Page 1

Channel Isolated RTD Input Module
User's Manual
-Q68RD3-G
-GX Configurator-TI (SW1D5C-QTIU-E)
Page 2

Page 3
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
(Read these precautions before use.)
Before using this product, please read this manual and the relevant manuals carefully and pay full attention
to safety to handle the product correctly.
In this manual, the safety precautions are classified into two levels: " WARNING" and " CAUTION".
WARNING
CAUTION
Under some circumstances, failure to observe the precautions given under " CAUTION" may lead to
serious consequences.
Observe the precautions of both levels because they are important for personal and system safety.
Make sure that the end users read this manual and then keep the manual in a safe place for future
reference.
Indicates that incorrect handling may cause hazardous conditions,
resulting in death or severe injury.
Indicates that incorrect handling may cause hazardous conditions,
resulting in minor or moderate injury or property damage.
[Design Precautions]
WARNING
Do not write any data to the "system area" of the buffer memory in the intelligent function module.
Also, do not use any "use prohibited" signals as an output signal from the programmable controller
CPU to the intelligent function module.
Doing so may cause malfunction of the programmable controller system.
CAUTION
Do not install the control lines or communication cables together with the main circuit lines or power
cables.
Keep a distance of 100mm (3.94 inches) or more between them.
Failure to do so may result in malfunction due to noise.
A - 1
Page 4
[Installation Precautions]
CAUTION
Use the programmable controller in an environment that meets the general specifications in the
user's manual for the CPU module used.
Failure to do so may result in electric shock, fire, malfunction, or damage to or deterioration of the
product.
To mount the module, while pressing the module mounting lever located in the lower part of the
module, fully insert the module fixing projection(s) into the hole(s) in the base unit and press the
module until it snaps into place.
Incorrect mounting may cause malfunction, failure or drop of the module.
When using the programmable controller in an environment of frequent vibrations, fix the module
with a screw.
Tighten the screw within the specified torque range.
Undertightening can cause drop of the screw, short circuit or malfunction.
Overtightening can damage the screw and/or module, resulting in drop, short circuit, or malfunction.
Shut off the external power supply (all phases) used in the system before mounting or removing the
module.
Failure to do so may result in damage to the product.
A module can be replaced online (while power is on) on any MELSECNET/H remote I/O station or in
the system where a CPU module supporting the online module change function is used.
Note that there are restrictions on the modules that can be replaced online, and each module has its
predetermined replacement procedure.
For details, refer to the relevant chapter in this manual.
Do not directly touch any conductive parts and electronic components of the module.
Doing so can cause malfunction or failure of the module.
A - 2
Page 5
[Wiring Precautions]
CAUTION
Individually ground the shielded cables of the programmable controller with a ground resistance of
Ω or less.
100
Failure to do so may result in electric shock or malfunction.
Connectors for external devices must be crimped or pressed with the tool specified by the
manufacturer, or must be correctly soldered.
Incomplete connections may cause short circuit, fire, or malfunction.
Prevent foreign matter such as dust or wire chips from entering the module.
Such foreign matter can cause a fire, failure, or malfunction.
A protective film is attached to the top of the module to prevent foreign matter, such as wire chips,
from entering the module during wiring.
Do not remove the film during wiring.
Remove it for heat dissipation before system operation.
A - 3
Page 6
[Wiring Precautions]
CAUTION
Place the cables in a duct or clamp them.
If not, dangling cable may swing or inadvertently be pulled, resulting in damage to the module or
cables or malfunction due to poor contact.
When disconnecting the cable from the module, do not pull the cable by the cable part.
For the cable with connector, hold the connector part of the cable.
Pulling the cable connected to the module may result in malfunction or damage to the module or
cable.
[Startup and Maintenance Precautions]
WARNING
Do not touch any terminal while power is on.
Doing so will cause electric shock or malfunction.
Shut off the external power supply (all phases) used in the system before cleaning the module or
retightening the terminal screws, connector screws, or module fixing screws.
Failure to do so may result in electric shock or cause the module to fail or malfunction.
Undertightening can cause drop of the screw, short circuit or malfunction.
Overtightening can damage the screw and/or module, resulting in drop, short circuit, or malfunction.
A - 4
Page 7
CAUTION
Do not disassemble or modify the modules.
Doing so may cause failure, malfunction, injury, or a fire.
Shut off the external power supply (all phases) used in the system before mounting or removing the
module.
Failure to do so may cause the module to fail or malfunction.
A module can be replaced online (while power is on) on any MELSECNET/H remote I/O station or in
the system where a CPU module supporting the online module change function is used.
Note that there are restrictions on the modules that can be replaced online, and each module has its
predetermined replacement procedure.
For details, refer to the relevant chapter in this manual.
After the first use of the product, do not mount/remove the module to/from the base unit more than
50 times (IEC 61131-2 compliant).
Exceeding the limit of 50 times may cause malfunction.
Do not touch any terminal while power is on.
Failure to do so may cause malfunction.
Shut off the external power supply (all phases) used in the system before cleaning the module or
retightening the module fixing screws.
Failure to do so may cause the module to fail or malfunction.
Undertightening can cause drop of the screw, short circuit or malfunction.
Overtightening can damage the screw and/or module, resulting in drop, short circuit, or malfunction.
Before handling the module, touch a grounded metal object to discharge the static electricity from
the human body.
Failure to do so may cause the module to fail or malfunction.
A - 5
Page 8

[Disposal Precautions]
CAUTION
When disposing of this product, treat it as industrial waste.
A - 6
Page 9

CONDITIONS OF USE FOR THE PRODUCT
(1) Mitsubishi programmable controller ("the PRODUCT") shall be used in conditions;
i) where any problem, fault or failure occurring in the PRODUCT, if any, shall not lead to any major
or serious accident; and
ii) where the backup and fail-safe function are systematically or automatically provided outside of
the PRODUCT for the case of any problem, fault or failure occurring in the PRODUCT.
(2) The PRODUCT has been designed and manufactured for the purpose of being used in general
industries.
MITSUBISHI SHALL HAVE NO RESPONSIBILITY OR LIABILITY (INCLUDING, BUT NOT
LIMITED TO ANY AND ALL RESPONSIBILITY OR LIABILITY BASED ON CONTRACT,
WARRANTY, TORT, PRODUCT LIABILITY) FOR ANY INJURY OR DEATH TO PERSONS OR
LOSS OR DAMAGE TO PROPERTY CAUSED BY the PRODUCT THAT ARE OPERATED OR
USED IN APPLICATION NOT INTENDED OR EXCLUDED BY INSTRUCTIONS, PRECAUTIONS,
OR WARNING CONTAINED IN MITSUBISHI'S USER, INSTRUCTION AND/OR SAFETY
MANUALS, TECHNICAL BULLETINS AND GUIDELINES FOR the PRODUCT.
("Prohibited Application")
Prohibited Applications include, but not limited to, the use of the PRODUCT in;
• Nuclear Power Plants and any other power plants operated by Power companies, and/or any
other cases in which the public could be affected if any problem or fault occurs in the PRODUCT.
• Railway companies or Public service purposes, and/or any other cases in which establishment of
a special quality assurance system is required by the Purchaser or End User.
• Aircraft or Aerospace, Medical applications, Train equipment, transport equipment such as
Elevator and Escalator, Incineration and Fuel devices, Vehicles, Manned transportation,
Equipment for Recreation and Amusement, and Safety devices, handling of Nuclear or
Hazardous Materials or Chemicals, Mining and Drilling, and/or other applications where there is a
significant risk of injury to the public or property.
Notwithstanding the above, restrictions Mitsubishi may in its sole discretion, authorize use of the
PRODUCT in one or more of the Prohibited Applications, provided that the usage of the PRODUCT
is limited only for the specific applications agreed to by Mitsubishi and provided further that no
special quality assurance or fail-safe, redundant or other safety features which exceed the general
specifications of the PRODUCTs are required. For details, please contact the Mitsubishi
representative in your region.
A - 7
Page 10
REVISIONS
* The manual number is given on the bottom left of the back cover.
Print Date *Manual Number Revision
Apr., 2008 SH(NA)-080722ENG-A First edition
May, 2008 SH(NA)-080722ENG-B
Sep., 2011 SH(NA)-080722ENG-C
Feb., 2012 SH(NA)-080722ENG-D
Correction
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS, GENERIC TERMS, ABBREVIATIONS, AND TERMS,
Section 2.1, 3.1, 4.1, 5.2.1, 5.3.1, 5.3.3, 7.1
Correction
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS, COMPLIANCE WITH EMC AND LOW VOLTAGE
DIRECTIVES, Section 6.2.3, WARRANTY
Addition
CONDTIONS OF USE FOR THE PRODUCT
Correction
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS, COMPLIANCE WITH EMC AND LOW VOLTAGE
DIRECTIVES, GENERIC TERMS, ABBREVIATIONS, AND TERMS, Chapter 1,
Section 1.1, 2.1 to 2.3, 3.1, 3.2, 3.2.1 to 3.2.3, 3.3.1, 3.3.2, 3.4.1, 3.4.4, 3.4.5,
3.4.10, 3.4.11, 4.1, 4.3, 4.4.1, 4.4.2, 4.5, 4.6, 5.2.1, 5.2.2, 5.3.1, 5.4, 5.5, 5.6.1,
5.6.2, 6.2.1, 6.2.2, 7.1, 7.3.1 to 7.3.6, 7.4, 7.5, 8.1, Appendix 1.2 to 1.4, Appendix 2
Deletion
Appendix 1
Japanese Manual Version SH-080721-D
This manual confers no industrial property rights or any rights of any other kind, nor does it confer any patent licenses.
Mitsubishi Electric Corporation cannot be held responsible for any problems involving industrial property rights which may
occur as a result of using the contents noted in this manual.
© 2008 MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORPORATION
A - 8
Page 11

INTRODUCTION
Thank you for choosing the Mitsubishi MELSEC-Q Series General Purpose Programmable Controllers.
Before using the equipment, please read this manual carefully to develop full familiarity with the functions
and performance of the Q series programmable controller you have purchased, so as to ensure correct use.
CONTENTS
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• A - 1
CONDITIONS OF USE FOR THE PRODUCT••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• A - 7
REVISIONS•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••A - 8
INTRODUCTION •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• A - 9
CONTENTS••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• A - 9
COMPLIANCE WITH EMC AND LOW VOLTAGE DIRECTIVES ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• A - 13
GENERIC TERMS, ABBREVIATIONS, AND TERMS •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• A - 14
PACKING LIST•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• A - 15
CHAPTER1 OVERVIEW 1 - 1 to 1 - 3
1.1 Features •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 1 - 2
CHAPTER2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION 2 - 1 to 2 - 8
2.1 Applicable Systems•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••2 - 1
2.2 When Using the Q68RD3-G with Redundant CPU••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 2 - 5
2.3 How to Check the Function Version, Serial No., and Software Version ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••2 - 6
CHAPTER3 SPECIFICATIONS 3 - 1 to 3 - 49
3.1 Performance Specifications ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 3 - 1
3.2 Function List ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 3 - 3
3.2.1 Temperature conversion system •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••3 - 4
3.2.2 Conversion setting for disconnection detection function••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 3 - 9
3.2.3 Warning output function•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 3 - 11
3.3 I/O Signals for Communicating with Programmable Controller CPU ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 3 - 17
3.3.1 I/O signal list ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 3 - 17
3.3.2 I/O signal details••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 3 - 18
3.4 Buffer Memory ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 3 - 24
3.4.1 Buffer memory assignment•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 3 - 24
3.4.2 Conversion enable/disable setting (Un\G0) •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 3 - 30
3.4.3 CH[] Time/Count/Moving average/Time constant setting (Un\G1 to Un\G8) •••••••••••••••••••• 3 - 31
3.4.4 Conversion completion flag (Un\G10) ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 3 - 32
3.4.5 CH[] Measured temperature value (Un\G11 to Un\G18) •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 3 - 33
3.4.6 Error code (Un\G19) •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 3 - 34
3.4.7 Setting range 1, 2 (Un\G20 and Un\G21)••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 3 - 34
3.4.8 Setting range 3 (Offset/gain setting) (Un\G22) •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 3 - 34
A - 9
Page 12

3.4.9 Averaging processing selection (Un\G24 and Un\G25)•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 3 - 35
3.4.10 Offset/gain setting mode (Un\G26 and Un\G27) •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 3 - 36
3.4.11 CH[] Offset/gain temperature setting values (Un\G28 to Un\G43) ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 3 - 37
3.4.12 Warning output enable/disable setting (Un\G46)•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 3 - 37
3.4.13 Warning output flag (Process alarm/Rate alarm) (Un\G47 and Un\G48)••••••••••••••••••••••••• 3 - 38
3.4.14 Disconnection detection flag (Un\G49)•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 3 - 39
3.4.15 CH[] Scaling value (Un\G50 to Un\G57) •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 3 - 41
3.4.16 Scaling valid/invalid setting (Un\G58) ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 3 - 42
3.4.17 CH[] Scaling range upper/lower limit values (Un\G62 to Un\G77) ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 3 - 43
3.4.18 CH[] Scaling width upper/lower limit values (Un\G78 to Un\G93)•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 3 - 43
3.4.19 CH[] Process alarm upper/lower limit values (Un\G94 to Un\G125)••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 3 - 44
3.4.20 CH[] Rate alarm warning detection period (Un\G126 to Un\G133) •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 3 - 45
3.4.21 CH[] Rate alarm upper/lower limit values (Un\G134 to Un\G149) ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 3 - 45
3.4.22 Mode switching setting (Un\G158 and Un\G159) ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 3 - 46
3.4.23 Conversion setting for disconnection detection (Un\G164 and Un\G165)•••••••••••••••••••••••• 3 - 47
3.4.24 CH[] Conversion setting value for disconnection detection (Un\G166 to Un\G173) •••••••••••• 3 - 48
3.4.25 Factory default offset/gain values, User range settings offset/gain values, User range settings
resistance offset/gain values (Un\G190 to Un\G253) •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 3 - 49
CHAPTER4 PROCEDURES AND SETTINGS BEFORE SYSTEM OPERATION
4 - 1 to 4 - 15
4.1 Handling Precautions •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 4 - 1
4.1.1 Fixing module with module fixing bracket ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••4 - 2
4.2 Procedures and Settings before System Operation •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 4 - 3
4.3 Part Names •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 4 - 4
4.4 Wiring ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 4 - 6
4.4.1 Wiring precautions ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••4 - 6
4.4.2 External wiring ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 4 - 7
4.5 Intelligent Function Module Switch Setting•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••4 - 8
4.6 Offset/Gain Setting ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 4 - 10
CHAPTER5 UTILITY PACKAGE (GX Configurator-TI) 5 - 1 to 5 - 25
5.1 Utility Package Functions •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••5 - 1
5.2 Installing and Uninstalling Utility Package ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 5 - 3
5.2.1 Precautions for use ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 5 - 3
5.2.2 Operating environment ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 5 - 6
5.3 Operating Utility Package ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 5 - 8
5.3.1 Common operations •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 5 - 8
5.3.2 Operation overview ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 5 - 11
5.3.3 Activating intelligent function module utility •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 5 - 13
5.4 Initial Setting ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 5 - 15
5.5 Auto Refresh Setting ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 5 - 17
5.6 Monitor/Test•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 5 - 19
5.6.1 Monitor/test screen•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 5 - 19
5.6.2 Offset/gain setting operation •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 5 - 22
5.6.3 OMC (Online Module Change) refresh data ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 5 - 25
A - 10
Page 13

CHAPTER6 PROGRAMMING 6 - 1 to 6 - 31
6.1 Programming Procedure •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 6 - 2
6.2 Using Programs in Normal System Configuration •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 6 - 4
6.2.1 Before creating a program••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 6 - 6
6.2.2 Program example when utility package is used •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••6 - 8
6.2.3 Program example when utility package is not used •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 6 - 13
6.3 Using Programs on Remote I/O Network •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 6 - 18
6.3.1 Before creating a program••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 6 - 20
6.3.2 Program example when utility package is used ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 6 - 21
6.3.3 Program example when utility package is not used •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 6 - 25
CHAPTER7 ONLINE MODULE CHANGE 7 - 1 to 7 - 37
7.1 Conditions Required for Online Module Change ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 7 - 2
7.2 Operations during Online Module Change •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••7 - 3
7.3 Procedures of Online Module Change ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••7 - 4
7.3.1 When factory default is used and initial setting has been made with GX Configurator-TI ••••••7 - 4
7.3.2 When factory default is used and initial setting has been made with sequence program••••••• 7 - 9
7.3.3 When user range setting is used and initial setting has been made with GX Configurator-TI
(Separate system is available)•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 7 - 13
7.3.4 When user range setting is used and initial setting has been made with GX Configurator-TI
(Separate system is not available) ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 7 - 18
7.3.5 When user range setting is used and initial setting has been made with sequence program
(Separate system is available)•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 7 - 24
7.3.6 When user range setting is used and initial setting has been made with sequence program
(Separate system is not available) ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 7 - 29
7.4 Range Reference Table ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 7 - 34
7.5 Precautions for Online Module Change •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 7 - 37
CHAPTER8 TROUBLESHOOTING 8 - 1 to 8 - 7
8.1 Error Code List •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 8 - 1
8.2 Troubleshooting ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 8 - 3
8.2.1 When "RUN" LED turns off •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 8 - 3
8.2.2 When "RUN" LED flashes ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 8 - 3
8.2.3 When "ERR" LED flashes ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 8 - 3
8.2.4 When "ERR" LED turns on ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••8 - 3
8.2.5 When "ALM" LED flashes ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 8 - 4
8.2.6 When "ALM" LED turns on •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 8 - 4
8.2.7 When Disconnection detection signal (XC) turns ON •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 8 - 4
8.2.8 When measured temperature value cannot be read •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••8 - 4
8.2.9 When measured temperature value is abnormal••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••8 - 5
8.2.10 Checking Q68RD3-G status using system monitor of GX Developer••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• 8 - 6
APPENDICES APPX - 1 to APPX - 14
Appendix 1 Dedicated Instructions •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• APPX - 1
Appendix 1.1 List of Dedicated Instructions and Available Devices•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••APPX - 1
A - 11
Page 14

Appendix 1.2 G(P).OFFGAN •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••APPX - 2
Appendix 1.3 G(P).OGLOAD ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• APPX - 4
Appendix 1.4 G(P).OGSTOR •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••APPX - 8
Appendix 2 External Dimensions •••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••• APPX - 13
INDEX INDEX - 1 to INDEX - 2
A - 12
Page 15

COMPLIANCE WITH EMC AND LOW VOLTAGE DIRECTIVES
(1) Method of ensuring compliance
To ensure that Mitsubishi programmable controllers maintain EMC and Low Voltage
Directives when incorporated into other machinery or equipment, certain measures
may be necessary. Please refer to one of the following manuals.
• QCPU User's Manual (Hardware Design, Maintenance and Inspection)
• Safety Guidelines
(This manual is included with the CPU module or base unit.)
The CE mark on the side of the programmable controller indicates compliance with
EMC and Low Voltage Directives.
(2) Additional measures
To ensure that this product maintains EMC and Low Voltage Directives, please refer
to Section 4.4.1.
A - 13
Page 16
GENERIC TERMS, ABBREVIATIONS, AND TERMS
Unless otherwise specified, this manual uses the following general terms, abbreviations,
and terms.
Generic term/
Abbreviation/Term
Q68RD3-G The abbreviation for the Q68RD3-G channel isolated RTD input module
Up scale A measurement range maximum value + 5% of the measurement range
Down scale A measurement range minimum value - 5% of the measurement range
GX Developer
GX Works2
GX Configurator-TI
QCPU (Q mode)
Process CPU A generic term for the Q02PHCPU, Q06PHCPU, Q12PHCPU, and Q25PHCPU
Redundant CPU A generic term for the Q12PRHCPU and Q25PRHCPU
Personal computer
RTD (Resistance
Temperature Detector)
Windows Vista
Windows XP
Windows 7
The product name of the software package for the MELSEC programmable controllers
The abbreviation for the thermocouple input module setting and monitor tool GX Configurator-
TI (SW1D5C-QTIU-E)
A generic term for the Q00JCPU, Q00CPU, Q01CPU, Q02CPU, Q02HCPU, Q06HCPU,
Q12HCPU, Q25HCPU, Q02PHCPU, Q06PHCPU, Q12PHCPU, Q25PHCPU, Q12PRHCPU,
Q25PRHCPU, Q00UJCPU, Q00UCPU, Q01UCPU, Q02UCPU, Q03UDCPU, Q04UDHCPU,
Q06UDHCPU, Q10UDHCPU, Q13UDHCPU, Q20UDHCPU, Q26UDHCPU, Q03UDECPU,
Q04UDEHCPU, Q06UDEHCPU, Q10UDEHCPU, Q13UDEHCPU, Q20UDEHCPU,
Q26UDEHCPU, Q50UDEHCPU, and Q100UDEHCPU
An IBM PC/AT or compatible computer with DOS/V
A generic term for the platinum RTD and nickel RTD
A generic term for the following:
Microsoft Windows Vista Home Basic Operating System,
Microsoft Windows Vista Home Premium Operating System,
Microsoft Windows Vista Business Operating System,
Microsoft Windows Vista Ultimate Operating System,
Microsoft Windows Vista Enterprise Operating System
A generic term for the following:
Microsoft Windows XP Professional Operating System,
Microsoft Windows XP Home Edition Operating System
A generic term for the following:
Microsoft Windows 7 Starter Operating System,
Microsoft Windows 7 Home Premium Operating System,
Microsoft Windows 7 Professional Operating System,
Microsoft Windows 7 Ultimate Operating System,
Microsoft Windows 7 Enterprise Operating System
Note that the 32-bit version is designated as "32-bit Windows 7", and the 64-bit version is
designated as "64-bit Windows 7".
Description
A - 14
Page 17

PACKING LIST
The product package contains the following.
Model Product Quantity
Q68RD3-G Q68RD3-G channel isolated RTD input module 1
SW1D5C-QTIU-E GX Configurator-TI Version1 (Single license product) (CD-ROM) 1
SW1D5C-QTIU-EA GX Configurator-TI Version1 (Volume license product) (CD-ROM) 1
A - 15
Page 18
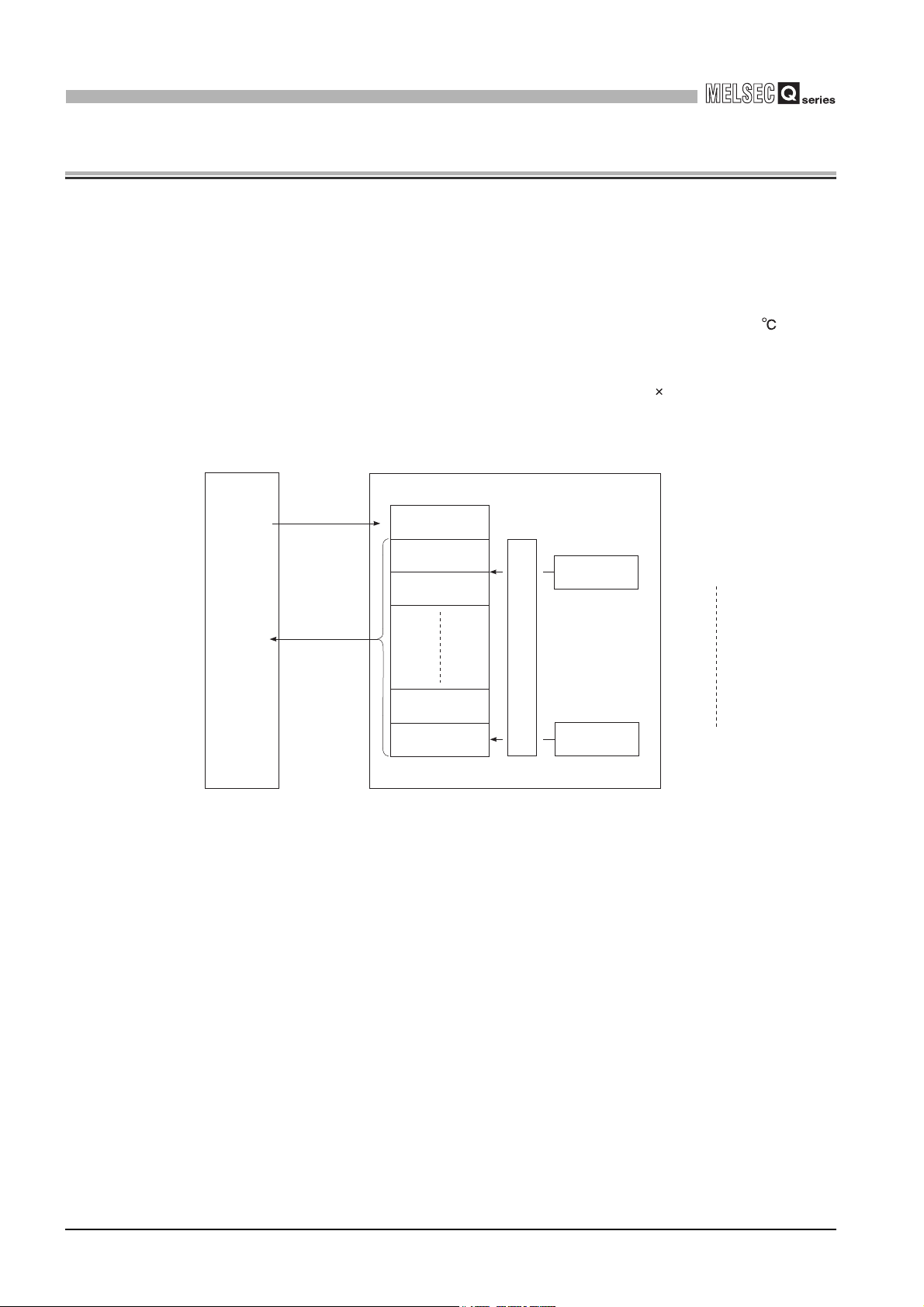
1
OVERVIEW
CHAPTER1 OVERVIEW
This user's manual provides the specifications, handling instructions, programming
procedures, and other information of the Q68RD3-G channel isolated RTD (Resistance
Temperature Detector) input module (hereinafter the "Q68RD3-G"), which is designed to
use with the MELSEC-Q series CPU module.
The Q68RD3-G is a RTD module (3-wire type) and converts temperature data [ ] input
from the Pt100 or JPt100 platinum RTDs (hereinafter the "Pt100" or "JPt100") or the Ni100
nickel RTD (hereinafter the "Ni100") to measured temperature values in 16-bit signed
binary data (stored as a value rounded off to one decimal place 10) or scaling values
(ratios (%)).
Programmable controller
CPU
TO
instruction
FROM
instruction
Initial setting
Measured
temperature
value, scaling
value reading
* For details on scaling values, refer to Section 3.4.15.
(Buffer memory)
Setting data
Measured
temperature
value
Scaling value
Measured
temperature
value
Scaling value
Q68RD3-G
*1
*1
Channel 1
Temperature measurement
Channel 8
RTD input
RTD input
1 - 1
Page 19

1
OVERVIEW
1.1 Features
(1) Isolated channels
The Q68RD3-G is a channel isolated module.
(2) Temperature measurement of eight channels available in one module
The Q68RD3-G can measure temperature of eight channels in one module.
The module can also convert the detected measured temperature values into scaling
values (ratios (%)).
(3) Conversion enable/disable setting
Conversion enable/disable setting is possible for each channel. Disabling conversion
for unused channels prevents unnecessary disconnection detection.
(4) Use of 3-wire RTDs conforming to standards
3-wire RTDs listed in the table below can be used.
Table 1.1 Available RTD
RTD Compliant standard
Platinum RTD
Nickel RTD Ni100 DIN 43760 1987
Pt100 JIS C 1604-1997, IEC 751 1983
JPt100 JIS C 1604-1981
1
2
3
4
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
Also, RTD type and measurement range can be set for each channel using GX
Developer.
(5) Disconnection detection
Disconnection status of RTD can be detected for each channel by Disconnection
detection flag.
Disconnection status can also be detected from the measured temperature value by
setting "Up scale", "Down scale" or "Given value" for the Conversion setting for
disconnection detection.
(6) Selection of sampling processing, time average processing, count
average processing, moving average processing, and primary delay
filter
A temperature conversion system: sampling processing, time average processing,
count average processing, moving average or primary delay filter can be selected for
each channel.
(7) Error compensation by offset/gain value setting
Error compensation is available by setting offset/gain values for each channel.
Offset/gain values can be selected from user range setting and factory default setting.
PROCEDURES AND
5
6
7
SETTINGS BEFORE
SYSTEM OPERATION
UTILITY PACKAGE
(GX CONFIGURATOR-TI)
PROGRAMMING
1.1 Features
1 - 2
ONLINE MODULE
CHANGE
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 20

1
OVERVIEW
(8) Warning output function
(a) Process alarm warning output
A warning can be output when the measured temperature value exceeds the input
range set by user.
Upper limit value and lower limit value can be set for each channel, and a setting
to have a difference (hysteresis) between warning output and warning clear is
also available.
(b) Rate alarm warning output
A warning can be output when the measured temperature value exceeds the rate
of temperature change set by user.
(9) Online module change
The module can be changed without stopping the system.
Furthermore, the following operations can be processed by using sequence
programs.
• Transferring the offset/gain set values to the replacement Q68RD3-G
• Transferring the offset/and gain set values to another Q68RD3-G mounted on the
other slot
(10)Easy settings using GX Configurator-TI
Using GX Configurator-TI which is sold separately, sequence programs can be
reduced since settings of the Q68RD3-G can be made on the screen.
Also, the set status or operating status of the module can be checked easily.
1 - 3
1.1 Features
Page 21
2
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
CHAPTER2 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
This chapter explains the system configuration of the Q68RD3-G.
2.1 Applicable Systems
This section describes the applicable systems.
(1) Applicable modules and base units, and No. of modules
(a) When mounted with CPU module
The table below shows the CPU modules and base units applicable to the
Q68RD3-G and quantities for each CPU model.
Depending on the combination with other modules or the number of mounted
modules, power supply capacity may be insufficient.
Pay attention to the power supply capacity before mounting modules, and if the
power supply capacity is insufficient, change the combination of the modules.
1
2
3
4
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
PROCEDURES AND
5
6
7
8
SETTINGS BEFORE
SYSTEM OPERATION
UTILITY PACKAGE
(GX CONFIGURATOR-TI)
PROGRAMMING
ONLINE MODULE
CHANGE
2.1 Applicable Systems
TROUBLESHOOTING
2 - 1
Page 22
2
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
Programmable
controller CPU
C Controller module
Table 2.1 Applicable modules, number of mountable modules, and applicable base units
Applicable CPU module
CPU type CPU model Main base unit Extension base unit
Q00JCPU Up to 16
Basic model QCPU
High Performance
model QCPU
Process CPU
Redundant CPU
Universal model QCPU
Safety CPU QS001CPU N/A
Q00CPU
Q01CPU
Q02CPU
Q02HCPU
Q06HCPU
Q12HCPU
Q25HCPU
Q02PHCPU
Q06PHCPU
Q12PHCPU
Q25PHCPU
Q12PRHCPU
Q25PRHCPU
Q00UJCPU Up to 16
Q00UCPU
Q01UCPU
Q02UCPU Up to 36
Q03UDCPU
Q04UDHCPU
Q06UDHCPU
Q10UDHCPU
Q13UDHCPU
Q20UDHCPU
Q26UDHCPU
Q03UDECPU
Q04UDEHCPU
Q06UDEHCPU
Q10UDHCPU
Q13UDEHCPU
Q20UDEHCPU
Q26UDEHCPU
Q50UDEHCPU
Q100UDEHCPU
Q06CCPU-V
Q06CCPU-V-B
Q12DCCPPU-V
No. of modules
Up to 24
Up to 64
Up to 64
Up to 53
Up to 24
Up to 64
Up to 64
*1
Base unit
*2
*3
:Applicable, :N/A
* 1 Limited within the range of I/O points for the CPU module.
* 2 Can be installed to any I/O slot of a base unit
* 3 An extension base unit cannot be connected to a safety CPU.
2 - 2
Remark
To use the Q68RD3-G with a C Controller module, refer to the user's manual for
the C Controller module.
2.1 Applicable Systems
Page 23
2
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
(b) Mounting to a MELSECNET/H remote I/O station
The table below shows the network modules and base units applicable to the
Q68RD3-G and quantities for each network module model.
Depending on the combination with other modules or the number of mounted
modules, power supply capacity may be insufficient.
Pay attention to the power supply capacity before mounting modules, and if the
power supply capacity is insufficient, change the combination of the modules.
Table 2.2 Applicable modules, number of mountable modules, and applicable base units
Applicable network
module
QJ72LP25-25
QJ72LP25G
QJ72LP25GE
QJ72BR15
* 1 Limited within the range of I/O points for the network module.
* 2 Can be installed to any I/O slot of a base unit.
Remark
No. of modules
Up to 64
1
OVERVIEW
2
*1
Main base unit of
remote I/O station
Base unit
*2
Extension base unit of
remote I/O station
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
:Applicable, :N/A
SPECIFICATIONS
4
The Basic model QCPU or C Controller module cannot create the MELSECNET/
H remote I/O network.
PROCEDURES AND
5
6
7
SETTINGS BEFORE
SYSTEM OPERATION
UTILITY PACKAGE
(GX CONFIGURATOR-TI)
PROGRAMMING
2.1 Applicable Systems
2 - 3
ONLINE MODULE
CHANGE
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 24
2
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
(2) Support of multiple CPU system
The function version of the Q68RD3-G has been "C" from the first release, supporting
the multiple CPU system.
When using the Q68RD3-G in a multiple CPU system, refer to the following manual
first.
• QCPU User's Manual (Multiple CPU System)
(a) Intelligent function module parameters
Write intelligent function module parameters only to the control CPU of the
Q68RD3-G.
(3) Support of online module change
The function version of the Q68RD3-G has been "C" from the first release, supporting
online module change.
For details, refer to CHAPTER 7.
(4) Supported software packages
Relation between the system containing the Q68RD3-G and software package is
shown in the following table.
GX Developer or GX Works2 is required to use the Q68RD3-G.
Table 2.3 Compatible software package and software version
System
Q00J/Q00/Q01CPU
Q02/Q02H/Q06H/
Q12H/Q25HCPU
Q02PH/Q06PHCPU
Q12PH/Q25PHCPU
Q12PRH/Q25PRHCPU Redundant system Version 8.45X or later
Q00UJ/Q00U/
Q01UCPU
Q02U/Q03UD/
Q04UDH/Q06UDHCPU
Q10UDH/Q20UDHCPU
Q13UDH/Q26UDHCPU
Q03UDE/Q04UDEH/
Q06UDEH/Q13UDEH/
Q26UDEHCPU
Q10UDEH/
Q20UDEHCPU
Q50UDEH/
Q100UDEHCPU
When mounted to MELSECNET/H remote I/O
station
Single CPU system Version 7 or later
Multiple CPU system Version 8 or later
Single CPU system Version 4 or later
Multiple CPU system Version 6 or later
Single CPU system
Multiple CPU system
Single CPU system
Multiple CPU system
Single CPU system
Multiple CPU system
Single CPU system
Multiple CPU system
Single CPU system
Multiple CPU system
Single CPU system
Multiple CPU system
Single CPU system
Multiple CPU system
Single CPU system
Multiple CPU system
Single CPU system
Multiple CPU system
GX Developer GX Configurator-TI GX Works2
Version 8.68W or later
Version 7.10L or later
Version 8.76E or later
Version 8.48A or later
Version 8.76E or later
Version 8.62Q or later
Version 8.68W or later
Version 8.76E or later
Cannot be used Cannot be used Version 1.25B or later
Version 6 or later
Software version
Version 1.26AC
or later
Version 1.26AC
or later
Version 1.15R or later
Cannot be used
Version 1.15R or later
Version 1.40S or later
2 - 4
2.1 Applicable Systems
Page 25
2
t
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
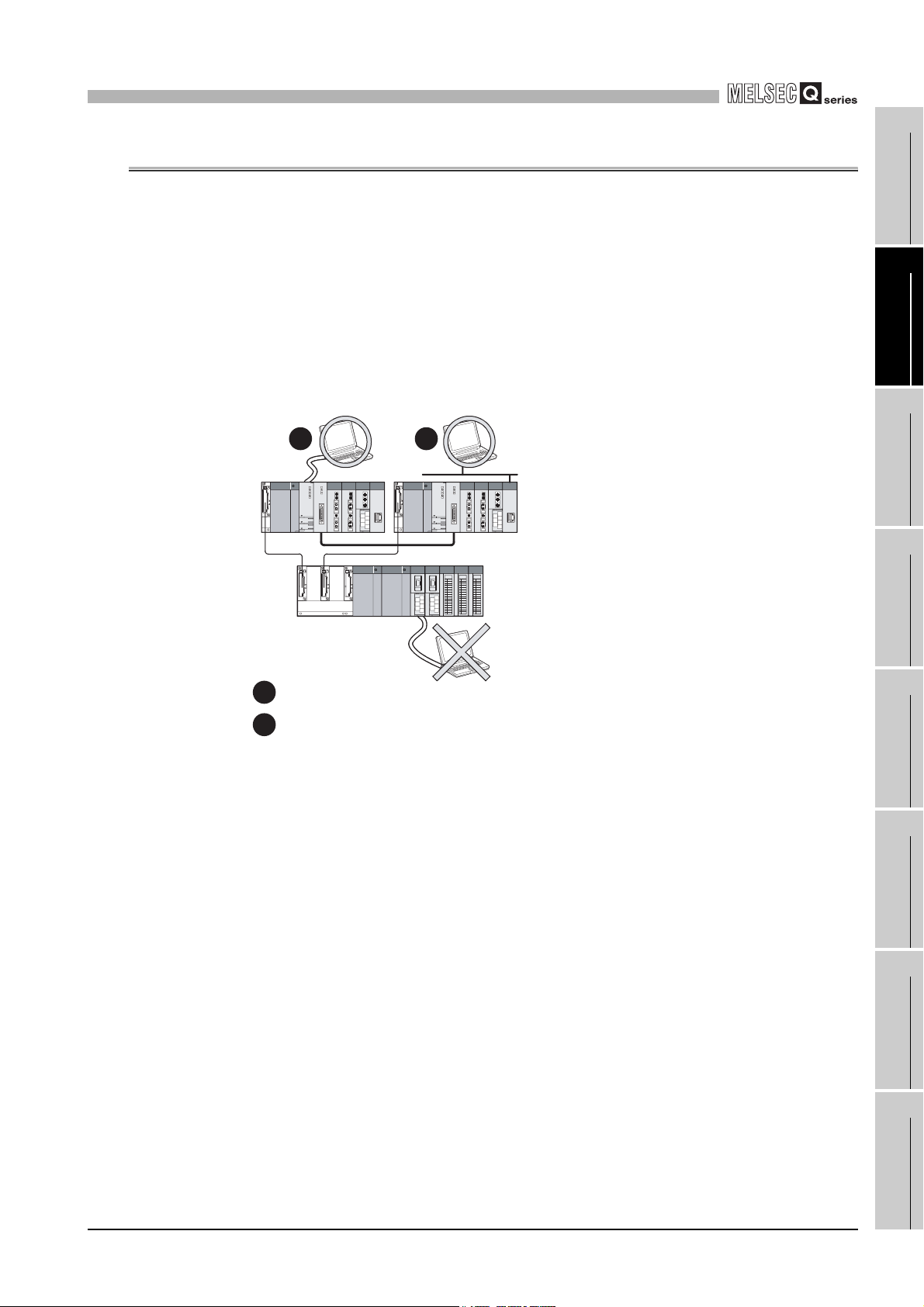
2.2 When Using the Q68RD3-G with Redundant CPU
This section describes the use of the Q68RD3-G with Redundant CPU.
1
(1) Dedicated instructions
Dedicated instructions cannot be used.
(2) GX Configurator-TI
GX Configurator-TI cannot be used when accessing Redundant CPU via an intelligent
function module on an extension base unit from GX Developer. Connect a personal
computer with a communication path indicated below.
1 2
Main base unit
Extension base unit
(GX Configurator-TI cannot be used.)
1
Connecting directly to a programmable controller CPU
PROCEDURES AND
2
3
4
5
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
SETTINGS BEFORE
SYSTEM OPERATION
2
Connecting to a programmable controller CPU via an intelligent function module
(Ethernet module, MELSECNET/H module or CC-Link module) on the main base uni
Figure 2.1 Communication path for GX Configrator-TI
6
7
8
UTILITY PACKAGE
(GX CONFIGURATOR-TI)
PROGRAMMING
ONLINE MODULE
CHANGE
2.2 When Using the Q68RD3-G with Redundant CPU
TROUBLESHOOTING
2 - 5
Page 26
2
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
2.3 How to Check the Function Version, Serial No., and Software
Version
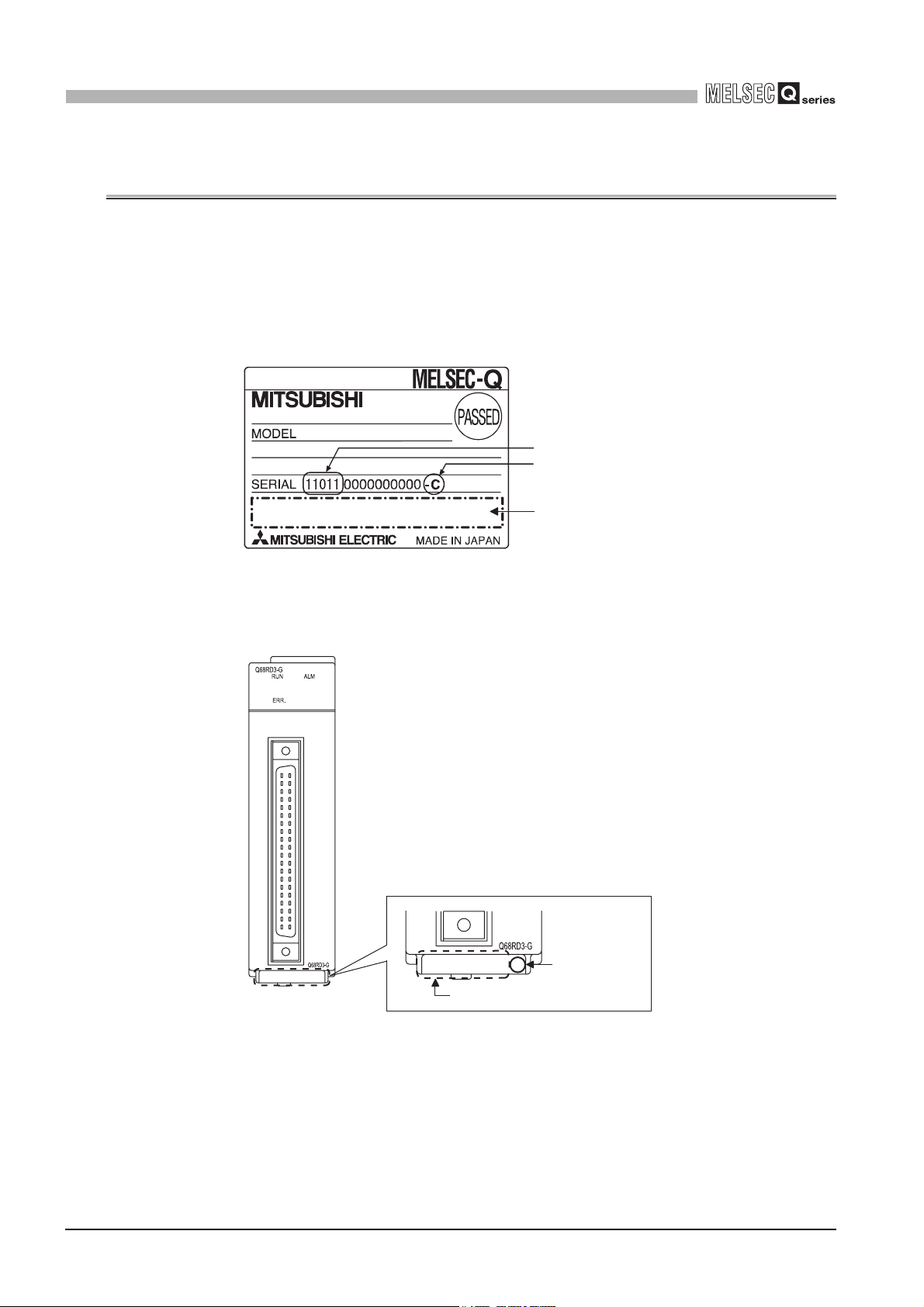
(1) Checking the function version and serial No.
The serial No. and function version of the Q68RD3-G can be checked on the rating
plate, front of the module, and system monitor of GX developer.
(a) On the rating plate
The rating plate is put on the side of the Q68RD3-G.
Serial No. (Upper 5 digits)
Function version
Relevant regulation standards
(b) On the front of the module
The function version and serial No. on the rating plate is also indicated on the
front of the module (lower part).
1101120000000000-C
Serial No.
Function version
2 - 6
2.3 How to Check the Function Version, Serial No., and Software Version
Page 27
2
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
1
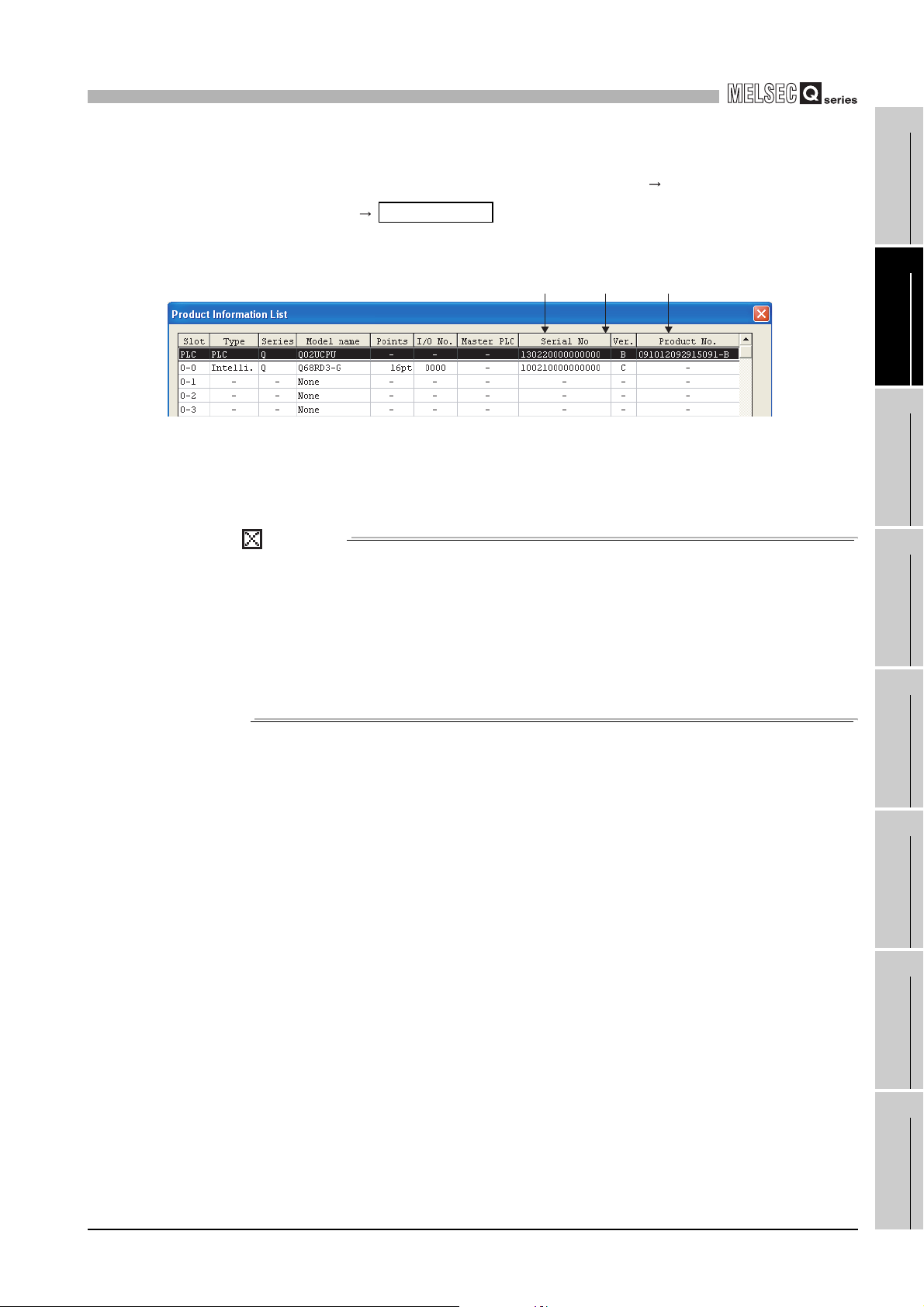
(c) On the system monitor (product information list)
To display the system monitor, select [Diagnostics] [System
monitor] of GX Developer.
1) Displaying the product No.
Since the Q68RD3-G do not support the production number display,
"-" is displayed in the "Product No." field.
Product Inf. List
Serial
No.
Function
version
Product
No.
POINT
The serial No. on the rating plate and the front of the module may be different from
the serial No.
• The serial No. on the rating plate and the front of the module indicates the
management information of the product.
• The serial No. displayed on the product information list in GX Developer
indicates the function information of the product. The function information
of the product is updated when a new function is added.
PROCEDURES AND
2
3
4
5
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
SETTINGS BEFORE
SYSTEM OPERATION
2.3 How to Check the Function Version, Serial No., and Software Version
2 - 7
UTILITY PACKAGE
(GX CONFIGURATOR-TI)
6
PROGRAMMING
7
ONLINE MODULE
CHANGE
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 28
2
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
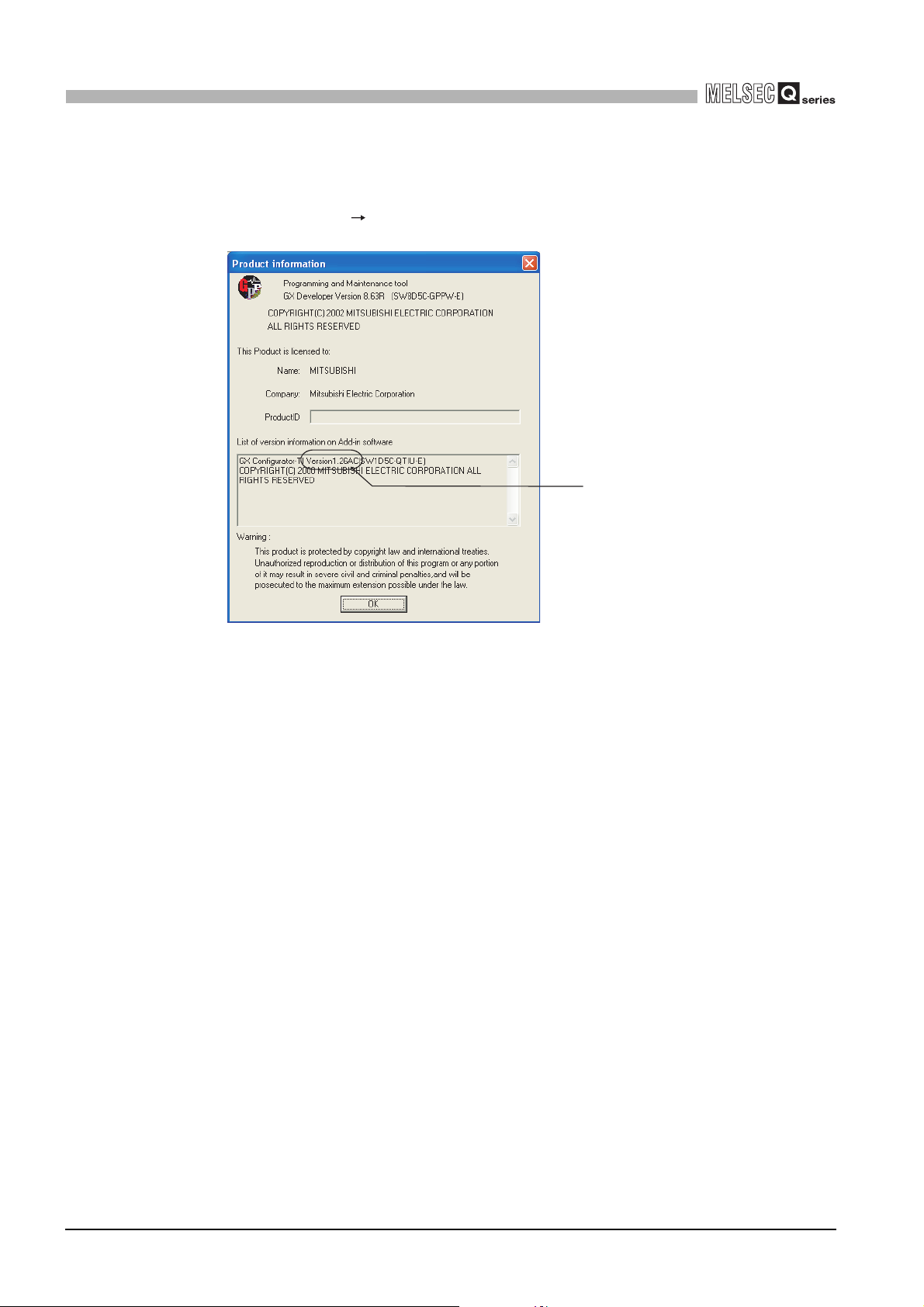
(2) Checking the software version of GX Configurator-TI
The software version of GX Configurator-TI can be checked on GX Developer by
clicking [Help] [Product information].
Software version
("Product information" screen of GX Developer Version 8)
2 - 8
2.3 How to Check the Function Version, Serial No., and Software Version
Page 29

3
SPECIFICATIONS
CHAPTER3 SPECIFICATIONS
3.1 Performance Specifications
The following table shows the performance specifications of the Q68RD3-G.
(1) List of performance specifications
Table 3.1 List of performance specifications
Item Specifications
Number of channels 8 channels
Output
Usable RTD
Measured
temperature
range
Temperature detecting output current 1.0mA or less
Conversion
accuracy
Resolution
Conversion speed
Number of analog input points 8 channels
Isolation specifications
Disconnection detection
Maximum number of writes to Flash memory 50,000
Number of I/O points occupied 16 points (I/O assignment: Intelligent 16 points)
External connection system 40-pin connector
Applicable wire size
External device connector (sold separately) A6CON1,A6CON2,A6CON4
Internal current consumption (5VDC) 0.54A
Weight 0.20kg
External dimensions
Temperature conversion value 16-bit signed binary (-2000 to 8500)
Scaling value 16-bit signed binary
*5
Pt100
JPt100
Ni100
-200 to 850
Pt100
*2
JPt100
Ni100
-20 to 120
0 to 200
-180 to 600
-20 to 120
0 to 200
-60 to 180
*1
*1
*1
*1
*1
*1
*1
Between RTD input and
programmable controller
power supply
Between RTD input channels
* 1 If the temperature out of the measurement range given in the table is input from the RTD, the
maximum and minimum values of the measurement range are used.
Pt100 (JIS C 1604-1997, IEC 751 1983), JPt100 (JIS C 1604-1981),
Ni100 (DIN 43760 1987)
-200 to 850
-180 to 600
-60 to 180
0.8 (Ambient temperature: 25 5 ), 2.4 (Ambient temperature: 0 to 55 )
0.3 (Ambient temperature: 25 5 ), 1.1 (Ambient temperature: 0 to 55 )
0.4 (Ambient temperature: 25 5 ), 1.2 (Ambient temperature: 0 to 55 )
0.8 (Ambient temperature: 25 5 ), 2.4 (Ambient temperature: 0 to 55 )
0.3 (Ambient temperature: 25 5 ), 1.1 (Ambient temperature: 0 to 55 )
0.4 (Ambient temperature: 25 5 ), 1.2 (Ambient temperature: 0 to 55 )
0.4 (Ambient temperature: 25 5 ), 1.2 (Ambient temperature: 0 to 55 )
0.1
320ms/8 channels
Specific isolated area
Available (each channel respectively)
0.3mm
0.088mm
2
Isolation
method
Transformer
isolation
Transformer
isolation
(AWG22) or less (for A6CON1, A6CON4)
2
to 0.24mm2(AWG28 to 24) (for A6CON2)
102(H) 27.4(W) 130(D)mm
3.1 Performance Specifications
*3
Dielectric
withstand
voltage
500VACrms for 1min.
1000VACrms for
1min.
*4
Isolation
resistance
500VDC
10M or
more
3 - 1
1
2
3
4
PROCEDURES AND
5
6
7
8
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
SETTINGS BEFORE
SYSTEM OPERATION
UTILITY PACKAGE
(GX CONFIGURATOR-TI)
PROGRAMMING
ONLINE MODULE
CHANGE
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 30
3
SPECIFICATIONS
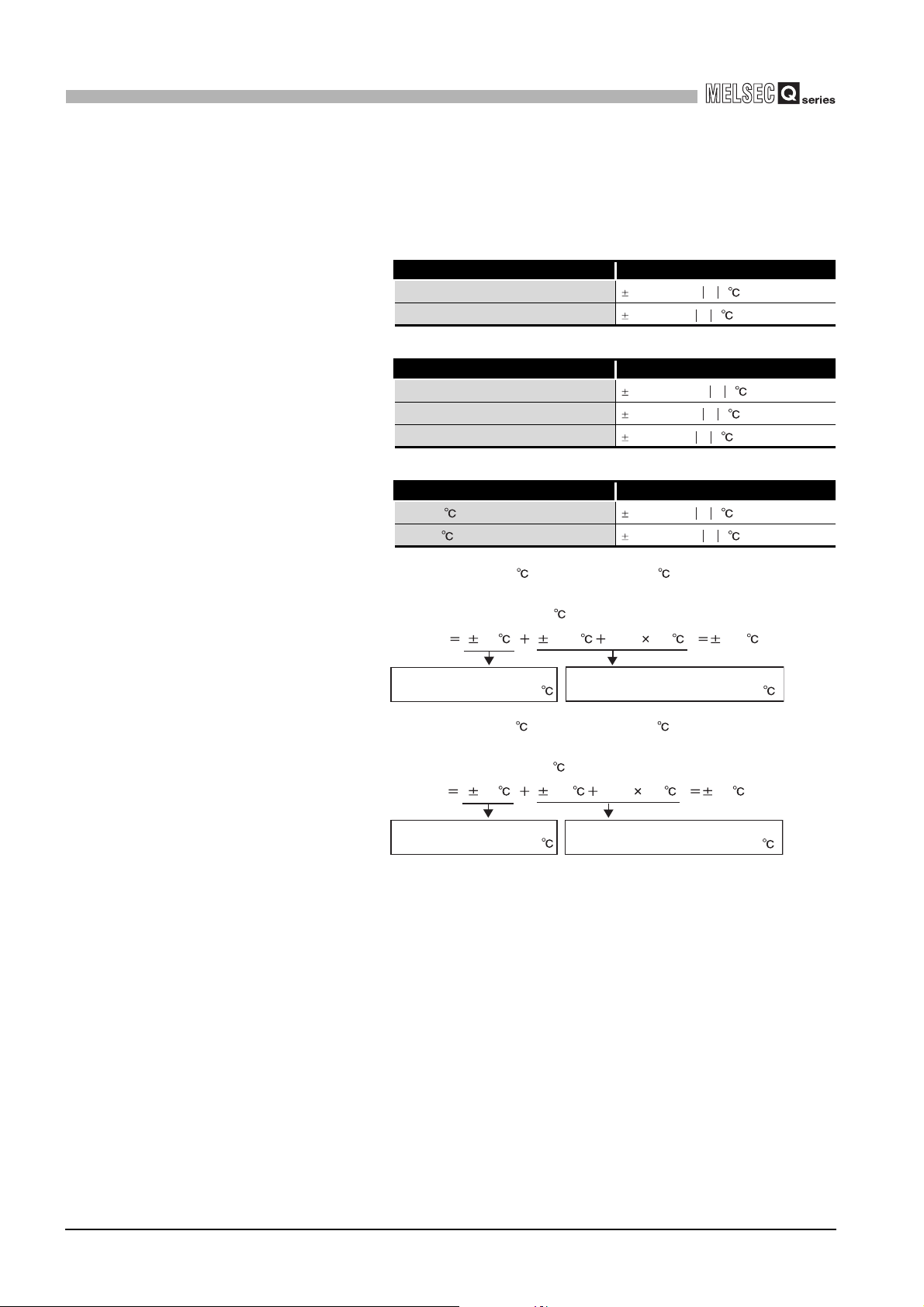
* 2 When a RTD is connected, the degree of accuracy will be the sum of the conversion accuracy of
the Q68RD3-G and the tolerance of the connected RTD.
Use the calculation formula below.
(Accuracy) = (Conversion accuracy) + (Tolerance of connected RTD)
Table 3.2 Pt100 Tolerance (JIS C 1604-1997, IEC 751 1983)
Class To lera nce
A
B
Table 3.3 JPt100 Tolerance (JIS C 1604-1981)
Class To lera nce
0.15
0.2
0.5
Table 3.4 Ni100 Tolerance (DIN 43760 1987)
Class To lera nce
0 to 250 (0.4+0.007 t )
-60 to 0 (0.4+0.0028 t )
(0.15+0.002 t )
(0.3+0.005 t )
(0.15+0.0015 t )
(0.15+0.002 t )
(0.3+0.005 t )
Example 1
Example 2
* 3 The conversion speed indicates the time required before the measured temperature values are
stored into the buffer memory when sampling processing is specified.
Regardless of the number of conversion-enabled channels, the measured temperature values of
all channels are batch-stored into the buffer memory every 320ms. (Refer to Section 3.2.1.)
* 4 When disconnection state is detected, output values are selected from "Up scale", "Down scale" or
"Given value". (Refer to Section 3.2.2.)
* 5 Only 3-wire RTDs can be used.
2-wire RTDs and 4-wire RTDs cannot be used.
Ambient temperature: 40 (for Pt100 (-200 to 850 ))
RTD type: Pt100 Class A
Measurement temperature: 800
(Accuracy) ( 2.4 ) { (0.15 0.002 800 )} 4.15
Conversion accuracy with
ambient temperature at 40
Ambient temperature: 25 (for Pt100 (-200 to 850 ))
RTD type: Pt100 Class B
Measurement temperature: 500
(Accuracy) ( 0.8 ) { (0.3 0.005 500 )} 3.6
Conversion accuracy with
ambient temperature at 25
Tolerance of Pt100 with measured
temperature of RTD class A at 800
Tolerance of Pt100 with measured
temperature of RTD class B at 500
3 - 2
3.1 Performance Specifications
Page 31

3
SPECIFICATIONS
3.2 Function List
The following table lists the Q68RD3-G functions.
1
Table 3.5 Function list
Item Description Reference
Temperature conversion
function
Temperature conversion
system
Conversion enable/disable
function
RTD type selection function,
Range switching function
Disconnection detection
function
Conversion setting for
disconnection detection
function
Warning output function
Scaling function
Offset/gain setting function This function compensates an error of measured temperature value.
Online module change
This function incorporates temperature data to a module by connecting a RTD.
Temperature data are stored into the buffer memory in 16-bit signed binary (-2000 to 8500).
(1) Sampling processing
This processing converts every temperature input value for each channel and outputs
a measured temperature value after every conversion.
(2) Averaging processing
(a) Time average
This processing averages temperature conversion by time for each channel and
stores the averaged value.
(b) Count average
This processing averages temperature conversion by count for each channel
and stores the averaged value.
(c) Moving average
This processing averages measured temperature values, which are measured
every sampling period for the specified number of times.
(3) Primary delay filter
This processing smooths measured temperature values by a preset time constant.
This function specifies temperature conversion availability (enable or disable) for each
channel.
Conversion time is 320ms/8 channels.
This function sets RTD type and measurement range for each channel. Section 4.5
This function detects disconnection of RTD which is connected to each conversion-enabled
channel.
This function is to select a value to be stored in the CH Measured temperature value
(Un\G11 to Un\G18) from "Up scale", "Down scale" or "Given value" when disconnection is
detected.
(1)
Process alarm
A warning is output when the measured temperature value is equal to or more than
the process alarm upper upper limit value, or equal to or less than the process alarm
lower lower limit value.
(2)
Rate alarm
A warning is output when the measured temperature value changes in a rate by
which the measured temperature value reaches the rate alarm upper limit value or
more, or the rate alarm lower limit value or less.
This function converts measured temperature value to scaling value (ratio (%)) and stores
the converted value into the buffer memory.
This function enables a module change without the system being stopped.
Section 3.4.5
Section 3.2.1
Section 3.4.2
Section 3.4.14
Section 3.2.2
Section 3.2.3
Section 3.4.15
to
Section 3.4.18
Section 3.4.11
Section 4.6
CHAPTER 7
PROCEDURES AND
2
3
4
5
6
7
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
SETTINGS BEFORE
SYSTEM OPERATION
UTILITY PACKAGE
(GX CONFIGURATOR-TI)
PROGRAMMING
3.2 Function List
3 - 3
ONLINE MODULE
CHANGE
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 32

3
SPECIFICATIONS
3.2.1 Temperature conversion system
The following shows the temperature measurement timing within each conversion period.
Temperatures of all channels, CH1 to CH8, are batch-updated every 320ms, regardless of
the Conversion enable/disable setting (Un\G0).
If the Conversion enable/disable setting (Un\G0) of a channel is set to "Enable" when the
temperature is measured, the measured temperature value is stored in the CH
Measured temperature value (Un\G11 to Un\G18). If the setting is set to "Disable", the
measured temperature value is not stored.
Regardless of the number of conversion-enabled channels, the measured temperature
values are stored in the buffer memory every 320ms.
The following shows the temperature measurement timing within each conversion period.
Conversion period (320ms) Conversion period (320ms) Conversion period (320ms)
Update timing
CH1 to CH8
Measured
temperature values
batch-updated
Update timing
CH1 to CH8
Measured
temperature values
batch-updated
Update timing
CH1 to CH8
Measured
temperature values
batch-updated
Update timing
CH1 to CH8
Measured
temperature values
batch-updated
3 - 4
3.2 Function List
3.2.1 Temperature conversion system
Page 33

3
SPECIFICATIONS
(1) Sampling processing
Measured temperature values that are measured every 320ms of sampling period are
stored in the buffer memory.
(2) Averaging processing
Averaging processing requires at least 2 times of conversion processing excluding the
maximum and the minimum values.
After the first averaging processing is completed, the corresponding bit for a channel
where processing has been completed of the Conversion completion flag (Un\G10)
turns ON (changes to "1").
(a) Time average
Conversion is performed for a set period of time. Then, the total value, excluding
the maximum and the minimum values, is averaged and the averaged value is
stored in the buffer memory.
The number of processing times within the set period of time is calculated in the
following formula.
Number of processing times = set period of time 320 (times)
1
2
3
4
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
Setting range of time average is 1280 to 5000ms.
If a value outside the setting range is set, an error (error code: 20 ) occurs.
[Example]
When six channels, channels 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6, are conversion-enabled and the
average time is set to 2000ms, temperature is measured six times and the averaged
value is output.
2000 320 = 6.25 (times)...... Drop the fractional part
(b) Count average
Conversion is performed for a preset number of times. Then, the total value,
excluding the maximum and the minimum values, is averaged and the averaged
value is stored in the buffer memory.
The processing time is calculated in the following formula.
Processing time = preset count 320 (ms)
Setting range of count average is 4 to 500 times.
If a value outside the setting range is set, an error (error code: 30 ) occurs.
[Example]
When six channels, channels 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6, are conversion-enabled and the
average count is set to 5 times, the averaged value is output every 1600ms.
5 320 = 1600 (ms)
PROCEDURES AND
5
6
7
SETTINGS BEFORE
SYSTEM OPERATION
UTILITY PACKAGE
(GX CONFIGURATOR-TI)
PROGRAMMING
3.2 Function List
3.2.1 Temperature conversion system
3 - 5
ONLINE MODULE
CHANGE
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 34

3
SPECIFICATIONS
(c) Moving average
Measured temperature values, which are measured every sampling period for the
specified number of times, are averaged and the averaged value is stored in the
buffer memory.
The latest measured temperature value can be obtained since averaging
processing is performed moving for each sampling period.
Measured
temperature value
16000
Moving average processing with 4-time setting
3)
2)
1)
4)
Sampling period (320ms)
5)
6)
7)
8)
9)
10)
12)
11)
8000
1st storage
2nd storage
3rd storage
0
Conversion completion flag turns ON (changes to "1").
Data transition in buffer memory
1st storage
1)+2)+3)+4) 2)+3)+4)+5) 3)+4)+5)+6)
444
2nd storage
3rd storage
Time [ms]
Buffer memory
Measured
temperature value
3 - 6
3.2 Function List
3.2.1 Temperature conversion system
Page 35

3
SPECIFICATIONS
(3) Primary delay filter
By a preset time constant, measured temperature value whose excessive noise has
been smoothed is output.
The degree of smoothness depends on the time constant.
Time constant is the time required for measured temperature value to reach 63.2% of
a steady-state value.
The relational expression between time constant and measured temperature value is
shown below.
1
OVERVIEW
2
[When n=1
Y
[When n=2]
Yn = yn-1 +
[When n 3]
Y
Yn: Current measured temperature
Yn-1: Preceding measured
n: Number of sampling times
TA: Time constant (320 to 5000ms)
* 1 Conversion completion flag turns ON (changes to "1") when n 2.
Setting range of time constant is 320 to 5000ms.
If a value outside the setting range is set, an error (error code: 32 ) occurs.
*1
]
n = 0
n = Yn-1 +
value
temperature value
t
t + TA
t
t + TA
(y
n - yn-1)
(yn - Yn-1)
yn: Measured temperature value
before smoothed
yn-1: Preceding measured
temperature value before
smoothed
Conversion period (320ms)
t:
PROCEDURES AND
3
4
5
6
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
SETTINGS BEFORE
SYSTEM OPERATION
UTILITY PACKAGE
(GX CONFIGURATOR-TI)
3.2 Function List
3.2.1 Temperature conversion system
3 - 7
PROGRAMMING
7
ONLINE MODULE
CHANGE
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 36

3
SPECIFICATIONS
[Example 1: Measured temperature value when the temperature input value is changed
from 250.0 to 260.0 ]
The measured temperature value changes as shown below when the time constant is
set to 3200ms (3.2s).
The measured temperature value reaches 63.2% (256.3 ) of the value converted
with sampling processing in 3200ms (3.2s) after the temperature input value has
reached to 260.0 .
262.0 2620
260.0
258.0
256.0
254.0
252.0
Temperature input value ( )
250.0
Temperture input value
0 3200
Elapsed time (ms)
Measured temperature value
2600
2580
2560
2540
2520
2500
Measured temperature value
[Example 2: Measured temperature value when the change of temperature input value is a
waveform with ringing]
The measured temperature value changes as shown below when the time constant is
set to 1280ms (1.28s) or 640ms (0.64s), and the moving average processing is set to
4 times, respectively.
Measured temperature value
(Time constant setting 640ms)
Measured temperature value
(Time constant setting 1280ms)
2620
262.0
Temperature input value
Measured temperature value
(Moving average processing 4 times)
260.0
258.0
256.0
254.0
252.0
Temperature input value ( )
250.0
0
1000
2000
3000
4000
Elapsed time (ms)
5000
6000
7000
2600
2580
2560
2540
2520
Measured temperature value
2500
3 - 8
3.2 Function List
3.2.1 Temperature conversion system
Page 37

3
SPECIFICATIONS
3.2.2 Conversion setting for disconnection detection function
(1) This function is to select a value to be stored in the CH Measured
temperature value (Un\G11 to Un\G18) from "Up scale", "Down scale" or
"Given value" when disconnection is detected.
The Conversion setting for disconnection detection (Un\G164 and
Un\G165) can be set for each channel.
(2) This function is effective for only conversion-enabled channels.
(3) When "Up scale" (0
or down scale value of the measurement range to be used is stored.
Table 3.6 Measured temperature value when disconnection is detected
Setting
RTD type
Pt100
JPt100
Ni100
* 1 RTD type to be used and measurement range are set in the intelligent function module switch
setting. (Refer to Section 4.5.)
Setting value
(4) When "Given value" (2H) is selected, set a value in the CH Conversion
setting value for disconnection detection (Un\G166 to Un\G173) in units
H) or "Down scale" (1H) is selected, an up scale value
Measurement
*1
0
H
1
H
4
H
2
H
3
H
5
H
8
H
range
-200 to 850 902.5 -252.5
-20 to 120 127.0 -27.0
0 to 200 210.0 -10.0
-180 to 600 639.0 -219.0
-20 to 120 127.0 -27.0
0 to 200 210.0 -10.0
-60 to 180 192.0 -72.0
Measured temperature value when
disconnection is detected
Up scale Down scale
PROCEDURES AND
1
2
3
4
5
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
SETTINGS BEFORE
SYSTEM OPERATION
of 0.1 .
The value set in the buffer memory above is stored in the CH
Measured temperature value (Un\G11 to Un\G18) when disconnection is
detected.
(5) It takes 320ms (maximum) to detect a disconnection state.
6
7
8
UTILITY PACKAGE
(GX CONFIGURATOR-TI)
PROGRAMMING
ONLINE MODULE
CHANGE
3.2 Function List
3.2.2 Conversion setting for disconnection detection function
TROUBLESHOOTING
3 - 9
Page 38

3
SPECIFICATIONS
(6) It takes 640ms (maximum) to obtain normal measured temperature
values after connection is restored.
Temperature conversion restarts 640ms after connection is restored.
When averaging processing is set, it takes another 640ms and time
required for averaging processing before normal measured temperture
values are stored to the CH Measured temperature value (Un\G11 to
Un\G18) after the restart of temperature conversion. During the time
before normal measured temperature values are stored in the buffer
memory, the measured temperature values remain the value specified in
the The Conversion setting for disconnection detection (Un\G164 and
Un\G165), such as "Down scale".
(7) For operation of the warning output function when disconnection is
detected or recovered, refer to Section 3.2.3.
3 - 10
3.2 Function List
3.2.2 Conversion setting for disconnection detection function
Page 39

3
SPECIFICATIONS
1
3.2.3 Warning output function
(1) Process alarm
Temperature
(a) Warning occurrence
When the detected measured temperature value is higher than or equal to the
process alarm upper upper limit value, or lower than or equal to the process alarm
lower lower limit value (when the value enters the warning output range), a
warning occurs.
When a warning occurs, "1" is stored to the bit of the corresponding channel in the
Warning output flag (Process alarm) (Un\G47), Warning output signal (XD) turns
ON, and the "ALM" LED turns on.
(b) Warning clearance
After a warning occurs, when the temperature value is lower than the process
alarm upper lower limit value or higher than the process alarm lower upper limit
value (when the value returns to within the setting range), the warning is cleared.
When the warning is cleared, "0" is stored to the bit of the corresponding channel
in the Warning output flag (Process alarm) (Un\G47).
Warning output signal (XD) turns OFF only when the values for all channels return
to within the setting range.
Warning output range section
Out of warning output range section
Included
Warning
clearance
Warning
clearance
Upper upper
limit value
Upper lower
limit value
CH1 measured
temperature value
Lower upper
limit value
CH2 measured
temperature value
Lower lower
limit value
Warning
occurence
Warning
occurence
Warning clearance
Warning occurence
PROCEDURES AND
2
3
4
5
6
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
SETTINGS BEFORE
SYSTEM OPERATION
UTILITY PACKAGE
(GX CONFIGURATOR-TI)
CH1 Process alarm upper
limit value (Un\G47.b0)
CH1 Process alarm lower
limit value (Un\G47.b1)
CH2 Process alarm upper
limit value (Un\G47.b2)
Warning output signal (XD)
Time
3.2 Function List
3.2.3 Warning output function
3 - 11
PROGRAMMING
7
ONLINE MODULE
CHANGE
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 40

3
RTD type
Pt100
(New JIS)
JPt100
(Old JIS)
Ni100
SPECIFICATIONS
(c) Settable temperature range and default value vary according to the RTD type to
be used and measurement range.
Values are set in units of 0.1 .
Table 3.7 Settable range and default value of process alarm
Measurement
range
-200 to 850
-20 to 120
0 to 200
-180 to 600
-20 to 120
0 to 200
-60 to 180
Process alarm
lower upper limit
value
(in units of 0.1 )
Default value
Process alarm
lower lower limit
value
(in units of 0.1 )
-2000 8500 -2000 to 8500
-200 1200 -200 to 1200
0 2000 0 to 2000
-1800 6000 -1800 to 6000
-200 1200 -200 to 1200
0 2000 0 to 2000
-600 1800 -600 to 1800
Process alarm
upper upper limit
value
(in units of 0.1 )
Process alarm
upper lower limit
value
(in units of 0.1 )
Settable temperature
range
(Accuracy guarantee
range)
(in units of 0.1 )
(d) When time average or count average is specified, process alarm processing is
executed for each preset time or count.
When other temperature conversion system (sampling processing, moving
average or primary delay filter) is specified, process alarm processing is executed
at every sampling period.
(e) When disconnection state is detected, the measured temperature value is
replaced with the setting in the Conversion setting for disconnection detection
(Un\G164 and Un\G165), such as "Down scale". As a result, a warning may occur.
3 - 12
3.2 Function List
3.2.3 Warning output function
Page 41

3
SPECIFICATIONS
(2) Rate alarm
(a) Warning occurrence
When the measured temperature value is monitored at every rate alarm warning
detection period and the changed portion from the preceding value is larger than
or equal to the rate alarm upper limit value, or smaller than or equal to the rate
alarm lower limit value, a warning occurs.
When a warning occurs, "1" is stored to the bit of the corresponding channel in the
Warning output flag (Rate alarm) (Un\G48), Warning output signal (XD) turns ON,
and the "ALM" LED turns on.
(b) Warning clearance
After a warning occurrence, when the changed portion of the measured
temperature value is smaller than the rate alarm upper limit value or larger than
the rate alarm lower limit value (when the value returns to within the setting
range), the warning is cleared.
When the warning is cleared, "0" is stored to the bit of the corresponding channel
in the Warning output flag (Rate alarm) (Un\G48).
Warning output signal (XD) turns OFF only when the values for all channels return
to within the setting range.
1
2
3
4
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
PROCEDURES AND
5
6
7
8
SETTINGS BEFORE
SYSTEM OPERATION
UTILITY PACKAGE
(GX CONFIGURATOR-TI)
PROGRAMMING
ONLINE MODULE
CHANGE
3.2 Function List
3.2.3 Warning output function
TROUBLESHOOTING
3 - 13
Page 42

3
SPECIFICATIONS
Measured
temperature
value
Change of
measured
temperature
value ( C)
Rate alarm
warning
detection
period
Rate alarm
warning
detection
period
Change of CH2
measured
temperature
value
Rate alarm
upper limit
value
Rate alarm
lower limit
value
CH1 measured
temperature
value
CH2
measured
temperature
value
Change of
CH1
measured
temperature
value
Time
CH1 Rate alarm upper
limit value (Un\G48.b0)
CH1 Rate alarm lower
limit value (Un\G48.b1)
CH2 Rate alarm upper
limit value (Un\G48.b2)
Warning output signal (XD)
Time
3 - 14
3.2 Function List
3.2.3 Warning output function
Page 43

3
SPECIFICATIONS
(c) The rate alarm upper limit/lower limit values are set in units of 0.1 for the
measured temperature range.
Setting range is -32768 to 32767 (-3276.8 to 3276.7 ).
The default value is set to "0".
(d) The rate alarm warning detection period is set based on the number of conversion
periods.
Setting range is 1 to 6000 (times).
Calculation method of the rate alarm warning detection period is below.
(Rate alarm warning detection period)
= (Setting value of the Rate alarm warning detection period) (Conversion
period) (320ms)
[Example 1: When setting the rate alarm warning detection period to 150 times with
sampling processing]
Rate alarm warning detection period = 150 times 320ms = 48000ms = 48s
1
2
3
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
[Example 2: When setting the rate alarm warning detection period to 150 times with
averaging processing (count average: 10 times)]
Rate alarm warning detection period = 150 times 10 times 320ms = 480000ms =
480s
(e) Rate alarm is effective to monitor a change of measured temperature values
within a limited range.
1) Setting example of the rate alarm upper/lower limit values for monitoring that a
measured temperature value increases within the specified range
Change of
measured
temperature
value ( C)
20.0
10.0
C
C
0
Rate alarm upper limit value
Rate alarm lower limit value
Time
PROCEDURES AND
4
5
6
7
SPECIFICATIONS
SETTINGS BEFORE
SYSTEM OPERATION
UTILITY PACKAGE
(GX CONFIGURATOR-TI)
PROGRAMMING
3.2 Function List
3.2.3 Warning output function
3 - 15
ONLINE MODULE
CHANGE
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 44

3
SPECIFICATIONS
2) Setting example of the rate alarm upper/lower limit values for monitoring that a
measured temperature value decreases within the specified range
Change of
measured
temperature
value ( C)
3) Setting example of the rate alarm upper/lower limit values for monitoring that a
measured temperature value changes within the specified range
-10.0
-20.0
0
Rate alarm upper limit value
C
C
Rate alarm lower limit value
Time
Change of
measured
temperature
value ( C)
Rate alarm upper limit value
C
10.0
0
C
-10.0
Rate alarm lower limit value
Time
(f) When disconnection state is detected, the measured temperature value is
replaced with the setting in the Conversion setting for disconnection detection
(Un\G164 and Un\G165), such as "Down scale". As a result, a warning may occur.
(g) After connection is restored, preceding values required for rate alarm occurrence
are cleared.
Therefore, a warning does not occur even though the changed portion of
measured temperature values before and after temperature conversion exceeds
the setting range when temperature conversion is restarted.
3 - 16
3.2 Function List
3.2.3 Warning output function
Page 45

3
SPECIFICATIONS
3.3 I/O Signals for Communicating with Programmable Controller
CPU
1
This section describes the I/O signal assignment and the function of each signal.
3.3.1 I/O signal list
The following table lists the I/O signals of the Q68RD3-G.
The I/O numbers (X/Y) described in this chapter and later indicate the case where the start
I/O number of the Q68RD3-G is set to "0".
Table 3.8 I/O signal list
Input signal
(Signal direction:
Programmable controller CPU Q68RD3-G)
Device No. Signal name Device No. Signal name
X0
X1
X2 Y2
X3 Y3
X4 Y4
X5 Y5
X6 Y6
X7 Y7
X8 Y8
X9 Operating condition setting completion flag Y9 Operating condition setting request
XA Offset/gain setting mode status flag YA User range write request
XB Channel change completion flag YB Channel change request
XC Disconnection detection signal YC
XD Warning output signal YD
XE Conversion completion flag YE
XF Error flag YF Error clear request
Module ready
Reserved
*1
Programmable controller CPU Q68RD3-G)
Y0
Y1
Reserved
Reserved
Output signal
(Signal direction:
*1
*1
POINT
The reserved signals marked *1 are used by the system and are not available for
the user. If they are turned ON/OFF in a sequence program, the functions of those
signals in the Q68RD3-G cannot be guaranteed.
PROCEDURES AND
2
3
4
5
6
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
SETTINGS BEFORE
SYSTEM OPERATION
UTILITY PACKAGE
(GX CONFIGURATOR-TI)
3.3 I/O Signals for Communicating with Programmable Controller CPU
3.3.1 I/O signal list
3 - 17
PROGRAMMING
7
ONLINE MODULE
CHANGE
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 46

3
SPECIFICATIONS
3.3.2 I/O signal details
This section describes details of the Q68RD3-G I/O signals.
(1) Module ready (X0)
(a) If the module is in the normal mode when the programmable controller is powered
ON or the reset operation of the CPU module is performed, this signal turns ON to
start conversion processing as soon as the module is ready.
(b) When this signal is OFF in the normal mode, conversion processing is not
performed. If the module is in the offset/gain setting mode, conversion processing
is performed even if this signal is OFF.
(c) In any of the following cases, this signal turns OFF.
• The module is in the offset/gain setting mode.
• A watchdog timer error occurs in the Q68RD3-G.
* 1 A watchdog timer error occurs when program operation does not complete within the intended time
due to errors such as a hardware failure of the Q68RD3-G. The "RUN" LED of the Q68RD3-G turns
off when a watchdog timer error occurs.
*1
(2) Operation condition setting completion flag (X9)
(a) When the following settings are changed, this signal is used as an interlock
condition to turn ON/OFF Operation condition setting request (Y9).
• Conversion enable/disable setting (Un\G0)
• CH Time/Count/Moving average/Time constant setting (Un\G1 to Un\G8)
• Averaging processing selection (Un\G24, Un\G25)
• Warning output enable/disable setting (Un\G46)
• Scaling valid/invalid setting (Un\G58)
• CH Scaling range upper/lower limit values (Un\G62 to Un\G77)
• CH Scaling width upper/lower limit values (Un\G78 to Un\G93)
• CH Process alarm upper/lower limit values (Un\G94 to Un\G125)
• CH Rate alarm warning detection period (Un\126 to Un\G133)
• CH Rate alarm upper/lower limit values (Un\G134 to Un\G149)
• Conversion setting for disconnection detection (Un\G164, Un\G165)
• CH Conversion setting value for disconnection detection (Un\G166 to
Un\G173)
(b) When this signal is OFF, conversion processing is not performed.
3 - 18
3.3 I/O Signals for Communicating with Programmable Controller CPU
3.3.2 I/O signal details
Page 47

3
SPECIFICATIONS
(c) In the following case, this signal turns OFF.
• Operating condition setting request (Y9) is ON.
Module ready (X0)
Operating condition
setting completion flag (X9)
Operating condition setting
request (Y9)
Conversion enable/disable
setting (Un\G0)
Conversion completion
flag (XE)
(3) Offset/gain setting mode status flag (XA)
(a) In offset/gain setting mode
1) This signal is used as an interlock condition to turn ON/OFF User range write
request (YA) when values adjusted by offset/gain setting are written.
Executed in Q68RD3-G
Executed in sequence program
Conversion
disabled
Conversion enabled
1
2
3
4
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
2) For offset/gain setting, refer to Section 4.6.
Executed in Q68RD3-G
Module ready (X0)
OFF
Offset/gain setting mode
status flag (XA)
User range write request (YA)
Executed in sequence program
(b) In normal mode
1) This signal is used as an interlock condition to turn ON/OFF User range write
request (YA) when the user range is restored.
2) For the user range restore function, refer to CHAPTER 7.
Executed in Q68RD3-G
Executed in sequence program
Module ready (X0)
Offset/gain setting mode status
flag (XA)
ON
PROCEDURES AND
5
6
7
SETTINGS BEFORE
SYSTEM OPERATION
UTILITY PACKAGE
(GX CONFIGURATOR-TI)
PROGRAMMING
User range write request (YA)
3.3 I/O Signals for Communicating with Programmable Controller CPU
3.3.2 I/O signal details
3 - 19
ONLINE MODULE
CHANGE
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 48

3
SPECIFICATIONS
(4) Channel change completion flag (XB)
(a) This signal is used as an interlock condition to turn ON/OFF Channel change
request (YB) when changing the channel targeted for offset/gain setting.
(b) For offset/gain setting, refer to Section 4.6.
Executed in Q68RD3-G
Executed in sequence program
Offset/gain setting mode
offset/gain specification
(Un\G26, Un\G27)
Channel change completion
flag (XB)
Channel change request (YB)
(5) Disconnection detection signal (XC)
(a) This signal turns ON when any input signal line in the input circuit of the
conversion-enabled channel is disconnected.
To identify the disconnected channel, check Disconnection detection flag
(Un\G49).
When this signal turns ON, conversion update for the conversion-enabled
channels stops.
(b) Measured temperature value when this signal turns ON can be selected from "Up
scale", "Down scale" or "Given value". (Refer to Section 3.2.2.)
(c) This signal turns OFF after eliminating the cause of disconnection and turning ON
Error clear request (YF).
(d) When connection is restored, the measured temperature value update is restarted
regardless of the reset of this signal.
(6) Warning output signal (XD)
(a) This signal turns ON when a process alarm or rate alarm is detected.
1) Process alarm
• This signal turns ON when the process alarm is enabled and a measured
temperature value exceeds the preset range of the Process alarm upper/
lower limit values (Un\G94 to Un\G125) in any of conversion-enabled
channels.
• This signal automatically turns OFF when the measured temperature
value returns to within the setting range for all conversion-enabled
channels. The "ALM" LED also turns off.
3 - 20
3.3 I/O Signals for Communicating with Programmable Controller CPU
3.3.2 I/O signal details
Page 49

3
SPECIFICATIONS
2) Rate alarm
• This signal turns ON when the rate alarm is enabled and the change of
• This signal automatically turns OFF when the change of measured
measured temperature value exceeds the preset range of the Rate alarm
upper/lower limit values (Un\G134 to Un\G149) in any of conversionenabled channels.
temperature value returns to within the setting range for all conversionenabled channels. The "ALM" LED also turns off.
Executed in Q68RD3-G
Warning output flag
(Un\G47, Un\G48)
Warning output
signal (XD)
0
Warning occurrence
(process alarm, rate alarm)
0
1
2
3
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
(7) Conversion completion flag (XE)
(a) This flag turns ON when measured temperature values of all conversion-enabled
channels are stored into the buffer memory after the programmable controller is
powered ON or the reset operation of the CPU module is performed.
(b) When averaging processing is specified, this signal also turns ON when the
converted measured temperature values are stored into the buffer memory after
completion of averaging processing.
(c) Status of this flag depends on the ON/OFF status of Operating condition setting
completion flag (X9).
1) When Operating condition setting completion flag (X9) turns ON (stop
conversion)
• Temperature conversion for conversion-enabled channels is started.
• After the measured temperature value is stored into the buffer memory,
the bit of corresponding channel in the Conversion completion flag
(Un\G10) turns ON (changes to "1").
• After the measured temperature values of all conversion-enabled
channels are stored into the buffer memory, this flag turns ON.
2) When Operating condition setting completion flag (X9) turns OFF (conversion
stop)
• The bits of all channels in the Conversion completion flag (Un\G10) are
turned OFF (changes to "0").
• This flag turns OFF.
Note that even though conversion has been stopped, the data
immediately before the stop are held in the Measured temperature values
stored in the buffer memory.
(d) Use this signal or the Conversion completion flag (Un\G10) as an interlock to read
out the measured temperature value.
PROCEDURES AND
4
5
6
7
8
SPECIFICATIONS
SETTINGS BEFORE
SYSTEM OPERATION
UTILITY PACKAGE
(GX CONFIGURATOR-TI)
PROGRAMMING
ONLINE MODULE
CHANGE
(e) This flag does not turn ON when all channels are set to conversion-disabled.
3.3 I/O Signals for Communicating with Programmable Controller CPU
3.3.2 I/O signal details
3 - 21
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 50

3
SPECIFICATIONS
(8) Error flag (XF)
(a) This signal turns ON when a write error occurs.
(b) To clear the error code, turn ON Error clear request (YF).
Error code (Un\G19)
Error flag (XF)
Error clear request (YF)
(9) Operating condition setting request (Y9)
Executed in Q68RD3-G
Executed in sequence program
Error occurrence
(a) This signal is turned ON when enabling the following settings.
• Conversion enable/disable setting (Un\G0)
• CH Time/Count/Moving average/Time constant setting (Un\G1 to Un\G8)
• Averaging processing selection (Un\G24, Un\G25)
• Warning output enable/disable setting (Un\G46)
• Scaling valid/invalid setting (Un\G58)
• CH Scaling range upper/lower limit values (Un\G62 to Un\G77)
• CH Scaling width upper/lower limit values (Un\G78 to Un\G93)
• CH Process alarm upper/lower limit values (Un\G94 to Un\G125)
• CH Rate alarm warning detection period (Un\G126 to Un\G133)
• CH Rate alarm upper/lower limit values (Un\G134 to Un\G149)
• Conversion setting for disconnection detection (Un\G164, Un\G165)
• CH Conversion setting value for disconnection detection (Un\G166 to
Un\G173)
(b) When this signal is turned ON, Disconnection detection signal (XC) and Warning
output signal (XD) turn OFF.
(c) For the ON/OFF timing, refer to the description for Operating condition setting
completion flag (X9).
3 - 22
3.3 I/O Signals for Communicating with Programmable Controller CPU
3.3.2 I/O signal details
Page 51

3
SPECIFICATIONS
1
(10)User range write request (YA)
(a) In offset/gain setting mode
1) This signal is turned ON when the offset/gain setting adjusted values are
written to the Flash memory.
2) For the ON/OFF timing, refer to the description for Offset/gain setting mode
status flag (XA).
For offset/gain setting, refer to Section 4.6.
(b) In normal mode
1) This signal is turned ON when the user range is restored.
2) For the ON/OFF timing, refer to the description for Offset/gain setting mode
status flag (XA).
For the user range restore function, refer to CHAPTER 7.
(11)Channel change request (YB)
(a) This signal is turned ON when changing the offset/gain setting target channel.
(b) For the ON/OFF timing, refer to the description for Channel change completion
flag (XB).
For offset/gain setting, refer to Section 4.6.
(12)Error clear request (YF)
(a) This signal is turned ON when clearing Error flag (XF) and Disconnection
detection signal (XC).
However, a setting value error of the intelligent function module switch setting
cannot be cleared.
Correct the setting value.
PROCEDURES AND
2
3
4
5
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
SETTINGS BEFORE
SYSTEM OPERATION
(b) For the ON/OFF timing, refer to the descriptions for Disconnection detection
signal (XC) and Error flag (XF).
3.3 I/O Signals for Communicating with Programmable Controller CPU
3.3.2 I/O signal details
3 - 23
UTILITY PACKAGE
(GX CONFIGURATOR-TI)
6
PROGRAMMING
7
ONLINE MODULE
CHANGE
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 52

3
SPECIFICATIONS
3.4 Buffer Memory
3.4.1 Buffer memory assignment
This section describes the assignment of the Q68RD3-G buffer memory.
POINT
Do not write data to the system area or the area where writing data from a
sequence program is disabled.
Doing so may cause a malfunction of the module.
Table 3.9 Buffer memory assignment (1/6)
Address
Hex. Dec.
00H 0 Conversion enable/disable setting 00FFH
01H 1 CH1 Time/Count/Moving average/Time constant setting 0
02H 2 CH2 Time/Count/Moving average/Time constant setting 0
03H 3 CH3 Time/Count/Moving average/Time constant setting 0
04H 4 CH4 Time/Count/Moving average/Time constant setting 0
05H 5 CH5 Time/Count/Moving average/Time constant setting 0
06H 6 CH6 Time/Count/Moving average/Time constant setting 0
07H 7 CH7 Time/Count/Moving average/Time constant setting 0
08H 8 CH8 Time/Count/Moving average/Time constant setting 0
09H 9 System area
0AH 10 Conversion completion flag 0 R Section 3.4.4
0BH 11 CH1 Measured temperature value 0 R
0CH 12 CH2 Measured temperature value 0 R
0DH 13 CH3 Measured temperature value 0 R
0EH 14 CH4 Measured temperature value 0 R
0FH 15 CH5 Measured temperature value 0 R
10H 16 CH6 Measured temperature value 0 R
11H 17 CH7 Measured temperature value 0 R
12H 18 CH8 Measured temperature value 0 R
13H 19 Error code 0 R Section 3.4.6
14H 20 Setting range (Input type CH1-4) 0 R
15H 21 Setting range (Input type CH5-8) 0 R
16H 22 Setting range (Offset/gain setting CH1-CH8) 0 R Section 3.4.8
17H 23 System area
18H 24 Averaging processing selection (CH1-CH4) 0
19H 25 Averaging processing selection (CH5-CH8) 0
1AH 26 Offset/gain setting mode (Offset specification) 0
1BH 27 Offset/gain setting mode (Gain specification) 0
1CH 28 CH1 Offset temperature setting value 0
1DH 29 CH1 Gain temperature setting value 0
1EH 30 CH2 Offset temperature setting value 0
1FH 31 CH2 Gain temperature setting value 0
20H 32 CH3 Offset temperature setting value 0
21H 33 CH3 Gain temperature setting value 0
22H 34 CH4 Offset temperature setting value 0
23H 35 CH4 Gain temperature setting value 0
Description Default value
Read/Write
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
Reference
*1
section
Section 3.4.2
Section 3.4.3
Section 3.4.5
Section 3.4.7
Section 3.4.9
Section 3.4.10
Section 3.4.11
3 - 24
3.4 Buffer Memory
3.4.1 Buffer memory assignment
Page 53

3
SPECIFICATIONS
Table 3.9 Buffer memory assignment (2/6)
Address
Hex. Dec.
24H 36 CH5 Offset temperature setting value 0
25H 37 CH5 Gain temperature setting value 0
26H 38 CH6 Offset temperature setting value 0
27H 39 CH6 Gain temperature setting value 0
28H 40 CH7 Offset temperature setting value 0
29H 41 CH7 Gain temperature setting value 0
2AH 42 CH8 Offset temperature setting value 0
2BH 43 CH8 Gain temperature setting value 0
2CH 44
2DH 45
2EH 46 Warning output enable/disable setting FFFFH
2FH 47 Warning output flag (Process alarm) 0 R
30H 48 Warning output flag (Rate alarm) 0 R
31H 49 Disconnection detection flag 0 R Section 3.4.14
32H 50 CH1 Scaling value 0 R
33H 51 CH2 Scaling value 0 R
34H 52 CH3 Scaling value 0 R
35H 53 CH4 Scaling value 0 R
36H 54 CH5 Scaling value 0 R
37H 55 CH6 Scaling value 0 R
38H 56 CH7 Scaling value 0 R
39H 57 CH8 Scaling value 0 R
3AH 58 Scaling valid/invalid setting 00FFH
3BH 59
to to
3DH 61
3EH 62 CH1 Scaling range lower limit value 0
3FH 63 CH1 Scaling range upper limit value 0
40H 64 CH2 Scaling range lower limit value 0
41H 65 CH2 Scaling range upper limit value 0
42H 66 CH3 Scaling range lower limit value 0
43H 67 CH3 Scaling range upper limit value 0
44H 68 CH4 Scaling range lower limit value 0
45H 69 CH4 Scaling range upper limit value 0
46H 70 CH5 Scaling range lower limit value 0
47H 71 CH5 Scaling range upper limit value 0
48H 72 CH6 Scaling range lower limit value 0
49H 73 CH6 Scaling range upper limit value 0
4AH 74 CH7 Scaling range lower limit value 0
4BH 75 CH7 Scaling range upper limit value 0
4CH 76 CH8 Scaling range lower limit value 0
4DH 77 CH8 Scaling range upper limit value 0
4EH 78 CH1 Scaling width lower limit value 0
4FH 79 CH1 Scaling width upper limit value 0
50H 80 CH2 Scaling width lower limit value 0
51H 81 CH2 Scaling width upper limit value 0
52H 82 CH3 Scaling width lower limit value 0
53H 83 CH3 Scaling width upper limit value 0
System area
System area
Description Default value
Read/Write
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
Reference
*1
section
Section 3.4.11
Section 3.4.12
Section 3.4.13
Section 3.4.15
Section 3.4.16
Section 3.4.17
Section 3.4.18
PROCEDURES AND
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
SETTINGS BEFORE
SYSTEM OPERATION
UTILITY PACKAGE
(GX CONFIGURATOR-TI)
PROGRAMMING
ONLINE MODULE
CHANGE
3.4 Buffer Memory
3.4.1 Buffer memory assignment
TROUBLESHOOTING
3 - 25
Page 54

3
SPECIFICATIONS
Table 3.9 Buffer memory assignment (3/6)
Address
Hex. Dec.
54H 84 CH4 Scaling width lower limit value 0
55H 85 CH4 Scaling width upper limit value 0
56H 86 CH5 Scaling width lower limit value 0
57H 87 CH5 Scaling width upper limit value 0
58H 88 CH6 Scaling width lower limit value 0
59H 89 CH6 Scaling width upper limit value 0
5AH 90 CH7 Scaling width lower limit value 0
5BH 91 CH7 Scaling width upper limit value 0
5CH 92 CH8 Scaling width lower limit value 0
5DH 93 CH8 Scaling width upper limit value 0
5EH 94 CH1 Process alarm lower lower limit value -2000
5FH 95 CH1 Process alarm lower upper limit value -2000
60H 96 CH1 Process alarm upper lower limit value 8500
61H 97 CH1 Process alarm upper upper limit value 8500
62H 98 CH2 Process alarm lower lower limit value -2000
63H 99 CH2 Process alarm lower upper limit value -2000
64H 100 CH2 Process alarm upper lower limit value 8500
65H 101 CH2 Process alarm upper upper limit value 8500
66H 102 CH3 Process alarm lower lower limit value -2000
67H 103 CH3 Process alarm lower upper limit value -2000
68H 104 CH3 Process alarm upper lower limit value 8500
69H 105 CH3 Process alarm upper upper limit value 8500
6AH 106 CH4 Process alarm lower lower limit value -2000
6BH 107 CH4 Process alarm lower upper limit value -2000
6CH 108 CH4 Process alarm upper lower limit value 8500
6DH 109 CH4 Process alarm upper upper limit value 8500
6EH 110 CH5 Process alarm lower lower limit value -2000
6FH 111 CH5 Process alarm lower upper limit value -2000
70H 112 CH5 Process alarm upper lower limit value 8500
71H 113 CH5 Process alarm upper upper limit value 8500
72H 114 CH6 Process alarm lower lower limit value -2000
73H 115 CH6 Process alarm lower upper limit value -2000
74H 116 CH6 Process alarm upper lower limit value 8500
75H 117 CH6 Process alarm upper upper limit value 8500
76H 118 CH7 Process alarm lower lower limit value -2000
77H 119 CH7 Process alarm lower upper limit value -2000
78H 120 CH7 Process alarm upper lower limit value 8500
79H 121 CH7 Process alarm upper upper limit value 8500
7AH 122 CH8 Process alarm lower lower limit value -2000
7BH 123 CH8 Process alarm lower upper limit value -2000
7CH 124 CH8 Process alarm upper lower limit value 8500
7DH 125 CH8 Process alarm upper upper limit value 8500
7EH 126 CH1 Rate alarm warning detection period 0
7FH 127 CH2 Rate alarm warning detection period 0
80H 128 CH3 Rate alarm warning detection period 0
81H 129 CH4 Rate alarm warning detection period 0
82H 130 CH5 Rate alarm warning detection period 0
Description Default value
Read/Write
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
Reference
*1
section
Section 3.4.18
Section 3.4.10
Section 3.4.20
3 - 26
3.4 Buffer Memory
3.4.1 Buffer memory assignment
Page 55

3
SPECIFICATIONS
Table 3.9 Buffer memory assignment (4/6)
Address
Hex. Dec.
83H 131 CH6 Rate alarm warning detection period 0
85H 133 CH8 Rate alarm warning detection period 0
86H 134 CH1 Rate alarm upper limit value 0
87H 135 CH1 Rate alarm lower limit value 0
88H 136 CH2 Rate alarm upper limit value 0
89H 137 CH2 Rate alarm lower limit value 0
8AH 138 CH3 Rate alarm upper limit value 0
8BH 139 CH3 Rate alarm lower limit value 0
8CH 140 CH4 Rate alarm upper limit value 0
8DH 141 CH4 Rate alarm lower limit value 0
8EH 142 CH5 Rate alarm upper limit value 0
8FH 143 CH5 Rate alarm lower limit value 0
90H 144 CH6 Rate alarm upper limit value 0
91H 145 CH6 Rate alarm lower limit value 0
92H 146 CH7 Rate alarm upper limit value 0
93H 147 CH7 Rate alarm lower limit value 0
94H 148 CH8 Rate alarm upper limit value 0
95H 149 CH8 Rate alarm lower limit value 0
96H 150
to to
9DH 157
9EH 158
9FH 159
A0H 160
to to
A3H 163
A4H 164 Conversion setting for disconnection detection1 (CH1-CH4) 1111H
A5H 165 Conversion setting for disconnection detection2 (CH5-CH8) 1111H
A6H 166 CH1 Conversion setting value for disconnection detection 0
A7H 167 CH2 Conversion setting value for disconnection detection 0
A8H 168 CH3 Conversion setting value for disconnection detection 0
A9H 169 CH4 Conversion setting value for disconnection detection 0
AAH 170 CH5 Conversion setting value for disconnection detection 0
ABH 171 CH6 Conversion setting value for disconnection detection 0
ACH 172 CH7 Conversion setting value for disconnection detection 0
ADH 173 CH8 Conversion setting value for disconnection detection 0
AEH 174
to to
BDH 189
BEH 190
BFH 191
C0H 192
C1H 193
C2H 194
C3H 195
System area
Mode switching setting 0
System area
System area
CH1 Factory default offset value
CH1 Factory default gain value
CH1 User range settings offset value
CH1 User range settings gain value
CH1 User range settings resistance offset value (L)
CH1 User range settings resistance offset value (H)
Description Default value
*3
*3
*3
*3
*3
*3
0
0
0
0
0
Read/Write
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
*2
R/W
Reference
*1
section
Section 3.4.2084H 132 CH7 Rate alarm warning detection period 0
Section 3.4.21
Section 3.4.22
Section 3.4.23
Section 3.4.24
Section 3.4.25
PROCEDURES AND
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
SETTINGS BEFORE
SYSTEM OPERATION
UTILITY PACKAGE
(GX CONFIGURATOR-TI)
PROGRAMMING
ONLINE MODULE
CHANGE
3.4 Buffer Memory
3.4.1 Buffer memory assignment
TROUBLESHOOTING
3 - 27
Page 56

3
SPECIFICATIONS
Address
Hex. Dec.
C4H 196
C5H 197
C6H 198
C7H 199
C8H 200
C9H 201
CAH 202
CBH 203
CCH 204
CDH 205
CEH 206
CFH 207
D0H 208
D1H 209
D2H 210
D3H 211
D4H 212
D5H 213
D6H 214
D7H 215
D8H 216
D9H 217
DAH 218
DBH 219
DCH 220
DDH 221
DEH 222
DFH 223
E0H 224
E1H 225
E2H 226
E3H 227
E4H 228
E5H 229
E6H 230
E7H 231
E8H 232
E9H 233
EAH 234
EBH 235
ECH 236
EDH 237
EEH 238
EFH 239
F0H 240
F1H 241
Table 3.9 Buffer memory assignment (5/6)
Description Default value
CH1 User range settings resistance gain value (L)
CH1 User range settings resistance gain value (H)
CH2 Factory default offset value
CH2 Factory default gain value
CH2 User range settings offset value
CH2 User range settings gain value
*3
*3
*3
*3
CH2 User range settings resistance offset value (L)
CH2 User range settings resistance offset value (H)
CH2 User range settings resistance gain value (L)
CH2 User range settings resistance gain value (H)
CH3 Factory default offset value
CH3 Factory default gain value
CH3 User range settings offset value
CH3 User range settings gain value
*3
*3
*3
*3
CH3 User range settings resistance offset value (L)
CH3 User range settings resistance offset value (H)
CH3 User range settings resistance gain value (L)
CH3 User range settings resistance gain value (H)
CH4 Factory default offset value
CH4 Factory default gain value
CH4 User range settings offset value
CH4 User range settings gain value
*3
*3
*3
*3
CH4 User range settings resistance offset value (L)
CH4 User range settings resistance offset value (H)
CH4 User range settings resistance gain value (L)
CH4 User range settings resistance gain value (H)
CH5 Factory default offset value
CH5 Factory default gain value
CH5 User range settings offset value
CH5 User range settings gain value
*3
*3
*3
*3
CH5 User range settings resistance offset value (L)
CH5 User range settings resistance offset value (H)
CH5 User range settings resistance gain value (L)
CH5 User range settings resistance gain value (H)
CH6 Factory default offset value
CH6 Factory default gain value
CH6 User range settings offset value
CH6 User range settings gain value
*3
*3
*3
*3
CH6 User range settings resistance offset value (L)
CH6 User range settings resistance offset value (H)
CH6 User range settings resistance gain value (L)
CH6 User range settings resistance gain value (H)
CH7 Factory default offset value
CH7 Factory default gain value
CH7 User range settings offset value
CH7 User range settings gain value
*3
*3
*3
*3
Reference
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
*1
*2
*2
*2
*2
*2
*2
*2
*2
*2
*2
*2
*2
*2
*2
*2
*2
*2
*2
*2
*2
*2
*2
*2
*2
*2
*2
*2
*2
*2
*2
*2
*2
*2
*2
*2
section
Section 3.4.25
Read/Write
*3
*3
0
0
0
0
0
*3
*3
*3
*3
0
0
0
0
0
0
*3
*3
*3
*3
0
0
0
0
0
0
*3
*3
*3
*3
0
0
0
0
0
0
*3
*3
*3
*3
0
0
0
0
0
0
*3
*3
*3
*3
0
0
0
0
0
0
3 - 28
3.4 Buffer Memory
3.4.1 Buffer memory assignment
Page 57

3
SPECIFICATIONS
Address
Hex. Dec.
F2H 242
F3H 243
F4H 244
F5H 245
F6H 246
F7H 247
F8H 248
F9H 249
FAH 250
FBH 251
FCH 252
FDH 253
Table 3.9 Buffer memory assignment (6/6)
Description Default value
CH7 User range settings resistance offset value (L)
CH7 User range settings resistance offset value (H)
CH7 User range settings resistance gain value (L)
CH7 User range settings resistance gain value (H)
CH8 Factory default offset value
CH8 Factory default gain value
CH8 User range settings offset value
CH8 User range settings gain value
CH8 User range settings resistance offset value (L)
CH8 User range settings resistance offset value (H)
CH8 User range settings resistance gain value (L)
CH8 User range settings resistance gain value (H)
* 1 Indicates an availability of reading/writing data from/to a sequence program.
R : Read enabled W : Write enabled
* 2 Data must be written to buffer memory under the interlock conditions (buffer memory write
conditions) of the following I/O signals.
• Operating condition setting
*3
*3
*3
*3
1
Reference
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
*1
*2
*2
*2
*2
*2
*2
*2
*2
section
Section 3.4.25
2
3
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
Read/Write
*3
*3
*3
*3
*3
*3
*3
*3
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
4
Buffer memory write condition
Y9 X9
Operating
Write
condition
request
setting request
* 3 This area is related with the user range save/restore functions, which allows users to re-set the
offset/gain values easily when performing online module change.
Operating
condition setting
completion flag
MOV
PROCEDURES AND
5
6
7
SETTINGS BEFORE
SYSTEM OPERATION
UTILITY PACKAGE
(GX CONFIGURATOR-TI)
PROGRAMMING
3.4 Buffer Memory
3.4.1 Buffer memory assignment
3 - 29
ONLINE MODULE
CHANGE
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 58

3
SPECIFICATIONS
3.4.2 Conversion enable/disable setting (Un\G0)
(1) Temperature conversion enable/disable status is set for each channel.
(2) Setting "Disable" for unused channels can prevent unnecessary
disconnection detection.
(3) The default value is set to "Disable" for all channels.
b15 b14 b13 b12 b11 b10 b9 b8 b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
CH8 CH7 CH6 CH5 CH4 CH3 CH2 CH100000000
Data for b8 to b15 are fixed to "0".
[Example]
b15 b14 b13 b12 b11 b10 b9 b8 b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
1111110000000000
Channel 1 and 2 are enabled for conversion.
(4) To activate the setting, turning ON/OFF Operating condition setting
request (Y9) is required.
0: Enable
1: Disable
3 - 30
3.4 Buffer Memory
3.4.2 Conversion enable/disable setting (Un\G0)
Page 59

3
SPECIFICATIONS
1
3.4.3 CH[] Time/Count/Moving average/Time constant setting (Un\G1
to Un\G8)
(1) Time average, count average, moving average or time constant for
primary delay filter is set for each channel that is specified for averaging
processing.
(2) The default value is set to "0000
H".
(3) To activate the setting, turning ON/OFF Operating condition setting
request (Y9) is required.
(4) The following table shows the settable range.
Table 3.10 Settable range
Processing method Setting value
Time average
Count average 4 to 500 (times)
Moving average 2 to 60 (times)
Primary delay filter
* 1 : Values can be set in units of 1ms; however, processing is performed in units of 320ms.
1280 to 5000 (ms)
320 to 5000 (ms)
*1
*1
POINT
When a value out of the above setting range is written, an error (error code: 20 ,
30 , 31 or 32 ) occurs on the channel. Then, Error flag (XF) turns ON and
conversion processing is performed with the setting before the error occurrence.
PROCEDURES AND
2
3
4
5
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
SETTINGS BEFORE
SYSTEM OPERATION
3.4 Buffer Memory
3.4.3 CH[] Time/Count/Moving average/Time constant setting (Un\G1 to Un\G8)
3 - 31
UTILITY PACKAGE
(GX CONFIGURATOR-TI)
6
PROGRAMMING
7
ONLINE MODULE
CHANGE
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 60

3
SPECIFICATIONS
3.4.4 Conversion completion flag (Un\G10)
(1) The bit of the corresponding channel in the Conversion completion flag
turns ON (changes to "1") when conversion of conversion-enabled
channels is completed.
When averaging processing is specified, the flag turns ON (changes to
"1") after the first averaged value is stored into the CH Measured
temperature value (Un\G11 to Un\G18).
Conversion completion flag (XE) turns ON when conversion of all
conversion-enabled channels is completed.
(2) When Operating condition setting request (Y9) is turned ON, the bit
returns to the default value of OFF ("0") and it turns ON ("1") after
conversion is completed.
b15 b14 b13 b12 b11 b10 b9 b8 b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
CH8 CH7 CH6 CH5 CH4 CH3 CH2 CH100000000
Data for b8 to b15 are fixed to "0".
(3) If disconnection is detected in the status where the bit of each channel
in the Conversion completion flag (Un\G10) has already been ON ("1"),
the bit remains ON ("1").
(4) Use this area or the Conversion completion flag (XE) as an interlock to
read out the measured temperature value.
0: During conversion or unused
1: Conversion completed
3 - 32
3.4 Buffer Memory
3.4.4 Conversion completion flag (Un\G10)
Page 61

3
SPECIFICATIONS
3.4.5 CH[] Measured temperature value (Un\G11 to Un\G18)
(1) Values input from RTD are converted into "temperature values" to detect
temperature.
(2) The measured temperature value rounded off to one decimal place is
multiplied by 10 and the result is stored into the buffer memory in 16-bit
signed binary. (Drop the second decimal place and later.)
(3) The default value is set to "0" for all channels.
[Example 1]
When the measured temperature value is 123.025 ..... 1230 is stored.
b15 b14 b13 b12 b11 b10 b9 b8 b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
1
2
3
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
1100111000000100
[Example 2]
When the measured temperature value is -123.025 ..... -1230 is stored.
b15 b14 b13
11111011
b12b11b10b9b8b7b6b5b4b3b2b1b0
00110010
(4) Use the Conversion completion flag (XE) or the Conversion completion
flag (Un\G10) as an interlock to read out the measured temperature
value.
PROCEDURES AND
4
5
6
7
SPECIFICATIONS
SETTINGS BEFORE
SYSTEM OPERATION
UTILITY PACKAGE
(GX CONFIGURATOR-TI)
PROGRAMMING
3.4 Buffer Memory
3.4.5 CH[] Measured temperature value (Un\G11 to Un\G18)
3 - 33
ONLINE MODULE
CHANGE
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 62

3
SPECIFICATIONS
3.4.6 Error code (Un\G19)
(1) Error code that is detected by the Q68RD3-G is stored.
(2) For details on error codes, refer to Section 8.1.
3.4.7 Setting range 1, 2 (Un\G20 and Un\G21)
(1) This area is for checking the measurement range of the Q68RD3-G,
which is set with Switch 1 and 2 in the intelligent function module switch
setting.
Setting values of the measurement range are stored into the area
indicated below for each channel.
Un\G20
(Setting range 1 CH1-4)
Un\G21
(Setting range 2 CH5-8)
b15
to
CH4 CH3 CH1
CH8 CH7 CH6 CH5
b12 b11
to
b8 b7
to
CH2
(2) The following table shows the measurement range and setting value for
each RTD.
Table 3.11 Measurement range and setting value
RTD Measurement range Setting value
0
H
1
H
H
4
2
H
3
H
5
H
8
H
Pt100
JPt100
Ni100
-200 to 850
-20 to 120
0 to 200
-180 to 600
-20 to 120
0 to 200
-60 to 180
3.4.8 Setting range 3 (Offset/gain setting) (Un\G22)
b4 b3
to
b0
3 - 34
(1) This area is for checking the offset/gain setting of the Q68RD3-G, which
is set with Switch 3 in the intelligent function module switch setting.
"0" is stored for factory default setting and "1" is stored for user range
setting.
b15 b14 b13 b12 b11 b10 b9 b8 b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
CH8 CH7 CH6 CH5 CH4 CH3 CH2 CH100000000
Data for b8 to b15 are fixed to "0".
3.4 Buffer Memory
3.4.6 Error code (Un\G19)
0: Factory default setting
1: User range setting
Page 63

3
SPECIFICATIONS
3.4.9 Averaging processing selection (Un\G24 and Un\G25)
(1) Sampling processing or averaging processing (time average, count
average, moving average or primary delay filter) is selected for each
channel.
(2) The default value is set to "Sampling processing" for all channels.
1
OVERVIEW
2
Un\G24 (Averaging processing
selection CH1-4)
Un\G25 (Averaging processing
selection CH5-8)
(3) To activate the setting, turning ON/OFF Operating condition setting
request (Y9) is required.
(4) The following table shows the settable range.
Table 3.12 Processing method and setting value
[Example]
To set count average, time average, primary delay filter, and sampling processing for
Channel 1, 2, 3, and 4 respectively, set "0412
b15 b12 b11 b8 b7 b4 b3 b0
Processing method Setting value
Sampling processing 0H
Moving average 3H
Primary delay filter 4H
to
CH4 CH3 CH2 CH1
CH8 CH7 CH6 CH5
Time average 1H
Count average 2H
to
H" in Un\G24.
to to
PROCEDURES AND
3
4
5
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
SETTINGS BEFORE
SYSTEM OPERATION
POINT
If a value out of the setting range is set, sampling processing is performed.
3.4 Buffer Memory
3.4.9 Averaging processing selection (Un\G24 and Un\G25)
3 - 35
UTILITY PACKAGE
(GX CONFIGURATOR-TI)
6
PROGRAMMING
7
ONLINE MODULE
CHANGE
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 64

3
SPECIFICATIONS
3.4.10 Offset/gain setting mode (Un\G26 and Un\G27)
(1) A channel targeted for adjusting offset/gain setting values in the offset/
gain setting mode is specified.
(2) Specify a channel for offset setting in Un\G26, and a channel for gain
setting in Un\G27.
(3) Multiple channels can be set at the same time. Though, specify different
channels for the offset and the gain settings; either one of Un\G26 or
Un\G27 must be set to 0 for a channel. If both settings are set to the
same channel, an error (error code 500) occurs.
(4) For details on offset/gain setting, refer to Section 4.6.
Un\G26
(Offset specification)
Un\G27
(Gain specification)
b15 b14 b13 b12 b11 b10 b9 b8
00000000
00000000
Data for b8 to b15 are fixed to "0". 1: Setting channel
b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
CH4 CH3 CH2 CH1CH8 CH7 CH6 CH5
CH4 CH3 CH2 CH1CH8 CH7 CH6 CH5
0: Setting disabled
3 - 36
3.4 Buffer Memory
3.4.10 Offset/gain setting mode (Un\G26 and Un\G27)
Page 65

3
SPECIFICATIONS
3.4.11 CH[] Offset/gain temperature setting values (Un\G28 to Un\G43)
(1) Offset/gain temperature setting values are specified in 16-bit signed
binary for each channel.
(2) A value is set in units of 0.1 .
(3) When Channel change request (YB) is turned ON in the offset/gain
setting mode, measured temperature value is compensated for the value
written in this area.
POINT
(1) High accuracy is ensured for the Offset/gain temperature setting values when
the minimum/maximum temperatures of the operating range are used to
compensate errors.
(2) Set the Offset/gain temperature setting values while reading measured
temperature values.
(3) Satisfy the following conditions when setting the Offset/gain temperature
setting values. If the conditions are not satisfied, an error (error code: 41 )
occurs.
Condition 1: Within the input enabled range
Condition 2:
(Gain temperature setting value) - (Offset temperature setting value) > 0.1[ ]
(4) The offset/gain temperature setting values are stored into the Flash memory
of the Q68RD3-G using the User range write request (YA), and the values are
not erased at power-off.
PROCEDURES AND
1
2
3
4
5
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
SETTINGS BEFORE
SYSTEM OPERATION
3.4.12 Warning output enable/disable setting (Un\G46)
(1) Enable/disable status of warning output for process alarm or rate alarm
is set for each channel.
(2) The default value is set to "Disable" for all channels.
b15 b14 b13 b12 b11 b10 b9 b8 b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
CH4 CH3 CH2 CH1CH8 CH7 CH6 CH5CH4 CH3 CH2 CH1CH8 CH7 CH6 CH5
Rate alarm setting
0: Enable,
1: Disable
(3) To activate the setting, turning ON/OFF Operating condition setting
request (Y9) is required.
3.4.11 CH[] Offset/gain temperature setting values (Un\G28 to Un\G43)
Process alarm setting
3.4 Buffer Memory
3 - 37
UTILITY PACKAGE
(GX CONFIGURATOR-TI)
6
PROGRAMMING
7
ONLINE MODULE
CHANGE
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 66

3
SPECIFICATIONS
3.4.13 Warning output flag (Process alarm/Rate alarm) (Un\G47 and
Un\G48)
(1) When a measured temperature value is out of the setting range of the
CH Process alarm upper/lower limit values (Un\G94 to Un\G125) or
CH Rate alarm upper/lower limit values (Un\G134 to Un\G149), the bit
of the corresponding channel turns ON (changes to "1").
(2) For both process alarm and rate alarm, whether the warning is for the
upper limit value or lower limit value can be checked for each channel.
(3) When the measured temperature value or the change of measured
temperature values returns to within the setting range, this flag will be
automatically reset.
(4) If a warning is detected on any of channels for which conversion and
warning output of process alarm or rate alarm are enabled, Warning
output signal (XD) also turns ON.
(5) When Operating condition setting request (Y9) is turned ON, this flag
will be cleared.
Un\G47 (Process alarm)
Un\G48 (Rate alarm)
b15 b14 b13 b12 b11 b10 b9 b8 b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
CH3 lower
CH8 lower
limit value
b15 b14 b13 b12 b11 b10 b9 b8 b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
CH8 lower
limit value
CH7 lower
limit value
CH8 upper
limit value
CH7 lower
limit value
CH8 upper
limit value
CH6 lower
CH7 upper
limit value
CH6 lower
CH7 upper
limit value
limit value
CH6 upper
limit value
limit value
CH6 upper
limit value
CH5 lower
limit value
CH5 upper
CH5 lower
limit value
CH5 upper
CH4 lower
limit value
limit value
CH4 lower
limit value
limit value
CH4 upper
limit value
CH3 lower
CH4 upper
limit value
limit value
CH3 upper
limit value
CH3 upper
limit value
limit value
CH2 lower
limit value
CH2 upper
CH2 upper
CH2 lower
limit value
CH1 lower
limit value
limit value
0: Normal
1: Alarm ON
CH1 lower
limit value
limit value
0: Normal
1: Alarm ON
CH1 upper
limit value
CH1 upper
limit value
3 - 38
3.4 Buffer Memory
3.4.13 Warning output flag (Process alarm/Rate alarm) (Un\G47 and Un\G48)
Page 67

3
SPECIFICATIONS
3.4.14 Disconnection detection flag (Un\G49)
(1) The flag of the corresponding channel turns ON (changes to "1") when
the disconnection state of RTD is detected.
(2) Disconnection detection is executed on conversion-enabled channels
only.
(3) Disconnection state is detectable for each channel.
(4) If disconnection is detected on any of conversion-enabled channels,
Disconnection detection signal (XC) also turns ON.
For a channel where disconnection is detected, a value based on the
Conversion setting for disconnection detection (Un\G164 and Un\G165)
is stored in the CH Measured temperature value (Un\G11 to Un\G18).
Conversion for the channels not disconnected is continued.
b15 b14 b13 b12 b11 b10 b9 b8 b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
CH8 CH7 CH6 CH5 CH4 CH3 CH2 CH100000000
1
2
3
4
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
Data for b8 to b15 is fixed to "0".
0: Normal
1: Disconnected
(5) When Operating condition setting request (Y9) or Error clear request
(YF) is turned ON, this flag will be cleared.
(6) The following table shows the relationship between the Disconnection
detection flag and conversion enable/disable setting.
Table 3.13 Relationship between the Disconnection detection flag and conversion enable/disable setting
Connection status
Without disconnection
Conversion enable/disable
setting
A
Enable
B
b
A
Disable
Enable ON
Disconnection detection
flag
OFF
B
With disconnection
b
A
Disable OFF
Enable ON
B
Without connection
b
Disable OFF
PROCEDURES AND
5
6
7
8
SETTINGS BEFORE
SYSTEM OPERATION
UTILITY PACKAGE
(GX CONFIGURATOR-TI)
PROGRAMMING
ONLINE MODULE
CHANGE
3.4 Buffer Memory
3.4.14 Disconnection detection flag (Un\G49)
TROUBLESHOOTING
3 - 39
Page 68

3
SPECIFICATIONS
POINT
(1) Always set "Disable" for any channel where no RTD is connected.
If "Enable" is set, the bit of the corresponding channel in the Disconnection
detection flag (Un\G49) turns ON (changes to "1").
(2) When the Disconnection detection flag (Un\G49) turns ON (changes to "1"), a
value to be stored in the Measured temperature value can be selected from
"Up scale", "Down scale" or "Given value". (Refer to Section 3.2.2.)
When connection is restored, updating of the measured temperature value
will be restarted.
(3) For wiring of RTD, refer to Section 4.4.
(4) For troubleshooting of disconnection detection, refer to Section 8.2.7.
3 - 40
3.4 Buffer Memory
3.4.14 Disconnection detection flag (Un\G49)
Page 69

3
SPECIFICATIONS
3.4.15 CH[] Scaling value (Un\G50 to Un\G57)
(1) Measured temperature values within the scaling range set in the CH
Scaling range upper/lower limit values (Un\G62 to Un\G77) are scaled to
the scaling width set in the CH Scaling width upper/lower limit values
(Un\G78 to Un\G93), and the result is stored.
(2) The following is how to calculate the scaling value.
Scaling value =
(scaling width upper limit value - scaling width lower limit value)
measured temperature value - scaling range lower limit value
scaling range upper limit value - scaling range lower limit value
[Example] To scale a temperature to percent
When the CH1 measured temperature value of 360 (measured temperature value =
3600) is scaled at the following settings:
Scaling range: -100 to 500 (lower limit value = -1000, upper limit value = 5000)
Scaling width: 0 to 100% (lower limit value = 0, upper limit value = 100)
Scaling value =
(100 - 0)
3600 - (-1000)
5000 - (-1000)
+ 0 =
76.666666
= 77[%]
Fractional portion is rounded off.
Stores into buffer memory address 50.
+ scaling width lower limit value
POINT
(1) If the upper limit value is less than the lower limit value in the settings of the
CH Scaling range upper/lower limit values (Un\G62 to Un\G77) or the CH
Scaling width upper/lower limit values (Un\G78 to Un\G93), it will not result in
an error and the scaling value calculated with the expression above will be
output.
(2) When the measured temperature is out of the range set in the Scaling range
upper/lower limit values, the value set in the Scaling width upper limit value or
lower limit value is stored into this buffer memory.
PROCEDURES AND
1
2
3
4
5
6
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
SETTINGS BEFORE
SYSTEM OPERATION
UTILITY PACKAGE
(GX CONFIGURATOR-TI)
3.4 Buffer Memory
3.4.15 CH[] Scaling value (Un\G50 to Un\G57)
3 - 41
PROGRAMMING
7
ONLINE MODULE
CHANGE
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 70

3
SPECIFICATIONS
3.4.16 Scaling valid/invalid setting (Un\G58)
(1) This area is for setting the scaling function valid/invalid status for each
channel.
(2) The default value is set to "Invalid" for all channels.
b15 b14 b13 b12 b11 b10 b9 b8 b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
CH8 CH7 CH6 CH5 CH4 CH3 CH2 CH100000000
Data for b8 to b15 is fixed to "0".
0: Valid
1: Invalid
(3) To activate the scaling function, turning ON/OFF Operating condition
setting request (Y9) after setting this area is required.
(4) Program example with a condition of the following is below.
Scaling range: -100 to 500 (lower limit value = -1000, upper limit
value = 5000)
Scaling width: 0 to 100% (lower limit value = 0, upper limit value = 100)
\
Sets CH1 scaling function to
"Enable".
\
Sets CH1 Scaling range lower
limit value.
\
Sets CH1 Scaling range upper
limit value.
\
Sets CH1 Scaling width lower
limit value.
\
Sets CH1 Scaling width upper
limit value.
Turns ON Operating condition
setting request (Y9).
Turns OFF Operating condition
setting request (Y9).
3 - 42
3.4 Buffer Memory
3.4.16 Scaling valid/invalid setting (Un\G58)
Page 71

3
SPECIFICATIONS
3.4.17 CH[] Scaling range upper/lower limit values (Un\G62 to Un\G77)
(1) A scaling range of measured temperature values is set for each channel
in units of 0.1 .
(2) The default value is set to "0".
(3) Settable scaling range is -32768 to 32767.
1
OVERVIEW
2
(4) To activate the setting, turning ON/OFF Operating condition setting
request (Y9) is required.
POINT
(1) When the measured temperature is out of the range set in the Scaling range
upper/lower limit values, the value set in the Scaling width upper limit value or
lower limit value is stored into the CH Scaling value (Un\G50 to Un\G57).
(2) Set "Valid" in the Scaling valid/invalid setting (Un\G58).
When "Disable" is set, the settings of CH Scaling range upper/lower limit
values (Un\G62 to Un\G77) take no effect.
(3) If the same value is set for the upper limit and the lower limit, an error (error
code: 91 ) occurs on the corresponding channel. Then, Error flag (XF) turns
ON and the module operates with the setting before the error occurrence.
3.4.18 CH[] Scaling width upper/lower limit values (Un\G78 to Un\G93)
(1) A width for scaling conversion is set for each channel.
(2) The default value is set to "0".
(3) Settable scaling range is -32768 to 32767.
PROCEDURES AND
3
4
5
6
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
SETTINGS BEFORE
SYSTEM OPERATION
UTILITY PACKAGE
(GX CONFIGURATOR-TI)
(4) To activate the setting, turning ON/OFF Operating condition setting
request (Y9) is required.
POINT
1) When "Invalid" is set in the Scaling valid/invalid setting (Un\G58), the settings
of CH Scaling width upper/lower limit values (Un\G78 to Un\G93) take no
effect.
(2) If the same value is set for the upper limit and the lower limit, an error (error
code: 91 ) occurs on the corresponding channel. Then, Error flag (XF) turns
ON and the module operates with the setting before the error occurrence.
3.4 Buffer Memory
3.4.17 CH[] Scaling range upper/lower limit values (Un\G62 to Un\G77)
3 - 43
PROGRAMMING
7
ONLINE MODULE
CHANGE
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 72

3
SPECIFICATIONS
3.4.19 CH[] Process alarm upper/lower limit values (Un\G94 to
Un\G125)
(1) Process alarm upper upper limit value, upper lower limit value, lower
upper limit value, and lower lower limit value are set.
(2) A range of measured temperature values is set for each channel in units
of 0.1 .
(3) Settable range and default value differ according to the RTD type and
measurement range.
Table 3.14 Process alarm settable range and default value
RTD type
(Measurement
range)
Pt100
(-200 to 850 )
Pt100
(-20 to 120 )
Pt100
(0 to 200 )
JPt100
(-180 to 600 )
JPt100
(-20 to 120 )
JPt100
(0 to 200 )
Ni100
(-60 to 180 )
Process alarm
lower upper limit
value
(in units of 0.1 )
Default value
Process alarm
lower lower limit
value
(in units of 0.1 )
-2000 8500 -2000 to 8500
-200 1200 -200 to 1200
0 2000 0 to 2000
-1800 6000 -1800 to 6000
-200 1200 -200 to 1200
0 2000 0 to 2000
-600 1800 -600 to 1800
Process alarm
upper upper limit
value
(in units of 0.1 )
Process alarm
upper lower limit
value
(in units of 0.1 )
Settable temperature
guarantee range)
(in units of 0.1 )
range (Accuracy
3 - 44
(4) To activate the setting, turning ON/OFF Operating condition setting
request (Y9) is required.
(5) For details on process alarm, refer to Section 3.2.3.
POINT
(1) If any of the following values are set, an error (error code: 6 ) occurs.
Then, Error flag (XF) turns ON and the module operates with the setting
before the error occurrence.
• A value out of the above settable range.
• A value that does not satisfy the following condition:
Process alarm lower lower limit value lower upper limit value upper
lower limit value upper upper limit value
(2) When "Disable" is set in the Warning output enable/disable setting (Un\G46),
the settings of CH Process alarm upper/lower limit values (Un\G94 to
Un\G125) take no effect.
3.4 Buffer Memory
3.4.19 CH[] Process alarm upper/lower limit values (Un\G94 to Un\G125)
Page 73

3
SPECIFICATIONS
3.4.20 CH[] Rate alarm warning detection period (Un\G126 to Un\G133)
(1) The number of conversion periods to check a change in measured
temperature values is set for each channel.
(2) Settable range is 1 to 6000 (times).
(3) The default value is set to "0".
(4) To activate the setting, turning ON/OFF Operating condition setting
request (Y9) is required.
(5) For details on rate alarm, refer to Section 3.2.3.
POINT
(1) When a value out of the above setting range is set, an error (error code: 70 )
occurs on the corresponding channel. Then, Error flag (XF) turns ON and the
module operates with the setting before the error occurrence.
(2) Set "Enable" in the Warning output enable/disable setting (Un\G46). When
"Disable" is set, the settings of CH Rate alarm warning detection period
(Un\G126 to Un\G133) take no effect.
1
2
3
4
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
3.4.21 CH[] Rate alarm upper/lower limit values (Un\G134 to Un\G149)
(1) A change portion for measured temperature values is set for each
channel.
(2) Settable range is -32768 to 32767 (-3276.8 to 3276.7 ) and set the value
in units of 0.1 .
[Example]
When setting the rate alarm upper limit value to 30 , store "300" into the buffer
memory.
(3) To activate the setting, turning ON/OFF Operating condition setting
request (Y9) is required.
(4) For details on rate alarm, refer to Section 3.2.3.
PROCEDURES AND
5
6
7
8
SETTINGS BEFORE
SYSTEM OPERATION
UTILITY PACKAGE
(GX CONFIGURATOR-TI)
PROGRAMMING
ONLINE MODULE
CHANGE
3.4 Buffer Memory
3.4.20 CH[] Rate alarm warning detection period (Un\G126 to Un\G133)
TROUBLESHOOTING
3 - 45
Page 74

3
SPECIFICATIONS
3.4.22 Mode switching setting (Un\G158 and Un\G159)
This area is used to switch the mode between normal mode and offset/gain setting mode.
The mode can be switched without resetting the programmable controller CPU.
(1) The setting value of the switching target mode is set.
(2) To switch the mode, turning ON/OFF Operating condition setting request
(Y9) after setting the value is required.
(3) When the mode is switched, this area is cleared to "0" and Operating
condition setting completion flag (X9) turns OFF.
After confirming that Operating condition setting completion flag (X9)
has turned OFF, turn OFF Operating condition setting request (Y9).
Table 3.15 Switching target mode and setting value
Switching target mode
Normal mode 0964H 4144H
Offset/gain setting mode 4144H 0964H
Buffer memory address 158 Buffer memory address 159
Setting Value
POINT
If a value other than the setting value above is written, mode switching is not
performed and only the operating condition is changed.
3 - 46
3.4 Buffer Memory
3.4.22 Mode switching setting (Un\G158 and Un\G159)
Page 75

3
SPECIFICATIONS
1
3.4.23 Conversion setting for disconnection detection (Un\G164 and
Un\G165)
(1) The value to be stored in the CH Measured temperature value (Un\G11
to Un\G18) when disconnection state is confirmed is selected from "Up
scale", "Down scale" or "Given value".
(2) When "Up scale"(0
stored in the CH Measured temperature value (Un\G11 to Un\G18).
(3) When "Down scale" (1
range is stored in the CH Measured temperature value (Un\G11 to
Un\G18).
(4) When "Given value"(2
Conversion setting value for disconnection detection (Un\G166 to
Un\G173) is stored in the CH Measured temperature value (Un\G11 to
Un\G18).
(5) The default value is set to "Down scale".
Un\G164 (Conversion setting for
disconnection detection CH1-4)
Un\G165 (Conversion setting for
disconnection detection CH5-8)
H) is selected, up-scale of the currently set range is
H) is selected, down-scale of the currently set
H) is selected, the value set in the CH
b15 b12 b11 b8 b7 b4 b3 b0
to
CH4 CH3 CH2 CH1
CH8 CH7 CH6 CH5
to
to
to
PROCEDURES AND
2
3
4
5
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
SETTINGS BEFORE
SYSTEM OPERATION
Measured temperature value at the
time of disconnection detection
Up scale
Down scale
Given value
Setting
value
0
H
1
H
2
H
(6) To activate the setting, turning ON/OFF Operating condition setting
request (Y9) is required.
(7) For details, refer to Section 3.2.2.
POINT
If a value out of the setting range is set, the module operates with the default
setting, "Down scale".
3.4 Buffer Memory
3.4.23 Conversion setting for disconnection detection (Un\G164 and Un\G165)
3 - 47
UTILITY PACKAGE
(GX CONFIGURATOR-TI)
6
PROGRAMMING
7
ONLINE MODULE
CHANGE
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 76

3
SPECIFICATIONS
3.4.24 CH[] Conversion setting value for disconnection detection
(Un\G166 to Un\G173)
(1) When "Given value" (2H) is set in the Conversion setting for
disconnection detection (Un\G164 and Un\G165), the value set in this
area is stored in the CH Measured temperature value (Un\G11 to
Un\G18) at the time of disconnection detection.
When "Up scale" (0
setting for disconnection detection, the settings in these area take no
effect.
H) or "Down scale" (1H) is set in the Conversion
(2) Setting range is from -32768 to 32767 (0000
[Example]
When setting the value to 0.3 Store "3" in the buffer memory.
(3) The default value is set to "0".
(4) To activate the setting, turning ON/OFF Operating condition setting
request (Y9) is required.
H to FFFFH) (in units of 0.1 ).
3 - 48
3.4 Buffer Memory
3.4.24 CH[] Conversion setting value for disconnection detection (Un\G166 to Un\G173)
Page 77

3
SPECIFICATIONS
1
3.4.25 Factory default offset/gain values, User range settings offset/gain values, User range settings resistance offset/gain values (Un\G190 to Un\G253)
(1) This area is related to the user range save/restore function to re-set the
offset/gain easily at online module change.
(2) When the offset/gain setting values of the user range setting are
restored, the data to be used are stored.
The data are stored (saved) in the following cases.
• When writing initial setting by the utility
• When setting the operating condition (Y9 turns from OFF to ON
• When writing the offset/gain values in the offset/gain setting mode (YA turns from
OFF to ON)
* 1 The data are not saved when a setting value has been written in the Mode switching setting
(Un\G158 and Un\G159).
*1
)
(3) To restore the offset/gain values of the user range setting, set the data
saved in this area to the corresponding area of the restoring target
module.
(4) Save buffer memory data during online module change in the following
procedure.
1) Turn OFF to ON Operating condition setting request (Y9).
2) Compare the values of the Factory default offset/gain values, the User range
settings offset/gain values, and the User range settings resistance offset/gain
values (Un\G190 to Un\G253) to the values in the range reference table. For
the range reference table, refer to Section 7.4.
PROCEDURES AND
2
3
4
5
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
SETTINGS BEFORE
SYSTEM OPERATION
3) When the values are appropriate, take down the buffer memory data
compared.
(5) For details on online module change, refer to CHAPTER 7.
POINT
This area is not used for offset/gain setting.
For offset/gain setting, refer to Section 4.6.
3.4 Buffer Memory
3.4.25 Factory default offset/gain values, User range settings offset/gain values, User range settings
3 - 49
UTILITY PACKAGE
(GX CONFIGURATOR-TI)
6
PROGRAMMING
7
ONLINE MODULE
CHANGE
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 78

PROCEDURES AND SETTINGS BEFORE SYSTEM
4
OPERATION
CHAPTER4 PROCEDURES AND SETTINGS BEFORE
SYSTEM OPERATION
4.1 Handling Precautions
(1) Do not drop or give a strong impact to the case.
(2) Do not remove the printed-circuit board of the module from the case.
Doing so may cause a failure.
(3) Be careful to prevent foreign matters such as cutting chips or wire chips
from entering the module.
Such foreign matter can cause a fire, failure, or malfunction.
(4) A protective film is attached to the module top to prevent foreign matter
such as wire chips from entering the module during wiring.
Do not remove the film during wiring.
Be sure to remove it for heat dissipation before system operation.
(5) Tighten the screws such as module fixing screws within the following
ranges.
Loose screws may cause short circuits, failures, or malfunctions.
Table 4.1 Tightening torque
Screw Tightening torque range
Module fixing screw (M3 screw)
Connector screw (M2.6 screw) 0.20 to 0.29N•m
(6) To mount the module, while pressing the module mounting lever located
in the lower part of the module, fully insert the module fixing projection
into the hole in the base unit and press the module until it snaps into
place.
Incorrect module mounting may cause a malfunction, failure, or drop of
the module.
0.36 to 0.48N•m
4 - 1
(7) Always make sure to touch the grounded metal to discharge the
electricity charged in the body, etc., before touching the module.
Failure to do so may cause a failure or malfunctions of the module.
4.1 Handling Precautions
Page 79

4
PROCEDURES AND SETTINGS BEFORE SYSTEM
OPERATION
1
4.1.1 Fixing module with module fixing bracket
Fix the Q68RD3-G with a module fixing bracket after it is mounted to the base unit.
POINT
Make sure that the module fixing bracket is hooked on the third slit viewed from
the front of the Q68RD3-G. Then, tighten the module fixing screw within the
specified torque range.
Module fixing bracket
3rd slit
Module fixing screw
Q68RD3-G
PROCEDURES AND
2
3
4
5
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
SETTINGS BEFORE
SYSTEM OPERATION
4.1 Handling Precautions
4.1.1 Fixing module with module fixing bracket
4 - 2
UTILITY PACKAGE
(GX CONFIGURATOR-TI)
6
PROGRAMMING
7
ONLINE MODULE
CHANGE
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 80

PROCEDURES AND SETTINGS BEFORE SYSTEM
4
OPERATION
4.2 Procedures and Settings before System Operation
Start
Module mounting
Mount the Q68RD3-G in the specified slot.
Wiring
Connect the RTD and the Q68RD3-G. When using a
relay terminal block, connect the RTD to the relay
terminal block and then connect the relay terminal block
to the Q68RD3-G.
(Refer to Section 4.4.2)
Intelligent function module switch setting
Make switch settings using GX Developer.
(See Section 4.5).
(Refer to Section 4.4.2).
(Refer to Section 4.5).
Use user range settings?
Use user range settings
Offset/gain setting
When using user range settings, perform offset/gain
Initial setting and Auto refresh setting
Programming and debugging
(Refer to Section 4.6).
setting.
(See Section 4.6).
Use the utility package?
YES
Make these settings using the utility package to simplify
sequence programs.
Create and check sequence programs.
(Refer to CHAPTER 5).
(See Chapter 5).
Use factory default settings
NO
4 - 3
4.2 Procedures and Settings before System Operation
Page 81

PROCEDURES AND SETTINGS BEFORE SYSTEM
r
4
OPERATION
4.3 Part Names
This section describes each part name of the Q68RD3-G.
1
Module fixing screw Module fixing bracket
2)
(Connector
terminal
number)
Table 4.2 Part name
Number Name Description
Indicates the operating status of the Q68RD3-G.
On: Normal operation
1)
RUN LED
2) ERR. LED
3) ALM LED
4) Serial No. display Displays the serial No. of the Q68RD3-G
*1
* 1 When the module is mounted on a MELSECNET/H remote I/O station, the RUN LED stays off until
Flashing: Offset/gain setting mode
Off:
Indicates the error status of the Q68RD3-G.
On: Error occurred
Flashing:
Off: Normal operation
Indicates the warning status of the Q68RD3-G.
On: Warning (process alarm, rate alarm) occurred (Refer to Section 3.4.13.)
Flashing: Disconnection detected
Off: Normal operation
a data link starts normally, even after the power is turned on. The RUN LED turns on once a data
link starts.
5V power supply interrupted, watchdog timer error occurred, or online module
change enabled
Switch setting error occurred
The setting value of the intelligent function module switch 5 is other than 0.
A1
A20
OVERVIEW
2
3)1)
(Connecto
terminal
number)
B1
3
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
4
B20
4)
PROCEDURES AND
SETTINGS BEFORE
SYSTEM OPERATION
5
UTILITY PACKAGE
(GX CONFIGURATOR-TI)
6
PROGRAMMING
7
4.3 Part Names
4 - 4
ONLINE MODULE
CHANGE
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 82

4
PROCEDURES AND SETTINGS BEFORE SYSTEM
OPERATION
Table 4.3 Signal name
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
A9
A10
A11
A12
A13
A14
A15
A16
A17
A18
A19
A20
Seen from the front
of the module
B1
B2
B3
B4
B5
B6
B7
B8
B9
B10
B11
B12
B13
B14
B15
B16
B17
B18
B19
B20
* 1 For actual wiring, refer to Section 4.4.2 External wiring.
Ter min al
number
A1 CH1 A1 B1 CH1 B1
A2 CH1 b1 B2
A3 B3 CH2 b2
A4 CH2 A2 B4 CH2 B2
A5 B5
A6 CH3 A3 B6 CH3 B3
A7 CH3 b3 B7
A8 B8 CH4 b4
A9 CH4 A4 B9 CH4 B4
A10 B10
A11 CH5 A5 B11 CH5 B5
A12 CH5 b5 B12
A13 B13 CH6 b6
A14 CH6 A6 B14 CH6 B6
A15 B15
A16 CH7 A7 B16 CH7 B7
A17 CH7 b7 B17
A18 B18 CH8 b8
A19 CH8 A8 B19 CH8 B8
A20 B20
Signal name
Ter minal
number
Signal name
(1) Connector for external wiring
The connectors for use with the Q68RD3-G should be purchased separately by the
user.The following tables show the connector types and the crimp-contact tool.
(a) Connector types
Typ e Model name Applicable wire size
Soldering type
(straight out)
Crimp-contact type
(straight out)
Soldering type
(straight out/diagonal out)
* 1 The A6CON3 (pressure-displacement type, straight out) connector cannot be used for the
A6CON1
A6CON2
A6CON4
Q68RD3-G.
(b) Crimp-contact too
Typ e Model name Applicable wire size Contact
Crimp-contact tool FCN-363T-T005/H
*1
0.088mm
2
0.3mm
(AWG22) (stranded)
0.088mm
0.3mm
2
to 0.24mm2(AWG28 to 24)
2
to 0.24mm2 (AWG28 to 24) (stranded)
2
(AWG22) (stranded)
FUJITSU COMPONENT LIMITED
http://www.fcl.fujitsu.com/en/
4 - 5
4.3 Part Names
Page 83

PROCEDURES AND SETTINGS BEFORE SYSTEM
4
OPERATION
4.4 Wiring
1
This section describes the wiring precautions and module connection example.
4.4.1 Wiring precautions
External wiring that is less susceptible to noise is required as a condition of configuring a
highly-reliable system and making full use of the capabilities of Q68RD3-G.
Precautions for external wiring are described below.
(1) Use separate cables for the AC control circuit and the external input
signals of the Q68RD3-G to avoid the influence of the AC side surges
and inductions.
(2) Always place a RTD at least 100mm (3.94 inch) away from the main
circuit cables and AC control circuit lines. Fully keep it away from highvoltage cables and circuits, which include high frequency waves, such
as an inverter's load circuit. Not doing so will cause the module more
susceptible to noises, surges, and inductions.
(3) The following wiring is required for the product to comply with the EMC
and Low Voltage Directives.
AD75CK
PROCEDURES AND
2
3
4
5
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
SETTINGS BEFORE
SYSTEM OPERATION
Q68RD3-G
In a control panel
External
device
connector
Relay
terminal
block
20 to 30cm (7.87 to 11.81 inch)
(a) Use shielded cables for every external wiring and use the AD75CK cable clamp to
ground to the panel. AD75CK can ground four cables together when using cables
with outer diameter of about 7mm (0.28 inch).
Use shielded cabled between the external device connector and the relay terminal
block, and ground it to the control panel. The cable must be 3m or shorter.
(b) Before touching the relay terminal block, always touch the grounded metal to
discharge the electricity charged in the body.
4.4.1 Wiring precautions
Strip off the
outer sheath
4.4 Wiring
4 - 6
UTILITY PACKAGE
(GX CONFIGURATOR-TI)
6
PROGRAMMING
7
ONLINE MODULE
CHANGE
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 84

4
PROCEDURES AND SETTINGS BEFORE SYSTEM
OPERATION
4.4.2 External wiring
(1) Wiring procedure
1) Install a relay terminal block.
2) Connect a RTD and the relay terminal block.
Wire Q68RD3-G to the relay terminal block using an external device
connector.
Q68RD3-G
Cable
(*1)
Relay
terminal block
CH1
A
B
b
CH8
A
B
b
* 1 Always use shielded cables.
In addition, always ground the shield.
Cable (*1)
External device
connector
CH1
A
B
b
CH8
A
B
b
A1
B1
A2
A19
B19
B18
ModulatorModulator
Demodulator
Demodulator
4 - 7
4.4 Wiring
4.4.2 External wiring
Page 85

PROCEDURES AND SETTINGS BEFORE SYSTEM
g
4
OPERATION
4.5 Intelligent Function Module Switch Setting
The intelligent function module switches are set on the I/O assignment tab of PLC
parameter in GX Developer.
(1) Setting item
There are five intelligent function module switches, Switch 1 to 5. Values are set with
16-bit data.
The default value when not setting the intelligent function module switches is "0" for
all Switch 1 to 5.
Table 4.4 Intelligent function module switch setting
Setting item
1
2
3
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
Switch 1
Switch 2
Switch 3
Measurement range
setting
(CH1 to CH4)
CH4 CH3 CH2 CH1
Measurement range
setting
(CH5 to CH8)
CH8 CH7 CH6 CH5
Offset/gain setting
00
Fixed to 0
H
H
b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
CH8 CH7 CH6 CH5 CH4 CH3 CH2 CH1
Mode setting
RTD Measurement range
New JIS
H
H
(Pt100)
Old JIS
(JPt100)
Ni100
Setting a value other than above results in a range setting
error (error code: 10 ) and measured temperature is not
converted. ( indicates the error corresponding channel
number.)
-200 to 850
-20 to 120
0 to 200
-180 to 600
-20 to 120
0 to 200
-60 to 180
Setting
value
0
H
1
H
4
H
2
H
3
H
5
H
8
H
PROCEDURES AND
4
5
SPECIFICATIONS
SETTINGS BEFORE
SYSTEM OPERATION
UTILITY PACKAGE
(GX CONFIGURATOR-TI)
6
0: Factory default settin
1: User range setting
Switch 4
Switch 5
000
Fixed to 0
* 1 Setting any value within the setting range will provide the same operation.
When the setting range is 1
* 2 Setting a value other than "0
H
H
0
H
: Normal mode
*1
H
to F
H
: Offset/gain setting mode
1
0H : Fixed
H to FH, set "1H" for example.
H" results in an error.
*2
4.5 Intelligent Function Module Switch Setting
4 - 8
PROGRAMMING
7
ONLINE MODULE
CHANGE
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 86

4
PROCEDURES AND SETTINGS BEFORE SYSTEM
OPERATION
(2) Operating procedure
Make settings on the I/O assignment tab of PLC parameter in GX Developer.
(a) I/O assignment tab
Set the following for the slot in which the Q68RD3-G is mounted.
The "Type" setting is mandatory, but other items are optional. Set them as
needed.
Type : Select "Intelli.".
Model name : Enter the module model name.
Points : Select "16points".
StartXY : Enter the start I/O number of the Q68RD3-G.
Detailed setting: Specify the control programmable controller of the Q68RD3-G.
It is unnecessary to set the "Error time output mode" and "H/W error time PLC
operation mode" since these settings are invalid for the Q68RD3-G.
4 - 9
(b) Switch setting for intelligent function module screen
Click the button on the I/O assignment tab to display the screen shown
below, then make settings for Switch 1 to 5.
The switches can be set easily if values are entered in hexadecimal. Change the
"Input format" to "HEX." (hexadecimal) and then enter setting values.
4.5 Intelligent Function Module Switch Setting
Page 87

PROCEDURES AND SETTINGS BEFORE SYSTEM
4
OPERATION
4.6 Offset/Gain Setting
Set offset/gain setting values in the following procedure.
When factory default settings are used, offset/gain setting is not required.
If the utility package is installed, set offset/gain setting values according to the procedure
described in Section 5.6.2.
(1) Setting procedure
With the intelligent function module switch
setting, set the RTD type to be used and the
temperature range for the measurement range
setting of a channel targeted for adjusting
offset/gain values.
2)
Switch to the offset/gain setting mode.
Check that the "RUN" LED is flashing to indicate
the offset/gain setting mode.
1)
Set "Enable" for the Conversion enable/disable
setting (Un\G0) of the offset/gain setting target
Identify the disconnected
channel with the
Disconnection detection flag
(Un\G49), review the wiring
of the corresponding
channel, and turn YF from
ON to OFF.
channel and turn Y9 from ON to OFF.
YES
Is Disconnection detection
Input a value used as an offset value to the
adjusting target channel using a RTD or
standard resistor.
Set the offset setting channel in the Offset/gain
setting mode (Offset specification) (Un\G26) and
set "0" in the Offset/gain setting mode (Gain
specification) (Un\G27).
Write the measurement setting value equivalent
to the input to the CH Offset temperature
setting value (Un\G28)
channel.
Start
signal (XC) ON?
NO
*3
of the adjusting target
1
OVERVIEW
2
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
Set the gain setting channel in the Offset/gain
*1
*2
setting mode (Gain specification) (Un\G27) and set
"0" in the Offset/gain setting mode (Offset
specification) (Un\G26).
Write the measurement setting value equivalent to
the input to the CH Gain temperature setting
value (Un\G29)
Turn ON Channel change request (YB).
Confirm that the Channel change completion flag
(XB) has turned ON.
Turn OFF Channel change request (YB).
Turn ON User range write request (YA).
Confirm that the Offset/gain setting mode status flag
(XA) has turned OFF.
*3
of the adjusting target channel.
Adjust other channels?
NO
YES
SPECIFICATIONS
4
PROCEDURES AND
SETTINGS BEFORE
SYSTEM OPERATION
5
1)
UTILITY PACKAGE
*4
(GX CONFIGURATOR-TI)
6
Turn ON Channel change request (YB).
Confirm that the Channel change completion
flag (XB) has turned ON.
Turn OFF Channel change request (YB).
Input a value used as a gain value to the
adjusting target channel using a RTD or
standard resistor.
Turn OFF User range write request (YA).
Is the "ERR." LED on?
NO
Switch to the normal mode.
End
4.6 Offset/Gain Setting
YES
2)
4 - 10
PROGRAMMING
7
ONLINE MODULE
CHANGE
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 88

4
PROCEDURES AND SETTINGS BEFORE SYSTEM
OPERATION
* 1 The following table shows the mode switching method (normal mode offset/gain setting mode
normal mode).
Table 4.5 Mode switching method
Mode switching method Reference
Dedicated instruction (G(P).OFFGAN)
Setting in the Mode switching setting (Un\G158, Un\G159) and turning
Operating condition setting request (Y9) from OFF to ON
Intelligent function module switch setting
(After setting the intelligent function module switches, power OFF ON or
reset the programmable controller CPU.)
* 2 Always set "Disable" to the Conversion enable/disable setting of unused channels or channels not
targeted for the offset/gain setting.
If all channels are set to "Enable", the Disconnection detection flag (Un\G49) of channels that are
not connecting a RTD turns ON (changes to "1").
* 3 Only buffer memory address of channel 1 is described in the chart. For buffer memory addresses
of other channels, refer to Section 3.4.1 Buffer memory assignment.
* 4 Do not perform the operations below during the steps indicated with *4. If they are performed, the
data inside a flash memory will have a problem, and the Q68RD3-G may not operate normally.
• Powering off the programmable controller CPU
• Resetting the programmable controller CPU
(2)(a) in this
section
(2)(b) in this
section
Section 4.5,
(2)(c) in this
section
4 - 11
4.6 Offset/Gain Setting
Page 89

4
PROCEDURES AND SETTINGS BEFORE SYSTEM
OPERATION
POINT
(1) Perform offset/gain setting in the actual operating status.
(2) Offset/gain values are stored in the Flash memory of the Q68RD3-G by
turning ON User range write request (YA). These values are not erased even
at power-off. To prevent unnecessary write to the Flash memory, an error
(error code: 162) occurs when values are written 26 times continuously.
(3) Set the offset/gain values within the range where the following conditions are
satisfied.
(Gain value) - (Offset value) > 0.1[ ]
Set the offset/gain temperature setting values within the range where the
following conditions are satisfied.
(Gain temperature setting value) - (Offset temperature setting value) > 0.1[ ]
(4) When User range write request (YA) is turned ON, consistency checks, for
offset value and gain value, and for offset temperature setting value and gain
temperature setting value, are executed.
If an error occurs on any channel, offset/gain values are not written to the
module.
Check the value in the Error code (Un\G19) and take a corrective action.
Then, perform offset/gain setting again.
(5) Offset/gain setting can be performed on multiple channels at the same time.
However, set the offset/gain channels separately.
If the offset/gain channels are set at the same time, an error (error code: 500)
occurs.
(6) It takes approximately 7 seconds before Channel change completion flag
(XB) turns ON after turning ON Channel change request (YB). During this
period, input to channels targeted for offset/gain setting must be constant.
In addition, if disconnection state is detected during this period, Channel
change completion flag (XB) turns ON earlier and an error (error code: 51 )
occurs at the same time. If this occurs, perform offset/gain setting again after
connection is restored.
(7) If an error (error code: 51 ) described at (6) occurs while performing offset/
gain setting simultaneously on multiple channels, values are not set only for
the disconnected channel but also normally-connected channels. Therefore,
perform offset/gain setting again for all adjusting target channels after
connection is restored.
(8) Module ready (X0) turns from OFF to ON when the offset/gain setting mode is
switched to the normal mode by the dedicated instruction (G(P).OFFGAN) or
the setting in the Mode switching setting (Un\G158 and Un\G159).
Note that initial setting processing will be executed if there is a sequence
program that performs initial settings when Module ready (X0) turns ON.
PROCEDURES AND
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
SETTINGS BEFORE
SYSTEM OPERATION
UTILITY PACKAGE
(GX CONFIGURATOR-TI)
PROGRAMMING
4.6 Offset/Gain Setting
4 - 12
ONLINE MODULE
CHANGE
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 90

4
PROCEDURES AND SETTINGS BEFORE SYSTEM
OPERATION
(2) Program examples
The program in the dotted area of (a) is common to all (a),(b), and (c).
In these examples, X/Y0 to X/YF are used as I/O numbers of the Q68RD3-G.
Table 4.6 List of devices
Device Function
M0 Mode switching
M1 Channel selection
M2 Channel conversion enabling
M3 Offset setting
M4 Gain setting
M5 Channel change instruction
M6 Offset/gain setting value write command to module
M50 Switching to the offset/gain setting mode
M51 Switching to the normal mode
D0 Dedicated instruction (G(P).OFFGAN) setting value storage device
D1
D2
D3 Offset temperature setting value storage device
D4 Gain temperature setting value storage device
Channel specification storage device
4 - 13
4.6 Offset/Gain Setting
Page 91

4
PROCEDURES AND SETTINGS BEFORE SYSTEM
OPERATION
(a) When switching the mode using the dedicated instruction (G(P).OFFGAN)
In this program example, the mode is switched to the offset/gain setting mode by
the dedicated instruction (G(P).OFFGAN), offset/gain setting target channels are
set, and the offset/gain values are written to the Q68RD3-G. Then, the mode is
switched back to the normal mode.
1
OVERVIEW
2
*1
Dedicated instruction
(G.OFFGAN)
Stores offset/gain setting
target channel.
Copies data of D1 into D2.
Inverts bit for conversion
enable/disable setting.
Sets conversion
enable/disable.
Turns ON Operating
condition setting request (Y9).
Turns OFF Operating
condition setting request (Y9).
Stores offset temperature
setting value into D3.
Writes value to Offset
temperature setting value.
Specifies offset setting
channel.
Sets "0" for gain setting
channel.
Stores gain temperature
setting value into D4.
Writes value to Gain
temperature setting value.
Sets "0" for offset setting
channel.
Specifies gain setting
channel.
PROCEDURES AND
3
4
5
6
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
SETTINGS BEFORE
SYSTEM OPERATION
UTILITY PACKAGE
(GX CONFIGURATOR-TI)
Processing in normal mode
*1 The program in the dotted area is a common program.
Turns ON Channel change
request (YB).
Turns OFF Channel change
request (YB).
Turns ON User range write
request (YA).
Turns OFF User range write
request (YA).
4.6 Offset/Gain Setting
4 - 14
PROGRAMMING
7
ONLINE MODULE
CHANGE
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 92

4
PROCEDURES AND SETTINGS BEFORE SYSTEM
OPERATION
(b) When switching the mode using the setting in the Mode switching setting
(Un\G158 and Un\G159) and Operating condition setting request (Y9)
Stores "H4144" in Un\G158.
Stores "H0964" in Un\G159.
Common program
Stores "H0964" in Un\G158.
Stores "H4144" in Un\G159.
Processing in normal mode
(c) When switching the mode using the intelligent function module switch setting
Only the common program is required.
4 - 15
4.6 Offset/Gain Setting
Page 93

5
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX Configurator-TI)
CHAPTER5 UTILITY PACKAGE (GX Configurator-TI)
5.1 Utility Package Functions
Table 5.1 lists the utility package functions.
Table 5.1 List of utility package (GX Configurator-TI) functions (1/2)
Function Description Reference
(1) Makes initial setting of the following items, which are required to operate the Q68RD3-G, for each
channel.
•Conversion enable/disable setting •Rate alarm warning detection period
•Averaging processing selection •Rate alarm upper limit value
•Time/count/moving average/time constant setting •Rate alarm lower limit value
•Process alarm warning output enable/disable setting •Scaling range lower limit value
•Setting range •Scaling range upper limit value
•Process alarm lower lower limit value •Scaling valid/invalid setting
Initial setting
Auto refresh
setting
•Process alarm lower upper limit value •Scaling width lower limit value
•Process alarm upper lower limit value •Scaling width upper limit value
•Process alarm upper upper limit value
•Rate alarm warning output enable/disable setting
(2) The initial setting data are registered in the parameter of the programmable controller CPU and
automatically written to the Q68RD3-G when the programmable controller CPU changes to the RUN
status.
(1) Sets the automatically refreshed Q68RD3-G buffer memory for each channel.
•Conversion completion flag •Setting range (Offset/gain setting CH1-CH8)
•CH Measured temperature value
•Error code •Warning output flag (Rate alarm)
•Setting range (Input type CH1-CH4) •Disconnection detection flag
•Setting range (Input type CH5-CH8)
(2) The values stored in the Q68RD3-G buffer memory where auto refresh setting has been made are
automatically read from/written to the device when the END instruction of the programmable controller
CPU is executed.
•Warning output flag (Process alarm)
•CH Scaling value
•Conversion setting for disconnection
detection
•Conversion setting value for disconnection
detection
Section 5.4
Section 5.5
PROCEDURES AND
1
2
3
4
5
6
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
SETTINGS BEFORE
SYSTEM OPERATION
UTILITY PACKAGE
(GX CONFIGURATOR-TI)
5.1 Utility Package Functions
5 - 1
PROGRAMMING
7
ONLINE MODULE
CHANGE
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 94

5
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX Configurator-TI)
Table 5.1 List of utility package (GX Configurator-TI) functions (2/2)
Function Description Reference
Monitors and tests the buffer memory and I/O signals of the Q68RD3-G.
•Module ready •Disconnection detection signal
•Operating condition setting completion flag •Warning output signal
•Operating condition setting request •Conversion completion flag
•Offset/gain setting mode status flag •Error flag
•User range write request •Error clear request
•Channel change completion flag •Mode switching setting
(1)
CH Monitor/test
•Conversion enable/disable setting •Rate alarm warning output enable/disable
setting
•Averaging processing selection •Rate alarm warning detection period
•Time/Count/Moving average/Time constant setting •Warning output flag (Rate alarm) lower
limit value
•Conversion completion flag •Warning output flag (Rate alarm) upper
limit value
•Measured temperature value •Rate alarm upper limit value
•Error code •Rate alarm lower limit value
•Setting range •Disconnection detection flag
•Process alarm warning output enable/disable setting •Scaling value
•Warning output flag (Process alarm) lower limit value •Scaling valid/invalid setting
•Warning output flag (Process alarm) upper limit value •Scaling range lower limit value
•Process alarm lower lower limit value •Scaling range upper limit value
•Process alarm lower upper limit value •Scaling width lower limit value
•Process alarm upper lower limit value •Scaling width upper limit value
Monitor/test
•Process alarm upper upper limit value •Conversion setting for disconnection
detection
•Conversion setting value for
disconnection detection
(2) Offset/gain setting
•Mode switching setting
•Mode switching setting status
•Conversion enable/disable setting
•Operating condition setting request •Channel change completion flag
•Setting range •Channel change request
•CH Offset setting channel setting •CH Measured temperature value
(3) X/Y Monitor/test
•Xn0: Module ready •Yn9: Operating condition setting request
•Xn9: Operating condition setting completion flag •YnA: User range write request
•XnA: Offset/gain setting mode status flag •YnB: Channel change request
•XnB: Channel change completion flag •YnF: Error clear request
•XnC: Disconnection detection signal
•XnD: Warning output signal
•XnE: Conversion completion flag
•XnF: Error flag
(4) OMC (Online Module Change) refresh data
•CH Factory default offset/gain values •CH User range settings offset/gain values
•CH User range settings resistance offset/gain values
•OMC (Online Module Change) refresh data write request
•CH Offset setting value
•CH Gain setting channel setting
•CH Gain setting value
•OMC (Online Module Change) refresh data
read request
Section 5.6
5 - 2
5.1 Utility Package Functions
Page 95

5
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX Configurator-TI)
5.2 Installing and Uninstalling Utility Package
For installation and uninstallation of an utility package, refer to the "Method of installing the
MELSOFT Series" provided with the utility package.
5.2.1 Precautions for use
This section describes the precautions for using GX Configurator-TI.
1
OVERVIEW
2
(1) Safety
Since GX Configurator-TI is add-in software for GX Developer, read "Safety
Precautions" and the basic operating procedures in the GX Developer Operating
Manual.
(2) Installation
GX Configurator-TI shall be added in GX Developer Version 4 or later. Therefore, it
must be installed on the personal computer that has already been GX Developer
Version 4 or later installed.
(3) Screen display error when intelligent function module utility is used
Insufficient system resource may cause inappropriate display of the screen when the
intelligent function module utility is used. If this occurs, close the intelligent function
module utility first, and subsequently GX Developer (such as programs and
comments) and other applications. Then, restart GX Developer and the intelligent
function module utility.
(4) Activating intelligent function module utility
(a) PLC series set in GX Developer
A project must be specified. When creating a new project, select "QCPU (Q
mode)" for the PLC series in GX Developer.
If any series other than "QCPU (Q mode)" is selected, or if no project is specified,
the intelligent function module utility cannot be activated.
PROCEDURES AND
3
4
5
6
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
SETTINGS BEFORE
SYSTEM OPERATION
UTILITY PACKAGE
(GX CONFIGURATOR-TI)
(b) Activation of multiple utilities
Multiple intelligent function module utilities can be activated.
Note, however, that "Open parameters" and "Save parameters" operations under
"Intelligent function module parameter" are allowed for one intelligent function
module utility only.
For the other utilities, only the "Monitor/test" operation is allowed.
5.2 Installing and Uninstalling Utility Package
5.2.1 Precautions for use
5 - 3
PROGRAMMING
7
ONLINE MODULE
CHANGE
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 96

5
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX Configurator-TI)
(5) Switching screens between two or more intelligent function module
utilities
When two or more intelligent function module utility screens cannot be displayed side
by side, select a screen to be displayed on the top of others using the task bar.
(6) Number of parameters that can be set in GX Configurator-TI
When multiple intelligent function modules are mounted, the number of parameter
settings must not exceed the following limit.
Table 5.2 Maximum number of parameter settings
When intelligent function modules
are installed to:
Q00J/Q00/Q01CPU 512 256
Q02/Q02H/Q06H/Q12H/Q25HCPU 512 256
Q02PH/Q06PH/Q12PH/Q25PHCPU 512 256
Q12PRH/Q25PRHCPU 512 256
Q00UJ/Q00U/Q01UCPU 512 256
Q02UCPU 2048 1024
Q03UD/Q04UDH/Q06UDH/
Q10UDH/Q13UDH/Q20UDH/
Q26UDH/Q03UDE/Q04UDEH/
Q06UDEH/Q10UDEH/Q13UDEH/
Q20UDEH/Q26UDEHCPU
Q50UDEH/Q100UDEHCPU Not available Not available
MELSECNET/H remote I/O station 512 256
Maximum number of parameter settings
Initial setting Auto refresh setting
4096 2048
For example, if multiple intelligent function modules are mounted to the MELSECNET/
H remote I/O station, make the settings in GX Configurator-TI so that the total number
of parameter settings set for all the intelligent function modules does not exceed the
maximum number of parameter settings of the MELSECNET/H remote I/O station.
Calculate the total number of parameter settings for initial setting and auto refresh
setting, respectively.
The following table shows the number of parameter settings that can be set for one
module in GX Configurator-TI.
Table 5.3 Number of parameter settings that can be set for one module
Target module Initial setting Auto refresh setting
Q68RD3-G
Example) Counting the number of parameter settings for the auto refresh setting
6 (Fixed)
24 (Max.)
5 - 4
5.2 Installing and Uninstalling Utility Package
5.2.1 Precautions for use
Page 97

5
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX Configurator-TI)
This one row is counted as one setting.
Blank rows are not counted.
Count up all the setting items on this
screen, and add the total to the number
of settings for other intelligent function
modules to get a grand total.
1
2
3
4
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
SPECIFICATIONS
PROCEDURES AND
5
6
7
8
SETTINGS BEFORE
SYSTEM OPERATION
UTILITY PACKAGE
(GX CONFIGURATOR-TI)
PROGRAMMING
ONLINE MODULE
CHANGE
5.2 Installing and Uninstalling Utility Package
5.2.1 Precautions for use
TROUBLESHOOTING
5 - 5
Page 98

5
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX Configurator-TI)
5.2.2 Operating environment
This section describes the operating environment of the personal computer that runs GX
Configurator-TI.
Table 5.4 Operating environment of personal computer
Item Description
Installation (Add-in) target
Computer A personal computer with any of the operating systems below
Hard disk space
Display
Operating system
*1
CPU
Required
memory
For installation 65MB or more
For operation 10MB or more
GX Developer Version 4 (English version) or later
Refer to the next page "Operating system and performance required for personal
computer".
800
600 dots or more resolution
Microsoft Windows 95 Operating System (English version)
Microsoft Windows 98 Operating System (English version)
Microsoft Windows Millennium Edition Operating System (English version)
Microsoft Windows NT Workstation Operating System Version 4.0
(English version)
Microsoft Windows 2000 Professional Operating System (English version)
Microsoft Windows XP Professional Operating System (English version) SP1 or
later
Microsoft Windows XP Home Edition Operating System (English version) SP1 or
later
Microsoft Windows Vista Home Basic Operating System (English version)
Microsoft Windows Vista Home Premium Operating System (English version)
Microsoft Windows Vista Business Operating System (English version)
Microsoft Windows Vista Ultimate Operating System (English version)
Microsoft Windows Vista Enterprise Operating System (English version)
Microsoft Windows 7 Starter Operating System (English version)
Microsoft Windows 7 Home Premium Operating System (English version)
Microsoft Windows 7 Professional Operating System (English version)
Microsoft Windows 7 Ultimate Operating System (English version)
Microsoft Windows 7 Enterprise Operating System (English version)
* 1 Install GX Configurator-TI in GX Developer Version 4 or later in the same language.
GX Developer (English version) and GX Configurator-TI (Japanese version) cannot be used in
combination, and GX Developer (Japanese version) and GX Configurator-TI (English version)
cannot be used in combination.
* 2 GX Configurator-TI can not be installed in GX Developer Version 3 or earlier.
* 3 When Windows Vista or Windows 7 is used, resolution of 1024 768 dots or more is
recommended.
* 4 When 32-bit Windows 7 is used, add GX Configurator-TI Version 1.28AE or later in GX Developer
Version 8.91V or later.
When 64-bit Windows 7 is used, add GX Configurator-TI Version 1.28AE or later in GX Developer
Version 8.98C or later.
*3
*2
*4
*4
*4
*4
*4
5 - 6
5.2 Installing and Uninstalling Utility Package
5.2.2 Operating environment
Page 99

5
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX Configurator-TI)
Table 5.5 Operating system and performance required for personal computer
Operating system
Windows 95 Pentium 133MHz or more
Windows 98 Pentium 133MHz or more
Windows Me Pentium 150MHz or more
Windows NT Workstation 4.0 Pentium 133MHz or more
Windows 2000 Professional Pentium 133MHz or more
Windows XP Pentium 300MHz or more
Windows Vista Pentium 1GHz or more
Windows 7 Pentium 1GHz or more
POINT
Performance required for personal computer
CPU Required memory
32MB or more
32MB or more
32MB or more
32MB or more
64MB or more
128MB or more
1GB or more
1GB or more (32-bit)
2GB or more (64-bit)
1
2
3
OVERVIEW
SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
(1) The functions shown below are not available for Windows XP, Windows
Vista , and Windows 7.
If any of the following functions is attempted, this product may not operate
normally.
• Start of application in Windows compatible mode
• Fast user switching
• Remote desktop
• Large fonts (Details setting of Display Properties)
Also, GX Configurator-TI is not supported by 64-bit Windows XP and 64-bit
Windows Vista .
(2) A user with USER authority or higher can access GX Configurator-TI for
Windows Vista and Windows 7.
(3) When Windows 7 is used, the following functions are not available.
• Windows XP Mode
• Windows Touch
PROCEDURES AND
4
5
6
7
SPECIFICATIONS
SETTINGS BEFORE
SYSTEM OPERATION
UTILITY PACKAGE
(GX CONFIGURATOR-TI)
PROGRAMMING
5.2 Installing and Uninstalling Utility Package
5.2.2 Operating environment
5 - 7
ONLINE MODULE
CHANGE
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 100

5
UTILITY PACKAGE (GX Configurator-TI)
5.3 Operating Utility Package
5.3.1 Common operations
(1) Control keys
The following table shows the special keys that can be used for operating the utility
package and their applications.
Delete
Back
Space
Table 5.6 Available control keys
Key Application
Esc
Ta b
Ctrl
Cancels the current entry in a cell.
Closes the window.
Moves between controls in the window.
Used in combination with the mouse operation to
select multiple cells for test execution.
Deletes the character where the cursor is
positioned.
When a cell is selected, clears all of the setting
contents in the cell.
Deletes the character where the cursor is
positioned.
Page
Up
Page
Down
Enter
Moves the cursor.
Moves the cursor one page up.
Moves the cursor one page down.
Completes the entry in the cell.
5 - 8
5.3 Operating Utility Package
5.3.1 Common operations
 Loading...
Loading...