
QCPU User's Manual (Multiple CPU System)
-Q00CPU -Q100UDEHCPU
-Q01CPU
-Q02(H)CPU
-Q06HCPU
-Q12HCPU
-Q25HCPU
-Q02PHCPU
-Q06PHCPU
-Q12PHCPU
-Q25PHCPU
-Q00UCPU
-Q01UCPU
-Q02UCPU
-Q03UDVCPU
-Q03UD(E)CPU
-Q04UDVCPU
-Q04UD(E)HCPU
-Q06UDVCPU
-Q06UD(E)HCPU
-Q10UD(E)HCPU
-Q13UDVCPU
-Q13UD(E)HCPU
-Q20UD(E)HCPU
-Q26UDVCPU
-Q26UD(E)HCPU
-Q50UDEHCPU

SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
WARNING
CAUTION
Indicates that incorrect handling may cause hazardous conditions,
resulting in death or severe injury.
Indicates that incorrect handling may cause hazardous conditions,
resulting in minor or moderate injury or property damage.
Overcurrent or overvoltage protection of
the power supply module is activated.
The CPU module detects an error such as a
watchdog timer error by the self-diagnostic function.
All outputs are turned off All outputs are turned off
All outputs are turned off
All outputs are held or turned off
according to the parameter setting.
Q series module AnS/A series module
(Read these precautions before using this product.)
Before using this product, please read this manual and the relevant manuals carefully and pay full attention
to safety to handle the product correctly.
In this manual, the safety precautions are classified into two levels: " WARNING" and " CAUTION".
Under some circumstances, failure to observe the precautions given under " CAUTION" may lead to
serious consequences.
Observe the precautions of both levels because they are important for personal and system safety.
Make sure that the end users read this manual and then keep the manual in a safe place for future
reference.
[Design Precautions]
WARNING
● Configure safety circuits external to the programmable controller to ensure that the entire system
operates safely even when a fault occurs in the external power supply or the programmable controller.
Failure to do so may result in an accident due to an incorrect output or malfunction.
(1) Configure external safety circuits, such as an emergency stop circuit, protection circuit, and
protective interlock circuit for forward/reverse operation or upper/lower limit positioning.
(2) The programmable controller stops its operation upon detection of the following status, and the
output status of the system will be as shown below.
All outputs may turn on when an error occurs in the part, such as I/O control part, where the
programmable controller CPU cannot detect any error. To ensure safety operation in such a case,
provide a safety mechanism or a fail-safe circuit external to the programmable controller. For a
fail-safe circuit example, refer to the QCPU User's Manual (Hardware Design, Maintenance and
Inspection).
(3) Outputs may remain on or off due to a failure of an output module relay or transistor. Configure an
external circuit for monitoring output signals that could cause a serious accident.
1
[Design Precautions]
WARNING
● In an output module, when a load current exceeding the rated current or an overcurrent caused by a
load short-circuit flows for a long time, it may cause smoke and fire. To prevent this, configure an
external safety circuit, such as a fuse.
● Configure a circuit so that the programmable controller is turned on first and then the external power
supply. If the external power supply is turned on first, an accident may occur due to an incorrect output
or malfunction.
● For the operating status of each station after a communication failure, refer to manuals relevant to the
network. Incorrect output or malfunction due to a communication failure may result in an accident.
● When connecting a peripheral with the CPU module or connecting an external device, such as a
personal computer, with an intelligent function module to modify data of a running programmable
controller, configure an interlock circuit in the program to ensure that the entire system will always
operate safely. For other forms of control (such as program modification or operating status change)
of a running programmable controller, read the relevant manuals carefully and ensure that the
operation is safe before proceeding. Especially, when a remote programmable controller is controlled
by an external device, immediate action cannot be taken if a problem occurs in the programmable
controller due to a communication failure. To prevent this, configure an interlock circuit in the
sequence program, and determine corrective actions to be taken between the external device and
CPU module in case of a communication failure.
[Design Precautions]
CAUTION
● Do not install the control lines or communication cables together with the main circuit lines or power
cables. Keep a distance of 100mm (3.94 inches) or more between them. Failure to do so may result in
malfunction due to noise.
● When a device such as a lamp, heater, or solenoid valve is controlled through an output module, a
large current (approximately ten times greater than normal) may flow when the output is turned from
off to on. Take measures such as replacing the module with one having a sufficient current rating.
● After the CPU module is powered on or is reset, the time taken to enter the RUN status varies
depending on the system configuration, parameter settings, and/or program size. Design circuits so
that the entire system will always operate safely, regardless of the time.
2
[Installation Precautions]
CAUTION
● Use the programmable controller in an environment that meets the general specifications in the
QCPU User's Manual (Hardware Design, Maintenance and Inspection). Failure to do so may result in
electric shock, fire, malfunction, or damage to or deterioration of the product.
● To mount the module, while pressing the module mounting lever located in the lower part of the
module, fully insert the module fixing projection(s) into the hole(s) in the base unit and press the
module until it snaps into place. Incorrect mounting may cause malfunction, failure or drop of the
module. When using the programmable controller in an environment of frequent vibrations, fix the
module with a screw. Tighten the screw within the specified torque range. Undertightening can cause
drop of the screw, short circuit, or malfunction. Overtightening can damage the screw and/or module,
resulting in drop, short circuit, or malfunction.
When using an extension cable, connect it to the extension cable connector of the base unit securely.
●
Check the connection for looseness. Poor contact may cause incorrect input or output.
● When using a memory card, fully insert it into the memory card slot. Check that it is inserted
completely. Poor contact may cause malfunction.
● When using an SD memory card, fully insert it into the SD memory card slot. Check that it is inserted
completely. Poor contact may cause malfunction.
● Securely insert an extended SRAM cassette into the cassette connector of a CPU module. After
insertion, close the cassette cover to prevent the cassette from coming off. Poor contact may cause
malfunction.
● Shut off the external power supply (all phases) used in the system before mounting or removing the
module. Failure to do so may result in damage to the product. A module can be replaced online (while
power is on) on any MELSECNET/H remote I/O station or in the system where a CPU module
supporting the online module change function is used. Note that there are restrictions on the modules
that can be replaced online, and each module has its predetermined replacement procedure. For
details, refer to the relevant sections in the QCPU User's Manual (Hardware Design, Maintenance
and Inspection) and in the manual for the corresponding module.
● Do not directly touch any conductive parts and electronic components of the module, memory card,
SD memory card, or extended SRAM cassette. Doing so can cause malfunction or failure of the
module.
● When using a Motion CPU module and modules designed for motion control, check that the
combinations of these modules are correct before applying power. The modules may be damaged if
the combination is incorrect. For details, refer to the user's manual for the Motion CPU module.
[Wiring Precautions]
WARNING
● Shut off the external power supply (all phases) used in the system before wiring. Failure to do so may
result in electric shock or damage to the product.
● After installation and wiring, attach the included terminal cover to the module before turning it on for
operation. Failure to do so may result in electric shock.
3
[Wiring Precautions]
CAUTION
● Individually ground the FG and LG terminals of the programmable controller with a ground resistance
of 100 or less. Failure to do so may result in electric shock or malfunction.
● Use applicable solderless terminals and tighten them within the specified torque range. If any spade
solderless terminal is used, it may be disconnected when the terminal screw comes loose, resulting in
failure.
● Check the rated voltage and terminal layout before wiring to the module, and connect the cables
correctly. Connecting a power supply with a different voltage rating or incorrect wiring may cause a fire
or failure.
● Connectors for external devices must be crimped or pressed with the tool specified by the
manufacturer, or must be correctly soldered. Incomplete connections may cause short circuit, fire, or
malfunction.
● Securely connect the connector to the module. Poor contact may cause malfunction.
● Do not install the control lines or communication cables together with the main circuit lines or power
cables. Keep a distance of 100mm (3.94 inches) or more between them. Failure to do so may result in
malfunction due to noise.
● Place the cables in a duct or clamp them. If not, dangling cable may swing or inadvertently be pulled,
resulting in damage to the module or cables or malfunction due to poor connection.
● Check the interface type and correctly connect the cable. Incorrect wiring (connecting the cable to an
incorrect interface) may cause failure of the module and external device.
● Tighten the terminal screws within the specified torque range. Undertightening can cause short circuit,
fire, or malfunction. Overtightening can damage the screw and/or module, resulting in drop, short
circuit, or malfunction.
● Prevent foreign matter such as dust or wire chips from entering the module. Such foreign matter can
cause a fire, failure, or malfunction.
● A protective film is attached to the top of the module to prevent foreign matter, such as wire chips,
from entering the module during wiring. Do not remove the film during wiring. Remove it for heat
dissipation before system operation.
● When disconnecting the cable from the module, do not pull the cable by the cable part. For the cable
with connector, hold the connector part of the cable. For the cable connected to the terminal block,
loosen the terminal screw. Pulling the cable connected to the module may result in malfunction or
damage to the module or cable.
● Mitsubishi programmable controllers must be installed in control panels. Connect the main power
supply to the power supply module in the control panel through a relay terminal block. Wiring and
replacement of a power supply module must be performed by qualified maintenance personnel with
knowledge of protection against electric shock. For wiring methods, refer to the QCPU User's Manual
(Hardware Design, Maintenance and Inspection).
4

[Startup and Maintenance Precautions]
WARNING
● Do not touch any terminal while power is on. Doing so will cause electric shock or malfunction.
● Correctly connect the battery connector. Do not charge, disassemble, heat, short-circuit, solder, or
throw the battery into the fire. Also, do not expose it to liquid or strong shock. Doing so will cause the
battery to produce heat, explode, ignite, or leak, resulting in injury and fire.
● Shut off the external power supply (all phases) used in the system before cleaning the module or
retightening the terminal screws, connector screws, or module fixing screws. Failure to do so may
result in electric shock or cause the module to fail or malfunction.
[Startup and Maintenance Precautions]
CAUTION
● Before performing online operations (especially, program modification, forced output, and operating
status change) for the running CPU module from the peripheral device connected, read relevant
manuals carefully and ensure the safety. Improper operation may damage machines or cause
accidents.
● Do not disassemble or modify the modules. Doing so may cause failure, malfunction, injury, or a fire.
● Use any radio communication device such as a cellular phone or PHS (Personal Handy-phone
System) more than 25cm (9.85 inches) away in all directions from the programmable controller.
Failure to do so may cause malfunction.
● Shut off the external power supply (all phases) used in the system before mounting or removing the
module. Failure to do so may cause the module to fail or malfunction. A module can be replaced
online (while power is on) on any MELSECNET/H remote I/O station or in the system where a CPU
module supporting the online module change function is used. Note that there are restrictions on the
modules that can be replaced online, and each module has its predetermined replacement procedure.
For details, refer to the relevant sections in the QCPU User's Manual (Hardware Design, Maintenance
and Inspection) and in the manual for the corresponding module.
● After the first use of the product, do not mount/remove the module to/from the base unit, and the
terminal block to/from the module, and do not insert/remove the extended SRAM cassette to/from the
CPU module more than 50 times (IEC 61131-2 compliant) respectively. Exceeding the limit of 50 times
may cause malfunction.
● After the first use of the product, do not insert/remove the SD memory card to/from the CPU module
more than 500 times. Exceeding the limit may cause malfunction.
● Do not drop or apply shock to the battery to be installed in the module. Doing so may damage the
battery, causing the battery fluid to leak inside the battery. If the battery is dropped or any shock is
applied to it, dispose of it without using.
● Before handling the module, touch a grounded metal object to discharge the static electricity from the
human body. Failure to do so may cause the module to fail or malfunction.
5

[Disposal Precautions]
CAUTION
● When disposing of this product, treat it as industrial waste. When disposing of batteries, separate
them from other wastes according to the local regulations. (For the Battery Directive in EU member
states, refer to the QCPU User's Manual (Hardware Design, Maintenance and Inspection).)
[Transportation Precautions]
CAUTION
● When transporting lithium batteries, follow the transportation regulations. (For details of the regulated
models, refer to the QCPU User's Manual (Hardware Design, Maintenance and Inspection).)
6

CONDITIONS OF USE FOR THE PRODUCT
(1) Mitsubishi programmable controller ("the PRODUCT") shall be used in conditions;
i) where any problem, fault or failure occurring in the PRODUCT, if any, shall not lead to any major
or serious accident; and
ii) where the backup and fail-safe function are systematically or automatically provided outside of
the PRODUCT for the case of any problem, fault or failure occurring in the PRODUCT.
(2) The PRODUCT has been designed and manufactured for the purpose of being used in general
industries.
MITSUBISHI SHALL HAVE NO RESPONSIBILITY OR LIABILITY (INCLUDING, BUT NOT
LIMITED TO ANY AND ALL RESPONSIBILITY OR LIABILITY BASED ON CONTRACT,
WARRANTY, TORT, PRODUCT LIABILITY) FOR ANY INJURY OR DEATH TO PERSONS OR
LOSS OR DAMAGE TO PROPERTY CAUSED BY the PRODUCT THAT ARE OPERATED OR
USED IN APPLICATION NOT INTENDED OR EXCLUDED BY INSTRUCTIONS, PRECAUTIONS,
OR WARNING CONTAINED IN MITSUBISHI'S USER, INSTRUCTION AND/OR SAFETY
MANUALS, TECHNICAL BULLETINS AND GUIDELINES FOR the PRODUCT.
("Prohibited Application")
Prohibited Applications include, but not limited to, the use of the PRODUCT in;
• Nuclear Power Plants and any other power plants operated by Power companies, and/or any
other cases in which the public could be affected if any problem or fault occurs in the PRODUCT.
• Railway companies or Public service purposes, and/or any other cases in which establishment of
a special quality assurance system is required by the Purchaser or End User.
• Aircraft or Aerospace, Medical applications, Train equipment, transport equipment such as
Elevator and Escalator, Incineration and Fuel devices, Vehicles, Manned transportation,
Equipment for Recreation and Amusement, and Safety devices, handling of Nuclear or
Hazardous Materials or Chemicals, Mining and Drilling, and/or other applications where there is a
significant risk of injury to the public or property.
Notwithstanding the above, restrictions Mitsubishi may in its sole discretion, authorize use of the
PRODUCT in one or more of the Prohibited Applications, provided that the usage of the PRODUCT
is limited only for the specific applications agreed to by Mitsubishi and provided further that no
special quality assurance or fail-safe, redundant or other safety features which exceed the general
specifications of the PRODUCTs are required. For details, please contact the Mitsubishi
representative in your region.
7
INTRODUCTION
Remark
This manual describes the system configurations, functions, and communication methods with external devices
required in a multiple CPU system.
Before using this product, please read this manual and the relevant manuals carefully and develop familiarity with the
functions and performance of the Q series programmable controller to handle the product correctly.
When applying the program examples introduced in this manual to the actual system, ensure the applicability and
confirm that it will not cause system control problems.
Relevant CPU modules:
CPU module Model
Basic model QCPU Q00CPU, Q01CPU
High Performance model QCPU Q02(H)CPU, Q06HCPU, Q12HCPU, Q25HCPU
Process CPU Q02PHCPU, Q06PHCPU, Q12PHCPU, Q25PHCPU
Q00UCPU, Q01UCPU, Q02UCPU, Q03UD(E)CPU, Q03UDVCPU,
Universal model QCPU
Q04UD(E)HCPU, Q04UDVCPU, Q06UD(E)HCPU, Q06UDVCPU,
Q10UD(E)HCPU, Q13UD(E)HCPU, Q13UDVCPU, Q20UD(E)HCPU,
Q26UD(E)HCPU, Q26UDVCPU, Q50UDEHCPU, Q100UDEHCPU
● This manual does not describe the specifications and precautions of the power supply modules, base units, extension
cables, memory cards, SD memory cards, extended SRAM cassettes, and batteries as well as the peripheral
configurations.
QCPU User's Manual (Hardware Design, Maintenance and Inspection)
● For the functions of CPU modules when used in a system other than a multiple CPU system, refer to the following.
User's Manual (Function Explanation, Program Fundamentals) for the CPU module used
8

Memo
9
CONTENTS
CONTENTS
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
CONDITIONS OF USE FOR THE PRODUCT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
INTRODUCTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
MANUALS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
MANUAL PAGE ORGANIZATION. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
TERMS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
CHAPTER 1 OVERVIEW 18
CHAPTER 2 CONCEPT OF MULTIPLE CPU SYSTEM 24
2.1 CPU Numbers. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
2.2 I/O Number Assignment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
2.2.1 I/O numbers of I/O modules and intelligent function modules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
2.2.2 I/O numbers of CPU modules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
CHAPTER 3 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION 31
3.1 System Using Basic Model QCPU as CPU No.1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
3.1.1 Available CPU modules, base units, power supply modules, and extension cables . . . . . . . 32
3.1.2 CPU module combinations and mounting positions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
3.1.3 Available I/O modules and intelligent function modules. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
3.2 System Using High Performance Model QCPU or Process CPU as CPU No.1. . . . . . . . . . . . 41
3.2.1 Available CPU modules, base units, power supply modules, and extension cables . . . . . . . 41
3.2.2 CPU module combinations and mounting positions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
3.2.3 Available I/O modules and intelligent function modules. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
3.3 System Using Universal Model QCPU as CPU No.1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
3.3.1 Available CPU modules, base units, power supply modules, and extension cables . . . . . . . 53
3.3.2 CPU module combinations and mounting positions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
3.3.3 Available I/O modules and intelligent function modules. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
3.4 Applicable Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .65
3.5 Precautions for System Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
CHAPTER 4 STARTING UP MULTIPLE CPU SYSTEM 75
4.1 Procedure Before Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
4.2 Operation Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
4.2.1 System configuration example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
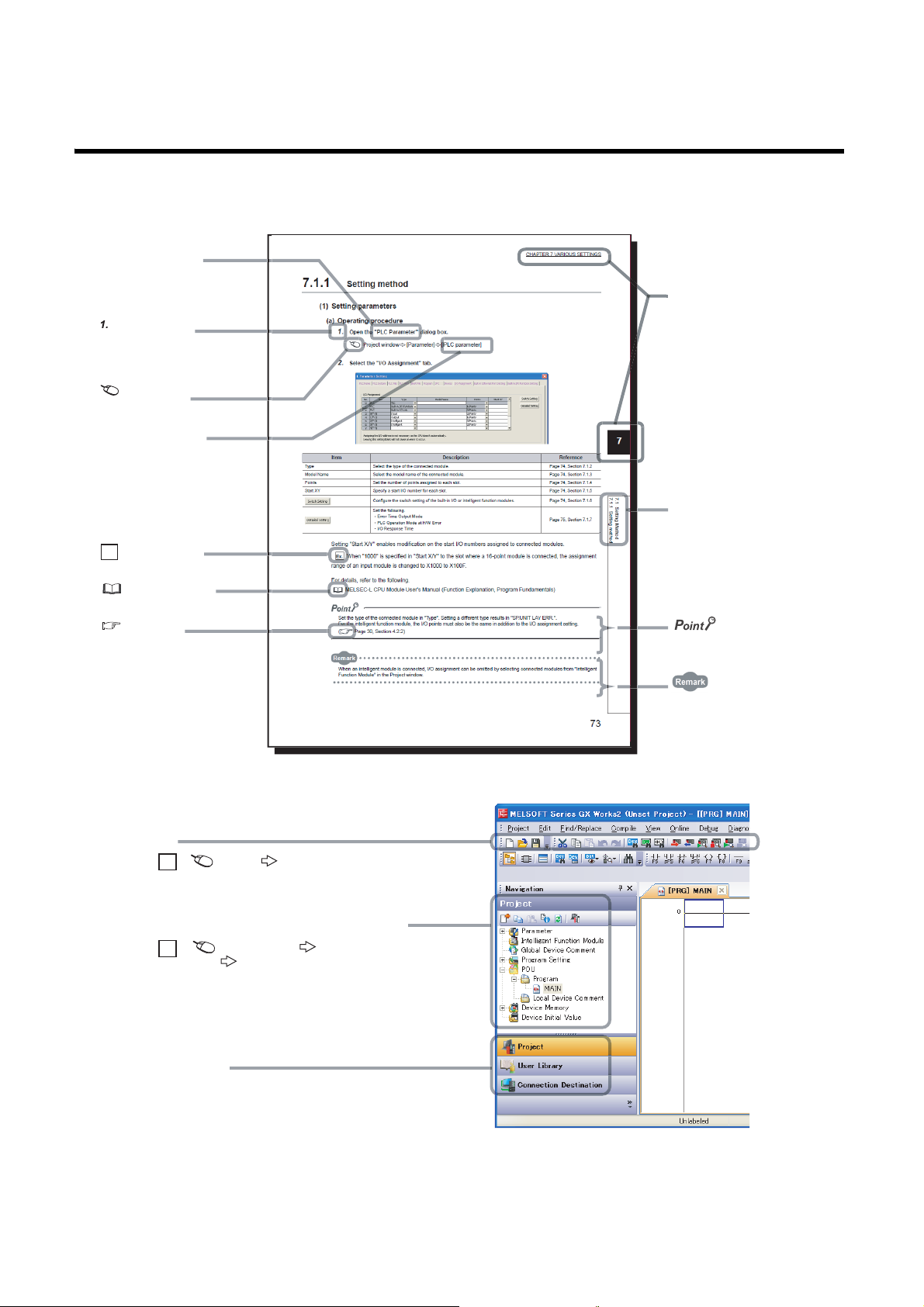
4.2.2 Parameter settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
4.3 Program Examples for Communications by Auto Refresh . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
4.3.1 Program examples for Basic model QCPU, High Performance model QCPU, and Process
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
CPU
4.3.2 Program examples for Universal model QCPU . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
4.4 Clock Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
4.4.1 Clock data of CPU modules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
4.4.2 Clock data of intelligent function modules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
4.5 Resetting a Multiple CPU System. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .101
4.6 System Operation When a Stop Error Occurs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .102
10
CHAPTER 5 ACCESS BETWEEN CPU MODULES AND OTHER MODULES 104
5.1 Access to Controlled Modules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
5.2 Access to Non-controlled Modules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .104
5.2.1 Loading input (X) data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
5.2.2 Loading output (Y) data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
5.2.3 Output to output modules and intelligent function modules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
5.2.4 Access to the intelligent function module buffer memory. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
5.2.5 Access using the link direct device . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
5.3 Access From a Programming Tool . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
5.4 Accessible QCPUs when GOT is connected . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .115
CHAPTER 6 COMMUNICATIONS AMONG CPU MODULES 116
6.1 Communications Using the CPU Shared Memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .118
6.1.1 Communications by auto refresh (using the auto refresh area) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 122
6.1.2 Communications by auto refresh (using the multiple CPU high speed transmission area)
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
6.1.3 Communications by programs using the CPU shared memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150
6.1.4 Communications among CPU modules when an error is detected . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 159
6.2 Control Directions from QCPU to Motion CPU . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 160
6.3 Communications Among CPU Modules By Dedicated Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .162
6.3.1 Reading/writing device data from/to Motion CPU . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 162
6.3.2 Starting interrupt programs from QCPU to C Controller module/PC CPU module. . . . . . . . 164
6.3.3 Reading/writing device data between QCPUs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 165
6.4 Multiple CPU Synchronous Interrupt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .166
6.5 Multiple CPU synchronous startup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .168
APPENDICES 170
Appendix 1 Parameters for a Multiple CPU System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .170
Appendix 1.1 List of parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 172
Appendix 2 Comparison with a Single CPU System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .175
Appendix 3 Precautions for Using AnS/A Series Modules. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .188
Appendix 4 Processing Time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .192
Appendix 4.1 Concept of scan time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 192
Appendix 4.2 Factors that increase scan time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 194
Appendix 4.3 Reducing processing time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 200
INDEX 201
REVISIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 204
WARRANTY . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 207
11
MANUALS
To understand the main specifications, functions, and usage of the CPU module, refer to the basic manuals. Read
other manuals as well when using a different type of CPU module and its functions. Order each manual as needed,
referring to the following lists.
The numbers in the "CPU module" and the respective modules are as follows.
Number CPU module Number CPU module
1) Basic model QCPU 3) Process CPU
2) High Performance model QCPU 4) Universal model QCPU
●: Basic manual, : Other CPU module manuals/Use them to utilize functions.
(1) CPU module user's manual
Manual name
<manual number (model code)>
QCPU User's Manual (Hardware Design,
Maintenance and Inspection)
<SH-080483ENG (13JR73)>
QnUCPU User's Manual (Function Explanation,
Program Fundamentals)
<SH-080807ENG (13JZ27)>
Qn(H)/QnPH/QnPRHCPU User's Manual
(Function Explanation, Program Fundamentals)
<SH-080808ENG (13JZ28)>
QnUCPU User's Manual (Communication via
Built-in Ethernet Port)
<SH-080811ENG (13JZ29)>
QnUDVCPU/LCPU User's Manual (Data
Logging Function)
<SH-080893ENG (13JZ39)>
Description
Specifications of the hardware (CPU modules, power
supply modules, base units, extension cables, memory
cards, SD memory cards, and extended SRAM
cassettes), system maintenance and inspection,
troubleshooting, and error codes
Functions, methods, and devices for programming ●
Functions, methods, and devices for programming ●●●
Detailed description of communication via the built-in
Ethernet ports of the CPU module
Detailed description of the data logging function of the
CPU module
CPU module
1) 2) 3) 4)
●●●●
12
(2) Programming manual
Manual name
<manual number (model code)>
MELSEC-Q/L Programming Manual (Common
Instruction)
<SH-080809ENG (13JW10)>
MELSEC-Q/L/QnA Programming Manual
(SFC)
<SH-080041 (13JF60)>
MELSEC-Q/L Programming Manual (MELSAP-
L)
<SH-080076 (13JF61)>
MELSEC-Q/L Programming Manual (Structured
Te xt )
<SH-080366E (13JF68)>
MELSEC-Q/L/QnA Programming Manual (PID
Control Instructions)
<SH-080040 (13JF59)>
MELSEC-Q Programming/Structured
Programming Manual (Process Control
Instructions)
<SH-080316E (13JF67)>
(3) Operating manual
Description
Detailed description and usage of instructions used in
programs
System configuration, specifications, functions,
programming, and error codes for SFC (MELSAP3)
programs
System configuration, specifications, functions,
programming, and error codes for SFC (MELSAP-L)
programs
System configuration and programming using structured
text language
Dedicated instructions for PID control
Dedicated instructions for process control
CPU module
1) 2) 3) 4)
●●●●
Manual name
<manual number (model code)>
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating Manual
(Common)
<SH-080779ENG (13JU63)>
GX Developer Version 8 Operating Manual
<SH-080373E (13JU41)>
Description
System configuration, parameter settings, and online
operations (common to Simple project and Structured
project) of GX Works2
Operating methods of GX Developer, such as
programming, printing, monitoring, and debugging
CPU module
1) 2) 3) 4)
●●●●
13
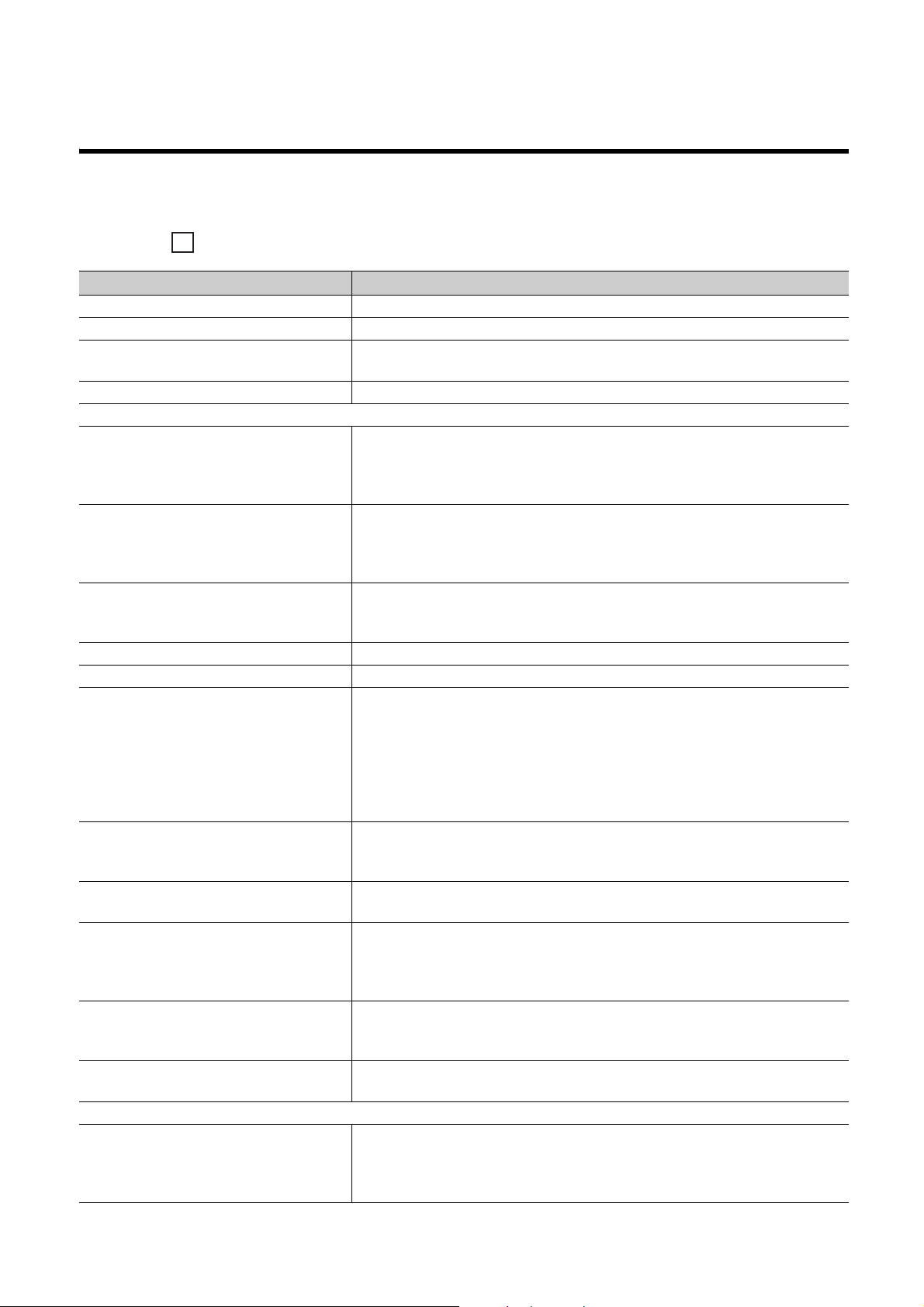
MANUAL PAGE ORGANIZATION
The section of
the current page is shown.
The chapter of
the current page is shown.
"" is used for window
names and items.
[ ] is used for items
in the menu bar and
the project window.
shows operating
procedures.
shows reference
manuals.
shows notes that
requires attention.
shows mouse
operations.
*1
shows
reference pages.
shows setting or
operating examples.
Ex.
shows useful
information.
A window selected in the view selection area is displayed.
View selection area
[Online] [Write to PLC...]
Select [Online] on the menu bar,
and then select [Write to PLC...].
Project window
[Parameter]
[PLC Parameter]
Select [Project] from the view selection
area to open the Project window.
Menu bar
Ex.
Ex.
In the Project window, expand [Parameter] and
select [PLC Parameter].
In this manual, pages are organized and the symbols are used as shown below.
The following page illustration is for explanation purpose only, and is different from the actual pages.
*1 The mouse operation example is provided below. (For GX Works2)
14
TERMS
Ex.
Unless otherwise specified, this manual uses the following generic terms and abbreviations.
* indicates a part of the model or version.
Q33B, Q35B, Q38B, Q312BQ3B
Ter m Description
Series
Q series The abbreviation for Mitsubishi MELSEC-Q series programmable controller
AnS series
A series The abbreviation for large types of Mitsubishi MELSEC-A series programmable controller
CPU module type
CPU module
QCPU
Basic model QCPU
High Performance model QCPU A generic term for the Q02CPU, Q02HCPU, Q06HCPU, Q12HCPU, and Q25HCPU
Process CPU A generic term for the Q02PHCPU, Q06PHCPU, Q12PHCPU, and Q25PHCPU
Universal model QCPU
Built-in Ethernet port QCPU
High-speed Universal model QCPU
Motion CPU
PC CPU module
C Controller module
CPU module model
QnU(D)(H)CPU
The abbreviation for compact types of Mitsubishi MELSEC-A series programmable
controller
A generic term for the Basic model QCPU, High Performance model QCPU, Process
CPU, Universal model QCPU, Motion CPU, C Controller module, and PC CPU module.
The term in this manual does not include the Redundant CPU because it cannot be used
in a multiple CPU system.
A generic term for the Basic model QCPU, High Performance model QCPU, Process
CPU, and Universal model QCPU.
The term in this manual does not include the Redundant CPU because it cannot be used
in a multiple CPU system.
A generic term for the Q00CPU and Q01CPU.
The term in this manual does not include the Q00JCPU because it cannot be used in a
multiple CPU system.
A generic term for the Q00UCPU, Q01UCPU, Q02UCPU, Q03UDCPU, Q03UDVCPU,
Q03UDECPU, Q04UDHCPU, Q04UDVCPU, Q04UDEHCPU, Q06UDHCPU,
Q06UDVCPU, Q06UDEHCPU, Q10UDHCPU, Q10UDEHCPU, Q13UDHCPU,
Q13UDVCPU, Q13UDEHCPU, Q20UDHCPU, Q20UDEHCPU, Q26UDHCPU,
Q26UDVCPU, Q26UDEHCPU, Q50UDEHCPU, and Q100UDEHCPU.
The term in this manual does not include the Q00UJCPU because it cannot be used in a
multiple CPU system.
A generic term for the Q03UDVCPU, Q03UDECPU, Q04UDVCPU, Q04UDEHCPU,
Q06UDVCPU, Q06UDEHCPU, Q10UDEHCPU, Q13UDVCPU, Q13UDEHCPU,
Q20UDEHCPU, Q26UDVCPU, Q26UDEHCPU, Q50UDEHCPU, and Q100UDEHCPU
A generic term for the Q03UDVCPU, Q04UDVCPU, Q06UDVCPU, Q13UDVCPU, and
Q26UDVCPU
A generic term for the Mitsubishi motion controllers: Q172CPUN, Q173CPUN,
Q172HCPU, Q173HCPU, Q172CPUN-T, Q173CPUN-T, Q172HCPU-T, Q173HCPU-T,
Q172DCPU, Q173DCPU, Q172DCPU-S1, Q173DCPU-S1, Q172DSCPU, and
Q173DSCPU
A generic term for the MELSEC-Q series-compatible PC CPU modules manufactured by
CONTEC Co., Ltd: PPC-CPU686(MS)-64, PPC-CPU686(MS)-128, and PPC-
CPU852(MS)-512
A generic term for the C Controller modules: Q06CCPU-V, Q06CCPU-V-B, Q12DCCPU-
V, Q24DHCCPU-V, and Q24DHCCPU-LS
A generic term for the Q00UCPU, Q01UCPU, Q02UCPU, Q03UDCPU, Q04UDHCPU,
Q06UDHCPU, Q10UDHCPU, Q13UDHCPU, Q20UDHCPU, and Q26UDHCPU.
The term in this manual does not include the Q00UJCPU because it cannot be used in a
multiple CPU system.
15
Term Description
QnUDVCPU
QnUDE(H)CPU
Q172CPUN(-T) A generic term for the Q172CPUN and Q172CPUN-T
Q173CPUN(-T) A generic term for the Q173CPUN and Q173CPUN-T
Q172HCPU(-T) A generic term for the Q172HCPU and Q172HCPU-T
Q173HCPU(-T) A generic term for the Q173HCPU and Q173HCPU-T
Q172DCPU(-S1) A generic term for the Q172DCPU and Q172DCPU-S1
Q173DCPU(-S1) A generic term for the Q173DCPU and Q173DCPU-S1
Base unit type
Base unit
Main base unit A generic term for the Q3B, Q3SB, Q3RB, and Q3DB
Extension base unit
Slim type main base unit Another term for the Q3SB
Redundant power main base unit Another term for the Q3RB
Redundant power extension base unit Another term for the Q6RB
Multiple CPU high speed main base unit Another term for the Q3DB
Redundant power supply base unit
Base unit model
Q3B A generic term for the Q33B, Q35B, Q38B, and Q312B main base units
Q3SB A generic term for the Q32SB, Q33SB, and Q35SB slim type main base units
Q3RB Another term for the Q38RB redundant power main base unit
Q3DB
Q5B A generic term for the Q52B and Q55B extension base units
Q6B A generic term for the Q63B, Q65B, Q68B, and Q612B extension base units
Q6RB Another term for the Q68RB redundant power extension base unit
QA1S5B
QA1S6B A generic term for the QA1S65B and QA1S68B extension base units
QA6B A generic term for the QA65B and QA68B extension base units
A5B A generic term for the A52B, A55B, and A58B extension base units
A6B A generic term for the A62B, A65B, and A68B extension base units
QA6ADP+A5B/A6B The abbreviation for A large type extension base unit where the QA6ADP is mounted
QA1S6ADP+A1S5B/A1S6B The abbreviation for A small type extension base unit where the QA1S6ADP is mounted
Power supply module
Power supply module
Q series power supply module
AnS series power supply module A generic term for the A1S61PN, A1S62PN, and A1S63P power supply modules
A generic term for the Q03UDVCPU, Q04UDVCPU, Q06UDVCPU, Q13UDVCPU, and
Q26UDVCPU
A generic term for the Q03UDECPU, Q04UDEHCPU, Q06UDEHCPU, Q10UDEHCPU,
Q13UDEHCPU, Q20UDEHCPU, Q26UDEHCPU, Q50UDEHCPU, and Q100UDEHCPU
A generic term for the main base unit, extension base unit, slim type main base unit,
redundant power main base unit, redundant power extension base unit, and multiple
CPU high speed main base unit.
The term in this manual does not include the redundant type extension base unit
because it cannot be used in a multiple CPU system.
A generic term for the Q5B, Q6B, Q6RB, QA1S5B, QA1S6B,
QA1S6ADP+A1S5B/A1S6B, QA6B, and QA6ADP+A5B/A6B.
The term in this manual does not include the Q6WRB because it cannot be used in a
multiple CPU system.
A generic term for the redundant power main base unit and redundant power extension
base unit
A generic term for the Q35DB, Q38DB, and Q312DB multiple CPU high speed main
base units
Another term for the QA1S51B extension base unit
A generic term for the Q series power supply module, AnS series power supply module,
A series power supply module, slim type power supply module, and redundant power
supply module
A generic term for the Q61P-A1, Q61P-A2, Q61P, Q61P-D, Q62P, Q63P, Q64P, and
Q64PN power supply modules
16
Ter m Description
A series power supply module
Slim type power supply module The abbreviation for the Q61SP slim type power supply module
Redundant power supply module A generic term for the Q63RP and Q64RP redundant power supply modules
Life detection power supply module The abbreviation for the Q61P-D life detection power supply module
Network module
CC-Link IE module
MELSECNET/H module The abbreviation for the MELSECNET/H network module
Ethernet module The abbreviation for the Ethernet interface module
CC-Link module The abbreviation for the CC-Link system master/local module
Network
CC-Link IE A generic term for the CC-Link IE Controller Network and CC-Link IE Field Network
MELSECNET/H The abbreviation for the MELSECNET/H network system
Memory extension
Memory card A generic term for SRAM card, Flash card, and ATA card
SRAM card
Flash card A generic term for the Q2MEM-2MBF and Q2MEM-4MBF Flash cards
ATA card A generic term for the Q2MEM-8MBA, Q2MEM-16MBA, and Q2MEM-32MBA ATA cards
SD memory card
Extended SRAM cassette
Software package
Programming tool A generic term for GX Works2 and GX Developer
GX Works2
GX Developer
Others
Control CPU
Controlled module I/O modules and intelligent function modules which are controlled by a control CPU
Non-controlled module
Extension cable
Battery
QA6ADP The abbreviation for the QA6ADP QA conversion adapter module
QA1S6ADP
GOT
A generic term for the A61P, A61PN, A62P, A63P, A68P, A61PEU, and A62PEU power
supply modules
A generic term for the CC-Link IE Controller Network module and CC-Link IE Field
Network module
A generic term for the Q2MEM-1MBS, Q2MEM-2MBS, Q3MEM-4MBS, and Q3MEM-
8MBS SRAM cards
A generic term for the L1MEM-2GBSD and L1MEM-4GBSD SD Secure Digital memory
cards. An SD card is a non-volatile memory card.
A generic term for the Q4MCA-1MBS, Q4MCA-2MBS, Q4MCA-4MBS, and Q4MCA-
8MBS extended SRAM cassettes
The product name for the MELSEC programmable controller software package
A CPU module which controls each I/O module and intelligent function module.
In a multiple CPU system, the CPU module which executes the control can be set for
each module.
I/O modules and intelligent function modules that are controlled by CPU modules other
than a control CPU
A generic term for the QC05B, QC06B, QC12B, QC30B, QC50B, and QC100B
extension cables
A generic term for the Q6BAT, Q7BAT, and Q8BAT CPU module batteries, Q2MEM-BAT
SRAM card battery, and Q3MEM-BAT SRAM card battery
A generic term for the QA1S6ADP and QA1S6ADP-S1 Q-AnS base unit conversion
adapter
A generic term for Mitsubishi Graphic Operation Terminal, GOT-A*** series, GOT-F***
series, and GOT1000 series
17
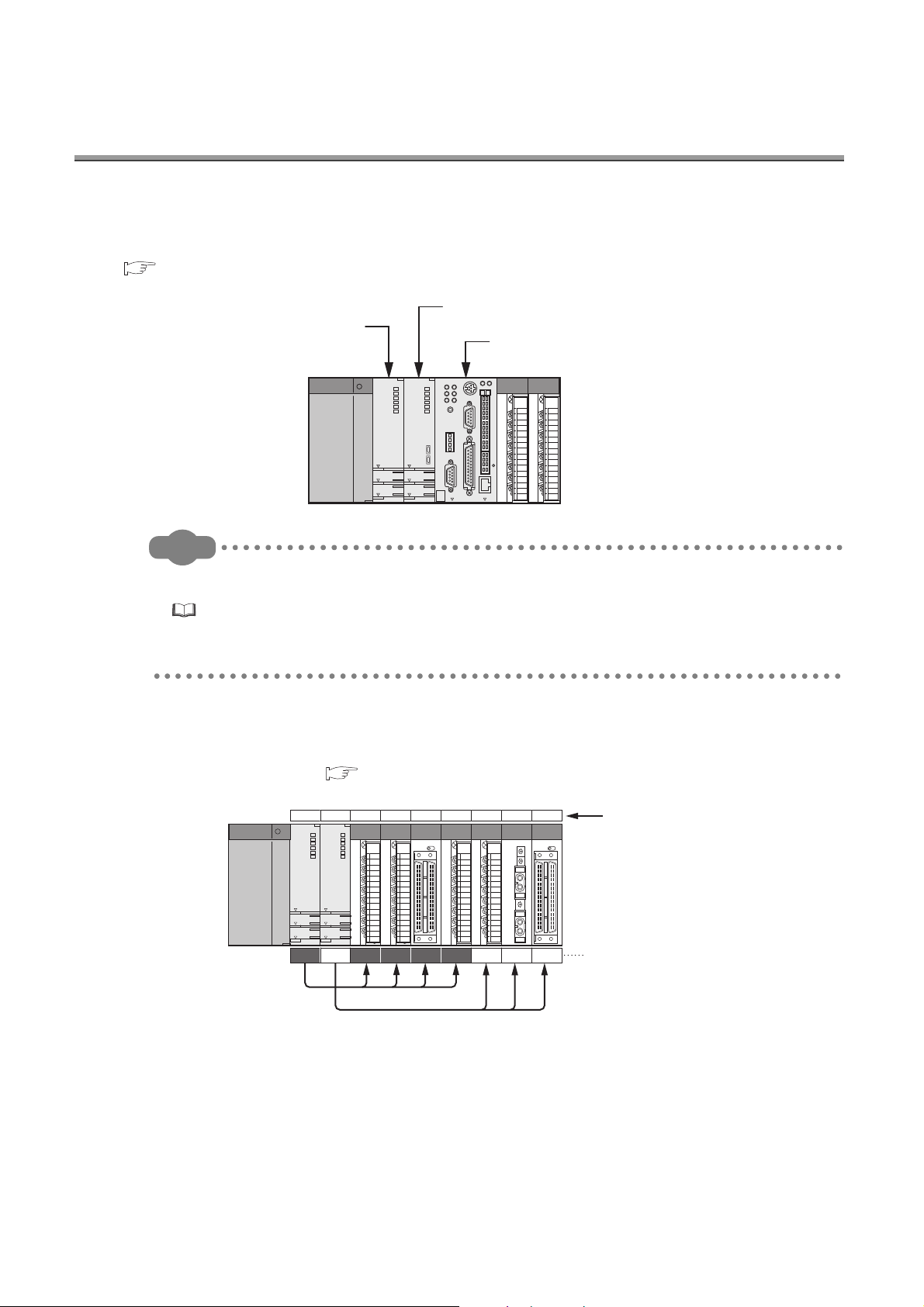
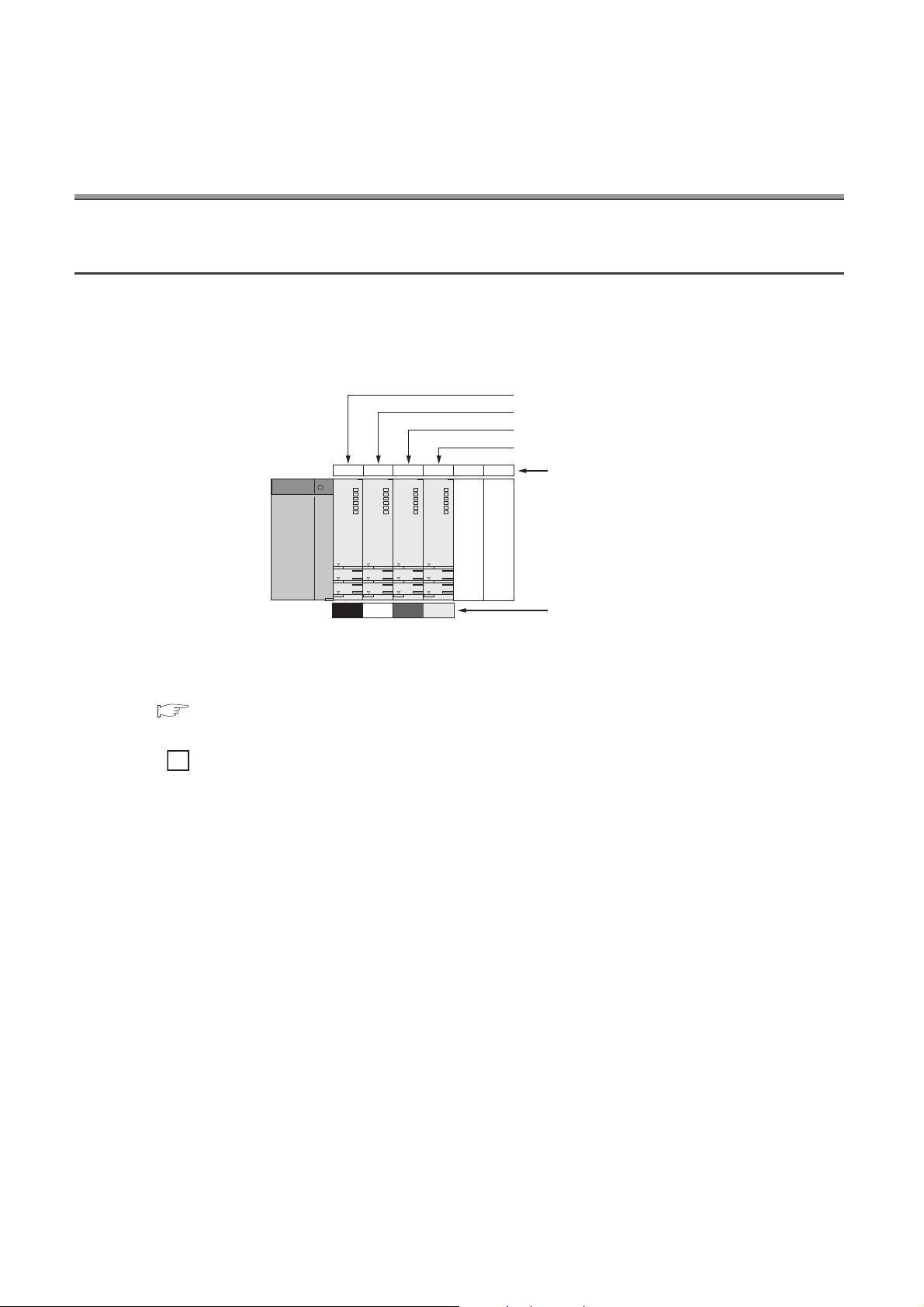
CHAPTER 1 OVERVIEW
Remark
QCPU
Motion CPU
PC CPU module
1 1 1 1
In a multiple CPU system, more than one CPU module is mounted on the main base unit and each CPU module
controls I/O modules and intelligent function modules separately.
QCPUs, Motion CPUs, C Controller modules, and PC CPU modules can be used in multiple CPU systems.
( Page 31, CHAPTER 3)
This manual describes the combinations of CPU modules and communications among CPU modules in a multiple CPU
system. For the uses, functions, and instruction availabilities of each CPU module, refer to the following.
Manual for the CPU module used
For PC CPU modules, contact CONTEC Co., Ltd.
http://www.contec.com/
(1) Distributed control
In a multiple CPU system, control can be distributed by specifying a control CPU module for each I/O module and
intelligent function module. ( Page 24, Section 2.1)
CPU01234567
112
Controlled by CPU No.1.
Controlled by CPU No.2.
222
Distributed control provides the advantages listed on the following page.
Slot number
Control CPU setting
18
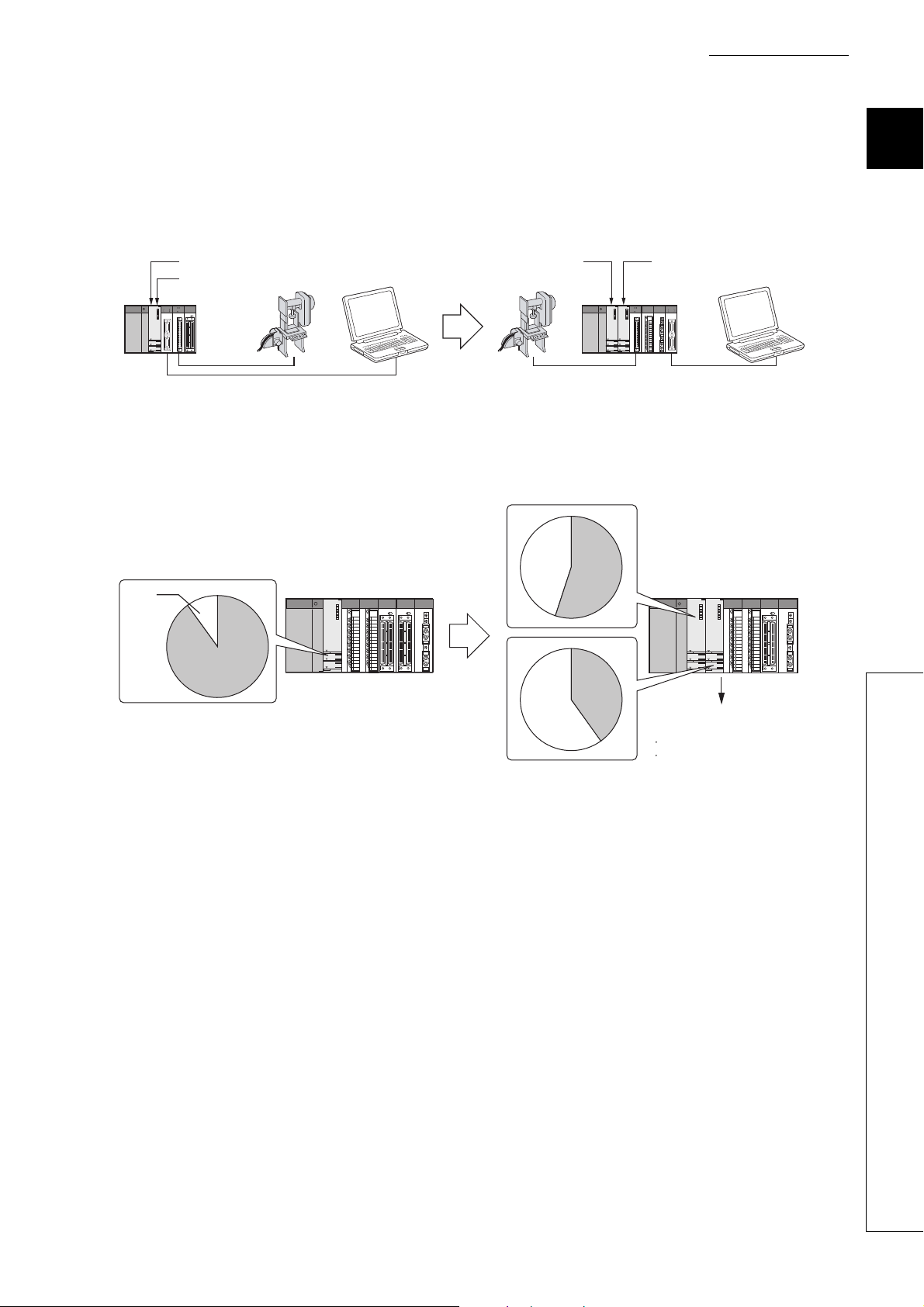
CHAPTER 1 OVERVIEW
Data processing (low speed)
A single QCPU controls an entire system.
Machine control (high speed)
(Processing speed:
1ms or less)
CPU module for
machine control
(Processing speed:
1 to several 10ms)
CPU module for
data processing
Machine control speed is further increased with
load distribution according to the control cycle.
Free
space
Used memory
Free
space
Free
space
Used
memory
Used
memory
Memory capacity can be expanded by
using more than one CPU module.
An additional CPU module can
expand the following:
Program memory
Device memory
(a) Distribution of processing
The overall system scan time can be reduced by distributing the high-load processing performed in a single
CPU module over multiple CPU modules.
(b) Distribution of memory
The memory capacity used for the entire system can be increased by distributing the memory areas over
multiple CPU modules.
1
(c) Distribution of functions
Programs can be developed easily by distributing the functions, for example, having different CPU modules
control production line A and production line B.
19
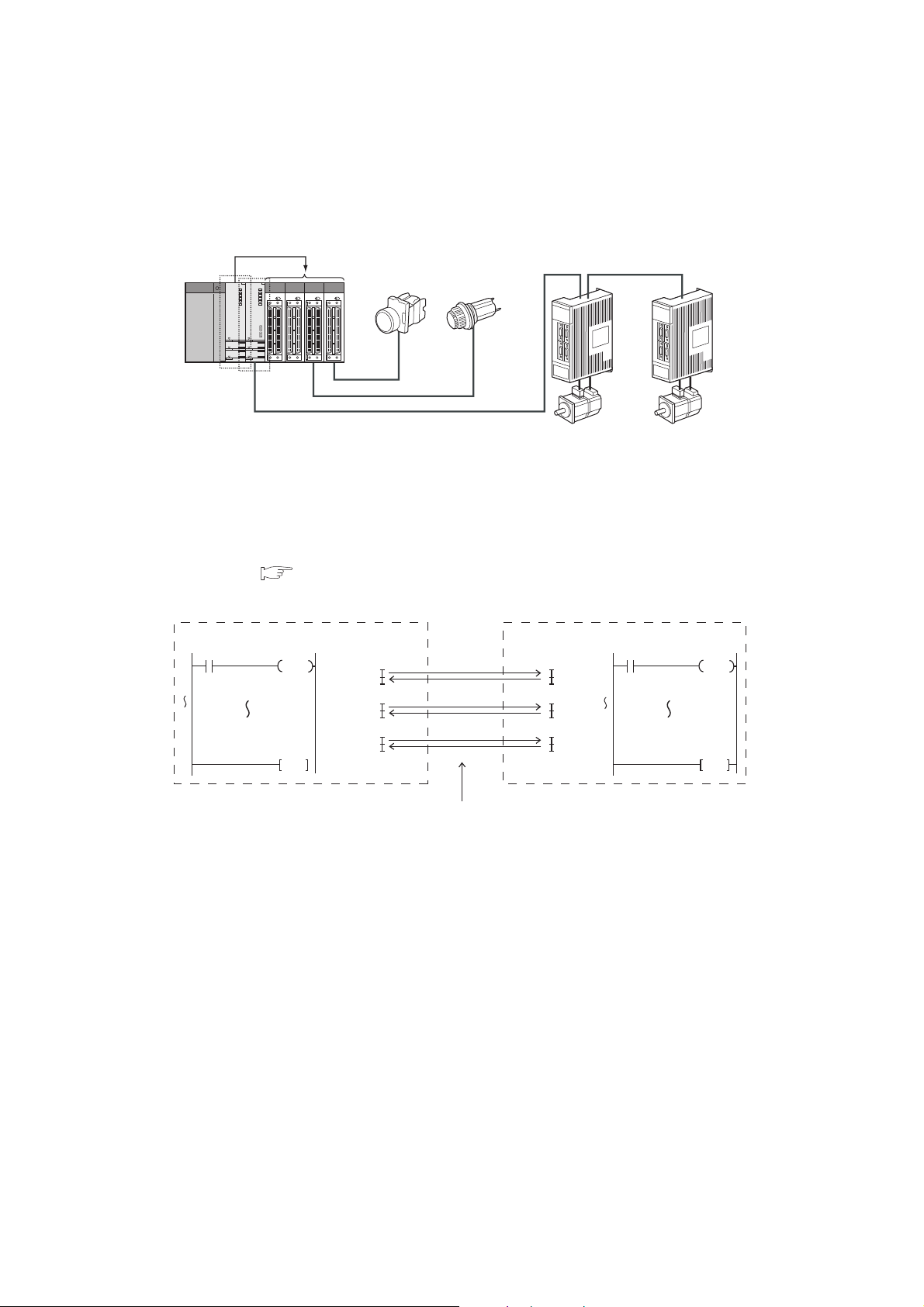
(2) Configuring sequence control and motion control systems on the same base
Control
Motion control
Sequence
control
SSCNET
Operation switch Operation status lamp
Servo
motor
Servo
motor
Servo
amplifier
Servo
amplifier
CPU No.1
Program Program
Multiple CPU high
speed transmission
Multiple CPU high
speed transmission
Data transfer
Data transfer
Data transfer
Data are transferred in parallel with programs.
X0
Y20
END
0
CPU No.2
X100
Y120
END
0
unit
In a multiple CPU system consisting of a QCPU and Motion CPU, sequence control and motion control can be
implemented together to achieve a high-level motion system.
Interaction with Motion CPUs for motion control is enhanced in Universal model QCPUs.
(a) High-speed data transfer between CPU modules
In a multiple CPU system, up to 14K-word data are transferred in parallel with programs between CPU
modules. This enables high-speed data transfer independent of scan time, and shortens the takt time of the
entire system. ( Page 150, Section 6.1.3)
20
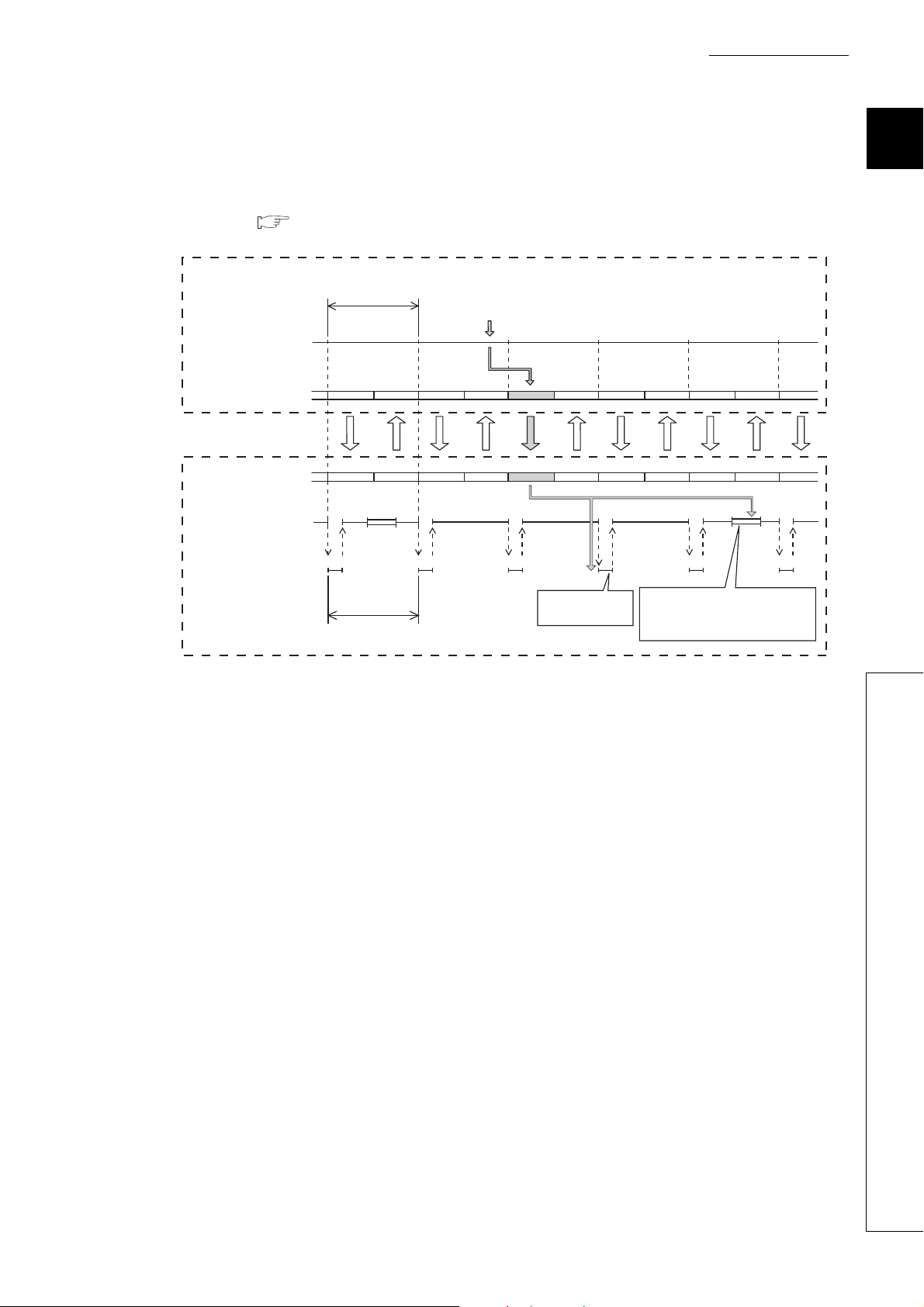
CHAPTER 1 OVERVIEW
Reading an imposition signal when
a multiple CPU synchronous
interrupt program is not used
Motion
CPU
Universal
model QCPU
Operation cycle
of a Motion CPU
Motion SFC program
Multiple CPU high
speed transmission
area
Multiple CPU high
speed transmission
Multiple CPU high
speed transmission
area
Multiple CPU
synchronous
interrupt program
Program
Reading an
imposition signal
Multiple CPU
high speed
transmission cycle
I45 IRET
END 0
I45 IRET I45 IRET
I45 IRET
END
I45 IRET
I45 IRET
Reading an
imposition signal
0
(b) Synchronous processing with a motion control
An interrupt program which is synchronized with the operation cycle of a Motion CPU (multiple CPU
synchronous interrupt program) can be executed. Command input or output from a Motion CPU can be
synchronized with the operation cycle of the Motion CPU, which enables high-speed data transfer independent
of scan time. ( Page 166, Section 6.4)
1
21

(c) Checking data send/receive timing between CPU modules
With the sampling trace function of Universal model QCPUs, the data communications timing with a Motion
CPU can be checked. Timing can also be checked between Universal model QCPUs.
The sampling trace function facilitates the processing for checking the data send/receive timing between CPU
modules, and reduces the time for debugging the multiple CPU system.
Sampling trace result display using a programming tool
The sampling trace of other CPU modules in the multiple CPU system can be executed, by specifying the following CPU
modules.
• Universal model QCPU (except the Q00UCPU, Q01UCPU, and Q02UCPU)
• Motion CPU (Q172DCPU(-S1), Q173DCPU(-S1), Q172DSCPU, or Q173DSCPU)
22

CHAPTER 1 OVERVIEW
(3) Data communications among CPU modules
The following data communications can be performed among CPU modules in a multiple CPU system.
(a) Transferring data among CPU modules
Data can be transferred among CPU modules by setting auto refresh using a programming tool.
( Page 122, Section 6.1.1 to Page 135, Section 6.1.2)
(b) Reading data from other CPU modules
Each CPU module can read data from other CPU modules whenever required using the following instructions.
( Page 150, Section 6.1.3)
• Read instruction from the CPU shared memory in another CPU module
• Cyclic transmission area device (U3En\G)
(c) Directing control to the Motion CPU
The QCPU can direct control to the Motion CPU using the following instruction. ( Page 160, Section 6.2)
• Motion dedicated instruction
(d) Reading/writing device data to/from the Motion CPU
The QCPU can read/write device data to/from the Motion CPU using the following instructions.
( Page 162, Section 6.3.1)
• Multiple CPU transmission dedicated instruction
• Multiple CPU high-speed transmission dedicated instruction
1
(e) Issuing events to the C Controller module or PC CPU module
The QCPU can issue events to the C Controller module or PC CPU module using the following instruction.
( Page 164, Section 6.3.2)
• Multiple CPU transmission dedicated instruction
The Universal model QCPU (except the Q00UCPU, Q01UCPU, and Q02UCPU) can execute the motion
dedicated instruction multiple times in one scan. Since the motion dedicated instruction can be executed
consecutively to different axis numbers, delay time of servo startup intervals can be shortened.
(f) Logging communication data among CPU modules
Communication data among CPU modules can be saved to an SD memory card in CSV format by logging the
cyclic transmission area device (U3EnG) using the data logging function of the CPU module.
The high-speed Universal model QCPU supports the data logging function.
( QnUDVCPU/LCPU User's Manual (Data Logging Function))
23
CHAPTER 2 CONCEPT OF MULTIPLE CPU
Ex.
1
3
SYSTEM
2.1 CPU Numbers
CPU numbers are assigned to identify CPU modules contained in a multiple CPU system.
A CPU module mounted in the CPU slot of a main base unit will be CPU No.1. CPU No.2, No.3, and No.4 will be
assigned sequentially to the right of CPU No.1.
CPU slot: CPU No.1
Slot 0: CPU No.2
Slot 1: CPU No.3
Slot 2: CPU No.4
CPU 0 1 2 3 4
Slot number
2
1
4
CPU number
(1) Available CPU numbers
Available CPU numbers differ depending on the QCPU used as CPU No.1 and the main base unit used.
( Page 31, CHAPTER 3)
When a Basic model QCPU is used as CPU No.1, the total number of mountable CPU modules is three
(CPU No.1 to No.3). However, when a slim type main base unit (Q3SB) or multiple CPU high-speed
main base unit (Q3
No.1 and No.2).
DB) is used, the number of mountable CPU modules is limited to one or two (CPU
24

(2) Uses of CPU numbers
Slot number
Control CPU setting
Controlled by CPU No.1.
Controlled by CPU No.2.
CPU01234567
11 2 1 1 1 1 222
CPU numbers are used for the following purposes.
CHAPTER 2 CONCEPT OF MULTIPLE CPU SYSTEM
(a) Setting control CPUs
CPU numbers are used to set a control CPU for each I/O module and intelligent function module.
Set control CPUs in PLC parameter ("I/O Assignment").
Project window [Parameter] [PLC Parameter] [I/O Assignment]
Set control CPUs.
2
2.1 CPU Numbers
25

(b) Specifying a connection target using a programming tool (personal computer)
1
3
<> K1 SD395
Set the CPU number to be compared.
SET F1
CPU numbers are used to specify a CPU module to which a programming tool is connected.
CPU 0 1 2
2
A programming tool
communicates with
CPU No.2.
4
Slot number
CPU number
Specify "PLC No.2".
(3) Checking the host CPU number
The host CPU number of a QCPU is stored in SD395 (Multiple CPU system information). A host CPU number
check program (refer to an example below) should be created. If created, the following status can be checked
easily.
• Incorrect mounting status of the QCPU
• Program writing status to other CPU modules using the programming tool
In the following program, if the QCPU to which the program is written is other than CPU No.1 (if the value in
SD395 is other than "1"), the annunciator (F1) turns on. Accordingly, the USER LED of the QCPU turns on.
The corresponding annunciator number is stored in SD62 (Annunciator number).
26

CHAPTER 2 CONCEPT OF MULTIPLE CPU SYSTEM
Ex.
2.2 I/O Number Assignment
A multiple CPU system uses the following two I/O numbers.
• I/O numbers used by CPU modules to communicate with I/O modules and intelligent function modules
( Page 27, Section 2.2.1)
• I/O numbers used by CPU modules to communicate with other CPU modules ( Page 30, Section 2.2.2)
2.2.1 I/O numbers of I/O modules and intelligent function modules
In the same way as in single CPU systems, I/O number "00H" is assigned to the I/O module or intelligent function
module mounted to the right of the CPU module. The subsequent I/O numbers are assigned sequentially to the right.
In multiple CPU systems, however, CPU modules may be mounted in slots 0 to 2 as well, and accordingly the start slot
of "00
" varies.
H
When two CPU modules are mounted
2
CPU01234567
I/O number: 00
H
Slot number
2.2 I/O Number Assignment
2.2.1 I/O numbers of I/O modules and intelligent function modules
27

● Some CPU modules occupy two or more slots. When this type of CPU module is used, the second slot and after are
treated as empty slots.
In the case of a PC CPU module, for example, the right slot of the occupied two slots is treated as an empty slot having
16 points. (An empty slot occupies 16 points by default.)
For this reason, the start I/O number of the module mounted on the right of the PC CPU module will be "10
".
H
CPU 0 1 2
Number of
CPU modules: 3
Note that the start I/O number can be changed to "00
Slot number
Empty slot:
00
H to 0FH occupied
" by setting "0 Point" to the number of points for the right slot of the
H
PC CPU module in PLC parameter ("I/O Assignment").
● The I/O numbers of the multiple CPU system can be checked on the System monitor window using a programming tool.
● In the same way as in single CPU systems, the position of I/O number "00
" can be changed to any slot in PLC
H
parameter ("I/O Assignment"). ( User's Manual (Function Explanation, Program Fundamentals) for the CPU module
used)
28

Ex.
Example of I/O number assignment
4th
extension
Q series power
supply module
CPU No.1
CPU No.2
CPU No.3
CPU No.4
1st
extension
2nd
extension
3rd
extension
Q312B (12 slots occupied)
Q612B (12 slots occupied)
Extension base unit .........When 32-point modules are mounted in each slot
Main base unit.........When 32-point modules are mounted in each slot
Q55B (5 slots occupied)
Q68B (8 slots occupied)
Q68B (8 slots occupied)
...... I/O number
...... Slot number
00 to 1F
20 to 3F
40 to 5F
60 to 7F
80 to 9F
A0 to BF
C0 to DF
E0 to FF
100 to 11F
120 to 13F
140 to 15F
160 to 17F
180 to 19F
1A0 to 1BF
1C0 to 1DF
1E0 to 1FF
200 to 21F
220 to 23F
240 to 25F
260 to 27F
280 to 29F
2A0 to 2BF
2C0 to 2DF
300 to 31F
320 to 33F
340 to 35F
360 to 37F
380 to 39F
3A0 to 3BF
3C0 to 3DF
3E0 to 3FF
400 to 41F
420 to 43F
4A0 to 4BF
4C0 to 4DF
4E0 to 4FF
500 to 51F
520 to 53F
440 to 45F
460 to 47F
480 to 49F
2E0 to 2FF
CPU 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23
24 25 26 27 28
29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36
45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52
5th
extension
Q68B (8 slots occupied)
540 to 55F
560 to 57F
580 to 59F
5A0 to 5BF
5C0 to 5DF
5E0 to 5FF
600 to 61F
620 to 63F
53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60
6th
extension
Q68B (8 slots occupied)
640 to 65F
660 to 67F
680 to 69F
6A0 to 6BF
6C0 to 6DF
6E0 to 6FF
700 to 71F
720 to 73F
61 62 63
7th
extension
Q65B (5 slots occupied)
740 to 75F
760 to 77F
780 to 79F
Use prohibited
Use prohibited
37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44
If modules are
mounted, an error
occurs.
CHAPTER 2 CONCEPT OF MULTIPLE CPU SYSTEM
2
2.2 I/O Number Assignment
2.2.1 I/O numbers of I/O modules and intelligent function modules
29

2.2.2 I/O numbers of CPU modules
In multiple CPU systems, I/O numbers are assigned to each CPU module to specify mounted CPU modules. The I/O
number for each CPU module is fixed at the corresponding slot, and cannot be changed in PLC parameter ("I/O
Assignment").
The following is the list of I/O numbers that can be assigned to CPU modules.
Item
Start I/O number
Available slots differ depending on the QCPU used as CPU No.1 and the main base unit used. ( Page 31,
CHAPTER 3)
CPU slot Slot 0 Slot 1 Slot 2
3E00
H
CPU module mounting position
3E10
H
3E20
H
(1) Uses of I/O numbers of CPU modules
The I/O numbers of CPU modules are used for the following purposes.
• Communications among CPU modules ( Page 116, CHAPTER 6)
• Specifying the communication-target CPU module under the MC protocol ( MELSEC-Q/L MELSEC
Communication Protocol Reference Manual)
3E30
H
30

CHAPTER 3 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
Remark
CHAPTER 3 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
In a multiple CPU system, QCPUs, motion CPUs, C Controller modules, and PC CPU modules can be mounted in the
CPU slot to slot 2 of the main base unit.
I/O modules and intelligent function modules are mounted to the right of CPU modules.
This chapter describes the system configurations according to the QCPU used as CPU No.1.
● For a multiple CPU system using a C Controller module as CPU No.1, refer to the manual for the C Controller module
used.
● For PC CPU modules, contact CONTEC Co., Ltd.
http://www.contec.com/
3
31
3.1 System Using Basic Model QCPU as CPU No.1
This section describes the system configuration using a Basic model QCPU as CPU No.1.
3.1.1 Available CPU modules, base units, power supply modules,
and extension cables
Available CPU modules and the number of mountable modules differ depending on the main base unit used.
(1) When a main base unit (Q3B) is used
(a) Available modules, the number of extension base units, and the number of
mountable modules
Item Description
3 CPU modules
Number of CPU
modules
Applicable CPU
*1
module
Maximum number of
extension base units
Maximum number of
mountable I/O
modules
Applicable main base
unit
Applicable extension
base unit
Applicable extension
cable
Applicable power
supply module
*1 For the CPU modules that can be combined and their mounting positions, refer to Page 37, Section 3.1.2.
*2 When using a Motion CPU, install operating system software on the CPU module. For models and versions of the
CPU No.1 (Basic model QCPU)
CPU No.2 (Motion CPU)
CPU No.3 (C Controller module or PC CPU module)
Basic model QCPU Q00CPU, Q01CPU Function version B or later
Motion CPU
C Controller module
PC CPU module
Type requiring no power supply
module (Q series)
Type requiring power supply module
(Q series)
operating system, refer to the manual for the Motion CPU used.
*2
QC05B, QC06B, QC12B, QC30B, QC50B, QC100B
Q61P-A1, Q61P-A2, Q61P, Q61P-D, Q62P, Q63P, Q64P, Q64PN
Q172CPUN(-T), Q173CPUN(-T),
Q172HCPU(-T), Q173HCPU(-T)
Q06CCPU-V, Q06CCPU-V-B,
Q12DCCPU-V, Q24DHCCPU-V,
Q24DHCCPU-LS
PPC-CPU686(MS)-64,
PPC-CPU686(MS)-128,
PPC-CPU852(MS)-512
4 extension base units
25 - (Number of CPU modules)
Q33B, Q35B, Q38B, Q312B
Q52B, Q55B
Q63B, Q65B, Q68B, Q612B
Manual for the Motion CPU
used
No function version restriction
Manual for the PC CPU
module used
32

CHAPTER 3 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
(b) Precautions
• If I/O modules are mounted exceeding the maximum number, "SP.UNIT LAY ERR" (error code: 2124)
occurs.
• "Number of CPU modules" indicates the number set in "No. of PLC" of PLC parameter ("Multiple CPU
Setting").
• When a C Controller module which occupies three slots is used, the maximum number of mountable I/O
modules will be two smaller than the number defined in the table on Page 32, Section 3.1.1 (1) (a).
• A PC CPU module occupies two slots. When this module is used, the maximum number of mountable I/O
modules will be one smaller than the number defined in the table on Page 32, Section 3.1.1 (1) (a).
3
3.1 System Using Basic Model QCPU as CPU No.1
3.1.1 Available CPU modules, base units, power supply modules, and extension cables
33

(2) When a redundant power main base unit (Q3RB) is used
(a) Available modules, the number of extension base units, and the number of
mountable modules
Item Description
Number of CPU
modules
Applicable CPU
*1
module
Maximum number of
extension base units
Maximum number of
mountable I/O
modules
Applicable main base
unit
Applicable extension
base unit
Applicable extension
cable
Applicable power
supply module
CPU No.1 (Basic model QCPU)
CPU No.2 (C Controller module)
Basic model QCPU Q00CPU, Q01CPU Function version B or later
C Controller module
Type requiring no power supply
module (Q series)
Redundant power extension base unit Q68RB
QC05B, QC06B, QC12B, QC30B, QC50B, QC100B
(The Q63RP and Q64RP can be mounted on the same redundant power supply base unit.)
2 CPU modules
Q24DHCCPU-V,
Q24DHCCPU-LS
4 extension base units
25 - (Number of CPU modules)
Q38RB
Q52B, Q55B
Q63RP, Q64RP
No function version restriction
(b) Precautions
• If I/O modules are mounted exceeding the maximum number, "SP.UNIT LAY ERR" (error code: 2124)
occurs.
• "Number of CPU modules" indicates the number set in "No. of PLC" of PLC parameter ("Multiple CPU
Setting").
• When a C Controller module which occupies three slots is used, the maximum number of mountable I/O
modules will be two smaller than the number defined in the table on Page 34, Section 3.1.1 (2) (a).
34

(3) When a slim type main base unit (Q3SB) is used
(a) Available modules, the number of extension base units, and the number of
mountable modules
Item Description
Number of CPU
modules
Applicable CPU
*1
module
Maximum number of
extension base units
Maximum number of
mountable I/O
modules
Applicable main base
unit
Applicable power
supply module
CPU No.1 (Basic model QCPU)
CPU No.2 (C Controller module)
Basic model QCPU Q00CPU, Q01CPU Function version B or later
C Controller module
Q32SB 1
Q33SB 2
Q35SB 4
Q06CCPU-V, Q06CCPU-V-B,
Q12DCCPU-V
2 CPU modules
Extension not allowed
Q32SB, Q33SB, Q35SB
CHAPTER 3 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
3
No function version restriction
Q61SP
(b) Precautions
Slim type main base units do not have an extension cable connector. Therefore, no extension base unit or GOT
can be bus-connected.
3.1 System Using Basic Model QCPU as CPU No.1
3.1.1 Available CPU modules, base units, power supply modules, and extension cables
35

(4) When a multiple CPU high speed main base unit (Q3DB) is used
(a) Available modules, the number of extension base units, and the number of
mountable modules
Item Description
Number of CPU
modules
Applicable CPU
*1
module
Maximum number of
extension base units
Maximum number of
mountable I/O
modules
Applicable main base
unit
Applicable extension
base unit
Applicable extension
cable
Applicable power
supply module
*1 For the CPU modules that can be combined and their mounting positions, refer to Page 37, Section 3.1.2.
CPU No.1 (Basic model QCPU)
CPU No.2 (C Controller module or PC CPU module)
Basic model QCPU Q00CPU, Q01CPU Function version B or later
Q06CCPU-V, Q06CCPU-V-B,
C Controller module
PC CPU module
Type requiring no power supply
module (Q series)
Type requiring power supply module
(Q series)
QC05B, QC06B, QC12B, QC30B, QC50B, QC100B
Q61P-A1, Q61P-A2, Q61P, Q61P-D, Q62P, Q63P, Q64P, Q64PN
Q12DCCPU-V, Q24DHCCPU-V,
Q24DHCCPU-LS
PPC-CPU686(MS)-64,
PPC-CPU686(MS)-128,
PPC-CPU852(MS)-512
Q52B, Q55B
Q63B, Q65B, Q68B, Q612B
2 CPU modules
4 extension base units
25 - (Number of CPU modules)
Q35DB, Q38DB, Q312DB
No function version restriction
Manual for the PC CPU
module used
36
(b) Precautions
• If I/O modules are mounted exceeding the maximum number, "SP.UNIT LAY ERR" (error code: 2124)
occurs.
• "Number of CPU modules" indicates the number set in "No. of PLC" of PLC parameter ("Multiple CPU
Setting").
• When a C Controller module which occupies three slots is used, the maximum number of mountable I/O
modules will be two smaller than the number defined in the table on Page 36, Section 3.1.1 (4) (a).
• A PC CPU module occupies two slots. When this module is used, the maximum number of mountable I/O
modules will be one smaller than the number defined in the table on Page 36, Section 3.1.1 (4) (a).

CHAPTER 3 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
B
B : Basic model QCPU
: Motion CPU
: C Controller module
: PC CPU module
CPU No.1 CPU No.2 CPU No.3
P
P
P
C
C
C
M
M
3.1.2 CPU module combinations and mounting positions
This section describes the combinations and mounting positions of CPU modules when a Basic model QCPU is used
as CPU No.1.
Note that the CPU modules that can be mounted differ depending on the main base unit used. ( Page 32, Section
3.1.1)
(1) Combinations
3
High
Performance
CPU No.1
Basic model
QCPU
model QCPU,
Process CPU,
Universal
model QCPU
Cannot be used
together.
*1 A C Controller module and a PC CPU module cannot be mounted on the same main base unit.
*2 A C Controller module (Q12DCCPU-V, Q24DHCCPU-V, or Q24DHCCPU-LS) and a Motion CPU (Q172CPUN(-T),
Q173CPUN(-T), Q172HCPU(-T), or Q173HCPU(-T)) cannot be mounted on the same main base unit.
(2) Mounting positions
The following shows the possible combinations of mounting positions of CPU modules in a multiple CPU system.
Number of CPU modules that can be mounted as CPU No.2 or others
Motion CPU
Q172CPUN(-T),
Q173CPUN(-T),
Q172HCPU(-T),
Q173HCPU(-T)
0 to 1
Q172DCPU(-S1),
Q173DCPU(-S1),
Q172DSCPU,
*2
Q173DSCPU
Cannot be used
together.
C Controller module
Q06CCPU-V,
Q06CCPU-V-B,
Q12DCCPU-V,
Q24DHCCPU-V
0 to 1 0 to 1 3
*1*2
PC CPU module
PPC-CPU686(MS)-64,
PPC-CPU686(MS)-128,
PPC-CPU852(MS)-512
*1
Maximum
number of
mountable
modules
(including
CPU No.1)
3.1 System Using Basic Model QCPU as CPU No.1
3.1.2 CPU module combinations and mounting positions
(a) Basic model QCPU
Only one Basic model QCPU can be mounted in the CPU slot (the slot on the right of the power supply module)
of the main base unit.
(b) Motion CPU
Only one Motion CPU can be mounted in slot 0 on the right of the Basic model QCPU. It cannot be mounted in
a slot other than slot 0.
37

(c) C Controller module or PC CPU module
Ex.
Ex.
Ex.
CPU 0 1 2
Slot number
Power supply
module
Basic model
QCPU
PC CPU
module
Motion CPU
CPU 0 1 2 CPU 0 1 2
Added Motion CPU
Slot number Slot number
Power supply
module
Basic model
QCPU
PLC (Empty)
Power supply
module
Basic model
QCPU
Motion CPU
CPU 0 1 2 CPU 0 1 2
Added PC CPU module
Slot number Slot number
Power supply
module
Basic model
QCPU
Motion CPU
PLC (Empty)
Power supply
module
Basic model
QCPU
Motion CPU
PC CPU
module
CPU 0 1 2 CPU 0 1 2
Added Motion CPU
Slot number Slot number
Power supply
module
Basic model
QCPU
PLC (Empty)
PC CPU
module
Power supply
module
Basic model
QCPU
Motion CPU
PC CPU
module
Either a C Controller module or PC CPU module can be mounted on the extreme right of the other CPU
module(s). No CPU module can be mounted on the right of the C Controller module or PC CPU module.
(d) Empty slot setting
Empty slots can be reserved for future addition of CPU modules. Set the number of CPU modules including
empty slots in "No. of PLC" of PLC parameter ("Multiple CPU Setting"). Then, set "PLC (Empty)" to the type of
a target slot in PLC parameter ("I/O Assignment").
Adding a Motion CPU in slot 0 in the future
Adding a PC CPU module in slot 1 in the future
Setting "PLC (Empty)" between CPU modules
38

CHAPTER 3 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
● When a Basic model QCPU is used, "PLC (Empty)" can be set between CPU modules. This is useful when adding a
Motion CPU to the system where a Basic model QCPU and a C Controller module or PC CPU module are used. No
program modification is required because the CPU number of the C Controller module or PC CPU module does not need
to be changed even after the new module is added.
● For a CPU module that occupies two slots or more, secure as many empty slots as needed for the module.
3
3.1 System Using Basic Model QCPU as CPU No.1
3.1.2 CPU module combinations and mounting positions
39

3.1.3 Available I/O modules and intelligent function modules
Remark
This section describes I/O modules and intelligent function modules that can be used.
(1) I/O modules and interrupt module
I/O modules (QX and QY) and interrupt module (QI60) can be used. Any CPU module can be set as a control
CPU.
(2) Intelligent function modules
Intelligent function modules with function version B or later can be used. Any CPU module can be set as a control
CPU.
Write parameters of each intelligent function module to the CPU module to be controlled.
The following modules can be used even if their function version is not B or later.
Module that can be used
even if its function version is not B or later
High-speed counter module (QD62, QD62D, QD62E)
Intelligent function modules with function version A (except high-speed counter modules (QD62, QD62D, and QD62E)) can
be used in the multiple CPU system only when CPU No.1 is set as a control CPU.
• External devices can access only the control CPU (CPU No.1) via a serial communication module.
• External devices cannot access CPU modules other than the control CPU (CPU No.1) via a MELSECNET/H
module or serial communication module.
• If any of CPU No.2 to No.4 is set as a control CPU, "SP.UNIT VER.ERR" (error code: 2150) will occur and the
multiple CPU system will not start up.
Modules with function version A can be used.
Any CPU module can be set as a control CPU.
Description
(3) Number of mountable modules
Refer to Page 68, Section 3.5.
(4) Access ranges of controlled and non-controlled modules
Each CPU module can access non-controlled modules by setting "I/O Sharing When Using Multiple CPUs" in
PLC parameter ("Multiple CPU Setting"). ( Page 104, Section 5.2)
40
If all of the following conditions are met, use a MELSECNET/H module with a serial number (first five digits) of "10042" or
later.
• A multiple CPU system containing a Built-in Ethernet port QCPU is configured.
• A programming tool or GOT is connected to an Ethernet port of the Built-in Ethernet port QCPU.
• A programming tool or GOT accesses another station via a MELSECNET/H module controlled by a CPU module
other than the control CPU.
• The access target on another station is an A/QnA series CPU module.

CHAPTER 3 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
3.2 System Using High Performance Model QCPU or
Process CPU as CPU No.1
This section describes the system configuration using a High Performance model QCPU or Process CPU as CPU
No.1.
3.2.1 Available CPU modules, base units, power supply modules,
and extension cables
Available CPU modules and the number of mountable modules differ depending on the main base unit used.
(1) When a main base unit (Q3B) is used
(a) Available modules, the number of extension bases units, and the number of
mountable modules
3
Item Description
Number of CPU
modules
Applicable CPU
*1
module
Applicable CPU
*1
module
Maximum number of
extension base units
High Performance model QCPU
Process CPU
Universal model QCPU
Motion CPU
C Controller module
PC CPU module
*2
4 CPU modules
• Function version B
Q02(H)CPU, Q06HCPU, Q12HCPU,
Q25HCPU
Q02PHCPU, Q06PHCPU, Q12PHCPU,
Q25PHCPU
Q03UD(E)CPU, Q03UDVCPU,
Q04UD(E)HCPU, Q04UDVCPU,
Q06UD(E)HCPU, Q06UDVCPU,
Q10UD(E)HCPU, Q13UD(E)HCPU,
Q13UDVCPU, Q20UD(E)HCPU,
Q26UD(E)HCPU, Q26UDVCPU,
Q50UDEHCPU, Q100UDEHCPU
Q172CPUN
Q172HCPU
Q06CCPU-V, Q06CCPU-V-B
Q12DCCPU-V
Q24DHCCPU-V
Q24DHCCPU-LS No function version restriction
PPC-CPU686(MS)-64,
PPC-CPU686(MS)-128,
PPC-CPU852(MS)-512
(-T)
, Q173CPUN
(-T)
, Q173HCPU
7 extension base units
(-T)
(-T)
,
• Function version B with a serial number
(first five digits) of "03051" or later when
used as CPU No.1 and with a PC CPU
module
No function version restriction
No function version restriction
Manual for the Motion CPU used
• Serial number (first five digits) of "10012"
or later when used with the
Q03UDECPU, Q04UDEHCPU,
Q06UDEHCPU, Q13UD(E)HCPU, or
Q26UD(E)HCPU
• Serial number (first five digits) of "10102"
or later when used with the
Q10UD(E)HCPU, Q20UD(E)HCPU,
Q50UDEHCPU, or Q100UDEHCPU
• Cannot be used with the QnUDVCPU.
Serial number (first five digits) of "14122" or
later when used with the QnUDVCPU
Serial number (first five digits) of "14122" or
later when used with the QnUDVCPU
Manual for the PC CPU module
used
Cannot be used with the QnUDVCPU.
3.2 System Using High Performance Model QCPU or Process CPU as CPU No.1
3.2.1 Available CPU modules, base units, power supply modules, and extension cables
41

Item Description
Maximum number of
mountable I/O modules
Applicable main base
unit
Applicable extension
base unit
Applicable extension
cable
Applicable power supply
module
*1 For the CPU modules that can be combined and their mounting positions, refer to Page 47, Section 3.2.2.
*2 When using a Motion CPU, install operating system software on the CPU module. For models and versions of the
*3 These units cannot be used in a multiple CPU system including a Process CPU. ( Page 188, Appendix 3)
*4 Since the QA1S51B does not have an extension cable connector (OUT), it cannot be used with the QA6B or
*5 When the QA1S6B is used as an extension base unit, the QA6ADP+A5B/A6B cannot be connected.
*6 When the QA1S6ADP+A1S5B/A1S6B is used, the maximum number of extension base units is 1, and the maximum
65 - (Number of CPU modules)
Q33B, Q35B, Q38B, Q312B
Type requiring no power supply module
(Q series)
Type requiring power supply module (Q
series)
Type requiring no power supply module
(AnS series)
Type requiring power supply module
(AnS series)
Type requiring no power supply module
(A series)
Type requiring power supply module (A
series)
Power supply module (Q series) Q61P-A1, Q61P-A2, Q61P, Q61P-D, Q62P, Q63P, Q64P, Q64PN
Power supply module (AnS series)
Power supply module (A series)
*3*4
*3*5
*3
*3
*3
Q52B, Q55B
Q63B, Q65B, Q68B, Q612B
QA1S51B, QA1S6ADP+A1S5B
QA1S65B, QA1S68B, QA1S6ADP+A1S6B
QA6ADP+A5B
QA65B, QA68B, QA6ADP+A6B
QC05B, QC06B, QC12B, QC30B, QC50B, QC100B
*3
A1S61PN, A1S62PN, A1S63P
A61P, A61PN, A62P, A63P, A61PEU, A62PEU
*6
*6
operating system, refer to the manual for the Motion CPU used.
QA6ADP+A5B/A6B.
number of I/O modules that can be mounted is 20 minus the number of CPU modules. When the QA1S6ADPS1+A1S5B/A1S6B is used, the maximum number of extension base units is 3, and the maximum number of I/O
modules that can be mounted is 36 minus the number of CPU modules.
(b) Precautions
• Extension base units, QA1S5B, QA1S6B, QA1S6ADP+A1S5B/A1S6B, QA6B, and
QA6ADP+A5
CPU of AnS/A series modules. ( Page 188, Appendix 3)
• If I/O modules are mounted exceeding the maximum number, "SP.UNIT LAY ERR" (error code: 2124)
occurs.
• "Number of CPU modules" indicates the number set in "No. of PLC" of PLC parameter ("Multiple CPU
Setting").
• When a C Controller module which occupies three slots is used, the maximum number of mountable I/O
modules will be two smaller than the number defined in the table on Page 41, Section 3.2.1 (1) (a).
• A PC CPU module occupies two slots. When this module is used, the maximum number of mountable I/O
modules will be one smaller than the number defined in the table on Page 41, Section 3.2.1 (1) (a).
B/A6B, can be connected when a High Performance model QCPU is set as the control
42

(2) When a redundant power main base unit (Q3RB) is used
(a) Available modules, the number of extension base units, and the number of
mountable modules
Item Description
Number of CPU
modules
Applicable CPU
*1
module
Maximum number of
extension base units
Maximum number of
mountable I/O modules
Applicable main base
unit
Applicable extension
base unit
Applicable extension
cable
Applicable power supply
module
*1 For the CPU modules that can be combined and their mounting positions, refer to Page 47, Section 3.2.2.
High Performance model QCPU
Process CPU
Universal model QCPU
C Controller module
Type requiring no power supply module
(Q series)
Redundant power extension base unit Q68RB
(The Q63RP and Q64RP can be mounted on the same redundant power supply base unit.)
Q02(H)CPU, Q06HCPU, Q12HCPU,
Q25HCPU
Q02PHCPU, Q06PHCPU, Q12PHCPU,
Q25PHCPU
Q03UD(E)CPU, Q03UDVCPU,
Q04UD(E)HCPU, Q04UDVCPU,
Q06UD(E)HCPU, Q06UDVCPU,
Q10UD(E)HCPU, Q13UD(E)HCPU,
Q13UDVCPU, Q20UD(E)HCPU,
Q26UD(E)HCPU, Q26UDVCPU,
Q50UDEHCPU, Q100UDEHCPU
Q24DHCCPU-V
Q24DHCCPU-LS No function version restriction
Q52B, Q55B
QC05B, QC06B, QC12B, QC30B, QC50B, QC100B
4 CPU modules
7 extension base units
65 - (Number of CPU modules)
Q38RB
Q63RP, Q64RP
CHAPTER 3 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
Function version B
No function version restriction
No function version restriction
Serial number (first five digits) of "14122" or
later when used with the QnUDVCPU
3
3.2 System Using High Performance Model QCPU or Process CPU as CPU No.1
3.2.1 Available CPU modules, base units, power supply modules, and extension cables
(b) Precautions
• If I/O modules are mounted exceeding the maximum number, "SP.UNIT LAY ERR" (error code: 2124)
occurs.
• "Number of CPU modules" indicates the number set in "No. of PLC" of PLC parameter ("Multiple CPU
Setting").
• When a C Controller module which occupies three slots is used, the maximum number of mountable I/O
modules will be two smaller than the number defined in the table on Page 43, Section 3.2.1 (2) (a).
43

(3) When a slim type main base unit (Q3SB) is used
(a) Available modules, the number of extension base units, and the number of
mountable modules
Item Description
Number of CPU
modules
Applicable CPU
*1
module
Maximum number of
extension base units
Maximum number of
mountable I/O modules
Applicable main base
unit
Applicable power supply
module
*1 For the CPU modules that can be combined and their mounting positions, refer to Page 47, Section 3.2.2.
High Performance model QCPU
Universal model QCPU
C Controller module
Q32SB 3 - (Number of CPU modules)
Q33SB 4 - (Number of CPU modules)
Q35SB 6 - (Number of CPU modules)
Q02(H)CPU, Q06HCPU, Q12HCPU,
Q25HCPU
Q03UD(E)CPU, Q03UDVCPU,
Q04UD(E)HCPU, Q04UDVCPU,
Q06UD(E)HCPU, Q06UDVCPU,
Q10UD(E)HCPU, Q13UD(E)HCPU,
Q13UDVCPU, Q20UD(E)HCPU,
Q26UD(E)HCPU, Q26UDVCPU,
Q50UDEHCPU, Q100UDEHCPU
Q06CCPU-V, Q06CCPU-V-B
Q12DCCPU-V
3 CPU modules
Extension not allowed
Q32SB, Q33SB, Q35SB
Function version B
No function version restriction
• Serial number (first five digits) of "10012"
or later when used with the
Q03UDECPU, Q04UDEHCPU,
Q06UDEHCPU, Q13UD(E)HCPU, or
Q26UD(E)HCPU
• Serial number (first five digits) of "10102"
or later when used with the
Q10UD(E)HCPU, Q20UD(E)HCPU,
Q50UDEHCPU, or Q100UDEHCPU
• Cannot be used with the QnUDVCPU.
Serial number (first five digits) of "14122" or
later when used with the QnUDVCPU
Q61SP
44
(b) Precautions
• Slim type main base units do not have an extension cable connector. Therefore, no extension base unit or
GOT can be bus-connected.
• Four CPU modules cannot be mounted because the power consumption of the CPU modules exceeds the
rated output current of the power supply module (Q61SP).
If a C Controller module is used, three CPU modules cannot be mounted.
• "Number of CPU modules" indicates the number set in "No. of PLC" of PLC parameter ("Multiple CPU
Setting").

CHAPTER 3 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
(4) When a multiple CPU high speed main base unit (Q3DB) is used
(a) Available modules, the number of extension base units, and the number of
mountable modules
Item Description
Number of CPU
modules
Applicable CPU
*1
module
Maximum number of
extension base units
Maximum number of
mountable I/O modules
Applicable main base
unit
Applicable extension
base unit
Applicable extension
cable
Applicable power supply
module
*1 For the CPU modules that can be combined and their mounting positions, refer to Page 47, Section 3.2.2.
High Performance model QCPU
Process CPU
Universal model QCPU
C Controller module
PC CPU module
Type requiring no power supply module (Q
series)
Type requiring power supply module (Q
series)
QC05B, QC06B, QC12B, QC30B, QC50B, QC100B
Q61P-A1, Q61P-A2, Q61P, Q61P-D, Q62P, Q63P, Q64P, Q64PN
Q02(H)CPU, Q06HCPU, Q12HCPU,
Q25HCPU
Q02PHCPU, Q06PHCPU,
Q12PHCPU, Q25PHCPU
Q03UD(E)CPU, Q03UDVCPU,
Q04UD(E)HCPU, Q04UDVCPU,
Q06UD(E)HCPU, Q06UDVCPU,
Q10UD(E)HCPU, Q13UD(E)HCPU,
Q13UDVCPU, Q20UD(E)HCPU,
Q26UD(E)HCPU, Q26UDVCPU,
Q50UDEHCPU, Q100UDEHCPU
Q06CCPU-V, Q06CCPU-V-B
Q12DCCPU-V
Q24DHCCPU-V
Q24DHCCPU-LS No function version restriction
PPC-CPU686(MS)-64,
PPC-CPU686(MS)-128,
PPC-CPU852(MS)-512
Q52B, Q55B
Q63B, Q65B, Q68B, Q612B
4 CPU modules
• Function version B
• Function version B with a serial number
(first five digits) of "03051" or later when a
module is used as CPU No.1 and used
with a PC CPU module
No function version restriction
No function version restriction
• Serial number (first five digits) of "10012"
or later when used with the Q03UDECPU,
Q04UDEHCPU, Q06UDEHCPU,
Q13UD(E)HCPU, or Q26UD(E)HCPU
• Serial number (first five digits) of "10102"
or later when used with the
Q10UD(E)HCPU, Q20UD(E)HCPU,
Q50UDEHCPU, or Q100UDEHCPU
• Cannot be used with the QnUDVCPU.
Serial number (first five digits) of "14122" or
later when used with the QnUDVCPU
Serial number (first five digits) of "14122" or
later when used with the QnUDVCPU
Cannot be used with the QnUDVCPU.
7 extension base units
65 - (Number of CPU modules)
Q35DB, Q38DB, Q312DB
Manual for the PC CPU module used
3
3.2 System Using High Performance Model QCPU or Process CPU as CPU No.1
3.2.1 Available CPU modules, base units, power supply modules, and extension cables
45

(b) Precautions
• If I/O modules are mounted exceeding the maximum number, "SP.UNIT LAY ERR" (error code: 2124)
occurs.
• "Number of CPU modules" indicates the number set in "No. of PLC" of PLC parameter ("Multiple CPU
Setting").
• A C Controller module (Q24DHCCPU-V) occupies three slots. When this module is used, the maximum
number of mountable I/O modules will be two smaller than the number defined in the table on Page 45,
Section 3.2.1 (4) (a).
• When a C Controller module which occupies three slots is used, the maximum number of mountable I/O
modules will be two smaller than the number defined in the table on Page 45, Section 3.2.1 (4) (a).
46

CHAPTER 3 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
3.2.2 CPU module combinations and mounting positions
This section describes the combinations and mounting positions of CPU modules when a High Performance model
QCPU or Process CPU is used as CPU No.1.
Note that the CPU modules that can be mounted differ depending on the main base unit used. ( Page 41, Section
3.2.1)
(1) Combinations
Number of CPUs that can be mounted as CPU No.2 or others
High
CPU No.1
High
Performance
model QCPU
Process CPU 0 to 3 0 to 3
Performance
model QCPU,
Process CPU,
Universal model
*1*2*5*6*7
QCPU
0 to 3 0 to 3
Q172CPUN(-T),
Q173CPUN(-T),
Q172HCPU(-T),
Q173HCPU(-T)
*1 The Q00UCPU, Q01UCPU, and Q02UCPU can be used only as CPU No.1.
*2 A Universal model CPU (except the Q00UCPU, Q01UCPU, and Q02UCPU) and a Motion CPU (Q172CPUN(-T),
Q173CPUN(-T), Q172HCPU(-T), or Q173HCPU(-T)) cannot be mounted on the same main base unit.
*3 A C Controller module and a PC CPU module cannot be mounted on the same main base unit.
*4 A C Controller module (Q12DCCPU-V, Q24DHCCPU-V, or Q24DHCCPU-LS) and a Motion CPU (Q172CPUN(-T),
Q173CPUN(-T), Q172HCPU(-T), or Q173HCPU(-T)) cannot be mounted on the same main base unit.
*5 A Universal model QCPU and a PC CPU module (PPC-CPU686(MS)-64 or PPC-CPU686(MS)-128) cannot be used
together. When a Universal model QCPU is used, use the PPC-CPU852(MS)-512.
*6 A QnUDVCPU and a C Controller module (Q06CCPU-V or Q06CCPU-V-B) cannot be mounted on the same main base
unit.
*7 A QnUDVCPU and a PC CPU module cannot be mounted on the same main base unit.
Motion CPU
Q172DCPU(-S1),
Q173DCPU(-S1),
*2*4
Q172DSCPU,
Q173DSCPU
Cannot be used
together.
Cannot be used
together.
C Controller module
Q06CCPU-V,
Q06CCPU-V-B,
Q12DCCPU-V
0 to 3 0 to 1 0 to 1 4
0 to 3 0 to 1 0 to 1 4
*3*4*6
Q24DHC
CPU-V,
Q24DHC
CPU-LS
PC CPU module
PPCCPU686
(MS)-64,
PPCCPU686
(MS)-128
*3*5*7
PPC-
CPU852
(MS)-512
Maximum
number of
mountable
modules
(including CPU
No.1)
3
3.2 System Using High Performance Model QCPU or Process CPU as CPU No.1
3.2.2 CPU module combinations and mounting positions
47

(2) Mounting positions
Q : QCPU
*1
: Motion CPU
: C Controller module
: PC CPU module
CPU No.1 CPU No.2 CPU No.3 CPU No.4
P
C
M
QQQQ
P
C
P
C
C
P
C
MM
P
P
C
C
CC
C
P
C
MMM
M
The following shows the possible combinations of mounting positions of CPU modules in a multiple CPU system.
*1 The QCPU used as CPU No.1 indicates a High Performance model QCPU or Process CPU.
The QCPU used as CPU No.2 or later indicates a High Performance model QCPU, Process CPU, or Universal model
QCPU (except the Q00UCPU, Q01UCPU, and Q02UCPU).
48

CHAPTER 3 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
CPU 0 1 2 CPU 0 1 2CPU 0 1 2
Slot numberSlot number
Power supply
module
QCPU
QCPU
Motion CPU
Motion CPU
Power supply
module
QCPU
Motion CPU
QCPU
Motion CPU
Correct mounting positions Incorrect mounting positions
(a) High Performance model QCPU or Process CPU
Up to four High Performance model QCPUs and/or Process CPUs can be mounted in the CPU slot (the slot on
the right of the power supply module) to slot 2 of the main base unit.
(b) Universal model QCPU
Up to three Universal model QCPUs can be mounted in slot 0 to slot 2 of the main base unit.
(c) Motion CPU
Up to three Motion CPUs can be mounted in the slot on the right of the High Performance model QCPU or
Process CPU to slot 2 of the main base unit. Only a Motion CPU, C Controller module, or PC CPU module can
be mounted on the right of the Motion CPU.
(d) C Controller module
Up to three C Controller modules can be mounted in slot 0 to slot 2 of the main base unit. For a C Controller
module which occupies three slots, only one module can be mounted.
Note that only a C Controller module can be mounted on the right of the C Controller module.
(e) PC CPU module
Only one PC CPU module can be mounted on the rightmost slot available for CPU modules. No CPU module
can be mounted on the right of the PC CPU module.
3
3.2 System Using High Performance Model QCPU or Process CPU as CPU No.1
3.2.2 CPU module combinations and mounting positions
CPU 0 1 2
PC CPU
Power supply
module
QCPU
module
Slot number
Motion CPU
49

(f) Empty slot setting
Ex.
CPU 0 1 2
Power supply
module
QCPU
QCPU
PLC (empty)
Motion CPU
CPU 0 1 2
Power supply
module
Motion CPU
PLC (empty)
QCPU
QCPU
Slot numberSlot number
Incorrect mounting positionsCorrect mounting positions
CPU01234
Add a CPU module.
Slot number
Set "PLC (Empty)" to slot 2.
Keep slot 3 empty.
Move to the right.
Power supply
module
High Performance
model QCPU
Motion CPU
Motion CPU
PC CPU
module
PC CPU
module
(Empty)
Input module
Power supply
module
High Performance
model QCPU
Motion CPU
Motion CPU
Input module
CPU 0 1 2 3 4
Slot number
Empty slots can be reserved for future addition of CPU modules. Set the number of CPU modules including
empty slots in "No. of PLC" of PLC parameter ("Multiple CPU Setting"). Then, set "PLC (Empty)" to the type of
a target slot from the right in PLC parameter ("I/O Assignment").
Setting the number of CPU modules to "4" in PLC parameter and mounting two High Performance model
QCPUs and one Motion CPU
Mount the High Performance model QCPUs in the CPU slot and slot 0, and the Motion CPU in slot 1, and
set "PLC (Empty)" to slot 2.
When a High Performance model QCPU or Process CPU is used, "PLC (Empty)" cannot be set between CPU modules. To
add a CPU module to the system where a C Controller module or PC CPU module is used, move the C Controller module or
PC CPU module to the right to allow addition of a CPU module.
50

CHAPTER 3 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
3.2.3 Available I/O modules and intelligent function modules
This section describes the I/O modules and intelligent function modules that can be used.
(1) I/O modules, interrupt modules, and intelligent function modules
Refer to the system configuration using a Basic model QCPU as CPU No.1. ( Page 40, Section 3.1.3 (1),
Page 40, Section 3.1.3 (2))
(2) Modules replaceable online
(a) I/O modules and intelligent function modules that can be replaced
Modules can be replaced online in a multiple CPU system including a Process CPU.
Modules controlled by the Process CPU are targeted.
The following table lists modules that can be replaced online.
Module can be replaced Restrictions
Input module
No function version restrictionOutput module
I/O combined module
Analog-digital converter module
Digital-analog converter module
Temperature input module
Intelligent function
module
Temperature control module
Pulse input module
Load cell input module
CT input module
Loop control module
Function version C
3
3.2 System Using High Performance Model QCPU or Process CPU as CPU No.1
3.2.3 Available I/O modules and intelligent function modules
(b) Applicable CPU modules
To replace a module controlled by the Process CPU online, configure a multiple CPU system with the CPU
modules listed below.
CPU module Model Restrictions
High Performance
model QCPU
Process CPU Q02PHCPU, Q06PHCPU, Q12PHCPU, Q25PHCPU
Universal model QCPU
Motion CPU
C Controller module
PC CPU module
Q02(H)CPU, Q06HCPU, Q12HCPU, Q25HCPU
Q03UD(E)CPU, Q03UDVCPU, Q04UD(E)HCPU,
Q04UDVCPU, Q06UD(E)HCPU, Q06UDVCPU,
Q10UD(E)HCPU, Q13UD(E)HCPU, Q13UDVCPU,
Q20UD(E)HCPU, Q26UD(E)HCPU, Q26UDVCPU,
Q50UDEHCPU, Q100UDEHCPU
Q172CPUN
Q173HCPU
Q06CCPU-V, Q06CCPU-V-B, Q12DCCPU-V,
Q24DHCCPU-V, Q24DHCCPU-LS
PPC-CPU686(MS)-64, PPC-CPU686(MS)-128,
PPC-CPU852(MS)-512
(-T)
, Q173CPUN
(-T)
(-T),
Q172HCPU
(-T)
,
Serial number (first five digits) of
"04012" or later
No function version restriction
Version A or later
Manual for the CPU module
used
51

(3) Number of mountable modules
Refer to Page 68, Section 3.5.
(4) Access ranges of controlled and non-controlled modules.
Refer to the system configuration using a Basic model QCPU as CPU No.1. ( Page 40, Section 3.1.3 (4))
52

CHAPTER 3 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
3.3 System Using Universal Model QCPU as CPU No.1
This section describes the system configuration using a Universal model QCPU as CPU No.1.
3.3.1 Available CPU modules, base units, power supply modules,
and extension cables
Available CPU modules and the number of mountable modules differ depending on the main base unit used.
(1) When a multiple CPU high-speed main base unit (Q3DB) is used
(a) Available modules, the number of extension base units, and the number of
mountable modules
Item Description
Number of CPU
modules
Applicable CPU
*1
module
Universal model QCPU
High Performance model QCPU
Process CPU
Motion CPU
C Controller module
*6
Q00UCPU, Q01UCPU, Q02UCPU
Q03UD(E)CPU, Q03UDVCPU,
Q04UD(E)HCPU, Q04UDVCPU,
Q06UD(E)HCPU, Q06UDVCPU,
Q10UD(E)HCPU, Q13UD(E)HCPU,
Q13UDVCPU, Q20UD(E)HCPU,
Q26UD(E)HCPU, Q26UDVCPU,
Q50UDEHCPU, Q100UDEHCPU
Q02(H)CPU, Q06HCPU, Q12HCPU,
Q25HCPU
Q02PHCPU, Q06PHCPU, Q12PHCPU,
Q25PHCPU
Q172DCPU(-S1), Q173DCPU(-S1),
Q172DSCPU, Q173DSCPU
Q06CCPU-V, Q06CCPU-V-B
Q12DCCPU-V
Q24DHCCPU-V
Q24DHCCPU-LS No function version restriction
4 CPU modules
The modules can be used as CPU No.1.
• No function version restriction
• Serial number (first five digits) of "09072"
or later when used with a PC CPU module
Function version B
No function version restriction
Manual for the Motion CPU
• Serial number (first five digits) of "10102"
or later when used with the Q00UCPU,
Q01UCPU, or Q02UCPU
• Serial number (first five digits) of "10012"
or later when used with the Q03UDECPU,
Q04UDEHCPU, Q06UDEHCPU,
Q13UD(E)HCPU, or Q26UD(E)HCPU
• Serial number (first five digits) of "10102"
or later when used with the
Q10UD(E)HCPU, Q20UD(E)HCPU,
Q50UDEHCPU, or Q100UDEHCPU
• Cannot be used with the QnUDVCPU.
Serial number (first five digits) of "14122" or
later when used with the QnUDVCPU
Serial number (first five digits) of "14122" or
later when used with the QnUDVCPU
3
*2
3.3 System Using Universal Model QCPU as CPU No.1
3.3.1 Available CPU modules, base units, power supply modules, and extension cables
53

Item Description
Applicable CPU
*1
module
Maximum number
of extension base
units
Maximum number
of mountable I/O
modules
Applicable main
base unit
Applicable
extension base
unit
Applicable
extension cable
Applicable power
supply module
PC CPU module PPC-CPU852(MS)-512
7 extension base units,
when the Q00UCPU, Q01UCPU, or Q02UCPU is used: 4 extension base units
65 - (Number of CPU modules),
when the Q00UCPU or Q01UCPU is used: 25 - (Number of CPU modules),
when the Q02UCPU is used: 37 - (Number of CPU modules)
Q35DB, Q38DB, Q312DB
Type requiring no power supply module (Q
series)
Type requiring power supply module (Q series) Q63B, Q65B, Q68B, Q612B
Type requiring no power supply module (AnS
*3*5
series)
Type requiring power supply module (AnS
*3*4
series)
Type requiring no power supply module (A
*3
series)
Type requiring power supply module (A
*3
series)
Power supply module (Q series) Q61P-A1, Q61P-A2, Q61P, Q62P, Q63P, Q64P, Q64PN
Power supply module (AnS series)
Power supply module (A series)
*3
*3
Q52B, Q55B
QA1S51B, QA1S6ADP+A1S5B
QA1S65B, QA1S68B, QA1S6ADP+A1S6B
QA6ADP+A5B
QA65B, QA68B, QA6ADP+A6B
QC05B, QC06B, QC12B, QC30B, QC50B, QC100B
A1S61PN, A1S62PN, A1S63P
A61P, A61PN, A62P, A63P, A61PEU, A62PEU
*1 For the CPU modules that can be combined and their mounting positions, refer to Page 60, Section 3.3.2.
*2 When the Q00UCPU, Q01UCPU, or Q02UCPU is used as CPU No.1, one more CPU module (CPU No.2) can be
mounted. The following CPU modules can be mounted as CPU No.2.
• Driver S/W (PPC-DRV-02) version 1.03 or
later when used with the Q00UCPU or
Q01UCPU
• Driver S/W (PPC-DRV-02) version 1.01 or
later when used with the Q02UCPU
• Driver S/W (PPC-DRV-02) version 1.01 or
later when used with the Q03UDCPU,
Q04UDHCPU, or Q06UDHCPU
• Driver S/W (PPC-DRV-02) version 1.02 or
later when used with the Q03UDECPU,
Q04UDEHCPU, Q06UDEHCPU,
Q13UD(E)HCPU, or Q26UD(E)HCPU
• Driver S/W (PPC-DRV-02) version 1.03 or
later when used with the Q10UDEHCPU,
Q20UDEHCPU, Q50UDEHCPU, or
Q100UDEHCPU
• Cannot be used with the QnUDVCPU.
*7
*7
54
CPU module Model
C Controller module Q06CCPU-V, Q06CCPU-V-B, Q12DCCPU-V, Q24DHCCPU-V, Q24DHCCPU-LS
PC CPU module PPC-CPU852(MS)-512
*3 These modules and units can be used when a Universal model QCPU with a serial number (first five digits) of "13102" or
later is set as the control CPU of AnS/A series modules. These modules and units cannot be used in a multiple CPU
system containing a Process CPU ( Page 188, Appendix 3)
*4 When the QA1S6B is used as an extension base unit, the QA6ADP+A5B/A6B cannot be connected.
*5 Since the QA1S51B does not have an extension cable connector (OUT), it cannot be used with the QA6B or
QA6ADP+A5B/A6B.
*6 When using a Motion CPU, install operating system software on the CPU module. For models and versions of the
operating system, refer to the manual for the Motion CPU used.
*7 When the QA1S6ADP+A1S5B/A1S6B is used, the maximum number of extension base units is 1, and the maximum
number of I/O modules that can be mounted is 20 minus the number of CPU modules. When the QA1S6ADP-
S1+A1S5B/A1S6B is used, the maximum number of extension base units is 3, and the maximum number of I/O
modules that can be mounted is 36 minus the number of CPU modules.

CHAPTER 3 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
(b) Precautions
• If I/O modules are mounted exceeding the maximum number, "SP.UNIT LAY ERR" (error code: 2124)
occurs.
• "Number of CPU modules" indicates the number set in "No. of PLC" of PLC parameter ("Multiple CPU
Setting").
• When a C Controller module which occupies three slots is used, the maximum number of mountable I/O
modules will be two smaller than the number defined in the table on Page 53, Section 3.3.1 (1) (a).
• A PC CPU module occupies two slots. When this module is used, the maximum number of mountable I/O
modules will be one smaller than the number defined in the table on Page 53, Section 3.3.1 (1) (a).
3
3.3 System Using Universal Model QCPU as CPU No.1
3.3.1 Available CPU modules, base units, power supply modules, and extension cables
55

(2) When a main base unit (Q3B) is used
(a) Available modules, the number of extension base units, and the number of
mountable modules
Item Description
Number of CPU
modules
Q00UCPU, Q01UCPU, Q02UCPU
Q03UD(E)CPU, Q03UDVCPU,
Q04UD(E)HCPU, Q04UDVCPU,
Q06UD(E)HCPU, Q06UDVCPU,
Q10UD(E)HCPU, Q13UD(E)HCPU,
Q13UDVCPU, Q20UD(E)HCPU,
Q26UD(E)HCPU, Q26UDVCPU,
Q50UDEHCPU, Q100UDEHCPU
Q02(H)CPU, Q06HCPU, Q12HCPU,
Q25HCPU
Q02PHCPU, Q06PHCPU, Q12PHCPU,
Q25PHCPU
Q172CPUN(-T), Q173CPUN(-T),
Q172HCPU(-T), Q173HCPU(-T)
Q06CCPU-V, Q06CCPU-V-B
Q12DCCPU-V
Q24DHCCPU-V
Q24DHCCPU-LS No function version restriction
7 extension base units,
Applicable CPU
*1
module
Maximum number
of extension base
units
Universal model QCPU
High Performance model QCPU
Process CPU
Motion CPU
C Controller module
PC CPU module PPC-CPU852(MS)-512
when the Q00UCPU, Q01UCPU, or Q02UCPU is used: 4 extension base units
4 CPU modules
The modules can be used as CPU No.1.
• No function version restriction
• Serial number (first five digits) of "09072" or later
when used with a PC CPU module
Function version B
No function version restriction
Manual for the Motion CPU
Can be used with the Q00UCPU, Q01UCPU, or
Q02UCPU.
• Serial number (first five digits) of "10102" or later
when used with the Q00UCPU, Q01UCPU, or
Q02UCPU
• Serial number (first five digits) of "10012" or later
when used with the Q03UDECPU,
Q04UDEHCPU, Q06UDEHCPU,
Q13UD(E)HCPU, or Q26UD(E)HCPU
• Serial number (first five digits) of "10102" or later
when used with the Q10UD(E)HCPU,
Q20UD(E)HCPU, Q50UDEHCPU, or
Q100UDEHCPU
• Cannot be used with the QnUDVCPU.
Serial number (first five digits) of "14122" or later
when used with the QnUDVCPU
Serial number (first five digits) of "14122" or later
when used with the QnUDVCPU
• Driver S/W (PPC-DRV-02) version 1.03 or later
when used with the Q00UCPU or Q01UCPU
• Driver S/W (PPC-DRV-02) version 1.01 or later
when used with the Q02UCPU
• Driver S/W (PPC-DRV-02) version 1.01 or later
when used with the Q03UDCPU, Q04UDHCPU,
or Q06UDHCPU
• Driver S/W (PPC-DRV-02) version 1.02 or later
when used with the Q03UDECPU,
Q04UDEHCPU, Q06UDEHCPU,
Q13UD(E)HCPU, or Q26UD(E)HCPU
• Driver S/W (PPC-DRV-02) version 1.03 or later
when used with the Q10UDEHCPU,
Q20UDEHCPU, Q50UDEHCPU, or
Q100UDEHCPU
• Cannot be used with the QnUDVCPU.
*2
56

Item Description
Maximum number
of mountable I/O
modules
Applicable main
base unit
Applicable
extension base
unit
Applicable
extension cable
Applicable power
supply module
when the Q00UCPU or Q01UCPU is used: 25 - (Number of CPU modules),
when the Q02UCPU is used: 37 - (Number of CPU modules)
Type requiring no power supply module
(Q series)
Type requiring power supply module (Q
series)
Type requiring no power supply module
(AnS series)
Type requiring power supply module
(AnS series)
Type requiring no power supply module
(A series)
Type requiring power supply module (A
series)
Power supply module (Q series) Q61P-A1, Q61P-A2, Q61P, Q62P, Q63P, Q64P, Q64PN
Power supply module (AnS series)
Power supply module (A series)
*3*5
*3*4
*3
*3
QC05B, QC06B, QC12B, QC30B, QC50B, QC100B
*3
*3
65 - (Number of CPU modules),
Q33B, Q35B, Q38B, Q312B
Q52B, Q55B
Q63B, Q65B, Q68B, Q612B
QA1S51B, QA1S6ADP+A1S5B
QA1S65B, QA1S68B, QA1S6ADP+A1S6B
QA6ADP+A5B
QA65B, QA68B, QA6ADP+A6B
A1S61PN, A1S62PN, A1S63P
A61P, A61PN, A62P, A63P, A61PEU, A62PEU
*1 For the CPU modules that can be combined and their mounting positions, refer to Page 60, Section 3.3.2.
*2 When the Q00UCPU, Q01UCPU, or Q02UCPU is used as CPU No.1, two more CPU modules (CPU No.2 and No.3) can
be mounted. The following CPU modules can be mounted as CPU No.2 and No.3.
CHAPTER 3 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
3
*6
*6
CPU module Model
Motion CPU Q172CPUN
C Controller module Q06CCPU-V, Q06CCPU-V-B, Q12DCCPU-V, Q24DHCCPU-V, Q24DHCCPU-LS
PC CPU module PPC-CPU852(MS)-512
*3 These modules and units can be used when a Universal model QCPU with a serial number (first five digits) of "13102" or
later is set as the control CPU of AnS/A series modules. These modules and units cannot be used in a multiple CPU
system containing a Process CPU ( Page 188, Appendix 3)
*4 When the QA1S6B is used as an extension base unit, the QA6ADP+A5B/A6B cannot be connected.
*5 Since the QA1S51B does not have an extension cable connector (OUT), it cannot be used with the QA6B or
QA6ADP+A5B/A6B.
*6 When the QA1S6ADP+A1S5B/A1S6B is used, the maximum number of extension base units is 1, and the maximum
number of I/O modules that can be mounted is 20 minus the number of CPU modules. When the QA1S6ADP-
S1+A1S5B/A1S6B is used, the maximum number of extension base units is 3, and the maximum number of I/O
modules that can be mounted is 36 minus the number of CPU modules.
(-T)
, Q173CPUN
(-T),
Q172HCPU
(-T)
, Q173HCPU
(-T)
(b) Precautions
• If I/O modules are mounted exceeding the maximum number, "SP.UNIT LAY ERR" (error code: 2124)
occurs.
• "Number of CPU modules" indicates the number set in "No. of PLC" of PLC parameter ("Multiple CPU
Setting").
• When a C Controller module which occupies three slots is used, the maximum number of mountable I/O
modules will be two smaller than the number defined in the table on Page 56, Section 3.3.1 (2) (a).
• A PC CPU module occupies two slots. When this module is used, the maximum number of mountable I/O
modules will be one smaller than the number defined in the table on Page 56, Section 3.3.1 (2) (a).
3.3 System Using Universal Model QCPU as CPU No.1
3.3.1 Available CPU modules, base units, power supply modules, and extension cables
57

(3) When a redundant power main base unit (Q3RB) is used
(a) Available modules, the number of extension base units, and the number of
mountable modules
Item Description
Number of CPU
modules
Applicable CPU
*1
module
Maximum number
of extension base
units
Maximum number
of mountable I/O
modules
Applicable main
base unit
Applicable
extension base
unit
Applicable
extension cable
Applicable power
supply module
*1 For the CPU modules that can be combined and their mounting positions, refer to Page 60, Section 3.3.2.
*2 When the Q00UCPU, Q01UCPU, or Q02UCPU is used as CPU No.1, one more CPU module (CPU No.2) can be
Q00UCPU, Q01UCPU, Q02UCPU
Q03UD(E)CPU, Q03UDVCPU,
Q04UD(E)HCPU, Q04UDVCPU,
Universal model QCPU
High Performance model QCPU
Process CPU
C Controller module
7 extension base units (when the Q00UCPU, Q01UCPU, or Q02UCPU is used: 4 extension base units)
when the Q00UCPU or Q01UCPU is used: 25 - (Number of CPU modules), when the Q02UCPU is used: 37 - (Number of CPU modules)
Type requiring no power supply module
(Q series)
Redundant power extension base unit Q68RB
(The Q63RP and Q64RP can be mounted on the same redundant power supply base unit.)
Q06UD(E)HCPU, Q06UDVCPU,
Q10UD(E)HCPU, Q13UD(E)HCPU,
Q13UDVCPU, Q20UD(E)HCPU,
Q26UD(E)HCPU, Q26UDVCPU,
Q50UDEHCPU, Q100UDEHCPU
Q02(H)CPU, Q06HCPU, Q12HCPU,
Q25HCPU
Q02PHCPU, Q06PHCPU, Q12PHCPU,
Q25PHCPU
Q24DHCCPU-V
Q24DHCCPU-LS No function version restriction
Q52B, Q55B
QC05B, QC06B, QC12B, QC30B, QC50B, QC100B
mounted. The following CPU modules can be mounted as CPU No.2.
4 CPU modules
65 - (Number of CPU modules)
Q38RB
Q63RP, Q64RP
The modules can be used as CPU No.1.
No function version restriction
Function version B
No function version restriction
Serial number (first five digits) of "14122" or later
when used with the QnUDVCPU
*2
58
CPU module Model
C Controller module Q24DHCCPU-V, Q24DHCCPU-LS
(b) Precautions
• If I/O modules are mounted exceeding the maximum number, "SP.UNIT LAY ERR" (error code: 2124)
occurs.
• "Number of CPU modules" indicates the number set in "No. of PLC" of PLC parameter ("Multiple CPU
Setting").
• When a C Controller module which occupies three slots is used, the maximum number of mountable I/O
modules will be two smaller than the number defined in the table on Page 58, Section 3.3.1 (3) (a).

(4) When a slim type main base unit (Q3SB) is used
(a) Available modules, the number of extension base units, and the number of
mountable modules
Item Description
Number of CPU
modules
Applicable CPU
*1
module
Maximum number
of extension base
units
Maximum number
of mountable I/O
modules
Applicable
extension cable
Applicable power
supply module
*1 For the CPU modules that can be combined and their mounting positions, refer to Page 60, Section 3.3.2.
*2 When the Q00UCPU, Q01UCPU, or Q02UCPU is used as CPU No.1, one more CPU module (CPU No.2) can be
Q00UCPU, Q01UCPU, Q02UCPU
Q03UD(E)CPU, Q03UDVCPU,
Q04UD(E)HCPU, Q04UDVCPU,
Universal model QCPU
High Performance model QCPU
C Controller module
Q32SB 3 - (Number of CPU modules)
Q33SB 4 - (Number of CPU modules)
Q35SB 6 - (Number of CPU modules)
Q06UD(E)HCPU, Q06UDVCPU,
Q10UD(E)HCPU, Q13UD(E)HCPU,
Q13UDVCPU, Q20UD(E)HCPU,
Q26UD(E)HCPU, Q26UDVCPU,
Q50UDEHCPU, Q100UDEHCPU
Q02(H)CPU, Q06HCPU, Q12HCPU,
Q25HCPU
Q06CCPU-V, Q06CCPU-V-B
Q12DCCPU-V
mounted. The following CPU modules can be mounted as CPU No.2.
3 CPU modules
Extension not allowed
Q32SB, Q33SB, Q35SB
Q61SP
CHAPTER 3 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
The modules can be used as CPU No.1.
No function version restriction
Function version B
• Serial number (first five digits) of "10102" or later
when used with the Q00UCPU, Q01UCPU, or
Q02UCPU
• Serial number (first five digits) of "10012" or later
when used with the Q03UDECPU,
Q04UDEHCPU, Q06UDEHCPU,
Q13UD(E)HCPU, or Q26UD(E)HCPU
• Serial number (first five digits) of "10102" or later
when used with the Q00UCPU, Q01UCPU,
Q02UCPU, Q10UD(E)HCPU, Q20UD(E)HCPU,
Q50UDEHCPU, or Q100UDEHCPU
• Cannot be used with the QnUDVCPU.
Serial number (first five digits) of "14122" or later
when used with the QnUDVCPU
*2
3
3.3 System Using Universal Model QCPU as CPU No.1
3.3.1 Available CPU modules, base units, power supply modules, and extension cables
CPU module Model
C Controller module Q06CCPU-V, Q06CCPU-V-B, Q12DCCPU-V
(b) Precautions
• Slim type main base units do not have an extension cable connector. Therefore, no extension base unit or
GOT can be bus-connected.
• Four CPU modules cannot be mounted because the power consumption of the CPU modules exceeds the
rated output current of the power supply module (Q61SP).
• "Number of CPU modules" indicates the number set in "No. of PLC" of PLC parameter ("Multiple CPU
Setting").
59

3.3.2 CPU module combinations and mounting positions
This section describes the combinations and mounting positions of CPU modules when a Universal model QCPU is
used as CPU No.1.
Note that the CPU modules that can be mounted differ depending on the main base unit used. ( Page 53, Section
3.3.1)
(1) Combinations
CPU No.1
Q00UCPU,
Q01UCPU,
Q02UCPU
Universal model
QCPU other than
the above
High
Performance
model QCPU,
Process CPU,
Universal model
*2*5*6
QCPU
Cannot be used
together.
0 to 3
Number of CPU modules that can be mounted as CPU No.2 or others
*1*5
Q24DHC
CPU-V,
Q24DHC
CPU-LS
Q172CPUN(-T),
Q173CPUN(-T),
Q172HCPU(-T),
Q173HCPU(-T)
0 to 1
Cannot be used
together.
Motion CPU
Q172DCPU(-S1),
Q173DCPU(-S1),
Q172DSCPU,
*3
Q173DSCPU
Cannot be used
C Controller module
Q06CCPU-V,
Q06CCPU-V-B,
Q12DCCPU-V,
*4
Q24DHCCPU-V
together.
0 to 3 0 to 3 0 to 1
0 to 1 0 to 1
PC CPU module
PPC-CPU686
(MS)-64,
PPC-CPU686
(MS)-128
Cannot be
used together.
Cannot be
used together.
*1*6
PPC-
CPU852
(MS)-512
0 to 1 3
0 to 1 4
Maximum
number of
mountable
modules
(including
CPU No.1)
*1 A C Controller module and a PC CPU module cannot be mounted on the same main base unit.
*2 The Q00UCPU, Q01UCPU, and Q02UCPU can be used only as CPU No.1.
*3 The module and a C Controller module (Q12DCCPU-V, Q24DHCCPU-V, Q24DHCCPU-LS) cannot be mounted on the
same main base unit.
*4 When the Q172DCPU(-S1), Q173DCPU(-S1), Q172DSCPU, or Q173DSCPU is used, only the following CPU modules
can be mounted on the same main base unit.
• Universal model QCPU (except the Q00UCPU, Q01UCPU, and Q02UCPU)
*5 A QnUDVCPU and a C Controller module (Q06CCPU-V or Q06CCPU-V-B) cannot be mounted on the same main base
unit.
*6 A QnUDVCPU and a PC CPU module cannot be mounted on the same main base unit.
60

CHAPTER 3 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
Q
Q : QCPU
*1
: Motion CPU
: C Controller module
: PC CPU module
CPU No.1 CPU No.2 CPU No.3
P
P
P
C
C
C
M
M
(2) Mounting positions
The following shows the possible combinations of mounting positions of CPU modules in a multiple CPU system.
• When the Q00UCPU, Q01UCPU, or Q02UCPU is used as CPU No.1
*1 The QCPU indicates the Q00UCPU, Q01UCPU, or Q02UCPU.
3
3.3 System Using Universal Model QCPU as CPU No.1
3.3.2 CPU module combinations and mounting positions
61

• When a CPU module other than the Q00UCPU, Q01UCPU, or Q02UCPU is used as CPU No.1
CPU No.1 CPU No.2 CPU No.3 CPU No.4
*2
QQQQ
M
C
P
*2
M
Q
M
C
P
C
C
P
*2*2
M
QQ
M
C
P
*2
M
Q
M
C
P
Q : QCPU
C
C
M
*1
: Motion CPU
P
62
C
CC
C
P
: C Controller module
P
: PC CPU module
*1 The QCPU used as CPU No.1 indicates a Universal model QCPU (except the Q00UCPU, Q01UCPU, and Q02UCPU).
The QCPU used as CPU No.2 or later indicates a High Performance model QCPU, Process CPU, or Universal model
QCPU (except the Q00UCPU, Q01UCPU, and Q02UCPU).
*2 The QCPU indicates a Universal model QCPU (except the Q00UCPU, Q01UCPU, and Q02UCPU).

CHAPTER 3 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
(a) Universal model QCPU
Only one Q00UCPU, Q01UCPU, or Q02UCPU can be mounted in the CPU slot (the slot on the right of the
power supply module).
Up to four Universal model QCPUs other than the Q00UCPU, Q01UCPU, and Q02UCPU can be mounted in
the CPU slot (the slot on the right of the power supply module) to slot 2 of the main base unit.
(b) High Performance model QCPU or Process CPU
When the Q00UCPU, Q01UCPU, or Q02UCPU is used, no High Performance model QCPU or Process CPU
can be mounted.
When a Universal model QCPU other than the Q00UCPU, Q01UCPU, and Q02UCPU is used, up to three High
Performance QCPUs and/or Process CPUs can be mounted in slot 0 to slot 2 of the main base unit.
(c) Motion CPU
When the Q00UCPU, Q01UCPU, or Q02UCPU is used, only one Motion CPU can be mounted in slot 0 of the
main base unit.
When a Universal model QCPU other than the Q00UCPU, Q01UCPU, and Q02UCPU is used, up to three
Motion CPUs can be mounted in slot 0 to slot 2.
Only a Universal model QCPU, Motion CPU, C Controller module, or PC CPU module can be mounted on the
right of the Motion CPU.
3
(d) C Controller module
When the Q00UCPU, Q01UCPU, or Q02UCPU is used, only one C Controller module can be mounted on the
rightmost slot available for CPU modules.
When a Universal model QCPU other than the Q00UCPU, Q01UCPU, and Q02UCPU is used, up to three C
Controller modules can be mounted on the right of the following CPU modules. For a C Controller module
which occupies three slots, only one module can be mounted.
• High Performance model QCPU
• Process CPU
• Universal model QCPU (except the Q00UCPU, Q01UCPU, and Q02UCPU)
• C Controller module
• Motion CPU (Q172DCPU(-S1), Q173DCPU(-S1), Q172DSCPU, or Q173DSCPU)
(e) PC CPU module
Only one PC CPU module can be mounted on the rightmost slot available for CPU modules. No CPU module
can be mounted on the right of the PC CPU module.
CPU 0 1 2
Power supply
module
QCPU
PC CPU
module
Motion CPU
Slot number
3.3 System Using Universal Model QCPU as CPU No.1
3.3.2 CPU module combinations and mounting positions
63

(f) Empty slot setting
Ex.
CPU
Power supply
module
Power supply
module
Universal model
QCPU
Universal model
QCPU
Universal model
QCPU
Universal model
QCPU
PLC (Empty)
Universal model
QCPU
Motion CPU
Motion CPU
012 CPU012
Added Universal model QCPU
Slot number Slot number
Empty slots can be reserved for future addition of CPU modules. Set the number of CPU modules including
empty slots in "No. of PLC" of PLC parameter ("Multiple CPU Setting"). Then, set "PLC (Empty)" to the type of
a target slot in PLC parameter ("I/O Assignment").
Setting "PLC (Empty)" between CPU modules
When a Universal model QCPU is used, "PLC (Empty)" can be set between CPU modules.
This is useful when adding a CPU module to the system in the future. No program modification is required because the CPU
number set as an empty slot can be assigned to the added CPU module.
Note, however, that when the following CPU module is used, "PLC (Empty)" cannot be set to the left of the CPU module.
• High Performance model QCPU
• Process CPU
To add a High Performance mode QCPU to the system where a C Controller module or PC CPU module is used, move the
C Controller module or PC CPU module to the right to allow addition of a CPU module.
Set "PLC (Empty)" to slot 2.
Keep slot 3 empty.
CPU
01234
Power supply
module
Universal model
QCPU
High Performance
Add a CPU module.
PC CPU
model QCPU
High Performance
model QCPU
module
(Empty)
Move to the right.
Slot number
Input module
CPU01234 Slot number
PC CPU
Power supply
module
Universal model
QCPU
High Performance
model QCPU
High Performance
model QCPU
module
Input module
3.3.3 Available I/O modules and intelligent function modules
Refer to the system configuration using a a High Performance model QCPU or Process CPU as CPU No.1.
( Page 51, Section 3.2.3)
64

3.4 Applicable Software
This section describes software packages applicable in a multiple CPU system.
(1) Applicable GX Works2, GX Developer, and PX Developer
The following table lists the applicable versions of GX Works2, GX Developer, and PX Developer.
CHAPTER 3 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
3
QCPU
Basic model QCPU
High Performance model QCPU 6.00A or later
Q02PHCPU,
Process CPU
Universal model
QCPU
*1 To use GX Works2 in combination with PX Developer, use GX Works2 version 1.98C or later.
*2 To use GX Developer in combination with PX Developer, use GX Developer version 7.12N or later.
Q06PHCPU
Q12PHCPU,
Q25PHCPU
Q00UCPU, Q01UCPU
Q02UCPU,
Q03UDCPU,
Q04UDHCPU,
Q06UDHCPU
Q10UDHCPU,
Q20UDHCPU
Q13UDHCPU,
Q26UDHCPU
Q03UDVCPU,
Q04UDVCPU,
Q06UDVCPU,
Q13UDVCPU,
Q26UDVCPU
Q03UDECPU,
Q04UDEHCPU,
Q06UDEHCPU,
Q13UDEHCPU,
Q26UDEHCPU
Q10UDEHCPU,
Q20UDEHCPU
Q50UDEHCPU,
Q100UDEHCPU
GX Works2 GX Developer PX Developer
1.15R or later
1.87R or later
1.15R or later
1.98C or later Use prohibited Use prohibited
1.15R or later
1.31H or later Use prohibited Use prohibited
8.00A or later
8.68W or later
7.10L or later
8.76E or later Use prohibited
8.48A or later Use prohibited
8.76E or later Use prohibited
8.62Q or later Use prohibited
8.68W or later Use prohibited
8.76E or later Use prohibited
Version
Use prohibited
1.18U or later
1.00A or later
*1
*1*2
3.4 Applicable Software
65

(2) Applicable GX Configurator
The following tables list the applicable versions of GX Configurator. Applicable GX Configurator versions differ
depending on the intelligent function module used. ( Manual for the intelligent function module used)
(a) When a Basic model QCPU, High Performance model QCPU, or Process CPU is
used
Ver sion
Product
GX Configurator-AD
GX Configurator-DA SW0D5C-QDAU 20C or later
GX Configurator-SC SW0D5C-QSCU 20C or later
GX Configurator-CT SW0D5C-QCTU 20C or later
GX Configurator-TI 1.00A or later
GX Configurator-TC SW0D5C-QCTU 00A or later
GX Configurator-FL SW0D5C-QFLU 00A or later
GX Configurator-QP 2.10L or later 2.00A or later 2.13P or later
GX Configurator-PT 1.10L or later 1.00A or later 1.13P or later
GX Configurator-MB 1.00A or later 1.00A or later 1.00A or later
GX Configurator-AS 1.13P or later 1.13P or later 1.13P or later
GX Configurator-DN 1.10L or later 1.00A or later 1.13P or later
GX Configurator-DP 7.00A or later 7.00A or later
*1 To use GX Configurator with the Q02PH/Q06PHCPU, use the version 7.04E or later.
Basic model QCPU
1.10L or later
High Performance model
QCPU
SW0D5C-QADU 20C or later
Process CPU
1.13P or later
7.00A or later
*1
66

(b) When a Universal model QCPU is used
Version compatible with the Universal model QCPU
Product
GX Configurator-AD
GX Configurator-DA
GX Configurator-SC
GX Configurator-CT
GX Configurator-TI
GX Configurator-TC
GX Configurator-FL
GX Configurator-QP 2.25B or later 2.29F or later
GX Configurator-PT
GX Configurator-MB
GX Configurator-AS
GX Configurator-DN
GX Configurator-DP
*6
*1 The software can be used by installing GX Developer version 8.48A or later.
*2 The software can be used by installing GX Developer version 8.62Q or later.
*3 The software can be used by installing GX Developer version 8.68W or later.
*4 The software can be used by installing GX Developer version 8.76E or later.
*5 GX Configurator-QP version 2.29F can also be used when connected via USB.
*6 To use GX Configurator with the Q50UDEH/Q100UDEHCPU, use the version 7.07H or later.
*7 To use GX Configurator with the Q02UCPU, use the version 7.03D or later.
Used with
Q02U/Q03UD/Q04UDH/
Q06UDHCPU
2.05F or later
2.06G or later
2.12N or later
1.25AB or later
1.24AA or later
1.23Z or later
1.23Z or later
1.23Z or later
1.08J or later
1.21X or later
1.23Z or later
7.02C or later
*1
*1
*1
*1
*1
*1
*1
*1
*1
*1
*1
*7
Used with
Q13UDH/Q26UDHCPU
2.05F or later
2.06G or later
2.12N or later
1.25AB or later
1.24AA or later
1.23Z or later
1.23Z or later
1.23Z or later
1.08J or later
1.21X or later
1.23Z or later
7.03D or later 7.03D or later 7.04E or later
CHAPTER 3 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
Used with
Q03UDE/Q04UDEH/
Q06UDEH/Q13UDEH/
Q26UDEHCPU
*2
*2
*2
*2
*2
*2
*2
2.05F or later
2.06G or later
2.17T or later
1.25AB or later
1.24AA or later
1.23Z or later
1.23Z or later
2.30G or later
*2
*2
*2
*2
1.23Z or later
1.08J or later
1.21X or later
1.24AA or later
*3
*3
*3
*3
*3
*3
*3
*5
*3
*3
*3
*3
Used with
Q00U/Q01U/Q10UDH/
Q20UDH/Q10UDEH/
Q20UDEHCPU
2.05F or later
2.06G or later
2.17T or later
1.25AB or later
1.24AA or later
1.23Z or later
1.23Z or later
2.32J or later
1.23Z or later
1.08J or later
1.21X or later
1.24AA or later
*4
*4
*4
*4
*4
*4
*4
*4
*4
*4
*4
3
3.4 Applicable Software
67
3.5 Precautions for System Configuration
This section describes restrictions and precautions on system configuration.
(1) Number of mountable modules
The number of mountable modules and supported functions are restricted depending on the CPU module used.
For the number of modules that can be connected to each Motion CPU, C Controller module, or PC CPU module,
refer to the manual for the CPU module used.
(a) When a Basic model QCPU is used
Product Model Maximum number of modules/units per system
CC-Link IE Controller Network
module
MELSECNET/H module
Ethernet interface module
CC-Link system master/local
module
• QJ71GP21-SX
• QJ71GP21S-SX
• QJ71LP21
• QJ71BR11
• QJ71LP21-25
• QJ71LP21S-25
• QJ71LP21G
• QJ71LP21GE
• QJ71NT11B
• QJ71E71
• QJ71E71-B2
• QJ71E71-B5
• QJ71E71-100
• QJ61BT11
• QJ61BT11N
Up to 4 modules (One
Q00CPU or Q01CPU can
control only one module.)
Up to 4 modules (One
Q00CPU or Q01CPU can
control only one module on
the PLC to PLC network.)
Only 1 module (Controlled only by the QCPUs)
Up to 10 modules
Up to 4 modules in total
*1
(One QCPU can control only two
modules.)
Interrupt module • QI60
• QX40H
High-speed input module
(Interrupt module)
High speed data logger module • QD81DL96
High speed data
communication module
GOT
*4
*1 Modules of function version B or later can be mounted.
*2 The number indicates interrupt modules with no interrupt pointer setting. With interrupt pointer setting, no restriction
applies.
*3 For the applicable GOT models, refer to the connection manual for the GOT used.
*4 The number of mountable modules is restricted when a high-speed input module is used as an interrupt module by
turning off the function switch (SW2).
• QX70H
• QX80H
• QX90H
• QJ71DC96
• GOT-A900 series (Bus connection only)
• GOT1000 series (Bus connection only)
Up to 3 modules
Only 1 module (Controlled by QCPUs or C Controller
Only 1 module (Controlled by QCPUs or C Controller
*3
*3
*2
(One QCPU can control only one
module.)
modules)
modules)
Up to 5 units
68

(b) When a High Performance model QCPU or Process CPU is used
Product Model Maximum number of modules/units per system
CC-Link IE Controller Network
*4
module
MELSECNET/H module
Ethernet interface module
CC-Link system master/local
module
AnS series
special function module
Interrupt module
High-speed input module
(Interrupt module)
High speed data logger module • QD81DL96
High speed data
communication module
GOT
*1 One CPU module can control the following number of modules by setting CC-Link network parameters.
*2 The module can be used only when a High Performance model QCPU is set to a control module. However, it cannot be
*3 For the applicable GOT models, refer to the connection manual for the GOT used.
*4 The module can be used with the following CPU modules.
*5 The number of mountable modules is restricted when a high-speed input module is used as an interrupt module by
*2
*5
• CPU module with a serial number (first five digits) of "08031" or earlier: Up to 4 modules
• CPU module with a serial number (first five digits) of "08032" or later: Up to 8 modules
There is no restriction on the number of mounted modules when the parameters are set with the CC-Link dedicated
instructions.
used if a Process CPU is used in combination. ( Page 188, Appendix 3)
• High Performance model QCPU with a serial number (first five digits) of "09012" or later
• Process CPU with a serial number (first five digits) of "10042" or later
turning off the function switch (SW2).
• QJ71GP21-SX
• QJ71GP21S-SX
• QJ71LP21
• QJ71BR11
• QJ71LP21-25
• QJ71LP21S-25
• QJ71LP21G
• QJ71LP21GE
• QJ71NT11B
• QJ71E71
• QJ71E71-B2
• QJ71E71-B5
• QJ71E71-100
• QJ61BT11
• QJ61BT11N
• A1SJ71PT32-S3
• A1SJ71T32-S3
• A1SD51S
• A1SD21-S1
• A1SJ71J92-S3
(When using GET/PUT service)
• A1SJ71AP23Q
• A1SJ71AR23Q
• A1SJ71AT23BQ
•A1SI61
•QI60
•QX40H
•QX70H
•QX80H
•QX90H
• QJ71DC96
• GOT-A900 Series (Bus connection only)
• GOT1000 Series (Bus connection only)
*2
CHAPTER 3 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
Up to 2 modules
Up to 4 modules in total
Up to 4 modules
Up to 4 modules
No restriction
No restriction (Auto refresh setting not allowed)
Up to 6 modules in total
Only 1 module
Up to 4 modules (Up to 3 modules when A1SI61 is used.
A QCPU can control only 1 module.)
Up to 4 modules (Controlled by QCPUs or C Controller
modules. A QCPU or C Controller module can control only
1 module.)
Up to 4 modules (Controlled by QCPUs or C Controller
modules. A QCPU or C Controller module can control only
1 module.)
*3
*3
Up to 5 units
*1
3
3.5 Precautions for System Configuration
69

Remark
For the restrictions on mounting A-series modules on the QA6B or QA6ADP+A5B/A6B, refer to the following.
QA65B/QA68B Extension Base Unit User's Manual
QA6ADP QA Conversion Adapter Module User's Manual
For the restrictions on mounting AnS-series modules on the QA1S6ADP+A1S5B/A1S6B, refer to the following.
QA1S6ADP Q-AnS Base Unit Conversion Adapter User's Manual
QA1S6ADP-S1 Q-AnS Base Unit Conversion Adapter User's Manual
70

(c) When a Universal model QCPU is used
Product Model Maximum number of modules/units per system
CC-Link IE Controller Network
*4
module
MELSECNET/H module
CC-Link IE Field Network
module
Ethernet interface module
CC-Link system master/local
module
AnS series
special function module
Interrupt module
High-speed input module
(Interrupt module)
High speed data logger
*9
module
High speed data
communication module
GOT
*8
*7
• QJ71GP21-SX
• QJ71GP21S-SX
• QJ71LP21
• QJ71BR11
• QJ71LP21-25
• QJ71LP21S-25
• QJ71LP21G
• QJ71LP21GE
• QJ71NT11B
• QJ71GF11-T2
• QJ71E71
• QJ71E71-B2
• QJ71E71-B5
• QJ71E71-100
• QJ61BT11
• QJ61BT11N
• A1SJ71PT32-S3
• A1SJ71T32-S3
• A1SD51S
• A1SD21-S1
• A1SJ71J92-S3
(When using GET/PUT service)
• A1SJ71AP23Q
• A1SJ71AR23Q
• A1SJ71AT23BQ
only)
*8
*2
•A1SI61
•QI60
•QX40H
•QX70H
•QX80H
•QX90H
• QD81DL96
• QJ71DC96
• GOT1000 Series (for bus connection
CHAPTER 3 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
Up to 4 modules in total
With the Q00UCPU, Q01UCPU, or Q02UCPU, the
maximum number of connectable modules is as follows:
• Q02UCPU: Up to 2 modules in total
• Q00UCPU or Q01UCPU: Only 1 module
No restriction
Up to 4 modules
With the Q00UCPU, Q01UCPU, or Q02UCPU, the
maximum number of connectable modules is as follows:
• Q02UCPU: Up to 2 modules
• Q00UCPU or Q01UCPU: Only 1 module
No restriction
No restriction (Auto refresh setting not allowed)
Up to 6 modules in total
Only 1 module
Up to 4 modules
Up to 4 modules (Controlled by QCPUs or C Controller
modules. A QCPU or C Controller module can control only
1 module.)
Up to 4 modules (Controlled by QCPUs or C Controller
modules. A QCPU or C Controller module can control only
1 module.)
Up to 5 units
*6
*1*5
*3
3
3.5 Precautions for System Configuration
71
*1 One CPU module can control the following number of modules by setting CC-Link network parameters.
Remark
• Q00UCPU or Q01UCPU: Up to 2 modules
• Q02UCPU: Up to 4 modules
• Other CPU modules: Up to 8 modules
There is no restriction on the number of mounted modules when the parameters are set with the CC-Link dedicated
instructions.
*2 For the applicable GOT models, refer to the connection manual for the GOT used.
*3 The number indicates interrupt modules with no interrupt pointer setting. With interrupt pointer setting, no restriction
applies.
*4 When one of the following CPU modules is used in the multiple CPU system, the number of modules can be mounted is
restricted to two.
• High Performance model QCPU
• Process CPU
*5 Modules of function version B or later can be mounted.
*6 One CPU module can control the following number of modules by setting CC-Link IE Field Network parameters using a
programming tool.
• Q00UCPU or Q01UCPU: Up to 2 modules
• Q02UCPU: Up to 4 modules
• Other CPU modules: Up to 8 modules
There is no restriction on the number of mounted modules when the parameters are set with the CC-Link IE Field
Network dedicated instructions.
*7 The number of mountable modules is restricted when a high-speed input module is used as an interrupt module by
turning off the function switch (SW2).
*8 The module can be used when a Universal model QCPU with a serial number (first five digits) of "13102" or later is set to
a control module. However, it cannot be used if a process CPU is used in combination. ( Page 188, Appendix 3)
*9 With a High-speed Universal model QCPU, only high-speed data logger modules with a serial number (first five digits)
"14122" or later can be used.
For the restrictions on mounting A-series modules on the QA6B or QA6ADP+A5B/A6B, refer to the following.
QA65B/QA68B Extension Base Unit User's Manual
QA6ADP QA Conversion Adapter Module User's Manual
For the restrictions on mounting AnS-series modules on the QA1S6ADP+A1S5B/A1S6B, refer to the following.
QA1S6ADP Q-AnS Base Unit Conversion Adapter User's Manual
QA1S6ADP-S1 Q-AnS Base Unit Conversion Adapter User's Manual
72

CHAPTER 3 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
Ex.
(2) Modules that have restrictions when used with an Universal model QCPU
For modules that have restrictions when used with an Universal model QCPU, refer to the following manual.
QnUCPU User's Manual (Function Explanation, Program Fundamentals)
(3) Combinations of power supply modules, base units, and QCPUs
There are some restrictions on combinations of power supply modules, base units, and QCPUs. ( QCPU
User's Manual (Hardware Design, Maintenance and Inspection)
Redundant power supply modules can be mounted only on redundant power main base units or
redundant power extension base units.
(4) Precautions for using a QCPU of function version A
If a QCPU of function version A is used in a multiple CPU system, an error occurs. To configure a multiple CPU
system with QCPUs, use CPU modules of function version B or later.
CPU No.1 Other than CPU No.1 Error in CPU No.1
QCPU (function version A) QCPU (function version A)
QCPU (function version A) QCPU (function version B)
QCPU (function version B) QCPU (function version A)
"UNIT VERIFY ERROR"
(error code: 2000)
"UNIT VERIFY ERROR"
(error code: 2000)
"MULTI EXE.ERROR"
(error code: 7010)
(5) Precautions for using the high-speed interrupt function
A High Performance model QCPU and High-speed Universal model QCPU support the high-speed interrupt
function.
If the parameter with the high-speed interrupt fixed scan interval setting is written, the functions of the CPU
module are partly restricted. The restrictions differ depending on the CPU module used. ( User's Manual
(Function Explanation, Program Fundamentals) for the CPU module used)
Note that the above restrictions do not apply to the High Performance model QCPU with a serial number (first five
digits) of "04011" or earlier because the module ignores the high-speed interrupt fixed scan interval setting.
Error in other than CPU
No.1
"SP.UNIT LAY ERROR"
(error code: 2125)
"MULTI EXE.ERROR"
(error code: 7010)
"SP.UNIT LAY ERROR"
(error code: 2125)
3
3.5 Precautions for System Configuration
(6) Precautions for using a Motion CPU (Q172DCPU(-S1), Q173DCPU(-S1),
Q172DSCPU, or Q173DSCPU)
The Q172DCPU(-S1), Q173DCPU(-S1), Q172DSCPU, or Q173DSCPU can only be mounted on a multiple CPU
high-speed main base unit.
Note that do not mount any Motion modules controlled by the Motion CPU in slot 0 to 2 of the multiple CPU high-
speed main base unit.
73

(7) Precautions for connecting a GOT
The following GOT series can be used.
• GOT-A900 series
• GOT-F900 series (The Q-mode compatible operating system and communication driver must be installed.)
• GOT1000 series
The GOT800 series, A77GOT, and A64GOT cannot be used.
*1 Universal model QCPUs do not support the GOT-A900 and GOT-F900 series.
*1
*1
74

CHAPTER 4 STARTING UP MULTIPLE CPU SYSTEM
Check box
Determine the role (controls and functions) of each CPU module used in
a multiple CPU system.
Study details of device assignment. To perform auto refresh of the CPU
shared memory, the refresh range must be set consecutively.
Select modules to be used in a multiple CPU system.
To the next page
Mount the selected modules on a main base unit and extension base
unit(s).
Set the RUN/STOP switch of the CPU No.1 to the STOP position, and
power on the system.
Study details of device assignment.
Determine the role of each CPU module.
Select modules.
Mount the modules.
Power on the system.
Page 116, CHAPTER 6
Page 31, CHAPTER 3
Page 31, CHAPTER 3
CHAPTER 4 STARTING UP MULTIPLE CPU
SYSTEM
This chapter describes the procedure for starting up a multiple CPU system.
4.1 Procedure Before Operation
4
4.1 Procedure Before Operation
75

Set the RUN/STOP switch of all the CPU modules to the RUN position.
Connect the CPU No.1 and a personal computer where a programming
tool has been installed.
*1
Write programs and parameters to the CPU modules. To write data to the
CPU No.2 and later, select the target CPU module in the Transfer Setup
window of the programming tool.
Reset the entire system by resetting the CPU No.1. Set the RUN/STOP
switch of the CPU No.1 to the RUN position again, and check whether no
error occurs in any CPU module in the system.
*2
Debug the program of each CPU module individually.
Run all the CPU modules.
Debug the system.
Connect to a programming tool.
Write data to the CPU modules.
Reset the CPU No.1.
Page 112, Section 5.3
*1 When a PC CPU module is used, the QCPU can be bus-connected to a programming tool by installing the programming
*2 If an error has occurred, check the error cause using the programming tool and take corrective action.
tool in the PC CPU module. Select "Q Series Bus" for the "PC side I/F" setting in the "Transfer Setup" window using the
programming tool.
An error in the CPU modules can be checked in the "PLC Diagnostics" window.
An error in the I/O modules and intelligent function modules can be checked in the "System Monitor" window.
( QCPU User's Manual (Hardware Design, Maintenance and Inspection))
76
CHAPTER 4 STARTING UP MULTIPLE CPU SYSTEM
No. of PLC
Online Module Change
Detailed Setting: Control PLC
: Setting required
: Same setting required for all CPU modules
Multiple CPU Setting
Operation Mode
*1
I/O Sharing When Using Multiple CPUs
Change Screens
CPU Specific Send Range
PLC Side Device
Refresh Setting
I/O Assignment I/O Assignment
Basic Setting Slots
PLC System Points Occupied by Empty Slot
: Individual setting allowed for each CPU module
4.2 Operation Settings
This section describes the settings required to operate a multiple CPU system. A system where three Universal model
QCPUs are mounted shall be used as an example.
(1) Parameters required
(a) Basic model QCPU, High Performance model QCPU, and Process CPU
Settings of parameters in double-lined squares, except some parameters, must be the same in all the CPU
modules used in a multiple CPU system. ( Page 172, Appendix 1.1)
4
*1 For Basic model QCPUs, the online module change setting is not available.
High Performance model QCPUs do not support the online change function, but the setting is required to replace
modules controlled by the Process CPU on the same base unit online.
4.2 Operation Settings
77

(b) Universal model QCPU
Multiple CPU Setting
Operation Mode
Multiple CPU Synchronous Startup Setting
Online Module Change
*1
Start
PLC Side Device
Advanced Setting
Use Multiple CPU High Speed
Transmission
CPU Specific Send Range
CPU Specific Send Range
Refresh Setting
Auto Refresh Points
I/O Sharing When Using Multiple CPUs
System Area
Multiple CPU High Speed Transmission
Area Setting
Host Station
I/O Assignment I/O Assignment
Basic Setting Slots
PLC System Points Occupied by Empty Slot
No. of PLC
Detailed Setting: Control PLC
: Setting required
: Same setting required for all CPU modules
: Individual setting allowed for each CPU module
Settings of parameters in double-lined squares, except some parameters, must be the same in all the CPU
modules used in a multiple CPU system. ( Page 172, Appendix 1.1)
*1 Universal model QCPUs do not support the online change function, but the setting is required to replace modules
controlled by the Process CPU on the same base unit online.
78

CHAPTER 4 STARTING UP MULTIPLE CPU SYSTEM
11 2 3 1 1 222
3 33
CPU 0 4 5 6 7
Slot number
Control CPU setting
312
89
Slot number
Control CPU setting
10 11 12 13 14 15
Personal computer (Programming tool)
Power supply module
Power supply module
Universal model QCPU
Universal model QCPU
Universal model QCPU
PLC (Empty)
Input module
Input module
Output module
Output module
Input module
Output module
Intelligent function module
Intelligent function module
4.2.1 System configuration example
This section describes the procedure for setting parameters required in a multiple CPU system, using the following
system as an example.
4
4.2 Operation Settings
4.2.1 System configuration example
79

4.2.2 Parameter settings
This section describes parameters required for the system configuration on Page 79, Section 4.2.1. Use a
programming tool to set parameters.
• Settings of parameters in double-lined squares on Page 77, Section 4.2 (1) must be the same in all the CPU
modules in a multiple CPU system.
• The necessity of parameters differs depending on the QCPU used. ( Page 77, Section 4.2 (1))
(1) Setting parameters (for the first time)
1. Set "Points Occupied by Empty Slot" in the "PLC System" window of PLC parameter.
Project window [Parameter] [PLC Parameter] [PLC System] "Points Occupied by
Empty Slot"
Item Description Default
Points Occupied by Empty Slot Set the number of points occupied by one empty slot. 16 points
2. Set parameters for the multiple CPU system in the "Multiple CPU Setting" window of PLC
parameter.
Project window [Parameter] [PLC Parameter] [Multiple CPU Setting]
80

No. of PLC
CHAPTER 4 STARTING UP MULTIPLE CPU SYSTEM
Item Description Default
Set the number of CPU modules mounted on the main base unit in the
multiple CPU system. The number of modules differs depending on the CPU
module used as CPU No.1 and the main base unit used. ( Page 31,
CHAPTER 3)
This parameter must be set.
Set this parameter to check the host CPU number in the multiple CPU system.
If this parameter is set, each CPU module checks its own CPU number with
the one set in this parameter to see if they match.
Host CPU number setting
1
4
Host Station
Operation Mode
The CPU module checks
if the CPU numbers match.
CPU
No.1
CPU No.2
CPU numbers are determined by their mounting positions.
• When "No Specification" is selected, the host CPU number is not checked.
• Host CPU numbers do not need to be set to all the CPU modules in the
system.
• To set the same "Multiple CPU Setting" parameters to all the CPU modules
used in the multiple CPU system, select "No Specification". Parameter
settings are shared by all the CPU modules used in the system.
The host CPU number can be checked when one of the following CPU
modules is used.
• Universal model QCPU (except the Q00UCPU, Q01UCPU, and Q02UCPU)
• Motion CPU (Q172DCPU(-S1), Q173DCPU(-S1), Q172DSCPU, or
Q173DSCPU)
• C Controller module (Q12DCCPU-V, Q24DHCCPU-V, or Q24DHCCPU-LS)
Select whether to stop or continue the operation of all the CPU modules when
a stop error occurs in a CPU module. Set this parameter to continue the
operation of other error-free CPU modules if a stop error occurs in a CPU
module other than CPU No.1.
For example, if the "All station stop by stop error of PLC2" checkbox is
unchecked, other CPU modules continue their operation even after a stop
error occurs in CPU No.2.
The operation mode of CPU No.1 cannot be changed. ( Page 102,
Section 4.6)
Set this parameter to enable synchronous startup of the CPU modules in the
multiple CPU system. ( Page 168, Section 6.5)
The CPU module checks
if the CPU numbers match.
CPU
No.3
No Specification
All items selected
4.2 Operation Settings
4.2.2 Parameter settings
Multiple CPU Synchronous
Startup Setting
Only Universal model QCPUs support this parameter.
Uncheck the checkbox of the corresponding CPU number if any of the
following CPU modules is used.
• High Performance model QCPU
• Process CPU
• C Controller module (Q06CCPU-V or Q06CCPU-V-B)
• PC CPU module
All items selected
81

Item Description Default
Online Module Change
I/O Sharing When Using
Multiple CPUs
Multiple CPU High Speed
Transmission Area Setting
Communication Area Setting
(Refresh Setting)
(1) Basic model QCPU
This parameter is not supported.
(2) Process CPU
Check the checkbox to enable online module change.
(3) High Performance model QCPU and Universal model QCPU
Check the checkbox if online module change is enabled with a Process
CPU. Modules controlled by a High Performance model QCPU or
Universal model QCPU cannot be replaced online.
Set this parameter to read the input (X) and output (Y) data from the I/O
modules and intelligent function modules controlled by other CPU modules.
• Loading input (X) data: Page 105, Section 5.2.1
• Loading output (Y) data: Page 107, Section 5.2.2
Set this parameter to enable automatic data communications between the
CPU modules in the system using the multiple CPU high speed transmission
area of the CPU shared memory.
Only Universal model QCPUs support this parameter.
Note that some conditions must be met on the main base units and CPU
modules to be used. ( Page 135, Section 6.1.2)
If the conditions cannot be satisfied, use "Communication Area Setting
(Refresh Setting)".
Set this parameter to enable automatic data communications between the
CPU modules in the system using the automatic refresh area of the CPU
shared memory. ( Page 122, Section 6.1.1)
Not selected
Not selected
"Use Multiple CPU High
Speed Transmission"
checkbox: Selected
-
Match "No. of PLC" with the number of CPU modules actually mounted. If the numbers do not match, an error will occur.
82

CHAPTER 4 STARTING UP MULTIPLE CPU SYSTEM
3. Set the types and points for the mounted modules in the "I/O Assignment" window of PLC
parameter.
Project window [Parameter] [PLC Parameter] [I/O Assignment]
4
Item Description Default
Select the type of a mounted module.
To reserve an empty slot for the future addition of a CPU module, select
"PLC (Empty)".
The slots where "PLC (Empty)" can be set differ depending on the CPU
module used as CPU No.1.
Type
Model Name
Points Set the number of I/O points for each module. Blank
• When a Basic model QCPU is used as CPU No.1
Page 38, Section 3.1.2 (2) (d)
• When a High Performance model QCPU or Process CPU is used as CPU
No.1
Page 50, Section 3.2.2 (2) (f)
• When a Universal model QCPU is used as CPU No.1
Page 64, Section 3.3.2 (2) (f)
Enter the model name of a mounted module.
This is a memo in the programming tool and does not affect the operation of
CPU modules.
Blank
4.2 Operation Settings
-
4.2.2 Parameter settings
83

Control PLC
4. Click the button in the "I/O Assignment" window, and set a control CPU for each I/O
module and intelligent function module.
Item Description Default
Set the CPU module that controls each I/O module and intelligent function
module mounted.
PLC No.1
5. Set other parameters required.
6. Save the project using the programming tool so that the multiple CPU system parameter settings
can be used in other CPU modules.
[Project] [Save As]
84

CHAPTER 4 STARTING UP MULTIPLE CPU SYSTEM
(2) Using the multiple CPU system parameters set to another CPU module
1. Click the button in the "Multiple CPU Setting" window of PLC parameter.
Select and open the project file from which the settings will be imported.
Project window [Parameter] [PLC Parameter] [Multiple CPU Setting]
4
The settings of a project file created with a different programming tool cannot be used. Reuse such settings as follows.
• To import the settings of a project file created with GX Developer to GX Works2, open the GX Developer project in
GX Works2 by using the [Open Other Project] function.
[Project] [Open Other Data] [Open Other Project]
• To import the settings of a project file created with GX Works2 to GX Developer, save the GX Works2 project in
the GX Developer format by using [Export to GX Developer Format File] function.
[Project] [Export to GX Developer Format File]
2. The following window appears. Click the button.
3. Check the settings in the "Multiple CPU Setting" window of PLC parameter.
To change the auto refresh setting devices, click the button and set new device ranges.
(Settings of parameters with "(*1)" must be the same in all the CPU modules in the system.)
4.2 Operation Settings
4.2.2 Parameter settings
85

4. Check the "Points Occupied by Empty Slot" setting in the "PLC System" window of PLC
parameter.
Project window [Parameter] [PLC parameter] [PLC System] "Points Occupied by
Empty slots"
5. Check the settings in the "I/O Assignment" window of PLC parameter.
Project window [Parameter] [PLC parameter] [I/O Assignment]
6. Click the button in the "I/O Assignment" window and check the "Control PLC" setting.
7. Set other parameters required.
8. Save the project using the programming tool.
[Project] [Save As]
86

CHAPTER 4 STARTING UP MULTIPLE CPU SYSTEM
1
1 1 1 1
4.3 Program Examples for Communications by Auto
Refresh
4.3.1 Program examples for Basic model QCPU, High Performance
model QCPU, and Process CPU
This section provides program examples for communicating data by auto refresh between the CPU modules in the
following system.
Personal computer (Programming tool)
4
CPU 0 4 5 6 732
Power supply module
High Performance
Point assigned
to each slot
1
1
Input
Output
A/D
X0 to XF
Y10 to Y1F
model QCPU
High Performance
model QCPU
222
X/Y20 to X/Y2F
(1) Parameter settings
(a) I/O assignment
Assign I/O points to the mounted modules. ( Page 27, Section 2.2)
Project window [Parameter] [PLC Parameter] [I/O Assignment]
D/A
Input
X/Y30 to X/Y3F
X40 to X4F
Output
16 16 16161616
Y50 to Y5F
Slot number
Control CPU setting
4.3 Program Examples for Communications by Auto Refresh
4.3.1 Program examples for Basic model QCPU, High Performance model QCPU, and Process CPU
87

(b) Auto refresh setting
Set auto refresh parameters. ( Page 123, Section 6.1.1 (2))
Project window [Parameter] [PLC Parameter] [Multiple CPU Setting] "Communication
Area Setting (Refresh Setting)"
88

CHAPTER 4 STARTING UP MULTIPLE CPU SYSTEM
Send
command
CPU No.1
send data (bit)
CPU No.1
send data (word)
(2) Program examples
(a) Sending bit data and word data from CPU No.1 to CPU No.2
• Devices used in CPU modules
Device used in CPU No.1 Device used in CPU No.2
M0
D0 and D1 D0 and D1
Send data from CPU No.1 to CPU No.2
-
• Program example of CPU No.1
M0
D100
Send data from CPU No.1 to CPU No.2
Storage device for data received from CPU
No.1
YE0 Data reception flag (for data from CPU No.1)
SM400 Always ON
4
• Program example of CPU No.2
SM400
Always ON CPU No.1
send data (bit)
CPU No.1
send data
(word)
CPU No.2
receive data
(bit)
CPU No.2
receive data
(word)
4.3 Program Examples for Communications by Auto Refresh
4.3.1 Program examples for Basic model QCPU, High Performance model QCPU, and Process CPU
89

(b) Continuously sending data from CPU No.1 to CPU No.2
SM400
Always ONCPU No.1
send flag
Send start data
Send end data
Send start
data
CPU No.1
send data
CPU No.1
send flag
CPU No.1
send flag
CPU No.2
receive
complete flag
CPU No.1
send data
CPU No.2
receive data
CPU No.2
receive
complete flag
CPU No.1
send flag
• Devices used in CPU modules
Device used in CPU No.1 Device used in CPU No.2
M40 Send data from CPU No.2 to CPU No.1 M40 Send data from CPU No.2 to CPU No.1
D10 to
D18
D81 to
D88
Send data from CPU No.1 to CPU No.2
Storage device of send data to CPU No.2
SM400 Always ON -
For handshake between CPU No.1 and No.2, refer to Page 132, Section 6.1.1 (3).
• Program example of CPU No.1
D10 to
D18
D121 to
D128
Send data from CPU No.1 to CPU No.2
Storage device for data received from CPU
No.1
90
• Program example of CPU No.2

CHAPTER 4 STARTING UP MULTIPLE CPU SYSTEM
(c) Continuously reading/writing data between CPU No.1 and No.2 using the user
setting area
Data can be read/write between CPU modules by programs using the user setting area in the CPU shared
memory.
The same number of points must be set for CPU No.1 and CPU No.2 in the auto refresh setting.
4
The auto refresh area occupies the memory addresses 0800H to 0821H, the area set by setting 1 and setting 2.
Consequently, the user setting area will be a range from 0822H to 0FFFH. ( Page 118, Section 6.1)
CPU shared memory
0000H
01FF
0200H
07FF
0800H
0FFF
Host CPU operation
to
information area
H
to
System area
H
Auto refresh area
to
User setting area
H
CPU No.1 memory
0800H
D0 to D31
081FH
0820H
M0 to M31
0821H
0822H
0850H
0881H
0FFFH
CPU No.2 memory
0800H
D32 to D63
081FH
0820H
M32 to M63
0821H
0822H
0850H
0881H
0FFFH
4.3 Program Examples for Communications by Auto Refresh
4.3.1 Program examples for Basic model QCPU, High Performance model QCPU, and Process CPU
91

• Devices used in CPU modules
CPU No.1 read
complete flag
Write complete bit
CPU No.2
write flag
CPU No.2
write flag
Write
complete bit
Write end
data
Write start
data
Write start
data
SM400
Always
ON
CPU No.2
write flag
Read
start data
CPU No.1
read
complete flag
Device used in CPU No.1 Device used in CPU No.2
M31 Send data from CPU No.1 to CPU No.2 M31 Send data from CPU No.1 to CPU No.2
M63 Send data from CPU No.2 to CPU No.1 M63 Send data from CPU No.2 to CPU No.1
D100 to
D149
Storage device for data received from CPU
No.2
-
D200 to
D249
Storage device of send data to CPU No.1
M100 Write completion bit of the S.TO instruction
SM400 Always ON
• Program example of CPU No.2
92
• Program example of CPU No.1

CHAPTER 4 STARTING UP MULTIPLE CPU SYSTEM
Input
X0 to XF
Output
Y10 to Y1F
A/D
X/Y20 to X/Y2F
D/A
X/Y30 to X/Y3F
Input
X40 to X4F
Output
Y50 to Y5F
Point assigned
to each slot
161616161616
1
1 2221 1 1 1
1
CPU 0 4 5 6 732
Slot number
Control CPU setting
Personal computer (Programming tool)
Power supply module
Universal model QCPU
Universal model QCPU
4.3.2 Program examples for Universal model QCPU
This section provides program examples for communicating data by auto refresh (using the multiple CPU high speed
transmission area) between the CPU modules in the following system.
4
(1) Parameter settings
(a) I/O assignment
Assign I/O points to the mounted modules. ( Page 27, Section 2.2)
Project window [Parameter] [PLC Parameter] [I/O Assignment]
4.3.2 Program examples for Universal model QCPU
4.3 Program Examples for Communications by Auto Refresh
93

(b) Auto refresh setting
Setting of CPU No.1 Setting of CPU No.2
Set auto refresh parameters. ( Page 138, Section 6.1.2 (3))
Project window [Parameter] [PLC Parameter] [Multiple CPU Setting] "Multiple CPU
High Speed Transmission Area Setting"
94

CHAPTER 4 STARTING UP MULTIPLE CPU SYSTEM
Send
command
CPU No.1
send data
(bit)
CPU No.1
send data
(word)
(2) Program examples
(a) Sending bit data and word data from CPU No.1 to CPU No.2
• Devices used in CPU modules
Device used in CPU No.1 Device used in CPU No.2
M0
D0 and D1 D0 and D1
Send data from CPU No.1 to CPU No.2
-
• Program example of CPU No.1
M0
D100
Send data from CPU No.1 to CPU No.2
Storage device for data received from CPU
No.1
YE0 Data reception flag (for data from CPU No.1)
SM400 Always ON
4
• Program example of CPU No.2
SM400
Always
ON
CPU No.1
send data
(bit)
CPU No.1
send data
(word)
CPU No.2
receive data
(bit)
CPU No.2
receive data
(word)
4.3.2 Program examples for Universal model QCPU
4.3 Program Examples for Communications by Auto Refresh
95

(b) Continuously sending data from CPU No.1 to CPU No.2
SM400
Always ONCPU No.1
send flag
Send start
data
Send end
data
Send start
data
CPU No.1
send data
CPU No.1
send flag
CPU No.1
send flag
CPU No.2
receive
complete flag
CPU No.1
send data
CPU No.2
receive data
CPU No.2
receive
complete flag
CPU No.1
send flag
• Devices used in CPU modules
Device used in CPU No.1 Device used in CPU No.2
M40 Send data from CPU No.2 to CPU No.1 M40 Send data from CPU No.2 to CPU No.1
D10 to
D18
D81 to
D88
Send data from CPU No.1 to CPU No.2
Storage device of send data to CPU No.2
SM400 Always ON -
For handshake between CPU No.1 and No.2, refer to Page 148, Section 6.1.2 (5).
• Program example of CPU No.1
D10 to
D18
D121 to
D128
Send data from CPU No.1 to CPU No.2
Storage device for data received from CPU
No.1
96
• Program example of CPU No.2

CHAPTER 4 STARTING UP MULTIPLE CPU SYSTEM
Setting of CPU No.1 Setting of CPU No.2
CPU shared memory
Host CPU operation
information area
System area
Auto refresh area
Auto refresh area
User setting area
CPU No.1
send area
CPU No.1
receive area
CPU No.2
receive area
User setting area
Auto refresh area
Use-prohibited area
Multiple CPU high
speed transmission area
3E0\G10000
3E0\G17133 3E0\G17133
3E0\G17133
3E1\G10000
CPU No.1 memory
Auto refresh area
User setting area
CPU No.2
send area
User setting area
Auto refresh area
3E0\G10000
3E1\G10000
CPU No.2 memory
3E1\G17133
to
to
(c) Continuously reading/writing data between CPU No.1 and CPU No.2 using the user
setting area in the multiple CPU high speed transmission area
Data can be read/write between CPU modules using the user setting area in the CPU shared memory.
The same number of points must be set for CPU No.1 and CPU No.2 in the auto refresh setting.
4
The user setting area will be 3E0\G10000 and later for CPU No.1 and 3E1\G10000 and later for CPU No.2.
4.3.2 Program examples for Universal model QCPU
4.3 Program Examples for Communications by Auto Refresh
97

• Devices used in CPU modules
CPU No.1 read
completed
CPU No.2
write flag
CPU No.2
write flag
Write
final data
Write
head data
Write
head data
Always ONCPU No.2
write flag
CPU No.2
write flag
Read
head data
CPU No.1
read
completed
Device used in CPU No.1 Device used in CPU No.2
M31 Send data from CPU No.1 to CPU No.2 M31 Send data from CPU No.1 to CPU No.2
M63 Send data from CPU No.2 to CPU No.1 M63 Send data from CPU No.2 to CPU No.1
D100 to
D149
Storage device for data received from CPU
No.2
D200 to
D249
Storage device of send data to CPU No.1
- SM400 Always ON
• Program example of CPU No.2
98
• Program example of CPU No.1
 Loading...
Loading...