Mitsubishi M37630E4FS, M37630E4FP, M37630M4T-XXXFS, M37630M4T-XXXFP, M37630E4T-XXXFP Datasheet
DESCRIPTION
g
g
g
g
guag
g
g
g
g
g
g
g
g
The 7630 group is a single chip 8-bit microcomputer designed with
CMOS silicon
equipped with a CAN (Controller Area Network) module cir-
Bein
cuit, the microcomputer is suited to drive automotive equipments.
The CAN module complies with CAN specification version 2.0, part
B and allows priority-based messa
In addition to the microcomputers simple instruction set, the ROM,
RAM and I/O addresses are placed in the same memory map to
enable easy pro
The built-in ROM is available as mask ROM or One Time PROM.
For development purposes, emulator- and EPROM-type microcomputers are available as well.
ate technology.
e management.
ramming.
FEATURES
z
Basic machine-lan
z
Minimum instruction execution time
(at 10 MHz oscillation frequency) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.2 µs
z
Memory size
ROM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16252 bytes (M37630M4T-XX XFP)
RAM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .512 bytes (M37630M4T-XXXFP)
z
I/O ports
rammable I/O ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35
Pro
Input . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1
e instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .71
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
7630 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
z
Interrupts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .24 sources, 24 vectors
z
Timers
16-bit Timers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 channels
8-bit Timers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3 channels
z
Serial I/Os
Clock synchronous. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 channel
UART . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 channel
z
CAN module
(CAN specification version 2.0, part B) . . . . . . . . . . .1 channel
z
A-D converter. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-bits x 8 channels
z
Watchdo
z
Clock Generatin
Built-in with internal feedback resistor
z
Power source volta
(at 10 MHz oscillation frequency). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.0 to 5.5 V
z
Power dissipation
In hi
(at 8 MHz oscillation frequency, at 5 V power source volta
z
Operatin
z
Packa
APPLICATION
Automotive controls
timer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
e
h-speed mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55 mW
temperature range. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –40 to 85 °C
e. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44QFP (44P6N-A)
e)
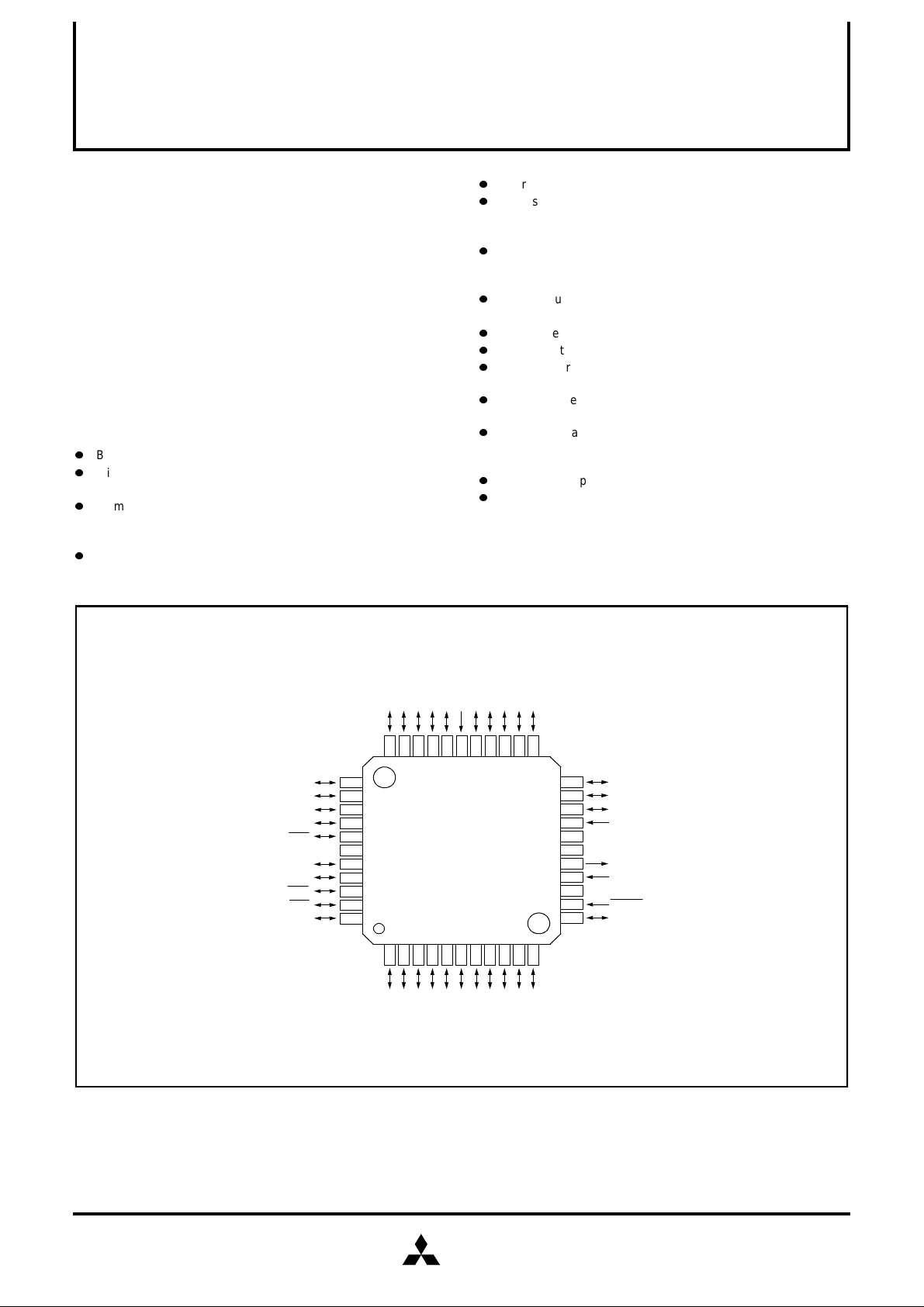
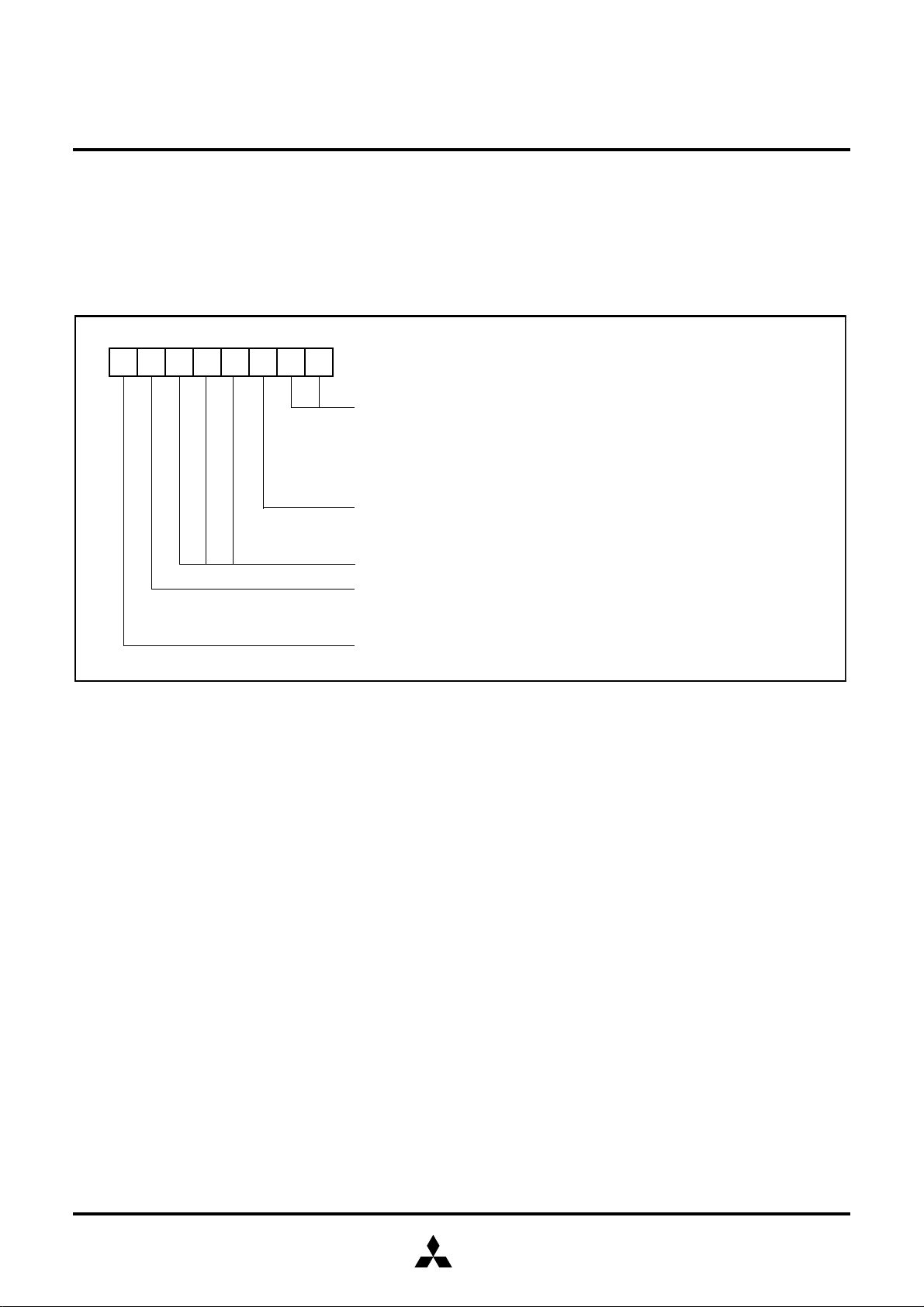
PIN CONFIGURATION (TOP VIEW)
P1
P20/S
P21/S
OUT
P22/S
CLK
P23/S
RDY
V
P24/URXD
P25/UTXD
P26/U
RTS
P27/U
CTS
P3
SS
34
7
35
IN
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
0
1
0
1
0
7
6
5
0
/CNTR
/CNTR
/INT
/TX
/PWM
5
6
P1
P1
3332313029282726252423
/INT
4
3
2
1
P1
P1
P1
P1
4
/AN
/AN
/AN
/AN
7
6
5
4
P0
P0
P0
P0
M37630M4T-XXXFP
M37630E4T-XXXFP
123456789
4
0
1
3
P3
P3
/CTX
1
P3
/CRX
2
P3
/KW
/KW
0
1
P4
P4
10
2
3
4
5
/KW
/KW
/KW
/KW
2
3
4
5
P4
P4
P4
P4
Package type: 44P6N-A
44-pin plastic molded QFP
3
/AN
3
P0
22
P02/AN
P01/AN
P00/AN
V
REF
AV
SS
V
CC
X
OUT
X
IN
V
SS
RESET
P47/KW
2
1
0
7
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
6
/KW
6
P4
Fig. 1 Pin configuration of M37630M4T–XXXFP
MITSUBISHI
ELECTRIC
1
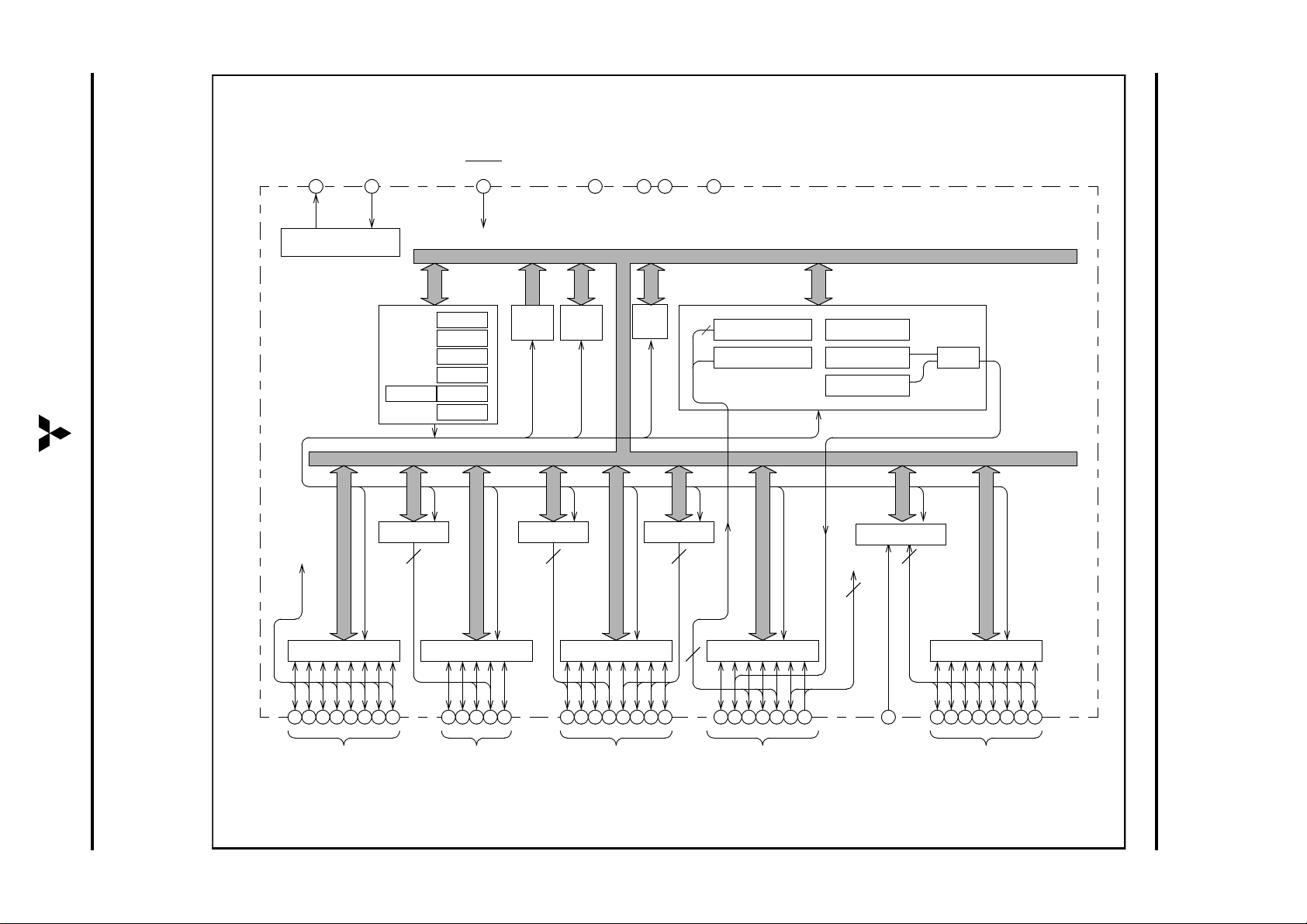
2
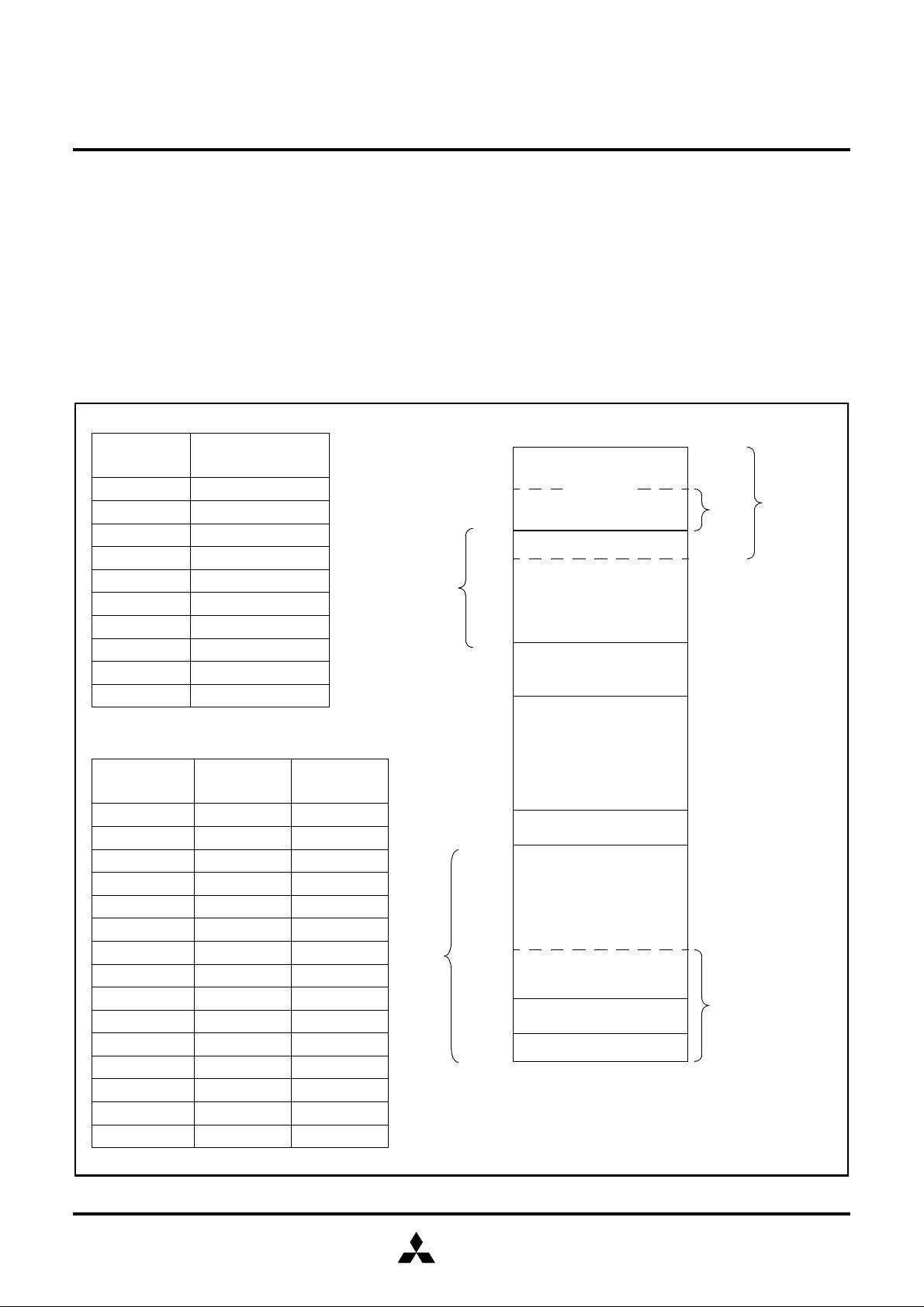
Fig. 2 Functional block diagram
M37630MXT-XXXFP FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM (PACKAGE: 44P6N-A)
Clock
output
X
OUT
Clock generating circuit
MITSUBISHI
ELECTRIC
key on
wake up
Clock
input
X
IN
1516 13 17 14 39 18
CPU
PCH (8)
2
RESET
A (8)
X (8)
Y (8)
S (8)
PCL (8)
PS (8)
Reset
input
UART
4
V
CC
RAMROM
V
WDT
SS
Serial I/OCAN
4
AV
SS
Time r X (16)
2
Time r Y (16)
Timer 1 (8)
Timer 2 (8)
Timer 3 (8)
A-D Converter
INT0, INT
PWM
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
8
1
12
P4 (8)
1011
I/O port P4
2
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
P3 (5)
56789
441234
P2 (8)
43
35363738404142
P1 (7)
3
28293031323334
19
V
input
REF
P0 (8)
I/O port P0I/O port P1I/O port P2I/O port P3
2021222324252627
7630 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
g
g
g
g
g
g
g
g
PIN DESCRIPTION
T a ble 1: Pin description
Pin Name Input/Output Description
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
7630 Group
V
AV
CC
, V
SS
SS
Power source
e
volta
Analog power
source volta
e
RESET Reset input Input
X
X
V
P0
P0
P1
P1
P1
P1
IN
OUT
REF
/AN0—
0
/AN
7
/INT
1
/INT
2
/TX
3
/CNTR
4
0
Clock input Input
Clock output Output
Reference volt-
e input
a
I/O port P0 I/O CMOS I/O ports or analog input ports
7
0
1
I/O port P1 I /O
0
Input Reference volta
Input
Power supply pins; apply 4.0 to 5.5 V to V
Ground pin for A-D converter. Connect to V
and 0 V to V
CC
SS
SS
Reset pin. This pin must be kept at “L” level for more than 2 µs, to enter the reset
state. If the crystal or ceramic resonator requires more time to stabilize, extend the
“L” level period.
Input and output pins of the internal clock
quartz–crystal resonator between the X
source is used, connect it to X
and leave X
IN
enerating circuit. Connect a ceramic or
and X
IN
pins. When an external clock
OUT
open.
OUT
e input pin for A-D converter
CMOS input port or external interrupt input port. The active ed
external interrupts can be selected. This pin will be used as V
ramming of One Time PROM Versions.
pro
e (rising or falling) of
pin during PROM
PP
CMOS I/O port or external interrupt input port. The active edge (rising or falling) of
external interrupts can be selected.
CMOS I/O port or input pin used in the bi-phase counter mode
CMOS I/O port or timer X input pin used for the event counter, pulse width measure-
ment and bi-phase counter mode
/CNTR
P1
5
/PWM
P1
6
P1
7
P2
0/SIN
P21/S
P22/S
P23/S
/URXD
P2
4
/UTXD
P2
5
P2
6/URTS
P27/U
P3
0
P3
/CTX
1
/CRX
P3
2
P3
—P3
3
P4
/KW0—
0
/KW
P4
7
OUT
CLK
RDY
CTS
1
I/O port P2
I/O port P3
4
I/O port P4 I /O
7
I/O
I/O
CMOS I/O port or timer Y input pin used for the event counter, pulse width and pulse
period measurement mode
CMOS I/O port or PWM output pin used in the PWM mode of timers 2 and 3
CMOS I/O port
CMOS I/O ports or clock synchronous serial I/O pins
CMOS I/O ports or asynchronous serial I/O pins
CMOS I/O port
CMOS I/O port or CAN transmit data pin
CMOS I/O port or CAN receive data pin
CMOS I/O port
CMOS I/O ports. These ports can be used for key-on wake-up when confi
ured as
inputs.
MITSUBISHI
ELECTRIC
3
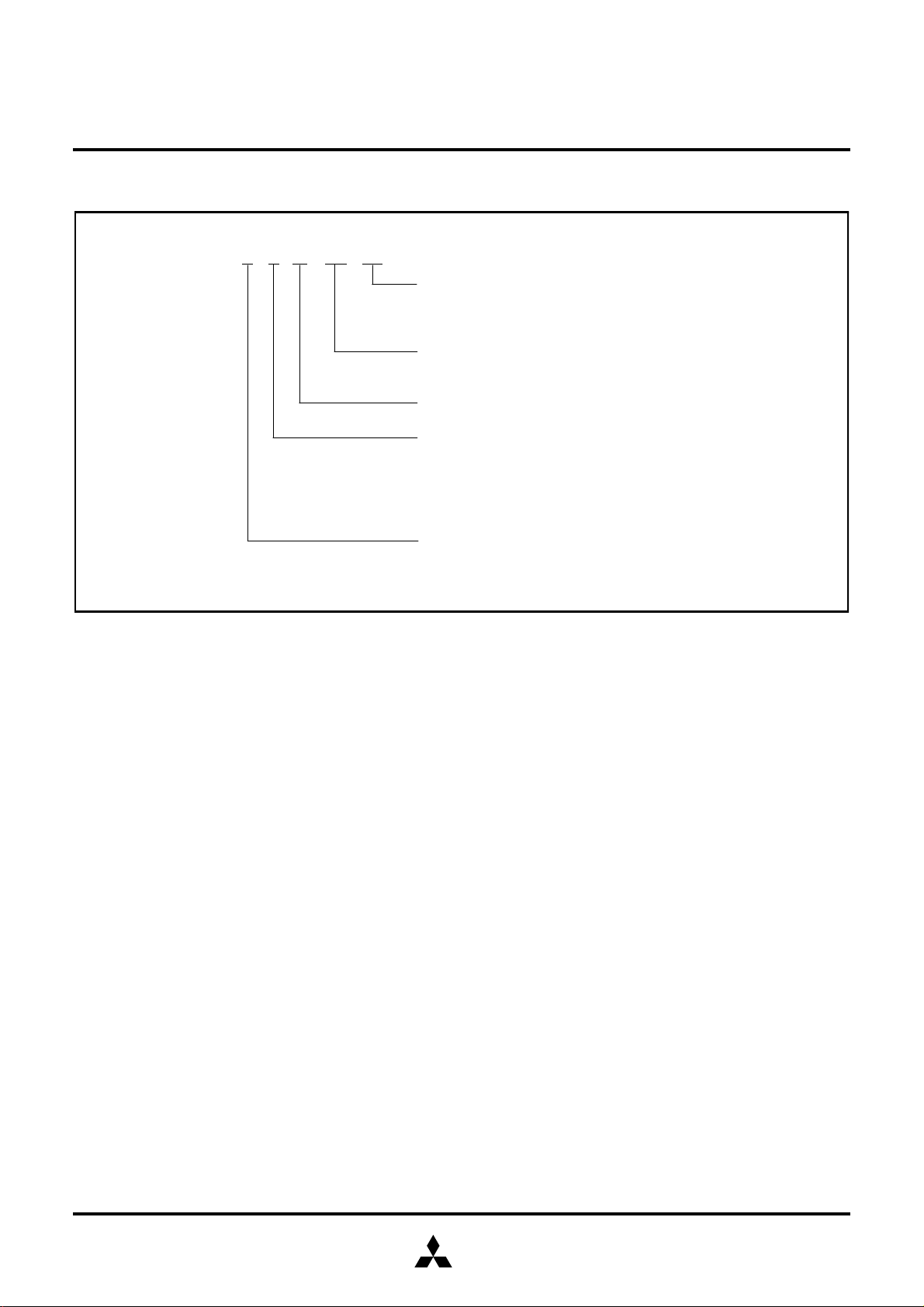
PART NUMBERING
g
g
g
Product M37630 M 4 T– XXX FP
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
7630 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
e type
Packa
FP: 44P6N-A packa
FS: 80D0 packa
ROM number
Omitted in One Time PROM version (blank) and EPROM version
T: Automotive use
ROM/PROM size
4: 16384 bytes
The first 128 bytes and the last 4 bytes of ROM are reserved areas.
They cannot be used.
e
e
Fig. 3 Part numbering
Memory type
M: Mask ROM version
E: EPROM or One Time PROM version
4
MITSUBISHI
ELECTRIC
GROUP EXPANSION
g
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
7630 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
Mitsubishi plans to expand the 7630 group as follows:
Memory Type
Support mask ROM, One Time PROM and EPROM versions.
ROM
External
60K
48K
32K
28K
24K
20K
M37630M4T
16K
12K
Mass product
M37630E4T
Memory Size
ROM/PROM size . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 6 Kb ytes
RAM size. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 512 bytes
Package
44P6N-A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.8mm-pitch plastic molded QFP
80D0 . . . . . . . . . . .0.8mm-pitch ceramic LCC (EPROM version)
Under development
8K
384 512 640 768 896 1024
RAM size (bytes)
Fig. 4 Memory expansion plan
Currently supported products are listed below:
Table 2: List of supported products
Product
M37630M4T-XXXFP Mask ROM version
M37630E4T-XXXFP 16384 512 44P6N-A One Time PROM version
M37630E4FP (16252) One Time PROM version (blank)
M37630E4FS 80D0 EPROM version
(P)ROM size (bytes)
ROM size for User ( )
RAM size (bytes) Packa
e Remarks
As of March 1998
MITSUBISHI
ELECTRIC
5
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
g
g
g
g
g
g
g
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
7630 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
The core of 7630 group microcomputers is the 7600 series CPU.
This core is based on the standard instruction set of 740 series;
however the performance is improved by allowin
same instructions as that of the 740 series in less cycles. Refer to
the 7600 Series Software Manual for details of the instruction set.
70
to execute the
CPU mode re
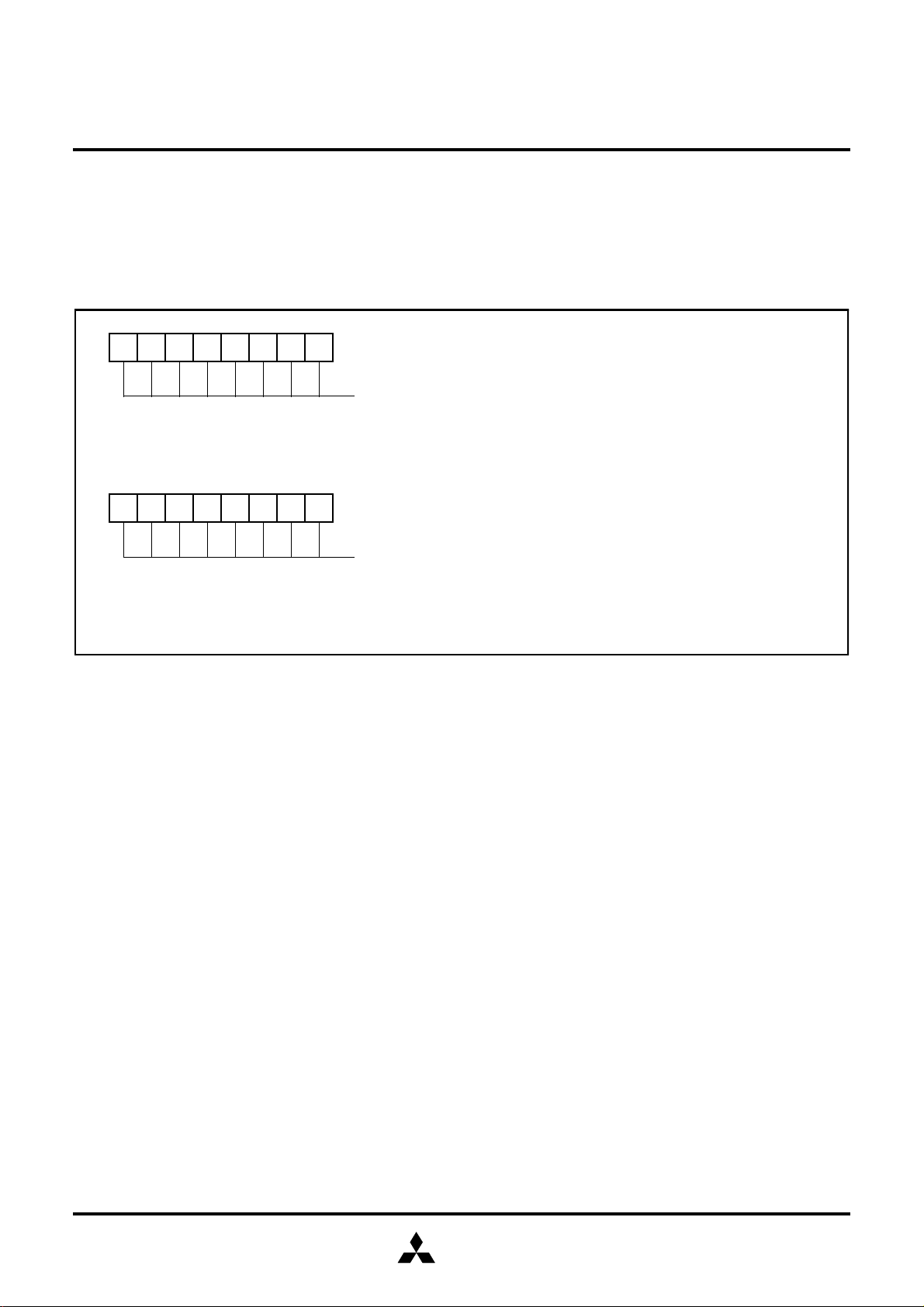
CPUM
Processor mode bits (set these bits to “00”)
b1 b0
0 0: Sin
0 1: Not used
1 0: Not used
1 1: Not used
Stack pa
Not used (“0” when read, do not write “1”)
Internal system clock selection bit
Not used (“0” when read, do not write “1”)
e selection bit
0 : 0 pa
1 : 1 pa
0 : φ=f(X
1 : φ=f(X
CPU Mode Register CPUM
The CPU mode register contains the stack page selection bit and
internal system clock selection bit. The CPU mode re
cated to address 0000
ister (address 000016)
le–chip mode
e
e
) divided by 2 (high–speed mode)
IN
) divided by 8 (middle–speed mode)
IN
.
16
ister is allo-
Fig. 5 Structure of CPU mode register
6
MITSUBISHI
ELECTRIC
MEMORY
g
g
g
g
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
7630 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
Special Function Register (SFR) Area
The special function register (SFR) area contains the registers
to functions such as I/O ports and timers.
relatin
RAM
RAM is used for data storage and for stack area of subroutine calls
and interrupts.
ROM
ROM is used for storing user’s program code as well as the interrupt vector area.
RAM area
RAM size
(byte)
192
256
384
512
640
768
896
1024
1536
2048
Address
XXXX
011F
015F
01DF
025F
02DF
035F
03DF
045F
06DF
085F
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
User RAM
Interrupt Vector Area
The interrupt vector area is for storing jump destination addresses
used at reset or when an interrupt is
enerated.
Zero Page
This area can be accessed most efficiently by means of the zero
e addressing mode.
pa
Special Page
This area can be accessed most efficiently by means of the s pecial
e addressing mode.
pa
0000
16
0040
0060
00FF
XXXX
0860
16
16
16
16
16
SFR area
CAN
SFRs
Zero page
ROM area
ROM size
(byte)
4096
8192
12288
16384
20480
24576
28672
32768
36864
40960
45056
49152
53248
57344
61440
Address
YYYY
F000
E000
D000
C000
B000
A000
9000
8000
7000
6000
5000
4000
3000
2000
1000
Fig. 6 Memory map diagram
Not used
Address
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
ZZZZ
F080
E080
D080
C080
B080
A080
9080
8080
7080
6080
5080
4080
3080
2080
1080
16
YYYY
ZZZZ
FF00
FFCA
FFFB
FFFC
FFFF
16
Reserved ROM area
16
16
16
Interrupt vector area
16
16
Reserved ROM area
16
Special page
16
16
16
16
16
16
ROM
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
MITSUBISHI
ELECTRIC
7

SPECIAL FUNCTION REGISTERS (SFR)
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
7630 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
0000
CPU mode register CPUM
16
0001
Not used
16
0002
Interrupt request register A IREQA
16
0003
Interrupt request register B IREQB
16
0004
Interrupt request register C IREQC
16
0005
Interrupt control register A ICONA
16
0006
Interrupt control register B ICONB
16
0007
Interrupt control register C ICONC
16
0008
Port P0 register P0
16
0009
Port P0 direction register P0D
16
000A
Port P1 register P1
16
000B
Port P1 direction register P1D
16
000C
Port P2 register P2
16
000D
Port P2 direction register P2D
16
000E
Port P3 register P3
16
000F
Port P3 direction register P3D
16
0010
Port P4 register P4
16
0011
Port P4 direction register P4D
16
0012
Serial I/O shift register SIO
16
0013
Serial I/O control register SIOCON
16
0014
A-D conversion register AD
16
0015
A-D control register ADCON
16
0016
Timer 1 T1
16
0017
Timer 2 T2
16
0018
Timer 3 T3
16
0019
Timer 123 mode register T123M
16
001A
Timer XL TXL
16
001B
Timer XH TXH
16
001C
Timer YL TYL
16
001D
Timer YH TYH
16
001E
Timer X mode register TXM
16
001F
Timer Y mode register TYM
16
0020
UART mode register UMOD
16
0021
UART baud rate generator UBRG
16
0022
UART control register UCON
16
0023
UART status register USTS
16
0024
UART transmit buffer register 1 UTBR1
16
0025
UART transmit buffer register 2 UTBR2
16
0026
UART receive buffer register 1 URBR1
16
0027
UART receive buffer register 2 URBR2
16
0028
Port P0 pull-up control register PUP0
16
0029
Port P1 pull-up control register PUP1
16
002A
Port P2 pull-up control register PUP2
16
002B
Port P3 pull-up control register PUP3
16
002C
Port P4 pull-up/down control register PUP4
16
002D
Interrupt polarity selection register IPOL
16
002E
Watchdog timer register WDT
16
002F
Polarity control register PCON
16
0030
CAN transmit control register CTRM
16
0031
CAN bus timing control register 1 CBTCON1
16
0032
CAN bus timing control register 2 CBTCON2
16
0033
CAN acceptance code register 0 CAC0
16
0034
CAN acceptance code register 1 CAC1
16
0035
CAN acceptance code register 2 CAC2
16
0036
CAN acceptance code register 3 CAC3
16
0037
CAN acceptance code register 4 CAC4
16
0038
CAN acceptance mask register 0 CAM0
16
0039
CAN acceptance mask register 1 CAM1
16
003A
CAN acceptance mask register 2 CAM2
16
003B
CAN acceptance mask register 3 CAM3
16
003C
CAN acceptance mask register 4 CAM4
16
003D
CAN receive control register CREC
16
003E
CAN transmit abort register CABORT
16
003F
Reserved
16
0040
CAN transmit buffer register 0 CTB0
16
0041
CAN transmit buffer register 1 CTB1
16
0042
CAN transmit buffer register 2 CTB2
16
0043
CAN transmit buffer register 3 CTB3
16
0044
CAN transmit buffer register 4 CTB4
16
0045
CAN transmit buffer register 5 CTB5
16
0046
CAN transmit buffer register 6 CTB6
16
0047
CAN transmit buffer register 7 CTB7
16
0048
CAN transmit buffer register 8 CTB8
16
0049
CAN transmit buffer register 9 CTB9
16
004A
CAN transmit buffer register A CTBA
16
004B
CAN transmit buffer register B CTBB
16
004C
CAN transmit buffer register C CTBC
16
004D
CAN transmit buffer register D CTBD
16
004E
Reserved
16
004F
Reserved
16
0050
CAN receive buffer register 0 CRB0
16
0051
CAN receive buffer register 1 CRB1
16
0052
CAN receive buffer register 2 CRB2
16
0053
CAN receive buffer register 3 CRB3
16
0054
CAN receive buffer register 4 CRB4
16
0055
CAN receive buffer register 5 CRB5
16
0056
CAN receive buffer register 6 CRB6
16
0057
CAN receive buffer register 7 CRB7
16
0058
CAN receive buffer register 8 CRB8
16
0059
CAN receive buffer register 9 CRB9
16
005A
CAN receive buffer register A CRBA
16
005B
CAN receive buffer register B CRBB
16
005C
CAN receive buffer register C CRBC
16
005D
CAN receive buffer register D CRBD
16
005E
Reserved
16
005F
Reserved
16
Fig. 7 Memory map of special register (SFR)
8
MITSUBISHI
ELECTRIC
I/O PORTS
g
g
g
g
g
g
g
g
g
g
g
The 7630 group has 35 programmable I/O pins and one input pin
ed in five I/O ports (ports P0 to P4). The I/O ports are con-
arran
trolled by the correspondin
ters; each I/O pin can be controlled separately.
When data is read from a port confi
latch’s contents are read instead of the port level. A port confi
port registers and port direction regis-
ured as an output port, the port
ured
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
7630 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
as an input port becomes floatin
written to this port will affect the port latch only; the port remains
.
floatin
Refer to Structure of port- and port direction re
port I/Os (1) and Structure of port I/Os (2).
and its level can be read. Data
isters, Structure of
70
Port Pi re
Pi
Port Pij control bit (j = 0 to 7)
0 : “L” level
1 : “H” level
Note : The control bits corresponding to P10, P35, P36 and P37 are not used
70
Port Pi direction re
PiD
Port Pij direction control bit (j = 0 to 7)
0 : Port confi
1 : Port confi
Note : The direction control bits corresponding to P10, P11, P35, P36 and
Fig. 8 Structure of port- and port direction registers
ister (i = 0 to 4) (address 000816 + 2 · i)
(“0” when read, do not write “1”).
ister (i = 0 to 4) (address 000916 + 2 · i)
ured as input
ured as output
P3
are not used (“0” when read, do not write “1”). Port direction re-
7
gisters are undefined when read (write only).
MITSUBISHI
ELECTRIC
9
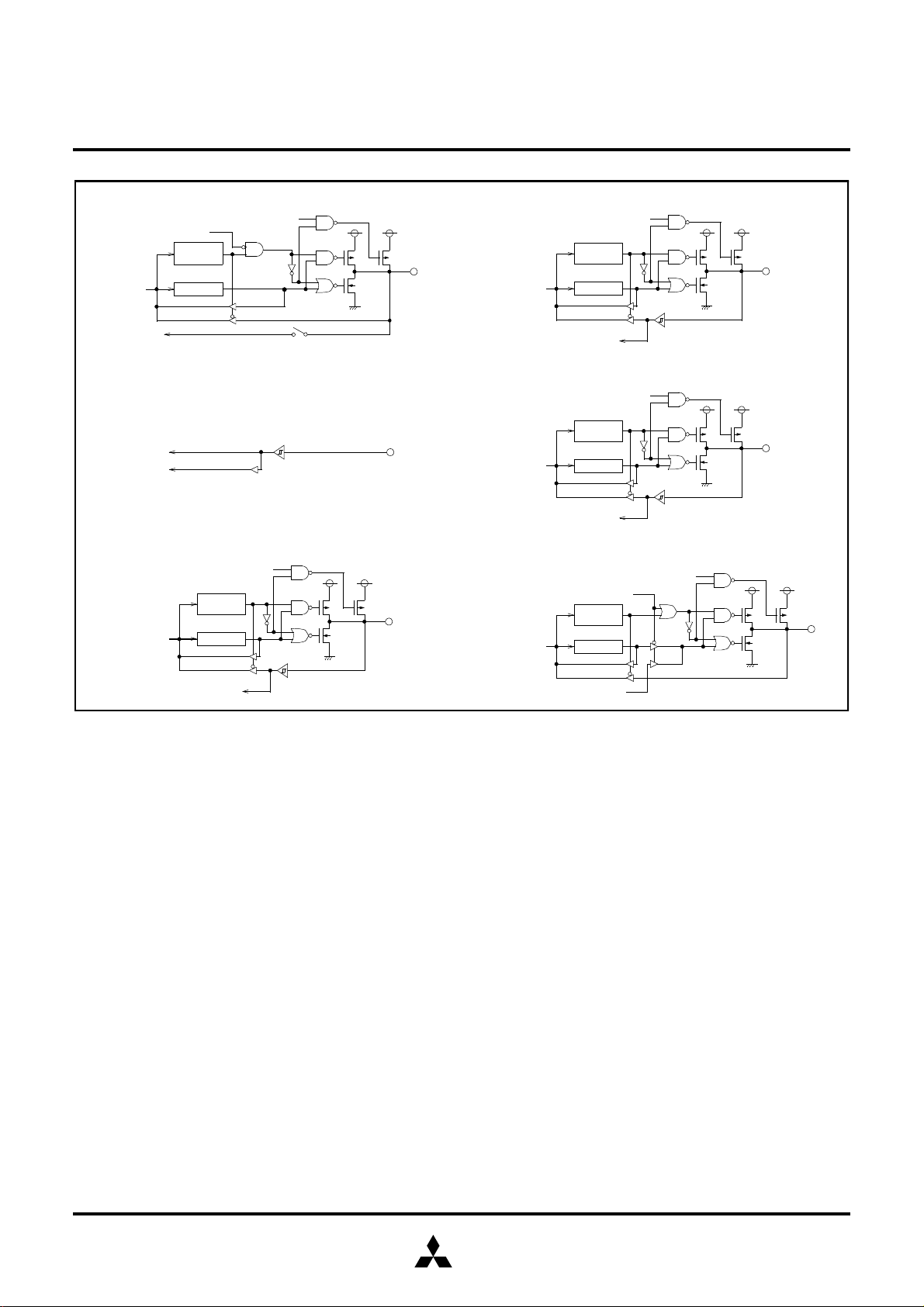
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
7630 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
(1) Ports P0
Data bus
/AN0 to P07/AN
0
Analog input selection
ADC input
(2) Port P11/INT
Interrupt input
Data bus
(3) Port P12/INT
Data bus
Direction
register
Port latch
0
1
Pull-up control bit
Direction
register
Port latch
7
Pull-up control bit
Analog input selection
(4) Port P13/TX
Timer bi-phase mode input
Data bus
0
Pull-up control bit
Port latch
direction
register
(5) Ports P14/CNTR0, P15/CNTR
Pull-up control bit
Direction
register
Data bus
Timer bi-phase mode input
Port latch
(6) Port P16/PWM
Pull-up control bit
PWM output enable
Direction
register
Data bus
Port latch
1
Interrupt input
Fig. 9 Structure of port I/Os (1)
PWM output
10
MITSUBISHI
ELECTRIC
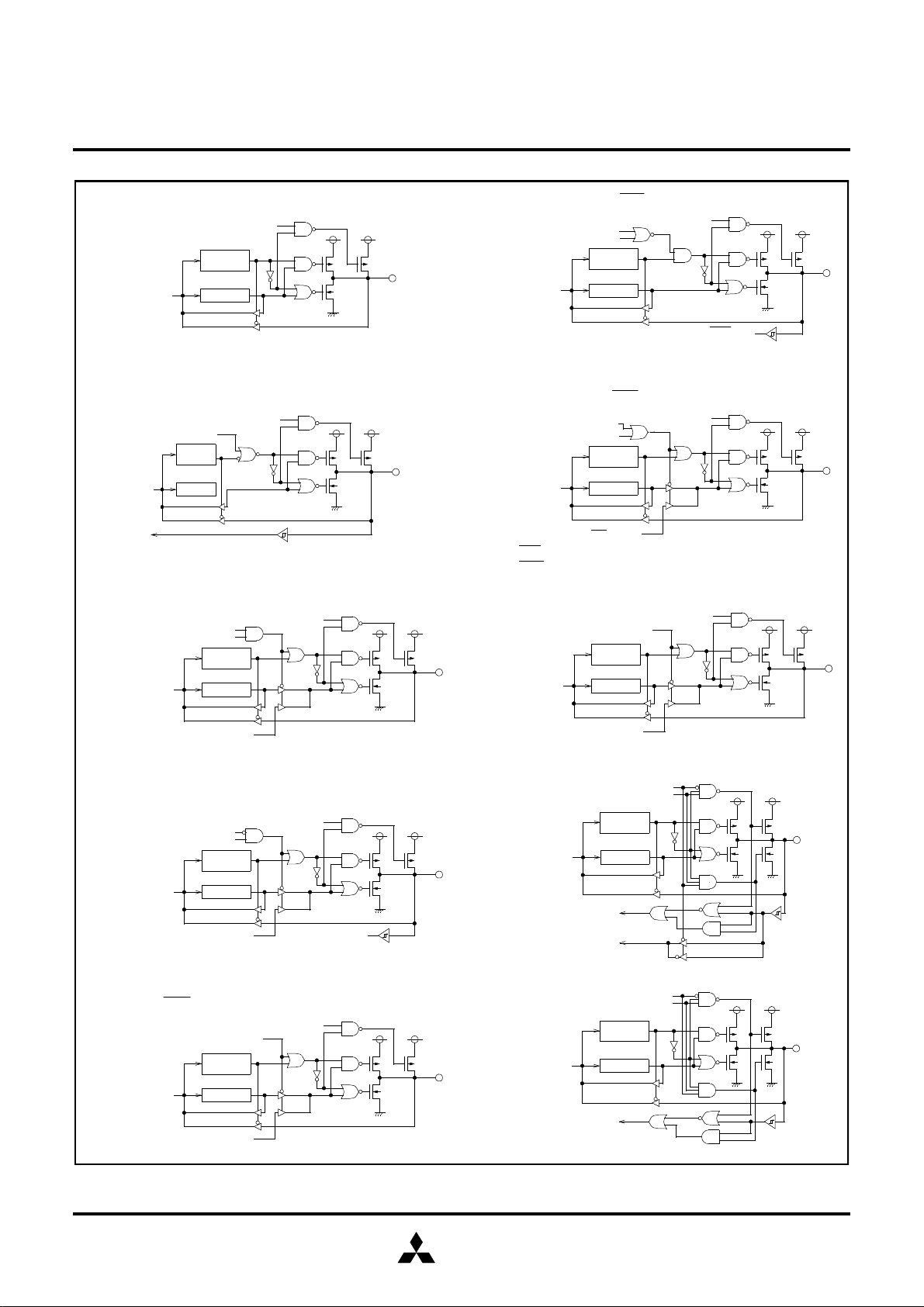
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
7630 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
(7) Ports P17, P30, P33, P3
Pull-up control bit
Direction
register
IN
Direction
register
Port latch
OUT
Port latch
Pull-up control bit
Direction
register
Port latch
Data bus
(8) Port P20/S
SIO Port Select
Data bus
SIO1 input
(9) Port P21/S
SIO port selection bit
Transmit complete signal
Data bus
4
Pull-up control bit
(12) Ports P24/URXD, P27/U
Transmission or reception* in
Transmit or receive* enable bit
Data bus
progress
Direction
register
Port latch
(13) Ports P25/UTXD, P26/U
Transmission or reception** in
Transmit or receive** enable bit
Data bus
(*) for U
CTS
(**) for U
RTS
progress
Direction
register
Port latch
U
or U
output
TXD
RTS
(14) Port P31/CTX
CAN port selection bit
Direction
register
Data bus
Port latch
CTS
Pull-up control bit
U
RTS
Pull-up control bit
Pull-up control bit
RXD
or U
CTS
input
SIO output
(10) Port P22/S
(11) Port P23/S
CLK
Clock selection bit
Port selection bit
direction
Data bus
SRDY output selection bit
Data bus
Port latch
SIO clock output
RDY
Direction
Port latch
SRDY output
Pull-up control bit
register
Pull-up control bit
register
Fig. 10 Structure of port I/Os (2)
External clock input
CTX output
(15) Port P3
/CRX
2
CAN dominant level control bit
Pull-up
/down control bit
Direction
register
Data bus
Port latch
CAN interrupt
CRX input
(16) Ports P40/KW0 to P47/KW
Key-on wake-up control bit
Pull-up
/down control bit
Direction
register
Data bus
Key-on wake-up interrupt
Port latch
7
MITSUBISHI
ELECTRIC
11
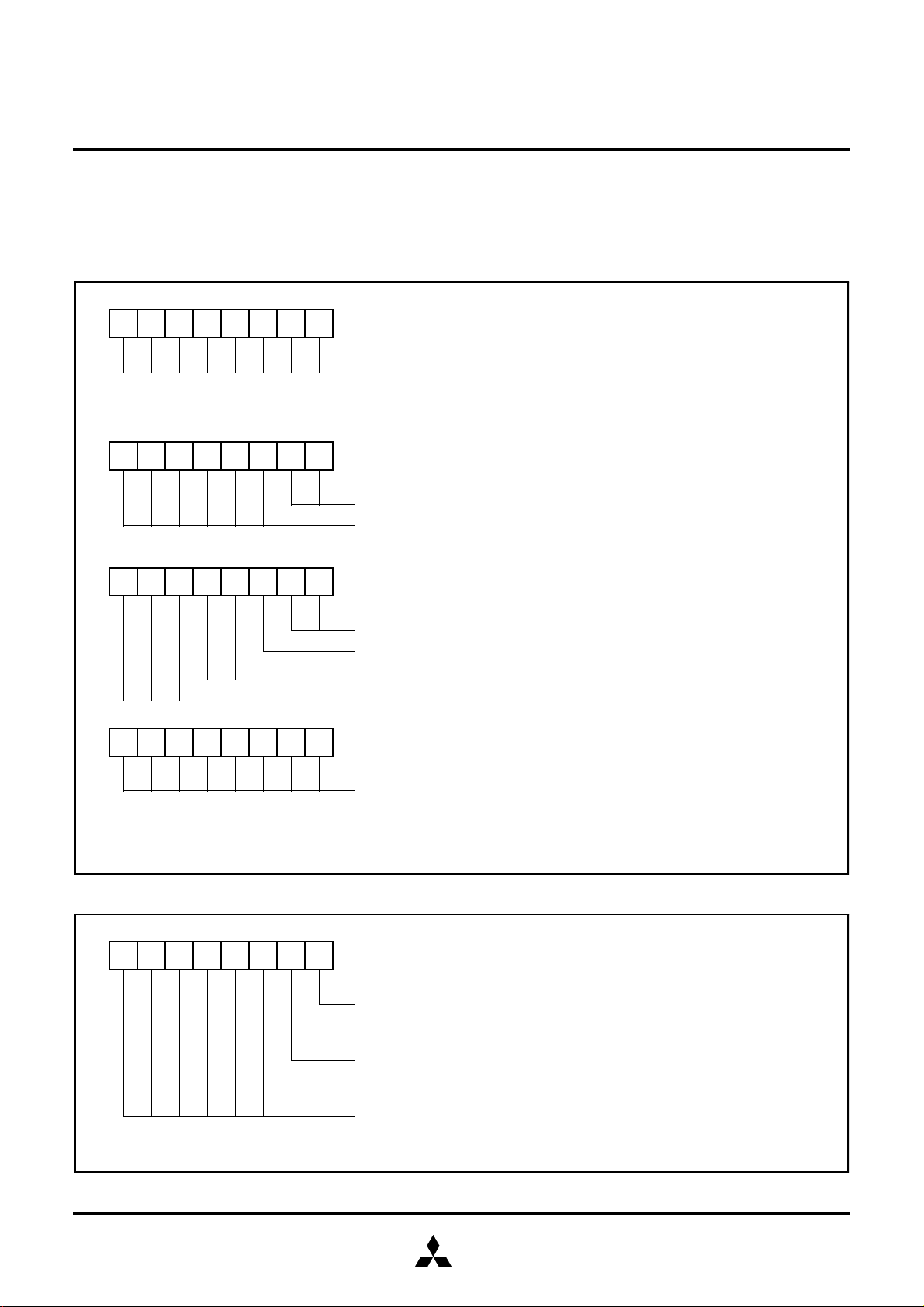
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
g
g
g
g
g
g
g
g
g
g
7630 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
Port Pull-up/pull-down Function
Each pin of ports P0 to P4 except P11 is equipped with a programmable pull-up transistor. P3
equipped with pro
pull-up function of P0 to P3 can be controlled by the correspondin
70
70
70
70
rammable pull-down transistors as well. The
/CRX and P40/KW0 to P47/KW7 are
2
Port Pi pull-up control re
PUP0, PUP2
Pij pull-up transistor control bit (j = 0 to 7)
0 : Pull-up transistor disabled
1 : Pull-up transistor enabled
Port P1 pull-up control register (address 002916)
PUP1
Not used (“0” when read, do not write “1”)
pull-up transistor control bit (j = 2 to 7)
P1
j
Port P3 pull-up control register (address 002B16)
PUP3
P3j pull-up transistor control bit (j = 0, 1)
P32 pull-up/down transistor control bit
pull-up transistor control bit (j = 3, 4)
P3
j
Not used (“0” when read, do not write “1”)
Port P4 pull-up/down control re
PUP4
port pull-up control registers (see Structure of port pull-up/down
control re
can be controlled by the correspondin
ters to
polarity control re
isters). The pull-up/down function of ports P32 and P4
port pull-up/pull-down regis-
ether with the polarity control register (see Structure of
ister).
ister (address 002816 + i) (i = 0, 2)
ister (address 002C16)
P4j pull-up/down transistor control bit (j = 0 to 7)
0 : Pull-up/down transistor disabled
1 : Pull-up/down transistor enabled
Fig. 11 Structure of port pull-up/down control regist ers
70
Polarity control register (address 002F16)
PCON
Key-on wake-up polarity control bit
0 : Low level active
1 : Hi
CAN module dominant level control bit
0 : Low level dominant
1 : Hi
Not used (undefined when read)
Fig. 12 Structure of polarity control register
h level active
h level dominant
12
MITSUBISHI
ELECTRIC

MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
g
g
g
g
g
g
g
g
g
g
7630 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
Port Overvoltage Application
When configured as input ports, P1 to P4 may be subjected to over-
e (VI>VCC) if the input current to the applicable port is limited
volta
to the specified values (see “Table 8:”). Use a serial resistor of
appropriate size to limit the input current. To estimate the resistor
value, assume the port volta
Notes:
• Subjectin
Assure to keep V
ports to overvoltage may effect the supply voltage.
CC
e to be VCC at overvoltage condition.
and VSS within the target limits.
• Avoid to subject ports to overvolta
5.5 V.
• The overvolta
the internal port protection circuits has a ne
ports noise immunity. Therefore, careful and intense testin
the tar
“countermeasures a
manual.
• Port P0 must not be subjected to overvolta
e condition causing input current flowing through
et system’s noise immunity is required. Refer to the
ainst noise” of the corresponding users
e causing VCC to rise above
ative effect on the
e conditions.
of
MITSUBISHI
ELECTRIC
13

INTERRUPTS
g
g
g
g
g
g
g
g
g
g
g
g
There are 24 interrupts: 6 external, 17 internal, and 1 software.
Interrupt Control
Each interrupt except the BRK instruction interrupt has both an
interrupt request bit and an interrupt enable bit, and is controlled by
the interrupt disable fla
interrupt request and enable bits are “1” and the interrupt dis-
in
able fla
software. Interrupt request bits can be cleared by software but cannot be set by software. The BRK instruction interrupt and reset cannot be disabled with any fla
except the BRK instruction interrupt and reset. If several interrupt
requests occur at the same time, the interrupt with the hi
ity is accepted first.
is “0”. Interrupt enable bits can be cleared or set by
Interrupt Operation
Upon acceptance of an interrupt, the following operations are automatically performed.
1. The processin
. An interrupt occurs when the correspond-
or bit. The I flag disables all interrupts
hest prior-
being executed is stopped.
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
7630 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
2. The contents of the pro
ister are automatically pushed onto the stack.
re
3. Concurrently with the push operation, the interrupt jump
destination address is read from the vector table into the
ram counter.
pro
4. The interrupt disable fla
request bit is cleared.
Notes on use
When the active edge of an external interrupt (INT0, INT1, CNTR0,
, CWKU or KOI) is changed, the corresponding interrupt
CNTR
1
request bit may also be set. Therefore, take the followin
(1) Disable the external interrupt which is selected.
(2) Chan
(3) Clear the interrupt request bit to “0”.
(4) Enable the external interrupt which is selected.
e the active edge in interrupt edge selection register.
(in the case of CNTR
: Timer Y mode register)
CNTR
1
ram counter and processor status
is set and the corresponding interrupt
sequence.
: Timer X mode register; in the case of
0
14
MITSUBISHI
ELECTRIC
.
g
g
g
g
g
g
g
g
g
g
g
g
g
g
g
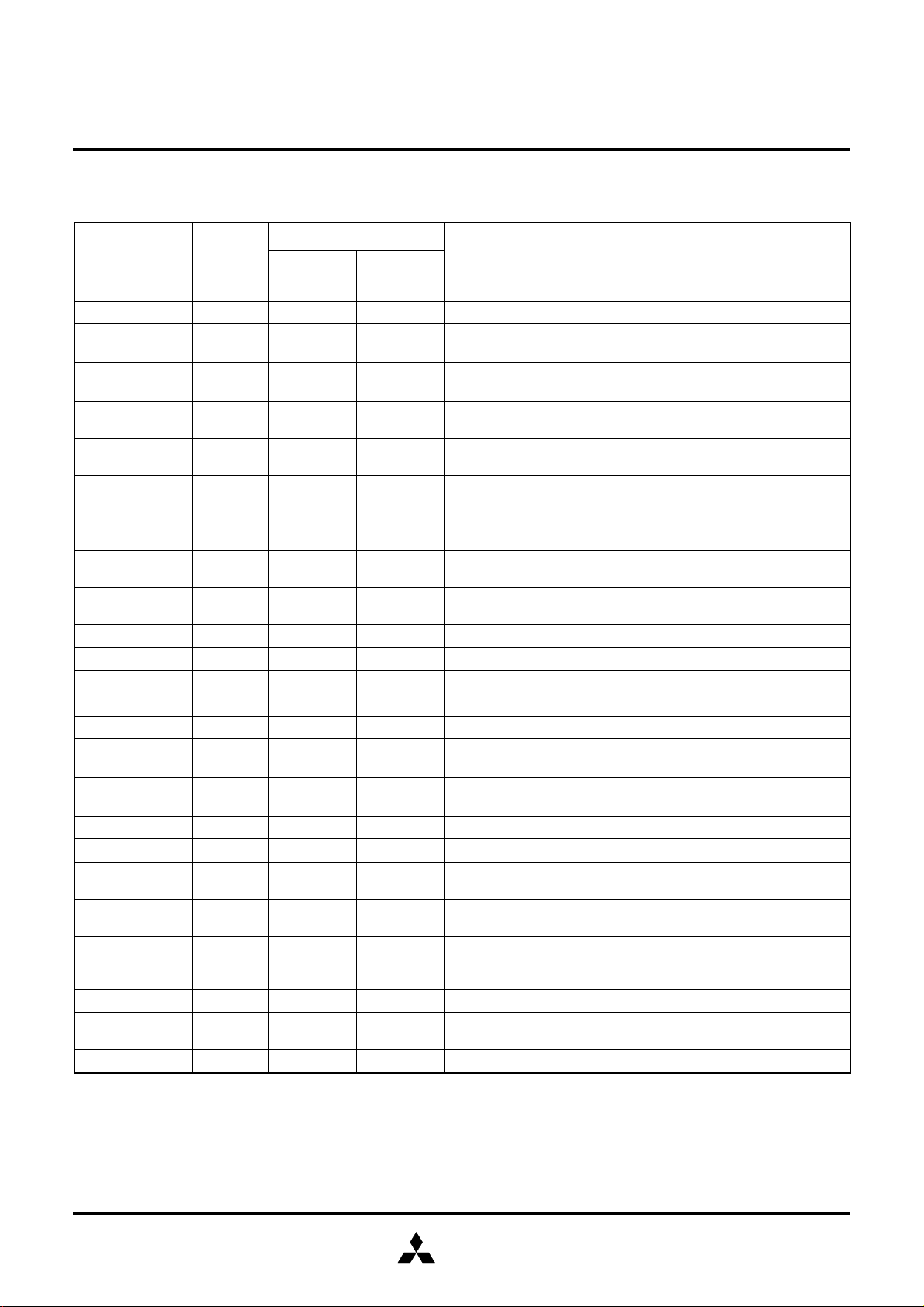
Table 3: Interrupt vector addresses and priority
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
7630 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
Interrupt source Priority
Reset (Note 2)
Watchdo
INT
INT
CAN
transmit
timer 2
0
1
successful
CAN successful
receive
CAN overrun 7
CAN error
passive
CAN error bus off 9
CAN wake up 10
Timer X 11
Timer Y 12
Timer 1 13
Timer 2 14
Timer 3 15
0
CNTR
CNTR
1
16
17
UART receive 18
UART transmit 19
UART transmit
buffer empty
UART receive
error
20
21
Vector Address (Note 1)
h Low
Hi
1
3
4
5
6
8
FFFB
FFF9
FFF7
FFF5
FFF3
FFF1
FFEF
FFED
FFEB
FFE9
FFE7
FFE5
FFE3
FFE1
FFDF
FFDD
FFDB
FFD9
FFD7
FFD5
FFD3
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
FFFA
FFF8
FFF6
FFF4
FFF2
FFF0
FFEE
FFEC
FFEA
FFE8
FFE6
FFE4
FFE2
FFE0
FFDE
FFDC
FFDA
FFD8
FFD6
FFD4
FFD2
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
Interrupt Request Generatin
Conditions
At Reset Non-maskable
At Watchdog timer underflow Non-maskable
At detection of either rising or falling
e of INT0 interrupt
ed
At detection of either rising or falling
e of INT1 interrupt
ed
At CAN module successful
transmission of messa
e
At CAN module successful reception
of messa
e
If CAN module receives message
when receive buffers are full.
When CAN module enters into error
passive state
When CAN module enters into bus
off state
When CAN module wakes up via
CAN bus
At Timer X underflow or overflow
At Timer Y underflow
At Timer 1 underflow
At Timer 2 underflow
At Timer 3 underflow
At detection of either rising or falling
e in CNTR0 input
ed
At detection of either rising or falling
e in CNTR1 input
ed
At completion of UART receive Valid when UART is selected
At completion of UART transmit Valid when UART is selected
At UART transmit buffer empty Valid when UART is selected
When UART reception error occurs. Valid when UART is selected
Remarks
External Interrupt
(active ed
e selectable)
External Interrupt
(active ed
e selectable)
Valid when CAN module is
activated and request transmit
Valid when CAN module is
activated
Valid when CAN module is
activated
Valid when CAN module is
active
Valid when CAN module is
active
External Interrupt
(active ed
e selectable)
External Interrupt
(active ed
e selectable)
Serial I/O 22
A-D conversion 23
Key-on wake-up 24
BRK instruction 25
FFD1
FFCF
FFCD
FFCB
16
16
16
16
FFD0
FFCE
FFCC
FFCA
At completion of serial I/O data
16
transmit and receive
At completion of A-D conversion
16
At detection of either rising or falling
16
16
e of P4 input
ed
At BRK instruction execution Non-maskable
Valid when serial I/O is
selected
External Interrupt
(active edge selectable)
Notes 1: Vector addresses contain interrupt jump destination address
2 : Reset function in the same way as an interrupt with the hi
hest priority
MITSUBISHI
ELECTRIC
15
 Loading...
Loading...