Page 1

MES Interface Module User's Manual
-QJ71MES96
-SW1DNC-MESIF-E
(MX MESInterface)
Page 2

Page 3
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
(Always read these precautions before using this equipment.)
Before using this product, please read this manual and the relevant manuals introduced in this manual
carefully and pay full attention to safety to handle the product correctly.
The precautions given in this manual are concerned with only this product. For the safety precautions of the
programmable controller system, please read the User's Manual for the CPU module used.
In this manual, the safety instructions are ranked as " WARNING" and " CAUTION".
WARNING
CAUTION
Note that the CAUTION level may lead to a serious consequence according to the circumstances.
Always follow the instructions of both levels because they are important to personal safety.
Please save this manual to make it accessible when required and always forward it to the end user.
Indicates that incorrect handling may cause hazardous conditions,
resulting in death or severe injury.
Indicates that incorrect handling may cause hazardous conditions,
resulting in minor or moderate injury or property damage.
[Design Precautions]
WARNING
When controlling a running programmable controller (e.g. data modification), create an interlock
circuit on sequence programs so that the whole system functions safely all the time.
Also, be sure to read the manual carefully and ensure safety before performing any other controls
such as operating status change.
Especially, when controlling a programmable controller from a remote location via network, problems
on the programmable controller side may not be dealt with promptly due to failure of data
communications.
Create an interlock circuit on a sequence program.
For the operation status of each station at a communication error, refer to the manual for that station.
Incorrect output or malfunctions may cause an accident.
Install a safety circuit external to the programmable controller that keeps the entire system safe even
when there are problems with the external power supply or the programmable controller.
Otherwise, trouble could result from erroneous output or erroneous operation.
When the programmable controller system security needs to be protected against illegal access from
an external device via a network, take measures at the user's discretion.
A
- 1
Page 4
[Design Precautions]
WARNING
Do not write any data to the "System area" in the buffer memory of the intelligent function module.
As for signals output from the programmable controller CPU to the intelligent function module, never
output (ON) a "Use prohibited" signal.
Doing these operations may cause malfunctions of the programmable controller system.
CAUTION
Do not bunch the control wires or communication cables with the main circuit or power wires, or
install them close to each other.
They should be installed 100 mm (3.94 inch) or more from each other.
Not doing so could result in noise that would cause erroneous operation.
During registering each setting, do not power OFF the mounted module or reset the programmable
controller CPU.
Otherwise, data in the CompactFlash card will be undefined. Therefore, resetting and re-registering
data are required.
This may also cause a module failure or malfunctions.
[Installation Precautions]
CAUTION
Use the programmable controller under the environment specified in the User's Manual.
Using this programmable controller in an environment outside the range of the general specifications
could result in electric shock, fire, erroneous operation, and damage to or deterioration of the
product.
To mount the module, while pressing the module mounting lever located in the lower part of the
module, fully insert the module fixing projection(s) into the hole(s) in the base unit and press the
module until it snaps into place.
Incorrect loading of the module can cause a malfunction, failure or drop.
When using the programmable controller in the environment of much vibration, tighten the module
with a screw.
A
- 2
Page 5
[Installation Precautions]
CAUTION
Completely turn off the externally supplied power used in the system before mounting or removing
the module.
Not doing so could result in damage to the product.
Tighten the screw in the specified torque range.
Undertightening can cause a drop, short circuit or malfunction.
Overtightening can cause a drop, short circuit or malfunction due to damage to the screw or module.
Do not directly touch the module's conductive parts or electronic components.
Touching the conductive parts could cause an operation failure or give damage to the module.
When connecting a connector, properly press, crimp, or solder it using the tools specified by the
manufacturer.
Incomplete connection may cause short-circuit, fire, and malfunctions.
Push the CompactFlash card into the CompactFlash card slot and install it securely.
After installing the CompactFlash card, check that it is inserted securely.
Failure to do so may cause malfunctions due to poor contact.
[Wiring Precautions]
CAUTION
Always store the communication cables and power cables connected to the module in the duct or fix
them in place with clamps.
Not doing so may cause swing, move, or poor connection of the cable, or damage of a module and/
or cable due to careless pull, resulting in malfunctions.
Install connectors securely to modules.
Tighten the screw in the specified torque range.
Undertightening can cause a drop, short circuit or malfunction.
Overtightening can cause a drop, short circuit or malfunction due to damage to the screw or module.
When disconnecting communication cables connected to the module, never pull on the cable
section.
When using a cable with a connector, disconnect it with holding the connector connected to the
module.
When the cable is pulled while connected to the module, this may cause malfunctions or module/
cable damage.
A
- 3
Page 6
[Wiring Precautions]
CAUTION
Be sure there are no foreign substances such as sawdust or wiring debris inside the module.
Such debris could cause fires, damage, or erroneous operation.
A protective film is attached to the top of the module to prevent foreign matter, such as wire chips,
from entering the module during wiring.
Do not peel this label during wiring.
Before starting system operation, be sure to peel this label because of heat dissipation.
[Start-up and Maintenance Precautions]
WARNING
Do not touch any terminal during power distribution.
Doing so may cause malfunctions.
Always switch OFF the external supply power used by the system in all phases before cleaning or
retightening terminal screws.
Failure to do so may cause a failure or malfunctions of the module.
Loose screws may cause a drop of the module, short-circuit, or malfunctions.
Tightening screws excessively may damage the screws and/or the module, resulting in a drop of the
module, short-circuit, or malfunctions.
CAUTION
Do not disassemble or transform the module.
Doing so may cause a failure, malfunctions, personal injuries, and/or a fire.
Always shut OFF the external supply power used by the system in all phases before mounting or
removing a module.
Failure to do so may cause a failure or malfunctions of the module.
Do not install/remove the module to/from the base unit more than 50 times after the first use of the
product. (IEC 61131-2 compliant)
Failure to do so may cause malfunction.
Do not drop or apply any impact to the battery.
Doing so may damage the battery, resulting in a battery fluid leakage inside the battery.
If any impact has been applied, discard the battery and never use it.
Before handling a module, touch a grounded metal object to discharge the static electricity from the
human body.
Failure to do so may cause a failure or malfunctions of the module.
A
- 4
Page 7
[Operation Precautions]
WARNING
Make sure safety before controlling a running programmable controller (e.g. data modification).
Do not write any data to the "System area" in the buffer memory of the intelligent function module.
As for signals output from the programmable controller CPU to the intelligent function module, never
output (ON) a "Use prohibited" signal.
Doing these operations may cause malfunctions of the programmable controller system.
[Disposal Precautions]
CAUTION
When disposing of the product, treat it as industrial waste.
When disposing of batteries, separate them from other wastes according to the local regulations.
(For details of the battery directive in EU member states, refer to Appendix 9.)
[Transportation Precautions]
CAUTION
When transporting lithium batteries, make sure to treat them based on the transportation regulations.
(Refer to Appendix 8 for details of the relevant models.)
A
- 5
Page 8

CONDITIONS OF USE FOR THE PRODUCT
(1) Mitsubishi programmable controller ("the PRODUCT") shall be used in conditions;
i) where any problem, fault or failure occurring in the PRODUCT, if any, shall not lead to any major
or serious accident; and
ii) where the backup and fail-safe function are systematically or automatically provided outside of
the PRODUCT for the case of any problem, fault or failure occurring in the PRODUCT.
(2) The PRODUCT has been designed and manufactured for the purpose of being used in general
industries.
MITSUBISHI SHALL HAVE NO RESPONSIBILITY OR LIABILITY (INCLUDING, BUT NOT
LIMITED TO ANY AND ALL RESPONSIBILITY OR LIABILITY BASED ON CONTRACT,
WARRANTY, TORT, PRODUCT LIABILITY) FOR ANY INJURY OR DEATH TO PERSONS OR
LOSS OR DAMAGE TO PROPERTY CAUSED BY the PRODUCT THAT ARE OPERATED OR
USED IN APPLICATION NOT INTENDED OR EXCLUDED BY INSTRUCTIONS, PRECAUTIONS,
OR WARNING CONTAINED IN MITSUBISHI'S USER, INSTRUCTION AND/OR SAFETY
MANUALS, TECHNICAL BULLETINS AND GUIDELINES FOR the PRODUCT.
("Prohibited Application")
Prohibited Applications include, but not limited to, the use of the PRODUCT in;
• Nuclear Power Plants and any other power plants operated by Power companies, and/or any
other cases in which the public could be affected if any problem or fault occurs in the PRODUCT.
• Railway companies or Public service purposes, and/or any other cases in which establishment of
a special quality assurance system is required by the Purchaser or End User.
• Aircraft or Aerospace, Medical applications, Train equipment, transport equipment such as
Elevator and Escalator, Incineration and Fuel devices, Vehicles, Manned transportation,
Equipment for Recreation and Amusement, and Safety devices, handling of Nuclear or
Hazardous Materials or Chemicals, Mining and Drilling, and/or other applications where there is a
significant risk of injury to the public or property.
Notwithstanding the above, restrictions Mitsubishi may in its sole discretion, authorize use of the
PRODUCT in one or more of the Prohibited Applications, provided that the usage of the PRODUCT
is limited only for the specific applications agreed to by Mitsubishi and provided further that no
special quality assurance or fail-safe, redundant or other safety features which exceed the general
specifications of the PRODUCTs are required. For details, please contact the Mitsubishi
representative in your region.
A
- 6
Page 9
REVISIONS
Correction
Addition
Change of a term
Correction
Correction
Addition
Correction
Correction
Addition
Change of section No.
Correction
Addition
The manual number is given on the bottom left of the back cover.
Print date Manual number Revision
Sept., 2006 SH(NA)-080644ENG-A First edition
Jan., 2007 SH(NA)-080644ENG-B
GENERIC TERMS AND ABBREVIATIONS, DEFINITIONS AND
DESCRIPTIONS OF TERMS, Chapter 1, Sections 2.2, 2.4.2, 2.5, 3.1, 3.2, 3.5,
4.2, 4.6.2, 5.2, 6.1.10, 7.7.1, 7.8.1, 7.9.1, 7.10.1, 7.11.1, 7.11.2, 7.12.5, 7.13.2,
7.13.4, 8.1, 8.2, 8.6, 10.2.1, 10.3.2, 10.3.3, Appendix 3.9
Sections 2.6, 2.6.1, 2.6.2, Appendix 1
Apr., 2007 SH(NA)-080644ENG-C
"PLC" was changed to "programmable controller".
GENERIC TERMS AND ABBREVIATIONS, Sections 2.2, 2.5, 3.2, 7.7, 7.7.1,
7.8.1, 7.11.1, 7.12.2, 10.2.1, Appendices 2, 4.6
Oct., 2007 SH(NA)-080644ENG-D
DEFINITIONS AND DESCRIPTIONS OF TERMS, PACKING LIST, Sections 2.2,
2.4.2, 2.6.2, 3.1, 3.3, 3.6.10, 4.1, 6.1.6, 6.1.9, 7.3.1, 7.4.5, 7.6.2, 7.6.4, 7.8.1,
7.8.3, 7.9.1, 7.10.1 to 7.10.3, 7.10.5, 7.11.1, 7.11.2, 7.12.5, 8.5, 8.8.1, 8.8.2,
10.2.1, Appendices 1.1, 3.1, 3.2, 3.8, 3.10, 3.13, 3.15, 3.16
Oct., 2007 SH(NA)-080644ENG-E
Jan., 2008 SH(NA)-080644ENG-F
Sept., 2008 SH(NA)-080644ENG-G
Sections 6.3.2, 7.8.2, Appendices 1.2, 3.5, 3.19, 3.20
Sections 3.3, 7.8, 7.11.1, 7.12.5, Appendices 3.8, 3.20
GENERIC TERMS AND ABBREVIATIONS, DEFINITIONS AND
DESCRIPTIONS OF TERMS, Sections 1.1, 2.2 to 2.4, 2.6.2, 3.1, 3.2, 4.4.1,
4.7.1, Chapter 5, Sections 6.1.9, 6.1.10, 7.2, 7.3.1, 7.3.4, 7.5 to 7.11, 7.12.5,
7.13.4, 8.1 to 8.3, 8.5, 10.2.1, 10.2.2, 10.3.3, Appendices 1.1, 3.3, 3.4, 3.6 to 3.13
Appendix 7
Appendix 7 Appendix 8
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS, COMPLIANCE WITH THE EMC AND LOW
VOLTAGE DIRECTIVES, GENERIC TERMS AND ABBREVIATIONS, Sections
2.1.1, 2.2, 2.4.1, 2.4.2, 2.5, 3.1, 3.2, 4.1, 4.7.2, 4.8.1, 5.1, 6.1.4, 7.11.1, 7.11.2,
8.2, 8.5, 10.1.3, 10.2.1, 10.3.3, Appendices 1.1, 4
Appendix 9
A
- 7
Page 10

The manual number is given on the bottom left of the back cover.
Correction
Correction
Addition
Correction
Correction
Correction
Correction
Correction
Addition
Change of section No.
Correction
Print date Manual number Revision
Jan., 2009 SH(NA)-080644ENG-H
Sections 2.2, 3.2, 6.1.4, 10.3.3, Appendices 1.1, 1.2
Jan., 2010 SH(NA)-080644ENG-I
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS, GENERIC TERMS AND ABBREVIATIONS,
DEFINITIONS AND DESCRIPTIONS OF TERMS, Sections 1.1, 2.3, 2.4.2, 2.5,
2.6.2, 3.1, 3.3, 4.3, 4.7.2, 4.8.1 to 4.8.3, 6.1.6, 6.1.9, 7.3.1, 7.3.4, 7.8.1, 7.9,
7.9.1, 7.10, 7.10.1, 7.11, 7.11.1, 7.12.5, 8.1, 8.2, 8.8.1, 10.2.1, 10.2.2, 10.3.2,
10.3.3,
Appendices 3.1, 3.10, 3.13 to 3.15, 3.19, 5, 7.1
CONDITIONS OF USE FOR THE PRODUCT
Sept., 2010 SH(NA)-080644ENG-J
HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL, GENERIC TERMS AND ABBREVIATIONS,
Sections 2.1 to 2.3, 2.4.1, 2.4.2, 3.1, 3.2, 5.1, 5.2, 7.7.1, 7.10.2, 7.12.6, 7.15, 8.3,
10.3.1, 10.3.3, Appendices 1.1, 3.7, 7.1, 7.2
Sept., 2011 SH(NA)-080644ENG-K
COMPLIANCE WITH THE EMC AND LOW VOLTAGE DIRECTIVES, Sections
2.4.1, 2.4.2, 2.6.2, 3.1, 3.2, 4.3, 7.7, 7.7.1, 7.9.1, 7.11.1, 7.11.2, 7.15, 8.2, 10.2.1,
10.3.3, Appendices 1.1, 3.7, 3.8, 3.10, 4.1, 4.2
Jun., 2012 SH(NA)-080644ENG-L
COMPLIANCE WITH EMC AND LOW VOLTAGE DIRECTIVES, Sections 2.2,
2.4.1, 2.4.2, 2.5, 3.2, 10.2.1, Appendix 3.7
Feb., 2013 SH(NA)-080644ENG-M
GENERIC TERMS AND ABBREVIATIONS, Sections 1.1, 1.2, 2.2, 2.4.2, 2.6.2,
3.1, 3.2, 3.3, 3.6.8, 5.1, 6.1.3, 7.3.1, 7.3.2, 7.8, 7.8.1, 7.8.2, 7.8.3, 7.9.1, 7.10.3,
7.10.5, 7.11, 7.11.1, 7.14, 7.15, 8.1, 8.2, 8.4.2, 8.5, 8.7, 8.8.1, 10.2.1, 10.2.2,
10.3.1, 10.3.3, Appendices 1.1, 3.8, 3.9, 3.10, 3.13, 3.14, 3.15
Oct., 2013 SH(NA)-080644ENG-N
GENERIC TERMS AND ABBREVIATIONS,
DEFINITIONS AND DESCRIPTIONS OF TERMS, Sections 1.1, 2.2, 2.4.1, 2.4.2,
2.5, 2.6.2, 3.1 to 3.3, 4.3, 5.1, 5.2, 6.1.2, 6.1.10, 7.6, 7.6.4, 7.9.1, 7.10, 7.10.1,
7.10.4, 7.11, 7.11.1, 7.13.5, 7.12.5, 8.1 to 8.3, 8.8.1, 8.8.2, 10.2.1, 10.2.2, 10.3.1,
10.3.3, Appendices 1.1, 1.2, 2.4, 3.3, 3.7, 3.10, 3.11, 3.13, 3.14, 7.1, 7.2
Jun., 2014 SH(NA)-080644ENG-O
A
- 8
Sections 6.1.7, 7.11.2, 7.11.3
Sections 6.1.7 to 6.1.10 6.1.8 to 6.1.11, 7.11.2 7.11.4
GENERIC TERMS AND ABBREVIATIONS, Sections 2.2, 2.4.1, 2.4.2, 3.1, 3.2,
3.3, 3.4.1, 3.4.2, 3.6.2, 3.6.3, 5.2, 6.1.7, 7.2, 7.7, 7.8.1, 7.9.1, 7.11.1, 7.13.6, 8.1,
8.2, 8.3, 10.2.1, 10.2.2, 10.3.1, 10.3.3, Appendices 1.1, 3.7, 3.10, 7.2
Page 11
The manual number is given on the bottom left of the back cover.
Correction
Addition
Correction
Print date Manual number Revision
Dec., 2014 SH(NA)-080644ENG-P
Sections 3.2, 4.7.1, 7.8.3, 10.2.1, 10.3.3
Sections 2.6.2
Feb., 2015 SH(NA)-080644ENG-Q
Sections 4.8.1
Japanese Manual Version SH-080643-R
This manual confers no industrial property rights or any rights of any other kind, nor does it confer any patent licenses.
Mitsubishi Electric Corporation cannot be held responsible for any problems involving industrial property rights which may
occur as a result of using the contents noted in this manual.
© 2006 MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORPORATION
A
- 9
Page 12

INTRODUCTION
Thank you for choosing the Mitsubishi MELSEC-Q Series of General Purpose Programmable Controllers.
Before using the equipment, please read this manual carefully to develop full familiarity with the functions
and performance of the Q series programmable controller you have purchased, so as to ensure correct use.
CONTENTS
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS .................................................................................................................................A - 1
CONDITIONS OF USE FOR THE PRODUCT.................................................................................................. A - 6
REVISIONS.......................................................................................................................................................A - 7
COMPLIANCE WITH EMC AND LOW VOLTAGE DIRECTIVES.................................................................. A - 16
HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL ....................................................................................................................... A - 17
GENERIC TERMS AND ABBREVIATIONS................................................................................................... A - 20
DEFINITIONS AND DESCRIPTIONS OF TERMS ........................................................................................ A - 22
PACKING LIST .............................................................................................................................................. A - 24
CHAPTER 1 OVERVIEW 1 - 1 to 1 - 8
1.1 Features........................................................................................................................................... 1 - 2
1.2 MX MESInterface Software Configuration .......................................................................................1 - 8
CHAPTER 2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION 2 - 1 to 2 - 22
2.1 System Configuration ...................................................................................................................... 2 - 1
2.1.1 Overall system configuration .................................................................................................... 2 - 1
2.1.2 System configuration for installation ......................................................................................... 2 - 2
2.1.3 System configuration for initial setup ........................................................................................ 2 - 3
2.1.4 System configuration for operation ........................................................................................... 2 - 4
2.2 Applicable Systems ......................................................................................................................... 2 - 5
2.3 Connection System Equipment ....................................................................................................... 2 - 7
2.4 Operating Environment .................................................................................................................... 2 - 9
2.4.1 Configuration computer ............................................................................................................ 2 - 9
2.4.2 Server computer ..................................................................................................................... 2 - 11
2.4.3 Computer for developing XML processing applications.......................................................... 2 - 15
2.5 Checking Function Version and Serial Number ............................................................................. 2 - 16
2.6 Precautions for System Configuration ........................................................................................... 2 - 19
2.6.1 Precautions for using Redundant CPU................................................................................... 2 - 19
2.6.2 Precautions for using multiple CPU system............................................................................ 2 - 20
2.6.3 Precautions for using database .............................................................................................. 2 - 21
CHAPTER 3 SPECIFICATIONS 3 - 1 to 3 - 38
3.1 Performance Specifications ............................................................................................................. 3 - 1
3.2 Accessible Devices and Ranges ..................................................................................................... 3 - 5
3.3 Function List .................................................................................................................................. 3 - 12
A
- 10
Page 13

3.4 I/O Signals for Programmable Controller CPU .............................................................................. 3 - 16
3.4.1 I/O signal list ........................................................................................................................... 3 - 16
3.4.2 I/O signals details ................................................................................................................... 3 - 18
3.5 Buffer Memory List......................................................................................................................... 3 - 21
3.6 Buffer Memory Details ................................................................................................................... 3 - 26
3.6.1 Module status area ................................................................................................................. 3 - 26
3.6.2 Network connection status area .............................................................................................3 - 26
3.6.3 Network settings status area .................................................................................................. 3 - 27
3.6.4 Current error area ................................................................................................................... 3 - 28
3.6.5 Error log area.......................................................................................................................... 3 - 29
3.6.6 Sampling/monitoring cycle area .............................................................................................3 - 31
3.6.7 Tag status area....................................................................................................................... 3 - 31
3.6.8 Current tag data value area .................................................................................................... 3 - 33
3.6.9 Access target CPU setting status area ................................................................................... 3 - 36
3.6.10 Information linkage function area ........................................................................................... 3 - 37
CHAPTER 4 SETTINGS AND PROCEDURE TO OPERATION 4 - 1 to 4 - 25
4.1 Handling Precautions....................................................................................................................... 4 - 1
4.2 Settings and Procedure to Operation .............................................................................................. 4 - 2
4.3 Parts Names .................................................................................................................................... 4 - 6
4.4 Wiring............................................................................................................................................... 4 - 8
4.4.1 Wiring ....................................................................................................................................... 4 - 8
4.4.2 Wiring precautions.................................................................................................................... 4 - 8
4.5 Intelligent Function Module Switch Settings .................................................................................... 4 - 9
4.6 Self-diagnostics Test ..................................................................................................................... 4 - 12
4.6.1 Self-loopback test ................................................................................................................... 4 - 12
4.6.2 Hardware test ......................................................................................................................... 4 - 13
4.7 CompactFlash Card....................................................................................................................... 4 - 14
4.7.1 Precautions for using a CompactFlash card........................................................................... 4 - 14
4.7.2 Installation/removing the CompactFlash card ........................................................................ 4 - 15
4.8 Battery ........................................................................................................................................... 4 - 20
4.8.1 Battery specifications.............................................................................................................. 4 - 20
4.8.2 Mounting of battery................................................................................................................. 4 - 20
4.8.3 Battery replacement ............................................................................................................... 4 - 21
4.9 Operation without Mounting Battery ............................................................................................. 4 - 24
4.10 Removing Battery for Storage ....................................................................................................... 4 - 25
CHAPTER 5 INSTALLATION AND UNINSTALLATION 5 - 1 to 5 - 11
5.1 Installation........................................................................................................................................ 5 - 1
5.2 Uninstallation ................................................................................................................................... 5 - 9
CHAPTER 6 FUNCTIONS 6 - 1 to 6 - 24
6.1 DB Interface Function ...................................................................................................................... 6 - 1
A
- 11
Page 14

6.1.1 DB interface function operation ................................................................................................ 6 - 1
6.1.2 Job execution procedure .......................................................................................................... 6 - 2
6.1.3 Tag function .............................................................................................................................. 6 - 4
6.1.4 Trigger monitoring function ....................................................................................................... 6 - 5
6.1.5 Trigger buffering function.......................................................................................................... 6 - 7
6.1.6 SQL text transmission (Communication action)...................................................................... 6 - 10
6.1.7 Stored procedure call function (Communication action) ......................................................... 6 - 11
6.1.8 Arithmetic processing function (Operation action) .................................................................. 6 - 12
6.1.9 Program execution function .................................................................................................... 6 - 12
6.1.10 DB buffering function .............................................................................................................. 6 - 13
6.1.11 Precautions............................................................................................................................. 6 - 20
6.2 XML Processing Function.............................................................................................................. 6 - 22
6.3 Time Synchronization Function ..................................................................................................... 6 - 23
6.3.1 Using the SNTP time query result in the programmable controller CPU ................................ 6 - 23
6.3.2 Daylight saving time function .................................................................................................. 6 - 24
CHAPTER 7 MES INTERFACE FUNCTION CONFIGURATION TOOL 7 - 1 to 7 - 147
7.1 MES Interface Function Configuration Tool ..................................................................................... 7 - 1
7.2 Starting the MES Interface Function Configuration Tool ................................................................. 7 - 1
7.3 Screen Structure.............................................................................................................................. 7 - 2
7.3.1 Screen structure ....................................................................................................................... 7 - 2
7.3.2 Menu configuration ................................................................................................................... 7 - 4
7.3.3 Toolbar configuration ................................................................................................................ 7 - 6
7.3.4 Operations using the Edit items tree......................................................................................... 7 - 7
7.4 Project File Handling........................................................................................................................ 7 - 9
7.4.1 Creating a new project.............................................................................................................. 7 - 9
7.4.2 Opening a project ..................................................................................................................... 7 - 9
7.4.3 Saving a project ...................................................................................................................... 7 - 10
7.4.4 Importing a project .................................................................................................................. 7 - 11
7.4.5 Importing a CSV file................................................................................................................ 7 - 13
7.4.6 Exporting a CSV file................................................................................................................ 7 - 16
7.4.7 Printing a setting information file............................................................................................. 7 - 16
7.5 Project Setting ............................................................................................................................... 7 - 17
7.6 System Setting............................................................................................................................... 7 - 18
7.6.1 Setting items in Network setting ............................................................................................. 7 - 19
7.6.2 Setting items in Time synchronization setting......................................................................... 7 - 20
7.6.3 Setting items in Account setting.............................................................................................. 7 - 24
7.6.4 Setting items in DB buffering setting....................................................................................... 7 - 27
7.7 Access Target CPU Setting ........................................................................................................... 7 - 33
7.7.1 Setting items in Access target CPU setting ............................................................................ 7 - 34
7.8 Device Tag Setting ........................................................................................................................ 7 - 38
7.8.1 Setting items in Device Tag setting ........................................................................................7 - 39
7.8.2 Setting items in Array setting .................................................................................................. 7 - 43
7.8.3 Setting items in Component setting ........................................................................................ 7 - 45
7.9 Server Service Setting ................................................................................................................... 7 - 53
7.9.1 Setting items in Server Service setting ................................................................................... 7 - 54
A
- 12
Page 15

7.10 Job Setting..................................................................................................................................... 7 - 58
7.10.1 Setting items in Job setting..................................................................................................... 7 - 59
7.10.2 Setting items in Trigger conditions ......................................................................................... 7 - 62
7.10.3 Setting items in Program execution ........................................................................................7 - 75
7.10.4 Setting items in DB Buffering.................................................................................................. 7 - 79
7.10.5 Setting items for job cancellation ............................................................................................ 7 - 80
7.11 Job Setting - Actions...................................................................................................................... 7 - 81
7.11.1 Setting items in Communication action .................................................................................. 7 - 85
7.11.2 Setting items in Communication action (Select/Update/Insert/MultiSelect/Delete) ................ 7 - 92
7.11.3 Setting items in Communication action (Stored procedure) ................................................. 7 - 116
7.11.4 Setting items in Operation action.......................................................................................... 7 - 119
7.12 Online .......................................................................................................................................... 7 - 123
7.12.1 Setting the target MES interface module .............................................................................. 7 - 123
7.12.2 Writing the MES interface function settings .......................................................................... 7 - 124
7.12.3 Reading the MES interface function settings........................................................................ 7 - 126
7.12.4 Verifying the MES interface function settings ....................................................................... 7 - 126
7.12.5 Checking the working log of the MES interface module ....................................................... 7 - 127
7.12.6 Executing a job as a one-shot task....................................................................................... 7 - 134
7.13 Online - Remote operation........................................................................................................... 7 - 135
7.13.1 Checking the operation status of the MES interface function ............................................... 7 - 136
7.13.2 Manipulating the operation status of the MES interface function ......................................... 7 - 137
7.13.3 Checking the connection of the previous job execution ....................................................... 7 - 139
7.13.4 Changing the job status ........................................................................................................ 7 - 140
7.13.5 Checking the operation status of DB buffering ..................................................................... 7 - 141
7.13.6 Operating the DB buffering ................................................................................................... 7 - 142
7.13.7 Checking the operation status of the trigger buffering .......................................................... 7 - 143
7.13.8 Formatting the CompactFlash card ...................................................................................... 7 - 143
7.14 Help ............................................................................................................................................. 7 - 144
7.15 Precautions.................................................................................................................................. 7 - 145
CHAPTER 8 DB CONNECTION SERVICE AND SETTING TOOL 8 - 1 to 8 - 31
8.1 DB Connection Service Functions ................................................................................................... 8 - 1
8.2 Setting ODBC to the Database........................................................................................................ 8 - 6
8.3 Starting DB Connection Service Setting Tool ................................................................................ 8 - 13
8.4 Screen Structure of DB Connection Service Setting Tool ............................................................. 8 - 14
8.4.1 Screen structure ..................................................................................................................... 8 - 14
8.4.2 Menu configuration ................................................................................................................. 8 - 15
8.5 Setting Items of DB Connection Service Setting Tool ................................................................... 8 - 16
8.6 Importing/Exporting Files .............................................................................................................. 8 - 21
8.7 Help ............................................................................................................................................... 8 - 23
8.8 Output Log Specifications.............................................................................................................. 8 - 24
8.8.1 Access log .............................................................................................................................. 8 - 25
8.8.2 SQL failure log........................................................................................................................ 8 - 31
A
- 13
Page 16

CHAPTER 9 XML MESSAGE FORMAT 9 - 1 to 9 - 6
9.1 XML Message Format Definition ..................................................................................................... 9 - 2
9.2 XML Message Format Sending Method .......................................................................................... 9 - 4
9.2.1 XML message format sending method ..................................................................................... 9 - 4
9.2.2 Sample program ....................................................................................................................... 9 - 5
CHAPTER 10 TROUBLESHOOTING 10 - 1 to 10 - 54
10.1 Error Codes ................................................................................................................................... 10 - 2
10.1.1 Finding an error code.............................................................................................................. 10 - 2
10.1.2 Error types .............................................................................................................................. 10 - 3
10.1.3 System monitor....................................................................................................................... 10 - 4
10.2 Error Code List............................................................................................................................... 10 - 7
10.2.1 Error codes for the MES interface module.............................................................................. 10 - 7
10.2.2 Error codes of DB Connection Service ................................................................................. 10 - 24
10.2.3 Error codes returned in XML response messages ............................................................... 10 - 36
10.3 Troubleshooting by symptom....................................................................................................... 10 - 37
10.3.1 When using MES Interface Function Configuration Tool...................................................... 10 - 37
10.3.2 When using DB Connection Service Setting Tool ................................................................ 10 - 44
10.3.3 When operating the MES interface module .......................................................................... 10 - 45
APPENDICES App - 1 to App - 76
Appendix 1 Functions Added in MES Interface Module and MX MESInterface .....................................App - 1
Appendix 1.1 Addition of new functions.............................................................................................App - 1
Appendix 1.2 Operations of former versions .....................................................................................App - 4
Appendix 2 Usable Characters and ASCII Code Tables ........................................................................App - 6
Appendix 2.1 ASCII code table..........................................................................................................App - 6
Appendix 2.2 Characters that can be used for item names, component names, variable names,
etc. in the product ........................................................................................................App - 7
Appendix 2.3 Characters available for character string constants, etc..............................................App - 8
Appendix 2.4 Characters available for field names, table names, stored procedure names,etc. ......App - 8
Appendix 3 Setting Information File Format (CSV File Format) .............................................................App - 9
Appendix 3.1 Setting information files list..........................................................................................App - 9
Appendix 3.2 Setting information file format and editing precautions.............................................. App - 10
Appendix 3.3 SYSTEM.CSV ...........................................................................................................App - 13
Appendix 3.4 ACCOUNT.CSV ........................................................................................................App - 15
Appendix 3.5 DST.CSV...................................................................................................................App - 17
Appendix 3.6 DBBUF.CSV..............................................................................................................App - 19
Appendix 3.7 CPU.CSV................................................................................................................... App - 20
Appendix 3.8 TAG.CSV...................................................................................................................App - 24
Appendix 3.9 COMPONENT.CSV................................................................................................... App - 26
Appendix 3.10 SERVER.CSV ...........................................................................................................App - 28
Appendix 3.11 JOB.CSV ...................................................................................................................App - 30
Appendix 3.12 CONDITION.CSV......................................................................................................App - 32
Appendix 3.13 ACTION.CSV.............................................................................................................App - 36
Appendix 3.14 ACFIELD.CSV...........................................................................................................App - 39
Appendix 3.15 ACCONDITION.CSV................................................................................................. App - 41
Appendix 3.16 ACEXCEPTION.CSV ................................................................................................App - 43
A
- 14
Page 17

Appendix 3.17 ACOPERATION.CSV................................................................................................ App - 45
Appendix 3.18 REMOTE.CSV........................................................................................................... App - 48
Appendix 3.19 ORDERBY.CSV ........................................................................................................App - 50
Appendix 3.20 MULTISELECT.CSV .................................................................................................App - 51
Appendix 4 Processing Time................................................................................................................App - 53
Appendix 4.1 Product whose first five digits of serial No. is "13092" or later .................................. App - 53
Appendix 4.2 Product whose first five digits of serial No. is "09102" or later and "13091" or
earlier ........................................................................................................................App - 56
Appendix 4.3 Product whose first five digits of serial No. is "09101" or earlier ............................... App - 59
Appendix 5 External Dimensions.......................................................................................................... App - 61
Appendix 6 Data Collection Method for CPUs that cannot be Accessed Directly ................................App - 62
Appendix 7 Warning Messages in Windows(R) ...................................................................................App - 64
Appendix 7.1 Overview of warning messages ................................................................................App - 64
Appendix 7.2 Methods for disabling warning messages ................................................................. App - 65
Appendix 8 Transportation Precautions ............................................................................................... App - 73
Appendix 8.1 Controlled model .......................................................................................................App - 73
Appendix 8.2 Handling for shipping.................................................................................................App - 73
Appendix 9 Handling of Batteries and Devices with Built-in Batteries in EU Member States............... App - 74
Appendix 9.1 Disposal precautions ................................................................................................. App - 74
Appendix 9.2 Exportation precautions.............................................................................................App - 75
INDEX Index - 1 to Index - 2
A
- 15
Page 18

COMPLIANCE WITH EMC AND LOW VOLTAGE DIRECTIVES
(1) Method of ensuring compliance
To ensure that Mitsubishi programmable controllers maintain EMC and Low Voltage
Directives when incorporated into other machinery or equipment, certain measures
may be necessary. Please refer to one of the following manuals.
• QCPU User's Manual (Hardware Design, Maintenance and Inspection)
• Safety Guidelines
(This manual is included with the CPU module or base unit.)
The CE mark on the side of the programmable controller indicates compliance with
EMC and Low Voltage Directives.
(2) Additional measures
To ensure that this product maintains EMC and Low Voltage Directives, please refer
to one of the manuals listed under (1).
A
- 16
Page 19

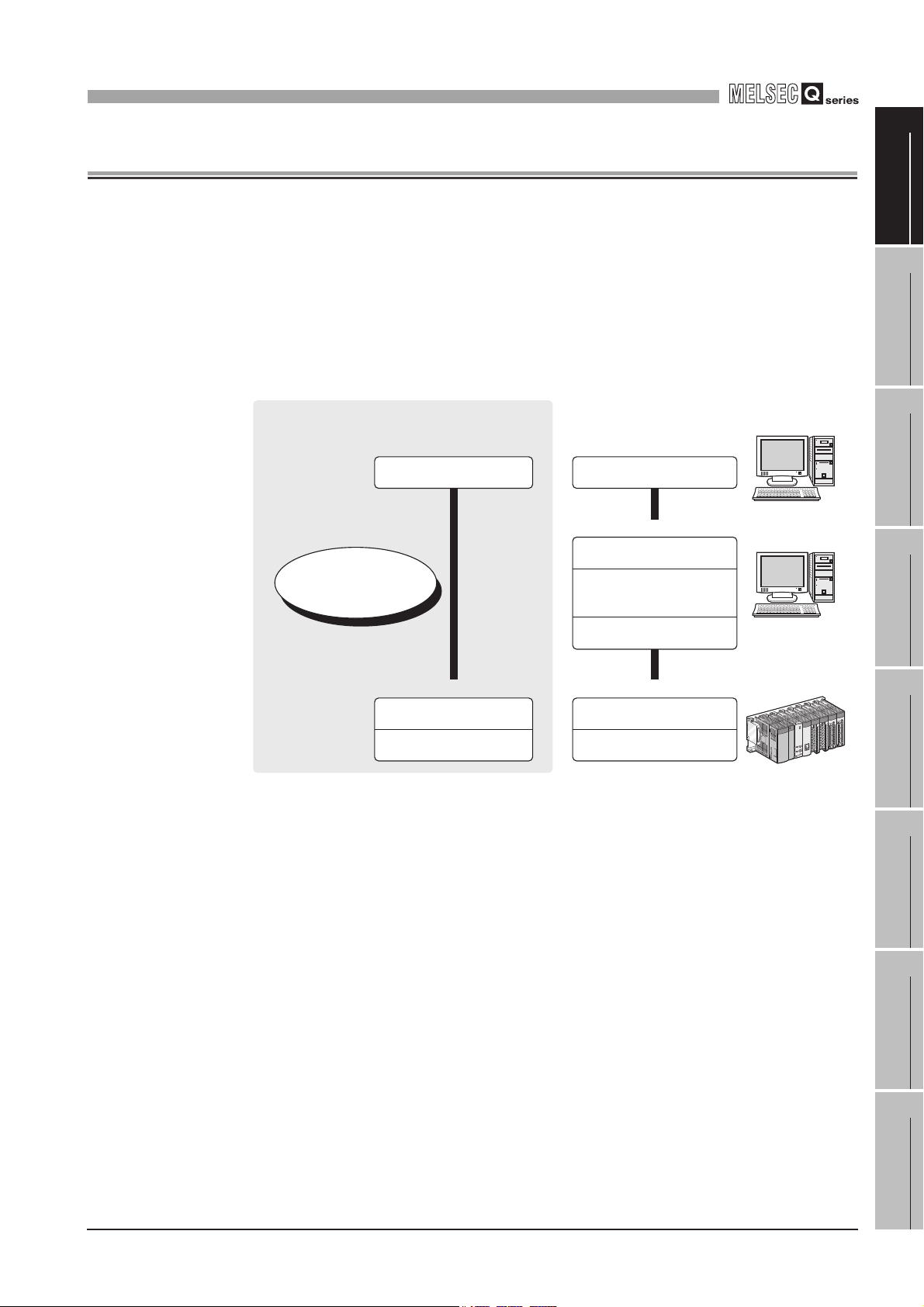
HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL
Section 7.6 ...... Explains a display method of the screen.
Section 7.6.1
Section 7.6.2
Section 7.6.3
Section 7.6.4
Explains setting items and
the setting methods of the screen.
* Sections 7.7 to 7.10 also provide explanations as indicated above.
This manual is organized by objective for using the QJ71MES96 MES interface module
and MX MESInterface Version 1 (SW1DNC-MESIF-E). Use this manual with referring to
the following.
(1) Features and software configuration
Section 1.1 covers the features.
Section 1.2 covers the MX MESInterface software configuration.
(2) System configuration, applicable systems, connection system equipment, and
operating environment
Section 2.1 covers the system configuration.
Section 2.2 covers the applicable systems.
Section 2.3 covers the connection system equipment.
Section 2.4 covers the operating environment.
(3) Performance specifications about the MES interface module
Section 3.1 covers the performance specifications.
Chapter 1 OVERVIEW
Chapter 2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
Chapter 3 SPECIFICATIONS
(4) Procedure up to MES interface Function module start-up
Chapter 4 SETTINGS AND PROCEDURE TO OPERATION
Section 4.2 covers the schematic procedure up to the MES interface module operation.
(5) Installation and uninstallation methods for MX MESInterface
Chapter 5 INSTALLATION AND UNINSTALLATION
CHAPTER 5 covers MX MESInterface installation and uninstallation methods.
(6) MES interface module functions
Chapter 6 FUNCTIONS
CHAPTER 6 covers the MES interface module functions.
(7) Setting method for MES Interface Function Configuration Tool
Chapter 7 MES INTERFACE FUNCTION CONFIGURATION TOOL
CHAPTER 7 covers the setting method of the MES Interface Function Configuration
Tool.
Section 7.6 to Section 7.10 provide explanations as indicated below.
A
- 17
Page 20

(8) Setting method for DB Connection Service
Chapter 8 DB CONNECTION SERVICE AND SETTING TOOL
CHAPTER 8 covers the functions and setting method for the DB Connection Service.
(9) XML message format
Chapter 9 XML MESSAGE FORMAT
CHAPTER 9 covers the XML message format.
(10)Methods for checking errors and the corrective actions
Chapter 10 TROUBLESHOOTING
CHAPTER 10 covers troubleshooting and lists the error codes.
A
- 18
Page 21
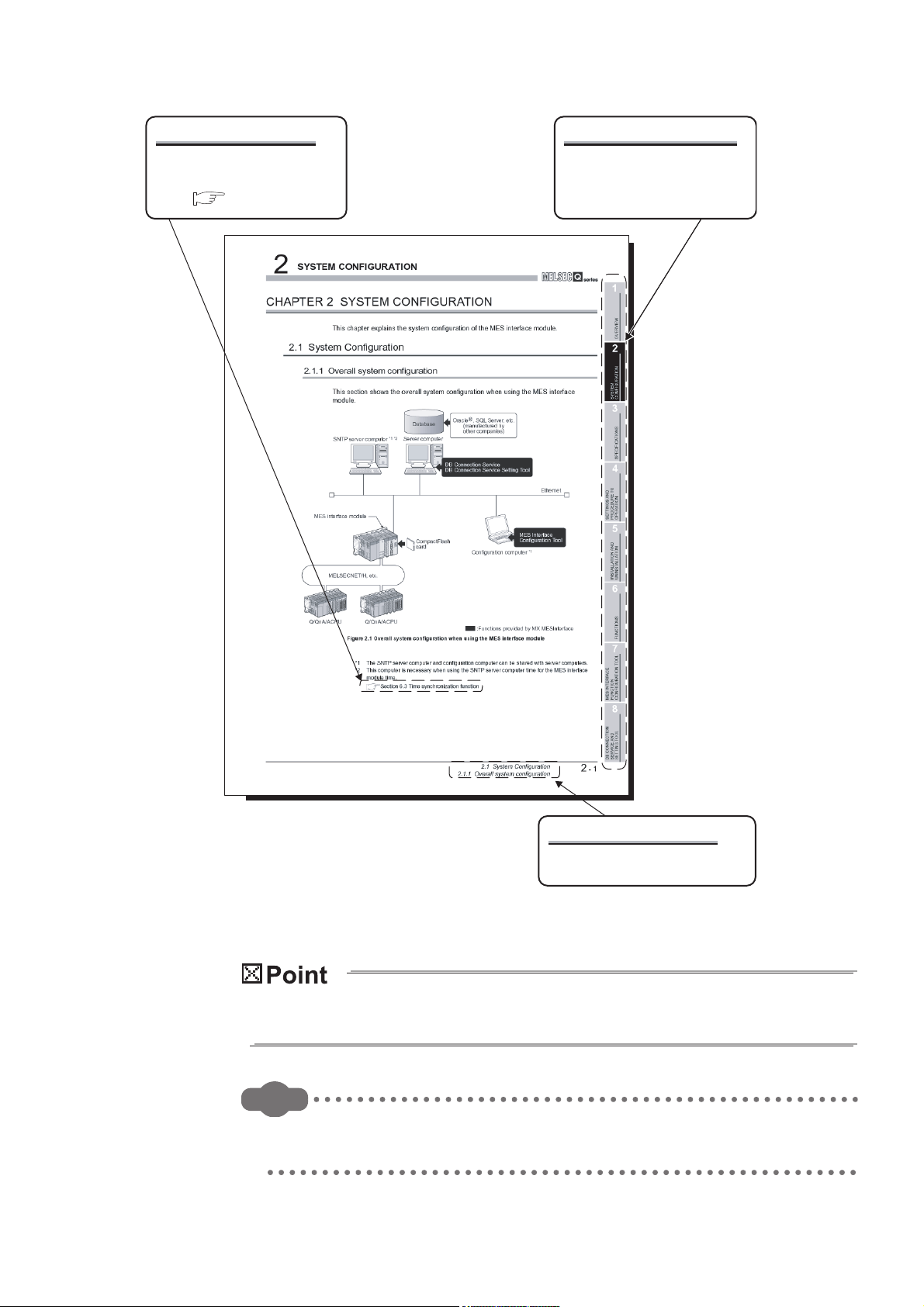
Remark
Displaying a reference
Displaying a chapter title
Reference in this manual and
reference manual are shown
with .
Index on the right of a page
clears the chapter of the page.
Displaying a section title
The section in which the open page
is included is clear.
The above is different from the actual page, as it is provided for explanation only.
In addition, this manual provides the following explanations.
Explains the matters to be especially noted, the functions and others related to the
description on that page.
Provides the reference destination related to the description on that page and the
convenient information.
A
- 19
Page 22
GENERIC TERMS AND ABBREVIATIONS
Unless otherwise specified, this manual uses the following generic terms and
abbreviations to explain the QJ71MES96 MES interface module and MX MESInterface
Version 1 (SW1DNC-MESIF-E).
Generic term/abbreviation Description
Generic term for the A1NCPU, A0J2HCPU, A1SCPU, A1SHCPU, A1SJCPU, A1SJHCPU,
ACPU
C Controller module
Ethernet Generic term for 100BASE-TX, 10BASE-T, 10BASE5, and 10BASE2 network systems
Ethernet module Generic term for the E71, QE71, Q series E71, and L series E71
E71
GX Developer
LCPU
L series E71 Another term for the LJ71E71-100
MELSECNET/H Abbreviation for MELSECNET/H network system supporting the Q series
MELSECNET/10 Abbreviation for MELSECNET/10 network system supporting the AnU and QnA/Q4AR
MES interface module Abbreviation for the QJ71MES96 MES interface module
MX MESInterface Product name for the model name SW1DNC-MESIF-E
QCPU (A mode) Generic term for the Q02CPU-A, Q02HCPU-A, and Q06HCPU-A
QCPU (Q mode)
QC24(N)
QE71
QnACPU
Q series C24
Q series E71 Generic term for the QJ71E71-100, QJ71E71-B5, and QJ71E71-B2
RCPU Generic term for R04CPU, R08CPU, R16CPU, R32CPU, R120CPU
R series E71 Another term for the RJ71EN71
UC24
A2CCPU, A2CJCPU, A2NCPU, A2NCPU-S1, A2SCPU, A2SHCPU, A2ACPU, A2ACPU-S1,
A2UCPU, A2UCPU-S1, A2USCPU, A2USCPU-S1, A2USHCPU-S1, A3NCPU, A3ACPU,
A3UCPU, and A4UCPU
Generic term for the Q06CCPU-V, Q06CCPU-V-B, Q12DCCPU-V, Q24DHCCPU-V, and
Q24DHCCPU-LS
Generic term for the AJ71E71N3-T, AJ71E71N-B5, AJ71E71N-B2, A1SJ71E71N3-T,
A1SJ71E71N-B5, and A1SJ71E71N-B2
Generic product name for the model names of the SWnD5C-GPPW-E, SWnD5C-GPPW-EA,
SWnD5C-GPPW-EV, and SWnD5C-GPPW-EVA. (n = Version 4 or later)
- A designates a multiple-license product; -V designates a version upgraded product.
Generic term for the L02SCPU, L02SCPU-P, L02CPU, L02CPU-P, L06CPU, L06CPU-P,
L26CPU, L26CPU-P, L26CPU-BT, and L26CPU-PBT
Generic term for the Q00JCPU, Q00CPU, Q01CPU, Q02CPU, Q02HCPU, Q06HCPU,
Q12HCPU, Q25HCPU, Q02PHCPU, Q06PHCPU, Q12PHCPU, Q25PHCPU, Q12PRHCPU,
Q25PRHCPU, Q00UJCPU, Q00UCPU, Q01UCPU, Q02UCPU, Q03UDCPU, Q04UDHCPU,
Q06UDHCPU, Q10UDHCPU, Q13UDHCPU, Q20UDHCPU, Q26UDHCPU, Q03UDECPU,
Q04UDEHCPU, Q06UDEHCPU, Q10UDEHCPU, Q13UDEHCPU, Q20UDEHCPU,
Q26UDEHCPU, Q50UDEHCPU, Q100UDEHCPU, Q03UDVCPU, Q04UDVCPU,
Q06UDVCPU, Q13UDVCPU, and Q26UDVCPU
Generic term for the AJ71QC24, AJ71QC24-R2, AJ71QC24-R4, A1SJ71QC24,
A1SJ71QC24-R2, AJ71QC24N, AJ71QC24N-R2, AJ71QC24N-R4, A1SJ71QC24N,
A1SJ71QC24N-R2, A1SJ71QC24N1, and A1SJ71QC24N1-R2
Generic term for the AJ71QE71N3-T, AJ71QE71N-B5, AJ71QE71N-B2, A1SJ71QE71N3-T,
A1SJ71QE71N-B5, and A1SJ71QE71N-B2
Generic term for the Q2ACPU, Q2ACPU-S1, Q2ASCPU, Q2ASCPU-S1, Q2ASHCPU,
Q2ASHCPU-S1, Q3ACPU, Q4ACPU, and Q4ARCPU
Generic term for the QJ71C24N, QJ71C24N-R2, QJ71C24N-R4, QJ71C24, and
QJ71C24-R2
Generic term for the AJ71UC24, A1SJ71UC24-R2, A1SJ71UC24-R4, A1SJ71UC24-PRF,
A1SJ71C24-R2, A1SJ71C24-R4, A1SJ71C24-PRF, A1SCPUC24-R2, A2CCPUC24, and
A2CCPUC24-PRF
(To the next page)
A
- 20
Page 23

Generic term/abbreviation Description
Generic term for the following:
®
Windows® 7 Starter Operating System
®
Windows® 7 Home Premium Operating System
Windows® 7
Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft® Windows® 7 Professional Operating System
Microsoft® Windows® 7 Ultimate Operating System
®
Microsoft
Windows® 7 Enterprise Operating System
Generic term for the following:
®
Windows® 8 Operating System
®
Windows® 8 Enterprise Operating System
Windows® 8
Microsoft
Microsoft® Windows® 8 Pro Operating System
Microsoft
Generic term for the following:
®
Windows® 8.1 Operating System
®
Windows® 8.1 Pro Operating System
®
Windows® 8.1 Enterprise Operating System
Windows® 8.1
Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft
Generic term for the following:
Microsoft® Windows Vista® Home Basic Operating System
Windows Vista
®
Microsoft® Windows Vista® Home Premium Operating System
®
Microsoft
Windows Vista® Business Operating System
Microsoft® Windows Vista® Ultimate Operating System
Microsoft® Windows Vista® Enterprise Operating System
Generic term for the following:
®
Windows® XP
Microsoft
Windows® XP Professional Operating System
Microsoft® Windows® XP Home Edition Operating System
Computer link module (Serial
communication module)
Generic term for the UC24, QC24(N), and Q series C24
Especially when referring to the QC24(N) and Q series C24, they are written as "Serial
communication module".
(From the previous page)
A
- 21
Page 24
DEFINITIONS AND DESCRIPTIONS OF TERMS
The following table shows the definitions and descriptions of the terms used in this
manual.
Term Description
CSV
DB buffering
HTTP
Tag for Wonderware®
Historian
MES
ODBC
SNTP
SNTP server computer
SQL
URL
URL encode
XML
Item One setting group unit included each setting type for editing
Account
Action
System switching
COMMIT Processing for finalizing the changes to a database
CompactFlash card
(CF card)
Abbreviation for Comma Separated Values
Text file in which the data are aligned and set off by commas and double quotations
Function temporarily stores SQL text that failed to be sent due to a communication error and
resends the text when the communications have been recovered
Abbreviation for Hyper Text Transfer Protocol
Protocol to exchange XML format messages between the MES interface module and user
applications in the XML processing function
Name for data unit in the data base Wonderware® Historian.
Abbreviation for Manufacturing Execution Systems
Systems for controlling and monitoring the plant status in real time to optimize production
activities
The systems enable to speed up the responses to production plan and status changes that lead
to efficient production processes and optimization of production activities.
Abbreviation for Open DataBase Connectivity
Standard specifications for software to access databases
Abbreviation for Simple Network Time Protocol
Protocol for synchronizing computer time via a TCP/IP network
Computer that provides time information to the MES interface module
This computer can be shared with a server computer.
Abbreviation for Structured Query Language
Data manipulation language and used for relational database operations
Abbreviation for Uniform Resource Locator
Notation method for indicating the locations of information resources on the Internet
Converts character strings into characters can be used in URLs.
This designates percent encoding defined by RFC3986.
Abbreviation for eXtensible Markup Language
Markup language for describing documentation, data meanings, and structures
Designates the right to use the MES interface module or server computer, or an ID necessary for
their use.
Unit for processing defined in a job
There are [Communication action] for communicating with a database and [Operation action] for
operating tag component values.
[Communication action] is a processing unit for sending one SQL text (Select, Update, Insert,
MultiSelect, or Delete) or one stored procedure execution request.
[Operation action] is a processing unit of up to 20 dyadic operations.
Function for the Redundant CPU to switch between control system and standby system of the
redundant system. (Switching from control system to standby system, and vice versa.)
Storage card regulated by the [CF+ and CompactFlash Specification] issued by the Compact
Flash Association
This memory card is necessary for the MES interface module to operate the MES interface
function.
(To the next page)
A
- 22
Page 25
Term Description
Generic term for the services can be offered by a server computer to which DB Connection
Service is installed
Server service
Server computer
Job Unit for accessing a database
Stored procedure
Update settings
Configuration computer
Time zone
Tag component
(Component)
Data source
Database (DB) or
relational database
(RDB)
Table
Device
Device tag (Tag)
Trigger condition Startup conditions for job operation
There are database server service and application server service.
The database server service is a service for accessing a database.
The application server service is a service for linking with a program.
There are database server computers and application server computers.
The database server computer is a personal computer with a relational database which links
information with the MES interface module.
The application server computer is a personal computer with a program that operates upon
request from the MES interface module.
Stored procedure combines sequential processing procedures into one program against the
database, and save it to the database management system.
This executes processing based on the arguments received from MES interface module, and
returns the processing results to MES interface module.
Processing updates the MES interface module settings from MES Interface Function
Configuration Tool
Personal computer for configuring various settings required for the MES interface function in the
MES interface module
This computer can be shared with a server computer.
Standard time zone for each region of the world
Each nation uses the time difference ( 12 hours maximum) from the time at the Greenwich
Observatory in the United Kingdom (GMT) as the standard time. The region using the same time
difference is called a time zone.
The standard time for Japan is 9 hours ahead of the GMT.
In some nations, daylight time in which the clock is advanced for one hour is used in summer.
Generic term for a component (Device data) making up a device tag (Tag)
This data organizes the communications path, data type, device, etc. for access to each
programmable controller CPU device data as a single data unit.
Connection information necessary for accessing data using ODBC
®
With Windows
database can be accessed via ODBC by specifying the data source name in the MES interface
function.
Data management method that follows relational data model logic
One data is expressed as a collection of multiple items (Fields) and the data collection is
expressed as a table.
Data can be easily merged and selected using key data.
Data management format managed with relational databases
It is a two-dimensional table format composed of rows and columns.
Variety of memory data in the programmable controller
There are devices handled in units of bits and devices handled in units of words.
Data table that contains a set of information (Component) required to access the device data in
the programmable controller CPUs on the network
The MES interface module collects device data in units of tags at an interval defined in the tag.
, a data source name is assigned to connection information for management. The
(From the previous page)
(To the next page)
A
- 23
Page 26

(From the previous page)
Term Description
When trigger conditions (conditions for data transmission) of multiple jobs are met in a
concentrated manner, their data and trigger times are buffered in the module's internal memory so
Trigger buffering
Data separation
Daylight saving
(Summer time)
Handshake
Field Corresponds to a column in a relational database and indicates a type of data (Record attribute).
Variable (Temporary
variable)
Record
Rollback Processing for canceling changes to a database
that actions (data operation/transmission) can be executed later using the buffered data.
Even if the frequency of data transmission triggers is high, jobs are executed without missing any
trigger.
New data and old data are mixedly exists in units of 16 bits (1 word) in 32 bits data (2 words) or
larger data due to data reception timing.
The system in which clocks are set one hour ahead of standard time in a specific period of time in
summer.
For highly reliable processing, programmable controller CPU devices are used to manage
processing between the programmable controller CPU and MES interface module.
Variable that can be used in a single job for temporary storage of values selected from a database
and for writing operation values to a database or tag components
Corresponds to a row in a relational database. One row (Record) stores the values of multiple
columns (Fields).
PACKING LIST
The following table shows the products included to the QJ71MES96 MES interface
module and MX MESInterface Version 1 (SW1DNC-MESIF-E).
Model Product name Quantity
QJ71MES96
SW1DNC-MESIF-E MX MESInterface Version 1 (with one license) (CD-ROM) 1
SW1DNC-MESIF-EA MX MESInterface Version 1 (with multiple licenses) (CD-ROM) 1
QJ71MES96MES interface module 1
Battery (Q6BAT) 1
A
- 24
Page 27
1
OVERVIEW
CHAPTER 1 OVERVIEW
This manual explains the specifications, preparatory procedures, functions, and
troubleshooting for the MELSEC-Q series QJ71MES96 MES interface module (hereafter,
abbreviated as MES interface module).
When applying the following program examples to the actual system, make sure to
examine the applicability and confirm that it will not cause system control problems.
The MES interface module links the programmable controller (Production equipment)
device data with information system (Manufacturing Execution System) database without
communication gateways.
1
2
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
Information linkage using the MES interface module
<Manufacturing Execution System>
Information system
(Database)
Computerization via
communication gateways
is unnecessary.
<Production equipment> <Production equipment>
MES interface module
Programmable controller CPU
Figure 1.1 Information linkage using the MES interface module
SQL
XML
(Device data)
Conventional information linkage
without the MES interface module
<Manufacturing Execution System>
Information system
(Database)
<Communication gateway>
Host information system
communication processing
Data processing
(Operation processing,
logging, etc.)
Controller communication
Communication module
Programmable controller CPU
(Device data)
3
SPECIFICATIONS
4
SETTINGS AND
PROCEDURE TO
OPERATION
5
INSTALLATION AND
UNINSTALLATION
6
FUNCTIONS
7
MES INTERFACE
FUNCTION
CONFIGURATION TOOL
8
DB CONNECTION
SERVICE AND
SETTING TOOL
1
- 1
Page 28
1
OVERVIEW
1.1 Features
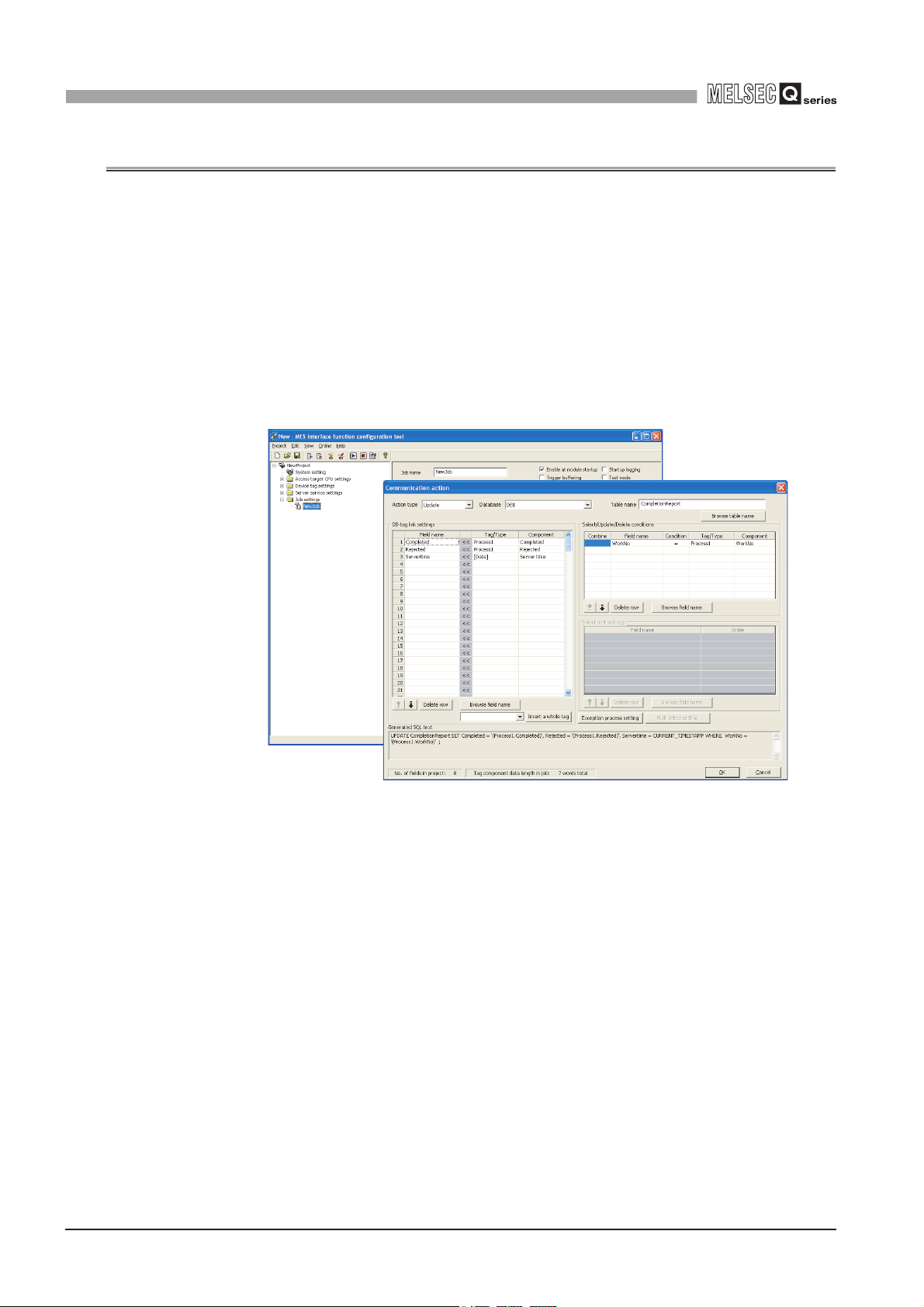
This section explains the features of MX MESInterface.
(1) Connection with the information system is enabled by simple settings without
program
Access to information system databases can be realized simply by making the
necessary settings with the setting tool.
There is no need to write programs for accessing databases, so the engineering costs
for system construction can be reduced and the work period can be shortened.
[MX MESInterface] - [MES interface function configuration tool]
1
- 2
Figure 1.2 [MX MESInterface] - [MES interface function configuration tool]
1.1 Features
Page 29
1
OVERVIEW
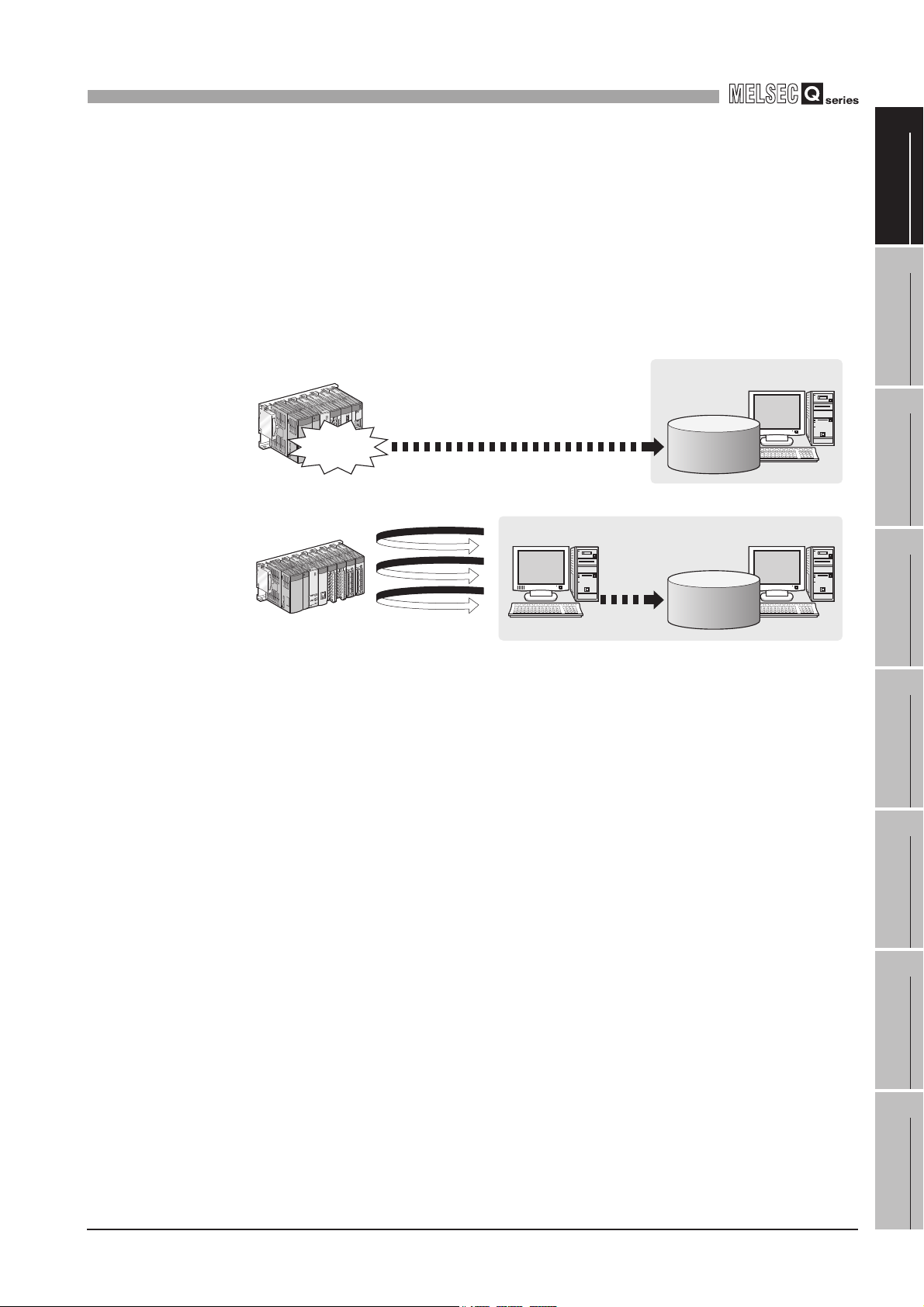
(2) The information system load can be reduced.
[MES interface module...]
Data can be monitored on the MES interface module side and when the conditions
are met, the data can be sent to the information system.
Also, the data can be operated and the results of the operations can be sent to the
information system.
This can reduce the information system loads compared to the conventional system
of constantly obtaining and monitoring data.
1
OVERVIEW
2
Conditions
met
[In the conventional system...]
Constantly obtaining/monitoring data
from information system are required.
Figure 1.3 Loads reduction of information system
Sends data as required.
<Information system>
<Information system>
Database
Database
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
SPECIFICATIONS
4
SETTINGS AND
PROCEDURE TO
OPERATION
5
INSTALLATION AND
UNINSTALLATION
1.1 Features
6
FUNCTIONS
7
MES INTERFACE
FUNCTION
CONFIGURATION TOOL
8
DB CONNECTION
SERVICE AND
SETTING TOOL
1
- 3
Page 30
1
OVERVIEW
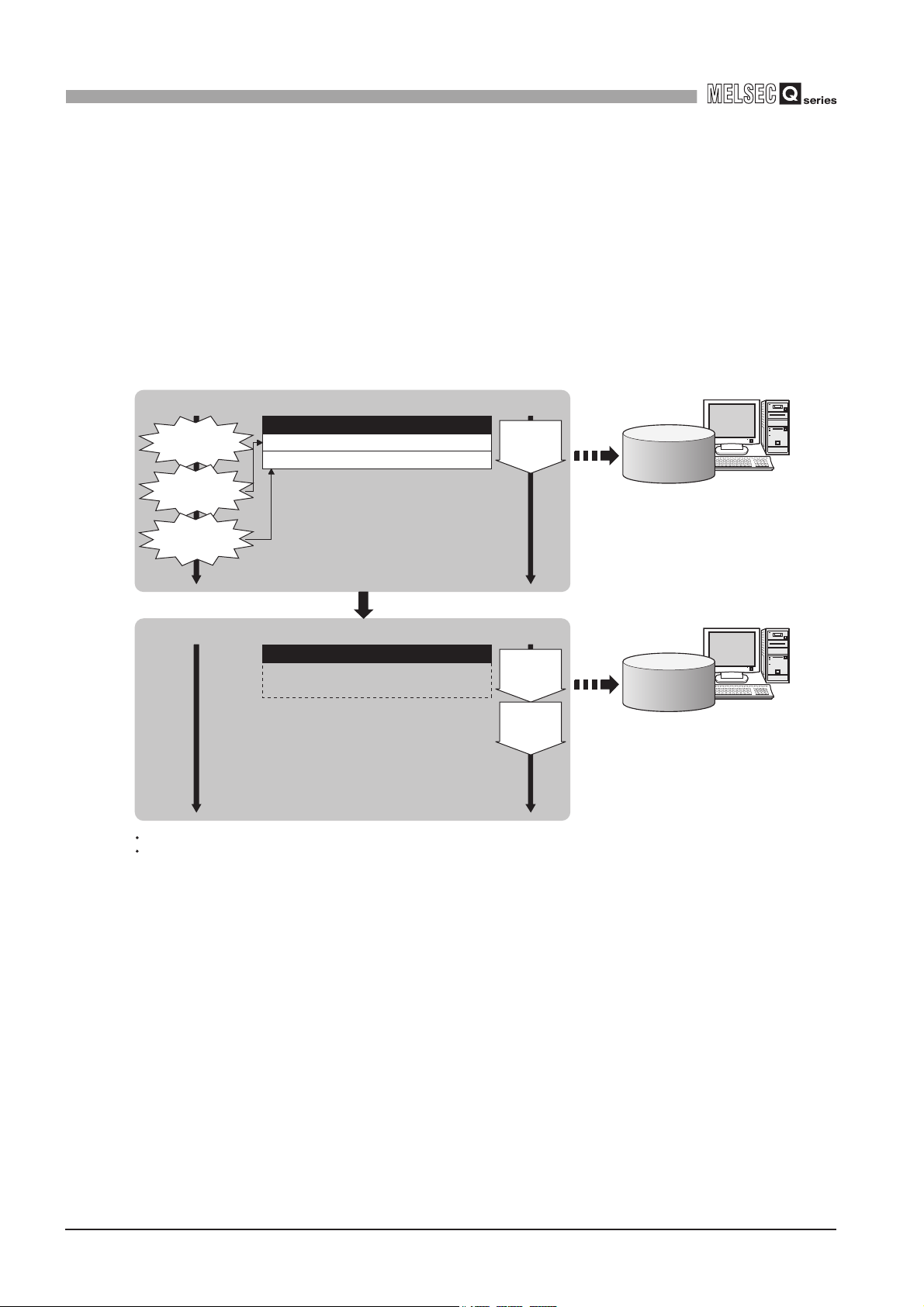
(3) Buffering function for reliable data acquisition/transmission
(a) Even if the frequency of data transmission triggers is high, no trigger will be
[MES interface module]
[When loads are concentrated]
Job 1-1)
Trigger conditions
met
Job 1-2)
Trigger conditions
met
Job 3-3)
Trigger conditions
met
Job 1-2) Trigger information (Tag data, time)
Job 3-3) Trigger information (Tag data, time)
missed. (Trigger buffering function)
When multiple sets of conditions for data transmission are met in a concentrated
manner, their data and trigger times can be buffered in the module's internal
memory.
After the loads are reduced, data operations and transmission are executed using
the buffered data.
Trigger buffer
Job 1-1)
Action
execution
Sending
data
Database
Executes action of Job 1-1), and
stores trigger information of Job 1-2)
and 3-3) in the trigger buffer.
Time
After loads have been reduced
[When loads are reduced]
Trigger buffer
Time Time
The numbers 1) to 3) show the order in which trigger conditions of respective jobs are met.
Job 1 and 3 are assumed to access the same database.
Figure 1.4 Data buffering in the case of load concentration
Job 1-2)
Action
execution
Job 3-3)
Action
execution
Time
Sending
data
After completing the action of Job 1-1),
executes actions of Job 1-2) and 3-3)
in this order based on the trigger buffer
information.
Database
1
- 4
1.1 Features
Page 31

1
OVERVIEW
(b) Data to be send to the database are protected even if a communication error
occurs. (DB buffering function)
When an error occurs during performing communication with a database, stored
procedure execution requests or the SQL texts failed to send can be stored in a
CompactFlash card.
After the recovery, the buffered SQL texts or stored procedure execution requests
are automatically sent to the database. (Manual operation is also possible.)
Disconnected
Database
Insert...
Insert...
Insert...
Update...
1
2
3
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
CompactFlash card
Recovered
Resend
Database
Insert...
Insert...
Insert...
Update...
CompactFlash card
Figure 1.5 Buffering of send data (SQL text) during a communication error
4
SETTINGS AND
PROCEDURE TO
OPERATION
5
INSTALLATION AND
UNINSTALLATION
6
FUNCTIONS
7
1.1 Features
MES INTERFACE
FUNCTION
CONFIGURATION TOOL
8
DB CONNECTION
SERVICE AND
SETTING TOOL
1
- 5
Page 32

1
OVERVIEW
(4) Log data are available in the event of an access error
After connection with a database, when there is a communication error, a log of the
error contents can be recorded to the database side.
Analyzing the log can protect data and analyze the error.
Database
DB Connection
Service
Access
log
Figure 1.6 Obtaining logs for access errors
(5) Directions from the information system can be realized.
Processing registered in the MES interface module can be started from information
system applications.
This enables to realize production directions from the information system.
Not only can data be sent to a database but it can also be received from a database.
This enables to download data such as production information from information
system databases.
<MES interface module>
2) Starts registered
processing.
(Job execution)
1) Instructs job execution.
3) Sends data.
SQL
failure
log
<Information system>
Database
1
- 6
<MES interface module>
1.1 Features
1) Instructs job execution.
2) Starts registered
processing.
(Job execution)
3) Sends data.
Figure 1.7 Realization of directions from the information system
<Information system>
Database
Page 33

1
OVERVIEW
(6) Supporting diverse databases
(7) Access independent of the database table configuration is possible.
When designing a new system, a wide range of database types can be selected.
Even when connecting to the existing system, the system can be transferred without
changing the existing database.
Freely designed database tables can be used for access to databases.
When designing a new system, not only the high flexibility of design, but when
connecting to the existing system, the system can be constructed without changing
the database tables.
1
2
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
(8) Time synchronization using SNTP is also possible.
The clocks for the MES interface module and the programmable controller CPU can
be set through communications with an SNTP server computer.
This enables to synchronize the time for the entire system.
3
SPECIFICATIONS
4
SETTINGS AND
PROCEDURE TO
OPERATION
5
INSTALLATION AND
UNINSTALLATION
6
1.1 Features
FUNCTIONS
7
MES INTERFACE
FUNCTION
CONFIGURATION TOOL
8
DB CONNECTION
SERVICE AND
SETTING TOOL
1
- 7
Page 34

1
OVERVIEW
1.2 MX MESInterface Software Configuration
This section explains the MX MESInterface software configuration.
Table 1.1 MX MESInterface software configuration
Item Description
Installs each execution software (MES Interface Function Configuration Tool, DB
Installer
MES Interface Function
Configuration Tool
DB Connection Service
DB Connection Service
Setting Tool
Connection Service, and DB Connection Service Setting Tool) in each operating
environment.
Operates on a configuration computer and configures various settings required for the
MES interface function.
In addition to the configuration, the application tool offers features such as the operation
status check, working log check, or stop/restart operation.
Operates on the server computer and links databases with the MES interface module
and the MES Interface Function Configuration Tool.
Operates on the server computer and changes the settings of the DB Connection
Service.
Reference
section
CHAPTER 5
CHAPTER 7
CHAPTER 8
CHAPTER 8
1
- 8
1.2 MX MESInterface Software Configuration
Page 35

2
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
CHAPTER 2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
This chapter explains the system configuration of the MES interface module.
2.1 System Configuration
2.1.1 Overall system configuration
1
OVERVIEW
2
This section shows the overall system configuration when using the MES interface
module.
R
Oracle , SQL Server, etc.
(manufactured by
other companies)
*3
DB Connection Service
DB Connection Service Setting Tool
Configuration computer
MES Interface Function
Configuration Tool
*1
SNTP server computer
MES interface module
MELSECNET/H, etc.
*1 *2
Server computer
Database
CompactFlash
card
Ethernet
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
SPECIFICATIONS
4
SETTINGS AND
PROCEDURE TO
OPERATION
5
INSTALLATION AND
UNINSTALLATION
Q/L/QnA/ACPU, C Controller module
Figure 2.1 Overall system configuration when using the MES interface module
*1 The SNTP server computer and configuration computer can be shared with server computers.
*2 This computer is necessary when using the SNTP server computer time for the MES interface
module time.
Section 6.3 Time Synchronization Function
*3 The redundant server system and database cannot be used.
:Functions provided by MX MESInterface
2.1 System Configuration
2.1.1 Overall system configuration
2
- 1
6
FUNCTIONS
7
MES INTERFACE
FUNCTION
CONFIGURATION TOOL
8
DB CONNECTION
SERVICE AND
SETTING TOOL
Page 36

2
Installation
Commercialized product
Configuration computer
MX MESInterface
MES Interface Function
Configuration Tool
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
2.1.2 System configuration for installation
This section shows system configurations for installing MX MESInterface.
(1) When installing DB Connection Service and DB Connection Service Setting
Tool on a server computer
MX MESInterface
Installation
DB Connection Service
DB Connection Service Setting Tool
Figure 2.2 Installing DB Connection Service and DB Connection Service Setting Tool
(1) When installing DB Connection Service on a database server computer, the
ODBC setting for the database used must be done beforehand.
Section 8.2 Setting ODBC to the Database
(2) When installing DB Connection Service on an application server computer, an
account for user program execution must be created beforehand.
Server computer
Commercialized product
(2) When installing MES Interface Function Configuration Tool on a configuration
computer
2
- 2
Figure 2.3 Installing MES Interface Function Configuration Tool
2.1 System Configuration
2.1.2 System configuration for installation
Page 37

2
Remark
r
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
2.1.3 System configuration for initial setup
This section shows system configurations for initial setup of the MES interface module
using MES Interface Function Configuration Tool.
MES interface module
Ethernet
MES interface module
Ethernet
Twisted pair cable
(Crossing cable)
or
Twisted pair cable
(Straight cable)
Configuration computer
1
2
3
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
Default value of
"MES interface module"
IP ADDRESS
Subnet mask
Hub
Figure 2.4 System configurations for initial setup of the MES interface module
Configuration compute
The following explains the network settings of the configuration computer when
connecting it to the MES interface module on a 1:1 basis.
1 Set the same network address as the one of the MES interface module in the
network settings for the configuration computer.
Set the values to be identical.
Set different values.
Network section
192.168.3. 3
255.255.255. 0
section
Figure 2.5 Network settings for configuration computer
Host
"Configuration computer"
IP ADDRESS
Subnet mask
Network section
192.168.3.
255.255.255. 0
Host
section
1
2 Make the network settings of the configuration computer in the [Internet Protocol
(TCP/IP) Properties] dialog box.
Example: Microsoft
®
Windows® XP Professional Operating System
SPECIFICATIONS
4
SETTINGS AND
PROCEDURE TO
OPERATION
5
INSTALLATION AND
UNINSTALLATION
6
FUNCTIONS
7
MES INTERFACE
FUNCTION
CONFIGURATION TOOL
8
Figure 2.6 [Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties] dialog box
3
DB CONNECTION
SERVICE AND
SETTING TOOL
2.1 System Configuration
2.1.3 System configuration for initial setup
2
- 3
Page 38

2
r
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
2.1.4 System configuration for operation
This section shows the system configuration when operating the MES interface module.
The MES interface module can only be connected with a LAN.
The module cannot be connected via the Internet.
MES interface module
Figure 2.7 System configuration for operating the MES interface module
Twisted pair cable
Ethernet
Intranet
Server computer
SNTP server computer
Configuration compute
2
- 4
2.1 System Configuration
2.1.4 System configuration for operation
Page 39

2
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
2.2 Applicable Systems
This section describes the applicable systems.
1
Programmable
controller CPU
(1) Applicable modules and base units, and No. of modules
(a) When mounted with a CPU module
The table below shows the CPU modules and base units applicable to the MES
interface module and quantities for each CPU model.
Depending on the combination with other modules or the number of mounted
modules, power supply capacity may be insufficient.
Pay attention to the power supply capacity before mounting modules, and if the
power supply capacity is insufficient, change the combination of the modules.
Table 2.1 Applicable modules and base units, and No. of modules
Applicable module
CPU type CPU model
Q00JCPU 8
Basic model QCPU
High Performance
model QCPU
Process CPU
Redundant CPU
Universal model
QCPU
*3*4
Q00CPU
Q01CPU
Q02CPU
Q02HCPU
Q06HCPU
Q12HCPU
Q25HCPU
Q02PHCPU
Q06PHCPU
Q12PHCPU
Q25PHCPU
Q12PRHCPU
Q25PRHCPU
Q00UJCPU
Q00UCPU
Q01UCPU
Q02UCPU
Q03UDCPU
Q04UDHCPU
Q06UDHCPU
Q10UDHCPU
Q13UDHCPU
Q20UDHCPU
Q26UDHCPU
Q03UDECPU
Q04UDEHCPU
Q06UDEHCPU
Q10UDEHCPU
Q13UDEHCPU
Q20UDEHCPU
Q26UDEHCPU
No. of modules
*6
*6
*6
*6
*6
*5
*5
*5
*5
*6
*6
*6
*6
*6
*6
*6
*6
*6
*6
*6
*1
Main base unit
24
64
64
53 ×
8
24
36
64
Base unit
*1
*2
Extension base unit
:Applicable ,
(To the next page)
×
:N/A
OVERVIEW
2
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
SPECIFICATIONS
4
SETTINGS AND
PROCEDURE TO
OPERATION
5
INSTALLATION AND
UNINSTALLATION
6
FUNCTIONS
7
MES INTERFACE
FUNCTION
CONFIGURATION TOOL
8
2.2 Applicable Systems
DB CONNECTION
SERVICE AND
SETTING TOOL
2
- 5
Page 40

2
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
Programmable
controller CPU
C Controller module
Table 2.1 Applicable modules and base units, and No. of modules (continue)
Applicable module
CPU type CPU model
Q50UDEHCPU
Q100UDEHCPU
Universal model
QCPU
RCPU
Safety CPU QS001CPU N/A ×
*1 Limited within the range of I/O points for the CPU module.
*2 Can be installed to any I/O slot of a base unit.
*3 Use the MES interface module whose serial No. (first five digits) is 09012 or later.
*4 Can access host station only. Cannot access other stations.
*5 Use the MES interface module whose serial No. (first five digits) is 09042 or later.
*6 Use the MES interface module whose serial No. (first five digits) is 10012 or later.
*7 An extension base unit cannot be connected to the safety CPU module.
*8 Use the MES interface module whose serial No. (first five digits) is 11052 or later.
*9 Use the MES interface module whose serial No. (first five digits) is 12092 or later.
Use the Q12DCCPU-V whose serial No. (first five digits) is 12042 or later.
*10 Use the MES interface module whose serial No. (first five digits) is 14122 or later.
*11 Use the MES interface module whose serial No. (first five digits) is 16072 or later.
*12 RCPU can be mounted on the RQ extension base unit or Q series extension base unit which is
routed from RQ extension base unit.
Q03UDVCPU
Q04UDVCPU
Q06UDVCPU
Q13UDVCPU
Q26UDVCPU
R04CPU
R08CPU
R16CPU
R32CPU
R120CPU
Q06CCPU-V
Q06CCPU-V-B
Q12DCCPU-V
Q24DHCCPU-V
Q24DHCCPU-LS
*11
*11
*11
*11
*11
*8
*8
*10
*10
*10
*10
*10
*9
*10
*10
No. of modules
64
59 ×
N/A × ×
64
62
*1
Main base unit
(From the previous page)
Base unit
*1
*2
Extension base unit
*12
*7
×
:Applicable , × :N/A
2
- 6
Use a MES interface module appropriate to each CPU module.
If an unsupported one is used for a CPU module, it does not function normally.
(b) When mounting to remote I/O station of MELSECNET/H
The MES interface module cannot be mounted to remote I/O station of the
MELSECNET/H.
Mount the MES interface module to a CPU module of the master station.
2.2 Applicable Systems
Page 41

2
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
(2) Application to multiple CPU system
When using the MES interface module in multiple CPU system, refer to the following
manual.
QCPU User's Manual (Multiple CPU System)
The MES interface module is compatible with the multiple CPU system with function
version B from the first product.
2.3 Connection System Equipment
This section explains the equipment can be connected to the MES interface module.
(1) CompactFlash card (sold separately)
The MES interface module requires one CompactFlash card.
Use a CompactFlash card manufactured by Mitsubishi listed in the following table.
Failure to do so may cause a problem such as data corruption in the CompactFlash
card and system stop.
1
2
3
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
Table 2.2 CompactFlash card (sold separately)
Model Description
GT05-MEM-128MC CompactFlash card 128 MB
GT05-MEM-256MC CompactFlash card 256 MB
QD81MEM-512MBC CompactFlash card 512MB
QD81MEM-1GBC CompactFlash card 1GB
(1) For CompactFlash card format, use the formatting function of MES Interface
Function Configuration Tool.
Section 7.13.8 Formatting the CompactFlash card
(2) A CompactFlash card has a service life (restriction on the number of writes).
For details, refer to the specifications of each product.
4
SETTINGS AND
PROCEDURE TO
OPERATION
5
INSTALLATION AND
UNINSTALLATION
6
FUNCTIONS
7
2.3 Connection System Equipment
MES INTERFACE
FUNCTION
CONFIGURATION TOOL
8
DB CONNECTION
SERVICE AND
SETTING TOOL
2
- 7
Page 42

2
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
(2) Twisted pair cable (sold separately)
Use twisted pair cable that meets IEEE 802.3 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX standards.
(a) For 100 Mbps
Either 1) or 2) of the following can be used.
1) Unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cable
Straight cable: Category 5 or higher
Crossing cable: Category 5 or 5e
2) Shielded twisted pair (STP) cable
Straight cable: Category 5 or higher
Crossing cable: Category 5 or 5e
(b) For 10 Mbps
Either 1) or 2) of the following can be used.
1) Unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cable
Straight cable: Category 3 or higher
Crossing cable: Category 3 to 5e
2) Shielded twisted pair (STP) cable
Straight cable: Category 3 or higher
Crossing cable: Category 3 or 5e
During high speed communication (100 Mbps) via 100BASE-TX connection,
communication errors may occur due to the effect of high frequency noise
generated from the equipment other than programmable controller, depending on
the installation environment.
Take the following countermeasures on the MES interface module side to
eliminate the effect of high frequency noise when constructing the network
system.
(1) Wiring
• Do not install the twisted pair cables together with the main circuit or
power lines, or bring them close to each other.
• Make sure to place the twisted pair cable in a duct.
(2) Cable
• In the environment where the cable is susceptible to noise, use the
shielded twisted pair cable (STP cable).
(3) 10 Mbps communication
• Connect the 10 Mbps-compatible equipment with the MES interface
module and transmit the data to the equipment at a transmission speed of
10 Mbps.
2
- 8
2.3 Connection System Equipment
Page 43

2
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
2.4 Operating Environment
2.4.1 Configuration computer
This section explains the operating environment for the configuration computer.
Table 2.3 Operating environment for configuration computer
Item Description
Computer
CPU
Required
memory
Hard disk available capacity 64 MB or more
Disc drive CD-ROM disc drive
Display Resolution 1024 × 768 pixels or higher
Operating system
(English version)
Interface Ethernet
Windows
See Table 2.4 "Performance required for personal computer and operating systems".
Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft
®
supported personal computer.
®
Windows® 2000 Professional Operating System Service Pack 2 or later
®
Windows® XP Professional Operating System
®
Windows® XP Home Edition Operating System
®
Windows® 2000 Server Operating System Service Pack 2 or later
®
Windows Server® 2003 Operating System
®
Windows Vista® Home Basic Operating System
®
Windows Vista® Home Premium Operating System
®
Windows Vista® Business Operating System
®
Windows Vista® Ultimate Operating System
®
Windows Vista® Enterprise Operating System
®
Windows® 7 Starter Operating System
®
Windows® 7 Home Premium Operating System
®
Windows® 7 Professional Operating System
®
Windows® 7 Ultimate Operating System
®
Windows® 7 Enterprise Operating System
®
Windows® 8 Operating System
®
Windows® 8 Pro Operating System
®
Windows® 8 Enterprise Operating System
®
Windows® 8.1 Operating System
®
Windows® 8.1 Pro Operating System
®
Windows® 8.1 Enterprise Operating System
1
OVERVIEW
2
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
SPECIFICATIONS
4
SETTINGS AND
PROCEDURE TO
OPERATION
5
INSTALLATION AND
UNINSTALLATION
6
FUNCTIONS
2.4 Operating Environment
2.4.1 Configuration computer
2
- 9
7
MES INTERFACE
FUNCTION
CONFIGURATION TOOL
8
DB CONNECTION
SERVICE AND
SETTING TOOL
Page 44

2
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
(1) Instructions for operating system
Operating system
Windows® 2000 Professional
Windows® XP
Windows® 2000 Server
Windows Server® 2003
Windows Vista
Windows® 7
Windows® 8
Windows® 8.1
®
(a) Performance required for personal computer and operating systems
Table 2.4 Performance required for personal computer and operating systems
Performance required for personal computer
CPU Required memory
®
300MHz or more
®
550MHz or more
Pentium® 1GHz or more
CoreTM2 Duo 2GHz or more
Intel
Pentium
Pentium
®
128 MB or more
256 MB or more
32-bit version: 1GB or more
64-bit version: 2GB or more
(b) Supported version
1GB or more
Table 2.5 Supported version of MX MESInterface
Operating system
Windows® 2000 Professional
Windows® XP(32-bit version)
Windows® 2000 Server
Windows Server® 2003(32-bit version)
Windows Vista®(32-bit version)
Windows® 7(32-bit version)
Windows® 7(64-bit version)
Windows® 8(32-bit version, 64-bit version)
Windows® 8.1(32-bit version, 64-bit version)
Supported version of MX
MESInterface
All versions
Version 1.04E or later
Version 1.06G or later
Version 1.08J or later
Version 1.10L or later
Version 1.12N or later
(c) User authority
Log on as a user having administrator authority.
• Installation, uninstallation are available only by the administrator's authority.
• Use the product as a user having a privilege higher than 'Standard user' or
'Administrator'.
(d) The functions cannot be used
The following functions cannot be used.
This product may not perform properly, when these functions are used.
• Activating the application with Windows
®
compatible mode
• Simplified user switch-over
• Remote desktop
• Large font size (Advanced setting of Display Properties)
• DPI setting other than 100% (set the size of text and illustration other than
[smaller-100%])
• Power save mode (Standby, Hibernate, Sleep)
• Windows XP Mode
• Windows Touch or Touch
• Modern UI
• Client Hyper-V
2
- 10
2.4 Operating Environment
2.4.1 Configuration computer
Page 45

2
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
1
2.4.2 Server computer
This section explains the operating environment for the server computer.
Table 2.6 Operating environment for server computer
Item Description
Computer
CPU
Required
memory
Hard disk available capacity 64 MB or more
Disc drive CD-ROM disc drive
Display Resolution 1024 × 768 pixels or higher
Operating system
(English version)
Interface Ethernet
Required software
Windows
See Table 2.7 "Performance required for personal computer and operating systems".
Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft
When using the DB interface function: relational database (English version)
When using the time synchronization function: SNTP server
(Equipped as a standard to Windows
Server
®
supported personal computer.
®
Windows® 2000 Professional Operating System Service Pack 2 or later
®
Windows® XP Professional Operating System
®
Windows® 2000 Server Operating System Service Pack 2 or later
®
Windows Server® 2003 Operating System
®
Windows Server® 2003 x64 Edition
®
Windows Server® 2008 Operating System
®
Windows Server® 2012 Operating System
®
Windows Vista® Business Operating System
®
Windows Vista® Ultimate Operating System
®
Windows Vista® Enterprise Operating System
®
Windows® 7 Professional Operating System
®
Windows® 7 Ultimate Operating System (English version)
®
Windows® 7 Enterprise Operating System
®
Windows® 8 Pro Operating System
®
Windows® 8 Enterprise Operating System
®
Windows® 8.1 Pro Operating System
®
Windows® 8.1 Enterprise Operating System
®
•Oracle
•Oracle
•Oracle
•Oracle
•Oracle
•Microsoft
•Microsoft
•Microsoft
•Microsoft
•Microsoft
•Microsoft
•Microsoft
•Microsoft
•Microsoft
•Microsoft
• Wonderware
8i (32 bits)
®
9i (32 bits)
®
10g (32 bits)
®
11g (32-bit, x 64)
®
12c (x 64)
®
SQL Server® 2000 (32 bits)
®
SQL Server® 2005 (32 bits)
®
SQL Server® 2008 (32-bit, x64)
®
SQL Server® 2012 (32-bit, x64)
®
SQL Server® 2000 Desktop Engine (MSDE 2000)
®
Access® 2000
®
Access® 2003
®
Access® 2007
®
Access® 2010 (32 bits)
®
Access® 2013 (32 bits)
®
Historian 9.0 (Industrial SQL Server®)
®
2008, and Windows Server® 2012)
®
2000 Server, Windows Server® 2003, Windows
OVERVIEW
2
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
SPECIFICATIONS
4
SETTINGS AND
PROCEDURE TO
OPERATION
5
INSTALLATION AND
UNINSTALLATION
6
FUNCTIONS
7
MES INTERFACE
FUNCTION
CONFIGURATION TOOL
8
2.4 Operating Environment
2.4.2 Server computer
2
- 11
DB CONNECTION
SERVICE AND
SETTING TOOL
Page 46

2
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
(1) Instructions for operating system
(a) Performance required for personal computer and operating systems
Table 2.7 Performance required for personal computer and operating systems
Operating system
Windows® 2000 Professional
Windows® XP Professional
Windows® 2000 Server
Windows Server® 2003
Windows Server® 2008 Pentium® 2GHz or more
Windows Vista® Business
Windows Vista® Ultimate
Windows Vista® Enterprise
Windows® 7 Professional
Windows® 7 Ultimate
Windows® 7 Enterprise
Windows® 8 Pro
Windows® 8 Enterprise
Windows® 8.1 Pro
Windows® 8.1 Enterprise
Windows Server® 2012
Pentium
Pentium
Intel
Performance required for personal computer
CPU Required memory
®
300MHz or more
®
550MHz or more
®
Pentium
Pentium
®
CoreTM2 Duo 2GHz or more
1GHz or more
®
1GHz or more
128 MB or more
256 MB or more
2GB or more
1GB or more
32-bit version: 1GB or more
64-bit version: 2GB or more
2GB or more
2
- 12
2.4 Operating Environment
2.4.2 Server computer
Page 47

2
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
(b) Supported version
Table 2.8 Supported version of MX MESInterface
Windows® 2000 Professional
Windows® XP(32-bit version)
Windows® 2000 Server
Windows Server® 2003(32-bit version)
Windows Server® 2003(64-bit version*1)
Windows Server® 2008(32-bit version, 64-bit version*1)
Windows Vista®(32-bit version)
Windows Vista®(64-bit version)
Windows® 7(32-bit version, 64-bit version)
Windows® 8(32-bit version, 64-bit version)
Windows Server® 2012
Windows® 8.1(32-bit version, 64-bit version)
*1 Itanium processor(IA-64) is not supported.
(c) User authority
• Installation, uninstallation are available only by the administrator's authority.
• MX MESInterface is available only by the administrator's authority.
Operating system
Supported version of
MX MESInterface
All versions
Version 1.05F or later
Version 1.04E or later
Version 1.05F or later
Version 1.06G or later
Version 1.10L or later
Version 1.12N or later
1
2
3
4
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
(d) The functions cannot be used
The following functions cannot be used.
This product may not perform properly, when these functions are used.
• Activating the application with Windows
®
compatible mode
• Simplified user switch-over
• Remote desktop
• Large font size (Advanced setting of Display Properties)
• DPI setting other than 100% (set the size of text and illustration other than
[smaller-100%])
• Power save mode (Standby, Hibernate, Sleep)
• Windows XP Mode
• Windows Touch or Touch
• Modern UI
• Client Hyper-V
• Server Core Installation
SETTINGS AND
PROCEDURE TO
OPERATION
5
INSTALLATION AND
UNINSTALLATION
6
FUNCTIONS
7
MES INTERFACE
FUNCTION
CONFIGURATION TOOL
2.4 Operating Environment
2.4.2 Server computer
2
- 13
8
DB CONNECTION
SERVICE AND
SETTING TOOL
Page 48

2
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
(2) Considerations for the database
The restrictions when using database are as follows:
• To use a relational database, a license based on the number of MES interfaces is
usually required. (Varies depending on the relational database type and license
type.)
For details, please consult the relational database vendor.
• The redundant relational data base cannot be used.
• For the operating environment, refer to the specifications of the relational
database used. Use 32-bit operating system for 32-bit relational database.
• For the precautions for using each database, refer to the following section.
Section 2.6.3 Precautions for using database
(a) Supported version
Table 2.9 Supported version of Databases
Database
Oracle® 8i
Oracle® 9i
Oracle® 10g
Oracle® 11g
Oracle® 12c
Microsoft® SQL Server® 2000
Microsoft® SQL Server® 2005
Microsoft® SQL Server® 2008
Microsoft® SQL Server® 2012
Microsoft® SQL Server® 2000 Desktop Engine
(MSDE 2000)
Microsoft® Access® 2000
Microsoft® Access® 2003
Microsoft® Access® 2007
Microsoft® Access® 2010
Microsoft® Access® 2013
Wonderware® Historian 9.0®(Industrial SQL Server®)
Serial No. (first five digits) of
MES interface module
All versions All versions
12012 or later
16072 or later
All versions All versions
09012 or later
12012 or later
14122 or later
All versions All versions
10012 or later
13092 or later
15102 or later
09012 or later
Supported version of
MX MESInterface
Version 1.05F or later
Version 1.12N or later
Version 1.01B or later
Version 1.05F or later
Version 1.09K or later
Version 1.04E or later
Version 1.08J or later
Version 1.10L or later
Version 1.01B or later
2
- 14
2.4 Operating Environment
2.4.2 Server computer
Page 49

2
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
2.4.3 Computer for developing XML processing applications
This section explains the operating environment of the computer for developing XML
processing applications.
Table 2.10 Operating environment of computer for developing XML processing applications
Item Description
Program development environment
Microsoft
Sun Microsystems J2SE v1.4.2
®
Visual Studio® .NET 2003
1
2
3
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
4
SETTINGS AND
PROCEDURE TO
OPERATION
5
INSTALLATION AND
UNINSTALLATION
6
FUNCTIONS
7
2.4 Operating Environment
2.4.3 Computer for developing XML processing applications
2
- 15
MES INTERFACE
FUNCTION
CONFIGURATION TOOL
8
DB CONNECTION
SERVICE AND
SETTING TOOL
Page 50

2
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
2.5 Checking Function Version and Serial Number
The serial No. and function version of the MES interface module can be confirmed on the
rating plate and GX Developer's system monitor.
(1) Confirming the serial number on the rating plate
The rating plate is situated on the side face of the MES interface module.
MAC ADD.
12012
Figure 2.8 "SERIAL" on the rating plate on the side of the MES interface module
Serial No. (first 5 digits)
Relevant regulation standards
2
- 16
2.5 Checking Function Version and Serial Number
Page 51

2
120121102450001-B
Function version
Serial number
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
(2) Checking on the front of the module
The serial No. and function version on the serial number display are also indicated on
the front of the module (lower part).
1
2
3
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
Figure 2.9 "SERIAL" on the serial number display on the front of the MES interface module
4
SETTINGS AND
PROCEDURE TO
OPERATION
5
INSTALLATION AND
UNINSTALLATION
6
FUNCTIONS
7
2.5 Checking Function Version and Serial Number
MES INTERFACE
FUNCTION
CONFIGURATION TOOL
8
DB CONNECTION
SERVICE AND
SETTING TOOL
2
- 17
Page 52

2
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
(3) Confirming the serial number on the system monitor (Product Information List)
To display the screen for checking the serial number and function version, select
[Diagnostics] [System monitor] in GX Developer.
Product inf. list
Serial
number
Figure 2.10 [Product Information List] of GX Developer
1 Production number display
2 Since the MES interface module does not support the production number display,
"-" is displayed.
The serial No. on the rated plate and on the front of the module may not match the
serial No. displayed in the product information list of GX Developer.
• The serial No. on the rated plate and on the front of the module indicates
the management information of the product.
• The serial No. displayed in the product information list of GX Developer
indicates the functional information of the product.
The functional information of the product is updated when some functions
are added.
Function
version
Product
number
2
- 18
2.5 Checking Function Version and Serial Number
Page 53

2
REMARKS
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
2.6 Precautions for System Configuration
This section describes precautions for system configuration.
1
2.6.1 Precautions for using Redundant CPU
The following describes the precautions for using the Redundant CPU.
(1) Mountable base unit
When using the MES interface module in a redundant system, be sure to mount the
MES interface module to the extension base unit for CPU or redundant power supply.
The MES interface module cannot be mounted to the main base unit in a redundant
system.
(2) [Access target CPU setting]
• When the MES interface module is mounted to the Redundant CPU, it can
access the CPU of host station only.
It cannot access the CPU of other station.
• When the MES interface module is mounted to other than the Redundant CPU, it
cannot access the Redundant CPU of other station.
(3) [Device Tag setting]
• When a system switching occurs to the Redundant CPU, collection of device tag
may stop for about 15 seconds.
• When selecting [High-speed sampling] from Sampling settings of Device Tag
setting, be sure to create system area for the user setting to the Redundant CPU
of both systems in the same capacity.
Section 7.8.1 (1) Creating a user-specified system area
OVERVIEW
2
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
SPECIFICATIONS
4
SETTINGS AND
PROCEDURE TO
OPERATION
5
(4) [Job setting]
When accessing the Redundant CPU, it is recommended to select [Handshake
operation] for the trigger condition of a job.
When other than [Handshake operation] is selected for the trigger condition, the
following phenomenon may occur at system switching of a redundant system.
• Data separation
• The write data is not reflected to the programmable controller CPU.
Section 7.10.2 (8) Handshake operation
2.6 Precautions for System Configuration
2.6.1 Precautions for using Redundant CPU
2
- 19
INSTALLATION AND
UNINSTALLATION
6
FUNCTIONS
7
MES INTERFACE
FUNCTION
CONFIGURATION TOOL
8
DB CONNECTION
SERVICE AND
SETTING TOOL
Page 54

2
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
2.6.2 Precautions for using multiple CPU system
The following describes the precautions for using the multiple CPU system.
(1) Access to each CPU module at start-up of multiple CPU system
In the system in which a MES interface module is mounted in the multiple CPU
system, an error may occur when accessing other CPU from the MES interface
module or accessing the other station via a network module controlled by other CPU
from the MES interface module due to the difference of start-up time of each CPU
module. In this case, clear the error in the MES interface module after starting up
other CPU.
Page 10-3, Section 10.1.2 (2)
The start-up of other CPUs can be checked with the special relays, SM220 to SM223.
User's manual for the CPU module used
2
- 20
2.6 Precautions for System Configuration
2.6.2 Precautions for using multiple CPU system
Page 55

2
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
1
2.6.3 Precautions for using database
The following shows the precautions for using database.
OVERVIEW
For characters that can be used for field and table names, refer to the following:
Appendix 2.4 Characters available for field names, table names, stored
procedure names,etc.
(1) Microsoft® SQL Server®
(a) Set "SQL Server and Windows" or "SQL Server and Windows Authentication
mode" for the security authentication mode.
•Microsoft
Configure the setting in [SQL Server Properties (Configure)].
®
SQL Server® 2000
2
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
SPECIFICATIONS
4
SETTINGS AND
PROCEDURE TO
OPERATION
5
Figure 2.11 [SQL Server Properties (Configure)]
•Microsoft
Set the security authentication mode into the Mixed Mode.
Specify the command parameter at installation of the MSDE 2000.
setup sapwd="sa" SECURITYMODE=SQL
(sa: Specify any password)
(b) For Microsoft
values, output arguments, and input/output arguments of a stored procedure
which returns a result set cannot be acquired.
®
SQL Server® 2000 Desktop Engine (MSDE 2000)
®
SQL Server® 2008, and Microsoft® SQL Server® 2012, return
2.6 Precautions for System Configuration
2.6.3 Precautions for using database
2
- 21
INSTALLATION AND
UNINSTALLATION
6
FUNCTIONS
7
MES INTERFACE
FUNCTION
CONFIGURATION TOOL
8
DB CONNECTION
SERVICE AND
SETTING TOOL
Page 56

2
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
(2) Microsoft® Access
(a) The number of fields to be updated (UPDATE) by the one [Communication action]
is up to 127.
(b) Do not make multiple accesses to one and the same file.
(Do not make access from multiple MES interface modules.)
(c) There are some restrictions for the data type which can be assigned to tag
component, constant value, and variable with MES Interface Function
Configuration Tool.
Section 7.11.1 (1) About tag components
Section 7.11.1 (2) About constants
Section 7.11.1 (3) About variables
(3) Wonderware® Historian
(a) The insertion (INSERT) only can be used with [Communication action].
(b) The rollback of insertion (INSERT) to the database is disabled.
®
2
- 22
2.6 Precautions for System Configuration
2.6.3 Precautions for using database
Page 57

3
SPECIFICATIONS
CHAPTER 3 SPECIFICATIONS
This chapter explains the performance specifications, functions, buffer memory, etc. of the
MES interface module and the MX MESInterface.
For general specifications of the MES interface module, refer to the following manual.
QCPU User's Manual (Hardware Design, Maintenance and Inspection)
3.1 Performance Specifications
1
OVERVIEW
2
This section explains the MES interface module and the MX MESInterface performance
specifications.
(1) Transmission and interface specifications
Table 3.1 Transmission and interface specifications
Item Specifications
Interface
Data transmission
rate
Transmission method Base band
Ethernet
CompactFlash card
Number of occupied I/O points 32 points/slot (I/O assignment: Intelli. 32 points)
Clock
5VDC internal current consumption 0.69A
External dimensions 98 (3.86) (H) × 27.4 (1.08) (W) × 90 (3.54) (D) [mm (inch)]
Weight 0.16 kg
No. of cascaded
stages
Maximum segment
length
Supported function
Supply power voltage 3.3V ± 5 %
Supply power
capacity
Card size TYPE I card
No. of installable
cards
*1
*1 The MES interface module distinguishes 10BASE-T from 100BASE-TX depending on the device
on other end.
For connection with a hub not having the auto-negotiation function, set the hub side to half-duplex
auto communication mode.
*2 This number applies when a repeater hub is used.
When using a switching hub, check the number of cascaded stages with the manufacturer of the
hub to be used.
*3 For the maximum segment length (a length between hubs), consult with the manufacturer of the
switching hub used.
10BASE-T 100BASE-TX
10 Mbps 100 Mbps
Maximum 4 stages
100m (length between a hub and a node)
The auto-negotiation function is available. (automatically distinguishes 10BASE-T from
100BASE-TX)
Maximum 150 mA
1
The clock data is obtained from a programmable controller CPU (in multiple CPU
system, CPU No.1) or the SNTP server computer.
Section 6.3 Time Synchronization Function
*2
Maximum 2 stages
*3
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
SPECIFICATIONS
4
*2
SETTINGS AND
PROCEDURE TO
OPERATION
5
INSTALLATION AND
UNINSTALLATION
6
FUNCTIONS
7
MES INTERFACE
FUNCTION
CONFIGURATION TOOL
8
3.1 Performance Specifications
DB CONNECTION
SERVICE AND
SETTING TOOL
3
- 1
Page 58
3
SPECIFICATIONS
(2) Software specifications
Table 3.2 MX MESInterface performance specifications
Item Specifications
No. of connected databases Maximum 32 items/project
No. of databases that can be connected
Allowable number of settings Maximum 64 items/project Section 7.10.1
Trigger buffering Maximum 128 times
DB interface
Job
Trigger
conditions
Action
Program
execution
No. of conditions can be
combined
Condition type
Allowable number of
settings
Type Select, update, insert, multiselect, delete, stored procedure, operation
No. of communication
action fields
No. of records/data
selectable for
communication action
No. of operations
possible for operation
action
Operators for operation
action
Allowable number of
settings
Maximum 2 conditions
(Combination can be selected either AND or OR)/job
Period: 1 to 32767 seconds
Time: Year, month, day, day of the week, hour, minute
Value monitoring
component value.
Compares tag component value and constant value.
Module startup
Handshake
Maximum 10 actions/job
Maximum 8192 fields/project
Up to 40000 records/MultiSelect communication action
Up to 45000 words/job
(Maximum 20 dyadic operations)/operation action
Addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, remainder, character
string combination
Maximum 2 programs/job
One program before execution of initial action + one program after
execution of final action
®
•Oracle
•Oracle
•Oracle
•Oracle
•Oracle
•Microsoft
•Microsoft
•Microsoft
•Microsoft
•Microsoft
•Microsoft
•Microsoft
•Microsoft
•Microsoft
•Microsoft
• Wonderware
• [DB-tag link settings](Select/Update/Insert/MultiSelect): Maximum
• [DB-tag link settings](Stored procedure): Maximum 257 rows/
• [Select/Update/Delete conditions]: Maximum 8 rows/communication
• [Select sort settings]: Maximum 8 rows/communication action
8i (32 bits)
®
9i (32 bits)
®
10g (32 bits)
®
11g (32-bit, x64)
®
12c (x64)
®
SQL Server® 2000 (32 bits)
®
SQL Server® 2005 (32 bits)
®
SQL Server® 2008 (32-bit, x64)
®
SQL Server® 2012 (32-bit, x64)
®
SQL Server® 2000 Desktop Engine (MSDE 2000)
®
Access® 2000
®
Access® 2003
®
Access® 2007
®
Access® 2010 (32 bits)
®
Access® 2013 (32 bits)
®
Historian 9.0 (Industrial SQL Server®)
*1
: Compares tag component value and tag
*1
256 rows/communication action
communication action
action
Reference
section
Section 7.9.1
Section 7.10.2
Section 7.11
Section 7.11.1
Section 7.11.4
Section 7.10.3
(To the next page)
3
- 2
3.1 Performance Specifications
Page 59

3
DB interface
XML processing
Working log
SPECIFICATIONS
Table 3.2 MX MESInterface performance specifications
Item Specifications
No. of access target
CPU settings
No. of tags 64 tags/project
No. of components
Device tag
Data type
Statistical processing
DB buffering
Command type One-shot execution of a job, enabling the job, disabling the job
Request message size Maximum 128 k bytes
Reception protocol HTTP1.0
User authentication
Error log capacity
Event log capacity
Buffering capacity during
communication error
*1 The monitoring interval is 1 to 600 (in units of 0.1 seconds) or 1 to 32767 (in units of seconds).
*2 When the database is Microsoft
*3 [No. of samples] can be set up to 20.
*4 The following shows the method for roughly calculating the buffering duration from the buffering
capacity.
Buffering duration = (No. of executable bufferings)(Execution frequency [times/hour]) [h]
No. of executable bufferings = (Usage capacity)(SQL text length + Overhead (4 bytes) [cases]
SQL text length = Total field character length + 6 × No. of fields + Total data length + 20 [bytes]
64 settings/project Section 7.7
*2
256 components
4096 components/project
Signed single-precision integer type (16 bits), signed doubleprecision integer type (32 bits), single-precision floating point type
(32 bits), bit type, character string type (1 to 32 characters),
16-bit BCD type, 32-bit BCD type
Average, maximum, minimum, moving average
maximum
Maximum capacity: CompactFlash card capacity - 32M bytes
*4
(16 M bytes to 512 M bytes)
No. of accounts: 16
User ID: 1 to 20 characters
Password: 6 to 14 characters
Maximum capacity: 1 M byte
• At least 4800 logs can be recorded.
Maximum capacity: 4 M bytes
• At least 4800 logs can be recorded. (When there is no detailed log)
• At least 2 logs can be recorded. (When there is a detailed log)
Section 2.6.3 Precautions for using database
*3
/tag
, moving minimum
®
Access® 2000/2003/2007/2010/2013, refer to the following.
*3
, moving
*3
(From the previous page)
Reference
section
Section 7.8.3
Section 7.6.4
CHAPTER 9
Section 7.12.5
1
OVERVIEW
2
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
SPECIFICATIONS
4
SETTINGS AND
PROCEDURE TO
OPERATION
5
INSTALLATION AND
UNINSTALLATION
6
[Calculation example]
Accessing to 256 fields with 1 job and 1 action and performing every 30 seconds when capacity:
64 M bytes, field name: 16 characters, data length: 32 characters
SQL text length = (16 × 256) + 6 × 256 + (32 × 256) + 20 = 13844 [bytes]
No. of executable bufferings = (64 × 1024 × 1024)(13844 + 4) 4846 [cases]
Buffering duration = 4846(6030 × 60) 40 [h]
3.1 Performance Specifications
3
- 3
FUNCTIONS
7
MES INTERFACE
FUNCTION
CONFIGURATION TOOL
8
DB CONNECTION
SERVICE AND
SETTING TOOL
Page 60

3
SPECIFICATIONS
Performance of the MES interface module and the system using the MES
interface module differs depending on the following factors.
Conduct a verification by user prior to starting the system.
• Operating environment (personal computer, network, and the
CompactFlash card)
• Loading status of the server computer and the network.
• Sequence scan time
• Accessing status from a personal computer, terminal display, or intelligent
function module to the programmable controller CPU.
• Access from a personal computer by [MES Interface Function
Configuration Tool] and XML processing.
• Settings of the MES interface module.
For the reference value of the processing time, refer to the following.
Appendix 4 Processing Time
3
- 4
3.1 Performance Specifications
Page 61

3
SPECIFICATIONS
3.2 Accessible Devices and Ranges
This section explains the accessible devices and ranges.
For inaccessible CPU modules, refer to the following.
Appendix 6 Data Collection Method for CPUs that cannot be Accessed Directly
(1) Accessible CPU modules
Table 3.3 Accessible CPU modules
PLC series
QCPU (Q mode)
*2
RCPU
LCPU
QnACPU
QCPU (A mode) Q02CPU-A, Q02HCPU-A, Q06HCPU-A
ACPU
C Controller module
*5
Basic model QCPU Q00JCPU, Q00CPU, Q01CPU
High Performance
model QCPU
Process CPU
Redundant CPU
Universal model
*2
QCPU
*2
*1 Cannot access the Redundant CPU of other station.
*2 Serial numbers of the MES interface module to be used are restricted. The restriction is the same
as the one for the applicable systems.
*3 Use the MES interface module whose serial No. (first five digits) is 12092 or later.
*4 Use the MES interface module whose serial No. (first five digits) is 14122 or later.
*5 Do not access directly the PLC series other than the above table.
If the CPU module is accessed directly by mistake, all access target CPU may not be accessed.
Q02CPU, Q02HCPU, Q06HCPU, Q12HCPU, Q25HCPU
Q02PHCPU
*1*2
Q12PRHCPU, Q25PRHCPU
Q00UJCPU, Q00UCPU, Q01UCPU, Q02UCPU, Q03UDCPU, Q04UDHCPU,
Q06UDHCPU, Q10UDHCPU, Q13UDHCPU, Q20UDHCPU, Q26UDHCPU,
Q03UDECPU, Q04UDEHCPU, Q06UDEHCPU, Q10UDEHCPU, Q13UDEHCPU,
Q20UDEHCPU, Q26UDEHCPU, Q50UDEHCPU, Q100UDEHCPU,
Q03UDVCPU, Q04UDVCPU, Q06UDVCPU, Q13UDVCPU, Q26UDVCPU
R04CPU, R08CPU, R16CPU, R32CPU, R120CPU
L02CPU
L06CPU
Q2ACPU, Q2ACPU-S1, Q2ASCPU, Q2ASCPU-S1, Q2ASHCPU, Q2ASHCPU-S1,
Q3ACPU, Q4ACPU, Q4ARCPU
A1NCPU, A0J2HCPU, A1SCPU, A1SHCPU, A1SJCPU, A1SJHCPU, A2CCPU,
A2CJCPU, A2NCPU, A2NCPU-S1, A2SCPU, A2SHCPU, A2ACPU, A2ACPU-S1,
A2UCPU, A2UCPU-S1, A2USCPU, A2USCPU-S1, A2USHCPU-S1, A3NCPU,
A3ACPU, A3UCPU, A4UCPU
Q12DCCPU-V, Q24DHCCPU-V, Q24DHCCPU-LS
Section 2.2 Applicable Systems
*2
, Q06PHCPU*2, Q12PHCPU, Q25PHCPU
*3
, L26CPU-BT*3, L02CPU-P*3, L26CPU-PBT*3, L02SCPU*4, L02SCPU-P*4,
*4
, L06CPU-P*4, L26CPU*4, L26CPU-P
Model
1
OVERVIEW
2
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
SPECIFICATIONS
4
*4
SETTINGS AND
PROCEDURE TO
OPERATION
5
INSTALLATION AND
UNINSTALLATION
6
FUNCTIONS
3.2 Accessible Devices and Ranges
7
MES INTERFACE
FUNCTION
CONFIGURATION TOOL
8
DB CONNECTION
SERVICE AND
SETTING TOOL
3
- 5
Page 62

3
MES interface
module
SPECIFICATIONS
(2) Accessible routes
(a) Single network
Network
module
Network 2 to 7
Request
source
The network is any of CC IE Control, NET/10(H), Ethernet, or CC IE Field.
The following lists CPU modules that can be used on the network communication route.
Relay station
Access target CPU
Network communication
route
CC IE Control, NET/10(H)
Ethernet
CC IE Field
*8 *1 *1 *1*10 *1 *2
*4 *5
Relay
station
Network communication route
Use a QCPU (Q mode) or RCPU as a control CPU for the MES interface module and network module.Request source
Use a QCPU (Q mode) or RCPU as a control CPU for the network module.
For accessible CPU modules, refer to the following.
QCPU (Q mode)
*7
Relay
station
Figure 3.1 Single network
Table 3.4 Single network
RCPU
*12
Network 8Network 1
Access target CPU (PLC series)
*11
LCPU QnACPU
×
Access target CPU
××
QCPU (A mode),
ACPU
××
: Accessible ×: Inaccessible
C Controller
module
*6
*9
MES interface
module
Request
source
The following lists CPU modules that can be used on the network communication route.
Network
module
Network
communication
route
Use a QCPU (Q mode) or RCPU as a control CPU for the MES interface module and network module.Request source
For accessible CPU modules, refer to the following. Access target CPU
Access target CPU
C24 multidrop
CC-Link
Figure 3.2 Single network
3
- 6
3.2 Accessible Devices and Ranges
Page 63

3
SPECIFICATIONS
1
Table 3.5 Single network
Network communication
route
CC-Link
C24 ××
QCPU (Q mode)
*1 For the network No. and station number, set the values same with the parameter settings of the Q
*2 For the QnACPU and QE71 on the access target CPU side, use products of the manufacturing
*3 For the CC-Link system master/local module on the access target CPU side, use modules of
*4 Use a MES interface module whose serial No. (first five digits) is "13092" or later.
*5 Use Universal model QCPU whose serial No. (first five digits) is "12012" or later.
*6 When a C Controller module is used as a control CPU of the access target network module, the
*7 Use QCPU (Q mode) or RCPU as a control CPU of the access target network module.
*8 Use an Ethernet module to access a programmable controller CPU over Ethernet.
*7
RCPU
series E71, QE71, L series E71 and R series E71 on access target CPU side.
Also, set [Station No. IP information] in the parameter settings of the Q series E71, QE71, L series
E71 and R series E71.
For the [Station No. IP information], specify the IP address computation method, table conversion
method, or both.
date 9707B or later.
software version "S" or later.
accessible CPU module is only the control CPU.
With the built-in Ethernet port of a programmable controller CPU, a programmable controller CPU
cannot be accessed.
Access target CPU (PLC series)
*11
LCPU QnACPU
QCPU (A mode),
ACPU
*3 *3 *6
: Accessible ×: Inaccessible
C Controller
module
2
SYSTEM
3
4
OVERVIEW
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
Example of accessible
module configuration
MES
interface
module
Ethernet
module
Figure 3.3 Access to the programmable controller CPU over Ethernet
Example of inaccessible
module configuration
Programmable
controller CPU
Ethernet Ethernet
*9 When the access target CPU is Q12DCCPU-V, the access is not possible.
*10 Use a MES interface module whose serial No. (first five digits) is "15102" or later.
*11 Use a MES interface module whose serial No. (first five digits) is "16072" or later.
*12 When the Network communication route is NET/10(H), the access is not possible.
Ethernet
module
MES
interface
module
Ethernet
module
Programmable
controller CPU
SETTINGS AND
PROCEDURE TO
OPERATION
5
INSTALLATION AND
UNINSTALLATION
6
FUNCTIONS
7
MES INTERFACE
FUNCTION
CONFIGURATION TOOL
3.2 Accessible Devices and Ranges
8
DB CONNECTION
SERVICE AND
SETTING TOOL
3
- 7
Page 64

3
Network 8Network 1
Network 2 to 7
C24 multidrop
CC-Link
MES interface
module
Network
module
Access target CPU
Network
communication
route
Co-existence network communication route
Relay
station
Relay
station
Relay
station
The network is any of CC IE Control, NET/10(H), Ethernet, or CC IE Field.
The following lists CPU modules that can be used on the network communication route and the communication
routes of other network types.
Use a QCPU (Q mode) or RCPU as a control CPU for the network module.
For accessible CPU modules, refer to the following.
Relay station
Access target CPU
Use a QCPU (Q mode) or RCPU as a control CPU for the MES interface module and network module.Request source
Request
source
SPECIFICATIONS
(b) Different network
MES interface
module
Request
source
The network is any of CC IE Control, NET/10(H), Ethernet, or CC IE Field.
The following lists CPU modules that can be used on the network communication route and the communication routes
of other network types.
Relay station
Access target CPU
Network
communication route
CC IE Control, NET/
10(H), Ethernet
CC IE Field
*7
*3
Network
module
Network 1
Co-existence
network route
CC-Link
C24
Network 2 to 7
Relay
station
Network communication route Co-existence
Use a QCPU (Q mode) or RCPU as a control CPU for the MES interface module and network module.Request source
Use a QCPU (Q mode) or RCPU as a control CPU for the network module.
For accessible CPU modules, refer to the following.
QCPU
(Q mode)
Relay
station
Figure 3.4 Different network
Table 3.6 Different network
RCPU
*6
Network 8
Access target CPU (PLC series)
*10
LCPU QnACPU
*11 *2 *2 *5
*11
C24 multidrop
CC-Link
Relay
station
Access target CPU
network
communication
route
QCPU (A mode),
ACPU
×× ×
C Controller
module
: Accessible ×: Inaccessible
3
- 8
3.2 Accessible Devices and Ranges
Figure 3.5 Different network
Page 65

3
SPECIFICATIONS
1
Table 3.7 Different network
Network
communication route
CC-Link, C24
Co-existence
network route
CC IE Control,
NET/10(H)
Ethernet
CC IE Field
*7 *1 *1 *1*9
*3 *4
*1 For the network No. and station number, set the values same with the parameter settings of the Q
*2 For the CC-Link system master/local module on the access target CPU side, use modules of
*3 Use a MES interface module whose serial No. (first five digits) is "13092" or later.
*4 Use Universal model QCPU whose serial No. (first five digits) is "12012" or later.
*5 When a C Controller module is used as a control CPU of the access target network module, the
*6 Use QCPU (Q mode) or RCPU as a control CPU of the access target network module.
*7 Use an Ethernet module to access a programmable controller CPU over Ethernet.
Access target CPU (PLC series)
QCPU
(Q mode)
series E71, QE71, L series E71 and R series E71 on access target CPU side.
Also, set [Station No. IP information] in the parameter settings of the Q series E71, QE71, L series
E71 and R series E71.
For the [Station No. IP information], specify the IP address computation method, table conversion
method, or both.
software version "S" or later.
accessible CPU module is only the control CPU.
With the built-in Ethernet port of a programmable controller CPU, a programmable controller CPU
cannot be accessed.
*6
RCPU
*11
*10
LCPU QnACPU
×× ×
×× ×
××
QCPU (A mode),
ACPU
: Accessible ×: Inaccessible
C Controller
module
*5
*8
2
3
4
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
Example of accessible
module configuration
MES
interface
module
Ethernet
module
Figure 3.6 Access to the programmable controller CPU over Ethernet
Example of inaccessible
module configuration
Programmable
controller CPU
Ethernet Ethernet
*8 When the access target CPU is Q12DCCPU-V, the access is not possible.
*9 Use a MES interface module whose serial No. (first five digits) is "15102" or later.
*10 Use a MES interface module whose serial No. (first five digits) is "16072" or later.
*11 When the Network communication route is NET/10(H), the access is not possible.
Ethernet
module
MES
interface
module
Ethernet
module
Programmable
controller CPU
SETTINGS AND
PROCEDURE TO
OPERATION
5
INSTALLATION AND
UNINSTALLATION
6
FUNCTIONS
7
MES INTERFACE
FUNCTION
CONFIGURATION TOOL
3.2 Accessible Devices and Ranges
8
DB CONNECTION
SERVICE AND
SETTING TOOL
3
- 9
Page 66

3
SPECIFICATIONS
(3) Accessible devices
Table 3.8 Accessible devices
*1
Device
(Device name)
Function input (FX) × × × × × × ×
Function output (FY) × × × × × × ×
Function register (FD) × × × × × × ×
Special relay (SM) (M)
Special register (SD) (D)
Input relay (X)
Output relay (Y)
Internal relay (M)
Latch relay (L)
Annunciator (F) ×
Edge relay (V) × × ×
Link relay (B)
Data register (D)
Link register (W)
Timer
Counter
Retentive timer
Link special relay (SB) × × ×
Link special register (SW) × × ×
Step relay (S)
Direct input (DX) × × × × × × ×
Direct output (DY) × × × × × × ×
Accumulator (A) × × × × × × ×
Index register
File register
Link direct device
Intelligent function module device (Un\G)
*2
*3
*9 *11
*9
Contact (TS) ×
Coil (TC) ×
Current value (T/TN)
Long timer(LT)
Contact (CS) ×
Coil (CC) ×
Current value (C/CN)
Long counter(LC)
Contact (SS) × × ×
Coil (SC) × × ×
Current value (ST/SN)
Long retentive timer(LST)
*9
(Z) × × ×
(V) × × × × × × ×
(R)
(ZR)
*5*10
(ERn\R)
Link input (Jn\X)
Link output (Jn\Y)
Link relay (Jn\B)
Link special relay (Jn\SB)
Link register (Jn\W)
Link special register (Jn\SW)
*4
*14
*4
*14
*4
*14
*6
*6
*6
*6
*6
*7
*6
QCPU
(Q mode)
××× ××××
××× ××××
××× ××××
×× ×× ×
*8
*8
×× ×× ×
RCPU
*16
QCPU
(A mode)
×××
×××
×× ×
×× ×
×× ×
×× ×
×× ×
×× ×
××
LCPU
QnACP
U
ACPU
C Controller
module
×
*13
*11
*13
×
×
×
3
- 10
3.2 Accessible Devices and Ranges
Page 67

3
SPECIFICATIONS
Module access
device
Module refresh
device
*1
Device
(Device name)
Cyclic transmission area
device (U3En\G)
Cyclic transmission area
device (U3En\HG)
Refresh data register(RD)
*12 *15
*12 *14
*1 The local devices of the Q/QnA series programmable controller CPU and file registers for
*2 For the QCPU (Q mode)/QnACPU, specify SM; for the QCPU (A mode)/ACPU, specify M9000 or
*3 For the QCPU (Q mode)/QnACPU, specify SD; for the QCPU (A mode)/ACPU, specify D9000 or
*4 For the device name, specify either of them.
*5 For "n", specify the block number.
*6 For "n", specify the network No.
*7 For "n", specify the intelligent function module/special function module I/O number.
*8 When using the Q00JCPU, the access is not possible.
*9 M, L, and S devices are in the same region, regardless of the parameter device setting.
*10 ER0\R cannot be specified.
*11 The devices can be accessed only when specifying [Use device function] on the device setting
*12 The device is available in a multiple CPU system only.
*13 When the access target CPU is Q12DCCPU-V, the access is not possible.
*14 The devices newly added to RCPU are not accessible.
*15 When the access target CPU is RCPU, only in the device range from ‘U3En\G0’ to ‘9999’ are
*16 When the access target CPU is RCPU, only in the device range that can be set for QCPU or C
QCPU
(Q mode)
××× ××××
*14
individual programs cannot be accessed by specifying the program name.
Do not use local devices and file registers for individual programs since they may not be read/
written correctly.
later.
later.
screen in the C Controller setting utility.
accessible.
Controller module are accessible.For the settable device range, refer to the following manuals.
QCPU User's Manual (Hardware Design, Maintenance and Inspection)
MELSEC-Q C Controller Module User's Manual
××× ××××
RCPU
*16
QCPU
(A mode)
××××
LCPU
QnACP
ACPU
U
: Accessible, ×: Inaccessible
C Controller
module
1
OVERVIEW
2
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
SPECIFICATIONS
4
SETTINGS AND
PROCEDURE TO
OPERATION
5
3.2 Accessible Devices and Ranges
INSTALLATION AND
UNINSTALLATION
6
FUNCTIONS
7
MES INTERFACE
FUNCTION
CONFIGURATION TOOL
8
DB CONNECTION
SERVICE AND
SETTING TOOL
3
- 11
Page 68

3
Database
SPECIFICATIONS
3.3 Function List
This section lists the MES interface module functions.
(1) Function summary
The following explains the function summary of the MES interface module and MX
MESInterface.
The functions of the items are listed (2) and the subsequent descriptions.
MX MESInterface
Database
Database
Products manufactured
by other companies
Windows
application
MES interface module
R
MES Interface Function
Configuration Tool
DB Connection
Service
DB interface
function
Figure 3.7 Function summary
User-created
application
XML processing
function
SNTP server
Time
synchronization
function
3
- 12
3.3 Function List
Page 69

3
SPECIFICATIONS
(2) MES interface module function list
Table 3.9 MES interface module function list
Function Description
DB interface function Executes access to the database in units of jobs.
Collects device data of the programmable controller CPUs on the network in units of
tags.
By allocating database fields to tag components, the DB interface function enables the
Tag function
Trigger monitoring
function
Trigger buffering
function
SQL text transmission
function
(Communication action)
Stored procedure call
function
(Communication action)
Arithmetic processing
function
(Operation action)
Program execution
function
DB buffering function
XML processing function
Time synchronization
function
following.
• Database value reading/writing
• Reading/writing of programmable controller CPU device data specified with tag
components
Monitors values such as the time and tag values, and when the trigger condition
changes from false to true (when the conditions are met), starts a job.
When multiple sets of conditions for data transmission are met in a concentrated
manner, their data and trigger times are buffered in the module's internal memory so that
actions (data operation/transmission) can be executed later using the buffered data.
Even if the frequency of data transmission triggers is high, jobs are executed without
missing any trigger.
Automatically creates an SQL text and communicates with the database.
The following commands can be selected for the SQL text.
• Select/MultiSelect
• Update
• Insert
• Delete
A function to startup stored procedure in the database. Section 7.11.3
Performs operations for tag component values.
Executes programs in the application server computer before execution of the first action
and after execution of the last one in a job.
Buffers SQL texts into a CompactFlash card when they cannot be sent due to network
disconnection or failure of the database server computer.
After recovery, the buffered SQL texts are automatically sent to the database. (Manual
operation is also possible.)
Processes execution of requests made by user applications using XML format
messages.
The XML processing function allows the following instructions for job execution.
• One-shot execution of a job
• Validating a job (The job is executed when the trigger conditions are met.)
• Invalidating a job (The job is not executed even if the trigger conditions are met.)
Makes the time of the MES interface module synchronized with the time of the SNTP
server computer on the network or a programmable controller CPU (No.1 CPU in the
multiple CPU system).
Reference
section
Section 6.1
Section 7.10
Section 7.11
Section 6.1.3
Section 7.8
Section 6.1.4
Section 7.10.2
Section 6.1.5
Section 7.10.1
Section 6.1.6
Section 7.11.2
Section 6.1.8
Section 7.11.4
Section 6.1.9
Section 7.10.3
Section 6.1.10
Section 7.6.4
Section 7.10.4
Section 7.13.6
Section 6.2
CHAPTER 9
Section 6.3
Section 7.6.2
1
OVERVIEW
2
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
SPECIFICATIONS
4
SETTINGS AND
PROCEDURE TO
OPERATION
5
INSTALLATION AND
UNINSTALLATION
6
FUNCTIONS
7
MES INTERFACE
FUNCTION
CONFIGURATION TOOL
3.3 Function List
8
DB CONNECTION
SERVICE AND
SETTING TOOL
3
- 13
Page 70

3
SPECIFICATIONS
(3) MES Interface Function Configuration Tool function list
Table 3.10 MES Interface Function Configuration Tool function list
Function Description
System Setting Configure the initial settings for the MES interface module. Section 7.6
Network settings
Time synchronization
setting
Account setting Set user authentication accounts used for access to the MES interface module. Section 7.6.3
DB buffering setting Configure the settings for the DB buffering function. Section 7.6.4
Access Target CPU setting Set a connection channel to the access target CPU. Section 7.7
Device tag settings Configure the settings for the tag function. Section 7.8
Array setting
Component setting Configure the settings for assigning programmable controller CPU devices to tags. Section 7.8.3
Server Service setting Configure the settings for access to a server computer. Section 7.9
Job settings Configure the settings for the DB interface function. Section 7.10
Trigger conditions Configure the settings for startup conditions of the job. Section 7.10.2
Trigger buffering Set whether to utilize the Trigger buffering function or not. Section 7.10.1
Communication action Configure the settings for communications with a database. Section 7.11.1
Operation action Configure the settings for operation of tag component values. Section 7.11.4
Program execution Configure the settings for the program execution function. Section 7.10.3
DB buffering Set whether to utilize the DB buffering function or not. Section 7.10.4
Online Perform online operations to the MES interface module connected to the network. Section 7.12
Communication setting Set the target MES interface module. Section 7.12.1
Write Write the MES interface function settings (project) to the MES interface module. Section 7.12.2
Read Read the MES interface function settings (project) from the MES interface module. Section 7.12.3
Verify
Remote operation
Working log The working log of the MES interface module can be checked. Section 7.12.5
One-shot execution of a
job
Help
Configure the settings necessary for connecting the MES interface module to the
network.
Make the time setting for the MES interface module. Section 7.6.2
Configure this setting when writing multiple records extracted from a database to the
same tag component.
The MES interface function settings in the MES interface module are compared with
those in the currently editing project.
Display or change the operation status of the MES interface module, or format a
CompactFlash card.
Execute a job as a one-shot task. Section 7.12.6
The product information of the MES Interface Function Configuration Tool and the
Connect to MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC FA Global Website screen can be displayed.
Reference
section
Section 7.6.1
Section 7.8.2
Section 7.12.4
Section 7.13
Section 7.14
3
- 14
3.3 Function List
Page 71

3
SPECIFICATIONS
(4) DB Connection Service function list
Table 3.11 DB Connection Service function list
Function Description
ODBC connection function Connects the MES interface module and the ODBC interface for database.
Program execution function
Table information/stored
procedure information browse
function
IP filter function
Access log
Log output
function
DB Connection Service Setting
Tool
SQL failure log
Executes a program on the application server computer upon request from the MES
interface module.
Acquires the table information and stored procedure information, and sends them to
table information browse function and stored procedure information browse function
of MES Interface Function Configuration Tool.
Specifies the IP address of the MES interface module that can connect to the DB
Connection Service to ensure the security of the server computer.
Outputs the communication contents between the MES interface module and DB
Connection Service to the access log.
The error contents are output to the SQL failure log when the SQL text or stored
procedure cannot be completed normally in the database due to the reason such as
no table exist.
Software changes the DB Connection Service settings Section 8.5
Reference
section
Section 8.1
1
2
3
4
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
SETTINGS AND
PROCEDURE TO
OPERATION
5
INSTALLATION AND
UNINSTALLATION
6
FUNCTIONS
7
MES INTERFACE
FUNCTION
CONFIGURATION TOOL
3.3 Function List
8
DB CONNECTION
SERVICE AND
SETTING TOOL
3
- 15
Page 72

3
SPECIFICATIONS
3.4 I/O Signals for Programmable Controller CPU
3.4.1 I/O signal list
The following lists the MES interface module I/O signals to the programmable controller
CPU.
The following I/O signal assignment is based on the case where the start I/O No. of the
MES interface module is "0000" (installed to slot 0 of the main base unit)
If the MES interface module is mounted other than slot 0, see the list with changing the I/O
signals by those of the mounted slot.
Device X indicates an input signal from the MES interface module to the programmable
controller CPU and device Y indicates an output signal from the programmable controller
CPU to the MES interface module.
Table 3.12 I/O signal list
Signal direction MES interface module
Programmable controller CPU
Device
No.
Module READY
X0
ON: Module prepared
OFF: Module being prepared
CompactFlash card status
X1
ON: Installed OFF: Not installed
File access status
X2
ON: Stopped OFF: Running
X3 Use prohibited Y3
Network status
X4
ON: Initialization completed (Connectable)
OFF: Initializing (Unconnectable)
Information linkage status
X5
ON: Executing OFF: Stopped
X6
X7 Y7
Use prohibited
X8 Y8
X9 Y9
XA YA
XB
XC
XD YD
XE YE
SNTP time query timing
ON: Query complete OFF: No query
Use prohibited
XF YF
Signal name
Signal direction programmable controller CPU
Device
No.
Y0
Use prohibited
Y1
File access stop request
Y2
ON: Stop request OFF: —
Y4
Y5
Y6
Use prohibited
YB
YC
MES interface module
Signal name
3
- 16
(To the next page)
3.4 I/O Signals for Programmable Controller CPU
3.4.1 I/O signal list
Page 73

3
SPECIFICATIONS
Table 3.12 I/O signal list
Signal direction MES interface module
Programmable controller CPU
Device
No.
X10
X11
X12
X13
X14 Y14
X15 Y15
X16
X17
X18 Y18
X19 Y19
X1A Y1A
X1B Y1B
X1C
X1D
X1E Y1E
X1F
ERR. LED status
ON: Lighting, flashing OFF: Extinction
Sampling error
ON: Error OFF: Normal
Information linkage error
ON: Error OFF: Normal
Use prohibited
Access target CPU error
ON: Error OFF: Normal
Use prohibited
Another error
ON: Error OFF: Normal
Use prohibited
Watchdog timer error
ON: Error OFF: Normal
Signal name
(From the previous page)
Signal direction programmable controller CPU
MES interface module
Device
No.
Y10
Y11
Y12
Y13
Y16
Y17
Y1C
Y1D
Y1F
Error clear request
ON: Error clear request OFF: —
Use prohibited
Signal name
1
OVERVIEW
2
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
SPECIFICATIONS
4
SETTINGS AND
PROCEDURE TO
OPERATION
5
As for I/O signals to a programmable controller CPU, do not output (ON) a "Use
prohibited" signal.
Doing so may cause malfunctions of the programmable controller system.
3.4 I/O Signals for Programmable Controller CPU
3.4.1 I/O signal list
3
- 17
INSTALLATION AND
UNINSTALLATION
6
FUNCTIONS
7
MES INTERFACE
FUNCTION
CONFIGURATION TOOL
8
DB CONNECTION
SERVICE AND
SETTING TOOL
Page 74

3
SPECIFICATIONS
3.4.2 I/O signals details
Device
No.
X0 Module READY
CompactFlash card
X1
status
X2 File access status
The following table shows the details of the I/O signals of the MES interface module.
(1) Input signals details
Table 3.13 Input signals details
Signal name Description
Turns ON when the MES interface module becomes ready after the programmable controller is
powered ON from OFF or the programmable controller CPU is reset.
(1) Turns ON when the CompactFlash card is installed and the file access status (X2) is OFF.
(2) Turns OFF when the CompactFlash card is not installed or the file access status (X2) is ON.
(1) Turns ON while file access is stopped.
(a) The following operations are available while file access is stopped.
Removing and installing a CompactFlash card
( Section 4.7.2 Installation/removing the CompactFlash card)
Powering OFF the programmable controller during operation without battery
( Section 4.9 Operation without Mounting Battery)
(b) While file access is stopped, the following status occurs.
Reading from or writing to a CompactFlash card is disabled.
The MES interface function is suspended.
Operation from MES Interface Function Configuration Tool is disabled.
(2) Turns OFF during file access operation.
Powering ON the programmable controller from OFF or resetting the programmable controller
CPU brings file access in operation.
File access stop request (Y2)
X4 Network status
File access status (X2)
Information linkage status (X5)
CompactFlash card status (X1)
(1) Turns ON when the MES interface module is initialized and became a connectable state.
(2) When powering ON from OFF or resetting the programmable controller CPU, the network of the
MES interface module is initialized.
(In operation) (During stop)
Replace the CompactFlash card.
Power OFF the programmable controller.
(To the next page)
3
- 18
3.4 I/O Signals for Programmable Controller CPU
3.4.2 I/O signals details
Page 75

3
SPECIFICATIONS
Device
No.
X5
Signal name Description
Information linkage
status
(From the previous page)
Table 3.13 Input signals details
(1) Turns ON when the MES interface function operation is enabled.
This indicates that MES interface function processing is executable.
(2) Turns OFF when the MES interface function is in stop.
The MES interface function processing stops in the following cases.
1) The period after the programmable controller is powered ON from OFF or the programmable
controller CPU is reset until the MES interface function starts
2) When the MES interface function processing stops with [Remote operation] of MES Interface
Function Configuration Tool ( Section 7.13 Online - Remote operation)
3) When a module stop error occurs in the MES interface module
( Section 10.3.1 When using MES Interface Function Configuration Tool)
4) During updating settings ( Section 7.13.2 Manipulating the operation status of the MES
interface function)
5) While file access is stopped ( Section 4.7 CompactFlash Card)
(1) Turns ON when [Synchronize with SNTP] is selected in [Time synchronization setting], and
after succeeding the time query and storing the time into the buffer memory.
(2) Reads time data from the SNTP time query results (Buffer memory address: 11501 to 11507),
while XB is ON.
(3) This device turns OFF 1 second after XB turns ON.
1
2
3
4
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
SNTP time query
XB
timing
X10 ERR. LED status
X11 Sampling error
X12
Information linkage
error
SNTP time query timing (XB)
"Time synchronization" setting status
(Buffer memory address: 11500)
SNTP time query result
(Buffer memory address:
11501 to 11507)
Time query processing
(1) Turns ON while the ERR. LED is ON (during a module continuation error) or flashing (during a
module stop error).
(2) Turns OFF when the ERR. LED is turned OFF by turning the Error clear request (Y10) ON with
the ERR. LED ON. (However, this is not possible while the ERR. LED is flashing.)
(3) While the ERR. LED is ON or flashing (when X10 is ON), any or some of X11, X12, X16, and
X1C turn(s) ON.
(1) Turns ON when an error regarding Sampling error occurs.
(2) When this device is ON, the error code is stored into the Tag status area (Buffer memory
address: 1000 to 1075).
(3) Turns OFF when the Error clear request (Y10) is turned ON.
(1) Turns ON when an error regarding information linkage occurs.
(2) When this device is ON, the error code is stored into the Error log area (Buffer memory
address: 150 to 247).
(3) Turns OFF when the Error clear request (Y10) is turned ON.
(Initial value: OFF)
(Initial value: 0)
(Initial value: 0)
Sets time
data
Inquires time
to the SNTP
server computer.
(Initial)
1 second
Sets time
data
Inquires time
to the SNTP
server computer.
(To the next page)
1 second
SETTINGS AND
PROCEDURE TO
OPERATION
5
INSTALLATION AND
UNINSTALLATION
6
FUNCTIONS
7
MES INTERFACE
FUNCTION
CONFIGURATION TOOL
8
3.4 I/O Signals for Programmable Controller CPU
3.4.2 I/O signals details
3
- 19
DB CONNECTION
SERVICE AND
SETTING TOOL
Page 76

3
SPECIFICATIONS
Device
No.
X16
X1C Another error
X1F
Device
No.
Y2
Y10 Error clear request
Signal name Description
Access target CPU
error
Watchdog timer
error
Signal name Description
File access stop
request
(From the previous page)
Table 3.13 Input signals details
(1) Turns ON when an error occurs in communications with the access target CPU.
(2) When this device is ON, the error code is stored into the Access target CPU setting status area
(Buffer memory address: 4000 to 4071).
(3) Turns OFF when the Error clear request (Y10) is turned ON.
(1) Turns ON when an error not corresponding to X11, X12, or X16 occurs.
(2) When this device is ON, the error code is stored into the Error log area (Buffer memory
address: 150 to 247).
(3) Turns OFF when the Error clear request (Y10) is turned ON. (Only in case of a module
continuation error)
Turns ON when a watchdog timer error occurs.
(2) Output signals details
Table 3.14 Output signals details
(1) Turns ON when file access is stopped.
(2) For ON/OFF timing, refer to the description of X2.
(1) By turning ON during a module continuation error (ERR. LED: ON) turns OFF the ERR. LED
and X10, X11, X16, and X1C.
During a module stop error (ERR. LED: flashing), turning this device ON does not turn OFF the
ERR. LED.
(2) Clears the Current error area (Buffer memory address: 140 to 145).
Clears the latest error code displayed on [System monitor] of GX Developer. ( Section
10.1.3 System monitor)
3
- 20
3.4 I/O Signals for Programmable Controller CPU
3.4.2 I/O signals details
Page 77

3
SPECIFICATIONS
3.5 Buffer Memory List
The buffer memory list is shown below.
1
Address
(Decimal(Hex))
0
H
)
(0
1
H
)
(1
2
H
)
(2
3
H
)
(3
4
H
)
(4
5 to 6
H
to 6H)
(5
7
H
)
(7
8 to 54
H
to 36H)
(8
55 to 56
H
to 38H)
(37
57 to 58
H
to 3AH)
(39
59 to 60
H
to 3CH)
(3B
61 to 70
H
to 46H)
(3D
71 to 72
H
to 48H)
(47
73 to 74
H
to 4AH)
(49
75 to 76
H
to 4CH)
(4B
77 to 139
H
to 8BH)
(4D
Table 3.15 Buffer memory list
Application Name
RUN LED status
0: OFF 1: ON
ERR. LED status
0: OFF 1: ON 2: Flash
Switch 1 status (Mode setting)
0000h: Online
0001h: Hardware test
0002h: Self-loopback test
Switch 2 status (Default operation setting/battery error detection setting)
(1) Default operation setting [Account setting] (b0)
0: Operates according to [Account setting].
Module status
area
Use prohibited System area
Network
connection
status area
Use prohibited System area — — —
Network
settings status
area
Use prohibited System area — — —
1: Operates according to the default.
(2) Default operation setting [Account setting] (b1)
0: Operates according to [Network settings].
1: Operates according to the default.
(3) Battery error detection setting (b2)
0: Detects battery errors.
1: Does not detect battery errors.
Switch 3 status (Response monitoring time setting)
15 to 255 (Second): Response monitoring time
System area — —
Battery status
0: Normal 1: Battery error
IP address 0 R
Subnetwork 0 R
Default gateway 0 R
IP address 0 R
Subnet mask 0 R
Default gateway 0 R
*1 Shows whether or not reading/writing is possible.
R: Only reading is possible. W: Only writing is possible.
R/W: Both reading and writing are possible.
Initial
value
Read/
write
0R
0R
0R
0R
0R
0R
—
Reference
*1
section
Section
3.6.1
——
Section
3.6.2
Section
3.6.3
(To the next page)
OVERVIEW
2
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
SPECIFICATIONS
4
SETTINGS AND
PROCEDURE TO
OPERATION
5
INSTALLATION AND
UNINSTALLATION
6
FUNCTIONS
7
MES INTERFACE
FUNCTION
CONFIGURATION TOOL
8
3.5 Buffer Memory List
DB CONNECTION
SERVICE AND
SETTING TOOL
3
- 21
Page 78

3
SPECIFICATIONS
Address
(Decimal(Hex))
140
H
)
(8C
141
H
)
(8D
142 to 145
H
to 91H)
(8E
146 to 149
H
to 95H)
(92
150
H
)
(96
151
H
)
(97
152
H
)
(98
153
H
)
(99
154 to 157
H
to 9DH)
(9A
158 to 163
H
to A3H)
(9E
164 to 169
H
to A9H)
(A4
170 to 175
H
to AFH)
(AA
176 to 181
H
to B5H)
(B0
182 to 187
H
to BBH)
(B6
188 to 193
H
to C1H)
(BC
194 to 199
H
to C7H)
(C2
200 to 205
H
to CDH)
(C8
206 to 211
H
to D3H)
(CE
212 to 217
H
to D9H)
(D4
218 to 223
H
to DFH)
(DA
224 to 229
H
to E5H)
(E0
230 to 235
H
to EBH)
(E6
236 to 241
H
to F1H)
(EC
242 to 247
H
to F7H)
(F2
(From the previous page)
Table 3.15 Buffer memory list
Application Name
Initial
value
Read/
write
Reference
*1
section
Error code 0 R
Current error
area
System area — —
Section
3.6.4
Time 0R
Use prohibited System area — — —
Error count 0 R
Error log write pointer 0 R
Error code 0 R
Error log 1
System area — —
Time 0 R
Error log 2 (Same as Error log 1)
Error log 3 (Same as Error log 1)
Error log 4 (Same as Error log 1)
Error log 5 (Same as Error log 1)
Error log 6 (Same as Error log 1)
Error log area
Error log 7 (Same as Error log 1)
Section
3.6.5
Error log 8 (Same as Error log 1)
Error log 9 (Same as Error log 1)
Error log 10 (Same as Error log 1)
Error log 11 (Same as Error log 1)
Error log 12 (Same as Error log 1)
Error log 13 (Same as Error log 1)
Error log 14 (Same as Error log 1)
Error log 15 (Same as Error log 1)
Error log 16 (Same as Error log 1)
*1 Shows whether or not reading/writing is possible.
R: Only reading is possible. W: Only writing is possible.
R/W: Both reading and writing are possible.
(To the next page)
3
- 22
3.5 Buffer Memory List
Page 79

3
Address
(Decimal(Hex))
248 to 799
(F8
800 to 801
(320
802 to 803
(322
804 to 999
(324
1000 to 1003
(3E8
1004 to 1007
(3EC
1008 to 1011
(3F0
1013 to 1075
(3F5
1076 to 1289
(434
1294 to 1299
(50E
1300 to 1811
(514
1812 to 3999
(714
4000 to 4003
(FA0
4004 to 4007
(FA4
4009 to 4071
(FA9
SPECIFICATIONS
H
to 31FH)
H
to 321H)
H
to 323H)
H
to 3E7H)
H
to 3EBH)
H
to 3EFH)
H
to 3F3H)
1012
H
)
(3F4
H
to 433H)
H
to 509H)
1290
H
)
(50A
1291
H
)
(50B
1292
H
)
(50C
1293
H
)
(50D
H
to 513H)
H
to 713H)
H
to F9FH)
H
to FA3H)
H
to FA7H)
4008
H
)
(FA8
H
to FE7H)
(From the previous page)
Table 3.15 Buffer memory list
Application Name
Use prohibited System area — — —
Sampling/
monitoring
cycle area
Use prohibited System area — — —
Tag status area
Use prohibited System area — — —
Current tag
data value area
Use prohibited System area — — —
Access target
CPU setting
status area
Current cycle (Unit: second) 0 R
Maximum cycle (Unit: second) 0 R
Tag setting information 0 R
Sampling information 0 R
Sampling error information 0 R
Sampling 1, error code 0 R
Sampling 2 to
64, error codes
No. of requested tag 0 R/W
No. of stored tag 0 R
Update count 0 R
No. of components 0 R
System area — —
Current tag data value 0 R
Access target CPU setting information 0 R
Access target CPU error information 0 R
Access target CPU 1, error code 0 R
Access target
CPU 2 to 64,
error codes
*1 Shows whether or not reading/writing is possible.
R: Only reading is possible. W: Only writing is possible.
R/W: Both reading and writing are possible.
The composition of each area is the same as that of the Sampling 1,
error code.
Refer to
The composition of each area is the same as that of the Access target
CPU 1, error code.
Refer to
*2
for the assignment of each area.
*3
for the assignment of each area.
Initial
value
Read/
write
Reference
*1
section
Section
Section
Section
Section
(To the next page)
3.6.6
3.6.7
3.6.8
3.6.9
1
OVERVIEW
2
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
SPECIFICATIONS
4
SETTINGS AND
PROCEDURE TO
OPERATION
5
INSTALLATION AND
UNINSTALLATION
6
FUNCTIONS
7
MES INTERFACE
FUNCTION
CONFIGURATION TOOL
8
3.5 Buffer Memory List
DB CONNECTION
SERVICE AND
SETTING TOOL
3
- 23
Page 80

3
Address
(Decimal(Hex))
4072 to 11499
(FE8
(2CEC
11501 to 11507
(2CED
11513 to 11519
(2CF9
11521 to 11583
(2D01
SPECIFICATIONS
H
to
H
)
2CEB
11500
H
)
H
to
H
)
2CF3
11508
H
)
(2CF4
11509
H
)
(2CF5
11510
H
)
(2CF6
11511
H
)
(2CF7
11512
H
)
(2CF8
H
to
H
)
2CFF
11520
H
)
(2D00
H
to
H
)
2D3F
(From the previous page)
Table 3.15 Buffer memory list
Application Name
Use prohibited System area — — —
"Time synchronization" setting status
0: [Synchronize with PLC CPU time]1: [Synchronize with SNTP]
SNTP time query result 0 R
System area — — —
Information
linkage function
area
Monitoring interval timeout count 0 R
No. of trigger buffer data 0 R
Trigger buffer overflow count 0 R
System area — — —
Trigger buffer overflow count for Job 1 0 R
Trigger buffer
overflow counts
for Jobs 2 to 64
The composition of each area is the same as that of the Trigger buffer
overflow count for Job 1.
*4
Refer to
for the assignment of each area.
Initial
value
Read/
*1
write
0R
Reference
section
Section
3.6.10
Section
3.6.10
Section
3.6.10
*1 Shows whether or not reading/writing is possible.
R: Only reading is possible. W: Only writing is possible.
R/W: Both reading and writing are possible.
*2 The following table shows the error code area assignment for Sampling 1 to 64 (Buffer memory
address: 1012 to 1075).
Table 3.16 Sampling 1 to 64, error code areas
Name
Sampling 1 to 10, error codes 1012 1013 1014 1015 1016 1017 1018 1019 1020 1021
Sampling 11 to 20, error codes 1022 1023 1024 1025 1026 1027 1028 1029 1030 1031
Sampling 21 to 30, error codes 1032 1033 1034 1035 1036 1037 1038 1039 1040 1041
Sampling 31 to 40, error codes 1042 1043 1044 1045 1046 1047 1048 1049 1050 1051
Sampling 41 to 50, error codes 1052 1053 1054 1055 1056 1057 1058 1059 1060 1061
Sampling 51 to 60, error codes 1062 1063 1064 1065 1066 1067 1068 1069 1070 1071
Sampling 61 to 64, error codes 1072 1073 1074 1075
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30
31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40
41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50
51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60
61 62 63 64
Sampling 1 to 64, error code areas
3
- 24
3.5 Buffer Memory List
Page 81

3
Trigger buffer overflow counts for Jobs 1 to 10 11520 11521 11522 11523 11524 11525 11526 11527 11528 11529
Trigger buffer overflow counts for Jobs 11 to 20 11530 11531 11532 11533 11534 11535 11536 11537 11538 11539
Trigger buffer overflow counts for Jobs 21 to 30 11540 11541 11542 11543 11544 11545 11546 11547 11548 11549
Trigger buffer overflow counts for Jobs 31 to 40 11550 11551 11552 11553 11554 11555 11556 11557 11558 11559
Trigger buffer overflow counts for Jobs 41 to 50 11560 11561 11562 11563 11564 11565 11566 11567 11568 11569
Trigger buffer overflow counts for Jobs 51 to 60 11570 11571 11572 11573 11574 11575 11576 11577 11578 11579
Trigger buffer overflow counts for Jobs 61 to 64 11580 11581 11582 11583
SPECIFICATIONS
*3 The following table shows the error code area assignment for the Access target CPUs 1 to 64
(Buffer memory address: 4008 to 4071).
Table 3.17 Access target CPU 1 to 64, error code areas
Name
Access target CPU 1 to 10, error codes 4008 4009 4010 4011 4012 4013 4014 4015 4016 4017
Access target CPU 11 to 20, error codes 4018 4019 4020 4021 4022 4023 4024 4025 4026 4027
Access target CPU 21 to 30, error codes 4028 4029 4030 4031 4032 4033 4034 4035 4036 4037
Access target CPU 31 to 40, error codes 4038 4039 4040 4041 4042 4043 4044 4045 4046 4047
Access target CPU 41 to 50, error codes 4048 4049 4050 4051 4052 4053 4054 4055 4056 4057
Access target CPU 51 to 60, error codes 4058 4059 4060 4061 4062 4063 4064 4065 4066 4067
Access target CPU 61 to 64, error codes 4068 4069 4070 4071
*4 The following table shows the assignment of the Trigger buffer overflow count areas for Jobs 1 to
64 (Buffer memory address: 11520 to 11583).
Table 3.18 Trigger buffer overflow count areas for Jobs 1 to 64
Name
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30
31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40
41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50
51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60
61 62 63 64
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30
31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40
41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50
51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60
61 62 63 64
Trigger buffer overflow count areas for Jobs 1 to 64
Access target CPU 1 to 64, error code areas
1
OVERVIEW
2
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
SPECIFICATIONS
4
SETTINGS AND
PROCEDURE TO
OPERATION
5
INSTALLATION AND
UNINSTALLATION
6
3.5 Buffer Memory List
FUNCTIONS
7
MES INTERFACE
FUNCTION
CONFIGURATION TOOL
8
DB CONNECTION
SERVICE AND
SETTING TOOL
3
- 25
Page 82

3
SPECIFICATIONS
3.6 Buffer Memory Details
This section explains the buffer memory details.
(1) The values stored in buffer memory are cleared when the programmable
controller is powered ON from OFF, or the programmable controller CPU is
reset.
(2) When a value of 65536 or more is stored in the area composed of one word, a
count is stopped at FFFFh (65535).
(3) If a value of more than two words is stored in the area composed of two
words, a count is stopped at FFFFFFFFh (4294967295).
3.6.1 Module status area
The ON/OFF status of the MES interface module LED, setting status of the intelligent
function module switches, and battery status are stored.
Refer to the following for details.
• Section 4.3 Parts Names
• Section 4.5 Intelligent Function Module Switch Settings
3.6.2 Network connection status area
The status of network connection to which the MES interface module is currently
connected is stored.
(1) Storage example of IP address (Buffer memory address: 55 to 56)
For 192. 168. 3. 3, each octet (192 (first octet). 168 (second octet). 3 (third octet). 3
(fourth octet)) is stored as follows:
b15 b8tob7 b0
Buffer memory address: 55
56
(2) Storage example of Subnet mask (Buffer memory address: 57 to 58)
For 255. 255. 255. 0, each octet (255 (first octet). 255 (second octet). 255 (third octet).
0 (fourth octet)) is stored as follows:
b15 b8tob7 b0
Buffer memory address: 57
to
03H (3)
Third octet value Fourth octet value
C0
H (192)
First octet value Second octet value
FFH (255)
Third octet value Fourth octet value
03
A8
00
H (3)
H (168)
to
H (0)
3
- 26
3.6 Buffer Memory Details
3.6.1 Module status area
58
FF
H (255)
First octet value Second octet value
FF
H (255)
Page 83

3
SPECIFICATIONS
(3) Storage example of Default gateway (Buffer memory address: 59 to 60)
For 192. 168. 3. 254, each octet (192 (first octet). 168 (second octet). 3 (third octet).
254 (fourth octet)) is stored as follows:
Buffer memory address: 59
FE
to
H (254)
b15 b8tob7 b0
03H (3)
Third octet value Fourth octet value
1
OVERVIEW
2
60
For network connection, refer to the following.
Section 7.6.1 Setting items in Network setting
3.6.3 Network settings status area
The values stored to the Network setting status area is the same as the Network
connection status area.For the storage examples of IP address (buffer memory address:
71 to 72), subnet mask (buffer memory address: 73 to 74), default gateway (buffer
memory address: 75 to 76), refer to the following section.
Section 3.6.2 Network connection status area
This network settings status of the MES interface module is stored.
For network settings, refer to the following.
Section 7.6.1 Setting items in Network setting
C0
H (192)
First octet value Second octet value
A8
H (168)
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
SPECIFICATIONS
4
SETTINGS AND
PROCEDURE TO
OPERATION
5
3.6 Buffer Memory Details
3.6.3 Network settings status area
3
- 27
INSTALLATION AND
UNINSTALLATION
6
FUNCTIONS
7
MES INTERFACE
FUNCTION
CONFIGURATION TOOL
8
DB CONNECTION
SERVICE AND
SETTING TOOL
Page 84

3
SPECIFICATIONS
3.6.4 Current error area
(1) Error code (Buffer memory address: 140)
An error code which indicates the error contents is stored.
For error codes, refer to the following:
Section 10.2 Error Code List
(2) Time (Buffer memory address: 142 to 145)
The time when the error occurred is stored in BCD code.
Buffer memory address: 142
b15 b8to b7 b0to
Month (01H to 12H)
143
144
145
Hour (00
Second (00
Year (00
two digits of the year
Figure 3.8 Error time area
H to 23H)
H to 59H)
H to 99H) The first
H to 99H) The last
Year (00
two digits of the year
Day (01
H to 31H)
Minute (00
Day of the week (0
H to 59H)
H to 6H)
(1) The information of the Current error area can be confirmed on the following
diagnostic screen.
(a) Select [System monitor] [Present Error] of GX Developer
( Section 10.1.3 System monitor)
(2) The Current error area can be cleared in either of the following methods.
(a) Turn ON the Error clear request (Y10).
(b) Power ON the programmable controller from OFF or reset the
programmable controller CPU.
3
- 28
3.6 Buffer Memory Details
3.6.4 Current error area
Page 85
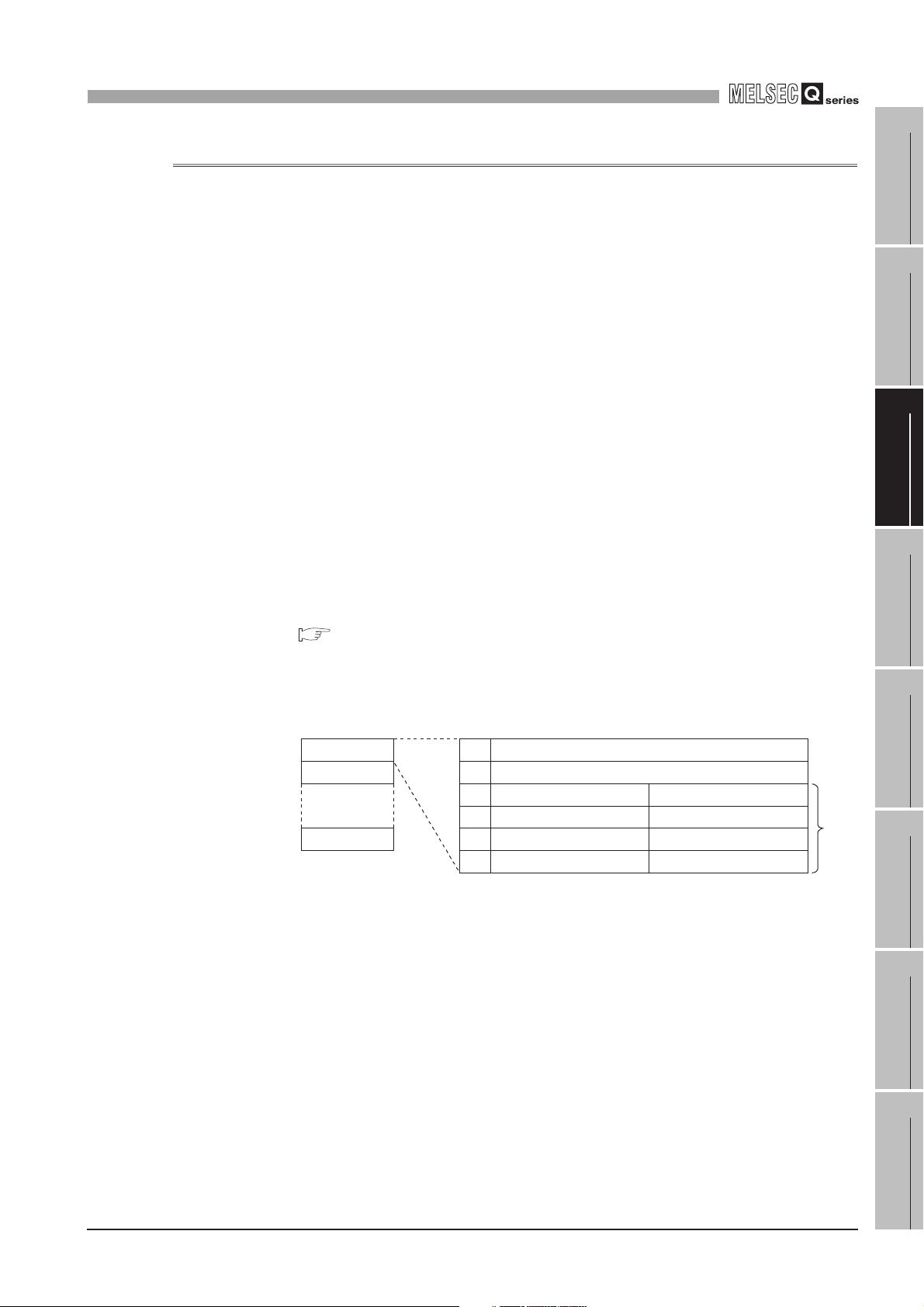
3
b15 to tob8 b7 b0
+2
+3
+4
+5
+1
System area (Use prohibited)
+0
Error code
Time
Buffer memory address: 152 to 157 Error log 1
Error log 2
Error log 16
158 to 163
242 to 247
Month (01
H
to 12H)
Hour (00
H
to 23H)
Second (00
H
to 59H)
Year (00H to 99H)
The first two digits of the year
Year (00
H
to 99H)
The last two digits of the year
Day (01H to 31H)
Minute (00
H
to 59H)
Day of the week (0
H
to 6H)
SPECIFICATIONS
1
3.6.5 Error log area
(1) Error count (Buffer memory address: 150)
(a) The cumulative number of registrations to the Error log area is stored.
(2) Error log write pointer (Buffer memory address: 151)
(a) The number of error log to which the latest error is registered is stored.
0: No error (No error log stored)
1 or more: Error log number of the latest error stored
*1 The pointer value of "16" indicates that the latest error has been registered into the error log area
of 16.
(b) If 17 or more errors occur, the excess errors are registered to the error log areas,
starting from the error log 1 area again.
*1
(3) Error log 1 to 16 (Buffer memory address: 152 to 247)
The error history is stored.
The Error log area is composed of 16 logs of the same data arrangement.
(a) Error code
An error code which indicates the error contents is stored.
For error codes, refer to the following:
Section 10.2 Error Code List
(b) Time
The time when the error occurred is stored in BCD code.
OVERVIEW
2
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
SPECIFICATIONS
4
SETTINGS AND
PROCEDURE TO
OPERATION
5
Figure 3.9 Error time area
(c) If an error that has already stored in the Error log area recurs, the error code is not
stored in the Error log area.
3.6 Buffer Memory Details
3.6.5 Error log area
3
- 29
INSTALLATION AND
UNINSTALLATION
6
FUNCTIONS
7
MES INTERFACE
FUNCTION
CONFIGURATION TOOL
8
DB CONNECTION
SERVICE AND
SETTING TOOL
Page 86

3
SPECIFICATIONS
(1) The information of the Error log area can be confirmed on the following
diagnostic screen.
Select [System monitor] [Error Display] of GX Developer (Section 10.1.3
System monitor)
(2) The Error log area can be cleared in either of the following methods.
(a) Power ON the programmable controller from OFF or reset the
programmable controller CPU.
(b) Select [Online] and click the [View working log] button.
( Section 7.12.5 Checking the working log of the MES interface module)
3
- 30
3.6 Buffer Memory Details
3.6.5 Error log area
Page 87

3
SPECIFICATIONS
3.6.6 Sampling/monitoring cycle area
The MES interface module monitors the device data sampling time and trigger conditions
alternately.
The time (cycle) required for this repetition can be confirmed in this area.
When the sampling/monitoring cycle is one second, device tag sampling and trigger
conditions are monitored based on the set values.
When it is longer than one second, delay of up to "sampling/monitoring cycle minus 1
second" may occur in the monitoring.
1
OVERVIEW
2
(1) Current cycle (buffer memory address: 800 to 801)
The current sampling/monitoring cycle value is stored. (Unit: Second)
(2) Maximum cycle (buffer memory address: 802 to 803)
The maximum sampling/monitoring cycle value up to the present moment is stored.
(Unit: Second)
3.6.7 Tag status area
(1) Tag setting information (Buffer memory address: 1000 to 1003)
(a) The information on whether [Device tag settings] have been made or not is stored.
(b) The bit corresponding to the preset tag setting No. is turned ON.
0: Not set
1: Set
Buffer memory address: 1000
b15 b12 b8 b7 b0b10 b9 b6b13b14 b11 b5b4b3b2b1
1001
1002
1003
Figure 3.10 Tag setting information area
26272829303132 18192021222324 1725
42434445464748 34353637383940 3341
58596061626364 50515253545556 4957
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
SPECIFICATIONS
4
SETTINGS AND
PROCEDURE TO
OPERATION
5
12345678910111213141516
INSTALLATION AND
UNINSTALLATION
6
(2) Sampling information (Buffer memory address: 1004 to 1007)
(a) The tag sampling result is stored.
(b) The bit corresponding to the tag setting No. which executed sampling is turned
ON.
0: Not collected
1: Collected
b15 b12 b8 b7 b0b10 b9 b6b13b14 b11 b5b4b3b2b1
Buffer memory address: 1004
1005
1006
1007
Figure 3.11 Sampling information area
3.6.6 Sampling/monitoring cycle area
26272829303132 18192021222324 1725
42434445464748 34353637383940 3341
58596061626364 50515253545556 4957
3.6 Buffer Memory Details
3
12345678910111213141516
- 31
FUNCTIONS
7
MES INTERFACE
FUNCTION
CONFIGURATION TOOL
8
DB CONNECTION
SERVICE AND
SETTING TOOL
Page 88

3
SPECIFICATIONS
(3) Sampling error information (Buffer memory address: 1008 to 1011)
(a) The tag sampling error information is stored.
(b) The bit corresponding to the tag setting No. to which the Sampling error occurred
is turned ON.
0: No sampling error
1: Sampling error detected
Buffer memory address: 1008
(c) The following results when a Sampling error occurs.
(Example) When an error occurred in the tag sampling of the tag setting number
• The Sampling error (X11) is turned ON.
• Sampling error information area (Buffer memory address: 1008 (bit 15)) is
• The error code is stored in the Sampling 16, error code area (Buffer memory
1009
1010
1011
Figure 3.12 Sampling error information area
16
turned ON.
address: 1027)
b15 b12 b8 b7 b0b10 b9 b6b13b14 b11 b5b4b3b2b1
12345678910111213141516
26272829303132 18192021222324 1725
42434445464748 34353637383940 3341
58596061626364 50515253545556 4957
(4) Sampling 1 to 64, error codes (Buffer memory address: 1012 to 1075)
The error code that indicates the error contents is stored in the corresponding tag
setting number area for which the Sampling error occurred.
For error codes, refer to the following:
Section 10.2 Error Code List
3
- 32
3.6 Buffer Memory Details
3.6.7 Tag status area
Page 89

3
SPECIFICATIONS
3.6.8 Current tag data value area
The specified current tag data is stored.
This section explains how to display the specified tag data in the Current tag data value
area.
1 Set the tag number displayed in the No. of requested tag (Buffer memory address:
*1
1290).
2 Check that the tag number is stored in the No. of stored tag (Buffer memory address:
1291) and that the Update count (Buffer memory address: 1292) is incremented by
*2
1.
3 Check that the tag component values for the No. of components (Buffer memory
address: 1293) are stored in the Current tag data value (Buffer memory address:
1300 to 1811).
*1 The tag numbers are the numbers beginning at 1 to 64 in the order set with MES Interface
Function Configuration Tool.
*2 If a value outside the range is set, the Current tag data value area is not updated.
*3 The Current tag data value area is updated each time the sampling is completed for the tag whose
number is set as the No. of requested tag (Buffer memory address: 1290).
*3
1
2
3
4
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
No. of requested tag
(Buffer memory address: 1290)
No. of stored tag
(Buffer memory address: 1291)
Update count
(Buffer memory address: 1292)
No. of components
(Buffer memory address: 1293)
Current tag data value
(Buffer memory address: 1300)
(1) No. of requested tag (Buffer memory address: 1290)
Specify the tag number whose current value is displayed as the Current tag data value
(Buffer memory address: 1300 to 1811).
(2) No. of stored tag (Buffer memory address: 1291)
The tag No. displayed as the Current tag data value (Buffer memory address: 1300 to
1811) is stored.
Specify tag No.
(Example) Specify "5".
Tag data is stored.
Figure 3.13 Current tag data value area
The current tag No. is stored.
(Example) "5" is stored.
The cumulative number
of updates is stored.
(Example) "1" is stored.
No. of components
is stored.
SETTINGS AND
PROCEDURE TO
OPERATION
5
INSTALLATION AND
UNINSTALLATION
6
FUNCTIONS
7
3.6 Buffer Memory Details
3.6.8 Current tag data value area
3
- 33
MES INTERFACE
FUNCTION
CONFIGURATION TOOL
8
DB CONNECTION
SERVICE AND
SETTING TOOL
Page 90

3
Remark
SPECIFICATIONS
(3) Update count (Buffer memory address: 1292)
(a) After the power is ON, the cumulative number of updates for the Current tag data
value (Buffer memory address: 1300 to 1811) is stored.
(b) After specifying the tag number displayed as the No. of requested tag (Buffer
memory address: 1290), when the update count is increased, the Current tag data
value (Buffer memory address: 1300 to 1811) is updated with the value of the
specified tag number.
(4) No. of components (Buffer memory address: 1293)
The No. of components displayed as the Current tag data value (Buffer memory
address: 1300 to 1811) is stored.
The following is an example where the current value of tag No. 5 is confirmed in
[Buffer memory batch monitor] of GX Developer .
1 Specify "5" as the No. of requested tag (Buffer memory
address: 1290) with [Buffer memory batch monitor] of
GX Developer.
2 Check that "5" is stored as the No. of stored tag (Buffer
memory address: 1291).
3 Check that the Update count (Buffer memory address:
1292) is updated.
4 Check that the No. of components for tag No. 5 is
stored in the No. of components (Buffer memory
address: 1293).
5 Check that the tag component value is stored in the
Current tag data value (Buffer memory address: 1300
to the address required for the No. of components).
3
- 34
3.6 Buffer Memory Details
3.6.8 Current tag data value area
Page 91

3
3
3
SPECIFICATIONS
(5) Current tag data value (Buffer memory address: 1300 to 1811)
(a) The current values of the tag components whose No. is specified with the No. of
requested tag (Buffer memory address: 1290) are stored.
(b) Two words are assigned per tag component.
1300
1301
1302
1303
Current value of
tag component 1
Current value of
tag component 2
1
2
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
1810
1811
Figure 3.14 Current tag data value area
Current value of
tag component 256
(c) Data are stored as follows depending on the data type for the tag component.
Upper word Lower word
Single precision:
Double precision:
Floating point:
Character string:
bit:
16-bit BCD:
32-bit BCD:
*1 When [Perform statistical processing] is set in [Device tag settings], data before the statistical
*2 Only the first four characters are stored.
*3 Data before the BCD conversion is stored.
0
Current value
Current value
0
0
Current value
Figure 3.15 Data type of tag component
processing is stored.
Current value
1st character2nd character3rd character4th character
0/1
Current value
*1
*1
*1
*2
*1*
*1*
3
SPECIFICATIONS
4
SETTINGS AND
PROCEDURE TO
OPERATION
5
INSTALLATION AND
UNINSTALLATION
6
3.6 Buffer Memory Details
3.6.8 Current tag data value area
3
- 35
FUNCTIONS
7
MES INTERFACE
FUNCTION
CONFIGURATION TOOL
8
DB CONNECTION
SERVICE AND
SETTING TOOL
Page 92

3
b15 b12 b8 b7 b0b10 b9 b6b13b14 b11 b5b4b3b2b1
12345678910111213141516
26272829303132 18192021222324 1725
42434445464748 34353637383940 3341
58596061626364 50515253545556 4957
4001
4002
4003
Buffer memory address: 4000
SPECIFICATIONS
3.6.9 Access target CPU setting status area
(1) Access target CPU setting information (Buffer memory address: 4000 to 4003)
(a) The information on whether [Access target CPU settings] have been made or not
is stored.
(b) The bit corresponding to the preset Access target CPU setting No. is turned ON.
0: Not set
1: Set
Figure 3.16 Access target CPU setting information area
(2) Access target CPU error information (Buffer memory address: 4004 to 4007)
(a) The access target CPU error information is stored.
(b) The bit corresponding to the Access target CPU setting number for which the
Access target CPU error has occurred is turned ON.
0: No Access target CPU error
1: Access target CPU error occurred
b15 b12 b8 b7 b0b10 b9 b6b13b14 b11 b5b4b3b2b1
Buffer memory address: 4004
4005
4006
4007
Figure 3.17 Access target CPU error information area
(c) The following results when the Access target CPU error occurs.
(Example) When an error occurred in the access target CPU for Access target
CPU setting No. 16
• Access target CPU error (X16) is turned ON.
• Access target CPU error information area (Buffer memory address: 4004 (bit
15)) is turned ON.
• The error code is stored in the Access target CPU 16, error code area (Buffer
memory address: 4023).
26272829303132 18192021222324 1725
42434445464748 34353637383940 3341
58596061626364 50515253545556 4957
12345678910111213141516
3
- 36
(3) Access target CPU 1 to 64, error codes (Buffer memory address: 4008 to
4071)
The error code showing the error contents is stored in the corresponding area of
access target CPU setting number for which the Access target CPU error has
occurred.
For error codes, refer to the following:
Section 10.2 Error Code List
3.6 Buffer Memory Details
3.6.9 Access target CPU setting status area
Page 93

3
SPECIFICATIONS
1
3.6.10 Information linkage function area
(1) "Time synchronization" setting status (Buffer memory address: 11500)
(a) The setting status of [Time synchronization setting] is stored.
For [Time synchronization setting], refer to the following.
Section 7.6.2 Setting items in Time synchronization setting
0: [Synchronize with PLC CPU time]
1: [Synchronize with SNTP]
(b) When selecting [Synchronize with SNTP] in [Time synchronization setting]
This area is set when the time information was obtained from the SNTP server
computer.
If the time information could not be obtained from the SNTP server computer, this
area is not set since the operation for when [Synchronize with PLC CPU time] is
selected is performed (Time is synchronized with the programmable controller
CPU).
(2) SNTP time query result (Buffer memory address: 11501 to 11507)
When [Synchronize with SNTP] is selected in [Time synchronization setting], the time
information obtained from the SNTP server is stored.
(When [Daylight saving setting] is enabled, time corrected to daylight saving time is
stored during the period of summer time.)
Table 3.19 SNTP time query result
Address
(Decimal)
11501 SNTP time query result (Year) The four-digit year data is stored.
11502
11503 SNTP time query result (Day) The day data, 01 to 31, is stored.
11504 SNTP time query result (Hour) The hour data, 00 to 23, is stored.
11505
11506
11507
SNTP time query result
(Month)
SNTP time query result
(Minute)
SNTP time query result
(Second)
SNTP time query result (Day of
the week)
Name Description Setting side
The month data, 01 to 12, is stored.
The minute data, 00 to 59, is stored.
The second data, 00 to 59, is stored.
The day of the week data is stored.
0: Sunday 1: Monday 2: Tuesday
3: Wednesday 4: Thursday 5: Friday
6: Saturday
Set on system
side
OVERVIEW
2
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
SPECIFICATIONS
4
SETTINGS AND
PROCEDURE TO
OPERATION
5
INSTALLATION AND
UNINSTALLATION
6
FUNCTIONS
(3) Monitoring interval timeout count (Buffer memory address: 11510)
The cumulative number of times that a monitoring interval timeout has occurred is
stored.
The monitoring interval timeout occurs when trigger detection has not been completed
within the monitoring interval.
If this timeout occurs, perform the following:
• Increase the monitoring interval
Increase the sampling interval of the tag that is used for trigger conditions.
• Reduce the trigger detection time.
Reduce the number of configured jobs.
3.6 Buffer Memory Details
3.6.10 Information linkage function area
3
- 37
7
MES INTERFACE
FUNCTION
CONFIGURATION TOOL
8
DB CONNECTION
SERVICE AND
SETTING TOOL
Page 94

3
SPECIFICATIONS
(4) No. of trigger buffer data (Buffer memory address: 11511)
The number of times the current trigger buffer has been used is stored.
If the number of times the trigger buffer has been used is always large, check the
number of jobs for which [Trigger buffering] is enabled and the trigger condition
setting. ( Section 7.10 Job Setting)
(5) Trigger buffer overflow count (Buffer memory address: 11512)
The cumulative number of trigger buffer overflows is stored.
If the trigger buffer overflows frequently, check the number of jobs for which [Trigger
buffering] is enabled and the trigger condition setting. ( Section 7.10 Job Setting)
(6) Trigger buffer overflow counts for Jobs 1 to 64 (Buffer memory address: 11520
to 11583)
The cumulative number of trigger buffer overflows for each job is stored.
3
- 38
3.6 Buffer Memory Details
3.6.10 Information linkage function area
Page 95

4
SETTINGS AND PROCEDURE TO OPERATION
CHAPTER 4 SETTINGS AND PROCEDURE TO OPERATION
This chapter explains the settings and procedure to operate the MES interface module in a
system.
(1) Before use, make sure to read SAFETY PRECAUTIONS at the beginning of
this manual.
(2) The mounting and installation environment of the MES interface module are
the same as those of a programmable controller CPU.
For details, refer to the following manual.
QCPU User's Manual (Hardware Design, Maintenance and Inspection)
4.1 Handling Precautions
1
2
3
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
This section explains the precautions for handling the MES interface module itself.
(1) Do not drop or apply severe shock to the module case since it is made of
resin.
(2) Before touching the module, always touch grounded metal, etc. to discharge
static electricity from human body, etc.
Not doing so can cause the module to fail or malfunction.
(3) Tighten the module fixing screws within the following range.
Table 4.1 Tightening torque
Screw Tightening torque range
Module fixing screw (usually not required) (M3 screw)
*1 The module can be easily fixed onto the base unit using the hook at the top of the module.
However, it is recommended to secure the module with the module fixing screw if the module is
subject to significant vibration.
*1
0.36 to 0.48 N·m
SPECIFICATIONS
4
SETTINGS AND
PROCEDURE TO
OPERATION
5
INSTALLATION AND
UNINSTALLATION
6
FUNCTIONS
4.1 Handling Precautions
7
MES INTERFACE
FUNCTION
CONFIGURATION TOOL
8
DB CONNECTION
SERVICE AND
SETTING TOOL
4
- 1
Page 96

4
Procedure to operation
SNTP server computer
*3
Database server computer
*1
Application server computer
*2
Server computer/SNTP server computer
Start the SNTP server.
Install the relational database
and design the table.
*4
Create a user program.
Set ODBC for the database.
Create an account for user program
execution.
*5
Install DB Connection Service and DB
Connection Service Setting Tool.
Change the settings of DB Connection
Service.
Install DB Connection Service and DB
Connection Service Setting Tool.
Change the settings of DB Connection
Service.
Operation
Section 8.2 Setting ODBC to the
Database
Section 5.1 Installation
Section 8.5 Setting Items of DB
Connection Service Setting Tool
Section 5.1 Installation
Section 8.5 Setting Items of DB
Connection Service Setting Tool
Section 2.6.3 Precautions for
using database
SETTINGS AND PROCEDURE TO OPERATION
4.2 Settings and Procedure to Operation
This section explains the schematic procedure up to operation for using the MES interface
function.
(1) Starting the server computer
Start the server computer, and then the MES interface module.
(2) Starting the MES interface module
4
- 2
4.2 Settings and Procedure to Operation
Figure 4.1 Server computer start-up procedure
*1 Be sure to make the settings to use the DB interface function.
*2 Make the settings when using the program execution function.
*3 Start it when using the SNTP server computer time with time synchronization function.
*4 Restart a personal computer after installing the relational database.
*5 Log on to the application server computer with the created account for user program execution
Section 6.1 DB Interface Function
Section 6.1.9 Program execution function
Section 6.3 Time Synchronization Function
If not, communication with the MES interface module may be impossible.
once before using the program execution function.
When using the application server computer to which the program execution function is set, log on
with an account other than the created account for user program execution.
Page 97

4
Section 5.1 Installation
Section 2.1.3 System configuration for initial setup
• Section 7.2 Starting the MES Interface Function
Configuration Tool
• Section 7.3 Screen Structure
• Section 7.4 Project File Handling
• Section 7.5 Project Setting
Section 7.13.8 Formatting the CompactFlash card
Section 7.6.1 Setting items in Network setting
SETTINGS AND PROCEDURE TO OPERATION
1
(2) Starting the MES interface module
Start the server computer, and then the MES interface module.
(1) Starting the server computer in this section
Procedure to operation
MES interface module
Mount a battery to the MES interface module.
Mount the MES interface module to a base unit.
Connect the MES interface module to the configuration computer on a 1:1 basis.
Power ON the programmable controller.
RUN LED is turned ON and ERR. LED flashes on the
MES interface module.
*1
Install MES Interface Function Configuration Tool.
*2
*3
Configuration computer
OVERVIEW
2
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
SPECIFICATIONS
4
SETTINGS AND
PROCEDURE TO
OPERATION
5
Install a CompactFlash card to the MES interface
module.
*4
Start MES Interface Function Configuration Tool.
Confirm the outline of MES Interface Function
Configuration Tool.
Format the CompactFlash card.
Figure 4.2 MES interface module start-up procedure
Select [System setting] and make [Network settings].
(To the next page)(To the next page)
4.2 Settings and Procedure to Operation
INSTALLATION AND
UNINSTALLATION
6
FUNCTIONS
7
MES INTERFACE
FUNCTION
CONFIGURATION TOOL
8
DB CONNECTION
SERVICE AND
SETTING TOOL
4
- 3
Page 98

4
Section 2.1.4 System configuration for operation
• Chapter 6 FUNCTIONS
• Section 7.6 System Setting
• Section 7.7 Access Target CPU Setting
• Section 7.8 Device Tag Setting
• Section 7.9 Server Service Setting
• Section 7.10 Job Setting
• Section 7.11 Job Setting - Actions
• Section 7.12.1 Setting the target MES interface
module
• Section 7.12.2 Writing the MES interface
function settings
• Section 7.12.1 Setting the target MES interface
module
• Section 7.12.2 Writing the MES interface
function settings
SETTINGS AND PROCEDURE TO OPERATION
(From the previous page) (From the previous page)
Set the target MES interface module.
Write a project to the MES interface module.
MES interface module
Power OFF the programmable controller.
According to [Network settings], connect the MES interface module and configuration computer to a network.
Power ON the programmable controller.
Check communications with the MES interface module by
When changing
the settings
executing the PING command in the command prompt
screen.
*5
Configure the settings in MES Interface Function
Configuration Tool for the MES interface function.
Configuration computer
Operation
4
- 4
4.2 Settings and Procedure to Operation
Set the target MES interface module.
Write the project to the MES interface module.
Figure 4.2 MES interface module start-up procedure
Page 99

4
SETTINGS AND PROCEDURE TO OPERATION
*1 As necessary, execute the self-diagnostic test for checking the communication function and
hardware of the MES interface module.
Section 4.6 Self-diagnostics Test
*2 For a battery, refer to the following:
Section 4.8 Battery
Section 4.9 Operation without Mounting Battery
Section 4.10 Removing Battery for Storage
*3 If an account is forgotten and therefore connection to the MES interface module cannot be made,
eject the CompactFlash card from the MES interface module, then follow the procedure in the
figure above
For details on how to eject the CompactFlash card, refer to the following.
*4 For details on how to insert/eject the CompactFlash card and precautions for use, refer to the
following.
*5 When the test has been completed abnormally, check the following and execute the PING
command again.
• Network settings for the MES interface module or configuration computer
• Connection status of the MES interface module or configuration computer
*3
and subsequent procedure.
Section 4.7.2 Installation/removing the CompactFlash card
Section 4.7 CompactFlash Card
1
2
3
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
4
SETTINGS AND
PROCEDURE TO
OPERATION
5
INSTALLATION AND
UNINSTALLATION
6
FUNCTIONS
7
4.2 Settings and Procedure to Operation
MES INTERFACE
FUNCTION
CONFIGURATION TOOL
8
DB CONNECTION
SERVICE AND
SETTING TOOL
4
- 5
Page 100

4
SETTINGS AND PROCEDURE TO OPERATION
4.3 Parts Names
This section explains the parts names of the MES interface module.
(1) With the LED cover closed
1)
1)
2)
Figure 4.3 With the LED cover closed
(2) With the LED cover open
3)
4)
5)
6)
4
- 6
4.3 Parts Names
7)
Figure 4.4 With the LED cover open
8)
 Loading...
Loading...