Mitsubishi PUHY-250YMF-B, PUY-200YMF-B, PUHY-P200YMF-B, PUHY-P250YMF-B, PUY-250YMF-B Service Handbook
...
AIR CONDITIONERS CITY MULTI
Models PUHY-200YMF-B, 250YMF-B
PUHY-P200YMF-B, P250YMF-B
PUY-200YMF-B, 250YMF-B
PURY-200YMF-B, 250YMF-B
PURY-P200YMF-B, P250YMF-B
CMB-P104, P105, P106, P108, P1010V-D
CMB-P104, P105, P106, P108, P1010, P1013, P1016V-E
Service Handbook
Service Handbook PUHY, PUY, PURY-200·250YMF-B/PUHY, PURY-P200·P250YMF-B/CMB-P-V-D, CMB-P-V-E


–1–
11
11
1 PRECAUTIONS FOR DEVICES THAT USE R407C REFRIGERANT
Caution
Do not use the existing refrigerant piping.
• The old refrigerant and refrigerator oil in the existing
piping contains a large amount of chlorine which may
cause the refrigerator oil of the new unit to deteriorate.
Use refrigerant piping made of C1220 (CU-DHP) phosphorus deoxidized copper as specified in the *JIS
H3300 “Copper and copper alloy seamless pipes and
tubes”. In addition, be sure that the inner and outer
surfaces of the pipes are clean and free of hazardous
sulphur, oxides, dust/dirt, shaving particles, oils,
moisture, or any other contaminant.
• Contaminants on the inside of the refrigerant piping
may cause the refrigerant residual oil to deteriorate.
*JIS: Japanese Industrial Standard
Store the piping to be used during installation indoors
and keep both ends of the piping sealed until just
before brazing. (Store elbows and other joints in a
plastic bag.)
• If dust, dirt, or water enters the refrigerant cycle,
deterioration of the oil and compressor trouble may
result.
Use ester oil, ether oil or alkylbenzene (small
amount) as the refrigerator oil to coat flares and
flange connections.
• The refrigerator oil will degrade if it is mixed with a
large amount of mineral oil.
Use liquid refrigerant to seal the system.
• If gas refrigerant is used to seal the system, the composition of the refrigerant in the cylinder will change
and performance may drop.
Do not use a refrigerant other than R407C.
• If another refrigerant (R22, etc.) is used, the chlorine
in the refrigerant may cause the refrigerator oil to deteriorate.
Use a vacuum pump with a reverse flow check valve.
• The vacuum pump oil may flow back into the refrigerant cycle and cause the refrigerator oil to deteriorate.
Do not use the following tools that have been used
with conventional refrigerants.
(Gauge manifold, charge hose, gas leak detector, reverse flow check valve, refrigerant charge base,
vacuum gauge, refrigerant recovery equipment)
• If the conventional refrigerant and refrigerator oil are
mixed in the R407C, the refrigerant may deteriorated.
• If water is mixed in the R407C, the refrigerator oil
may deteriorate.
• Since R407C does not contain any chlorine, gas
leak detectors for conventional refrigerants will not
react to it.
Do not use a charging cylinder.
• Using a charging cylinder may cause the refrigerant
to deteriorate.
Be especially careful when managing the tools.
• If dust, dirt, or water gets in the refrigerant cycle, the
refrigerant may deteriorate.
If the refrigerant leaks, recover the refrigerant in the
refrigerant cycle, then recharge the cycle with the
specified amount of the liquid refrigerant indicated
on the air conditioner.
• Since R407C is a nonazeotropic refrigerant, if additionally charged when the refrigerant leaked, the composition of the refrigerant in the refrigerant cycle will
change and result in a drop in performance or abnormal stopping.
–2–
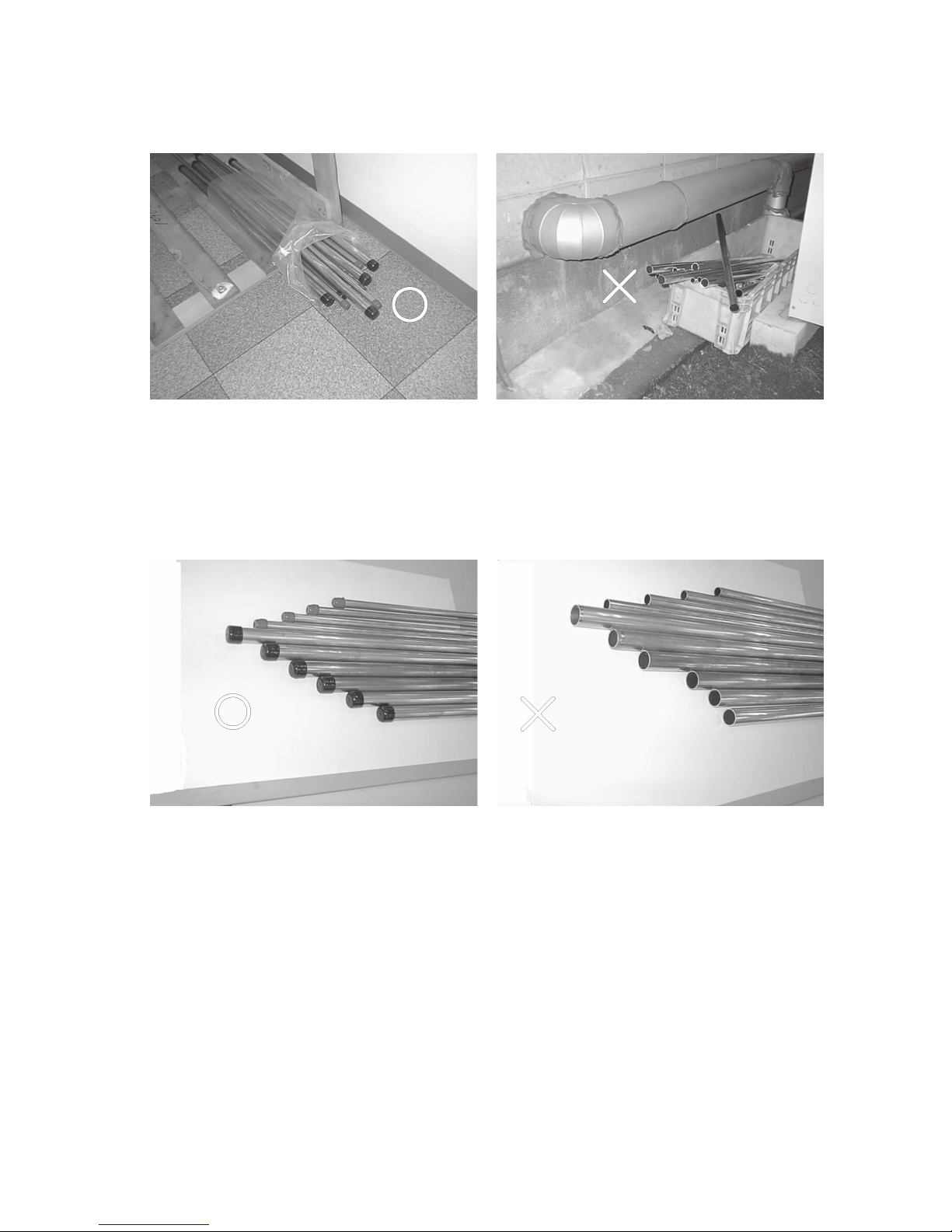
[1] Storage of Piping Material
(1) Storage location
Store the pipes to be used indoors. (Warehouse at site or owner’s warehouse)
Storing them outdoors may cause dirt, waste, or water to infiltrate.
(2) Pipe sealing before storage
Both ends of the pipes should be sealed until immediately before brazing.
Wrap elbows and T’s in plastic bags for storage.
* The new refrigerator oil is 10 times more hygroscopic than the conventional refrigerator oil (such as Suniso). Water
infiltration in the refrigerant circuit may deteriorate the oil or cause a compressor failure. Piping materials must be
stored with more care than with the conventional refrigerant pipes.

–3–
[2] Piping Machining
Use ester oil, ether oil or alkylbenzene (small amount) as the refrigerator oil to coat flares and flange connections.
Use only the necessary minimum quantity of oil !
Reason :
1. The refrigerator oil used for the equipment is highly hygroscopic and may introduce water inside.
Notes :
• Introducing a great quantity of mineral oil into the refrigerant circuit may also cause a compressor failure.
• Do not use oils other than ester oil, ether oil or alkylbenzene.

–4–
[3] Necessary Apparatus and Materials and Notes on Their Handling
The following tools should be marked as dedicated tools for R407C.
<<Comparison of apparatus and materials used for R407C and for R22>>
Apparatus Used Use R22 R407C
Gauge manifold Evacuating, refrigerant filling Current product
Charging hose Operation check Current product
Charging cylinder Refrigerant charging Current product Do not use.
Gas leakage detector Gas leakage check Current product Shared with R134a
Refrigerant collector Refrigerant collection R22 For R407C use only
Refrigerant cylinder Refrigerant filling R22
Vacuum pump Vacuum drying Current product
Vacuum pump with a check valve Current product
Flare tool Flaring of pipes Current product
Bender Bending of pipes Current product
Application oil Applied to flared parts Current product
Torque wrench Tightening of flare nuts Current product
Pipe cutter Cutting of pipes Current product
Welder and nitrogen cylinder Welding of pipes Current product
Refrigerant charging meter Refrigerant charging Current product
Vacuum gauge Checking the vacuum degree Current product
Symbols :
To be used for R407C only. Can also be used for conventional refrigerants.
Tools for R407C must be handled with more care than those for conventional refrigerants. They must not come into contact
with any water or dirt.
Identification of dedicated use for R407C
: Record refrigerant
name and put brown
belt on upper part of
cylinder.
Can be used by
attaching an adapter
with a check valve.
Ester oil or Ether oil or
Alkybenzene (Small
amount)
–5–
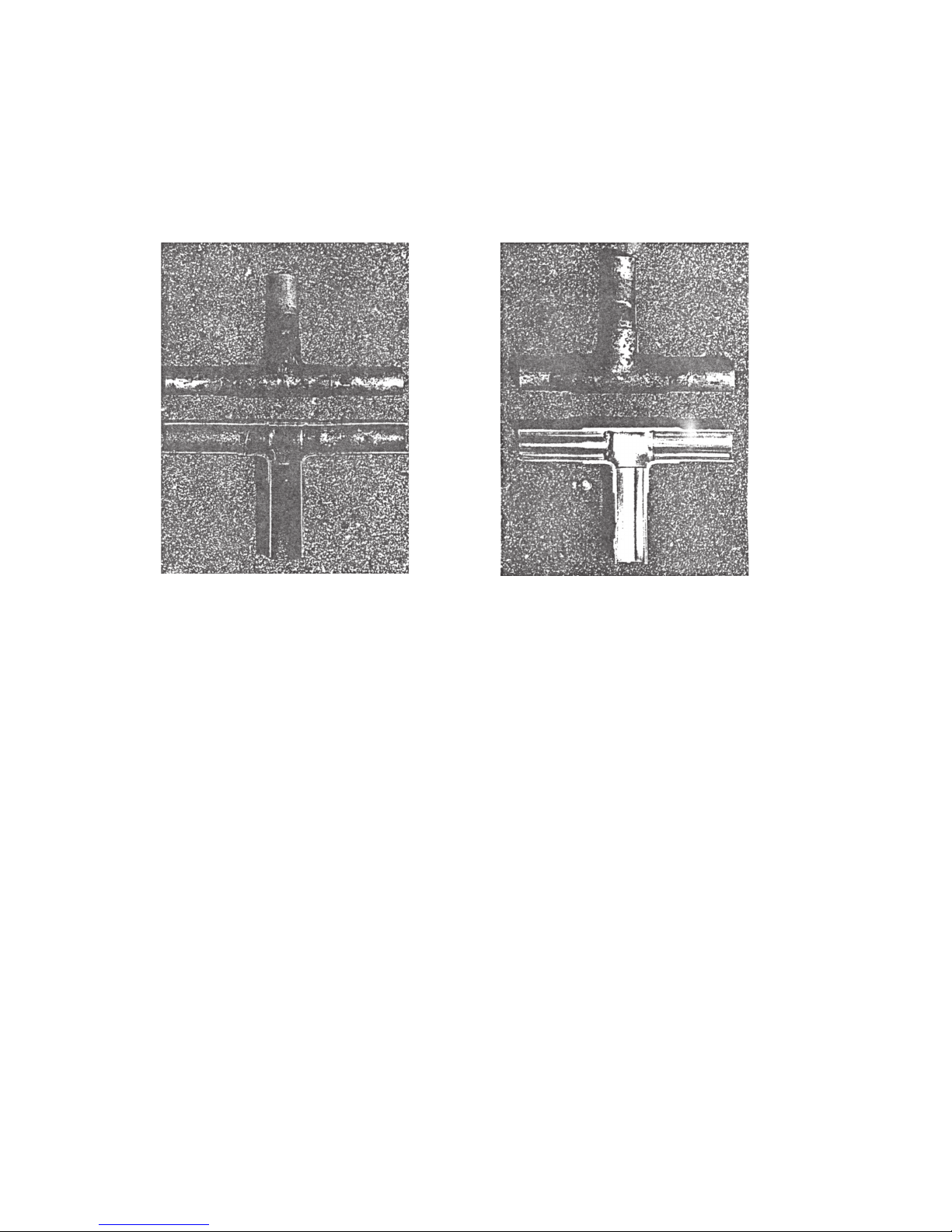
[4] Brazing
No changes from the conventional method, but special care is required so that foreign matter (ie. oxide scale, water, dirt,
etc.) does not enter the refrigerant circuit.
Example : Inner state of brazed section
When non-oxide brazing was not used When non-oxide brazing was used
Items to be strictly observed :
1. Do not conduct refrigerant piping work outdoors on a rainy day.
2. Apply non-oxide brazing.
3. Use a brazing material (Bcup-3) which requires no flux when brazing between copper pipes or between a copper pipe
and copper coupling.
4. If installed refrigerant pipes are not immediately connected to the equipment, then braze and seal both ends of them.
Reasons :
1. The new refrigerant oil is 10 times more hygroscopic than the conventional oil. The probability of a machine failure if
water infiltrates is higher than with conventional refrigerant oil.
2. A flux generally contains chlorine. A residual flux in the refrigerant circuit may generate sludge.
Note :
• Commercially available antioxidants may have adverse effects on the equipment due to its residue, etc. When
applying non-oxide brazing, use nitrogen.
–6–
[5] Airtightness Test
No changes from the conventional method. Note that a refrigerant leakage detector for R22 cannot detect R407C
leakage.
Halide torch R22 leakage detector
Items to be strictly observed :
1. Pressurize the equipment with nitrogen up to the design pressure and then judge the equipment’s airtightness, taking
temperature variations into account.
2. When investigating leakage locations using a refrigerant, be sure to use R407C.
3. Ensure that R407C is in a liquid state when charging.
Reasons :
1. Use of oxygen as the pressurized gas may cause an explosion.
2. Charging with R407C gas will lead the composition of the remaining refrigerant in the cylinder to change and this
refrigerant can then not be used.
Note :
• A leakage detector for R407C is sold commercially and it should be purchased.
[6] Vacuuming
1. Vacuum pump with check valve
A vacuum pump with a check valve is required to prevent the vacuum pump oil from flowing back into the refrigerant
circuit when the vacuum pump power is turned off (power failure).
It is also possible to attach a check valve to the actual vacuum pump afterwards.
2. Standard degree of vacuum for the vacuum pump
Use a pump which reaches 0.5 Torr (500 MICRON) or below after 5 minutes of operation.
In addition, be sure to use a vacuum pump that has been properly maintained and oiled using the specified oil. If the
vacuum pump is not properly maintained, the degree of vacuum may be too low.
3. Required accuracy of the vacuum gauge
Use a vacuum gauge that can measure up to 5 Torr. Do not use a general gauge manifold since it cannot measure a
vacuum of 5 Torr.
4. Evacuating time
• Evacuate the equipment for 1 hour after –755 mmHg (5 Torr) has been reached.
• After envacuating, leave the equipment for 1 hour and make sure the that vacuum is not lost.
5. Operating procedure when the vacuum pump is stopped
In order to prevent a backflow of the vacuum pump oil, open the relief valve on the vacuum pump side or loosen the
charge hose to drawn in air before stopping operation.
The same operating procedure should be used when using a vacuum pump with a check valve.
–7–
[7] Charging of Refrigerant
R407C must be in a liquid state when charging, because it is a non-azeotropic refrigerant.
For a cylinder with a syphon attached For a cylinder without a syphon attached
Cylinder color identification R407C-Gray Charged with liquid refrigerant
R410A-Pink
Reasons :
1. R407C is a mixture of 3 refrigerants, each with a different evaporation temperature. Therefore, if the equipment is
charged with R407C gas, then the refrigerant whose evaporation temperature is closest to the outside temperature is
charged first while the rest of refrigerants remain in the cylinder.
Note :
• In the case of a cylinder with a syphon, liquid R407C is charged without turning the cylinder up side down. Check the
type of cylinder before charging.
[8] Dryer
1. Replace the dryer when the refrigerant circuit is opened (Ex. Change the compressor, full gas leakage). Be sure to
replace the dryer with a CITY MULTI Series Y (For use with R407C).
If any other product is used, the unit will be damaged.
2. Opening the refrigerant circuit after changing to a new dryer is less than 1 hour. The replacement of the dryer should
be the last operation performed.
Cylin-
der
Cylin-
der
Val ve
Val ve
Liquid
Liquid
–8–
22
22
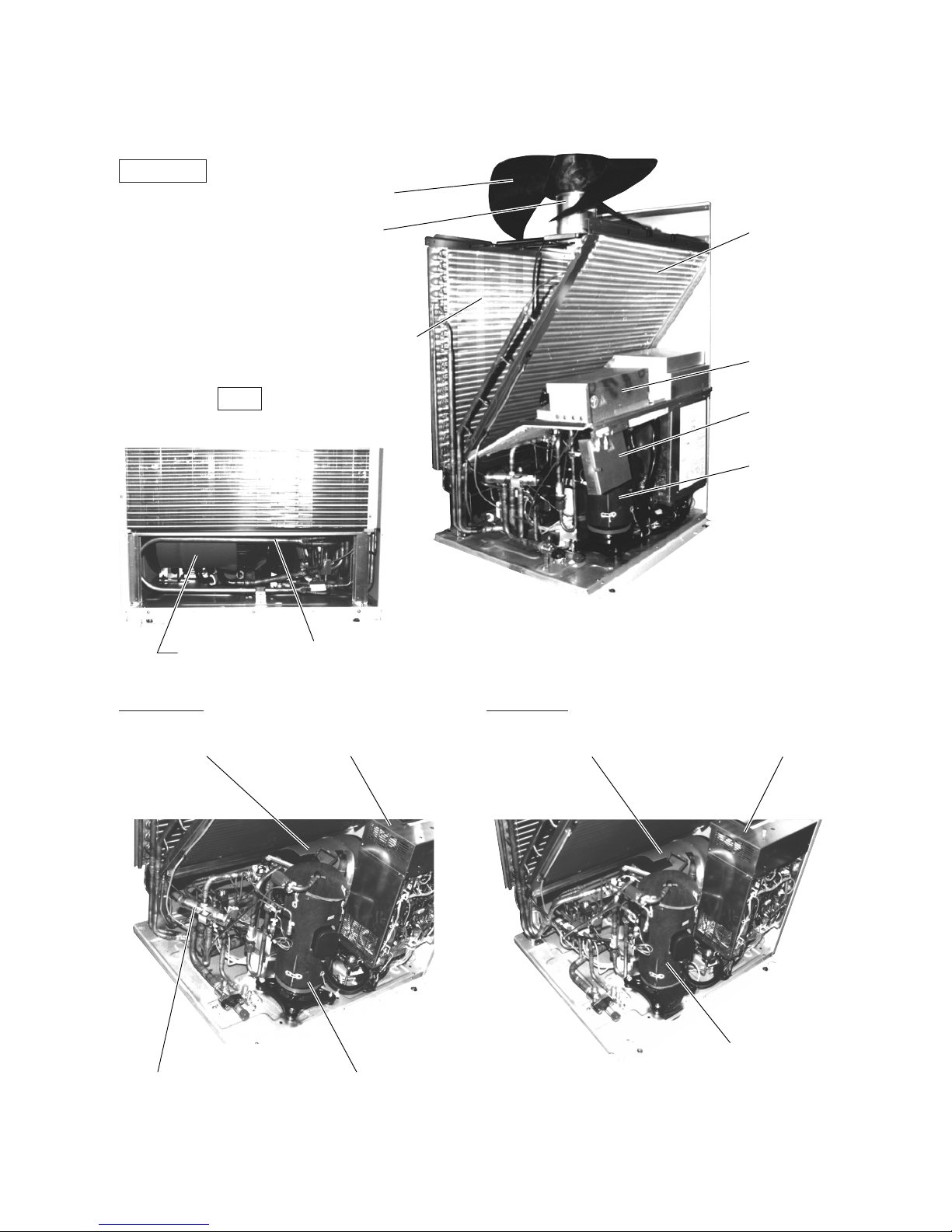
2 COMPONENT OF EQUIPMENT
[1] Appearance of Components
Outdoor unit
• PU(H)Y-200, 250YMF-B
Rear
PUHY-YMF-B PUY-YMF-B
Propeller fan
Fan motor
Heat exchanger
(front)
Noise
filter
Heat exchanger
(rear)
Terminal
Box
Compressor
Accumulator
SCC
Accumulator Control Box Accumulator Control Box
4-way valve Compressor
Compressor
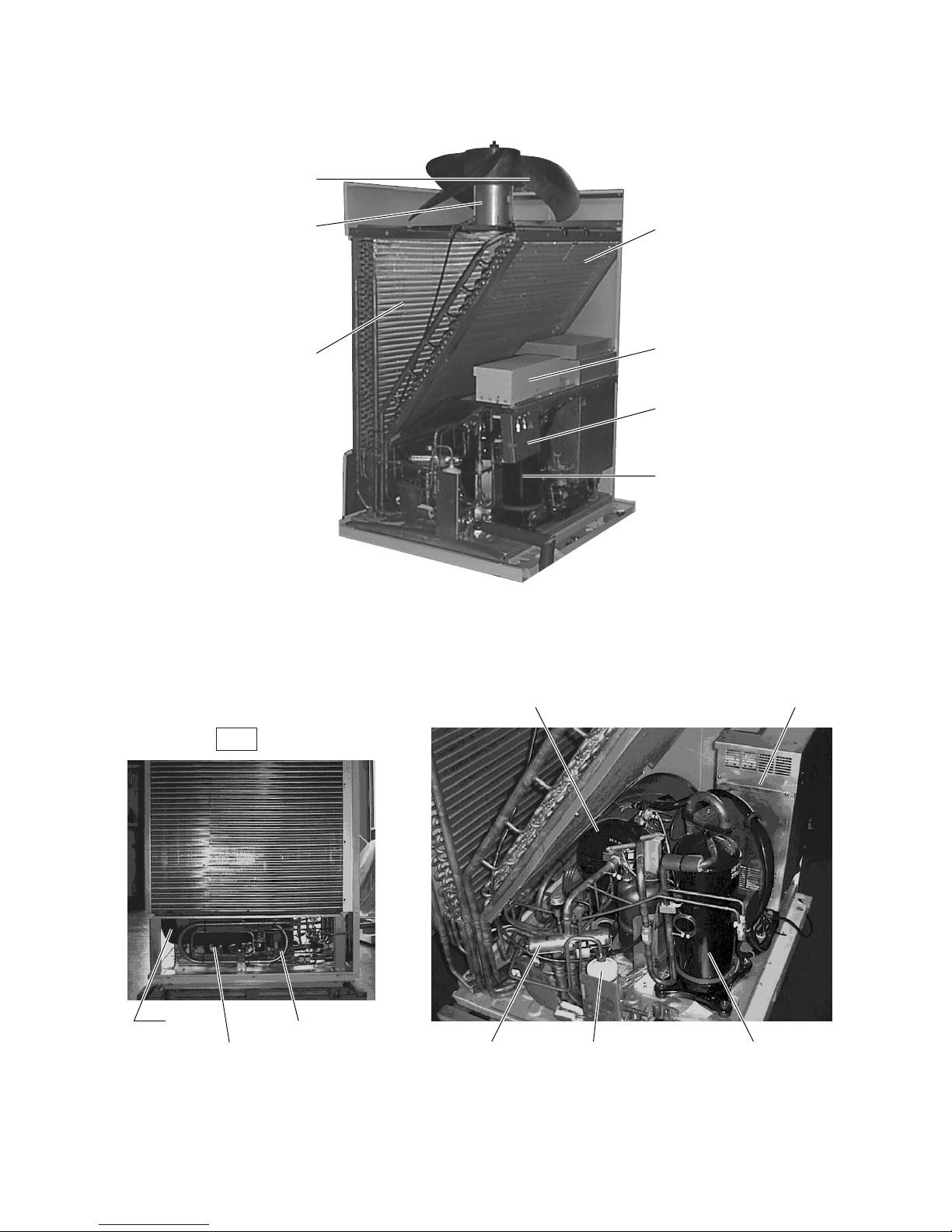
–9–
• PUHY-P200·250YMF-B
Propeller fan
Fan motor
Heat exchanger (front)
Heat exchanger (rear)
Noise filter
Terminal Box
Compressor
Drier
Accumulator Control Box
4-way valve Compressor
SCC
Accumulator
Rear
Heat exchanger
of CS circuit
–10–
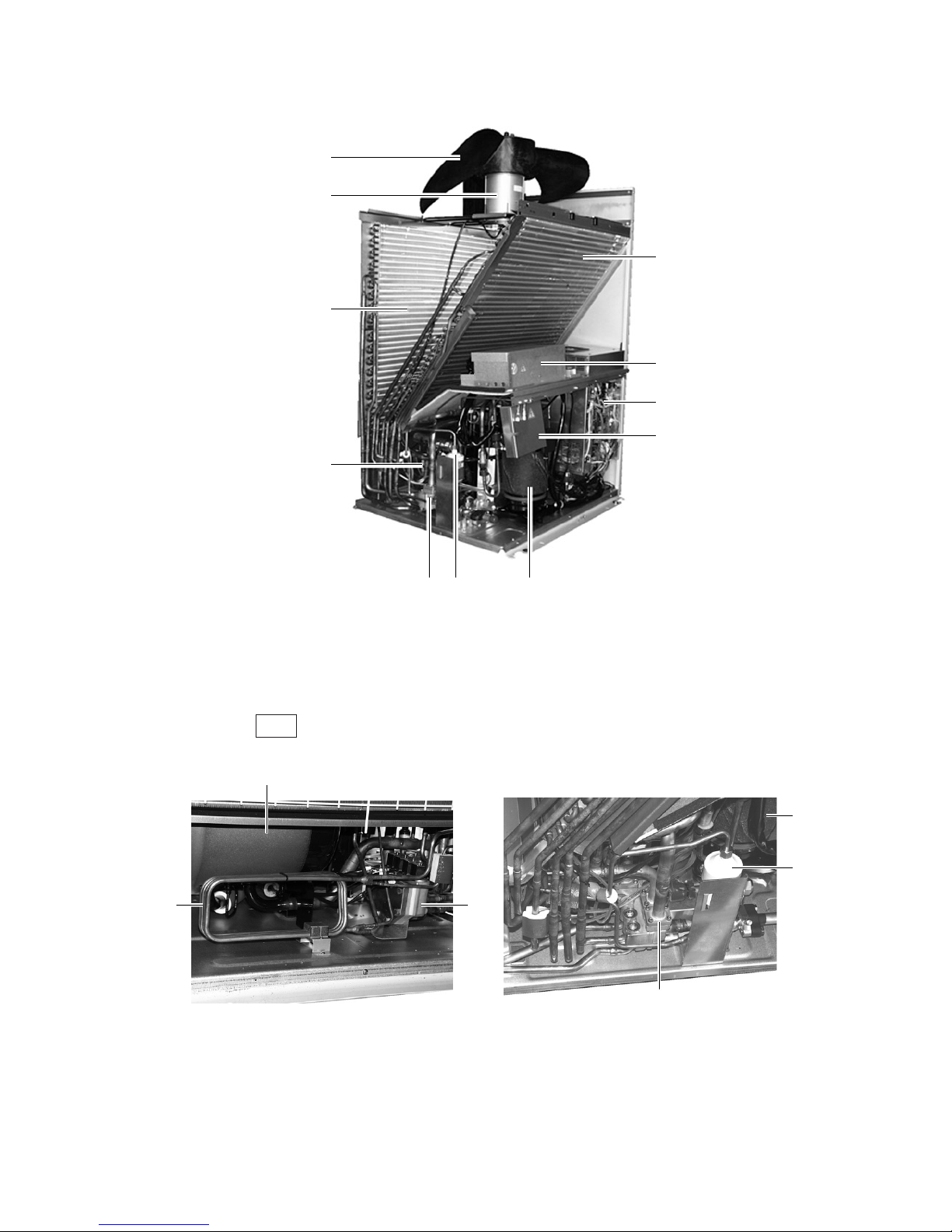
• PURY-P200·250YMF-B
Propeller fan
Solenoid Valves
(SV) Block
Fan motor
Heat exchanger
(rear)
Accumulator
Compressor
Terminal Box
Check Valves
(CV) Block
Drier
CV block
Rear
SV
block
Heat
exchanger
of CS circuit
Compressor
Drier
Heat exchanger
(front)
Noise filter
Control Box
–11–
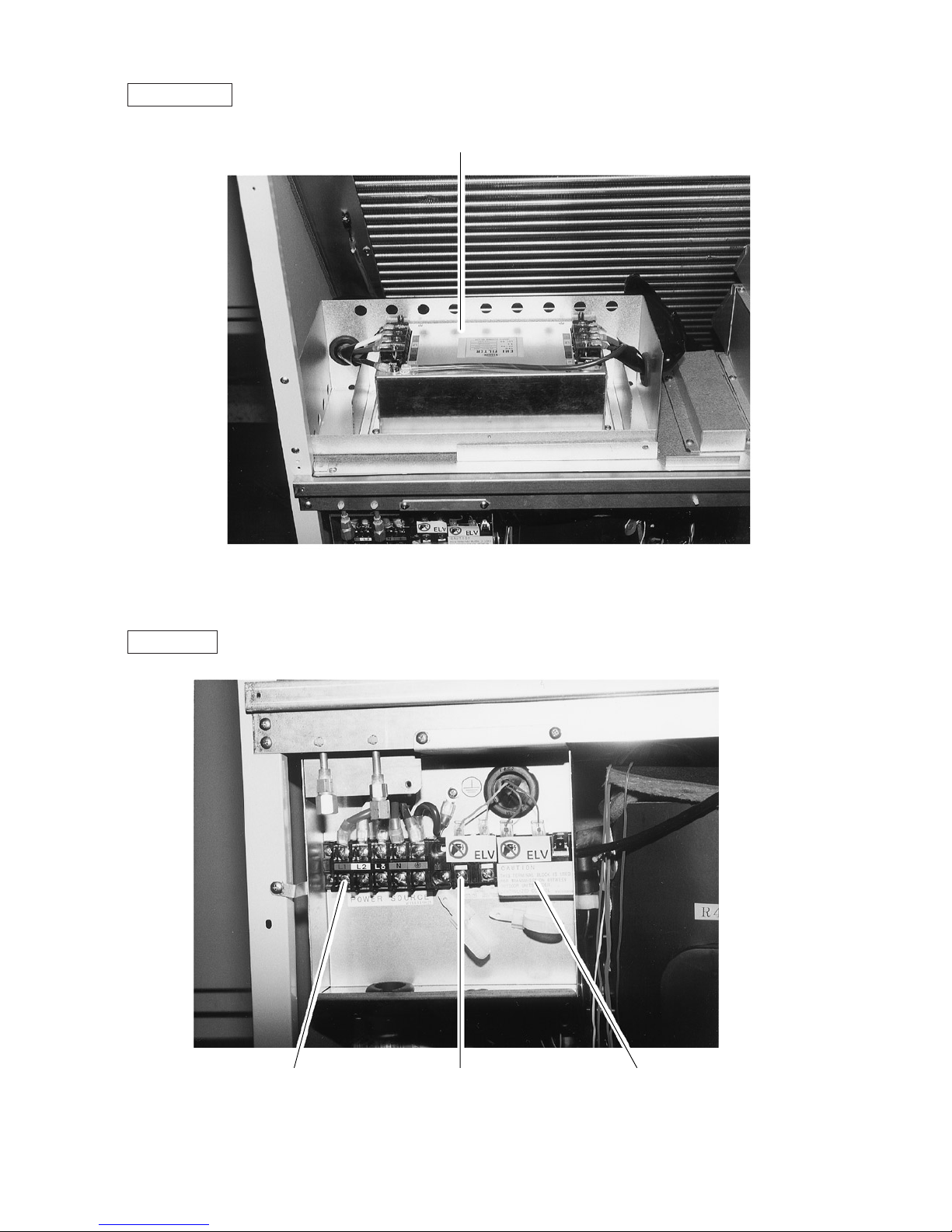
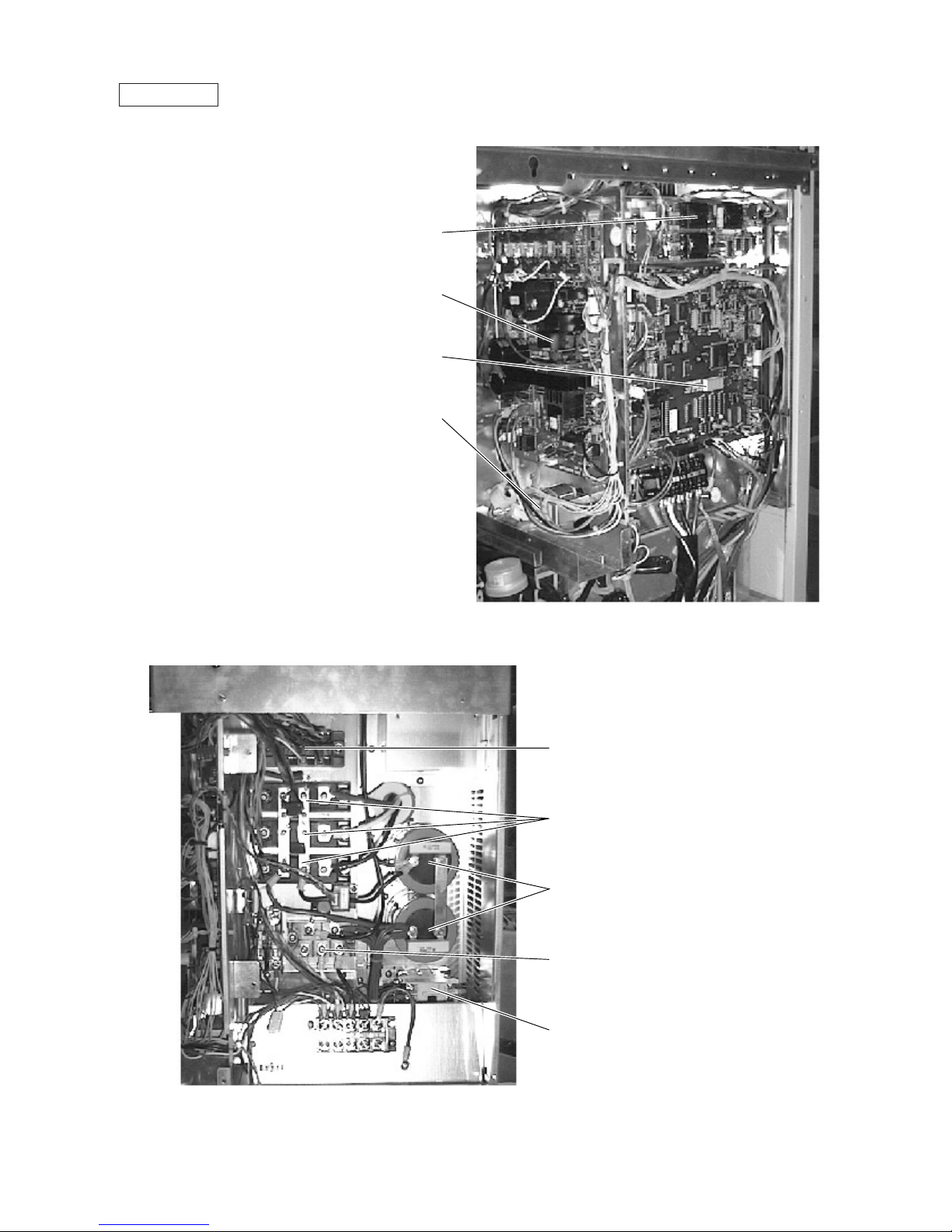
Noise Filter Box
Terminal Box
Noise filter
Terminal block TB3
Transmission
Terminal block TB1
Power source
Terminal block TB7
Transmission (Centralized control)
–12–
Controller Box
FANCON board
Choke coil (L2)
INV board
MAIN board
Thyristor module (SCRM)
Diode stack (DS)
Transistor module (TRM)
Capacitor (C2, C3)
(Smoothing capacitor)
Magnetic contactor (52C)
–13–
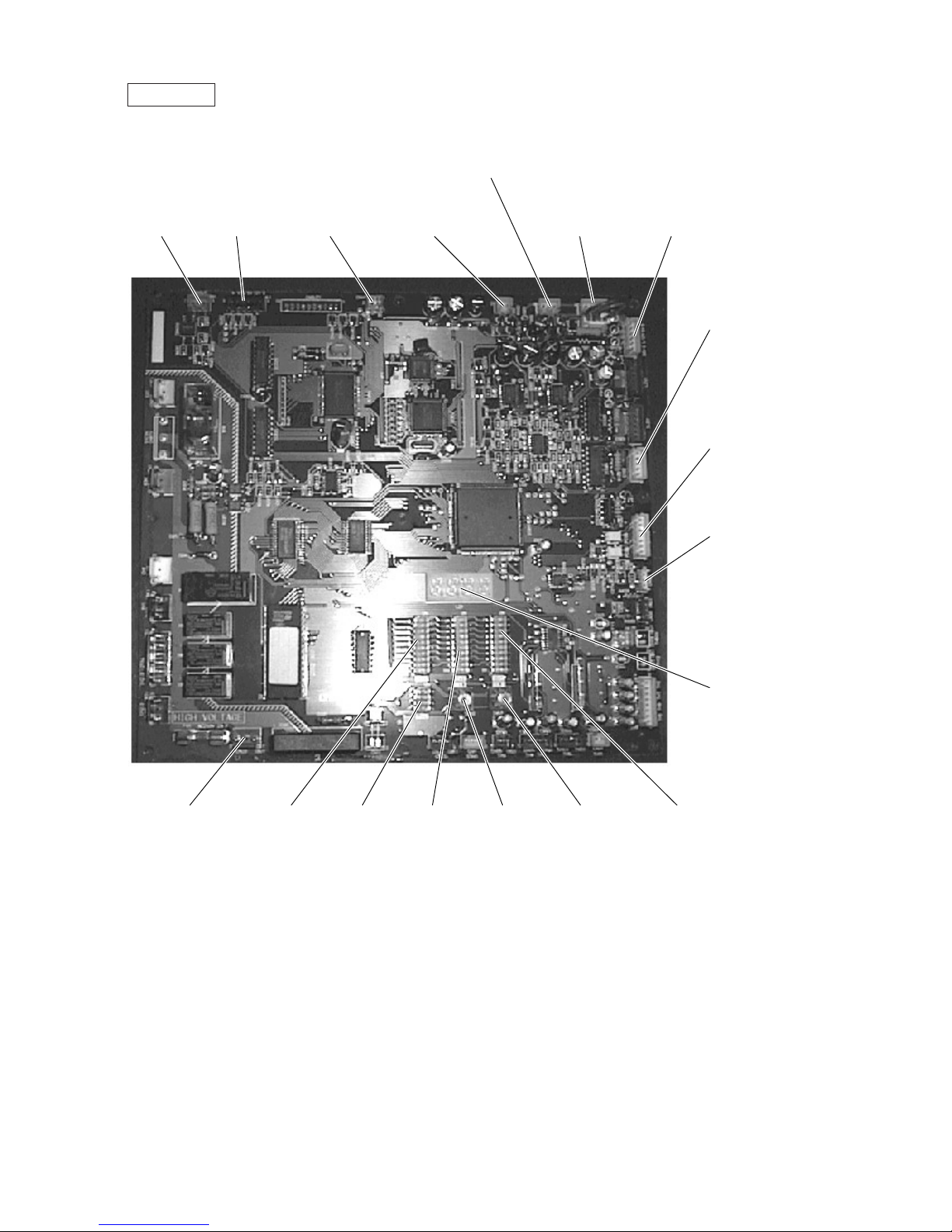
MAIN board
• PUHY
CN51
Indication distance
3-4 Compressor
ON/OFF
3-5 Trouble
LD1
Service LED
CNRS3
Serial transmission to
INV board
CN3D
Cooling/Heating auto
changeover
SW1
CNTR CNFC1
CNVCC4
Power source for
control
CNVCC3
Power source for
control
1-2 30V, 1-3 30V
4-6 12V, 5-6 5V
CNS1
M-NET transmision
CNS2
M-NET transmission
(Centralized control)
CN40
M-NET transmission
power supply
CN20
Power supply
3 L1
1 N
SW3 SW4 SW2 SWU2 SWU1

–14–
MAIN board
• PURY
CN51
Indication distance
3-4 Compressor
ON/OFF
3-5 Trouble
LD1
Service LED
CNRS3
Serial transmission to
INV board
CNTR CNFC1
CNVCC4
Power source for
control
CNVCC3
Power source for
control
1-2 30V, 1-3 30V
4-6 12V, 5-6 5V
CNS2
M-NET transmission
(Centralized control)
CNS1
M-NET
transmission
CN20
Power supply
3 L1
1 N
SW3 SW4 SW2
CN40
M-NET transmission
power supply
SWU2 SWU1 SW1
–15–
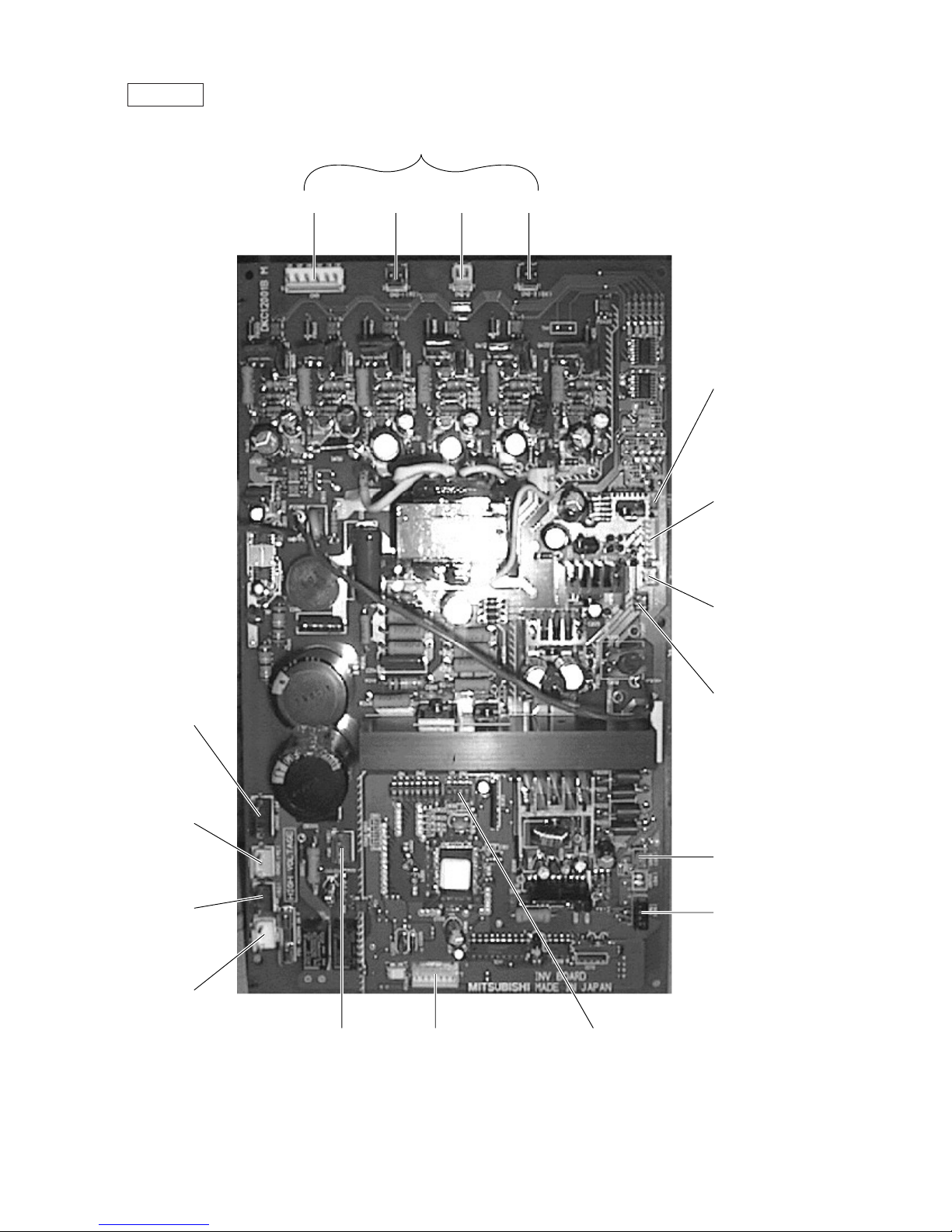
INV board
CN3 CN2-1 CN2-2 CN2-3
Output to transistor module (INVERTER)
CNL2
Choke coil
CNTH
CN30V
CNVCC1
Power supply
1-2 30V, 1-3 30V
4-6 12V, 5-6 5V
CNVCC2
Power supply (5V)
CNCT
CNVDC
1-4
DC-560V
CNAC2
Powe r
source
1 L2
3 N
CN52C
Control for
52C
CNFAN
Control
for MF1
CNR CNRS2
Serial transmission
to MAIN board
SW1
–16–
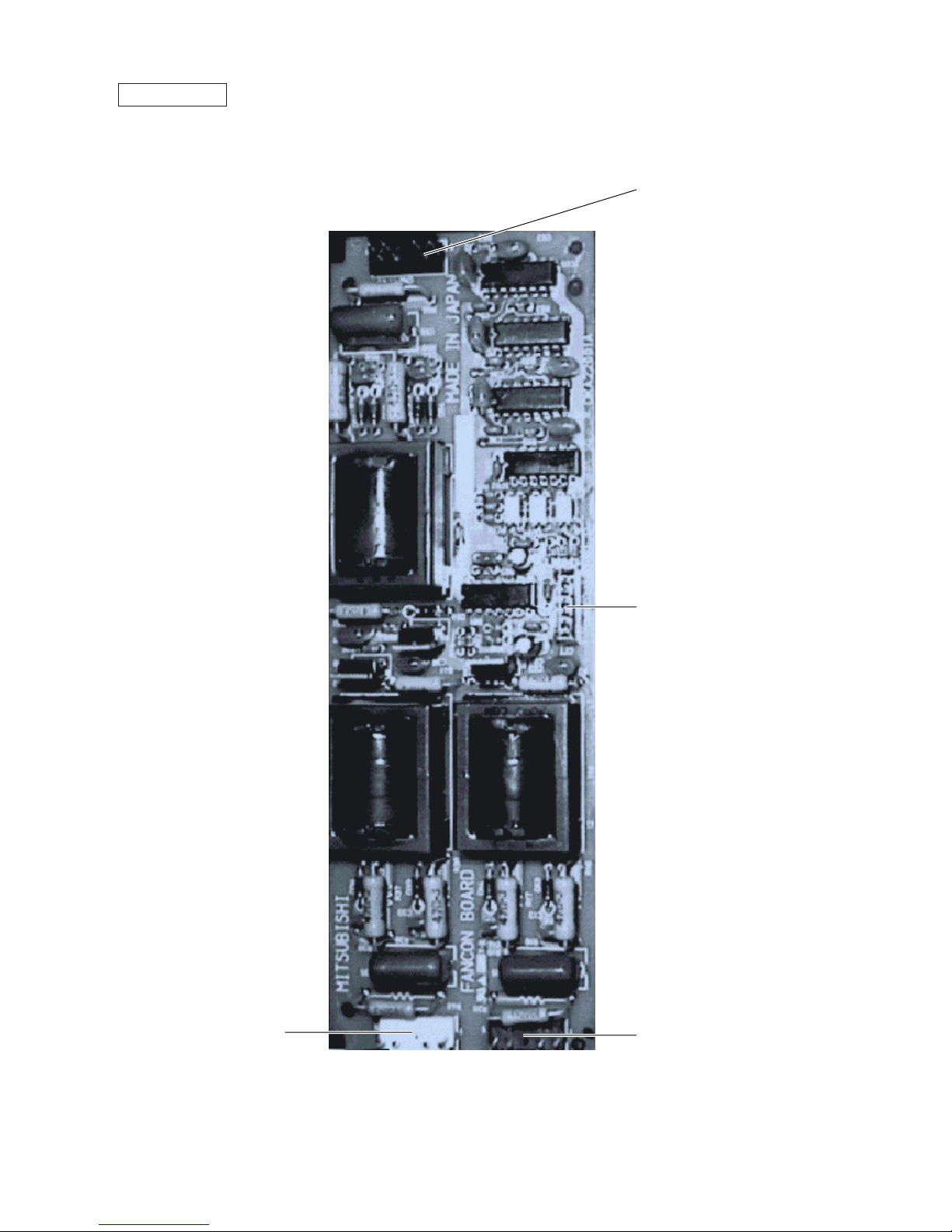
FANCON board
CNFC2
CNU
CNW
CNV
–17–
BC controller
CNTR
CN02
M-NET
transmission
CN03
CN12
Power
supply
1 EARTH
3 N
5 L
SW4 SW2 SW1
–18–
TH1
TH6
TH7
TH8
TH5
TH3
TH4
TH2
Indoor units
CJ1
O/S
63HS
CJ1
Comp
HEX2
HEX1
SCC
LEV1
ST7
BV2
ST2
BV1
ST1
CJ2
CV1
ST6
SV1
CP1
SV2ST5
CP2
CP4
ST3
ST4
SLEV
SA
MA
CP3
63H
6-2
27
8
40 6
CH
93 80
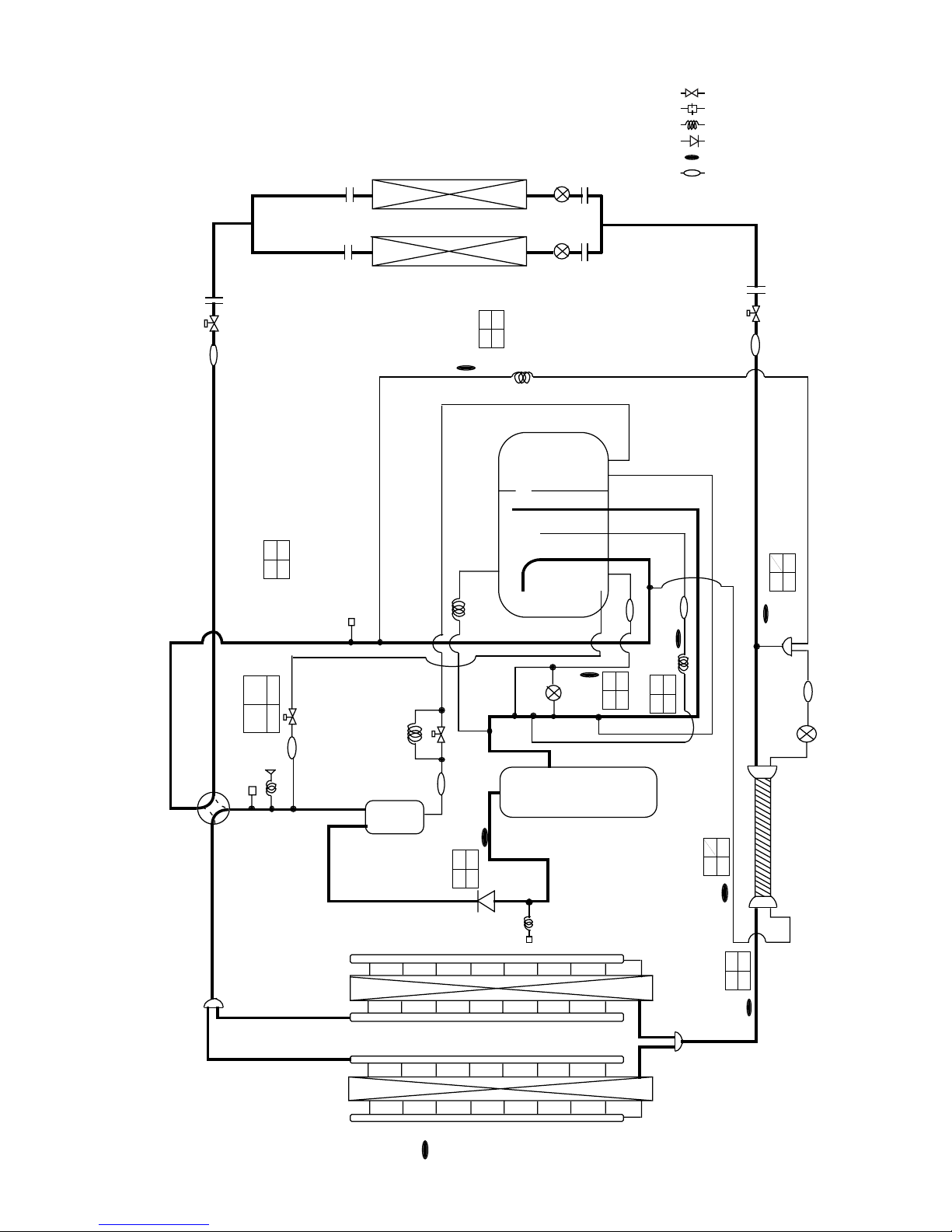
*Operation data of PUHY-200YMF-B
Standard operation data are shown for cooling
in the C column and heating in the H column.
Units for each value are : ˚C for TH1
˜
TH8
: kg/cm
2
G (MPa) for HPS
*
6-1
30 36
20.3
(1.99)
17.5
(1.72)
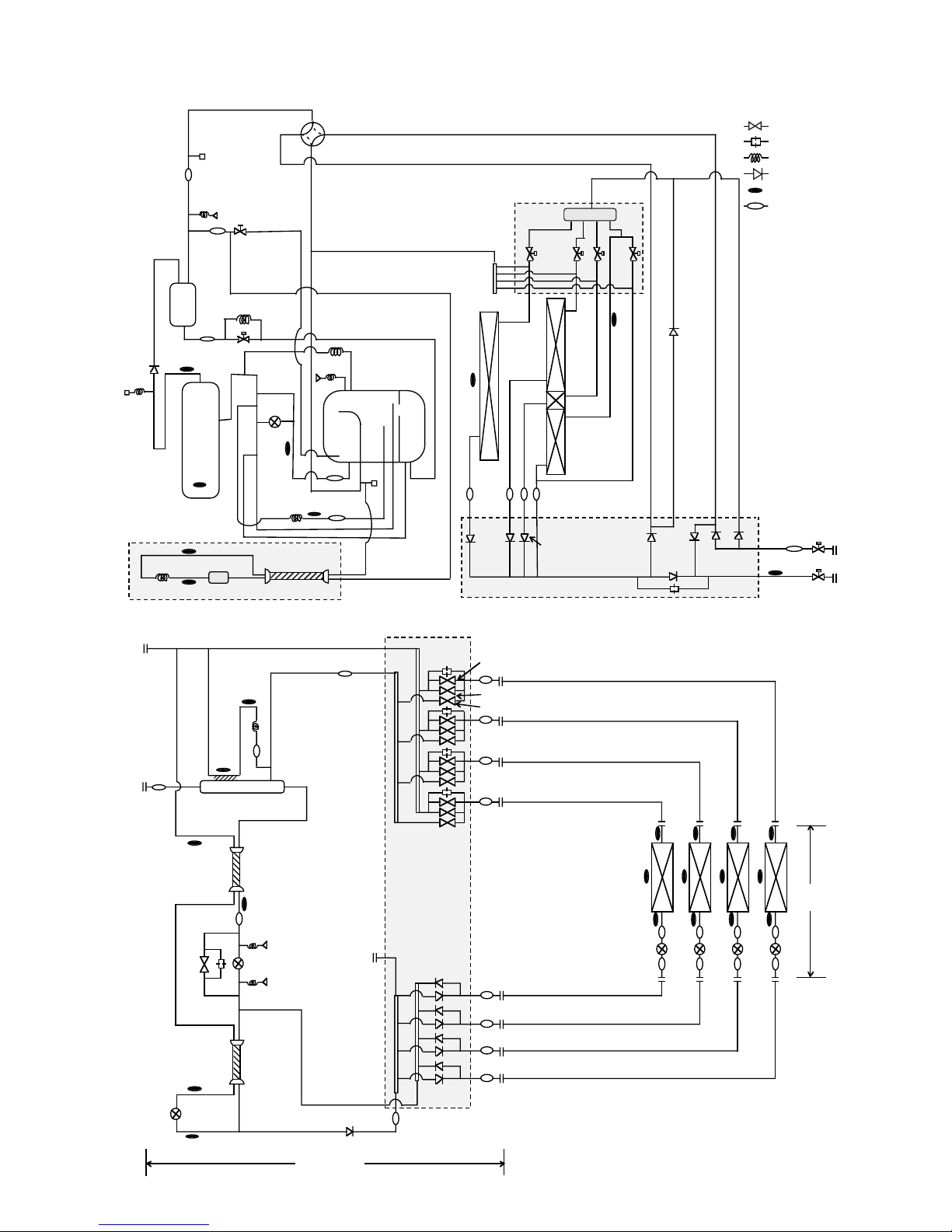
[2] Refrigerant Circuit Diagram and Thermal Sensor
1PUHY-200YMF-B, 250YMF-B
: Solenoid valve
: Orifice
: Capillary
: Check valve
: Thermal sensor
: Strainer
SP : Service port
ACC : Accumulator
–19–
TH1
TH6
TH7
TH8
TH5
TH3
TH4
TH2
Indoor units
CJ1
O/S
63HS
CJ1
Comp
HEX2
HEX1
SCC
LEV1
ST7
BV2
ST2
BV1
ST1
CJ2
CV1
ST6
SV1
CP1
SV2ST5
CP2
CP4
ST3
ST4
SLEV
SA
MA
CP3
63H
6
27
8
40
C
93
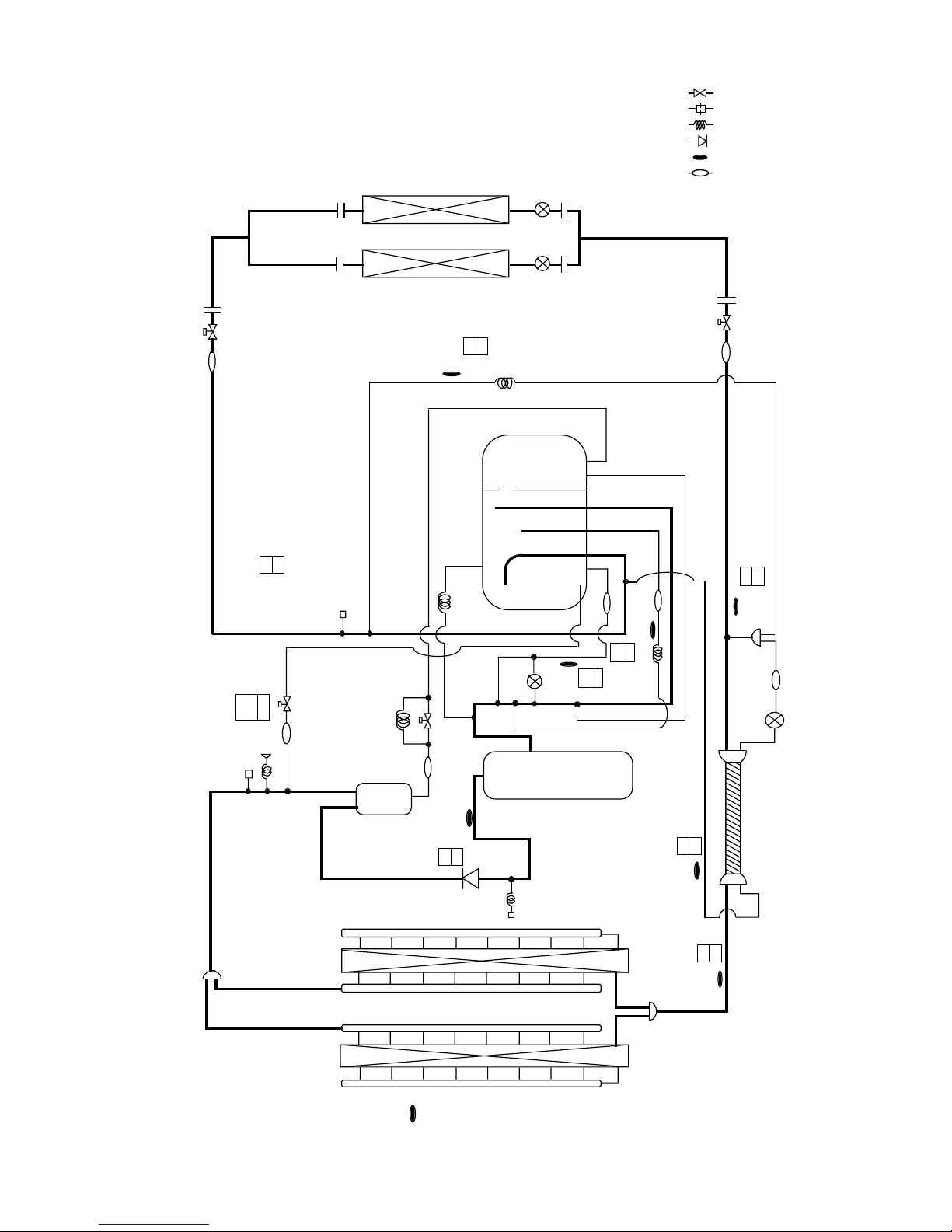
*Operation data of PUY-200YMF-B
Standard operation data are shown for cooling
in the C.
Units for each value are : ˚C for TH1
˜
TH8
: kg/cm
2
G (MPa) for HPS
*
6
30
20.3
(1.99)
: Solenoid valve
: Orifice
: Capillary
: Check valve
: Thermal sensor
: Strainer
SP : Service port
ACC : Accumulator
2PUY-200YMF-B, 250YMF-B

–20–
SCC
11 0
85 70
21.9
(2.15)
21.4
(2.10)
96 78
111 87
34 36
3.93 3.67
19 -3
0.23 0.28
-1 -3
42 -1
CH
8
27
85 0
LEV1
HEX f HEX b
TH6
CS-Circuit
SV2
CP1
CJ1
CJ2
63HS
SV1
ST6
CV1
CP3
O/S
63H
63LS
MA SA
ST8
ST4
TH4
TH3
TH7
ST7
LEV1
ST2
BV2
Indoor units
ST1 BV1
ST3
Comp
Drier
TH9
TH10
CP2
TH2
TH8
TH5
SLEV
ST5
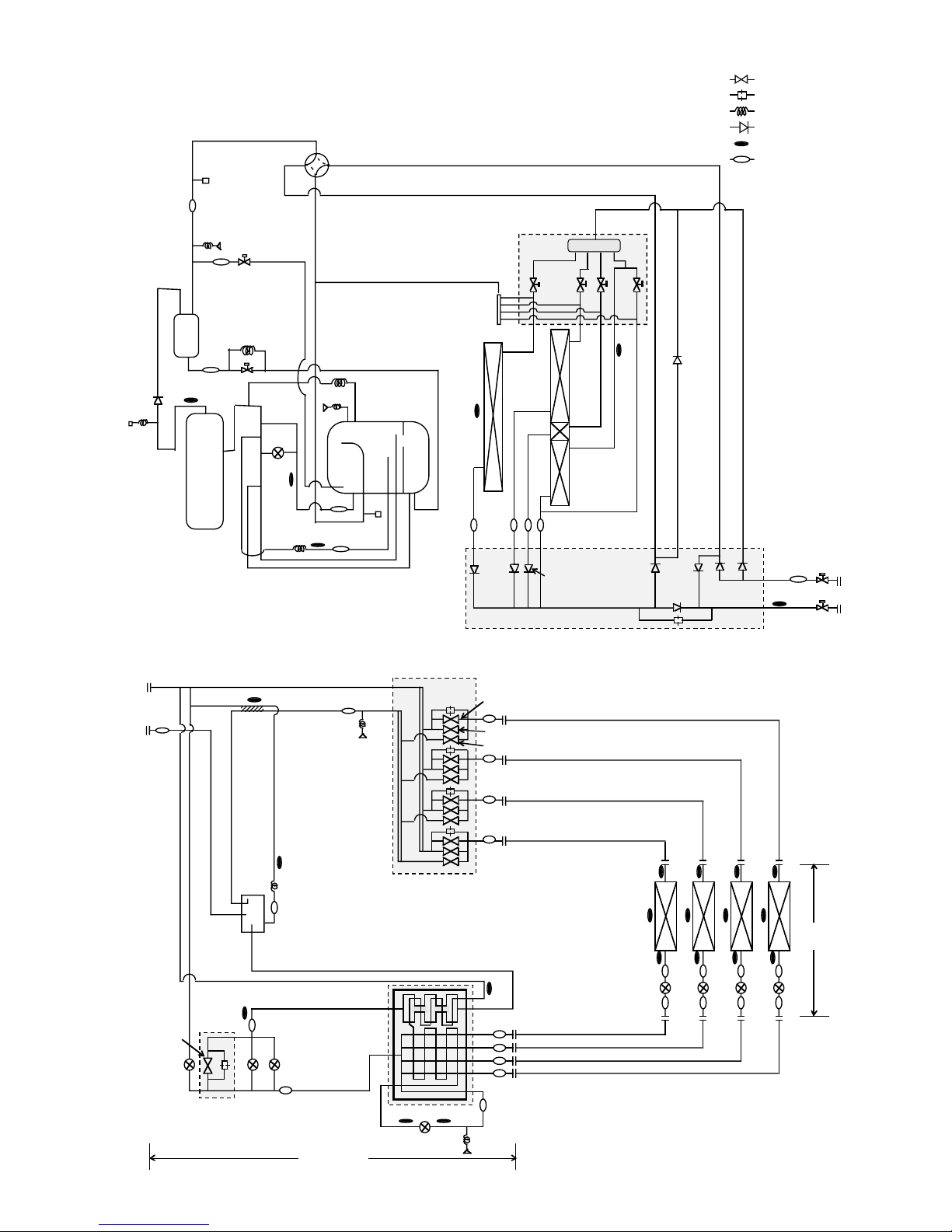
Circulating Configuration : αOC
❈
❈ Operation data of PUHY-P250YMF-B
Standard operation data are shown for cooling in the C column and for heating in
the H column.
TH1~TH5, TH7~TH10 : ˚C
LEV1,SLEV : pulse
HPS, LPS : kg/cm
2
G (MPa)
➂PUHY-P200YMF-B, P250YMF-B
TH1
: Solenoid valve
: Orifice
: Capillary
: Check valve
: Thermal sensor
: Strainer
SP : Service port
ACC : Accumulator
–21–
: Solenoid valve
: Orifice
: Capillary
: Check valve
: Thermal sensor
: Strainer
SP : Service port
ACC : Accumulator
➃PURY-200YMF-B, 250YMF-B
TH1
TH5
TH3
TH4
TH23
TH21
TH22
LEV
TH13
PS1
SVC
SVA
SVB
A Block
B Block
C Block
Indoor
units
BC controller
Gas/liquid separator
LEV2
LEV1
SVM
LEV4
LEV3
TH15 TH16
PS3
TH12
O/S
63HS
SP1
Comp
BV2
BV1
ST1
Solenoid Valves
Block
SP2
Check Valves Block
CV1
ST6
SV1
CP1
SV2
ST5
CP2
CP3
ST3
ST4
SLEV
SA
MA
63H
TH6
HEXb
SV6
CV7
SV5
SV3
SV4
HEXf3
HEXf2
HEXf1
CV10
CV3
CV2
CV5
CV4
CV9
CV8
CV6
63LS
TH14
TH11
Distributor
TH7
ACC
CMB-P104V-D
–22–
TH1
TH9
Drier
TH5
TH3
TH4
TH2
O/S
63HS
63LS
SP1
Comp
BV2
BV1
ST1
SP2
CS(Composition Sensing) circuit
CV1
ST6
SV1
CP1
SV2
ST5
CP2
CP3
ST3
ST4
SLEV
SA
MA
CP3
63H
TH10
TH6
HEXb
CV7
HEXf3
HEXf2
HEXf1
CV10
CV3
CV2
CV5
CV4
CV9CV8
CV6
TH7
Check Valves Block
Valves Block
ACC
Solenoid Valves
Block
SV6
SV5
SV3
SV4
Distributor
➄PURY-P200YMF-B, P250YMF-B
: Solenoid valve
: Orifice
: Capillary
: Check valve
: Thermal sensor
: Strainer
SP : Service port
ACC : Accumulator
TH23
TH21
TH22
LEV
TH13
SVC
SVA
SVB
Indoor
units
BC controller
CMB-P104V-E
Gas/liquid separator
PS1
LEV1
SVM
PS3
LEV3
TH14
TH12
TH11
TH15
TH16
–23–
ON/OFF
–
STAND BY
DEFROST
ERROR CODE
OA UNIT ADDRESS NO.
CENTRALLY CONTROLLED
CLOCK
ON
OFF
˚C
1Hr.
NOT AVAILABLE
˚C
CHECK MODE
FILTER
CHECK
TEST RUN
ON
OFF
CLOCK
FILTER
CHECK
TEST RUN
REMOTE CONTROLLER
NETWORK
PAR-F25MA
TEMP. TIMER SET
INDOOR UNIT
ADDRESS NO.
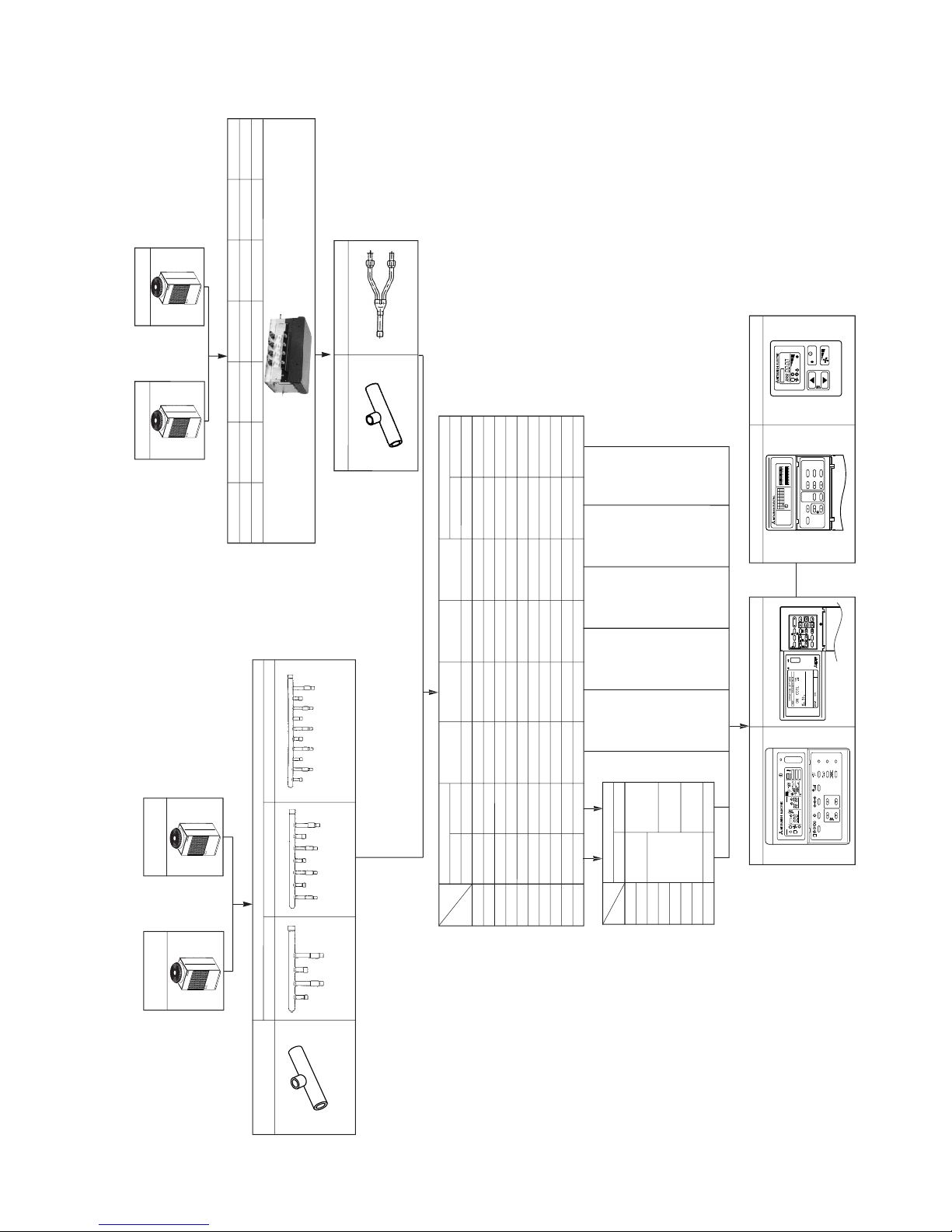
[3] Equipment Composition
40LW-F
A. Outdoor Unit
PURY-200YMF-B
PURY-P200YMF-B
PURY-250YMF-B
PURY-P250YMF-B
B. BC controller
Branch pipe kit
CMY-Y102S-F CMY-Y102L-F
D. Indoor Unit
Cassette ceiling
Ceiling concealed Wall mounted Ceiling suspended
Floor standing
Exposed Concealed
PLFY-P PLFY-P PEFY-P PKFY-P PCFY-P PFFY-P PFFY-P
4-way flow 2-way flow
20 - 20VLMD 20VM 20VAM - 20VLEM 20VLRM
25 - 25VLMD 25VM 25VAM - 25VLEM 25VLRM
32 32VKM 32VLMD 32VM 32VGM - 32VLEM 32VLRM
40 40VKM 40VLMD 40VM 40VGM 40VGM 40VLEM 40VLRM
50 50VKM 50VLMD 50VM 50VGM - 50VLEM 50VLRM
63 63VKM 63VLMD 63VM - 63VGM 63VLEM 63VLRM
80 80VKM 80VLMD 80VM - - - -
100 100VKM 100VLMD 100VM - 100VGM - -
125 125VKM 125VLMD 125VM -
125VGM
--
E. Option (Panel)
Decoration panel
PLP- CMP-
20
25
32
40
50
63
80
100, 125
3GB
6GB
32LW-F
63LW-F
125LW-F
Model
Capacity
Model
Capacity
PAR-F25MA
F. Remote Controller
C. Branch pipe kit/joint pipe kit
4-branch type
CMB-P104V-D
5-branch type
CMB-P105V-D
6-branch type
CMB-P106V-D
8-branch type
CMB-P108V-D
10-branch type
CMB-P1010V-D
13-branch type
––
16-branch type
CMB-P104V-E CMB-P105V-E CMB-P106V-E CMB-P108V-E CMB-P1010V-E CMB-P1013V-ECMB-P1016V-E
Joint pipe kit
CMY-R160-F: for V-D type
CMY-R160-G: for V-E type
Ceiling mounted
built-in
71
-
-
-
PDFY-P
20VM
25VM
32VM
40VM
50VM
63VM
80VM
100VM
125VM
71VM
-
-
--
MJ-103MTRA
PAC-SC32PTA
PAC-SE51CRA
A. Outdoor Unit
PUHY-200YMF-B
PUY-200YMF-B
PUHY-P200YMF-B
PUHY-250YMF-B
PUY-250YMF-B
PUHY-P250YMF-B
B. Branch pipe kit
Branch joint
Branch header
4-connection 7-connection 10-connection
CMY-Y107-ECMY-Y104-E CMY-Y1010-ECMY-Y102S-F CMY-Y102L-F
12
6
3
GROUP
SELECT
MODE
TEST RUN
AIR
DIRECTION
FAN SPEED
ON/OFF
0
87
54
CLOCK/
PATTERN
PROHIBITION
TIMER
MODE
TEMP.
REMOTE
MJ-103MTRA
CENTRAL CONTROLLER
9
INS.
DEL.
SCREEN
BACK
ENTER
VENTILATION
RESET
ON/OFF
SMTWTFS
SET
SET BACK
036912
12 15 18 21 24
SET/MONITOR TODAY
WEEKLY
SETTING
PROGRAM TIMER
PAC-SC32PTA
DAILY
SETTING
ON
SET BACK ON
CLOCK
OFF
DAILY TIMER
OFF
SET BACK
CENTRAL
TEMP.CHECK
˚C
TEMP.
ON/OFF
PAC-SE51CRA
–24–
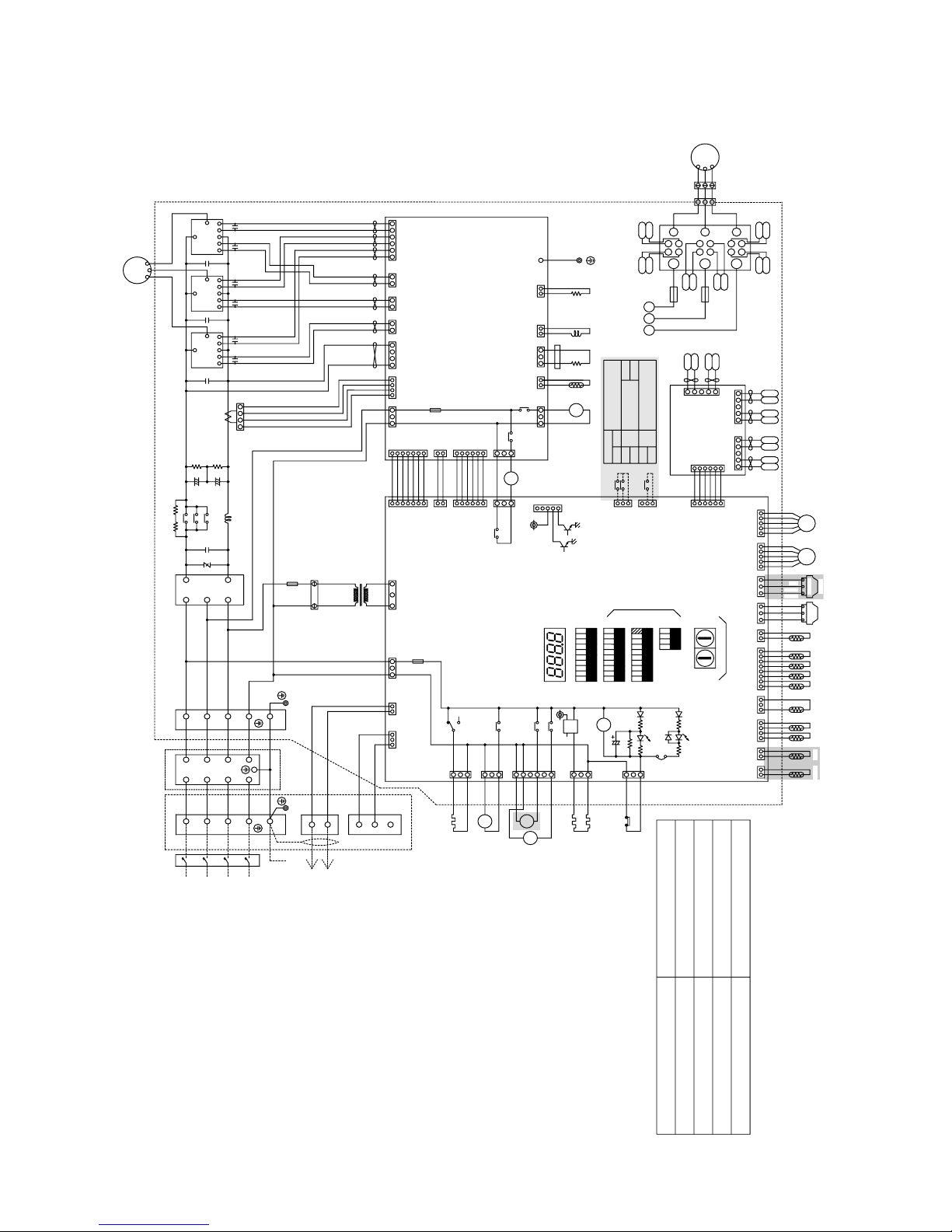
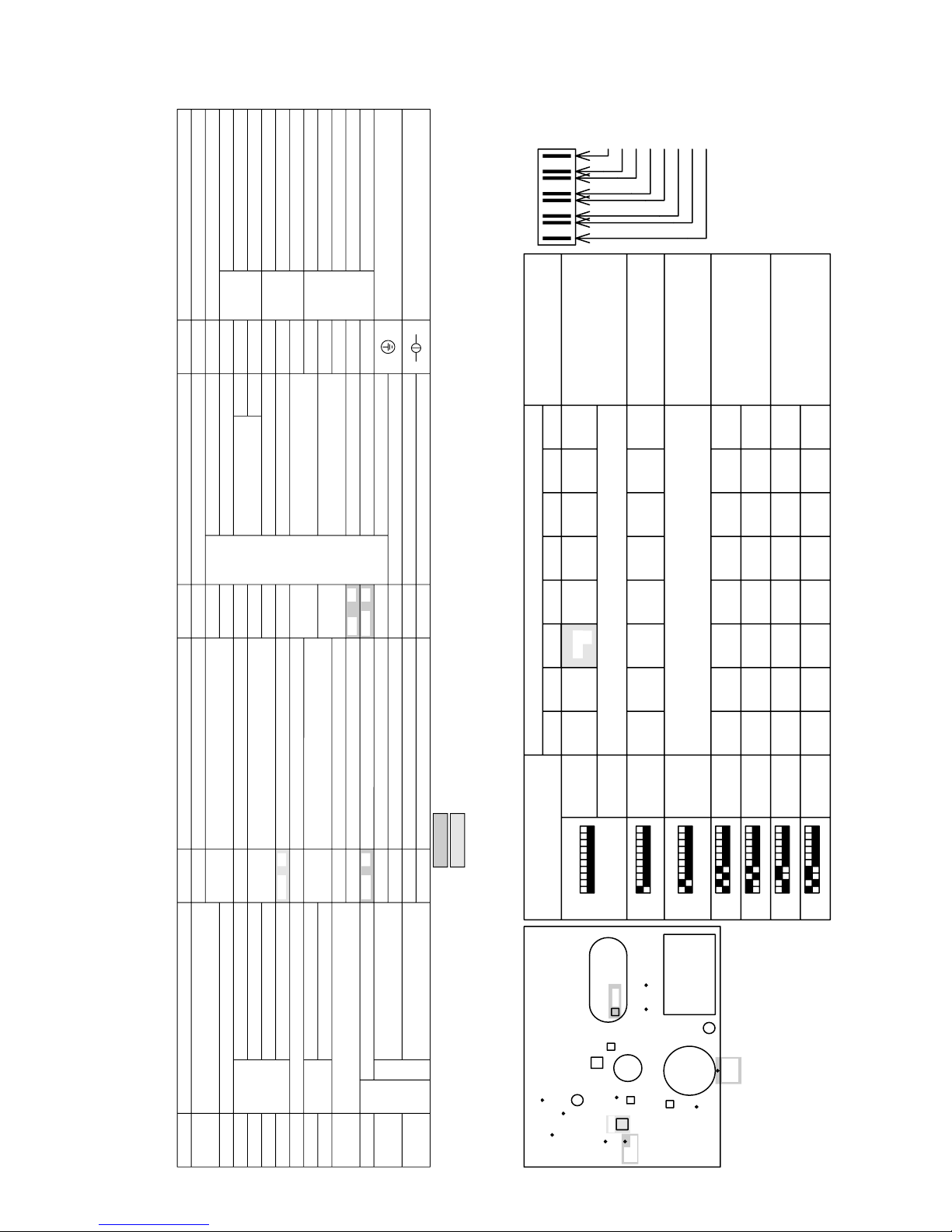
[4] Electrical Wiring Diagram
1 PU(H)Y-(P)200·250YMF-B
kQ
r
lQ
lP
kP
P
m
kR
od
@@
ioQ
qU
kdc@
|
T
Q
f
j
f
j
f
j
f
j
f
j
f
j
bmle
vfQ
tjP
tfQ
rbql
tfP
t
tjQ
vjP
vjQ
v
vfP
ujP
ufP
ujQ
ufQ
u
t
kP
q
kQ
eQ
kP
v
kR
v
kQ
eP
UOOu‘b
W‘@e
kR
le
S
P
Q
R
UOOu‘b
W‘@e
a
bmOS
u
q
tfQ
S
v
a
T
tfP
tjP
tjQ
T
U
TSRQPPQRST
R
Q
P
vfQ
e@
@
@ie@j
vjQ
vfP
vjP
ufQ
ujQ
ufP
ujP
@ @nm@ @l @QTOD
@rvR|PO@ @nee@ @l @QOOD
PQ P SQ
R
PRQ
P
RQS
S
PPQR UV
P
W
R
P
Q
QP
P
Q
P
R
V
PQ
U
R
Q
P
T
QR
S
S
R
T
R
P
Q
Q
P
RS
P
T
T
Q
U
R
P
S
Q
Q
R
T
P
Q
R
S
T
U
eOP
QTOu‘b
Q‘@e
bmOX
iQoj
R
bmOU
iQoj
bmRR
iRoj
P
P
bmRc
iRoj
bmRT
iRoj
bmRr
iRoj
R
bmQO
iRoj
Q
bmebP
iUoj
Q
bmRS
iUoj
R
Q
Q
P
bmQ|R
iQoj
U
P
T
bmubbS
iQoj
S
R
R
Q
P
P
R
bmrP
iQoj
Q
bmTP
iToj
P
bm‘bQ
iRoj
P
Q
Q
bmrQ
iRoj
R
P
bmwPO
iRoj
bmq
iRoj
Q
bmTQb
iRoj
R
bmucb
iSoj
bmRW
iRoj
bmsg
iQoj
wOQ
wOP
PPO
e
@
PO
t@
@
@
nmFP
PPO
rvP
rvtQ rvtP
neeFO
nmFP
rvQ
neeFO
rvR
POP
neeFO
nmFP
kcP
P
r|
@
ie @rvPFP‘PO
@
@@
@j
PQu
me@a
m
TFs
SFb
@nm^nee
bOSV
m
wPO
kR
o@
Rm‘
RWO^SOO^SPTu
TOg
qORX
cQS
qORV
obOP
qORW
obOV
cQT
qPTW
qPTV
c‘OSO
anw@ancx
b
@
@
il‘hm@ j
f^
x
a
SR
QP
a
q
v
rrq
wOS
wOT
me
ruP
kduP
bgP
QPrS
saP‘
ruQ
kP
bgQ
kQ
bgR
kQ
eP
QTOu‘b
Q‘@e
URg
kR
m
kP
kQ
kR
m
PQR
sgP
sgQ
sgVsgWsgT
sgU
sgRsgS
a
v
q
URgr
kP
rkdu
kR
kQ
od
s
@@@@@a
kP
od
saP
v
q
a
a
f/
x
b
@
h
@
t@
saR
lP
lQ
saV
‘
cr
bP
‘|
‘
{
ymqS
bP
qT
qP
TQb
{
sqlP
{
cbk
bQ
bR
qQ
qR
sOP
eR
QTOu‘b
P‘@e
bmsqP
sqlQ
bP
bQdP
aQ
dQ
dQ
dP
aP
aP
dP
dQ
dQ
aQ
bQdP
bP
sqlR
bQdP
aQ
dQ
dQ
dP
aP
bPS
bPT
bPU
SR
cbbs
QP
v
bQT
t
bQQbQP
bQSbQR
bQO
v
lb
u
lib
j
qa
RQ P
ef
PQ
Q
RS
P
PQ
Q
RS Q
PR
PQ
Q
PQ
P
PP
Q
QR
P
ST
R
U
Q
Q
R
S
P
Q
P
V
U
T
S
R
Q
P
T
U
P
Q
R
TQb
wOQ
wOP
wPO
bmqrQ
iVoj
bmubbQ
iQoj
bmubbR
iUoj
bmbs
iSoj
bmubbP
iUoj
bmqrR
iVoj
bmOT
iSoj
bme‘m
iRoj
bmOR
iRoj
bmQ|Q
iQoj
bmOQ
iWoj
sggr
bmOP
iQoj
bmg
iRoj
bmQ|P
iQoj
bmk
iRoj
bmRQ
iRoj
bmkuP
iToj
bmsq
iRoj
bmkuQ
iToj
bmR
iUoj
bmkQ
iQoj
bmROu
iQoj
leP
o
qV
eaU
a
x
n
kQ
o@
@
ihmu@
j
anw@ancx
h
b
@a
q
a
a
o
a
x
v
q
a
n
q
a
bmv
iToj
bmu
iToj
bmebQ
iUoj
bmt
iToj
vhqhmf@ch‘fq‘l
P|Q
nm
nee
nm
nee
P|R
nm
nee
bmRc
l
‘
m
gd‘s
bnnk
nmFP
neeFO
rvS
PS
Appliance
PUHY-P200/250YMF-B
PUY-P200/250YMF-B
PUHY-200/250YMF-B
PUY-200/250YMF-B
Difference
All exists
” 1” are not existed
” 2” are not existed
” 1” and ” 2” are not existed
1
2
2
1
<Difference of appliance>
URkr
PQR
a
v
q
sgPO sgX
–25–
sgT
f
kduP
sgQ
q
sgW
f
sgV
v
W
Q
P
neeFO
nmFP
P
mDQ
mDPTmDPSmDPQmDPO
mDWmDUmDS
mDPU
mDP
mDPRm DPPmDX
mDVmDTmDR
mDQ mDT
mDX mDPR m DPU
mDU
mDPO m DPS
mDV
mDPP
mDP mDS mDW
mDPQ m DPT
TSRQPW
nmFP
neeFO
c
|
@
i@ @ j
ek‘ fVek‘ fP
QPrS
b
b@
Q
ruP
ek‘ fU
c
‘
n
@@ |
@
irvPj @kdc@
WPQRSTUV
Q
W
nmFP
neeFO
VU
UV
neeFO
nmFP
R
nmFP
WPQRST
neeFO
S
TSRQPW
nmFP
neeFO
VU
VU
UV
neeFO
nmFP
W
R
T
PQRST
VU
ST
c
@ @kdc@
i
jq
@rvP@
ek‘ fRek‘ fSek‘ fQ
ruQ
ek‘ fT
OOOO‘ XXXX
c
@@
@@ @
@@
rrq
OOOO‘ XXXX
c
@@
@@
@
@@
mDR
kdc@
h
@
··
PUHY-P
·
YMF-B
ek‘ f
ek‘ f
ek‘ f
ek‘ f
ek‘ f
ek‘ f
ek‘ f
ek‘ f
kcP
q@
ik
j
b@
P
ia
j
q@
@Q
h@
h@
h@
h@
ek‘ fW
sgU
lb
rkdu
sgP
URgr
URg
n
ruQ
ruP
‘ bbtltk
‘ snq
sgR
a
sgS
x
h
b
a
ie j
ek‘ fW@
@
@
@
nm
k
@@
@@ @ C
s@@@
k
@@
a@@
s@@@^
k
@@
@
s@@@
X
X
X
X
X
X
XPO
PO
PO
PO
PO
PO
PO
sgR
sgT
sgS
sgQ
q@
@
qQCqR
u
b
bQCbR
m@@@r
o@
g@
i@
@
j
i
@QSOu@
@ODPP‘ j
leP
cbk
eP‘ R
saPi‘ j
saV
r
le
q
@
e
r
r@
io @
@
j
q
c
rxlank@dwok
‘ m ‘ shnm
b@is
j
ruPCruQ
kQ
cb@
i ‘
@
@
@
j
cbbs
o@
saR
TQb
sgP
b
@r
qU
qV
ih
@@
j
sggr
qPCqT
q@
@
bPCPSCPTCPU
ymqS
lblb
@@@@@@@@@ir | @ @
j
d
@
@
in @
j
URgr
URg g @
@
b@
bgQCbgR
r
@
@
ic
|
@
j
kduP
S| @QPrS
1
rkdu
g@
@
k@
@
URkr
m@@@r
rvQCRCS
r@
rvtP‘ Q
b
@@D
q
@
@D@
k
r
e
@
‘ D@
k
@
t
‘
@
@
@@ D@
g@
@
@D
n ‘ @D@
o@ D@
@
@D@
@@@ @r | @
@
@D@
@@@ @r | @
m@ @ @
eaU
e
l
@
m@@@
rrq r @
@
s
sP
ib
@
@
@
j
bgP b
@
ib
j
d
@
@
cr c @
sqlP‘ Ro @
@
me m @e
sgPO
sgX
sgW
sgV
sgU
wPCQCSCTCPO
kcP
bQO‘ QT
e
@
t@
@
c
@
@|
r
s
rvPr
@D
@D@
c
@@D@
s
s
s
i
b
@
bmbs
bmqrQCR
b
bmubbPCR
bmebPCQ
bmubbQCS
b
l|h@s
u
u
o@
@
d@
q@
PUHY-P
·
YMF-B only
H/P unit (PUHY) only
1
2
2
2
2
1
2
2
sgPO
a
URkr
sgX
o
QPrS
1 PU(H)Y-(P)200·250YMF-B
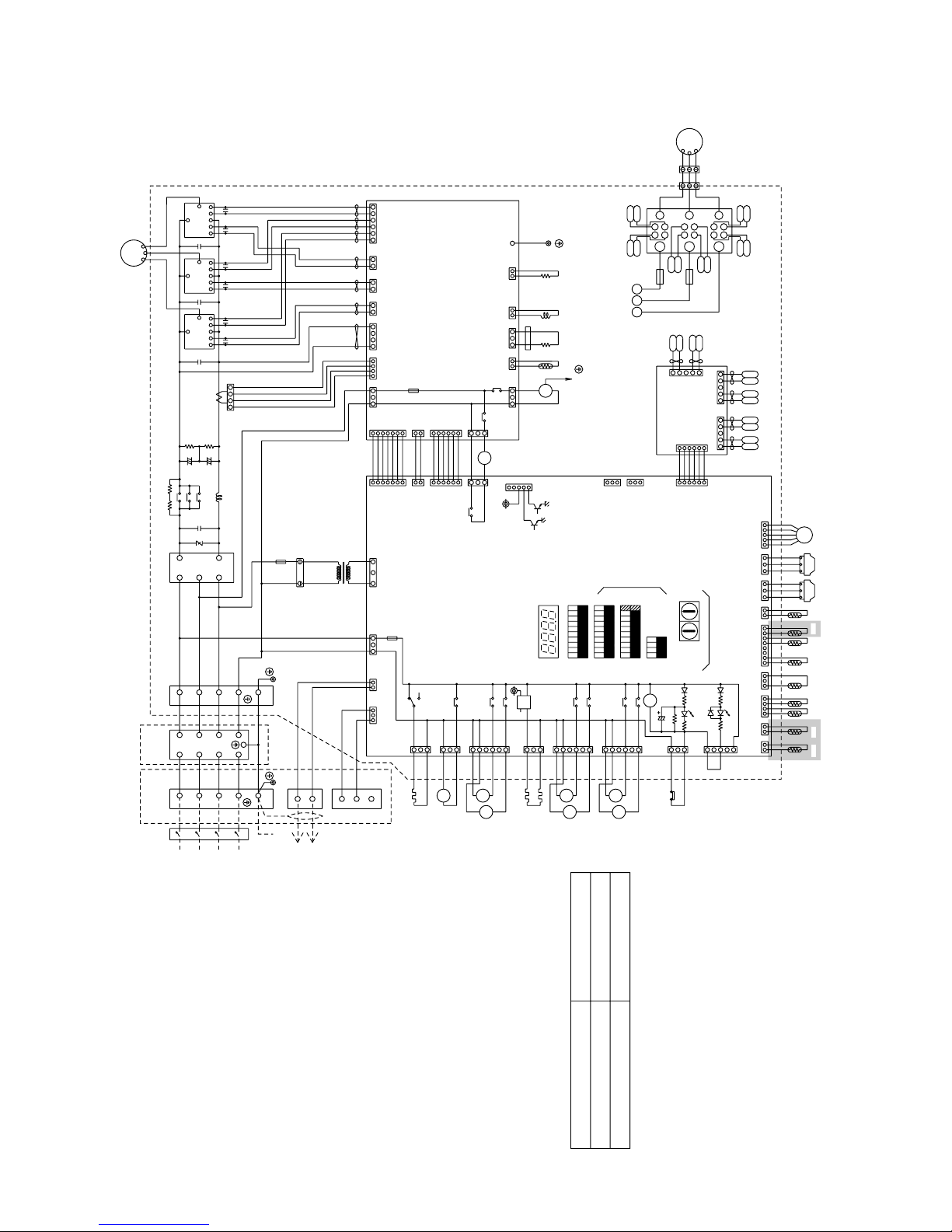
–26–
CNTR
(3P)
CN3
(6P)
CNL2
(2P)
CN30V
(2P)
MF1
Purple
R7
FB6
Black
Yellow
Orange
L2
Power circuit board
(INV board)
BOX BODY
Inverter
Controller Box
Red
Brown
Black
Purple
Black
Yellow
White
Red
Brown
Orange
Red
Blue
CNW
(5P)
CNV
(5P)
CNFC2
(6P)
CNU
(5P)
SW4
41
OFF:0
ON:1
SV4
X07
X06
12345
6
(6P)
CN36
SV6
X09
X08
12345
6
(6P)
CN37
SV3
SV5
22
(5P)
CNLV1
(3P)
CN32
(3P)
CNL
(2P)
CN2-1
(3P)
CNH
(2P)
CN01
THHS
(8P)
CN02
(2P)
CN2-2
(3P)
CN03
(3P)
CNFAN
(4P)
CN05
(7P)
CNRS3
(6P)
CNVCC1
(4P)
CNCT
(6P)
CNVCC3
(2P)
CNVCC2
(7P)
CNRS2
X10
X01
X02
52C
32165
1234567121432
2
6
3
54
1
32
2
11
1
21
2
21
31
243
2
21
1
43
2
21
FG
123
BlackRed
Motor (Compressor)
V
MC
W
C20
C23 C24
C21 C22
U
C25
White
12
DCCT
34
C16
C15
C14
B1
E1
E2
E2
B2
C2E1
TRM3
C1
C2E1
B2
E2
E2
E1
B1
B1
E1
E2
E2
B2
C2E1
C1
TRM2
CNTR1
1A F
250VAC
F3
T01
R3
R2
C3
C2
DCL
+
TRM1
+
52C
R1
R5
C1
ZNR4
+
~
-~
C1
DS
~
TB7
M2
M1
TB3
Unit body
controller
remote
Indoor and
Connect to
Yellow
Green/
Blue
Black
Red
White
TB1
PE
L1
Terminal Box
PE
L2
L3
SLEV
L1
63LS
Red
White
Black
321
63HS
Red
White
Black
TH4 TH3
TH6
TH5
TH7
TH2
TH1
321
N
L3
L2
L1
N
L3
63H
2A F
250VAC
F1
L2
CH3
L2
CH2
L1
SV2
TB1A
21S4
CH1
SV1
NF
X05
X04
SSR
White
Red
Black
12
34
Blue
Yellow
Green/
(MAIN board)
Control circuit board
BOX BODY
DA040
R157
R158
D25
PC07
R038
PC01
R037
D24
R039
50Hz
380/400/415V
3N~
Power source
L3
X10
N
C047
4:Compressor ON/OFF
5:Trouble
N
NF Box
12V
switch
the following table)
(For SW1:1~10display see
Self-diagnosis selector
1
LD1
ON:1
OFF:0
110
*1
SW3
OFF:0
SW2
ON:1
OFF:0
SWU1SWU2
SW1
101
ON:1
*1
Unit address setting switch
10
switch
Function selector
101
X01
X02
(2P)
CNTH
(3P)
CN38
(4P)
CNVDC
3
(3P)
CN52C
2
(3P)
CNR
(3P)
CNX10
1
3
(3P)
CNS2
221
(3P)
CNAC2
1
(5P)
CN51
2
(2P)
CNS1
3112334
(2P)
CNVCC4
516
(2P)
CN2-3
122
3
(6P)
CN34
2
(6P)
CNFC1
2
(3P)
CN20
3
(3P)
CN3S
(3P)
CN35
(3P)
CN3D
1
1
(3P)
CN33
(2P)
CN06
3
(2P)
CN09
2A F
250VAC
F01
65432
1
5322413
625
112
3
5
3
4
4325
1
2
3
6217
3
1
2
1122
1
3
8
1
763211
4
423
1
231
3
24121
SW3-10 are OFF for Model 200.
and ON for Model 250.
VK1
VG1
VK2
VG2
WK1
WG1
WK2
(Fancon board)
Fan control board
WG2
123
54321 12345
6
5
UK2
UK1
UG1
5
Black
White
4
UG2
Red
V
CN04
Black
8A F
600VAC
321
4
MF
L3
8A F
600VAC
F1
L2
W
L3
White
L1
F2
L2
Red
L1
U
V
VG2
VK2
VG1
VK1
WG1
W
WK2
WK1
UK2
U
UG1
SCRM
UG2
UK1
WG2
CNMF
K
G
K
G
K
G
K
G
K
G
K
G
2
5
display
self-diagnosis
LED for
R6
5
TH10
PE
L3
N
1
L1
M1
M2
S
L2
4
3
CNRT1
(5P)
1
2
Terminal
Block
Noise
Filter
Crank case heater
(Compressor)
Cord heater
(Accumulator liquid
level detect)
switch
High Pressure
Fan motor
(Heat exchanger)
Fuse
Fuse
Fuse
Terminal Block
Diode stack
to TB1A
TH9
Appliance
PURY-P200/250YMF-B
PURY-200/250YMF-B
Difference
All exists
” 2” are not existed
<Difference of appliance>
2 PURY-(P)200·250YMF-B
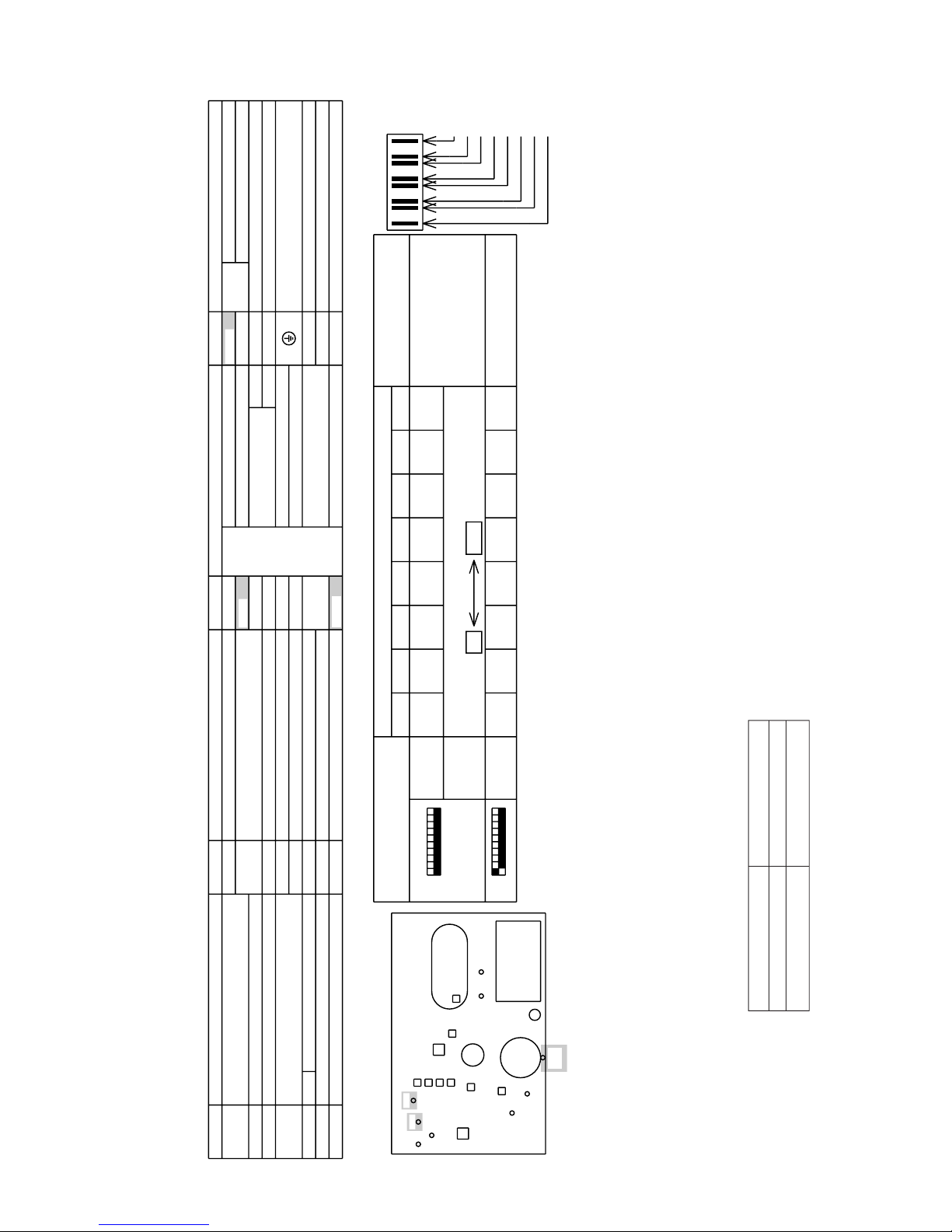
–27–
FLAG8 always lights at
microcomputer power
ON
(Front)
Inverter
Controller
Box
TH4TH3
ACCUMULATOR
63LS
SV1
SV2
TH10
Blown
Oil
separator
21S4
63H
63HS
TH1
SLEV
MC
FLAG8
Check display1
(Blinking)
Relay output
display
(Lighting)
LD1
FLAG8
FLAG1
FLAG2
FLAG3
FLAG4
FLAG5
FLAG6
FLAG7
<Internal layout>
<LED display>
FLAG5
SV2
FLAG2 FLAG4FLAG3
Display at LED lighting(blinking)Remarks SW1 operation
76543218
<Operation of self-diagnosis switch(SW1)and LED display>
Always
lighting
Display
FLAG6
SV1
Crankcase
heater
21S4
FLAG1 FLAG7
(at factory shipment)
During
compres-
sor run
ON:1
OFF:0
<SYMBOL EXPLANATION>
109
For PURY-(P)200/250YMF-B
*2
*2
51 1102
*please refer to the service handbook about other switch settings of LED display.
SV6
SV5
SV4
SV3
TH2
TH9
TH7
TH6
*2
TH5
Display the address and error code by turns
76543218
ON:1
OFF:0
109
SV3 SV4
SV5 SV6 SSR
NameSymbol
MF1
DCL
Symbol
Radiator panelFan
(Power factor improvement)
Choke coil(Transmission)L2
SV1,SV2
DC reactor
DCCT
52C
TH1
Current Sensor
(Inverter main circuit)
THHS
ZNR4 Electronic expansion valve(Oil return)
63HS
Solenoid valve (Discharge-suction bypass)
4-way valve21S4
SLEV
High pressure sensor
Low pressure sensor63LS
NameSymbol
Compressor shell temp.
Radiator panel temp. detect
Lower
Symbol
Aux. relay
Upper
Accumurator liquid
High pressure liquid temp.
temp. detect
OA temp. detect
Iiquid outlet temp.detect
Pipe temp. detect
at Sub-cool coil
Name
Magnetic contactor
Name
SSR Solid state relay TRM1~3 Power transistor module
TH10 *2
TH9 *2
TH7
TH6
X1,2,4~10
Saturation evapo. temp. detect
Discharge pipe temp. detectThermistor
Earth terminal
(Heat exchanger capacity control)
SV3~SV6
FB6 Ferrite core
Solenoid valve
Varistor
TH2 *2
TH4
TH5
TH3
Thermistor
<Difference of appliance>
Appliance Difference
PURY-P200/250YMF-B All exists
PURY-200/250YMF-B ”*2” are not existed
2 PURY-(P)200·250YMF-B
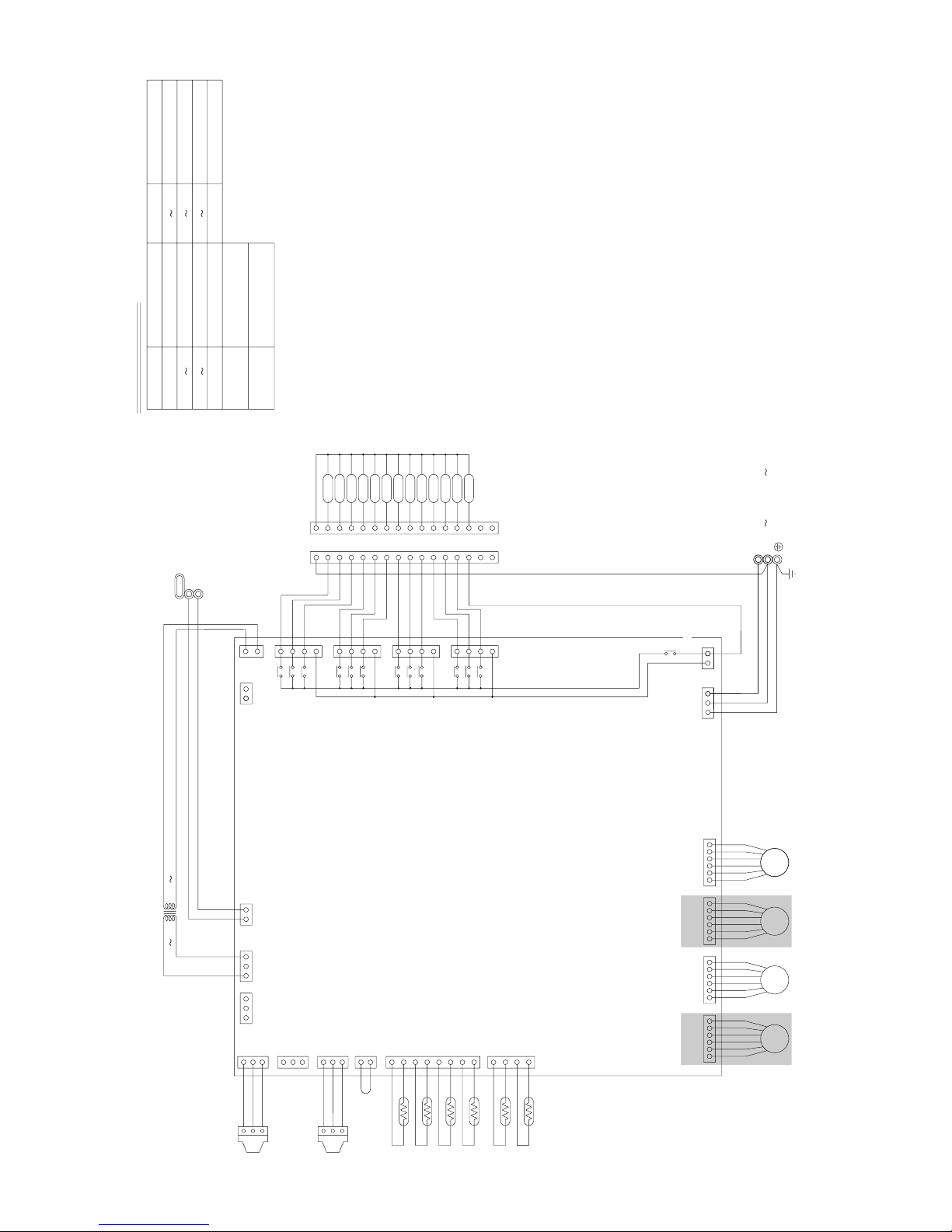
–28–
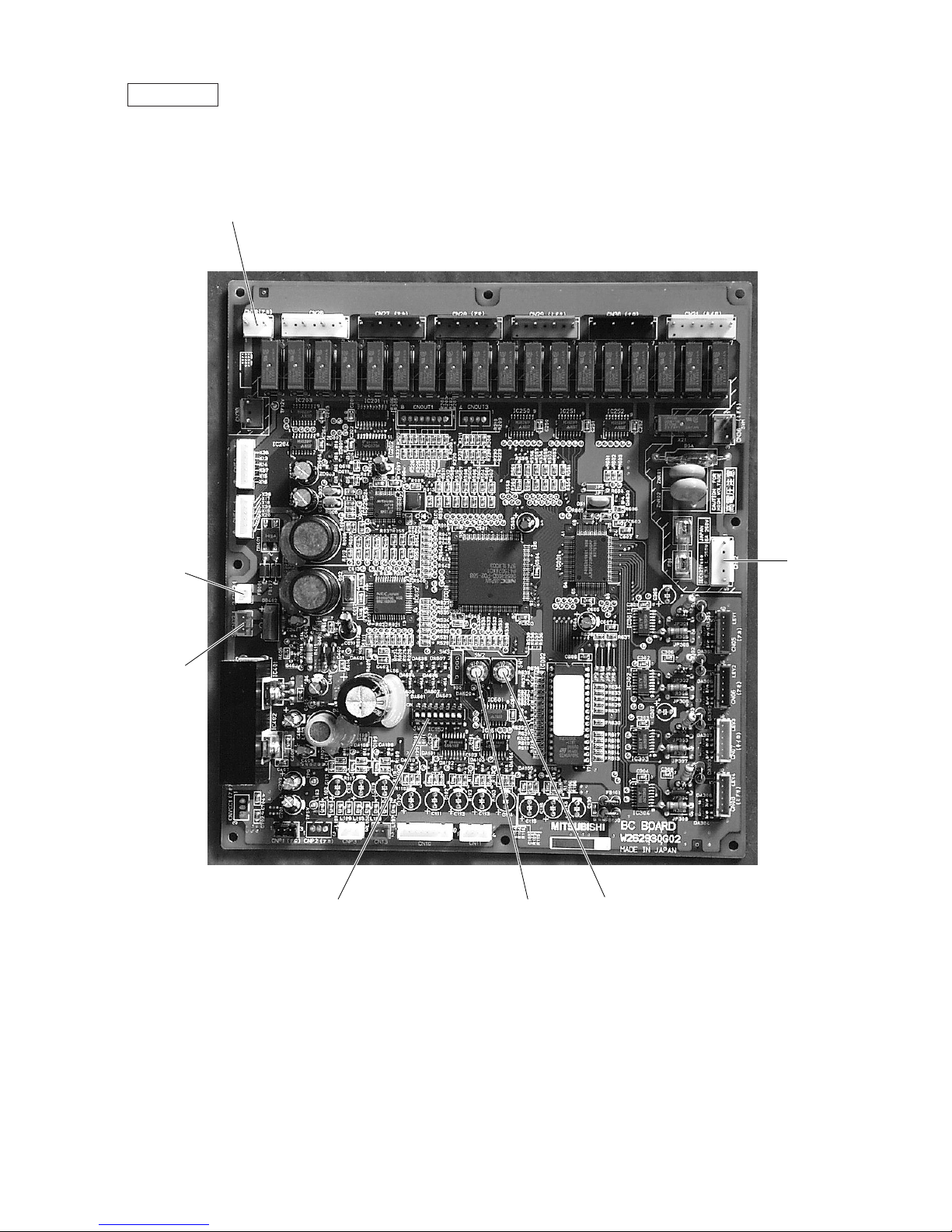
Symbol explanation
PE
3
2
1
3
2
1
EARTH
Terminal block
(for Transmission)
TB02
Terminal block
(for power source)
TB01
Note:TB02 is terminal block for transmission.
Never connect power line to it.
NameSymbol
Solenoid valve
Solenoid valve
Solenoid valve
Solenoid valve
Expansion valve
Thermister sensor
Transformer
NameSymbol
SV1 4A
SV1 4B
SV1 4C
SVM
TR
TH11 16
LEV1 4
PS1,3 Pressure sensor
Transmission line
Shield wire
* Only for CMB-P-V-D
/N 220V 240V 50Hz
Power source
BC Board
31
LEV1
TB01
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
SVM
SV4B
SV4A
SV4C
SV3B
SV3A
SV3C
SV2B
SV2A
SV2C
SV1C
SV1A
SV1B
}
CN38
3
1
CNTR
CN02
CN12
153
31
7
5
3
1
7
5
3
1
7
5
3
1
7
5
3
1
TR
3
CNVCC1
12
X2
X1
X30
X4
X3
X31
X6
X5
X32
X8
X7
X33
X21
}
DC 30V
123456 654321654321654321
LEV4 LEV3 LEV2
1
2
3
CNP1
1
2
3
CNP2
1
2
3
CNP3
2
1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
4
3
2
1
12321
CN03
CN13
CN10
CN11
CN08 CN07 CN06 CN05
L
N
TH11
TH12
TH13
TH14
TH15
TH16
PS1
PS3
20 22V
TB02
M2
M1
CN26
CN27
CN28
CN29
TB01
220 240V
CN36
3 CMB-P104V-D
CMB-P104V-E
 Loading...
Loading...