Page 1

MELSEC-L CPU Module User's Manual
(Function Explanation, Program Fundamentals)
-L02SCPU
-L02SCPU-P
-L02CPU
-L02CPU-P
-L06CPU
-L06CPU-P
-L26CPU
-L26CPU-P
-L26CPU-BT
-L26CPU-PBT
Page 2

Page 3
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
WARNING
CAUTION
Indicates that incorrect handling may cause hazardous conditions,
resulting in death or severe injury.
Indicates that incorrect handling may cause hazardous conditions,
resulting in minor or moderate injury or property damage.
(Read these precautions before using this product.)
Before using this product, please read this manual and the relevant manuals carefully and pay full attention
to safety to handle the product correctly.
In this manual, the safety precautions are classified into two levels: " WARNING" and " CAUTION".
Under some circumstances, failure to observe the precautions given under " CAUTION" may lead to
serious consequences.
Observe the precautions of both levels because they are important for personal and system safety.
Make sure that the end users read this manual and then keep the manual in a safe place for future
reference.
1
Page 4
[Design Precautions]
WARNING
● Configure safety circuits external to the programmable controller to ensure that the entire system
operates safely even when a fault occurs in the external power supply or the programmable controller.
Failure to do so may result in an accident due to an incorrect output or malfunction.
(1) Emergency stop circuits, protection circuits, and protective interlock circuits for conflicting
operations (such as forward/reverse rotations or upper/lower limit positioning) must be configured
external to the programmable controller.
(2) Machine OPR (Original Point Return) of the positioning function is controlled by two kinds of data:
an OPR direction and an OPR speed. Deceleration starts when the near-point dog signal turns on.
If an incorrect OPR direction is set, motion control may continue without deceleration. To prevent
machine damage caused by this, configure an interlock circuit external to the programmable
controller.
(3) When the CPU module detects an error during control by the positioning function, the motion
slows down and stops.
(4) When the programmable controller detects an abnormal condition, it stops the operation and all
outputs are:
• Turned off if the overcurrent or overvoltage protection of the power supply module is activated.
• Held or turned off according to the parameter setting if the self-diagnostic function of the CPU
module detects an error such as a watchdog timer error.
(5) All outputs may be turned on if an error occurs in a part, such as an I/O control part, where the
CPU module cannot detect any error. To ensure safety operation in such a case, provide a safety
mechanism or a fail-safe circuit external to the programmable controller. For a fail-safe circuit
example, refer to "General Safety Requirements" in the MELSEC-L CPU Module User's Manual
(Hardware Design, Maintenance and Inspection).
(6) Outputs may remain on or off due to a failure of a component such as a transistor in an output
circuit. Configure an external circuit for monitoring output signals that could cause a serious
accident.
● In an output circuit, when a load current exceeding the rated current or an overcurrent caused by a
load short-circuit flows for a long time, it may cause smoke and fire. To prevent this, configure an
external safety circuit, such as a fuse.
● Configure a circuit so that the programmable controller is turned on first and then the external power
supply. If the external power supply is turned on first, an accident may occur due to an incorrect output
or malfunction.
● Configure a circuit so that the external power supply is turned off first and then the programmable
controller. If the programmable controller is turned off first, an accident may occur due to an incorrect
output or malfunction.
● For the operating status of each station after a communication failure, refer to relevant manuals for
each network. Incorrect output or malfunction due to a communication failure may result in an
accident.
2
Page 5
WARNING
● When changing data from a peripheral connected to the CPU module to the running programmable
controller, configure an interlock circuit in the program to ensure that the entire system will always
operate safely. For other forms of control (such as program modification or operating status change)
of a running programmable controller, read the relevant manuals carefully and ensure that the
operation is safe before proceeding. Especially, when a remote programmable controller is controlled
by an external device, immediate action cannot be taken if a problem occurs in the programmable
controller due to a communication failure. To prevent this, configure an interlock circuit in the program,
and determine corrective actions to be taken between the external device and CPU module in case of
a communication failure.
● An absolute position restoration by the positioning function may turn off the servo-on signal (servo off)
for approximately 20ms, and the motor may run unexpectedly. If this causes a problem, provide an
electromagnetic brake to lock the motor during absolute position restoration.
[Design Precautions]
CAUTION
● Do not install the control lines or communication cables together with the main circuit lines or power
cables. Keep a distance of 100mm or more between them. Failure to do so may result in malfunction
due to noise.
● During control of an inductive load such as a lamp, heater, or solenoid valve, a large current
(approximately ten times greater than normal) may flow when the output is turned from off to on.
Therefore, use a module that has a sufficient current rating.
● After the CPU module is powered on or is reset, the time taken to enter the RUN status varies
depending on the system configuration, parameter settings, and/or program size. Design circuits so
that the entire system will always operate safely, regardless of the time.
[Installation Precautions]
WARNING
● Shut off the external power supply (all phases) used in the system before mounting or removing a
module. Failure to do so may result in electric shock or cause the module to fail or malfunction.
3
Page 6
[Installation Precautions]
CAUTION
● Use the programmable controller in an environment that meets the general specifications in the
MELSEC-L CPU Module User's Manual (Hardware Design, Maintenance and Inspection). Failure to
do so may result in electric shock, fire, malfunction, or damage to or deterioration of the product.
● To interconnect modules, engage the respective connectors and securely lock the module joint levers
until they click. Incorrect interconnection may cause malfunction, failure, or drop of the module.
● Do not directly touch any conductive parts and electronic components of the module. Doing so can
cause malfunction or failure of the module.
● Securely connect an extension cable to the connectors of a branch module and an extension module.
After connections, check that the cable is inserted completely. Poor contact may cause malfunction.
● When using an SD memory card, fully insert it into the SD memory card slot. Check that it is inserted
completely. Poor contact may cause malfunction.
● Do not directly touch any conductive parts and electronic components of the module or SD memory
card. Doing so can cause malfunction or failure of the module.
[Wiring Precautions]
WARNING
● Shut off the external power supply (all phases) used in the system before wiring. Failure to do so may
result in electric shock or cause the module to fail or malfunction.
● After installation and wiring, attach the included terminal cover to the module before turning it on for
operation. Failure to do so may result in electric shock.
4
Page 7
[Wiring Precautions]
CAUTION
● Individually ground the FG terminal of the programmable controller with a ground resistance of 100
or less. Failure to do so may result in electric shock or malfunction.
● Use applicable solderless terminals and tighten them within the specified torque range.
If any spade solderless terminal is used, it may be disconnected when a terminal block screw comes
loose, resulting in failure.
● Check the rated voltage and terminal layout before wiring to the module, and connect the cables
correctly. Connecting a power supply with a different voltage rating or incorrect wiring may cause a fire
or failure.
● Connectors for external devices must be crimped or pressed with the tool specified by the
manufacturer, or must be correctly soldered. Incomplete connections may cause short circuit, fire, or
malfunction.
● Securely connect the connector to the module.
● Do not install the control lines or communication cables together with the main circuit lines or power
cables. Failure to do so may result in malfunction due to noise.
● Place the cables in a duct or clamp them. If not, dangling cable may swing or inadvertently be pulled,
resulting in damage to the module or cables or malfunction due to poor contact.
● Check the interface type and correctly connect the cable. Incorrect wiring (connecting the cable to an
incorrect interface) may cause failure of the module and external device.
● Tighten the terminal block screws within the specified torque range. Undertightening can cause short
circuit, fire, or malfunction. Overtightening can damage the screw and/or module, resulting in drop,
short circuit, fire, or malfunction.
● When disconnecting the cable from the module, do not pull the cable by the cable part. For the cable
with connector, hold the connector part of the cable. For the cable connected to the terminal block,
loosen the terminal screw. Pulling the cable connected to the module may result in malfunction or
damage to the module or cable.
● Prevent foreign matter such as dust or wire chips from entering the module. Such foreign matter can
cause a fire, failure, or malfunction.
● A protective film is attached to the top of the module to prevent foreign matter, such as wire chips,
from entering the module during wiring. Do not remove the film during wiring. Remove it for heat
dissipation before system operation.
● To use the high-speed counter function, ground the shield cable on the encoder side (relay box).
Always ground the FG and LG terminals to the protective ground conductor. Failure to do so may
cause malfunction.
● Mitsubishi programmable controllers must be installed in control panels. Connect the main power
supply to the power supply module in the control panel through a relay terminal block.
Wiring and replacement of a power supply module must be performed by qualified maintenance
personnel with knowledge of protection against electric shock.
For wiring methods, refer to the MELSEC-L CPU Module User's Manual (Hardware Design,
Maintenance and Inspection).
5
Page 8
[Startup and Maintenance Precautions]
WARNING
● Do not touch any terminal while power is on. Doing so will cause electric shock or malfunction.
● Correctly connect the battery connector. Do not charge, disassemble, heat, short-circuit, solder, or
throw the battery into the fire. Also, do not expose it to liquid or strong shock.
Doing so will cause the battery to produce heat, explode, ignite, or leak, resulting in injury and fire.
● Shut off the external power supply (all phases) used in the system before cleaning the module or
retightening the terminal block screws or connector screws. Failure to do so may result in electric
shock.
[Startup and Maintenance Precautions]
CAUTION
● Before performing online operations (especially, program modification, forced output, and operating
status change) for the running CPU module from the peripheral connected, read relevant manuals
carefully and ensure the safety. Improper operation may damage machines or cause accidents.
● Do not disassemble or modify the module. Doing so may cause failure, malfunction, injury, or a fire.
● Use any radio communication device such as a cellular phone or PHS (Personal Handy-phone
System) more than 25cm away in all directions from the programmable controller. Failure to do so
may cause malfunction.
● Shut off the external power supply (all phases) used in the system before mounting or removing a
module. Failure to do so may cause the module to fail or malfunction.
● Tighten the terminal block screws or connector screws within the specified torque range.
Undertightening can cause drop of the component or wire, short circuit, or malfunction. Overtightening
can damage the screw and/or module, resulting in drop, short circuit, or malfunction.
● After the first use of the product (module, display unit, and terminal block), the number of
connections/disconnections is limited to 50 times (in accordance with IEC 61131-2). Exceeding the
limit may cause malfunction.
● After the first use of the SD memory card, do not insert/remove the memory card more than 500 times.
Exceeding the limit may cause malfunction.
● Do not drop or apply shock to the battery to be installed in the module. Doing so may damage the
battery, causing the battery fluid to leak inside the battery. If the battery is dropped or any shock is
applied to it, dispose of it without using.
● Before handling the module, touch a conducting object such as a grounded metal to discharge the
static electricity from the human body. Failure to do so may cause the module to fail or malfunction.
● Before testing the operation by the positioning function, set a low speed value for the speed limit
parameter so that the operation can be stopped immediately upon occurrence of a hazardous
condition.
6
Page 9

[Disposal Precautions]
CAUTION
● When disposing of this product, treat it as industrial waste. When disposing of batteries, separate
them from other wastes according to the local regulations. (For details on battery regulations in EU
member states, refer to the MELSEC-L CPU Module User's Manual (Hardware Design, Maintenance
and Inspection).)
[Transportation Precautions]
CAUTION
● When transporting lithium batteries, follow the transportation regulations. (For details on the regulated
models, refer to the MELSEC-L CPU Module User's Manual (Hardware Design, Maintenance and
Inspection).)
7
Page 10

CONDITIONS OF USE FOR THE PRODUCT
(1) Mitsubishi programmable controller ("the PRODUCT") shall be used in conditions;
i) where any problem, fault or failure occurring in the PRODUCT, if any, shall not lead to any major
or serious accident; and
ii) where the backup and fail-safe function are systematically or automatically provided outside of
the PRODUCT for the case of any problem, fault or failure occurring in the PRODUCT.
(2) The PRODUCT has been designed and manufactured for the purpose of being used in general
industries.
MITSUBISHI SHALL HAVE NO RESPONSIBILITY OR LIABILITY (INCLUDING, BUT NOT
LIMITED TO ANY AND ALL RESPONSIBILITY OR LIABILITY BASED ON CONTRACT,
WARRANTY, TORT, PRODUCT LIABILITY) FOR ANY INJURY OR DEATH TO PERSONS OR
LOSS OR DAMAGE TO PROPERTY CAUSED BY the PRODUCT THAT ARE OPERATED OR
USED IN APPLICATION NOT INTENDED OR EXCLUDED BY INSTRUCTIONS, PRECAUTIONS,
OR WARNING CONTAINED IN MITSUBISHI'S USER, INSTRUCTION AND/OR SAFETY
MANUALS, TECHNICAL BULLETINS AND GUIDELINES FOR the PRODUCT.
("Prohibited Application")
Prohibited Applications include, but not limited to, the use of the PRODUCT in;
• Nuclear Power Plants and any other power plants operated by Power companies, and/or any
other cases in which the public could be affected if any problem or fault occurs in the PRODUCT.
• Railway companies or Public service purposes, and/or any other cases in which establishment of
a special quality assurance system is required by the Purchaser or End User.
• Aircraft or Aerospace, Medical applications, Train equipment, transport equipment such as
Elevator and Escalator, Incineration and Fuel devices, Vehicles, Manned transportation,
Equipment for Recreation and Amusement, and Safety devices, handling of Nuclear or
Hazardous Materials or Chemicals, Mining and Drilling, and/or other applications where there is a
significant risk of injury to the public or property.
Notwithstanding the above, restrictions Mitsubishi may in its sole discretion, authorize use of the
PRODUCT in one or more of the Prohibited Applications, provided that the usage of the PRODUCT
is limited only for the specific applications agreed to by Mitsubishi and provided further that no
special quality assurance or fail-safe, redundant or other safety features which exceed the general
specifications of the PRODUCTs are required. For details, please contact the Mitsubishi
representative in your region.
8
Page 11
INTRODUCTION
Remark
Thank you for purchasing the Mitsubishi Electric MELSEC-L series programmable controllers.
This manual describes the memory maps, functions, and devices of the CPU module, and programming.
Before using this product, please read this manual and the relevant manuals carefully and develop familiarity with the
functions and performance of the MELSEC-L series programmable controller to handle the product correctly.
When applying the program examples introduced in this manual to an actual system, ensure the applicability and
confirm that it will not cause system control problems.
Relevant CPU modules
CPU module Model
LCPU
This manual does not describe the details of the instructions, error codes, special relay (SM), and special register (SD).
● For the instructions, refer to the following.
MELSEC-Q/L Programming Manual (Common Instruction)
● For the error codes, special relay(SM), and special register (SD), refer to the following.
MELSEC-L CPU Module User's Manual (Hardware Design, Maintenance and Inspection)
L02SCPU, L02SCPU-P, L02CPU, L02CPU-P, L06CPU, L06CPU-P, L26CPU, L26CPU-P,
L26CPU-BT, L26CPU-PBT
9
Page 12
RELEVANT MANUALS
(1) CPU module user's manual
Manual name
<manual number (model code)>
MELSEC-L CPU Module User's Manual (Hardware Design, Maintenance and
Inspection)
<SH-080890ENG, 13JZ36>
MELSEC-L CPU Module User's Manual (Built-In Ethernet Function)
<SH-080891ENG, 13JZ37>
MELSEC-L CPU Module User's Manual (Built-In I/O Function)
<SH-080892ENG, 13JZ38>
QnUDVCPU/LCPU User's Manual (Data Logging Function)
<SH-080893ENG, 13JZ39>
(2) Programming manual
Manual name
<manual number (model code)>
MELSEC-Q/L Programming Manual (Common Instruction)
<SH-080809ENG, 13JW10>
MELSEC-Q/L/QnA Programming Manual (SFC)
<SH-080041, 13JF60>
MELSEC-Q/L Programming Manual (MELSAP-L)
<SH-080076, 13JF61>
MELSEC-Q/L Programming Manual (Structured Text)
<SH-080366E, 13JF68>
MELSEC-Q/L/QnA Programming Manual (PID Control Instructions)
<SH-080040, 13JF59>
Description
Specifications of the CPU modules, power supply modules, display unit,
branch module, extension module, SD memory cards, and batteries,
information on how to establish a system, maintenance and inspection, and
troubleshooting
The built-in Ethernet function of the CPU module
The general-purpose I/O function, interrupt input function, pulse catch
function, positioning function, and high-speed counter function of the CPU
module
The data logging function of the CPU module
Description
Detailed description and usage of instructions used in programs
System configuration, specifications, functions, programming, and error codes
for SFC (MELSAP3) programs
System configuration, specifications, functions, programming, and error codes
for SFC (MELSAP-L) programs
System configuration and programming using structured text language
Dedicated instructions for PID control
(3) Operating manual
Manual name
<manual number (model code)>
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating Manual (Common)
GX Developer Version 8 Operating Manual
<SH-080779ENG, 13JU63>
<SH-080373E, 13JU41>
Description
System configuration, parameter settings, and online operations of GX
Works2, which are common to Simple projects and Structured projects
Operating methods of GX Developer, such as programming, printing,
monitoring, and debugging
10
Page 13
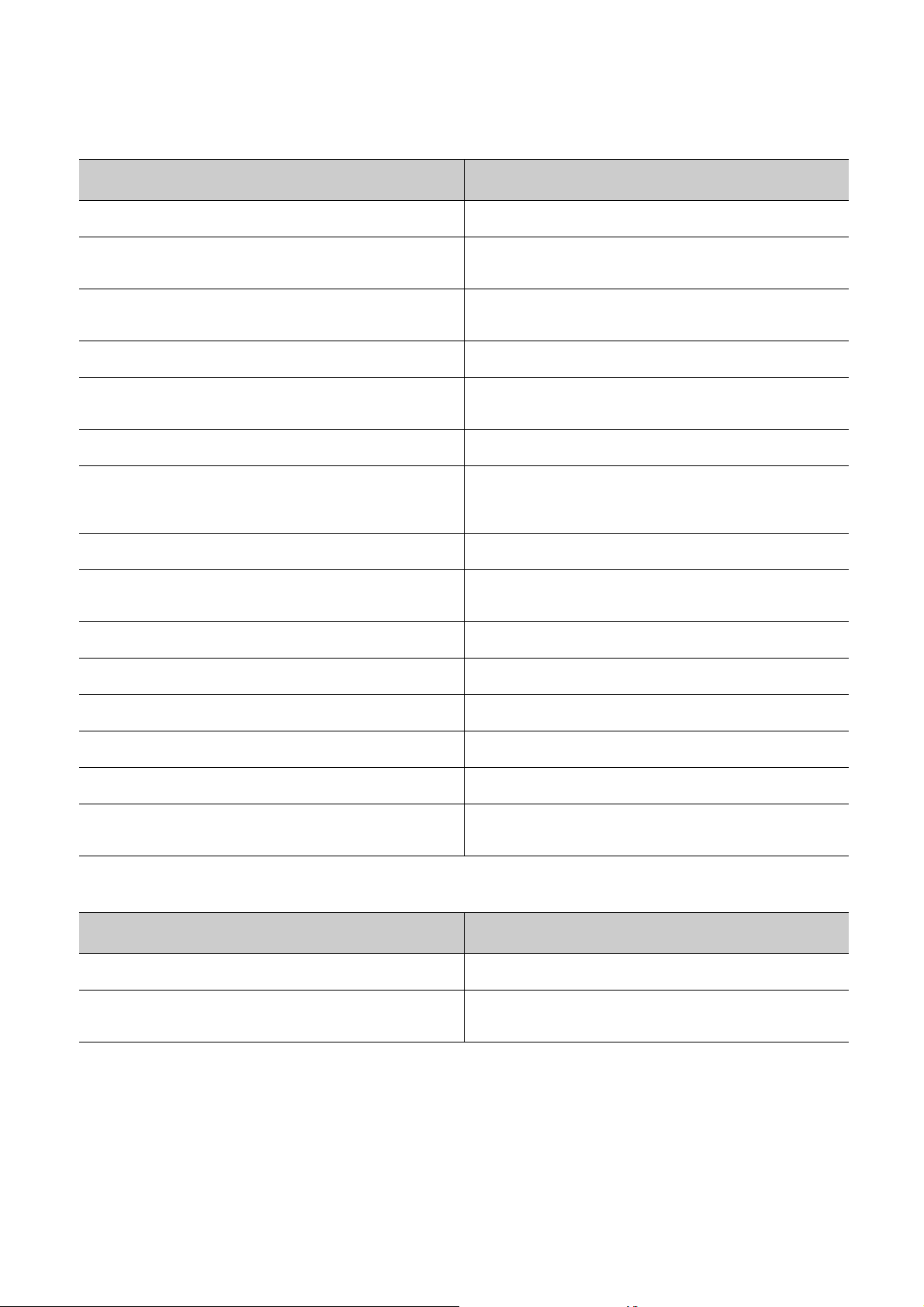
(4) I/O module and intelligent function module manual
Manual name
<manual number (model code)>
MELSEC-L I/O Module User's Manual
<SH-080888ENG, 13JZ34>
MELSEC-L Ethernet Interface Module User's Manual (Basic)
<SH-081105ENG, 13JZ73>
MELSEC-L Serial Communication Module User’s Manual (Basic)
<SH-080894ENG, 13JZ40>
MELSEC Communication Protocol Reference Manual
<SH-080008, 13JF89>
MELSEC-L CC-Link System Master/Local Module User's Manual
<SH-080895ENG, 13JZ41>
MELSEC-L CC-Link/LT Master Module User's Manual
<SH-081012ENG, 13JZ65>
MELSEC-L CC-Link IE Field Network Master/Local Module User's Manual
<SH-080972ENG, 13JZ54>
MELSEC-L Analog-Digital Converter Module User's Manual
<SH-080899ENG, 13JZ42>
MELSEC-L Dual Channel Isolated High Resolution Analog-Digital Converter
Module User's Manual
<SH-081103ENG, 13JZ72>
MELSEC-L Digital-Analog Converter Module User's Manual
<SH-080900ENG, 13JZ43>
MELSEC-L Analog Input/Output Module User's Manual
<SH-081167ENG, 13JZ87>
MELSEC-L LD75P/LD75D Positioning Module User's Manual
<SH-080911ENG, 13JZ46>
MELSEC-L High-Speed Counter Module User's Manual
<SH-080920ENG, 13JZ49>
MELSEC-L Temperature Control Module User's Manual
<SH-081000ENG, 13JZ64>
MELSEC-L Multiple Input (Voltage/Current/Temperature) Module User's
Manual
<SH-081365ENG, 13JZ76>
Specifications and troubleshooting of the I/O module
Specifications, procedures for data communication with external devices, line
connection (open/close), fixed buffer communication, random access buffer
communication, and troubleshooting of the Ethernet module
System configuration, specifications, procedures before operation, data
communication methods (basic), and troubleshooting of the serial
communication module
Details of MELSEC communication protocol (MC protocol) that is used for
data communication between a target device and a CPU module
Settings, specifications, handling, data communication methods, and
troubleshooting of the built-in CC-Link function of the CPU module or the CCLink system master/local module
Settings, specifications, handling, data communication methods, and
troubleshooting of the CC-Link/LT master module
Overview of CC-Link IE Field Network, and specifications, procedures before
operation, system configuration, installation, wiring, settings, functions,
programming, and troubleshooting of the MELSEC-L series CC-Link IE Field
Network master/local module
System configuration, specifications, settings, and troubleshooting of the
analog-digital converter module
System configuration, specifications, settings, and troubleshooting of the dual
channel isolated high resolution analog-digital converter module
System configuration, specifications, settings, and troubleshooting of the
digital-analog converter module
System configuration, specifications, settings, and troubleshooting of the
analog input/output module
System configuration specifications settings and troubleshooting of the
positioning module
System configuration specifications settings and troubleshooting of the highspeed counter module
System configuration specifications settings and troubleshooting of the
temperature control module
System configuration, specifications, settings, and troubleshooting of the
multiple input module
Description
(5) Others
Manual name
<manual number (model code)>
iQ Sensor Solution Reference Manual
CC-Link IE Field Network Basic Reference Manual
<SH-081133ENG, 13JV28>
<SH-081684ENG, 13JX62>
Description
Operating methods of iQ Sensor Solution, such as programming and
monitoring
Specifications, procedures before operation, system configuration,
programming, functions, parameter settings, and troubleshooting of CC-Link
IE Field Network Basic
11
Page 14

CONTENTS
CONTENTS
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
CONDITIONS OF USE FOR THE PRODUCT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
INTRODUCTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
RELEVANT MANUALS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
MANUAL PAGE ORGANIZATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
TERMS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
PART 1 PROGRAMMING
CHAPTER 1 BASIC PROCEDURE FOR PROGRAMMING 20
1.1 System Configuration Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
1.2 Creating a Project. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
1.3 Creating a Program . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
1.3.1 Prior knowledge for creating a program . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
1.3.2 How to create a program . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .24
1.4 Converting a Program. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
1.5 Writing a Project to the CPU Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
1.5.1 Formatting a memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
1.5.2 Writing to the CPU module. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
1.6 Checking an Operation of the CPU Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
1.7 Saving a Project . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
CHAPTER 2 APPLICATION OF PROGRAMMING 31
2.1 Memory and Files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
2.1.1 Memory configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
2.1.2 Parameter-valid drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .34
2.1.3 Files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35
2.2 I/O Number . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
2.2.1 Concept of I/O number assignment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41
2.2.2 I/O number assignment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .43
2.3 Scan Time Structure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
2.3.1 Initial processing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .45
2.3.2 Refresh processing of input/output modules or intelligent function modules . . . . . . . . . . . . . .46
2.3.3 Program operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .46
2.3.4 END processing. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .47
2.4 Operation Processing of the CPU Module for Each Operating Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
2.5 Operation Processing During Momentary Power Failure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
2.6 Processing of Inputs and Outputs. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .51
2.6.1 Refresh processing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .51
2.6.2 Direct processing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .54
2.7 Interrupt Program . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
2.8 Executing Multiple Programs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
2.8.1 Initial execution type program . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .63
2.8.2 Scan execution type program . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .65
2.8.3 Standby type program . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .66
12
Page 15

2.8.4 Fixed scan execution type program . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .69
2.8.5 Changing the program execution type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .72
2.9 Boot Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
2.10 Programming Language . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
2.11 Communications with Intelligent Function Modules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
PART 2 FUNCTIONS
CHAPTER 3 CPU MODULE FUNCTIONS 82
3.1 Function List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
3.2 Constant Scan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
3.3 Watchdog Timer (WDT) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
3.4 Latch Function . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
3.5 Initial Device Value . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
3.6 Service Processing Setting. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
3.7 Output Mode at Operating Status Change (STOP to RUN) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
3.8 Input Response Time Setting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
3.9 Error Time Output Mode Setting. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
3.10 PLC Operation Mode at H/W Error Setting. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
3.11 Security Function . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
3.11.1 File Password 32 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .105
3.11.2 Remote Password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
3.12 Remote Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
3.12.1 Remote RUN/STOP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .112
3.12.2 Remote PAUSE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 114
3.12.3 Remote RESET . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .116
3.12.4 Remote Latch Clear . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .117
3.13 Scan Time Measurement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
3.14 Program List Monitor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
3.15 Interrupt Program List Monitor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 122
3.16 Monitor condition setting. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
3.17 Local Device Monitor/Test. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 128
3.18 External Input/Output Forced On/Off . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
3.19 Executional Conditioned Device Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
3.20 Sampling Trace. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 143
3.21 Realtime Monitor Function . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150
3.22 Writing Programs in RUN Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 151
3.22.1 Online change (ladder mode). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .151
3.22.2 Online change (files) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .152
3.22.3 Precautions for online change . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .153
3.23 Debug from Multiple Programming Tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 158
3.23.1 Simultaneous monitoring from multiple programming tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .159
3.23.2 Online change from multiple programming tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .160
3.24 Self-Diagnostic Function. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 161
13
Page 16

3.25 Error Clear . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 166
3.26 LED Control Function . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 169
3.26.1 Methods for turning off the LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .169
3.26.2 LED indication priority . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .170
3.27 Module Error Collection Function . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 171
3.28 Latch Data Backup to Standard ROM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 175
3.28.1 Latch data backup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .176
3.28.2 Restoring backup data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .179
3.29 Writing/Reading Device Data to/from Standard ROM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 180
3.30 Module Model Name Read. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 181
3.31 CPU Module Change Function with SD Memory Card. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 182
3.31.1 Backup to SD memory card . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .184
3.31.2 Backup data restoration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .192
3.32 Clock Function . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 196
3.33 Battery Life-Prolonging Function . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 198
3.34 Memory Check Function. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 199
3.35 Program Cache Memory Auto Recovery Function . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 200
3.36 Project Data Batch Save/Load Function. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 202
3.36.1 Batch save . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .203
3.36.2 Batch load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .209
3.37 Predefined Protocol Function . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 215
3.37.1 Communications via Ethernet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .215
3.37.2 Communications via RS-232 and RS-422/485 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .216
3.38 Serial Communication Function . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 227
3.39 iQ Sensor Solution Function. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 234
CHAPTER 4 DISPLAY UNIT FUNCTIONS 236
4.1 Function List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 240
4.2 CPU Monitor/Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 241
4.2.1 Device monitor/test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .241
4.2.2 Device clear . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .249
4.2.3 Forced on/off . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .251
4.2.4 Scan time monitor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .254
4.2.5 Built-in I/O function monitor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .255
4.2.6 Error display/clear . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .259
4.3 CPU Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 263
4.3.1 Clock setting. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .263
4.4 Module Monitor/Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 265
4.4.1 Buffer memory monitor/test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .265
4.5 Module Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 270
4.5.1 Initial setting change . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .270
4.6 User Message. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 273
4.7 Memory Card Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 274
4.7.1 File list/delete . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .274
4.7.2 Free space display . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .279
4.7.3 Batch save . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .280
14
Page 17

4.7.4 Batch load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .281
4.8 Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 283
4.8.1 Language setting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .283
4.8.2 Contrast adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .284
4.8.3 Lighting period setting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .285
4.8.4 Pop-up display . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .286
PART 3 DEVICES, CONSTANTS
CHAPTER 5 DEVICES 288
5.1 Device List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 288
5.2 Internal User Devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 290
5.2.1 Input (X) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .293
5.2.2 Output (Y). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .293
5.2.3 Internal relay (M) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .294
5.2.4 Latch relay (L) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .294
5.2.5 Link relay (B) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .294
5.2.6 Annunciator (F) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .295
5.2.7 Link special relay (SB) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .298
5.2.8 Edge relay (V) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .298
5.2.9 Step relay (S). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .299
5.2.10 Timer (T, ST) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .299
5.2.11 Counter (C) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .308
5.2.12 Data register (D). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .311
5.2.13 Link register (W). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .312
5.2.14 Link special register (SW) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .313
5.3 Internal System Devices. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 314
5.3.1 Function devices (FX, FY, FD) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .314
5.3.2 Special relay (SM) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .316
5.3.3 Special register (SD) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .316
5.4 Link Direct Devices. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 317
5.5 Module Access Devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 320
5.5.1 Intelligent function module device . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .320
5.6 Index Register/Standard Device Register (Z). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 322
5.6.1 Index Register (Z) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .322
5.6.2 Standard device register (Z). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .323
5.6.3 Saving and restoration of the index register. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .324
5.7 File Register (R, ZR). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 326
5.8 Extended Data Register (D) and Extended Link Register (W) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 330
5.9 Nesting (N) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 335
5.10 Pointer (P). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 336
5.10.1 Local pointer. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .337
5.10.2 Common pointer. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .338
5.11 Interrupt Pointer (I) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 339
5.12 Other Devices. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 340
15
Page 18
5.12.1 SFC block device (BL) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .340
5.12.2 I/O No. specification device (U) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .340
5.12.3 Macro instruction argument device (VD) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .341
CHAPTER 6 CONSTANTS 342
6.1 Decimal Constant (K) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 342
6.2 Hexadecimal Constant (H) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 342
6.3 Real Number (E). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 343
6.4 Character String (" "). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 343
CHAPTER 7 CONVENIENT USAGE OF DEVICES 344
7.1 Global Device . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 344
7.2 Local Device . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 345
APPENDICES 350
Appendix 1 Parameter Setting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 350
Appendix 1.1 List of parameter numbers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .350
Appendix 1.2 PLC parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .353
Appendix 1.3 Network parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .374
Appendix 1.4 Remote password setting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .375
Appendix 2 Added and Changed Functions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 376
Appendix 3 CPU Module Processing Time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 378
Appendix 3.1 Time required for each processing in a scan time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .378
Appendix 3.2 Factors that increase the scan time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .385
Appendix 3.3 Realtime monitor function processing time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .388
Appendix 4 Data Used in the CPU Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 389
Appendix 5 Character Codes Available in the Display Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 391
Appendix 6 Differences Between LCPU and QnUCPU . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 403
Appendix 6.1 Specifications comparison . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .403
Appendix 6.2 Precautions for utilizing programs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .404
Appendix 7 Precautions for Using GX Works2 and Differences with GX Developer . . . . . . . . . . . . 405
Appendix 8 Device Point Assignment Sheet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 406
INDEX 407
REVISIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 410
WARRANTY . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 413
TRADEMARKS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 414
16
Page 19
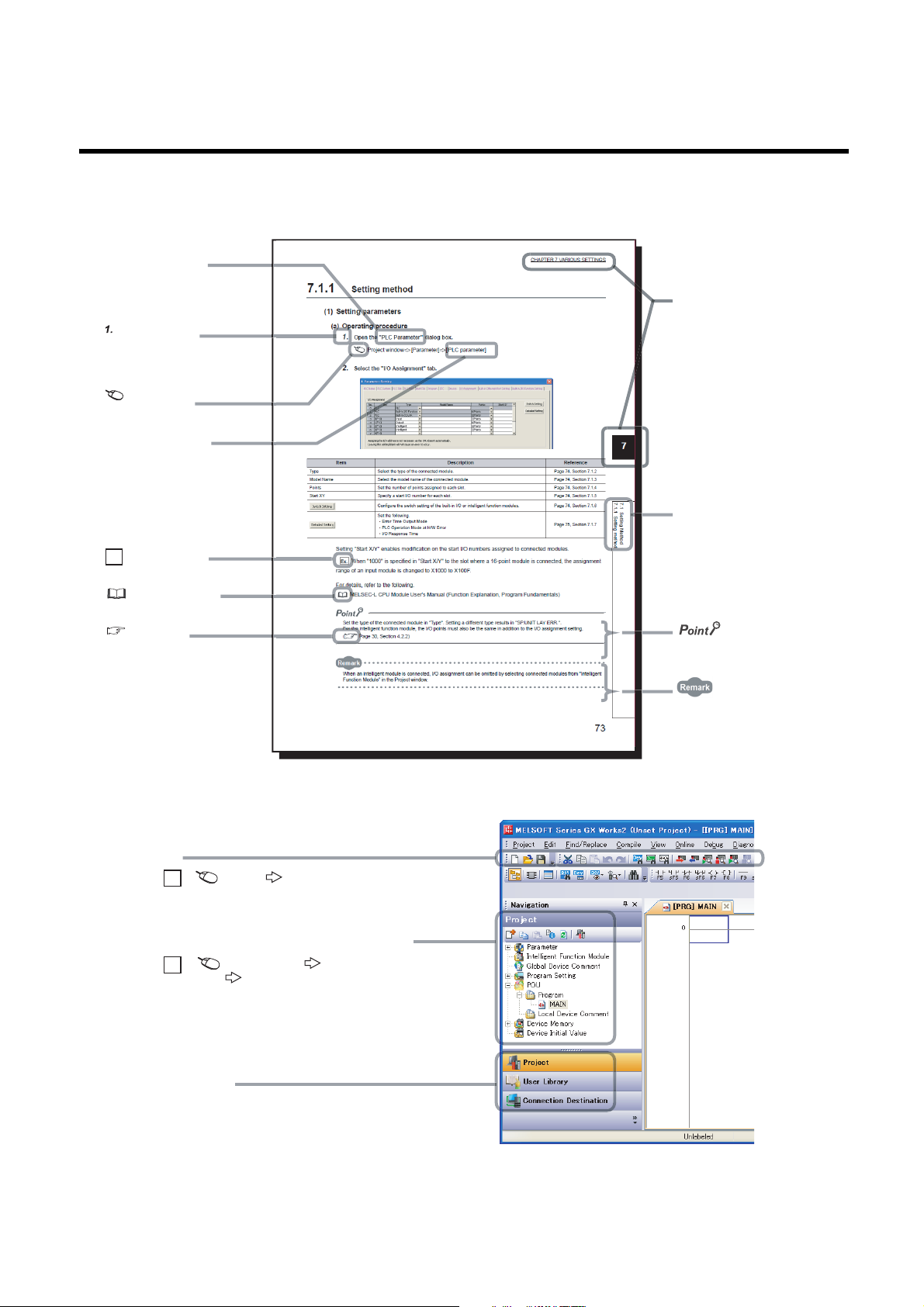
MANUAL PAGE ORGANIZATION
The section of
the current page is shown.
The chapter of
the current page is shown.
"" is used for
screen names and items.
[ ] is used for items
in the menu bar and
the project window.
shows operating
procedures.
shows reference
manuals.
shows notes that
requires attention.
shows mouse
operations.
*1
shows
reference pages.
shows setting or
operating examples.
Ex.
shows useful
information.
A window selected in the view selection area is displayed.
View selection area
[Online] [Write to PLC...]
Select [Online] on the menu bar,
and then select [Write to PLC...].
Project window
[Parameter]
[PLC Parameter]
Select [Project] from the view selection
area to open the Project window.
Menu bar
Ex.
Ex.
In the Project window, expand [Parameter] and
select [PLC Parameter].
In this manual, pages are organized and the symbols are used as shown below.
The following illustration is for explanation purpose only, and should not be referred to as an actual documentation.
*1 The mouse operation example (for GX Works2) is provided below.
17
Page 20
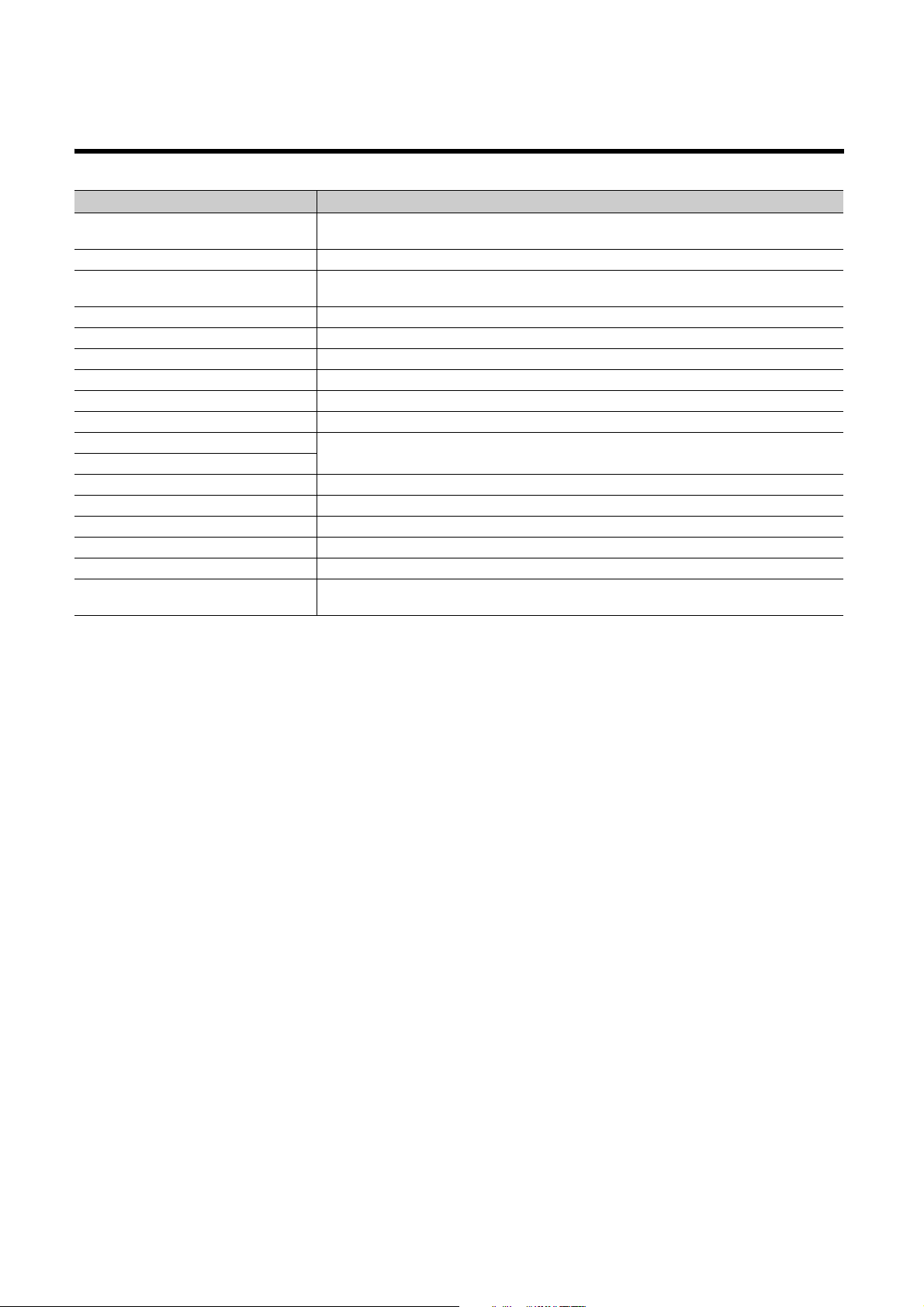
TERMS
Unless otherwise specified, this manual uses the following terms.
Ter m Description
Battery
Branch module The abbreviation for the MELSEC-L series branch module
Built-in Ethernet port LCPU
CPU module The abbreviation for the MELSEC-L series CPU module
Display unit A liquid crystal display to be attached to the CPU module
END cover A cover to be attached to the right side of the rightmost MELSEC-L series module
Extension block A block where an extension module is connected in an extension system
Extension cable The abbreviation for the MELSEC-L series extension cable
Extension module The abbreviation for the MELSEC-L series extension module
GX Works2
GX Developer
LCPU Another term for the MELSEC-L series CPU module
Main block A block where a CPU module is connected in an extension system
Power supply module The abbreviation for the MELSEC-L series power supply module
Programming tool A generic term for GX Works2 and GX Developer
QnUCPU Another term for the MELSEC-Q series Universal model QCPU
SD memory card
A battery to be installed in the CPU module and used for backing up data such as the standard RAM data
and latch device data in case of power failure. The Q6BAT and Q7BAT are available.
A generic term for the L02CPU, L02CPU-P, L06CPU, L06CPU-P, L26CPU, L26CPU-P, L26CPU-BT, and
L26CPU-PBT
The product name of the software package for the MELSEC programmable controllers
Secure Digital Memory Card, which is a flash memory device. The NZ1MEM-2GBSD, NZ1MEM-4GBSD,
NZ1MEM-8GBSD, NZ1MEM-16GBSD, L1MEM-2GBSD, and L1MEM-4GBSD are available.
18
Page 21
PART 1 PROGRAMMING
In this part, fundamental knowledge of programming is described.
CHAPTER 1 BASIC PROCEDURE FOR PROGRAMMING. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
CHAPTER 2 APPLICATION OF PROGRAMMING. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
19
Page 22
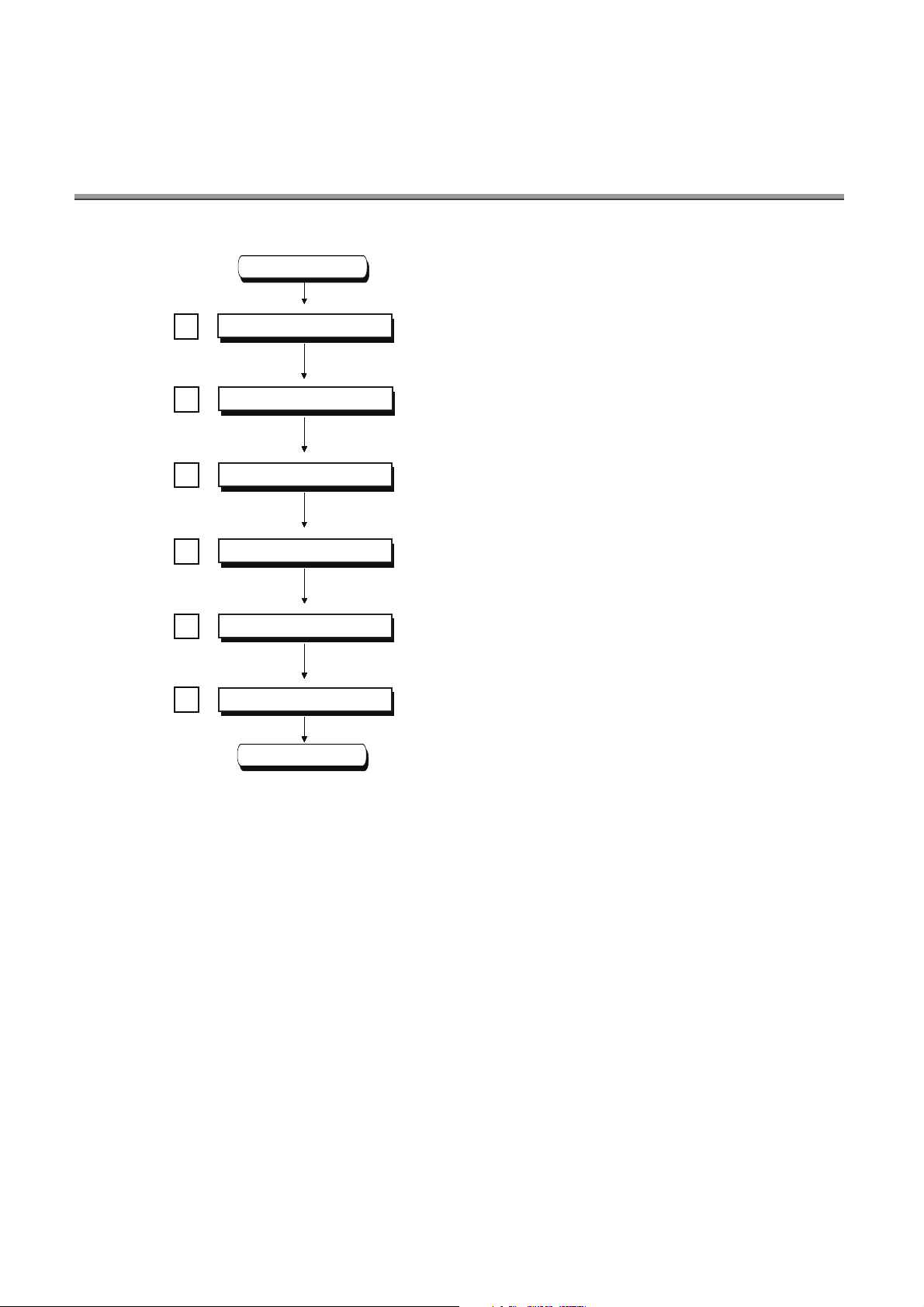
CHAPTER 1 BASIC PROCEDURE FOR
Creating projects
Creating programs
Converting programs
Writing projects
Checking operations
PROGRAMMING
This chapter describes the basic procedure for programming.
Start
Check column
Create projects with GX Works2.
( Page 22, Section 1.2)
Create programs.
( Page 23, Section 1.3)
Convert created programs into ones that can be processed by
the CPU module.
( Page 25, Section 1.4)
Write the projects to the CPU module.
For the first use of the CPU module, format the used memory
beforehand.
( Page 26, Section 1.5)
Debug the programs using the monitoring function.
( Page 28, Section 1.6)
Saving projects
End
Save the projects.
( Page 30, Section 1.7)
20
Page 23
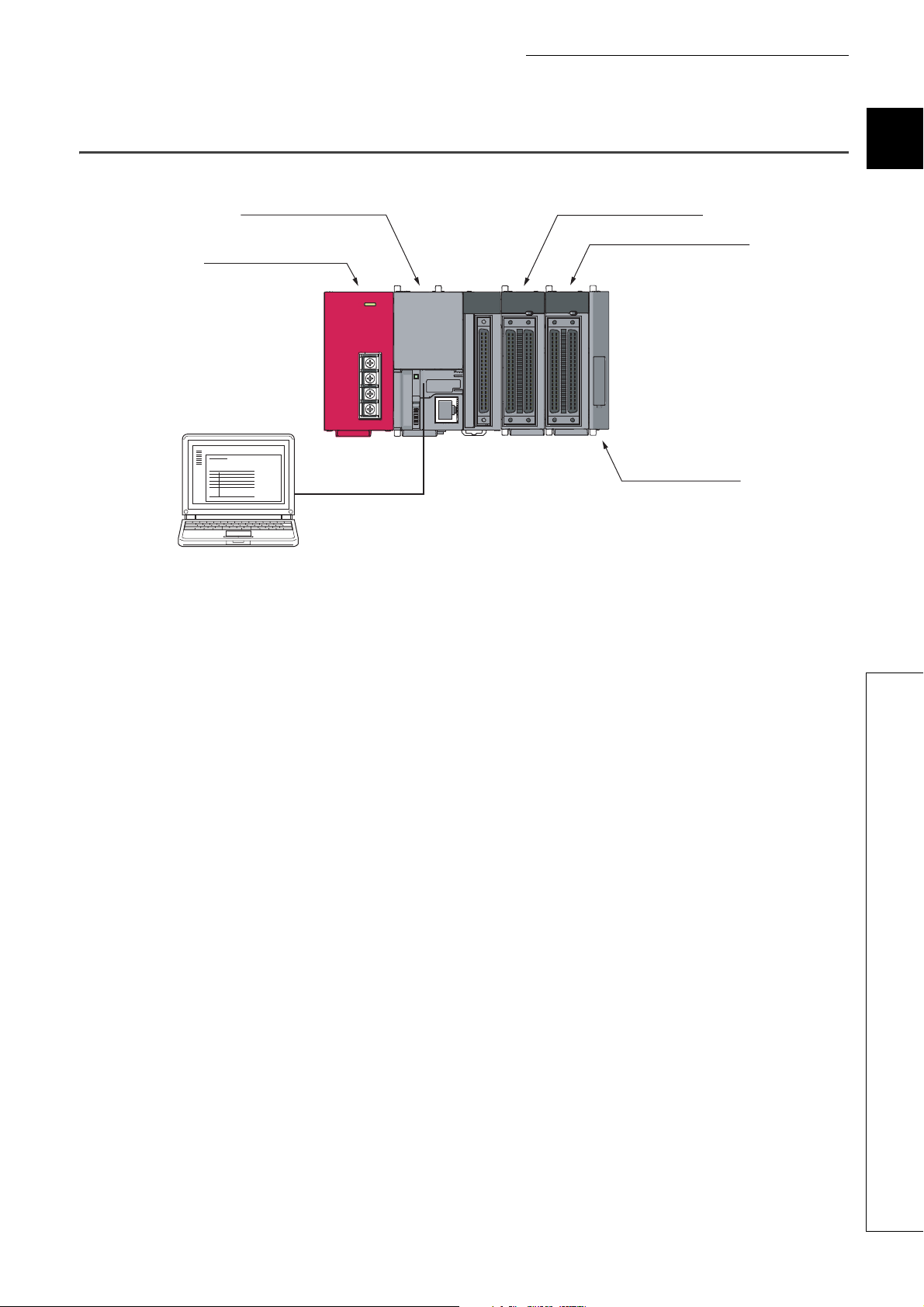
CHAPTER 1 BASIC PROCEDURE FOR PROGRAMMING
CPU module (L02CPU)
Power supply module (L61P)
GX Works2
Input module (LX42C4)
Output module (LY42NT1P)
END cover (L6EC)
USB connection
1.1 System Configuration Example
The following system configuration is used for description throughout this chapter.
*1 Wiring of the power supply module and I/O modules are omitted in this illustration.
1
1.1 System Configuration Example
21
Page 24

1.2 Creating a Project
A project is a set of information, such as programs and parameters, which is necessary to operate a programmable
controller.
The following two projects are available.
• Simple project
• Structured project
Create a new project using GX Works2.
[Project] [New...]
Item Description
Project Type
PLC Series Select a series of the CPU module to use in the project. In this chapter, "LCPU" is selected.
PLC Type Select a type of the CPU module (CPU module model) to use in the project. In this chapter, "L02/L02-P" is selected.
Language Select a language of the program data to use for the new project. In this chapter, "Ladder" is selected.
When performing communication between a programming tool and a CPU module through GOT or a network module, check
the PLC type because the modules could be connected with wrong model names. If the modules are connected with wrong
model names, data may not be written or read properly.
Select a type of project to create. In this chapter, "Simple Project" is selected.
Use Label Select this checkbox when using a label for programming. In this chapter, this is not selected.
22
Page 25
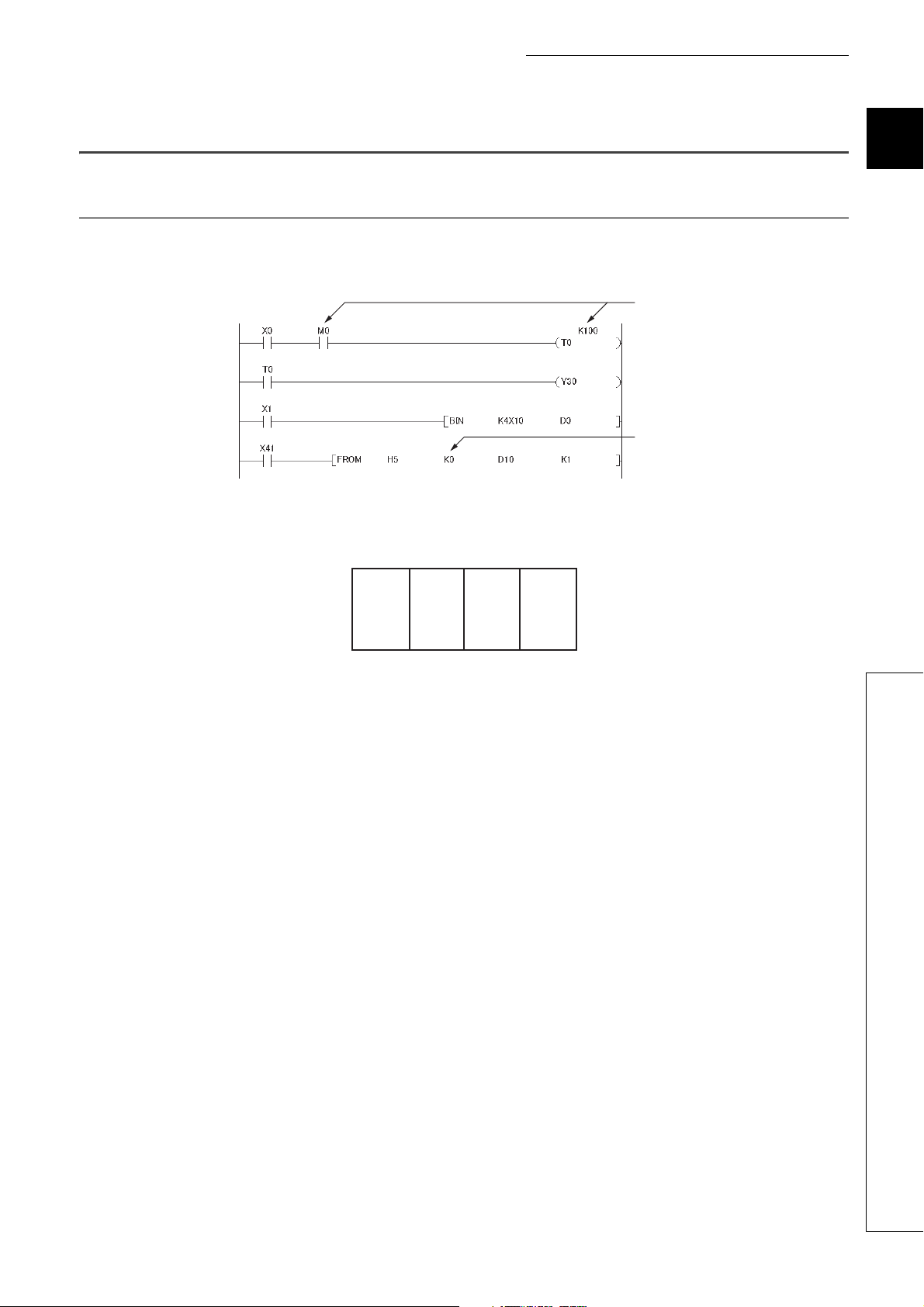
CHAPTER 1 BASIC PROCEDURE FOR PROGRAMMING
Device
Constant
1.3 Creating a Program
1.3.1 Prior knowledge for creating a program
(1) Device and constants
Devices and constants, such as shown below, are used for creating a program. ( Page 288, CHAPTER 5)
(2) Concept of I/O numbers
I/O numbers are automatically assigned.
Power
supply
module
CPU
module
0000
to
000F
Input
module
64
points
X0010
to
X004F
Output
module
64
points
Y0050
to
Y008F
1.3.1 Prior knowledge for creating a program
1
1.3 Creating a Program
Users can also assign I/O numbers according to their purposes. ( Page 41, Section 2.2)
(3) Program configuration
A main routing program, subroutine program, ( Page 46, Section 2.3.3), and interrupt program ( Page
56, Section 2.7) can be included in a program.
23
Page 26
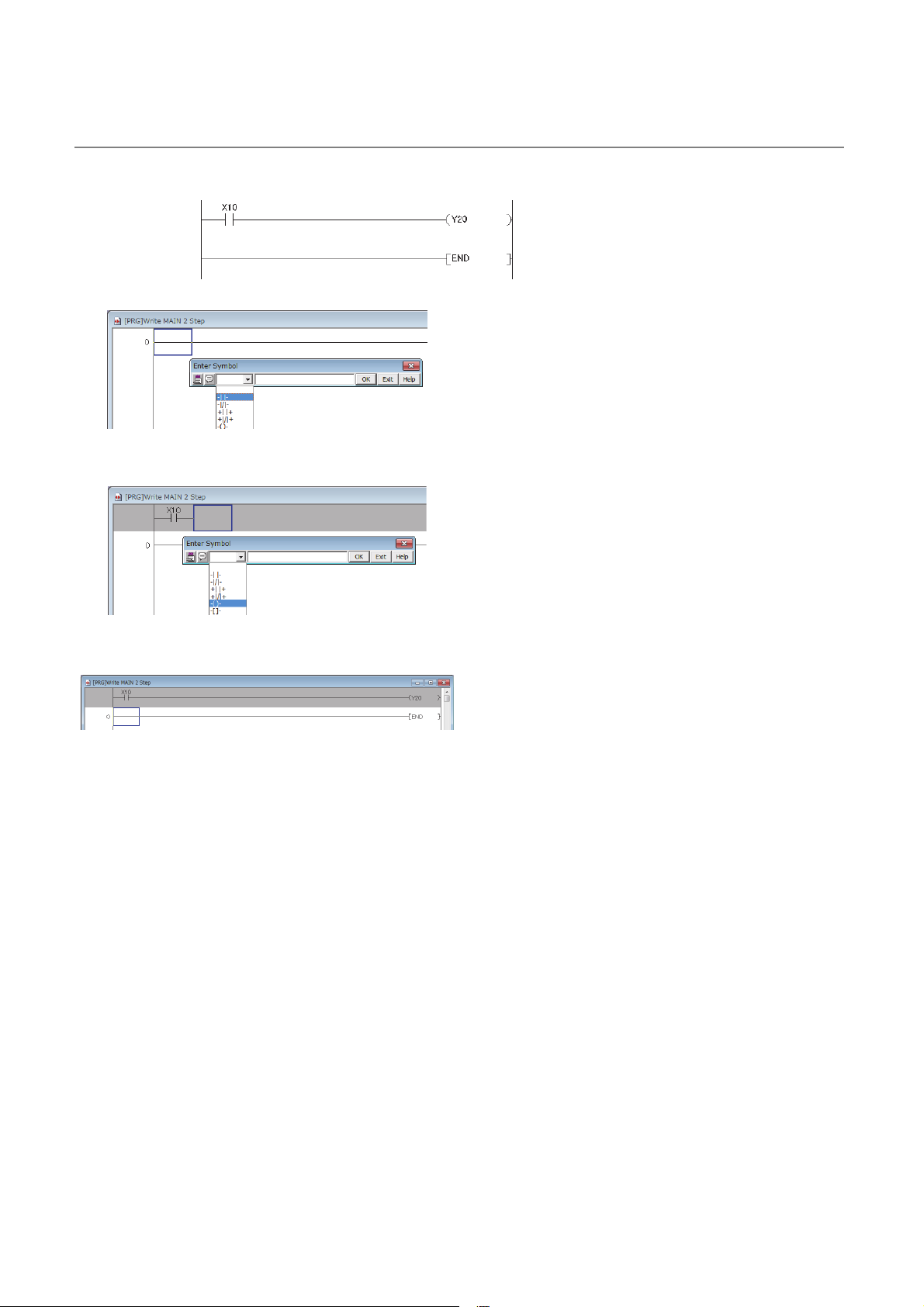
1.3.2 How to create a program
This section shows how to create the following sample program.
When X10 is turned on, Y20 turns on.
1. To enter X10, type X10 at the original cursor
position and select the contact shown in the left
figure.
2. To enter Y20, type Y20 and select the coil shown in
the left figure.
The program has been created. In the next procedure, convert the program.
24
Page 27

CHAPTER 1 BASIC PROCEDURE FOR PROGRAMMING
1.4 Converting a Program
Operation of a program is defined after converting its ladder.
[Compile] [Build]
The program has been converted. In the next procedure, write the program to a CPU module.
● To use a label, the program must be compiled.
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating Manual (Common)
● After modifying a program, it must be compiled.
1
1.4 Converting a Program
25
Page 28
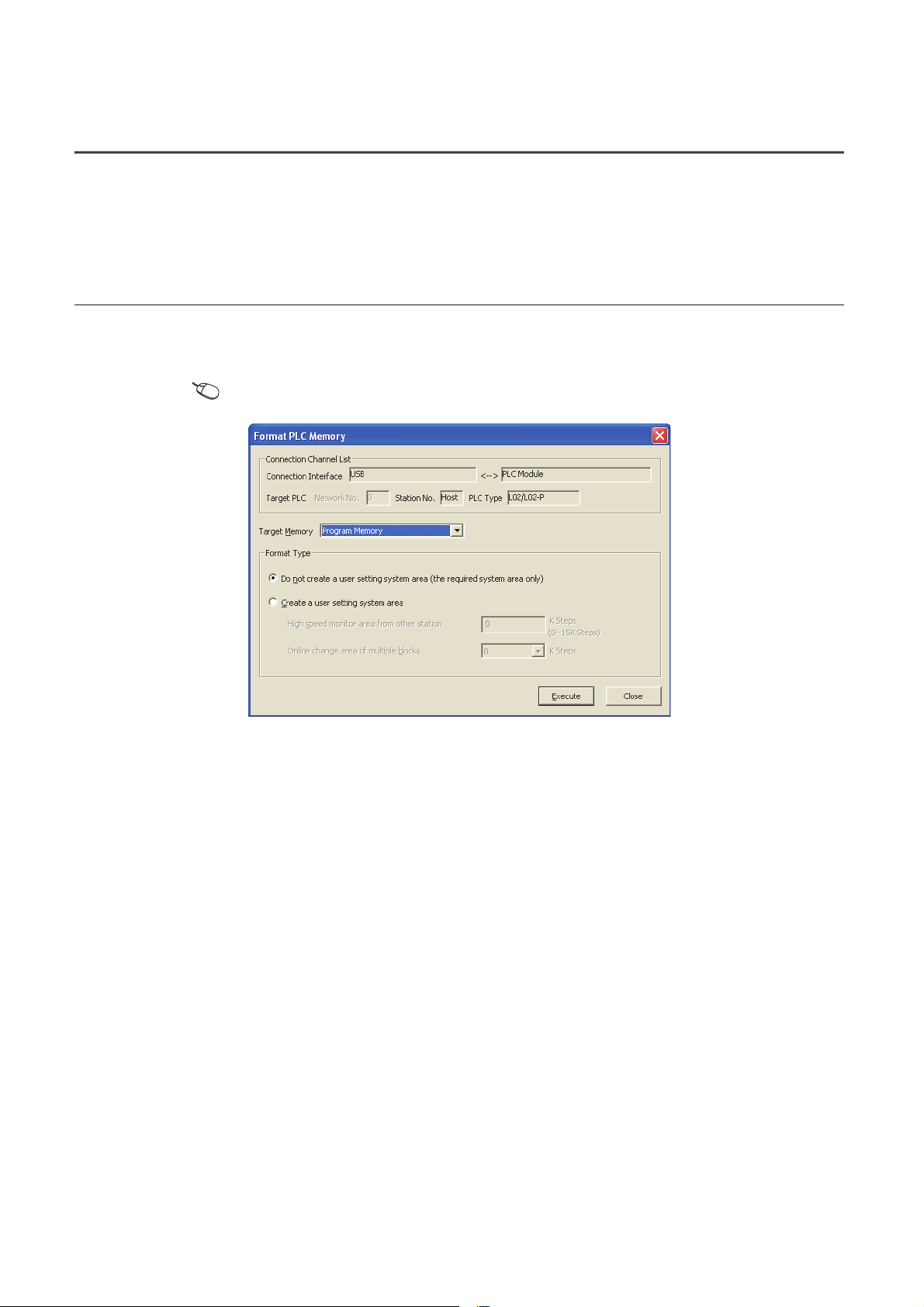
1.5 Writing a Project to the CPU Module
Write the project (the program and parameters described in Section 1.4.) to the CPU module. Note that, when the
program is new, the memory ( Page 31, Section 2.1.1) is formatted so that a program can be written to it.
1.5.1 Formatting a memory
To format a memory, open the "Format PLC Memory" dialog box. In this chapter, a program memory is formatted so
that a program can be written to it.
[Online] [PLC Memory Operation] [Format PLC Memory...]
To check the capacity of the memory after formatting, open the "Online Data Operation" dialog box.
26
Page 29
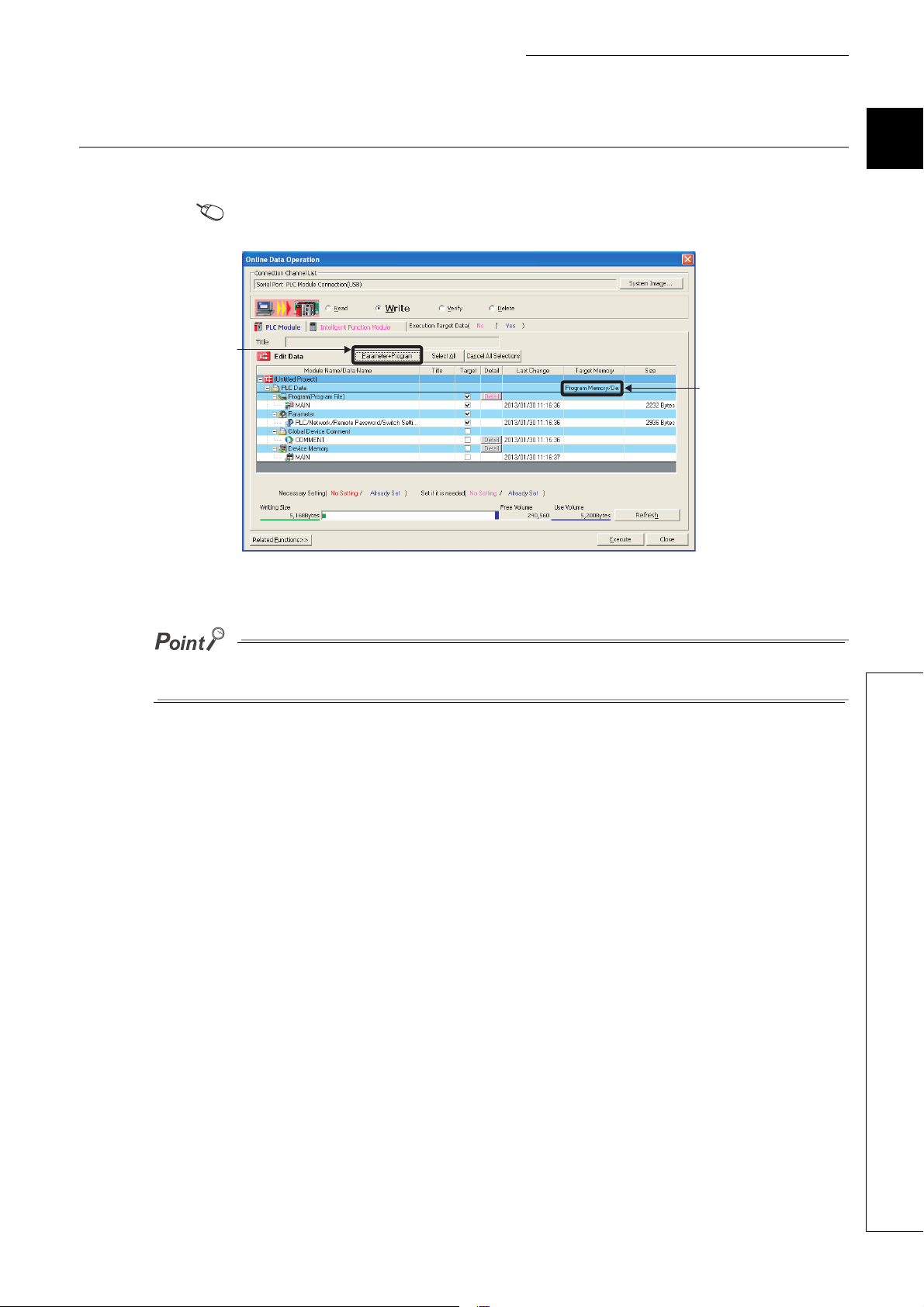
CHAPTER 1 BASIC PROCEDURE FOR PROGRAMMING
1) Select the program
memory.
2) Click this button to
select the parameter
and program
checkboxes
automatically.
1.5.2 Writing to the CPU module
Open the "Online Data Operation" dialog box. In this chapter, a project is written to the program memory.
[Online] [Write to PLC...]
1
The project has been written. In the next procedure, execute the program.
Note that parameter setting is required to operate CPU modules. In this chapter, the procedure for parameter setting is not
introduced since default values are used.( Page 350, Appendix 1)
1.5 Writing a Project to the CPU Module
1.5.2 Writing to the CPU module
27
Page 30

1.6 Checking an Operation of the CPU Module
On (green)
Off
Flashing (red)
MODE:
RUN :
ERR. :
On (green)
Off
Flashing (red)
MODE:
RUN :
ERR. :
MODE:
RUN :
ERR. :
On (green)
Off
Off
MODE:
RUN :
ERR. :
On (green)
On (green)
Off
To check an operation, execute the program written to the CPU module. In this chapter, operation is checked through
the monitoring screen of GX Works2.
(1) Executing a program
Before operating the CPU module, data written to the CPU module must be validated. To validate, power off and
then on or reset the CPU module.
1. Before resetting the CPU module, check the current
LED status.
2. Move the switch on the front of the CPU module to
the RESET position. (One second or longer)
3. Hold the switch until the ERR. LED turns off after
flashing.
In the next procedure, run the CPU module. To run, use the switch on the CPU module.
4. Move the switch to the RUN position.
When the RUN LED is lit green, the program is being executed successfully.
By remote operation, CPU modules can be operated without using switches. ( Page 112, Section 3.12)
28
Page 31

CHAPTER 1 BASIC PROCEDURE FOR PROGRAMMING
Enter a device to be
turned on or off.
(2) Checking operation
Conductivity and power distribution status of contacts and coils can be checked by switching GX Works2 to the
monitor mode.
[Online] [Monitor] [Start Monitoring]
When X0 and X1 are turned on, Y10 turns on. (to turn on X0 and X1, place the cursor on them and double-click
while holding the key.) While contacts and coils are conducting, they are shown in blue.
Alternatively, device states can be checked through a display unit. ( Page 241, Section 4.2.1)
Debug can be performed by forcibly turn on or off devices in the "Modify Value" dialog box.
[Debug] [Modify Value...]
Shift
1
1.6 Checking an Operation of the CPU Module
For details on current value changing, refer to the following.
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating Manual (Common)
If a program is edited during debugging, the program can be written to the CPU module even while the CPU
module is in the RUN status. ( Page 158, Section 3.23)
29
Page 32

1.7 Saving a Project
To save a project, open the "Save As" dialog box.
[Project] [Save As...]
Item Description
Enter the storage destination folder (drive or path) of the workspace. Folders can be browsed for selection by
Save Folder Path
Workspace/Project List Select a workspace. Double-click "Workspace" to display a project list.
Workspace Name Enter a name for the workspace.
Project Name Enter a name for the project.
*1
Titl e
*1 Projects can also be saved without titles.
clicking the button.
Enter a title for the project.
30
Page 33

CHAPTER 2 APPLICATION OF PROGRAMMING
<Drive 3>
Standard RAM
(SRAM)
<Drive 4>
Standard ROM
(flash ROM)
<Drive 0>
Program
memory
(flash ROM)
Inside CPU module
Programming tool
1) Data are written to the program
cache memory first.
2) After writing to the program
cache memory, the data are
automatically transferred to
the program memory.
Program
cache
memory
(SRAM)
CHAPTER 2 APPLICATION OF PROGRAMMING
This chapter describes applications of programming.
2.1 Memory and Files
2.1.1 Memory configuration
The following table lists the memory configuration of the CPU module.
CPU module Memory configuration
L02SCPU, L02SCPU-P Program memory, standard RAM, standard ROM
L02CPU, L02CPU-P, L06CPU, L06CPU-P, L26CPU, L26CPU-P,
L26CPU-BT, L26CPU-PBT
(1) Program memory
This memory stores programs and parameters required in processing of the CPU module.
(a) Processing a program
When a program is executed, data in the program memory are transferred to the program cache memory*1 at
the following timings.
• Initial processing at power-on
• Initial processing at reset
Program memory, standard RAM, standard ROM, SD memory card
2.1.1 Memory configuration
2
2.1 Memory and Files
*1 The program cache memory is used for program operations.
(b) Writing to the program memory
When a program is written to the program memory, it is temporarily written to the program cache memory, and
then automatically transferred back to the program memory.
While the CPU module is in the RUN status, automatic data transfer to the program memory can be disabled by setting.
( Page 153, Section 3.22.3)
31
Page 34

(c) Transfer confirmation to the program memory
Program transfer to the program memory can be checked by the following.
• On the dialog box below
• SM681 and SD681
Whether the transfer is in execution or complete can be checked by SM165.
(2) Standard RAM
This memory stores file register files, local device files, sampling trace files, and module error collection files.
(3) Standard ROM
This memory stores data such as device comments and PLC user data.
(4) SD memory card
This memory stores programs and parameters. To execute a program stored in the SD memory card, perform a
boot operation. ( Page 74, Section 2.9)
An SD card memory is required when using the data logging function.
(5) Memory capacity
The following table shows the memory capacity of each memory.
CPU module Program memory Standard RAM Standard ROM SD memory card
L02SCPU, L02SCPU-P
L02CPU, L02CPU-P
L06CPU, L06CPU-P 240K bytes
L26CPU, L26CPU-P,
L26CPU-BT, L26CPU-PBT
80K bytes 128K bytes 512K bytes
1040K bytes 2048K bytes
768K bytes
1024K bytes
Capacity of the SD memory card
used
32
Page 35

CHAPTER 2 APPLICATION OF PROGRAMMING
(6) Memory and data to be stored
: Storable, : Not storable
Program
File type
Memory
Drive 0 Drive 3 Drive 4 Drive 2
Parameter PARAM.QPA One file per drive
Intelligent function module
parameters
Program ***.QPG
Device comment ***.QCD
Initial device value ***.QDI
File register
Local device
Sampling trace
PLC user data ***.CSV/BIN
Symbolic information
Drive heading QN.DAT
Device data storage file DEVSTORE.QST
Module error collection file
Boot setting file AUTOEXEC.QBT
Remote password 00000000.QTM
Latch data backup file LCHDAT00.QBK
Backup data file MEMBKUP0.QBP
System file for project batch
save/load
Device data file DEVDATA.QDT
Data logging setting file
Data logging file
Menu definition file MENUDEF.QDF
System file for the iQ Sensor Solution
function (data backup/restoration)
Backup data file for the iQ Sensor
Solution function (data
backup/restoration)
Predefined protocol setting file
*1
*4
IPARAM.QPA
SVLDINF.QSL
SSBRINF.QSI
Standard
RAM
*2
*2
*2
*2
Standard
ROM
SD memory card
File name and
extension (any
given name for ***)
***.QDR
***.QDL
***.QTD
*5
IERRLOG.QIE
LOGCOM.QLG,
LOG01 to 10.QLG
*3
***.CSV
*6
***.QBR
ECPRTCL.QPT,CPRT
CL.QPT
Remarks
One data per
drive
One file per
module
2.1.1 Memory configuration
2
2.1 Memory and Files
*1 Store parameters (PARAM.QPA) and intelligent function module parameters (IPARAM.QPA) in the same drive.
Otherwise the intelligent function module parameters are invalid.
*2 Only one file can be stored.
*3 This drive cannot be selected as a storage file by the data logging function. To write data to this drive, perform Write PLC
User Data.
*4 This is the data of label program configuration information.
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating Manual (Common)
*5 For Simple project (with a label): SRCINF1M.C32 and SRCINF2M.C32. For Structured project: SRCINF1I.C32 and
SRCINF2I.C32.
*6 This file name depends on the connection type of the iQ Sensor Solution data backup/restoration. ( iQ Sensor
Solution Reference Manual)
33
Page 36

2.1.2 Parameter-valid drive
CPU modules operate according to parameter settings. Systems automatically select parameters from those stored in
the drives for CPU module operation, according to the following priority order.
[Priority order]
1) Drive 0 (program memory)
2) Drive 2 (SD memory card)
3) Drive 4 (standard ROM)
● If parameters are set to be booted to an SD memory card, the above priority order is applied after the parameters are
booted to the specified destination. ( Page 74, Section 2.9)
● The parameters used by the CPU module can be checked at "Parameter Valid Drive Information" under "PLC Status
Information" on the "PLC Diagnostics" dialog box. ( Page 376, Appendix 2)
[Diagnostics] [PLC Diagnostics]
(1) Timing that the parameters take effect
The CPU module automatically searches for parameters in the following timing and operates according to the
parameters stored in the drive.
• When the CPU module is powered off and then on
• When the CPU module is reset
(2) Precautions
Note that if the parameters are written while the CPU module is in operation, the timing that the parameters take
effect varies.
(a) To write a parameter to the drive other than the one in operation:
The CPU module keeps operating according to the current parameters. When the CPU module is turned off
and then on or is reset, newly written parameters take effect according to the priority order.
(b) To write a parameter to the drive where another parameter is currently processed:
Only the device settings become effective immediately after writing is complete. To make all the parameters
effective, power off and then on or reset the CPU module.
34
Page 37

CHAPTER 2 APPLICATION OF PROGRAMMING
2.1.3 Files
For the files written to the CPU module, information such as written date, file name (if created), and file size are
appended to the file. By monitoring the file through Read from PLC, the file is displayed as shown below.
[Online] [Read from PLC...]
2
Item Description
A file name consists of a name (up to 8 one-byte or 4 two-byte characters) and an extension.
• File name: Create with uppercase characters only.
• Extension: It is automatically appended according to the specified file type.
File name
Update date The date and time when the file was written to the CPU module is displayed.
Size
The following cannot be used as a file name since they are the reserved words of Microsoft Windows
COM1 to COM9, PRN, LPT1 to LPT9, NULL, AUX, CLOCK$, and CON
When using characters, recognition of uppercase and lowercase differs depending on the memory.
• Program memory, standard RAM, standard ROM: Not case-sensitive ("ABC" and "abc" are both considered to be "ABC".)
• SD memory card: Case-sensitive
Except for file registers, at least 64 bytes are added to the capacity of the file created by a user.
To display the latest data, click the "Refresh" button.
2.1 Memory and Files
2.1.3 Files
.
35
Page 38

(1) Handling
(a) Power-off during online data operation (including reset)
Files in memory are not discarded if the CPU module is powered off or reset during online operation.
However, for SD memory cards, doing so may result in data corruption. Stop accessing to an SD memory card,
and then power off or reset the CPU module. All of SD memory card operations can be disabled by SM606 (SD
memory card forced disable instruction). For the forced disablement of SD card, refer to the following.
MELSEC-L CPU Module User's Manual (Hardware Design, Maintenance and Inspection)
(b) Simultaneous writing to the same file from multiple programming tools
While a file is being written, accessing the file from another programming tool is not allowed. Also, while a file is
being accessed, writing data to the file from another programming tool is not allowed.
To write data to the same file from multiple programming tools, perform one by one.
(c) Simultaneous accessing to different files from multiple programming tools
Up to ten different files in a CPU module can be simultaneously accessed from multiple programming tools.
(d) File access into the SD memory card
Accessing into the SD memory card with the SP.FREAD or SP.FWRITE instruction may extend the scan time
as the number of files stored in the SD memory card increases.
36
Page 39

(2) File size
The size of a file used in the CPU module depends on the file type. Calculate the rough size of each file, referring
to the following table.
File type File size (unit: byte)
Default
• L02SCPU, L02SCPU-P: 2760 (The size can be increased by parameter setting.)
• L02CPU, L02CPU-P: 2936 (The size can be increased by parameter setting.)
• L06CPU, L06CPU-P, L26CPU, L26CPU-P, L26CPU-BT, L26CPU-PBT: 2964 (The size can be increased by parameter
*1
Parameter
Intelligent function module
parameter
Program
Device comment
Initial device value
File register 2 (number of device points)
setting.)
Reference
• Boot setting 84 + (18 (number of files))
• With CC-Link setting ( MELSEC-L CC-Link System Master/Local Module User's Manual)
• With CC-Link IE Field Network setting (MELSEC-L CC-Link IE Field Network Master/Local Module User's Manual)
• With Ethernet setting ( MELSEC-L Ethernet Interface Module User's Manual (Basic))
• With remote password setting 92 + (the number of target modules 10)
76 + (28 the number of modules set) + parameter size for each utility
*3
+ 4 ((number of steps) + (number of steps reserved for online change))
228
74 + 72 + 8 + (total comment data size of each device)
Comment data size per device = 10 + 10240 a + 40 b
• a: Quotient of ((number of device points) 256)
• b: remainder of ((number of device points 256)
66 + 44 (number of settings of the initial device value) + 2 (total number of device points set to the initial device value) + 72
+ 8
70 + 6 (set device type) + (Am + Av + B + Ct + Cst + Cc) n
CHAPTER 2 APPLICATION OF PROGRAMMING
2
*1
*1
*2
*2
, Up to an increment of 172
*2
• Am, Av = (((a1 + a2) 16) - ((a1 + 1) 16) + 1) 2
•B = b 2
• Ct, Cst, Cc = ((((c1 + c2) 2) 16) - ((c1 2 + 1) 16) + 1) 2 + c2 2
Local device
Sampling trace file
PLC user data Depends on the value and the number of data
Source information Depends on the specifications of the programming tool
Drive heading 72
Device data storage file
Module error collection file 76 + 64 (64 (value set for the number of storable errors))
System file for project batch
save/load
Device data file
*4
*5
• Am, Av: Save area sizes of M (internal relay) and V (edge relay), respectively
a1: Start device number of M or V
a2: Number of points of M or V
• B: Save area size of D (data register) and Z (index register)
b: Total number of points of D and Z
• Ct, Cst, Cc: Save area sizes of T (timer), ST (retentive timer), and C (counter), respectively
c1: Start device number of T, ST, or C
c2: Number of points of T, ST, or C
• n: Number of programs (only the ones using local devices)
362 + (number of word device points + number of bit device points) 12 + (N1 + N2 + number of word device points 2 +
(number of bit device points 16) 2) the number of traces (total number of executions)
Apply the following values for N1 and N2 according to the items selected under Additional Information on the "Condition
setting" tab of the "Trace Setting" dialog box.
• N1: When "Time" is selected, apply "4".
• N2: When "Program Name" is selected, apply "8".
L02SCPU, L02SCPU-P, L02CPU, L02CPU-P: Setting value at formatting (2K to 32K)
L06CPU, L06CPU-P, L26CPU, L26CPU-P, L26CPU-BT, L26CPU-PBT: Setting value at formatting (2K to 1024K)
136 + (34 (number of target drives) + 34 (number of target files
• a: Total size of target file names (including " " . , and extension)
• b: Add "34" when sampling trace is registered.
• c: Add "34" when data logging is registered.
70 + 8 (number of target devices*6) + ((number of word device points) + (a 16) + (18 b 16)) 2
• a: Number of bit device points (other than timer, retentive timer, and counter)
• b: Number of bit device points (timer, retentive timer, and counter)
*7
)) + a + b + c
2.1.3 Files
2.1 Memory and Files
37
Page 40

File type File size (unit: byte)
Data logging setting file
System file for the iQ Sensor
Solution function (data
backup/restoration)
Backup data file for the iQ
Sensor Solution function (data
backup/restoration)
Predefined protocol setting file 65532
Refer to the following.
QnUDVCPU/LCPU User's Manual (Data Logging Function)
Refer to the following.
iQ Sensor Solution Reference Manual
*1 The value is adjusted by the system so that the total number of bytes including the network parameter settings becomes
multiple of four.
*2 The value is adjusted by the system so that the number of bytes becomes multiple of four.
*3 This value (228) is set by default. (It varies depending on parameter settings.)
*4 After the decimal point of a value obtained by a division part in the formula is rounded up.
*5 This file is used only when the project data batch save/load function is used.
*6 Count a contact and coil together as one device for the timer, retentive timer, and counter.
*7 The device data file is not included in the number of files.
38
Page 41

(3) Program file structure
Program file structure
File header
Execution program
Reserved area for
online change
57 steps
(default)
500 steps
These areas are reserved
in increments of file size units.
The following shows a program file structure.
Item Description
File header
Execution program This area stores the created program.
Reserved area for
online change
This area stores data such as the name, size, and created date of files. The file header size ranges from 43 to 59 steps (172 to 236
bytes) depending on the setting made in the Device tab of the PLC Parameter dialog box.
This area is used when the number of steps is increased after writing data in the RUN status. (Default: 500 steps (2000 bytes) After the
online change is complete, remaining number of steps for this area is displayed. The setting value can be changed in the "Online Data
Operation" dialog box. (It can be changed while online change is performed.)
CHAPTER 2 APPLICATION OF PROGRAMMING
2
2.1.3 Files
2.1 Memory and Files
39
Page 42

(4) Memory capacity
Ex.
(a) File size unit for each memory area
When a file is written to the memory area, the unit of the stored file depends on the CPU module and memory
area to be written. This unit is referred to as a file size unit.
CPU module
L02SCPU, L02SCPU-P
L02CPU, L02CPU-P, L06CPU,
L06CPU-P
L26CPU, L26CPU-P, L26CPU-BT,
L26CPU-PBT
Program memory Standard RAM Standard ROM SD memory card
1 step (4 bytes) 128 steps (512 bytes)
(b) Calculation example of memory capacity
Memory capacity when the parameters and program are written to the program memory.
[Conditions]
• Program file to be written: MAIN.QPG (525 steps (2100 bytes))
• Parameter file to be written: PARAM.QPA (2936 bytes)
• Reserved area for online change: 500 steps (2000 bytes)
Memory area
128 steps (512 bytes)
512 steps (2048 bytes)
32K bytes
The memory capacity is calculated in units of file sizes of the CPU module to be written. For a program
memory, the file size unit is 1 step (4 bytes).
• Calculation of program file size
The program file size can be found by the program size + reserved area for online change. Since a program
is stored in units of file sizes (1 step), only the amount equal to the program size is occupied.
525 + 500 = 1025 steps (4100 bytes)
• Calculation of parameter file size
Since the parameter file capacity is 2936 bytes, it occupies 734 steps (2936 bytes) in the program memory.
[Result] Program size + parameter file capacity = 1025 + 734 = 1759 steps (7036 bytes)
Memory capacity can also be calculated from a programming tool.
[Tool] [Confirm Memory Size...]
For calculation of memory capacity using a programming tool, refer to the following.
Manual for the programming tool used
40
Page 43

CHAPTER 2 APPLICATION OF PROGRAMMING
2.2 I/O Number
This section describes the I/O number assignment required for data communication between the CPU module or its
built-in functions and I/O modules or intelligent function modules.
2.2.1 Concept of I/O number assignment
(1) Purpose of I/O number assignment
I/O numbers can be assigned with any given number for the following purposes.
(a) Reserving points for future module changes
The number of points can be reserved to prevent the I/O number modification when the current module is
changed in the future to the one with the different number of occupied I/O points.
(b) Preventing I/O numbers from being changed
The change in the I/O numbers can be prevented when an I/O module or intelligent function module, whose
occupied I/O points are other than 16, is removed due to failure.
2
(c) Changing the I/O numbers to those used in the program
When the I/O numbers used in the actual system differ from those in the program, the I/O numbers of each
module can be changed to the ones in the program. If any of the I/O modules whose number of I/O points are
other than 16 fails without I/O assignment setting, the I/O numbers assigned following to the failed module may
change, leading to a malfunction. For this reason, making the I/O assignment setting is recommended.
2.2 I/O Number
2.2.1 Concept of I/O number assignment
41
Page 44

(2) I/O number assignment
Power
supply
module
CPU module
(built-in I/O
function and
built-in CC-Link
function)
Input
module
Intelligent
function
module
Input
module
Output
module
0030
to
003F
0040
to
005F
0060
to
006F
0070
to
007F
16
points
32
points
16
points
16
points
Output
module
0080
to
008F
16
points
0000
to
002F
Power
supply
module
Input
module
Intelligent
function
module
Input
module
Output
module
00D0
to
00DF
00B0
to
00CF
0090
to
009F
00A0
to
00AF
16
points
32
points
16
points
16
points
Main block
Extension block 1
Branch
module
Extension
module
The I/O numbers are represented in hexadecimal. The following is an example of an I/O number assignment to
the L26CPU-BT.
The start I/O numbers are as below.
L02SCPU, L02SCPU-P, L02CPU,
Tar get
L02CPU-P, L06CPU, L06CPU-P,
L26CPU, L26CPU-P
Default I/O assignment Default I/O assignment
Built-in I/O
Built-in CC-Link
Following modules (Main block)
• The module to the right of a CPU module (when a
branch module is not connected, or connected to
the left of the END cover)
• The module to the right of a branch module (when
a branch module is connected to the right of a CPU
module)
Following modules (Extension block)
• The module to the right of an extension module
(when a branch module is connected to the left of
the END cover)
• The module to the right of a branch module (when
a branch module is connected to the right of an
extension module)
0000
H
0010
H
Consecutive
number from the
previous block
Change allowed
Change allowed
Change allowed
L26CPU-BT, L26CPU-PBT
0000
H
0010
H
0030
H
Consecutive
number from the
previous block
Change allowed
Change allowed
Change allowed
Change allowed
42
The start I/O number does not need to be assigned for the built-in Ethernet port, branch module, extension
module, RS-232 adapter, RS-422/485 adapter, and END cover.
Page 45

2.2.2 I/O number assignment
(1) Setting method
To assign I/O numbers, open the I/O Assignment tab. ( Page 353, Appendix 1.2)
Project window [PLC Parameter] [Parameter] [I/O Assignment]
CHAPTER 2 APPLICATION OF PROGRAMMING
2
In the I/O Assignment tab, the following settings are also available
• Response time from I/O (I/O Response Time) ( Page 102, Section 3.8)
• CPU module operation upon an error ( Page 103, Section 3.9)
• CPU module operation upon hardware failure of an intelligent function module ( Page 104, Section 3.10)
• Switch setting of intelligent function modules
2.2 I/O Number
2.2.2 I/O number assignment
43
Page 46

(2) Precautions
(a) Type setting
The type set in the I/O Assignment tab must be the same as that of the connected module. Setting a different
type may result as follows.
Connected modules
• Input module
• Output module
• I/O combined module
Intelligent function module
Branch module
Modules other than a branch module Empty Regarded as Empty
Other combinations
Type specified in the I/O
Assignment tab
• Intelligent
•Branch
• Branch (for LA1S
Extension)
• Input
•Output
•I/O Mix
•Branch
• Branch (for LA1S
Extension)
•Empty
• Input
•Output
•I/O Mix
• Intelligent
Results
"SP.UNIT.LAY.ERR." occurs.
Error does not occur but incorrect operation may be caused. Or
"PARAMETER ERROR" (error code: 3000) is detected.
For intelligent function modules, the number of I/O points must be the same.
(b) I/O points of modules
The number of I/O points for each module selected in the I/O Assignment tab is set in priority to those of
connected modules.
• If the preset number of I/O points is less than those of connected I/O modules, the available points for the
connected I/O module are decreased. (For example, If the number of I/O points is set to 16 points in the
I/O Assignment tab to the module where a 32-point input module is connected, the second half 16 points
of the 32-point input module are invalid.)
• If the preset number of I/O points exceeds those of connected I/O modules, the exceeded number of
points will not be used.
Set the last I/O number within the I/O point range. Failure to do so causes "SP. UNIT LAY ERR.".
(c) Start XY setting
Note that, in the following two cases, the start XY setting may be duplicated. ("SP.UNIT.LAY.ERR." occurs if the
start X/Y is duplicated.)
• Start XY values are not in the correct order.
• Modules with and without the start XY setting (automatically assigned module) are mixed.
44
Page 47

CHAPTER 2 APPLICATION OF PROGRAMMING
Power-on or reset
Scan time
Initial processing
Refresh processing
Program operation
END processing
2.3 Scan Time Structure
A CPU module sequentially performs the following processing in the RUN status. Scan time is the time required for all
processing and executions to be performed.
( Page 45, Section 2.3.1)
( Page 46, Section 2.3.2)
( Page 46, Section 2.3.3)
( Page 47, Section 2.3.4)
2
2.3.1 Initial processing
The CPU module performs preprocessing required for program operations. The preprocessing is executed only once
when any of the operations described in the following table is performed to the CPU module. When initial processing is
completed, the CPU module is placed in the operation status set by the switch. ( Page 48, Section 2.4)
: Performed, : Not performed
CPU module status
Initial processing item
The I/O module initialization
Boot from an SD memory card
PLC parameter check
Initialization of devices outside the latch range (bit device: off, word
device: 0)
Automatic I/O number assignment to connected modules
CC-Link IE Field Network information setting
Intelligent function modules switch setting
CC-Link information setting
Ethernet information setting
Initial device value setting
*1 The operation indicates that the status is changed back to RUN without resetting the module after any program or
parameter was changed in the STOP status. (The switch is set from STOP to RUN (the RUN LED will flash), then back
to STOP and to RUN again.)
Note that the PLS, P instruction (instruction for pulse conversion) may not be executed properly with the above
operation. This is because the previous information may not be inherited depending on the program changes.
Powered-on Reset
Changed from STOP to
*1
RUN
2.3.1 Initial processing
2.3 Scan Time Structure
45
Page 48

2.3.2 Refresh processing of input/output modules or intelligent
END/FEND
instructions
END/FEND
1 scan (After completion
of END processing,
an operation is repeated
starting from step 0.)
Step 0
Program
execution
END processing
Main routine program
function modules
The CPU module performs the following before program operations.
• On/off data input from the input module or intelligent function module to the CPU module
• On/off data output from the CPU module to the output module or intelligent function module
For details on refresh processing, refer to Page 51, Section 2.6.
2.3.3 Program operation
A main routine program repeatedly executes its operation from the step 0 to the END or FEND instruction. This
program is executed from the step 0 for every scan.
A main routine program can be divided to main routine and subroutine programs. A subroutine program is from a
pointer (P ) to the RET instruction, and is created between the FEND and END instructions. This program is
executed only when it is called by a subroutine program call instruction (such as CALL(P), FCALL(P)) from a main
routine program.
Program A
Main routine program
Subroutine
program 1
Subroutine
program 2
Subroutine
program 3
1
Pointer*
*1 Pointer numbers do not need to be specified in ascending order.
46
Page 49

Use a subroutine program for the purposes such as the following.
• Handle the program that is executed several times in one scan as a subroutine program so that the entire
number of steps can be reduced
• Handle the program that is executed under the specific condition as a subroutine program so that the scan
time can be decreased
● A subroutine programs can be managed as one separate program (standby type program). ( Page 66, Section 2.8.3)
● Subroutine programs can be configured with the nesting. ( Page 335, Section 5.9)
● Using an interrupt pointer in a subroutine program changes the program to an interrupt program. ( Page 56, Section
2.7)
2.3.4 END processing
END processing includes the following.
• Link refresh with CC-Link IE Field Network master/local module
• Link refresh with CC-Link IE Field Network Basic
• Auto refresh with intelligent function module
• Intelligent function module dedicated instruction processing
• Device data latch processing
• Service processing
• Watchdog time reset
• Self-diagnostics processing
• Special relay/special register value setting (only for those that should be set during END processing)
CHAPTER 2 APPLICATION OF PROGRAMMING
2
2.3.4 END processing
2.3 Scan Time Structure
When a constant scan is set, the results of processing performed in END processing are held for the period between after
END processing is completed and until the next scan starts.
47
Page 50

2.4 Operation Processing of the CPU Module for Each
Operating Status
There are three types of operating status for the CPU module.
• RUN status
•STOP status
• PAUSE status
(1) Operation processing in the RUN status
RUN status is a status where program operations are repeatedly performed in a loop between the step 0 and the
END (FEND) instruction.
(a) Output status when entering the RUN status
The CPU module outputs either of the following according to the output module parameter setting when its
status is changed to RUN. ( Page 101, Section 3.7)
• Output (Y) status saved immediately before entering the STOP status
• Result of operations performed for one scan after entering the RUN status
(b) Processing time required before operations
The processing time required for the CPU module to start program operations after its operating status is
changed from STOP to RUN varies depending on the system configuration and/or parameter settings.
(Normally, it takes one to three seconds.)
(2) Operation processing in the STOP status
Stop status is a status where the operation is stopped. The CPU module status will be changed to STOP when a
stop error occurs.
(a) Output status when entering the STOP status
When entering the STOP status, the CPU module saves data in the output (Y) and turns off all outputs. The
device memory other than that of the output (Y) will be held.
(3) Operation processing in the PAUSE status
PAUSE status is a status where program operations are stopped after operations are performed for one scan,
holding the output and device memory status.
48
Page 51

CHAPTER 2 APPLICATION OF PROGRAMMING
(4) Operation processing when operating status of the CPU module changed
The operation processing of CPU module performs the following according to the RUN/STOP status.
CPU module operation processing
RUN/STOP
status
RUN STOP
STOP RUN
Program
operation
processing
The CPU module
executes the
program until the
END instruction
and stops.
The CPU module
executes the
program from the
step 0.
External output
The CPU module saves the
output (Y) status immediately
before its status is changed to
STOP and turns off all the
outputs.
The CPU module outputs data
according to the output mode
parameter setting. ( Page
101, Section 3.7)
Device memory
M, L, S, T, C, D Y
The CPU module holds the device memory
status immediately before its status is
changed to STOP.
The CPU module holds the device memory
status immediately before its status is
changed to STOP.
Note that the CPU module uses initial
device values if those values are present.
Local device data are cleared.
The CPU module saves the
output (Y) status immediately
before its status is changed to
STOP and turns off all the
outputs.
The CPU module outputs data
according to the output mode
parameter setting. ( Page
101, Section 3.7)
2
The CPU module performs the following in any of the RUN, STOP, or PAUSE status.
• Refresh processing with I/O modules
• Refresh processing with CC-Link IE Field Network master/local module
• Refresh processing with CC-Link IE Field Network Basic
• Auto refresh processing with intelligent function modules
• Intelligent function module dedicated instruction processing (completion processing only)
• Self-diagnostics processing
• Service processing
• Special relay/special register value setting (only for those that should be set during END processing)
Even if the CPU module is in the STOP or PAUSE status, the following operations can be executed.
• I/O monitor or test operation from a programming tool
• Read/Write data from/to external devices using the MC protocol
2.4 Operation Processing of the CPU Module for Each Operating Status
49
Page 52

2.5 Operation Processing During Momentary Power Failure
Ex.
ENDEND
0
END
0
Instantaneous power
failure occurred.
Power recovery
The CPU module suspends
its program operation.
When the input voltage supplied to the power supply module drops below the specified range, the CPU module detects
a momentary power failure and performs the following operation.
(1) When a momentary power failure occurs for a period shorter than the
allowable power failure time
The CPU module registers error data and suspends the operation processing. The CPU module, however,
continues measurement in the timer device and holds the output status.
• When resume start is specified for the SFC program, data in the system is saved.
• The CPU module restarts its operation processing.
• Even if operation processing is suspended due to a momentary power failure, the CPU module continues the
measurement of the watchdog timer (WDT).
When the WDT setting of PLC parameter is 200ms and the scan time is 190ms, if a momentary power
failure occurs for 15ms, "WDT ERROR" occurs.
(2) When a momentary power failure occurs for a period longer than the allowable
power failure time
The CPU module starts its operations initially and the operation processing will be the same as that when either
of the following is performed.
• Powering off and then on the CPU module
• Resetting the CPU module
50
Page 53

CHAPTER 2 APPLICATION OF PROGRAMMING
2.6 Processing of Inputs and Outputs
The CPU module can batch-access the general-purpose I/O*1, I/O modules, and intelligent function modules before
program operation (refresh processing). Note that I/O processing can be performed upon execution of an instruction
by using a direct access device in the program. (direct processing)
Compared to the refresh processing, data acquisition is faster in direct processing while more time is required for
processing of each instruction.
*1 The general-purpose input is an input signal received by the general-purpose input function of the built-in I/O function.
The general-purpose output is an output signal sent by the general-purpose output function of the built-in I/O function.
2.6.1 Refresh processing
(1) Outline of the processing
The following describes the details of the refresh processing.
2
(a) Input
Before starting a program operation, the ON/OFF data in the general-purpose module and input module are
collectively loaded to the General-purpose input/input module access area of the CPU module. When a
program is executed, the ON/OFF data in the input (X) device memory are used for operation.
(b) Output
The program operation result for output (Y) is output to the output (Y) device memory for every operation.
Before starting a program operation, the ON/OFF data in the output (Y) device memory are collectively output
to the general purpose output or output module.
2.6.1 Refresh processing
2.6 Processing of Inputs and Outputs
51
Page 54

(c) Process flowchart
CPU module
CPU (operation processing area)
3)
4)
to
5)
X0
Y22
Input (X)
device
memory
General-purpose
input/input
module access
area
Output (Y)
device
memory*
3
Input
refresh
Network module
Input module
Output module
1)
Output
refresh
2)
Remote input
refresh area*
1
Programming
tool input
area*
2
Y20
Built-in CC-Link*
4
General-purpose output
General-purpose
input
Built-in
CC-Link*
4
Network module
*1 The remote input refresh area indicates the area to be used when refresh is set to the input (X) in CC-Link IE Field
*2 Data in the programming tool input area can be turned on or off by the following:
*3 Data in the output (Y) device memory can be turned on or off by the following operation.
*4 This applies only to the L26CPU-BT and L26CPU-PBT.
*5 This applies only to the Built-in Ethernet port LCPU.
Input refresh
Output refresh Before program operation, data in the output (Y) device memory (2)) are collectively output to the output module.
Execution of an input
contact instruction
Execution of an output
contact instruction
Execution of the OUT
instruction
Network, CC-Link IE Field Network Basic, or CC-Link. Data in the remote input refresh area are refreshed during END
processing.
Test operation of a programming tool
Writing data from a network module
Writing data from an external device using the MC protocol
Writing data using the simple PLC communication function
Test operation of a programming tool
Writing data using a program
Writing data from a network module
Writing data from an external device using the MC protocol
Writing data using the simple PLC communication function
Item Description
Before program operation, input data (1)) are collectively read out from the general-purpose input and input
modules, the OR processing with the programming tool input area and remote input refresh area is executed, and
then the data are stored in the input (X) device memory.
Input data (3)) are read out from the input (X) device memory and the program is executed.
Output data (4)) are read from the output (Y) device memory and the program is executed.
The operation result of the program (5)) are stored to the output (Y) device memory.
52
Page 55

CHAPTER 2 APPLICATION OF PROGRAMMING
(2) Response delay
An output response which corresponds to the status change in the input module delays for two scans (maximum)
depending on the on timing of an external contact. The following shows response delay examples.
[Example]
A program that turns on the output Y5E
when the input X5 is turned on.
• Y5E turns on at the earliest timing
0 END END00
X5
Y5E
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
External contact
CPU module
devices
External load
• Y5E turns on at the slowest timing
0 END END00
ON
X5
Y5E
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
External contact
CPU module
devices
External load
(maximum 1 scan)
56
ON
ON
ON
Delay time
(minimum 1 scan)
56
ON
ON
Delay time
: Input refresh
: Output refresh
ON
: Input refresh
: Output refresh
ON
2.6.1 Refresh processing
2
2.6 Processing of Inputs and Outputs
53
Page 56

2.6.2 Direct processing
CPU module
CPU
(operation processing area)
4)
5)
6)
DX0
DY20
Input (X)
device
memory
Output (Y)
device
memory*
2
1)
2)
DY25
Programming
tool input
area*
1
Input module
Output module
General-purpose
input
General-purpose
output
3)
(1) Outline of the processing
Data input and output are performed using a direct access input (DX) or direct access output (DY).
*1 Data in the programming tool input area can be turned on or off by the following:
Test operation of a programming tool
Writing data from a network module
Writing data from an external device using the MC protocol
Writing data using the simple PLC communication function
*2 Data in the output (Y) device memory can be turned on or off by the following operation.
Test operation of a programming tool
Writing data to a program
Writing data from a network module
Writing data from an external device using the MC protocol
Writing data using the simple PLC communication function
Item Description
Execution of an input
contact instruction
Execution of an output
contact instruction
Execution of the OUT
instruction
The OR processing is performed between the input information of the input module (1)) and the input data of the
programming tool (2)) or general-purpose input(3)). The result is stored in the input (X) device memory and is
used as input data (4)) to execute the program.
Output data in the output (Y) device memory are read out (5)) and the program is executed.
The operation result of the program (6)) are output to the general-purpose output and output module, and stored
in the output (Y) device memory.
54
Page 57

CHAPTER 2 APPLICATION OF PROGRAMMING
OFF
ON
055 56
External contact
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
DX5
(External contact)
DY5E
(External load)
CPU module
devices
Delay time
(
maximum
1 scan)
END 0
55 56
: Input refresh
: Output refresh
(2) Response delay
An output response which corresponds to the status change in the input module delays for one scan (maximum)
depending on the on timing of an external contact. The following shows response delay examples.
[Example]
A program that turns on the output Y5E
when the input X5 is turned on.
• DY5E turns on at the earliest timing
05556
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
Delay time
CPU module
devices
External contact
DX5
(External contact)
DY5E
(External load)
2
• DY5E turns on at the slowest timing
2.6 Processing of Inputs and Outputs
2.6.2 Direct processing
55
Page 58

2.7 Interrupt Program
Main routine
program
Interrupt
program (I0)
Interrupt
program (I29)
An interrupt factor for
I0 occurred.
An interrupt factor for
interrupt program (I29) occurred.
Execution
Execution
Execution Execution
IRET
Execution
IRET
Time
An interrupt program is from an interrupt pointer (I) to the IRET instruction.
Main routine
program
Interrupt
program (I0)
Interrupt
program (I29)
Interrupt pointer
Indicates the end
of the main routine
program.
The interrupt pointer number (I) varies depending on the interrupt factor. ( Page 339, Section 5.11) When an
interrupt factor occurs, an interrupt program of the interrupt pointer number corresponding to that factor is executed.
(Interrupt program are executed only after the corresponding interrupt factor occurs.)
56
Page 59

CHAPTER 2 APPLICATION OF PROGRAMMING
Interrupt
program
Main routine program
Program A
Interrupt pointer
*1 *2
(1) Creating an interrupt program
Create interrupt programs between the FEND and END instructions in the main routine program. Before
executing any of interrupt programs of I0 to I15, I23 to I31, or I50 to I255, allow an interrupt by the EI instruction.
2
(2) Restrictions on creating an interrupt program
(a) PLS and PLF instructions
*1 The pointer numbers do not need to be specified in ascending order.
*2 Ensure that there is no overlap of interrupt pointer numbers.
Interrupt programs can be managed as one separate program (standby type program). ( Page 66, Section 2.8.3)
The PLS and PLF instructions perform off processing in the next scan of which the instruction is executed.
Therefore, the device which is turned on by the instruction remains on until the same instruction is reexecuted.
X0
M0
OFF
OFF
END 0
X0
PLS
M0
IRETEND 0 END 0 I0 IRET END 0
I0
ON
ON
Turns on by executing the PLS M0 instruction at the rise of X0 (off on).
X0
PLS
M0
Turns off by executing the PLS M0 instruction.
2.7 Interrupt Program
(b) EI and DI instructions
Do not execute the EI or DI instruction during interrupt program execution.
(c) Timer (T) and counter (C)
Do not use the timer (T) and counter (C) in interrupt programs.
57
Page 60

(3) Operation when an interrupt factor occurs
Main routine
program
Interrupt
program
Interrupt factor occurred.
Interrupt enabled (EI)
STOP/ PAUSE RUN
RUN
Execution
Not executed since
the CPU module is in
the STOP or PAUSE
status.
Executed after the CPU module exits
the STOP or PAUSE status and enters
the RUN status, and execution status of
the interrupt program becomes enabled.
The following restrictions are applied to the interrupt program depending on the interrupt factor occurrence
timing.
(a) When an interrupt factor occurs before the interrupt program execution status is
enabled
The CPU module stores the interrupt factor occurred. As soon as the interrupt program execution status is
enabled, the CPU module executes the interrupt program corresponding to the stored interrupt factor.
Interrupt factor occurred.
Main routine
program
Interrupt enabled (EI)
Interrupt
program
Not executed since
execution status of the
interrupt program is
disabled (DI).
Execution
Executed when execution
status of the interrupt program
becomes enabled.
When the same interrupt factor occurs more than one time before the interrupt program execution status is
enabled, the interrupt factors of I0 to I15, I28 to I31, I45, I50 to I255, and fixed scan execution type programs
are stored only once. Note that all interrupt factors occurred are discarded if they are masked by the IMASK
instruction.
(b) When an interrupt factor occurs in the STOP or PAUSE status
The CPU module executes the interrupt program as soon as the interrupt program execution status is enabled
after the CPU module status is changed to RUN.
58
Page 61

CHAPTER 2 APPLICATION OF PROGRAMMING
I50 I100
I150
Main routine
program
Interrupt program
(I50)
Interrupt program
(I100)
Interrupt program
(I150)
High
Low
Priority
Interrupt
enabled (EI)
Concurrence of multiple
interrupt factors
Execution
IRET
Execution
Wait status
IRET
Execution
Wait status
IRET
(c) When multiple interrupt factors simultaneously occur in the interrupt program
execution enabled status
The interrupt programs are executed in the order of priority of the interrupt pointers (I) ( Page 339,
Section 5.11).
Other interrupt programs have to wait until processing of the interrupt program being executed is completed.
2
(d) When the same interrupt factor as that of the interrupt program being executed
occurs
When the same interrupt factor as that of the interrupt program being executed occurs more than one time
before completion of interrupt program processing, the interrupt factors of I0 to I15, I45, and I50 to I255 are
stored only once, and then the interrupt program corresponding to each stored interrupt factor is executed after
completion of current interrupt program execution. The interrupt factors of I28 to I31 and fixed scan execution
type programs are all stored, and then all the interrupt programs corresponding to interrupt factors are
executed after completion of current interrupt program execution.
(e) When an interrupt factor occurs during link refresh
The link refresh is suspended and an interrupt program is executed. Even if the Block data assurance per
station setting is enabled in the CC-Link IE or MELSECNET/H network, this setting does not work when a
device set as a refresh target is used in the interrupt program. In the interrupt program, do not use any refresh
target device. For the Block data assurance per station setting, refer to the following.
MELSEC-L CC-Link IE Field Network Master/Local Module User's Manual
10ms 10ms 10ms 10ms
Interrupt factor
2.7 Interrupt Program
Interrupt program execution
Link refresh execution
Link refresh is suspended and
interrupt program is executed.
59
Page 62

(f) When an interrupt factor occurs during END processing
When the constant scan function is used and an interrupt factor occurs during the waiting time in END
processing, an interrupt program corresponding to the interrupt factor is executed.
(g) When an interrupt factor occurs during access to another module
When an interrupt factor occurs during access to another module (during service processing or instruction
processing), the interrupt program becomes standby status until the service processing or the instruction in
execution is completed. To shorten the wait time of the interrupt, reduce the amount of data that access to other
modules.
(4) Processing at program execution type change
When the program execution type is changed from the scan execution type to the interrupt, the CPU module
saves and restores the following data. ( Page 324, Section 5.6.3)
• Data in the index register
• File register block number
Whether to save and restore the data above can be set by parameter. When the data are not saved or restored,
the overhead time of the corresponding interrupt program can be shortened. ( Page 378, Appendix 3.1)
(5) Precautions
(a) When the same device is used
During execution of an instruction in a main routine program, an interrupt program may be executed,
suspending the processing of the instruction being executed, resulting in a device data inconsistency. Take the
following measures to prevent device data inconsistency.
• Do not directly specify the device where the data are written by the interrupt program in the main routine
program. Use the data in another device by moving the data with the transfer instruction.
• Disable interrupts with the DI instruction if instructions that may cause inconvenience for the main routine
program are used. Note that interrupts do not occur during accessing the device of the corresponding
argument of the instruction. For this reason, data inconsistency does not occur in units of arguments.
60
Page 63

CHAPTER 2 APPLICATION OF PROGRAMMING
Control data A
Control data B
Control data n
Control data A
Program A
Control data B
Program B
Control data n
Program n
Divide a program
on the basis of each
control data and
register them.
Control by one program
Dividing one program
into multiple programs.
Programs are executed
in this order.
2.8 Executing Multiple Programs
Multiple programs can be stored in the CPU module by changing the file names of programs. Dividing a program by
process or function allows simultaneous programming by multiple engineers.
2
The following settings are required after creating multiple programs.
Project window [Parameter] [PLC Parameter] [Program]
Setting item Description Reference
Program Name
"Initial" (initial execution type program)
"Scan" (scan execution type)
"Wait" (standby type program) This program is executed only when requested.
Execute Type
"Fixed Scan" (fixed scan execution type
program)
Enter the name (file name) of the program to be executed in the CPU
module.
This program is executed only once when the CPU module is powered on
or its status is switched from STOP to RUN.
This program is executed once in every scan, starting in the next scan of
which the initial execution type program is executed and later.
This program is executed at time intervals specified in "Fixed scan interval"
and "In Unit".
• Fixed Scan Interval: Enter the execution interval of fixed scan execution
type program. The setting range varies depending on the setting unit.
When the unit is "ms": 0.5 to 999.5ms (in increments of 0.5ms)
When the unit is "s": 1 to 60s (in increments of 1s)
• In Unit: Select the unit ("ms" or "s") of the fixed scan interval.
2.8 Executing Multiple Programs
Page 63,
Section 2.8.1
Page 65,
Section 2.8.2
Page 66,
Section 2.8.3
Page 69,
Section 2.8.4
How to use a local device file can be set for each program by proceeding to another dialog box. ( Page 347,
Section 7.2 (2))
61
Page 64

(1) Program sequence in the CPU module
Power-on or STOP RUN
Initial execution
type program
Fixed scan execution
type program
Scan execution
type program
Standby type
program
END processing
Executed once when
the CPU module is
powered on or switched
from STOP to RUN.
Executed at specified
intervals.
Program execution sequence
Program execution when
a subroutine program or
interrupt program is called
Executed upon request.
The following shows the program sequence after the CPU module is powered on or its operating status is
changed from STOP to RUN. Use an appropriate type of program as required.
62
Page 65

CHAPTER 2 APPLICATION OF PROGRAMMING
Creating an initial execution type program
Program A
Program B
Control by one program
Processing
performed once
Processing performed
in every scan
Initial execution
type program
Scan execution
type program
One program is divided into
an initial execution type program
and scan execution type program.
2.8.1 Initial execution type program
Initial execution type program is executed only once when the CPU module is powered on or its operating status is
changed from STOP to RUN.
This type of program can be used as a program that need not be executed from the next scan and later once it is
executed, like initial processing to an intelligent function module.
(1) Processing
After completion of all the initial execution type program execution, END processing is performed. In the next
scan and later, scan execution type programs are executed.
Power-on or STOP RUN
2
Initial execution
type program A
Initial execution
type program B
Initial execution
type program n
END processing
Scan execution
type program
1 scan
If there are multiple initial execution
type programs, the CPU module
executes them starting from the one
that was set first.
2.8 Executing Multiple Programs
2.8.1 Initial execution type program
63
Page 66

(2) Initial scan time
Ex.
Ex.
SD522 SD523
Stores the initial scan time of 1ms or less (unit: s)
Stores the initial scan time. (in increments of 1ms)
Initial scan time is the execution time of initial execution type program. When multiple programs are executed, the
initial scan time will be the time required for completing all the initial execution type program execution.
Since the CPU module stores the initial scan time into the special register (SD522 and SD523), the initial scan
time can be checked by monitoring SD522 and SD523. (Accuracy: 0.1ms)
If the stored values in SD522 and SD523 are 3 and 400 respectively, the initial scan time is 3.4ms. Even if
the WDT instruction (instruction that resets the watchdog timer) is executed in the program, the
measurement of the initial scan time continues.
When an interrupt program or fixed scan execution type program is executed before completion of the initial execution type
program execution, the execution time of the executed program will be added to the initial scan time.
(3) Initial execution monitoring time
Initial execution monitoring time is a timer for monitoring initial scan time.
Project window [Parameter] [PLC Parameter] [PLC RAS]
Set initial execution monitoring time.
The setting range is 10 to 2000ms (in increments of 10ms). No default value is set.
(4) Precautions on programming
Initial execution type programs do not support the instructions that require several scans (instructions with
completion device).
SEND, RECV and similar instructions
64
Page 67

CHAPTER 2 APPLICATION OF PROGRAMMING
1st scan 2nd scan 3rd scan 4th scan
STOP RUN
Power-on RUN
END processing
Initial execution type program
Scan execution type program A
Scan execution type program C
Scan execution type program B
Scan time
0 END
0 END
0 END
0 END
0 END
0 END
0 END
0
2.8.2 Scan execution type program
Scan execution type program is executed once in every scan, starting in the next scan of which the initial execution
type program is executed and later.
2
When multiple scan execution type programs are executed, the scan time will be the time required for completing all
the scan execution type program execution. If an interrupt program or fixed scan execution type program is executed,
execution time of the executed program will be added to the scan time.
2.8.2 Scan execution type program
2.8 Executing Multiple Programs
65
Page 68

2.8.3 Standby type program
P100
I0
P100
I0
Scan execution type program
Main routine
program
Subroutine
program
Interrupt
program
Scan execution type program
Main routine
program
Standby type program
Subroutine
program
Interrupt
program
Standby type program is executed only when its execution is requested. This type of program can be changed to any
desired execution type by a program instruction. This program is mainly used for the following purposes.
• Program library
Standby type program is used as a program library, a collection of subroutine programs and/or interrupt
programs, and managed separately from a main routine program. Multiple subroutine programs and/or
interrupt programs can be created and managed in a single standby type program.
• Program type change
Standby type program is used to create and store programs available in all systems. Only required programs
will be executed. For example, a program preset as a standby ("Wait") type program in the PLC Parameter
dialog box can be changed to a scan execution type program and executed in the program.
(1) Execution method
Execute standby type programs in either of the following methods.
• Create subroutine and interrupt programs in a standby type program and execute the standby program upon
interrupt or a call such as by a pointer.
• Change a standby type program to any other execution type using instructions.
66
Page 69

CHAPTER 2 APPLICATION OF PROGRAMMING
Use a common pointer.
Main routine program
Program A
Program B (standby type program)
P100 RET
I0 IRET
END processing
CALL P100 instruction execution
END processing
Interrupt factor occurred.
END processing
Main routine program
Subroutine program in
a standby type program
Interrupt program in
a standby type program
(a) Executing upon an interrupt or a call such as by a pointer
When creating subroutine and/or interrupt programs in a single standby type program, start the program from
the step 0. The FEND instruction used in creation of a subroutine or interrupt program is not required after a
main routine program.
2
After execution of the standby type program, the CPU module re-executes the program that called a program in
the standby type program.
Use common pointers. ( Page 336, Section 5.10) If local pointers are used, subroutine programs in a standby type
program cannot be executed from any other program.
2.8 Executing Multiple Programs
2.8.3 Standby type program
67
Page 70

(b) Changing the program execution type using instructions
Use the PSCAN, PSTOP, or POFF instruction to change a program execution type. ( Page 72, Section
2.8.5)
In the following figure, the PSCAN instruction changes the program "DEF" to a scan execution type program
and the PSTOP instruction changes the program "ABC" to a standby type program.
The program execution type is changed in END processing. Therefore, the execution type will not be changed
in the middle of program execution. If different types are set to the same program in the same scan, the
program will be changed to the type specified by the last instruction executed.
(2) Restrictions on creating a execution type program
Unavailable devices depend on the program type (subroutine program or interrupt program) or the execution type
changed by an instruction.
68
Page 71

CHAPTER 2 APPLICATION OF PROGRAMMING
2.8.4 Fixed scan execution type program
Fixed scan execution type program is a program executed at specified time intervals. This type of programs, unlike
interrupt programs, can be interrupted in units of files without interrupt pointers or the IRET instruction. For the
restrictions on programming, refer to Page 57, Section 2.7 (2). The restrictions on programming are the same as
those for interrupt programs.
Fixed scan interval
2
END processing
Scan execution
type program
Fixed scan execution
type program
To execute a fixed scan execution type program, execute the EI instruction in the initial execution type program or scan
execution type program to enable interrupts.
Condition
established
Condition
established
2.8 Executing Multiple Programs
2.8.4 Fixed scan execution type program
69
Page 72

(1) Processing
Fixed scan interval
END processing
Scan execution
type program
Fixed scan execution
type program
*1: Waiting time
*2: If processing is not completed within
the waiting time, the scan time increases.
Condition
established
Constant scan
*
2
*
1
(a) When two or more fixed scan execution type programs exist
Each fixed scan execution type program is executed at specified time intervals. If two or more fixed scan
execution type programs reach the specified time at the same timing, programs will be executed in ascending
order of the numbers set in the Program tab of the PLC Parameter dialog box.
(b) When both fixed scan execution type program and interrupt program exist
When a fixed scan execution type program and an interrupt program (I28 to I31) reach the specified time at the
same timing, the interrupt program will be given priority.
(c) When the execution condition is established during END processing
When the execution condition is established during the waiting time of the constant scan execution or the END
instruction, a fixed scan execution type program is executed.
(2) Processing at program execution type change
For how to save and restore data in the index register when the program execution type is changed, refer to
Page 60, Section 2.7 (4). The method is the same as that for interrupt programs.
70
Page 73

CHAPTER 2 APPLICATION OF PROGRAMMING
Ex.
Highest common factor of fixed
scan execution intervalal
*1
< Interrupt disabled time Condition 1
(3) Precautions
(a) Execution interval of a fixed scan execution type program
Execution interval of a fixed scan execution type program may increase from the preset interval depending on
the time set for disabling interrupts by the DI instruction (interrupt disabled time). If the interrupt disabled time
by the DI instruction becomes too long, use an interrupt program by fixed scan interrupt (I28 to I31) instead of a
fixed scan execution type program.
*1 This is the highest common factor of execution interval set to multiple fixed scan execution type programs.
When the condition 1) is satisfied, the actual execution interval of a fixed scan execution type program may
increase from the preset interval by the time shown in the expression below.
Interrupt disabled time
Highest common factor of fixed
scan execution interval
Fixed scan execution interval set to
the corresponding program
2
Increase in execution time of a fixed scan execution type program.
• Fixed scan execution interval10ms, 5ms, 1ms, 0.5ms
• Highest common factor of fixed scan execution interval0.5ms
• Interrupt disabled time (DI)5ms (Interrupt enabled time (EI)less than 0.5ms)
With the settings above, the condition 1) will be 0.5ms < 5ms.
n + 1 th scans
DI
EI
Enabled
Less than 0.5ms
Disabled
Program execution
operation
Interrupt
enabled status
nth scan(s)
DI
Disabled
Interrupt disabled time = 5ms Interrupt disabled time = 5ms
EI
Enabled
Less than 0.5ms
END END
Disabled
The execution time of a fixed scan execution type program whose execution interval is set to 10ms increases
100ms (5 0.5 10 = 100) at the most.
2.8 Executing Multiple Programs
2.8.4 Fixed scan execution type program
71
Page 74

2.8.5 Changing the program execution type
The execution type of programs can be changed using instructions even during execution. Use the PSCAN, PSTOP, or
POFF instruction to change a program execution type.
PSCAN
Initial execution
type program
instruction
Scan execution
type program
PSTOP
and POFF
instructions
Standby type
program
Execution type before
change
Scan execution type Remains unchanged. Changes to the standby type.
Initial execution type
Standby type
Fixed scan execution type
Changes to the scan execution
type.
Changes to the scan execution
type.
Changes to the scan execution
type.
PSCAN PSTOP POFF
PSTOP
and POFF
instructions
PSCAN
instruction
Fixed scan execution
PSTOP
and POFF
instructions
type program
Instruction
Changes to the standby type.
Remains unchanged. No processing
Changes to the standby type.
Once the fixed scan execution type program is changed to another execution type, the type cannot be returned to the fixed
scan execution type.
PSCAN
instruction
Turns off outputs in the next scan.
Changes to the standby type in two scans later.
Turns off outputs in the next scan.
Changes to the standby type in two scans later.
Turns off outputs in the next scan.
Changes to the standby type in two scans later.
72
Page 75

CHAPTER 2 APPLICATION OF PROGRAMMING
Ex.
: ABC
: DEF
: GHI : JKL
When M0 turns on,
the program "ABC" is
changed from a standby
type to a scan execution
type program.
When M1 turns on,
the program "ABC" is
changed from a scan
execution type to a standby
type program.
Control program
The PSCAN instruction changes
the program "ABC" to a scan
execution type program.
The PSTOP instruction changes
the program "ABC" to a standby
type program.
Standby
type
program
Standby
type
program
Standby
type
program
Standby
type
program
In a control program, a standby type program matching the preset condition is changed to a scan
execution type program in the course of program execution. (An unused scan execution type program
can also be changed to a standby type program.)
2
2.8 Executing Multiple Programs
2.8.5 Changing the program execution type
73
Page 76

2.9 Boot Operation
Remark
CPU modules can be operated according to the program and parameters stored in an SD memory card. Operating a
CPU module by reading out (boot) those data are called boot operation. The files that can be booted are as follows.
: Bootable, : Not bootable
File type Boot source
Parameter
Device comment
Device initial value
Symbolic information
*1 The intelligent function parameter is included.
*2 This is the data of label program configuration information.
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating Manual (Common)
The L02SCPU and L02SCPU-P do not support the boot operation.
*1
Program
SD memory card
*2
Program memory Standard ROM
Boot destination
(1) Executing a program
The programs specified in the Boot File tab are booted to the program memory when:
• the CPU module is powered off and then on or
• the CPU module is reset.
(a) Boot operation procedure
1. Create a program.
2. Configure the setting for a boot operation.
Specify the file name and transfer destination to boot.
Project window [Parameter] [PLC Parameter] [Boot File]
74
Page 77

CHAPTER 2 APPLICATION OF PROGRAMMING
3. Insert an SD memory card.
4. Write the setting to the SD memory card (parameters and the files set in the Boot File tab).
Reset the CPU module after the above operation. The boot operation is complete.
(b) Checking whether a boot is complete
The following indicates completion of boot operation.
• SM660 turns on
• There is no BOOT ERROR.
• Data in the transfer destination and in the program memory are found matched by a data verification.
[Online] [Verify with PLC...]
(c) Operation for stopping boot operation
To stop boot operation and operate the CPU module by the parameters and program files written to the
program memory, perform the following operations.
1. Remove the memory card and write parameters without boot file setting to the program memory.
2. Power off and then off or rest the CPU module.
2
(d) Boot operation precautions
• Set the maximum number of settable boot files in the Boot File tab of the PLC Parameter dialog box so that
it is the same with the number of files storable to the program memory. However, the number of boot files is
reduced by one when:
• a heading is set
• the parameters set in the Boot File tab of the PLC Parameter dialog box and stored in the SD memory card
is booted.
• The size unit of a file stored in each memory differs between the SD memory card and the program memory.
Therefore, note that files transferred from the SD memory card to the program memory differ in memory
capacity between before and after the transfer.
• Set the same model name of the CPU module in the "PLC type" (model name of the CPU module) for the
program written to the SD memory card (program set in the Boot File tab) and for the CPU module to boot.
2.9 Boot Operation
75
Page 78

2.10 Programming Language
Remark
The following programming languages are supported in the programming tool.
• Ladder
•ST
•SFC
• Structured ladder
(1) Ladder
A graphical programming language which uses contacts and coils. For a project with a label, the inline ST
function can be used in the ladder editor which allows a user to edit an ST program.
X0
M0
T0
X1
BIN K4X10 D0
X41
FROM H5 K0 D10 K1
K100
T0
Y30
Sequence instruction
Basic instruction
Application instruction
Data indicating the execution status of an operation in a sequence program step is referred to as "signal flow".
(2) ST
A text language such as C language, and is preferred by computing engineers.
(3) SFC
A graphical programming language where the execution order and conditions are clearly defined for the program.
(4) Structured ladder
A graphical programming language that uses contacts and coils.
For the projects that support these programming languages, refer to the following.
Manual for the programming tool used
76
Page 79

CHAPTER 2 APPLICATION OF PROGRAMMING
2.11 Communications with Intelligent Function Modules
The intelligent function module allows the CPU module to process analog quantity and high-speed pulses that cannot
be processed by the I/O modules. The following is some of the intelligent modules.
• Serial communication module
• Analog module
• Positioning module
• High-speed counter module
• Temperature control module
The intelligent function module is equipped with a memory (buffer memory) to store the data taken in from or output to
external devices. The CPU module writes or reads data to or from the buffer memory of the intelligent function module.
(1) Setting method of intelligent function module parameters
Open the "New Module" dialog box.
Project window [Intelligent function module] Right-click [New Module...]
2
Item Description
Module Selection
Mount Position
Title Setting Title Enter a title.
Module Type Select a type of the CPU module.
Module Name Select a model name of the CPU module.
Mounted Slot No. Select a slot No. where he CPU module is connected.
Acknowledge I/O Assignment
Specify start X/Y address Enter the start I/O number.
The I/O assignment settings in the PLC Parameter dialog box can be
checked.
2.11 Communications with Intelligent Function Modules
77
Page 80

Upon completion of the setting above, parameters for the intelligent function module appear in the "Project"
window.
To set the intelligent module parameters, refer to the following.
Manual for the intelligent function module used
(2) Communications with the FROM and TO instructions
The FROM instruction stores data read from the buffer memory of the intelligent function module to the specified
device.
The TO instruction writes data stored in the specified device to the buffer memory of the intelligent function
module.
For details on the FROM and TO instructions, refer to the following.
MELSEC-Q/L Programming Manual (Common Instruction)
(3) Communications using the intelligent function module device
The intelligent function module device represents the buffer memory of the intelligent function module as one of
the CPU module devices. ( Page 320, Section 5.5.1)
The difference from the FROM and TO instructions is that, with this device, both reading and writing data from
and to the intelligent function module cab be processed with one instruction.
78
Page 81

CHAPTER 2 APPLICATION OF PROGRAMMING
Ex.
b15 b0
to
S2
+ 0
+ 1
+ 2
CPU module Serial communication module
Channel 1
Channel 2
Send
Send
Set channels to be used in
control data.
(4) Communications using the intelligent function module dedicated instruction
This instruction enables easy programming for the use of functions of the intelligent function module.
Serial communication module dedicated instruction (OUTPUT instruction)
The OUTPUT instruction allows communications with external device by nonprocedural protocol regardless
of the buffer memory address of the serial communication module.
(a) Processing of the intelligent function module dedicated instruction
When using multiple intelligent function module dedicated instructions to one intelligent function module,
execute the dedicated instructions one by one after the completion device turns on. This completion device
turns on for one scan when an instruction is completed. If the CPU module status is changed from RUN to
STOP before the completion device turns on, the completion device does not turn on until one scan after the
next RUN of CPU module.
For details on the intelligent function module dedicated instructions and the completion device, refer to the
following.
Manual for the intelligent function module used
2
2.11 Communications with Intelligent Function Modules
79
Page 82

Memo
80
Page 83

PART 2 FUNCTIONS
In this part, the functions of the CPU module and display unit are described.
CHAPTER 3 CPU MODULE FUNCTIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
CHAPTER 4 DISPLAY UNIT FUNCTIONS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 236
81
Page 84

CHAPTER 3 CPU MODULE FUNCTIONS
This chapter describes the functions for a CPU module.
3.1 Function List
The following table lists the functions of the LCPU.
Item Description Reference
Boot operation
Constant scan Executes a program at a set interval regardless of its scan time. Page 85, Section 3.2
Watchdog timer (WDT)
Latch function Holds the device data of the CPU module. Page 88, Section 3.4
Initial device value Registers data used in programs without programs. Page 91, Section 3.5
Service processing setting Specifies the service processing count or time to be executed in END processing. Page 94, Section 3.6
Output mode at operating status change
(STOP to RUN)
Input response time setting Sets input response time for modules such as an input module. Page 102, Section 3.8
Error time output mode setting
PLC operation mode at H/W error setting
*2
File password 32
Security
function
Remote RUN/STOP Changes the CPU module status to RUN or STOP without using switches.
Remote PAUSE
Remote RESET Resets the CPU module when it is in the STOP status, without using switches.
Remote latch clear
Scan time measurement Measures the execution time of the specified steps in a program.
Program list monitor Displays the scan time and execution status of the program being executed.
Interrupt program list monitor Displays the number of executions of an interrupt programs.
Monitor condition setting Monitors the CPU module under specified conditions.
Device monitor/test Monitors and/or tests the local devices of the specified program.
External input/output forced on/off Forcibly turns on/off the external input/output of the CPU module.
Executional conditioned device test Changes a device value for the specified step of a program.
Remote Password Prevents unauthorized access from external devices.
Block password Prevents access to program contents by setting a block password for each POU.
Boots data stored in an SD memory card to the program memory or the standard ROM
when the CPU module is powered off and on or reset.
Monitors operational delays caused by hardware failure or program error of the CPU
module.
Sets the status of the outputs(Y) when the operation status of the CPU module is
changed from STOP to RUN.
Sets whether to clear or hold the output status to each module when a stop error occurs
in the CPU module.
Sets a operation mode of the CPU module when a hardware error (CPU module
detects SP.UNIT DOWN) occurred in an intelligent function module.
Protects data in the CPU module against tampering and theft by unauthorized persons.
Prohibits writing/reading data to/from each file in the CPU module using a programming
tool. Sets write password and read password for each file stored in the CPU module.
Changes the CPU module status to PAUSE without using switches, holding the status
of outputs (Y).
Clears latch data of the CPU module when the module is in the STOP status, without
using switches.
Page 74, Section 2.9
Page 87, Section 3.3
Page 101, Section 3.7
Page 103, Section 3.9
Page 104, Section
3.10
Page 105, Section
3.11
Page 105, Section
3.11.1
Page 110, Section
3.11.2
GX Works2 Version 1
Operating Manual
(Common)
Page 112, Section
3.12.1
Page 114, Section
3.12.2
Page 116, Section
3.12.3
Page 117, Section
3.12.4
Page 118, Section
3.13
Page 121, Section
3.14
Page 122, Section
3.15
Page 123, Section
3.16
Page 128, Section
3.17
Page 131, Section
3.18
Page 135, Section
3.19
82
Page 85

CHAPTER 3 CPU MODULE FUNCTIONS
Item Description Reference
Sampling trace Continuously collects data of the specified device at a specified timing.
Realtime monitor function
Online change (ladder mode) Writes programs while the CPU module is in the RUN status.
Online change (files) Collectively writes files while the CPU module is in the RUN status.
Debug from multiple programming tools Enables simultaneous debugging from multiple programming tools.
Self-diagnostic function Self-diagnoses the CPU module to see whether an error exists or not.
Error clear Clears continuation errors by error type. User can specify continuation errors to clear.
LED control function
Module error collection function Lists descriptions of errors occurred in the intelligent function module.
Latch data backup to standard ROM Backs up latch data such as device data and error history without using a battery.
Writing/reading device data to/from
standard ROM
Module model name read Reads the model name of a module connected.
CPU module change function with SD
memory card
Clock function Controls the clock data of the CPU module.
Battery-life prolonging function Prolongs a battery life by limiting the data to be latched to clock data only.
Memory check function
Program cache memory auto recovery
function
Project data batch save/load function
Predefined
protocol
function
Serial communication function
Writing/reading data to/from refresh
devices with the specified station
number
Data logging function
Built-in I/O function
*2
*1
*1
*1*2
*1*2
*1
Communications via
*2
Ethernet
Communications via RS-
232, RS-422/485
*2
*2
*1*2
Monitors the data in the specified device of the CPU module at a specified interval or at
a desired timing in real time.
Sets the timing to turn off and indication of the LEDs located on the front of the CPU
module.
Writes/reads device data to/from the standard ROM using an instruction.
Saves the data in a CPU module to an SD memory card when changing the CPU
module.
Checks that data in the memories of the CPU module are not changed due to
excessive electric noise.
Restores the error location automatically by using data in the program memory, which
are stored in the flash ROM, when the memory check function detects an error in the
program cache memory.
Saves data in the CPU module to an SD memory card, and also reads the data saved
*1*2
in an SD memory card to the CPU module.
Sends and receives packets predefined by using GX Works2, enabling easy
communications with external devices (such as measuring instruments and bar code
readers).
Communicates data with external devices, such as personal computers and HMIs,
connected with an RS-232 or RS-422/485 cable using the MC protocol.
Writes/reads data by specifying the station number of the target station, without
considering the assignment of refresh devices.
Collects data from the specified device of a CPU module at a specified timing. The data
logging file can be transferred from a CPU module to the FTP server using the data
logging file transfer function.
Performs the following dedicated functions: general-purpose input function, generalpurpose output function, interrupt input function, pulse catch function, positioning
function, and high-speed counter function.
Page 143, Section
3.20
Page 150, Section
3.21
Page 151, Section
3.22.1
Page 152, Section
3.22.2
Page 158, Section
3.23
Page 161, Section
3.24
Page 166, Section
3.25
Page 169, Section
3.26
Page 171, Section
3.27
Page 175, Section
3.28
Page 180, Section
3.29
Page 181, Section
3.30
Page 182, Section
3.31
Page 196, Section
3.32
Page 198, Section
3.33
Page 199, Section
3.34
Page 200, Section
3.35
Page 202, Section
3.36
MELSEC-L CPU
Module User's Manual
(Built-In Ethernet
Function)
Page 215, Section
3.37
Page 227, Section
3.38
MELSEC-Q/L
Programming Manual
(Common Instruction)
QnUDVCPU/LCPU
User's Manual (Data
Logging Function)
MELSEC-L CPU
Module User's Manual
(Built-In I/O Function)
3
3.1 Function List
83
Page 86

Item Description Reference
Socket communication
*2
function
File transfer function
(FTP server)
File transfer function
(FTP client)
Simple PLC
Built-in
Ethernet
*2
function
Built-in CC-Link function
iQ Sensor Solution function
CC-Link IE Field Network Basic function
communication
function
IP address change
function
IP packet transfer
function
E-mail send/receive
function
SLMP frame send
instruction
*1
*1*2
*1*2
*1
*1
*2
*1*2
*1 Availability depends on the version of the CPU module. ( Page 376, Appendix 2)
*2 Some models do not support those functions. For the availability, refer to the reference sections of each function.
*3 Only the Built-in Ethernet port LCPU supports this function.
Enables MC protocol communications and the following functions by using built-in
Ethernet ports.
Communicates data (using TCP/UDP) with external devices connected on the Ethernet
network. The function is executed by dedicated instructions.
Works as a server of the FTP (File Transfer Protocol), which is used to transfer files
between the CPU module and external devices.
External devices with the FTP client function can directly access to the files in the CPU
module.
Works as a client of the FTP (File Transfer Protocol), which is used to transfer files
between the CPU module and external devices.
The CPU module can transfer files to the FTP server on a LAN by using the file transfer
function instructions.
Allows data communications between specified devices at the specified timing just by
doing simple settings from a programming tool.
Changes the IP address of the built-in Ethernet port by storing the value in the special
relay or special register, instead of setting the value in the built-in Ethernet port setting
parameter.
Communicates with the following devices that correspond to IP address specified via a
CC-Link IE Controller Network module or CC-Link IE Field Network module, using a
protocol such as the FTP or HTTP via a built-in Ethernet port from an Ethernet device
such as a personal computer.
• External devices on the CC-Link IE Field Network
• External devices on the Ethernet network, which are connected through the built-in
Ethernet ports
Sends/receives e-mail to/from an electronic device, such as a mobile phone, smart
phone, and personal computer. Device data can be read/written by describing an MC
protocol command in the body of the e-mail sent to the CPU module.
Sends MC protocol messages (QnA-compatible 3E frame) from the CPU module to
external devices connected on the Ethernet network.
Allows data communications over CC-Link.
A set of functions that can be used in iQ Sensor Solution
*1*3
A set of functions that can be used in CC-Link IE Field Network Basic
MELSEC-L CPU
Module User's Manual
(Built-In Ethernet
Function)
MELSEC-L CC-Link
System Master/Local
Module User's Manual
Page 234, Section
3.39
iQ Sensor Solution
Reference Manual
CC-Link IE Field
Network Basic
Reference Manual
84
For details on the special relay (SM) and special register (SD) used for each function, refer to the following.
MELSEC-L CPU Module User's Manual (Hardware Design, Maintenance and Inspection)
Page 87

CHAPTER 3 CPU MODULE FUNCTIONS
END
5ms
0
END
0
2ms 6ms
END
0
1ms
5ms
END
0
2ms
7ms7ms 7ms
Program execution
END processing
Waiting time
Enter a value.
3.2 Constant Scan
Scan time of the CPU module is not constant because the processing time varies depending on the execution status of
instructions used in a program. By using this function, scan time can be maintained constant.
(1) Application
I/O refresh is performed before program execution. By using this function, the constant I/O refresh intervals can
be maintained even the time required for program execution changes.
• Scan time without constant scan setting
Program execution
END
0 END 0 END 0 END 0
END processing
3
5ms
6ms
• Scan time with constant scan setting (7ms)
• Scan time for multiple programs with constant scan setting (10ms)
Execution of program A
Execution of program B
Execution of program C
END processing
Waiting time
8ms 2ms
10ms
(2) Constant scan time setting
The setting range is from 0.5 to 2000ms (in increments of 0.5ms).
When not using the constant scan function, leave the setting box blank.
9ms
10ms
5ms
3.2 Constant Scan
1ms
Project window [Parameter] [PLC Parameter] [PLC RAS]
The constant scan accuracy is 0.01ms. However, constant scan time may increase when an interrupt program or
a fixed scan execution type program is being executed.
85
Page 88

(a) Condition
0 0 END 0END 0END 0END
3.5ms
4ms 4ms
3.8ms 3.4ms
4ms5.3ms
0.2ms
0.5ms
0.6ms
When constant scan time is set to 4ms
Program execution
Scan where scan time is increased
Set a value that satisfies the following relational expression.
WDT setting time > Constant scan setting time > Maximum scan time of the program
If the program scan time is longer than the constant scan setting time, the CPU module detects "PRG. TIME
OVER" (error code: 5010). In this case, the constant scan setting is ignored and the program scan time is
applied.
If the program scan time is longer than the WDT setting time, the CPU module detects "WDT ERROR". In this
case, the program execution is stopped.
(3) Waiting time from when END processing is executed until next scan starts
• When an interrupt factor occurs during waiting time, either of an interrupt program or fixed scan execution
type program is executed.
• When a service processing parameter is set, a communication service processing with peripherals and
intelligent function modules is performed.
86
Page 89

CHAPTER 3 CPU MODULE FUNCTIONS
Enter a value.
3.3 Watchdog Timer (WDT)
WDT is an internal timer of the CPU module that detects CPU module hardware failures and program errors.
(1) Setting
Open the tab for watchdog timer setting. The setting range is 10 to 2000ms (in increments of 10ms). 200ms is set
by default.
Project window [Parameter] [PLC Parameter] [PLC RAS]
A precision error is observed within the range of 0 to 10ms.
3
(2) Reset
WDT is reset in END processing. The watchdog timer times up when the scan time is extended due to a factor
such as an interrupt, and the END/FEND instruction were not executed within the setting value of watchdog timer.
When the watchdog timer times up, "WDT ERROR" is detected and the following status occurs.
• The CPU module turns off all outputs.
• The RUN LED turns off and the ERR.LED starts flashing.
• SM1 turns on and the error codes 5000 and 5001 are stored in SD0.
The watchdog timer can be reset by executing the WDT instruction in a program. To avoid the time up of
watchdog timer while a program is repeatedly executed between the FOR and NEXT instructions, reset the
watchdog timer by the WDT instruction.
Repeatedly executed program
WDT reset
Note that the scan time value is not reset even after the watchdog timer is reset. The scan time is measured up to
the END instruction.
Repeated by
1,000 times.
3.3 Watchdog Timer (WDT)
87
Page 90

3.4 Latch Function
Set latch ranges by the start and
end device numbers.
This function holds data in each device of the CPU module when:
• the CPU module is powered off and then on,
• the CPU module is reset, or
• a power failure occurred exceeding the allowable momentary power failure time.
Data in each device of the CPU module are cleared and set back to its default (bit device: off, word device: 0) when
this function is not used. By using this function, the operation can be continued with the previous data even after
powering off the CPU module while the data are managed by a sequential control. Program operation does not change
regardless of the latch
(1) Devices that can be latched
Set the device to latch among the following. (By default, only the latch relay is latched.)
• Latch relay (L) • Link relay (B) • Annunciator (F)
• Edge relay (V) • Timer (T) • Retentive timer (ST)
• Counter (C) • Data register (D) • Link register (W)
The following devices also can be set when a file register is set to be used in the PLC file.
• File register (ZR) • Extended data register (D) • Extended link register (W)
When the battery life-prolonging function is set, the latch function is disabled. ( Page 198, Section 3.33)
(2) Latch range setting
Set the following.
Project Window [Parameter] [PLC Parameter] [Device]
• Latch clear operation enable range (Latch (1) Start/End): Data in this range can be cleared by a latch clear
operation.
• Latch clear operation disable range (Latch (2) Start/End): Data in this range cannot be cleared by a latch
clear operation.
88
Page 91

CHAPTER 3 CPU MODULE FUNCTIONS
Remark
(3) Effect on the scan time
Data latch processing is performed during END processing therefore the scan time increases. Consider the effect
on the scan time when latching devices. ( Page 378, Appendix 3.1)
To reduce the scan time increase due to latch*1, minimize the number of latch points (latch (1) setting, latch (2) setting, and
latch relay) as much as possible by performing the following.
• Move data to be latched to the file register.
• Store device data that is less frequently updated in the standard ROM with the SP.DEVST instruction. (The device
data stored in the standard ROM can be read with the S(P).DEVLD instruction. ( Page 180, Section 3.29)
*1 For file registers (including an extended data register (D) and an extended link register (W)), the scan time is not
increased due to latch.
(4) Latch data clear methods
(a) Data in the latch clear operation enable range (Latch (1) Start/End)
Perform either of the following.
• Remote latch clear
Perform the operation using a programming tool. ( Page 117, Section 3.12.4)
• Latch clear by using the special relay and special register areas
1. Change the operating status of the CPU module to STOP.
2. Set "5A01
" in SD339.
H
3. Turn on SM339.
3
3.4 Latch Function
Data can be cleared only when the CPU module is in STOP status. If the operation is performed when the CPU module is
not in STOP status, no processing is performed (data cannot be cleared).
Before clearing data by using the special relay and special register areas, check the version of the CPU module used.
( Page 376, Appendix 2)
89
Page 92

(b) Data in the latch clear operation disable range (Latch (2) Start/End) and in the file
register
Perform any of the following.
• Perform the data clear operation using the display unit. ( Page 249, Section 4.2.2)
• Reset data by using the RST instruction.
• Transfer K0 by using the MOV or FMOV instruction. ( MELSEC-Q/L Programming Manual (Common
Instruction))
• Set parameters ("Clear Device's whole Memory" or "Clear all File Registers").
[Online] [PLC Memory Operation] [Clear PLC Memory] "Clear Device's whole
Memory"/"Clear all File Registers"
(5) Precautions
• The latch setting does not take effect if the device is specified as a local device or the initial device value is
specified for the device.
• A battery is required to retain the device data that are set in the latch range. If the battery connecter is
removed during power-off, the device data within the latch range are discarded and undefined values may
replace. (A battery is required also in the boot operation to latch devices.)
90
Page 93

CHAPTER 3 CPU MODULE FUNCTIONS
Using an initial device value can omit creating device data
setting program in an initial processing program.
Initial device value
Device memory
Device memory
3.5 Initial Device Value
This function registers data used in a program to the device or the buffer memory of the intelligent function module
without a program. By using this function, creating a device data setting program can be omitted in the initial
processing program.
3
(1) Timing when initial device values are written to the specified device
The CPU module writes data in the specified initial device value file to the specified device or the buffer memory
of the intelligent function module when:
• the CPU module is powered off and then on,
• the CPU module is reset, or
• the CPU module status is switched from STOP to RUN.
(2) Devices that can be used
The following shows devices that can be used for initial device value.
• Current timer value (T) • Current retentive timer value (ST)
• Current counter value (C) • Data register (D)
• Link register (W) • Link special register (SW)
• Special register (SD)
• File register (R, ZR) • Extended data register (D)
• Extended link register (W)
*1 The initial device value setting has a priority over the latch setting.
*2 To use an intelligent function module, select "Module Synchronization" because the initial device value may not be
correctly set to the target module. ( Page 350, Appendix 1)
*1
• Intelligent function module device (U\G)
3.5 Initial Device Value
*2
91
Page 94

(3) Initial device value setting
1. Specify a memory and name to store initial device
values.
Project Window [Parameter] [PLC
Parameter] [PLC File]
2. Specify a name to store initial device values.
Project Window [Device Initial Value] Rightclick [Add New Data...]
3. Clicking the button on the dialog box
above opens the dialog box shown on the left. Enter
the range for initial device values.
92
Page 95

CHAPTER 3 CPU MODULE FUNCTIONS
4. Configure the device memory.
Project Window [Device Memory] [MAIN]
Right-click [Input Device...]
5. Store the initial device value file in the program
memory of the CPU module, standard ROM, or an
SD memory card.
[Online] [Write to PLC]
3
Whenever the initial device value range is changed, execute "Device Memory Diversion" on the "Device Initial Value MAIN"
dialog box. For details on creating initial device value data, refer to the following.
Manual for the programming tool used
(4) Precautions
Initial device values also take effect when the CPU module status is switched from STOP to RUN. Therefore,
they cannot be used for the data that are to be changed in a program after being set at CPU module power-on
from off. Use an instruction such as the MOV instruction in the main routine program so that the initial device
values are set to the specified devices. For the intelligent function module, use the TO instruction to write data to
the buffer memory.
3.5 Initial Device Value
93
Page 96

3.6 Service Processing Setting
This function allows to set the time and the number of times of service processing performed at END processing by
parameters.
Processing for requests from peripherals to the CPU module are performed with this function. The processing speed
for the communication response to the requests varies depending on the scan time and communication load. Set the
parameter of the service processing time as follows to achieve an optimal service processing environment for the
system used.
• Setting a longer time can improve the processing speed for the communication response.
• Setting a shorter time can avoid a prolonged scan time caused by the service processing.
Communications from multiple peripherals to the CPU module may slow down the processing speed for the
communication response. Adjust the settings for the system by specifying a longer service processing time or
modifying the parameter settings of the peripherals to set longer timeout times taking the processing speed for the
communication response and increases in scan times into consideration.
● The service processing setting can be configured for the following communications:
• Communication via an intelligent function module (not including refresh with a network module)
• Communication via a USB cable, RS-232 adapter, RS-422/485 adapter, and the built-in Ethernet ports
(communication with a programming tool or GOT, or using the built-in Ethernet function)
● Using the COM instruction enables the service processing during program execution while the processing is normally
performed during END processing. Use this function when the scan time is long.
94
Page 97

(1) Setting method
Configure the setting of the service processing.
"Execute the process as the scan time proceeds" is selected by default.
Item Description Setting range Remarks
Execute the process as the
scan time proceeds
Specify service process time
*1*2*3*6
Specify service process
execution counts
Execute it while waiting for
constant scan setting.
*6
*4*5
*2*6
Project Window [Parameter] [PLC Parameter] [PLC System]
Select any one option button.
Deselected parameters remain
unavailable.
Set the percentage of service processing for
one scan.
Set the time of service processing for one scan.
Set the number of service processing for one
scan.
Set whether to perform service processing
during waiting time for constant scan setting.
• Range: 1 to 99%
• Unit: 1%
• Range: 0.2ms to 1000ms
• Unit: 0.1ms
• Range: 1 to 10 times
• Unit: 1 time
CHAPTER 3 CPU MODULE FUNCTIONS
3
Default when selected = 10%
Default when selected = 0.2ms
Default when selected = 1 time
Even when the waiting time is 0.2ms
or less, the service processing time of
0.2ms is added to the scan time.
*1 There is a margin of error between -20s to +30s against actual processing time.
*2 The response performance of service processing significantly reduces in the following cases. Set service processing
time considering the time-out time of the peripheral.
Service processing time is set much shorter than the scan time.
Setting "Execute it while waiting for constant scan setting" results in increase in the scan time and decrease in the
service processing time.
*3 For the following functions, scan time will be increased longer than the specified time during service processing even if
the service processing time specification is set.
Online change
Change T/C setting
Local device monitor
Program memory backup
Writing to/reading from the file register or the buffer memory of an intelligent function module (The scan time is
increased when the write or read size is large.)
Diagnostic function of a network module (CC IE Field diagnostics, CC-Link/ CC-Link/LT diagnostics)
Monitor function (module access device, link direct device)
*4 Note that the scan time is increased much longer if the CPU module simultaneously receives multiple requests while the
service processing count specification is set many.
*5 If a data communication is performed over Ethernet when "Specify service process execution counts" is selected in
parameter, the scan time will increase by the service processing time (approx. 500ms). To keep the scan time 500ms or
less, select an item other than "Specify service process execution counts" in parameter. (For example, select "Specify
service process time." and set a time value to 500ms or less.)
*6 If communications in the MC protocol are performed with an item other than "Specify service process execution counts"
selected, data inconsistency may occur. To prevent data inconsistency, select "Specify service process execution
counts".
3.6 Service Processing Setting
95
Page 98

(2) Operation for service processing setting
Program execution
END processing
Request 1)
Program execution
END processing
Request 2)-1
Program execution
END processing
Request 3)
Peripheral
Request 2)-2
1ms
1ms
1.2ms
The service processing time depends on the
scan time (program execution time).
When time required for processing one request
exceeds 10% of one scan time, the service
processing is suspended and the remaining
requests are processed at the END processing
in the next scan.
1st scan
(10ms)
2nd scan
(10ms)
3rd scan
(12ms)
Request 1)
Request 2)
Request 3)
Request 4)
Request 5)
Operations for each service processing setting is described below.
(a) Execute the process as the scan time proceeds
Operation when 10% is set is as shown below.
● When the constant scan is set, ( Page 99, Section 3.6 (2) (d)), the calculation of the service processing time is a
calculation of the percentage of the time excluding the waiting time of the constant scan from the scan time, not a
calculation of the percentage of the scan time.
Example: Operation when 50% is set
0% 50% 100%
Program execution
END processing
Service processing
Service processing time
Scan time (constant scan setting)
Waiting time
● If no request data for service processing exists, END processing speeds up by the amount of request processing time.
(The CPU module does not wait for requests.)
96
Page 99

(b) Specify service process time
Program execution
END processing
Request 1)
Program execution
END processing
Peripheral
Program execution
END processing
Request 2)
Request 2)
Request 3)
1ms
Request 3)
Request 4)
Multiple requests are processed until the processing time
exceeds the set service processing time (1ms).
When the service processing time is exceeded, the service
processing is suspended and the remaining requests are
processed at the END processing in the next scan.
Regardless of the number of requests to be
processed in the END processing, the increase
in scan time will be kept constant.
Request 1)
Request 2)
Request 3)
Request 4)
Request 5)
1st scan
2nd scan
3rd scan
Operation when 1ms is set is as shown below.
CHAPTER 3 CPU MODULE FUNCTIONS
3
If no request data for service processing exists, END processing speeds up by the amount of request processing time. (The
CPU module does not wait for requests.)
3.6 Service Processing Setting
97
Page 100

(c) Specify service process execution counts
Program execution
END processing
Request 1)
Program execution
END processing
Request 2)
Program execution
END processing
Request 3)
Peripheral
Regardless of request data size, one
request is processed at one END processing.
Even if the program execution time is the same,
the scan time depends on service processing time.
Request 1)
Request 2)
Request 3)
Request 4)
Request 5)
1st scan
2nd scan
3rd scan
Operation when 1 time is set is as shown below.
Operation when 2 times is set is as shown below.
Request 1)
Program execution
1st scan
END processing
Request 1)
Request 2)
Request 2)
Regardless of request data size, two requests
are processed at one END processing.
Request 4)
Request 3)
Request 5)
Peripheral
Program execution
2nd scan
END processing
Request 3)
Request 4)
● When several devices are connected to one CPU module, each device requests service processing. When the CPU
module simultaneously receives requests from several devices, a single END processing can simultaneously accept
several requests if the service processing count is set to the number of connected devices. This improves response
performance. Note that the scan time increases by the amount of service processing time.
● If no request data for service processing exists, END processing speeds up by the amount of request processing time.
(The CPU module does not wait for requests.)
98
 Loading...
Loading...