thermal part of thermo label is black.
2. Note the highest temperature of thermal part. Note
the temperature periodically, and check the abnor-
mality of temperature alteration.
Note: For damper temperature limit and inspection, re-
fer to "Damper - Inspect" (8-
4).
Fig. 3-18 Thermo label of damper
Air pressure
gauge
Air pressure
gauge
valve
If the abnormality of temperature alteration is found,
consult a dealer of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
75 80 85 90 95
100 105 110 115 120
50 55 60 65 70
Thermo label
ࠨࡕࡌ࡞
ࠨࡕࡌ࡞
ࠨࡕࡌ࡞
5E-75
5E-100
5E-50
5E-75
5E-100
5E-50
5E-75
5E-100
5E-50
5E-75
5E-100
5E-50
(Display example)
When thermal part of the thermo label is
black until 80, it indicates that the maximum
temperature of damper during operating is
from 80°C [176°F] to 85°C [185°F].
Page 46

3-12
Chapter 3 OPERATION
Start
The starting method varies depending on the application and specifications. Start the engine according to the spec-
ified procedure.
Warming-up Operation
After the engine starts, operate the engine in a no load condition at low idling speed for 5 to 10 minutes to warm-up
the engine.
Checking Engine Oil Pressure
During warm-up operation, check if the oil pressure is
in the range of standard value (0.3 MPa {3.1 kgf/cm
2
}
[21 psi] or more).
Also, make sure the oil pressure gauge is actuated
properly.
External Inspection During Warm-up
During warm-up operation, walk around the engine
and check for fuel, oil, coolant or exhaust gas leaks.
Before starting the engine, check to make sure no one is near the engine and that tools are not left on or near the
engine. In a loud voice, notify people in the area when starting the engine.
Do not apply a load to the engine at starting. (Disengage the clutch if equipped.)
Continuous operation of the starter will drain the battery power and cause the starter to seize. Do not use the
starter for more than 10 seconds at a time. When the engine does not start, wait for more than 1 minute before
cranking again.
Do not approach rotating parts during operation. Entanglement by rotating parts can result in serious injury.
Page 47

3-13
Chapter 3 OPERATION
Run
Cautions During Operation
Inspection During Operation
Check for abnormal engine noises or vibrations such
as knocking or the exterior of engine such as piping
joints for leaks.
Carefully check the following items whether there is
any abnormality.
Note: (a) If the engine stops because of decreasing
engine oil press ure, be sure to loc ate the
cause of problem and correct it before re-
starting the engine.
(b) When the thermo switch is activated during
normal operation, run the engine with the idle
speed at low Rpms for 5 or 6 minutes to cool
the engine before stopping the engine. Be
sure to locate the cause of problem and cor-
rect it before restarting the engine.
Do not approach rotating parts during operation.
Entanglement by rotating parts can result in serious
injury.
Do not touch any hot part of the engine such as
exhaust pipes during operation or immediately after
shut down. A hot engine can cause burns.
Always provide adequate ventilation in the engine
room. If air supply to the engine room is not sufficient,
the room temperature rises and can affect engine
output and performance.
For the first 50 hours of the new engine or after the
overhaul, operate the engine under a light load for
break-in operation. Operating the new engine under
heavy load or severe conditions during the break-in
period can shorten the service life of the engine.
Do not turn the battery switch OFF when the engine
is running. Turning off the battery switch during oper-
ation not only stops the instrument operations but
also may deteriorate the alternator diode and regula-
tor.
Never turn the key to the "START" position during
operation. The starter may be damaged.
When operating the engine with a 30 % of rated load
or lower, limit each operation to an hour. Prolonged
warm-up operation causes carbon build-up in the cyl-
inders that leads to incomplete combustion. Operate
the engine with a 30 % of rated load or more for over
5 minutes after continuous operation for an hour to
prevent causing carbon build-up.
Table 3-1 Inspection During Operation
Item to be inspected Criterion/Reference value
Warning indicator
lamps/Instruments
Lighting/Numerical
anomaly
Engine speed/Frequency
No large fluctuation
Breather mist volume As usual
Exhaust color As usual
Damper temperature 90°C [194°F] or lower
Engine oil pressure
0.39 MPa {4 kgf/cm
2
}
[57 psi] or more
Oil Temperature
(oil pan)
110 °C [230 °F] or lower
Coolant temperature 70 to 90°C [158 to 194°F]
Exhaust temperature 550°C [1022°F] or lower
Intake air pressure
0.15 to 0.25 MPa
{1.5 to 2.5 kgf/cm
2
}
[10.85 to 18.08 psi]
Page 48

3-14
Chapter 3 OPERATION
Stop
Engine stopping method varies depending on the specifications.
To stop the engine, follow the instructions of the equipment.
Emergency Stop
To perform the emergency stop, pull the manual stop
lever to the arrow direction. Continue pulling the lever
until the engine stops completely.
Note: When the engine does not stop even if the man-
ual stop lever is pulled, stop fuel supply.
Fig. 3-19 Manual Stop Lever
Inspection After St opping
Inspect the engine for fuel, oil or coolant leaks. If any leak is found, repair the leak or contact a dealer of Mitsubishi
Heavy Industries, Ltd.
Stopping the engine abruptly while engine parts are hot due to high-speed operation can be a cause for heat up of
the engine parts and shorten the engine life. Before stopping the engine, run the engine with the idle speed at low
Rpms for 5 or 6 minutes to cool the engine, and check the engine for abnormalities.
Never accelerate the engine immediately before shutting it down.
Do not restart the engine immediately after abnormal shut down. When the engine stops with alarms, be sure to
locate the cause of the problem and correct the problem before restarting the engine. After restarting the opera-
tion, check the engine for abnormalities again. If the engine has an abnormality, repair it immediately.
When stopping the engine by pulling the manual
stop lever, continue pulling the lever until the engine
stops completely. If not, the engine may start again.
STOP
Page 49

4-1
Chapter 4 FUEL
Recommended Fuel
Use fuel that meets the values specified in the following Table 4-1 of "Recommended Fuel" and Table 4-2 of "Rec-
ommended Limit and Use Limit of Fuel Property".
It is necessary to use fuel that has a pour point suitable for the ambient temperature.
Note: Please use the fuel that meet the control of the countries or areas where the engine is used, if the control is
applied.
Handling Fuel
When using fuel from a storage tank, leave it to sit for more than 24 hours so that dust and water can settle at the
bottom. Then, use the upper clean fuel.
Fill up the fuel tank or service tank after each operation.
This prevents water from mixing with fuel in the tank and also gives time for dust and water to separate and settle at
the bottom of the tank.
Before refilling, clean the areas around the caps thoroughly and remove the caps from the drum and tank. Also
clean your hands and the hose before refueling. When using a hand-operated pump, be careful not to pump water
or sediment accumulated at the bottom of the storage tank.
Be sure to use a strainer when filling fuel tank. For a complete filtration, it is recommended to use a clean lint-free
cloth together with the strainer.
Use a fuel specified in this manual only. Do not refill the fuel tank more than the specified level. Otherwise, fire may
result.
Table 4-1 Recommended Fuel
Specification Classification
ISO 8217 DMX-CLASS
ASTM D975 No.1-D, No.2-D
BS 2869 CLASS A1, CLASS A2
DIN 51601 DIESEL-FUEL
JIS K2204 TYPE1, TYPE2, TYPE3
EN 590 DIESEL-FUEL
Page 50

4-2
Chapter 4 FUEL
Fuel Specification
Use fuel which meets the requirements specified in the table below.
Table 4-2 Recommended Limit and Use Limit of Fuel Property
Item Recommended limit Use limit Test method
Flash point
50°C [122°F] or higher
(In accordance with the regulation)
JIS K 2265
:2007
ISO 3769
ISO 2719
Distillation
Initial boiling point 170°C [338°F] or higher
JIS K 2254
:1998
ISO 3405
90 % distillate temperature
330 to 380°C [626 to 716°F]
Pour point (PP) 6°C [42.8°F] or lower than ambient temperature
JIS K 2269
:1987
ISO 3016
Cloud point (CP) Below ambient temperature
JIS K 2269
:1987
ISO 3015
Cold filter plugging point (CFPP) 3 °C [37.4 °F] or lower than ambient temperature
JIS K 2288
:2000
IP 309/96
Carbon residue (10 % residual oil) 0.4 weight % or lower 1.0 weight % or lower
JIS K 2270
:2000
ISO 6615
ISO 10370
Cetane number 45 or higher
JIS K 2280
:1996
ISO 5165
Cetane index (new type) 45 or higher
JIS K 2280
:1996
ISO/DIS 4264
Kinetic viscosity
2.0 mm
2
/s [0.0031 in2/s] or more at 30 °C [86 °F]
8.0 mm
2
/s [0.0124 in2/s] or more at 30 °C [86 °F]
JIS K 2283
:2000
ISO 3104
Sulfur content 0.2 weight % or lower
1.0 weight % or lower
(Shorten lub. oil change
intervals)
JIS K 2541
:2000
(The content
should be as
low as the diesel fuel.)
ISO 4260
ISO 8754
Water content and sediment 0.1 volume % or lower
JIS K 2275
:1996
ISO 3733
Ash content 0.01weight % or lower 0.03 weight % or lower
JIS K 2272
:1998
ISO 6245
Copper corrosion
(3 hrs at 50 °C [122 °F])
Color change = Copper plate No.3 or less
JIS K 2513
:2000
ISO 2160
Density at 15 °C [59 °F]
0.83 to 0.87 g/cm
3
[49.9424 to 54.3123 lb/ft
3
]
0.80 to 0.87 g/cm
3
[49.9424 to 54.3123 lb/ft
3
]
JIS K 2249
:1995
ISO 3675
Caulking
24 hrs at 250 °C
[482 °F]
75 % carbonization or less 80 % carbonization or less
Fed 791B
24 hrs at 230 °C
[446 °F]
55 % carbonization or less -
48 hrs at 180 °C
[356 °F]
Ta r- f re e -
Aromatics substances (by HPLC) 38 % by volume or less
JIS K 2536
:2003
ISO 3837
Polycyclic aromatic content 8 volume % or lower
Asphaltene 0.1 weight % or lower -
Page 51

4-3
Chapter 4 FUEL
Foreign substances
(foreign materials at engine fuel
inlet)
5.0 mg/liter or less
JIS B 9931
:2000
ISO 4405
Lubricity: MWSD (Measured mean
Wear Scar Diameter) by HFRR
wear test at 60 °C [140 °F] fuel temperature
460 µm [0.02 in.] or less
(calculated wear scar diame-
ter at WS 1.4 kPa {0.0143
kgf/cm
2
} [0.2031 psi])
- ISO 12156-1
BDF: Biodiesel fuel (FAME: Fatty
Acid Methyl Ester)
BDF quality shall meet JIS K 2390, or ASTM-D 6751 or
EN14214,
BDF blending of 5 % by volume or less is approved
JIS K 2390
:2008
(FAME for
mixing)
ASTM D 6751
EN 14214
Engine applications
for regular (prime) use
(Regular)
for emergency use
(Emergency)
Selection
according to
application
Table 4-2 Recommended Limit and Use Limit of Fuel Property
Item Recommended limit Use limit Test method
Page 52

Page 53

5-1
Chapter 5 ENGINE OIL
Recommended Engine Oil
Engine Oil Grade
Many oil standards, which are established through
special engine tests, are available to determine the
quality of oil depending on the engines to which they
will be applied and on operating conditions. Among
those standards, API (American Petroleum Institute)
service classifications are mostly used to classify
engine oils. SAE specifies the viscosity only, while the
API service classification indicates the quality level of
engine oil.
For engine lubrication oil, please use API service clas-
sification CF or CH-4.
When using the CF class engine oil, it must be certi-
fied according to API service classification CF by 2009
and satisfied the following Table 5-1 Recommended
limit of engine oil property.
When using the CH-4 class engine oil, the sulfur con-
tent of fuel must be 0.2 weight % or lower.
Fig. 5-1 Engine Oil Grade
Use the engine oils recommended in this manual only. Never use oil other than that specified in this manual.
The use of inappropriate or inferior oils will result in sticking of piston rings, seizure between piston and cylinder, or
premature wear of bearings and moving parts, and significantly shortens the service life of the engine.
OILOIL
Class CH-4
API Service
Classification
API Service
Classification
Class CF
Page 54

5-2
Chapter 5 ENGINE OIL
Engine Oil Specification
Use engine oil which meets the requirements specified in the table below.
Table 5-1 Table of Recommended Limit of Engine Oil Properties
Item Unit Recommended limit Test method
API/JASO CF class *1 -
SAE viscosity - 15W-40 -
Color ASTM - L4.0
JIS K 2580
ISO 2049
Density 15°C [59°F] g/cm
3
0.87 to 0.90
JIS K 2249
ISO 3675
ISO3838
ISO 649-4
ISO 91-1
Kinetic Viscosity:
40°C [104°F]
mm
2
/s
100 to 110 JIS K 2283
ISO 3107
ISO 2904
150°C [302°F] 13.5 to 15.5
Viscosity - -
JIS K 2283
ISO 3107
ISO 2904
Flash point °C [°F]
225 to 250
[437 to 482]
JIS K 2265
ISO 3679
ISO 2719
ISO 2592
Base
number
Hydrochloric
acid method
Sulfur contents
of fuel
1.0 weight %
or lower
mgKOH/g
10 or higher
(up to 13)
JIS K 2501
ISO 3771
ISO 6618
ISO 6619
ISO 7537
0.2 weight %
or lower
8 or higher
(up to 13)
Perchloric
acid method
Sulfur contents
of fuel
1.0 weight %
or lower
mgKOH/g
13 or higher
(up to 16)
0.2 weight %
or lower
11 or higher
(up to 16)
Acid number mgKOH/g 1.5 to 2.0
JIS K 2501
ISO 3771
ISO 6618
ISO 6619
ISO 7537
Sulfur content % 0.5 or less
JIS K 2541
ISO 4260
ISO 8754
Sulfuric acid ash % 2.0 or lower
JIS K 2272
ISO 3987
ISO 6245
Carbon residue content % 2.0 or lower
JIS K 2270
ISO 10370
ISO 6615
High temperature shear viscosity
150°C
[302°F]
mP·aS 3.7 or higher JPI-5S-36-91
Pour point °C [°F] -25 [-13]or lower
JIS K 2269
ISO 3015
ISO 3016
Page 55

5-3
Chapter 5 ENGINE OIL
*1 It must have been certified API service classification CF by 2009.
*2 Temperature of test I (24°C [75.2°F]), Temperature of test II (93.5°C [200.3°F]), Temperature of test III (24°C
[75.2°F] after 93.5°C [200.3°F])
*3 Temperature of aluminum panel: 300°C [572°F] and 325°C [617°F]
Temperature of engine oil: 100°C [212°F]
Splatter time: 15 seconds
Downtime: 45 seconds
Test time: 8 hours
the properties are the weight of solid product.
Selection of Oil Viscosity
Use the following chart to select the appropriate oil
viscosity according to the ambient temperature.
Excessively high oil viscosity causes power loss and
an abnormal rise of oil temperature, while excessively
low oil viscosity accelerates wear due to inadequate
lubrication, and also causes a decrease in engine out-
put due to leakage of combustion gas.
Fig. 5-2 Selection of Oil Viscosity
Handling Engine Oil
When handling a large amount of engine oil more than the legally specified quantities, be sure to have the work per-
formed by a service station operated under the provision of the law. When removing oil from the engine or oil can,
use an oil pump. Do not suck oil using you mouth and a pipe.
Be sure to close the cap on the oil can after use.
Keep oil in a well-ventilated place and out of direct sunlight.
Be sure to obtain the MSDS of the engine oil and follow the instructions of the MSDS.
Bubbling test
*2
I
mL
10/0
JIS K 2518
ISO 6247
II 30/0
III 10/0
Panel caulking test
*3
300°C
[572°F]
mg
140 or lower
FED791-3462
325°C
[617°F]
300 or lower
Table 5-1 Table of Recommended Limit of Engine Oil Properties
Item Unit Recommended limit Test method
SAE10W
SAE30
SAE40
SAE15W-40
Temperature
°C [°F]
Engine oil
viscosity
-30
[-21]
-20
[-4]
-10
[14]
10
[50]20[68]30[86]40[104]50[122]
0
[32]
Before filling the engine with engine oil, stop the engine and make sure there are no open flames and other fire
hazards near the engine. Leaked or spilled oil on hot surfaces or electrical components can cause a fire. Wipe off
any spilled oil immediately and thoroughly. After filling oil, securely close the filler cap.
Page 56

5-4
Chapter 5 ENGINE OIL
Service Limits of Engine Oil
Engine oil degrades through the use and by lapse of time.
The quality of engine oil and fuel, and the operating condition of the engine affect the deterioration of the engine oil.
Replace the engine oil in accordance with Chapter 7 MAINTENACE SCHEDULE. However, only if the operating
load is stable and engine oil analyze result allows, oil replacement interval may be changed.
Refer to the following table for the determination of engine oil performance. If any of the following properties
exceeds the limit, replace the engine oil with new oil.
Table 5-2 Table of engine oil properties
Properties Standard Test method
Kinetic Viscosity:
mm
2
/s [in2/s]
@100°C [212°F]
+30 % or less rate of change from
new oil
10 mm
2
/s [0.155 in2/s] or more
JIS K 2283
:2007
ISO 3107
ISO 2909
+30 % or less rate of change from
new oil
-20 % or less rate of change from
new oil
Base number mgKOH/g
2.0 or more with hydrochloric acid
(HCL) method
1/2 of new oil or more with perchlo-
ric acid (PCA) method
JIS K 2501
:2003
ISO 3771
Acid number mgKOH/g Up to +3.0 of new oil
JIS K 2501
:2003
ISO 3771
Water Content Vol % 0.2 or less
JIS K 2275
:1996
ISO 9029
Flash point (open cup) °C [°F] 180 [356] or higher
JIS K 2265
:2007
ISO 3769
ISO 2719
Pentane insoluble Wt % 0.5 or less
Compliance with ASTM D
893
Pentane insoluble coagulated
Wt % 3.0 or less
Compliance with ASTM D
893
Page 57

5-5
Chapter 5 ENGINE OIL
Definition of Properties of Engine Oil
Kinetic Viscosity
Kinetic viscosity is a basic physical property of engine
oil and is considered as the most important aspect
when evaluating oil.
Contamination of oil by blow-by gas and deterioration
of oil by its natural aging increase the kinetic viscosity
and degrade the performance of viscosity, which will
cause the deposition of sludge inside the engine and
oil filter clogging. Contamination of oil by fuel and
sheared molecules of viscosity index improver in oil
decrease the viscosity and degrade the performance
of viscosity, which will cause insufficient lubrication
and friction/wear of engine parts.
Base Number
Base number shows the ability to neutralize acids
such as organic acid due to engine oil oxidation, or
sulfurous or sulfuric acid due to the sulfur content of
fuel.
Because base number indicates the amount of disper-
sant detergent in oil, it can be used to estimate con-
sumption of basic dispersant detergent. The ability to
disperse sludge declines as dispersant detergent is
used up.
Acid Number
The acid number in oil increases as the organic acid is
being derived by the engine oil oxidation, or sulfurous
acid or sulfuric acid derived by the combustion of sul-
fur content of fuel, or the oil becomes contaminated
with imperfect combustion products.
An increase in the acid number will result in corrosion
or wear of the inner parts of the engine (such as cylin-
der liners or metal) due to sulfur content, and piston
ring seizure due to sludge.
Water Content
Water in oil promotes corrosion/wear, and decreases
lubricity in sliding parts.
Flash Point
The flash point is lowered by contamination with fuels.
Flash point is measured to check the dilution of fuel.
The dilution of fuel reduces oil film, and causes insuffi-
cient lubrication that will cause friction or wear of
engine parts.
Insoluble
Insoluble includes acid products of engine oil, imper-
fect combustion products, sludge or soot, metal abra-
sive particles and dust. Insoluble is an indication of
degradation/contamination of oil.
Dispersant detergent, which is an additive in engine
oil, absorbs sludge particles, and disperses them as
fine particles in oil. Total insoluble density and
remaining dispersibility can be obtained by measuring
insoluble and coagulated insoluble (chemical speciali-
ties which stop action of disperse detergent and col-
lect the sludge dispersed in oil) to understand engine
oil contamination level, and thereby, piston ring sei-
zure or premature wear can be prevented before it
occurs.
Page 58

5-6
Chapter 5 ENGINE OIL
Engine Oil Analysis Service
For a long term service life of engine, it is recommended to get an engine oil analysis service.
It is a system to understand the availability of the engine oil using in your engine by sampling it with the special sam-
pling tools.
The engine oil analysis service provides the followings:
The quantity of fine metal powder in engine oil due to abrasion, by which worn parts can be located.
Water, LLC or salt that should not be in engine oil can be detected.
Engine oil deteriorating conditions, by which appropriate engine oil renewal intervals, operating conditions, proper
inspection and maintenance schedule can be planned.
The engine oil analysis service can diagnose the internal condition of the engine, which is necessary when disas-
sembling the engine. It is highly recommended to take advantage of our engine oil analysis service so that you can
learn the engine condition before any malfunction occurs to the engine.
Page 59

6-1
Chapter 6 COOLANT
Note: In this operation manual, the word "coolant" represents a mixture of water and LLC.
Recommended Water for Coolant
Use soft water (such as tap water) for the engine cooling system. The water quality must meet the requirements in
the Table below. Basically, the water quality should be within the recommended value, however, up to the limit is
acceptable.
Note: Other than those above, turbidity must be below 15 mg/liter.
Long Life Coolant (LLC)
Be sure to use Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. genuine long life coolant (LLC) "GLASSY long life coolant (Ethyl-
ene glycol type)" or "PG GLASSY long life coolant (Non-amine type)" as coolant. When using other brand LLCs by
necessity, be sure to use the non-amine type LLC that meets the specification in Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
Mitsubishi heavy industries disclaims the warranty claims about malfunctions due to the use of LLC that does not
meet the following specification.
Genuine LLC
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. recommends the use
of our genuine long life coolant "GLASSY long life
coolant (Ethylene glycol type)", and Eco-friendly prod-
uct "PG GLASSY long life coolant (propylene glycol
type)", which are most appropriate coolant for Mitsubi-
shi diesel engines. Be sure to use our Genuine LLC.
Fig. 6-1 GLASSY - LLC
Table 6-1 Water Quality Standards
Item
Chemical
symbol
Unit
Recommend
value
Limit Main adverse effect
pH (25°C [77°F]) - - 6.5 to 8.0 6.5 to 8.5
Corrosion and rust, scale
formation
Electrical conductivity
(25°C [77°F])
- mS/m < 25 < 40
Corrosion and rust, scale
formation
Total hardness CaCO
3 ppm < 95 < 100 Scale formation
M alkalinity CaCO
3 ppm < 70 < 150 Scale formation
Chlorine ion Cl
-
ppm < 100 < 100 Corrosion and rust
Sulfuric acid ion SO
4
2-
ppm < 50 < 100 Corrosion and rust
Total iron Fe ppm < 1.0 < 1.0 Scale formation
Silica SiO
2 ppm < 30 < 50 Scale formation
Residue from evaporation - ppm < 250 < 400 Scale formation
Should coolant or LLC be accidentally swallowed, induce vomiting immediately and seek medical attention. If LLC
should enter eyes, flush immediately with plenty of water and seek medical attention.
Page 60

6-2
Chapter 6 COOLANT
Other Brand LLCs
When using LLC other than Mitsubishi Heavy Indus-
tries, Ltd. genuine long life coolant (LLC) "GLASSY
long life coolant (Ethylene glycol type)" or "PG
GLASSY long life coolant (propylene glycol type)", be
sure to use the LLC which meets specification in Mit-
subishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
The quality and performance of commercially avail-
able LLCs as well as their component variations are
the responsibility of LLC suppliers.
Before purchasing commercial LLC, be sure to dis-
cuss the suitability of LLC with the LLC supplier.
Use all-season LLC (non-amine type) only. Do not use
antifreeze alone instead of LLC.
Standard for Other Brand
LLC
When using other brand LLCs by necessity, be sure to
use the LLC that meets the following specification.
Mitsubishi heavy industries, Ltd. disclaims the war-
ranty claim concerning malfunctions caused by the
use of LLC that does not meet the following specifica-
tion.
General Demands of LLC
LLC must be a homogeneous liquid without sedi-
ment.
When the LLC is diluted to 30 to 60% density, the LLC
shall not cause troubles such as corrosion and precip-
itation deposits in the engine cooling system.
LLC shall be mixed with other LLC that satisfies this
specification, and shall not separate elements each
other, and shall not decrease the performance each
other.
LLC shall not allow the container to be corroded, and
shall not has precipitation products etc. even if LLC is
left in the container for 6 months.
LLC shall not has extraction products etc. even if LLC
is kept in -20 to -25°C [-4 to -13°F].
The validity term of the quality that provides with this
specification is 2 years after it delivers with the indoor
normal temperature keeping.
Never mix Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. genuine
LLC with other brand LLCs. Mixing with other brand
LLCs degrades the performance of the Mitsubishi
Heavy Industries, Ltd. genuine LLC.
Page 61

6-3
Chapter 6 COOLANT
LLC Specification
LLC shall be examined according to JIS K2234, Section 7 (Test method), and satisfy this requirements. General
matters and the specimen sampling shall comply with JIS K2234.
Table 6-2 LLC Specification
Property Standard
Appearance No precipitation
Density
Minimum 1.112 g/cm
3
[69.4199 lb/ft3] (20/
20°C) [68/68°F]
(Stock solution)
Water content Maximum 5.0 weight % (Stock solution)
Frozen temperature
30 vol % Maximum -14.5°C [6°F]
50 vol % Maximum -34.0°C [-29°F]
Boiling temperature 155°C [311°F] or higher (Stock solution)
pH 7.0 to 11.0 (30 vol %)
Bubbling character
(ASTM D3306-01)
30 vol % 4.0 ml or less
33
1/3 vol %
150 ml [0.032 gal] or less, Disappearance of
bubble within 5 seconds.
Hard water adaptability 1.0 or less (50 vol %)
Metallic causticity
(88±2°C
[190.4±35.6°F],
336±2 Hr,
30 vol % (E.G),
50 vol % (P.G))
Metal specimen
Mass
change
Aluminum ± 0.30 mg/cm
2
Cast iron ±0.15 mg/cm
2
Steel ± 0.15 mg/cm
2
Brass ± 0.15 mg/cm
2
Solder ± 0.30 mg/cm
2
Copper ± 0.15 mg/cm
2
Appearance of the specimen
after testing
No visible signs of corrosion on the surface
excluding the area contacting to spacer.
However, discoloration is acceptable.
Bubbling during the test Not bubbling overflow
Properties of
liquid after the
test
pH 6.5 to 11.0
pH change ±1.0
Precipitation 0.5 vol % or less
Appearance of liquid
No remarkable discoloration, separation
and gel generation.
Page 62

6-4
Chapter 6 COOLANT
Circulation metallic causticity
(98±2°C
[208.4±35.6°F],
1000 Hr,
30 vol %
(E.G)
50 vol %
(P.G)
Metal specimen
Mass
change
Aluminum, Cast
iron, Steel, Brass,
Solder, Copper
±0.30 mg/cm
2
Appearance of the specimen
after testing
No visible signs of corrosion on the surface
excluding the area contacting to spacer.
However, discoloration is acceptable.
Properties of
liquid after the
test
pH 7.0 to 9.0
pH change ±1.0
Pre-alkalinity change ±15 %
Precipitation 1.0 vol % or less
Appearance of liquid
No remarkable discoloration, separation
and gel generation.
Density
of ion
Fe, Cu, Al, Zn, Pb,
NH
4
+
10 ppm or less
Circulation metallic causticity
(88±3°C
[190.4±37.4°F],
1000±2 Hr,
30 vol %
(E.G)
Metal specimen
Mass
change
Aluminum ± 0.60 mg/cm
2
Cast iron ±0.30 mg/cm
2
Steel ± 0.30 mg/cm
2
Brass ± 0.30 mg/cm
2
Solder ± 0.60 mg/cm
2
Copper ± 0.30 mg/cm
2
Appearance of the specimen
after testing
No visible signs of corrosion on the surface
excluding the area contacting to spacer.
However, discoloration is acceptable.
Properties of
liquid after the
test
pH 6.5 to 11.0
pH change Maximum ±1.0
Appearance of liquid
No remarkable discoloration, separation
and gel generation.
Condition of
parts
Pump seal
Free from any malfunction, liquid leak and
abnormal noise during operation.
Inside of pump case and blade Free from remarkable corrosion
Rubber adaptability
(30 vol %,
115°C [239°F],
360 Hr)
Silicon
Tensile strength change -60 to 0 %
Elongation change -40 to +20 %
Volume change 0 to +40 %
Hardness change -20 to +10 %
Acrylonitrile
butadiene rubber
Tensile strength change 0 to +10 %
Elongation change -15 to +15 %
Volume change 0 to +40 %
Hardness change -10 to 0 %
Ethylene propylene diene
monomer
Tensile strength change 0 to +10 %
Elongation change -30 to 0 %
Volume change 0 to +10 %
Hardness change -10 to 0 %
Table 6-2 LLC Specification
Property Standard
Page 63

6-5
Chapter 6 COOLANT
Storage stability vol % (30 vol %, room temperature, 6 Hr) 0.3 or less
Table 6-2 LLC Specification
Property Standard
Page 64

6-6
Chapter 6 COOLANT
Maintenance of LLC
Replacement Intervals of LLC
When a coolant mixed with the LLC recommended by our company is used, replace coolant every 8000 hours or 2
years, whichever comes first.
LLC Concentration
Keep the LLC concentration of 30 % (GLASSY) and 40 % (PG GLASSY) on any temperature conditions. LLC of
less than 30 % concentration does not provide sufficient corrosion protection. If the LLC concentration is lower than
10 %, it may accelerate corrosion.
When adding coolant, do not add plain water. Always use coolant with the same LLC concentration.
Note: (a) If the outside air temperature is -30°C [-22°F] or lower, use "GLASSY."
(b) The concentration above is based on Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. genuine LLC "GLASSY long life
coolant (Ethylene glycol type)" or "PG GLASSY long life coolant (Non-amine type)."
For determining the accurate LLC concentration, refer to the instructions for the LLC used.
Should coolant or LLC be accidentally swallowed, induce vomiting immediately and seek medical attention. If LLC
should enter eyes, flush immediately with plenty of water and seek medical attention.
LLC is toxic. Never dispose of coolant containing LLC drained from engine into regular sewage. For disposal of
used coolant, consult LLC distributor.
Be sure to renew LLC (coolant) at the intervals specified in this manual.
Failure to renew LLC may cause malfunctions due to performance degradation of preventing rust and cavitation.
Table 6-3 Recommended LLC Concentration
Item Type
Appear-
ance
Lowest ambient temperature
-10°C [14°F]
or above
-20°C [-4°F]
or above
-30°C [-22°F]
or above
-45°C [-49°F]
or above
LLC concentration
(%)
GLASSY Green 30 40 50 60
PG GLASSY Red 40 55 70 -
Page 65

6-7
Chapter 6 COOLANT
Importance of LLC
Today's trend is toward smaller and lighter engines
offering greater output, lower fuel consumption and
lower exhaust emission levels.
Conditions to which engine coolant is subjected,
therefore, are becoming severer due to longer operat-
ing hours, higher coolant temperature and higher cool-
ant circulating speed.
Many different materials such as steel, aluminum,
copper, solder and rubber are used in the cooling sys-
tem, and they are also subjected to the severe condi-
tions described above. Those materials have different
ionization characteristics, and this difference acceler-
ates corrosion through the medium of engine coolant.
To prevent such a problem, it is necessary to use the
LLC having the additive that prevents rust.
Characteristics of LLC
Additive and Important
Notes
LLC contains several chemicals in such proportions
as to produce chemical reactions that suppress corro-
sion (ionization) of engine parts in contact with the
coolant. LLC loses its effectiveness by hours of use as
well as lapse of time.
Moreover, if the chemicals in LLC are not maintained,
certain chemicals in the LLC become rapidly used up
and result in dissolution of metals instead of protecting
metals from corrosion. Consequently, other corrosion
preventing chemicals react with dissolving metals and
accelerate corrosion. This condition generates more
severe corrosion than when plain soft water is used.
This is a typical problem caused by the use of inap-
propriate LLC.
Examples of Abnormalities Caused by LLC
(Amine Type)
Pitting of Iron Parts
Amines are generally effective in suppressing the rust-
ing of ferrous metals, but they are said to cause prob-
lems for copper parts.
Dissolved copper (copper corrosion) in the cooling
system deposits on iron parts and the copper deposits
cause corrosion and then pitting on iron parts that
have a high ionization characteristics due to galvanic
or local-cell action.
Corrosion of Aluminum Parts
Silicate is highly effective in protecting aluminum
against rusting. However, it is unstable in a solution in
which the pH is 9 or lower, and can turn to gel and pre-
cipitate in the solution. For this reason, the pH is usu-
ally specified to be about 10 to ensure a high alkaline
level.
This means, after silicate is used up, the high alkalinity
causes chemical attacks on aluminum. To prevent this
problem, proper maintenance of the coolant is
required. For case example, rapid wear of mechanical
seals in the water pump due to secondary effects of
silicate gel formed. Corrosion of aluminum parts after
silicate is consumed.
Pitting and Clogging of the Heat
Exchange Equipment
When LLC deteriorates or when its concentration in
the coolant is too low, the anti-corrosion performance
of LLC lowers and results in the corrosion of metals.
Brass and solder tend to corrode faster than other
metals, and corrosion of these metals is said to cause
water leakage and clogs. Example: Holes and clogs in
heat exchange equipment.
Page 66

Page 67

7-1
Chapter 7 MAINTENANCE SCHEDULE
How to Use the Maintenance Schedule
Periodic inspection not only extends the service life of the engine but also serves to ensure safe operation. Be sure
to conduct inspections and maintenance according to the maintenance schedule.
The maintenance schedule shows the standard service intervals. If you notice any abnormalities such as abnormal
noise, black exhaust smoke, white exhaust smoke, extremely high temperature of exhaust gas, abnormal vibration,
and fuel, oil or exhaust gas leakage, make sure to conduct the inspection and maintenance work, regardless of rec-
ommended service intervals in the "Maintenance schedule."
Note: Appropriate service intervals vary depending on the usage and operating conditions as well as consump tion
of fuel, oil and coolant. Check the operating record of the engine to determine the most ap propriate service
intervals. (Feel free to consult a dealer of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. regarding service intervals.)
Service the items at multiples of the original requirement. For example, at 1000 service hours, also service those
items listed under every 250 service hours and every 50 service hours.
Periodic Maintenance Chart
Appropriate service intervals vary depending on the engine specifications. Perform all daily inspection and mainte-
nance items in an accordance with the following 3 categories.
Periodic Maintenance Chart for Regular Use Engine
When the engine is used as a regular use engine, perform the periodic inspection and maintenance in accordance
with the "Periodic Maintenance Chart for Engine in Regular Use".
Periodic Maintenance Chart for Emergency Engine
When the engine is used as an emergency engine, perform the periodic inspection and maintenance in accordance
with the "Periodic Maintenance Chart for Emergency Engine". Due to the nature of application, an engine for emer-
gency use is subject to demanding operating conditions such as a quick startup and immediate supply of power. In
addition, it must operate reliably in the event of an emergency. Therefore, be sure to perform the daily inspection
and also conduct the following operation for maintenance purposes. Once every week: Operate the engine under
no load (for 3 to 5 minutes). (When operating the engine for the adjustment of peripheral devices, limit the operating
time to 10 minutes.) Once every month: Operate the engine under load (for 15 to 30 minutes with more than 1/2
load). If the engine cannot be operated under load every month, operate the engine under load (more than 1/2 load)
for more than 2 hours. During the engine maintenance operation, check the ease of startup, oil pressure, and
exhaust color and vibration.
Periodic maintenance chart for general purpose engine
If the engine is used for different purposes other than the above usage, do maintenance according to the "Periodic
Maintenance Chart for General-Purpose Power Supply Engine".
Page 68

7-2
Chapter 7 MAINTENANCE SCHEDULE
General Definition of Engine
General Definition of Regular Use Engine
An engine operated with a constant base load for the purpose of generating electric power, which is used indepen-
dently or in combination with commercial power supply. An engine operated under a fluctuating load throughout a
day for supplying rated electric power in lieu of commercial power.
General definition of emergency engine
An engine used for emergency power generation such as main power supply and commercial power supply.
General Definition of General-purpose Engine
An engine used for a purpose other than power generation - for example, to drive a pump, as the main engine for a
ship, and for an industrial vehicle - and operated under constant or cyclically varying load and speed.
Page 69

7-3
Periodic Maintenance Chart for Regular Use Engine
Table 7-1 Periodic Maintenance Chart for Regular Use Engine
Interval and Service item
Refer-
ence
page
Every 50 service hours or
every month
Fuel Tank - Drain Water*1 8-6
Water Separator - Drain Water*1 8-7
First 50 service hours for
a new or overhauled
engine
Bolts and Nuts on the Engine - Retighten *2
Engine Oil, Oil Filter and Bypass Oil Filter - Replace
It is recommended to check the engine oil characteristics at the same time.
The oil filters must be replaced when the filter alarm lights.
8-12
Every 250 service hours
Engine Oil, Oil Filter and Bypass Oil Filter - Replace
It is recommended to check the engine oil characteristics at the same time.
The oil filters must be replaced when the filter alarm lights.
8-12
First 250 service hours
for a new or overhauled
engine
Valve Clearance - Inspect and Adjust
(Check valve mechanism at the same time.)
*2
Every 1000 service hours
Fuel Filter - Replace 8-9
Water Separator Element - Replace *1 8-7
Gauze Filter - Clean 8-8
Belt and Belt Tension - Inspect and Adjust 8-2
Every 2000 hours
Fuel Tank - Drain Water (Replace Parts as Necessary) *1 8-6
Valve Clearance - Inspect and Adjust
(Check valve mechanism at the same time.)
*2
Fuel Injection Timing - Inspect and Adjust *2
Fuel Injection Nozzle - Nozzle Tip Replacement
(Check the spray condition and adjust the fuel injection pressure after
replacement)
*2
Checking Movement of the Rack (During Operation) of the Fuel Injection
Pump (Including the Governor)
*2
Fuel Pipe - Inspect 8-11
Oil Pipe - Inspect 8-15
Every 4000 service hours
Top End of the Engine - Overhaul
Remove the cylinder head, and inspect and service the combustion chambers.
*2
Turbocharger - Inspect 8-19
Damper - Inspect 8-4
Starter - Inspect 8-24
Protection Devices Operation - Inspect *2
Unit Seal and Oil Seal of Water Pump - Replace *2
Checking LLC Concentration Level in the Coolant *2
Page 70

7-4
Chapter 7 MAINTENANCE SCHEDULE
*1 If it is not a item supplied from Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, maintain the part following the manufacture's opera-
tion manual as required.
*2 Items require special tools or large equipment. For the servicing of those items, contact a dealer of Mitsubishi
Heavy Industries, Ltd.
Every 8000 hours
Engine - Major Overhaul
Disassemble engine, clean, check and change major parts.
[Parts to be changed at major overhaul.]
Inlet and exhaust valves, inlet and exhaust valve seats, valve rotators, valve
cotters, rocker arm adjusting screws, valve push rods, bridge caps, camshaft
bushings, camshaft expansion plugs, main bearings, cylinder liners, main
bearing cap bolts and washers, piston rings, connecting rod bearings,
damper, crankcase thrust plate and consumable items (gaskets, oil seals, Orings, etc.)
[At second overhaul, replace the following parts in addition to the parts listed
above]>
Cylinder head bolts, valve guides, valve bridge guides, valve bridges, valve
springs, tappets, camshaft thrust plates, pistons, piston pins, connecting rod
bolts, connecting rod bushings, rocker bushings, fuel pipe assembly, oil pipe
assembly
*2
Fuel Injection Pump - Inspect and Test (Replace Parts as Necessary) *2
Governor - Inspect and Test (Replace Parts as Necessary) *2
Protective Devices - Repair or Replace
High coolant temperature, low oil pressure, overspeeding, starting failure,
water supply failure, undervoltage, overvoltage, overcurrent, low coolant
level in tank, low fuel level in tank, low air pressure in tank, etc.
*2
Auxiliary Devices Operation - Check
Water heater, oil heater, oil priming pump, fuel transfer pump, governor
motor, etc.
*2
Every 8000 service hours
or every 2 years
Coolant - Change 8-16
As required
Fuel System - Bleed Air *1 3-2
Radiator Fins - Check and Clean *1 8-18
Air Cleaner Element - Clean, Check and Replace *1 8-21
Cleaning the Inside of the Engine Breathers *2
Stop Solenoid - Inspect or Replace *2
Couplings - Inspect or Replace *1 *2
Inspecting the Vibration-isolating Rubber *1 *2
Table 7-1 Periodic Maintenance Chart for Regular Use Engine
Interval and Service item
Refer-
ence
page
Page 71

7-5
Chapter 7 MAINTENANCE SCHEDULE
Periodic Maintenance Chart for Emergency Engine
Table 7-2 Periodic Maintenance Chart for Emergency Engine
Interval and service item
Refer-
ence
page
Every week
Engine External - Inspect
(Check for leakage of fuel, oil and coolant)
3-8
Fuel Tank Oil Level - Check *1 3-9
Engine Oil Level - Check *1 3-9
Coolant Level - Check 3-10
Air Tank Air Pressure - Check
(Air motor type or direct inlet type)
3-11
Water Leakage of Aircooler - Inspect -
Operating the Engine for Maintenance
(Operate the engine under no load for 5 to 10 minutes)
Check for ease of starting, color of exhaust smoke, abnormal vibration,
abnormal noise, abnormal smell and gauge indication (oil pressure gauge,
coolant temperature gauge, oil temperature gauge, exhaust temperature
gauge, tachometer, etc.)
-
Every month
Engine Oil for Mixing of Fuel and Water - Inspect 8-14
Fuel Control Link - Check 3-9
Battery Electrolyte Level - Inspect *1 8-23
Air Tank - Drain Water 8-25
Air compressor Oil Level - Inspect and Refill -
Conducting Engine Maintenance Operation
(Operate the engine with more than 1/2 load for 15 to 30 minutes)
Check for ease of starting, color of exhaust smoke, abnormal vibration,
abnormal noise, abnormal smell and gauge indication (oil pressure gauge,
coolant temperature gauge, oil temperature gauge, exhaust temperature
gauge, tachometer, etc.)
Check fuel injection pump and the movement and rack of governor, check
temperature of damper, check damper visually.
-
Every 6 months
Checking LLC Concentration Level in the Coolant *2
Cleaning the Inside of the Coolant Tank *1 -
Page 72

7-6
Chapter 7 MAINTENANCE SCHEDULE
Every one year
Basic engine
Belt and Belt Tension - Inspect and Adjust 8-2
Bolts and Nuts on the Engine - Check and Retighten *2
Damper - Inspect 8-4
Valve Clearance - Inspect and Adjust
(Check valve mechanism at the same time.)
*2
Inspecting the Vibration-isolating Rubber *1 *2
Foundation Bolts - Inspect *1 *2
Couplings - Inspect or Replace *1 *2
Fuel system
Fuel Tank - Drain Water*1 8-6
Water Separator - Drain Water*1 8-7
Fuel Injection Nozzle Spray Condition and Spray Pressure - Inspect and Adjust
*2
Fuel Injection Timing - Inspect and Adjust *2
Fuel Pipe - Inspect 8-11
Lubricating
system
Oil Pipe - Inspect 8-15
Engine Oil Properties - Analyze *2
Engine Oil Pressure (Maintenance Operation) - Inspect
and Adjust
*2
Table 7-2 Periodic Maintenance Chart for Emergency Engine
Interval and service item
Refer-
ence
page
Page 73

7-7
Chapter 7 MAINTENANCE SCHEDULE
Every one year
Cooling system
Water Pump - Inspect *2
Solenoid Valve and Pressure Reducing Valve of the Cooling System - Inspect, Disassemble and Clean *1
*2
Strainer (Including With Ball Tap) of Cooling Water Inspect, Disassemble and Clean *1
*2
Coolant Properties (When Only Soft Water is Used) Inspect
(Change coolant according to the analysis results)
*2
Air intake system Air Cleaner Element - Clean, Check and Replace *1 8-21
Electrical system
Starter - Inspect 8-24
Alternator - Inspect 8-24
Specific Gravity of Battery Electrolyte - Check*1 8-23
Air Heater - Inspect -
Air starter
system
Air Strainer - Drain Water and Clean 8-25
Air Tank - Inspect Safety Valve Operation 8-26
Air Starter Valve - Inspect *2
Solenoid Valve and Pressure Reducing Valve - Inspect
and Clean
*2
Air Distribution Valve - Inspect *2
Air Compressor Belt Tension - Inspect *2
Auxiliary Devices Operation - Check *1
High coolant temperature, low oil pressure, overspeeding, starting failure,
water supply failure, undervoltage, overvoltage, overcurrent, low coolant
level in tank, low fuel level in tank, low air pressure in tank, etc.
*2
Auxiliary Devices Operation - Check
Engine control, fuel transfer pump, governor motor, room ventilating fan,
solenoid, storage pump, water tank ball tap, water heater, oil heater, oil priming pump, etc.
*2
Every 2 years
Engine Oil, Oil Filter and Bypass Oil Filter - Replace
It is recommended to check the engine oil characteristics at the same time.
The oil filters must be replaced when the filter alarm lights.
8-12
Fuel Filter - Replace 8-9
Water Separator Element - Replace *1 8-7
Gauze Filter - Clean 8-8
Fuel Control Link Ball Joint - Inspect
(Replace parts as necessary)
8-10
Coolant - Change 8-16
Thermostat - Inspect *2
Turbocharger - Inspect 8-19
Exhaust Muffler - Drain Water *1 8-19
Air Compressor Overhaul (Air motor type or direct inlet type) *2
Table 7-2 Periodic Maintenance Chart for Emergency Engine
Interval and service item
Refer-
ence
page
Page 74

7-8
Chapter 7 MAINTENANCE SCHEDULE
*1 If it is not a item supplied from Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, maintain the part following the manufacture's opera-
tion manual as required.
*2 Items require special tools or large equipment. For the servicing of those items, contact a dealer of Mitsubishi
Heavy Industries, Ltd.
Every 4 years
Top End of the Engine - Overhaul
Remove the cylinder head, and inspect and service the combustion chambers.(If the abnormalities of first and second cylinders are found, inspect all
cylinders. )
*2
Checking Oil Cooler for Contamination, Clogging and Leakage *2
Checking Oil Pump for Discoloration and Other External Defects *2
Governor Oil Filter - Change 8-15
Fuel Tank - Clean *1 8-6
Fuel Injection Pump - Inspect and Test (Replace parts as necessary) *2
Governor - Inspect and Test (Replace parts as necessary) *2
Radiator Fins - Check and Clean *1 8-18
Rubber Hose - Replace *2
Air Cleaner Element - Clean, Check and Replace *1 8-21
Protective Devices - Repair or Replace *1
Oil pressure gauge, coolant temperature gauge, oil temperature gauge,
exhaust temperature gauge, tachometer
*2
Every 8 years
Engine - Major Overhaul
Disassemble engine, clean, check and change major parts.
*2
Damper - Replace *2
Oil Pump - Repair or Replace *2
Fuel Injection Nozzle - Nozzle Tip Replacement
(Check the spray condition and adjust the fuel injection pressure after
replacement)
*2
Rubber Parts and O-rings - Replace *2
Unit Seal and Oil Seal of Water Pump - Replace *2
Turbocharger - Disassemble and Inspect *2
Aircooler - Disassemble and Clean *2
Vibration-isolating Rubber - Repair or Replace *1 *2
Couplings - Repair or Replace *1 *2
Protective Devices - Repair or Replace *1 *2
Protective Devices - Repair or Replace *1 *2
Stop Solenoid - Inspect or Replace *2
Ball Tap of Water Tank - Repair or Replace *1 *2
Other Consumables - Replace *2
Table 7-2 Periodic Maintenance Chart for Emergency Engine
Interval and service item
Refer-
ence
page
Page 75

7-9
Chapter 7 MAINTENANCE SCHEDULE
Periodic Maintenance Chart for General Purpose Engine
Table 7-3 Periodic Maintenance Chart for General Purpose Engine
Interval and service item
Refer-
ence
page
Every 50 service hours or
every month
Fuel Control Link Ball Joint - Inspect 8-10
Air Strainer - Drain Water and Clean (Air motor type or direct inlet type) 8-25
Air Tank - Drain Water (Air motor type or direct inlet type) 3-10
First 50 service hours for
a new or overhauled
engine
Bolts and Nuts on the Engine - Retighten *2
Engine Oil, Oil Filter and Bypass Oil Filter - Replace
It is Recommended to Check the Engine Oil Characteristics at the Same
time.
The Oil Filters Must be Replaced When the Filter Alarm Lights.
8-12
Every 250 service hours
or every 1 year
Engine Oil, Oil Filter and Bypass Oil Filter - Replace
The Oil Filters Must be Replaced When the Filter Alarm Lights.
8-12
Governor Oil Filter - Change 8-15
Belt and Belt Tension - Inspect and Adjust 8-2
Radiator Fins - Check and Clean *1 8-18
Exhaust Muffler - Drain Water *1 8-19
Air Tank - Inspect Safety Valve Operation 8-26
First 250 service hours
for a new or overhauled
engine
Valve Clearance - Inspect and Adjust
(Check valve mechanism at the same time.)
*2
Every 1000 service hours
or every 2 years
Fuel Filter - Replace 8-9
Water Separator Element - Replace *1 8-7
Gauze Filter - Clean 8-8
Air Strainer - Drain Water and Clean (Air motor type or direct inlet type) 8-25
Zinc Rod - Replace *2
Every 2000 service hours
or every 3 years
Bolts and Nuts on the Engine - Retighten *2
Valve Clearance - Inspect and Adjust
(Check valve mechanism at the same time.)
*2
Fuel Injection Timing - Inspect and Adjust *2
Fuel Pipe - Inspect 8-11
Oil Pipe - Inspect 8-15
Fuel Injection Nozzle - Nozzle Tip Replacement
(Check the spray condition and adjust the fuel injection pressure after
replacement)
*2
Protection Devices Operation - Inspect
(High water temperature, low oil pressure, overspeed)
*2
Page 76

7-10
Chapter 7 MAINTENANCE SCHEDULE
*1 If it is not a item supplied from Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, maintain the part following the manufacture's opera-
tion manual as required.
*2 Items require special tools or large equipment. For the servicing of those items, contact a dealer of Mitsubishi
Heavy Industries, Ltd.
Every 4000 service hours
or every 5 years
Top End of the Engine - Overhaul
Remove the Cylinder Head, and Inspect and Service the Combustion Chambers.
*2
Fuel Control Link Ball Joint - Inspect 8-10
Damper - Inspect 8-4
Air Cleaner - Clean *2
Heat Exchanger - Wash *2
8000 hours
Engine - Major Overhaul
Disassemble Engine, Clean, Check and Change Major Parts.
*2
Fuel Injection Pump - Inspect and Test (Replace parts as necessary) *2
Governor - Inspect and Test (Replace parts as necessary) *2
Protective Devices - Repair or Replace *2
Auxiliary Devices Operation - Check *2
Every 8000 service hours
or every 2 years
Coolant - Change 8-16
As required
Fuel System - Bleed Air 3-2
Air Cleaner Element - Clean, Check and Replace *1 8-21
Table 7-3 Periodic Maintenance Chart for General Purpose Engine
Interval and service item
Refer-
ence
page
Page 77

8-1
Chapter 8 PERIODIC INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES
Basic Engine
Engine External - Inspect
Inspect the engine exterior as described below.
1. Make sure there is no combustible material near the engine or battery. Also, check to make sure that the engine
and battery are clean. If combustible materials or dust are found near the engine or battery, remove them.
2. Check the electrical wiring for such components as the starter and alternator for looseness.
3. Check the whole engine for leaks of fuel, engine oil or coolant. If leaks are found, repair or contact your local
dealer.
4. Check that valves, plugs or cocks are properly positioned.
Fuel feed valve: Open
Coolant drain cock (plug): Closed
Engine oil drain plug: Closed
Be sure to keep combustible materials away from the engine, especially from the hot engine parts such as exhaust
manifolds, or the battery. Check for fuel and oil leaks. Remove dust from the top surface of the battery. A fire can
be caused by combustible materials placed near hot engine parts. If any abnormality is found, be sure to repair it
or contact your local dealer.
Page 78

8-2
Chapter 8 PERIODIC INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES
Belt and Belt Tension - Inspect and Adjust
Belt - Inspect
1. Inspect the belt visually for separation or damage. If any abnormality is found, replace the belt with a new one.
2. Inspect belt tension (deflection) and pressing force.
V-belt
Push the belt downward at the midway between pulleys with approximately 98 to 147 N {10 to 15 kgf} [22.05 to
33.05 lbf]. If the deflection is 10 to 15 mm [0.39 to 0.59 in.], the tension is correct. If the deflection of belt is not within
the standard, adjust the belt tension.
Ribbed belt
Refer to Table 8-1 "Ribbed Belt Tension Force", adjust the pressing force if it is not average level when pushing the
belt downward till 15 mm [0.59 in.] at the midway between pulleys with gauge.
Belt Tension (Alternator Side) - Adjust
1. Remove the belt cover.
2. Loosen all retaining bolts of the alternator and ad-
justing rod.
3. Loosen the upper and lower lock nuts on the ad-
justing rod.
Note: That the lower nut on the adjusting rod has left-
hand threads.
4. Turn the adjusting rod to adjust the belt tension.
5. After adjusting deflection, fix the upper and lower
lock nuts.
6. Tighten all retaining bolts of the alternator and ad-
justing plate.
7. Reinstall the belt cover and front cover.
Fig. 8-1 Belt and Belt Tension - Inspect and Adjust
If defects such as cuts or surface separations are found during inspection, replace the belt.
Keep oil and grease away from the belt. They may cause the belt to slip and shorten the service life.
Excessive belt tension can cause rapid wear of the alternator bearing and shorten the service life of the belt.
Adjust the belt tension accurately by following the procedures below.
Adjusting rod
Fixing bolt
V-belt
Ribbed belt
Gauge
Lock nut (left-hand thread)
Lock nut (left-hand thread)
Approx.
10 to 15 mm
[0.39 to 0.59 in.]
15 mm [0.59 in.]
Pressing force
Width Approx.
10 mm [0.39 in.]
Page 79

8-3
Chapter 8 PERIODIC INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES
The pressing force when pressing the belt downward till 15 mm [0.59 in.] at the midway of the belt direct distance.
Table 8-1 Ribbed Belt Tension Force
Item
Num-
ber of
ribs
Belt direct distance (mm)
Up to 300
300 or more
Up to 400
400 or more
Up to 500
500 or more
Up to 600
600 or more
When
attaching a
new belt
3
74 N {7.55 kgf }
[16.64 lbf]
49 N {5.00 kgf }
[11.02 lbf]
37 N {3.77 kgf }
[8.31 lbf]
29 N {2.96 kgf }
[6.53 lbf]
25 N {2.55 kgf }
[5.62 lbf]
4
88 N {8.97 kgf }
[19.78 lbf]
59 N {6.02 kgf }
[13.27 lbf]
44 N {4.49 kgf }
[9.90 lbf]
35 N {3.57 kgf }
[7.87 lbf]
29 N {2.96 kgf }
[6.53 lbf]
5
103 N {10.50 kgf }
[23.15 lbf]
69 N {7.04 kgf }
[15.52 lbf]
51 N {5.20 kgf }
[11.46 lbf]
41 N {4.18 kgf }
[9.22 lbf]
34 N {3.47 kgf }
[7.65 lbf]
6
118 N {12.03 kgf }
[26.52 lbf]
79 N {8.06 kgf }
[17.77 lbf]
59 N {6.02 kgf }
[13.27 lbf]
47 N {4.79 kgf }
[10.56 lbf]
39 N {3.98 kgf }
[8.77 lbf]
7
132 N {13.46 kgf }
[29.67 lbf]
88 N {8.97 kgf }
[19.78 lbf]
66 N {6.73 kgf }
[14.84 lbf]
53 N {5.40 kgf }
[11.90 lbf]
44 N {4.49 kgf }
[9.90 lbf]
8
147 N {14.99 kgf }
[33.05 lbf]
98 N {9.99 kgf}
[22.02 lbf]
74 N {7.55 kgf }
[16.64 lbf]
59 N {6.02 kgf }
[13.27 lbf]
49 N {5.00 kgf }
[11.02 lbf]
9
162 N {16.52 kgf }
[36.42 lbf]
108 N {11.01 kgf }
[24.27 lbf]
81 N {8.26 kgf }
[18.21 lbf]
65 N {6.63 kgf }
[14.62 lbf]
54 N {5.51 kgf }
[12.15 lbf]
10
176 N {17.95 kgf }
[39.57 lbf]
118 N {12.03 kgf }
[26.52 lbf]
88 N {8.97 kgf }
[19.78 lbf]
71 N {7.24 kgf }
[15.96 lbf]
59 N {6.02 kgf }
[13.27 lbf]
11
191 N {19.48 kgf }
[42.95 lbf]
127 N {12.95 kgf }
[28.55 lbf]
96 N {9.79 kgf }
[21.58 lbf]
76 N {7.75 kgf }
[17.09 lbf]
64 N {6.53 kgf }
[14.40 lbf]
12
206 N {
21.01 kgf }
[46.32 lbf]
137 N {13.97 kgf }
[30.80 lbf]
103 N {10.50 kgf }
[23.15 lbf]
82 N {8.36 kgf }
[18.43 lbf]
69 N {7.04 kgf }
[15.52 lbf]
Reused
3
51 N {5.20 kgf }
[11.46 lbf]
34 N {3.47 kgf }
[7.65 lbf]
26 N {2.65 kgf }
[5.84 lbf]
21 N {2.14 kgf }
[4.72 lbf]
17 N {1.73 kgf }
[3.81 lbf]
4
62 N {6.32 kgf }
[13.93 lbf]
41 N {4.18 kgf }
[9.22 lbf]
31 N {3.16 kgf }
[6.97 lbf]
25 N {2.55 kgf }
[5.62 lbf]
21 N {2.14 kgf }
[4.72 lbf]
5
72 N {7.34 kgf }
[16.18 lbf]
48 N {4.89 kgf }
[10.78 lbf]
36 N {3.67 kgf }
[8.09 lbf]
29 N {2.96 kgf }
[6.53 lbf]
24 N {2.45 kgf }
[5.40 lbf]
6
82 N {8.36 kgf }
[18.43 lbf]
55 N {5.61 kgf }
[12.37 lbf]
41 N {4.18 kgf }
[9.22 lbf]
33 N {3.37 kgf }
[7.43 lbf]
27 N {2.75 kgf }
[6.06 lbf]
7
93 N {9.48 kgf}
[20.90 lbf]
62 N {6.32 kgf }
[13.93 lbf]
46 N {4.69 kgf }
[10.34 lbf]
37 N {3.77 kgf }
[8.31 lbf]
31 N {3.16 kgf }
[6.97 lbf]
8
103 N {10.50 kgf }
[23.15 lbf]
69 N {7.04 kgf }
[15.52 lbf]
51 N {5.20 kgf }
[11.46 lbf]
41 N {4.18 kgf }
[9.22 lbf]
34 N {3.47 kgf }
[7.65 lbf]
9
113 N {11.52 kgf }
[25.40 lbf]
75 N {7.65 kgf }
[16.87 lbf]
57 N {5.81 kgf }
[12.81 lbf]
45 N {4.59 kgf }
[10.12 lbf]
38 N {3.87 kgf }
[8.53 lbf]
10
123 N {12.54 kgf }
[27.65 lbf]
82 N {8.36 kgf }
[18.43 lbf]
62 N {6.32 kgf }
[13.93 lbf]
49 N {5.00 kgf }
[11.02 lbf]
41 N {4.18 kgf }
[9.22 lbf]
11
134 N {
13.66 kgf }
[30.12 lbf]
89 N {9.08 kgf }
[20.02 lbf]
67 N {6.83 kgf }
[15.06 lbf]
54 N {5.51 kgf }
[12.15 lbf]
45 N {4.59 kgf }
[10.12 lbf]
12
144 N {14.68 kgf }
[32.36 lbf]
96 N {9.79 kgf }
[21.58 lbf]
72 N {7.34 kgf }
[16.18 lbf]
58 N {5.91 kgf }
[13.03 lbf]
48 N {4.89 kgf }
[10.78 lbf]
Page 80

8-4
Chapter 8 PERIODIC INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES
Damper - Inspect
Damper - Check Visually
Check the vibration damper for oil leakage, scratches,
deformation, discoloration and peeling of paint. Check
carefully for swelling on the cover (use a scale), oil
leaks from the shim, discoloration and peeling of paint
due to heat.
Note: If defects are found in the damper, contact a
dealer of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
Fig. 8-2 Damper - Check Visually
Damper Temperature Management
For making damper function well, heat of damper must be dissipated from its surface to prevent excessive damper
heating. Mitsubishi inspects each engine before shipment to ensure proper operating temperature of the vibration
damper. However, the vibration damper temperature varies depending on ambient conditions. Therefore, observe
the following suggestions and provide sufficient ventilation for the vibration damper and equipment.
1. Make sure the temperature of the outside damper surface does not exceed the temperature that described in the
following table when operating the engine with rated power for an hour.
2. When installing a safety cover to damper, check ventilation carefully and make sure the damper temperature re-
mains below the temperature specified above, with the cover in place.
3. It is recommended to use the thermo label for the temperature management of damper in regular use engine.
When installing a damper protective cover to the
engine, do not use a cover that encloses the damper.
It may cause serious engine problems because the
damper deteriorates by heat or not deliver enough its
performance.
Silicon oil
Cover
Table 8-2 Damper Temperature Management
Type of damper Continuous Standby
Viscous damper 90°C [194°F] 100°C [212°F]
Viscous rubber damper 80°C [176°F] 90°C [194°F]
Page 81

8-5
Chapter 8 PERIODIC INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES
Thermo Label - Handle
The white thermal part of thermo label becomes black when reaching the specified value.
Note: The thermal part that becomes black once does not return to white. Therefore, if the engine stops and then the
temperature of damper drops, the thermo label continues indicating the maximum temperature while engine is
running.
1. Attach a thermo label to the periphery or front end of damper.
2. Note the maximum temperature to check the thermal part of thermo label when engine stops. Note the temper-
ature periodically, and check the abnormality of temperature alteration.
Note: (a) When the temperature of thermo label increased, identify the abnormality of engine or other cause. Then,
reattach new thermo label, and check the change of temperature.
(b) If the temperature indication of thermo label comes close to the limit temperature of damper or the abnor-
mality is found in change of temperature, contact a dealer of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
(c) For damper temperature limit and inspection, refer to "Damper - Inspect" (8-4).
Fig. 8-3 Damper Temperature Management
Table 8-3 Thermo Label for Temperature Management
Part
Name
Part No.
Temperature
measuring
range
Thermo
label
100-120
32522-04211
20 labels set: 32522-04200
100 to 120°C
[212 to 248°F]
Thermo
label
75-95
32522-04111
20 labels set: 32522-04100
75 to 95°C
[167 to 203°F]
Thermo
label
50-70
32522-04311
20 labels set: 32522-04300
50 to 70°C
[122 to 158°F]
<5E-75>
75 80 85 90 95
<5E-100>
100 105 110 115 120
<5E-50>
50 55 60 65 70
Thermo Label
Page 82

8-6
Chapter 8 PERIODIC INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES
Fuel System
Fuel System - Inspect
Fuel Tank - Clean
1. Close the fuel feed valve to cut off the fuel supply to the engine.
2. Place a drip tray under the drain cock.
3. Drain all fuel in the tank from drain cock on the bottom of fuel tank.
4. Clean the inside of fuel tank.
5. Add fuel to the fuel tank.
6. Open the fuel feed valve, and bleed air for the fuel system.
Note: (a) For bleeding fuel system, refer to "Fuel System - Bleed Air" (3-2).
(b) If the specification of fuel tank differs from the contents of this operation manual, follow the manufacturer's
operation manual.
Fuel Tank - Drain Water
If fuel gets mixed with particles of foreign material
such as dust, dirt, or water, it can cause not only
decrease of output but also malfunctions of the fuel
system. To avoid such a problem, drain fuel tank as
described below.
1. Prepare the oil pan (capacity of 2 L [0.5 U.S. gal.]
or more) under the drain cock of fuel tank.
2. Open the drain cock of fuel tank and drain fuel at
least 1 to 2 liters.
3. Make sure that water and particles of foreign mate-
rial discharged with fuel. Close the drain cock.
Note: If the specification of fuel tank d iffers from the
contents of this opera tion manual, follow the
manufacturer's operation manual.
Fig. 8-4 Fuel Tank - Drain Water
When handling fuel, make sure there are no open flames or other fire hazards near the engine.
Wipe off any spilled fuel completely. Spilled fuel can ignite and cause a fire.
For fuel to be used, refer to "FUEL" (4-1).
Drain cock
Water
Page 83

8-7
Chapter 8 PERIODIC INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES
Water Separator - Drain Water
1. Prepare a plate, and place it under the drain cock
of water separator.
2. Open the drain cock, and drain water in the water
separator.
3. Close the all drain cocks after draining.
Note: If the specification of water separator differs from
the contents of this operation manual, follow the
manufacturer's operation manual.
Fig. 8-5 Water Separator - Drain Water
Water Separator Element - Replace
1. Close the inlet cock and outlet cock.
2. Turn the T-handle, and remove the water separator
cover.
3. Open the drain cock, and drain fuel in the water
separator.
4. Close the all drain cocks after draining.
5. Replace the element with a new one.
6. Fill the water separator with fuel.
7. Attach the water separator cover, and tighten the T-
handle.
8. Open the inlet cock and outlet cock.
9. After replacing the element, open the fuel feed
valve to the engine, then bleed air from the fuel
system.
Note: (a) For bleeding fuel system, refer to "Fuel Sys-
tem - Bleed Air" (3-2).
(b) If the specification of water separator differs
from the contents of this operation manual,
follow the manufacturer's operation manual.
Fig. 8-6 Water Separator Element - Replace
Inlet cock
Outlet cock
Drain cock
Open the inlet valve slowly to prevent overflowing fuel. Wrap a cloth around the water separator before the fuel
may spill.
Element
Inlet cock
Drain cock
Outlet cock
Page 84

8-8
Chapter 8 PERIODIC INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES
Gauze Filter - Clean
If the gauze filter is clogged, the fuel supply becomes
insufficient, resulting in decrease in power output or
engine stall.
1. Remove the eye bolt at the inlet port of fuel feed
pump.
2. Using a screw driver, remove the gauze filter that is
fitted inside the eye bolt.
3. Soak the gauze filter in the fuel, and clean it with a
brush.
4. After cleaning, install the gauze filter into the eye
bolt using a screw driver.
5. Install the eye bolt to the fuel feed pump.
6. Bleed the air from the fuel filter.
Note: For bleeding the fuel filter, refer to "Fuel Filter -
Bleed Air" (3-2).
Fig. 8-7 Gauze Filter - Clean
Fuel feed pump
Gauze filter
Eyebolt
Page 85

8-9
Chapter 8 PERIODIC INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES
Fuel Filter - Replace
1. Clean the area around the fuel filters.
2. Prepare a drip pan, and place it under the fuel fil-
ters.
3. Using a filter wrench, remove the fuel filters.
4. Wipe off fuel on the fuel filter cartridge mounting
surface of the filter bracket with a waste cloth.
5. Check new fuel filters for proper seating of the gas-
ket.
6. Apply clean fuel to the gasket of the new fuel filter.
7. Install the fuel filter to the filter bracket. When the
gasket contacts the mounting surface of the filter
bracket, further rotate 3/4 to a full turn.
8. After installing the new fuel filter, bleed the fuel fil-
ter.
Note: For bleeding the fuel filter, refer to "Fuel Filter -
Bleed Air" (3-2).
9. Start the engine and run it at idle speed for several
minutes.
10. Make sure that there is no fuel leak during the en-
gine operation. If fuel leakage is found, loosen the
fuel filter and check the gaskets for damage. If
there is no damage, retighten the fuel filter.
Fig. 8-8 Fuel Filter - Replace
Fig. 8-9 Fuel Filter
Do not use a filter with the dented case. Filter dam-
age or fuel leakage may occur and it can cause fire
hazard.
Do not use a filter wrench to install the fuel filter.
Do not dent or scratch the fuel filter surfaces.
Apply fuel to
the gasket.
Page 86

8-10
Chapter 8 PERIODIC INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES
Fuel Control Link Ball Joint - Inspect
Check ball joint in the fuel control link for play. If the
amount of play is 0.1 mm [0.004 in.] or more, replace
the ball joint with the new one.
If the ball joints are integrated in the control link,
replace the control link when the ball joints have loos-
ened. When installing ball joints, be sure to tighten the
nuts firmly.
Fig. 8-10 Ball Joints For Looseness - Inspect
Fig. 8-11 Fuel Control Link - Remove
If the sealed ball joints are found loosened, contact a
dealer of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. If the seal
on the ball joint is broken, the warranty is invalidated.
Ball joint
Rod
Lever
0.1 mm
[0.004 in.]
0.1 mm
[0.004 in.]
Ball joint
Control link
Page 87

8-11
Chapter 8 PERIODIC INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES
Fuel Pipe - Inspect
High Pressure Fuel Injection Pipe and Clamp Seat - Inspect and Replace
Visual Inspection in Every 2000 Service Hours
Check clamp seat cracks and wear, or high pressure
fuel injection pipe wear. If defective, replace the clamp
seat with a new one. Replace the high pressure fuel
injection pipe with a new one as needed.
In Every Major Overhaul
Replace clamp seat with a new one. Also, check high
pressure fuel injection pipe wear. If defective, replace
the high pressure fuel injection pipe with a new one.
In Every Other Major Overhaul
Replace all clamp seats and high pressure fuel injec-
tion pipes with new ones.
Fig. 8-12 High Pressure Fuel Injection Pipe and
Clamp Seat - Inspect and Replace
Low Pressure Fuel Pipe and Clip - Inspect
Visual Inspection in Every 2000 Service Hours
Loosen clamp fixing bolt and check clip wear and pipe
metal contact with clamp. If defective, replace the pipe
assembly with a new one.
In Every Other Major Overhaul
Replace the pipe assembly with a new one.
Fig. 8-13 Low Pressure Fuel Pipe and Clip - Inspect
Clamp plate
Clamp seat
Clamp
Clip
Page 88

8-12
Chapter 8 PERIODIC INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES
Lubricating System
Engine Oil, Oil Filter and Bypass Oil Filter - Replace
Engine Oil - Drain
After stopping the engine, drain the engine oil form the engine oil drain port of oil pan.
When draining engine oil, check that the oil temperature is low.
When draining oil or changing the oil filter, wear gloves. Hot engine oil and parts may cause burns.
Do not dump waste oil. It is forbidden by law. For disposal of waste oil, consult a dealer of Mitsubishi Heavy Indus-
tries, Ltd.
Change the engine oil, oil filter and bypass oil filter at the same time.
Also checking and analyzing the oil properties is recommended when changing the engine oil.
Do not reuse the oil filter element, as it is a paper type. When replacing filters, always replace gasket with new
ones.
Page 89

8-13
Chapter 8 PERIODIC INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES
Engine Oil - Refill
1. Remove the cap from the oil filler.
2. Fill the engine oil pan with specified engine oil to
the specified level.
Note: For engine oil, refer to "ENGINE OIL" (5-1). For
engine oil capacity, refer to "MAIN SPECIFICA-
TIONS" (12-1).
3. Check the oil level in the oil pan as follows:
4. Pull out the oil level gauge and wipe it clean with a
waste cloth.
5. Insert the oil level gauge fully into the oil level
gauge guide and then pull it out again.
6. The proper oil level is between the high and low
marks on the oil level gauge.
If the engine oil goes over the high marks on the oil
level gauge, open the engine oil drain valve to drain
oil. If the engine oil is low, refill the specified engine
oil.
7. Install the oil filler cap after adding engine oil.
8. Check the oil pan and other area for oil leaks. Re-
pair the oil leakage if any.
9. While pulling the stop lever, rotate the crankshaft
for approx. 10 seconds to turn on the starter. Stop
the operation for 1 minute, then, repeat the opera-
tion two or three times. Circulate engine oil to each
engine parts.
Note: Prepare for the cooling system.
10. Check the oil level with the oil level gauge again,
and add oil to the specified level.
Fig. 8-14 Oil Filler and Oil Level Gauge
Refilling engine oil must be specified level. If the
refilling oil goes over the high marks on the oil level
gauge, engine oil may blow out.
H
L
Oil filler
Oil level gauge
Oil level gauge
High
Low
Improper
Improper
Proper
Page 90

8-14
Chapter 8 PERIODIC INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES
Oil Filter and Bypass Oil Filter - Replace
1. Clean around the oil filters.
2. Prepare drip pans, and place them under oil filters
and a bypass oil filter.
3. Using a filter wrench, remove oil filters and a by-
pass oil filter.
Note: Disconnect the removed oil filters and a bypass
oil filter, and check elements for metal particles.
If metal particles are found, contact a dealer of
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
4. Thoroughly wipe off oil on the oil filter mounting
surface of the filter bracket with a cloth.
5. Check the new oil filters and a bypass filter for
proper seating of gasket.
6. Apply clean engine oil to gasket.
7. Install oil filters and a bypass oil filter to the filter
bracket. When the gasket contacts the mounting
surface of the filter bracket, further rotate 3/4 to a
full turn.
Fig. 8-15 Oil Filter and Bypass Oil Filter -
Replace
Fig. 8-16 Oil Filter
Engine Oil for Mixing of Fuel and Water - Inspect
Sample 1 to 2 L [0.26 to 0.53 U.S. gal.] of engine oil, and check for abnormal odor and discoloration to determine
the mixing of fuel and water.
If fuel is mixed with the engine oil, the oil will smell like fuel.
If water is mixed with the engine oil, the oil will be milky white.
If fuel or water is detected in the engine oil, find the cause of the problem, and repair. If the problem cannot be cor-
rected easily, contact a dealer of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
Do not use a filter with the dented case. Filter dam-
age or oil leakage may occur and it can cause fire
hazard.
Do not use a filter wrench to install the oil filter and
bypass oil filter.
Do not dent or scratch the oil filter surfaces.
Bypass oil filter
Oil filter
Oil tray
Filter wrench
Apply engine oil
to gasket.
If the engine continues to operate with engine oil mixed with fuel or water, the engine oil viscosity decreases and
this can cause serious accidents such as seizing of bearings.
Page 91

8-15
Chapter 8 PERIODIC INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES
Governor Oil Filter - Change
1. Prepare a drip pan and place it under the governor
oil filter.
2. Loosen the air vent plug and remove the drain plug.
Drain oil from the filter into the drip pan.
3. Remove the oil pipe from the center bolt.
4. Remove the center bolt and remove the case from
the bracket. Remove the used element from the
case.
5. Put a new element in the case using the center
bolt.
6. Install the case to the filter bracket. Tighten the
center bolt.
7. Install the oil pipe to the center bolt.
8. Install the drain plug.
9. Remove the air vent plug. Fill up the filter with en-
gine oil.
10. After filling up, reinstall the air vent plug.
Fig. 8-17 Governor oil filter - Drain
Fig. 8-18 Governor oil filter - Change
Oil Pipe - Inspect
Oil Pipe and Clip - Inspect and Replace
Visual Inspection at Overhaul
Loosen clamp fixing bolt and check clip wear and pipe
wear. If defective, replace the pipe assembly with a
new one.
In Every Other Major Overhaul
Replace the pipe assembly with a new one.
Fig. 8-19 Oil Pipe and Clip - Inspect and Replace
When draining oil or changing the oil filter, wear
gloves. Hot engine oil and parts may cause burns.
Air vent plug
Drain plug
Oil pipe
Center bolt
Element
Case
Clamp
Clip
Page 92

8-16
Chapter 8 PERIODIC INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES
Cooling System
Coolant - Change
Radiator Cap - Open/Close
Note: If the specification of radiator differs from the
contents of this opera tion manual, follow the
manufacturer's operation manual.
Fig. 8-20 Radiator Cap
Coolant - Drain
1. When draining coolant immediately after engine
operation, idle the engine in low gear for 5 to 6 min-
utes to lower the coolant temperature to 70 to 80 °C
[158 to 176 °F].
2. Open the coolant inlet.
3. Place coolant receiving cans under the drain cocks
and plugs, and open the coolant drain cocks and
plugs to drain the coolant.
Fig. 8-21 Coolant Drain Cock (Engine)
The service life of LLC is 2 years. Be sure to change coolant at least once every 2 years.
When using the engine with radiator cooling system,
remove the radiator cap only after the engine has
cooled to the room temperature. Place a waste cloth
over the cap, and loosen the cap about a half-turn or
stand the lever to the upright position to release inter-
nal pressure. Opening the radiator cap of coolant
expansion tank while the engine is hot causes steam
and hot coolant to blow out and can result in skin
burns.
Turn the cap about
half a turn
Stand the lever to
the upright position
Coolant
drain cocks
Left side
Right side
The coolant drain cocks located in the crankcase
respectively (behind the each fuel injection pump
accessory drive unit).
Page 93

8-17
Chapter 8 PERIODIC INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES
Cooling System - Clean
1. Close coolant drain cocks and plugs.
2. Pour in a cleaning solution (a solution that is non-
corrosive to rubber and metals) in the cooling sys-
tem, and operate the engine at 800 to 900 min
-1
for
about 15 minutes, then drain the cleaning solution.
3. Close coolant drain cocks and plugs.
4. Pour in fresh water, and operate the engine at 800
to 900 min
-1
for about 10 minutes.
Repeat the above rinsing steps until the draining
water becomes clear and clean.
Fig. 8-22 Coolant Drain Cock (Water Pump)
Coolant - Refill
1. Close coolant drain cocks and plugs firmly.
2. Open the coolant filler and add a mixture of water
and coolant having the specified concentration.
Note: Determine the amounts of LLC and wa ter to be
added by using the LLC concentration chart.
For the coolant, refer to "COOLANT" (6-1) . For
the coolant capacity, refer to "MAIN SPECIFICA-
TIONS" (12-1).
3. Check the heat exchange equipment and other
parts for coolant leaks. If a coolant leak is found, re-
pair it.
4. When coolant reaches the full level, close the cool-
ant filler securely.
5. While pulling the manual stop lever, rotate the
crankshaft for approx. 10 seconds using the starter.
Stop the operation for 1 minute, then, repeat the
operation two or three times to bleed the cooling
system.
Note: Prepare for the engine oil system.
6. Check the level of coolant.
Clean the cooling system when operating the engine
or heat exchange equipment first time, or restarting
the engine after storage with coolant drained.
Coolant
drain cock
Always use the coolant having the same concentra-
tion.
Page 94

8-18
Chapter 8 PERIODIC INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES
Radiator Fins - Check and Clean
Check the radiator fins for holes and cracks.
To clean the radiator fins, blow compressed air from
the opposite direction of the normal air flow.
Note: If the specification of radiator differs from the
contents of this opera tion manual, follow the
manufacturer's operation manual.
Fig. 8-23 Radiator fins - Clean
When handling compressed air, wear safety goggles,
a hardhat, gloves and other necessary protective
gear. Working without wearing proper protective gear
could result in serious injuries.
Page 95

8-19
Chapter 8 PERIODIC INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES
Inlet and Exhaust Systems
Turbocharger - Inspect
Disconnect the pipe from the air inlet side. Hold the
compressor wheel nut by hand and turn the wheel to
check for looseness or rotation smoothness. Replace
the turbocharger if any abnormal movement is found.
Note: When removing an d inspecting turbocharger,
contact a dealer of Mitsubishi Heavy Indu stries,
Ltd.
Also, inspect that there is any disc oloration or
damage on the compressor wheel fins.
Fig. 8-24 Turbocharger - Inspect
Exhaust Muffler - Drain Water
Remove the drain plug and allow water to drain from
the exhaust muffler.
Note: If the specification of exhaust muffler differs from
the contents of this operation manual, follow the
manufacturer's operation manual.
Fig. 8-25 Draining Water From the Exhaust Muffler
Check the turbocharger when the engine is cold.
Also, make sure that the compressor wheel is not
rotating before inspecting the turbocharger.
If the color of the exhaust gas is abnormal, also
inspect the turbocharger.
The exhaust muffler is very hot immediately after
operation. Never touch the exhaust muffler by hand.
Work must be conducted after the exhaust muffler
cools at the room temperature.
Drain plug
Page 96

8-20
Chapter 8 PERIODIC INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES
Air Cleaner - Check for Clogging
1. Check the air cleaner indicator for the element
clogging.
2. If the element is clogged, the red signal mark will
be displayed.
3. Immediately clean or replace the air cleaner ele-
ment when the signal turns red.
Note: (a) For cleaning of the air cleaner element, refer
to "Air Cleaner Element - Clean, Check and
Replace" (8-21).
(b) If the specification of air cleaner differs from
the contents of this operation manual, follow
the manufacturer's operation manual.
Fig. 8-26 Air Cleaner - Check for Clogging
Reset button
Signal
(red)
Page 97

8-21
Chapter 8 PERIODIC INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES
Air Cleaner Element - Clean, Check and Replace
1. Remove the air cleaner cap and wing bolt.
2. Remove the air cleaner element from the body.
3. Blow compressed air (0.69 MPa {7 kgf/cm
2
} [100
psi] or lower) onto the inside surface of the element
to remove foreign materials.
4. To remove dust stuck on the air cleaner element,
blow dry compressed air onto the outside surface
from a distance.
Blow compressed air on the inside surface toward
the outside along the pleats. Then, blow com-
pressed air on the outside and inside surface
again.
5. After cleaning, hold the air cleaner element near a
light bulb to illuminate the inside, to check for de-
fects such as cuts, pinholes or local wear.
6. If any defect is found, replace the air cleaner ele-
ment with a new one.
7. Reassemble the air cleaner element as it was.
Fig. 8-27 Air Cleaner Element - Remove
Fig. 8-28 Air Cleaner Element - Clean and Check
When handling compressed air, wear safety goggles, a dust mask, a hardhat, gloves and other necessary protec-
tive gear. Working without wearing proper protective gear could result in serious injuries.
Never perform maintenance on the air cleaner while the engine is running. Servicing the pre-cleaner while the
engine is running can cause particles of foreign material to enter the engine and result in rapid wear of parts, lead-
ing to a shorter service life of the engine. Never tap, hit or wash the air cleaner element.
If defects such as cuts, pinholes or local wear are found in the element, or if the air cleaner indicator shows a red
sign soon after the cleaned element is installed, change it for new one. Remove the air cleaner slowly to prevent
foreign materials accumulated on the element from falling off.
After removing the air cleaner, immediately cover the air inlet with plastic sheet or similar means to prevent foreign
materials from entering the engine.
Air cleaner
element
Body
Wing
bolt
Clean Check
Page 98

8-22
Chapter 8 PERIODIC INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES
8. After cleaning or replacing the air cleaner element,
press the reset button to reset the indicator.
Note: If the specification of air cleaner differs from the
contents of this opera tion manual, follow the
manufacturer's operation manual.
Fig. 8-29 Air Cleaner - Check for Clogging
Reset button
Signal
(red)
Page 99

8-23
Chapter 8 PERIODIC INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES
Electrical System
Battery - Check
Note: If the specification of battery differs from the c ontents of this operation manual, follow the manufacturer's op-
eration manual.
Battery Electrolyte Level - Inspect
Battery electrolyte evaporates during use and the
electrolyte level gradually decreases. The proper elec-
trolyte surface level is between the LOWER LEVEL
and UPPER LEVEL lines.
For the battery without level lines, the proper electro-
lyte surface level is about 10 to 15 mm [0.39 to 0.59
in.] above the top of the plates.
If the electrolyte level is low, remove the caps and add
distilled water to the proper level.
Note: When adding distilled water, add little by little.
Fig. 8-30 Battery Electrolyte Level - Inspect
Specific Gravity of Battery Electrolyte - Check
If the specific gravity measured at 20°C [68°F] is lower
than 1.22, then charge the electrolyte.
Fig. 8-31 Specific Gravity of Battery Electrolyte -
Check
If battery electrolyte is spilled on your skin or clothes, flush immediately with plenty of water. If battery electrolyte
get into your eyes, flush them immediately with plenty of water and then get medical attention.
Do not use open flames or other fire hazards near the battery. When handling the battery, be careful of sparks gen-
erated by accidental shorting.
UPPER LEVEL
LOWER LEVEL
10 to 15 mm
[0.39 to 0.59 in.]
Proper
Table 8-4 Specific gravity of electrolyte
Specific gravity
at 20 °C [68 °F]
Condition Remedy
From 1.26 to 1.28 Fully charged -
From 1.22 to 1.26 Charged Charge
Less than 1.22 Discharged Charge
Float
Electrolyte
surface
Electrolyte
Glass tube
Page 100

8-24
Chapter 8 PERIODIC INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES
Starter - Inspect
Visually check the starter for damage.
Note: If the starter is defective, consult a dealer of Mit-
subishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
Fig. 8-32 Starter - Inspect
Alternator - Inspect
Visually check the alternator for damage.
Remove the belt, and turn the pulley by hand to make
sure that it rotates smoothly.
Note: If the alternator is defectiv e, consult a dealer of
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
Fig. 8-33 Alternator - Inspect
Starter
Alternator
 Loading...
Loading...