

SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
(Always read these instructions before using this equipment.)
Before using this product, please read this manual, the relevant manuals introduced in this manual,
standard PLC manuals, and the safety standard carefully and pay full attention to safety to handle the
product correctly.
In this manual, the safety instructions are ranked as "DANGER" and "CAUTION".
DANGER
CAUTION
Note that the CAUTION level may lead to a serious consequence according to the circumstances.
Always follow the instructions of both levels because they are important to personal safety.
Please save this manual to make it accessible when required and always forward it to the end user.
Indicates that incorrect handling may cause hazardous conditions,
resulting in death or severe injury.
Indicates that incorrect handling may cause hazardous conditions,
resulting in medium or slight personal injury or physical damage.
A - 1
[Design Precautions]
DANGER
When a safety PLC detects an error in an external power supply or a failure in PLC main module, it
turns off all the outputs.
Create an external circuit to securely stop the power of hazard by turning off the outputs.Incorrect
configuration may result in an accident.
Create short current protection for a safety relay, and a protection circuit such as a fuse, and
breaker, outside a safety PLC.
When data/program change, or status control is performed from a PC to a running safety PLC,
create an interlock circuit outside the sequence program and safety PLC to ensure that the whole
system always operates safely.
For the operations to a safety PLC, pay full attention to safety by reading the relevant manuals
carefully, and establishing the operating procedure.
Furthermore, for the online operations performed from a PC to a safety CPU module, the corrective
actions against a communication error due to a cable connection fault, etc. should be predetermined
as a system.
All output signals from a safety CPU module to the CC-Link Safety system master module are
prohibited to use.
These signals can be found in the CC-Link Safety System Master Module User's Manual.
Do not turn ON or OFF these signals by sequence program, since turning ON/OFF these output
signals of the PLC system may cause malfunctions and safety operation cannot be guaranteed.
When a safety remote I/O module has detected a CC-Link Safety error, it turns off all the outputs.
Note that the outputs in a sequence program are not automatically turned off.
If a CC-Link Safety error has been detected, create a sequence program that turns off the outputs in
the program.
If the CC-Link Safety is restored with the outputs on, it may suddenly operate and result in an
accident.
To inhibit restart without manual operation after safety functions was performed and outputs were
turned OFF, create an interlock program which uses a reset button for restart.
CAUTION
Do not bunch the wires of external devices or communication cables together with the main circuit or
power lines, or install them close to each other.They should be installed 100 mm (3.94 inch) or more
from each other.Not doing so could result in noise that would cause erroneous operation.
A - 2
[Installation Precautions]
CAUTION
Use a safety PLC in the environment that meets the general specifications described in this manual.
Using this PLC in an environment outside the range of the general specifications could result in
electric shock, fire, erroneous operation, and damage to or deterioration of the product.
While pressing the installation lever located at the bottom of module, insert the module fixing tab into
the fixing hole in the base unit until it stops. Then, securely mount the module with the fixing hole as
a supporting point.
Incorrect loading of the module can cause a failure or drop.
Secure the module to the base unit with screws.
Tighten the screw in the specified torque range.
If the screws are too loose, it may cause a drop of the screw or module.
Over tightening may cause a drop due to the damage of the screw or module.
Completely turn off the externally supplied power used in the system before mounting or
removingthe module.
Not doing so could result in damage to the product.
Do not directly touch the module's conductive parts or electronic components.
Doing so may cause malfunctions or a failure.
[Wiring Precautions]
DANGER
Be sure to shut off all phases of the external supply power used by the system before wiring.
Not completely turning off all power could result in electric shock or damage to the product.
When energizing or operating the module after installation or wiring, be sure to close the attached
terminal cover.
Not doing so may result in electric shock.
A - 3
[Wiring Precautions]
CAUTION
Be sure to ground the FG terminals and LG terminals to the protective ground conductor.
Not doing so could result in electric shock or erroneous operation.
Use a solderless terminal with insulation sleeve for wiring of a terminal block.
Use up to two solderless terminals for a single terminal.
Use applicable solderless terminals and tighten them with the specified torque.
If any solderlessspade terminal is used, it may be disconnected when the terminal screw comes
loose, resultingin failure.
Wire the module correctly after confirming the rated voltage and terminal layout.
Connecting a power supply of a different rated voltage or incorrect wiring may cause a fire or failure.
Tighten a terminal block mounting screw, terminal screw, and module fixing screw within the
specified torque range.
If the terminal block mounting screw or terminal screw is too loose, it may cause a short circuit, fire,
or malfunctions.
If too tight, it may damage the screw and/or the module, resulting in a drop of the screw or module, a
short circuit or malfunctions.
If the module fixing screw is too loose, it may cause a drop of the screw or module.
Over tightening the screw may cause a drop due to the damage of the screw or module.
Be sure there are no foreign substances such as sawdust or wiring debris inside the module.
Such debris could cause a fire, failure, or erroneous operation.
The module has an ingress prevention label on its top to prevent foreign matter, such as wire offcuts,
from entering the module during wiring.
Do not peel this label during wiring.Before starting system operation, be sure to peel this label
because of heat dissipation.
Install our PLC in a control panel for use.
Wire the main power supply to the power supply module installed in a control panel through a
distribution terminal block.
Furthermore, the wiring and replacement of a power supply module have to be performed by a
maintenance worker who acquainted with shock protection.
(For the wiring methods, refer to Section 10.3.)
A - 4
[Startup and Maintenance precautions]
DANGER
Do not touch the terminals while power is on.
Doing so could cause shock or erroneous operation.
Correctly connect the battery.Also, do not charge, disassemble, heat, place in fire, short circuit, or
solder the battery.
Mishandling of battery can cause overheating or cracks which could result in injury and fires.
Turn off all phases of the external supply power used in the system when cleaning the module or
retightening the terminal block mounting screws, terminal screws, or module fixing screws.
Not doing so could result in electric shock.Tighten a terminal block mounting screw, terminal screw,
and module fixing screw within the specified torque range.
If the terminal block mounting screw or terminal screw is too loose, it may cause a short circuit, fire,
or malfunctions.
If too tight, it may damage the screw and/or the module, resulting in a drop of the screw or module, a
short circuit or malfunctions.
If the module fixing screw is too loose, it may cause a drop of the screw or module.
Over tightening the screw may cause a drop due to the damage of the screw or module.
A - 5
[Startup and Maintenance precautions]
CAUTION
The online operations performed from a PC to a running safety PLC (Program change when a safety
CPU is RUN, device test, and operating status change such as RUN-STOP switching) have to be
executed after the manual has been carefully read and the safety has been ensured.
Following the operating procedure predetermined at designing, the operation has to be performed by
an instructed person.
When changing a program while a safety CPU is RUN (Write during RUN), it may cause a program
breakdown in some operating conditions.
Fully understand the precautions described in the GX Developer's manual before use.
Do not disassemble or modify the modules.
Doing so could cause a failure, erroneous operation, injury, or fire.
If the product is repaired or remodeled by other than the specified FA centers or us, the warranty is
not covered.
Use any radio communication device such as a cellular phone or a PHS phone more than 25cm(9.85
inch) away in all directions of the PLC.
Not doing so can cause a malfunction.
Completely turn off the externally supplied power used in the system before mounting or
removingthe module.
Not doing so may result in a failure or malfunctions of the module.
Restrict the mounting/removal of a module, base unit, and terminal block up to 50 times
(IEC61131-2-compliant), after the first use of the product.
Failure to do so may cause the module to malfunction due to poor contact of connector.
Do not drop or give an impact to the battery mounted to the module.
Doing so may damage the battery, causing the battery fluid to leak inside the battery.
If the battery is dropped or given an impact, dispose of it without using.
Before touching the module, always touch grounded metal, etc. to discharge static electricity
fromhuman body, etc.
Not doing so may result in a failure or malfunctions of the module.
A - 6
[Disposal Precautions]
CAUTION
When disposing of this product, treat it as industrial waste.
When disposing of batteries, separate them from other wastes according to the local regulations.
(For details of the battery directive in EU member states, refer to Appendix 4.)
[Transportation Precautions]
CAUTION
When transporting lithium batteries, make sure to treat them based on the transport regulations.
(For details of the controlled models, refer to Appendix 3.)
A - 7

REVISIONS
The manual number is given on the bottom left of the back cover.
Print Date Manual Number Revision
Sep., 2006 SH(NA)-080626ENG-A First edition
May, 2007 SH(NA)-080626ENG-B
Apr., 2008 SH(NA)-080626ENG-C
Sep., 2008 SH(NA)-080626ENG-D
Correction
Section 2.2, 4.1, 5.1, 6.1, 9.1.1, 9.1.3, 10.1, 10.3.1, 10.3.2, 12.2.1, 12.2.10
Addition
Section 12.2.12
Correction
ABOUT MANUALS, GENERIC TERMS AND ABBREVIATIONS, Section 1.1,
2.1, 4.2, 4.3, 4.4, 5.1, 5.3, 6.2, 8.1, 9.1.3, 9.1.4, 9.2.1, 10.2.1, 10.2.3, 10.3.1,
10.3.2, 11.1, 11.2, 12.2.1, 12.2.3, 12.2.4, 12.2.5, 12.2.7, 12.2.8, 12.2.9, 12.2.12,
12.3.1, 12.3.3, 12.3.4, 12.3.5, 12.3.6, 12.3.7, 12.3.8, 12.6, 12.7
Addition
Section 2.1.1, Appendix 2
Correction
Section 10.2.1
Addition
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS, Section 7.1, Appendix 4
Japanese Manual Version SH-080607-D
This manual confers no industrial property rights or any rights of any other kind, nor does it confer any patent licenses.
Mitsubishi Electric Corporation cannot be held responsible for any problems involving industrial property rights which may
occur as a result of using the contents noted in this manual.
C
2006 MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORPORATION
A - 8

INTRODUCTION
Thank you for choosing the Mitsubishi MELSEC-QS Series of Safety Programmable Controllers.
Before using the equipment, please read this manual carefully to develop full familiarity with the functions
and performance of the QS series PLC you have purchased, so as to ensure correct use.
CONTENTS
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• A - 1
REVISIONS•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••A - 8
INTRODUCTION •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• A - 9
CONTENTS••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• A - 9
ABOUT MANUALS ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• A - 16
HOW THIS MANUAL IS ORGANIZED ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• A - 18
HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• A - 20
GENERIC TERMS AND ABBREVIATIONS ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• A - 21
PRECAUTIONS FOR USE ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• A - 22
CHAPTER1 OVERVIEW 1 - 1 to 1 - 6
1.1 Features •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 1 - 3
CHAPTER2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION 2 - 1 to 2 - 6
2.1 System Configuration ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••2 - 1
2.1.1 Precautions for system configuration•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 2 - 3
2.2 Configuration of Peripheral Devices••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 2 - 4
2.3 Confirming Serial No. and Function Version••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 2 - 5
CHAPTER3 GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS 3 - 1 to 3 - 1
CHAPTER4 CPU MODULE 4 - 1 to 4 - 7
4.1 Performance Specifications••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 4 - 1
4.2 Part Names •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 4 - 3
4.3 Switch Operation after Writing a Program ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 4 - 5
4.4 Reset Operation••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 4 - 6
CHAPTER5 POWER SUPPLY MODULE 5 - 1 to 5 - 5
5.1 Specifications •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 5 - 1
5.2 Precaution when connecting the uninterruptive power supply ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 5 - 3
5.3 Names of Parts and Settings ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 5 - 4
A - 9

CHAPTER6 BASE UNIT 6 - 1 to 6 - 2
6.1 Specification ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 6 - 1
6.2 Part Names •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 6 - 2
CHAPTER7 BATTERY 7 - 1 to 7 - 2
7.1 Battery (Q6BAT) •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 7 - 1
7.1.1 Battery Specifications •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 7 - 1
7.1.2 Installation of Battery ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 7 - 2
CHAPTER8 CPU MODULE START-UP PROCEDURES 8 - 1 to 8 - 3
8.1 Procedure before Operating in SAFETY MODE •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 8 - 1
CHAPTER9 EMC AND LOW VOLTAGE DIRECTIVES 9 - 1 to 9 - 12
9.1 Requirements for Conformance to EMC Directive •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••9 - 1
9.1.1 Standards relevant to the EMC Directive ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 9 - 1
9.1.2 Installation instructions for EMC Directive •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 9 - 3
9.1.3 Cables •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••9 - 4
9.1.4 Power Supply Module ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••9 - 6
9.1.5 Others ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 9 - 7
9.2 Requirement to Conform to the Low Voltage Directive •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 9 - 9
9.2.1 Standard applied for MELSEC-QS series PLC•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 9 - 9
9.2.2 MELSEC-QS series PLC selection •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 9 - 9
9.2.3 Power supply••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 9 - 10
9.2.4 Control panel ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 9 - 10
9.2.5 Grounding••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 9 - 12
9.2.6 External wiring ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 9 - 12
CHAPTER10 LOADING AND INSTALLATION 10 - 1 to 10 - 22
10.1 Calculating Heat Generation of PLC •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 10 - 3
10.2 Module Installation•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 10 - 5
10.2.1 Precaution on installation •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 10 - 5
10.2.2 Instructions for mounting the base unit ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••10 - 12
10.2.3 Installation and removal of module •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••10 - 15
10.3 Wiring ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••10 - 18
10.3.1 The precautions on the wiring •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••10 - 18
10.3.2 Connecting to the power supply module•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••10 - 22
CHAPTER11 MAINTENANCE AND INSPECTION 11 - 1 to 11 - 10
11.1 Daily Inspection ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 11 - 3
11.2 Periodic Inspection ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 11 - 4
11.3 Battery Life and Replacement Procedure •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 11 - 5
11.3.1 Battery lives of CPU modules••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 11 - 6
11.3.2 Replacement Procedure of the CPU Module Battery •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 11 - 8
A - 10

11.4 When PLC Has been Stored without a Battery ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 11 - 9
11.5 When Battery Has Gone Flat during Storage of a PLC•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••11 - 10
CHAPTER12 TROUBLESHOOTING 12 - 1 to 12 - 86
12.1 Troubleshooting Basics •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 12 - 1
12.2 Troubleshooting Flowchart •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 12 - 2
12.2.1 Troubleshooting category flow •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 12 - 2
12.2.2 Flowchart for when the ERR terminal (negative logic) is off (opened) •••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 12 - 3
12.2.3 Flowchart for when the "POWER" LED turns off •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 12 - 5
12.2.4 When the "ALIVE" LED does not turn on or turns off •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 12 - 7
12.2.5 Flowchart for when the "RUN" LED turns off •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 12 - 9
12.2.6 When the "RUN" LED flashes •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••12 - 10
12.2.7 Flowchart for when the "ERR." LED turns on or flashes••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••12 - 11
12.2.8 When the "USER" LED turns on ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••12 - 14
12.2.9 When the "BAT." LED turns on ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••12 - 15
12.2.10 Flowchart for when a program cannot be read •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••12 - 16
12.2.11 Flowchart for when a program cannot be written ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••12 - 17
12.2.12 Flowchart for when the CPU cannot communicate with the GX Developer•••••••••••••••••••••12 - 18
12.3 Error Code List •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••12 - 20
12.3.1 Error codes ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••12 - 21
12.3.2 Reading an error code ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••12 - 21
12.3.3 Error code list (1000 to 1999) ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••12 - 22
12.3.4 Error code list (2000 to 2999) ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••12 - 28
12.3.5 Error code list (3000 to 3999) ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••12 - 34
12.3.6 Error code list (4000 to 4999) ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••12 - 42
12.3.7 Error code list (5000 to 5999) ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••12 - 46
12.3.8 Error code list (8000 to 9000) ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••12 - 48
12.4 Canceling Errors •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••12 - 56
12.5 Error codes returned to request source during communication with CPU module ••••••••••••••••••12 - 58
12.6 Special Relay List••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••12 - 67
12.7 Special Register List ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••12 - 71
APPENDICES App- 1 to App - 7
Appendix 1 External Dimensions •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• App- 1
Appendix 1.1 CPU module •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• App- 1
Appendix 1.2 Power supply module••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• App- 2
Appendix 1.3 Main base unit ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• App- 3
Appendix 2 Safety CPU Module Upgrade ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• App- 4
Appendix 3 Precautions for Battery Transportation •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• App- 5
Appendix 4 Handling of Batteries and Devices with Built-in Batteries in EU Member States•••••••••••••• App- 6
Appendix 4.1 Disposal precautions ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• App- 6
Appendix 4.2 Exportation precautions •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• App- 7
INDEX Index- 1 to Index- 2
A - 11

(Related manual).................QSCPU User's Manual (Function Explanation, Program Fundamentals)
CONTENTS
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
REVISIONS
INTRODUCTION
CONTENTS
ABOUT MANUALS
HOW TO SEE THIS MANUAL IS ORGANIZED
HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL
GENERIC TERMS AND ABBREVIATIONS
CHAPTER1 OVERVIEW
1.1 Features
1.2 Program Storage and Operation
1.3 Devices and Instructions Convenient for Programming
1.4 How to Check the Serial No. and Function Version
CHAPTER2 PERFORMANCE SPECIFICATION
CHAPTER3 SEQUENCE PROGRAM CONFIGURATION AND EXECUTION CONDITIONS
3.1 Sequence Program
3.1.1 Sequence program description method
3.1.2 Sequsence program operation
3.2 Concept of Scan Time
3.3 Operation Processing
3.3.1 Initial processing
3.3.2 CC-Link Safety, MELSECNET/H refresh
3.3.3 I/O refresh
3.3.4 END processing
3.4 RUN, STOP, PAUSE Operation Processing
3.5 Operation Processing during Momentary Power Failure
3.6 Data Clear Processing
3.7 Numeric Values which can be Used in Sequence Programs
3.7.1 BIN (Binary Code)
3.7.2 HEX (Hexadecimal)
3.7.3 BCD (Binary Coded Decimal)
CHAPTER4 I/O NUMBER ASSIGNMENT
4.1 Definition of I/O Number
4.2 Concept of I/O Number Assignment
A - 12

4.2.1 I/O numbers of base unit
4.2.2 I/O numbers of remote station
4.3 I/O Assignment by GX Developer
4.3.1 Purpose of I/O assignment by GX Developer
4.3.2 Concept of I/O assignment using GX Developer
4.3.3 Examples of I/O Number Assignment
4.4 Checking the I/O Numbers
CHAPTER5 MEMORIES AND FILES HANDLED BY CPU MODULE
5.1 Memories by CPU Module
5.1.1 Memory configuration and storable data
5.1.2 Program memory
5.1.3 Standard ROM
5.1.4 Standard ROM program execution (boot run) and writing
5.2 Program File Structure
5.3 File Operation by GX Developer and Handling Precautions
5.3.1 File operation
5.3.2 Precautions for handling files
5.3.3 Memory capacities of files
5.3.4 File size units
CHAPTER6 FUNCTIONS
6.1 Function List
6.2 Safety CPU Operation Mode
6.2.1 Safety CPU operation mode
6.2.2 Checking safety CPU operation mode
6.2.3 Safety CPU operation mode switching
6.2.4 Operation of each function in each safety CPU operation mode and CPU operation status
6.2.5 Online operations that can be executed on the CPU module from GX Developer
6.3 CPU access password
6.4 PLC memory initialization
6.5 Setting to prevent continuous RUN in TEST MODE
6.6 Checking the ROM write count
6.7 Self-diagnostics Function
6.7.1 LED display for error
6.7.2 Cancel the error
6.8 Recording the operation contents and self-diagnostics error occurrence contents (operation
history function)
6.9 Constant scan
• error
6.10 Setting of Output (Y) Status when Changing between STOP and RUN
6.11 Clock Function
6.12 Remote Operation
6.12.1 Remote RUN/STOP
6.12.2 Remote RESET
A - 13

6.12.3 Relationship of remote operation and CPU's RUN/STOP status
6.13 Monitor Function
6.14 Writing in Program during CPU Module RUN
6.14.1 Online change in ladder mode
6.15 Watchdog Timer(WDT)
6.16 Remote password
6.17 CPU Module System Display by GX Developer
6.18 LED Display
6.18.1 Method to turn off the LED
CHAPTER7 COMMUNICATION WITH INTELLIGENT FUNCTION MODULE
7.1 Communication with CC-Link Safety master module
7.2 Communication with CC-Link IE Controller Network Module or MELSECNET/H Module
7.3 Communication with Ethernet Module
7.4 Communication using intelligent function module dedicated instructions
CHAPTER8 PARAMETERS
8.1 PLC Parameters
8.2 Network Parameters
8.3 Remote Password
CHAPTER9 DEVICE EXPLANATION
9.1 Device List
9.2 Internal User Devices
9.2.1 Input (X)
9.2.2 Output (Y)
9.2.3 Internal relay (M)
9.2.4 Annunciator (F)
9.2.5 Edge relay (V)
9.2.6 Link relay (B)
9.2.7 Link special relay (SB)
9.2.8 Timer (T)
9.2.9 Counter (C)
9.2.10 Data register (D)
9.2.11 Link register (W)
9.2.12 Link special register (SW)
9.3 Internal System Devices
9.3.1 Special relay (SM)
9.3.2 Special register (SD)
9.4 Nesting (N)
9.5 Constants
9.5.1 Decimal constant (K)
9.5.2 Hexadecimal constant (H)
A - 14

CHAPTER10 CPU MODULE PROCESSING TIME
10.1 Scan Time
10.1.1 Scan time structure
10.1.2 Time required for each processing included in scan time
10.1.3 Factors that increase the scan time
10.2 Other Processing Times
CHAPTER11 PROCEDURE FOR WRITING PROGRAM TO CPU MODULE
11.1 Items to be examined for program creation
11.2 Procedure for writing program
11.3 Boot run procedure
APPENDICES
Appendix 1 Special Relay List
Appendix 2 Special Register List
Appendix 3 List of Parameter No
Appendix 4 Restrictions on Using CC-Link IE Controller Network Module with Safety CPU Module
Appendix 5 Restrictions on Using MELSECNET/H Module with Safety CPU Module
Appendix 6 Restrictions on Using Ethernet Module with Safety CPU Module
Appendix 7 Dedicated Instructions which can be used in Safety CPU Module
Appendix7.1 List of dedicated instructions
Appendix7.2 Programming using dedicated instructions
Appendix 8 Safety CPU Module Upgrade
Appendix 9 Access Range for Safety CPU Module
Appendix 10 Precautions for Battery Transportation
INDEX
A - 15

ABOUT MANUALS
Introduction Manual
Before constructing or designing the safety-related system, be sure to read
the following manual.
Manual Name
Safety Application Guide
Explains the overview, construction method, laying and wiring examples, and application programs
of the safety-related system.
(Sold separately)
Related Manuals
The following manuals are also related to this product.
If necessary, order them by quoting the details in the tables below.
Manual No.
(Model Code)
SH-080613ENG
(13JR90)
Manual Name
QSCPU User's Manual (Function Explanation, Program Fundamentals)
Explains the functions, programming methods, devices and others that are necessary to create
programs with the QSCPU.
(Sold separately)
QSCPU Programming Manual (Common Instructions)
Explains how to use the sequence instructions, basic instructions, application instructions, and
QSCPU dedicated instructions.
(Sold separately)
CC-Link Safety System Master Module User's Manual
Explains the specifications, procedures and settings before system operation, parameter setting,
and troubleshooting of the QS0J61BT12 CC-Link Safety system master module.
(Sold separately)
CC-Link Safety System Remote I/O Module User's Manual
Explains the specifications, procedures and settings before system operation, parameter setting,
and troubleshooting of the CC-Link Safety system remote I/O module.
(Sold separately)
CC-Link IE Controller Network Reference Manual
Explains the specifications, procedures and settings before system operation, parameter setting,
programming, and troubleshooting of a CC-Link IE controller network.
(Sold separately)
Q Corresponding MELSECNET/H Network System Reference Manual (PLC to PLC
network)
Explains the specifications, procedures and settings before system operation, parameter setting,
programming, and troubleshooting of a MELSECNET/H network system for PLC to PLC network.
(Sold separately)
Q Corresponding Ethernet Interface Module User's Manual (Basic)
Explains the specifications, procedures for data communication with external devices, line
connection (open/close), fixed buffer communication, random access buffer communication, and
troubleshooting of the Ethernet module.
(Sold separately)
Q Corresponding Ethernet Interface Module User's Manual (Application)
Explains the e-mail function, programmable controller CPU status monitoring function,
communication function via CC-Link IE controller network, MELSECNET/H or MELSECNET/10,
communication function using the data link instructions, file transfer function (FTP server) of the
Ethernet module.
(Sold separately)
Manual No.
(Model Code)
SH-080627ENG
(13JR93)
SH-080628ENG
(13JW01)
SH-080600ENG
(13JR88)
SH-080612ENG
(13JR89)
SH-080668ENG
(13JV16)
SH-080049
(13JF92)
SH-080009
(13JL88)
SH-080010
(13JL89)
A - 16
Manual Name
Q Corresponding MELSEC Communication Protocol Reference Manual
Explains the communication methods and control procedures using the MC protocol, which is used
by external devices to read and write data of the programmable controller CPU via the serial
communication module or Ethernet module.
(Sold separately)
GX Developer Version 8 Operating Manual
Explains the online functions of GX Developer, such as the programming, printout, monitoring, and
debugging methods.
(Sold separately)
GX Developer Version 8 Operating Manual (Safety Programmable Controller)
Explains the GX Developer functions added and modified for the compatibility with the safety
programmable controller.
(Sold separately)
Remark
Printed materials are separately available for single item purchase. Order the
manual by quoting the manual number on the table above (Model code).
Manual No.
(Model Code)
SH-080008
(13JF89)
SH-080373E
(13JU41)
SH-080576ENG
(13JU53)
A - 17
HOW THIS MANUAL IS ORGANIZED
Reference destination
A reference destination or
reference manual is marked
.
Chapter heading
The index on the right side of the page
shows the chapter of the open page at a
glance.
A - 18
Section title
The section of the open page is shown at a
glance.

In addition, this manual provides the following explanations.
POINT
Explains the matters to be especially noted, the functions and others related to the
description on that page.
Remark
Provides the reference destination related to the description on that page and the
convenient information.
A - 19
HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL
This manual is prepared for users to understand the hardware specifications of those
modules such as the CPU modules, power supply modules, and base units, maintenance
and inspections of the system, and troubleshooting required when you use QS series
PLCs.
The manual is classified roughly into three sections as shown below.
1) Chapters 1 and 2 Describe the outline of the CPU module and the system
2) Chapters 3 to 7 Describe the general specifications indicating the operating
3) Chapters 8 to 12 Describe the overall maintenance such as the installation of the
configuration.
The basics of the system configuration of CPU module are
described.
environments of the CPU module, power supply module, and base
units, and the performance specifications of these modules.
CPU module, daily inspections, and troubleshooting.
Remark
This manual does not explain the functions of the CPU module.
For these functions, refer to the manual shown below.
QSCPU User's Manual (Function Explanation, Program Fundamentals)
A - 20
GENERIC TERMS AND ABBREVIATIONS
Unless otherwise specified, this manual uses the following generic terms and
abbreviations to explain the QS series CPU modules.
Generic Term/Abbreviation Description
Safety PLC
Standard PLC
QS series Abbreviation for Mitsubishi safety PLC MELSEC-QS series
QS001CPU Abbreviation for the QS001CPU type safety CPU module
CPU module Other name for the QS001CPU
GX Developer
QS034B Abbreviation for the QS034B type safety main base unit
Base unit Other name for the QS034B
QS061P Abbreviation for the QS061P-A1 and QS061P-A2 type safety power supply modules
Power supply module Other name for the QS061P
QS0J61BT12 Abbreviation for the QS0J61BT12 type CC-Link Safety system master module
CC-Link Safety Abbreviation for the CC-Link Safety system
CC-Link Safety master module Other name for the QS061BT12
CC-Link IE controller network
module
MELSECNET/H Abbreviation for the MELSECNET/H network system
MELSECNET/H module
Ethernet Abbreviation for the Ethernet network system
Ethernet module
Intelligent function module
QS0J65BTS2-8D Abbreviation for the QS0J65BTS2-8D CC-Link Safety remote I/O module
QS0J65BTS2-4T Abbreviation for the QS0J65BTS2-4T CC-Link Safety remote I/O module
QS0J65BTB2-12DT Abbreviation for the QS0J65BTB2-12DT type CC-Link Safety remote I/O module
CC-Link Safety remote I/O
module
Q series CPU module
Standard CPU module
Battery Abbreviation for the Q6BAT type battery
Blank cover Abbreviation for the QG60 type blank cover
GOT
Generic term for safety CPU module, safety power supply module, safety main base
unit, CC-Link safety master module and CC-Link safety remote I/O module.
Generic term of each module for MELSEC-Q series, MELSEC-QnA series, MELSEC-A
series and MELSEC-FX series. (Used for distinction from safety PLC.)
General product name for the models SW8D5C-GPPW-E, SW8D5C-GPPW-EA,
SW8D5C-GPPW-EV and SW8D5C-GPPW-EVA
Abbreviation for the QJ71GP21-SX and QJ71GP21S-SX CC-Link IE controller network
module
Abbreviation for the QJ71LP21-25, QJ71LP21S-25, QJ71LP21G, QJ71BR11
MELSECNET/H network module
Abbreviation for the QJ71E71-100, QJ71E71-B5, QJ71E71-B2 Ethernet interface
module
Generic term for the CC-Link Safety master module, CC-Link IE controller network
module, MELSECNET/H module, and Ethernet module
Generic term for the QS0J65BTS2-8D, QS0J65BTS2-4T, QS0J65BTB2-12DT
Generic term for the Q00JCPU, Q00CPU, Q01CPU, Q02CPU, Q02HCPU, Q06HCPU,
Q12HCPU, Q25HCPU, Q12PHCPU, Q25PHCPU, Q12PRHCPU and Q25PRHCPU
modules
Other name for the Q series CPU module (Used for distinction from safety CPU
modules.)
Generic term for the Mitsubishi Graphic Operation Terminal GOT-A*** series, GOT-F***
series and GOT1000 series
A - 21
PRECAUTIONS FOR USE
Precautions for the first use of Q series a CPU module
Precautions on battery
(1) When running the CPU module that has been stored without battery
(2) When running the CPU module that has been stored with battery longer than
When using a CPU module for the first time, the PLC memory needs to be initialized
using GX Developer.
For details of PLC memory initialization, refer to the following manual.
GX Developer Operating Manual (Safety PLC)
When, in the TEST MODE, running the CPU module that has been stored with the
battery removed, the memory needs to be formatted using GX Developer.
( Section 11.4)
the battery life
When, in the TEST MODE, running the CPU module that has been stored with the
battery exceeding its life, the memory needs to be formatted using GX Developer.
( Section 11.5)
A - 22
1
OVERVIEW
CHAPTER1 OVERVIEW
This Manual describes the hardware specifications and handling methods of the QS
Series CPU Module QS001CPU. The Manual also includes descriptions related to the
specifications of the power supply module, base unit and battery.
For the functions, programs, and devices of the QS Series CPU Module, refer to the
manual below.
QSCPU User's Manual (Function Explanation, Program Fundamentals)
1
2
3
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
GENERAL
SPECIFICATIONS
4
5
6
7
CPU MODULE
POWER SUPPLY
MODULE
BASE UNIT
1 - 1
8
BATTERY
CPU MODULE START-
UP PROCEDURES
1
OVERVIEW
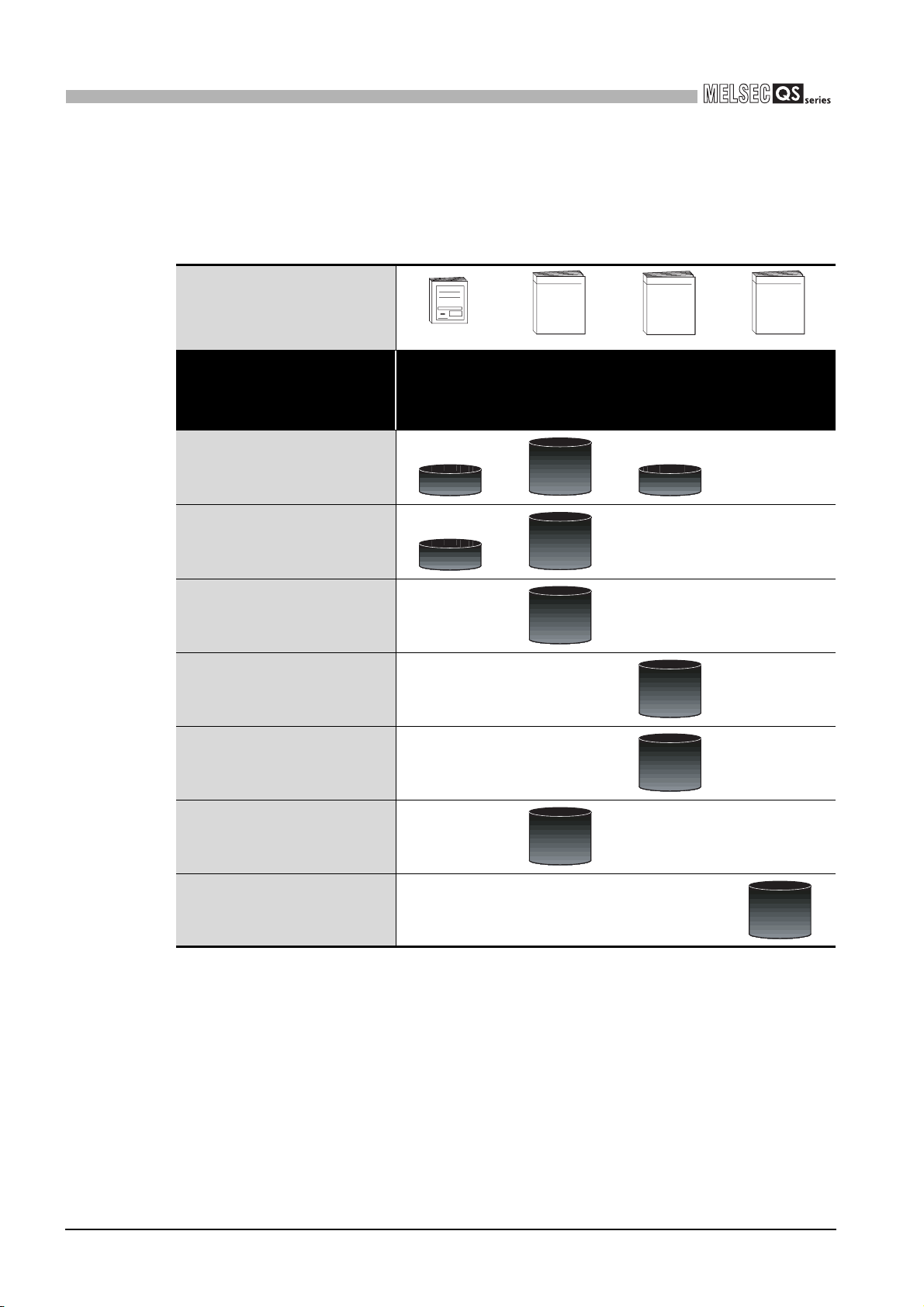
(1) List of QS Series CPU Module manuals
The QS series CPU module manuals are as shown below.
For details such as manual numbers, refer to "About Manuals" in this manual.
Table1.1 List of manuals of QS Series CPU module
Purpose
Confirmation of part names and
specifications of the CPU module
Confirmation of connection methods
for the power supply module,and base
unit
Construction of the CPU system
(confirmation of start-up procedure
and I/O number assignment)
Confirmation of the sequence program
configuration and memory
Hard
ware
(Packed)
QSCPU CPU
Module User's
Manual (Hardware)
Outline
Outline
Maintenance
and Inspection
QSCPU User's
Manual (Hardware
Design,
Maintenance and
inspection)
Details
Details
Details
Program
Fundamentals
QSCPU User's
Manual (Function
Explanation,
Program
Fundamentals)
Outline
Details
Common
Instructions
QSCPU
Programming
Manual (Common
Instruction)
Confirmation of the functions,
parameters, and devices of the CPU
module
Confirmation of the troubleshooting
and error codes
Confirmation of usage of sequence
instructions, basic instructions,
application instructions, etc.
Details
Details
Details
1 - 2
1
OVERVIEW
1.1 Features
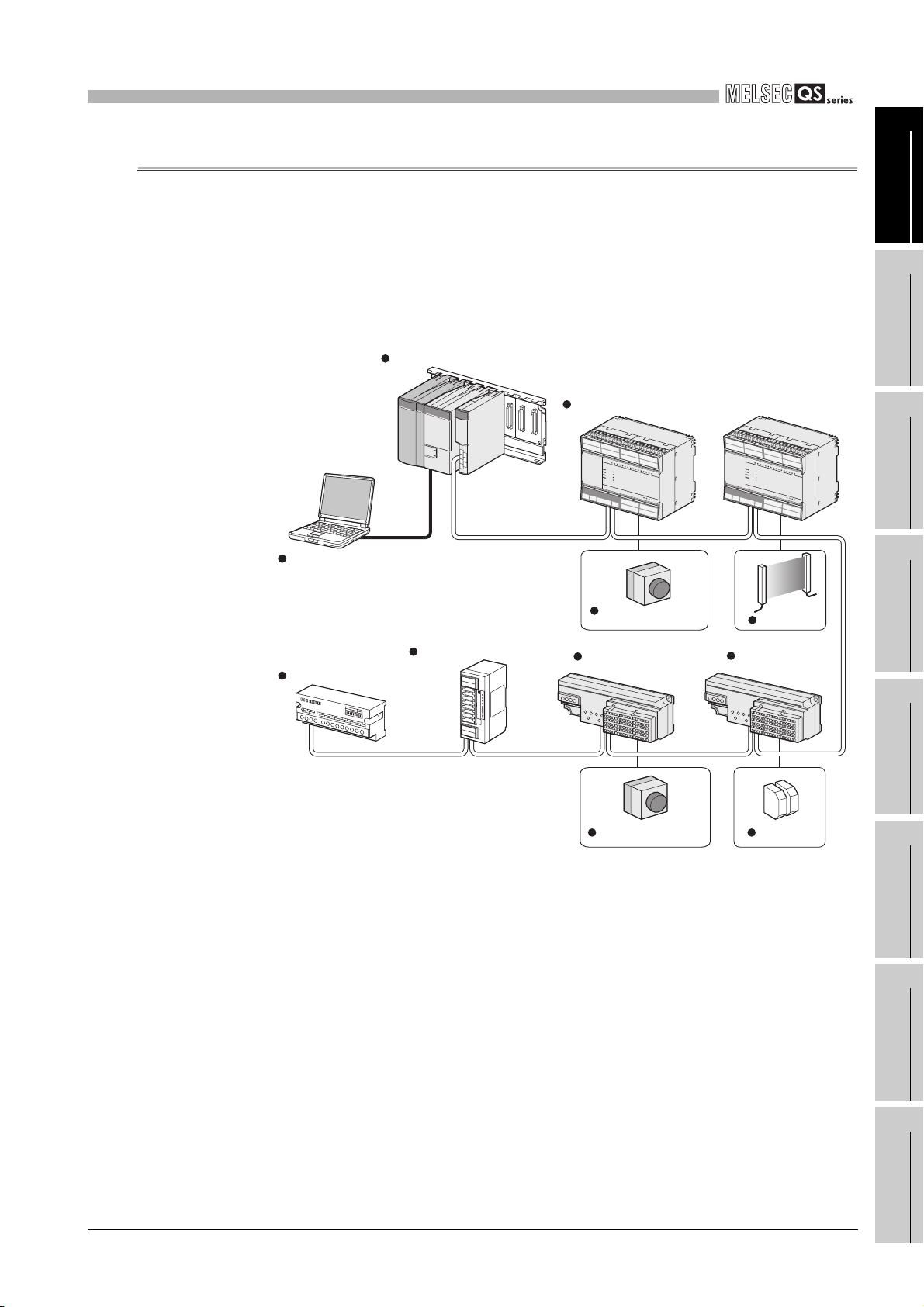
The QS series CPU module has the following new features:
(1) Safety PLC system can be constructed
The QS series programmable controllers have obtained the highest safety level
(IEC61508 SIL3, EN954-1/ISO13849-1 Category 4, IEC62061) applicable to
programmable controllers.
Power supply/CPU/CC-Link Safety master module
1
2
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
GX Developer
(Version 8.40S or later)*1
Standard remote I/O station
CC-Link Safety
Standard Remote device station
Figure 1.1 Safety PLC system
CC-Link Safety remote I/O station
Emergency stop switch
CC-Link Safety
remote I/O station
Emergency stop switch
Light curtain
CC-Link Safety
remote I/O station
Safety relay
3
4
5
6
GENERAL
SPECIFICATIONS
CPU MODULE
POWER SUPPLY
MODULE
* 1 : The available functions vary depending on the versions. For details, refer to Appendix 2.
1.1 Features
1 - 3
7
8
BASE UNIT
BATTERY
CPU MODULE START-
UP PROCEDURES
1
OVERVIEW
(2) The safety CPU operation mode is equipped for safe system operation
The CPU module is equipped with two safety CPU operation modes. "SAFETY
MODE" for safe system operation and "TEST MODE" for system construction and
maintenance.
These two modes prevent the user's erroneous operations for safe system operation.
(a) SAFETY MODE
SAFETY MODE is a mode for safe system operation. This mode prohibits the
write operation from a programming tool and the device test operation during the
system operation.
(b) TEST MODE
TEST MODE is a mode for maintenance. This mode enables the write operation
from a programming tool and the device test operation to debug or maintain the
sequence program.
For the details of operations available in the SAFETY MODE and TEST MODE, refer
to the following manual.
QSCPU User's Manual (Function Explanation, Program Fundamentals)
(3) Enriched operation history and error history
The CPU module can record a total of 3000 details of the CPU module operation by
the user and errors occurred in the CPU module or CC-Link Safety as operation/error
history data.
Recording the details of the CPU module operation by the user into the operation/
error history clarifies the occurrence order of operations and errors.
Troubleshooting becomes easier by confirming the operation/error history.
The contents recorded in the operation/error history are shown in Table1.2.
Table1.2 Recorded contents of operation/error history
Information Contents History Information per Entry
• Operation code
• Operation message
• Operation execution date
• Result code
• Operation attached information
• Error code
• Error message
• Occurrence date
• Error information category (common
information/individual information)
• Error information (common
information/individual information)
Operation
history
information
Error history
information
User's operations for the CPU module are
stored as a history.
(Operations which change the CPU module
status are recorded.)
The following errors are stored as a history.
• Error/failure detected by self-diagnostics
• Hardware error
• Error detected by CC-Link Safety
1 - 4
1.1 Features
1
OVERVIEW
(4) Enhanced RAS
(a) Enhanced memory diagnostics
The memory diagnostics equipped with the CPU module are enhanced.
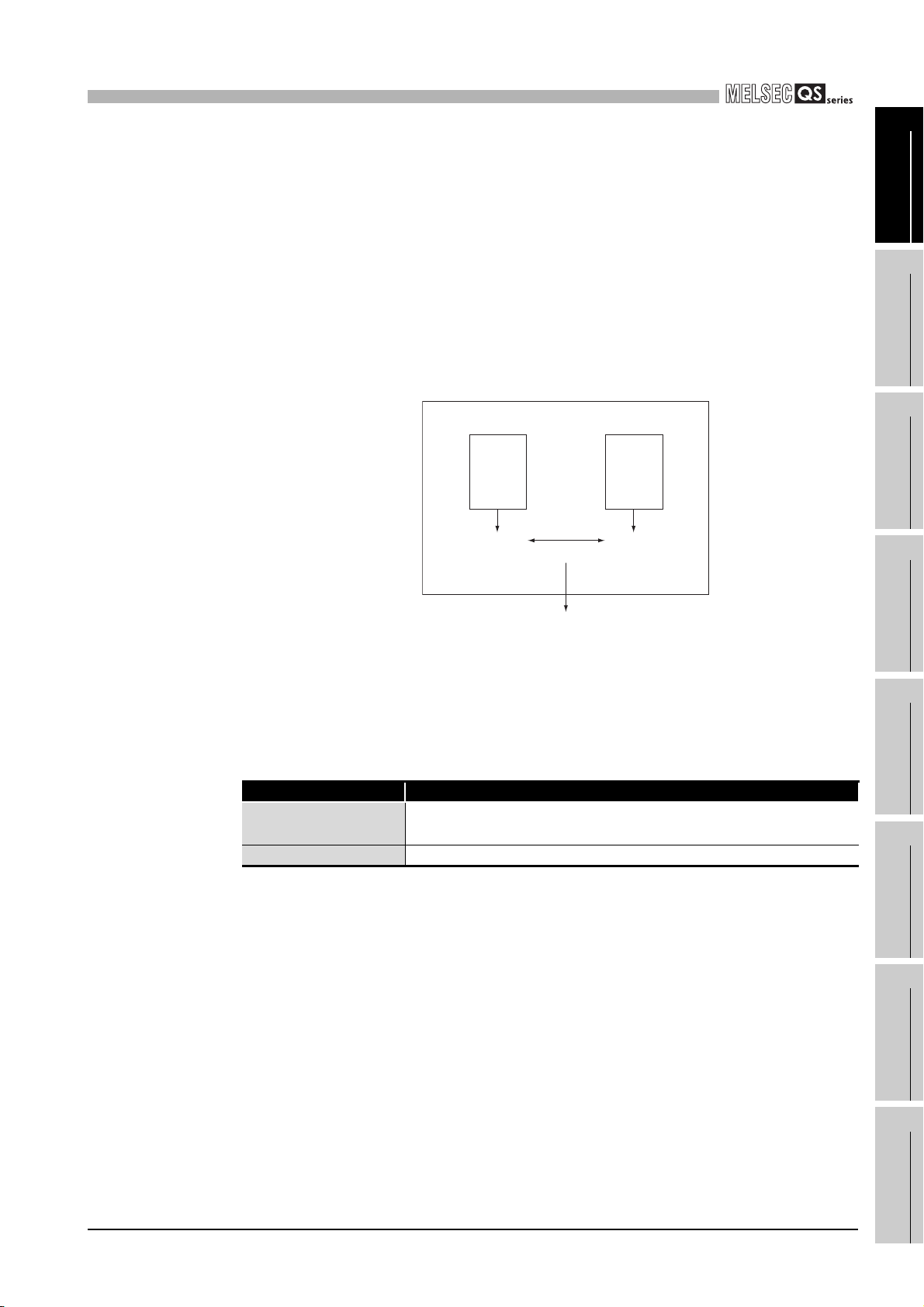
(b) Redundant CPU
The CPU module has two CPUs (CPU A and CPU B). The operation results of
CPU A/CPU B are compared, and output only when the results are matched so
that incorrect outputs can be prevented. (When the compared results are
mismatched, the system stops.)
CPU module
1
2
3
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
CPU
A
Operation
result
Figure 1.2 Redundant CPU
(c) Enhanced hardware diagnostics by hardware circuit
The diagnostic functions of the Table1.3 prevents incorrect outputs when a
hardware error which cannot be detected by the OS occurs.
Table1.3 Hardware diagnostics function added to the QS series CPU module
Diagnostics Diagnosis Contents
Overvoltage/
undervoltage detection
Clock stop detection The input clock stop to the CPU module internal circuit is detected.
Overvoltage or undervoltage is detected for the power supply voltage
provided from the power supply module to the CPU module.
Compare
CPU
B
Operation
result
Output when matched
4
5
6
GENERAL
SPECIFICATIONS
CPU MODULE
POWER SUPPLY
MODULE
1.1 Features
1 - 5
7
8
BASE UNIT
BATTERY
CPU MODULE START-
UP PROCEDURES
1
r
r
OVERVIEW
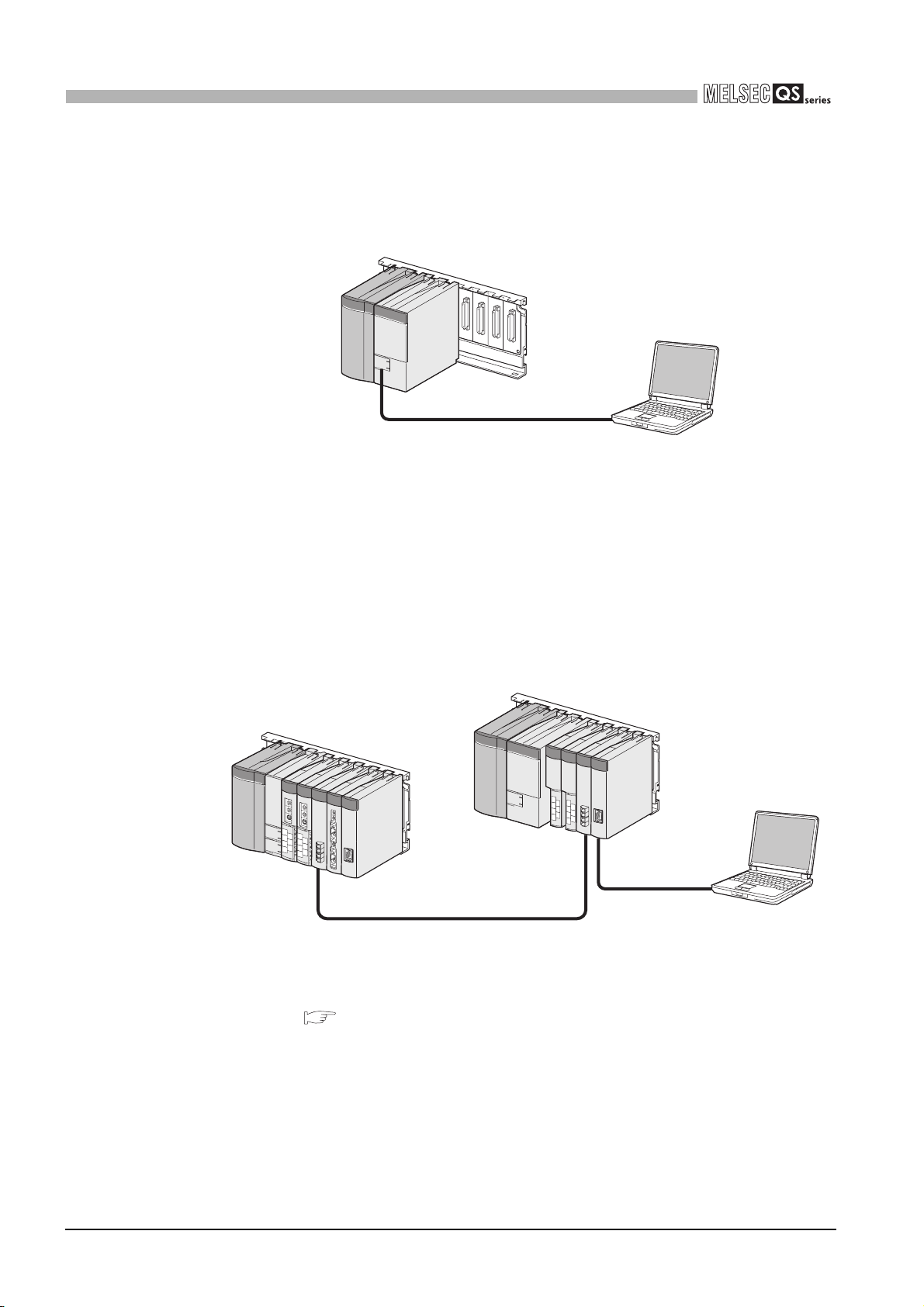
(5) USB interface is equipped
(6) Connectable with personal computers and standard programmable controllers
The CPU module is equipped with the USB interface to communicate with a
programming tool.
USB
Personal compute
Figure 1.3 Connection to a personal computer using USB
The CPU module can read data from the MELSOFT products installed in the personal
computer and also can communicate data between safety programmable controller
and standard programmable controller using dedicated instructions via CC-Link IE
controller network, MELSECNET/H, and/or Ethernet
Besides, the data of ladder monitor, device monitor, and operation/error history in the
safety programmable controller can be read using GOT.
*1
.
1 - 6
1.1 Features
Personal compute
Figure 1.4 Connection with personal computer and standard programmable controller
* 1 : For an access range from GX Developer and a GOT to a safety CPU module, refer to the following
manual.
QSCPU User's Manual (Function Explanation, Program Fundamentals)
* 2 : An access to the CPU module can be restricted by using the remote password function.

2
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
CHAPTER2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
This section describes the system configuration of the QS series CPU module cautions on
use of the system, and configured equipment.
2.1 System Configuration
The following figure shows the system configuration of the safety PLC system when the
QS series CPU module is used.
(1) System configuration when the CPU(QS001CPU) is used
1
2
3
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
GENERAL
SPECIFICATIONS
Battery for a CPU
(Q6BAT)
QS001CPU CPU module
QS034B base unit
Power supply/intelligent function module
Figure 2.1 System configuration
* 1 : For mountable modules, refer to Section 2.1.1 "Precautions for system configuration".
4
CPU MODULE
5
POWER SUPPLY
MODULE
6
*1
BASE UNIT
7
2.1 System Configuration
2 - 1
8
BATTERY
CPU MODULE START-
UP PROCEDURES

2
r
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
(2) System configuration overview
Table2.1 Base unit and power supply module applicable to system configuration
Base unit model name QS034B
Maximum number of monted
modules
Power supply module model
name
Base unit (QS034B)
CPU 0 1 2 3
00 to 0F
CPU modulePower supply module
Figure 2.2 System configuration
QS061P-A1, QS061P-A2
10 to 1F
20 to 2F
4 modules
Slot numbe
I/O number
30 to 3F
Precautions
• The extension base unit cannot be connected.
• The multiple CPU system cannot be configured.
• The modules which can be mounted on the I/O slot are the CC-Link Safety
master module, CC-Link IE controller network module, MELSECNET/H
module, Ethernet module, and blank cover only.
If a module other than the ones mentioned above is mounted, "MODULE
LAYOUT ERROR" (error code: 2125) is detected.
Note, however, that a "MODULE LAYOUT ERROR" is not detected for the
slot where "Empty" has been set in the I/O assignment setting of PLC
parameter.
• GOTs cannot be connected.
2 - 2
2.1 System Configuration

2
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
2.1.1 Precautions for system configuration
(1) Modules mountable on the main base unit
Table2.2 lists the modules that can be mounted on the main base unit.
The number of mounted modules and functions are restricted depending on the
module type.
Table2.2 Modules mountable on the main base unit
Module Model
CPU module • QS001CPU Only one ---
Power supply module
CC-Link Safety master
module
CC-Link IE controller network
module
MELSECNET/H module
Ethernet module
Blank cover • QG60 Up to four ---
• QS061P-A1
• QS061P-A2
• QS0J61BT12 Up to two ---
• QJ71GP21-SX
• QJ71GP21S-SX
• QJ71LP21-25
• QJ71LP21S-25
• QJ71LP21G
• QJ71LP21GE
• QJ71BR11
• QJ71E71-B2
• QJ71E71-B5
• QJ71E71-B100
Number of modules
mounted in one system
Only one (only one of the module
models)
Only one (only one of the models
among CC-Link IE controller network
modules and MELSECNET/H
modules)
Only one (only one of the module
models)
Remarks
• The first five digits of the serial
number are “10041” or higher
• Function version D or later
---
---
---
1
2
3
4
5
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
GENERAL
SPECIFICATIONS
CPU MODULE
2.1 System Configuration
2.1.1 Precautions for system configuration
2 - 3
6
7
8
POWER SUPPLY
MODULE
BASE UNIT
BATTERY
CPU MODULE START-
UP PROCEDURES

2
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
2.2 Configuration of Peripheral Devices
This section describes the configuration of the peripheral devices usable in the safety PLC
system.
QS001CPU
Personal computer
(GX Developer Version 8.40S or later)
USB cable*1
* 1: For details of the USB cable, refer to "About the USB cable (QCPU (Q mode) compatible)" of the
following manual.
GX Developer Operating Manual
Figure 2.3 Configuration of peripheral devices
2 - 4
2.2 Configuration of Peripheral Devices
2.1.1 Precautions for system configuration

2
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
2.3 Confirming Serial No. and Function Version
The serial No. and function version of the CPU module can be confirmed on the rated
plate and GX Developer's system monitor.
1
OVERVIEW
(1) Confirming the serial No. on the rated plate
The rated plate is situated on the side face of the CPU module.
PASSED
MODEL
Serial No. (first 5 digits)
function version
SERIAL
080910000000000-A
Standard symbol for
conformance is described.
MADE IN JAPAN
Figure 2.4 The rated plate
(2) Checking on the front of the module
The serial number written on the rating plate is displayed on the front (at the bottom)
of the module.
2
3
4
5
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
GENERAL
SPECIFICATIONS
CPU MODULE
Q S 0 0 1 C P U
A L I V E
R U N
E R R.
PULL
U S B
T E S T
U S E R
B A T.
Figure 2.5 CPU module front display
090911090910001-B
Serial No.
6
7
8
POWER SUPPLY
MODULE
BASE UNIT
BATTERY
2.3 Confirming Serial No. and Function Version
2 - 5
CPU MODULE START-
UP PROCEDURES

2
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
Remark
The serial number is displayed on the front of the module from March 2008
production.
Products manufactured during switching period may not have the serial number
on the front of the module.
(3) Confirming the serial No. on the system monitor (Product Information List)
To display the System monitor screen, select [Diagnostics] [System monitor] and
click the Product Information List button in GX Developer.
On the system monitor, the serial No. and function version of the intelligent function
module can also be confirmed.
Serial number function version
2 - 6
Figure 2.6 System monitor
POINT
The serial number displayed on the Product information list screen of GX
Developer may differ from that on the rating plate and on the front of the module.
• The serial No. on the rated plate describes the management information
of the product.
• The serial No. displayed on the product information of GX Developer
describes the function information of the product.
The function information of the product is updated when adding functions.
2.3 Confirming Serial No. and Function Version

3
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
CHAPTER3 GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
The performance specifications of PLC are shown in Table3.1.
Table3.1 General specifications
Item Specifications
Operating ambient
temperature
Storage ambient
temperature
Operating ambient
humidity
Storage ambient
humidity
Conforming
Vibration
resistance
Shock resistance
Operating
ambience
Operating
*3
altitude
Installation location Inside control panel
Overvoltage
category
Pollution level
Equipment
category
*1
*2
to
JIS B 3502,
IEC 61131-2
Conforming to JIS B 3502, IEC 61131-2 (147 m/s
Under
intermittent
vibration
Under
continuous
vibration
directions respectively by sine half-wave pulse)
5 to 95%RH , non-condensing
5 to 95%RH , non-condensing
0 to 55
-40 to 75
Frequency
range
5 to 9Hz ----
9 to 150Hz
5 to 9Hz ----
9 to 150Hz
No corrosive gases
2000m (6562ft.) max.
II max.
2 max.
Class I
Constant
acceleration
9.8m/s
4.9m/s
2
, duration of action 11ms, three times in X, Y, Z
Half amplitude Sweep count
3.5mm
(0.14inch)
2
2
----
1.75mm
(0.07inch)
----
10 times each in
X, Y, Z
directions
respectively
1
2
3
4
5
6
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
GENERAL
SPECIFICATIONS
CPU MODULE
POWER SUPPLY
MODULE
*1 : This indicates the section of the power supply to which the equipment is assumed to be connected between the public
electrical power distribution network and the machinery within premises. Category II applies to equipment for which
electrical power is supplied from fixed facilities.
The surge voltage withstand level for up to the rated voltage of 300 V is 2500 V.
*2 : This index indicates the degree to which conductive material is generated in terms of the environment in which the
equipment is used.
Pollution level 2 is when only non-conductive pollution occurs. A temporary conductivity caused by condensing must be
expected occasionally.
*3 : Do not use or store the PLC under pressure higher than the atmospheric pressure of altitude 0m.
Doing so can cause a malfunction.
When using the PLC under pressure, please contact your sales representative.
3 - 1
7
8
BASE UNIT
BATTERY
CPU MODULE START-
UP PROCEDURES

4
CPU MODULE
CHAPTER4 CPU MODULE
4.1 Performance Specifications
Table4.1 shows the performance specifications of the CPU module.
Table4.1 Performance Specifications
Item QS001CPU Remarks
Control method Repetitive operation of stored program ----
I/O control mode Refresh mode ---Program
language
Processing speed
(sequence
instruction)
Constant scan
(Function for keeping regular scan
time)
Program capacity
Memory
*1
capacity
Max. number of
files stored
Sequence control
language
LD X0
MOV D0 D1
*1
Program memory
(drive 0)
Standard ROM
(drive 4)
Program memory
Standard ROM
Relay symbol language, function block. ----
0.10 s
0.35 s
1 to 2000ms
(Setting available in1ms unit.)
14k steps
(56k bytes)
128k bytes ----
128k bytes ----
*2
3
*2
3
----
----
Setting by parameters.
----
----
----
No. of times of writing data into the
standard ROM
No. of I/O device points 6144 points(X/Y0 to 17FF)
No. of I/O points 1024 points(X/Y0 to 3FF)
*1 : The maximum number of executable sequence steps is as shown below.(Program capacity) - (File heade size (default: 34 steps))
For the details, refer to the manual below.
QSCPU User's Manual (Function Explanation, Program Fundamentals)
*2 : Each of parameter, sequence program, SFC program, and device comment files can be stored.
Max.100000 times ----
No. of points
usable on
program
No. of points
accessible to the
actual I/O module
4 - 1
4.1 Performance Specifications

4
CPU MODULE
Table4.1 Performance Specifications (Continue)
Item QS001CPU Remarks
Internal relay [M] 6144 points by default (M0-6143) (changeable)
Link relay [B] 2048 points by default (B0 to 7FF) (changeable)
512 points by default (T0 to 511) (changeable)
(Sharing of low- and high-speed timers)
The low- and high-speed timers are specified by the instructions.
Timer [T]
Retentive timer [ST]
No. of device points
Counter [C] Normal counter: 512 points by default (C0 to 511) (changeable)
Data register [D] 6144 points by default (D0 to 6143) (changeable)
Link register [W] 2048 points by default (W0 to 7FF) (changeable)
Annunciator [F] 1024 points by default (F0 to 1023) (changeable)
Edge relay [V] 1024 points by default (V0 to 1023) (changeable)
Link special relay [SB] 1536 points (SB0 to 5FF)
Link special register [SW] 1536 points (SW0 to 5FF)
Special relay [SM] 5120 points (SM0 to 5119)
Special register [SD] 5120 points (SD0 to 5119)
RUN/PAUSE contact
Timer function
Allowable instantaneous power failure
period
5VDC internal current consumption 0.43A ----
H 98mm (3.86inch) ----
External dimensions
Weight 0.29kg ----
Protection of degree IP2X ----
W 55.2mm (2.17inch) ----
D 113.8mm (4.48inch) ----
The measurement unit of the low- and high-speed timers is set up by
parameters.
(Low-speed timer: 1 to 1000ms, 1ms unit, 100ms by default)
(High-speed timer: 0.1 to 100ms, 0.1ms unit, 10ms by default)
0 point by default
(sharing of the low- and high-speed retentive timers) (changeable)
The low- and high-speed retentive timers are specified
by the instructions.
The measurement unit of the low- and high-speed retentive timers
is set up by parameters.
(Low-speed retentive timer: 1 to 1000ms, 1ms unit, 100ms by default)
(High-speed retentive timer: 0.1 to 100ms, 0.1ms unit, 10ms by default)
One contact can be set up in X0 to 17FF for each of RUN. No PAUSE
contact.
Year, month, date, hour, minute, second and day-of-week
(leap year automatically identified)
Accuracy: -3.18 to +5.25s (TYP.+2.14s)/d at 0
Accuracy: -3.18 to +2.59s (TYP.+2.07s)/d at 25
Accuracy: -12.97 to +3.63s (TYP.-3.16s)/d at 55
Varies depending on the power supply module. ----
The number of points
can be changed within
the setting range.
( QSCPU User's
Manual
(Function
Explanation,
Program
Fundamentals)
The number of device
points is fixed.
Setting by parameters.
----
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
GENERAL
SPECIFICATIONS
CPU MODULE
POWER SUPPLY
MODULE
BASE UNIT
Remark
For the general specifications, refer to CHAPTER 3.
4.1 Performance Specifications
4 - 2
8
BATTERY
CPU MODULE START-
UP PROCEDURES

4
W
y
CPU MODULE
4.2 Part Names
1)
QS001CPU
2)
4)
5)
hen opening the cover, put
our finger here.
ALIVE
RUN
ERR.
PULL
USB
TEST
USER
BAT.
15)
1)
3)
6)
7)
13)
14)
10)
9)
ALIVE
RUN
ERR.
TEST
USER
BAT.
BAT.
RESET RUN
PULL
STOP
Figure 4.1 Front face Figure 4.2 With front cover open
11)
12)
8)
Figure 4.3 Side Face
4 - 3
4.2 Part Names

4
*1
*1
*1
*1
(
)
CPU MODULE
No. Name Application
1) Module fixing hook Hook used to fix the module to the base unit.
"ALIVE" LED
2)
(Green)
"TEST" LED
3)
(Yellow)
"RUN" LED
4)
(Green)
"ERR." LED
5)
(Red)
On :
Off : When the hardware watchdog timer error is detected
Indicates the operating mode of the CPU module.
On :
Flash : When TEST MODE is switched to SAFETY MODE
Off : SAFETY MODE
Indicates the operating status of the CPU module.
On :
Off : During stop in "STOP" or when the error which stops the operation is detected
Flash : When parameters/program is written during STOP and the RUN/STOP/RESET
On :
Off : Normal
Flash : When the self-diagnostics error that will stop operation is detected
Table4.2 Part Names
Normal
("ERR." LED is On.)
TEST MODE
The "TEST" LED turns off after reset.
(Flash interval: On 200ms/Off 200ms)
During operation in "RUN"
switch is moved from "STOP" to "RUN"
(Flash interval: On 200ms/Off 200ms)
When the self-diagnostics error that will not stop operation, other than a battery
error, is detected
(Flash interval: On 200ms/Off 200ms)
When the reset operation is performed
(Flash interval: On 60ms/Off 60ms)
*1
1
2
3
4
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
GENERAL
SPECIFICATIONS
CPU MODULE
"USER" LED
6)
(Red)
"BAT." LED
7)
(Yellow)
8) Module loading lever Used to load the module to the safety base unit.
9)
USB connector
10)
RUN/STOP/RESET switch
11) Module fixing screw Screw used to fix a module to the base unit. (M3 screw)
12) Module fixing latch Latch used to fix a module to the base unit.
13) Battery Backup battery for the power failure compensation function of program memory.
14) Battery connector pin
15) Serial number display Displays the serial number on the rating plate.
*1 : Turns On during the initial processing (self-diagnostics, etc.) right after the power-on or reset cancel.
*2 : When a cable is to be connected to the USB connector at all times, clamp the cable to prevent a loose connection,
shifting, or disconnection by pulling due to carelessness.
*3 : Operate the RUN/STOP/RESET switche with your fingertips.
Do not use any tool such as a screwdriver because the switch part might be damaged.
*2
On :
Off : Normal
On :
Off : Normal
Connector used to connect to the USB compatible peripheral devices.
(Connector type B)
Can be connected by the USB dedicated cable.
RUN : Executes sequence program operation.
*3
STOP : Stops sequence program operation.
RESET :
For connection of the battery lead wires (When shipped from the factory, the lead wires
are disconnected from the connector to prevent the battery from discharging.)
When the anunciator (F) turns ON
When a battery error has occurred due to the CPU battery voltage drop
Performs hardware reset and operation initialization when an operation
error occurs.
Section 4.4
4.2 Part Names
*1
4 - 4
5
6
7
8
POWER SUPPLY
MODULE
BASE UNIT
BATTERY
CPU MODULE START-
UP PROCEDURES

4
CPU MODULE
4.3 Switch Operation after Writing a Program
Programs can be written to the CPU module in either the STOP or RUN status.
(1) When writing a program with the CPU module set to "STOP"
(a) Set the RUN/STOP/RESET switch to STOP.
The "RUN" LED turns Off, and the module is placed in the STOP status.
Write a program from GX Developer to the CPU module in the STOP status.
(b) Reset with the RUN/STOP/RESET switch.
The CPU module is reset. ( Section 4.4)
(c) Set the RUN/STOP/RESET switch to RUN.
The "RUN" LED turns on, and the CPU module is placed in the RUN status.
(2) When writing a program during RUN
When writing a program during RUN, the operation for the RUN/STOP/RESET switch
is not required.
POINT
1. The program modified online during boot operation is written to the program
memory.
After making online program change, also write the program to the standard
ROM of the boot source memory. If the program is not written in the standard
ROM, the old program will be executed at the next boot operation.
For details of the boot operation, refer to the manual below.
QSCPU User's Manual (Function Explanation, Program Fundamentals)
2. To stop the CPU module, the remote operation of GX Developer can also be
used.
In this case, the operation for the RUN/STOP/RESET switch is not required.
For details on the remote operation of GX Developer, refer to the following
manual.
GX Developer Version 8 Operating Manual
4 - 5
4.3 Switch Operation after Writing a Program

4
CPU MODULE
4.4 Reset Operation
For the CPU module, the RUN/STOP/RESET switch of the CPU module is used to switch
between the "RUN status" and "STOP status" and to perform "RESET operation".
When using the RUN/STOP/RESET switch to reset the CPU module, moving the RUN/
STOP/RESET switch to the reset position will not reset it immediately.
POINT
Perform reset operation with the RUN/STOP/RESET switch as shown in Figure 4.4.
Hold the RUN/STOP/RESET switch in the RESET position until reset processing
is complete (the flashing ERR. LED turns off).
If you release your hand from the RUN/STOP/RESET switch during reset
processing (during rapid flashing of ERR. LED), the switch will return to the STOP
position and reset processing cannot be completed.
Start
Hold the RUN/STOP/RESET switch
.......................
in the "RESET" position.
Reset operation is started using
the RUN/STOP/RESET switch.
1
2
3
4
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
GENERAL
SPECIFICATIONS
STOP
RESET
The ERR. LED flashes several times
Return the RUN/STOP/RESET
switch to the "STOP" position.
RUN
(3 to 4 times) rapidly.
ALIVE
RUN
ERR.
The "ERR. LED" turns off .
ALIVE
RUN
ERR.
RUN/STOP/RESET
switch
TEST
USER
BAT.
flashing
TEST
USER
BAT.
Off.
.......................
.......................
Reset is accepted and reset
processing is performed.
Reset is completed.
Reset is canceled.
5
6
7
CPU MODULE
POWER SUPPLY
MODULE
BASE UNIT
STOP
RUN
RESET
Termination , completed , end
RUN/STOP/RESET
switch
Figure 4.4 Reset Operation
:
Releasing your hand from the
RUN/STOP/RESET switch returns it
to the STOP position.
4.4 Reset Operation
4 - 6
8
BATTERY
CPU MODULE START-
UP PROCEDURES

4
CPU MODULE
POINT
Operate the RUN/STOP/RESET switch with your fingertips.
Do not use any tool such as a screwdriver because the switch part might be
damaged.
4 - 7
4.4 Reset Operation

5
POWER SUPPLY MODULE
CHAPTER5 POWER SUPPLY MODULE
This section describes the specifications of the power supply modules applicable for the
PLC system and how to select the most suitable module.
5.1 Specifications
Table5.1 shows the specifications of the power supply modules.
1
OVERVIEW
2
Table5.1 Power supply module specifications
Item
Base loading position QS series power supply module loading slot
Applicable base unit QS034B
Input power supply
Input frequency
Input voltage distortion factor
Max. input apparent power 125VA
Inrush current
Rated output
current
Overcurrent
protection
Overvoltage
protection
Efficiency 70% or more
Allowable momentary power
failure period
Dielectric withstand voltage
Insulation resistance
Noise durability
Operation indication LED indication (Normal: On (green), Error: Off)
Fuse Built-in (Unchangeable by user)
*1
*2
5VDC 6A
5VDC 6.6A or more
5VDC 5.5 to 6.5V
*3
Across inputs/LG and outputs/FG
1780VAC rms/3 cycles (2000 m (6562 ft.))
Across inputs/LG and outputs/FG, across inputs and LG, across outputs and FG 10M
or more by insulation resistance tester
• By noise simulator of 1500Vp-p noise voltage, 1 s noise width and 25 to 60Hz noise
frequency
• Noise voltage IEC61000-4-4, 2kV
QS061P-A1 QS061P-A2
100 to 120VAC
(85 to 132VAC)
Performance Specifications
+10%
-15%
50/60Hz 5%
Within 5% ( Section 5.2)
20A within 8ms
Within 20ms
*4
Across inputs/LG and outputs/FG
2830VAC rms/3 cycles (2000 m (6562 ft.))
200 to 240VAC
(170 to 264VAC)
+10%
-15%
3
4
5
6
7
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
GENERAL
SPECIFICATIONS
CPU MODULE
POWER SUPPLY
MODULE
BASE UNIT
5.1 Specifications
5 - 1
8
BATTERY
CPU MODULE START-
UP PROCEDURES

5
POWER SUPPLY MODULE
Table5.1 Power supply module specifications (Continue)
Item
Application
Rated switching
voltage, current
Minimum switching
load
Response time OFF to ON: 10ms max. ON to OFF: 12ms max.
Life
Contact output section
Surge suppressor No
Fuse No
Terminal screw size M3.5 screw
Applicable wire size
Applicable solderless terminal RAV1.25 to 3.5, RAV2 to 3.5 (0.8mm or less thick)
Applicable tightening torque 0.66 to 0.89N•m
External
dimensions
Weight 0.40kg
H 98mm (3.86inch)
W 55.2mm (2.17inch)
D 115mm (4.53inch)
Electrical : More than 100 thousand times at rated switching voltage, current
QS061P-A1 QS061P-A2
Performance Specifications
contact ( Section 5.3)
ERR.
24VDC, 0.5A
5VDC, 1mA
Mechanical : More than 20 million times
0.75 to 2mm
2
POINT
*1: Overcurrent protection
The overcurrent protection function shuts off the 5 VDC circuit and stops the system if
the current flowing in the circuit exceeds the specified value.
The LED of the power supply module is turned off or lights up in dim green when
voltage is lowered. If this device is activated, switch the input power supply OFF and
eliminate the cause such as insufficient current capacity or short. Then, a few minutes
later, switch it ON to restart the system.
The initial start for the system takes place when the current value becomes normal.
*2: Overvoltage protection
The overvoltage protection function shuts off the 5 VDC circuit and stops the system if
a voltage of 5.5 VDC or above is applied to the circuit.
When this device is activated, the power supply module LED is turned OFF.
For restart of the system, turn OFF the input power supply, and then turn ON in a few
minutes. This allows the system to start up with initial start. If the system doesn't start
up and a LED indication remains off, replacement of a power supply module is
required.
*3: Allowable momentary power failure period
• An instantaneous power failure lasting less than 20ms will cause AC down to be
detected, but operation will continue.
• An instantaneous power failure lasting in excess of 20ms may cause the
operation to continue or initial start to take place depending on the power supply
load.
*4: Inrush current
When power is switched on again immediately (within 5 seconds) after power-off, an
inrush current of more than the specified value (2ms or less) may flow. Reapply power
5 or more seconds after power-off. When selecting a fuse and breaker in the external
circuit, take account of the blowout, detection characteristics and above matters.
5 - 2
5.1 Specifications

5
POWER SUPPLY MODULE
5.2 Precaution when connecting the uninterruptive power supply
Be sure of the following terms when connecting the QS Series CPU Module system to the
uninterruptive power supply (abbreviated as UPS hereafter):
1
OVERVIEW
As for UPS, use the online power system or online interactive system with a voltage
distortion rate of 5% or less.
For the UPS of the commercial online power system, use Mitsubishi Electric's F Series
UPS (serial number P or later) (Ex.: FW-F10-0.3K/0.5K).
Do not use any UPS of the commercial online power system other than the F series
mentioned above.
2
3
4
5
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
GENERAL
SPECIFICATIONS
CPU MODULE
5.2 Precaution when connecting the uninterruptive power supply
5 - 3
6
7
8
POWER SUPPLY
MODULE
BASE UNIT
BATTERY
CPU MODULE START-
UP PROCEDURES

5
POWER SUPPLY MODULE
5.3 Names of Parts and Settings
The names of the parts of each power supply module are described below.
QS061P-A1 100 to 120VAC input, 5VDC 6A output
QS061P-A2 200 to 240VAC input, 5VDC 6A output
<For QS061P-A1>
1)7)
QS061P-A1
8)
POWER
Figure 5.1 Power supply module
QS061P-A1
POWER
6)
2)
3)
4)
9),10)
5)
5 - 4
5.3 Names of Parts and Settings

5
POWER SUPPLY MODULE
Table5.2 Part names
No. Name Application
On (green): Normal (5VDC output, instantaneous power failure within 20ms)
Off : • AC power supply is ON, however, the power supply module is out of
order.
1) "POWER" LED
• Turned ON when the whole system operates normally.
2) ERR. terminal
3) FG terminal
4) LG terminal
5) Terminal screw M3.5 screw
6) Terminal cover Protective cover of the terminal block
7) Module fixing screw
8) Module loading lever Used to load the module to the base unit.
9) Power input terminal Power input terminal for the QS061P-A1 and connected to a 100VAC power supply.
10) Power input terminal Power input terminal for the QS061P-A2 and connected to a 200VAC power supply.
• Turns OFF (opens) when the AC power is not input, a stop error (including a reset)
occurs in the CPU module, or the fuse is blown.
Ground terminal connected to the shielding pattern of the printed-circuit board.
This terminal is functional grounding terminal.
Grounding for the power filter. The potential of the QS061P-A1 and QS061P-A2 ter-
minals are one-half of the input voltage.
This terminal is protective grounding terminal.
Used to fix the module to the base unit.
M3 screw (Tightening torque : 0.36 to 0.48N•m)
(5VDC error, overload, internal circuit failure, fuse blown)
• AC power supply is not ON.
• Power failure (including an instantaneous power failure of 20ms or
more)
1
2
3
4
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
GENERAL
SPECIFICATIONS
CPU MODULE
POINT
1. The QS061P-A1 is dedicated for inputting a voltage of 100 VAC.
Do not input a voltage of 200 VAC into it or trouble may occur on the
QS061P-A1.
Table5.3 Precaution
Power module
type
QS061P-A1 Operates normally.
Power supply module does not
QS061P-A2
2. Ensure that the earth terminals LG and FG are grounded.
3. ERR.
terminal cannot be used as a safety output.
Connect the cable for ERR.
cause trouble.
CPU module cannot be
operated.
100VAC 200VAC
contact of 30m or less in length in a control panel.
Supply power voltage
Power supply module causes
trouble.
Operates normally.
5
6
7
8
POWER SUPPLY
MODULE
BASE UNIT
BATTERY
5.3 Names of Parts and Settings
5 - 5
CPU MODULE START-
UP PROCEDURES

6
BASE UNIT
CHAPTER6 BASE UNIT
This section describes the specifications of the base units used in the PLC
system.
6.1 Specification
The base unit is a unit to which the CPU module, power supply module and/or intelligent
function module are installed.
Table6.1 Base unit specifications
Item
Number of I/O modules installed 4
Possibility of extension Disable
Applicable module QS series modules
5 VDC internal current consumption 0.10A
Mounting hole size
H 98mm (3.86inch)
External dimensions
Weight 0.28kg
Attachment
DIN rail mounting Adapter type Q6DIN2
W 245mm (9.65inch)
D 44.1mm (1.74inch)
Mounting screw M4 14 4 pieces (DIN rail mounting adapter to be sold separately)
M4 screw hole or 4.5 hole (for M4 screw)
Type
QS034B
6 - 1
6.1 Specification

6
BASE UNIT
6.2 Part Names
1)
The names of the parts of the base unit are described below.
4) 3)
OUT
a1
b1
2)
5)
MODEL
SERIAL
MADE IN JAPAN
POWER
PASSED
BD992C202H01
Figure 6.1 Base unit (QS034B)
1
OVERVIEW
2
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
I/O3I/O2I/O1I/O0CPU
3
GENERAL
SPECIFICATIONS
4
Table6.2 Part Names
No. Name Application
1) Base cover Cover for protecting the printed-circuit board of the base unit
Connector for installing the QS series power supply module, CPU module and
2) Module connector
3) Module fixing screw hole
4) Base mounting hole Hole for mounting this base unit onto the panel of the control panel (for M4 screw)
5) DIN rail adapter mounting hole Hole for mounting DIN rail adapter
intelligent function module.
For the reserved connector where no module is mounted, attach a supplied
connector cover or a blank cover (QG60) to prevent entry of dust.
Screw hole for fixing the module to the base unit. Screw size: M3 12
5
6
7
CPU MODULE
POWER SUPPLY
MODULE
BASE UNIT
6.2 Part Names
6 - 2
8
BATTERY
CPU MODULE START-
UP PROCEDURES

7
BATTERY
CHAPTER7 BATTERY
This section describes the specifications of the batteries available for the QS Series CPU
Module and how to handle them.
7.1 Battery (Q6BAT)
Batteries (Q6BAT) are installed in the CPU module to retain data of the program memory,
and Error•operation history in case of power failure.
7.1.1 Battery Specifications
This section describes the specifications of the battery used for the CPU module.Note1
Table7.1 Battery Specifications
Item
Classification Manganese dioxide lithium primary battery
Initial voltage 3.0V
Nominal current 1800mAh
Storage life Actually 5 years (room temperature)
Total power failure
time
Application Power failure backup for program memory, operation/error history
Remark
1. Refer to Section 11.3.1 for the battery life.
2. For the battery directive in EU member states, refer to Appendix 4.
Type
Q6BAT
Section 11.3.1.
Note1
7 - 1
7.1 Battery (Q6BAT)
7.1.1 Battery Specifications

7
BAT.
BATTERY
7.1.2 Installation of Battery
The battery for the CPU module is shipped with its connector disconnected. Connect
the connector as follows.
Refer to Section 11.3 for the service life of the battery and how to replace the battery.
1
OVERVIEW
2
Open the CPU module front cover.
Confirm that the battery is loaded
correctly.
Insert the battery connector into the
connector pin on the case. Be sure that
the insertion direction is correct.
Completed
Figure 7.1 Q6BAT battery setting procedure
Connector
CPU module
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
.
T
BA
LL
PU
STOP
RUN
RESET
3
GENERAL
SPECIFICATIONS
4
CPU MODULE
5
7.1 Battery (Q6BAT)
7.1.2 Installation of Battery
7 - 2
6
7
8
POWER SUPPLY
MODULE
BASE UNIT
BATTERY
CPU MODULE START-
UP PROCEDURES

8
k
u
CPU MODULE START-UP PROCEDURES
CHAPTER8 CPU MODULE START-UP PROCEDURES
This chapter describes the procedure for starting up the CPU module.
It is assumed that programs and parameters have been created separately.
8.1 Procedure before Operating in SAFETY MODE
This section describes the procedure before operating the CPU module in SAFETY
MODE.
The default operation mode of the CPU module is TEST MODE. Switch the mode to
SAFETY MODE to operate the CPU module.
Start
Installing a base unit
Install a base unit to a panel.
Installing modules
Install modules required for the system configuration to the base unit.
Fixing modules by screws
Fix the modules to the base unit with screws to prevent the displacement by vibrations or
other causes.
Wiring
1) Wire the power supply to the power supply module.
2) Install wiring between the CC-Link Safety master module and the CC-Link Safety remote
I/O module.
3) Wire external device(s) to the CC-Link Safety remote I/O module.
4) Install wiring between network modules.
Making initial settings of modules
1) Set the RUN/STOP/RESET switch of the CPU module to the STOP position.
(Set the CPU module to stop status.)
2) Make switch settings for the MELSECNET/H module.
(To the next page)
• • • CHAPTER 10
• • • CHAPTER 2,
CHAPTER 10
• • • CHAPTER 10
• • • CHAPTER 10
• • • CHAPTER 4
MELSECNET/H Networ
System Reference Man
(PLC to PLC network)
8 - 1
8.1 Procedure before Operating in SAFETY MODE

8
CPU MODULE START-UP PROCEDURES
1
(Continued from the previous page)
Installing a battery
Install a battery to the CPU module.
Powering ON the power supply module
Confirm the following items of the safety PLC system, and then turn on the power supply.
Wiring of the power supply
Power supply voltage
Operating status of the CPU module Stop status (The RUN/STOP/RESET switch is
in the STOP position.)
Confirming the CPU module LEDs
Confirm that the "ALIVE" LED and "TEST" LED of the CPU module are on.
(Confirm that the CPU module is in TEST MODE.)
Connecting a personal computer in which GX Developer is installed
1) Start up GX Developer on the personal computer in which GX Developer is installed.
2) Connect the personal computer with GX Developer installed, to the CPU module.
Initializing the PLC memory of the CPU module
Initialize the PLC memory of the CPU module with GX Developer.
Registering the CPU access password with the CPU module
Register the CPU access password with the CPU module by using GX Developer.
Setting clock data and clearing history data of the CPU module
When the safety CPU module is operated for the first time after purchase, take the following
actions for the CPU module with GX Developer.
Set the clock with "Clock setup".
Clear the error history of the CPU module with "PLC diagnostics".
1
Writing the parameters and programs to the CPU module
Write the parameters and user programs created by GX Developer to the CPU module.
• • • CHAPTER 7
• • • CHAPTER 4,
CHAPTER 5,
CHAPTER 10
• • • CHAPTER 4
• • • GX Developer Version 8
Operating Manual
• • • GX Developer Version 8
Operating Manual
(Safety PLC)
• • • GX Developer Version 8
Operating Manual
(Safety PLC)
• • • GX Developer Version 8
Operating Manual
GX Developer Version 8
Operating Manual
(Safety PLC)
• • • GX Developer Version 8
Operating Manual
2
3
4
5
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
GENERAL
SPECIFICATIONS
CPU MODULE
POWER SUPPLY
MODULE
Restarting the system
Turn off and then turn on the system power supply, or reset the CPU module.
Running the CPU module
Set the RUN/STOP/RESET switch of the CPU module to the RUN position.
Confirm that the "ALIVE" LED, "RUN" LED, and "TEST" LED of the CPU module are on.
Checking the user program operation
Check the user program operation, cables, and inputs/outputs.
When the "ERR." LED of the CPU module is on or flashing, identify the error cause by the
diagnostics*
When the error is related to the parameters or programs, correct them.
2
of GX Developer to eliminate the error cause.
(To the next page)
*2: The following types of diagnostics are available.
PLC diagnostics
Ethernet diagnostics
CC IE Control diagnostics
MELSECNET diagnostics
CC-Link / CC-Link/LT diagnostics
System monitor
8.1 Procedure before Operating in SAFETY MODE
• • • CHAPTER 4
• • • CHAPTER 4
• • • CHAPTER 4
8 - 2
6
7
8
BASE UNIT
BATTERY
CPU MODULE START-
UP PROCEDURES

8
CPU MODULE START-UP PROCEDURES
(Continued from the previous page)
Stopping the CPU module
Set the RUN/STOP/RESET switch of the CPU module to the STOP position.
Switching to SAFETY MODE
Switch the mode from TEST MODE to SAFETY MODE by selecting the menu option,
"Switch safety CPU operation mode", in GX Developer.
Confirming the CPU module LEDs
After the operation mode has been switched from TEST MODE to SAFETY MODE using
GX Developer, confirm that the "TEST" LED of the CPU module is flashing while the
"ALIVE" LED is on.
Restarting the system
Turn the system power supply OFF and then ON, or perform the reset operation on the
CPU module.
Running the CPU module
Set the RUN/STOP/RESET switch of the CPU module to the RUN position.
Confirm that the "ALIVE" LED and "RUN" LED of the CPU module are on, and the "TEST"
LED is off.
YES
Correct the program?
• • • CHAPTER 4
• • • GX Developer Version 8
Operating Manual
(Safety PLC)
• • • CHAPTER 4
• • • CHAPTER 4
• • • CHAPTER 4
NO
End
Stopping the CPU module
Set the RUN/STOP/RESET switch of the CPU module to the STOP position.
Switching to TEST MODE
Switch the mode from SAFETY MODE to TEST MODE by selecting the menu option,
"Switch safety CPU operation mode", in GX Developer.
Confirming the CPU module LEDs
After the operation mode has been switched from SAFETY MODE to TEST MODE using
GX Developer, confirm that both the "TEST" LED and "ALIVE" LED of the CPU module are on.
Correcting the program
Correct the program with GX Developer.
1
• • • CHAPTER 4
• • •
Operating Manual
(Safety PLC)
• • • CHAPTER 4
• • •
Operating Manual
GX Developer Version 8
GX Developer Version 8
8 - 3
8.1 Procedure before Operating in SAFETY MODE

9
EMC AND LOW VOLTAGE DIRECTIVES
CHAPTER9 EMC AND LOW VOLTAGE DIRECTIVES
For the products sold in European countries, the conformance to the EMC Directive, which
is one of the European directives, has been a legal obligation since 1996. Also,
conformance to the Low Voltage Directive, another European Directive, has been a legal
obligation since 1997.
Manufacturers who recognize their products must conform to the EMC and Low Voltage
Directives are required to declare that their products conform to these Directives and put a
"CE mark" on their products.
9.1 Requirements for Conformance to EMC Directive
The EMC Directive specifies that products placed on the market must "be so constructed
that they do not cause excessive electromagnetic interference (emissions) and are not
unduly affected by electromagnetic interference (immunity)".
The applicable products are requested to meet these requirements. The Section 9.1.1
through Section 9.1.5 summarize the precautions on conformance to the EMC Directive of
the machinery constructed using the MELSEC-QS series PLCs.
The details of these precautions has been prepared based on the control requirements
and the applicable standards control. However, we will not assure that the overall
machinery manufactured according to these details conforms to the above-mentioned
directives. The method of conformance to the EMC Directive and the judgment on whether
or not the machinery conforms to the EMC Directive must be determined finally by the
manufacturer of the machinery.
9
EMC AND LOW
VOLTAGE
10
LOADING AND
11
MAINTENANCE AND
12
DIRECTIVES
INSTALLATION
INSPECTION
TROUBLESHOOTING APPENDICES INDEX
9.1.1 Standards relevant to the EMC Directive
The standards relevant to the EMC Directive are listed in Table9.1.
Table9.1 Standards relevant to the EMC Directive
Specification Test Item Test Details Standard Value
30M-230MHz QP:
40dB V/m (10m (32.81 ft.) in
*1
: 79dB
: 66dB
: 73dB
: 60dB
EN61131-2 :
2003
EN55011(CISPR11)
Radiated emission
EN55011(CISPR11)
Conducted emission
Radio waves from the product
*2
are measured.
Noise from the product to the
power line is measured.
measurement range)
230M-1000MHz QP:
47dB V/m(10m (32.81 ft.) in
measurement range)
150k-500kHz QP
Mean
500k-30MHz QP
Mean
*1
9.1 Requirements for Conformance to EMC Directive
9.1.1 Standards relevant to the EMC Directive
9 - 1

9
EMC AND LOW VOLTAGE DIRECTIVES
Table9.1 Standards relevant to the EMC Directive (Continue)
Specification Test Item Test Details Standard Value
EN61000-4-2
Electrostatic discharge
immunity
EN61000-4-3
Radiated electromagnetic
field immunity
EN61000-4-8
Power frequency
magnetic field immunity
EN61000-4-4
Electrical fast transient/
burst immunity
EN61131-2 :
2003
EN61000-4-5
Surge immunity
EN61000-4-6
Conducted disturbances
immunity
*1: QP : Quasi-peak value, Mean : Average value
*2: The PLC is an open type device (device installed to another device) and must be installed in a conductive control panel.
The tests for the corresponding items were performed while the PLC was installed inside a control panel.
*2
*2
*2
*2
*2
Immunity test in which
electrostatic is applied to the
cabinet of the equipment.
Immunity test in which electric
fields are irradiated to the
product.
Immunity test in which the
product is installed in the
magnetic field of the induction
*2
coil.
Immunity test in which burst
noise is applied to the power line
and signal line.
Immunity test in which lightning
surge is applied to the power line
and signal line.
Immunity test in which high
frequency noise is applied to the
power line and signal line.
8kV Air discharge
4kV Contact discharge
1.4GHz-2.0GHz, 80-1000MHz, 10V/m,
80%AM modulation 1kHz
50Hz/60Hz, 30A/m
AC power line: 2kV
DC power line: 2kV
DC I/O, analog, communication line: 1kV
AC power line:
Common mode 2kV, differential
mode 1kV
DC power line:
Common mode 1kV, differential
mode 0.5kV
DC I/O, analog, communication (shielded):
Common mode 1kV
DC I/O, analog (unshielded):
Common mode 0.5kV, differential
mode 0.5kV
Communication (unshielded):
1kV
0.15-80MHz, 80%AM modulation 1kHz,
3Vrms
9 - 2
9.1 Requirements for Conformance to EMC Directive
9.1.1 Standards relevant to the EMC Directive

9
EMC AND LOW VOLTAGE DIRECTIVES
9.1.2 Installation instructions for EMC Directive
The PLC is open equipment and must be installed within a control panel for use.*
This not only ensures safety but also ensures effective shielding of PLC-generated
electromagnetic noise.
* : CC-Link Safety remote station should be used having the control panel installed.
(1) Control panel
• Use a conductive control panel.
• When attaching the control panel's top plate or base plate, mask painting and
weld so that good surface contact can be made between the panel and plate.
• To ensure good electrical contact with the control panel, mask the paint on the
installation bolts of the inner plate in the control panel so that contact between
surfaces can be ensured over the widest possible area.
• Earth the control panel with a thick wire so that a low impedance connection to
ground can be ensured even at high frequencies.
• Holes made in the control panel must be 10 cm (3.94 inch) diameter or less. If
the holes are 10 cm (3.94 inch) or larger, radio frequency noise may be emitted.
In addition, because radio waves leak through a clearance between the control
panel door and the main unit, reduce the clearance as much as practicable.
The leakage of radio waves can be suppressed by the direct application of an
EMI gasket on the paint surface.
9
EMC AND LOW
VOLTAGE
10
LOADING AND
11
MAINTENANCE AND
12
DIRECTIVES
INSTALLATION
INSPECTION
Our tests have been carried out on a panel having the damping characteristics of
37 dB max. and 30 dB mean (measured by 3 m method with 30 to 300 MHz).
(2) Connection of power and earth wires
Earthing and power supply wires for the PLC system must be connected as described
below.
• Provide an earthing point near the power supply module. Earth the power
supply's LG and FG terminals (LG : Line Ground, FG : Frame Ground) with the
thickest and shortest wire possible. (The wire length must be 30 cm (11.81 inch)
or shorter.) The LG and FG terminals function is to pass the noise generated in
the PLC system to the ground, so an impedance that is as low as possible must
be ensured. As the wires are used to relieve the noise, the wire itself carries a
large noise content and thus short wiring means that the wire is prevented from
acting as an antenna.
• The earth wire led from the earthing point must be twisted with the power supply
wires. By twisting with the earthing wire, noise flowing from the power supply
wires can be relieved to the earthing. However, if a filter is installed on the power
supply wires, the wires and the earthing wire may not need to be twisted.
TROUBLESHOOTING APPENDICES INDEX
9.1 Requirements for Conformance to EMC Directive
9.1.2 Installation instructions for EMC Directive
9 - 3

9
EMC AND LOW VOLTAGE DIRECTIVES
9.1.3 Cables
The cables pulled out from the control panel contain a high frequency noise component.
On the outside of the control panel, therefore, they serve as antennas to emit noise.
To prevent noise emission, use shielded cables when pulling out the cables which are
connected to CC-Link Safety master module, MELSECNET/H module, Ethernet module,
and CC-Link Safety remote I/O module and using them outside of the control panel.
The use of shielded cables also increases noise immunity.
For signal lines (including common line) of CC-Link Safety master module, MELSECNET/
H module, Ethernet module, and CC-Link Safety remote I/O module, the noise immunity
satisfies the standard value on the condition that the shielded cables are used for
grounding.
If shielded cables are not used or not grounded correctly, the noise immunity does not
meet the specified requirements.
(1) Shield grounding processing of shielded cables
• Provide a grounding point on the shielded cable as near the module as possible
so that the wiring between the module and grounding point is not induced
electromagnetically by the other parts of wiring on the cable.
• Take appropriate measures so that the exposed shield part of the shielded cable,
where the cable jacket was partly removed, is grounded to the control panel on
the wildest contact surface.
A clamp may also be used as shown in Figure 9.2.
In this case, however, a mask painting is required for the inner wall of the control
panel which comes into contact with the clamp.
Screw
Shield part
Mask painting
Figure 9.1 Part to be exposed Figure 9.2 Shield grounding (Good example)
Note) If a wire is soldered onto the shield part of the shielded cable for grounding
as shown below, the high-frequency impedance rises, resulting in a loss of
shield effect.
Shield cable
Wire
Solderless terminal
Figure 9.3 Shield grounding (Bad example)
Clamp
Shield cable
9 - 4
9.1 Requirements for Conformance to EMC Directive
9.1.3 Cables

9
EMC AND LOW VOLTAGE DIRECTIVES
(2) MELSECNET/H module
Be sure to use double-shielded coaxial cables (MITSUBISHI CABLE INDUSTRIES,
LTD.: 5C-2V-CCY) for the coaxial cables of MELSECNET/H module. Radiated noise
in the range of 30HMz or higher can be suppressed by using double-shielded coaxial
cables. Ground the double-shielded coaxial cable by connecting its outer shield to the
ground.
9
EMC AND LOW
VOLTAGE
10
DIRECTIVES
Shield
Figure 9.4 Double-shielded coaxial cable grounding
Refer to (1) for the shield grounding processing.
Earth here
(3) Ethernet module
Precautions for using AUI cables, twisted pair cables, and coaxial cables are
described below.
• Be sure to ground the AUI cables
the AUI cable is of the shielded type, ground the exposed shield section of the
cable, where the cable jacket was partly removed as shown in Figure 9.5, on the
wildest contact surface.
AUI cable
Shield
Figure 9.5 AUI cable grounding
Refer to (1) for the shield grounding processing.
* 1 : Make sure to install a ferrite core for the cable.
The ZCAT2032 ferrite core manufactured by TDK is recommended.
*1
connected to the 10BASE5 connectors. Since
LOADING AND
11
MAINTENANCE AND
12
INSTALLATION
INSPECTION
TROUBLESHOOTING APPENDICES INDEX
Use shielded twisted pair cables for the twisted pair cables connected to the 10BASET/100BASE-TX connectors. Ground the exposed shield section of the shielded
twisted pair cable, where the cable jacket was partly removed as shown in Figure 9.6,
on the wildest contact surface.
Shielded twisted pair cable
Shield
Figure 9.6 Shielded twisted pair cable groundng
Refer to (1) for the shield grounding processing.
9.1 Requirements for Conformance to EMC Directive
9.1.3 Cables
9 - 5

9
EMC AND LOW VOLTAGE DIRECTIVES
Be sure to use double-shielded coaxial cables for the coaxial cables*2 connected to
the 10BASE2 connectors. Ground the double-shielded coaxial cable by connecting its
outer shield to the ground
Shield
Figure 9.7 SDouble-shielded coaxial cable grounding
Refer to (1) for the shield grounding processing.
* 1 : Make sure to install a ferrite core for the cable.
The ZCAT2032 ferrite core manufactured by TDK is recommended.
(4) I/O signal lines and other communication cables
If the I/O signal lines (including common line) and other communication cables (such
as CC-Link Safety) are pulled out from the control panel, be sure to ground the shieldsections of the cables as described in (1).
9.1.4 Power Supply Module
Always ground the LG and FG terminals after short-circuiting them.
Ground here
9 - 6
9.1 Requirements for Conformance to EMC Directive
9.1.4 Power Supply Module

9
EMC AND LOW VOLTAGE DIRECTIVES
9.1.5 Others
(1) Ferrite core
A ferrite core has the effect of reducing conduction noise in around 10MHz band and
radiated noise in the 30MHz to 100MHz band.
It is recommended to fit ferrite cores if shielded cables pulled out of the panel do not
provide sufficient shielding effects or if the emission of conduction noise from the
power supply line has to be suppressed.
It is also recommended to fit a ferrite core to the USB cable which connects the CPU
and the personal computer as measures against noise.
Regarding the number of winding to the ferrite core, the more the better. The two turns
or more is recommended as the number of winding.
9
EMC AND LOW
VOLTAGE
10
LOADING AND
11
MAINTENANCE AND
DIRECTIVES
INSTALLATION
INSPECTION
Figure 9.8 For number of winding is two turns or more
Note that the ferrite cores should be fitted to the cables in the position immediately
before they are pulled out of the panel. If the fitting position is improper, the ferrite will
not produce any effect.
12
TROUBLESHOOTING APPENDICES INDEX
9.1 Requirements for Conformance to EMC Directive
9.1.5 Others
9 - 7

9
EMC AND LOW VOLTAGE DIRECTIVES
(2) Noise filter (power supply line filter)
A noise filter is a component which has an effect on conducted noise.
It is not required to fit the noise filter to the power supply line, but fitting it can further
suppress noise.
(The noise filter has the effect of reducing conducted noise of 10 MHz or less.)
The precautions required when installing a noise filter are described below.
• Do not bundle the wires on the input side and output side of the noise filter. When
bundled, the output side noise will be induced into the input side wires from which
the noise was filtered.
Input side
(power supply side)
Induction
Filter
Output side
(device side)
The noise will be included when the
input and output wires are bundled.
Figure 9.9 Precautions on noise filter
• Earth the noise filter earthing terminal to the control cabinet with the shortest wire
possible (approx. 10 cm (3.94 inch)).
Remark
Table9.2 Noise filer specifications
Noise Filter Model Name FN343-3/01 FN660-6/06 ZHC2203-11
Manufacturer SCHAFFNER SCHAFFNER TDK
Rated current 3A 6A 3A
Rated voltage 250V
Input side
(power supply side)
Filter
Output side
(device side)
Separate and lay the input
and output wires.
9 - 8
9.1 Requirements for Conformance to EMC Directive
9.1.5 Others

9
EMC AND LOW VOLTAGE DIRECTIVES
9.2 Requirement to Conform to the Low Voltage Directive
The Low Voltage Directive requires each device that operates with the power supply
ranging from 50 to 1000VAC and 75 to 1500VDC to satisfy the safety requirements.
In Section 9.2.1 to Section 9.2.6, cautions on installation and wiring of the MELSEC-QS
series PLC to conform to the Low Voltage Directive are described.
These descriptions are based on the requirements and standards of the regulation,
however, it does not guarantee that the entire machinery manufactured based on the
descriptions conforms to the above-mentioned directive. The method and judgment for the
conformity to the low voltage directive must be left to the manufacturer's own discretion.
9.2.1 Standard applied for MELSEC-QS series PLC
The standard applied for MELSEC-QS series PLC is EN61131-2 safety of devices used in
measurement rooms, control rooms, or laboratories.
The MELSEC-QS series PLC modules which operate at the rated voltage of 50VAC/
75VDC or above are also developed to conform to the above standard.
The modules which operate at the rated voltage of less than 50VAC/75VDC are out of the
Low Voltage Directive application range.
For products with the CE mark, refer to the "Standard Compliance" menu of the
MELFANSweb homepage.
9
EMC AND LOW
VOLTAGE
10
LOADING AND
11
MAINTENANCE AND
12
DIRECTIVES
INSTALLATION
INSPECTION
9.2.2 MELSEC-QS series PLC selection
(1) Power supply module
There are dangerous voltages (voltages higher than 42.4V peak) inside the power
supply modules of the 100/200VAC rated input voltages. Therefore, the CE marked
models are enhanced in insulation internally between the primary and secondary.
(2) CPU module, base unit
Using 5VDC circuits inside, the above modules are out of the Low Voltage Directive
application range.
(3) CC-Link Safety master module, CC-Link IE controller network module,
MELSECNET/H module, Ethernet module
These modules are out of the scope of the Low Voltage Directive because the rated
voltage is 24VDC or less.
TROUBLESHOOTING APPENDICES INDEX
9.2 Requirement to Conform to the Low Voltage Directive
9.2.1 Standard applied for MELSEC-QS series PLC
9 - 9

9
EMC AND LOW VOLTAGE DIRECTIVES
9.2.3 Power supply
The insulation specification of the power supply module was designed assuming
installation category II. Be sure to use the installation category II power supply to the PLC.
The installation category indicates the durability level against surge voltage generated by
a thunderbolt. Category I has the lowest durability; category IV has the highest durability.
Category IV Category III Category II Category I
Figure 9.10 Installation category for power supply module
Category II indicates a power supply whose voltage has been reduced by two or more
levels of isolating transformers from the public power distribution.
9.2.4 Control panel
Because the PLC is an open device (a device designed to be stored within another
module), be sure to use it after storing in the control panel.*
* : Also, each network remote station needs to be installed inside the control panel.
(1) Electrical shock prevention
The control panel must be handled as shown below to protect a person who does not
have adequate knowledge of electricity from an electric shock.
• Lock the control panel so that only those who are trained and have acquired
enough knowledge of electric facilities can open the control panel.
• The control panel must have a structure which automatically stops the power
supply when the box is opened.
• For electric shock protection, use IP20 or greater control panel.
9 - 10
9.2 Requirement to Conform to the Low Voltage Directive
9.2.3 Power supply

9
EMC AND LOW VOLTAGE DIRECTIVES
(2) Dustproof and waterproof features
The control panel also has the dustproof and waterproof functions. Insufficient
dustproof and waterproof features lower the insulation withstand voltage, resulting in
insulation destruction.
The insulation in our PLC is designed to cope with the pollution level 2, so use in an
environment with pollustion level 2 or below.
Pollution level 1 : An environment where the air is dry and conductive dust
does not exist.
Pollution level 2 : An environment where conductive dust
does not usually exist, but occasional temporary
conductivity occurs due to the accumulated dust.
Generally, this is the level for inside the control box
equivalent to IP54 in a control room or on the floor of a
typical factory.
Pollution level 3 : An environment where conductive dust exits and
conductivity may be generated due to the accumulated
dust.
An environment for a typical factory floor.
Pollution level 4 : Continuous conductivity may occur due to rain, snow, etc.
An outdoor environment.
9
EMC AND LOW
VOLTAGE
10
LOADING AND
11
MAINTENANCE AND
12
DIRECTIVES
INSTALLATION
INSPECTION
As shown above, the PLC can realize the pollution level 2 when stored in a control
panel equivalent to IP54.
TROUBLESHOOTING APPENDICES INDEX
9.2 Requirement to Conform to the Low Voltage Directive
9.2.4 Control panel
9 - 11

9
EMC AND LOW VOLTAGE DIRECTIVES
9.2.5 Grounding
There are the following two different grounding terminals.
Use either grounding terminal in an earthed status.
Protective grounding : Maintains the electrical safety of the PLC and improves the
noise resistance.
Functional grounding : Improves the noise resistance.
9.2.6 External wiring
(1) 24VDC external power supply
This power supply must include a reinforced insulation for 24VDC circuit to prevent
dangerous voltage for CC-Link Safety remote I/O module.
(2) External devices
When a device with a hazardous voltage circuit is externally connected to the PLC,
use the device whose interface circuit section to the PLC has the reinforced insulation
against the hazardous voltage circuit.
(3) Reinforced insulation
The reinforced insulation covers the withstand voltages shown in Table9.3.
Table9.3 Reinforced Insulation Withstand Voltage
(Installation Category II, source : IEC664)
Rated voltage of hazardous
voltage area
150VAC or below 2500V
300VAC or below 4000V
Surge withstand voltage
(1.2/50 s)
9 - 12
9.2 Requirement to Conform to the Low Voltage Directive
9.2.5 Grounding

10
LOADING AND INSTALLATION
CHAPTER10 LOADING AND INSTALLATION
In order to increase the reliability of the system and exploit the maximum performance of
its functions, this section describes the methods and precautions for the mounting and
installation of the system.
9
EMC AND LOW
VOLTAGE
10
DIRECTIVES
DANGER
When a safety PLC detects an error in an external power supply or a fail-
ure in PLC main module, it turns off all the outputs.
Create an external circuit to securely stop the power of hazard by turning
off the outputs.Incorrect configuration may result in an accident.
Create short current protection for a safety relay, and a protection circuit
such as a fuse, and breaker, outside a safety PLC.
When data/program change, or status control is performed from a PC to
a running safety PLC, create an interlock circuit outside the sequence
program and safety PLC to ensure that the whole system always operates safely.
For the operations to a safety PLC, pay full attention to safety by reading
the relevant manuals carefully, and establishing the operating procedure.
Furthermore, for the online operations performed from a PC to a safety
CPU module, the corrective actions of the whole system should be predetermined in case that a communication error occurs due to a cable
connection fault, etc.
All output signals from a safety CPU module to the CC-Link Safety sys-
tem master module are prohibited to use.
These signals can be found in the CC-Link Safety System Master Module User's Manual.
Do not turn ON or OFF these signals by sequence program, since turning ON/OFF these output signals of the PLC system may cause malfunctions and safety operation cannot be guaranteed.
When a safety remote I/O module has detected a CC-Link Safety error, it
turns off all the outputs.
Note that the outputs in a sequence program are not automatically
turned off.
If a CC-Link Safety error has been detected, create a sequence program
that turns off the outputs in the program.
If the CC-Link Safety is restored with the outputs on, it may suddenly
operate and result in an accident.
LOADING AND
11
MAINTENANCE AND
12
INSTALLATION
INSPECTION
TROUBLESHOOTING APPENDICES INDEX
To inhibit restart without manual operation after safety functions was
performed and outputs were turned OFF, create an interlock program
which uses a reset button for restart.
10 - 1

10
LOADING AND INSTALLATION
CAUTION
Do not bunch the wires of external devices or communication cables
together with the main circuit or power lines, or install them close to each
other.They should be installed 100 mm (3.94 inch) or more from each
other.Not doing so could result in noise that would cause erroneous
operation.
10 - 2

10
10.1 Calculating Heat Generation of PLC
LOADING AND INSTALLATION
The ambient temperature inside the panel storing the PLC must be suppressed to an
ambient temperature of 55 or less, which is specified for the PLC.
For the design of a heat releasing panel, it is necessary to know the average power
consumption (heating value) of the devices and instruments stored inside.
Here the method of obtaining the average power consumption of the PLC system is
described.
From the power consumption, calculate a rise in ambient temperature inside the panel.
How to calculate average power consumption
The power consuming parts of the PLC are roughly classified into six blocks as shown
below.
9
EMC AND LOW
VOLTAGE
10
LOADING AND
11
DIRECTIVES
INSTALLATION
(1) Power consumption of power supply module
The power conversion efficiency of the power supply module is approx. 70 %, while
30 % of the output power is consumed as heat. As a result, 3/7 of the output power is
the power consumption.
Therefore the calculation formula is as follows.
3
PW =
W
I
5V
×(I5v×5) (W)
7
: Current consumption of logic 5 VDC circuit of each module
(2) Total power consumption for 5VDC logic circuits of all modules
(including CPU module)
The power consumption of the 5 VDC output circuit section of the power supply
module is the power consumption of each module (including the current consumption
of the base unit).
W
= I5V5 (W)
5V
The total of the power consumption values calculated for each block becomes the power
consumption of the overall sequencer system.
W = WPW+W
5V
MAINTENANCE AND
12
INSPECTION
TROUBLESHOOTING APPENDICES INDEX
From this overall power consumption (W), calculate the heating value and a rise in
ambient temperature inside the panel.
The outline of the calculation formula for a rise in ambient temperature inside the panel is
shown below.
W
=
T
C
UA
W : Power consumption of overall sequencer system (value obtained above)
A : Surface area inside the panel
U : When the ambient temperature inside the panel is uniformed by a fan........ 6
When air inside the panel is not circulated ................................................... 4
10.1 Calculating Heat Generation of PLC
10 - 3

10
LOADING AND INSTALLATION
POINT
If the temperature inside the panel has exceeded the specified range, it is
recommended to install a heat exchanger to the panel to lower the temperature.
If a normal ventilating fan is used, dust will be sucked into the PLC together with
the external air, and it may affect the performance of the PLC.
(3) Example of calculation of average power consumption
(a) System configuration
QS061P-A1 QS001CPU
QS034
QS0J61BT12
Figure 10.1 System configuration
(b) 5 VDC current consumption of each module
QS001CPU : 0.43(A)
QS0J61BT12 : 0.46(A)
QS034B : 0.10(A)
(c) Power consumption of power supply module
W
PW = 3/7 (0.43 + 0.46 + 0.10) 5 = 2.12(W)
(d) Total power consumption for 5 VDC logic circuits of all module
W
5V = (0.43 + 0.46 + 0.10) 5 = 4.95(W)
(e) Power consumption of overall system
W = 2.12 + 4.95 = 7.07(W)
10 - 4
10.1 Calculating Heat Generation of PLC

10
10.2 Module Installation
LOADING AND INSTALLATION
9
10.2.1 Precaution on installation
CAUTION
Use a safety PLC in the environment that meets the general specifica-
tions described in this manual.
Using this PLC in an environment outside the range of the general specifications could result in electric shock, fire, erroneous operation, and
damage to or deterioration of the product
While pressing the installation lever located at the bottom of module,
insert the module fixing tab into the fixing hole in the base unit until it
stops.
Then, securely mount the module with the fixing hole as a supporting
point.Incorrect loading of the module can cause a failure or drop.
Secure the module to the base unit with screws.Tighten the screw in the
specified torque range.If the screws are too loose, it may cause a drop of
the screw or module.
Over tightening may cause a drop due to the damage of the screw or
module.
Completely turn off the externally supplied power used in the system
before mounting or removingthe module.
Not doing so could result in damage to the product.
EMC AND LOW
VOLTAGE
10
LOADING AND
11
MAINTENANCE AND
12
DIRECTIVES
INSTALLATION
INSPECTION
TROUBLESHOOTING APPENDICES INDEX
Do not directly touch the module's conductive parts or electronic compo-
nents.
Doing so may cause malfunctions or a failure.
10.2 Module Installation
10.2.1 Precaution on installation
10 - 5

10
LOADING AND INSTALLATION
This section gives instructions for handling the CPU, and power supply modules, base unit
and so on.
• Do not drop the module case and main module or subject them to strong impact.
• Do not remove modules' printed circuit boards from the enclosure in order to
avoid changes in operation.
• Tighten the screws such as module fixing screws within the following ranges.
Location of Screw Tightening Torque Range
Module fixing screw (M3 12 screw)
Power supply module terminal screw (M3.5 screw) 0.66 to 0.89N•m
* 1 The module can be easily fixed onto the base unit using the hook at the top of the module.
However, it is recommended to secure the module with the module fixing screw if the module is
subject to significant vibration.
• Be sure to install a power supply module in the power supply installation slot of
QS034B.
Install a base unit (by screwing) in the following procedure.
Table10.1 Tightening torque range
*1
0.36 to 0.48N•m
1) Fit the two base unit top mounting screws into the enclosure.
Panel
Figure 10.2 Install a base unit
2) Place the right-hand side notch of the base unit onto the right-hand side screw.
Panel
Figure 10.3 Install a base unit
3) Place the left-hand side pear-shaped hole onto the left-hand side screw.
10 - 6
Panel
Figure 10.4 Install a base unit
10.2 Module Installation
10.2.1 Precaution on installation

10
LOADING AND INSTALLATION
4) Fit the mounting screws into the holes at the bottom of the base unit, and then
retighten the 4 mounting screws.
Note1 : Install the base unit to a panel, with no module loaded in the right-end
slot.
Remove the base unit after unloading the module from the right-end
slot.
Note the following points when mounting a DIN rail.
Mounting a DIN rail needs special adaptors (optional), which are to be user-prepared.
(a) Applicable adaptor types
For QS034B : Q6DIN2
Table10.2 Parts included with dinrail mounting adaptors included parts
9
EMC AND LOW
VOLTAGE
10
LOADING AND
11
DIRECTIVES
INSTALLATION
DIN rail mounting
adaptors
Q6DIN2 23222
Adaptor(Large) Adaptor(small)
(b) Adaptor installation method
Quantity of included parts
Mounting screw
(M5 10)
Square washer Stopper
MAINTENANCE AND
12
The way to install the adaptors for mounting a DIN rail to the base unit is given in
Figure 10.5.
Base unit rear
Place the hook of the adaptor
(small) in the lower hole.
Push the top of the adaptor
(small) far enough until it
"clicks".
INSPECTION
TROUBLESHOOTING APPENDICES INDEX
Insert the adaptor (large) into the grooves of
the base unit from below.
Push the bottom of the adaptor (large) far enough
until it "clicks".
Figure 10.5 Adaptor installation method
10.2.1 Precaution on installation
10.2 Module Installation
10 - 7

10
LOADING AND INSTALLATION
(c) Applicable DIN rail types (IEC 60715)
TH35-7.5Fe
TH35-7.5AI
TH35-15Fe
(d) DIN rail mounting screw intervals
When using either the TH35-7.5Fe or TH35-7.5Al DIN rail, rail mounting screws
should be inserted in 200 mm (7.88 inch) interrals or less in order to ensure that
the rail has sufficient strength.
DIN rail
35mm
(1.38 inch)
PPP
Figure 10.6 DIN rail mounting screw intervals
DIN rail mounting screw
(obtained by user)
P=200mm (7.88 inch) or less
When installing the DIN rail in a large vibration and/or shock prone environment,
insert the mounting screws in 200mm interrals or less by the following method
show below.
Screw the DIN rail in two places using the mounting screws and square washers
included with the adaptors in ‘Position A’ (bottom of base unit).
B *3
DIN rail
35mm
Mounting screws
A *2B *3
(included with adaptors)
Square washers necessary *1
Mounting screws (obtained by user)
No square washers
10 - 8
Stopper
* 1
Square washer
Mountiong screws
(M5 10)
* 2: Screw the DIN rail to a control panel using the mounting screws and square washers included
* 3: Screw the DIN rail with mounting screws(obtained by user) in ‘Position B’ (Where the base unit is
10.2 Module Installation
10.2.1 Precaution on installation
DIN rail
Side view A
with the adaptors in ‘Position A’ (bottom of base unit).
not installed). In this method the supplied mounting screws and square washeres are not used.
Stopper
P
Figure 10.7 DIN rail mounting screw intervals
Figure 10.8 Square washer
PP
P=200mm (7.88 inch) or less
square washer
DIN railMountiong screws
Mounting side
(e.g. Control panel)
Side view A

10
LOADING AND INSTALLATION
POINT
(1) Use only one washer for each mounting screw. Use only the square washers
supplied with the adaptors.
If two or more washers are used together for one mounting screw, the screw
may interfere with the base unit.
(2) Make sure to align the square washer sides with the DIN rail.
DIN railsquare washer DIN railsquare washer
Figure 10.9 Precautions when mounting a square washer
(3) Use the DIN rail that is compatible with M5 size screws.
9
EMC AND LOW
VOLTAGE
10
LOADING AND
11
MAINTENANCE AND
DIRECTIVES
INSTALLATION
INSPECTION
12
TROUBLESHOOTING APPENDICES INDEX
10.2 Module Installation
10.2.1 Precaution on installation
10 - 9

10
LOADING AND INSTALLATION
(e) Stopper mounting
When using the DIN rail in a large vibration and/or shock prone environment,
install the base unit using the stoppers supplied with the DIN rail mounting
adaptors indicated in (a).
1)
Loosen the screw at the top of the
stopper. (2 stoppers)
2)
Hitch the lower hook of the stopper
to the bottom of the DIN rail. Install
the stopper with the arrowhead side
facing up.
Hitch the upper hook of the stopper
3)
to the top of the DIN rail.
Slide the stopper to the end of the
4)
base unit so that they are fully in
contact.
5)
Tighten the screw of the stopper
with a screwdriver.
(Tightening torque 1.00 to 1.35N m)
1)
Stopper
Hook
Hook
DIN rail
Stopper
4)
3)
Hitch hook to top of
DIN rail
2)
Hitch hook to bottom
of DIN rail
(Left side)
5)
Make sure that the left and right
stoppers are fixed securely to the
DIN rail.
Complete
Figure 10.10 Fixture mounting procedure
Stopper
4)
5)
(Right side)
Stopper Stopper
DIN rail
10 - 10
10.2 Module Installation
10.2.1 Precaution on installation

10
LOADING AND INSTALLATION
POINT
When stoppers are used, the dimension of stoppers need to be considered in the
unit installation dimensions. Refer to a CPU user’s manual for the base unit
dimensions (W).
9
EMC AND LOW
VOLTAGE
DIRECTIVES
Stopper Stopper
35(1.38)
DIN rail
(f) Dimensions when DIN rail is attached (Side view).
DIN rail depth (D)
TH35-7.5Fe, TH35-7.5Al:7.5 (0.30)
TH35-15Fe:15 (0.59)
DIN rail adaptor
Base unit
Base unit width : W
W+18(0.71)
Figure 10.11 Base unit external dimensions (Front view)
Board side
Power supply module
5
(0.20)
7.5D
(0.30)
5
Base unit
DIN rail center
Unit: mm (inch)
49 49
(1.93)
(1.93)
98(3.86)
10
LOADING AND
11
MAINTENANCE AND
12
INSTALLATION
INSPECTION
TROUBLESHOOTING APPENDICES INDEX
DIN rail: TH35-7.5Fe,
TH35-7.5Al,
TH35-15Fe
35 (1.38)
115 (4.53)
Figure 10.12 External dimensions (Side view)
(49 (1.93))(49 (1.93))
98 (3.86)
3
(0.12)
Unit: mm (inch)
10.2 Module Installation
10.2.1 Precaution on installation
10 - 11

10
LOADING AND INSTALLATION
10.2.2 Instructions for mounting the base unit
When mounting the PLC to an enclosure or similar, fully consider its operability,
maintainability and environmental resistance.
(1) Module mounting position
Keep the clearances shown in Figure 10.13 or Figure 10.19 between the top/bottom
faces of the module and other structures or parts to ensure good ventilation and
facilitate module replacement.
(a) In case of base unit
Indicates the panel top, wiring duct or any
part position.
5mm (0.20 inch) or more
30mm(1.18 inch)
or more
*1
Panel
30mm(1.18 inch)
or more
5mm (0.20 inch) or more
* 1: For wiring duct with 50mm (1.97 inch) or less height.
40nm (1.58inch) or more for other cases.
Figure 10.13 Module mounting position
Programmable
logic controller
20mm
(0.79 inch)
or more
Door
10 - 12
10.2 Module Installation
10.2.2 Instructions for mounting the base unit

10
LOADING AND INSTALLATION
(2) Module mounting orientation
• Install the PLC in the orientation in Figure 10.14 to ensure good ventilation for
heat release.
Figure 10.14 Orientation in which modules can be mounted
• Do not mount it in either of the orientations shown in Figure 10.15.
9
EMC AND LOW
VOLTAGE
10
LOADING AND
11
MAINTENANCE AND
DIRECTIVES
INSTALLATION
INSPECTION
Vertical mounting Horizontal installation
Horizontal mounting
Figure 10.15 Orientation in which modules cannot be mounted
12
TROUBLESHOOTING APPENDICES INDEX
10.2 Module Installation
10.2.2 Instructions for mounting the base unit
10 - 13

10
LOADING AND INSTALLATION
(3) Installation surface
Mount the base unit on a flat surface. If the mounting surface is not even, this may
strain the printed circuit boards and cause malfunctions.
(4) Installation of unit in an area where the other devices are installed
Avoid mounting base unit in proximity to vibration sources such as large magnetic
contractors and no-fuse circuit breakers; mount these on a separate panel or at a
distance.
(5) Distances from the other devices
In order to avoid the effects of radiated noise and heat, provide the clearances
indicated below between the PLC and devices that generate noise or heat (contactors
and relays).
• Required clearance in front of PLC : at least 100 mm
• Required clearance on the right and left of PLC : at least 50 mm
(3.94 inch)
(1.97 inch).
*
At least
100mm
(3.94 inch)
Contactor, relay, etc.
At least
50mm (1.97 inch)
At least
50mm (1.97 inch)
Figure 10.16 Distances from the other devices
10 - 14
10.2 Module Installation
10.2.2 Instructions for mounting the base unit

10
LOADING AND INSTALLATION
10.2.3 Installation and removal of module
This section explains how to install and remove a power supply, CPU, I/O, intelligent
function or another module to and from the base unit.
9
EMC AND LOW
VOLTAGE
DIRECTIVES
(1) Installation and removal of the module from the QS034B
(a) Installation of module on the QS034B
Securely insert the module
fixing latch(*1) into the module
fixing hole so that the latch is
not misaligned.
Using the module fixing hole as
a fulcrum, push the module in
the direction of arrow to mount
it into the base unit.
Check that the module is
inserted in the base unit
securely and then fix it with the
module fixing screws.
Completed
* 1: The power supply module and CPU module has two module fixing latches. Insert the two module
Base unit
Base unit
Unit fixing
hook (*2)
Module
Module connector
Base unit
Module fixing
latch (*1)
Module loading
lever
Module fixing hole
Figure 10.17 Module mounting procedure
fixing latches on the right and left into the module fixing holes so that they are not misaligned.
Unit/Module
fixing latch
Module fixing hole
Module loading
lever
10
LOADING AND
11
MAINTENANCE AND
12
INSTALLATION
INSPECTION
TROUBLESHOOTING APPENDICES INDEX
Module fixing hook
Base unit hook
Power supply module
Center top
Push
Figure 10.18 Mounting the power supply module and CPU module
* 2: The power supply module and CPU module has two module fixing hooks on its top. Push the
center top of the power supply module and CPU module and mount the module so that the two
module fixing hooks on the right and left are securely engaged with the base unit hooks.
10.2 Module Installation
10.2.3 Installation and removal of module
10 - 15

10
LOADING AND INSTALLATION
POINT
1. When mounting the module, always insert the module fixing latch into the
module fixing hole of the base unit.
At that time, securely insert the module fixing latch so that it does not come off
from the module fixing hole.
If the module is forcibly mounted without the latch being inserted, the module
connector and module will be damaged.
2. Do not mount/remove the module onto/from base unit more than 50 times
(IEC61131-2-compliant), after the first use of the product. Failure to do so
may cause the module to malfunction due to poor contact of connector.
10 - 16
10.2 Module Installation
10.2.3 Installation and removal of module

10
LOADING AND INSTALLATION
(b) Removal from the QS034B
Remove the module fixing screw.
Then support the module with both
and securely press the
hands
module fixing hook*1 with your
finger.
Pull the module based on the
supporting point of module bottom
while pressing the module fixing
hook .
While lifting the module, take the
module fixing latch(*2) off the
module fixing hole.
Push
Module fixing
hook *1
Module
connector
Unit/Module
Base unit
Module fixing hole
Lifting
9
EMC AND LOW
VOLTAGE
10
LOADING AND
11
DIRECTIVES
INSTALLATION
Completed
Figure 10.19 Module removal procedure
* 1: The power supply module and CPU module has two module fixing hooks on its top. Push the two
module fixing hooks on the right and left of the module top simultaneously with your fingers until
they stop.
Push simultaneously
Module fixing hooks
Figure 10.20 Power supply module and CPU module removal procedure
* 2: The power supply module and CPU module has two module fixing latches. Remove the two
module fixing latches on the right and left of the module bottom from the module fixing holes.
MAINTENANCE AND
12
INSPECTION
TROUBLESHOOTING APPENDICES INDEX
POINT
When removing the module, always remove the module fixing screw(s) first, and
then remove the module fixing projection(s) from the module fixing hole(s).
Attempting to remove the module by force may damage the module fixing latch.
10.2 Module Installation
10.2.3 Installation and removal of module
10 - 17

10
10.3 Wiring
LOADING AND INSTALLATION
10.3.1 The precautions on the wiring
DANGER
Be sure to shut off all phases of the external supply power used by the
system before wiring.
Not completely turning off all power could result in electric shock or damage to the product.
When energizing or operating the module after installation or wiring, be
sure to close the attached terminal cover.
Not doing so may result in electric shock.
10 - 18
10.3 Wiring
10.3.1 The precautions on the wiring

10
LOADING AND INSTALLATION
9
CAUTION
Be sure to ground the FG terminals and LG terminals to the protective
ground conductor.Not doing so could result in electric shock or erroneous
operation.
Use a solderless terminal with insulation sleeve for wiring of a terminal
block.
Use up to two solderless terminals for a single terminal.
Use applicable solderless terminals and tighten them with the specified
torque.
If any solderlessspade terminal is used, it may be disconnected when the
terminal screw comes loose, resultingin failure.
Wire the module correctly after confirming the rated voltage and terminal
layout.
Connecting a power supply of a different rated voltage or incorrect wiring
may cause a fire or failure
Tighten a terminal block mounting screw, terminal screw, and module fix-
ing screw within the specified torque range.
If the terminal block mounting screw or terminal screw is too loose, it may
cause a short circuit, fire, or malfunctions.
If too tight, it may damage the screw and/or the module, resulting in a
drop of the screw or module, a short circuit or malfunctions.
If the module fixing screw is too loose, it may cause a drop of the screw
or module.
Over tightening the screw may cause a drop due to the damage of the
screw or module.
EMC AND LOW
VOLTAGE
10
LOADING AND
11
MAINTENANCE AND
12
DIRECTIVES
INSTALLATION
INSPECTION
TROUBLESHOOTING APPENDICES INDEX
Be sure there are no foreign substances such as sawdust or wiring debris
inside the module.
Such debris could cause a fire, failure, or erroneous operation.
The module has an ingress prevention label on its top to prevent foreign
matter, such as wire offcuts, from entering the module during wiring.
Do not peel this label during wiring.
Before starting system operation, be sure to peel this label because of
heat dissipation.
Install our PLC in a control panel for use.
Wire the main power supply to the power supply module installed in a
control panel through a distribution terminal block.
Furthermore, the wiring and replacement of a power supply module have
to be performed by a maintenance worker who acquainted with shock
protection.
(For the wiring methods, refer to Section 10.3.)
The precautions on the connection of the power cables are described below.
10.3 Wiring
10.3.1 The precautions on the wiring
10 - 19

10
LOADING AND INSTALLATION
(1) Power supply wiring
• Separate the PLC's power supply line from the lines for I/O devices and power
devices as shown below.
When there is much noise, connect an insulation transformer.
• Taking rated current or inrush current into consideration when wiring the power
supply, be sure to connect a breaker or an external fuse that have proper blown
and detection.
When using a single PLC, a 10A breaker or an external fuse are recommended
for wiring protection.
Insulation
Transformer
T1
PLC
I/O equipment
Main circuit equipment
200VAC
Main
power supply
Relay
terminal block
On a control panel
Figure 10.21 Power supply connection diagram
PLC
power supply
I/O power supply
Main circuit
power supply
• 100VAC and 200VAC wires should be twisted as dense as possible.
Connect the modules with the shortest distance.
Also, to reduce the voltage drop to the minimum, use the thickest wires possible
(maximum 2mm
2
).
• Do not bundle the 100VAC and 200VAC wires with, or run them close to, the main
circuit (high voltage, large current) and I/O signal lines (including common line).
Reserve a distance of at least 100 mm from adjacent wires.
• Momentary power failure may be detected or the CPU module may be reset due
to serge caused by lightening.
As measures against serge caused by lightening, connect a surge absorber for
lightening as shown in Figure 10.22.
Using the surge absorber for lightening can reduce the influence of lightening.
10 - 20
AC
E1 E1
E1
Figure 10.22 Connecting a lightning surge absorber
10.3 Wiring
10.3.1 The precautions on the wiring
PLC
I/O devices
E2
Surge absorber for lightening

10
LOADING AND INSTALLATION
POINT
1. Separate the ground of the surge absorber for lightening (E1) from that of the
PLC (E2).
2. Select a surge absorber for lightening whose power supply voltage does no
exceed the maximum allowable circuit voltage even at the time of maximum
power supply voltage elevation.
(2) Grounding
For grounding, perform the following:
• Use a dedicated grounding wire as far as possible. (Grounding resistance of
100 or less.)
• When a dedicated grounding cannot be performed, use (2) Common Grounding
shown below.
9
EMC AND LOW
VOLTAGE
10
LOADING AND
11
DIRECTIVES
INSTALLATION
Another
equipment
Grounding
Another
equipment
Figure 10.23 Grounding procedures
PLC
(1) Independent grounding Best (2) Common grounding Good
PLC
• For grounding a cable, use the cable of 2 mm
Grounding
Another
equipment
2
PLC
(3) Joint grounding Not allowed
or more.
Position the ground-contact point as closely to the sequencer as possible, and
reduce the length of the grounding cable as much as possible.
MAINTENANCE AND
12
INSPECTION
TROUBLESHOOTING APPENDICES INDEX
10.3 Wiring
10.3.1 The precautions on the wiring
10 - 21

10
A
w
LOADING AND INSTALLATION
10.3.2 Connecting to the power supply module
The following figure shows the wiring example of power lines, grounding lines, etc. to the
unit.
100/110VAC
C
Fuse
AC
DC
24VDC
Connect to 24VDC
terminals of module
that requires 24VDC
internally.
* 1: The ERR. terminal turns ON/OFF as described below.
The terminal turns OFF (opens) when the AC power is not input, a CPU module stop error
(including a reset) occurs, or the fuse of the power supply module is blown.
Main base unit
(QS034B)
QS061P-A1
Grounding
Figure 10.24 Wiring example
CPU module
Ground wire
1
ERR
FG
LG
INPUT
100-120VAC
POINT
1. Use the thickest possible (max. 2 mm2 (14 AWG)) wires for the 100/200 VAC
and 24 VDC power cables. Be sure to twist these wires starting at the connection terminals. For wiring a terminal block, be sure to use a solderless terminal. To prevent short-circuit due to loosening screws, use the solderless
terminals with insulation sleeves of 0.8 mm (0.03 inch) or less thick. The number of the solderless terminals to be connected for one terminal block are limited to 2.
Solderless terminals
ith insulation sleeves
Terminal block
2.The ERR
for ERR
10 - 22
10.3 Wiring
10.3.2 Connecting to the power supply module
. terminal can not be used as a safety output. In addition, set the cable
. contact in the control panel and its length to 30m (98.43 ft.) or less.

11
MAINTENANCE AND INSPECTION
CHAPTER11 MAINTENANCE AND INSPECTION
Do not touch the terminals while power is on.
DANGER
Doing so could cause shock or erroneous operation.
Correctly connect the battery.
Also, do not charge, disassemble, heat, place in fire, short circuit,
or solder the battery.
Mishandling of battery can cause overheating or cracks which
could result in injury and fires.
Turn off all phases of the external supply power used in the system
when cleaning the module or retightening the terminal block
mounting screws, terminal screws, or module fixing screws.
Not doing so could result in electric shock.
Tighten a terminal block mounting screw, terminal screw, and
module fixing screw within the specified torque range.
If the terminal block mounting screw or terminal screw is too loose,
it may cause a short circuit, fire, or malfunctions.
If too tight, it may damage the screw and/or the module, resulting
in a drop of the screw or module, a short circuit or malfunctions.
If the module fixing screw is too loose, it may cause a drop of the
screw or module.
Over tightening the screw may cause a drop due to the damage of
the screw or module.
9
EMC AND LOW
VOLTAGE
10
LOADING AND
11
MAINTENANCE AND
12
DIRECTIVES
INSTALLATION
INSPECTION
TROUBLESHOOTING APPENDICES INDEX
11 - 1

11
MAINTENANCE AND INSPECTION
The online operations performed from a PC to a running safety
CAUTION
PLC (Program change when a safety CPU is RUN, device test,
and operating status change such as RUN-STOP switching) have
to be executed after the manual has been carefully read and the
safety has been ensured.
Following the operating procedure predetermined at designing, the
operation has to be performed by an instructed person.
When changing a program while a safety CPU is RUN (Write
during RUN), it may cause a program breakdown in some
operating conditions.
Fully understand the precautions described in the GX Developer's
manual before use.
Do not disassemble or modify the modules.
Doing so could cause a failure, erroneous operation, injury, or fire.
If the product is repaired or remodeled by other than the specified
FA centers or us, the warranty is not covered.
Use any radio communication device such as a cellular phone or a
PHS phone more than 25cm (9.85 inch) away in all directions of
the PLC.
Not doing so can cause a malfunction.
Completely turn off the externally supplied power used in the sys-
tem before mounting or removing the module.
Not doing so may result in a failure or malfunctions of the module.
Restrict the mounting/removal of a module, base unit, and terminal
block up to 50 times (IEC61131-2-compliant), after the first use of
the product.
Failure to do so may cause the module to malfunction due to poor
contact of connector.
Do not drop or give an impact to the battery mounted to the
module.
Doing so may damage the battery, causing the battery fluid to leak
inside the battery.
If the battery is dropped or given an impact, dispose of it without
using.
Before touching the module, always touch grounded metal, etc. to
discharge static electricity from human body, etc.
Not doing so may result in a failure or malfunctions of the module.
11 - 2
In order that you can use the PLC in normal and optimal condition at all times, this
section describes those items that must be maintained or inspected daily or at regular
intervals.

11
11.1 Daily Inspection
MAINTENANCE AND INSPECTION
The items that must be inspected daily are listed in Table11.1.
Table11.1 Daily inspection
9
EMC AND LOW
VOLTAGE
DIRECTIVES
Item Inspection Item Inspection Judgment Criteria Remedy
1 Installation of base unit
Installation of power supply
2
module and CPU module
3 Connecting conditions
Power supply module
"POWER" LED
CPU module "ALIVE"
LED
CPU module "RUN"
4
LED
CPU module "ERR."
LED
Module indication LED
CPU module "TEST"
LED
CPU module "BAT."
LED
Check that fixing screws are
not loose and the cover is
not dislocated.
Check that the module is not
dislocated and the unit fixing
hook is engaged securely.
Check that the module fixing
screws are securely
tightened.
Check for loose terminal
screws.
Check for distance between
solderless terminals.
Check that the LED is On
(green).
Check that the LED is On
(green).
Check that the LED is On
(green).
Check that the LED is Off.
Check that the LED is Off.
Check that the LED is Off.
The screws and cover must
be installed securely
The module fixing hook
must be engaged and
installed securely.
The module fixing screws
must be securely tightened.
Screws should not be loose.
The proper clearance
should be provided between
Solderless terminals.
The LED must be On
(green).
(Abnormal if the LED is Off.)
The LED must be On
(green).
(Abnormal if the LED is Off.)
The LED must be On
(green).
(Abnormal if the LED is Off.)
The LED must be Off.
(Abnormal if the LED is On
or flashing.)
The LED must be Off.
(Abnormal if the LED is On.)
The LED must be Off.
(Abnormal if the LED is On.)
Retighten the screws.
Securely engaged the unit
fixing hook.
Securely tighten the
module fixing screws.
Retighten the terminal
screws.
Correct.
Since the status other
than indicated on the
left is in the status other
than normal operation
perform the
troubleshooting
referring to Section
12.2.
10
LOADING AND
INSTALLATION
11
MAINTENANCE AND
INSPECTION
12
TROUBLESHOOTING APPENDICES INDEX
*1
,
*1: Normal operation indicates the following conditions.
• Safety CPU operation mode is in the SAFETY MODE.
• The CPU operation status is in the RUN status.
11.1 Daily Inspection
11 - 3

11
MAINTENANCE AND INSPECTION
11.2 Periodic Inspection
The items that must be inspected one or two times every 6 months to 1 year are listed
below.
When the equipment is moved or modified, or layout of the wiring is changed, also perform
this inspection.
Table11.2 Periodic Inspection
Item Inspection Item Inspection Judgment Criteria Remedy
Ambient temperature
Ambient humidity 5 to 95 %RH
1
Atmosphere
Ambient environment
2 Power voltage
Measure with a
thermometer and a
hygrometer.
Measure corrosive gas.
Measure a voltage across
the terminals of 100/
200VAC.
0 to 55
Corrosive gas must not be
present.
85 to 132VAC
170 to 264VAC
When the sequencer is
used in the board, the
ambient temperature in the
board becomes the
ambient temperature.
Change the power supply.
Looseness, rattling
3
Installation
Adhesion of dirt and
foreign matter
Looseness of terminal
screws
4
5Battery
6
7 Clock
Proximity of solderless
terminals to each other
Connection
Looseness of
connectors
Number of writes to
standard ROM
Move the module to check
for looseness and rattling.
Check visually.
Try to further tighten screws
with a screwdriver.
Check visually.
Check visually.
Check "BAT." LED on the
front face of the CPU
module.
Check the period after the
purchase of the battery.
Check in the monitoring
mode of GX Developer that
SM51 or SM52 is turned
OFF.
Check the values of SD232
and SD233 in the monitoring
mode of GX Developer.
Check the current time at
the clock setting of GX
Developer.
The module must be
installed fixedly.
Dirt and foreign matter must
not be present.
Screws must not be loose.
Solderless terminals must
be positioned at proper
intervals.
Connectors must not be
loose.
The LED must be Off.
The period must be five
years or less.
SM51 or SM52 must be
OFF.
The number of writes to the
standard ROM must be
100,000 times or less.
There is no time lag
between the time checked
at the time setting of GX
Developer and the actual
time.
Retighten the screws.
If the CPU, or power
supply module is loose, fix
it with screws.
Remove and clean.
Retighten the terminal
screws.
Correct.
Retighten the connector
fixing screws.
If the LED is On, replace
the battery.
If the battery is used for
more than 5 years, replace
the battery.
If SM51 or SM52 is ON,
replace the battery.
If the number of writes to
the standard ROM
exceeds 100,000 times,
replace the CPU module.
Change the time at the
time setting of GX
Developer.
11 - 4
11.2 Periodic Inspection

11
11.3 Battery Life and Replacement Procedure
MAINTENANCE AND INSPECTION
The battery installed in the CPU module is used for data retention during the power failure
of the program memory and error/operation history. Special relays SM51 and SM52 turn
on due to the decrease of battery voltage. Even if the special relays turn on, the program
and error/operation history data are not erased immediately.
After relay SM51 turns on, replace the battery quickly within the data retention time for
power failure (3 minutes).
POINT
SM51 turns on when the battery voltage falls below the specified value, and
remains ON even after the voltage is recovered to the normal value.
SM52 turns on when the battery voltage falls below the specified value, and turns
OFF when the voltage is recovered to the normal value.
After SM51 and/or SM52 turns on, replace the battery quickly.
9
EMC AND LOW
VOLTAGE
10
LOADING AND
11
DIRECTIVES
INSTALLATION
SM51 and SM52 turn on when the battery voltage of the CPU module is lowered.
The battery voltage drop can be checked with the contents of the special registers SD51
and SD52.
b15 b1 b0to
SD51, SD52
For details of SD51 and SD52, refer to Section 12.7.
Fixed at 0
Error of a CPU
module battery
Figure 11.1 Bit pattern
When the battery
voltage is low, the
value is "1."
MAINTENANCE AND
12
INSPECTION
TROUBLESHOOTING APPENDICES INDEX
11.3 Battery Life and Replacement Procedure
11 - 5

11
MAINTENANCE AND INSPECTION
11.3.1 Battery lives of CPU modules
Table11.3 Battery lives
CPU Module
Typ e
QS001CPU
* 1: The power-on time ratio indicates the ratio of PLC power-on time to one day (24 hours).
* 2: The guaranteed battery service life; equivalent to the total power failure time that is calculated
* 3: The actual battery service life; equivalent to the total power failure time that is calculated based on
* 4: In the following status, the backup time after power OFF is 3 minutes.
Power-on Time
*1
Ratio
0%
30%
50%
70%
100%
(When the total power-on time is 12 hours and the total power-off time is 12 hours, the power-on
time ratio is 50%.)
based on the characteristics value of the memory (SRAM) supplied by the manufacturer and
under the storage ambient temperature range of -40 to 75 (operating ambient temperature of 0
to 55 ).
the measured value and under the storage ambient temperature of 40 . This value is intended
for reference only, as it varies with characteristics of the memory.
•The battery connector is disconnected.
•The lead wire of the battery is broken.
value (70 )
Guaranteed
26,000hr
2.96 years
37,142hr
4.23 years
43,800hr
5.00 years
43,800hr
5.00 years
43,800hr
5.00 years
Battery lives
Actual service
value (Reference
*2
value)
43,800hr
5.00 years
43,800hr
5.00 years
43,800hr
5.00 years
43,800hr
5.00 years
43,800hr
5.00 years
*3
(40 )
After SM52 ON
(Backup time after
*4
alarm
)
710hr
30 days
710hr
30 days
710hr
30 days
710hr
30 days
710hr
30 days
11 - 6
11.3 Battery Life and Replacement Procedure
11.3.1 Battery lives of CPU modules

11
MAINTENANCE AND INSPECTION
POINT
1. Do not use the battery exceeding its guaranteed life.
If it is expected that the battery may exceed its guaranteed life, take the
following measures:
• Back up programs and the error/operation history in advance after SM52
turns on (within the power failure compensation time after alarm
occurrence).
2. The life of Q6BAT is 5 years when not connected to a CPU module.
3. When the battery-low special relay SM52 turns on, immediately change the
battery.
If an alarm has not yet occurred, it is recommended to replace the battery
periodically according to the conditions of use.
9
EMC AND LOW
VOLTAGE
10
LOADING AND
11
MAINTENANCE AND
DIRECTIVES
INSTALLATION
INSPECTION
12
TROUBLESHOOTING APPENDICES INDEX
11.3 Battery Life and Replacement Procedure
11.3.1 Battery lives of CPU modules
11 - 7

11
BAT.
MAINTENANCE AND INSPECTION
11.3.2 Replacement Procedure of the CPU Module Battery
Replace the battery by the following procedure when the Q6BAT battery of the CPU
module comes to the end of its life. The battery replacement can be performed regardless
of the SAFETY MODE or TEST MODE.
The PLC power must be on for 10 minutes or longer before dismounting the battery.
Data in the memory are backed up for a while by a capacitor even after the battery is
removed. However, since data in the memory may be erased if the time for replacement
exceeds the backup time shown in Table11.4, replace the battery quickly.
Table11.4 Backup time
Backup time
3 minutes
Battery replacement
Save the error/operation history data
as a file with GX Developer. (*1)
Turn off the PLC.
Open the CPU module front cover.
Remove the old battery from its
holder.
Insert a new battery into the holder
in the correct direction. Connect the
lead connector to the connector.
Close the CPU module front cover.
Turn on the PLC.
The CPU module backs up the error/operation history data with a
*1:
battery. In the SAFETY MODE, sequence programs and parameters
are saved in the standard ROM. When replacing the battery, save
the error/operation history data as a backup file with GX Developer.
For details, refer to the GX Developer Version 8 Operating Manual
(Safety PLC).
CPU module
BAT.
PULL
STOP
RUN
RESET
Connector of
CPU module side
Connector
of battery side
11 - 8
Monitor
SM51 to verify
ON/OFF.
ON
Monitor
SD52 to check if bit 0 is
ON.
Bit 0 is ON.
Failure of the replaced battery
Figure 11.2 Replacement procedure for the Q6BAT battery
OFF
Bit 0 is OFF.
11.3 Battery Life and Replacement Procedure
11.3.2 Replacement Procedure of the CPU Module Battery
Completed

11
11.4 When PLC Has been Stored without a Battery
MAINTENANCE AND INSPECTION
When the PLC operation is to be resumed after being stored with the battery removed, the
memories in the CPU module may be corrupted.
Hence, before resuming operation, always format the memories using GX Developer.
After formatting the memories, write the memory contents backed up prior to storage to
each memory.
The relationships between battery and battery-backed memorie are shown in Table11.5.
9
EMC AND LOW
VOLTAGE
10
DIRECTIVES
Table11.5 Relationships between the battery and battery-backed memories
Memory
CPU module
Format the battery-backed memories in Table11.5 using GX Developer before resuming
operation.
For information about the memory formatting, refer to the manual below.
GX Developer Operating Manual
Program memory
Standard ROM ---- (Battery backup not needed)
: Battery backed, : Not battery backed
Battery
Q6BAT
POINT
1. Before storing the PLC, always back up the contents of each memory.
2. The operation/error history cannot be written to the memory from GX
Developer.
LOADING AND
11
MAINTENANCE AND
12
INSTALLATION
INSPECTION
TROUBLESHOOTING APPENDICES INDEX
11.4 When PLC Has been Stored without a Battery
11 - 9

11
11.5 When Battery Has Gone Flat during Storage of a PLC
MAINTENANCE AND INSPECTION
When the PLC is to be used after being stored for some period of time and the battery has
gone flat during storage, the memories in the CPU module may be corrupted.
Hence, before resuming operation, always format the memories using GX Developer.
After formatting the memories, write the memory contents backed up prior to storage to
each memory.
The relationships between battery and battery-backed memorie are shown in Table11.6.
Table11.6 Relationships between the battery and battery-backed memories
Memory
CPU module
Format the battery-backed memories in Table11.6 using GX Developer before resuming
operation.
For information about the memory formatting, refer to the manual below.
GX Developer Operating Manual
Program memory
Standard ROM ---- (Battery backup not needed)
: Battery backed, : Not battery backed
Battery
Q6BAT
POINT
1. Before storing the PLC, always back up the contents of each memory.
2. The operation/error history cannot be written to the memory from GX
Developer.
11 - 10
11.5 When Battery Has Gone Flat during Storage of a PLC
 Loading...
Loading...