
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
(Please read these instructions before using this equipment.)
Before using this product, please read this manual and the relevant manuals introduced in this manual
carefully and pay full attention to safety to handle the product correctly.
These precautions apply only to this product. Refer to the Q173CPU(N)/Q172CPU(N) Users manual for a
description of the Motion controller safety precautions.
In this manual, the safety instructions are ranked as "DANGER" and "CAUTION".
Indicates that incorrect handling may cause hazardous
Depending on circumstances, procedures indicated by
results.
In any case, it is important to follow the directions for usage.
Please save this manual to make it accessible when required and always forward it to the end user.
DANGER
CAUTION
conditions, resulting in death or severe injury.
Indicates that incorrect handling may cause hazardous
conditions, resulting in medium or slight personal injury or
physical damage.
CAUTION may also be linked to serious
A - 1
For Safe Operations
1. Prevention of electric shocks
DANGER
Never open the front case or terminal covers while the power is ON or the unit is running, as this
may lead to electric shocks.
Never run the unit with the front case or terminal cover removed. The high voltage terminal and
charged sections will be exposed and may lead to electric shocks.
Never open the front case or terminal cover at times other than wiring work or periodic
inspections even if the power is OFF. The insides of the Motion controller and servo amplifier are
charged and may lead to electric shocks.
Completely turn off the externally supplied power used in the system before mounting or
removing the module, performing wiring work, or inspections. Failing to do so may lead to electric
shocks.
When performing wiring work or inspections, turn the power OFF, wait at least ten minutes, and
then check the voltage with a tester, etc. Failing to do so may lead to electric shocks.
Be sure to ground the Motion controller, servo amplifier and servomotor. (Ground resistance :
or less) Do not ground commonly with other devices.
100
The wiring work and inspections must be done by a qualified technician.
Wire the units after installing the Motion controller, servo amplifier and servomotor. Failing to do
so may lead to electric shocks or damage.
Never operate the switches with wet hands, as this may lead to electric shocks.
Do not damage, apply excessive stress, place heavy things on or sandwich the cables, as this
may lead to electric shocks.
Do not touch the Motion controller, servo amplifier or servomotor terminal blocks while the power
is ON, as this may lead to electric shocks.
Do not touch the built-in power supply, built-in grounding or signal wires of the Motion controller
and servo amplifier, as this may lead to electric shocks.
2. For fire prevention
CAUTION
Install the Motion controller, servo amplifier, servomotor and regenerative resistor on
incombustible. Installing them directly or close to combustibles will lead to fire.
If a fault occurs in the Motion controller or servo amplifier, shut the power OFF at the servo
amplifier’s power source. If a large current continues to flow, fire may occur.
When using a regenerative resistor, shut the power OFF with an error signal. The regenerative
resistor may abnormally overheat due to a fault in the regenerative transistor, etc., and may lead
to fire.
Always take heat measures such as flame proofing for the inside of the control panel where the
servo amplifier or regenerative resistor is installed and for the wires used. Failing to do so may
lead to fire.
Do not damage, apply excessive stress, place heavy things on or sandwich the cables, as this
may lead to fire.
A - 2
3. For injury prevention
CAUTION
Do not apply a voltage other than that specified in the instruction manual on any terminal.
Doing so may lead to destruction or damage.
Do not mistake the terminal connections, as this may lead to destruction or damage.
Do not mistake the polarity ( + / - ), as this may lead to destruction or damage.
Do not touch the heat radiating fins of controller or servo amplifier, regenerative resistor and
servomotor, etc., while the power is ON and for a short time after the power is turned OFF. In this
timing, these parts become very hot and may lead to burns.
Always turn the power OFF before touching the servomotor shaft or coupled machines, as these
parts may lead to injuries.
Do not go near the machine during test operations or during operations such as teaching.
Doing so may lead to injuries.
4. Various precautions
Strictly observe the following precautions.
Mistaken handling of the unit may lead to faults, injuries or electric shocks.
(1) System structure
CAUTION
Always install a leakage breaker on the Motion controller and servo amplifier power source.
If installation of an electromagnetic contactor for power shut off during an error, etc., is specified in
the instruction manual for the servo amplifier, etc., always install the electromagnetic contactor.
Install the emergency stop circuit externally so that the operation can be stopped immediately and
the power shut off.
Use the Motion controller, servo amplifier, servomotor and regenerative resistor with the correct
combinations listed in the instruction manual. Other combinations may lead to fire or faults.
Use the Motion controller, base unit and motion module with the correct combinations listed in the
instruction manual. Other combinations may lead to faults.
If safety standards (ex., robot safety rules, etc.,) apply to the system using the Motion controller,
servo amplifier and servomotor, make sure that the safety standards are satisfied.
Construct a safety circuit externally of the Motion controller or servo amplifier if the abnormal
operation of the Motion controller or servo amplifier differ from the safety directive operation in the
system.
In systems where coasting of the servomotor will be a problem during the forced stop, emergency
stop, servo OFF or power supply OFF, use dynamic brakes.
Make sure that the system considers the coasting amount even when using dynamic brakes.
In systems where perpendicular shaft dropping may be a problem during the forced stop,
emergency stop, servo OFF or power supply OFF, use both dynamic brakes and electromagnetic
brakes.
A - 3
CAUTION
The dynamic brakes must be used only on errors that cause the forced stop, emergency stop, or
servo OFF. These brakes must not be used for normal braking.
The brakes (electromagnetic brakes) assembled into the servomotor are for holding applications,
and must not be used for normal braking.
The system must have a mechanical allowance so that the machine itself can stop even if the
stroke limits switch is passed through at the max. speed.
Use wires and cables that have a wire diameter, heat resistance and bending resistance
compatible with the system.
Use wires and cables within the length of the range described in the instruction manual.
The ratings and characteristics of the parts (other than Motion controller, servo amplifier and
servomotor) used in a system must be compatible with the Motion controller, servo amplifier and
servomotor.
Install a cover on the shaft so that the rotary parts of the servomotor are not touched during
operation.
There may be some cases where holding by the electromagnetic brakes is not possible due to the
life or mechanical structure (when the ball screw and servomotor are connected with a timing belt,
etc.). Install a stopping device to ensure safety on the machine side.
(2) Parameter settings and programming
CAUTION
Set the parameter values to those that are compatible with the Motion controller, servo amplifier,
servomotor and regenerative resistor model and the system application. The protective functions
may not function if the settings are incorrect.
The regenerative resistor model and capacity parameters must be set to values that conform to
the operation mode, servo amplifier and servo power supply module. The protective functions
may not function if the settings are incorrect.
Set the mechanical brake output and dynamic brake output validity parameters to values that are
compatible with the system application. The protective functions may not function if the settings
are incorrect.
Set the stroke limit input validity parameter to a value that is compatible with the system
application. The protective functions may not function if the setting is incorrect.
Set the servomotor encoder type (increment, absolute position type, etc.) parameter to a value
that is compatible with the system application. The protective functions may not function if the
setting is incorrect.
Set the servomotor capacity and type (standard, low-inertia, flat, etc.) parameter to values that
are compatible with the system application. The protective functions may not function if the
settings are incorrect.
Set the servo amplifier capacity and type parameters to values that are compatible with the
system application. The protective functions may not function if the settings are incorrect.
Use the program commands for the program with the conditions specified in the instruction
manual.
A - 4
CAUTION
Set the sequence function program capacity setting, device capacity, latch validity range, I/O
assignment setting, and validity of continuous operation during error detection to values that are
compatible with the system application. The protective functions may not function if the settings
are incorrect.
Some devices used in the program have fixed applications, so use these with the conditions
specified in the instruction manual.
The input devices and data registers assigned to the link will hold the data previous to when
communication is terminated by an error, etc. Thus, an error correspondence interlock program
specified in the instruction manual must be used.
Use the interlock program specified in the intelligent function module's instruction manual for the
program corresponding to the intelligent function module.
(3) Transportation and installation
CAUTION
Transport the product with the correct method according to the mass.
Use the servomotor suspension bolts only for the transportation of the servomotor. Do not
transport the servomotor with machine installed on it.
Do not stack products past the limit.
When transporting the Motion controller or servo amplifier, never hold the connected wires or
cables.
When transporting the servomotor, never hold the cables, shaft or detector.
When transporting the Motion controller or servo amplifier, never hold the front case as it may fall
off.
When transporting, installing or removing the Motion controller or servo amplifier, never hold the
edges.
Install the unit according to the instruction manual in a place where the mass can be withstood.
Do not get on or place heavy objects on the product.
Always observe the installation direction.
Keep the designated clearance between the Motion controller or servo amplifier and control panel
inner surface or the Motion controller and servo amplifier, Motion controller or servo amplifier and
other devices.
Do not install or operate Motion controller, servo amplifiers or servomotors that are damaged or
that have missing parts.
Do not block the intake/outtake ports of the Motion controller, servo amplifier and servomotor with
cooling fan.
Do not allow conductive matter such as screw or cutting chips or combustible matter such as oil
enter the Motion controller, servo amplifier or servomotor.
The Motion controller, servo amplifier and servomotor are precision machines, so do not drop or
apply strong impacts on them.
Securely fix the Motion controller, servo amplifier and servomotor to the machine according to
the instruction manual. If the fixing is insufficient, these may come off during operation.
A - 5
CAUTION
Always install the servomotor with reduction gears in the designated direction. Failing to do so
may lead to oil leaks.
Store and use the unit in the following environmental conditions.
Environment
Ambient
temperature
Ambient humidity
Storage
temperature
Atmosphere
Altitude
Vibration
Motion controller/Servo amplifier Servomotor
According to each instruction manual.
According to each instruction manual.
According to each instruction manual.
Indoors (where not subject to direct sunlight).
No corrosive gases, flammable gases, oil mist or dust must exist
1000m (3280.84ft.) or less above sea level
According to each instruction manual
Conditions
0°C to +40°C (With no freezing)
(32°F to +104°F)
80% RH or less
(With no dew condensation)
-20°C to +65°C
(-4°F to +149°F)
When coupling with the synchronous encoder or servomotor shaft end, do not apply impact such
as by hitting with a hammer. Doing so may lead to detector damage.
Do not apply a load larger than the tolerable load onto the synchronous encoder and servomotor
shaft. Doing so may lead to shaft breakage.
When not using the module for a long time, disconnect the power line from the Motion controller
or servo amplifier.
Place the Motion controller and servo amplifier in static electricity preventing vinyl bags and store.
When storing for a long time, please contact with our sales representative.
Also, execute a trial operation.
A - 6
(4) Wiring
CAUTION
Correctly and securely wire the wires. Reconfirm the connections for mistakes and the terminal
screws for tightness after wiring. Failing to do so may lead to run away of the servomotor.
After wiring, install the protective covers such as the terminal covers to the original positions.
Do not install a phase advancing capacitor, surge absorber or radio noise filter (option FR-BIF)
on the output side of the servo amplifier.
Correctly connect the output side (terminal U, V, W) and ground. Incorrect connections will lead
the servomotor to operate abnormally.
Do not connect a commercial power supply to the servomotor, as this may lead to trouble.
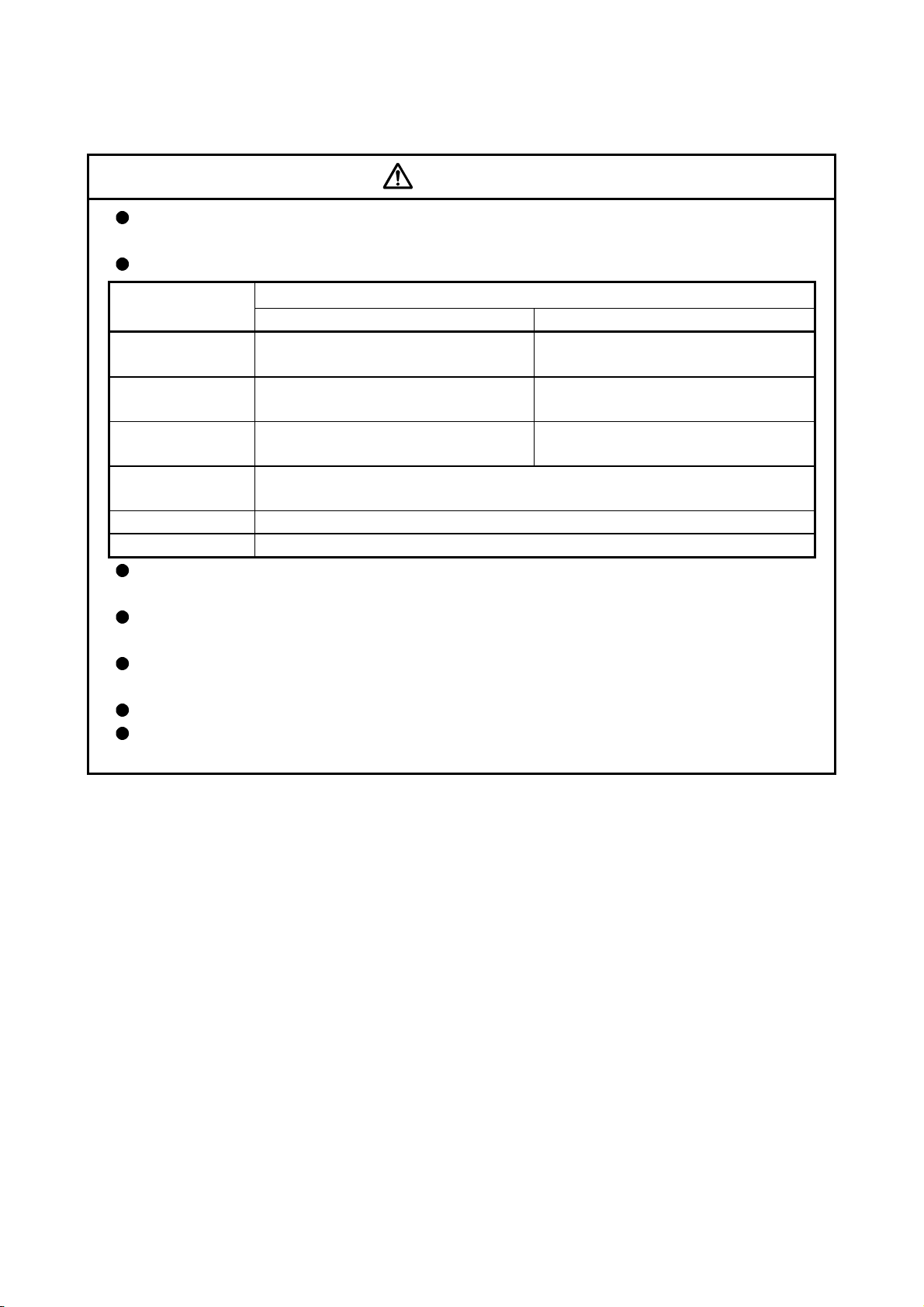
Do not mistake the direction of the surge absorbing diode
installed on the DC relay for the control signal output of brake
signals, etc. Incorrect installation may lead to signals not being
output when trouble occurs or the protective functions not
functioning.
Do not connect or disconnect the connection cables between
each unit, the encoder cable or PLC expansion cable while the
power is ON.
Securely tighten the cable connector fixing screws and fixing mechanisms. Insufficient fixing may
lead to the cables combing off during operation.
Do not bundle the power line or cables.
Servo amplifier
VIN
(24VDC)
Control output
signal
RA
(5) Trial operation and adjustment
CAUTION
Confirm and adjust the program and each parameter before operation. Unpredictable
movements may occur depending on the machine.
Extreme adjustments and changes may lead to unstable operation, so never make them.
When using the absolute position system function, on starting up, and when the Motion
controller or absolute value motor has been replaced, always perform a home position return.
A - 7
(6) Usage methods
CAUTION
Immediately turn OFF the power if smoke, abnormal sounds or odors are emitted from the
Motion controller, servo amplifier or servomotor.
Always execute a test operation before starting actual operations after the program or
parameters have been changed or after maintenance and inspection.
Do not attempt to disassemble and repair the units excluding a qualified technician whom our
company recognized.
Do not make any modifications to the unit.
Keep the effect or electromagnetic obstacles to a minimum by installing a noise filter or by using
wire shields, etc. Electromagnetic obstacles may affect the electronic devices used near the
Motion controller or servo amplifier.
When using the CE Mark-compliant equipment, refer to the "EMC Installation Guidelines" (data
number IB(NA)-67339) for the Motion controllers and refer to the corresponding EMC guideline
information for the servo amplifiers, inverters and other equipment.
Use the units with the following conditions.
Item Conditions
Input power According to each instruction manual.
Input frequency According to each instruction manual.
Tolerable momentary power failure According to each instruction manual.
(7) Corrective actions for errors
CAUTION
If an error occurs in the self diagnosis of the Motion controller or servo amplifier, confirm the
check details according to the instruction manual, and restore the operation.
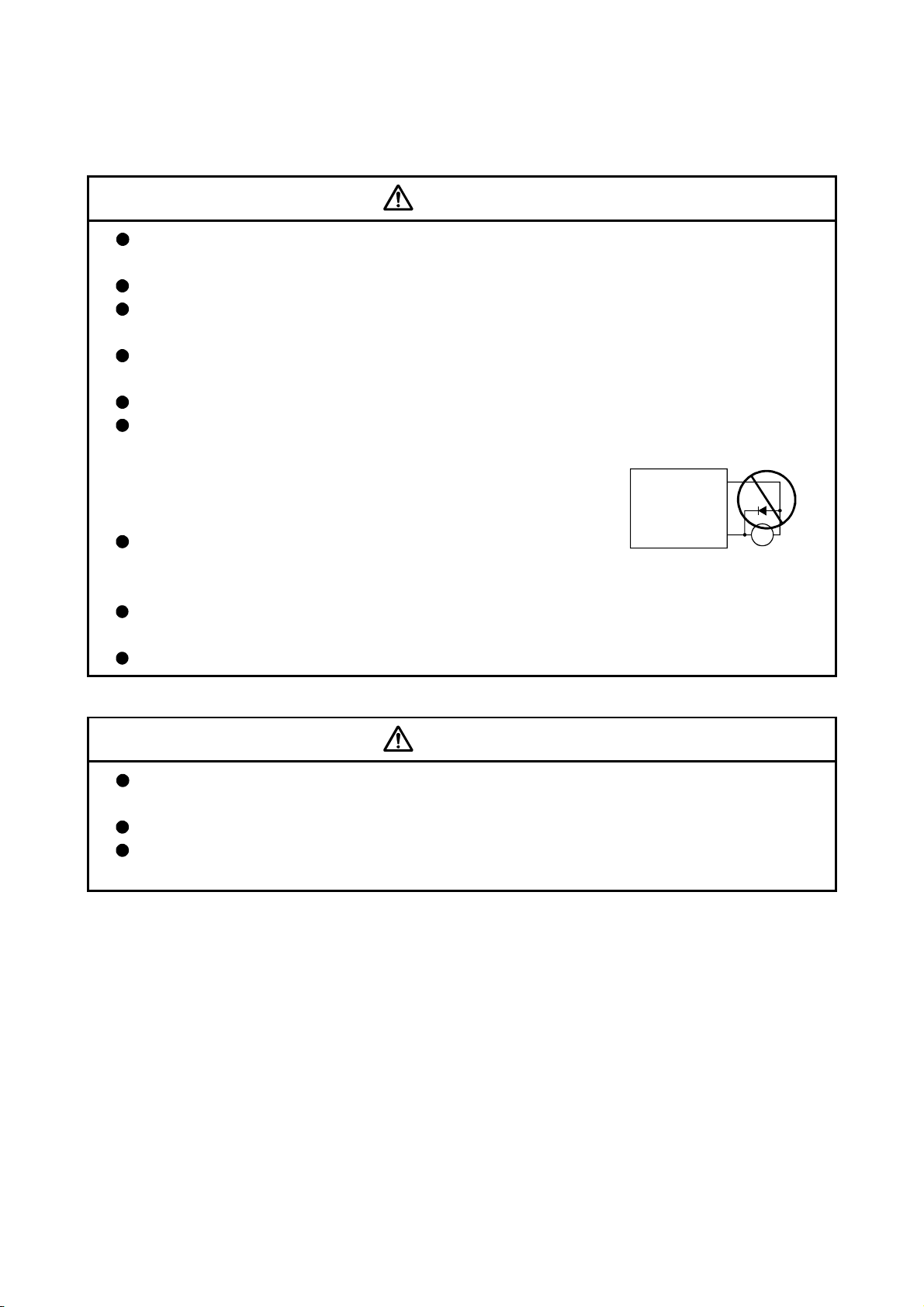
If a dangerous state is predicted in case of a power failure or product failure, use a servomotor
with electromagnetic brakes or install a brake mechanism externally.
Use a double circuit construction so that the electromagnetic brake operation circuit can be
operated by emergency stop signals set externally.
Shut off with servo ON signal OFF,
alarm, electromagnetic brake signal.
Servomotor
Electromagnetic
brakes
RA1 EMG
Shut off with the
emergency stop
signal (EMG).
24VDC
If an error occurs, remove the cause, secure the safety and then resume operation after alarm
release.
The unit may suddenly resume operation after a power failure is restored, so do not go near the
machine. (Design the machine so that personal safety can be ensured even if the machine
restarts suddenly.)
A - 8
(8) Maintenance, inspection and part replacement
CAUTION
Perform the daily and periodic inspections according to the instruction manual.
Perform maintenance and inspection after backing up the program and parameters for the Motion
controller and servo amplifier.
Do not place fingers or hands in the clearance when opening or closing any opening.
Periodically replace consumable parts such as batteries according to the instruction manual.
Do not touch the lead sections such as ICs or the connector contacts.
Before touching the module, always touch grounded metal, etc. to discharge static electricity from
human body. Failure to do so may cause the module to fail or malfunction.
Do not directly touch the module's conductive parts and electronic components.
Touching them could cause an operation failure or give damage to the module.
Do not place the Motion controller or servo amplifier on metal that may cause a power leakage
or wood, plastic or vinyl that may cause static electricity buildup.
Do not perform a megger test (insulation resistance measurement) during inspection.
When replacing the Motion controller or servo amplifier, always set the new module settings
correctly.
When the Motion controller or absolute value motor has been replaced, carry out a home
position return operation using one of the following methods, otherwise position displacement
could occur.
1) After writing the servo data to the Motion controller using programming software, switch on the
power again, then perform a home position return operation.
2) Using the backup function of the programming software, load the data backed up before
replacement.
After maintenance and inspections are completed, confirm that the position detection of the
absolute position detector function is correct.
Do not drop or impact the battery installed to the module.
Doing so may damage the battery, causing battery liquid to leak in the battery. Do not use the
dropped or impacted battery, but dispose of it.
Do not short circuit, charge, overheat, incinerate or disassemble the batteries.
The electrolytic capacitor will generate gas during a fault, so do not place your face near the
Motion controller or servo amplifier.
The electrolytic capacitor and fan will deteriorate. Periodically replace these to prevent secondary
damage from faults. Replacements can be made by our sales representative.
Lock the control panel and prevent access to those who are not certified to handle or install
electric equipment.
Do not burn or break a module and servo amplifier. Doing so may cause a toxic gas.
A - 9
(9) About processing of waste
When you discard Motion controller, servo amplifier, a battery (primary battery) and other option
articles, please follow the law of each country (area).
CAUTION
This product is not designed or manufactured to be used in equipment or systems in situations
that can affect or endanger human life.
When considering this product for operation in special applications such as machinery or systems
used in passenger transportation, medical, aerospace, atomic power, electric power, or
submarine repeating applications, please contact your nearest Mitsubishi sales representative.
Although this product was manufactured under conditions of strict quality control, you are strongly
advised to install safety devices to forestall serious accidents when it is used in facilities where a
breakdown in the product is likely to cause a serious accident.
(10) General cautions
All drawings provided in the instruction manual show the state with the covers and safety
partitions removed to explain detailed sections. When operating the product, always return the
covers and partitions to the designated positions, and operate according to the instruction
manual.
A - 10
REVISIONS
The manual number is given on the bottom left of the back cover.
Print Date Manual Number Revision
Jun., 2002 IB(NA)-0300042-A First edition
Feb., 2004 IB(NA)-0300042-B [Addition model]
Q173CPUN-T/Q172CPUN-T, A31TU-D3K13/A31TU-DNK13,
Q172EX-S1, Q173PX-S1, Q00CPU, Q01CPU, 64AD, Q68ADV, Q68ADI,
Q62DA, Q64DA, Q68DAV, Q68DAI, Q170TUD3CBL3M,
Q170TUDNCBL3M, Q170TUDNCBL03M-A, Q170TUTM, A31TUD3TM,
FR-V5
0- , Software for SV43
[Addition function]
For WindowsXP, Home position return function, ROM operation function,
Online change function
[Additional correction/partial correction]
Safety precautions, About processing of waste, Startup slow of the
Multiple CPU system, User file list, Error code list, etc.
[partial correction]
Mar., 2006 IB(NA)-0300042-C [Addition model]
Q62P, Q172EX-S2, Q172EX-S3, Q170ENC
[Addition function]
Cam axis command signal, Smoothing clutch complete signal, Gain
changing signal, Real mode axis information register, Motion SFC
instruction "FMOV", Bit device setting by Motion SFC instruction, Security
function
[Additional correction/partial correction]
Safety precautions, User file list, Error code list, Warranty, Manual model
code (1CT781
1XB781), etc.
Apr., 2010 IB(NA)-0300042-D [Additional correction/partial correction]
Safety precautions, "1.6.1 I/O No. for I/O modules and intelligent function
modules", Warranty
Japanese Manual Version IB(NA)-0300023
This manual confers no industrial property rights or any rights of any other kind, nor does it confer any patent
licenses. Mitsubishi Electric Corporation cannot be held responsible for any problems involving industrial property
rights which may occur as a result of using the contents noted in this manual.
© 2002 MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORPORATION
A - 11
INTRODUCTION
Thank you for choosing the Q173CPU(N)/Q172CPU(N) Motion Controller.
Please read this manual carefully so that equipment is used to its optimum.
CONTENTS
Safety Precautions .........................................................................................................................................A- 1
Revisions ........................................................................................................................................................A-11
Contents .........................................................................................................................................................A-12
About Manuals ...............................................................................................................................................A-18
1. OVERVIEW 1- 1 to 1-96
1.1 Overview................................................................................................................................................... 1- 1
1.2 Features ................................................................................................................................................... 1- 3
1.2.1 Features of Motion CPU ................................................................................................................... 1- 3
1.2.2 Basic specifications of Q173CPU(N)/Q172CPU(N)......................................................................... 1- 6
1.2.3 Operation control/transition control specifications ........................................................................... 1- 9
1.2.4 Differences between Q173CPU(N)/Q172CPU(N)and A173UHCPU/A172SHCPUN.................... 1-13
1.2.5 Positioning dedicated devices/special relays/special registers ....................................................... 1-15
1.3 Hardware Configuration ........................................................................................................................... 1-55
1.3.1 Motion system configuration ............................................................................................................. 1-55
1.3.2 Q173CPU(N) System overall configuration...................................................................................... 1-61
1.3.3 Q172CPU(N) System overall configuration...................................................................................... 1-63
1.3.4 Software packages............................................................................................................................ 1-65
1.3.5 Restrictions on motion systems ........................................................................................................1-69
1.4 Multiple CPU System ...............................................................................................................................1-71
1.4.1 Overview ............................................................................................................................................ 1-71
1.4.2 Installation of PLC CPU and Motion CPU ........................................................................................ 1-72
1.4.3 Precautions for using Q series I/O modules and intelligent function modules................................ 1-73
1.4.4 Modules subject to installation restrictions ....................................................................................... 1-74
1.4.5 Processing time of the Multiple CPU system ...................................................................................1-75
1.4.6 How to reset the Multiple CPU system .............................................................................................1-76
1.4.7 Processing at a CPU DOWN error occurrence by a PLC CPU or Q173CPU(N)/Q172CPU(N).... 1-77
1.5 System Settings .......................................................................................................................................1-80
1.5.1 System data settings .........................................................................................................................1-80
1.5.2 Common system parameters ........................................................................................................... 1-81
1.5.3 Individual parameters ........................................................................................................................1-87
1.6 Assignment of I/O No. ..............................................................................................................................1-92
1.6.1 I/O No. for I/O modules and intelligent function modules ................................................................ 1-92
1.6.2 I/O No. of PLC CPU and Q173CPU(N)/Q172CPU(N)..................................................................... 1-95
1.6.3 Setting I/O No. ................................................................................................................................... 1-96
2. STARTING UP THE MULTIPLE CPU SYSTEM 2- 1 to 2- 2
2.1 Startup Flow of the Multiple CPU System ............................................................................................... 2- 1
A - 12
3. COMMUNICATION BETWEEN THE PLC CPU AND THE MOTION CPU IN
THE MULTIPLE CPU SYSTEM 3- 1 to 3-26
3.1 Automatic Refresh Function of The Shared CPU Memory .................................................................... 3- 1
3.2 Control Instruction from the PLC CPU to The Motion CPU (Motion dedicated instructions) ................ 3-20
3.3 Reading/Writing Device Data .................................................................................................................. 3-21
3.4 Shared CPU Memory............................................................................................................................... 3-22
4. STRUCTURE OF THE MOTION CPU PROGRAM 4- 1 to 4- 4
4.1 Motion Control in SV13/SV22 Real Mode ............................................................................................... 4- 2
4.2 Motion Control in SV22 Virtual Mode ......................................................................................................4- 3
5. MOTION DEDICATED PLC INSTRUCTION 5- 1 to 5-48
5.1 Motion Dedicated PLC Instruction ........................................................................................................... 5- 1
5.1.1 Restriction item of the Motion dedicated PLC instruction ................................................................5- 1
5.2 Motion SFC Start Request from The PLC CPU to The Motion CPU:
S(P).SFCS (PLC instruction:
S(P).SFCS
) ............................................................................................ 5- 9
5.3 Servo Program Start Request from The PLC CPU to The Motion CPU:
S(P).SVST (PLC instruction:
S(P).SVST
) ........................................................................................... 5-12
5.4 Current Value Change Instruction from The PLC CPU to The Motion CPU:
S(P).CHGA (PLC instruction:
S(P).CHGA
) ..........................................................................................5-17
5.5 Speed Change Instruction from The PLC CPU to The Motion CPU:
S(P).CHGV (PLC instruction:
S(P).CHGV
) ..........................................................................................5-30
5.6 Torque Limit Value Change Request Instruction from The PLC CPU to The Motion CPU:
S(P).CHGT (PLC instruction:
5.7 Write from The PLC CPU to The Motion CPU: S(P).DDWR (PLC instruction:
5.8 Read from The Devices of The Motion CPU: S(P).DDRD (PLC instruction:
5.9 Interrupt Instruction to The Other CPU: S(P).GINT (PLC instruction:
S(P).CHGT
)........................................................................................... 5-34
S(P).DDRD
S(P).GINT
S(P).DDWR
).............................. 5-46
)............. 5-38
) ................. 5-42
6. MOTION SFC PROGRAMS 6- 1 to 6-28
6.1 Motion SFC Program Configuration ........................................................................................................6- 1
6.2 Motion SFC Chart Symbol List ................................................................................................................ 6- 2
6.3 Branch and Coupling Chart List............................................................................................................... 6- 5
6.4 Motion SFC Program Name .................................................................................................................... 6- 9
6.5 Steps......................................................................................................................................................... 6-10
6.5.1 Motion control step ............................................................................................................................6-10
6.5.2 Operation control step....................................................................................................................... 6-11
6.5.3 Subroutine call/start step................................................................................................................... 6-12
6.5.4 Clear step .......................................................................................................................................... 6-14
6.6 Transitions ................................................................................................................................................ 6-15
6.7 Jump, Pointer ........................................................................................................................................... 6-17
6.8 END .......................................................................................................................................................... 6-17
6.9 Branches, Couplings ................................................................................................................................6-18
6.9.1 Series transition................................................................................................................................. 6-18
A - 13

6.9.2 Selective branch, selective coupling................................................................................................. 6-19
6.9.3 Parallel branch, parallel coupling...................................................................................................... 6-20
6.10 Y/N Transitions....................................................................................................................................... 6-22
6.11 Motion SFC Comments ......................................................................................................................... 6-26
7. OPERATION CONTROL PROGRAMS 7- 1 to 7-96
7.1 Operation Control Programs.................................................................................................................... 7- 1
7.2 Device Descriptions ................................................................................................................................. 7- 7
7.3 Constant Descriptions .............................................................................................................................. 7- 9
7.4 Binary Operations .................................................................................................................................... 7-10
7.4.1 Substitution : =................................................................................................................................... 7-10
7.4.2 Addition : +......................................................................................................................................... 7-12
7.4.3 Subtraction :
7.4.4 Multiplication : * ................................................................................................................................. 7-15
7.4.5 Division : / .......................................................................................................................................... 7-16
7.4.6 Remainder : %................................................................................................................................... 7-17
7.5 Bit Operations........................................................................................................................................... 7-18
7.5.1 Bit inversion(Complement) : ~ .......................................................................................................... 7-18
7.5.2 Bit logical AND : & ............................................................................................................................. 7-19
7.5.3 Bit logical OR : | ................................................................................................................................. 7-20
7.5.4 Bit exclusive logical OR : ^................................................................................................................ 7-21
7.5.5 Bit right shift : >>................................................................................................................................ 7-22
7.5.6 Bit left shift : << .................................................................................................................................. 7-23
7.5.7 Sign inversion(Complement of 2) :
7.6 Standard Functions ..................................................................................................................................7-25
7.6.1 Sine : SIN........................................................................................................................................... 7-25
7.6.2 Cosine : COS..................................................................................................................................... 7-26
7.6.3 Tangent : TAN ................................................................................................................................... 7-27
7.6.4 Arcsine : ASIN ...................................................................................................................................7-28
7.6.5 Arccosine : ACOS .............................................................................................................................7-29
7.6.6 Arctangent : ATAN ............................................................................................................................ 7-30
7.6.7 Square root : SQRT .......................................................................................................................... 7-31
7.6.8 Natural logarithm : LN .......................................................................................................................7-32
7.6.9 Exponential operation : EXP ............................................................................................................. 7-33
7.6.10 Absolute value : ABS ......................................................................................................................7-34
7.6.11 Round-off : RND.............................................................................................................................. 7-35
7.6.12 Round-down : FIX ...........................................................................................................................7-36
7.6.13 Round-up : FUP .............................................................................................................................. 7-37
7.6.14 BCD
7.6.15 BIN
7.7 Type Conversions .................................................................................................................................... 7-40
7.7.1 Signed 16-bit integer value conversion : SHORT ............................................................................ 7-40
7.7.2 Unsigned 16-bit integer value conversion : USHORT ..................................................................... 7-41
7.7.3 Signed 32-bit integer value conversion : LONG............................................................................... 7-42
7.7.4 Unsigned 32-bit integer value conversion : ULONG ........................................................................ 7-43
7.7.5 Signed 64-bit floating-point value conversion : FLOAT ................................................................... 7-44
7.7.6 Unsigned 64-bit floating-point value conversion : UFLOAT ............................................................ 7-45
BCD conversion : BCD........................................................................................................ 7-39
.................................................................................................................................. 7-13
............................................................................................... 7-24
BIN conversion : BIN ......................................................................................................... 7-38
A - 14

7.8 Bit Device Statuses .................................................................................................................................. 7-46
7.8.1 ON (Normally open contact) : (None) ............................................................................................... 7-46
7.8.2 OFF (Normally closed contact) : ! .....................................................................................................7-47
7.9 Bit Device Controls................................................................................................................................... 7-48
7.9.1 Device set : SET................................................................................................................................ 7-48
7.9.2 Device reset : RST ............................................................................................................................ 7-50
7.9.3 Device output : DOUT ....................................................................................................................... 7-52
7.9.4 Device input : DIN ............................................................................................................................. 7-53
7.9.5 Bit device output : OUT .................................................................................................................... 7-54
7.10 Logical Operations ................................................................................................................................. 7-56
7.10.1 Logical acknowledgement : (None) ................................................................................................7-56
7.10.2 Logical negation : ! ..........................................................................................................................7-57
7.10.3 Logical AND : * ................................................................................................................................ 7-58
7.10.4 Logical OR : +.................................................................................................................................. 7-59
7.11 Comparison Operations......................................................................................................................... 7-60
7.11.1 Equal to : == ....................................................................................................................................7-60
7.11.2 Not equal to : != ...............................................................................................................................7-61
7.11.3 Less than : < .................................................................................................................................... 7-62
7.11.4 Less than or equal to : <= ............................................................................................................... 7-63
7.11.5 More than : > ................................................................................................................................... 7-64
7.11.6 More than or equal to : >=............................................................................................................... 7-65
7.12 Motion-Dedicated Functions(CHGV, CHGT) ........................................................................................7-66
7.12.1 Speed change request : CHGV ......................................................................................................7-66
7.12.2 Torque limit value change request : CHGT.................................................................................... 7-72
7.13 Other Instructions................................................................................................................................... 7-74
7.13.1 Event task enable : EI ..................................................................................................................... 7-74
7.13.2 Event task disable : DI ....................................................................................................................7-75
7.13.3 No operation : NOP......................................................................................................................... 7-76
7.13.4 Block transfer : BMOV .................................................................................................................... 7-77
7.13.5 Same data block transfer : FMOV ..................................................................................................7-80
7.13.6 Write device data to shared CPU memory of the self CPU : MULTW ..........................................7-82
7.13.7 Read device data from shared CPU memory of the other CPU: MULTR..................................... 7-85
7.13.8 Write device data to intelligent function module/special function module : TO............................. 7-88
7.13.9 Read device data from intelligent function module/special function module : FROM .................. 7-91
7.13.10 Time to wait : TIME .......................................................................................................................7-94
7.14 Comment Statement : //......................................................................................................................... 7-96
8. TRANSITION PROGRAMS 8- 1 to 8- 2
8.1 Transition Programs................................................................................................................................. 8- 1
9. MOTION CONTROL PROGRAMS 9- 1 to 9-22
9.1 Servo Instruction List................................................................................................................................ 9- 1
9.2 Servomotor/Virtual Servomotor Shaft Current Value Change................................................................ 9-14
9.3 Synchronous Encoder Shaft Current Value Change Control (SV22 Only)............................................ 9-17
9.4 Cam Shaft Within-One-Revolution Current Value Change Control (SV22 Only) .................................. 9-20
A - 15
9.5 Programming Instructions........................................................................................................................ 9-22
9.5.1 Cancel • start ..................................................................................................................................... 9-22
9.5.2 Indirect designation using motion devices........................................................................................ 9-22
10. MOTION DEVICES 10- 1 to 10- 6
10.1 Motion Registers (#0 to #8191) ............................................................................................................ 10- 1
10.2 Coasting Timer (FT) ..............................................................................................................................10- 6
11. MOTION SFC PARAMETER 11- 1 to 11-20
11.1 Task Definitions.................................................................................................................................... 11- 1
11.2 Number of Consecutive Transitions and Task Operation ..................................................................11- 2
11.2.1 Number of consecutive transitions ...............................................................................................11- 2
11.2.2 Task operation............................................................................................................................... 11- 3
11.3 Execution Status of The Multiple Task................................................................................................ 11- 7
11.4 Task Parameters.................................................................................................................................. 11- 8
11.5 Program Parameters............................................................................................................................ 11-10
11.6 How to Start The Motion SFC Program .............................................................................................. 11-16
11.6.1 Automatic start .............................................................................................................................. 11-16
11.6.2 Start from the Motion SFC program ............................................................................................. 11-16
11.6.3 Start from PLC (PLC instruction S(P).SFCS
)............................................................................ 11-16
11.7 How to End The Motion SFC Program ............................................................................................... 11-17
11.8 How to Change from One Motion SFC Program to Another.............................................................. 11-17
11.9 How to Manage The Executing Program ............................................................................................ 11-17
11.10 Operation Performed at CPU Power-Off or Reset ..........................................................................11-18
11.11 Operation Performed when CPU is Switched from RUN/STOP ...................................................... 11-18
11.12 Operation Performed when PLC Ready flag (M2000) Turns OFF/ON ............................................ 11-19
11.13 Operation at The Error Occurrence................................................................................................... 11-20
12. USER FILES 12- 1 to 12- 8
12.1 Projects................................................................................................................................................. 12- 1
12.2 User File List ........................................................................................................................................ 12- 2
12.3 Online Change in The Motion SFC Program ...................................................................................... 12- 3
12.3.1 Operating method for The Online Change ................................................................................... 12- 4
12.3.2 Transfer of program ...................................................................................................................... 12- 7
13. LIMIT SWITCH OUTPUT FUNCTION 13- 1 to 13- 8
13.1 Operations............................................................................................................................................ 13- 1
13.2 Limit Output Setting Data..................................................................................................................... 13- 4
14. ROM OPERATION FUNCTION 14- 1 to 14-12
14.1 About the ROM Operation Function .................................................................................................... 14- 1
14.2 Specifications of LED • Switch............................................................................................................. 14- 3
14.3 ROM Operation Function Details ........................................................................................................ 14- 5
14.4 Operating Procedure of "ROM writing" ............................................................................................... 14-11
A - 16
15. SECURITY FUNCTION 15- 1 to 15- 6
15.1 Password Registration/change............................................................................................................ 15- 1
15.2 Password Clearance............................................................................................................................ 15- 3
15.3 Password Check ..................................................................................................................................15- 4
15.4 Password Save .................................................................................................................................... 15- 5
15.5 Clear All ................................................................................................................................................ 15- 6
16. COMMUNICATIONS VIA NETWORK 16- 1 to 16-10
16.1 Specifications of The Communications via Network........................................................................... 16- 2
16.2 Access Range of The Communications via Network ......................................................................... 16- 3
16.2.1 Network configuration via the MELSECNET/10(H) or the Ethernet............................................ 16- 3
16.2.2 Network configuration via the CC-Link ......................................................................................... 16- 5
16.2.3 Network configuration via the RS422/485.................................................................................... 16- 6
16.2.4 Network configuration which MELSECNET/10 (H), Ethernet, CC-Link, RS422/485 were mixed
.................................................................................................................................................................. 16- 7
17. MONITOR FUNCTION OF THE MAIN CYCLE 17- 1 to 17- 2
18. SERVO PARAMETER READING FUNCTION 18- 1 to 18- 2
18.1 About The Servo Parameter Read Request Devices......................................................................... 18- 1
18.2 Operating Procedure of The Servo Parameter Reading Function..................................................... 18- 2
19. ERROR CODE LISTS 19- 1 to 19-18
19.1 Reading Procedure for Error Codes.................................................................................................... 19- 1
19.2 Motion SFC Error Code List ................................................................................................................ 19- 2
19.3 Motion SFC Parameter Errors ............................................................................................................. 19-11
19.4 Multiple CPU Error Codes ................................................................................................................... 19-13
19.4.1 Self-diagnosis error code ..............................................................................................................19-13
19.4.2 Release of self-diagnosis error ..................................................................................................... 19-18
APPENDICES APP- 1 to APP-32
APPENDIX 1 Processing Times...............................................................................................................APP- 1
APPENDIX 1.1 Processing time of operation control/Transition instruction .......................................APP- 1
APPENDIX 2 Sample Program ................................................................................................................APP- 9
APPENDIX 2.1 Program example to execute the Multiple CPU dedicated instruction continuously.APP- 9
APPENDIX 2.2 The program example to execute plural Multiple CPU instruction by the instructions of
one time........................................................................................................................APP-11
APPENDIX 2.3 Motion control example by Motion SFC program.......................................................APP-13
APPENDIX 2.4 Continuation execution example at the subroutine re-start by the Motion SFC program
.....................................................................................................................................APP-24
APPENDIX 2.5 Continuation execution example after the stop by the Motion SFC program............APP-28
A - 17
About Manuals
The following manuals are related to this product.
Referring to this list, please request the necessary manuals.
Related Manuals
(1) Motion controller
Q173CPU(N)/Q172CPU(N) Motion controller User's Manual
This manual explains specifications of the Motion CPU modules, Q172LX Servo external signal interface
module, Q172EX Serial absolute synchronous encoder interface module, Q173PX Manual pulse
generator interface module, Teaching units, Power supply modules, Servo amplifiers, SSCNET cables,
synchronous encoder cables and others.
(Optional)
Q173CPU(N)/Q172CPU(N) Motion controller (SV13/SV22) Programming Manual
(REAL MODE)
This manual explains the servo parameters, positioning instructions, device list, error list and others.
(Optional)
Manual Name
Manual Number
(Model Code)
IB-0300040
(1XB780)
IB-0300043
(1XB782)
Q173CPU(N)/Q172CPU(N) Motion controller (SV22) Programming Manual
(VIRTUAL MODE)
This manual describes the dedicated instructions use to the synchronous control by virtual main shaft,
mechanical system program create mechanical module.
This manual explains the servo parameters, positioning instructions, device list, error list and others.
(Optional)
Q173CPU(N)/Q172CPU(N) Motion controller (SV43) Programming Manual
This manual describes the dedicated instructions to execute the positioning control by Motion program of
EIA language (G-code).
This manual explains the Multiple CPU system configuration, performance specifications, functions,
programming, debugging, servo parameters, positioning instructions, device list error list and others.
(Optional)
IB-0300044
(1XB783)
IB-0300070
(1CT784)
A - 18
(2) PLC
QCPU User's Manual (Hardware Design, Maintenance and Inspection)
This manual explains the specifications of the QCPU modules, power supply modules, base units,
extension cables, memory card battery, and the maintenance/inspection for the system, trouble shooting,
error codes and others.
(Optional)
Qn(H)/QnPH/QnPRHCPUCPU User's Manual (Function Explanation, Program
Fundamentals)
This manual explains the functions, programming methods and devices and others to create programs
with the QCPU.
(Optional)
QCPU User's Manual (Multiple CPU System)
This manual explains Multiple CPU system overview, system configuration, I/O modules, communication
between CPU modules and communication with the I/O modules or intelligent function modules.
(Optional)
Manual Name
Manual Number
(Model Code)
SH-080483ENG
(13JR73)
SH-080808ENG
(13JZ28)
SH-080485ENG
(13JR75)
QCPU Programming Manual (Common Instructions)
This manual explains how to use the sequence instructions, basic instructions, application instructions and
micro computer program.
(Optional)
QCPU (Q Mode)/QnACPU Programming Manual (PID Control Instructions)
This manual explains the dedicated instructions used to exercise PID control.
(Optional)
QCPU (Q Mode)/QnACPU Programming Manual (SFC)
This manual explains the system configuration, performance specifications, functions, programming,
debugging, error codes and others of MELSAP3.
(Optional)
I/O Module Type Building Block User's Manual
This manual explains the specifications of the I/O modules, connector, connector/terminal block
conversion modules and others.
(Optional)
SH-080809ENG
(13JW10)
SH-080040
(13JF59)
SH-080041
(13JF60)
SH-080042
(13JL99)
A - 19

MEMO
A - 20
1 OVERVIEW
1. OVERVIEW
1.1 Overview
This programming manual describes the Motion SFC program and Multiple CPU
system of the operating system software packages "SW6RN-SV13Q
Generic term/Abbreviation Description
Q173CPU(N)/Q172CPU(N) or
Motion CPU (module)
Q172LX/Q172EX/Q173PX
or Motion module
MR-H-BN Servo amplifier model MR-H BN
MR-J2 -B Servo amplifier model MR-J2S- B/MR-J2M-B/MR-J2- B/MR-J2-03B5
AMP or Servo amplifier
QCPU, PLC CPU
or PLC CPU module
Multiple CPU system
or Motion system
CPUn
Programming software package General name for "MT Developer" and "GX Developer"
Operating system software General name for "SW RN-SV Q "
SV13
SV22
SV22Q
In this manual, the following abbreviations are used.
" for Motion CPU module(Q173CPU(N)/Q172CPU(N)).
Q173CPUN/Q172CPUN/Q173CPUN-T/Q172CPUN-T/Q173CPU/Q172CPU
Motion CPU module
Q172LX Servo external signals interface module/
Q172EX(-S1/-S2/-S3) Serial absolute synchronous encoder interface module
Q173PX(-S1) Manual pulse generator interface module
General name for "Servo amplifier model MR-H
MR-J2- B/MR-J2-03B5, Vector inverter FREQROL-V500 series"
Qn(H)CPU
Abbreviation for "Multiple PLC system of the Q series"
Abbreviation for "CPU No.n (n= 1 to 4) of the CPU module for the Multiple CPU
system"
Operating system software for conveyor assembly use (Motion SFC) :
SW6RN-SV13Q
Operating system software for automatic machinery use (Motion SFC) :
SW6RN-SV22Q
BN/MR-J2S- B/MR-J2M-B/
", "SW6RN-
(Note-1)
1
/
MT Developer Abbreviation for Integrated start-up support software package "MT Developer"
GX Developer
Manual pulse generator
or MR-HDP01
Serial absolute synchronous encoder
or MR-HENC/Q170ENC
SSCNET
Absolute position system
Cooling fan unit Cooling fan unit (Q170FAN)
Dividing unit Dividing unit (Q173DV)
Battery unit Battery unit (Q170BAT)
(Note-2)
Abbreviation for MELSEC PLC programming software package "GX Developer
(Version 6 or later)"
Abbreviation for "Manual pulse generator (MR-HDP01)"
Abbreviation for "Serial absolute synchronous encoder (MR-HENC/Q170ENC)"
High speed serial communication between Motion controller and servo amplifier
General name for "System using the servomotor and servo amplifier for absolute
position"
1 - 1
1 OVERVIEW
Generic term/Abbreviation Description
A 0BD-PCF A10BD-PCF/A30BD-PCF SSC I/F board
SSC I/F communication cable Abbreviation for "Cable for SSC I/F board/card"
Teaching Unit
or A31TU-D3 /A31TU-DN
Intelligent function module
Vector inverter (FR-V500) Vector inverter FREQROL-V500 series
A31TU-D3
Abbreviation for "MELSECNET/H module/Ethernet module/CC-Link module/
Serial communication module"
/A31TU-DN Teaching unit
(Note-3)
(Note-1) : Q172EX can be used in SV22.
(Note-2) : SSCNET: S
(Note-3) : Teaching unit can be used in SV13.
ervo System Controller NETwork
REMARK
For information about the each module, design method for program and parameter,
Motion CPU module/Motion unit Q173CPU(N)/Q172CPU(N) User’s Manual
PLC CPU, peripheral devices for PLC program design, I/O
modules and intelligent function module
Operation method for MT Developer Help of each software
• Design method for positioning control
SV13/SV22
SV22
(Virtual mode)
• Design method for positioning control
• Design method for mechanical system
refer to the following manuals relevant to each module.
Item Reference Manual
Manual relevant to each module
program in the real mode
parameter
program
Q173CPU(N)/Q172CPU(N) Motion controller
(SV13/SV22) Programming Manual (REAL MODE)
Q173CPU(N)/Q172CPU(N) Motion controller (SV22)
Programming Manual (VIRTUAL MODE)
1 - 2

1 OVERVIEW
1.2 Features
The Motion CPU and Multiple CPU system have the following features.
1.2.1 Features of Motion CPU
(1) Q series PLC Multiple CPU system
(a) The load of control processing for each CPU can be distributed by
controlling the complicated servo control with the Motion CPU, and the
machine control or information control with the PLC CPU, and flexible
system configuration can be realized.
(b) The Motion CPU and PLC CPU are selected flexibly, and the Multiple CPU
system up to 4 CPU modules can be realized.
The Motion CPU module for the number of axis to be used can be selected.
The PLC CPU module for the program capacity to be used can be selected.
(One or more PLC CPU is necessary with the Multiple CPU system.)
(c) The device data of other CPU can be used as the device data of self CPU
because the Multiple CPU automatic refresh may do automatically data
giving and receiving between each CPU of the Multiple CPU system.
(d) The device data access of the Motion CPU and the Motion SFC program
start can be executed from PLC CPU by the Motion dedicated PLC
instruction.
(2) Programming in the Motion SFC programs
(a) Since a program intelligible for anyone can be created in flow chart form by
macking a sequence of machine operation correspond to each operation
step, maintenance nature improves.
(b) Since transition conditions are judged with Motion CPU side and positioning
starts, there is not dispersion in the response time influenced by PLC scan
time.
Q173CPU(N) : Up to 32 axes
Q172CPU(N) : Up to 8 axes
Q00CPU : 8k steps
Q01CPU : 14k steps
Q02CPU, Q02HCPU : 28k steps
Q06HCPU : 60k steps
Q12HCPU : 124k steps
Q25HCPU : 252k steps
1 - 3

1 OVERVIEW
(c) High speed and high response processing is realizable with the step
processing method (only active steps) of Motion SFC.
(d) Not only positioning control but also numerical operations, device SET/RST,
etc. can be processed with Motion CPU side, making via PLC CPU is
unnecessary and a tact time can be shortened.
(e) By transition condition description peculiar to Motion SFC, the instructions to
servo amplifier is possible at completion of starting condition.
(f) By transition condition description peculiar to Motion SFC, after starting,
transition to next step is possible without waiting for positioning completion.
(g) Motion SFC program that responds and executes it at high speed for
interrupt input from external source can be set.
(h) Motion SFC program executed in the fixed cycle (0.88ms, 1.77ms, 3.55ms,
7.11ms, 14.2ms) by synchronizing to the Motion operation cycle can be set.
(3) High speed operation processing
(a) The minimum operation cycle of the Motion CPU is made 0.88[ms] (so far,
the ratio of 4 times), and it correspond with high frequency operation.
(b) High speed PLC control is possible by the Q series PLC CPU.
(For LD instruction)
Q02HCPU, Q06HCPU, Q12HCPU, Q25HCPU
Q02CPU
Q00CPU
Q01CPU
: 0.034[µs]
: 0.079[µs]
: 0.16[µs]
: 0.10[µs]
(4) Connection between the Motion controller and servo amplifier with
high speed serial communication by SSCNET
High speed serial communication by SSCNET connect between the Motion
controller and servo amplifier, and batch control the charge of servo parameter,
servo monitor and test operation, etc.
It is also realised reduce the number of wires.
(5) The operating system software package for your application needs
By installing the operating system software for applications in the internal flash
memory of the Motion CPU, the Motion controller suitable for the machine can be
realized.
And, it also can correspond with the function improvement of the software
package.
(a) Conveyor assembly use (SV13)
Offer liner interpolation, circular interpolation, helical interpolation, constantspeed control, speed control, fixed-pitch feed and etc. by the dedicated
servo instruction. Ideal for use in conveyors and assembly machines.
1 - 4

1 OVERVIEW
(b) Automatic machinery use (SV22)
Provides synchronous control and offers electronic cam control by
mechanical support language. Ideal for use in automatic machinery.
(c) Machine tool peripheral use (SV43)
Offer liner interpolation, circular interpolation, helical interpolation, constantspeed positioning and etc. by the EIA language (G-code). Ideal for use in
machine tool peripheral.
1 - 5
1 OVERVIEW
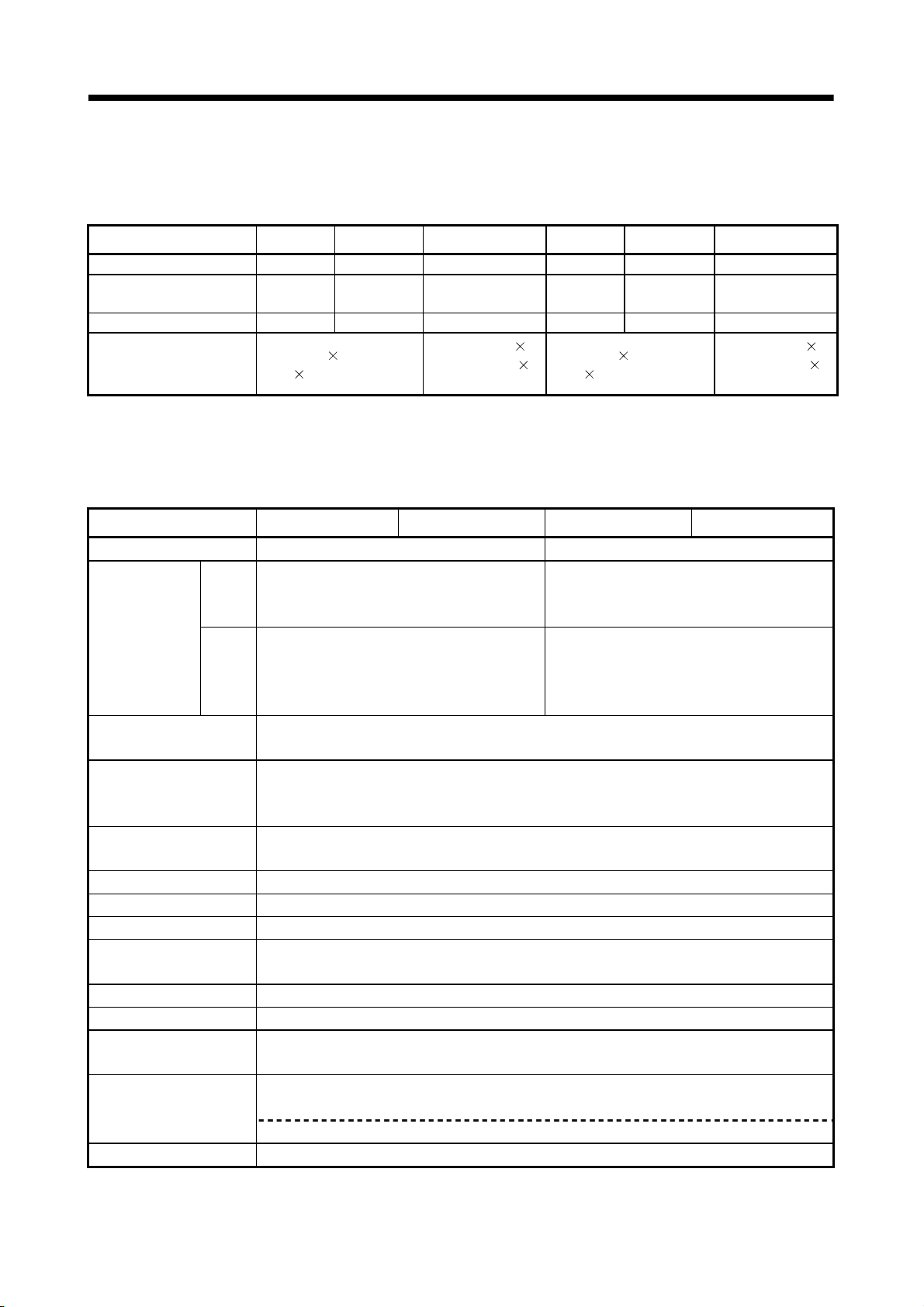
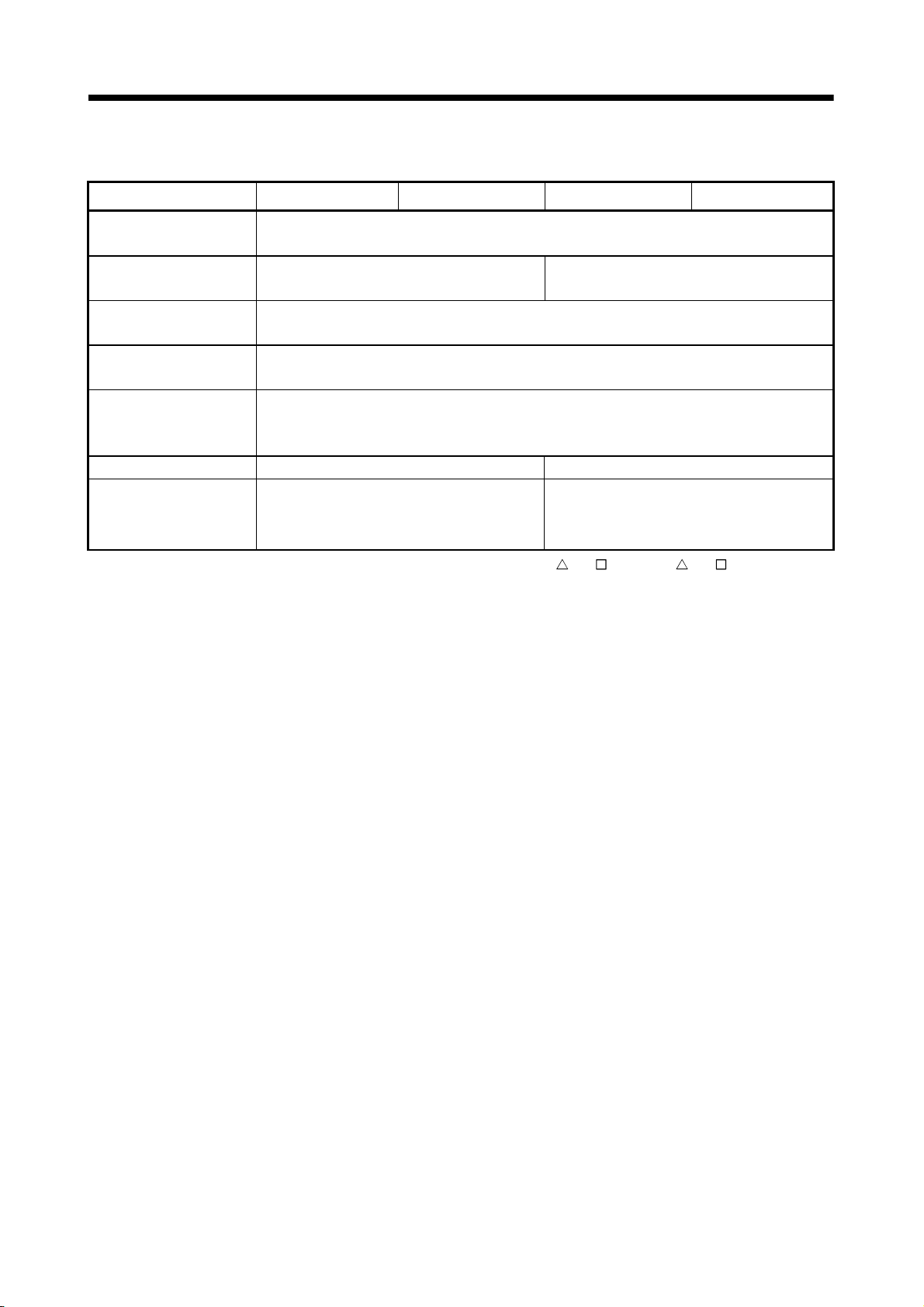
1.2.2 Basic specifications of Q173CPU(N)/Q172CPU(N)
Item Q173CPUN Q173CPUN-T Q173CPU Q172CPUN Q172CPUN-T Q172CPU
Teaching unit —— Usable —— —— Usable ——
Internal current
consumption(5VDC) [A]
Mass [kg] 0.23 0.24 0.22 0.22 0.23 0.21
Exterior dimensions
[mm(inch)]
(1) Module specifications
1.25 1.56
98(3.86)(H) 27.4(1.08)(W)
114.3(4.50)(D)
(Note)
1.75 1.14 1.45
118(4.65)(H)
27.4(1.08)(W)
89.3(3.52)(D)
(Note)
1.62
98(3.86)(H)
(Note) : Current consumption 0.26[A] of the teaching unit is included.
27.4(1.08)(W)
114.3(4.50)(D)
118(4.65)(H)
27.4(1.08)(W)
89.3(3.52)(D)
(2) SV13/SV22 Motion control specifications/performance
specifications
Item Q173CPUN(-T) Q173CPU Q172CPUN(-T) Q172CPU
Number of control axes Up to 32 axes Up to 8 axes
SV13
Operation cycle
(default)
SV22
Interpolation functions
Control modes
Acceleration/
deceleration control
Compensation Backlash compensation, Electronic gear
Programming language Motion SFC, Dedicated instruction, Mechanical support language (SV22)
Servo program capacity 14k steps
Number of positioning
points
Programming tool IBM PC/AT
Peripheral I/F USB/RS-232/SSCNET
Teaching operation
function
Home position return
function
JOG operation function Provided
(a) Motion control specifications
0.88ms/ 1 to 8 axes
1.77ms/ 9 to 16 axes
3.55ms/17 to 32 axes
0.88ms/ 1 to 4 axes
1.77ms/ 5 to 12 axes
3.55ms/13 to 24 axes
7.11ms/25 to 32 axes
Linear interpolation (Up to 4 axes), Circular interpolation (2 axes),
Helical interpolation (3 axes)
PTP(Point to Point) control, Speed control, Speed-position control, Fixed-pitch feed,
Constant speed control, Position follow-up control, Speed switching control,
High-speed oscillation control, Synchronous control (SV22)
Automatic trapezoidal acceleration/deceleration,
S-curve acceleration/deceleration
3200 points
(Positioning data can be designated indirectly)
Provided (Q173CPUN-T/Q172CPUN-T, SV13 use)
Proximity dog type (2 types), Count type (3 types), Data set type (2 types), Dog cradle type,
Stopper type (2 types), Limit switch combined type
(Home position return re-try function provided, home position shift function provided)
0.88ms/1 to 8 axes
0.88ms/1 to 4 axes
1.77ms/5 to 8 axes
1 - 6
1 OVERVIEW
Item Q173CPUN(-T) Q173CPU Q172CPUN(-T) Q172CPU
Motion control specifications (continued)
Manual pulse generator
operation function
Synchronous encoder
operation function
M-code function
Limit switch output
function
Absolute position system
Number of SSCNET I/F 5CH
Motion related interface
module
(Note-1) : Use the Dividing unit(Q173DV) or dividing cable(Q173J2B CBL M/Q173HB CBL M).
(Note-2) : When using the incremental synchronous encoder (SV22 use), you can use avobe number of modules.
When connecting the manual pulse generator, you can use only 1 module.
Possible to connect 12 modules Possible to connect 8 modules
Made compatible by setting battery to servo amplifier.
(Possible to select the absolute data method or incremental method for each axis)
(Note) : When the vector inverter is used, only the increment method.
Q172LX : 4 modules usable Q172LX : 1 module usable
Q172EX : 6 modules usable Q172EX : 4 modules usable
Q173PX : 4 modules usable
Possible to connect 3 modules
M-code output function provided
M-code completion wait function provided
Number of output points 32 points
Watch data: Motion control data/Word device
(Note-1)
2CH
(Note-2)
Q173PX : 3 modules usable
(Note-2)
1 - 7
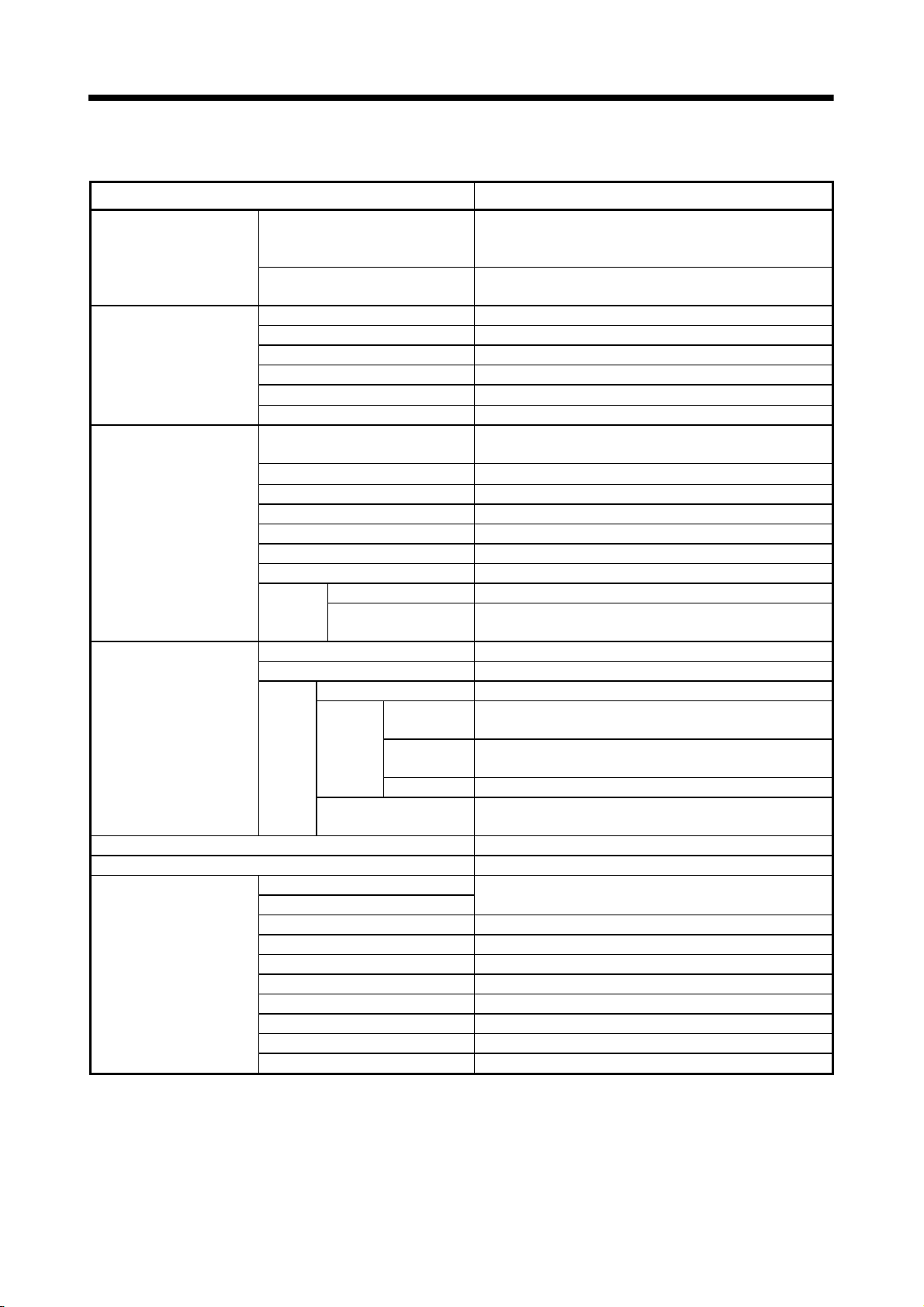
1 OVERVIEW
Motion SFC program capacity
Motion SFC program
Operation control program
(F/FS)
/
Transition program
(G)
Execute specification
Number of I/O points (X/Y) 8192 points
Number of real I/O points (PX/PY) 256 points
Number of devices
(Device In the Motion CPU
only)
(Included the positioning
dedicated device)
(b) Motion SFC Performance Specifications
Item Q173CPU(N)/Q172CPU(N)
Code total
(Motion SFC chart+ Operation control
+ Transition)
Text total
(Operation control + Transition)
Number of Motion SFC programs 256 (No.0 to 255)
Motion SFC chart size/program Up to 64k bytes (Included Motion SFC chart comments)
Number of Motion SFC steps/program Up to 4094 steps
Number of selective branches/branch 255
Number of parallel branches/branch 255
Parallel branch nesting Up to 4 levels
Number of operation control programs
Number of transition programs 4096(G0 to G4095)
Code size/program Up to approx. 64k bytes (32766 steps)
Number of blocks(line)/program Up to 8192 blocks (in the case of 4 steps(min)/blocks)
Number of characters/block (line) Up to 128 (comment included)
Number of operand/block Up to 64 (operand: constants, word device, bit devices)
( ) nesting/block Up to 32 levels
Descriptive
expression
Number of multi executed programs Up to 256
Number of multi active steps Up to 256 steps/all programs
Executed
task
Internal relays (M)
Latch relays (L)
Link relays (B) 8192 points
Annunciators (F) 2048 points
Special relays (M) 256 points
Data registers (D) 8192 points
Link registers (W) 8192 points
Special registers (D) 256 points
Motion registers (#) 8192 points
Coasting timers (FT)
Operation control program Calculation expression/bit conditional expression
Transition program
Normal task Executed in motion main cycle
Event task
(Execution
can be
masked.)
NMI task
Fixed cycle
External
interrupt
PLC interrupt Executed with interrupt instruction (S(P).GINT) from PLC CPU.
4096 with F(Once execution type) and FS(Scan execution type)
combined. (F/FS0 to F/FS4095)
Calculation expression/bit conditional expression/
comparison conditional expression
(0.88ms, 1.77ms, 3.55ms, 7.11ms, 14.2ms)
Executed when input ON is set among interrupt module QI60
Executed when input ON is set among interrupt module QI60
287k bytes
224k bytes
Executed in fixed cycle
(16 points).
(16 points).
Total (M + L) : 8192 points
1 point (888µs)
1 - 8
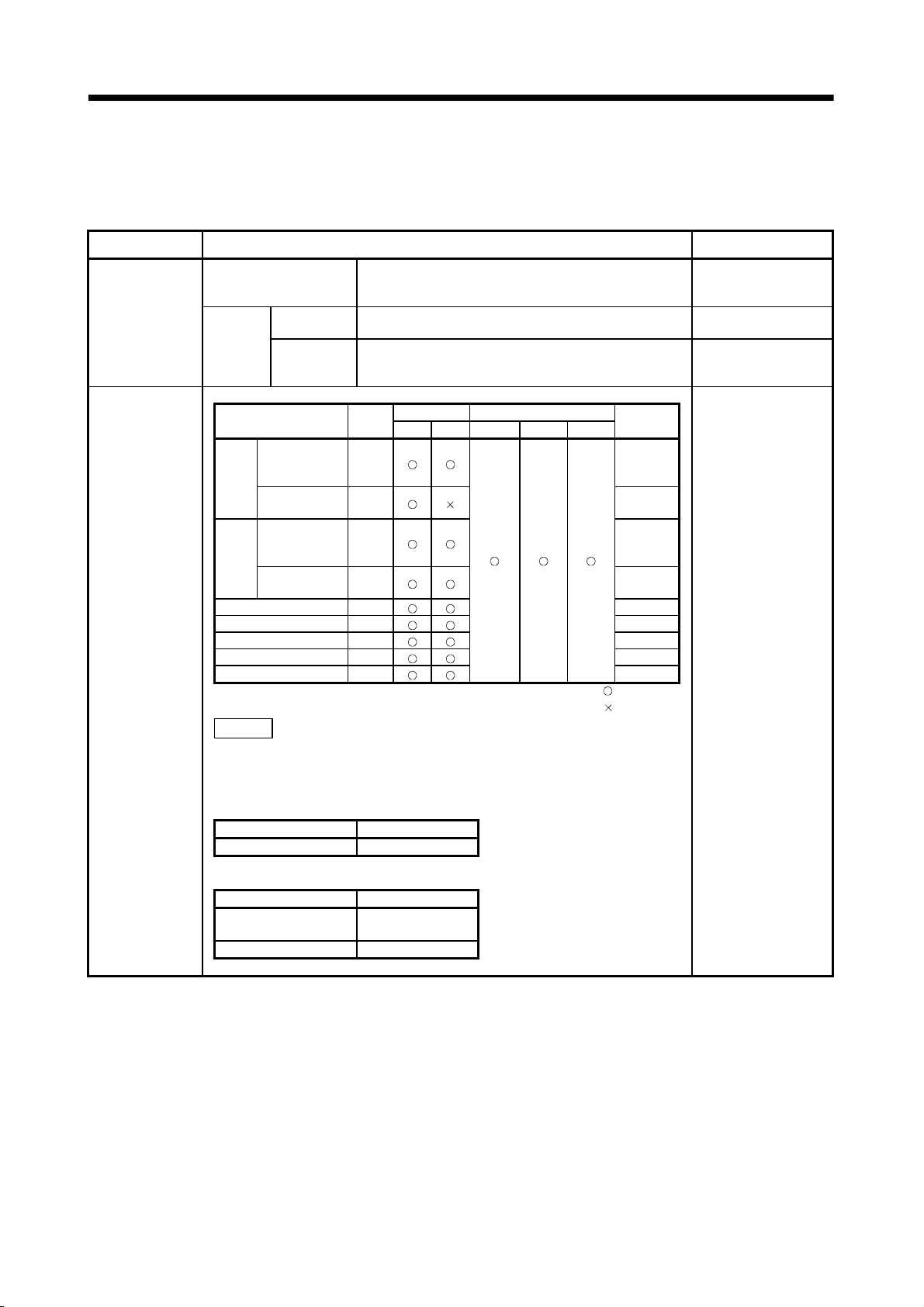
1 OVERVIEW
1.2.3 Operation control/transition control specifications
Expression
Bit devices
(1) Table of the operation control/transition control specifications
Item Specifications Remark
Calculation expression
Bit conditional
Conditional
expression
Accessibility Usable tasks
Input
Output
Internal relay M
Latch relay L
Link relay B
Annunciator F
Special relay M
CAUTION
<Restrictions on write-enabled bit devices>
1) Write to device X is allowed only within the input module non-installed range.
2) Special relay has predetermined applications in the system.
(Note) : SET/RST is disabled in the following device ranges.
SET/RST disable range Remark
M2001 to M2032 Start accept device
(Note) : DOUT output disabled in the following device ranges.
DOUT output disable range Remark
Designation including
M2000 to M2127
M9000 to M9255 Special relay
expression
Comparison
conditional
expression
Device Symbol
Input module
non-loaded
range
Input module
loaded range
Output module
non-loaded
range
Output module
loaded range
Do not perform write to other than the user setting device.
Returns a numeric result.
Expressions for calculating indirectly specified data using constants
and word devices.
Returns a true or false result.
Expression for judging ON or OFF of bit device.
Expressions for comparing indirectly specified data and calculation
expressions using constants and word devices.
Description
Read Write Normal Event NMI
X
PX
Y
example
X100
PX180
Y100
PY
Dedicated device
PY1E0
M20
L1000
B3FF
F0
M9000
: usable
: unusable
D100+1,SIN(D100), etc.
M0, !M0, M1*M0,
(M1+M2)*(!M3+M4), etc.
D100==100
D10<D102+D10, etc.
The input X/output Y are
written with the actual input
PX/actual output PY.
It does the layput of the I/O
numbers of PX, PY by a set
up of as system.
(In the operation control
program/transition program,
automatically represented
as PX/PY according to the
system setting information.)
1 - 9

1 OVERVIEW
Table of the operation control/transition control specification(continued)
Item Specifications Remark
K10, D100, etc.
2000000000, W100L, etc.
K-100, H0FFL, etc.
'K' may be omitted.
Word devices
Data type
Constant
Number of
instructions
of input PX, output PY
Accessibility Usable tasks
Data register D
Link register W
Special register D
Motion register #
Coasting timer FT
CAUTION
<Restrictions on write-enabled word devices>
1) Special register has predetermined applications in the system.
(None)
Binary operation 6
Bit operation 6
Sign 1
Standard function 15
Type conversion 6
Bit device status 2
Bit device control 5
Logical operation 4
Comparison operation 6
Motion dedicated function 2
Others 10
Input response Direct read control at instruction execution. Read/write response
Output response Direct write control at instruction execution.
Devices Symbol
Read Write Normal Event NMI
Do not perform write to other than the user-set device.
16-bit integer type (signed) -32768 to 32767
16-bit integer type (unsigned) 0 to 65535
32-bit integer type (signed) -2147483648 to 2147483647
L
32-bit integer type (unsigned) 0 to 4294967295
64-bit floating-point type
F
(double precision real number type)
Decimal
K
H
constant
Hexadecimal
constant
The above data type symbol 'L' or '. (decimal point)' provided at the end
indicates the data type. The constant without the data type is regarded
as the applicable minimum type.
IEEE format 1.23, #10F, etc.
63 in total
Description
example
DOL
W1F : F
D9000
#0F
FT
: usable
: unusable
1 - 10

1 OVERVIEW
(2) Table of the operation control/transition instruction
Classification Symbol Function Format Basic steps
Usable step
F/FS G
Y/N
transition's
conditional
expression
Section of
reference
= Substitution (D)=(S)
+ Addition (S1)+(S2)
Binary operation
Bit operation
Sign - Sign inversion (complement of 2) -(S) 2
Standard function
Type conversion
Bit device status
Bit device control
- Subtraction (S1)-(S2)
* Multiplication (S1)*(S2)
/ Division (S1)/(S2)
% Remainder (S1)%(S2)
~
Bit inversion (complement)
& Bit logical AND (S1)&(S2) 4
| Bit logical OR (S1)|(S2) 4
^ Bit exclusive OR (S1)^(S2) 4
>> Bit right shift (S1)>>(S2) 4
<< Bit left shift (S1)<<(S2) 4
SIN Sine SIN(S) 2
COS Cosine COS(S) 2
TAN Tangent TAN(S) 2
ASIN Arcsine ASIN(S) 2
ACOS Arccosine ACOS(S) 2
ATAN Arctangent ATAN(S) 2
SQRT Square root SQRT(S) 2
LN Natural logarithm LN(S) 2
EXP Exponential operation EXP(S) 2
ABS Absolute value ABS(S) 2
RND Round-off RND(S) 2
FIX Round-down FIX(S) 2
FUP Round-up FUP(S) 2
BCD
BIN
BCD
SHORT Convert into 16-bit integer type (signed) SHORT(S) 2
USHORT Convert into 16-bit integer type (unsigned) USHORT(S) 2
LONG Convert into 32-bit integer type (signed) LONG(S) 2
ULONG Convert into 32-bit integer type (unsigned) ULONG(S) 2
FLOAT
UFLOAT
(None) ON (normally open contact) (S) 2
! OFF (normally closed contact) !(S) 2
SET Device set
RST Device reset
DOUT Device output DOUT(D),(S) 4
DIN Device input DIN(D),(S) 4
OUT Bit device output
BIN conversion
BIN
BCD conversion
Regard as signed data and convert into 64bit floating point type
Regard as unsigned data and convert into
64-bit floating point type
~
(S) 2
BIN(S) 2
BCD(S) 2
FLOAT(S) 2
UFLOAT(S) 2
SET(D) 3
SET(D)= (conditional
expression)
RST(D) 3
RST(D)=(conditional
expression)
OUT(D)=(conditional
expression)
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
— 7.4.1
— 7.4.2
— 7.4.3
— 7.4.4
— 7.4.5
— 7.4.6
— 7.5.1
— 7.5.2
— 7.5.3
— 7.5.4
— 7.5.5
— 7.5.6
— 7.5.7
— 7.6.1
— 7.6.2
— 7.6.3
— 7.6.4
— 7.6.5
— 7.6.6
— 7.6.7
— 7.6.8
— 7.6.9
— 7.6.10
— 7.6.11
— 7.6.12
— 7.6.13
— 7.6.14
— 7.6.15
— 7.7.1
— 7.7.2
— 7.7.3
— 7.7.4
— 7.7.5
— 7.7.6
7.8.1
7.8.2
—
—
—
—
— 7.9.3
— 7.9.4
— 7.9.5
7.9.1
7.9.2
1 - 11

1 OVERVIEW
Table of the operation control/transition instruction (continued)
Classification Symbol Function Format Basic steps
(None) Logical acknowledgment (Conditional expression) 0
! Logical negation !(Conditional expression) 2
Logical operation
Comparison
operation
Motion dedicated
function
Others
* Logical AND
+ Logical OR
== Equal to
!= Not equal to
< Less than
<= Less than or equal to
> More than
>= More than or equal to
CHGV Speed change request CHGV((S1),(S2)) 4
CHGT Torque limit value change request CHGT((S1),(S2)) 4
EI Event task enable EI 1
DI Event task disable DI 1
NOP No operation NOP 1
BMOV Block transfer BMOV(D),(S),(n) 6
FMOV Same data block transfer FMOV(D),(S),(n) 6
MULTW
Write device data to shared CPU memory
of the self CPU
Read device data from shared CPU
MULTR
memory of the other CPU
Write device data to intelligent function
TO
module/special function module.
Read device data from intelligent function
FROM
module/special function module.
TIME Time to wait TIME(S) 7 —
(Conditional expression) *
(conditional expression)
(Conditional expression) +
(conditional expression)
(Conditional expression) ==
(conditional expression)
(Conditional expression) !=
(conditional expression)
(Conditional expression) <
(conditional expression)
(Conditional expression) <=
(conditional expression)
(Conditional expression) >
(conditional expression)
(Conditional expression) >=
(conditional expression)
MULTW(D),(S),(n),(D1) 8
MULTR(D),(S1),(S2),(n) 7
TO(D1),(D2),(S),(n) 7
FROM(D),(S1),(S2),(n) 7
(3) Rough calculation expression of singleprogram for operation
control/transition program
2 + (1 + Total number of basic steps in 1 block
+ Number of 32-bit constants/1 block
+ Number of 64-bit constants/1 block
(1 step = 2 bytes)
1
Number of blocks (steps)
3)
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
Usable step
F/FS G
: Usable —: Unusable
Y/N
transition's
conditional
expression
Section of
reference
7.10.1
7.10.2
7.10.3
7.10.4
7.11.1
7.11.2
7.11.3
7.11.4
7.11.5
7.11.6
— 7.12.1
— 7.12.2
— 7.13.1
— 7.13.2
— 7.13.3
— 7.13.4
— 7.13.5
— 7.13.6
— 7.13.7
— 7.13.8
— 7.13.9
— 7.13.10
1 - 12

1 OVERVIEW
1.2.4 Differences between Q173CPU(N)/Q172CPU(N) and A173UHCPU/A172SHCPUN
(1) Differences between Q173CPU(N)/Q172CPU(N) and
A173UHCPU/A172SHCPUN
Item Q173CPU(N) Q172CPU(N) A173UHCPU A172SHCPUN
Number of control axes Up to 32 axes Up to 8 axes Up to 32 axes Up to 8 axes
0.88ms/1 to 8 axes
1.77ms/9 to 16 axes
SV13
Operation cycle
SV22
Servo program capacity 14k steps 13k steps
Number of positioning points 3200 points/axis (Positioning data can be designated indirectly.)
Programming tool IBM PC/AT, A31TU-D PC9800 series, IBM PC/AT, A30TU, A31TU
Peripheral devices I/F USB/RS-232/SSCNET RS-422/SSCNET
Motion control
Home position return function
Manual pulse generator operation
function
Syncronous encoder operation
function
Limit switch output function Output points : 32points, watch data : motion control data/word device
Number of SSCNET Interfaces
(Included SSCNET interface 1CH to
the parsonal computer)
Number of motion slots
Number of Motion related modules
Normal task Executed in motion main cycle
Fixed
Event task
(Execution
Excuted
task
Motion SFC
Execute specification
Number of I/O (X/Y) points 8192 points 2048 points
Number of real I/O (PX/PY) points Total 256 points
can be
masked.)
NMI task
cycle
External
interrupt
PLC
interrupt
3.55ms/17 to 32 axes
(Default)
(It can be set up by
the parameters.)
0.88ms/1 to 4 axes
1.77ms/5 to 12 axes
3.55ms/13 to 24 axes
7.11ms/25 to 32 axes
(Default)
(It can be set up by
the parameters.)
Proximity dog type(2 types), Count type(3 types),
Data set type(2 types), Dog cradle type,
Stopper type(2 types), Limit switch conbined type
(Home position return retry function provided,
Home position shift function provided)
Possible to connect
12 modules
(Note-1)
5CH
(Up to 7 extension bases of the Q series)
Q172LX : 4 modules
Q172EX : 6 modules
Q173PX : 4 modules
(0.88ms, 1.77ms, 3.55ms, 7.11ms, 14.2ms)
Executed when input on is set among interrupt
Executed with interrupt instruction (GINT) from
Executed when input on is set among interrupt
2CH 4CH 2CH
Up to 64 slots
(Note-2)
Executed in fixed cycle
module(QI60) 16 points.
module(QI60) 16 points.
0.88ms/1 to 8 axes
(Default)
(It can be set up by
the parameters.)
0.88ms/1 to 4 axes
1.77ms/5 to 8 axes
(Default)
(It can be set up by
the parameters.)
Possible to connect 3 modules
Possible to connect
8 modules
Q172LX : 1 module
Q172EX : 4 modules
Q173PX : 3 modules
PLC CPU.
(Note-2)
1 - 13
3.55ms/1 to 20 axes
7.11ms/21 to 32 axes
3.55ms/1 to 12 axes
7.11ms/13 to 24 axes
14.2ms/25 to 32 axes
Proximity dog type, count type,
data set type 1
Possible to connect
4 modules
8 slots 2 slots
A172SENC : 4 modules A172SENC : 1 module
Executed in fixed cycle
(1.77ms, 3.55ms, 7.11ms, 14.2ms)
Executed when input on is set among
interrupt module(A1SI61) 16 points.
Executed when 1 interrupt point is provided
from PLC CPU.
Executed when input on is set among
interrupt module(A1SI61) 16 points.
3.55ms/1 to 8 axes
3.55 ms/1 to 8 axes
Possible to connect
1 module

1 OVERVIEW
Item Q173CPU(N) Q172CPU(N) A173UHCPU A172SHCPUN
Differences Between Q173CPU(N)/Q172CPU(N) and
A173UHCPU/A172SHCPUN(continued)
Internal relays (M)
Latch relays (L)
Link relays (B) 8192 points 1024 points
Annunciators (F) 2048 points 256 points
Timer contacts (TT) — 2048 points 256 points
Timer coils (TC) — 2048 points 256 points
Number of
Devices
(internal
motion
Motion SFC
CPU only)
Device memory Independence Commonness
Data exchange of PCPU and SCPU
Fixed
parameters
Others
PLC ready flag (M2000)
Forced stop input
Back-up battery for internal memory
(Note-1) : Use the Dividing unit (Q173DV) or dividing cable (Q173J2B CBL M/Q173HB CBL M).
(Note-2) : When using the incremental synchronous encoder (SV22 use), you can use above number of modules. When connecting the Manual
(Note-3) : When adding the external battery (A6BAT/MR-BAT), Q173DV (Q173CPU(N) use.), or Q170BAT (Q172CPU(N) use.) is used.
Counter contacts (CT) — 1024 points 256 points
Counter coils (CC) — 1024 points 256 points
Special relays (M) 256 points
Data registers (D) 8192 points 1024 points
Link registers (W) 8192 points 1024 points
Currnet value timers (T) — 2048 points 256 points
Currnet value counters (C) — 1024 points 256 points
Special registers (D) 256 points
Motion registers (#) 8192 points
Coasting timer (FT)
The data exchange method by automatic refresh
Number of pulses per
revolutions
Amount of pulses per
revolutions
Magnification —
M2000 turn it on with switch (STOP
or M2000 turn it on when both of switch RUN and
setting register is set "1".
An optional bit device(PX, M) is specified in the
parameter. (Emergency stop terminals of the
(Set the external battery (A6BAT/MR-BAT) if
continuous power off time is longer for 1 month or
pulse generator, you can use only 1 module.
Total M+L : 8192 points
1 point (888µs)
between the multiple CPU's.
1 to 2147483647[PLS] 1 to 65535[PLS]
In the case of the unit setup [PLS].
1 to 2147483647[PLS]
RUN),
servo amplifiers can be used.)
Internal rechargeable battery
(Note-3)
more.)
Total M+L(S) :
8192 points
The direct data exchange method which
made a device memory 2 port memory.
In the case of the unit setup [PLS].
1 to 65535[PLS]
1 time, 10 times,
100 times, 1000 times
M2000 turn on by PLC program
Emergency stop of the CPU base unit.
(Forced stop terminals of the servo amplifiers
cannot be used.)
A6BAT/MR-BAT
Total M+L(S) :
2048 points
1 - 14

1 OVERVIEW
1.2.5 Positioning dedicated devices/special relays/special registers
(1) Positioning dedicated devices
The following section describes the positioning dedicated devices.
A range of up to 32 axes is valid in Q173CPU(N), and a range of up to 8 axes is
valid in Q172CPU(N).
Refer to the "Q173CPU(N)/Q172CPU(N) Motion controller (SV13/SV22)
Programming Manual (REAL MODE)", "Q173CPU(N)/Q172CPU(N) Motion
controller (SV22) Programming Manual (VIRTUAL MODE)" for details of the
positioning dedicated devices.
(a) Table of the internal relays
Overall configuration
SV13 SV22
Device No. Purpose Device No. Purpose
M0 M0
to
M2000 M2000
to
M2320 M2320
to
M2400 M2400
to
M3040 M3040
to
M3072 M3072
to
M3136 M3136
to
M3200 M3200
to
M3840
to
M4799
User device
(2000 points)
Common device
(320 points)
Special relay allocated device (Status)
(80 points)
Axis status
(20 points
Unusable
Common device (Command signal)
(64 points)
Special relay allocated device
(Command signal)
(64 points)
Axis command signal
(20 points
User device
(960 points)
32 axes)
32 axes)
to
to
to
to
to
to
to
to
M3840
to
M4000
to
M4640
to
M4688
to
M4799
User device
(2000 points)
Common device
(320 points)
Special relay allocated device (Status)
(80 points)
Axis status
(20 points
Real mode……Each axis
Virtual mode….Output module
Unusable
Common device (Command signal)
(64 points)
Special relay allocated device
(Command signal)
(64 points)
Axis command signal
(20 points
Real mode……Each axis
Virtual mode….Output module
Unusable
(160 points)
Virtual servomotor axis status
(20 points 32 axes)
(Mechanical system setting axis only)
Synchronous encoder axis
status
Unusable
32 axes)
32 axes)
(Note-1)
(Note-2)
(4 points 12 axes)
(Note-1)
(Note-1,2)
1 - 15

1 OVERVIEW
Overall configuration(Continued)
SV13 SV22
Device No. Purpose Device No. Purpose
to
M8191
User device
(3392 points)
M4800 M4800
to
M5440
to
M5488
to
M5520
to
M5584
to
M5600
to
M8191
(Note-1) : It can be used as an user device in the SV22 real mode only.
(Note-2) : Do not set the M4000 to M5599 as a latch range in the virtual mode.
Virtual servomotor axis command
(Note-1, 2)
signal
(20 points
(Mechanical system setting axis only)
Synchronous encoder axis
command signal
(4 points
Cam axis command signal
(1 point
(Mechanical system setting axis only)
Smoothing clutch complete signal
(Note-1, 2)
(2 points 32 axes)
Unusable
(16 points)
User device
(2592 points)
32 axes)
(Note-2)
12 axes)
32 axes)
(Note-1)
(Note-1, 2)
1 - 16

1 OVERVIEW
MEMO
1 - 17

1 OVERVIEW
1) Table of the axis statuses (SV13/SV22)
Device No. Signal name Device No. Signal name
M2400
to
M2419
M2420
to
M2439
M2440
to
M2459
M2460
to
M2479
M2480
to
M2499
M2500
to
M2519
M2520
to
M2539
M2540
to
M2559
M2560
to
M2579
M2580
to
M2599
M2600
to
M2619
M2620
to
M2639
M2640
to
M2659
M2660
to
M2679
M2680
to
M2699
M2700
to
M2719
Axis 1 status
Axis 2 status
Axis 3 status
Axis 4 status
Axis 5 status
Axis 6 status
Axis 7 status
Axis 8 status
Axis 9 status
Axis 10 status
Axis 11 status
Axis 12 status
Axis 13 status
Axis 14 status
Axis 15 status
Axis 16 status
M2720
to
M2739
M2740
to
M2759
M2760
to
M2779
M2780
to
M2799
M2800
to
M2819
M2820
to
M2839
M2840
to
M2859
M2860
to
M2879
M2880
to
M2899
M2900
to
M2919
M2920
to
M2939
M2940
to
M2959
M2960
to
M2979
M2980
to
M2999
M3000
to
M3019
M3020
to
M3039
Axis 17 status
Axis 18 status
Axis 19 status
Axis 20 status
Axis 21 status
Axis 22 status
Axis 23 status
Axis 24 status
Axis 25 status
Axis 26 status
Axis 27 status
Axis 28 status
Axis 29 status
Axis 30 status
Axis 31 status
Axis 32 status
1 - 18

1 OVERVIEW
Detailes of each axis
Device No. Signal name
M2400 + 20n Positioning start complete
M2401 + 20n Positioning complete
M2402 + 20n In-position
M2403 + 20n Command in-position
M2404 + 20n Speed controlling
M2405 + 20n Speed/position switching latch signal
M2406 + 20n Zero pass signal
M2407 + 20n Error detection signal
M2408 + 20n Servo error detection signal
M2409 + 20n Home position return request signal
M2410 + 20n Home position return completion signal
M2411 + 20n FLS signal
M2412 + 20n RLS signal
M2413 + 20n STOP signal
M2414 + 20n
M2415 + 20n Servo ready signal
M2416 + 20n Torque limiting signal
M2417 + 20n Unusable
M2418 + 20n
M2419 + 20n M-code outputting signal
(Note-1) : "n" in the above device No. shows the numerical value which
correspond to axis No.
Q173CPU(N) : Axis No.1 to No.32 (n=0 to 31)
Q172CPU(N) : Axis No.1 to No.8 (n=0 to 7)
(Note-2) : Device area of 9 axes or more is unusable in the Q172CPU(N).
External
signals
DOG/CHANGE signal
Virtual mode continuation operation disable
warning signal (SV22)
1 - 19

1 OVERVIEW
2) Table of the axis command signals (SV13/SV22)
Device No. Signal name Device No. Signal name
M3200
to
M3219
M3220
to
M3239
M3240
to
M3259
M3260
to
M3279
M3280
to
M3299
M3300
to
M3319
M3320
to
M3339
M3340
to
M3359
M3360
to
M3379
M3380
to
M3399
M3400
to
M3419
M3420
to
M3439
M3440
to
M3459
M3460
to
M3479
M3480
to
M3499
M3500
to
M3519
Axis 1 command signal
Axis 2 command signal
Axis 3 command signal
Axis 4 command signal
Axis 5 command signal
Axis 6 command signal
Axis 7 command signal
Axis 8 command signal
Axis 9 command signal
Axis 10 command signal
Axis 11 command signal
Axis 12 command signal
Axis 13 command signal
Axis 14 command signal
Axis 15 command signal
Axis 16 command signal
M3520
to
M3539
M3540
to
M3559
M3560
to
M3579
M3580
to
M3599
M3600
to
M3619
M3620
to
M3639
M3640
to
M3659
M3660
to
M3679
M3680
to
M3699
M3700
to
M3719
M3720
to
M3739
M3740
to
M3759
M3760
to
M3779
M3780
to
M3799
M3800
to
M3819
M3820
to
M3839
Axis 17 command signal
Axis 18 command signal
Axis 19 command signal
Axis 20 command signal
Axis 21 command signal
Axis 22 command signal
Axis 23 command signal
Axis 24 command signal
Axis 25 command signal
Axis 26 command signal
Axis 27 command signal
Axis 28 command signal
Axis 29 command signal
Axis 30 command signal
Axis 31 command signal
Axis 32 command signal
1 - 20

1 OVERVIEW
Detailes of each axis
Device No. SV13 SV22
M3200 + 20n Stop command Stop command
M3201 + 20n Rapid stop command Rapid stop command
M3202 + 20n
M3203 + 20n
M3204 + 20n Complete signal OFF command Complete signal OFF command
M3205 + 20n
M3206 + 20n Unusable Unusable
M3207 + 20n Error reset command Error reset command
M3208 + 20n Servo error reset command Servo error reset command
M3209 + 20n
M3210 + 20n
M3211 + 20n
M3212 + 20n
M3213 + 20n
M3214 + 20n
M3215 + 20n Servo OFF command Servo OFF command
M3216 + 20n Gain changing command Gain changing command
M3217 + 20n
M3218 + 20n
M3219 + 20n FIN signal FIN signal
(Note-1) : "n" in the above device No. shows the numerical value which correspond to axis No.
(Note-2) : Device area of 9 axes or more is unusable in the Q172CPU(N).
Forward rotation JOG start
command
Reverse rotation JOG start
command
Speed/position switching enable
command
External stop input disable at start
command
Unusable Unusable
Feed current value update request
command
Unusable
Unusable Unusable
Q173CPU(N) : Axis No.1 to No.32 (n=0 to 31)
Q172CPU(N) : Axis No.1 to No.8 (n=0 to 7)
Forward rotation JOG start command
Reverse rotation JOG start comannd
Speed/position switching enable
comannd
External stop input disable at start
command
Feed current value update request
command
Address clutch reference setting
command
Cam reference position setting
command
1 - 21

1 OVERVIEW
3) Table of the virtual servomotor axis statuses (SV22 only)
Device No. Signal name Device No. Signal name
M4000
to
M4019
M4020
to
M4039
M4040
to
M4059
M4060
to
M4079
M4080
to
M4099
M4100
to
M4119
M4120
to
M4139
M4140
to
M4159
M4160
to
M4179
M4180
to
M4199
M4200
to
M4219
M4220
to
M4239
M4240
to
M4259
M4260
to
M4279
M4280
to
M4299
M4300
to
M4319
Axis 1 status
Axis 2 status
Axis 3 status
Axis 4 status
Axis 5 status
Axis 6 status
Axis 7 status
Axis 8 status
Axis 9 status
Axis 10 status
Axis 11 status
Axis 12 status
Axis 13 status
Axis 14 status
Axis 15 status
Axis 16 status
M4320
to
M4339
M4340
to
M4359
M4360
to
M4379
M4380
to
M4399
M4400
to
M4419
M4420
to
M4439
M4440
to
M4459
M4460
to
M4479
M4480
to
M4499
M4500
to
M4519
M4520
to
M4539
M4540
to
M4559
M4560
to
M4579
M4580
to
M4599
M4600
to
M4619
M4620
to
M4639
Axis 17 status
Axis 18 status
Axis 19 status
Axis 20 status
Axis 21 status
Axis 22 status
Axis 23 status
Axis 24 status
Axis 25 status
Axis 26 status
Axis 27 status
Axis 28 status
Axis 29 status
Axis 30 status
Axis 31 status
Axis 32 status
1 - 22

1 OVERVIEW
Detailes of each axis
Device No. Signal name
M4000 + 20n Positioning start complete
M4001 + 20n Positioning complete
M4002 + 20n Unusable
M4003 + 20n Command in-position
M4004 + 20n Speed controlling
M4005 + 20n
M4006 + 20n
M4007 + 20n Error detection
M4008 + 20n
M4009 + 20n
M4010 + 20n
Unusable
M4011 + 20n
M4012 + 20n
M4013 + 20n
M4014 + 20n
M4015 + 20n
M4016 + 20n
M4017 + 20n
M4018 + 20n
M4019 + 20n M-code outputting signal
(Note-1) : "n" in the above device No. shows the numerical value which
correspond to axis No.
Q173CPU(N) : Axis No.1 to No.32 (n=0 to 31)
Q172CPU(N) : Axis No.1 to No.8 (n=0 to 7)
(Note-2) : The unused axis areas in the mechanical system program can be used as an
user device.
Unusable
1 - 23

1 OVERVIEW
4) Table of the virtual servomotor axis command signals
(SV22 only)
Device No. Signal name Device No. Signal name
M4800
to
M4819
M4820
to
M4839
M4840
to
M4859
M4860
to
M4879
M4880
to
M4899
M4900
to
M4919
M4920
to
M4939
M4940
to
M4959
M4960
to
M4979
M4980
to
M4999
M5000
to
M5019
M5020
to
M5039
M5040
to
M5059
M5060
to
M5079
M5080
to
M5099
M5100
to
M5119
Axis 1 command signal
Axis 2 command signal
Axis 3 command signal
Axis 4 command signal
Axis 5 command signal
Axis 6 command signal
Axis 7 command signal
Axis 8 command signal
Axis 9 command signal
Axis 10 command signal
Axis 11 command signal
Axis 12 command signal
Axis 13 command signal
Axis 14 command signal
Axis 15 command signal
Axis 16 command signal
M5120
to
M5139
M5140
to
M5159
M5160
to
M5179
M5180
to
M5199
M5200
to
M5219
M5220
to
M5239
M5240
to
M5259
M5260
to
M5279
M5280
to
M5299
M5300
to
M5319
M5320
to
M5339
M5340
to
M5359
M5360
to
M5379
M5380
to
M5399
M5400
to
M5419
M5420
to
M5439
Axis 17 command signal
Axis 18 command signal
Axis 19 command signal
Axis 20 command signal
Axis 21 command signal
Axis 22 command signal
Axis 23 command signal
Axis 24 command signal
Axis 25 command signal
Axis 26 command signal
Axis 27 command signal
Axis 28 command signal
Axis 29 command signal
Axis 30 command signal
Axis 31 command signal
Axis 32 command signal
1 - 24

1 OVERVIEW
Detailes of each axis
Device No. Signal name
M4800 + 20n Stop command
M4801 + 20n Rapid stop command
M4802 + 20n Forward rotation JOG start command
M4803 + 20n Reverse rotation JOG start command
M4804 + 20n Complete signal OFF command
M4805 + 20n
M4806 + 20n
M4807 + 20n Error reset command
M4808 + 20n Unusable
M4809 + 20n External stop input disable at start command
M4810 + 20n
M4811 + 20n
M4812 + 20n
M4813 + 20n
M4814 + 20n
M4815 + 20n
M4816 + 20n
M4817 + 20n
M4818 + 20n
M4819 + 20n FIN signal
(Note-1) : "n" in the above device No. shows the numerical value which
correspond to axis No.
Q173CPU(N) : Axis No.1 to No.32 (n=0 to 31)
Q172CPU(N) : Axis No.1 to No.8 (n=0 to 7)
(Note-2) : The unused axis areas in the mechanical system program can be used as an
user device.
Unusable
Unusable
1 - 25

1 OVERVIEW
5) Table of the synchronous encoder axis statuses
(SV22 only)
Device No. Signal name
M4640 Error detection
M4641 External signal TREN
M4642 Virtual mode continuation operation disable warning
M4643
M4644 Error detection
M4645 External signal TREN
M4646 Virtual mode continuation operation disable warning
M4647
M4648 Error detection
M4649 External signal TREN
M4650 Virtual mode continuation operation disable warning
M4651
M4652 Error detection
M4653 External signal TREN
M4654 Virtual mode continuation operation disable warning
M4655
M4656 Error detection
M4657 External signal TREN
M4658 Virtual mode continuation operation disable warning
M4659
M4660 Error detection
M4661 External signal TREN
M4662 Virtual mode continuation operation disable warning
M4663
M4664 Error detection
M4665 External signal TREN
M4666 Virtual mode continuation operation disable warning
M4667
M4668 Error detection
M4669 External signal TREN
M4670 Virtual mode continuation operation disable warning
M4671
M4672 Error detection
M4673 External signal TREN
M4674 Virtual mode continuation operation disable warning
M4675
M4676 Error detection
M4677 External signal TREN
M4678 Virtual mode continuation operation disable warning
M4679
M4680 Error detection
M4681 External signal TREN
M4682 Virtual mode continuation operation disable warning
M4683
M4684 Error detection
M4685 External signal TREN
M4686 Virtual mode continuation operation disable warning
M4687
Axis 1
Unusable
Axis 2
Unusable
Axis 3
Unusable
Axis 4
Unusable
Axis 5
Unusable
Axis 6
Unusable
Axis 7
Unusable
Axis 8
Unusable
Axis 9
Unusable
Axis 10
Unusable
Axis 11
Unusable
Axis 12
Unusable
(Note-1) : The range of axis No.1 to 8 is valid in the Q172CPU(N).
(Note-2) : Device area of 9 axes or more is unusable in the Q172CPU(N).
1 - 26

1 OVERVIEW
6) Table of the syncronous encoder axis command signals
(SV22 only)
Device No. Signal name
M5440 Error reset
M5441 Unusable
M5442 Unusable
M5443
M5444 Error reset
M5445 Unusable
M5446 Unusable
M5447
M5448 Error reset
M5449 Unusable
M5450 Unusable
M5451
M5452 Error reset
M5453 Unusable
M5454 Unusable
M5455
M5456 Error reset
M5457 Unusable
M5458 Unusable
M5459
M5460 Error reset
M5461 Unusable
M5462 Unusable
M5463
M5464 Error reset
M5465 Unusable
M5466 Unusable
M5467
M5468 Error reset
M5469 Unusable
M5470 Unusable
M5471
M5472 Error reset
M5473 Unusable
M5474 Unusable
M5475
M5476 Error reset
M5477 Unusable
M5478 Unusable
M5479
M5480 Error reset
M5481 Unusable
M5482 Unusable
M5483
M5484 Error reset
M5485 Unusable
M5486 Unusable
M5487
Axis 1
Unusable
Axis 2
Unusable
Axis 3
Unusable
Axis 4
Unusable
Axis 5
Unusable
Axis 6
Unusable
Axis 7
Unusable
Axis 8
Unusable
Axis 9
Unusable
Axis 10
Unusable
Axis 11
Unusable
Axis 12
Unusable
(Note-1) : The range of axis No.1 to 8 is valid in the Q172CPU(N).
(Note-2) : Device area of 9 axes or more is unusable in the Q172CPU(N).
1 - 27

1 OVERVIEW
7) Table of the cam axis command signals (SV22 only)
Device No. Signal name
M5488 Axis 1 cam/ballscrew switching
M5489 Axis 2 cam/ballscrew switching
M5490 Axis 3 cam/ballscrew switching
M5491 Axis 4 cam/ballscrew switching
M5492 Axis 5 cam/ballscrew switching
M5493 Axis 6 cam/ballscrew switching
M5494 Axis 7 cam/ballscrew switching
M5495 Axis 8 cam/ballscrew switching
M5496 Axis 9 cam/ballscrew switching
M5497 Axis 10 cam/ballscrew switching
M5498 Axis 11 cam/ballscrew switching
M5499 Axis 12 cam/ballscrew switching
M5500 Axis 13 cam/ballscrew switching
M5501 Axis 14 cam/ballscrew switching
M5502 Axis 15 cam/ballscrew switching
M5503 Axis 16 cam/ballscrew switching
M5504 Axis 17 cam/ballscrew switching
M5505 Axis 18 cam/ballscrew switching
M5506 Axis 19 cam/ballscrew switching
M5507 Axis 20 cam/ballscrew switching
M5508 Axis 21 cam/ballscrew switching
M5509 Axis 22 cam/ballscrew switching
M5510 Axis 23 cam/ballscrew switching
M5511 Axis 24 cam/ballscrew switching
M5512 Axis 25 cam/ballscrew switching
M5513 Axis 26 cam/ballscrew switching
M5514 Axis 27 cam/ballscrew switching
M5515 Axis 28 cam/ballscrew switching
M5516 Axis 29 cam/ballscrew switching
M5517 Axis 30 cam/ballscrew switching
M5518 Axis 31 cam/ballscrew switching
M5519 Axis 32 cam/ballscrew changing
(Note-1) : The range of axis No.1 to 8 is valid in the Q172CPU(N).
(Note-2) : Device area of 9 axes or more is unusable in the Q172CPU(N).
(Note-3) : The unused aixs areas in the cam axis command signal can be used as an user
device.
1 - 28

1 OVERVIEW
Device No. Signal name Refresh cycle Fetch cycle Signal direction Remark
M5520 Main shaft side
M5521
M5522 Main shaft side
M5523
M5524 Main shaft side
M5525
M5526 Main shaft side
M5527
M5528 Main shaft side
M5529
M5530 Main shaft side
M5531
M5532 Main shaft side
M5533
M5534 Main shaft side
M5535
M5536 Main shaft side
M5537
M5538 Main shaft side
M5539
M5540 Main shaft side
M5541
M5542 Main shaft side
M5543
M5544 Main shaft side
M5545
M5546 Main shaft side
M5547
M5548 Main shaft side
M5549
M5550 Main shaft side
M5551
M5552 Main shaft side
M5553
M5554 Main shaft side
M5555
M5556 Main shaft side
M5557
M5558 Main shaft side
M5559
M5560 Main shaft side
M5561
M5562 Main shaft side
M5563
M5564 Main shaft side
M5565
M5566 Main shaft side
M5567
M5568 Main shaft side
M5569
M5570 Main shaft side
M5571
M5572 Main shaft side
M5573
M5574 Main shaft side
M5575
M5576 Main shaft side
M5577
M5578 Main shaft side
M5579
M5580 Main shaft side
M5581
M5582 Main shaft side
M5583
Output axis 1
Output axis 2
Output axis 3
Output axis 4
Output axis 5
Output axis 6
Output axis 7
Output axis 8
Output axis 9
Output axis 10
Output axis 11
Output axis 12
Output axis 13
Output axis 14
Output axis 15
Output axis 16
Output axis 17
Output axis 18
Output axis 19
Output axis 20
Output axis 21
Output axis 22
Output axis 23
Output axis 24
Output axis 25
Output axis 26
Output axis 27
Output axis 28
Output axis 29
Output axis 30
Output axis 31
Output axis 32
8) Table of the smoothing clutch complete signals
(SV22 only)
Auxiliary input side
Auxiliary input side
Auxiliary input side
Auxiliary input side
Auxiliary input side
Auxiliary input side
Auxiliary input side
Auxiliary input side
Auxiliary input side
Auxiliary input side
Auxiliary input side
Auxiliary input side
Auxiliary input side
Auxiliary input side
Auxiliary input side
Auxiliary input side
Operation cycle Status signal
Auxiliary input side
Auxiliary input side
Auxiliary input side
Auxiliary input side
Auxiliary input side
Auxiliary input side
Auxiliary input side
Auxiliary input side
Auxiliary input side
Auxiliary input side
Auxiliary input side
Auxiliary input side
Auxiliary input side
Auxiliary input side
Auxiliary input side
Auxiliary input side
(Note-1) : The range of axis No.1 to 8 is valid in the Q172CPU(N).
(Note-2) : Device area of 9 axes or more is unusable in the Q172CPU(N).
(Note-3) : The unused aixs areas in the mechanical system program can be used as an user device.
1 - 29

1 OVERVIEW
9) Table of the common devices (SV13/SV22)
SV13 SV22
Device No. Signal name Device No. Signal name
M2000 PLC ready flag M2000 PLC ready flag
M2001 Axis1 M2001 Axis1
to to to to
M2032 Axis32
Start accept flag
(32 points)
M2032 Axis32
Start accept flag
(32 points)
Refresh
cycle
Operation
cycle
Fetch
cycle
Main
cycle
Signal
direction
Command
signal
(Note-1)
Status
signal
(Note-2, 3)
M2033 Unusable M2033 Unusable — — —
M2034
M2035
Personal computer link
communication error flag
Motion SFC error history clear
request flag
(Note-5)
M2034
M2035
Personal computer link
communication error flag
Motion SFC error history clear
request flag
(Note-5)
Operation
cycle
Main
cycle
Status
signal
Command
signal
Remark
(Note-4)
M3072
M3080
M2036 M2036
M2037
M2037
M2038 Motion SFC debugging flag M2038 Motion SFC debugging flag
M2039 Motion SFC error detection flag M2039 Motion SFC error detection flag
Unusable
M2040
Speed switching point specified
flag
M2040
M2041 System setting error flag M2041 System setting error flag
M2042 All axes servo ON command M2042 All axes servo ON command
M2043 M2043
M2044 M2044
Unusable
M2045 M2045
M2046
M2046 Out-of-sync warning
M2047 Motion slot fault detection flag M2047 Motion slot fault detection flag
M2048
JOG operation simultaneous start
command
M2048
M2049 All axes servo ON accept flag M2049 All axes servo ON accept flag
Unusable — — —
At debug
Speed switcing point specified
flag
Real mode/virtual mode
switching request
mode
transition
Operation
cycle
Immedi-
ate
At start
Operation
cycle
At virtual
mode
transition
Real mode/virtual mode
switching status
Real mode/virtual mode
switching error detection flag
JOG operation simultaneous start
command
At virtual
mode
transition
Operation
cycle
Operation
cycle
Main
cycle
M2050 Unusable M2050 Unusable — —
M2051
M2052
M2053
Manual pulse generator 1 enable
flag
Manual pulse generator 2 enable
flag
Manual pulse generator 3 enable
flag
M2051
M2052
M2053
Manual pulse generator 1 enable
flag
Manual pulse generator 2 enable
flag
Manual pulse generator 3 enable
flag
Main
cycle
Status
signal
Status
signal
Command
signal
(Note-1)
Status
signal
Command
signal
(Note-1)
Status
signal
Command
signal
(Note-1)
Status
signal
—
Command
signal
(Note-1)
M3073
M3074
M3075
M3076
M3077
M3078
M3079
1 - 30

1 OVERVIEW
Table of the common devices (SV13/SV22) (continued)
SV13 SV22
Device No. Signal name Device No. Signal name
M2054 Operation cycle over flag M2054 Operation cycle over flag
M2055 M2055
to to
M2060
Unusable
M2060
Unusable — — —
M2061 Axis 1 M2061 Axis 1
to to to to
Speed changing flag
(32 axes)
M2092 Axis 32
M2092 Axis 32
Speed changing flag
(32 axes)
M2093 M2093
to
Unusable — — —
M2100
Synchronous encoder
current value changing
flag
(12 axes)
to
Unusable
M2101 Axis 1
to to
M2112 Axis 12
M2113
to
Unusable — — —
Refresh
cycle
Operation
cycle
Operation
cycle
Operation
cycle
Fetch
cycle
Signal
direction
Status
signal
Status
signal
(Note-2, 3)
Status
signal
(Note-2, 3)
Remark
(Note-4)
M2127
M2128 Axis 1 M2128 Axis 1
to to to to
M2159 Axis 32
Automatic decelerating
flag
(32 axes)
M2160 M2160
to
Unusable
M2127
Automatic decelerating
flag
M2159 Axis 32
(32 axes)
Main shaft
side
Auxiliary input
side
M2161
Output
axis 1
to to to
M2222
M2223
Output
axis 32
Main shaft
side
Auxiliary input
side
Clutch
status
(Note-6)
M2224
to
M2239
M2240 Axis 1 M2240 Axis 1
to to to to
M2271 Axis 32
Speed change "0"
accepting flag
(32 axes)
M2239
M2271 Axis 32
Unusable — — —
Speed change "0"
accepting flag
(32 axes)
M2272 M2272
to to
M2319
Unusable
M2319
Unusable — — —
Operation
cycle
Operation
cycle
Status
signal
(Note-2, 3)
Status
signal
(Note-2, 3)
1 - 31

1 OVERVIEW
No. Function Bit device Request register
1 PLC ready flag M2000 D704
2 Speed switching point specified flag M2040 D705
3 All axes servo ON command M2042 D706
4 Real mode/virtual mode switching request (SV22) M2043 D707
5 JOG operation simultaneous start command M2048 D708
6 Manual pulse generator 1 enable flag M2051 D755
7 Manual pulse generator 2 enable flag M2052 D756
8 Manual pulse generator 3 enable flag M2053 D757
Explanation of the request register
(Note-1) : Handling of D704 to D708 and D755 to D757 register
Because cannot be turn ON/OFF for every bit from the PLC CPU, the above
bit devices are assigned to D register, and each bit device becomes on with
the lowest rank bit 0
with 1
0.
Use it when the above functions are requested from the PLC CPU using the
S(P).DDRD and S(P).DDWR instruction. Refer to "5 MOTION DEDICATED
PLC INSTRUCTION " for S(P).DDRD and S(P).DDWR instruction.
(Note-2) : Device area of 9 axes or more is unusable in the Q172CPU(N).
(Note-3) : The range of axis No.1 to 8 is valid in the Q172CPU(N).
(Note-4) : It can also be ordered the device of a remark column.
(Note-5) : M3080 does not turn off automatically. Turn it off as an user side.
(Note-6) : It is unusable in the SV22 real mode.
1 of each register, and each bit device becomes off
CAUTION
The data executed later becomes effective when the same device is executed simultaneously
in the Motion SFC and PLC program.
1 - 32

1 OVERVIEW
Device No. Signal name Refresh cycle Fetch cycle Signal direction
M2320 Fuse blown detection
10) Table of the special relay allocated devices (Status)
(SV13/SV22)
Remark
M9000
(Note)
M2321 AC/DC DOWN detection
M2322 Battery low
M2323 Battery low latch
M2324 Self-diagnostic error
M2325 Diagnostic error
M2326 Always ON
M2327 Always OFF
M2328 Clock data error
M2329 PCPU WDT error flag
M2330 PCPU READY complete flag
M2331 Test mode ON flag
M2332 External forced stop input flag
M2333
Manual pulse generator axis setting
error flag
M2334 TEST mode request error flag
M2335 Servo program setting error flag
M2336 CPU No.1 reset flag
Error
occurrence
Main
operation
Error
occurrence
At request
Operation
cycle
Error
occurrence
M9005
M9006
M9007
M9008
M9010
M9036
M9037
M9026
M9073
M9074
M9075
M9076
M9077
Status signal
M9078
M9079
M9240
M2337 CPU No.2 reset flag
M2338 CPU No.3 reset flag
M2339 CPU No.4 reset flag
M2340 CPU No.1 error flag
At Status
change
M2341 CPU No.2 error flag
M2342 CPU No.3 error flag
M2343 CPU No.4 error flag
M2344 Servo parameter reading flag At request
M2345 CPU No.1 MULTR complete flag
M2346 CPU No.2 MULTR complete flag
M2347 CPU No.3 MULTR complete flag
At instruction
completion
M2348 CPU No.4 MULTR complete flag
M2349
to
Unusable — — — —
M2399
M9241
M9242
M9243
M9244
M9245
M9246
M9247
M9105
M9216
M9217
M9218
M9219
(Note) : The same status as a remark column is output.
1 - 33

y
1 OVERVIEW
Device No. Signal name Refresh cycle Fetch cycle Signal direction
M3072 PLC ready flag
11) Table of the common devices (Command signal)
(SV13/SV22)
Main cycle
Remark
(Note-1) , (Note-2)
M2000
M3073 Speed switching point specified flag At start
M3074 All axes servo ON command
M3075
M3076
M3077 Manual pulse generator 1 enable flag
M3078 Manual pulse generator 2 enable flag
M3079 Manual pulse generator 3 enable flag
M3080
M3081
to
M3135
(Note-1) : The device of a remarks column turns ON by OFF to ON of the above device, and the device of a remarks column turns
(Note-2) : It can also be ordered the device of a remark column.
(Note-3) : M3080 does not turn off automatically. Turn it off as an user side.
Real mode/virtual mode change request
(SV22)
JOG operation simultaneous start
command
Motion SFC error history clear request
(Note-3)
flag
Unusable — — — —
OFF by ON to OFF of the above device. The state of a device is not in agreement when the device of a remarks column
is turned on directly. In addition, when the request from a data register and the request from the above device are
performed simultaneously, the request from the above device becomes effective.
Operation
c
cle
At virtual mode
transition
Main cycle
Command
signal
M2040
M2042
M2043
M2048
M2051
M2052
M2053
M2035
12) Table of the special relay allocated devices (Command
signal) (SV13/SV22)
Device No. Signal name Refresh cycle Fetch cycle Signal direction
M3136 Clock data set request
Remark
(Note-1), (Note-2)
M9025
M3137 Clock data read request
M3138 Error reset
M3139 Servo parameter read request flag
M3140
to
M3199
(Note-1) : The device of a remarks column turns ON by OFF to ON of the above device, and the device of a remarks column turns
(Note-2) : It can also be ordered the device of a remark column.
Unusable — — — —
OFF by ON to OFF of the above device. The state of a device is not in agreement when the device of a remarks column
is turned on directly.
Main cycle
Command
signal
M9028
M9060
M9104
1 - 34

1 OVERVIEW
Device No. Application Device No. Application
D0 D0
to
D640 D640
to
D704 D704
to
D758 D758
to
D800 D800
(b) Table of the data registers
Overall configuration
SV13 SV22
Axis monitor device
(Note)
(Note)
32 axes)
32 axes)
(10 points
32 axes)
12 axes)
(Note)
Axis monitor device
(20 points
Control change register
(2 points
Common device (Command signal)
(54 points)
Common device (Monitor)
(42points)
32 axes)
32 axes)
to
to
to
to
to
D1120
to
D1240
to
D1560
(20 points
Real mode……Each axis
Virtual mode….Output module
Control change register
(2 points 32 axes)
Common device (Command signal)
(54 points)
Common device (Monitor)
(42points)
Virtual servomotor axis monitor
device
(10 points
(Mechanical system setting axis only)
Syncronous encoder axis monitor
device
Cam axis monitor device
(10 points
to
D8191
User device
(7392 points)
to
D8191
(Note) : It can be used as an user device in the SV22 real mode only.
User device
(6632 points)
1 - 35

1 OVERVIEW
1) Table of the each axis monitor devices (SV13/SV22)
Device No. Signal name Device No. Signal name
D0
to
D19
D20
to
D39
D40
to
D59
D60
to
D79
D80
to
D99
D100
to
D119
D120
to
D139
D140
to
D159
D160
to
D179
D180
to
D199
D200
to
D219
D220
to
D239
D240
to
D259
D260
to
D279
D280
to
D299
D300
to
D319
Axis 1 monitor device
Axis 2 monitor device
Axis 3 monitor device
Axis 4 monitor device
Axis 5 monitor device
Axis 6 monitor device
Axis 7 monitor device
Axis 8 monitor device
Axis 9 monitor device
Axis 10 monitor device
Axis 11 monitor device
Axis 12 monitor device
Axis 13 monitor device
Axis 14 monitor device
Axis 15 monitor device
Axis 16 monitor device
D320
to
D339
D340
to
D359
D360
to
D379
D380
to
D399
D400
to
D419
D420
to
D439
D440
to
D459
D460
to
D479
D480
to
D499
D500
to
D519
D520
to
D539
D540
to
D559
D560
to
D579
D580
to
D599
D600
to
D619
D620
to
D639
Axis 17 monitor device
Axis 18 monitor device
Axis 19 monitor device
Axis 20 monitor device
Axis 21 monitor device
Axis 22 monitor device
Axis 23 monitor device
Axis 24 monitor device
Axis 25 monitor device
Axis 26 monitor device
Axis 27 monitor device
Axis 28 monitor device
Axis 29 monitor device
Axis 30 monitor device
Axis 31 monitor device
Axis 32 monitor device
1 - 36

1 OVERVIEW
Detailes of each axis
Device No. SV13/SV22(Real mode) SV22(Virtual mode) Signal derection
D0 + 20n
D1 + 20n
D2 + 20n
D3 + 20n
D4 + 20n
D5 + 20n
D6 + 20n Minor error code Minor error code
D7 + 20n Major error code Major error code
D8 + 20n Servo error code Servo error code
D9 + 20n
D10 + 20n
D11 + 20n
D12 + 20n Execute program No. —
D13 + 20n M-code —
D14 + 20n Torque limit value Torque limit value
D15 + 20n
D16 + 20n
D17 + 20n
D18 + 20n
D19 + 20n
(Note-1) : "n" in the above device No. shows the numerical value which correspond to axis No.
(Note-2) : Device area of 9 axes or more is unusable in the Q172CPU(N).
Feed current value
Real current value Real current value
Deviation counter value Deviation counter value
Home position return re-travel
value
Travel value after proximity dog
ON
Data set pointer for constantspeed control
Travel value change register —
Real current value at stop input Hold Monitor device
Q173CPU(N) : Axis No.1 to No.32 (n=0 to 31)
Q172CPU(N) : Axis No.1 to No.8 (n=0 to 7)
Feed current value/roller cycle
speed
Monitor device
Hold
Hold
—
Command
device
1 - 37

1 OVERVIEW
2) Table of the control change registers (SV13/SV22)
Device No. Signal name Device No. Signal name
D640
D641
D642
D643
D644
D645
D646
D647
D648
D649
D650
D651
D652
D653
D654
D655
D656
D657
D658
D659
D660
D661
D662
D663
D664
D665
D666
D667
D668
D669
D670
D671
Axis 1 JOG speed
setting register
Axis 2 JOG speed
setting register
Axis 3 JOG speed
setting register
Axis 4 JOG speed
setting register
Axis 5 JOG speed
setting register
Axis 6 JOG speed
setting register
Axis 7 JOG speed
setting register
Axis 8 JOG speed
setting register
Axis 9 JOG speed
setting register
Axis 10 JOG speed
setting register
Axis 11 JOG speed
setting register
Axis 12 JOG speed
setting register
Axis 13 JOG speed
setting register
Axis 14 JOG speed
setting register
Axis 15 JOG speed
setting register
Axis 16 JOG speed
setting register
D672
D673
D674
D675
D676
D677
D678
D679
D680
D681
D682
D683
D684
D685
D686
D687
D688
D689
D690
D691
D692
D693
D694
D695
D696
D697
D698
D699
D700
D701
D702
D703
Axis 17 JOG speed
setting register
Axis 18 JOG speed
setting register
Axis 19 JOG speed
setting register
Axis 20 JOG speed
setting register
Axis 21 JOG speed
setting register
Axis 22 JOG speed
setting register
Axis 23 JOG speed
setting register
Axis 24 JOG speed
setting register
Axis 25 JOG speed
setting register
Axis 26 JOG speed
setting register
Axis 27 JOG speed
setting register
Axis 28 JOG speed
setting register
Axis 29 JOG speed
setting register
Axis 30 JOG speed
setting register
Axis 31 JOG speed
setting register
Axis 32 JOG speed
setting register
1 - 38

1 OVERVIEW
MEMO
1 - 39

1 OVERVIEW
3) Table of the virtual servomotor axis monitor devices
(SV22 only)
Device No. Signal name Device No. Signal name
D800
to
D809
D810
to
D819
D820
to
D829
D830
to
D839
D840
to
D849
D850
to
D859
D860
to
D869
D870
to
D879
D880
to
D889
D890
to
D899
D900
to
D909
D910
to
D919
D920
to
D929
D930
to
D939
D940
to
D949
D950
to
D959
Axis 1 monitor device
Axis 2 monitor device
Axis 3 monitor device
Axis 4 monitor device
Axis 5 monitor device
Axis 6 monitor device
Axis 7 monitor device
Axis 8 monitor device
Axis 9 monitor device
Axis 10 monitor device
Axis 11 monitor device
Axis 12 monitor device
Axis 13 monitor device
Axis 14 monitor device
Axis 15 monitor device
Axis 16 monitor device
1 - 40
D960
to
D969
D970
to
D979
D980
to
D989
D990
to
D999
D1000
to
D1009
D1010
to
D1019
D1020
to
D1029
D1030
to
D1039
D1040
to
D1049
D1050
to
D1059
D1060
to
D1069
D1070
to
D1079
D1080
to
D1089
D1090
to
D1099
D1100
to
D1109
D1110
to
D1119
Axis 17 monitor device
Axis 18 monitor device
Axis 19 monitor device
Axis 20 monitor device
Axis 21 monitor device
Axis 22 monitor device
Axis 23 monitor device
Axis 24 monitor device
Axis 25 monitor device
Axis 26 monitor device
Axis 27 monitor device
Axis 28 monitor device
Axis 29 monitor device
Axis 30 monitor device
Axis 31 monitor device
Axis 32 monitor device

1 OVERVIEW
Detailes of each axis
Device No. Signal name
D800 + 10n
D801 + 10n
D802 + 10n Minor error code
D803 + 10n Major error code
D804 + 10n Execute program No.
D805 + 10n M-code
D806 + 10n
D807 + 10n
D808 + 10n Error search output axis No.
D809 + 10n Data set pointer for constant-speed control
(Note-1) : "n" in the above device No. shows the numerical value which
correspond to axis No.
Q173CPU(N) : Axis No.1 to No.32 (n=0 to 31)
Q172CPU(N) : Axis No.1 to No.8 (n=0 to 7)
(Note-2) : The unused axis areas in the mechanical system program can be used as an
user device.
Feed current value
Current value after virtual sevomotor axis main
shaft's differential gear
1 - 41

1 OVERVIEW
4) Table of the synchronous encoder axis monitor devices
(SV22 only)
Device No. Signal name
D1120
to
D1129
D1130
to
D1139
D1140
to
D1149
D1150
to
D1159
D1160
to
D1169
D1170
to
D1179
D1180
to
D1189
D1190
to
D1199
D1200
to
D1209
D1210
to
D1219
D1220
to
D1229
D1230
to
D1239
Axis 1 monitor device
Axis 2 monitor device
Axis 3 monitor device
Axis 4 monitor device
Axis 5 monitor device
Axis 6 monitor device
Axis 7 monitor device
Axis 8 monitor device
Axis 9 monitor device
Axis 10 monitor device
Axis 11 monitor device
Axis 12 monitor device
1 - 42

1 OVERVIEW
Detailes of each axis
Device No. Signal name
D1120 + 10n
D1121 + 10n
D1122 + 10n Minor error code
D1123 + 10n Major error code
D1124 + 10n
D1125 + 10n
D1126 + 10n
D1127 + 10n
D1128 + 10n Error search output axis No.
D1129 + 10n Unusable
(Note-1) : "n" in the above device No. shows the numerical value which
correspond to axis No.
Q173CPU(N) : Axis No.1 to No.12 (n=0 to 11)
Q172CPU(N) : Axis No.1 to No.8 (n=0 to 7)
(Note-2) : Device area of 9 axes or more is unusable in the Q172CPU(N).
Current value
Unusable
Current value after synchronous encoder axis
main shaft's differential gear
1 - 43

1 OVERVIEW
5) Table of the cam axis monitor devices (SV22 only)
Device No. Signal name Device No. Signal name
D1240
to
D1249
D1250
to
D1259
D1260
to
D1269
D1270
to
D1279
D1280
to
D1289
D1290
to
D1299
D1300
to
D1309
D1310
to
D1319
D1320
to
D1329
D1330
to
D1339
D1340
to
D1349
D1350
to
D1359
D1360
to
D1369
D1370
to
D1379
D1380
to
D1389
D1390
to
D1399
Axis 1 monitor device
Axis 2 monitor device
Axis 3 monitor device
Axis 4 monitor device
Axis 5 monitor device
Axis 6 monitor device
Axis 7 monitor device
Axis 8 monitor device
Axis 9 monitor device
Axis 10 monitor device
Axis 11 monitor device
Axis 12 monitor device
Axis 13 monitor device
Axis 14 monitor device
Axis 15 monitor device
Axis 16 monitor device
D1400
to
D1409
D1410
to
D1419
D1420
to
D1429
D1430
to
D1439
D1440
to
D1449
D1450
to
D1459
D1460
to
D1469
D1470
to
D1479
D1480
to
D1489
D1490
to
D1499
D1500
to
D1509
D1510
to
D1519
D1520
to
D1529
D1530
to
D1539
D1540
to
D1549
D1550
to
D1559
Axis 17 monitor device
Axis 18 monitor device
Axis 19 monitor device
Axis 20 monitor device
Axis 21 monitor device
Axis 22 monitor device
Axis 23 monitor device
Axis 24 monitor device
Axis 25 monitor device
Axis 26 monitor device
Axis 27 monitor device
Axis 28 monitor device
Axis 29 monitor device
Axis 30 monitor device
Axis 31 monitor device
Axis 32 monitor device
1 - 44

1 OVERVIEW
Detailes of each axis
Device No. Signal name
D1240 + 10n Unusable
D1241 + 10n Execute cam No.
D1242 + 10n
D1243 + 10n
D1244 + 10n
D1245 + 10n
D1246 + 10n
D1247 + 10n
D1248 + 10n
D1249 + 10n
(Note-1) : "n" in the above device No. shows the numerical value which
correspond to axis No.
Q173CPU(N) : Axis No.1 to No.32 (n=0 to 31)
Q172CPU(N) : Axis No.1 to No.8 (n=0 to 7)
(Note-2) : The unused aixs areas in the mechanical system program can be used as an
user device.
Execute stroke amount
Current value within 1 cam shaft revolution
Unusable
1 - 45

1 OVERVIEW
6) Table of the common devices (SV13/SV22)
Device No. Signal name
D704 PLC ready flag request D740 Axis 21
D705
D706 All axes servo ON command request D742 Axis 23
D707
D708
D709 Unusable — D745 Axis 26
D710 D746 Axis 27
to
D713
D714
D715
D716
D717
D718
D719
D720 Axis 1 D755 Manual pulse generator 1 enable flag request
D721 Axis 2 D756 Manual pulse generator 2 enable flag request
D722 Axis 3 D757 Manual pulse generator 3 enable flag request
D723 Axis 4 D758 Unusable —
D724 Axis 5
D725 Axis 6
D726 Axis 7
D727 Axis 8
D728 Axis 9
D729 Axis 10 D790
D730 Axis 11
D731 Axis 12 D792
D732 Axis 13
D733 Axis 14 D799
D734 Axis 15
D735 Axis 16
D736 Axis 17
D737 Axis 18
D738 Axis 19
D739 Axis 20
Speed switching point specified flag
request
Real mode/virtual mode switching
request (SV22)
JOG operation simultaneous start
command request
JOG operation simultaneous start
axis setting register
Manual pulse generator axis 1 No.
setting register
Manual pulse generator axis 2 No.
setting register
Manual pulse generator axis 3 No.
setting register
Manual pulse generators 1
pulse input magnification
setting register
(Note-1, 2)
Signal
derecrtion
Command
device
Command
device
Device No. Signal name
D741 Axis 22
D743 Axis 24
D744 Axis 25
D747 Axis 28
D748 Axis 29
D749 Axis 30
D750 Axis 32
D751 Axis 32
D752
D753
D754
D759
D760
to
D789
D791
to
(Note-1) : The range of axis No.1 to 8 is valid in the Q172CPU(N).
(Note-2) : Device area of 9 axes or more is unusable in the Q172CPU(N).
Manual pulse generator 1 smoothing
magnification setting register
Manual pulse generator 2 smoothing
magnification setting register
Manual pulse generator 3 smoothing
magnification setting register
PCPU ready complete flag status
(0 : OFF/1 : ON)
Unusable —
Real mode axis information register (SV22)
Servo amplifier type
Manual pulse generators 1
pulse input magnification
setting register
(Note-1, 2)
Signal
derecrtion
Command
device
Monitor
device
Monitor
device
1 - 46

1 OVERVIEW
(2) Special relays
Special relays are internal relays whose applications are fixed in the Motion
CPU. For this reason, they cannot be used in the same way as the normal
internal relays by the Motion SFC programs.
However, they can be turned ON/OFF as needed in order to control the Motion
CPU.
The headings in the table that follows have the following meanings.
Item Explanation
No. • Indicates the device No. of the special relay.
Name • Indicates the name of the special relay.
Meaning • Indicates the nature of the special relay.
Details • Indicates detailed information about the nature of the special relay.
• Indicates whether the relay is set by the system or user, and, if it is set by system, when
setting is performed.
<Set by>
S : Set by system (Motion CPU)
U : Set by user (Motion SFC program or test operation using a peripheral device)
S/U : Set by both system (Motion CPU) and user
Set by
(When set)
<When set>
Main process : Set during each main processing (free time processing of the CPU)
Initial process : Set only during initial processing (when power supply is turned ON, or
Status change : Set only when there is a change in status
Error : Set when error is occurred.
Request : Set only when there is a user request (Special reray, etc.)
Operation cycle : Set during each operation cycle of the Motion CPU.
Indicated only if setting is done by system (Motion CPU) .
when executed the reset)
1 - 47

1 OVERVIEW
Special relay list
No. Name Meaning Details
• Turn on when there is one or more output modules control
of self CPU which fuse has been blown.
Remains on if normal status is restored.
• Turn on if a momentary power interruption of less than
20ms occurred during use of the AC power supply
module, and reset by turning power off to on.
• Turn on if a momentary power interruption of less than
10ms occurred during use of the DC power supply
module, and reset by turning power off to on.
• Turned on when the voltage of the external battery
reduces to less than specified value. Turn off when the
voltage of the external battery becomes normal.
• Synchronizes with "BAT. LED"
• Check the voltage of the external battery, only when it is
set with "external battery use" by system setting.
• Turn on when the voltage of the external battery reduces
to less than specified value. Remains on if normal status
is restored.
• Synchronizes with "BAT. LED"
• Check the voltage of the external battery, only when it is
set with "external battery use" by system setting.
• Turn on when error is found as a result of self-diagnosis.
Remains on if normal status is restored.
• Turn on when error is found as a result of diagnosis.
Remains on if normal status is restored.
• Write clock data stored in D9025 to D9028 to the clock
element when M9025 has changed from off to on.
• Turn on by clock data (D9025 to D9028) error. S(Request)
• Read clock data from D9025 to D9028 in BCD when
M9028 is on.
• Turn on without regard to position of RUN/STOP switch
on.
• Turn off without regard to position of RUN/STOP switch
on.
• A reset of the diagnostic error is executed. U
• Turn on when a "watchdog timer error" is detected by the
Motion CPU self-diagnosis function.
When the Motion CPU detects a WDT error, it executes
an immediate stop without deceleration of the operating
axes.
• The error cause is stored in the "Motion CPU WDT error
cause (D9184)".
• When the PLC ready flag (M2000) turn off to on, the
fixed parameters, servo parameters and limit switch
output data, etc., are checked, and if no error is detected
this flag turns on.
• Turn off when the PLC ready (M2000) signal turns off.
• This flag status indicates whether a TEST mode
established from a peripheral device is currently in
effect.
• If the TEST mode is not established in response to a
TEST mode request from a peripheral device, the
"TEST mode request error flag (M9078)" will turn on.
• This flag status indicate whether the forced stop. S(Operation cycle)
M9000 Fuse blown detection flag
AC/DC DOWN detection
M9005
flag
M9006 Battery low flag
M9007 Battery low latch flag
M9008 Self-diagnostic error flag
M9010 Diagnostic error flag
M9025 Clock data set request
M9026 Clock data error
M9028 Clock data read request
M9036 Always ON
M9037 Always OFF
M9060 Diagnostic error reset
M9073 PCPU WDT error flag
PCPU READY complete
M9074
flag
M9075 Test mode ON flag
External forced stop
M9076
input flag
OFF : Normal
ON : Fuse blown module
detected
OFF : AC/DC DOWN
not detected
ON : AC/DC DOWN
detected
OFF : Normal
ON : Battery low
OFF : Normal
ON : Battery low
OFF : No error
ON : Error
OFF : No error
ON : Error
OFF : Ignored
ON : Set request present
used
OFF : No error
ON : Error
OFF : Ignored
ON : Read request
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
OFF
ON : Abnormal
OFF : Normal
ON : PCPU READY
OFF : PCPU READY
ON : TEST mode is in
OFF : TEST mode is not in
ON : Forced stop OFF
OFF : Forced stop ON
ON : Diagnostic
error reset
completion
uncompletion
effect.
effect.
Set by
(When set)
S(Occur an error)
U
U
S(Main processing)
S(Occur an error)
S(Request)
S(Request)
(Note-1) : It adds newly at the Motion controller Q series.
Remark
New
(Note-1)
New
(Note-1)
1 - 48

1 OVERVIEW
Special relay list (continued)
No. Name Meaning Details
• This flag indicates whether the setting designated at the
manual pulse generator axis setting register (D714 to D719)
is normal or abnormal.
• When this relay turn on, the error content is stored at the
manual pulse generator axis setting error register (D9185 to
D9187).
• Turn on if the TEST mode is not established in response to a
TEST mode request from a peripheral device.
• When this relay turns on, the error content is stored at the
TEST mode request error register (D9182 to D9183).
• This flag status indicates whether the positioning data of the
servo program(K) specified with the Motion SFC program is
normal or abnormal, and if error is detected this flag turns
on.
• The content of a servo program setting error is stored at
D9189 and D9190.
• The servo parameter of servo parameter read request axis
set as D9104 is reflected in the Motion CPU from the servo
amplifier at the time of OFF to ON.
• This flag turn on while having read the servo amplifier
to the Motion CPU. It turn off automatically after reading
completion.
• Turn on when the data read from CPU No.1 is performed
normally by MULTR instruction.
• Turn on when the data read from CPU No.2 is performed
normally by MULTR instruction.
• Turn on when the data read from CPU No.3 is performed
normally by MULTR instruction.
• Turn on when the data read from CPU No.4 is performed
normally by MULTR instruction.
• Turn off at reset release of the CPU No.1.
• Turn on during reset of the CPU No.1. (It also contains when a
CPU is removed from the base unit.)
• The other CPU is also resetting.
• Turn off at reset release of the CPU No.2.
• Turn on during reset of the CPU No.2. (It also contains when a
CPU is removed from the base unit.)
• The error of the "MULTI CPU DOWN" (error code : 7000)
occurs in the other CPU.
• Turn off at reset release of the CPU No.3.
• Turn on during reset of the CPU No.3. (It also contains when a
CPU is removed from the base unit.)
• The error of the "MULTI CPU DOWN" (error code : 7000)
occurs in the other CPU.
• Turn off at reset release of the CPU No.4.
• Turn on during reset of the CPU No.4. (It also contains when a
CPU is removed from the base unit.)
• The error of the "MULTI CPU DOWN" (error code : 7000)
occurs in the other CPU.
Manual pulse generator
M9077
axis setting error flag
TEST mode request
M9078
error flag
Servo program setting
M9079
error flag
Servo parameter read
M9104
request flag
Servo parameter reading
M9105
flag
CPU No.1 MULTR
M9216
complete flag
CPU No.2 MULTR
M9217
complete flag
CPU No.3 MULTR
M9218
complete flag
CPU No.4 MULTR
M9219
complete flag
M9240 CPU No.1 resetting flag
M9241 CPU No.2 resetting flag
M9242 CPU No.3 resetting flag
M9243 CPU No.4 resetting flag
ON : At least one D714 to
D719 setting is
abnormal.
OFF : All D714 to D719
settings are normal.
ON : Abnormal
OFF : Normal
ON : Abnormal
OFF : Normal
OFF to ON :
Servo parameter read
ON : Servo parameter
reading.
OFF : Except servo
parameter reading.
OFF to ON :
CPU No.1 read completion
OFF to ON :
CPU No.2 read completion
OFF to ON :
CPU No.3 read completion
OFF to ON :
CPU No.4 read completion
OFF : CPU No.1 reset
release
ON : CPU No.1 resetting
OFF : CPU No.2 reset
release
ON : CPU No.2 resetting
OFF : CPU No.3 reset
release
ON : CPU No.3 resetting
OFF : CPU No.4 reset
release
ON : CPU No.4 resetting
(Note-1) : It adds newly at the Motion controller Q series.
(Note-2) : The CPU No.1 is reset after the factor of the stop error is removed to cancel a stop error.
Set by
(When set)
S(Occur an error)
S(Occur an error)
S(Occur an error)
U
S(Reading)
S(Read completion)
S(Change status)
Resetting is cancelled.
Remark
New
(Note-1)
1 - 49

1 OVERVIEW
Special relay list (continued)
No. Name Meaning Details
M9244 CPU No.1 error flag
M9245 CPU No.2 error flag
M9246 CPU No.3 error flag
M9247 CPU No.4 error flag
OFF : CPU No.1 normal
ON : On CPU No.1 stop
error
OFF : CPU No.2 normal
ON : On CPU No.2 stop
error
OFF : CPU No.3 normal
ON : On CPU No.3 stop
error
OFF : CPU No.4 normal
ON : On CPU No.4 stop
error
(Note-1) : It adds newly at the Motion controller Q series.
(Note-2) : The CPU No.1 is reset after the factor of the stop error is removed to cancel a stop error.
• Turn off when the CPU No.1 is normal. (It contains at
continuation error.)
• Turn on during stop error of the CPU No.1.
• Turn off when the CPU No.2 is normal. (It contains at
continuation error.)
• Turn on during stop error of the CPU No.2.
• Turn off when the CPU No.3 is normal. (It contains at
continuation error.)
• Turn on during stop error of the CPU No.3.
• Turn off when the CPU No.4 is normal. (It contains at
continuation error.)
• Turn on during stop error of the CPU No.4.
(Note-2)
(Note-2)
(Note-2)
(Note-2)
Set by
(When set)
S(Change status)
Resetting is cancelled.
Remark
New
(Note-1)
1 - 50

1 OVERVIEW
(3) Special registers
Special registers are internal registers whose applications are fixed in the
Motion CPU. For this reason, it is not possible to use these registers in Motion
SFC programs in the same way that normal registers are used.
However, data can be written as needed in order to control the Motion CPU.
Data stored in the special registers are stored as BIN values if no special
designation has been made to the contrary.
The headings in the table that follows have the following meanings.
Item Explanation
Number • Indicates the No. of the special register.
Name • Indicates the name of the special register.
Meaning • Indicates the nature of the special register.
Details • Indicates detailed information about the nature of the special register.
• Indicates whether the register is set by the system or user, and, if it is set by system,
when setting is performed.
<Set by>
S : Set by system (Motion CPU)
U : Set by user (Motion SFC program or test operation using a peripheral device)
S/U : Set by both system (Motion CPU) and user
Set by
(When set)
<When set>
Main process : Set during each main processing (free time processing of the CPU)
Initial process : Set only during initial processing (when power supply is turned ON, or
Status change : Set only when there is a change in status
Error : Set when error is occurred.
Request : Set only when there is a user request (Special reray , etc.)
Operation cycle : Set during each operation cycle of the Motion CPU.
Indicated only if setting is done by system (Motion CPU) .
when executed the reset)
1 - 51

)2)
1 OVERVIEW
Special register list
No. Name Meaning Details
D9000 Fuse blown No.
AC/DC DOWN
D9005
counter No.
D9008 Diagnostic error
D9010
Diagnostic error
D9011
occurrence time
D9012
Error information
D9013
classfication
D9014 Error information Error information
Module No. with
blown fuse
Number of times
for AC/DC DOWN
Dignostic error
number
Diagnostic error
occurrence
(Year, Month)
Diagnostic error
occurrence time
(Day, Hour)
Diagnostic error
occurrence time
(Minute, Second)
Error information
classfication code
• When fuse blown modules are detected, the lowest I/O module No. is stored
in D9000.
• 1 is added to the stored value each time the input voltage becomes
85[%](AC power supply/65[%] DC power supply) or less of the rating while
the CPU module is performing an operation, and the value is stored in BIN
code.
• When error is found as a result of self-diagnosis, error No. is stored in BIN
code.
• Refer to "19.4 Multiple CPU Error Codes" for details of the error code.
• The age (A.D, the rightmost two digits) when data on D9008 are updated,
and the month stored with a BCD code two digits.
• The day when data on D9008 are updated, and the hour stored with a BCD
code two digits.
• The minute when data on D9008 are updated, and the second stored with a
BCD code two digits.
• The classification code to judge the error information stored in the eror
information (D9014) is stored.
• The following code is stored.
0 : None
1 : Module No./CPU No./Base No.
2 : Parameter No.
• Error information to comply with the diagnostic error (D9008) is stored.
There are following two types informations to be stored.
1) Module No./CPU No./Base No.
•
Module No. or CPU No. is stored according to the error which occurred
in the case of the Multiple CPU system.
(Refer to each error code which is stored.)
CPU No.1 : 1, CPU No.2 : 2, CPU No.3 : 3, CPU No.4 : 4
2) Parameter No.
• The operation states of CPU as shown below are stored in D9015.
to to
B15 B7B0B8
Year(0 to 99) Month(1 to 12)
to to
B15 B7 B0B8
Day(1 to 31) Hour(0 to 23)
to to
B15 B7 B0B8
Minute(0 to 59) Second(0 to 59)
B15 B12 B11 B8 B7 B4 B3 B0
Example : October 1995
H9510
Example : 25st, 10 a.m
H2510
Example : 35 min., 48 sec.
H3548
Set by
(When set)
Remark
S(Occur an error)
New
(Note)
1
Operating state of
D9015
CPU
D9017 Scan time
Maximum scan
D9019
time
D9025 Clock data
Operating state of
CPU
Scan time
(1ms units)
Maximum scan
time (1ms units)
Clock data
(Year, month)
1) Operating state of CPU
2) STOP cause
Note : Priority is earliest first
• Main cycle is stored in the unit 1ms.
• Setting range (0 to 65535[ms])
• The maximum value of the main cycle is stored in the unit 1ms.
• Setting range (0 to 65535[ms])
• Stores the year (2 lower digits) and month in BCD.
B15 B12toB11 B8toB7 B4toB3 B0
Year Month
0 : RUN
2 : STOP
0 : RUN/STOP switch
4 : Error
to
Example : July,1993
H9307
(Note) : It adds newly at the Motion controller Q series.
S(Main processing)
New
(Note)
S/U(Request)
1 - 52

1 OVERVIEW
Special register list (continued)
No. Name Meaning Details
• Stores the day and hour in BCD.
B15 B12to B11 B8to B7 B4to B3 B0to
D9026 Clock data
Clock data
(Day, hour)
Example : 31st, 10 a.m.
H3110
Set by
(When set)
Remark
D9027 Clock data
Clock data
(Minute, second)
• Stores the minute and second in BCD.
Day Hour
B15 B12to B11 B8to B7 B4to B3 B0to
Minute
• Stores the day of the week in BCD.
B15 B12to B11 B8to B7 B4to B3 B0to
Second
Example : 35 min., 48 sec.
H3548
Example :
S/U(Request)
Friday
H0005
D9028 Clock data
Clock data
(Day of week)
"0" must be set here.
Diagnostic error
D9060
reset error No.
D9061 Multiple CPU No. Multiple CPU No. • CPU No. of the self CPU is stored. S(Initial processing)
Servo parameter
D9104
read request axis
No.
D9182
Test mode
D9183
request error
Motion CPU WDT
D9184
error cause
D9185
Manual pulse
D9186
generator axis
D9187
setting error
Error No. of
releasing an error
Servo parameter
read axis No.
It is operating in
requirement error
occurrence of the
test mode, axis
information
Error meaning of
WDT error occurs
Manual pulse
generator axis
setting error
information
• Error No. of canceling error is stored. U
• Axis No. of servo amplifier which begins to read servo parameter is setting.
Q173CPU(N) : 1 to 32 (Axis1 to 32)
Q172CPU(N) : 1 to 8 (Axis1 to 8)
• Each axis is stopping : 0/Operating : 1, information is stored as a bit data.
D9182 : b0 to b15(Axis 1 to Axis 16)
D9183 : b0 to b15(Axis 17 to Axis 32)
The following error codes are stored in D9184.
1 : S/W fault 1
2 : Operation cycle over
3 : Q bus WDT error
4 : WDT error
30 : Information processor H/W error
201 to 215 : Q bus H/W fault
250 to 253 : Servo amplifier interface H/W fault
300 : S/W fault3
301 : 15 CPSTART instructions of 8 or more points were started
simultaneously.
302 : During ROM operation, system setting data, program and
parameter written to internal FLASH ROM are fault.
• Contents of the manual pulse generator axis setting error is stored when the
manual pulse generator axis setting error flag(M9077) turn on.
(Normal : 0/Setting error : 1)
D9185 : The manual pulse generator axis setting error is stored in b0 to b2
(P1 to P3).
The smoothing magnification setting is stored in b3 to b5 (P1 to
P3).
D9186 : One pulse input magnification setting error is stored in b0 to b15
(axis 1 to axis 16).
D9187 : One pulse input magnification setting error is stored in b0 to b15
(axis 17 to axis 32).
Day of week
Sunday
0
Monday
1
Tuesday
2
3
Wednesday
4
Thursday
5
Friday
6
Saturday
U
S(Occur an error)
(Note) : It adds newly at the Motion controller Q series.
New
(Note)
1 - 53

)2)4)3)5)6)8)7)
1 OVERVIEW
Special register list (continued)
No. Name Meaning Details
D9188
D9189
D9190
D9191
D9192
D9193
D9194
D9195
D9196
D9197
Motion operation
cycle
Error program
No.
Error item
information
Servo amplifier
loading
information
Real mode/virtual
mode switching
error information
PC link
communication
error codes
Operation cycle
of the Motion
CPU setting
Motion operation
cycle
Error program No. of
servo program
Error code of servo
program
Servo amplifier
loading information
Real mode/virtual
mode Switching
error code
PC link
communication error
codes
Operation cycle of
the Motion CPU
setting
• The time when the motion operation cycle is stored in the [µs] unit.
When the servo program setting error flag (M9079) turns on, the erroneous
servo program No. will be stored.
When the servo program setting error flag (M9079) turns on, the error
code corresponding to the erroneous setting item will be stored.
• The loading status(loading : 1/non-loading : 0) of the servo amplifier
checked in initial process, and stored as the bit data.
D9191 : b0 to b15(axis 1 to axis 16)
D9192 : b0 to b15(axis 17 to axis 32)
• The axis which turned from non-loading to loading status after power-on is
handled as loaded. (However, the axis which turned from loading to nonloading status remains as loaded.)
• When a mode switching error occurs in real-to-virtual or virtual-to-real
mode switching, or a mode continuation error occurs in the virtual mode,
its error information is stored.
• The following error code is stored.
00 : No error
01 : Receiving timing error
02 : CRC error
03 : Communication response code error
04 : Received frame error
05 : Communication task start error
(Each error code is reset to "00" when normal communication is
restarted.)
• The time when the setting operation cycle is stroed in the [µs] unit.
• The CPU switch status is stored in the following format.
B15 B12B11
B7 B4 B3 B0
B8
Set by
(When set)
S(Operation cycle)
S(Occur an error)
S(Initial processing)
S(Occur an error)
S(Initial processing)
Remark
New
(Note)
D9200 State of switch State of CPU switch
D9201 State of LED State of CPU-LED
1) CPU switch status 0 : RUN
2) Memory card switch Always OFF
3) Dip switch
3)
1 : STOP
2 : L.CLR
B8 through B12 correspond to SW1
through SW5 of system setting switch 1.
0 : OFF/1 : ON
B13 through B15 is not used.
No used.
1)2)
• Information concerning which of the following states the LEDs on the CPU
are in is stored in the following bit patterns.
• 0 is off, 1 is on, and 2 is flicker
B15 B12 B11 B8 B7 B4 B3 B0
1
1) : RUN 5) : BOOT
2) : ERROR 6) : No used
3) : M.RUN 7) : No used
4) : BAT.ALARM 8) : MODE
Bit patterns for MODE
0 : OFF 1 : Green
2 : Orange
(Note) : It adds newly at the Motion controller Q series.
1 - 54
S(Main processing)
S(Change status)
New
(Note)
New
(Note)
.

1 OVERVIEW
1.3 Hardware Configuration
This section describes the Q173CPU(N)/Q172CPU(N) system configuration,
precautions on use of system and configured equipments.
1.3.1 Motion system configuration
This section describes the equipment configuration, configuration with peripheral
devices and system configuration in the Q173CPU(N)/Q172CPU(N) system.
1 - 55

1 OVERVIEW
(1) Equipment configuration in Q173CPU(N) system
(a) When using the Dividing unit/external battery
Extension of the Q series module
Motion module
(Q172LX, Q172EX, Q173P X)
(Note-1)
MITSUBISHI
LITHIUM BATT ERY
Battery
(A6BAT/MR-BAT)
Power supply module/
QCPU/ I/O module/ Intelligent
function module of the Q series
CPU base unit
(Q33B, Q35B, Q38B, Q312B)
Motion CPU module
(Q173CPU(N))
SSCNET cable
(Q173DVCBL M)
SSCNET CN1
SSCNET CN2
SSCNET CN3
SSCNET CN4
MITSUBISHI
LITHIUM BATTE RY
Q173CPU
Dividing unit
(Q173DV)
(Note-5)
Extension cable
(QC B)
(Note-2)
Short-circuit connector for
the teaching unit
(Q170TUTM)
(Note-3)
Cable for the teaching unit
(Q170TUD CBL M(-A))
(Note-4)
Short-circuit connector for
the teac hing unit
(A31TUD3TM)
Motion module
(Q172LX, Q172EX, Q173PX)
Q6 B extension base unit
(Q63B, Q65B, Q68B, Q612B)
Power supply module/
I/O module/Intelligent function
module of the Q series
(Note-5) (Note-6)
SVO ON
Teaching unit
(A31TU-D3 , A31TU-DN )
SSCNET cable
for MR-H-BN
(MR-J2HBUS M- A) (MR-J2HBUS M)
Servo amplifier
(MR-H-BN)
SSCNET cable
for MR-J2 -B
MITSUBISHI
Servo amplifier
(MR-J2 -B)
1 - 56
It is possible to select the best according to the system.
(Note-1) : When using the external battery, be sure to set the
Battery(A6BAT/MR-BAT) to the Dividing unit(Q173DV).
Battery(A6BAT/MR-BAT) is optional.
(Note-2) : It is possible to use only Q173CPUN-T.
It is packed together with Q173CPUN-T.
(Note-3) : It varies by the connecting teaching unit.
(Note-4) : It is packed together with Q170TUD CBL M.
(Note-5) : When using the A31TU-D3 /A31TU-DN , be sure to use
the Q173CPUN-T.
(Note-6) : A31TU-D3 /A31TU-DN corresponds to only Japanese.
It does not correspond to display for English.

p
1 OVERVIEW
(b) When using the Dividing cable
Extension of the Q series module
Motion module
(Q172LX, Q172EX, Q173PX)
Power supply module/
QCPU/ I/O module/ Intelligent
function module of the Q series
CPU base unit
(Q33B, Q35B, Q38B, Q312B)
Motion CPU module
(Q173CPU(N) )
SSCNET cable
for MR-H-BN
(Q173HB CBL M)
SSCNET cable
for MR-J2 -B
(Q173J2B CBL M )
MITSUBIS HI
(Note-4)
Extension cable
(QC B)
(Note-1)
Short-circuit connector for
the teaching unit
(Q170TUTM)
(Note-2)
Cable for the teaching un it
(Q170TUD CBL M(-A))
(Note-3)
Motion module
(Q172LX, Q172EX, Q173PX)
Q6 B extension base unit
(Q63B, Q65B, Q68B, Q612B)
Power supply module/
I/O module/Intelligent function
module of the Q series
(Note-5)
(Note-4)
SVO ON
Teaching unit
(A31TU-D3 , A31TU-DN )
Servo amplifier
(MR-H-BN)
Servo amplifier
(MR-J2 -B)
1 - 57
Short-circuit connector for the
teaching unit
(A31TUD3TM)
It is possible to select the best according to the system.
(Note-1) : It is possible to use only Q173CPUN-T. It is packed
together with Q173CPUN-T.
(Note-2) : It varies by the connecting teaching unit.
(Note-3) : It is packed together with Q170TUD CBL M.
(Note-4) : When using the A31TU-D3 /A31TU-DN , be sure to use
the Q173CPUN-T.
(Note-5) : A31TU-D3 /A31TU-DN corresponds to only Japanese.
It does not corres
ond to display for English.

1 OVERVIEW
(2) Equipment configuration in Q172CPU(N) system
(a) When using the external battery
Extension of the Q series module
Motion module
(Q172LX, Q172EX, Q173PX)
(Note-1)
BAT
LITHIUM BATTERY
CPU
PASSED
Battery unit
(Q170BAT)
MITSUBISHI
Power supply module/
QCPU/ I/O module/ Intelligent
function module of the Q series
CPU base unit
(Q33B, Q35B, Q38B, Q312B)
(Note-5)
Motion CPU module
(Q172CPU(N))
Extension cable
(QC B)
(Note-2)
Short-circuit connector for
the teaching unit
(Q170TUTM)
(Note-3)
Q17BAT
DATE
SSCNET cable
for MR-H-BN
(Q172HBCBL -M) (Q172J2BCBL M-B)
SSCNET cable
for MR-J2 -B
Cable for the teaching unit
(Q170TUD CBL M(-A))
Motion module
(Q172LX, Q172EX, Q173PX)
Q6 B extension base unit
(Q63B, Q65B, Q68B, Q612B)
Power supply module/
I/O module/Intelligent function
module of the Q series
(Note-6)
(Note-5)
SVO ON
Teaching unit
(A31TU-D3 , A31TU-DN )
(Note-4)
MITSUBISHI
MITSUBISHI
LITHIUM BATTERY
Battery
(A6BAT/MR-BAT)
Servo amplifier
(MR-H-BN)
Servo amplifier
(MR-J2 -B)
1 - 58
Short-circuit connector for
the teaching unit
(A31TUD3TM)
It is possible to select the best according to the system.
(Note-1) : When using the external battery, be sure to use the
SSCNET cable(Q172J2BCBL M-B/Q172HBCBL M-B)
and to set the battery (A6BAT/MR-BAT). Also install
the battery(A6BAT/MR-BAT)in the Battery unit(Q170BAT).
Battery(A6BAT/MR-BAT) is optional.
(Note-2) : It is possible to use only Q172CPUN-T.
It is packed together with Q172CPUN-T.
(Note-3) : It varies by the connecting teaching unit.
(Note-4) : It is packed together with Q170TUD CBL M.
(Note-5) : When using the A31TU-D3 /A31TU-DN , be sure to use
the Q172CPUN-T.
(Note-6) : A31TU-D3 /A31TU-DN corresponds to only Japanese.
It does not correspond to display for English.

1 OVERVIEW
(b) When not using the external battery
Extension of the Q series module
Motion module
(Q172LX, Q172EX, Q173PX)
Power supply module/
QCPU/ I/O module/ Intelligent
function module of the Q series
CPU base unit
(Q33B, Q35B, Q38B, Q312B)
Motion CPU module
(Q172CPU(N))
SSCNET cable
for MR-H-BN
(Q172HBCBL M) (Q172J2B CBL M)
SSCNET cable
for MR-J2 -B
MITSUBISHI
(Note-4)
Extension cable
(QC B)
(Note-1)
Short-circuit connector for
the teaching unit
(Q170TUTM)
(Note-2)
Cable for the teaching unit
(Q170TUD CBL M(-A))
(Note-3)
Motion module
(Q172LX, Q172EX, Q173PX)
Q6 B extension base unit
(Q63B, Q65B, Q68B, Q612B)
Power supply module/
I/O module/Intelligent function
module of the Q series
(Note-4)
(Note-5)
SVO ON
Teaching unit
(A31TU-D3 , A31TU-DN )
Servo amplifier
(MR-H-BN)
Servo amplifier
(MR-J2 -B)
Short-circuit connector for
the teaching unit
(A31TUD3TM)
It is possible to select the best according to the system.
(Note-1) : It is possible to use only Q172CPUN-T. It is packed
together with Q172CPUN-T.
(Note-2) : It varies by the connecting teaching unit.
(Note-3) : It is packed together with Q170TUD CBL M.
(Note-4) : When using the A31TU-D3 /A31TU-DN , be sure to use
the Q172CPUN-T.
(Note-5) : A31TU-D3 /A31TU-DN corresponds to only Japanese.
It does not correspond to display for English.
1 - 59

1 OVERVIEW
(3) Peripheral device configuration for the Q173CPU(N)/Q172CPU(N)
The following (a)(b)(c) can be used.
(a) RS-232 configuration
(b) USB configuration
(c) SSCNET configuration
Motion CPU module
(Q173CPU(N), Q172CPU(N))
RS-232 cable
(QC30R2)
Personal computer
Motion CPU module
(Q173CPU(N), Q172CPU(N))
USB cable
Personal computer
(Windows 98/2000/XP only)
R
Motion CPU module
(Q173CPU(N), Q172CPU(N))
SSC I/F communication cable
(Q170CDCBL M,
Q170BDCBL M)
MITSUBISHI
SSCNET
CARD
A30CD-PCF
SSC I/F Card/Board
(A30CD-PCF/A 0BD-PCF)
Personal computer
(Note) : For information about GPP functions of PLC CPU, refer to the operating
manual of PLC. Also, refer to the help of each software for information about
operation of each programming software package.
1 - 60

p
1 OVERVIEW
1.3.2 Q173CPU(N) System overall configuration
Motion CPU control module
e
e
l
l
u
u
d
d
e
o
o
s
l
m
m
u
r
p
o
r
e
e
t
l
c
c
e
a
a
r
a
a
d
f
f
u
e
r
o
r
n
c
n
e
e
a
t
t
n
e
n
n
i
e
i
g
M
QI60
Serial absolute synchronous encoder cable
(MR-JHSCBL M-H/Q170ENCCBL M)
Serial absolute synchronous encoder 2/module
E
(MR-HENC/Q170ENC)
FLS : Upper stroke limit
RLS : Lower stroke limit
STOP : Stop signal
DOG/CHANGE : Proximity dog/
Speed-position switching
SSCNET SYS TEM2
Terminal
connector
CPU base
unit
(Q3 B)
Q61P-A
100/200VAC
Personal Computer
IBM PC/AT
USB/RS-232
Teaching unit
A31TU-D3 /A31TU-DN
Panel Personal Computer
(WinNT/Win98/Win2000/WinXP)
Computer link SSC
(Note-1)
Cable for the teaching
unit
(Q170TUD CBL M(-A))
SSC I/F
Communication
cable
(Q170CDCBL M/
Q170BDCBL M)
SSC I/F Card/Board
(A30CD-PCF/A 0BD-PCF)
PLC CPU/
Motion CPU
Q173
Qn(H)
CPU(N)
CPU
Dividing unit
(Q173DV)
MITSUBISHI
LITHIUM BATTERY
e
l
l
u
a
d
s
n
o
u
r
o
e
m
t
n
x
e
o
e
r
c
s
l
h
a
o
f
a
c
r
v
n
r
n
e
t
g
y
e
i
n
S
s
i
S
Q172EX
Q172LX Q172PX
SSCNET cable
SSCNET SYSTEM1
QX
Q6 AD
QY
Q6 DA
I/O module of the Q Series or
Special function module
Analogue input/output
Input/output (Up to 256 points)
Interrupt signals (16 points)
Manual pulse generator 3/module
P
(MR-HDP01)
External input signals
d8d1
(Up to 1 mo dule)
(Up to 6 modules)
SSCNET SYST EM3
Terminal
connector
d8d1
Number of Inputs
8 axes/module
(Up to 4 modules)
SSCNET SYSTEM4
Terminal
connector
d1
d8
d1
Terminal
connector
d8
Extension
cable
Extension base unit
(Q6 B)
y
l
p
p
u
s
e
r
l
e
u
d
w
o
o
P
m
UP to 7 extensions
M
E
MR-H BN/MR-J2S- B/MR-J2M-B/MR-J2- B/MR-J2-03B5 model
Servo amplifier, Vector inverter(FR-V500), Up to 32 axes
M
M
E
(Note-1) : Be sure to use the Q173CPUN-T.
A31TU-D3 /A31TU-DN corresponds to only Japanese.
It does not corres
M
E
E
M
E
ond to display for English.
1 - 61
M
E
M
M
E
E

1 OVERVIEW
CAUTION
Construct a safety circuit externally of the Motion controller or servo amplifier if the abnormal
operation of the Motion controller or servo amplifier differ from the safety directive operation in
the system.
The ratings and characteristics of the parts (other than Motion controller, servo amplifier and
servomotor) used in a system must be compatible with the Motion controller, servo amplifier
and servomotor.
Set the parameter values to those that are compatible with the Motion controller, servo amplifier,
servomotor and regenerative resistor model and the system application. The protective
functions may not function if the settings are incorrect.
When a teaching unit is used, the cable for the teaching unit is necessary between the Motion
CPU (Q173CPUN-T/Q172CPUN-T) and teaching unit. And, connect the short-circuit connector
for teaching unit, after removing the teaching unit or when not using it.
1 - 62

p
1 OVERVIEW
1.3.3 Q172CPU(N) System overall configuration
Motion CPU control module
e
e
l
l
u
u
d
d
e
o
o
s
l
m
m
u
r
p
o
r
e
e
t
l
c
c
e
a
a
r
a
a
d
f
f
u
e
r
o
r
n
c
n
e
e
a
t
t
n
e
n
n
i
e
i
g
M
QI60
Serial absolute synchronous encoder cable
(MR-JHSCBL M-H/Q170ENCCBL M)
Serial absolute synchronous encoder 2/module
E
(MR-HENC/Q170ENC)
FLS : Upper stroke limit
RLS : Lower stroke limit
STOP : Stop signal
DOG/CHANGE : Proximity dog/
Speed-position switching
d1 d2 d3
CPU base
unit
(Q3 B)
100/200VAC
Battery unit
(Q170BAT)
Personal Computer
IBM PC/AT
USB/RS-232
Teaching unit
A31TU-D3 /A31TU-DN
(Note-1)
Cable for the teaching
unit
(Q170TUD CBL M(-A))
SSC I/F Card/Board
(A30CD-PCF/A 0BD-PCF)
PLC CPU/
Motion CPU
Qn(H)
Q61P-A
CPU
MITSUBISHI
LITHIUM BATTERY
SSC I/F
Communication
cable
(Q170CDCBL M/
Q170BDCBL M)
l
a
n
r
e
t
x
e
o
v
r
e
S
Q172
Q172LX Q172PX
CPU(N)
SSCNET cable
SSCNET SYSTEM1
s
l
a
n
g
i
s
e
l
u
d
s
o
u
o
m
n
e
o
r
c
h
a
f
c
r
n
e
t
y
n
S
i
Q172EX
QX
Q6 AD
QY
Q6 DA
I/O module of the Q Series or
Special function module
Analogue input/output
Input/output (Up to 256 points)
Interrupt signals (16 points)
Manual pulse generator 3/module
P
(MR-HDP01)
External input signals
(Up to 1 mo dule)
(Up to 4 modules)
Number of Inputs
8 axes/module
(Up to 1 module)
Terminal
connector
d8
Panel Personal Computer
(WinNT/Win98/Win2000/WinXP)
Computer link SSC
Extension base unit
(Q6 B)
y
l
p
Extension
cable
p
u
s
e
l
r
e
u
d
w
o
o
m
P
UP to 7 extensions
M
E
M
E
MR-H BN/MR-J2S- B/MR-J2M-B/MR-J2- B/
MR-J2-03B5 model Servo amplifier,
Vector inverter(FR-V5 00), Up to 8 axes
(Note-1) : Be sure to use the Q172CPUN-T.
A31TU-D3 /A31TU-DN corresponds to only Japanese.
It does not corres
M
E
1 - 63
M
E
ond to display for English.

1 OVERVIEW
CAUTION
Construct a safety circuit externally of the Motion controller or servo amplifier if the abnormal
operation of the Motion controller or servo amplifier differ from the safety directive operation in
the system.
The ratings and characteristics of the parts (other than Motion controller, servo amplifier and
servomotor) used in a system must be compatible with the Motion controller, servo amplifier
and servomotor.
Set the parameter values to those that are compatible with the Motion controller, servo amplifier,
servomotor and regenerative resistor model and the system application. The protective
functions may not function if the settings are incorrect.
When a teaching unit is used, the cable for the teaching unit is necessary between the Motion
CPU (Q173CPUN-T/Q172CPUN-T) and teaching unit. And, connect the short-circuit connector
for teaching unit, after removing the teaching unit or when not using it.
1 - 64

1 OVERVIEW
1.3.4 Software packages
(1) Software packages
Part name Model name Details
SW6RNCGSVPROE
MT Developer
SW6RNCGSVSETE
(Note) : Operating environment of the MT Developer is WindowsNTR4.0/WindowsR98/WindowsR2000/WindowsRXP
English version only.
(a) Operating system software packages
Application
For conveyor assembly SV13
(Motion SFC)
For automatic machinery SV22
(Motion SFC)
Q173CPU(N) Q172CPU(N)
SW6RN-SV13QB SW6RN-SV13QD
SW6RN-SV22QA SW6RN-SV22QC
Software package
(b) Integrated start-up support software package
Conveyor assembly software : SW6RN-GSV13P
Automatic machinery software : SW6RN-GSV22P
SW6RNC-GSVE
(Integrated start-up support software
(1 CD-ROM) )
SW6RNC-GSVHELPE (Operation manual (1 CD-ROM) )
A30CD-PCF(SSC I/F card (PCMCIA TYPE II 1CH/card) )
Q170CDCBL3M (A30CD-PCF cable 3m (9.84ft.) )
Machine tool peripheral software : SW6RN-GSV43P
Cam data creation software : SW3RN-CAMP
Digital oscilloscope software : SW6RN-DOSCP
Communication system software : SW6RN-SNETP
Document print software
Installation manual
SW6RNC-GSVPROE
: SW3RN-DOCPRNP,
SW20RN-DOCPRNP
(2) Operating environment of the personal computer
Operating environment is as follows.
IBM PC/AT with which WindowsNTR/WindowsR98/WindowsR2000/WindowsRXP
Item
CPU Pentium133MHz or more Pentium II 233MHz or more Pentium II 450MHz or more
Memory capacity Recommended 32MB or more Recommended 64MB or more Recommended 192MB or more
Hard disk free space Hard disk free space is as following list.
Disk drive 3.5inch (1.44MB) floppy disk drive, CD-ROM disk drive
Display 800×600 pixels, 256 colors or more
English version operates normally.
WindowsNT
(Service Pack 2 or later)
or Windows
R
4.0
(Note)
R
98
WindowsR2000 WindowsRXP
(Note) : Impossible to use USB connection.
1 - 65

Size
1 OVERVIEW
It is necessary the following capacity depending on the installed software.
Model name
SW6RNC-GSVE SW6RNC-GSVHELPE
SW6RN-GSV13P 65MB 40MB
SW6RN-GSV22P 66MB 45MB
SW6RN-GSV43P 55MB 32MB
SW3RN-CAMP 5MB 3MB
SW6RN-DOSCP 35MB 10MB
Standard 60MB
SW6RN-SNETP
Custom (When all selection) 60.5MB
3MB
SW3RN-DOCPRNP 45MB 5MB
SW20RN-DOCPRNP 45MB 5MB
(Note-1) : WindowsNTR, WindowsRare either registered trademarks or trademarks of Microsoft Corporation
in the United States and/or other countries.
(Note-2) : Pentium
United States and other countries.
R
are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the
POINT
(1) When the operation of Windows is not unclear in the operation of this software,
refer to the manual of Windows or guide-book from the other supplier.
(2) The screen might not be correctly displayed depending on the system font size
of WindowsNT
Be sure to use the small size fonts.
R
4.0/WindowsR98/WindowsR2000/WindowsRXP.
(3) Operating system(OS) type/version
(a) Confirmation method in the operating system(OS)
SOFTWARE
PACKAGE
3.5
inch
1)
2)
3)
T
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORPORATION ALL
RIGHTS RESERVED
4)
5)
1) OS software TYPE
2) Software version
3) OS software version
4) Serial number
5) Number of FD
Example) When using the Q173CPU(N), SV13 and version A.
1) SW6RN-SV13QB
2) BCD-B14W276
3) A
(b) Confirmation method in the SW6RN-GSV P
The operating system(OS) type/version of the connected CPU is displayed
(Motion SFC-compatible OS)
on the installation screen of the SW6RN-GSV
SV 1 3 QBVER3
A or B : Q173CPU(N)
C or D : Q172CPU(N)
Indicates Motion SFC compatibility.
1 - 66
P.
00 A
OS version
Indicates teaching unit usable.
U

1 OVERVIEW
(4) Restrictions of the function and PLC CPU by the Motion CPU and
software version
The function and PLC CPU which can be used has restrictions by version of the
Motion CPU module, operating system software and programming software.
Function
ROM operation H C M N Chapter 14
ROM operation (For additional parameter
(Home position return parameter, etc.))
Online change J F Section 12.3
Auto refresh function improvement of the CPU
shared memory
Communications via network H C M
Main operation cycle monitor D
Read the servo parameter from the servo
amplifier.
MULTR D
MULTW D
Motion SFC
instruction
Motion dedicated instruction
(SVST instruction and etc.)
Vector inverter connectable K F
Basic model QCPU (Function version "B")
(Q00CPU, Q01CPU)
Home position return functions added L F
Security function R K
MR-J2S-B Servo parameter "No.41 and later"
setting in the Motion controller
Operation setting for incompletion of home
position return
Bit device setting by Motion SFC instruction
(BMOV, FMOV, MULTW, MULTR, TO, FROM)
Mixed function of virtual mode with real mode
(SV22)
Cam/ball screw switching function (SV22) R K
Clutch for slippage system (linear acceleration/
deceleration system) for mechanical system
program (SV22)
Q170ENC (SV22) R K
(Note-1) : SV13/SV22 is the completely same version.
(Note-2) : Q173CPUN-T/Q172CPUN-T corresponds from the version A.
(Note-3) : Q173CPU(N)/Q172CPU(N) Motion controller (SV13/SV22) Programming Manual (REAL MODE).
(Note-4) : Q173CPU(N)/Q172CPU(N) Motion controller (SV22) Programming Manual (VIRTUAL MODE).
OUT D
TO H C Section 7.13.8
FROM H C
FMOV R K
The combination of each version and a function is shown below.
Q172
CPU
N
N
K
N
(Note-2)
Q172
CPUN
Operating system
software version
(Note-1)
N C T M U M
H C M
D
H
M
R K
R K
S K
R K
R K
Programming
software version
CPU module version
Q173
Q173
CPU
CPUN
J
M
: There is no restriction by the version.
Section of
reference
Section 3.1 (3)
Chapter 16
Chapter 17
Chapter 18
Section 7.13.7
Section 7.13.6
Section 7.9.5
Section 7.13.9
Section 7.13.5
Section 5.3 to 5.6
Chapter 15
Section 6.22.1
(Note-3)
Section
7.13.4 to 7.13.9
Section 10.1
(Note-4)
Section 10.2
(Note-4)
Section 7.2
(Note-4)
1 - 67

1 OVERVIEW
(5) Relevant software packages
(a) PLC software package
Model name Software package
GX Developer SW D5C-GPPW-E
(Note) : =used "6" or later.
1 - 68

1 OVERVIEW
1.3.5 Restrictions on motion systems
(1) It is not allowed to use the Motion CPU as the control CPU of a module installed
on the QA1S6
CPU.
(2) The connector for installation of memory card on the Motion CPU module is for
future function expansion.
(3) Motion CPU module cannot be used as standalone module. It must always be
used in combination with the PLC CPU module (version that supports Multiple
CPU systems). Moreover, it must be installed on the right side of PLC CPU
module. PLC CPU module cannot be installed in a position to the right of Motion
CPU module.
(4) Personal computer CPU unit must be installed on the right side of Motion CPU
module. Motion CPU module cannot be installed in a position to the right of
personal computer CPU unit.
(5) Make sure to use the PLC CPU module in the
(6) Motion CPU module cannot be set as the control CPU of intelligent function
module or Graphic Operation Terminal (GOT).
(7) SSCNET cable which connects the Motion CPU and servo amplifier, and the
teaching unit connecting cable which connects the Motion CPU and A31TU-D3
A31TU-DN
sufficient space for pulling out the cable when designing the control panel.
(8) Motion CPU module is one module element of Q series Multiple CPU system. It
must be set the parameters of Q series Multiple CPU system for each PLC CPU.
Motion CPU module must also be set to support the Multiple CPU system in the
system settings.
(9) Make sure to use the Motion CPU as the control CPU of motion modules
dedicated for Motion CPU (e.g., Q172LX, Q172EX
operate correctly if PLC CPU is set and installed as the control CPU by mistake.
Motion CPU is treated as a 32-point intelligent module by PLC CPU of other CPU.
It cannot be accessed from other CPU.
(10) When a Multiple CPU system is configured, make sure to configure the modules
so that the total current consumption of individual modules on the CPU base
does not exceed the 5 VDC output capacity of power supply module.
(Note-1)
B extension base unit. PLC CPU must be used as the control
"Q mode".
are pulled from the bottom part of unit. Make sure to secure
(Note-2)
, Q173PX). They will not
/
1 - 69

1 OVERVIEW
(11) Motion modules (Q172LX, Q172EX, Q173PX) is to do selection whether to be
necessary referring to the "3. DESIGN" of the "Q173CPU(N)/Q172CPU(N)
User's Manual" for the system design.
(12) Installation position of the Q172EX-S2/S3
(Note-2)
is only CPU base unit.
(Note-1) : Teaching unit can be used in SV13. It cannot be used in SV22.
(Note-2) : Q172EX can be used in SV22. It cannot be used in SV13.
1 - 70

1 OVERVIEW
1.4 Multiple CPU System
1.4.1 Overview
(1) Multiple CPU System
(2) Distributed system configuration
(3) Communication among the CPUs in the Multiple CPU system
Multiple (up to 4 modules) PLC CPUs and Motion CPUs are installed to the CPU
base unit, and each CPU controls the I/O modules and intelligent function
modules of the CPU base unit/extension base unit slot by slot in the Multiple
CPU system.
Each Motion CPU controls the servo amplifiers connected by SSCNET cable.
(a) By distributing such tasks as servo control, machine control and information
control among multiple processors, the flexible system configuration can be
realized.
(b) You can increase the number of control axes by using a multiple Motion
CPUs. It is possible to control up to 96 axes by using three Q173CPU(N)s.
(c) You can reduce the PLC scan time of the overall system by using a multiple
PLC CPUs and distributing the PLC control load among them.
(a) Transmission of data among the CPUs in the Multiple CPU system is
performed automatically using the multiple CPU automatic refresh function.
This makes it possible to use the device data of the other CPUs as the
device data of the self CPU.
(b) You can access the device data and start the Motion SFC program from the
PLC CPU to the Motion CPU by Motion dedicated PLC instruction.
1 - 71

1 OVERVIEW
1.4.2 Installation of PLC CPU and Motion CPU
Up to a total four PLC CPUs and Motion CPUs can be installed in the CPU base unit,
in the four slots starting from the CPU slot (the slot located to the immediate right of the
power supply module) to slot 2 in series.
There must be no non-installation slot left, between a PLC CPU and a Motion CPU, or
between Motion CPUs.
When two or more Motion CPUs are installed, they are installed together in the slots
provided to the right of one or more PLC CPUs. (PLC CPU cannot be installed to the
right of a Motion CPU.)
(1) When the high performance model PLC CPU is used.
Number of
CPUs
Installation positions of PLC CPUs/Motion CPUs
012
CPU
2
I/O, etc.
Power supply
PLC CPU
Motion CPU
012
CPU
I/O, etc.
012
CPU
3
PLC CPU
Power supply
CPU
Power supply
4
CPU
Power supply
PLC CPU
012
PLC CPU
PLC CPU
012
PLC CPU
Motion CPU
I/O, etc.
Motion CPU
PLC CPU
Motion CPU
Motion CPU
Motion CPU
PLC CPU
Power supply
CPU
Power supply
Motion CPU
012
PLC CPU
PLC CPU
I/O, etc.
Motion CPU
Motion CPU
Motion CPU
(2) When the basic model PLC CPU is used.
Multiple CPU system up to 3 modules (PLC CPU 1, Motion CPU 1,
Personal computer CPU
1).
1 - 72

1 OVERVIEW
1.4.3 Precautions for using Q series I/O modules and intelligent function modules
(1) Modules controllable by the Motion CPU
I/O modules (QX , QX -S1, QY , QH , QX Y , Q6 AD , Q6 AD- ,
DA , Q6 DA- ), interrupt module (QI60) and motion modules (Q172LX,
Q6
Q172EX, Q173PX) can be controlled by the Motion CPU.
(2) Compatibility with the Multiple CPU system
(a) All I/O modules (QX , QX -S1, QY , QH , QX Y , Q6 AD ,
Q6
AD- , Q6 DA , Q6 DA- ) support the Multiple CPU system.
(b) The interrupt module (QI60), which is currently not subject to function
upgrade, supports the Multiple CPU system.
(c) The intelligent function modules support the Multiple CPU system only when
their function version is B or later. These modules cannot be controlled by
the Motion CPU, so be sure to use the PLC CPU as a control CPU.
(d) All motion modules (Q172LX, Q172EX, Q173PX) support the Multiple CPU
system. These modules cannot be controlled by the PLC CPU, so be sure to
use the Motion CPU as a control CPU.
(3) Access range from a non-control CPU
(a) The Motion CPU can access only the modules controlled by the self CPU. It
Buffer memory
cannot access the modules controlled by other CPUs.
(b) Access range from a non-control CPU for the modules controlled by the
Motion CPU are shown below.
I/O setting from outside the group
Access target
Not received Received
Input (X)
Output (Y)
Read
Write
(setting from the PLC CPU)
REMARK
• The function version of an intelligent function module can be checked on the rated
plate of the intelligent function module or in the GX Developer's system monitor
product information list.
• Refer to the "Q173CPU(N)/Q172CPU(N) User's Manual" for the model name
which can be controlled by the Motion CPU.
1 - 73

1 OVERVIEW
1.4.4 Modules subject to installation restrictions
(1) Modules subject to installation restrictions in the Motion CPU are sown below.
Description Model name
Servo external signals
interface module
Serial absolute synchronous
interface module
Manual pulse generator
interface module
Input module QX
Output module QY
Input/output composite module
Analogue input module
Analogue output module
Interrupt module QI60 1 module
(Note-1) : SV22 only.
(Note-2) : When the Manual pulse generator and the serial encoder are used at the same time with the SV22, the
Q173PX installed in the slot of the smallest number is used for manual pulse generator input.
(Note-3) : A maximum of 4 modules, analogue input modules and analogue output modules, can be used.
Use within the restrictions listed below.
Maximum installable modules per CPU
Q173CPU(N) Q172CPU(N)
Q172LX 4 modules 1 module
(Note-3)
(Note-3)
Q172EX
(Note-1)
Q173PX
(Note-2)
QX -S1
QH
Y
QX
AD
Q6
Q6 AD-
DA
Q6
DA-
Q6
(When using the incremental
(When using only the Manual
6 modules 4 modules
4 modules
serial encoder.)
pulse generator.)
(Note-1)
1 module
(When using the incremental
(When using only the Manual
Total 256 points
3 modules
serial encoder.)
1 module
pulse generator.)
(2) Modules controlled by a Motion CPU cannot be installed in the extension base
unit QA1S6
B.
Q6
B. Install them in the CPU base unit Q3 B or extension base unit
(3) A total of eight base units including one CPU base unit and seven extension base
units can be used. However, the usable slots (number of modules) are limited to
64 per system including vacant slots. If a module is installed in slot 65 or
subsequent slot, an error (SP. UNIT LAY ERROR) will occur. Make sure all
modules are installed in slots 1 to 64. (Even when the total number of slots
provided by the CPU base unit and extension base units exceeds 65 (such as
when six 12-slot base units are used), an error does not occur as long as the
modules are installed within slots 1 to 64.)
(Note-1)
1 - 74

1 OVERVIEW
1.4.5 Processing time of the Multiple CPU system
(1) Processing of the Multiple CPU system
Each CPU module of the Multiple CPU system accesses to the modules
controlled by self CPU with which the CPU base unit or extension base unit is
installed, and the other CPU through the bus (base unit patterns and extension
cables). However, a multiple CPU module cannot use the bus simultaneously.
When a multiple CPUs have accessed the bus simultaneously, the CPUs which
performed buss access later remain in "waiting state" until the CPU currently
using the bus completes its processing. In a Multiple CPU system, the above
waiting time (duration while a CPU remains in waiting state) causes an I/O delay
or prolonged scan time.
(2) When the waiting time becomes the longest
In the Multiple CPU system, the wait time of self CPU becomes the longest in the
following conditions:
• When is using a total of four PLC CPUs/Motion CPUs are used in the Multiple
CPU system.
• When the extension base units are used.
• When the intelligent function modules handling large volumes of data are
installed in the extension base unit(s).
• When a total of four CPUs are used and the four CPUs have simultaneously
accessed a module installed in an extension base unit.
• When there are many automatic refresh points between a PLC CPU and a
Motion CPU.
(3) When shortening the processing time of the Multiple CPU system
The processing time of the Multiple CPU system can be shortened in the
following methods:
• Install all modules with many access points such as MELSECNET/10(H) and
CC-Link refreshes together in the CPU base unit.
• Control all modules with many access points such as MELSECNET/10(H) and
CC-Link refreshes using only one PLC CPU so that they are not accessed by
two or more CPUs simultaneously.
• Reduce the number of refresh points of MELSECNET/10(H), CC-Link, etc.
• Reduce the number of automatic refresh points of the PLC CPUs/Motion
CPUs.
1 - 75

1 OVERVIEW
1.4.6 How to reset the Multiple CPU system
With the Multiple CPU system, resetting the PLC CPU of CPU No. 1 resets the entire
system.
When the PLC CPU of CPU No. 1 is reset, the CPUs, I/O modules and intelligent
function modules of all CPUs will be reset.
To recover any of the CPUs in the Multiple CPU system that generated a CPU stop
error, reset the PLC CPU of CPU No. 1 or restart the power (i.e., turning the power
ON, OFF and then ON).
(If the PLC CPUs or Motion CPUs of CPU Nos. 2 through 4 generated a CPU stop
error, they can not be recovered by resetting the corresponding CPU.)
01234
Q173
Q173
Qn(H)
CPU
CPU
(N)
CPU
(N)
Q173
CPU
567
(N)
Power supply
CPU
No. 1
CPU
No. 2
CPU
No. 3
CPU
No. 4
These CPUs must not be reset.
If one of them is reset, all CPU
in the Multiple CPU system generate
CPU No. 1 can reset the entire Multiple CPU system.
a MULTI CPU DOWN error.
POINT
(1) In a Multiple CPU system, the PLC CPUs/Motion CPUs of CPU No. 2, 3 or 4
cannot be reset individually.
When a PLC CPU or Motion CPU of CPU No. 2, 3 or 4 is reset while the
Multiple CPU system is operating, the other CPUs generate a MULTI CPU
DOWN error (error code: 7000) and the entire system stops.
Note that depending on the timing at which the PLC CPU or Motion CPU of
CPU No. 2, 3 or 4 is reset, the PLC CPU of a the other CPU may stop due to
an error other than MULTI CPU DOWN.
(2) Resetting CPU No. 2, 3 or 4 generates a MULTI CPU DOWN error regardless
of the operation mode set in the Multiple CPU Settings tab. (Stop/continue all
CPUs upon error in CPU No. 2, 3 or 4.) (Refer to section 1.4.7 for the setting
of operation mode in Multiple CPU Settings.)
1 - 76

1 OVERVIEW
1.4.7 Processing at a CPU DOWN error occurrence by a PLC CPU or Q173CPU(N)/ Q172CPU(N)
In the Multiple CPU system, the system operates differently when CPU No. 1
generated a CPU DOWN error as compared with when CPU No. 2, 3 or 4 did.
(1) When CPU No. 1 generated a CPU DOWN error
(a) When the PLC CPU of CPU No. 1 generated a CPU DOWN error, all PLC
CPU/Q173CPU(N)/Q172CPU(N) of CPU Nos. 2, 3 and 4 generate a MULTI
CPU DOWN error (error code: 7000) and the Multiple CPU system stops.
(Note-1)
(b) Recover the system using the procedure below:
1) Check the cause of the error that occurred in CPU No. 1 using the PC
diagnostic function of GX Developer.
2) Remove the cause of the error.
3) Reset the PLC CPU of CPU No. 1 or restart the power.
Resetting the PLC CPU of CPU No. 1 or restarting the power resets all
CPUs in the Multiple CPU system and the system is recovered.
(2) When CPU No. 2, 3 or 4 generated a CPU DOWN error
If the PLC CPU, Q173CPU(N) or Q172CPU(N) of CPU No. 2, 3 or 4 generated a
CPU DOWN error, the entire system may or may not stop depending on the
setting of "Operation Mode" in the Multiple CPU Settings tab.
By default value, all CPUs will stop when any of the CPUs generates a CPU stop
error. If you do not wish to stop all CPUs following an error generated in the PLC
CPU, Q173CPU(N) or Q172CPU(N) of a specific CPU or CPUs, click and
uncheck the CPU or CPUs that will not stop all CPUs upon generating an error.
(See arrow A.)
A
1 - 77

1 OVERVIEW
(a) When a CPU DOWN error occurs in the CPU of the CPU in a checked "Stop
all CPUs upon error in CPU No. n" item, all PLC CPU/Q173CPU(N)/
Q172CPU(N) of the other CPUs will generate a MULTI CPU DOWN error
(error code: 7000) and the Multiple CPU system will stop.
(b) When a CPU DOWN error occurs in the CPU of the PLC in an unchecked
"Stop all CPUs upon error in CPU No. n" item, all CPUs of the other CPUs
will generate a MULTI CPU ERROR (error code: 7020) and continue their
operation.
POINT
(Note-1) : When a CPU DOWN error occurs, the CPU detecting the error will generate a
MULTI CPU DOWN error.
Therefore, the system may enter a MULTI CPU DOWN mode after detecting the
CPU DOWN error in the CPU generating a MULTI CPU DOWN error, instead of
the error in the CPU that generated the CPU DOWN error in the first place. In
this case, the common error-data area may store a CPU number different from
one corresponding to the CPU that generated the CPU DOWN error first.
When recovering the system, remove the cause of the error present in the CPU
not stopped by a MULTI CPU DOWN error.
In the screen below, the cause of the error present in CPU No. 2, which does
not have a MULTI CPU DOWN error, should be removed.
(Note-1)
1 - 78

1 OVERVIEW
(c) Use the following procedure to recover the system:
1) Check the CPU generating the error and cause of the error using the PC
diagnostic function of GX Developer.
2) If the error occurred in a Q173CPU(N)/Q172CPU(N) and the error code
is 10000, check the cause of the error using error list of SW6RNGSV
3) Remove the cause of the error.
4) Reset the PLC CPU of CPU No. 1 or restart the power.
P.
5) Resetting the PLC CPU of CPU No. 1 or restarting the power resets all
CPUs in the Multiple CPU system and the system will be recovered.
(3) Operation at a Motion CPU error
Category Type of error Operation Remark
System setting error
WDT error Varies depending on the error.
Operation
disable errors
Operation
continuous
enable errors
Self-diagnosis error Stops at a CPU DOWN error.
Other CPU DOWN error
Self-diagnosis error
Motion SFC error
Minor error
Major error
Servo error
Servo program setting
error
Operations at a Motion CPU error are shown below.
Does not operate from the
beginning (does not run).
Operation corresponding to
STOP (M2000 OFF). Depends
on the "Operation mode upon
CPU stop error" setting.
Operation continues when the
continuous error occurred.
Processing stops for each
program or axis instead of the
Motion CPU stopping all the
processing.
• All actual output PY points turn OFF.
No effect on other CPUs.
• All actual output PY points turn OFF.
Other CPUs may also stop depending on
the parameter setting.
• All actual output PY points turn OFF.
• Only the applicable program stops (the
program may continue depending on the
type of error).
• Actual output PY retains output.
• No effect on other CPUs.
1 - 79
 Loading...
Loading...