Mitsubishi M37212M8-XXXSP, M37212M6-XXXSP, M37212M6-XXXFP, M37212EFSP, M37212EFFP Datasheet

To all our customers
Regarding the change of names mentioned in the document, such as Mitsubishi
Electric and Mitsubishi XX, to Renesas Technology Corp.
The semiconductor operations of Hitachi and Mitsubishi Electric were transferred to Renesas
Technology Corporation on April 1st 2003. These operations include microcomputer, logic, analog
and discrete devices, and memory chips other than DRAMs (flash memory, SRAMs etc.)
Accordingly, although Mitsubishi Electric, Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, Mitsubishi
Semiconductors, and other Mitsubishi brand names are mentioned in the document, these names
have in fact all been changed to Renesas Technology Corp. Thank you for your understanding.
Except for our corporate trademark, logo and corporate statement, no changes whatsoever have been
made to the contents of the document, and these changes do not constitute any alteration to the
contents of the document itself.
Note : Mitsubishi Electric will continue the business operations of high frequency & optical devices
and power devices.
Renesas Technology Corp.
Customer Support Dept.
April 1, 2003

MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37212M4/M8–XXXSP, M37212M6–XXXSP/FP
M37212EFSP/FP
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER for VOLTAGE SYNTHESIZER
with ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
1. DESCRIPTION
The M37212M6-XXXSP/FP, M37212M4/M8-XXXSP are single-chip
microcomputers designed with CMOS silicon gate technology. They
have a OSD, I2C-BUS interface, and PWM, so it is useful for a channel selection system for TV.
The feature of the M37212EFSP/FP are similar to those of the
M37212M6-XXXSP/FP except that these chips have a built-in PROM
which can be written electrically. The differences between the
M37212M6-XXXSP/FP and M37212M4/M8-XXXSP are the ROM size
and the RAM size as shown below. Accordingly, the following descriptions will be for M37212M6-XXXSP/FP unless otherwise noted.
2. FEATURES
●Number of basic instructions ..................................................... 71
●Memory size
ROM............... .........16K bytes (M37212M4-XXXSP)
24K bytes (M37212M6-XXXSP/FP)
32K bytes (M37212M8-XXXSP)
62K bytes (M37212EFSP/FP)
RAM .........................320 bytes (M37212M4-XXXSP)
384 bytes (M37212M6-XXXSP/FP)
576 bytes (M37212M8-XXXSP)
1280 bytes (M37212EFSP/FP)
(*ROM correction memory included)
●The minimum instruction execution time
.........................................0.5 µs (at 8 MHz oscillation frequency)
●Power source voltage .................................................. 5 V ± 10 %
●Subroutine nesting
maximum 96 levels (M37212M4/M8-XXXSP, M37212M6-XXXSP/FP)
maximum 128 levels (M37212EFSP/FP)
●Interrupts........................................................ 14 types, 14 vectors
●8-bit timers ................................................................................... 4
●Programmable I/O ports
(Ports P0, P10–P14, P2, P30, P31, P40, P41) ............................. 25
●Input ports (Ports P15–P17, P32–P37, P42) ............................... 10
●Output ports (Ports P52–P55, P60–P63)....................................... 8
●12 V withstand ports .................................................................. 12
●LED drive ports ............................................................................ 4
●Serial I/O............................................................. 8-bit ✕ 1 channel
●Multi-master I
●A-D comparator (6-bit resolution) .................................8 channels
●PWM output circuit..........................................14-bit ✕ 1, 8-bit ✕ 8
●Power dissipation..............................................................165 mW
●ROM correction function ................................................. 2 vectors
Note: Only M37212M8-XXXSP and M37212EFSP/FP have ROM
2
C-BUS interface ............................... 1 (2 systems)
(at 8 MHz oscillation frequency, VCC=5.5V, at OSD display)
correction function.
●OSD function
Display characters ................................... 24 characters ✕ 2 lines
(It is possible to display 3lines or more by software)
Kinds of characters ........................................................256 kinds
Character display area..............................................12 ✕ 16 dots
Kinds of character sizes..................................................... 3 kinds
Kinds of character colors .................................. 8 colors (R, G, B)
Coloring unit................... character, character background, raster
Display position.............................................................................
Horizontal: 64 levels Vertical: 128 levels
Attribute ..............................................................................border
3. APPLICA TION
TV
Rev. 1.0

M37212M4/M8–XXXSP, M37212M6–XXXSP/FP
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER for VOLTAGE SYNTHESIZER
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. DESCRIPTION ..........................................................................1
2. FEAUTURES .............................................................................1
3. APPLICATION............................................................................1
4. PIN CONFIGURATION ..............................................................3
5. FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM .............................................5
6. PERFORMANCE OVERVIEW...................................................6
7. PIN DESCRIPTION ...................................................................8
8. FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION.................................................12
8.1 CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT (CPU) .................... 12
8.2 MEMORY ..................................................................13
8.3 INTERRUPTS ...........................................................19
8.4 TIMERS.....................................................................24
8.5 SERIAL I/O................................................................27
8.6 MULTI-MASTER I2C-BUS INTERFACE....................31
8.7 PWM OUTPUT CIRCUIT ..........................................44
8.8 A-D COMPARA TOR ..................................................49
8.9 ROM CORRECTION FUNCTION .............................51
8.10 OSD FUNCTIONS...................................................52
8.10.1 Display Position .......................................56
8.10.2 Character Size.........................................60
8.10.3 Clock for OSD..........................................62
8.10.4 Memory for OSD......................................63
8.10.5 Color Register..........................................66
8.10.6 Border......................................................68
8.10.7 Multiline Display.......................................69
8.10.8 OSD Output Pin Control ..........................70
8.10.9 Raster Coloring Function.........................71
8.11. SOFTWARE RUNAWAY DETECT FUNCTION......72
8.12. RESET CIRCUIT....................................................73
8.13. CLOCK GENERATING CIRCUIT...........................74
8.14. DISPLAY OSCILLATION CIRCUIT ........................75
8.15. AUTO-CLEAR CIRCUIT .........................................75
8.16. ADDRESSING MODE ............................................75
8.17. MACHINE INSTRUCTIONS...................................75
9. PROGRAMMING NOTES........................................................75
10. ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS .........................................76
11. RECOMMENDED OPERATING CONDITIONS.....................76
12. ELECTRIC CHARACTERISTICS ..........................................77
13. A-D COMPARISON CHARACTERISTICS.............................79
14.
MULTI-MASTER I2C-BUS BUS LINE CHARACTERISTICS ...........
15. PROM PROGRAMMING METHOD.......................................80
16. DATA REQUIRED FOR MASK ORDERS..............................81
17. MASK CONFIRMATION FORM.............................................82
18. MARK SPECIFICATION FORM.............................................91
19.
ONE TIME PROM VERSIONS M37212EFSP/FP MARKING ....
20. APPENDIX .............................................................................94
21. PACKAGE OUTLINE ........................................................... 117
79
93
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37212EFSP/FP
with ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
Rev. 1.0
2
0
2
3
4
5
6
7
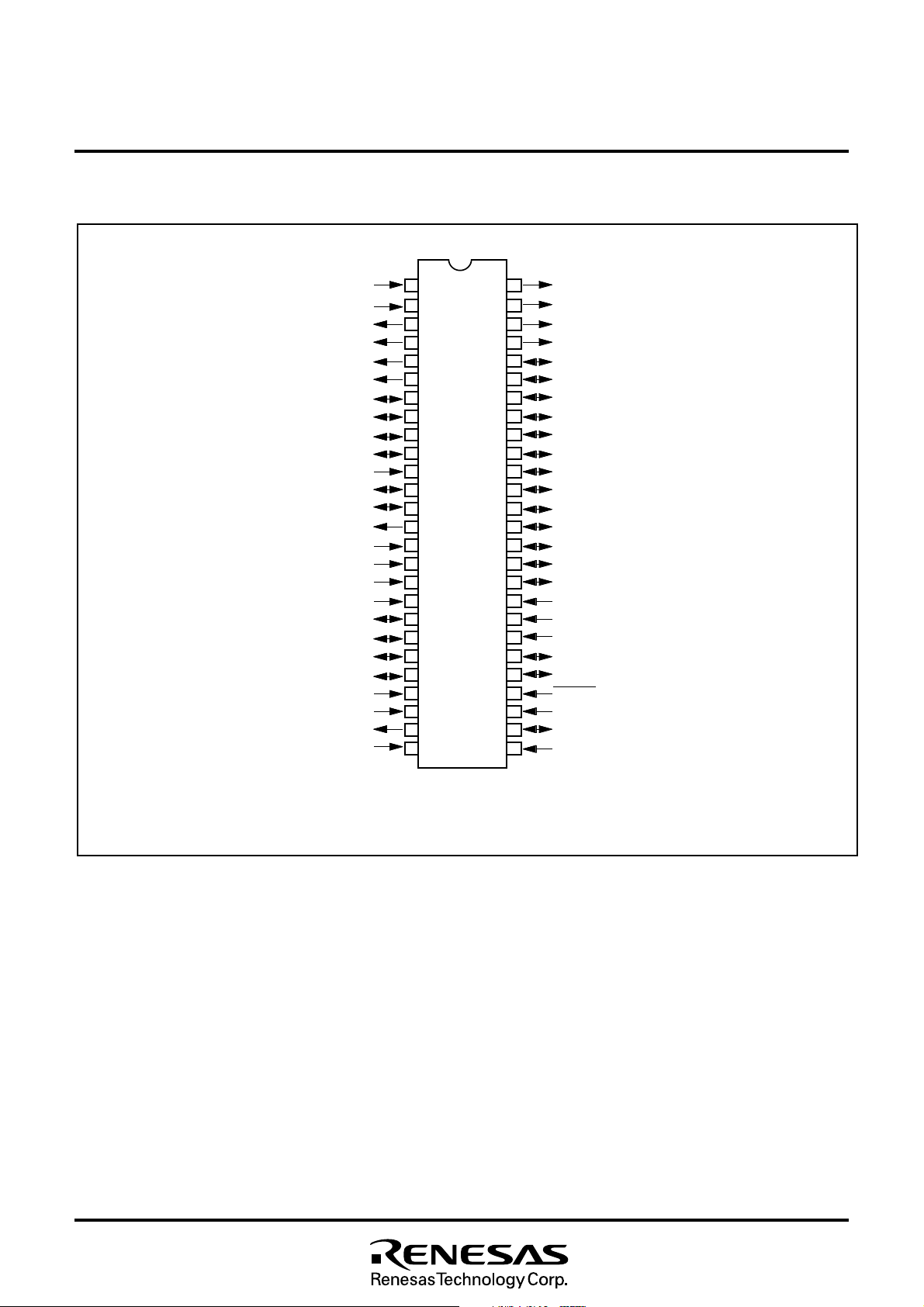
4. PIN CONFIGURATION
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37212M4/M8–XXXSP, M37212M6–XXXSP/FP
M37212EFSP/FP
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER for VOLTAGE SYNTHESIZER
with ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
3 7 2 1 2 M 4 / M 6 / M 8 - X X X S P , M 3 7 2 1 2 E F S
H
P 60/ P W M
P 61/ P W M 1
P 6
P 63/ P W M
P 00/ P W M
P 01/ P W M
P 02/ P W M
P 03/ P W M
P 42/ S
P 41/ S
C L K
P 40/ S
O U T ( / I N )
P 35/ I N T 2 / A - D 4
P 3
P 33/ T I M 3
P 3
V
2
/ P W M
I N
/ A - D 5
/ A - D 6
/ A - D 7
4
/ I N T 1
2
/ T I M 2
C N V
X
S Y N C
S Y N C
D A
P 2
P 2
P 2
P 2
X
O U T
V
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1 0
1 1
1 2
1 3
1 4
1 5
1 6
1 7
1 8
4
1 9
5
2 0
6
2 1
7
2 2
S S
2 3
I N
2 4
2 5
2 6
S S
M
P
5 2
5 1
5 0
4 9
4 8
4 7
4 6
4 5
4 4
4 3
4 2
4 1
4 0
3 9
3 8
3 7
3 6
3 5
3 4
3 3
3 2
3 1
3 0
2 9
2 8
2 7
P 52/ R
P 53/ G
P 54/ B
P 55/ O U T 1
0
P 2
P 2
1
P 2
2
P 2
3
P 0
4
P 0
5
P 0
6
P 0
7
P 10/ O U T 2 / A - D 8
1
/ S C L 1
P 1
P 12/ S C L 2
P 13/ S D A 1
4
/ S D A 2
P 1
P 15/ I N T 3 / A - D 1
P 16/ A - D 2
P 17/ A - D 3
0
P 3
P 31
R E S E T
O S C 1 / P 3
O S C 2 / P 3
V
6
7
C C
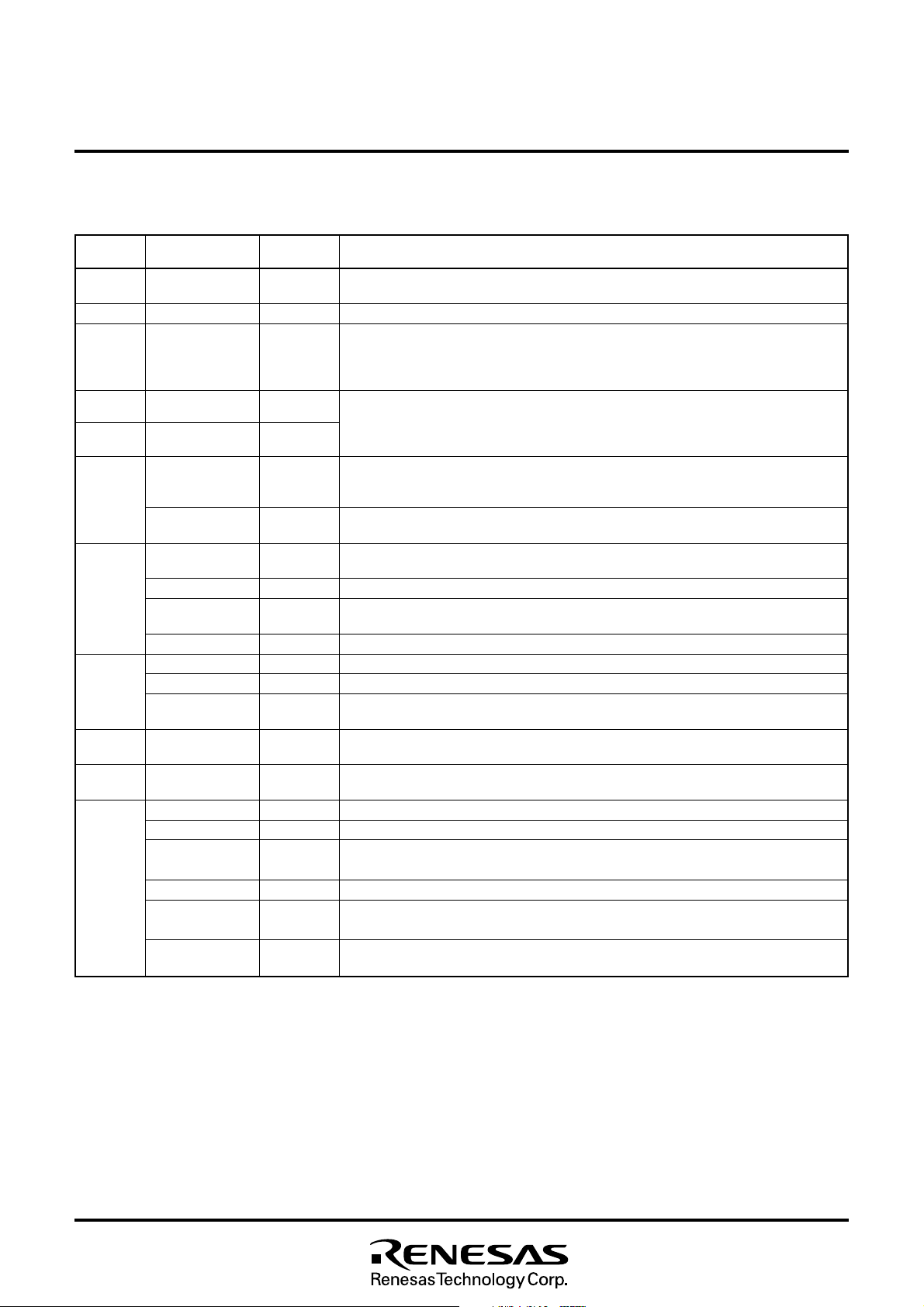
Fig. 4.1 Pin Configuration 1 (Top View)
Rev. 1.0
Outline 52P4B
3
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37212M4/M8–XXXSP, M37212M6–XXXSP/FP
M37212EFSP/FP
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER for VOLTAGE SYNTHESIZER
with ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
8
/
5
1
I N T 3 / A - D 1P
A - D 2
P
/
/
6
7
C
1
C
1
A - D 3
P
N
N
CN
CN
2
2
/
S C L
/
2
1
S D A 1P
/
3
4
C
1
1
P
S D A
N
/
2
3
C
N
CN
CN
CN
4
2
2
0
P
P
P
75
5
6
0
0
0
P
P
P
/
0
1
C
1
1
O U T 2 / A - D
P
S C L 1P
P
N
P 2
N C
P 2
5
/ O U T 1
P 5
P 5
4
/ B
3
/ G
P 5
P 52/ R
N C
N C
H
S Y N C
V
S Y N C
P 60/ P W M 0
P 6
1
/ P W M 1
P 6
2
/ P W M 2
N C
P 6
3
/ P W M 3
3
1
8
9
7
4
6
6
6
1
0
6 5
6 6
6 7
6 8
6 9
7 0
7 1
7 2
7 3
7 4
7 5
7 6
7 7
7 8
7 9
8 0
1234567
C
N
C
C
N
N
5
6
6
M 3 7 2 1 2 M 6 - X X X F P , M 3 7 2 1 2 E F F P
5
4
C
N
/
/
1
0
0
0
P
P
P W M
P W M
0
1
3
2
6
4
5
6
/
2
0
P
P W M
5
5
5
5
5
0
1
8
9
7
C
N
/
3
0
P
P W M
2
1
1
1
7
5
6
/
/
/
)
K
N
I
S
C
/
2
S
/
4
1
O
P
4
S
/
P
0
4
A - D
A - D
L
P
A - D
U T ( / I N
0
2
5
3
1
A
D
9
5
5
4
4
5
6
1
1
1
1
4
3
/
/
4
3
3
3
P
P
/
5
I N T
3
T I M
P
I N T 2 / A - D
6
7
8
4
4
4
7
8
9
1
1
1
5
4
2
2
2
P
P
/
2
3
P
T I M
3
4
5
4
4
0
1
2
2
6
C
2
N
P
1
2
4
4
4
2
2
C
N
4 0
3 9
3 8
3 7
3 6
3 5
3 4
3 3
3 2
3 1
3 0
2 9
2 8
2 7
2 6
2 5
4
3
2
2
C
C
N
N
P 3
0
N C
P 31
R E S E T
O S C 1 / P 3
O S C 2 / P 3
V
C C
N C
N C
V
S S
X
O U T
X
I N
C N V
S S
P
2
7
N C
N C
6
7
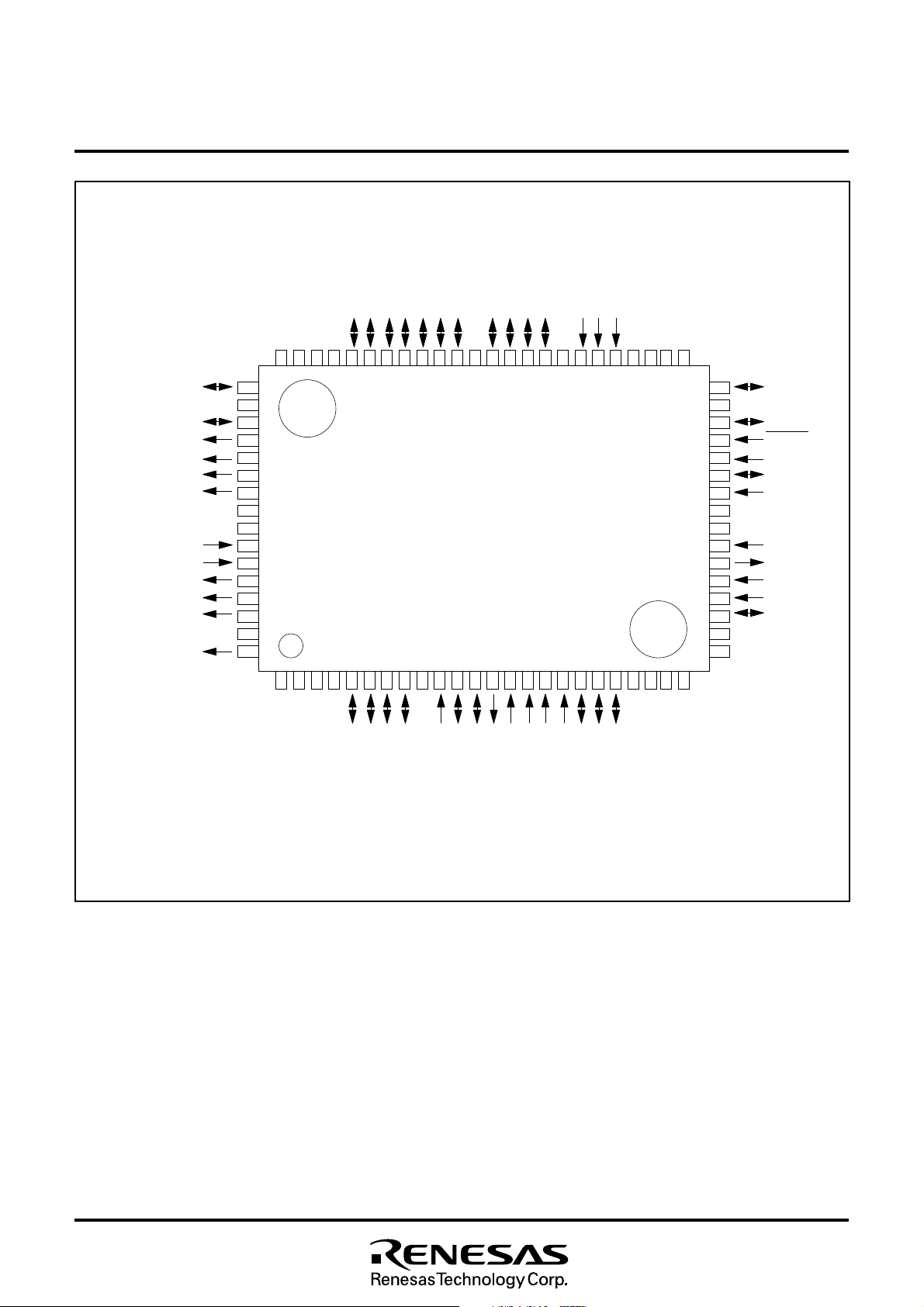
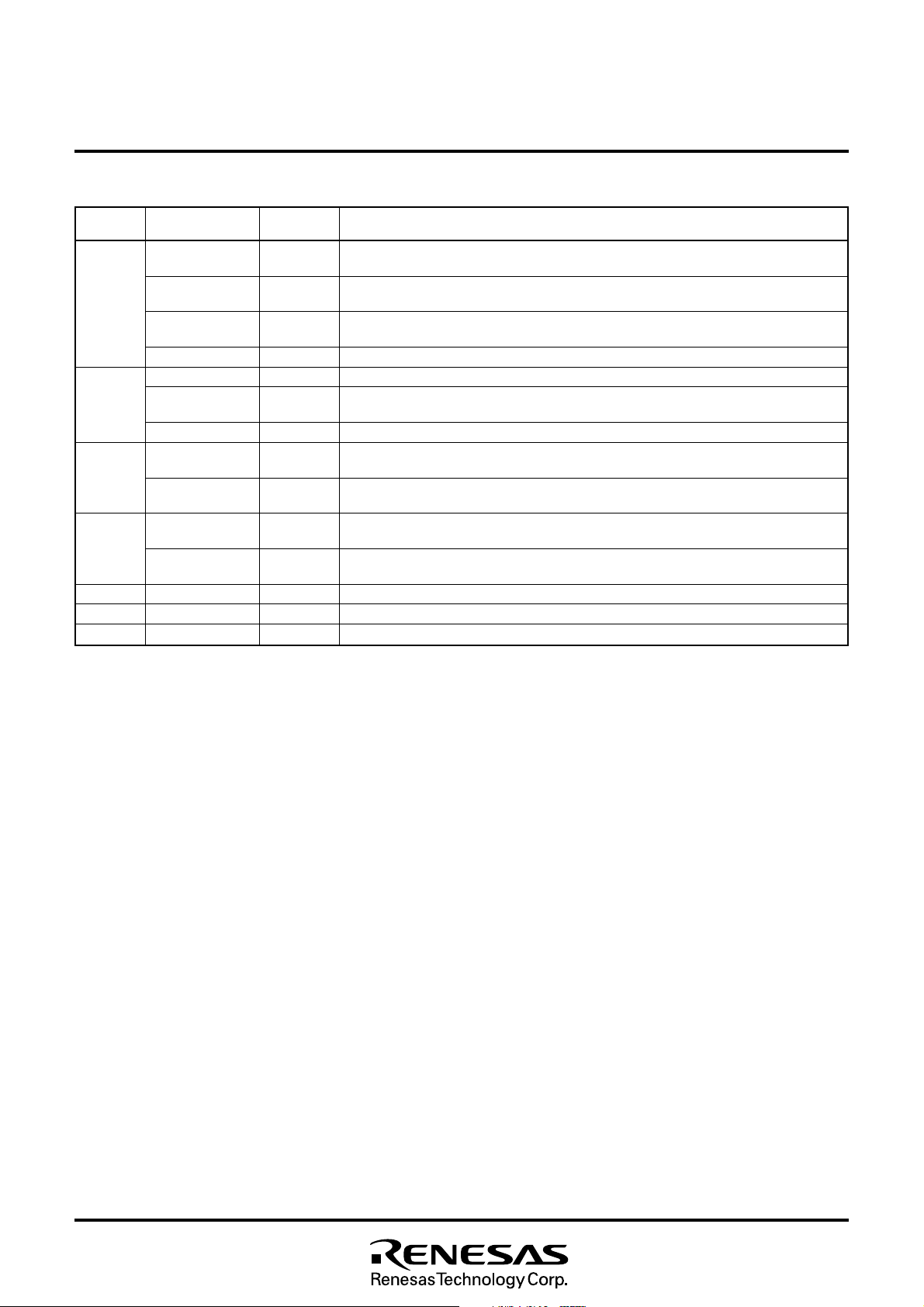
Fig. 4.2 Pin Configuration 2 (Top View)
4
Outline 80P6N-A
NC : Unconnected
Rev. 1.0
M37212M4/M8–XXXSP, M37212M6–XXXSP/FP
OUT1
Clock input Clock output
X
IN
X
OUT
Reset input
V
CC
V
SS
CNV
SS
Clock output for display
Input ports P3
6,
P3
7
OSC1 OSC2
Clock input for display
INT2
INT1
P5 (4)
B
G
R
H
SYNC
V
SYNC
A-D
comparator
14-bit
PWM circuit
8-bit PWM circuit
Accumulator
A (8)
Timer 4
T4 (8)
Timer 3
T3 (8)
Timer 2
T2 (8)
Timer 1
T1 (8)
Timer count source
selection circuit
TIM2
TIM3
Instruction
register (8)
Instruction
decoder
Control signal
CRT circuit
Stack
pointer
S (8)
Index
register
Y (8)
Index
register
X (8)
Processor
status
register
PS (8)
8-bit
arithmetic
and
logical unit
ROM
Program
counter
PC
L
(8)
Program
counter
PC
H
(8)
RAM
Data bus
Clock
generating
circuit
RESET
Output ports P5
2
–P5
5
Address bus
SI/O(8)
S
IN
S
CLK
S
OUT(/IN)
INT3
4142 434410 9 8 7
I/O port P0
3334353637383940
P1 (8)
I/O ports P1
0
–P1
4
2221 201945 464748
P2 (8)
I/O port P2
I/O ports P3
0
, P3
1
18 313214
P3 (6)
Multi-master
I C-BUS interface
P0 (8)
SDA
SCL
49 5051
52 2 1
2524
30
27 26
23
29
28
( ) Timing output
OUT2
DA
2
1516 17
P4 (3)
111213
PWM5
PWM4
PWM3
PWM2
PWM1
PWM0
PWM7
PWM6
Input ports P1
5
–P1
7
Input ports P3
2
–P3
5
P6 (4)
Output ports P6
0
–P6
3
6
5 4 3
I/O ports P4
0
, P4
1
Input port P4
2
Output for display
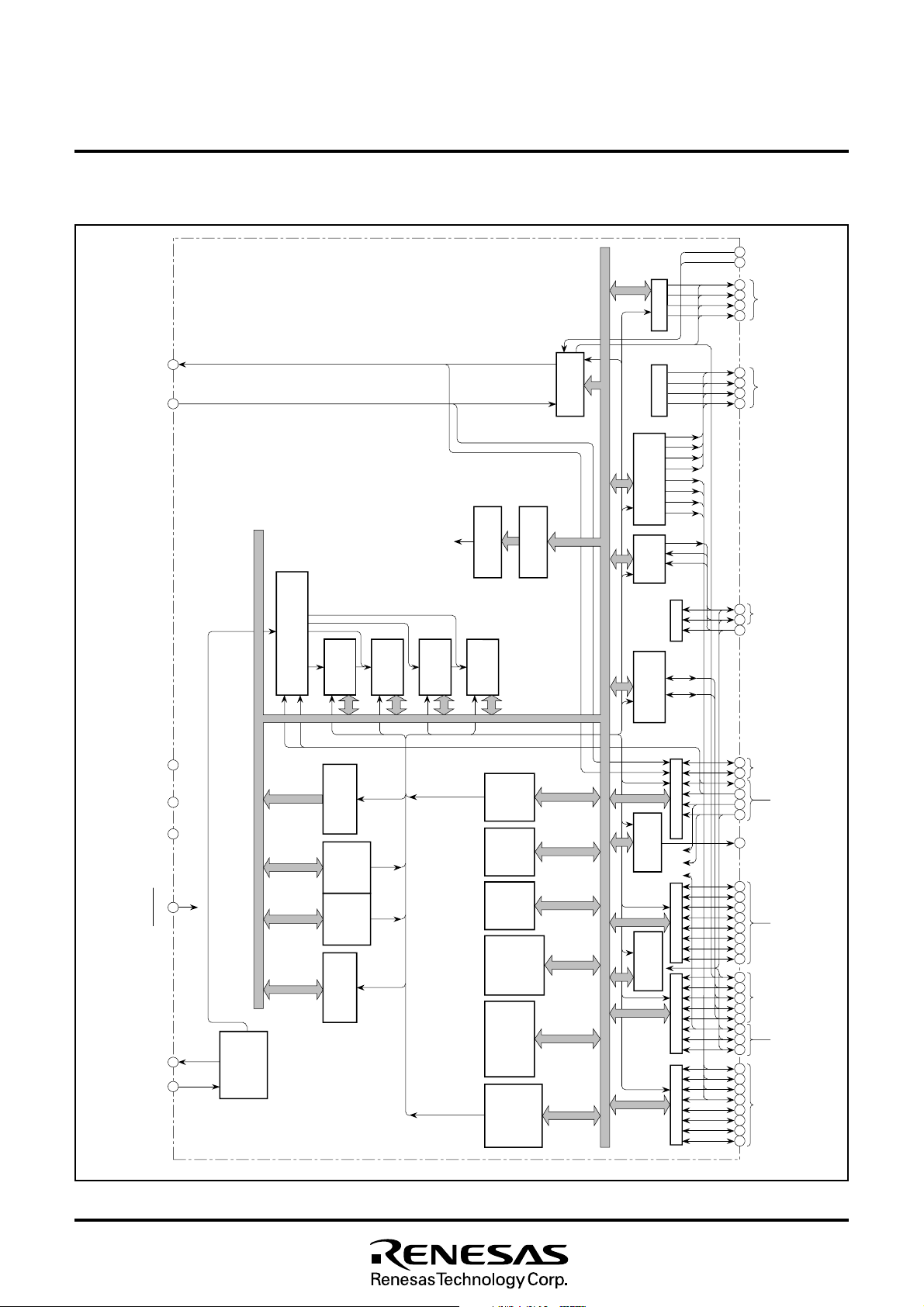
5. FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37212EFSP/FP
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER for VOLTAGE SYNTHESIZER
with ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
Fig. 5.1 Functional Block Diagram of M37212
Rev. 1.0
5
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37212M4/M8–XXXSP, M37212M6–XXXSP/FP
M37212EFSP/FP
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER for VOLTAGE SYNTHESIZER
with ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
6. PERFORMANCE OVERVIEW
Table 6.1 Performance Overview
Parameter Functions
Number of basic instructions 71
Number of basic instructions 0.5 µs (the minimum instruction execution time, at 8 MHz oscillation fre
Instruction execution time 8 MHz (maximum)
Memory size ROM M37212M4-XXXSP 16K bytes
M37212M6-XXXSP/FP
M37212M8-XXXSP 32K bytes
M37212EFSP/FP 62K bytes
RAM M37212M4-XXXSP 320 bytes
M37212M6-XXXSP/FP
M37212M8-XXXSP 576 bytes (ROM correction memory included)
M37212EFSP/FP 1280 bytes (ROM correction memory included)
OSD ROM 8 K bytes
OSD RAM 96 bytes
Input/Output ports P0 I/O 8-bit ✕ 1 (N-channel open-drain output structure, can be used as PWM
P10–P14 I/O 5-bit ✕ 1 (CMOS input/output output structure, however, N-channel open-
P15–P17 Input 3-bit ✕ 1 (can be used as INT input pin, A-D input pins)
P20–P27 I/O 8-bit ✕ 1 (CMOS input/output structure)
P30, P31 I/O 2-bit ✕ 1 (CMOS input/output structure)
P32–P37 Input 6-bit ✕ 1 (can be used as external clock input pins, INT input pins, OSD
P40, P41 I/O 2-bit ✕ 1 (N-channel open-drain output structure, can be used as serial I/O
P42 Input 1-bit ✕ 1(can be used as serial input pin, A-D input pin)
P52–P55 Output 4-bit ✕ 1 (CMOS output structure, can be used as OSD output pins)
P60–P63 Output 4-bit ✕ 1 (N-channel open-drain output structure, can be used as PWM
Serial I/O 8-bit ✕ 1
Multi-master I2C-BUS interface 1 (2 systems)
A-D comparator 8 channels (6-bit resolution)
PWM output circuit 14-bit ✕ 1, 8-bit ✕ 8
Timers 8-bit timer ✕ 4
Subroutine nesting 96 levels (maximum)
Interrupt <14 sources>
Clock generating circuit 2 built-in circuits (externally connected a ceramic resonator or a quartz-
quency)
24K bytes
384 bytes
output pins)
drain output structure, when P11–P14 are used as multi-master I2C-BUS
interface, can be used as OSD output, A-D input, multi-master I2C-BUS
interface)
display clock I/O pins, A-D input pins)
pins, A-D input pins)
output pins)
INT external interrupt ✕ 3, Internal timer interrupt ✕ 4, Serial I/O interrupt ✕
OSD interrupt ✕ 1, Multi-master I2C-BUS interface interrupt ✕ 1, f(XIN)/
interrupt ✕ 1, VSYNC interrupt ✕ 1, BRK interrupt ✕ 1, Reset ✕ 1
crystal oscillator)
1,
4096
Rev. 1.0
6

MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37212M4/M8–XXXSP, M37212M6–XXXSP/FP
M37212EFSP/FP
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER for VOLTAGE SYNTHESIZER
with ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
Table 6.2 Performance Overview (continued)
Parameter Functions
OSD display Number of display characters 24 characters ✕ 2 lines
function
Power source voltage 5 V ± 10 %
Power dissipation OSD ON 165 mW typ. (at oscillation frequency f(XIN) = 8 MHz, fOSC = 8 MHz)
Operating temperature range –10 °C to 70 °C
Device structure CMOS silicon gate process
Package M37212M4/M6/M8-XXXSP, M37212EFSP 52-pin plastic molded SDIP
Dot structure 12 ✕ 16 dots
Kinds of characters 254 kinds
Kinds of character sizes 3 kinds
Character font coloring 1 screen: 8 kinds (per character unit)
Display position Horizontal: 64 levels, Vertical: 128 levels
OSD OFF 110 mW typ. (at oscillation frequency f(XIN) = 8 MHz)
In stop mode 1.65 mW (maximum)
M37212M6-XXXFP, M37212EFSP 80-pin plastic molded QFP
Rev. 1.0
7
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37212M4/M8–XXXSP, M37212M6–XXXSP/FP
M37212EFSP/FP
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER for VOLTAGE SYNTHESIZER
with ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
7. PIN DESCRIPTION
Table 7.1 Pin Description
Pin Name
VCC, Power source Apply voltage of 5 V ± 10 % to (typical) VCC, and 0 V to VSS.
VSS.
CNVSS CNVSS This is connected to VSS.
______
RESET Reset input Input To enter the reset state, the reset input pin must be kept at a “L” for 2 µs or more (under
XIN Clock input Input This chip has an internal clock generating circuit. To control generating frequency, an
XOUT Clock output Output XOUT. If an external clock is used, the clock source should be connected to the XIN pin and
P00/PWM4–
P03/PWM7,
P04–P07 is N-channel open-drain output. (See note)
P10/OUT2/
A-D8,
P11/SCL1,
P12/SCL2,
P13/SDA1, I2C-BUS interface I2C-BUS interface is used. The output structure is N-channel open-drain output.
P14/SDA2, Analog input Input P10 pin is also used as analog input pin A-D8.
P15/INT3/ Input port P1 Input Port P15–P17 are a 3-bit input port and has basically the same functions as port P0.
A-D1,
P16/A-D2,
P17/A-D3 input
P20–P27 I/O port P2 I/O Port P2 is an 8-bit I/O port and has basically the same functions as port P0. The output
P30, P31 I/O port P3 I/O Ports P30, P31 are a 2-bit I/O port and has basically the same functions as port P0. The
P32/TIM2, Input port P3 Input Ports P32–P37 are a 6-bit input port and has basically the same functions as port P0.
P33/TIM3,
P34/INT1, External interrupt Input Pins P34, P35 are also used as INT external interrupt input pins INT1, INT2 respectively.
P35/INT2/
A-D4, Analog input Input P35 pin is also used as analog input pin A-D4.
P36/OSC1,
P37/OSC2
I/O port P0 I/O Port P0 is an 8-bit I/O port with direction register allowing each I/O bit to be individually
PWM output Output Pins P00–P03 are also used as PWM output pins PWM4–PWM7 respectively. The output
I/O port P1 I/O Port P10–P14 are a 5-bit I/O port and has basically the same functions as port P0. The
OSD output Output Pins P10 is also used as OSD output pin OUT2. The output structure is CMOS output.
Multi-master I/O Pins P11–P14 are used as SCL1, SCL2, SDA1 and SDA2 respectively, when multi-master
Analog input Input Pins P15–P17 are also used as analog input pins A-D1 to A-D3 respectively.
External interrupt Input P15 pin is also used as INT external interrupt input pin INT3.
External clock input
input
Clock input for Input P36 pin is also used as OSD display clock input pin OSC1.
OSD display
Clock output for Output P37 pin is also used as OSD display clock output pin OSC2. The output structure is CMOS
OSD display output.
Input/
Output
normal VCC conditions).
If more time is needed for the quartz-crystal oscillator to stabilize, this “L” condition should
be maintained for the required time.
external ceramic resonator or a quartz-crystal oscillator is connected between pins XIN and
the XOUT pin should be left open.
programmed as input or output. At reset, this port is set to input mode. The output structure
structure is N-channel open-drain output.
output structure is CMOS output.
structure is CMOS output. (See note)
output structure is CMOS output.
Input Pins P32, P33 are also used as external clock input pins TIM2, TIM3 respectively.
Functions
Rev. 1.0
8
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37212M4/M8–XXXSP, M37212M6–XXXSP/FP
M37212EFSP/FP
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER for VOLTAGE SYNTHESIZER
with ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
Table 7.2 Pin Description (continued)
Pin Name
P40/SOUT(/IN)/
A-D7, output structure is N-channel open-drain output.
P41/SCLK/ Serial I/O data I/O Pin P40 is also used as serial I/O data input/output pin SOUT(/IN). The output structure is NA-D6, input/output channel open-drain output.
P42/SIN/ Input port P4 Input Port P42 is a 1-bit input port and has basically the same functions as port P0.
A-D5, Serial I/O data Input Pin P42 is also used as serial I/O data input pin SIN.
P52/R, Output port P5 Output Ports P52–P55 are a 4-bit output port and has basically the same functions as port P0. The
P53/G,
P54/B,
P55/OUT1 structure is CMOS output.
P60PWM0–
P63/PWM3
HSYNC HSYNC input Input This is a horizontal synchronizing signal input for OSD.
VSYNC VSYNC input Input This is a vertical synchronizing signal input for OSD.
DA DA output Output This is a 14-bit PWM output pin.
Note : Port Pi (i = 0 to 3) has the port Pi direction register which can be used to program each bit as an input (“0”) or an output (“1”). The pins programmed as “1” in
I/O port P4 I/O Ports P40, P41 are a 2-bit I/O port and has basically the same functions as port P0. The
Serial I/O synchronizing
clock input/output structure is N-channel open-drain output.
Analog input pin Input Pin P40, P41 are also used as analog input pins A-D7, A-D6 respectively.
input
Analog input Input Pin P42 is also used as analog input pin A-D5.
OSD output Output Pins P52–P55 are also used as OSD output pins R, G, B, OUT1 respectively. The output
Output port P6 Output Ports P60–P63 are a 4-bit I/O port and has basically the same functions as port P0. The
PWM output Output Pins P60–P63 are also used as PWM output pins PWM0–PWM3 respectively. The output
the direction register are output pins. When pins are programmed as “0,” they are input pins. When pins are programmed as output pins, the output data are
written into the port latch and then output. When data is read from the output pins, the output pin level is not read but the data of the port latch is read. This
allows a previously-output value to be read correctly even if the output “L” voltage has risen, for example, because a light emitting diode was directly driven.
The input pins are in the floating state, so the values of the pins can be read. When data is written into the input pin, it is written only into the port latch, while
the pin remains in the floating state.
Input/
Output
I/O Pin P41 is also used as serial I/O synchronizing clock input/output pin S CLK. The output
output structure is CMOS output.
output structure is N-channel open-drain output.
structure is N-channel open-drain output.
Functions
Rev. 1.0
9
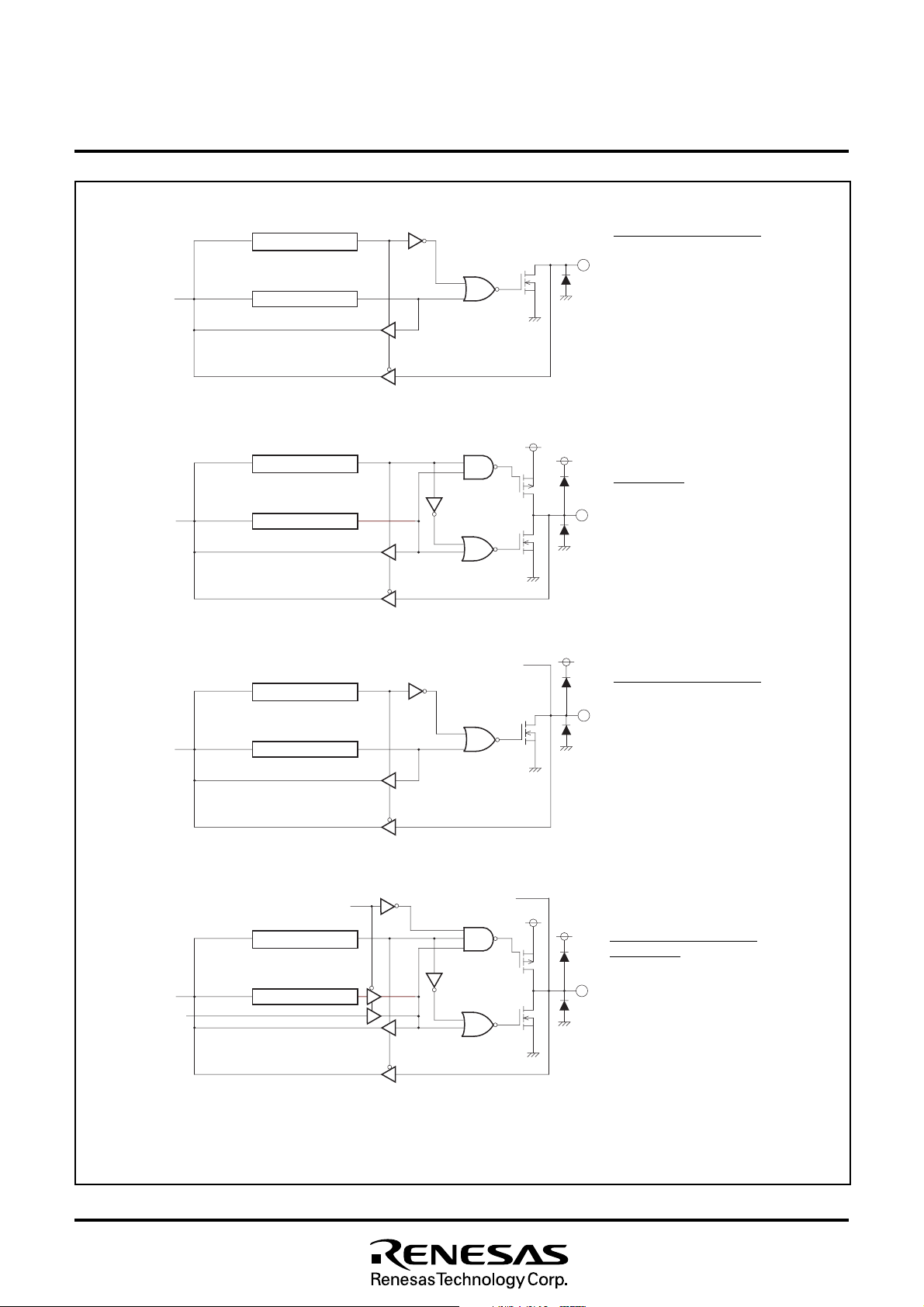
Port P0
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37212M4/M8–XXXSP, M37212M6–XXXSP/FP
M37212EFSP/FP
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER for VOLTAGE SYNTHESIZER
with ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
N-channel open-drain output
Direction register
Port P0
Data bus
Ports P10, P2, P30, P3
Data bus
Ports P4
0, P41
Data bus
1
Port latch
Direction register
Port latch
Direction register
Port latch
SIN, S
CLK
Note :Each port is also used as follows :
P00–P03 : PWM4–PWM7
CMOS output
Ports P10, P2, P30, P31
Note :Port P10 is also used as OUT2/
A-D8.
N-channel open-drain output
Ports P40, P41
Note :Each port is also used as follows :
P40 : SOUT(/IN)/A-D7
P41 : SCLK/A-D6
Ports P11–P1
Data bus
I2C-BUS clock
2
I
C-BUS data
4
Fig. 7.1 I/O Pin Block Diagram (1)
10
BSEL0
BSEL1
Direction register
Port latch
SCL1, SCL2,
SDA1, SDA2
N-channel open-drain output
CMOS output
Ports P11–P14
Notes 1: Each port is also used as follows :
P11 : SCL1
P12 : SCL2
P13 : SDA1
P14 : SDA2
2: The output structure of ports P11–
P14 is N-channel open-drain output
when using as multi-master I2CBUS interface (it is the same with
ports P40 and P41).
Rev. 1.0
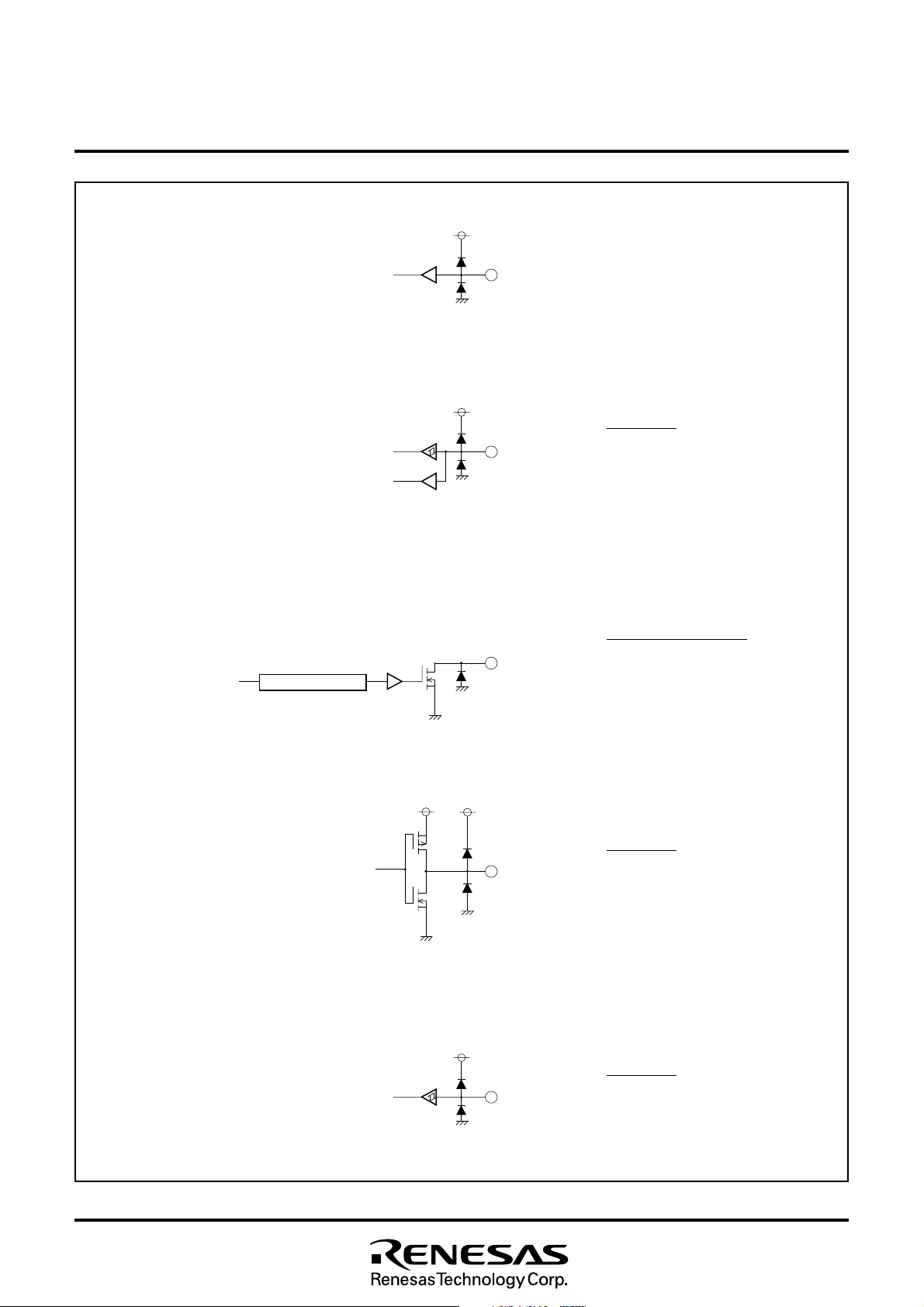
Ports P1
6
, P1
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37212M4/M8–XXXSP, M37212M6–XXXSP/FP
M37212EFSP/FP
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER for VOLTAGE SYNTHESIZER
with ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
7
Ports P1
5
, P32–P37, P4
Ports P60–P6
Data bus
Data bus
2
TIM2, TIM3,
INT1,
IN
INT2, S
3
Port latch
, INT3
Data bus
Ports P16, P17
Note : Each port is also used as follows :
P16 : A-D2
P17 : A-D3
Schmidt input
Ports P15, P32–P37, P42
Note : Each port is also used as follows :
P15 : INT3/A-D1
P32 : TIM2
P33 : TIM3
P34 : INT1
P35 : INT2/A-D4
P36 : OSC1
P37 : OSC2
P42 : SIN/A-D5
N-chanel open drain output
Ports P60–P63
Note :Each port is also used as follows :
P60–P63 : PWM0–PWM3
D-A, R, G, B, OUT1 , OUT2
H
SYNC
, V
SYNC
Fig. 7.2 I/O Pin Block Diagram (2)
Rev. 1.0
Internal circuit
Internal circuit
CMOS output
Ports D-A, R, G, B, OUT1, OUT2
Note : Each pin is also used as follows :
R : P52
G : P53
B : P54
OUT1 : P55
OUT2 : P10/A-D8
Schmidt input
Ports HSYNC, VSYNC
11
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
0
0
W
W
M37212M4/M8–XXXSP, M37212M6–XXXSP/FP
M37212EFSP/FP
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER for VOLTAGE SYNTHESIZER
with ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
8. FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
8.1 CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT (CPU)
This microcomputer uses the standard 740 Family instruction set.
Refer to the table of 740 Family addressing modes and machine
instructions or the SERIES 740 <Software> User’s Manual for details on the instruction set.
Machine-resident 740 Family instructions are as follows:
The FST, SLW instruction cannot be used.
The MUL, DIV, WIT and STP instructions can be used.
C P U M o d e R e g i s t e r
b 7b 6b 5b 4b 3 b 2b 1b 0
1
1
111
C P U m o d e r e g i s t e r ( C M ) [ A d d r e s s 0 0 F B
B
0 , 1
S t a c k p a g e s e l e c t i o n
2
b i t ( C M 2 ) ( S e e n o t e )
N a m eF
F i x t h e s e b i t s t o “ 0 . ”
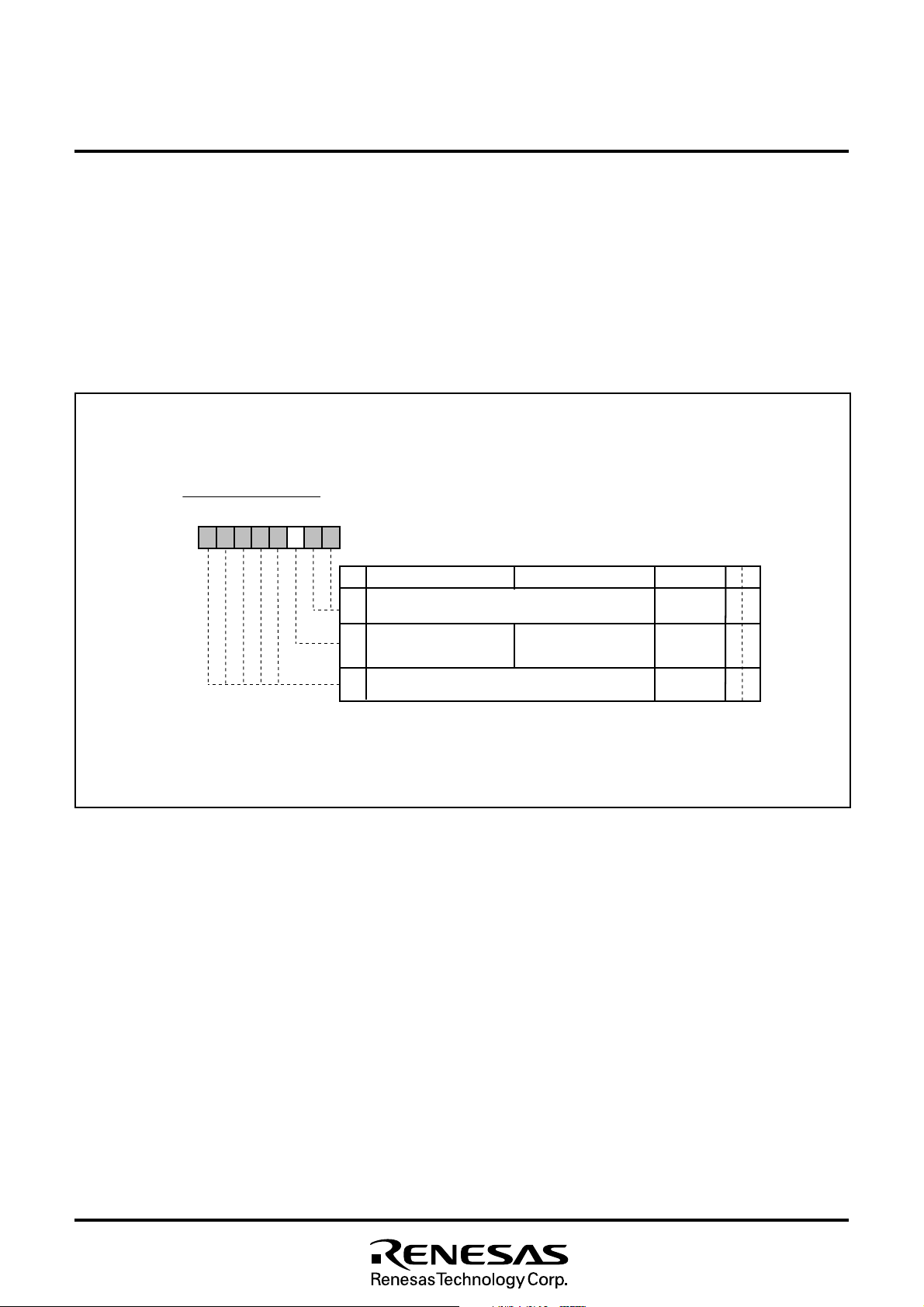
8.1.1 CPU Mode Register
The CPU mode register contains the stack page selection bit and
internal system clock selection bit. The CPU mode register is allocated at address 00FB16.
1 6
]
u n c t i o n
0 : 0 p a g e
1 : 1 p a g e
s
A f t e r r e s e t
I n d e t e r m i n a t e
1
RW
R
RW
Fig. 8.1.1 CPU Mode Register
F i x t h e s e b i t s t o “ 1 . ”
3 t o 7
N o t e : T h i s b i t i s s e t t o “ 1 ” a f t e r t h e r e s e t r e l e a s e .
I n d e t e r m i n a t e
R
Rev. 1.0
12
M37212M4/M8–XXXSP, M37212M6–XXXSP/FP
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER for VOLTAGE SYNTHESIZER
8.2 MEMORY
8.2.1 Special Function Register (SFR) Area
The special function register (SFR) area in the zero page contains
control registers such as I/O ports and timers.
8.2.2 RAM
RAM is used for data storage and for stack area of subroutine calls
and interrupts.
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37212EFSP/FP
with ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
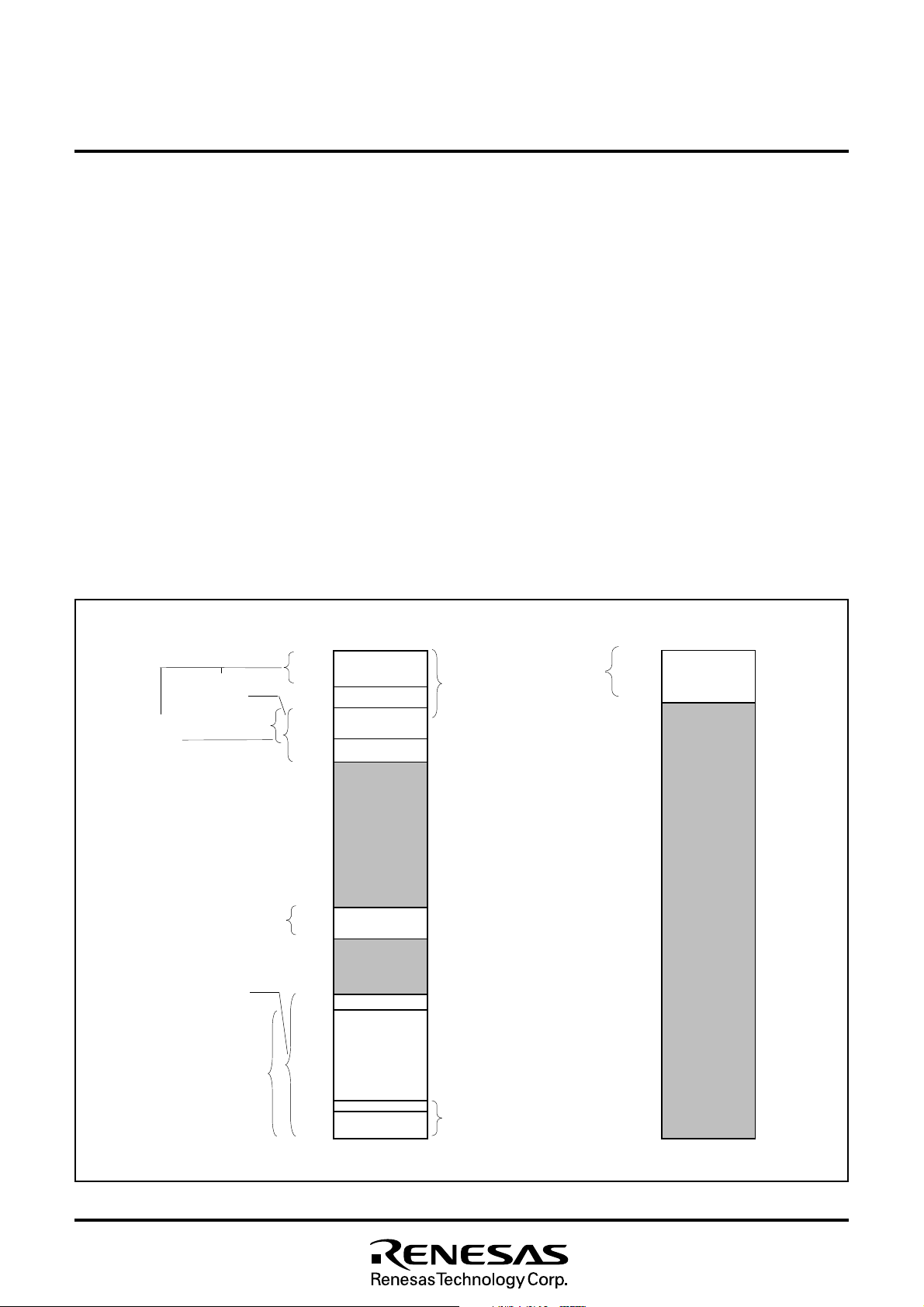
8.2.7 Zero Page
The 256 bytes from addresses 000016 to 00FF16 are called the zero
page area. The internal RAM and the special function registers (SFR)
are allocated to this area.
The zero page addressing mode can be used to specify memory and
register addresses in the zero page area. Access to this area with
only 2 bytes is possible in the zero page addressing mode.
8.2.3 ROM
ROM is used for storing user programs as well as the interrupt vector
area.
8.2.4 OSD RAM
RAM for display is used for specifying the character codes and colors to display.
8.2.5 OSD ROM
ROM for display is used for storing character data.
8.2.6 Interrupt Vector Area
The interrupt vector area contains reset and interrupt vectors.
■ M 3 7 2 1 2 M 4 / M 8 - X X X S P , M 3 7 2 1 2 M 6 - X X X S P / F P
0 0 0 0
1 6
M 3 7 2 1 2 M 4 -
X X X S P
R A M
( 3 2 0 b y t e s )
M 3 7 2 1 2 M 6 -
X X X S P / F P
R A M
( 3 8 4 b y t e s )
0 0 B F
0 0 C 0
0 0 F F
0 1 0 0
0 1 7 F
0 1 B F
1 6
1 6
S F R a r e a
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
8.2.8 Special Page
The 256 bytes from addresses FF0016 to FFFF16 are called the special page area. The special page addressing mode can be used to
specify memory addresses in the special page area. Access to this
area with only 2 bytes is possible in the special page addressing
mode.
8.2.9 ROM Correction Memory (RAM)
This is used as the program area for ROM correction.
Note: Only M37212M8-XXXSP and M37212EFSP/FP have ROM correction
memory.
1 0 0 0 0
Z e r o p a g e
O S D R O M
( 8 K b y t e s )
1 1 F F F
1 6
1 6
N o t u s e d
M 3 7 2 1 2 M 6 -
X X X S P / F P
R O M
( 2 4 K b y t e s )
M 3 7 2 1 2 M 4 -
X X X S P
R O M
( 1 6 K b y t e s )
O S D R A M
( 9 6 b y t e s )
( S e e n o t e )
0 6 0 0
0 6 B 7
A 0 0 0
C 0 0 0
F F 0 0
F F D E
F F F F
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
I n t e r r u p t v e c t o r a r e a
1 6
N o t u s e d
S p e c i a l p a g e
Fig. 8.2.1 Memory Map (M37212M4/M8-XXXSP, M37212M6-XXXSP/FP)
Rev. 1.0
N o t u s e d
1 F F F F
1 6
N o t e : R e f e r t o T a b l e 8 . 1 0 . 3 O S D R A M .
13
M37212M4/M8–XXXSP, M37212M6–XXXSP/FP
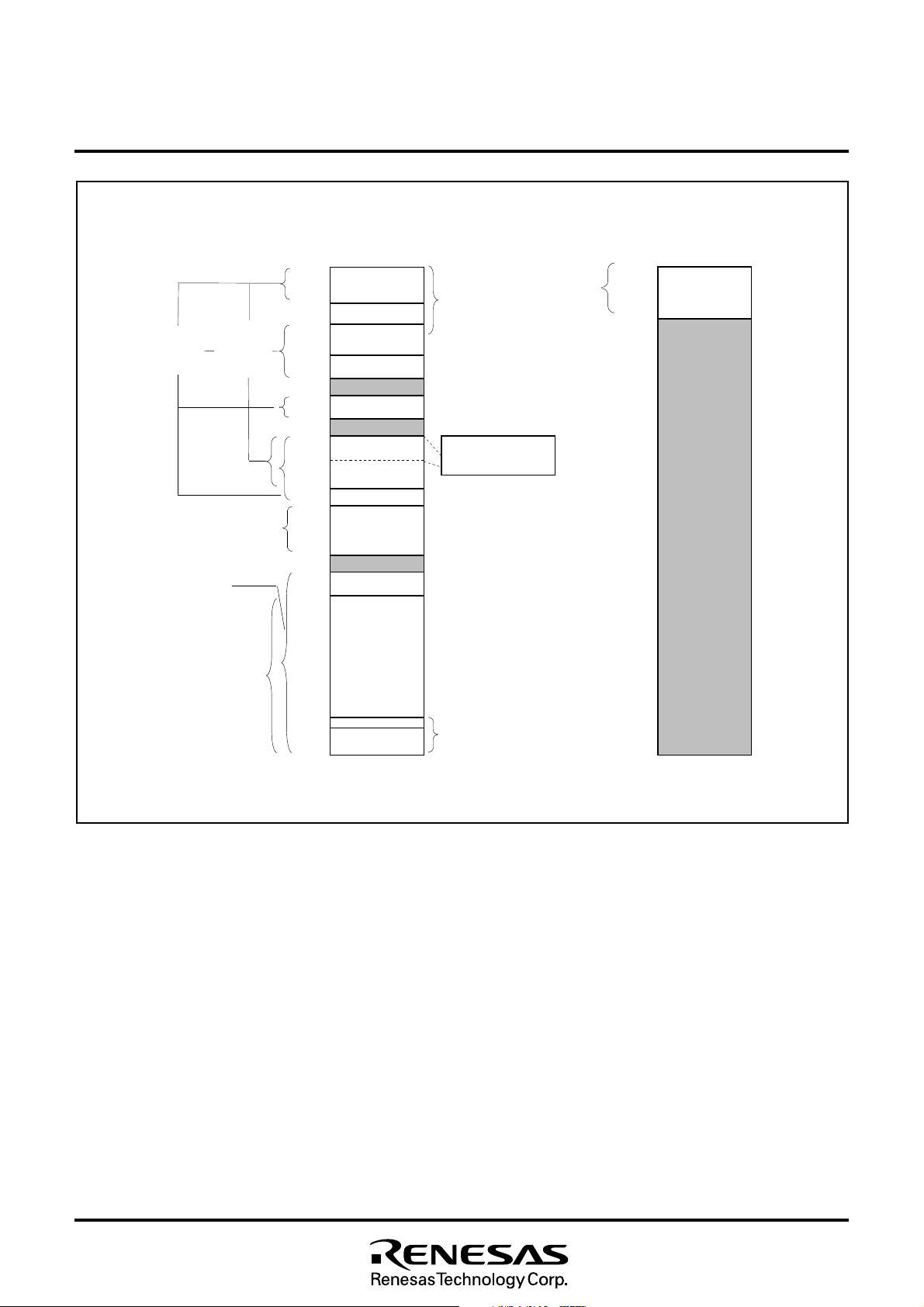
■ M 3 7 2 1 2 M 8 - X X X S P , M 3 7 2 1 2 E F S P / F P
0 0 0 0
1 6
0 0 B F
1 6
0 0 C 0
1 6
0 0 F F
M 3 7 2 1 2 E F S P
R A M
( 1 2 8 0 b y t e s )
M 3 7 2 1 2 E F S P
( 6 2 K b y t e s )
R O M
M 3 7 2 1 2 M 8 -
X X X S P
R A M
( 5 7 6 b y t e s )
O S D R A M
( 9 6 b y t e s )
( S e e n o t e )
0 1 0 0
0 1 F F
0 2 1 7
0 2 1 B
0 2 C 0
0 2 E 0
0 3 3 F
0 5 F F
0 6 0 0
0 6 B 7
0 8 0 0
8 0 0 0
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37212EFSP/FP
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER for VOLTAGE SYNTHESIZER
with ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
1 0 0 0 0
S F R a r e a
N o t u s e d
2 p a g e r e g i s t e r
N o t u s e d
N o t u s e d
Z e r o p a g e
R O M c o r r e c t i o n f u n c t i o n
V e c t o r 1 : a d d r e s s 0 2 C 0
V e c t o r 2 : a d d r e s s 0 2 E 0
O S D R O M
( 8 K b y t e s )
1 6
1 6
1 1 F F F
1 6
1 6
N o t u s e d
M 3 7 2 1 2 M 8 -
X X X S P
R O M
( 3 2 K b y t e s )
F F 0 0
1 6
F F D E
1 6
I n t e r r u p t v e c t o r a r e a
F F F F
1 6
Fig. 8.2.2 Memory Map (M37212M8-XXXSP, M37212EFSP/FP)
S p e c i a l p a g e
1 F F F F
1 6
N o t e : R e f e r t o T a b l e 8 . 1 0 . 3 O S D R A M
14
Rev. 1.0
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
K
M37212M4/M8–XXXSP, M37212M6–XXXSP/FP
M37212EFSP/FP
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER for VOLTAGE SYNTHESIZER
with ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
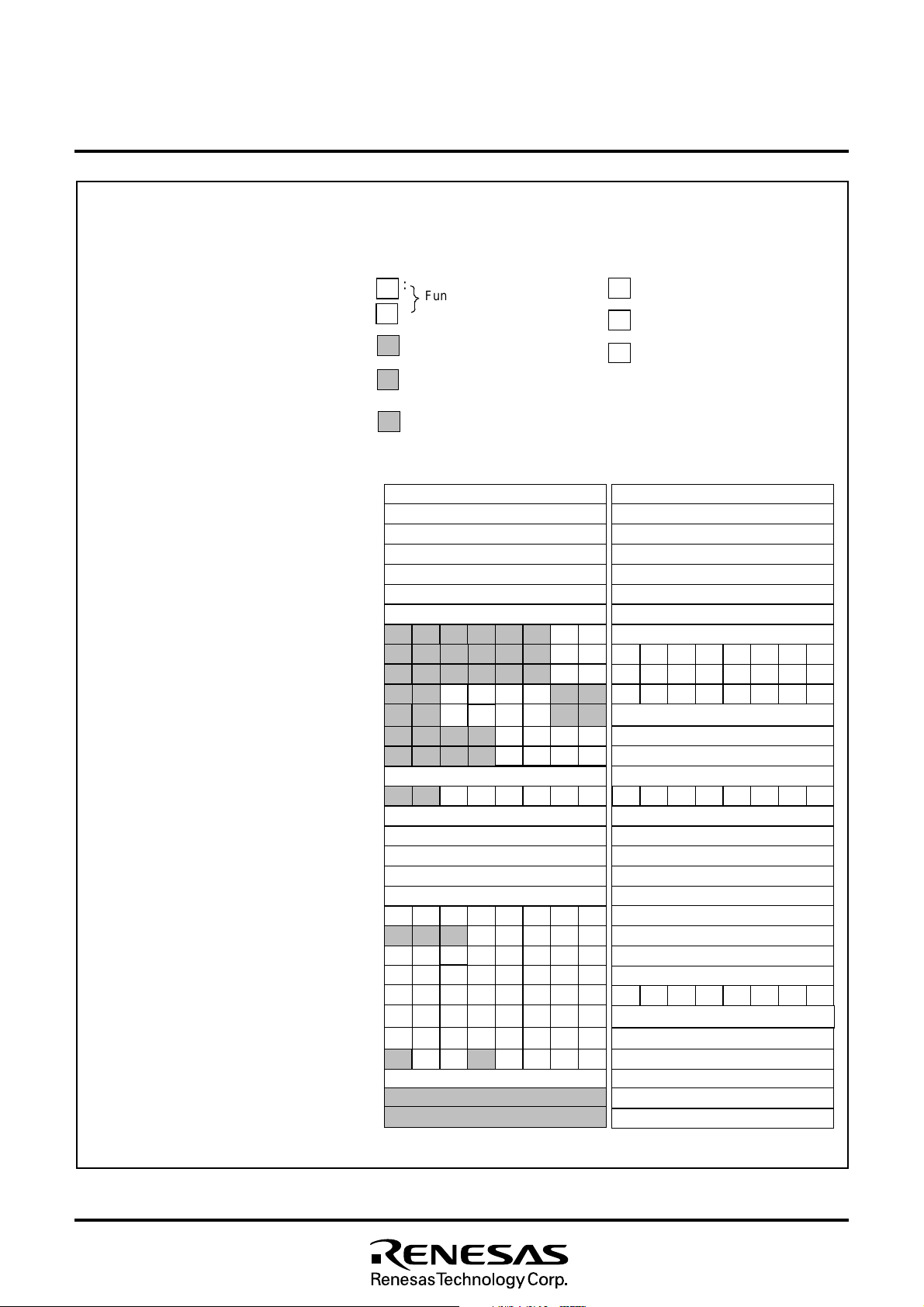
■ S F R a r e a ( a d d r e s s e s C 0
A d d r e s s
C 0
1 6
C 1
1 6
C 2
1 6
C 3
1 6
C 4
1 6
C 5
1 6
C 6
1 6
C 7
1 6
C 8
1 6
C 9
1 6
C A
1 6
C B
1 6
C C
1 6
C D
1 6
C E
1 6
C F
1 6
D 0
1 6
D 1
1 6
D 2
1 6
D 3
1 6
D 4
1 6
D 5
1 6
D 6
1 6
D 7
1 6
D 8
1 6
D 9
1 6
D A
1 6
D B
1 6
D C
1 6
D D
1 6
D E
1 6
D F
1 6
R e g i s t e r
P o r t P 0 ( P 0 )
P o r t P 0 d i r e c t i o n r e g i s t e r ( D 0 )
P o r t P 1 ( P 1 )
P o r t P 1 d i r e c t i o n r e g i s t e r ( D 1 )
P o r t P 2 ( P 2 )
P o r t P 2 d i r e c t i o n r e g i s t e r ( D 2 )
P o r t P 3 ( P 3 )
P o r t P 3 d i r e c t i o n r e g i s t e r ( D 3 )
P o r t P 4 ( P 4 )
P o r t P 4 d i r e c t i o n r e g i s t e r ( D 4 )
P o r t P 5 ( P 5 )
P o r t P 5 d i r e c t i o n r e g i s t e r ( D 5 )
P o r t P 6 ( P 6 )
D A - H r e g i s t e r ( D A - H )
D A - L r e g i s t e r ( D A - L )
P W M 0 r e g i s t e r ( P W M 0 )
P W M 1 r e g i s t e r ( P W M 1 )
P W M 2 r e g i s t e r ( P W M 2 )
P W M 3 r e g i s t e r ( P W M 3 )
P W M 4 r e g i s t e r ( P W M 4 )
P W M o u t p u t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 1 ( P W )
P W M o u t p u t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 2 ( P N )
2
I
C d a t a s h i f t r e g i s t e r ( S 0 )
2
C a d d r e s s r e g i s t e r ( S 0 D )
I
I2C s t a t u s r e g i s t e r ( S 1 )
I2C c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r ( S 1 D )
2
I
C c l o c k c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r ( S 2 )
S e r i a l I / O m o d e r e g i s t e r ( S M )
S e r i a l I / O r e g i s t e r ( S I O )
1 6
t o D F
1 6
)
B i t a l l o c a t i o n
:
F u n c t i o n b i t
:
N a m e
:
N o f u n c t i o n b i t
: F i x t o t h i s b i t t o “ 0 ”
0
( d o n o t w r i t e t o “ 1 ” )
: F i x t o t h i s b i t t o “ 1 ”
1
( d o n o t w r i t e t o “ 0 ” )
B i t a l l o c a t i o n S t a t e i m m e d i a t e l y a f t e r r e s e t
b 7
P 5 4
P 5 5
S E L
S E L
A
1 0 B I T
B S E L 0B S E L 1
S
A C K
B I T
F A S T
M O D E
D
A C
0
P 5 3
S E L
P 6 3
S t a t e i m m e d i a t e l y a f t e r r e s e t
: “ 0 ” i m m e d i a t e l y a f t e r r e s e t
0
: “ 1 ” i m m e d i a t e l y a f t e r r e s e t
1
: I n d e t e r m i n a t e i m m e d i a t e l y
?
a f t e r r e s e t
b 0
b 7
P 3 1 DP 3 0 D
P 5 2P 5 3P 5 4P 5 5
P 5 2
S E L
P 4 1P 4 0
P 4 1 DP 4 0 D
00
P 6 1P 6 0P 6 2
0
0
0
0
0????00
0
1111
00
P W 0P W 1P W 2P W 3P W 4P W 5P W 6P W 7
P N 2P N 3P N 4
P N 0P N 1
D 1D 2D 3D 4D 5D 6D 7D
0
S A D 0S A D 1S A D 2S A D 3S A D 4S A D 5S A D 6
R B W
L R BA D 0A A SA LP I NB BT R XM S T
B C 0B C 1B C 2E S OA L S
C C R 0C C R 1C C R 2C C R 3C C R 4
S M 0S M 1S M 2S M 3S M 5S M 6
00
b 0
?
1 6
0 0
?
1 6
0 0
?
0 0
1 6
?
0 0
1 6
00
00
0 0
0 F
0 F
1 6
1 6
1 6
?0
?0
??
??
?
??????
?
?
?
?
?
1 6
0 0
0 0
1 6
?
0 0
1 6
?00010
0 0
1 6
0 0
1 6
0 0
1 6
?
?
?
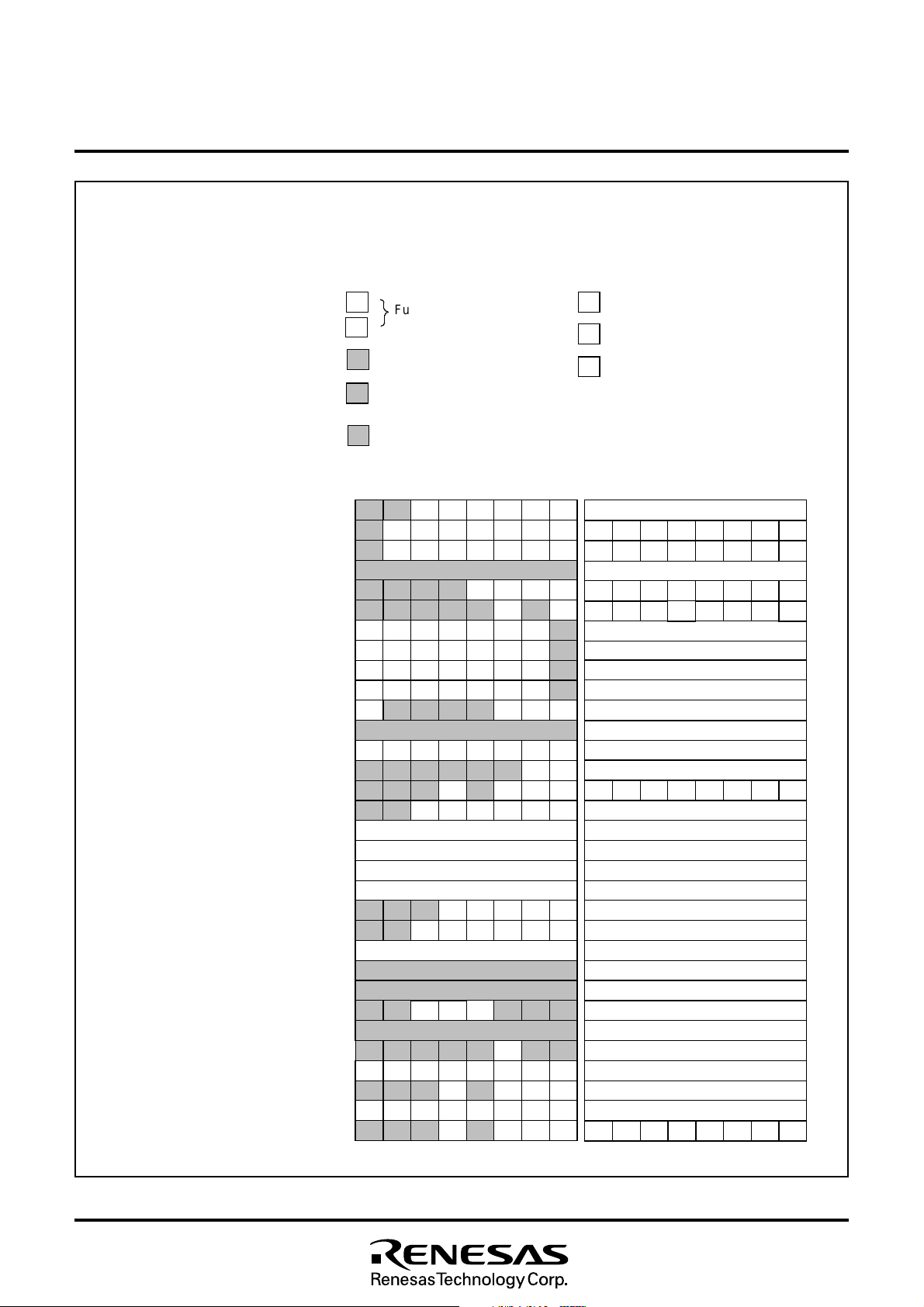
Fig. 8.2.3 Memory Map of Special Function Register (SFR) (1)
Rev. 1.0
15
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
6
M37212M4/M8–XXXSP, M37212M6–XXXSP/FP
M37212EFSP/FP
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER for VOLTAGE SYNTHESIZER
with ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
■ S F R a r e a ( a d d r e s s e s E 0
A d d r e s s
E 0
1 6
E 1
1 6
E 2
1 6
E 3
1 6
E 4
1 6
E 5
1 6
E 6
1 6
E 7
1
E 8
1 6
E 9
1 6
E A
1 6
E B
1 6
E C
1 6
E D
1 6
E E
1 6
E F
1 6
F 0
1 6
F 1
1 6
F 2
1 6
F 3
1 6
F 4
1 6
F 5
1 6
F 6
1 6
F 7
1 6
F 8
1 6
F 9
1 6
F A
1 6
F B
1 6
F C
1 6
F D
1 6
F E
1 6
F F
1 6
R e g i s t e r
H o r i z o n t a l p o s i t i o n r e g i s t e r ( H R )
V e r t i c a l p o s i t i o n r e g i s t e r 1 ( C V 1 )
V e r t i c a l p o s i t i o n r e g i s t e r 2 ( C V 2 )
C h a r a c t e r s i z e r e g i s t e r ( C S )
B o r d e r s e l e c t i o n r e g i s t e r ( M D )
C o l o r r e g i s t e r 0 ( C O 0 )
C o l o r r e g i s t e r 1 ( C O 1 )
C o l o r r e g i s t e r 2 ( C O 2 )
C o l o r r e g i s t e r 3 ( C O 3 )
C R T c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r ( C C )
C R T p o r t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r ( C R T P )
C R T c l o c k s e l e c t i o n r e g i s t e r ( C K )
A - D m o d e r e g i s t e r ( A D M )
A - D c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r ( A D C )
T i m e r 1 ( T 1 )
T i m e r 2 ( T 2 )
T i m e r 3 ( T 3 )
T i m e r 4 ( T 4 )
T i m e r 1 2 m o d e r e g i s t e r ( T 1 2 M )
T i m e r 3 4 m o d e r e g i s t e r ( T 3 4 M )
P W M 5 r e g i s t e r ( P W M 5 )
P W M 6 r e g i s t e r ( P W M 6 )
P W M 7 r e g i s t e r ( P W M 7 )
I n t e r r u p t i n p u t p o l a r i t y r e g i s t e r ( R E )
C P U m o d e r e g i s t e r ( C M )
I n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t r e g i s t e r 1 ( I R E Q 1 )
n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t r e g i s t e r 2 ( I R E Q 2
I
I n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 1 ( I C O N 1 )
n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 2 ( I C O N 2
I
1 6
t o F F
1 6
)
B i t a l l o c a t i o n
:
F u n c t i o n b i t
:
N a m e
:
N o f u n c t i o n b i t
: F i x t o t h i s b i t t o “ 0 ”
0
( d o n o t w r i t e t o “ 1 ” )
: F i x t o t h i s b i t t o “ 1 ”
1
( d o n o t w r i t e t o “ 0 ” )
B i t a l l o c a t i o nS
b 7
C C 7
O P 7
00
0000
0
R E5
1111
O S D R
V S C RI T 3 R
I I C R
)
0
I I C E
)
00
C K 0M S R
O S D E
V S C EI T 3 E
0
S t a t e i m m e d i a t e l y a f t e r r e s e t
: “ 0 ” i m m e d i a t e l y a f t e r r e s e t
0
: “ 1 ” i m m e d i a t e l y a f t e r r e s e t
1
: I n d e t e r m i n a t e i m m e d i a t e l y
?
a f t e r r e s e t
t a t e i m m e d i a t e l y a f t e r r e s e
b 0
b 7
H R 0H R 1H R 2H R 3H R 4H R 5
C V 1 1C V 1 2C V 1 3C V 1 4C V 1 5C V 1 6
C V 1 0
C V 2 0C V 2 1C V 2 2C V 2 3C V 2 4C V 2 5C V 2 6
0 0
??? ????0
??? ????0
0 0
C S 1 0C S 1 1C S 2 0C S 2 1
M D 1 0M D 2 0
C O 0 1C O 0 2C O 0 3C O 0 5C O 0 4C O 0 6C O 0 7
C O 1 1C O 1 2C O 1 3C O 1 5C O 1 4C O 1 6C O 1 7
C O 2 1C O 2 2C O 2 3C O 2 5C O 2 4C O 2 6C O 2 7
C O 3 1C O 3 2C O 3 3C O 3 5C O 3 4C O 3 6C O 3 7
C C 0C C 1C C 2
S Y
V S Y CR / G / BO U T 2O P 5 O U T 1O P 6H
A D M1A D M2A D M4
A D C1A D C2A D C3A D C4A D C5
C
C K0C K1
A D M0
A D C0
000 ????0
000 0?0?0
0 0
0 0
0 0
0 0
0 0
0 0
0 0
0 0
?00 00000
0 0
F F
0 7
F F
0 7
T 1 2 M 0T 1 2 M 1T 1 2 M 2T 1 2 M 3T 1 2 M 4
T 3 4 M 0
T 3 4 M 1T 3 4 M 2T 3 4 M 3T 3 4 M 4T 3 4 M 5
0 0
0 0
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
t
b 0
?
?
?
R E3R E4
00
0 0
1 6
?
C M 2
S 1 R
S 1 EM S E
001
T M 1 RT M 2 RT M 3 RT M 4 R
I T 1 RI T 2 R
T M 1 ET M 2 ET M 3 ET M 4 E
I T 1 EI T 2 E
?00 00000
FC
0 0
0 0
0 0
1 6
1 6
1 6
1 6
Fig. 8.2.4 Memory Map of Special Function Register (SFR) (2)
Rev. 1.0
16
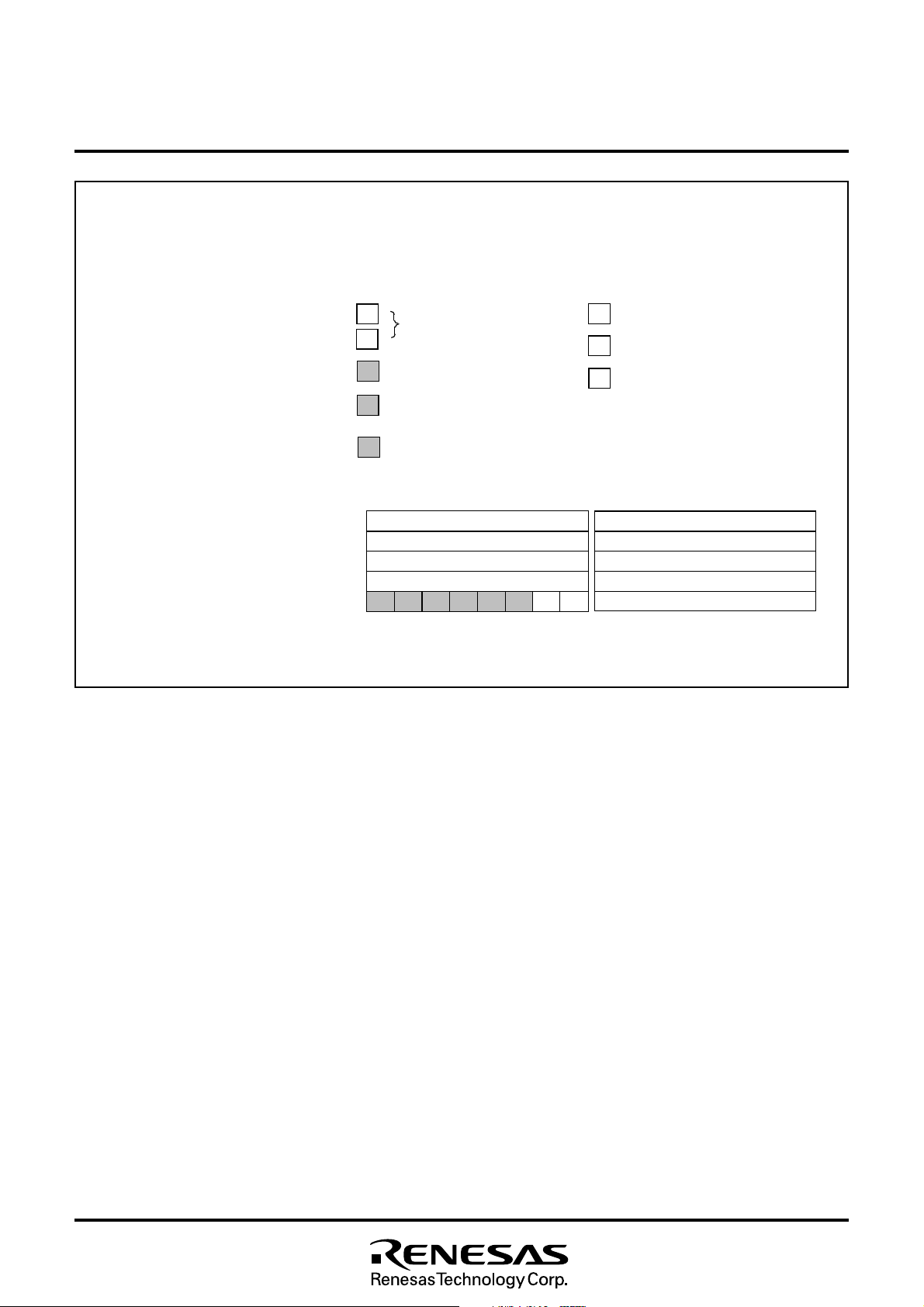
M37212M4/M8–XXXSP, M37212M6–XXXSP/FP
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER for VOLTAGE SYNTHESIZER
t o 2 1
■ 2 p a g e r e g i s t e r a r e a ( a d d r e s s e s 2 1 71
< B i t a l l o c a t i o n ><
:
F u n c t i o n b i t
:
N a m e
o f u n c t i o n b i
: N
: F i x t o t h i s b i t t o “ 0 ”
0
( d o n o t w r i t e t o “ 1 ” )
: F i x t o t h i s b i t t o “ 1 ”
1
( d o n o t w r i t e t o “ 0 ” )
A d d r e s s
2 1 71
6
2 1 81
6
2 1 91
6
2 1 A1
6
2 1 B1
6
R e g i s t e r
R O M c o r r e c t i o n a d d r e s s 1 ( h i g h - o r d e r )
O M c o r r e c t i o n a d d r e s s 1 ( l o w - o r d e r
R
R O M c o r r e c t i o n a d d r e s s 2 ( h i g h - o r d e r )
O M c o r r e c t i o n a d d r e s s 2 ( l o w - o r d e r
R
R O M c o r r e c t i o n e n a b l e r e g i s t e r ( R C R )
b 7b
)
)
B i t a l l o c a t i o nS
6
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
with ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
B1
6)
S t a t e i m m e d i a t e l y a f t e r r e s e t
0
1
t
?
t a t e i m m e d i a t e l y a f t e r r e s e
0b
7b
R C R 1R C R 0
00 0 01
M37212EFSP/FP
: “ 0 ” i m m e d i a t e l y a f t e r r e s e t
: “ 1 ” i m m e d i a t e l y a f t e r r e s e t
: I n d e t e r m i n a t e i m m e d i a t e l y
a f t e r r e s e t
0 01
6
0 01
6
0 01
6
0 01
6
6
>
t
0
N o t e : O n l y M 3 7 2 1 2 M 8 - X X X S P a n d M 3 7 2 1 2 E F S P / F P h a v e 2 p a g e r e g i s t e r .
Fig. 8.2.5 Memory Map of 2 Page Register Area
Rev. 1.0
17
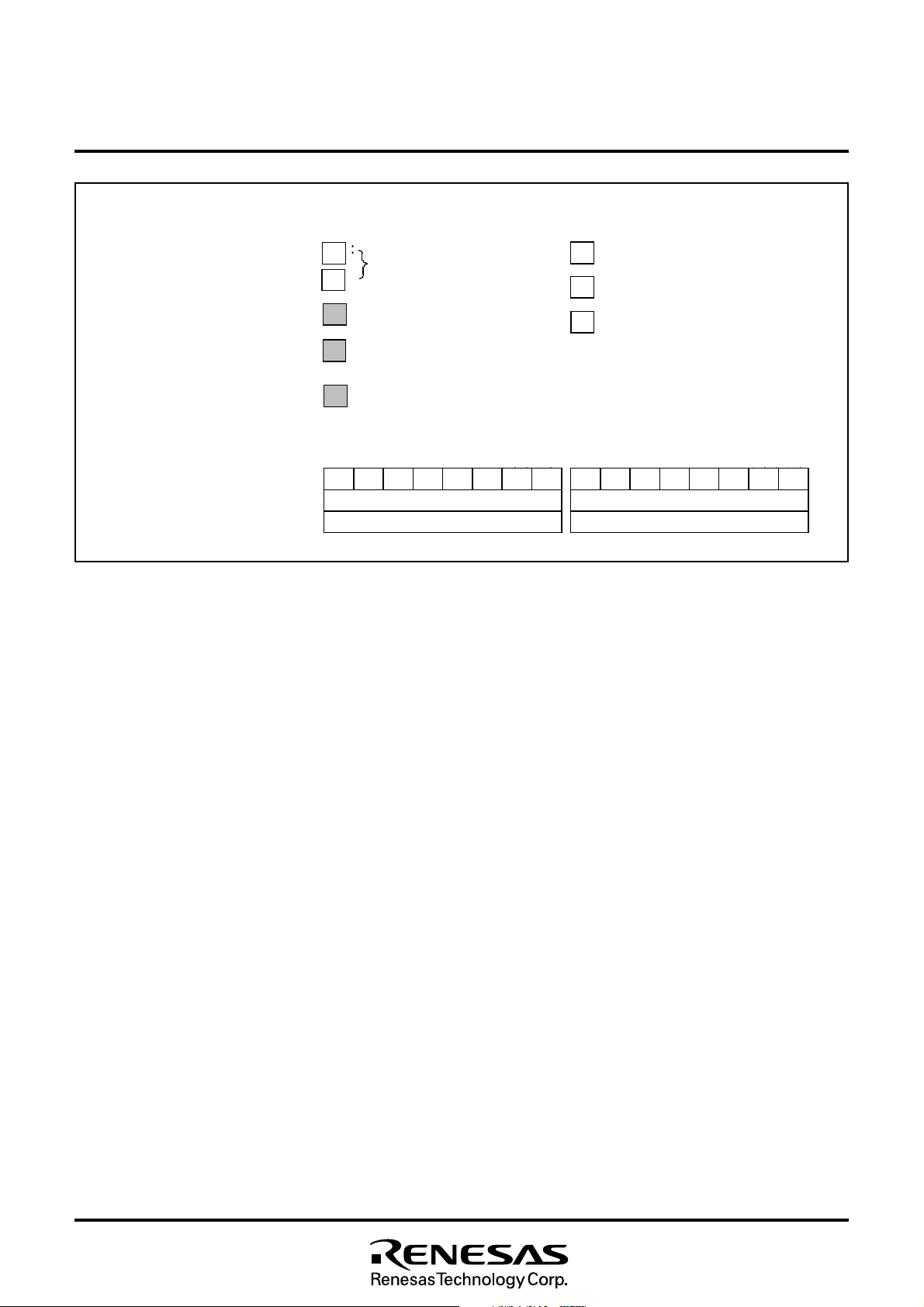
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37212M4/M8–XXXSP, M37212M6–XXXSP/FP
M37212EFSP/FP
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER for VOLTAGE SYNTHESIZER
with ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
< B i t a l l o c a t i o n ><
:
F u n c t i o n b i t
:
N a m e
:
N o f u n c t i o n b i t
: F i x t o t h i s b i t t o “ 0 ”
0
( d o n o t w r i t e t o “ 1 ” )
: F i x t o t h i s b i t t o “ 1 ”
1
( d o n o t w r i t e t o “ 0 ” )
R e g i s t e r
b 7
P r o c e s s o r s t a t u s r e g i s t e r ( P S )
P r o g r a m c o u n t e r ( P CH)
P r o g r a m c o u n t e r ( P CL)
Fig. 8.2.6 Internal State of Processor Status Register and Program Counter at Reset
B i t a l l o c a t i o nS
b 0
I Z CDBTVN???????
S t a t e i m m e d i a t e l y a f t e r r e s e t
: “ 0 ” i m m e d i a t e l y a f t e r r e s e t
0
: “ 1 ” i m m e d i a t e l y a f t e r r e s e t
1
: I n d e t e r m i n a t e i m m e d i a t e l y
?
a f t e r r e s e t
t a t e i m m e d i a t e l y a f t e r r e s e
b 7
1
C o n t e n t s o f a d d r e s s F F F F
C o n t e n t s o f a d d r e s s F F F E
>
t
b 0
1 6
1 6
18
Rev. 1.0
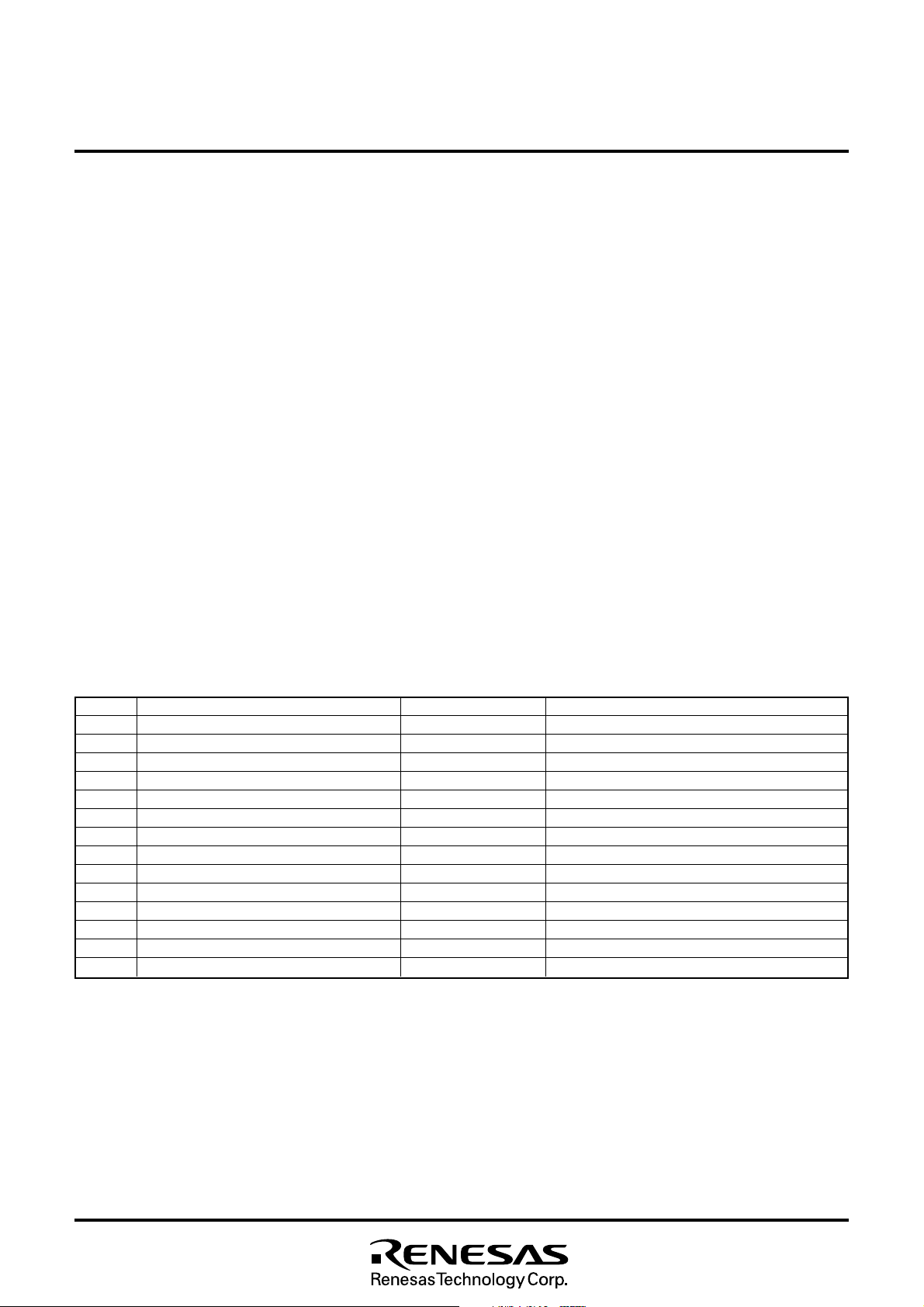
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37212M4/M8–XXXSP, M37212M6–XXXSP/FP
M37212EFSP/FP
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER for VOLTAGE SYNTHESIZER
with ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
8.3 INTERRUPTS
Interrupts can be caused by 14 different sources consisting of 4 external, 8 internal, 1 software, and reset. Interrupts are vectored interrupts with priorities as shown in Table 8.3.1. Reset is also included in
the table because its operation is similar to an interrupt.
When an interrupt is accepted,
① The contents of the program counter and processor status regis-
ter are automatically stored into the stack.
➁ The interrupt disable flag I is set to “1” and the corresponding
interrupt request bit is set to “0.”
➂ The jump destination address stored in the vector address enters
the program counter.
Other interrupts are disabled when the interrupt disable flag is set to
“1.”
All interrupts except the BRK instruction interrupt have an interrupt
request bit and an interrupt enable bit. The interrupt request bits are
in interrupt request registers 1 and 2 and the interrupt enable bits are
in interrupt control registers 1 and 2. Figures 8.3.2 to 8.3.6 show the
interrupt-related registers.
Interrupts other than the BRK instruction interrupt and reset are accepted when the interrupt enable bit is “1,” interrupt request bit is “1,”
and the interrupt disable flag is “0.” The interrupt request bit can be
set to “0” by a program, but not set to “1.” The interrupt enable bit can
be set to “0” and “1” by a program.
Reset is treated as a non-maskable interrupt with the highest priority.
Figure 8.3.1 shows interrupt control.
8.3.1 Interrupt Causes
SYNC, OSD interrupts
(1) V
The VSYNC interrupt is an interrupt request synchronized with
the vertical sync signal.
The OSD interrupt occurs after character block display to the
CRT is completed.
(2) INT1 to INT3 external interrupts
The INT1 to INT3 interrupts are external interrupt inputs, the system detects that the level of a pin changes from LOW to HIGH or
from HIGH to LOW, and generates an interrupt request. The input active edge can be selected by bits 3 to 5 of the interrupt
input polarity register (address 00F916) : when this bit is “0,” a
change from LOW to HIGH is detected; when it is “1,” a change
from HIGH to LOW is detected. Note that both bits are cleared to
“0” at reset.
(3) Timers 1 to 4 interrupts
An interrupt is generated by an overflow of timers 1 to 4.
Table 8.3.1 Interrupt Vector Addresses and Priority
Priority
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
Reset
OSD interrupt
INT2 external interrupt
INT1 external interrupt
Timer 4 interrupt
f(XIN)/4096 interrupt
VSYNC interrupt
Timer 3 interrupt
Timer 2 interrupt
Timer 1 interrupt
Serial I/O interrupt
Multi-master I2C-BUS interface interrupt
INT3 external interrupt
BRK instruction interrupt
Interrupt Source
Vector Addresses
FFFF16, FFFE16
FFFD16, FFFC16
FFFB16, FFFA16
FFF916, FFF816
FFF516, FFF416
FFF316, FFF216
FFF116, FFF016
FFEF16, FFEE16
FFED16, FFEC16
FFEB16, FFEA16
FFE916, FFE816
FFE716, FFE616
FFE516, FFE416
FFDF16, FFDE16
Remarks
Non-maskable
Active edge selectable
Active edge selectable
Active edge selectable
Non-maskable
Rev. 1.0
19
M37212M4/M8–XXXSP, M37212M6–XXXSP/FP
t
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER for VOLTAGE SYNTHESIZER
(4) Serial I/O interrupt
This is an interrupt request from the clock synchronous serial I/O
function.
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37212EFSP/FP
with ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
(5) f(XIN)/4096 interrupt
The f (XIN)/4096 interrupt occurs regularly with a f(XIN)/4096 period. Set bit 0 of PWM output control register 1 to “0.”
(6) Multi-master I2C-BUS interface interrupt
This is an interrupt request related to the multi-master I2C-BUS
interface.
(7) BRK instruction interrupt
This software interrupt has the least significant priority. It does
not have a corresponding interrupt enable bit, and it is not affected by the interrupt disable flag I (non-maskable).
Interrupt request bi
Interrupt enable bit
Interrupt disable flag I
Fig. 8.3.1 Interrupt Control
BRK instruction
Reset
Interrupt
request
20
Rev. 1.0
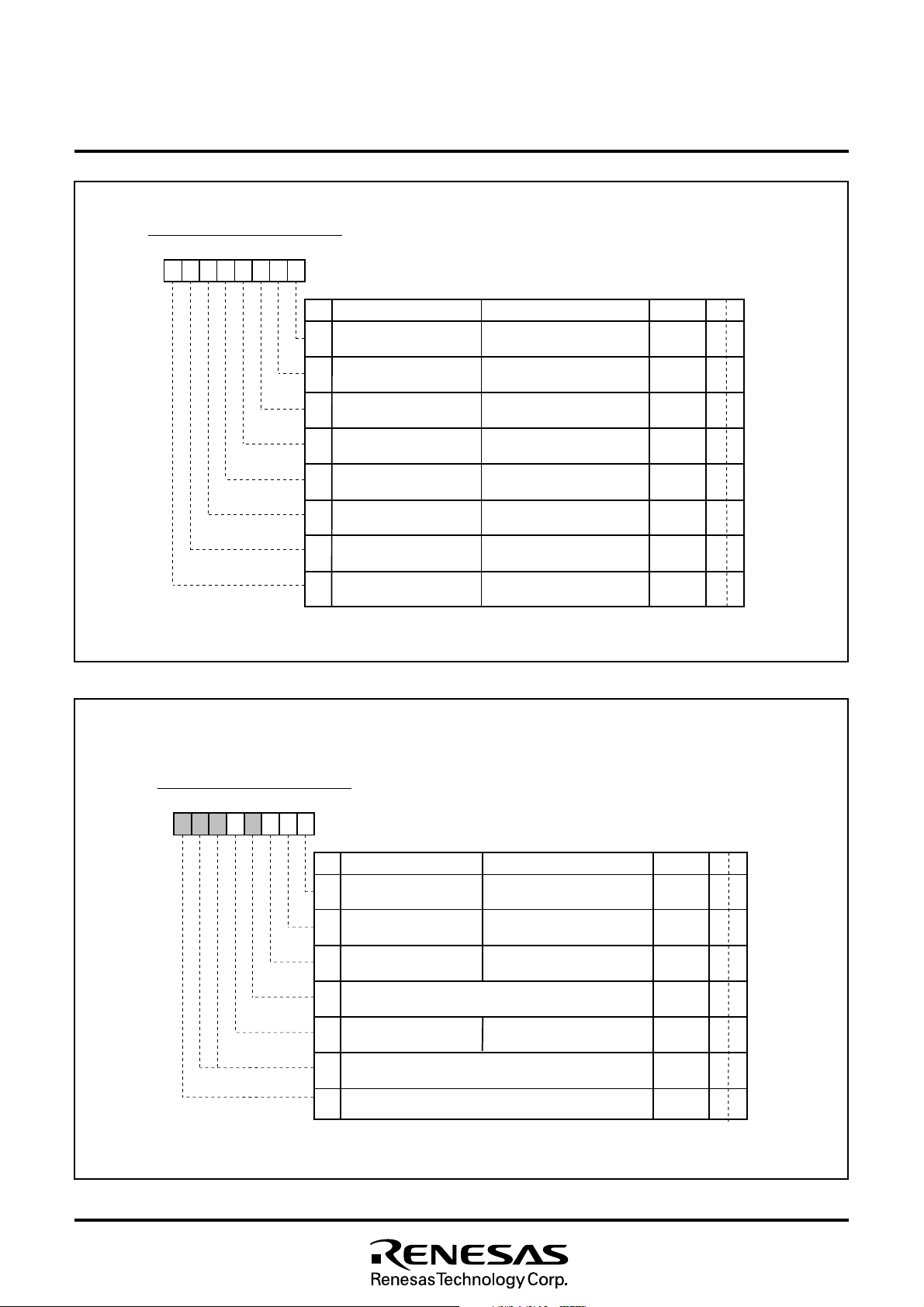
M37212M4/M8–XXXSP, M37212M6–XXXSP/FP
e
6
e
W
I n t e r r u p t R e q u e s t R e g i s t e r 1
b 7b 6 b 5b 4b 3 b 2b 1b 0
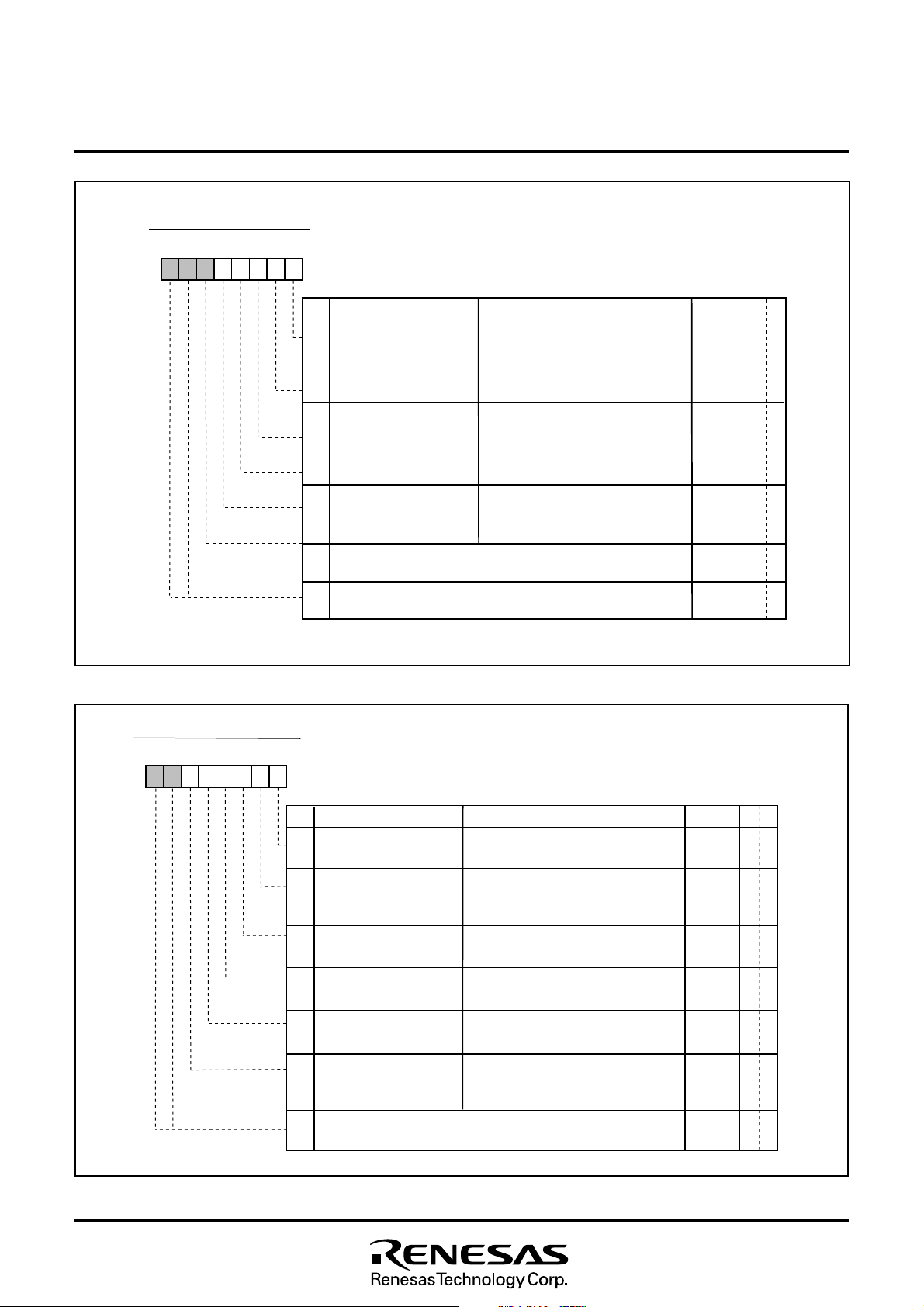
I n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t r e g i s t e r 1 ( I R E Q 1 ) [ A d d r e s s 0 0 F C
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37212EFSP/FP
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER for VOLTAGE SYNTHESIZER
with ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
1 6
]
Fig. 8.3.2 Interrupt Request Register 1
BN
0
T i m e r 1 i n t e r r u p t
r e q u e s t b i t ( T M 1 R )
1
2
3T i m e r 4 i n t e r r u p t
4
5
6
7
a m
T i m e r 2 i n t e r r u p t
r e q u e s t b i t ( T M 2 R )
T i m e r 3 i n t e r r u p t
r e q u e s t b i t ( T M 3 R )
r e q u e s t b i t ( T M 4 R )
O S D i n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t
b i t ( O S D R )
S Y N C
i n t e r r u p t
V
r e q u e s t b i t ( V S C R )
M u l t i - m a s t e r I2C - B U S i n t e r f a c e
i n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t b i t ( I I C R )
I N T 3 e x t e r n a l i n t e r r u p t
r e q u e s t b i t ( I T 3 R )
F u n c t i o n s
N o i n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t i s s u e d
0 :
1 :
I n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t i s s u e d
N o i n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t i s s u e d
0 :
1 :
I n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t i s s u e d
0 :
N o i n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t i s s u e d
1 :
I n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t i s s u e d
0 :
N o i n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t i s s u e d
1 :
I n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t i s s u e d
0 :
N o i n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t i s s u e d
1 :
I n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t i s s u e d
0 :
N o i n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t i s s u e d
1 :
I n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t i s s u e d
0 :
N o i n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t i s s u e d
1 :
I n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t i s s u e d
0 :
N o i n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t i s s u e d
1 :
I n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t i s s u e d
✽: “ 0 ” c a n b e s e t b y s o f t w a r e , b u t “ 1 ” c a n n o t b e s e t .
A f t e r r e s e t
0
0
0
0 ✽
0
0
0
0
RW
R
✽
R
✽
R
✽
R
✽
R
✽
R
✽
R
✽
R
I n t e r r u p t R e q u e s t R e g i s t e r 2
b 7b
b 5b 4b 3 b 2b 1b 0
0
Fig. 8.3.3 Interrupt Request Register 2
I n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t r e g i s t e r 2 ( I R E Q 2 ) [ A d d r e s s 0 0 F D
BN
0
1
2
3
a m
I N T 1 e x t e r n a l i n t e r r u p t
r e q u e s t b i t ( I T 1 R )
I N T 2 e x t e r n a l i n t e r r u p t
r e q u e s t b i t ( I T 2 R )
S e r i a l I / O i n t e r r u p t
r e q u e s t b i t ( S 1 R )
0 :
1 :
0 :
1 :
0 :
1 :
F u n c t i o n s
N o i n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t i s s u e d
I n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t i s s u e d
N o i n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t i s s u e d
I n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t i s s u e d
N o i n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t i s s u e d
I n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t i s s u e d
N o t h i n g i s a s s i g n e d . T h i s b i t i s a w r i t e d i s a b l e b i t .
W h e n t h i s b i t i s r e a d o u t , t h e v a l u e i s “ 0 . ”
f ( X
I N
4
5 , 6
) / 4 0 9 6 i n t e r r u p t
r e q u e s t b i t ( M S R )
0 :
N o i n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t i s s u e d
1 :
I n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t i s s u e d
N o t h i n g i s a s s i g n e d . T h e s e b i t s a r e w r i t e d i s a b l e b i t s .
W h e n t h e s e b i t s a r e r e a d o u t , t h e v a l u e s a r e “ 0 . ”
F i x t h i s b i t t o “ 0 . ”
7
✽: “ 0 ” c a n b e s e t b y s o f t w a r e , b u t “ 1 ” c a n n o t b e s e t .
1 6
]
A f t e r r e s e t
RW
0
R
✽
0
0
0R
0
0
0
✽
R
✽
R
—
✽
R
—
R
R
Rev. 1.0
21
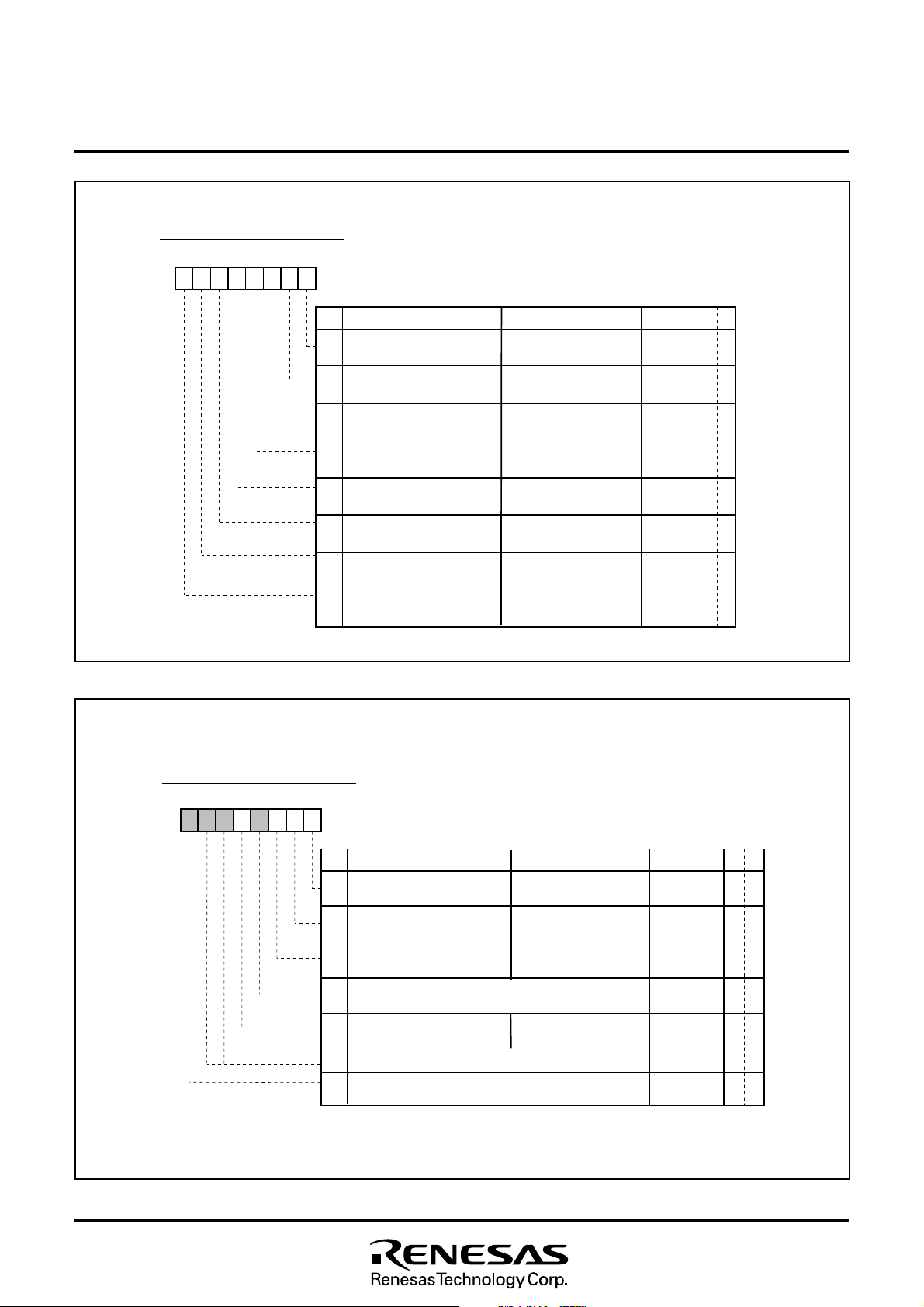
M37212M4/M8–XXXSP, M37212M6–XXXSP/FP
7
I n t e r r u p t C o n t r o l R e g i s t e r 1
b 7b 6 b 5b 4b 3 b 2b 1b 0
I n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 1 ( I C O N 1 ) [ A d d r e s s 0 0 F E
BN
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37212EFSP/FP
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER for VOLTAGE SYNTHESIZER
with ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
1 6
]
a m
eF
T i m e r 1 i n t e r r u p t
e n a b l e b i t ( T M 1 E )
T i m e r 2 i n t e r r u p t
e n a b l e b i t ( T M 2 E )
T i m e r 3 i n t e r r u p t
e n a b l e b i t ( T M 3 E )
T i m e r 4 i n t e r r u p t
e n a b l e b i t ( T M 4 E )
O S D i n t e r r u p t e n a b l e b i t
( O S D E )
V
S Y N C
i n t e r r u p t e n a b l e
b i t ( V S C E )
n t e r r u p t e n a b l e b i t ( I I C E
M u l t i - m a s t e r I2C - B U S i n t e r f a c e
i
)
I N T 3 e x t e r n a l i n t e r r u p t
e n a b l e b i t ( I T 3 E )
u n c t i o n
s RW
0 : I n t e r r u p t d i s a b l e d
1 : I n t e r r u p t e n a b l e d
0 : I n t e r r u p t d i s a b l e d
1 : I n t e r r u p t e n a b l e d
0 : I n t e r r u p t d i s a b l e d
1 : I n t e r r u p t e n a b l e d
0 : I n t e r r u p t d i s a b l e d
1 : I n t e r r u p t e n a b l e d
0 : I n t e r r u p t d i s a b l e d
1 : I n t e r r u p t e n a b l e d
0 : I n t e r r u p t d i s a b l e d
1 : I n t e r r u p t e n a b l e d
0 : I n t e r r u p t d i s a b l e d
1 : I n t e r r u p t e n a b l e d
0 : I n t e r r u p t d i s a b l e d
1 : I n t e r r u p t e n a b l e d
A f t e r r e s e t
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
R
W
Fig. 8.3.4 Interrupt Control Register 1
I n t e r r u p t C o n t r o l R e g i s t e r 2
b 7b 6 b 5b 4b 3 b 2b 1b 0
00
0
I n t e r r u p t c o n t r o l r e g i s t e r 2 ( I C O N 2 ) [ A d d r e s s 0 0 F F
BN
0
a m
eF
I N T 1 e x t e r n a l i n t e r r u p t
e n a b l e b i t ( I T 1 E )
I N T 2 e x t e r n a l i n t e r r u p t
1
e n a b l e b i t ( I T 2 E )
S e r i a l I / O i n t e r r u p t
2
e n a b l e b i t ( S 1 E )
F i x t h i s b i t t o “ 0 . ”
3
f ( X
I N
4
) / 4 0 9 6 i n t e r r u p t
e n a b l e b i t ( M S E )
F i x t h e s e b i t s t o “ 0 . ”
5 , 6
N o t h i n g i s a s s i g n e d . T h e s e b i t s a r e w r i t e d i s a b l e b i t s . W h e n
7
t h e s e b i t s a r e r e a d o u t , t h e v a l u e s a r e “ i n d e t e r m i n a t e . ”
u n c t i o n
s
0 : I n t e r r u p t d i s a b l e d
1 : I n t e r r u p t e n a b l e d
0 : I n t e r r u p t d i s a b l e d
1 : I n t e r r u p t e n a b l e d
0 : I n t e r r u p t d i s a b l e d
1 : I n t e r r u p t e n a b l e d
0 : I n t e r r u p t d i s a b l e d
1 : I n t e r r u p t e n a b l e d
1 6
]
A f t e r r e s e t
0
0
0
0
0
0
i n d e t e r m i n a t e
RW
RW
RW
RW
R
RW
RWW
–
R
Fig. 8.3.5 Interrupt Control Register 2
Rev. 1.0
22
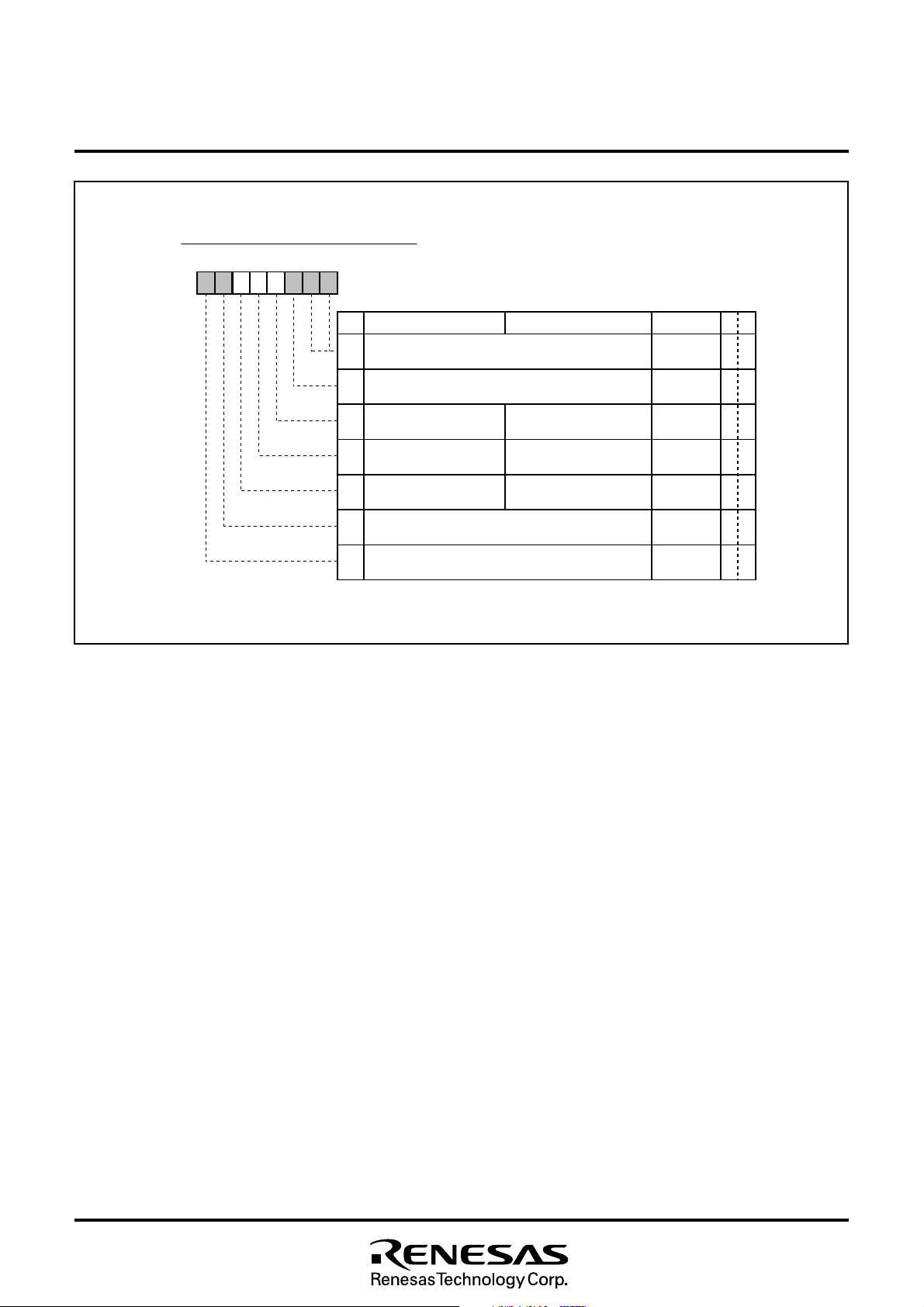
M37212M4/M8–XXXSP, M37212M6–XXXSP/FP
(
s
f
t
W
“
“
WRWRWRW
W
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER for VOLTAGE SYNTHESIZER
I n t e r r u p t I n p u t P o l a r i t y R e g i s t e r
b 7b 6b 5b 4b 3b 2b 1b 0
00
R E ) [ A d d r e s s 0 0 F
I n t e r r u p t i n p u t p o l a r i t y r e g i s t e r
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37212EFSP/FP
with ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
1 6
]
9
Fig. 8.3.6 Interrupt Input Polarity Register
BN
0 , 1
N o t h i n g i s a s s i g n e d . T h e s e b i t s a r e w r i t e d i s a b l e b i t s .
W h e n t h e s e b i t s a r e r e a d o u t , t h e v a l u e s a r e “ 0 . ”
0 .
20
F i x t h i s b i t t o
I N T 1 p o l a r i t y s w i t c h b i t
3
( R E 3 )
4
I N T 2 p o l a r i t y s w i t c h b i t
( R E 4 )
5
I N T 3 p o l a r i t y s w i t c h b i t
( R E 5 )
6
N o t h i n g i s a s s i g n e d . T h i s b i t i s a w r i t e d i s a b l e b i t .
W h e n t h i s b i t i s r e a d o u t , t h e v a l u e i s “ 0 . ”
0 .
7
F i x t h i s b i t t o
a m
eF
”
0 : P o s i t i v e p o l a r i t y
1 : N e g a t i v e p o l a r i t y
0 : P o s i t i v e p o l a r i t y
1 : N e g a t i v e p o l a r i t y
0 : P o s i t i v e p o l a r i t y
1 : N e g a t i v e p o l a r i t y
”
u n c t i o n
t e r r e s e
A
R
R—
0
R
0
0
0
0
R—
R
0
Rev. 1.0
23

MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37212M4/M8–XXXSP, M37212M6–XXXSP/FP
M37212EFSP/FP
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER for VOLTAGE SYNTHESIZER
with ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
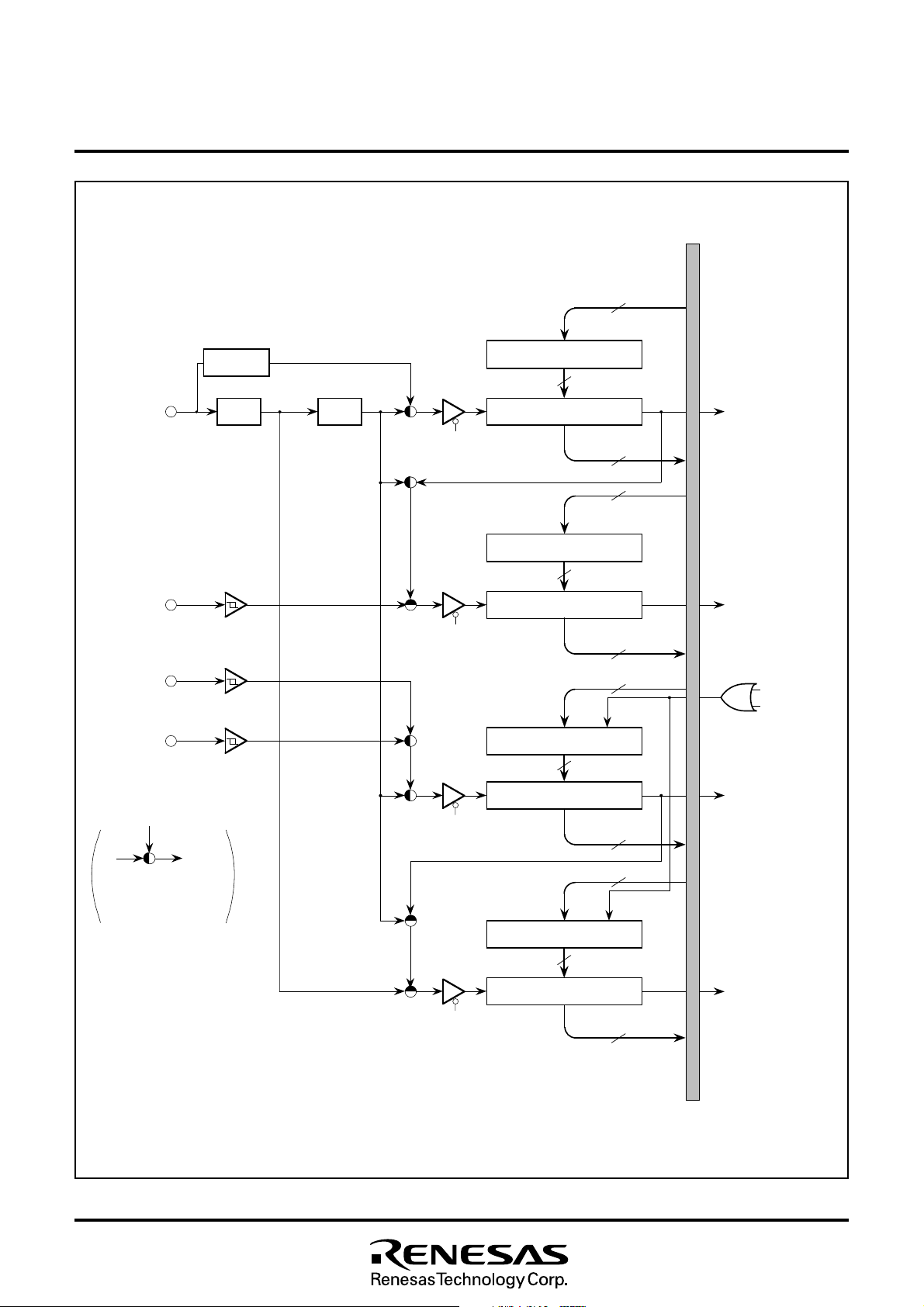
8.4 TIMERS
This microcomputer has 4 timers: timers 1 to 4. All timers are 8-bit
timers with the 8-bit timer latch. The timer block diagram is shown in
Figure 8.4.3.
All of the timers count down and their divide ratio is 1/(n+1), where n
is the value of timer latch. By writing a count value to the corresponding timer latch (addresses 00F016 to 00F316 : timers 1 to 4), the value
is also set to a timer, simultaneously.
The count value is decremented by 1. The timer interrupt request bit
is set to “1” by a timer overflow at the next count pulse, after the
count value reaches “0016.”
8.4.1 Timer 1
Timer 1 can select one of the following count sources:
• f(XIN)/16
• f(XIN)/4096
The count source of timer 1 is selected by setting bit 0 of timer 12
mode register 1 (address 00F416).
Timer interrupt request occurs at timer 1 overflow.
8.4.2 Timer 2
Timer 2 can select one of the following count sources:
• f(XIN)/16
• Timer 1 overflow signal
• External clock from the TIM2 pin
The count source of timer 2 is selected by setting bits 4 and 1 of
timer 12 mode register (address 00F416). When timer 1 overflow
signal is a count source for the timer 2, the timer 1 functions as an 8bit prescaler.
Timer 2 interrupt request occurs at timer 2 overflow.
At reset, timers 3 and 4 are connected by hardware and “FF16” is
automatically set in timer 3; “0716” in timer 4. The f(XIN)/16 is selected as the timer 3 count source. The internal reset is released by
timer 4 overflow in this state and the internal clock is connected.
At execution of the STP instruction, timers 3 and 4 are connected by
hardware and “FF16” is automatically set in timer 3; “0716” in timer 4.
However, the f(XIN)/16 is not selected as the timer 3 count source.
So set both bit 0 of timer 34 mode register (address 00F516) and bit
6 at address 00C716 to “0” before execution of the STP instruction
(f(XIN)/16 is selected as the timer 3 count source). The internal STP
state is released by timer 4 overflow in this state and the internal
clock is connected.
As a result of the above procedure, the program can start under a
stable clock.
The timer-related registers is shown in Figures 8.4.1 and 8.4.2.
8.4.3 Timer 3
Timer 3 can select one of the following count sources:
• f(XIN)/16
• External clock from the HSYNC pin
• External clock from the TIM3 pin
The count source of timer 3 is selected by setting bits 5 and 0 of
timer 34 mode register (address 00F516).
Timer 3 interrupt request occurs at timer 3 overflow.
8.4.4 Timer 4
Timer 4 can select one of the following count sources:
• f(XIN)/16
• f(XIN)/2
• Timer 3 overflow signal
The count source of timer 3 is selected by setting bits 1 and 4 of
timer 34 mode register (address 00F516). When timer 3 overflow
signal is a count source for the timer 4, the timer 3 functions as an 8bit prescaler.
Timer 4 interrupt request occurs at timer 4 overflow.
24
Rev. 1.0
e
2
3
T i m e r 1 2 M o d e R e g i s t e r
234
e
5
b 7b 6 b 5b 4b 3 b 2b 1b 0
0
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37212M4/M8–XXXSP, M37212M6–XXXSP/FP
M37212EFSP/FP
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER for VOLTAGE SYNTHESIZER
with ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
T i m e r m o d e r e g i s t e r ( T 1 2 M ) [ A d d r e s s 0 0 F 4
1 6
]
Fig. 8.4.1 Timer 12 Mode Register
T i m e r 3 4 M o d e R e g i s t e r
b 7b 6 b 5b 4b 3 b 2b 1b 0
B
0
N a m
T i m e r 1 c o u n t s o u r c e
s e l e c t i o n b i t 1 ( T 1 2 M 0 )
1
T i m e r 2 c o u n t s o u r c e
s e l e c t i o n b i t ( T 1 2 M 1 )
T i m e r 1 c o u n t
s t o p b i t ( T 1 2 M 2 )
T i m e r 2 c o u n t s t o p b i t
( T 1 2 M 3 )
T i m e r 2 i n t e r n a l c o u n t
s o u r c e s e l e c t i o n b i t 2
0 : f ( X
1 : f ( X
0 : I n t e r r u p t c l o c k s o u r c e
1 : E x t e r n a l c l o c k f r o m T I M 2 p i n
0 : C o u n t s t a r t
1 : C o u n t s t o p
0 : C o u n t s t a r t
1 : C o u n t s t o p
0 : f ( X
1 : T i m e r 1 o v e r f l o w
I N
) / 1 6
I N
) / 4 0 9 6
I N
) / 1 6
F u n c t i o n s
( T 1 2 M 4 )
F i x t h i s b i t t o “ 0 . ”
6 , 7N o t h i n g i s a s s i g n e d . T h e s e b i t s a r e w r i t e d i s a b l e b i t s .
W h e n t h e s e b i t s a r e r e a d o u t , t h e v a l u e s a r e “ 0 . ”
1 6
T i m e r 3 4 m o d e r e g i s t e r ( T 3 4 M ) [ A d d r e s s 0 0 F 5
]
A f t e r r e s e t
0
0
0
0
0
0
0—R
R
W
WR
WR
WR
WR
WR
WR
Fig. 8.4.2 Timer 34 Mode Register
Rev. 1.0
B
0
1
N a m
T i m e r 3 c o u n t s o u r c e
s e l e c t i o n b i t ( T 3 4 M 0 )
T i m e r 4 i n t e r n a l
i n t e r r u p t c o u n t s o u r c e
F u n c t i o n s
I N
0 : f ( X
) / 1 6
1 : E x t e r n a l c l o c k s o u r c e
0 : T i m e r 3 o v e r f l o w s i g n a l
1 : f ( X
I N
) / 1 6
s e l e c t i o n b i t ( T 3 4 M 1 )
T i m e r 3 c o u n t s t o p b i t
( T 3 4 M 2 )
T i m e r 4 c o u n t s t o p b i t
( T 3 4 M 3 )
T i m e r 4 c o u n t s o u r c e
4
s e l e c t i o n b i t ( T 3 4 M 4 )
5
T i m e r 3 e x t e r n a l c o u n t
s o u r c e s e l e c t i o n b i t
0 : C o u n t s t a r t
1 : C o u n t s t o p
0 : C o u n t s t a r t
1 : C o u n t s t o p
0 : I n t e r n a l c l o c k s o u r c e
1 : f ( X
I N
) / 2
0 : T I M 3 p i n i n p u t
1 : H
S Y N C
p i n i n p u t
( T 3 4 M 5 )
6 , 7N o t h i n g i s a s s i g n e d . T h e s e b i t s a r e w r i t e d i s a b l e b i t s .
W h e n t h e s e b i t s a r e r e a d o u t , t h e v a l u e s a r e “ 0 . ”
A f t e r r e s e t
RW
0 RW
0RW
0
RW
0
RW
RW
0
RW
0
0—R
25
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37212M4/M8–XXXSP, M37212M6–XXXSP/FP
M37212EFSP/FP
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER for VOLTAGE SYNTHESIZER
with ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
Data bus
8
TIM2
H
TIM3
X
SYNC
1/4096
IN
1/2
1/8
T12M0
T12M4
T12M1
T12M2
T12M3
T34M5
Timer 1 latch (8)
8
Timer 1 (8)
Timer 2 latch (8)
8
Timer 2 (8)
Timer 3 latch (8)
Timer 1
interrupt request
8
8
Timer 2
interrupt request
8
8
FF
16
Reset
STP
instruction
8
Timer 3
interrupt request
T34M0
T34M2
Timer 3 (8)
8
Selection gate :
Connected to black
colored side at reset
T34M1
T12M : Timer 12 mode register
T34M : Timer 34 mode register
T34M4
T34M3
Notes 1: “H” pulse width of external clock inputs TIM2 and TIM3 needs 4 machine cycles or more.
2: When the external clock source is selected, timers 2 and 3 are counted at a rising edge of input signal.
3: In the stop mode or the wait mode, external clock inputs TIM2 and TIM3 cannot be used.
Timer 4 latch (8)
8
Timer 4 (8)
Fig. 8.4.3 Timer Block Diagram
26
8
07
16
Timer 4
interrupt request
8
Rev. 1.0
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37212M4/M8–XXXSP, M37212M6–XXXSP/FP
M37212EFSP/FP
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER for VOLTAGE SYNTHESIZER
with ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
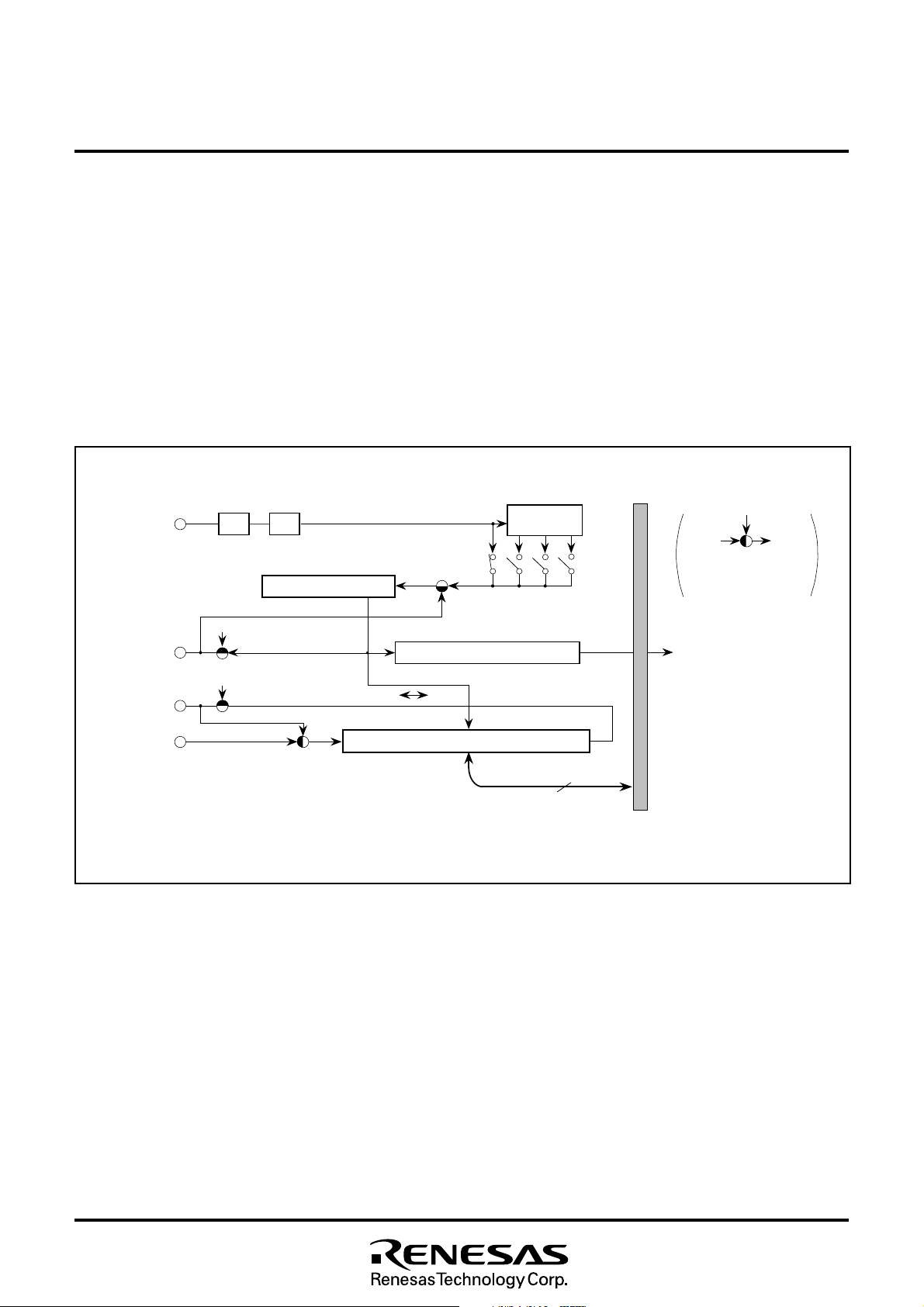
8.5 SERIAL I/O
This microcomputer has a built-in serial I/O which can either transmit
or receive 8-bit data serially in the clock synchronous mode.
The serial I/O block diagram is shown in Figure 8.5.1. The synchronous clock I/O pin (SCLK), data output pin (SOUT), and data input pin
(SIN) also functions as port P4.
Bit 3 of the serial I/O mode register (address 00DC16) selects whether
the synchronous clock is supplied internally or externally (from the
SCLK pin). When an internal clock is selected, bits 1 and 0 select
whether f(XIN) or f(XCIN) is divided by 4, 16, 32, or 64. To use SIN pin
for serial I/O, set the corresponding bit of the port P2 direction register (address 00C516) to “0.”
IN
S
OUT(/IN)
X
S
CLK
S
IN
P4
P4
1/2
1
latch
SM3
0
latch
SM3
1/2
Synchronization circuit
SM5
SM6
SM2
Serial I/O counter (8)
: LSB
MSB
Serial I/O shift register (8)
The operation of the serial I/O is described below. The operation of
the serial I/O differs depending on the clock source; external clock or
internal clock.
Data bus
Frequency
divider
1/81/4 1/16
SM1
S
(See note)
(Address 00DD16)
SM0
8
Selection gate :
Connected to black
colored side at reset.
SM : Serial I/O mode register
Serial I/O interrupt
request
Note : When the data is set in the serial I/O register (address 00DD
Fig. 8.5.1 Serial I/O Block Diagram
Rev. 1.0
16
), the register functions as the serial I/O shift register.
27
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
k
M37212M4/M8–XXXSP, M37212M6–XXXSP/FP
M37212EFSP/FP
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER for VOLTAGE SYNTHESIZER
with ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
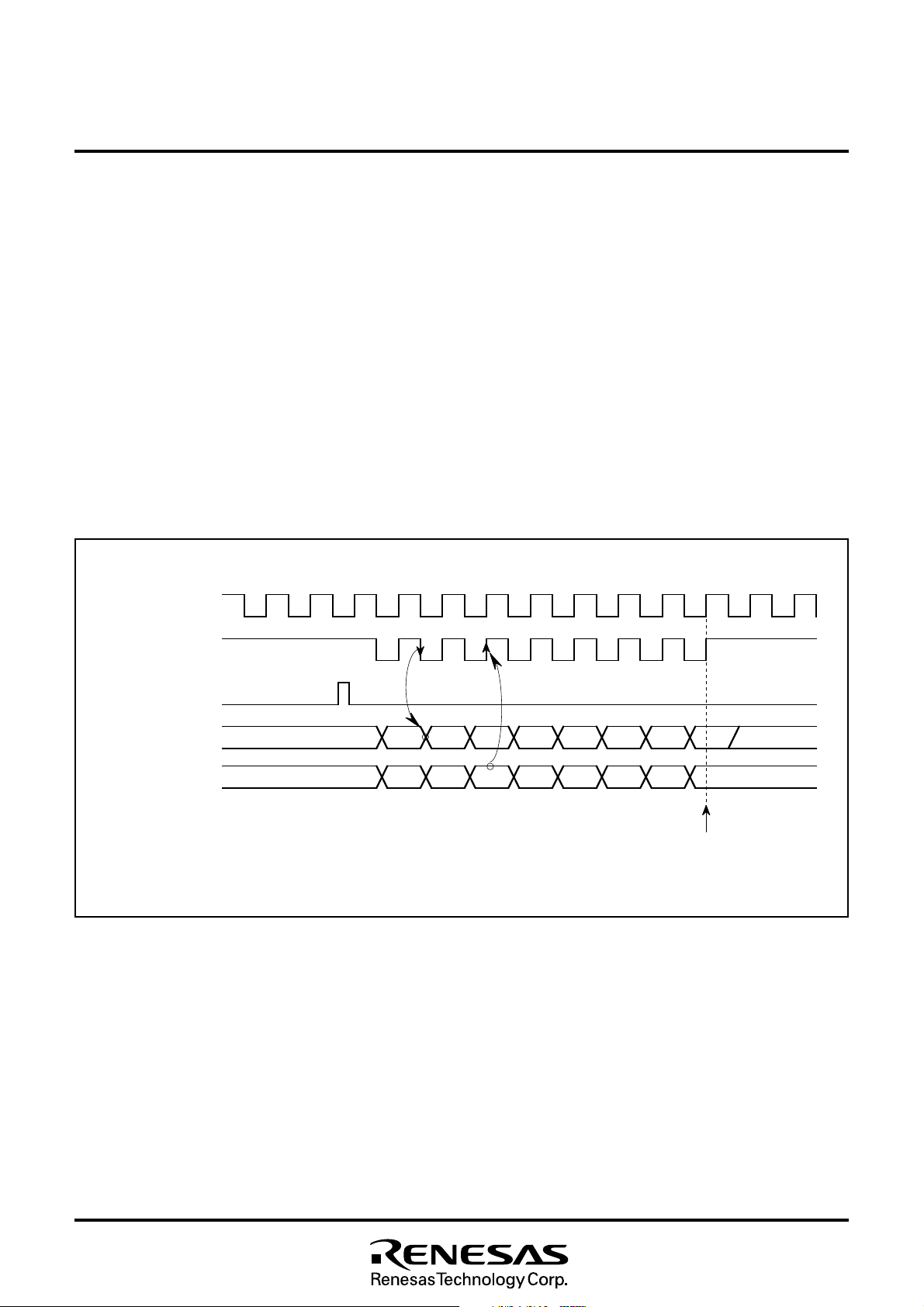
Internal clock : The serial I/O counter is set to “7” during the write
cycle into the serial I/O register (address 00DD16), and the transfer
clock goes HIGH forcibly. At each falling edge of the transfer clock
after the write cycle, serial data is output from the SOUT pin. Transfer
direction can be selected by bit 5 of the serial I/O mode register. At
each rising edge of the transfer clock, data is input from the SIN pin
and data in the serial I/O register is shifted 1 bit.
After the transfer clock has counted 8 times, the serial I/O counter
becomes “0” and the transfer clock stops at HIGH. At this time the
interrupt request bit is set to “1.”
S y n c h r o n o u s c l o c
External clock : The an external clock is selected as the clock source,
the interrupt request is set to “1” after the transfer clock has been
counted 8 counts. However, transfer operation does not stop, so the
clock should be controlled externally. Use the external clock of 1 MHz
or less with a duty cycle of 50%.
The serial I/O timing is shown in Figure 8.5.2. When using an external clock for transfer, the external clock must be held at HIGH for
initializing the serial I/O counter. When switching between an internal clock and an external clock, do not switch during transfer. Also,
be sure to initialize the serial I/O counter after switching.
Notes 1: On programming, note that the serial I/O counter is set by writing to
the serial I/O register with the bit managing instructions, such as SEB
and CLB.
2:When an external clock is used as the synchronous clock, write trans-
mit data to the serial I/O register when the transfer clock input level is
HIGH.
T r a n s f e r c l o c k
S e r i a l I / O r e g i s t e r
w r i t e s i g n a l
S e r i a l I / O o u t p u t
S
O U T
S e r i a l I / O i n p u t
S
I N
N o t e : W h e n a n i n t e r n a l c l o c k i s s e l e c t e d , t h e S
Fig. 8.5.2 Serial I/O Timing (for LSB first)
D
0
D
1
D
2
D
3
D
4
D
O U T
p i n i s a t h i g h - i m p e d a n c e a f t e r t r a n s f e r i s c o m p l e t e d .
( S e e n o t e )
5
D
6
D
7
I n t e r r u p t r e q u e s t b i t i s s e t t o “ 1 ”
28
Rev. 1.0
r
4
W
S e r i a l I / O M o d e R e g i s t e
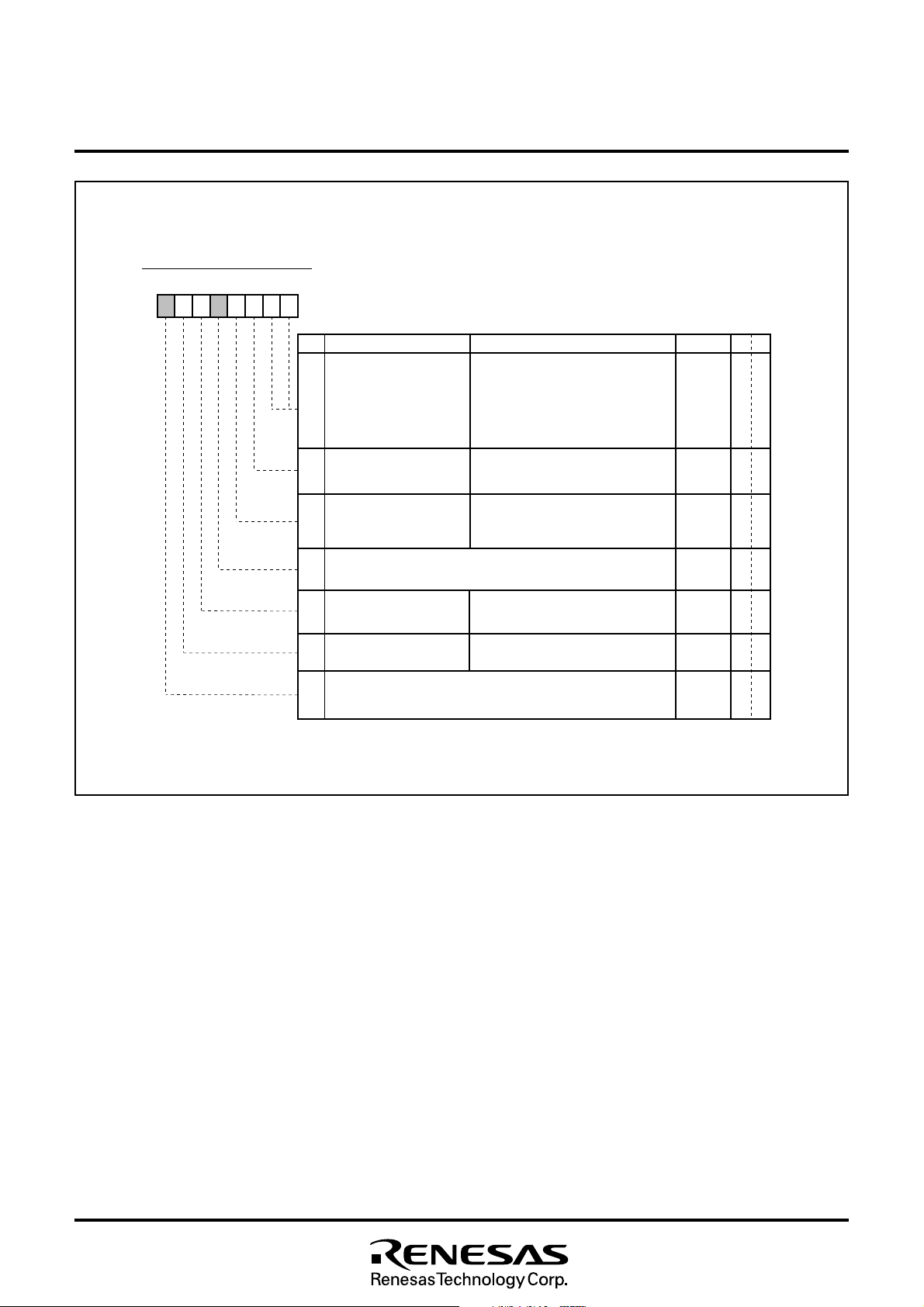
b 7b 6 b 5b 4b 3 b 2b 1b 0
0
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
M37212M4/M8–XXXSP, M37212M6–XXXSP/FP
M37212EFSP/FP
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER for VOLTAGE SYNTHESIZER
with ON-SCREEN DISPLAY CONTROLLER
1 6
S e r i a l I / O m o d e r e g i s t e r ( S M ) [ A d d r e s s 0 0 D C
BN
a m
eF
0 , 1I n t e r n a l s y n c h r o n o u s
c l o c k s e l e c t i o n b i t s
( S M 0 , S M 1 )
2
S y n c h r o n o u s c l o c k
s e l e c t i o n b i t ( S M 2 )
b 1 b 0
0 0 : f ( X
0 1 : f ( X
1 0 : f ( X
1 1 : f ( X
0 : E x t e r n a l c l o c k
1 : I n t e r n a l c l o c k
I N
I N
I N
I N
u n c t i o n
) / 4
) / 1 6
) / 3 2
) / 6 4
]
s
A f t e r r e s e t
RW
0RW
0
RW
Fig. 8.5.3 Serial I/O Mode Register
S e r i a l I / O p o r t
3
s e l e c t i o n b i t ( S M 3 )
0 : P 4
1 : S
0
, P 4
O U T ( / I N )
1
, S
C L K
F i x t h i s b i t t o “ 0 . ”
T r a n s f e r d i r e c t i o n
5
s e l e c t i o n b i t ( S M 5 )
S e r i a l i n p u t p i n
6
s e l e c t i o n b i t ( S M 6 )
N o t h i n g i s a s s i g n e d . T h i s b i t i s a w r i t e d i s a b l e b i t .
7
0 : L S B f i r s t
1 : M S B f i r s t
0 : I n p u t s i g n a l f r o m S
1 : I n p u t s i g n a l f r o m S
W h e n t h i s b i t i s r e a d o u t , t h e v a l u e i s “ 0 . ”
I N
O U T
p i n .
p i n .
0
RW
0
R
0
RW
0
RW
0R
—
Rev. 1.0
29
 Loading...
Loading...