Mitsubishi M37560MF-XXXGP, M37560MF-XXXFP, M37560ME-XXXGP, M37560ME-XXXFP, M37560MD-XXXGP Datasheet
...
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
7560 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
DESCRIPTION
The 7560 group is the 8-bit microcomputer based on the 740 family core technology.
The 7560 group has the LCD drive control circuit, an 8-channel AD/D-A converter, UART and PWM as additional functions.
The various microcomputers in the 7560 group include variations
of internal memory size and packaging. For details, refer to the
section on part numbering.
For details on availability of microcomputers in the 7560 Group,
refer the section on group expansion.
FEATURES
Basic machine-language instructions....................................... 71
•
The minimum instruction execution time............................ 0.5 µs
•
Memory size
•
ROM ................................................................ 32 K to 6 0 K bytes
RAM ............................................................... 1024 to 2560 bytes
Programmable input/output ports ............................................. 55
•
Software pull-up resistors .................................................... Built-in
•
Output ports ................................................................................. 8
•
Input ports .................................................................................... 1
•
Interrupts .................................................. 17 sources, 16 vectors
•
(at 8 MHz oscillation frequency)
(includes key input interrupt)
Timers ........................................................... 8-bit ✕ 3, 16-bit ✕ 2
•
Serial I/O1 ..................... 8-bit ✕ 1 (UART or Clock-synchronous)
•
Serial I/O2 .................................... 8-bit ✕ 1 (Clock-synchronous)
•
PWM output .................................................................... 8-bit ✕ 1
•
A-D converter .................................................. 8-bit ✕ 8 channels
•
D-A converter .................................................. 8-bit ✕ 2 channels
•
LCD drive control circuit
•
Bias ................................................................................... 1/2, 1/3
Duty ............................................................................ 1/2, 1/3, 1/4
Common output .......................................................................... 4
Segment output......................................................................... 40
2 Clock generating circuits
•
(connect to external ceramic resonator or quartz-crystal oscillator)
Watchdog timer ............................................................. 14-bit ✕ 1
•
Power source voltage ................................................ 2.2 to 5.5 V
•
Power dissipation
•
In high-speed mode ...........................................................40 mW
(at 8 MHz oscillation frequency, at 5 V power source voltage)
In low-speed mode..............................................................6 0 µW
(at 32 kHz oscillation frequency, at 3 V power source voltage)
Operating temperature range ...................................– 20 to 85°C
•
APPLICATIONS
Camera, household appliances, consumer electronics, etc.
PIN CONFIGURATION (TOP VIEW)
0
1
2
3
4
5
1
1
1
1
1
G
G
G
G
G
S
S
E
S
E
S
E
E
S
E
1
7
6
4
5
L
N
N
N
N
V
/
/
/
/
7
6
5
4
6
6
6
6
P
P
P
P
A
A
A
A
A
L K 2
S E G
S E G
S E G
S E G
S E G
S E G
S E G
S E G
S E G
S E G
V
A V
C O M
C O M
C O M
C O M
V
R E F
V
V
1
G
S
E
E
8 1
9
8 2
8
8 3
7
8 4
6
8 5
5
8 6
4
8 7
3
8 8
2
8 9
1
9 0
0
9 1
C C
9 2
9 3
S S
9 4
3
9 5
2
9 6
1
9 7
0
9 8
L 3
9 9
L 2
10 0
C
2
1 234567891 01 11 21 314151617181 9202 122232425262 72 82 93 0
1
C
9
8
0
1
2
3
5
6
7
8
1
1
G
G
6
7
1
1
/
/
G
G
1
0
3
3
S E
S E
S E
P
S
S
E
P
4
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
G
G
G
G
G
G
G
G
/
/
/
/
2
3
4
5
3
3
3
3
S E
S E
S E
S E
P
P
P
P
G
/
/
/
/
/
6
7
0
1
2
3
0
0
3
0
S E
S E
S E
S E
S E
P
P
P
P
P
M37560MF-XXXFP
2
1
1
0
1
0
2
3
N
N
/
/
1
2
C
C
S
S
/
/
2
3
6
6
A
U T
P
P
A
L K 2
1
0
A
A
N
N
R
R
/
/
/
2
2
6
5
I
/
/
P
D
5
4
S
O
/
/
R T
5
5
0
S
7
/
P
P
6
C N T
C N T
5
1
P
A
N
6
P
A D T / D
P
1
1
0
P
P
M
M
R
S
/
/
/
3
2
/
/
7
0
1
5
5
4
5
5
P
P
R T
L K
P
D Y
P
P
P W
P W
9
0
1
2
4
5
6
7
8
3
2
3
3
3
3
3
G
G
G
G
G
G
/
/
/
/
/
/
3
4
5
6
7
0
0
0
0
0
0
S E
P
1
C
S
/
6
4
P
1
S E
S E
S E
S E
P
P
P
S E
P
P
2
1
T
D
D
T
T
X
X
O
T
R
/
T
/
/
/
5
4
2
1
4
4
/φ/
4
4
3
P
P
P
P
I N
I N
4
U
P
9
3
3
3
3
3
G
G
G
G
G
/
/
/
/
/
1
2
3
4
5
1
1
1
1
1
S E
S E
S E
P
P
P
S E
P
P
51525 35 45 55 65 7585 96 06 162636 46 56 66 76 86 97 0717 27 37 47 57 67 77 87 98 0
5 0
P 1
4 9
4 8
4 7
46
4 5
4 4
4 3
4 2
4 1
4 0
3 9
3 8
3 7
3 6
3 5
3 4
3 3
3 2
3 1
6
0
7
5
4
4
7
7
7
7
P
P
P
P
P
6
P 1
7
P 2
0
P 2
1
P 2
2
P2
3
P 2
4
P2
5
P 2
6
P 2
7
V
SS
X
OUT
X
IN
X
COUT
X
CIN
R E S E T
P 70/ I N T
P 7
1
P 7
2
P 7
3
0
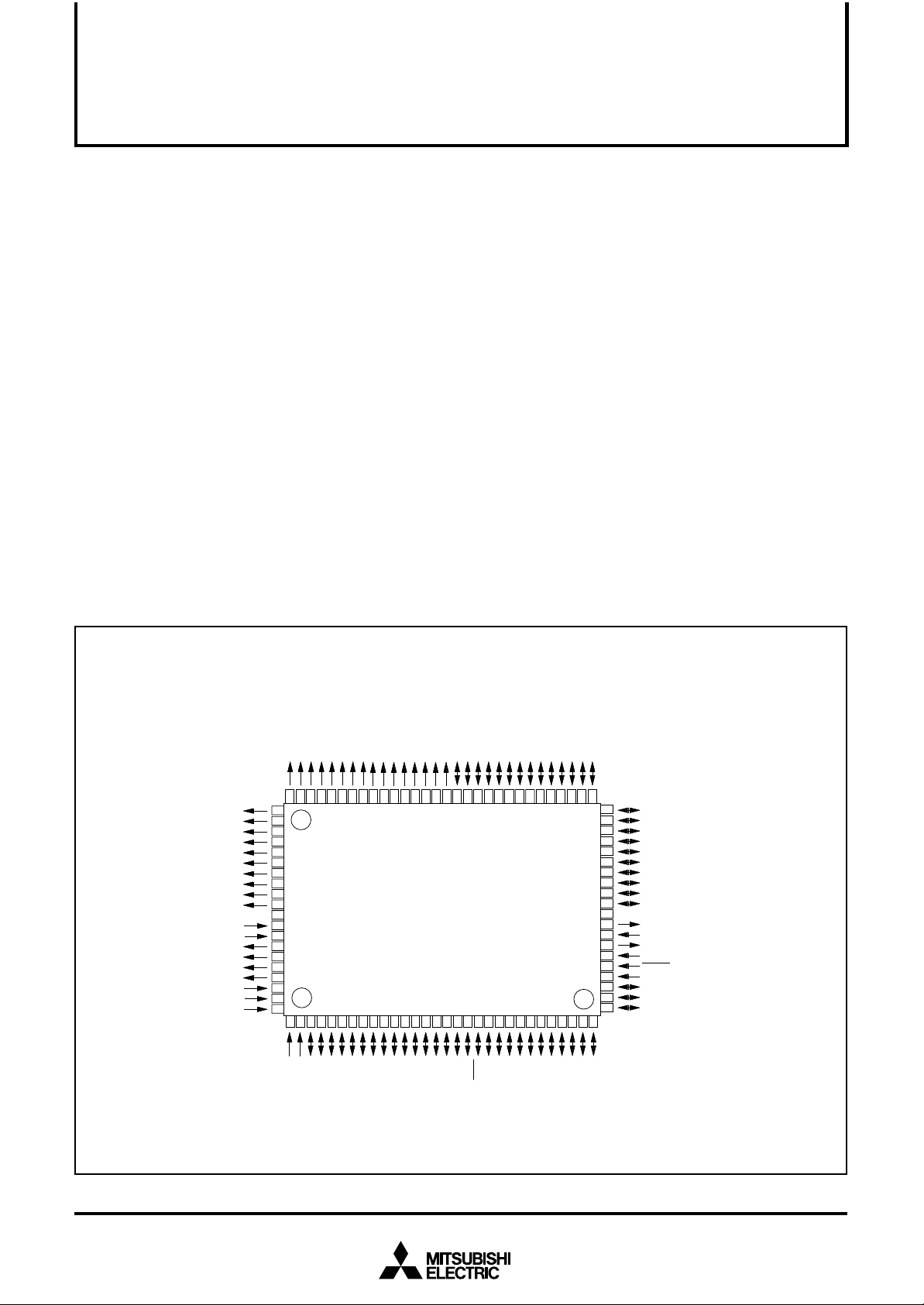
Package type : 100P6S-A
Fig. 1 Pin configuration of M37560MF-XXXFP
PIN CONFIGURATION (TOP VIEW)
3
4
5
6
1
1
1
1
G
G
G
G
S
E
S
E
S
E
S
E
S E G
S E G
S E G
S E G
S E G
S E G
S E G
SEG
S E G
S E G
SEG
SEG
S E G
V
AV
C O M
C O M
COM
COM
V
REF
V
V
V
1 2
1 1
1 0
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
CC
SS
3
2
1
0
L 3
L2
C
2
C
1
L 1
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
0 01
1 2345678910111 21 31 41 51 61 71 81 92 02 12 22 32 42 5
9
8
0
1
2
4
5
1
1
G
G
7
1
/
/
G
1
0
3
3
S E
S E
S E
P
P
S
E
3
2
2
2
2
2
G
G
/
/
2
3
3
3
S E
S E
P
P
2
G
G
G
G
/
/
/
/
4
5
6
7
3
3
3
3
S E
S E
S E
P
P
P
P
M37560MF-
6
2
G
/
0
0
S E
S E
P
XXX
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
7560 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
8
9
0
1
3
4
7
2
2
2
3
G
/
1
0
S E
P
3
G
G
G
G
/
/
/
/
2
3
4
5
0
0
0
0
S E
S E
S E
S E
P
P
P
P
GP
5
2
3
G
/
6
0
S E
P
6
3
G
/
7
0
S E
P
7
3
3
3
3
G
G
G
G
/
/
/
/
0
1
2
3
1
1
1
1
S E
S E
S E
P
P
P
P
5 15253545556575859606 1626364656 66 76 86 97 07 17 27 37 47 5
5 0
4 9
4 8
4 7
4 6
45
4 4
4 3
42
41
4 0
3 9
3 8
3 7
3 6
35
3 4
33
3 2
31
30
29
2 8
2 7
2 6
P14/SEG
P15/SEG
P1
6
P1
7
P2
0
P2
1
P2
2
P2
3
P2
4
P2
5
P2
6
P2
7
V
SS
X
OUT
X
IN
X
COUT
X
CIN
RESET
P70/INT
P7
1
P7
2
P7
3
P7
4
P7
5
P7
6
38
39
0
7
6
5
N
N
N
/
/
/
6
5
7
6
6
6
A
A
A
A
P
P
P
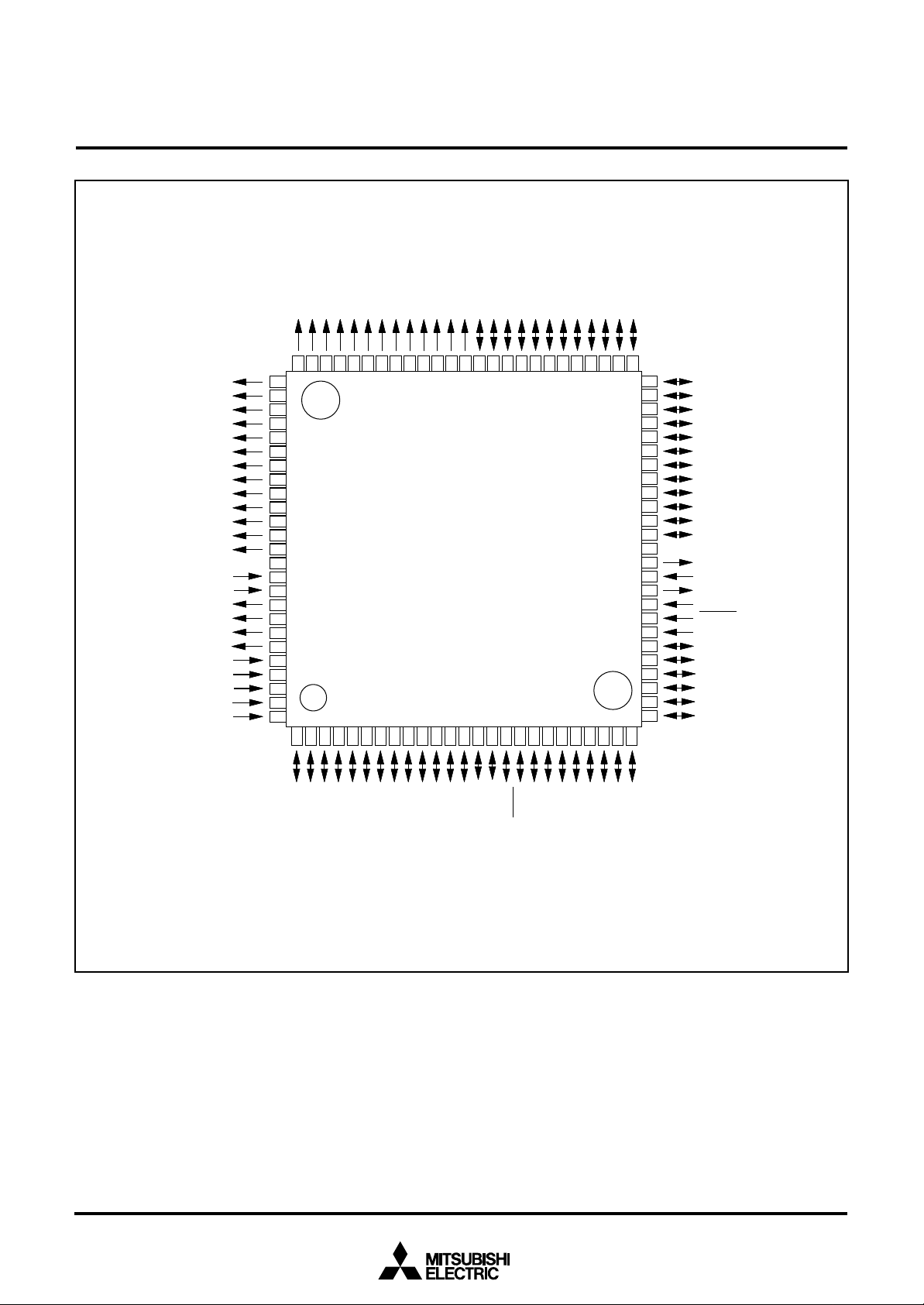
Package type : 100P6Q-A
Fig. 2 Pin configuration of M37560MF-XXXGP
4
2
3
N
N
N
/
/
/
4
1
2
6
P
C
C
S
S
/
/
2
3
6
6
A
U T
A
L K 2
A
P
P
L K 2
1
1
0
2
1
0
A
N
N
/
/
2
2
I
D
S
O
/
/
0
S
7
/
6
5
1
N
A
P
A D T / D
6
P
P
1
A
/
6
5
P
C N T
0
P
P
R
R
/
/
3
2
/
/
5
5
5
4
R T
R T
P
P
5
5
P W
C N T
P
P
1
1
0
1
D
D
X
M
/
1
5
P W
P
X
M
C
T
R
R
/
/
S
5
4
S
/
/
4
/
0
5
D Y
P
4
6
7
4
P
P
4
P
L K
P
U
0
7
1
2
T
4
7
T
T
P
P
O
/
/
T
1
2
4
4
/φ/
3
I N
I N
P
P
4
P
2
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
I
N
T
1
,
I
N
T
2
N
T
R
0
,
C
N
T
R
1
D
A
1
A
D
T
C
P
U
A
X
S
P
C
H
C
L
P
S
R
E S E
T
C
C
V
S
S
5
V
)
0
V
)
R O
M
A
M
5
9
1
0
P
4 ( 8 )P
2 ( 8
)
0 ( 8
)
P
1 ( 8
)
P
6 ( 8
)
P
7 ( 8
)
P
3 ( 8
)
P
5 ( 8
)
1
2
0
0
9
8
9
7
9
6
5
4
0
8
9
8
7
6
5
8
4
3
2
1
0
9
7
8
7
6
5
7
4
7
3
7
8
5
9
0
1
6
2
3
4
9
0
1
2
5
3
4
5
6
1
4
2
3
4
5
4
6
7
8
5
6
7
8
9
0
1
2
9
0
2
1
2
2
3
4
2
5
6
6
7
2
7
8
9
0
3
1
2
3
4
4
5
6
8
9
0
3
2
1
2
3
1
4
5
6
7
8
C
I
N
X
C
O U
T
X
N U
T
X
C
O U
T
X
I
N
I
/
O
1
(
8
)
V
R
E
F
A
V
S
S
L
1
1
2
L
2
V
L
3
C
O
M
0
C
O
M
1
C
O
M
2
C
O
M
3
E
G
0
E
G
1
E
G
2
S
E
G
3
S
E
G
4
S
E
G
5
S
E
G
6
S
E
G
7
S
E
G
8
S
E
G
9
E
G
1
0
E
G
1
1
E
G
1
2
E
G
1
3
E
G
1
4
S
E
G
1
5
S
E
G
1
6
S
E
G
1
7
φ
X
C
I
N
C
O U
T
X
3
8
9
S
I / O 2 ( 8
)
P
W M ( 8
)
φ
I
N
T
0
D
- A
2
-
A
1
A
2
T
O
U
T
L
C
D
d
r
i
v
e
c
o
n
t
r
o
l
c
i
r
c
u
i
t
L
C
D
d
i
s
p
l
a
y
R
A
M
(
2
0
b
y
t
e
s
)
T
i m e r X ( 1 6
)
T
i m e r Y ( 1 6
)
T
i m e r 1 ( 8
)
T
i m e r 2 ( 8
)
T
i m e r 3 ( 8
)
a
t
a
b
u
s
C
l
o
c
k
g
e
n
e
r
a
t
i
n
g
c
i
r
c
u
i
t
C
l o c
k
i
n p u
t
C
l o c
k
o
u t p u
t
u
b
-
c
l
o
c
k
u
t
p
u
t
S
u b - c l o c
k
i
n p u
t
e
s
e
t
K
e y i n p u t ( K e y - o n w a k e u p ) i n t e r r u p
t
R
e a l t i m e p o r t f u n c t i o
n
A
- D c o n v e r t e r ( 8
)
I
/ O p o r t P
0
I
/ O p o r t P
1
I
/
O
p
o
r
t
P
2
I
/ O p o r t P
4
I
/ O p o r t P
5
I
/
O
p
o
r
t
P
6
O
u
t
p
u
t
p
o
r
t
P
3
I
/
O
p
o
r
t
P
7
e
s
e
t
i
n
p
u
t
C
O
U
T
u
b
l
o
c
k
u
t
p
u
t
X C I
N
S
u b
c
l o c
k
i
n p u
t
W
a t c h d o g
t
i m e
r
7560 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
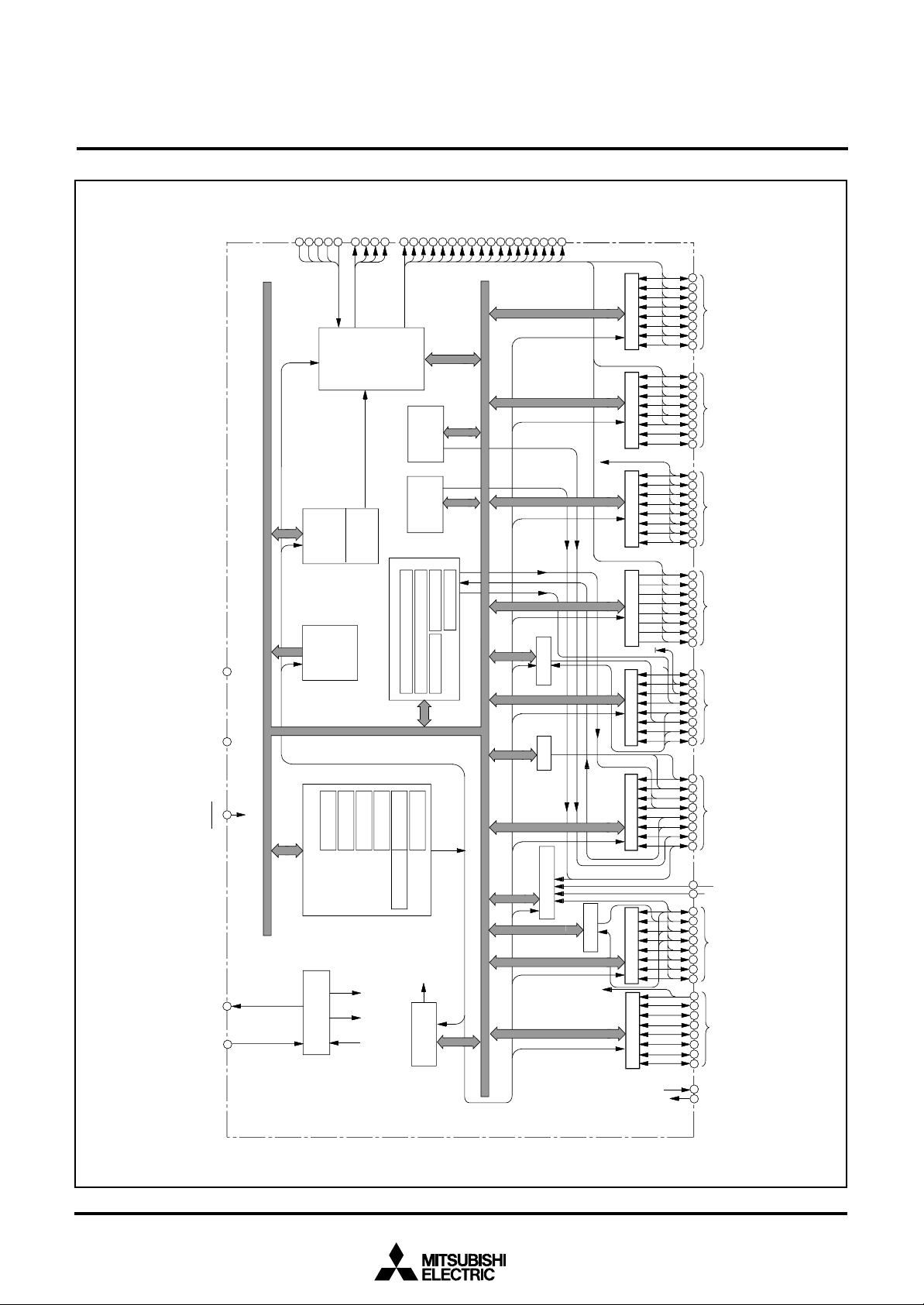
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM (Package : 100P6S-A)
Fig. 3 Functional block diagram
3
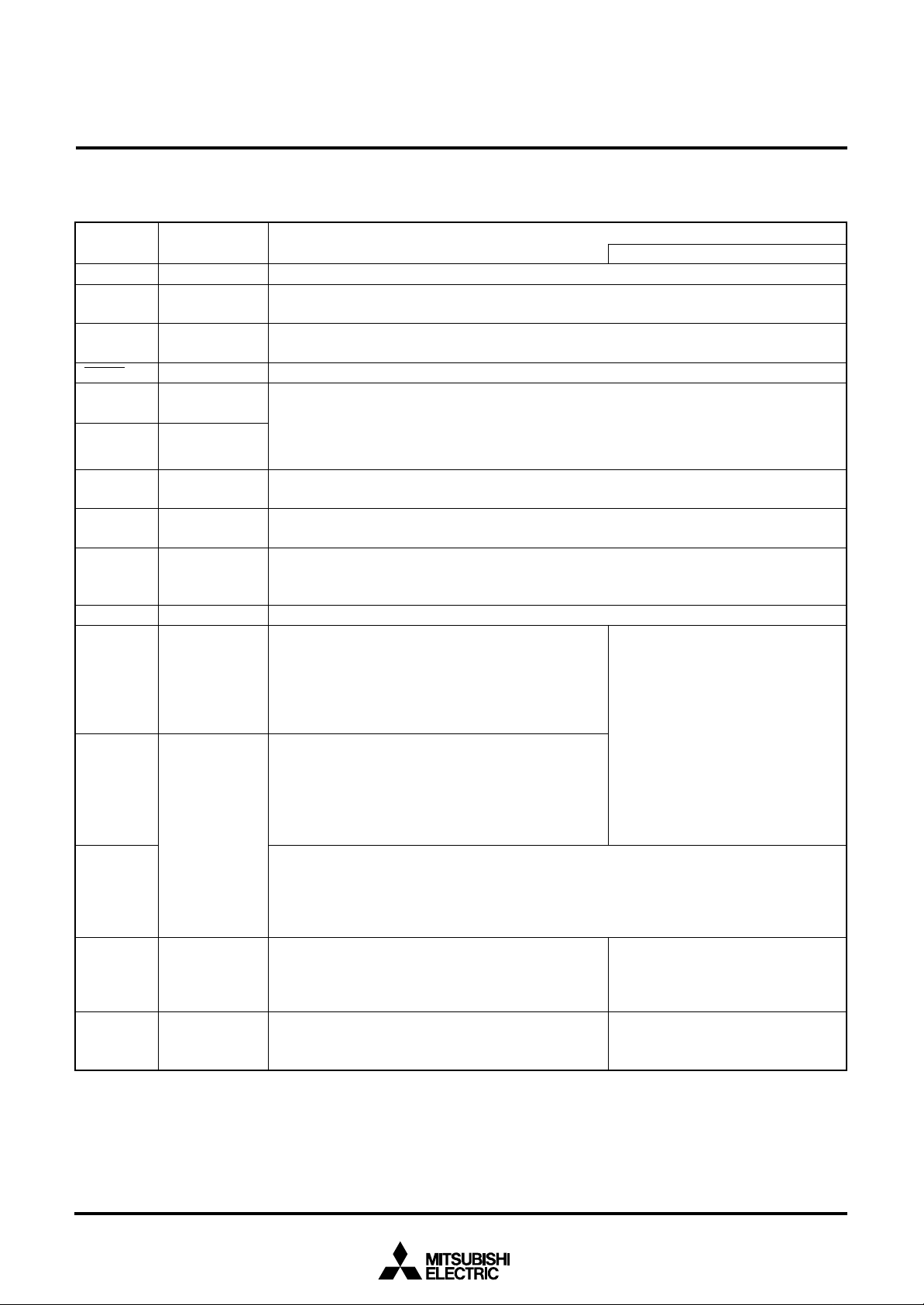
PIN DESCRIPTION
Table 1 Pin description (1)
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
7560 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
V
CC, VSS
VREF
AVSS
RESET
XIN
XOUT
VL1–VL3
C1, C2
COM0–COM
SEG0–SEG
P00/SEG26–
P07/SEG33
P10/SEG34–
P15/SEG39
P16, P17
P20 – P27
P30/SEG18 –
P37/SEG
25
FunctionPin Name
Power source •Apply voltage of 2.2 V to 5.5 V to VCC, and 0 V to VSS.
Analog refer-
ence voltage
Analog power
source
Reset input
Clock input
Clock output
LCD power
source
Charge-pump
capacitor pin
Common output
3
17
Segment output
I/O port P0
I/O port P1
I/O port P2
Output port P3
•Reference voltage input pin for A-D converter.
•GND input pin for A-D converter.
•Connect to VSS.
•Reset input pin for active “L”.
•Input and output pins for the main clock generating circuit.
•Connect a ceramic resonator or a quartz-crystal oscillator between the XIN and XOUT pins to set
the oscillation frequency.
•If an external clock is used, connect the clock source to the XIN pin and leave the XOUT pin open. A
feedback resistor is built-in.
•Input 0 ≤ VL1 ≤ VL2 ≤ VL3 voltage.
•Input 0 – VL3 voltage to LCD. (0 ≤ VL1 ≤ VL2 ≤ VL3 when a voltage is multiplied.)
•External capacitor pins for a voltage multiplier (3 times) of LCD contorl.
•LCD common output pins.
•COM2 and COM3 are not used at 1/2 duty ratio.
•COM3 is not used at 1/3 duty ratio.
•LCD segment output pins.
•8-bit I/O port.
•CMOS compatible input level.
•CMOS 3-state output structure.
•Pull-up control is enabled.
•I/O direction register allows each 8-bit pin to be pro-
grammed as either input or output.
•6-bit I/O port with same function as port P0.
•CMOS compatible input level.
•CMOS 3-state output structure.
•Pull-up control is enabled.
•I/O direction register allows each 6-bit pin to be pro-
grammed as either input or output.
•2-bit I/O port.
•CMOS compatible input level.
•CMOS 3-state output structure.
•I/O direction register allows each pin to be individually programmred as either input or output.
•Pull-up control is enabled.
•8-bit I/O port with same function as P16 and P17.
•CMOS compatible input level.
•CMOS 3-state output structure.
•Pull-up control is enabled.
•8-bit output port with same function as port P0.
•CMOS 3-state output structure.
•Port output control is enabled.
Function except a port function
•LCD segment output pins
•Key input (key-on wake-up) interrupt
input pins
•LCD segment output pins
4
Table 2 Pin description (2)
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
7560 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
P40
P41/INT1,
P42/INT2
P43/φ/TOUT
P44/RXD,
P45/TXD,
P46/SCLK1,
P47/SRDY1
P50/PWM0,
P51/PWM1
P52/RTP0,
P53/RTP1
P54/CNTR0,
P55/CNTR1
P56/DA1,
P57/ADT/DA
P60/AN0/S
IN2,
P61/AN1/S
OUT2,
P62/AN2/S
CLK21,
P63/AN3/S
CLK22
P64/AN4–
P67/AN7
P70/INT0
P71–P77
XCOUT
XCIN
I/O port P4
I/O port P5
2
I/O port P6
Input port P7
I/O port P7
Sub-clock output
Sub-clock input
FunctionPin Name
•1-bit I/O port with same function as P16 and P17.
•CMOS compatible input level.
•N-channel open-drain output structure.
•7-bit I/O port with same function as P16 and P17.
•CMOS compatible input level.
•CMOS 3-state output structure.
•Pull-up control is enabled.
•8-bit I/O port with same function as P16 and P17.
•CMOS compatible input level.
•CMOS 3-state output structure.
•Pull-up control is enabled.
•8-bit I/O port with same function as P16 and P17.
•CMOS compatible input level.
•CMOS 3-state output structure.
•Pull-up control is enabled.
•1-bit input port.
•7-bit I/O port with same function as P16 and P17.
•CMOS compatible input level.
•N-channel open-drain output structure.
•Sub-clock generating circuit I/O pins.
(Connect a resonator. External clock cannot be used.)
Function except a port function
•Interrupt input pins
•φ clock output pin
•Timer 2 output pin
•Serial I/O1 I/O pins
•PWM function pins
•Real time port function pins
•Timer X, Y function pins
•D-A conversion output pins
•A-D conversion input pins
•Serial I/O2 I/O pins
•A-D conversion input pins
•Interrupt input pin
5
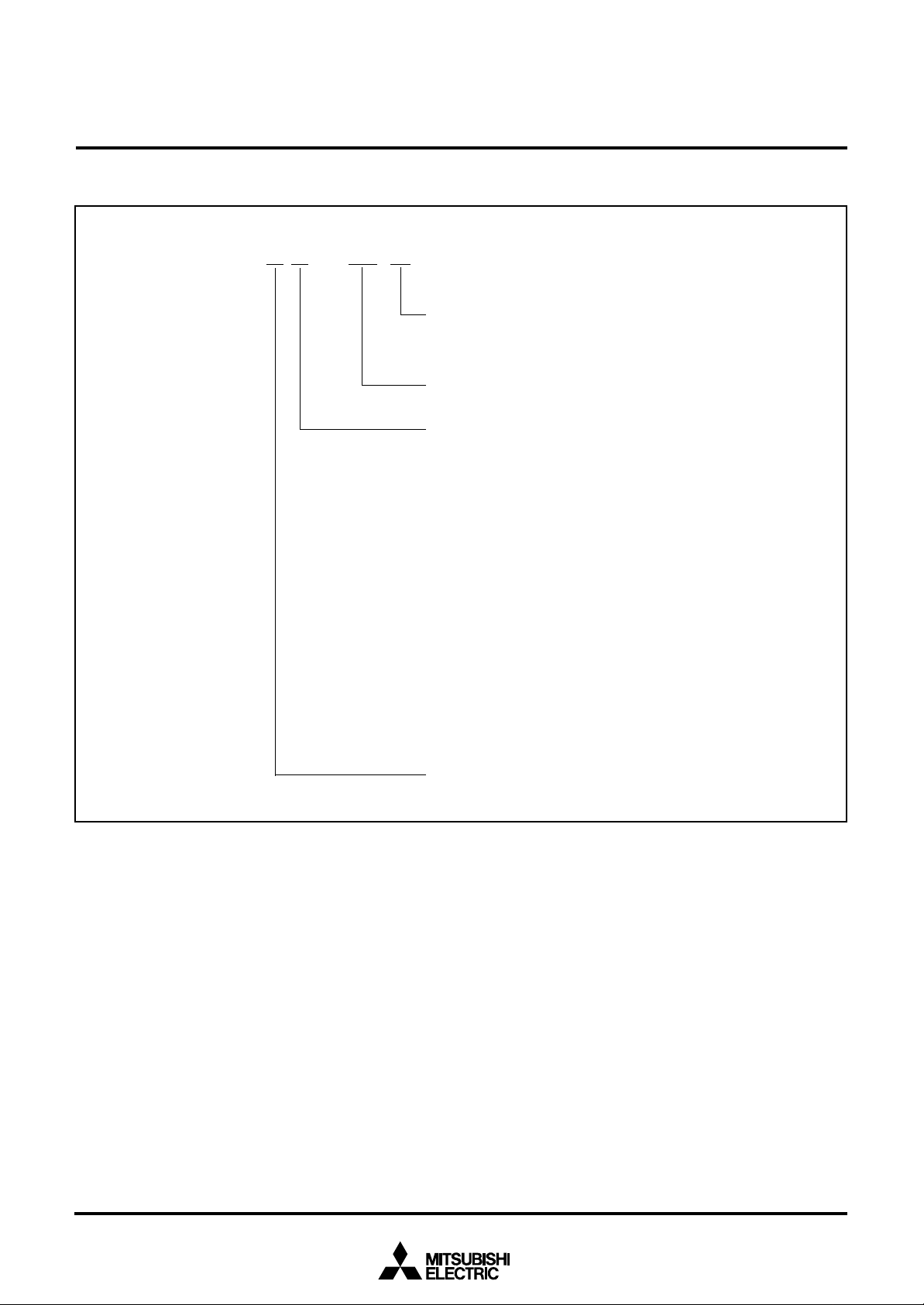
PART NUMBERING
M
M
X X X
F P
P
ROM/PROM si
b
The fi
ROM
M
Mask ROM
R O M
Pack
r o d u c
3 7 5 6 0
t
F –
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
7560 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
age type
FPGP: 100P6S-A pac kage
: 100P6Q-A package
n u m b e
1
: 4096
2
: 8192 byt es
3
: 12288 bytes
4
: 16384 bytes
5
: 20480 bytes
6
: 24576 bytes
7
: 28672 bytes
8
: 32768 bytes
9
: 36864 bytes
A
: 40960 bytes
B
: 45056 bytes
C
: 49152 bytes
D
: 53248 bytes
E
: 57344 bytes
F
: 61440 bytes
rst 128 bytes and the last 2 bytes of
are reser ved areas ; they cannot be used.
emory type
M :
r
ze
ytes
version
Fig. 4 Part numbering
6
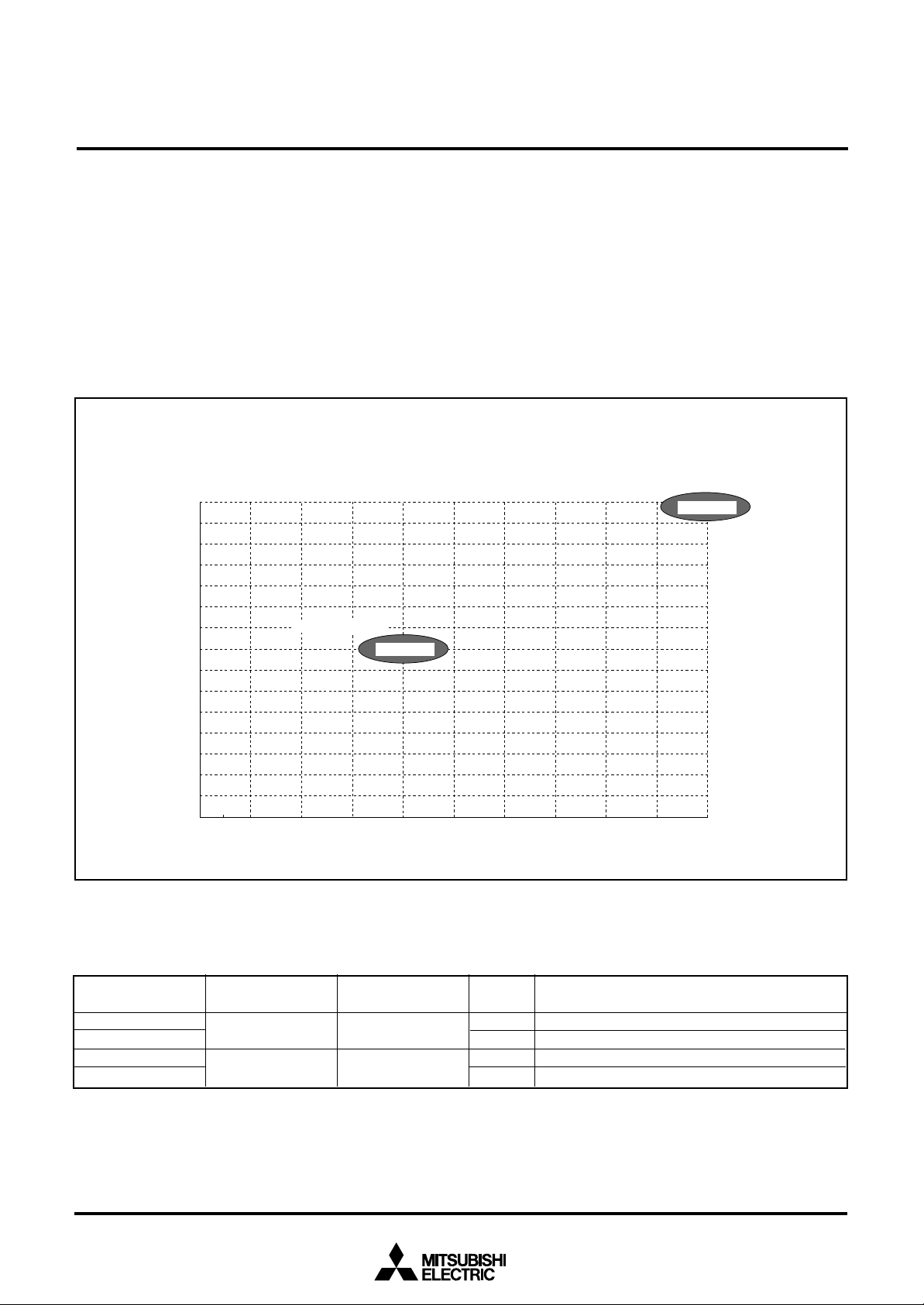
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
7560 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
GROUP EXPANSION
Mitsubishi plans to expand the 7560 group as follows.
Memory Type
Support for mask ROM version.
Memory Size
ROM size ........................................................... 32 K to 60 K bytes
RAM size .......................................................... 1024 to 2560 bytes
Memory Expansion Plan
ROM size (bytes)
60K
56K
52K
4 8 K
4 4 K
4 0 K
3 6 K
32K
28K
24K
20K
16K
1 2 K
8 K
4K
Under development
M37560M8
Packages
100P6Q-A .................................. 0.5 mm-pitch plastic molded QFP
100P6S-A ................................ 0.65 mm-pitch plastic molded QFP
Under development
M 3 7 5 6 0 M F
2 5 65
Fig. 5 Memory expansion plan
Currently products are listed below.
Table 3. List of products
Product
M37560M8-XXXFP
M37560M8-XXXGP
M37560MF-XXXFP
M37560MF-XXXGP
ROM size (bytes)
ROM size for User in ( )
32768
(32638)
61440
(61310)
1
27 6 81
0 2
RAM size (bytes)
1024
2560
41 2 8 01 5 3 61 7 9 2192 2 0 4 8 2304 2560
RAM size (bytes)
Package
100P6S-A
100P6Q-A
100P6S-A
100P6Q-A
Mask ROM version
Mask ROM version
Mask ROM version
Mask ROM version
Remarks
As of Mar. 2001
7
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
7560 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT (CPU)
The 7560 group uses the standard 740 family instruction set. Refer to the table of 740 family addressing modes and machine
instructions or the 740 Family Software Manual for details on the
instruction set.
Machine-resident 740 family instructions are as follows:
The FST and SLW instruction cannot be used.
The STP, WIT, MUL, and DIV instruction can be used.
[Accumulator (A)]
The accumulator is an 8-bit register. Data operations such as data
transfer, etc., are executed mainly through the accumulator.
[Index Register X (X)]
The index register X is an 8-bit register. In the index addressing
modes, the value of the OPERAND is added to the contents of
register X and specifies the real address.
[Index Register Y (Y)]
The index register Y is an 8-bit register. In partial instruction, the
value of the OPERAND is added to the contents of register Y and
specifies the real address.
[Stack Pointer (S)]
The stack pointer is an 8-bit register used during subroutine calls
and interrupts. This register indicates start address of stored area
(stack) for storing registers during subroutine calls and interrupts.
The low-order 8 bits of the stack address are determined by the
contents of the stack pointer. The high-order 8 bits of the stack
address are determined by the stack page selection bit. If the
stack page selection bit is “0” , the high-order 8 bits becomes
“0016”. If the stack page selection bit is “1”, the high-order 8 bits
becomes “0116”.
The operations of pushing register contents onto the stack and
popping them from the stack are shown in Figure 7.
Store registers other than those described in Figure 7 with program when the user needs them during interrupts or subroutine
calls.
[Program Counter (PC)]
The program counter is a 16-bit counter consisting of two 8-bit
registers PCH and PCL. It is used to indicate the address of the
next instruction to be executed.
b7
b0
A Accumulator
b7
b0
X Index register X
b7
b0
Y Index register Y
b7 b0
S Stack pointer
b7b15 b0
H
PC
L
Program counterPC
b7 b0
N V T B D I Z C Processor status register (PS)
Carry flag
Zero flag
Interrupt disable flag
Decimal mode flag
Break flag
Index X mode flag
Overflow flag
Negative flag
Fig. 6 740 Family CPU register structure
8
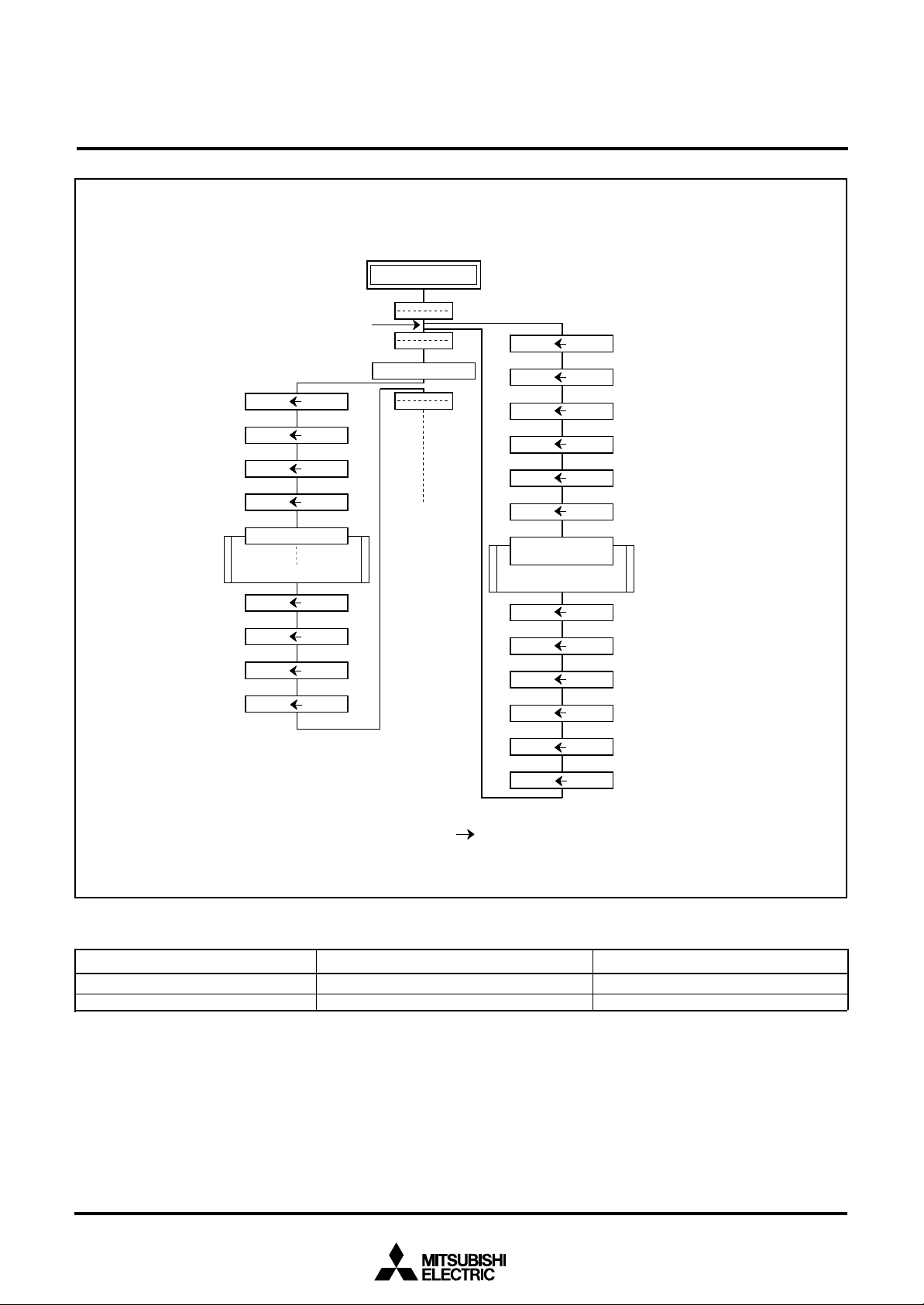
On-going Routin
e
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
7560 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
P u s h r e t u r n a d d r e s s
o n s t a c k
P O P re t u r n
a d d r e s s f r o m s t a c k
I n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t
M ( S )( P CH)
(S)
M ( S )( P CL)
( S )
S u b r o u t i n e
E x e c u t e R T S
( S )
( P CL)M ( S )
(S)
( P CH)M ( S )
(S) – 1
( S ) – 1
( S ) + 1
(S) + 1
( N o t e )
Execute JSR
M (S) (PCH)
(S) – 1
(S)
M ( S )( P CL)
( S )
( S ) – 1
M (S) (PS)
( S )
( S ) – 1
I n t e r r u p t
S e r v i c e R o u t i n e
E x e c u t e R T I
(S)
(S) + 1
( P S )M ( S )
(S)
(S) + 1
( P CL)M ( S )
(S)
(S) + 1
P u s h r e t u r n a d d r e s s
o n s t a c k
P u s h c o n t e n t s o f p r o c e s s o r
s t a t u s r e g i s t e r o n s t a c k
I F l a g i s s e t f r o m “ 0 ” t o “ 1 ”
F e t c h t h e j u m p v e c t o r
POP contents of
processor status
register from stack
P O P r e t u r n
a d d r e s s
f r o m s t a c k
(PCH)M (S)
N o t e: C o n d i t i o n f o r a c c e p t a n c e o f a n i n t e r r u p t I n t e r r u p t e n a b l e f l a g i s “ 1 ”
Fig. 7 Register push and pop at interrupt generation and subroutine call
Table 4 Push and pop instructions of accumulator or processor status register
Push instruction to stack
Accumulator
Processor status register
Interrupt disable flag is “0”
PHA
PHP
Pop instruction from stack
PLA
PLP
9
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
7560 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
[Processor status register (PS)]
The processor status register is an 8-bit register consisting of 5
flags which indicate the status of the processor after an arithmetic
operation and 3 flags which decide MCU operation. Branch operations can be performed by testing the Carry (C) flag , Zero (Z) flag,
Overflow (V) flag, or the Negative (N) flag. In decimal mode, the Z,
V, N flags are not valid.
• Bit 0: Carry flag (C)
The C flag contains a carry or borrow generated by the arithmetic logic unit (ALU) immediately after an arithmetic operation.
It can also be changed by a shift or rotate instruction.
• Bit 1: Zero flag (Z)
The Z flag is set if the result of an immediate arithmetic operation
or a data transfer is “0”, and cleared if the result is anything other
than “0”.
• Bit 2: Interrupt disable flag (I)
The I flag disables all interrupts except for the interrupt generated by the BRK instruction.
Interrupts are disabled when the I flag is “1”.
• Bit 3: Decimal mode flag (D)
The D flag determines whether additions and subtractions are
executed in binary or decimal. Binary arithmetic is executed
when this flag is “0”; decimal arithmetic is executed when it is
“1”.
Decimal correction is automatic in decimal mode. Only the ADC
and SBC instructions can be used for decimal aritmetic.
• Bit 4: Break flag (B)
The B flag is used to indicate that the current interrupt was generated by the BRK instruction. The BRK flag in the processor
status register is always “0”. When the BRK instruction is used to
generate an interrupt, the processor status register is pushed
onto the stack with the break flag set to “1”.
• Bit 5: Index X mode flag (T)
When the T flag is “0”, arithmetic operations are performed between accumulator and memory. When the T flag is “1”, direct
arithmetic operations and direct data transfers are enabled between memory locations.
• Bit 6: Overflow flag (V)
The V flag is used during the addition or subtraction of one byte
of signed data. It is set if the result exceeds +127 to -128. When
the BIT instruction is executed, bit 6 of the memory location operated on by the BIT instruction is stored in the overflow flag.
• Bit 7: Negative flag (N)
The N flag is set if the result of an arithmetic operation or data
transfer is negative. When the BIT instruction is executed, bit 7
of the memory location operated on by the BIT instruction is
stored in the negative flag.
Table 5 Set and clear instructions of each bit of processor status register
Set instruction
Clear instruction
C flag
SEC
CLC
Z flag
–
–
I flag
SEI
CLI
D flag
SED
CLD
B flag
–
–
T flag
SET
CLT
V flag
–
CLV
N flag
–
–
10
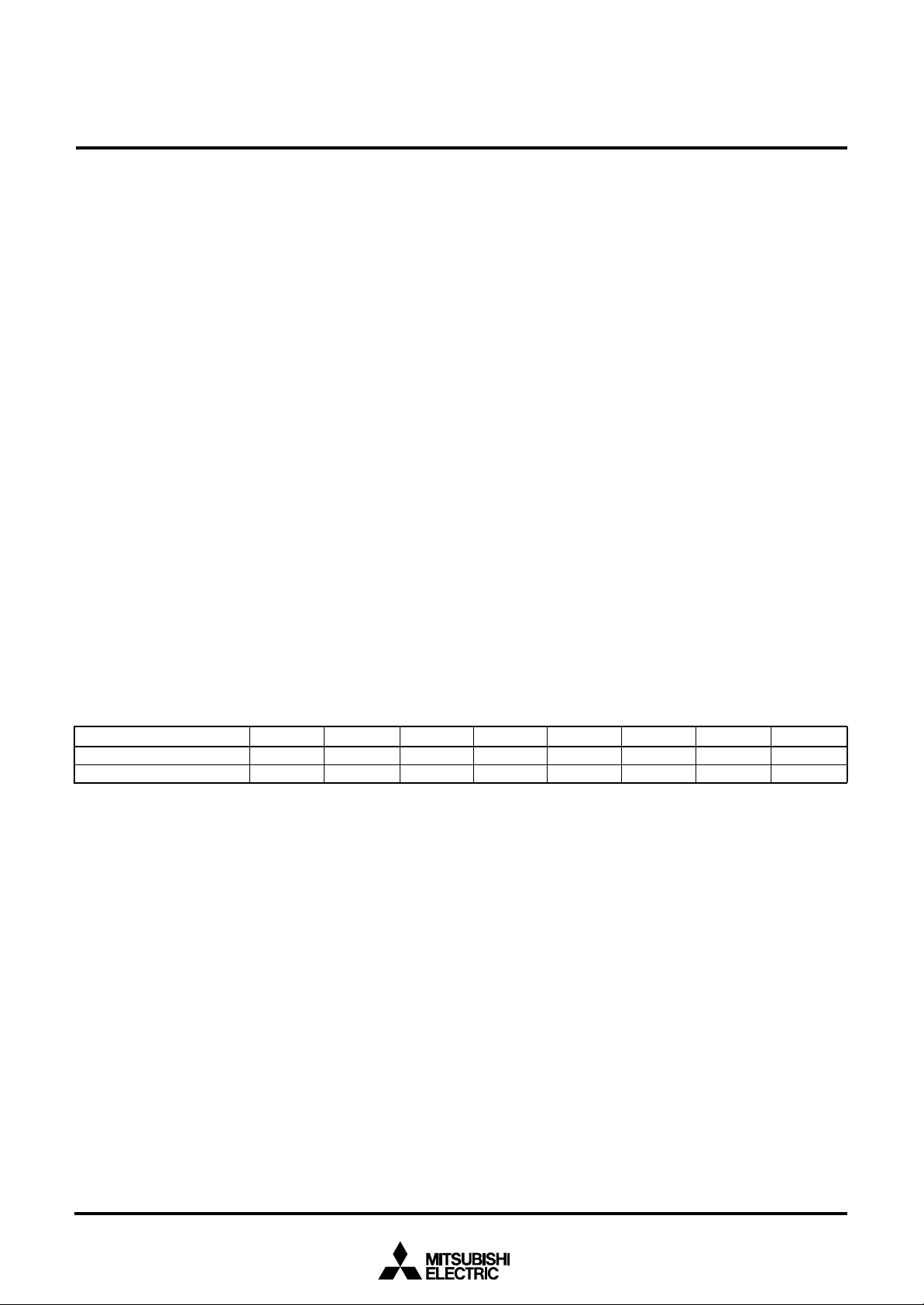
[CPU Mode Register (CPUM)] 003B16
N
P
CPU
( C P U M
B
)
b
b
The CPU mode register contains the stack page selection bit and
the internal system clock selection bit.
The CPU mode register is allocated at address 003B16.
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
7560 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
7
Fig. 8 Structure of CPU mode register
0
mode register
( C M ) : a d d r e s s 0 0 3
rocessor mode bits
b1 b0
0 0 : Single-chip mode
0 1 :
1 0 :
1 1 :
Stack page selection bit
0 : 0 page
1 : 1 page
Not used (returns “1” when read)
(Do not write “0” to this bit)
Port X
0 : Oscillation stop
1 : X
Main clock (X
0 : Oscillating
1 : Stopped
Main clock division ratio selection bit
0 : f(X
1 : f(XIN)/8 (middle-s peed mode)
Internal system clock selection bit
0 : X
1 : XCIN–XCOUT selected ( low-speed m ode)
ot available
C switch bit
CIN–XCOUT oscillating function
IN–XOUT) stop bit
IN)/2 (high-speed m ode)
IN–XOUT selected (m iddle-/high-speed mode)
1 6
11
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
FF
RAM
RAM si
Add
6
2
8
4
0
6
2
8
4
0
6
2
8
4
0
F
F
ROM
ROM si
Add
Add
F F
FFDC
FFFE
FFFF
XXXX
YYYY
ZZZZ
RAM
R O M
R
SFR
N
)
I
a
R
ROM
Z
S
LCD displ
RAM
R
ROM
N
RAM
7560 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
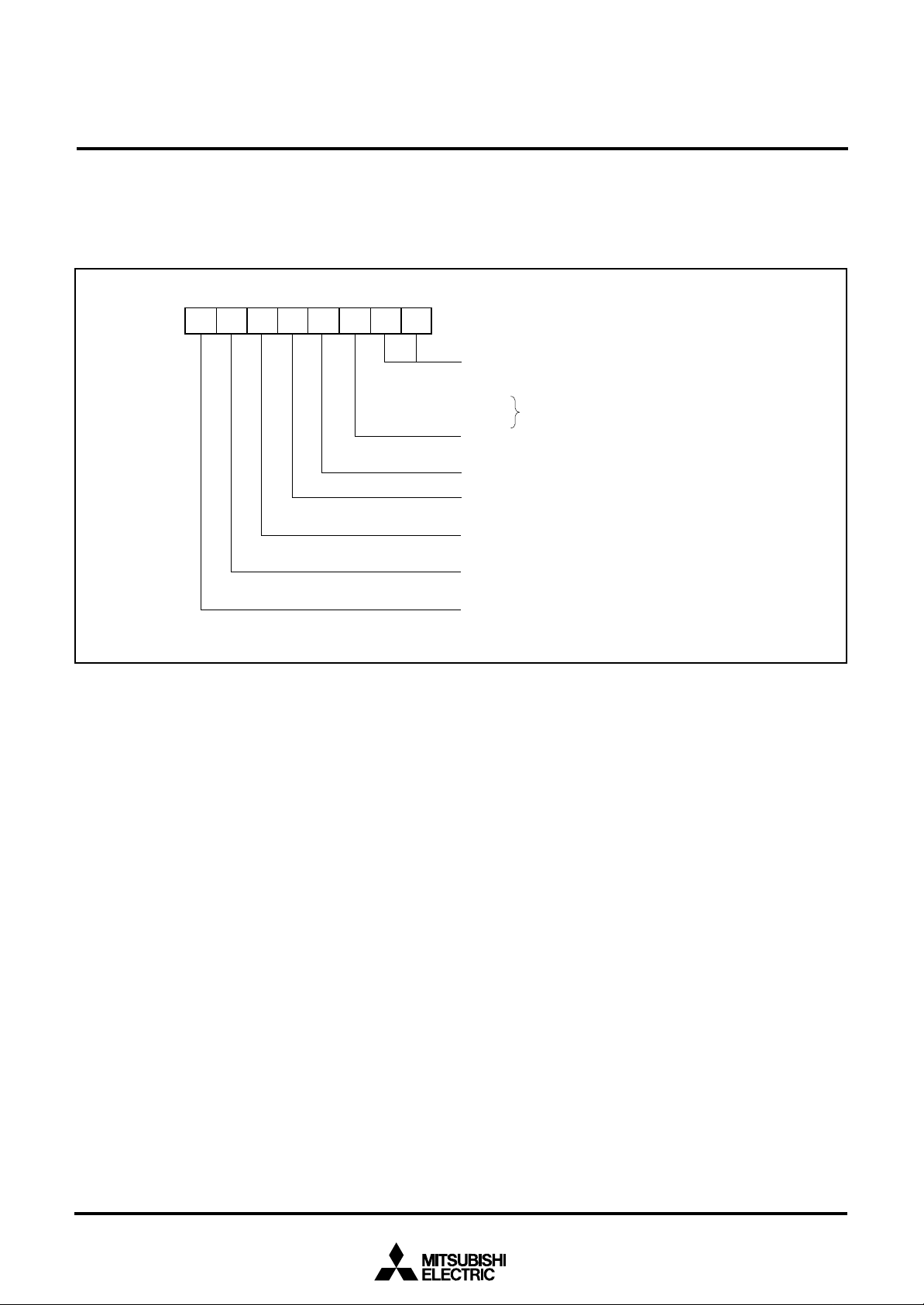
MEMORY
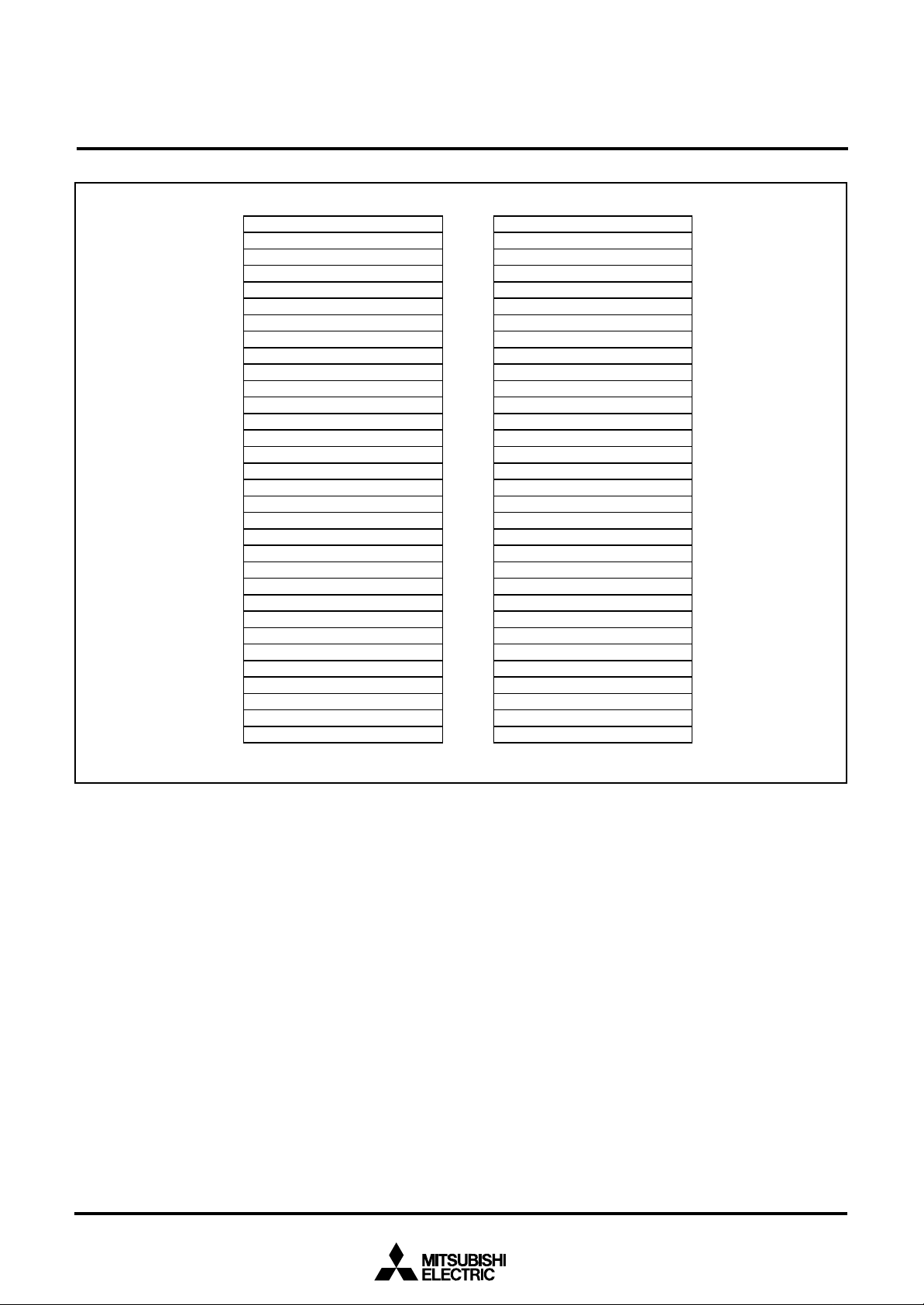
Special Function Register (SFR) Area
The Special Function Register area in the zero page contains control registers such as I/O ports and timers.
RAM
RAM is used for data storage and for stack area of subroutine
calls and interrupts.
ROM
The first 128 bytes and the last 2 bytes of ROM are reserved for
device testing and the rest is user area for storing programs.
Interrupt Vector Area
The interrupt vector area contains reset and interrupt vectors.
area
ze
(bytes)
1 9 2
2 5 6
3 8 4
5 1 2
6 4 0
7 6 8
8 9 6
1 0 2 4
1 5 3 6
2 0 4 8
2 5 6 0
ress
XXXX
00
013F
01BF
023F
02BF
033F
03BF
043F
063F
083F
0A3F
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
Zero Page
The 256 bytes from addresses 000016 to 00FF16 are called the
zero page area. The internal RAM and the special function registers (SFR) are allocated to this area.
The zero page addressing mode can be used to specify memory
and register addresses in the zero page area. Access to this area
with only 2 bytes is possible in the zero page addressing mode.
Special Page
The 256 bytes from addresses FF0016 to FFFF16 are called the
special page area. The special page addressing mode can be
used to specify memory addresses in the special page area. Access to this area with only 2 bytes is possible in the special page
addressing mode.
0 0 0 0
1 6
0040
0054
0 1 0 0
0440
area
16
16
1 6
16
ay
area
eserved area
16
e r o p a g
e
area
ze
(bytes)
409
819
1228
1638
2048
2457
2867
3276
3686
4096
4505
4915
5324
5734
6144
ote: When
area exceeds 1024 bytes, the areas shown the table are us ed.
Fig. 9 Memory map diagram
12
YYYY
000
E000
D000
C000
B000
A000
9000
8000
7000
6000
5000
4000
3000
2000
1000
ress
ot used (Note
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
ZZZZ
080
E080
D080
C080
B080
A080
9080
8080
7080
6080
5080
4080
3080
2080
1080
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
ress
16
eserved
area
(128 by tes)
16
0
1 6
0
16
16
16
nterrupt vector are
eserved
area
p e c i a l p a g
e
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
A
B
C
D
E
F
A
B
C
D
E
F
A
B
C
D
E
F
A
B
C
D
E
F
P
)
P
)
P
)
P
)
P
)
P
)
P
)
P
)
P
)
P
D)
P
)
P
)
P
)
P
)
Serial I/O
(SIO1STS)
Serial I/O
(SIO1CON)
UART
(UARTCON)
B
)
I
)
T i
)
Ti
(TXM)
( I N T E D G E )
CPU
(CPUM)
I
)
I
)
I
)
T i
)
T i
)
T i
)
T i
)
T i
)
Ti
(high) (TYH)
PULL
(PULLA)
P U L L
)
Ti
(TYM)
Ti
M)
T
(CKOUT)
S
(SEG)
L C D
)
A-D
(ADCON)
A-D
(AD)
T
(TB/RB)
R
K
(KIC)
P
)
P
)
R
Serial I/O
(SIO2CON)
S
)
PWM
(PWMCON)
P W M
)
P W M
)
R
R
R
R
D-A
(DA1)
D-A
(DA2)
D
A
l
)
7560 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
0 0 0 0
0001
0002
0 0 0 3
0 0 0 4
0 0 0 5
0 0 0 6
0 0 0 7
0 0 0 8
0 0 0 9
000
000
0 0 0
0 0 0
0 0 0
000
0010
0 0 1 1
0 0 1 2
0 0 1 3
0014
0015
0016
0017
0 0 1 8
0 0 1 9
001
001
001
001
001
0 0 1
o r t P 0 ( P 0
1 6
o r t P 0 d i r e c t i o n r e g i s t e r ( P 0 D
16
16
ort P1 (P1
o r t P 1 d i r e c t i o n r e g i s t e r ( P 1 D
1 6
o r t P 2 ( P 2
1 6
o r t P 2 d i r e c t i o n r e g i s t e r ( P 2 D
1 6
o r t P 3 ( P 3
1 6
o r t P 3 o u t p u t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r ( P 3 C
1 6
o r t P 4 ( P 4
1 6
o r t P 4 d i r e c t i o n r e g i s t e r ( P 4 D
1 6
16
ort P5 (P5
16
ort P5 direction register (P5
o r t P 6 ( P 6
1 6
o r t P 6 d i r e c t i o n r e g i s t e r ( P 6 D
1 6
o r t P 7 ( P 7
1 6
o r t P 7 d i r e c t i o n r e g i s t e r ( P 7 D
16
16
1 6
1 6
1 6
e s e r v e d a r e
16
16
ey input control register
16
r e g i s t e r B ( P U L L B
16
1 6
ransmit/Receive buffer register
1 6
16
16
a u d r a t e g e n e r a t o r ( B R G
16
16
e s e r v e d a r e
16
e r i a l I / O 2 r e g i s t e r ( S I O 2
1 6
a
register A
1 status register
1 control register
control register
2 control register
a
m e r X ( l o w ) ( T X L
0 0 2 0
1 6
m e r X ( h i g h ) ( T X H
0021
16
m e r Y ( l o w ) ( T Y L
0022
16
0 0 2 3
1 6
mer Y
m e r 1 ( T 1
0 0 2 4
1 6
m e r 2 ( T 2
0 0 2 5
1 6
m e r 3 ( T 3
0 0 2 6
1 6
0 0 2 7
1 6
0 0 2 8
0 0 2 9
002
002
0 0 2
0 0 2
002
002
0030
0 0 3 1
0 0 3 2
0 0 3 3
0034
0035
0036
0037
0 0 3 8
0 0 3 9
003
003
003
003
003
003
mer X mode register
1 6
mer Y mode register
1 6
mer 12 3 mode register (T123
16
OUT
/φ output cont rol register
16
control register
p r e s c a l e r ( P R E P W M
1 6
r e g i s t e r ( P W M
1 6
e s e r v e d a r e
16
e s e r v e d a r e
16
e s e r v e d a r e
16
1 6
eserved area
1 6
1 6
16
16
-
r e g i s t e r ( D A C O N
16
16
W a t c h d o g t i m e r c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r ( W D T C O N )
1 6
egment output enable register
m o d e r e g i s t e r ( L M
1 6
16
I n t e r r u p t e d g e s e l e c t i o n r e g i s t e r
16
n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t r e g i s t e r 1 ( I R E Q 1
16
n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t r e g i s t e r 2 ( I R E Q 2
16
n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 1 ( I C O N 1
16
n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 2 ( I C O N 2
16
a
a
a
1 conversion register
2 conversion register
control register
conversion register
c o n t r o
mode register
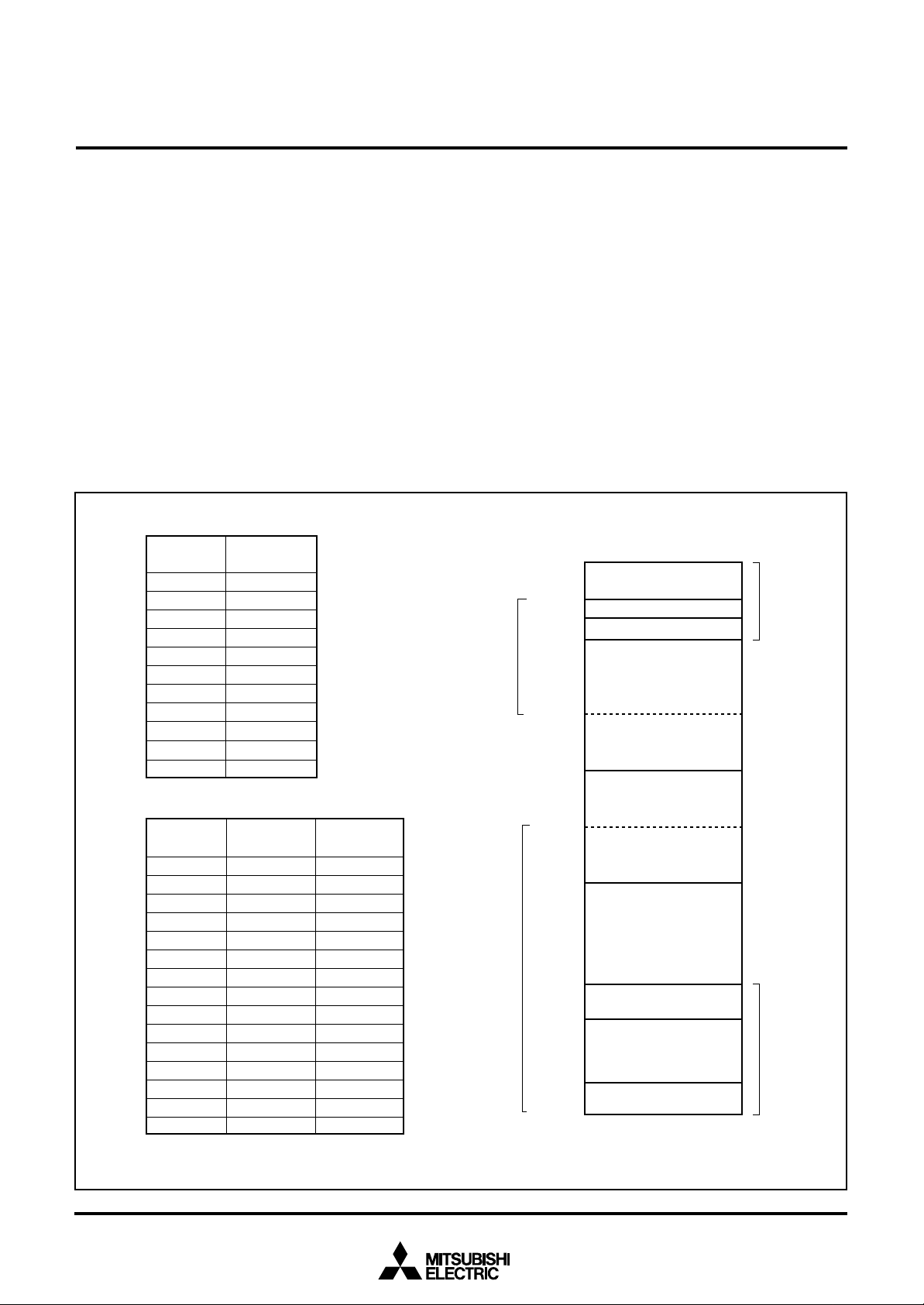
Fig. 10 Memory map of special function register (SFR)
13
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
P
P U L L
A
b
b
P
D i
PULL
B
b
b
N
PULL
PULL
7560 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
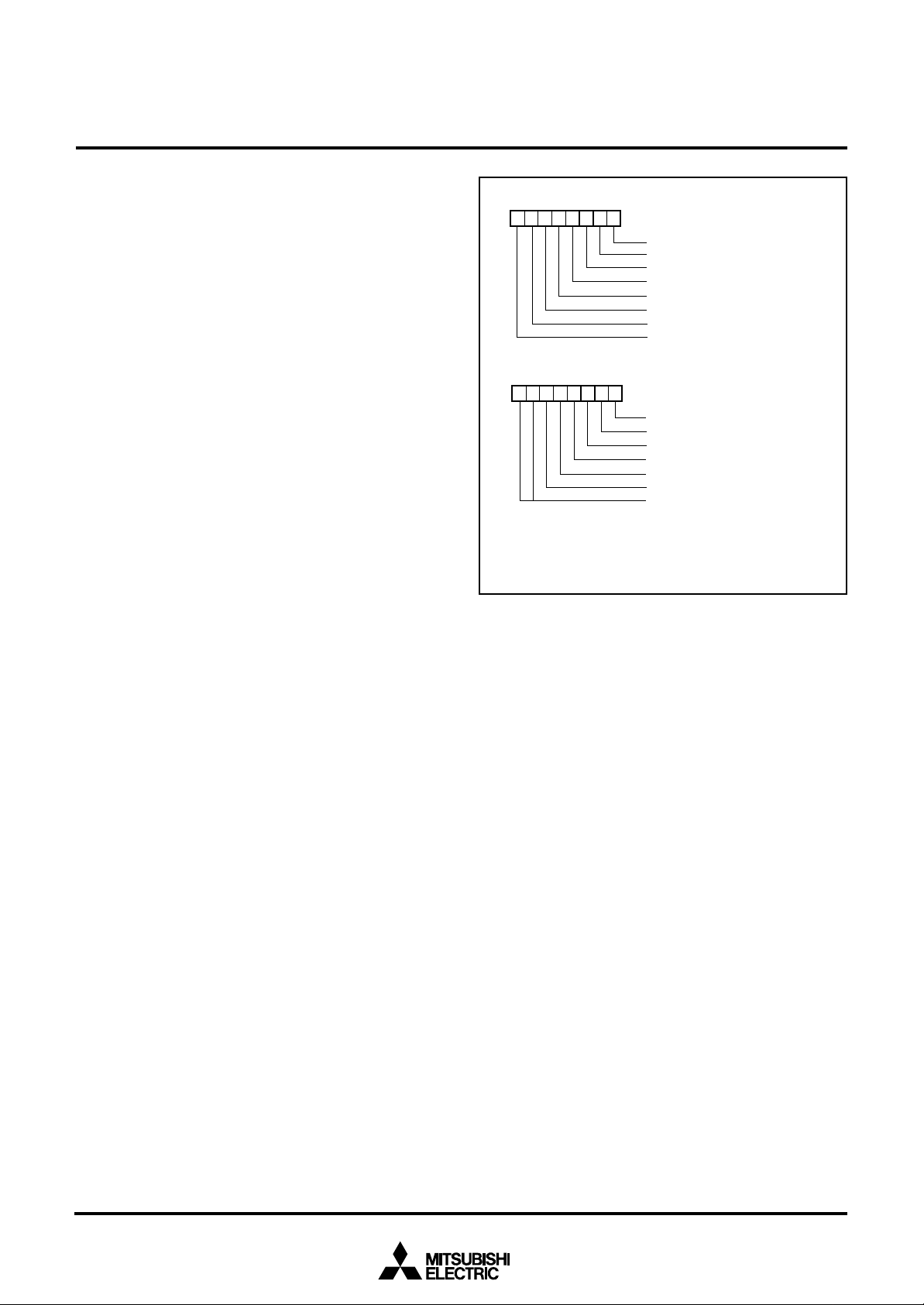
I/O PORTS
Direction Registers
The I/O ports (ports P0, P1, P2, P4, P5, P6, P71–P77) have direction registers which determine the input/output direction of each
individual pin. (Ports P00–P07 are shared with bit 0 of the port P0
direction register, and ports P10–P15 shared with bit 0 of the port
P1 direction register.) Each bit in a direction register corresponds
to one pin, and each pin can be set to be input port or output port.
When “0” is written to the bit corresponding to a pin, that pin becomes an input pin. When “1” is written to that bit, that pin becomes an output pin.
If data is read from a pin set to output, the value of the port output
latch is read, not the value of the pin itself. Pins set to input are
floating. If a pin set to input is written to, only the port output latch
is written to and the pin remains floating.
Port P3 Output Control Register
Bit 0 of the port P3 output control register (address 000716) enables control of the output of ports P30–P37.
When the bit is set to “1”, the port output function is valid.
When resetting, bit 0 of the port P3 output control register is set to
“0” (the port output function is invalid) and pulled up.
Pull-up Control
By setting the PULL register A (address 001616) or the PULL register B (address 001716), ports P0 to P2, P4 to P6 can control pullup with a program.
However, the contents of PULL register A and PULL register B do
not affect ports programmed as the output ports.
The PULL register A setting is invalid for pins set to segment output with the segment output enable register.
7
7
ote:The contents of
do not affect ports programmed as the output port.
0
r e g i s t e r
( P U L L A : a d d r e s s 0 0 1 61
00, P01 pull-up
P0
2, P03 pull-up
P0
4–P07 pull-up
P1
0–P13 pull-up
P1
4, P15 pull-up
P1
6, P17 pull-up
P2
0–P23 pull-up
P2
4–P27 pull-up
0
register
(PULLB : addr ess 001716)
41–P43 pull-up
P4
4–P47 pull-up
P5
0–P53 pull-up
P5
4–P57 pull-up
P6
0–P63 pull-up
P6
4–P67 pull-up
Not used (return “0” when read)
register A and
6)
s a b l
0 :
1 : E n a b l e
register B
e
Fig. 11 Structure of PULL register A and PULL register B
14
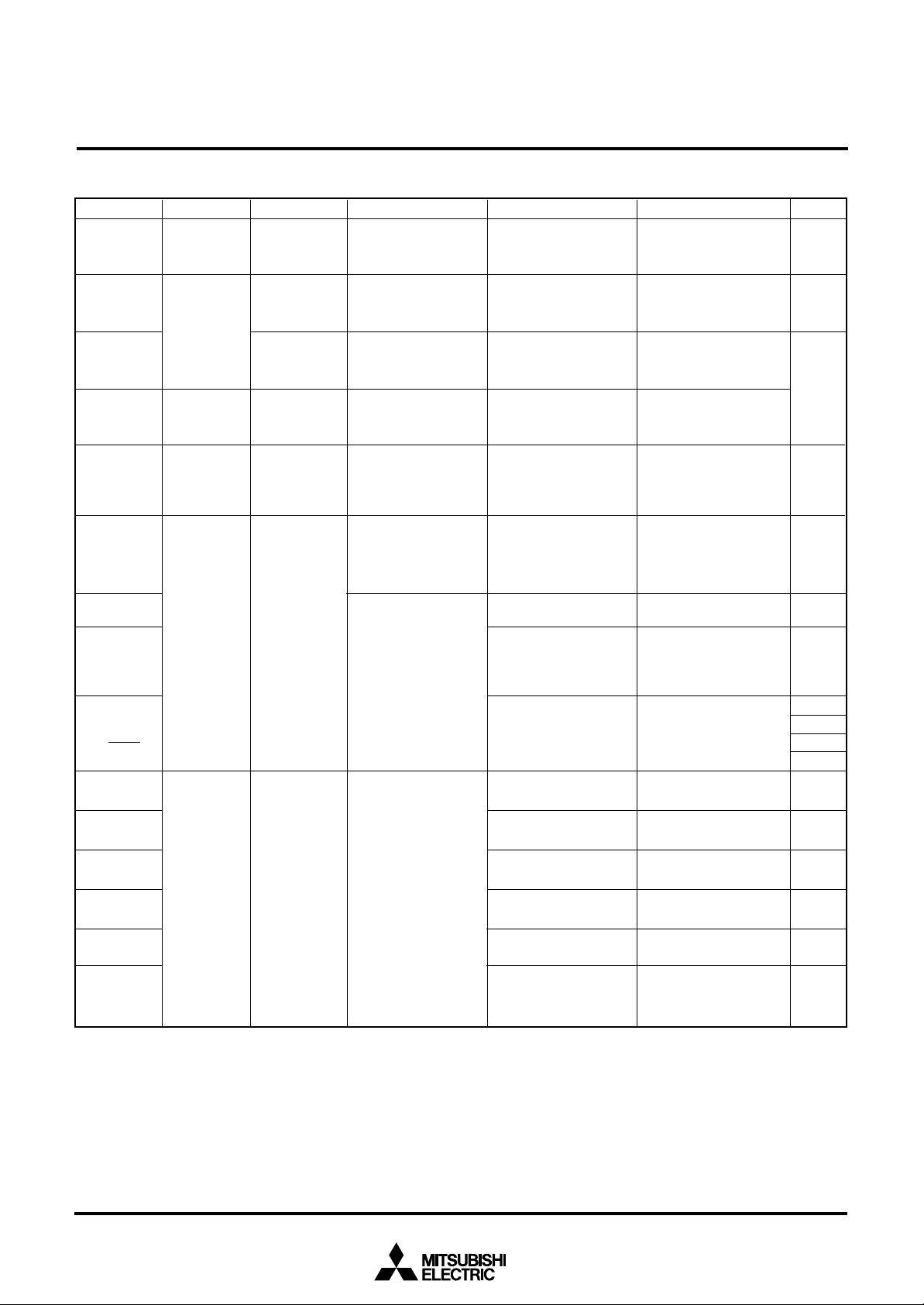
Table 6 List of I/O port function (1)
Pin
P00/SEG26–
P07/SEG33
P10/SEG34–
P15/SEG39
P16 , P17
P20–P27
P30/SEG18–
P37/SEG25
Port P0
Port P1
Port P2
Port P3
Input/OutputName
Input/output,
byte unit
Input/output,
6-bit unit
Input/output,
individual bits
Input/output,
individual bits
Output
I/O Format
CMOS compatible
input level
CMOS 3-state output
CMOS compatible
input level
CMOS 3-state output
CMOS compatible
input level
CMOS 3-state output
CMOS compatible
input level
CMOS 3-state output
CMOS 3-state output
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
Non-Port Function
LCD segment output
LCD segment output
Key input (key-on
wake-up) interrupt
input
LCD segment output
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
7560 Group
Related SFRs
PULL register A
Segment output enable
register
PULL register A
Segment output enable
register
PULL register A
PULL register A
Interrupt control register2
Key input control register
Segment output enable
register
P3 output enable register
Diagram No.
(1)
(2)
(1)
(2)
(4)
(3)
P40
P41/INT1,
P42/INT2
P43/φ/TOUT
P44/RXD,
P45/TXD,
P46/SCLK1,
P47/SRDY1
P50/PWM0,
P51/PWM1
P52/RTP0,
P53/RTP1
P54/CNTR0
P55/CNTR1
P56/DA1
P57/ADT/
DA2
Port P4
Port P5
Input/output,
individual bits
Input/output,
individual bits
CMOS compatible
input level
N-channel open-drain
output
CMOS compatible
input level
CMOS 3-state output
CMOS compatible
input level
CMOS 3-state output
External interrupt input
Timer output
φ output
Serial I/O1 function I/O
PWM output
Real time port
function output
Timer X function I/O
Timer Y function input
DA1 output
DA2 output
A-D trigger input
Interrupt edge selection
register
PULL register B
Timer 123 mode register
TOUT/φ output control
register
PULL register B
Serial I/O1 control register
Serial I/O1 status register
UART control register
PULL register B
PWM control register
PULL register B
Timer X mode register
PULL register B
Timer X mode register
PULL register B
Timer Y mode register
PULL register B
D-A control register
PULL register B
D-A control register
A-D control register
(13)
(4)
(12)
(5)
(6)
(7)
(8)
(10)
(9)
(11)
(14)
(15)
(15)
15
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
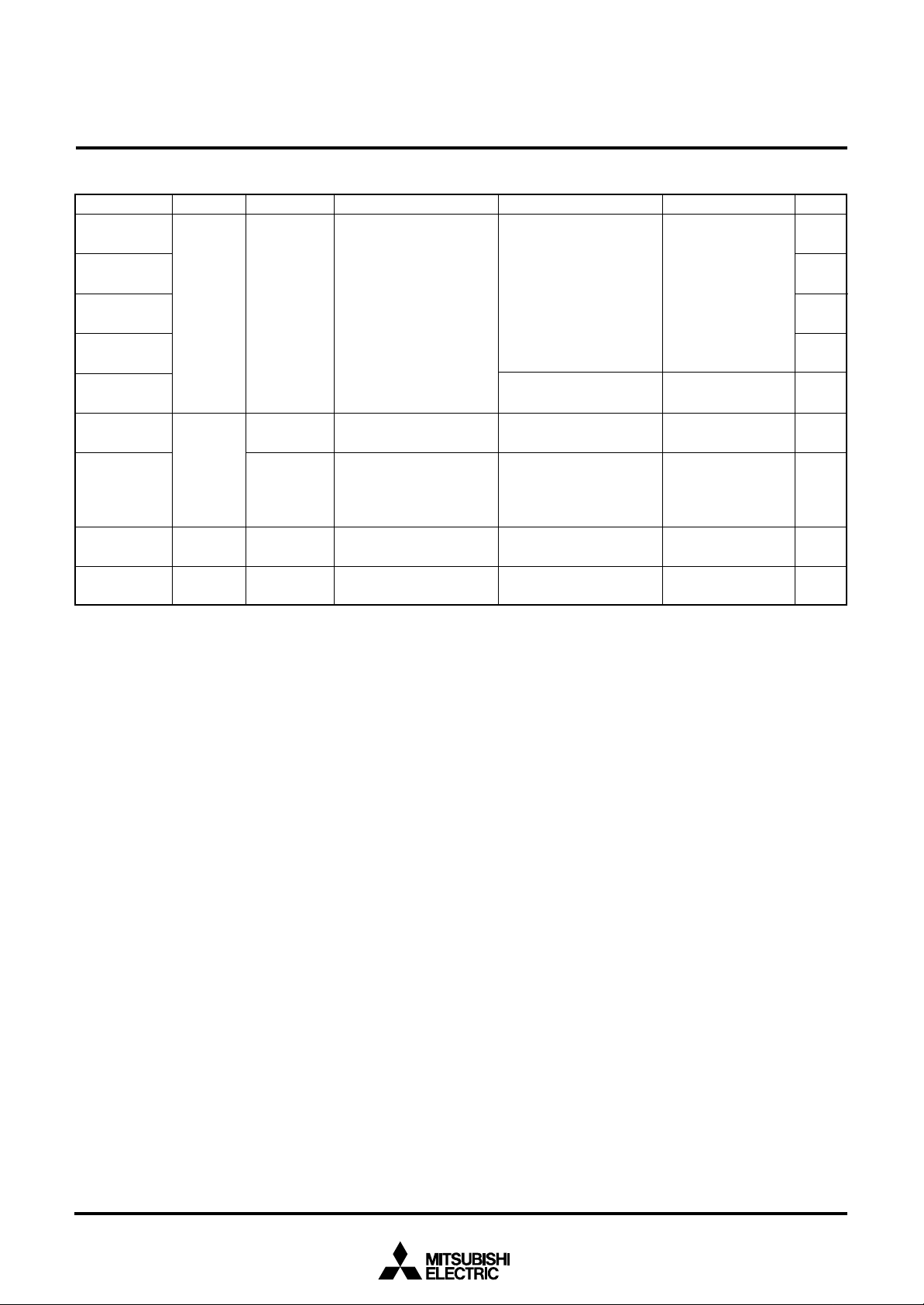
Table 7 List of I/O port function (2)
Pin Name I/O Format Non-Port Function Related SFRS
P60/SIN2/AN0
P61/SOUT2/
AN1
P62/SCLK21/
AN2
P63/SCLK22 /
AN3
P64/AN4–
P67/AN7
P70/INT0
P71–P77
Port P6
Port P7
Input/Output
Input/
output,
individual
bits
Input
Input/
output,
individual
bits
CMOS compatible input
level
CMOS 3-state output
CMOS compatible input
level
CMOS compatible input
level
N-channel open-drain
output
A-D conversion input
Serial I/O2 function I/O
A-D conversion input
External interrupt input
PULL register B
A-D control register
Serial I/O2 control
register
A-D control register
PULL register B
Interrupt edge
selection register
7560 Group
Diagram No.
(17)
(18)
(19)
(20)
(16)
(23)
(13)
COM0–COM3
SEG0–SEG17
Notes1: How to use double-function ports as function I/O ports, refer to the applicable sections.
2: Make sure that the input level at each pin is either 0 V or V
tential, a current will flow V
Common
Segment
Output
Output
CC to VSS through the input-stage gate.
LCD common output
LCD segment output
CC during execution of the STP instruction. When an input level is at an intermediate po-
LCD mode register
(21)
(22)
16
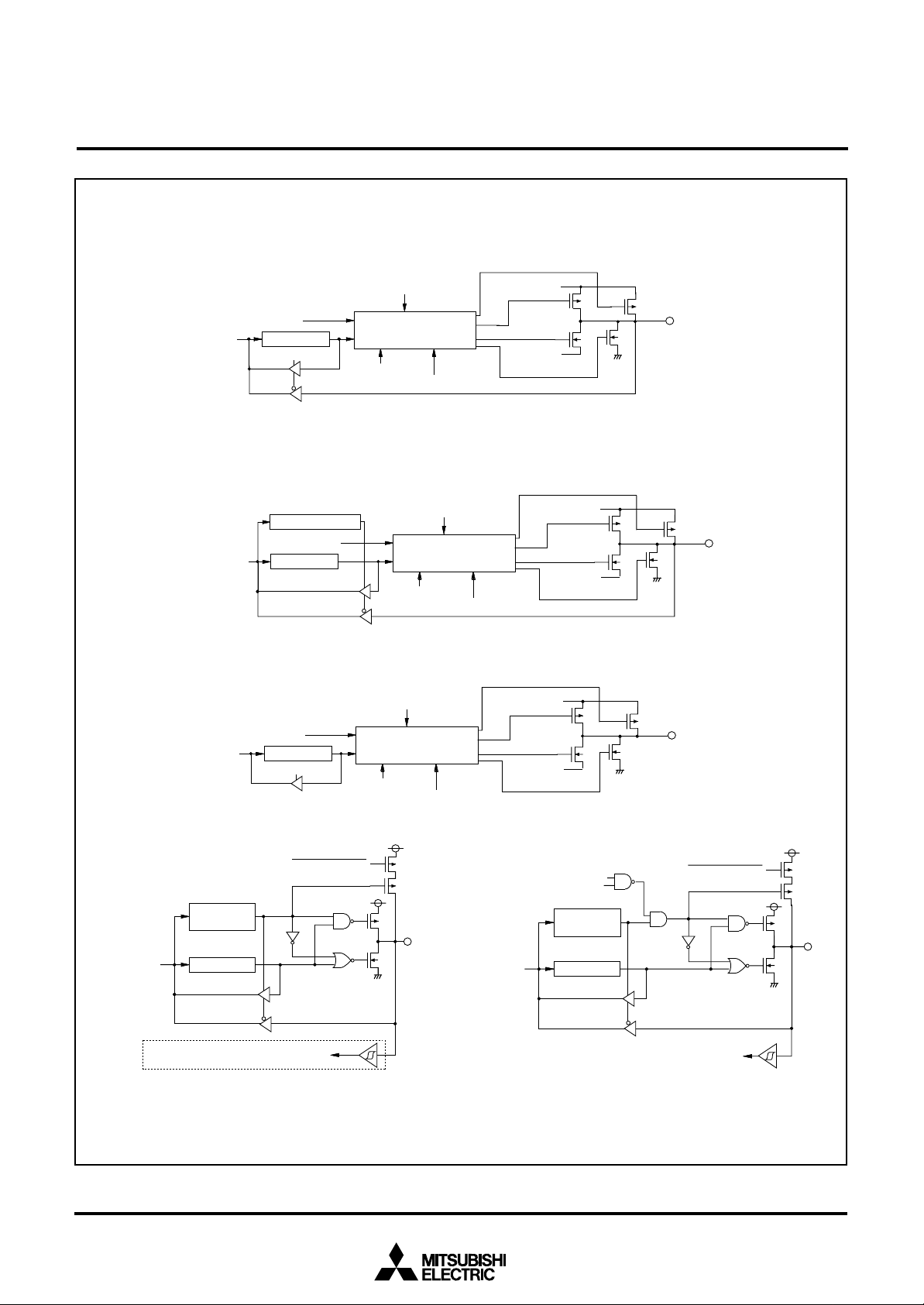
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
7560 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
( 1 ) P o r t s P 01– P 07, P 11– P 1
S e g m e n t d a t a
D a t a b u s
(2) Ports P00, P1
D a t a b u sP
P o r t l a t c h
P o r t d i r e c t i o n r e g i s t e r
0
D i r e c t i o n r e g i s t e r
S e g m e n t d a t a
o r t l a t c
h
( 3 ) P o r t P 3
Segment data
D a t a b u s
Port latch
5
L C D d r i v e t i m i n g
I n t e r f a c e l o g i c l e v e l
s h i f t c i r c u i t
P o r t / S e g m e n t
LCD drive timing
Port/Segment
LCD drive timing
I n t e r f a c e l o g i c l e v e l
s h i f t c i r c u i t
Port/Segment
Port direction register
Interface logic level
shift circuit
Port direction register
Output control
P u l l - u p
VL2/VL3/V
S e g m e n t / P o r t
S e g m e n t
V
L 1
/ V
P o r t
VL2/VL3/V
S e g m e n t / P o r t
Segment
Pull-up
V
L 2
/ V
L 3
/ V
Segment/Port
S e g m e n t
VL1/V
P o r t
CC
S S
Pull-up
Port
C C
SS
VL1/V
CC
SS
( 4 ) P o r t s P 16, P 17, P 2 , P 41, P 4
D i r e c t i o n
r e g i s t e r
D a t a b u s
Fig. 12 Port block diagram (1)
Port latch
Key-on wake up interrupt input
1
, INT2 interrupt input
INT
2
E x c e p t P 1
Pull-up control
6
, P 1
7
(5) Port P4
S e r i a l I / O 1 e n a b l e b i t
R e c e p t i o n e n a b l e b i t
Data bus
4
D i r e c t i o n
r e g i s t e r
Port latch
P u l l - u p c o n t r o l
S e r i a l I / O 1 i n p u t
17
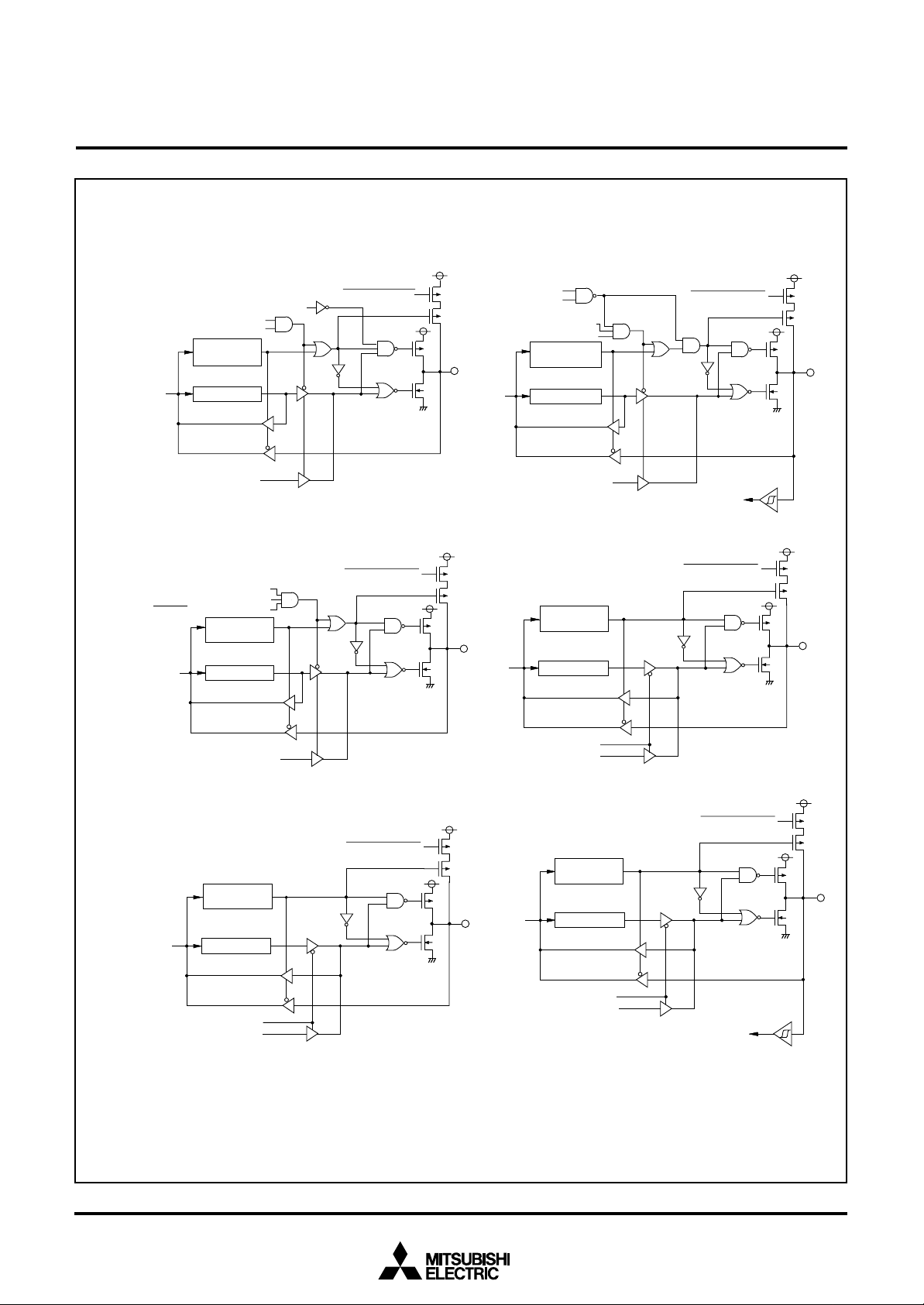
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
7560 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
( 6 ) P o r t P 4
5
P 4
D a t a b u s
( 8 ) P o r t P 4
S e r i a l I / O 1 m o d e s e l e c t i o n b i t
Data bus
5
/ T x D P - c h a n n e l o u t p u t d i s a b l e b i t
S e r i a l I / O 1 e n a b l e b i t
T r a n s m i s s i o n e n a b l e b i t
S
D i r e c t i o n
r e g i s t e r
P o r t l a t c h
S e r i a l I / O 1 o u t p u t
7
S e r i a l I / O 1 e n a b l e b i t
R D Y 1
o u t p u t e n a b l e b i t
D i r e c t i o n
r e g i s t e r
Port latch
P u l l - u p c o n t r o l
P u l l - u p c o n t r o l
( 7 ) P o r t P 4
Serial I/O1 synchronization
clock selection bit
S e r i a l I / O 1 e n a b l e b i t
Serial I/O1 mode selection bit
Data bus
( 9 ) P o r t s P 52, P 5
Data bus
6
Serial I/O1 enable bit
Serial I/O1 clock output
D i r e c t i o n
r e g i s t e r
P o r t l a t c h
3
D i r e c t i o n
r e g i s t e r
Port latch
P u l l - u p c o n t r o l
S e r i a l I / O 1 c l o c k i n p u t
Pull-up control
Serial I/O1 ready output
(10) Ports P50,P5
Data bus
P W M f u n c t i o n e n a b l e b i t
P W M o u t p u t
1
Direction
register
Port latch
P u l l - u p c o n t r o l
Real time control bit
Real time port data
( 1 1 ) P o r t P 5
D a t a b u s
Pulse output mode
4
D i r e c t i o n
r e g i s t e r
P o r t l a t c h
Timer output
Pull-up control
CNTR0 interrupt input
Fig. 13 Port block diagram (2)
18
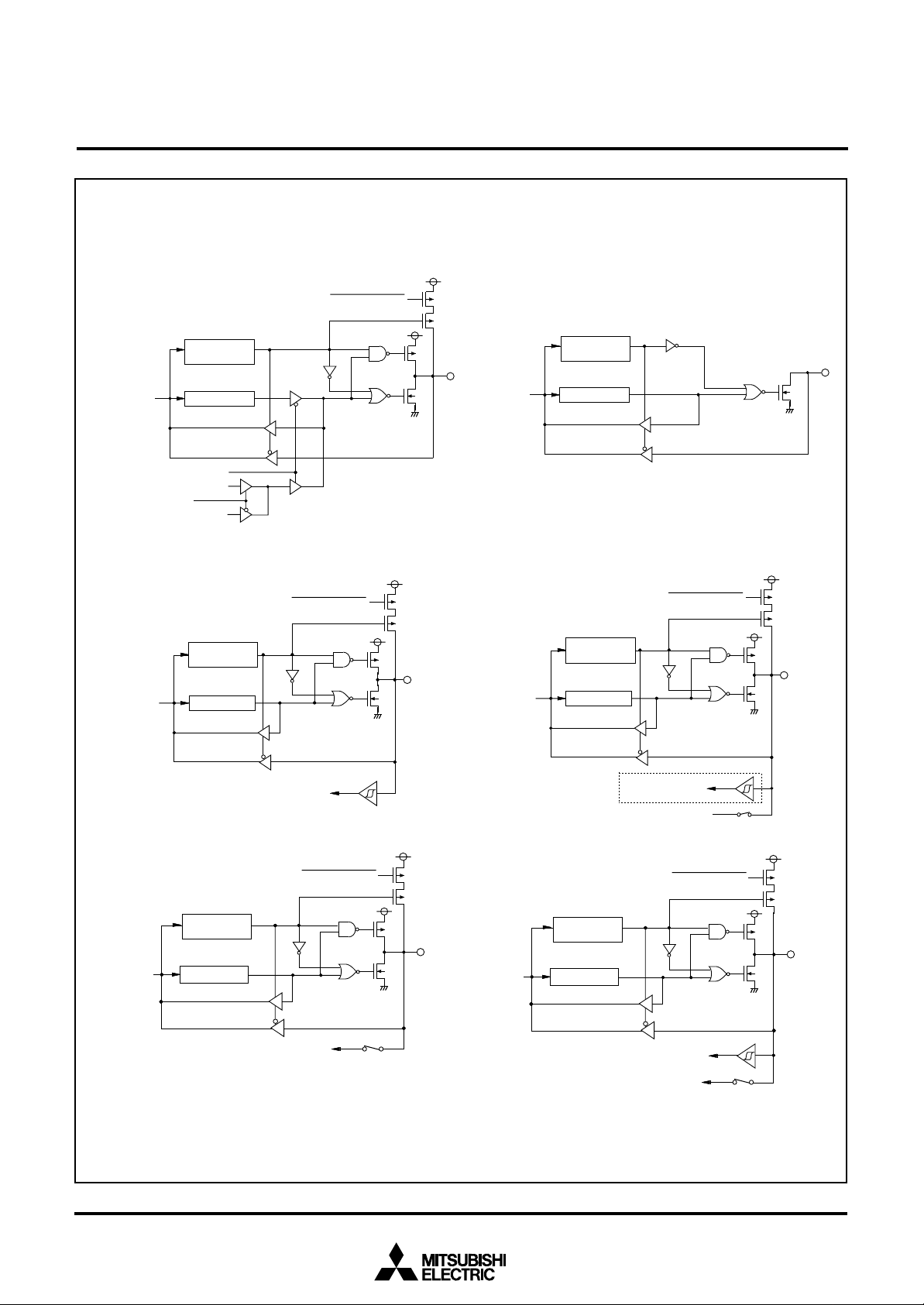
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
7560 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
( 1 2 ) P o r t P 4
T
OUT
/φ output control
T
O U T
/φ s e l e c t i o n b i t
( 1 4 ) P o r t P 5
Data bus
3
D i r e c t i o n
r e g i s t e r
P o r t l a t c hD a t a b u s
Timer output
φ o u t p u t
5
Direction
register
P o r t l a t c h
P u l l - u p c o n t r o l
P u l l - u p c o n t r o l
( 1 3 ) P o r t s P 40, P 71– P 7
Direction
register
P o r t l a t c hData bus
(15) Ports P56,P5
D a t a b u s
7
D i r e c t i o n
r e g i s t e r
Port latch
7
P u l l - u p c o n t r o l
C N T R1 i n t e r r u p t i n p u t
( 1 6 ) P o r t s P 64– P 6
Data bus
7
D i r e c t i o n
r e g i s t e r
P o r t l a t c h
A - D c o n v e r s i o n i n p u t
Fig. 14 Port block diagram (3)
Pull-up control
Analog input pin selection bit
(17) Port P6
Data bus
E x c e p t P 5
0
Port latch
6
D - A c o n v e r t e r o u t p u t
D i r e c t i o n
r e g i s t e r
A-D conversion input
A - D t r i g g e r i n p u t
D-A
Pull-up control
S e r i a l I / O 2 i n p u t
Analog input pin selection bit
1
,D-A2 output enable bit
19
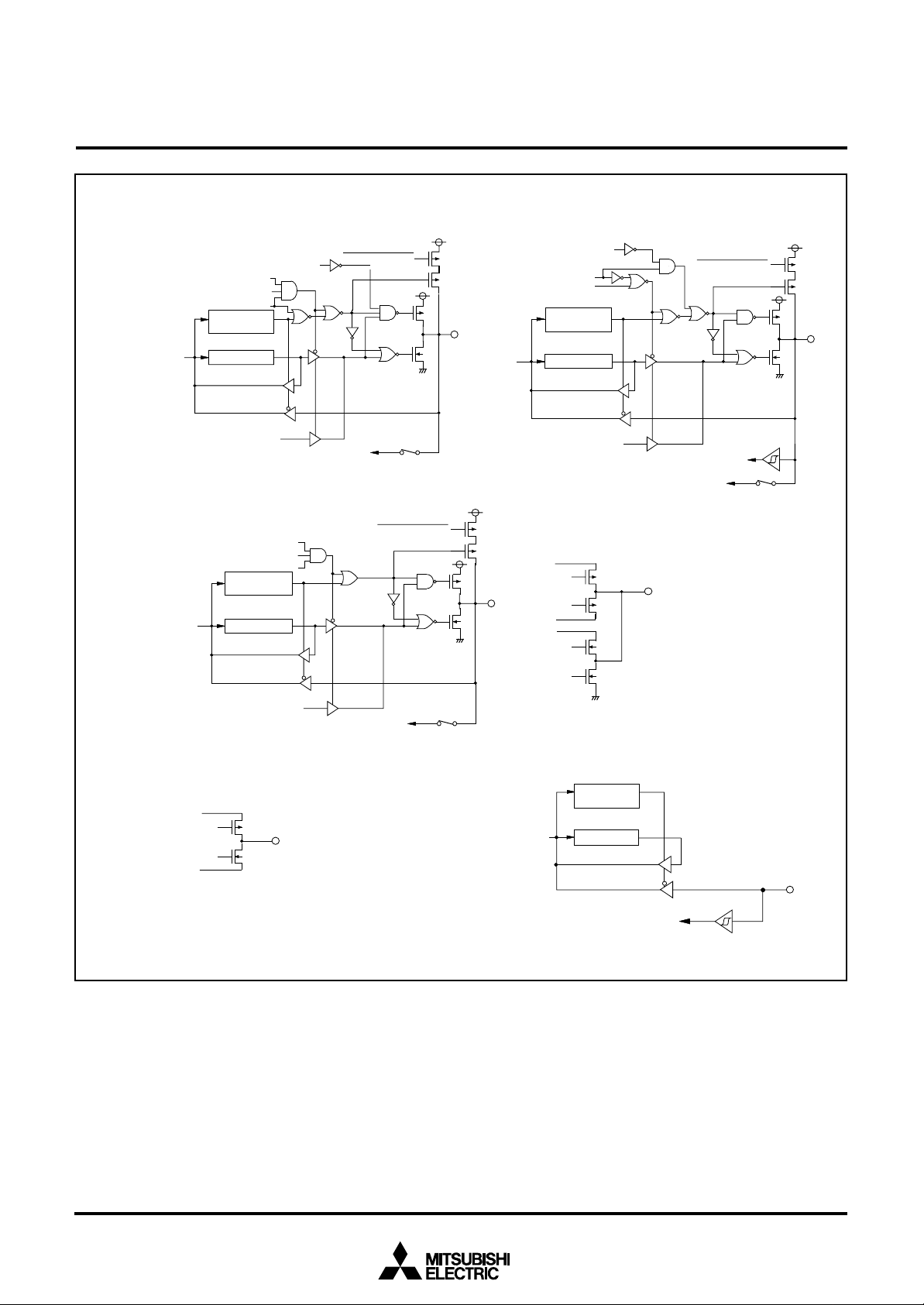
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
t
t
7560 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
( 1 8 ) P o r t P 6
P61/S
OUT2
S e r i a l I / O 2 t r a n s m i t e n d s i g n a l
S y n c h r o n o u s c l o c k s e l e c t i o n b i
S e r i a l I / O 2 p o r t s e l e c t i o n b i
( 2 0 ) P o r t P 6
Synchronous clock selection bit
Synchronous clock output pin selection bit
1
P-channel output disable bit
D i r e c t i o n
r e g i s t e r
Port latchD a t a b u s
S e r i a l I / O 2 o u t p u t
3
Serial I/O2 port selection bit
A - D c o n v e r s i o n i n p u t
Direction
register
P o r t l a t c hD a t a b u s
Pull-up control
Synchronous clock output pin
Analog input pin selection bit
Pull-up control
(19) Port P6
S y n c h r o n o u s c l o c k s e l e c t i o n b i t
Serial I/O2 port selection bit
2
selection bit
D i r e c t i o n
r e g i s t e r
Port latchD a t a b u s
S e r i a l I / O 2 c l o c k o u t p u t
(21)COM0–COM
V
L 3
V
L 2
V
L1
Pull-up control
S e r i a l I / O 2 c l o c k i n p u t
A-D conversion input
Analog input pin selection bit
3
The gate input signal of each
transistor is controlled by the LCD
duty ratio and the bias value.
S e r i a l I / O 2 c l o c k o u t p u t
( 2 2 ) S E G0– S E G
VL2/V
V
L 1
/ V
S S
1 7
L3
Fig. 15 Port block diagram (4)
A-D conversion input
Analog input pin selection bit
T h e v o l t a g e a p p l i e d t o t h e s o u r c e s o f P c h a n n e l a n d N - c h a n n e l t r a n s i s t o r s i s t h e
c o n t r o l l e d v o l t a g e b y t h e b i a s v a l u e .
( 2 3 ) P o r t P 7
Data bus
0
V
SS
Direction
register
Port latch
I N T0 i n p u t
20
 Loading...
Loading...