MITEL MH8841AS, MH8841AE, MH8841AN Datasheet
5-11
Features
• 1200 baud BELL 202 and CCITT V.23
Frequenc y Shift K eying (FSK) demo dulati on
• Compat ible wit h Bell core TR -NW T-000030 and
SR-TSV-002476
• High inpu t sens itivi ty: -36dB m
• Simple serial 3-wire data interface eliminating
the need for a UA RT
• Power do wn mo de
• Intern al gain ad ju stable a mp lifier
• Carrie r detec t statu s outp ut
• Uses 3.579545 MHz crystal or ceramic
resonator
• Single 5V powe r supp ly
• Low pow er CMO S tech nolog y
Applications
• Calling Num ber De livery (CND), Ca lling Na me
Delivery (CNAM) and Calling Identity on Call
Waiting (CIDCW) feat ures of Bellcore CL AS S
SM
service
• Featur e phone s
• Phone s et adj unc t boxes
• FAX machines
• Telephone An swer ing m achine s
• Database query systems
Description
The MT8841 Calling Number Identification Circuit
(CNIC) is a CMOS integrated circuit providing an
interface to various calling line information delivery
services that utilize 1200 baud BELL 202 or CCITT
V.23 FSK voiceband data transmission schemes.
The CNIC receives and demodulates the signal and
outputs d ata in to a simple 3-w ire se r ial in te rface.
Typically, the FSK modulated data containing
information on the calling line is sent before alerting
the called par ty or during the silent interval between
the first and second ring using either CCITT V.23
recommendations or Bell 202 specifications.
The CNIC accepts and demodulates both CCITT
V.23 and BELL 202 signals. Along with serial data
and clock, the CNIC provides a data ready signal to
indicate the reception of every 8-bit character sent
from the Central Office. The received data can be
processed externally by a microcontroller, stored in
memory, or displayed as is, depending on the
application.
Ordering Information
MT8841AE 16 Pin Plastic D IP
MT8841AS 16 Pin SOIC
MT8841A N 20 Pin SSO P
-40 °C to +85 °C
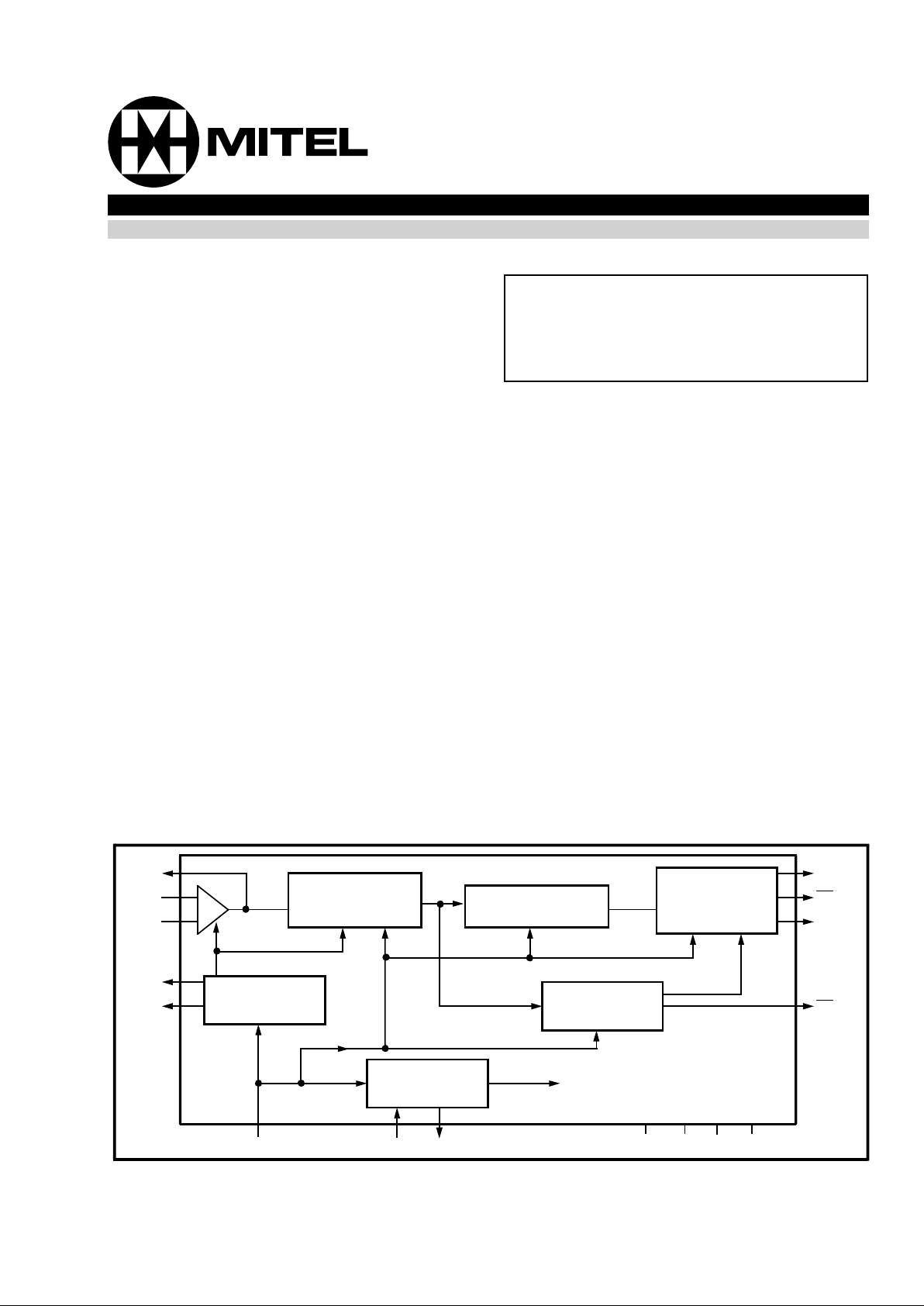
Figure 1 - Functional Block Diagram
CLASSSM is a service mark o f B ellcore
GS
IN-
IN+
CAP
V
Ref
DATA
DR
DCLK
CD
PWDN OSC1 OSC2
V
SSVDD
IC1 IC2
Receive
Bandpass
Filter
Bias
Generator
FSK
Demodulator
Data and Timin g
Carrier
Detector
Clock
Generat or
Recovery
to other
circuits
-
+
ISSUE 4 May 1995
MT8841
Calling Number Identification Circuit
CMOS
MT8841
5-12
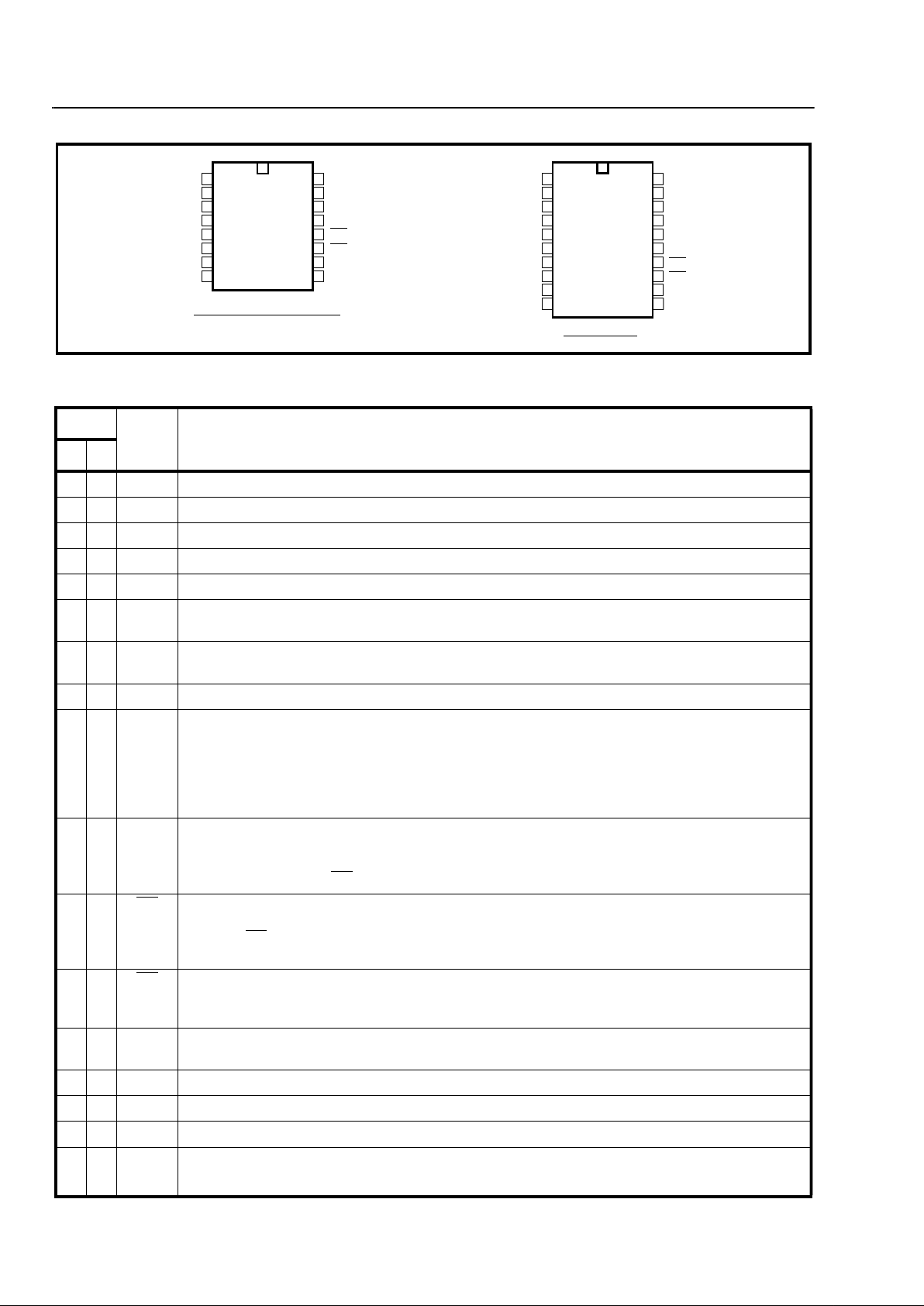
Figure 2 - Pin Connections
Pin Description
Pin #
Name Description
16 20
11 IN+Non-inverting Op-Amp (Input).
22 IN-Inverting Op-Amp (Input).
33 GSGai n Sel ect (Outpu t). Gives access to op-amp out put for connection of feedback resistor.
44 V
Ref
Voltage Reference (Output). Nominally V
DD/2
. This is used to bias the op-amp inputs.
55 CAPCapacitor. Connect a 0.1µF capacitor to V
SS
.
67OSC1Oscillator (Input). Crystal or ceramic resonator connection. This pin can be driven directly
from an external clocking source.
79OSC2Oscillator (Output). Crystal or ceramic resonator connection. When OSC1 is driven by an
external clock, this pin should b e left open.
810 V
SS
Power supply ground.
9 11 DCLK Data Clock (Output). Outputs a clock burst of 8 low going pulses at 1202.8Hz (3.5795MHz
divided by 2976). Every clock burst is initiated by the DATA stop bit start bit sequence. When
the input DATA is 1202.8 baud, the positive edge of each DCLK pulse coincides with the
middle of the data bits output at the DATA pin. No DCLK pulses are generated during the start
or stop bits. Typically, DCLK is used to clock the eight data bits from the 10 bit data word into a
serial-to-parallel converter.
10 12 DATA Data (Outp ut). Serial data out put correspondi ng to the FSK inpu t and switching at the input
baud rate. Mark frequency at the input corresponds to a logic high, while space frequency
corresponds to a logic low at the DATA output. With no FSK input, DATA is at logic high. This
output stay s high un til CD
has become active.
11 13 DR
Data Ready (Open Drain Output ). This output goes low after the last DCLK pulse of each
word. This can be used to identify the data (8-bit word) boundary on the serial output stream.
Typically, DR
is used to latch the eight data bits from the serial-to -p arallel convert er into a
microcontroller.
12 14 CD
Carrier Detect (Open Drain Output). A logic low indicates that a carrier has been present for
a specified time on the line. A time h ysteresis is provided to allow for mom ent ary di sconti nuit y
of carrier.
13 15 PWDN Power Down (Input). Active high, Schmitt Trigger input. Powers down the device including the
input op-amp and the oscillator.
14 16 IC1 Internal Connection 1. Connect to V
SS
.
15 19 IC2 Internal Connection 2. Internally connected, leave open circuit.
16 20 V
DD
Positive power supply voltage.
6,8
17,
18
NC No Connection.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
IN+
INGS
VRef
CAP
OSC1
OSC2
VSS
VDD
IC2
IC1
PWDN
CD
DR
DATA
DCLK
16 PIN PLASTIC DIP/SOIC
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
IN+
IN-
GS
VRef
CAP
NC
OSC1
NC
OSC2
VSS
20 PIN SSOP
VDD
IC2
NC
NC
PWDN
CD
DR
DATA
DCLK
IC1
MT8841
5-13
Functional Description
The MT8841 Calling Number Identification Circuit
(CNIC) is a device compatible with the Bellcore
proposal (TR-NWT-000030) on generic requirements
for transmitting asynchronous voiceband data to
Customer Premises Equipment (CPE) from a serving
Stored Program Controlled Switching System
(SPCS) or a Central Office (CO). This data
transmission technique is applicable in a variety of
services like Calling Number Delivery (CND), Calling
Name Delivery (CNAM) or Calling Identity Delivery
on Call Waiting (CIDCW) as specified in Custom
Local Area Signalling Service (CLASS
SM
) calling
information delivery features by Bellcore.
With CND, CNAM and CIDCW service, the called
subscriber has the capability to display or to store
the information on the calling party which is sen t by
the CO and received by the CNIC.
In the CND service, information about a calling party
is embedded in the silent interval between the first
and second ring. During this period, the CNIC
receives and demodulates the 1200 baud FSK signal
(compatible with Bell-202 specification) and outputs
data into a 3 - wir e se ria l i nte rfa c e.
In the CIDCW service, information about a second
calling party is sent to the subscriber, while they are
engaged in another call. During thi s period, the CNIC
receives and demodulates the FSK signal as in the
CND case.
The CNIC is designed to provide the data
transmission interface required for the above service
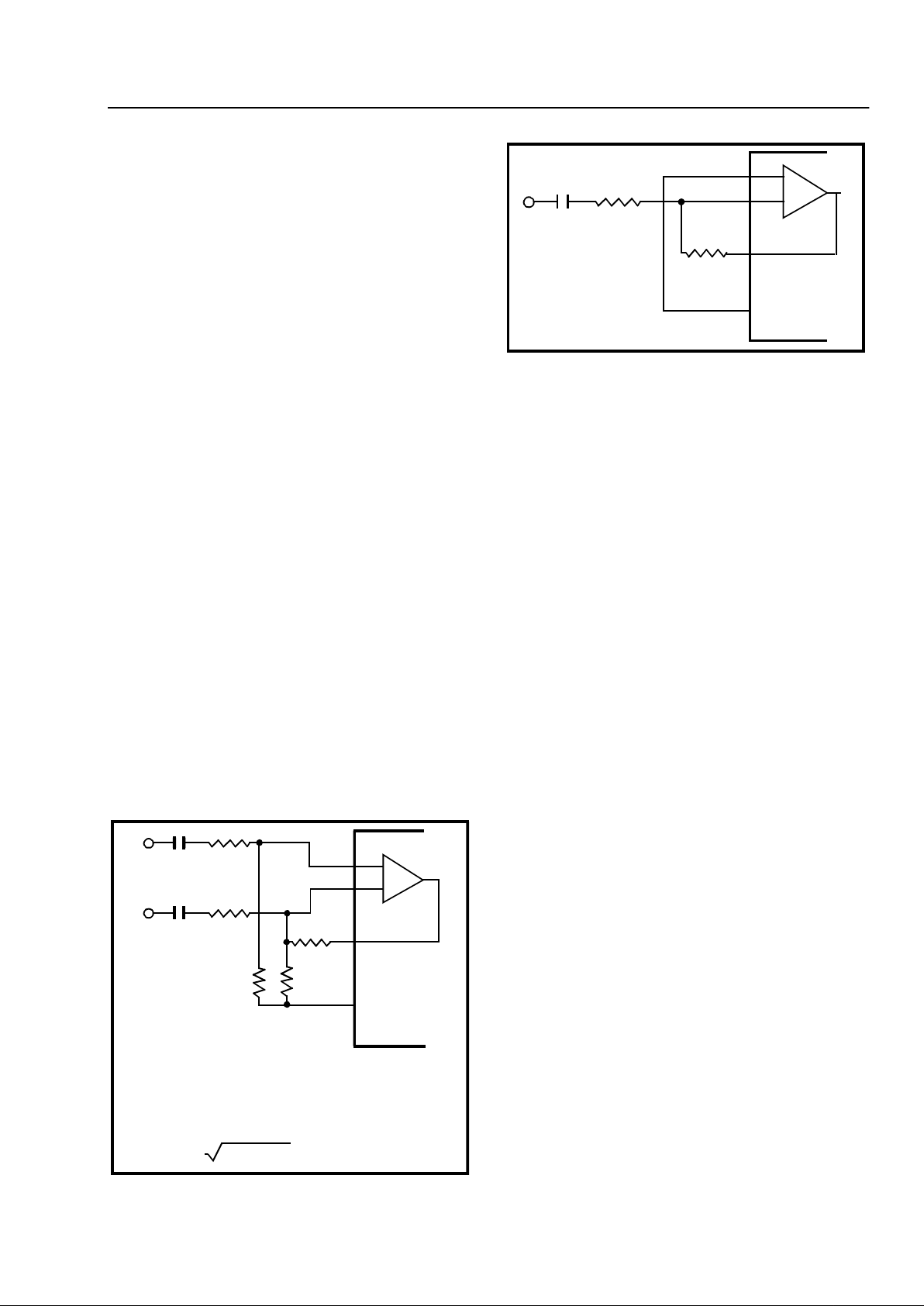
Figure 3 - Differential Input Configuration
C1
R1
C2
R4
R3
R2
R5
IN+
IN-
GS
V
Ref
MT8841
DIFFERENTIAL INPUT AMPLIFIER
C1 = C2 = 10 nF
R1 = R4 = R5 = 100 kΩ
R2 = 60kΩ, R3 = 37.5 kΩ
R3 = (R2R5) / (R2 + R5)
VOLTAGE GAIN
(A
V
diff) = R5/R1
INPUT IMPEDANCE
(Z
IN
diff) = 2
R1
2
+ (1/ωC)
2
Figure 4 - Single-Ended Input Configuration
at the called subscriber location either in the on-hook
case as in CND, or the off-hook case, as in
CIDCW. The functional block diagram of the CNIC
is shown in Figure 1. Note however, for CIDCW
applications, a separate CAS (CPE Alerting Signal)
detector is required.
In Europe, Caller ID and CIDCW services are being
proposed. These schemes may be different from
their North American counterparts. In most cases,
1200 baud CCITT V.23 FSK is used instead of Bell
202. Because the CNIC can also demodulate 1200
baud CCITT V.23 with the same performance, it is
suitable for these applications.
Although the main application of the CNIC is to
support CND and CIDCW service, it may also be
used in any application where 1200 baud Bell 202
and/or CCITT V.23 FSK data reception is required.
Input Configuration
The input arrangement of the MT8841 provides an
operational amplifier, as well as a bias source (V
Ref
)
which is u se d to b i as the inputs a t V
DD/2
. Provision is
made for connection of a feedback resistor to the opamp output (GS) for adjustment of gain. In a singleended configuration, the input pins are connected as
shown in Figure 4.
Figure 3 shows the necessary connections for a
differential input configuration.
User Interface
The CNIC provides a powerful 3-pin interface which
can reduce the external hardware and software
requirements. The CNIC receives the FSK signal,
demodulates it, and outputs the extracted data to the
DATA pin. For each received stop bit start bit
sequence, the CNIC outputs a fixed frequency clock
string of 8 pulses at the DCLK pin. Each clock rising
C
R
IN
IN+
IN-
GS
V
Ref
MT8841
VOLTAGE GAIN
(A
V
) = RF / R
IN
R
F
 Loading...
Loading...