Page 1
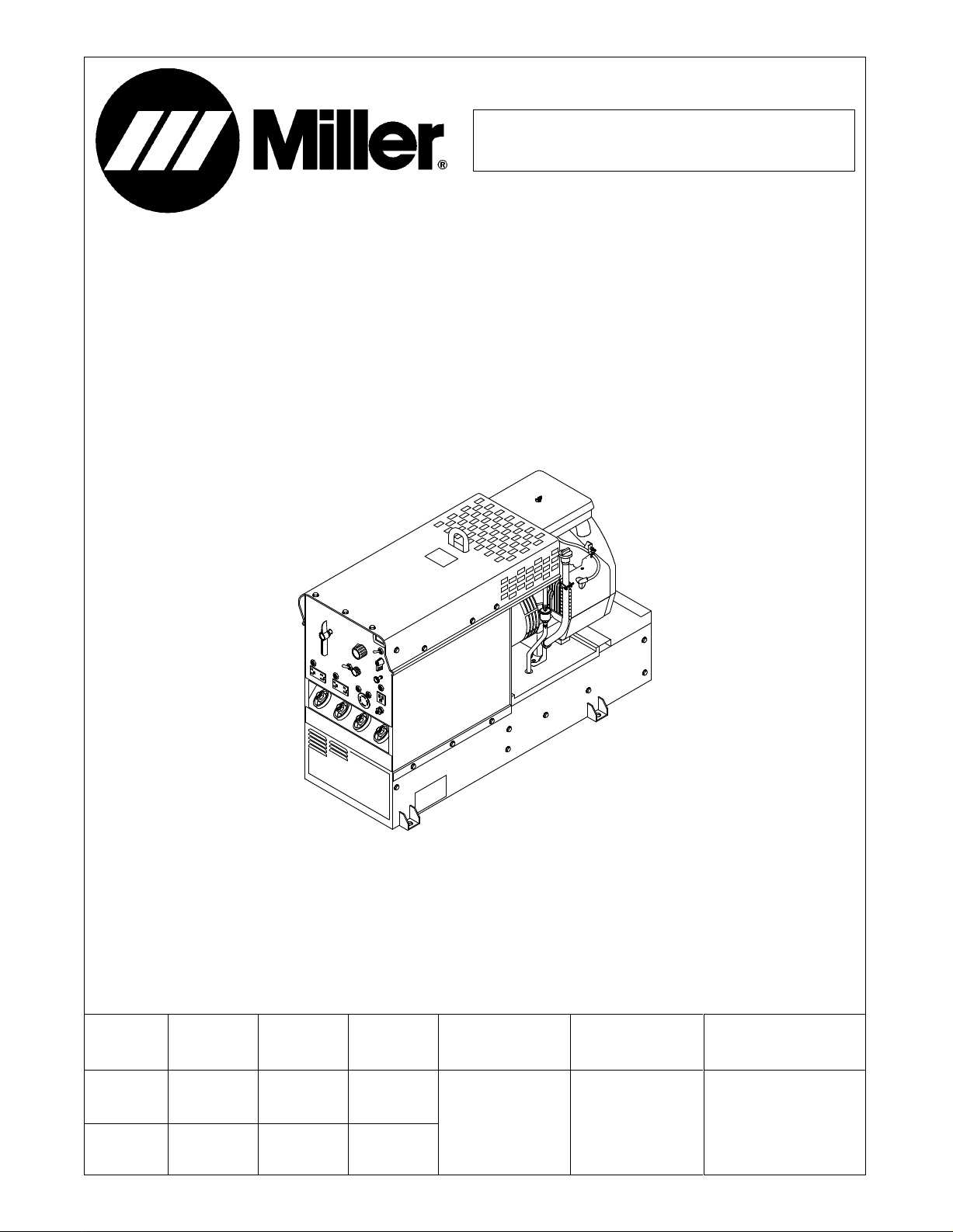
February 1996 Form: TM-428
T
Effective With Serial No. JH242114
TECHNICAL MANUAL
Service And Parts
Miller Legend
(Formerly The Legend AEAD-200LE)
CC AC/DC Welding Generator For SMAW, GMAW, GTAW Welding
Welding
Mode
CC/AC 35
CC/DC
cover_tm 4/95 – ST-140 091-E PRINTED IN USA
Weld
Output
Range
– 225 A
25 – 200 A
Rated
Welding
Output
225 A, 25 V
100% Duty
Cycle
200 A, 25 V
100% Duty
Cycle
Maximum
Open-Circu
it Voltage
,
,
Auxiliary Power
Rating
Single-Phase,
80
72
5 kVA/kW
120/240 V AC, 60 Hz
And
Single-Phase,
1 kVA/kW
1
15 V AC, 100 Hz
1996 MILLER Electric Mfg. Co.
, 42/21 A,
, 9 A,
Fuel Capacity Engine
Onan P218 Air-Cooled,
-
7.5 gal (28 L) T
ank
wo-Cylinder, Four-Cycle,
Gasoline Engine
-
Page 2
TABLE OF CONTENTS
SECTION 1 – SAFETY PRECAUTIONS FOR SERVICING 1.
1-1. Symbol Usage 1.
1-2. Servicing Hazards 1.
1-3. EMF Information 2.
SECTION 2 – INSTALLATION 3.
2-1. Installing Welding Generator 3.
2-2. Dimensions, Weights, And Operating Angles 3.
2-3. Fuel Consumption 4.
2-4. Engine Prestart Checks 4.
2-5. Connecting The Battery 5.
2-6. Connecting To Weld Output Terminals 5.
2-7. Selecting Weld Cable Sizes 6.
2-8. Remote 14 Receptacle RC1 Information 6.
SECTION
3 – OPERA
3-1. Front Panel Controls 7.
3-2. Remote Control (Optional) 8.
3-3. Duty Cycle 8.
3-4. Volt-Ampere Curves 9.
SECTION
4 – OPERA
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
TING WELDING GENERATOR 7.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
TING AUXILIAR
Y EQUIPMENT
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-1. 100 Hz Auxiliary Power Receptacle And Circuit Breaker 10.
4-2. AC Auxiliary Power Curve 10.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-3. 60 Hz Auxiliary Power Receptacles And Circuit Breakers 11.
SECTION 5 – THEOR
Y OF OPERA
TION 12.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
10.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SECTION 6 – TROUBLESHOOTING 15.
6-1. Troubleshooting Tables 15.
6-2. Troubleshooting Circuit Diagram For Welding Generator 18.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6-3. Troubleshooting Circuit Diagram For Welding Generator With Optional Remote Control 20.
6-4. Waveforms For Sections 6-2 And 6-3 22.
6-5. Idle Control Board/Module PC1 Testing Information 23.
6-6. Troubleshooting Flowcharts For Idle Control Board/Module PC1 24.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6-7. Voltage Regulator Board PC2 Testing Information Prior To Serial No. KE604176 26.
6-8. Voltage Regulator Board PC2 Test Point Values Prior To Serial No. KE604176 26.
6-9. Voltage Regulator Board PC2 Testing Information Effective With Serial No. KE604176 27.
6-10. Voltage Regulator Board PC2 Test Point Values Effective With Serial No. KE604176 27.
6-11. Optional Remote Control Board PC3 Testing Information 28.
6-12. Optional Remote Control Board PC3 Test Point Values 28.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6-13. Optional Remote Capacitor Board PC5 Testing Information Effective With
Serial No. KD346698 29.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6-14. Optional Remote Capacitor Board PC5 Test Point Values Effective With
Serial No. KD346698 29.
6-15. Replacing Brushes And Cleaning Slip Rings 30.
6-16. Checking Unit Output After Servicing 32.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
WHO DO I CONTACT FOR HELP?
H CALL:
Miller Customer Service
Department at
414-735-4505
H FAX:
800-637-2348
or
414-735-4136 (outside USA)
(in USA),
H WRITE:
Miller Electric Mfg. Co.
P
.O. Box 1079
Appleton, WI 54912 USA
.
. . . . . . .
. . . . . . . .
. .
. . .
Always provide Model Name and Serial or Style Number
OM-428N 1/96 – SPM-428C 6/94
Page 3

SECTION 7 – DISASSEMBL
7-1. Disassembly Of Unit 33.
7-2. Disassembly Of Generator 34.
SECTION 8 – MAINTENANCE 35.
8-1. Routine Maintenance 35.
8-2. Maintenance Label 36.
8-3. Servicing Air Cleaner 37.
8-4. Changing Engine Oil, Oil Filter, And Fuel Filter 38.
8-5. Adjusting Engine Speed 39.
8-6. Overload Protection 40.
8-7. Inspecting And Cleaning Optional Spark Arrestor 40.
SECTION 9 – ELECTRICAL DIAGRAMS 41.
Y AND REASSEMBL
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Y 33.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SECTION 10 – PARTS LIST 51.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Page 4

Page 5

SECTION 1 – SAFETY PRECAUTIONS FOR SERVICING
safety_rtm1 4/95
1-1. Symbol Usage
Y
Means Warning! Watch Out! There are possible hazards with this
procedure!
The possible hazards are shown in the adjoining symbols.
This group of symbols means Warning! Watch Out! possible ELECTRIC SHOCK, MOVING
and HOT PARTS hazards. Consult symbols and related instructions below for necessary
PARTS,
actions
to avoid the hazards.
1-2. Servicing Hazards
WARNING
The symbols shown below are used throughout this manual to call attention to and identify possible
hazards. When you see the symbol, watch out, and follow the related instructions to avoid the hazard.
Only qualified persons should service, test, maintain, and repair this unit.
During servicing, keep everybody, especially children, away.
Marks a special safety message.
.
Means NOTE; not safety related.
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill.
1. Do
not touch live electrical parts.
2. Stop
3. Insulate yourself from ground by standing or
4.
5. When
engine before testing or repairing unit unless
the procedure specifically requires an energized
unit.
working on dry insulating mats big enough to
contact with the ground.
prevent
Do not leave live unit unattended.
testing live unit, use
Do not put both hand inside unit. Keep one
free.
the one-hand method.
hand
MOVING PARTS can cause injury.
1. Keep
2. Have only qualified people remove guards or
3. Keep hands, hair, loose clothing, and tools away
4. Before
5. Block
6.
FLYING
away from moving
and
rotors.
covers for maintenance and troubleshooting as
necessary.
moving parts.
from
working on generator
or injectors to keep engine from kicking back or
starting.
flywheel so that it will not
on
generator components.
Reinstall panels or
servicing is finished and before starting engine.
PIECES
parts such as fans, belts,
, remove spark plugs
turn while working
guards and close doors when
OF MET
AL or DIRT can
cause injury.
1. Always wear safety glasses with side shields or
face
shield during servicing.
2. Be
careful not to short metal tools, parts, or wires
together
during testing and servicing.
STATIC
ELECTRICITY
can damage parts
on circuit boards.
1. Put on grounded wrist strap BEFORE handling
boards
or parts.
2. Use proper static-proof bags to store, move, or
ship
PC boards.
ENGINE EXHAUST GASES can kill.
1. Do
not breathe exhaust fumes.
2. Use in open, well-ventilated areas, or vent
exhaust outside and away from any building air
intakes.
ENGINE FUEL can cause fire or
explosion.
1. Stop
2. Do not fuel while smoking or near sparks or
3. Do
engine before fueling.
flames.
not overfill tank; clean up any spilled fuel.
BATTERY EXPLOSION can BLIND and
INJURE.
1. Always wear a face shield when working on a
battery.
2. Stop engine before disconnecting or connecting
battery
cables.
3. Do
not allow tools to cause sparks when working
on a battery
4. Do
not use welder to charge batteries or jump
vehicles.
5. Observe
.
start
correct polarity (+ and –) on batteries.
BATTERY ACID can BURN SKIN.
1. Do
not tip.
2.
Replace damaged battery
Flush eyes and skin immediately with water
3.
.
.
STEAM AND PRESSURIZED HOT
COOLANT can burn face, eyes, and
skin.
1. Check coolant level when
scalding.
2. If the engine is warm and checking is needed,
3. Wear
4. Turn cap slightly and let pressure escape slowly
steps 3 and 4.
follow
safety glasses and gloves and put a rag over
cap.
completely removing cap.
before
engine is cold to avoid
FALLING EQUIPMENT can cause
serious personal injury and equipment
damage.
1. Use equipment of adequate capacity to lift
components.
a lifting eye to lift unit only, NOT running gear
2. Use
gas cylinders, or any other accessories.
3.
Securely attach components to lifting
equipment.
,
Miller Legend
TM-428 Page 1
Page 6
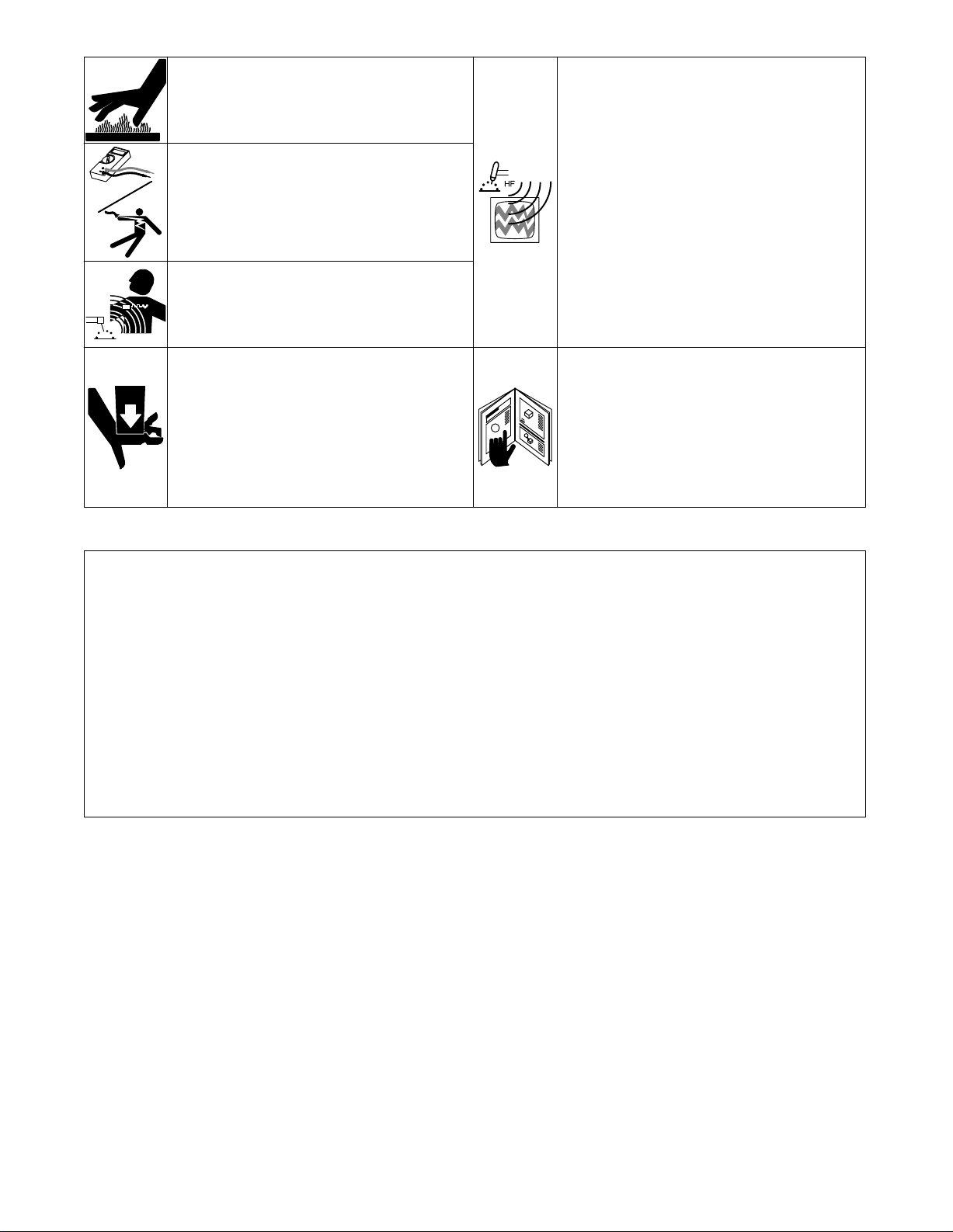
HOT PARTS can cause severe burns.
1. Allow
2. Wear
cooling period before servicing.
protective gloves and clothing when working
on
a hot engine.
ELECTRIC SHOCK HAZARD from
incorrect use of test equipment.
1. Stop engine before making or changing meter
connections.
lead
2. At
least one meter lead should be a self-retaining
spring
clip such as an alligator clamp.
3.
Read instructions for test equipment.
MAGNETIC FIELDS FROM HIGH
CURRENTS can affect pacemaker
operation.
1. Pacemaker wearers keep away from servicing
areas
until consulting your doctor
.
UNCONTROLLED TILTING OR TIPPING
OF UNIT can result in personal injury
and equipment damage.
1. Do
not put any body part under unit while lifting.
2. Use adequate blocks to support components as
needed
during job.
PINCH POINTS can injure.
1. Be careful when working on stator and rotor
assemblies.
HIGH-FREQUENCY RADIATION can
interfere with radio navigation, safety
services, computers, and
communications equipment.
1. Have only qualified persons familiar with
electronic
2. The user is responsible for having a qualified
electrician promptly correct any interference
problem
3. If notified by the FCC about interference, stop
using
4. Have the installation regularly checked and
maintained.
5. Keep high-frequency source doors and panels
tightly shut, keep spark gaps at correct setting,
and use grounding and shielding to minimize the
possibility
equipment perform this installation.
resulting from the installation.
the equipment at once.
of interference.
READ INSTRUCTIONS.
1. Use MILLER Testing Booklet (Part No. 150 853)
when
servicing this unit.
2. Consult the Owner’s Manual for welding safety
precautions.
3. Use
only genuine MILLER replacement parts.
4. Reinstall injectors and bleed air from fuel system
according to engine manual.
1-3. EMF Information
Considerations
Electric
The
following is a quotation from the
of
the U.S. Congress, Of
Effects of Power Frequency Electric & Magnetic Fields –
Background Paper
Government Printing Office, May 1989): “. . . there is now a very
large volume of scientific findings based on experiments at the
cellular
establish that low frequency magnetic fields can interact with, and
produce
very high quality, the results are complex. Current scientific
understanding does not yet allow us to interpret the evidence in a
single coherent framework. Even more frustrating, it does not yet
allow us to draw definite conclusions about questions of possible
risk
or to of
or
avoid potential risks.”
About W
And Magnetic Fields
level and from studies with
changes in, biological systems.
fer clear science-based advice on strategies to minimize
elding And The Ef
fice of T
echnology Assessment,
, OTA-BP-E-53 (Washington, DC: U.S.
animals and people which clearly
fects Of Low
General Conclusions Section
While most of this work is of
Frequency
Biological
To reduce magnetic fields in the workplace, use the following
procedures:
1. Keep
2.
3.
4.
5.
About Pacemakers:
The above procedures are also recommended for pacemaker
wearers.
cables close together by twisting or taping them.
Arrange cables to one side and away from the operator
Do not coil or drape cables around the body
Keep welding power source and cables as far away as
practical.
Connect work clamp to workpiece as close to the weld as
possible.
Consult your doctor for complete information.
.
.
TM-428 Page 2
Miller Legend
Page 7
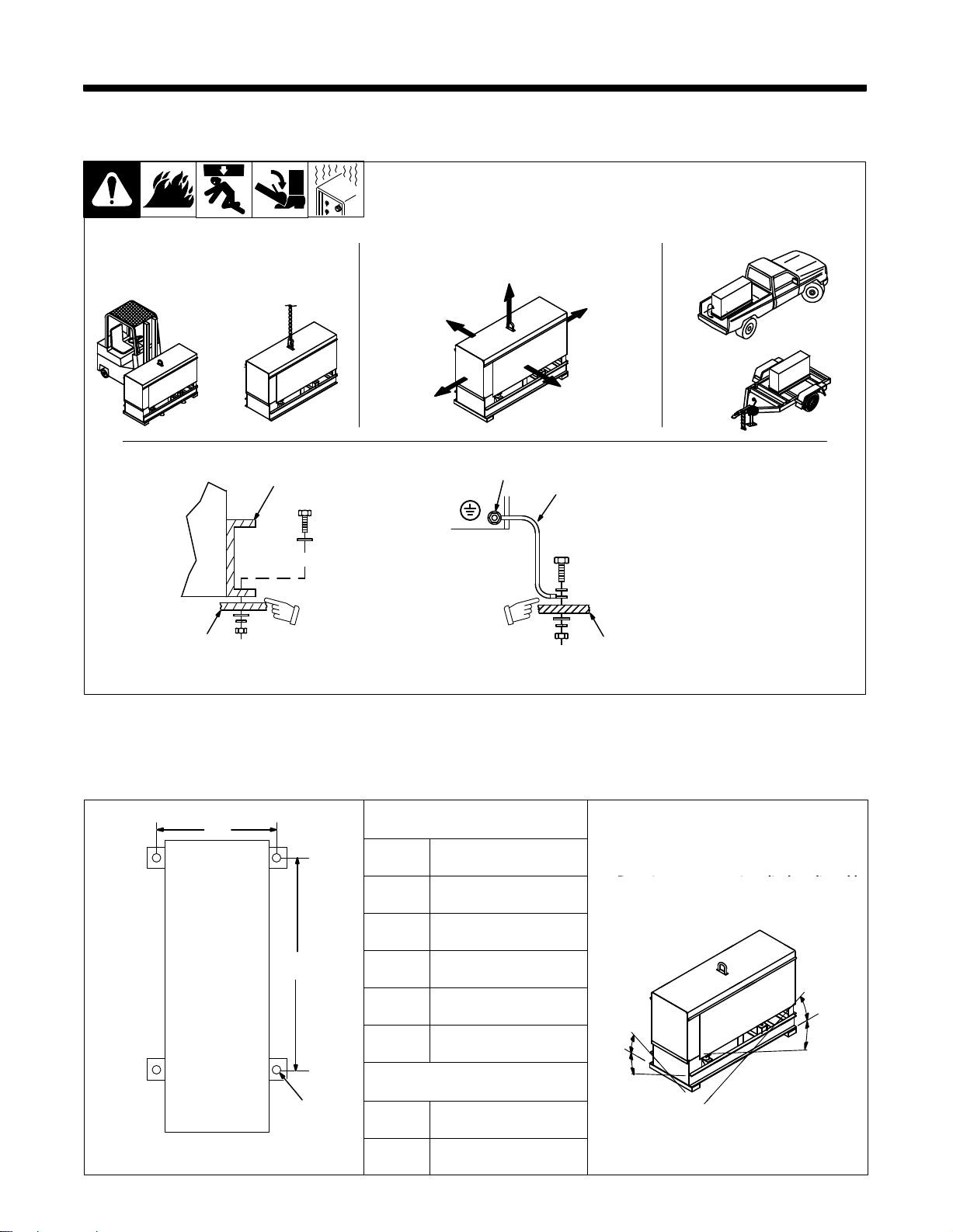
SECTION 2 – INSTALLATION
A
2-1. Installing Welding Generator
Movement Airflow Location
Y Do Not Lift Unit From End
18 in
(460 mm)
OR
18 in
(460 mm)
18 in
(460 mm)
OR
18 in
(460 mm)
Grounding
1
OR
Electrically
2
vehicle frame by metal-to-metal
contact.
bond
generator frame to
3
GND/PE
2-2. Dimensions, Weights, And Operating Angles
A
Height 31-5/8
Width 18
Dimensions
in (803 mm)
in (457 mm)
18 in
(460 mm)
1 Generator Base
Metal V
4
2
install1 10/95 – Ref. ST-800 652 / Ref. ST-800 477-A / ST-158 936-A / S-0854
Y Do not exceed operating angles while
running
Y Do
tip.
2
3
4
Use #10 AWG or larger insulated
copper
Y If unit does not have GFCI
or engine damage will occur
not move or operate unit where it could
ehicle Frame
Equipment Grounding
Terminal
Grounding Cable
wire.
receptacles, use GFCI-pro-
extension cord.
tected
.
Miller Legend
Engine End
Depth 45
B
A 16-1/2
B 32-3/4
C 13/16
in (1
143 mm)
in (419 mm)
in (832 mm)
in (21 mm) Dia.
25°
25°
25°
25°
°
Weight
C
Net 559
Ship 600
lb (254 kg)
lb (272 kg)
TM-428 Page 3
Page 8
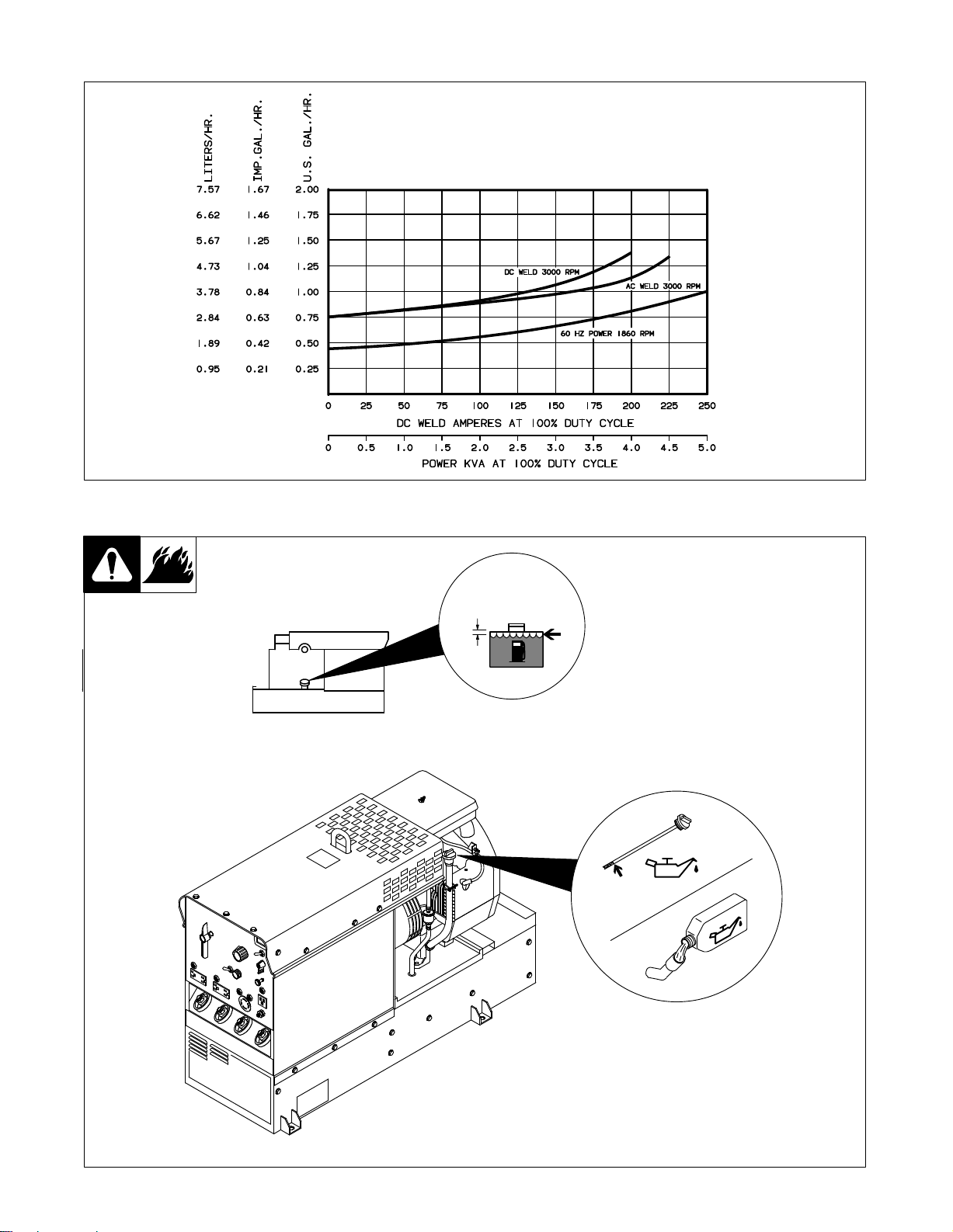
2-3. Fuel Consumption
SB-115 572
2-4. Engine Prestart Checks
1/2 in
(13 mm)
Full
Check
all fluids daily
be
cold and on a level surface.
Engine stops if oil pressure gets
low
.
too
Full
. Engine must
TM-428 Page 4
ST-140 091-E / Ref. ST-151 983
Miller Legend
Page 9
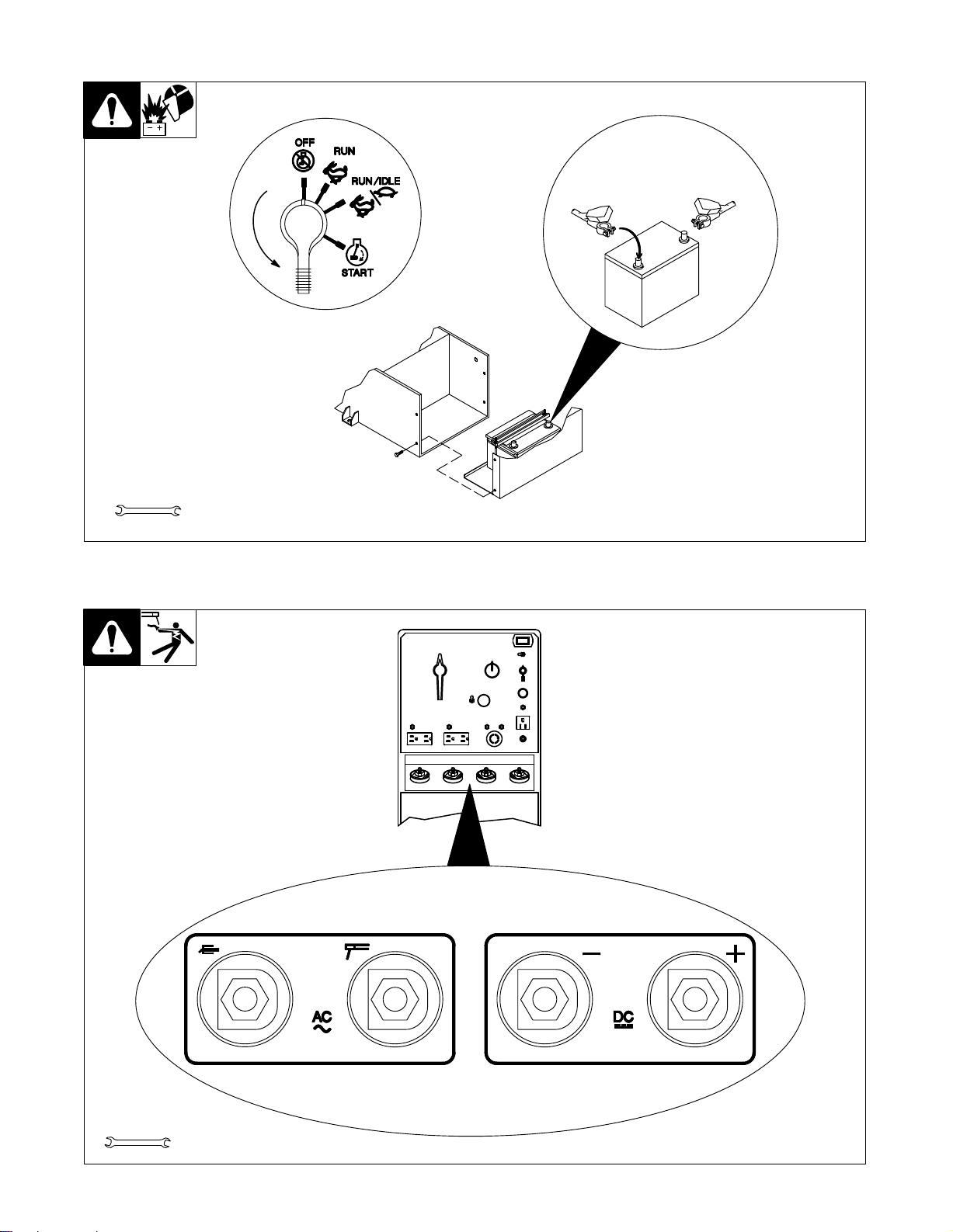
2-5. Connecting The Battery
Y
Connect (–) cable last.
Tools
Needed:
3/8, 1/2 in
2-6. Connecting To Weld Output Terminals
+
–
Ref. ST-144 839-F / Ref. ST-168 046 / Ref. S-0756-D
Y Use ONLY one set of termi-
nals at a time. Disconnect
cables from
weld
output
terminals not in use.
set of weld
Tools
Miller Legend
Needed:
3/4 in
ST-140 092-B / Ref. ST-168 046
TM-428 Page 5
Page 10
2-7. Selecting Weld Cable Sizes
B
A
Total Cable (Copper) Length In Weld Circuit Not Exceeding
100 ft (30 m) Or Less
Welding
Amperes
100 4 4 4 3 2 1 1/0 1/0
150 3 3 2 1 1/0 2/0 3/0 3/0
200 3 2 1 1/0 2/0 3/0 4/0 4/0
250 2 1 1/0 2/0 3/0 4/0 2-2/0 2-2/0
300 1 1/0 2/0 3/0 4/0 2-2/0 2-3/0 2-3/0
350 1/0 2/0 3/0 4/0 2-2/0 2-3/0 2-3/0 2-4/0
Weld cable size (A
10 – 60%
Duty Cycle
WG) is based on either a 4 volts or less drop or a current density of at least 300 circular mils per ampere.
60 – 100%
Duty Cycle
150 ft
(45 m)
200 ft
(60 m)
250 ft
(70 m)
300 ft
(90 m)
10 – 100% Duty Cycle
350 ft
(105 m)
2-8. Remote 14 Receptacle RC1 Information
Socket* Socket Information
400 ft
(120 m)
S-0007-D
AJ
K
B
L
C
D
*The remaining sockets are not used.
I
NH
M
G
F
E
ST-140 092-B
A Contact
B 15 volts dc.
C +4.5
D Remote
E 0
K Chassis
closure to B completes 15 volts dc contactor control
circuit.
volts dc output to remote control.
control circuit common.
to +4.5 volts dc input command signal from remote control.
common.
TM-428 Page 6
Miller Legend
Page 11
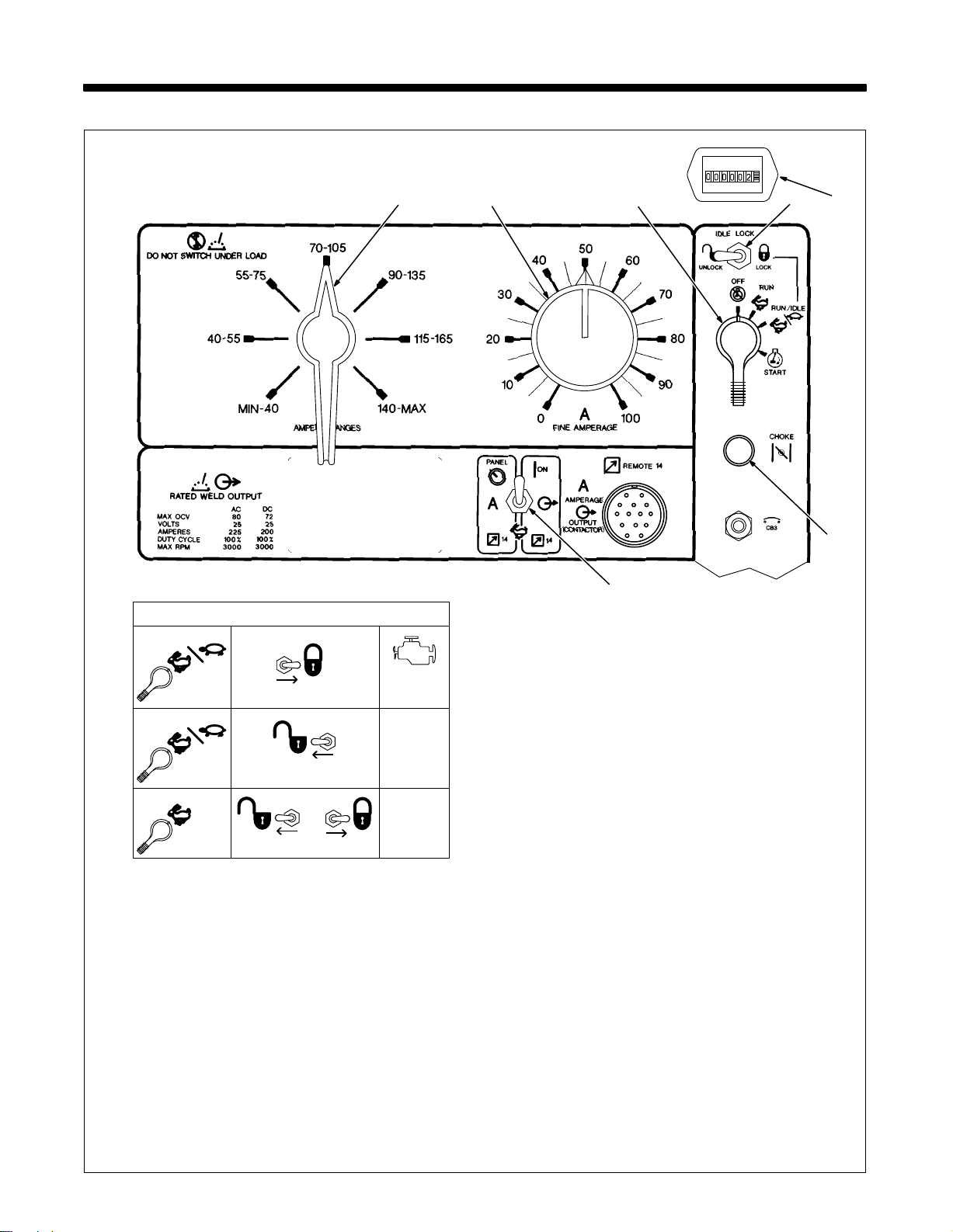
SECTION 3 – OPERATING WELDING GENERATOR
3-1. Front Panel Controls
RUN/IDLE
Using Idle Lock Switch
6 7
15
2
3
4
LOCK
RUN/IDLE
UNLOCK
RUN
OR
1 Engine
Control Switch S2
Use switch to start engine, select speed,
and stop engine. In Run/Idle position, en-
runs at power/idle rpm at no load, and
gine
weld/power
iary
engine
2
rpm under weld or 100 Hz auxil
power receptacle load. In Run
runs at weld rpm.
Idle Lock Switch S1
position,
Use switch to lock engine at power/idle
speed (see Table). In Unlock position, Engine Control switch and optional Remote
switch determine engine speed.
Control
3
Engine Choke Control
1860 rpm
(Power/Idle)
No Load:
1860 rpm
(Power/Idle)
Load:
3000 rpm
(Weld)
3000 rpm
LOCKUNLOCK
(Weld)
Use control to change engine air-fuel mix.
To Start: pull out choke and turn Engine
Control switch to Start position. Release
switch and slowly push choke in when en-
-
gine starts. Do not crank engine while fly-
is turning.
wheel
To Stop: turn Engine Control switch to Off
position.
4 Remote
Control Switch S4
Use switch to select front panel or remote
amperage
5
control (see Section 3-2).
Ampere Ranges Switch S5
Ref. ST-168 046
Use
switch to select weld amperage range.
.
For best arc starts, use lowest amper-
range possible.
age
6
Fine Amperage Control R1
Use
control to select
weld amperage within
the range selected by the Ampere Ranges
Control
switch.
Scale is
ing.
may be adjusted while weld
for reference only
. W
eld output
would be 88 A DC with control settings as
(50% of 70 to 105 A).
shown
7
Engine Hour Meter HM
-
Miller Legend
TM-428 Page 7
Page 12
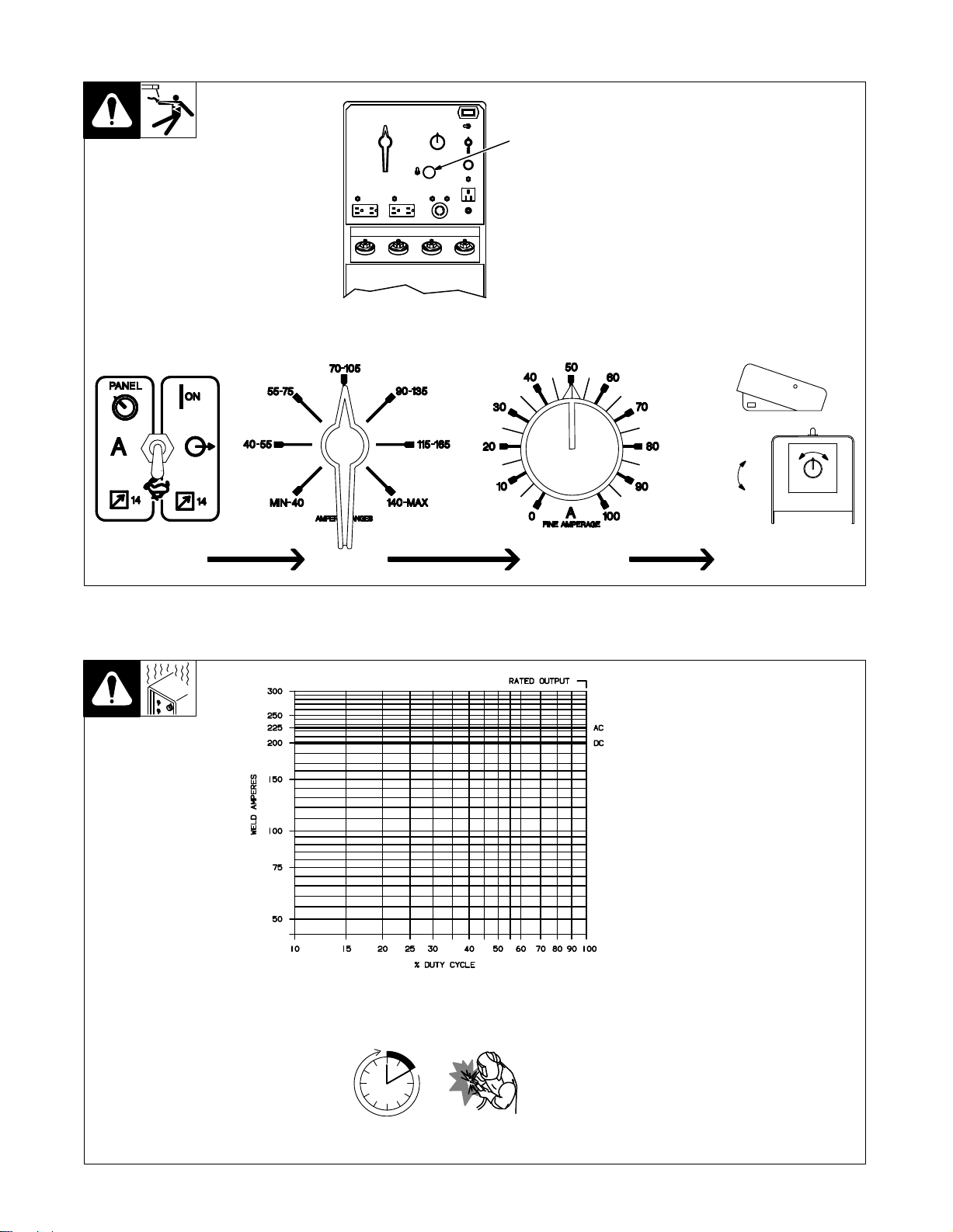
3-2. Remote Control (Optional)
Y Weld output terminals are
energized when Remote
1
Control switch S4 is in Pan-
position and engine is
el/On
running.
1 Remote
Connect
RC1
Percentage Of Range = 50%
Max = 88 A DC (50% of 70 to 105)
14 Receptacle RC1
optional remote control
(see Section 2-8).
In Example:
Min = 70
A DC
to
Set Switch
3-3. Duty Cycle
Set Range
Set Percentage
Max (88
Min (70
Duty
minutes
load
Y Exceeding duty cycle can
A DC)
A DC)
Adjust Remote Control
cycle is the percentage of 10
that unit can weld at
without overheating.
damage unit and void warranty.
ST-140 092-B
rated
TM-428 Page 8
100% Duty Cycle at 225 Amperes AC
Continuous Welding
SB-115 570
Miller Legend
Page 13
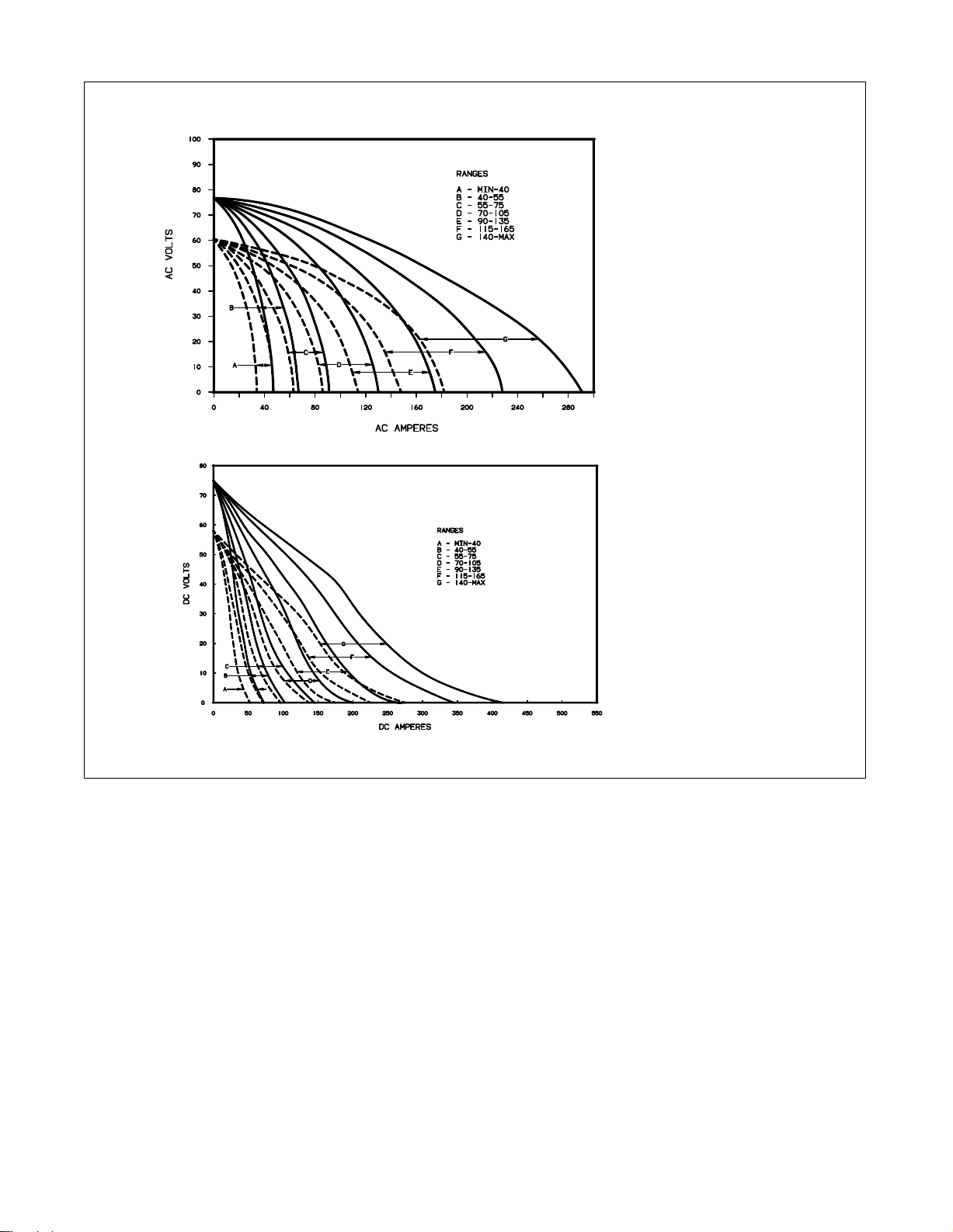
3-4. Volt-Ampere Curves
The volt-ampere curves show the
minimum and maximum voltage
and amperage output capabilities
the welding generator
of
other settings fall between the
shown.
curves
. Curves of
Miller Legend
SB-115 529-A / SB-115 528-A
TM-428 Page 9
Page 14
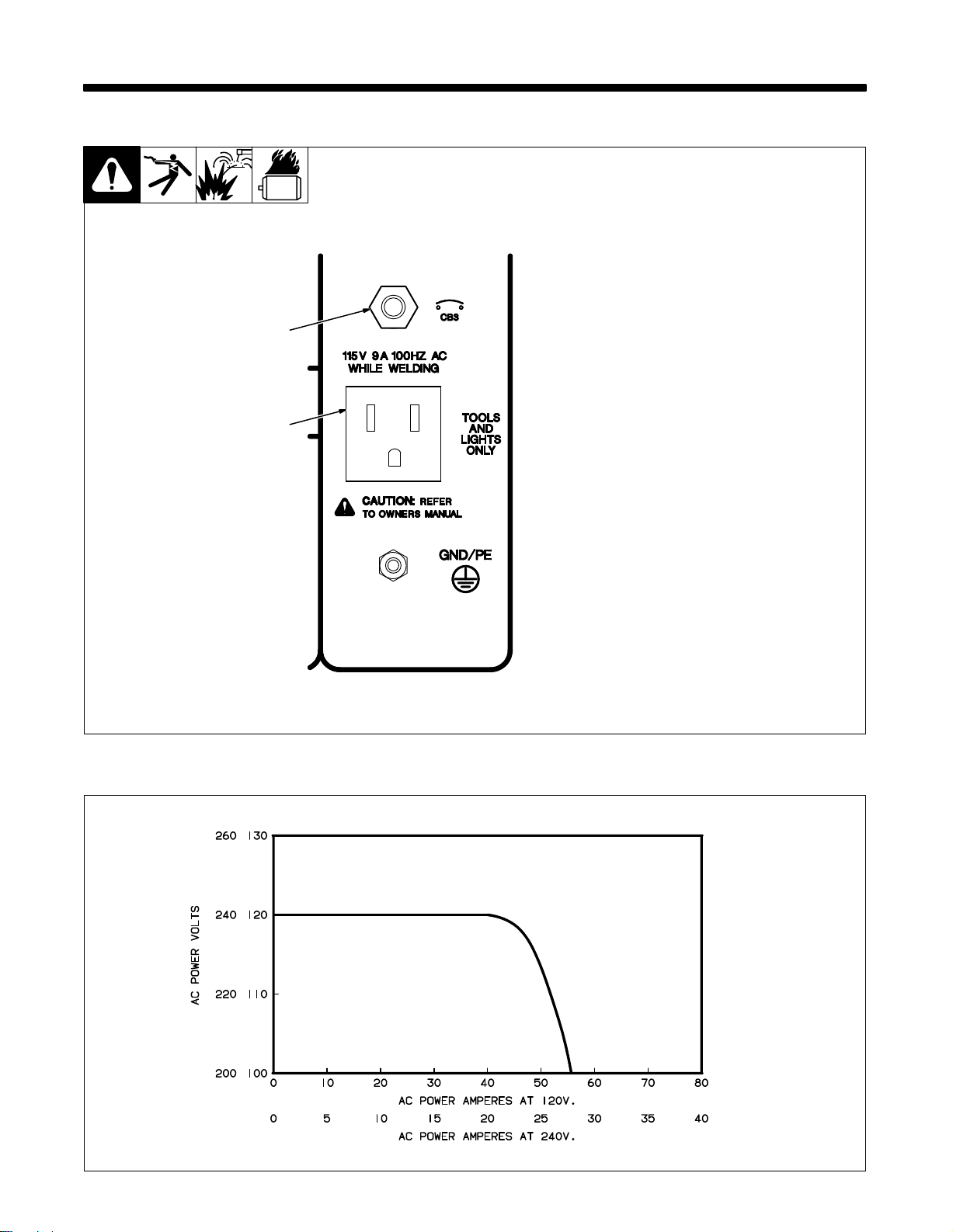
SECTION 4 – OPERATING AUXILIARY EQUIPMENT
4-1. 100 Hz Auxiliary Power Receptacle And Circuit Breaker
2
1
Y Do not operate 50/60 Hz or
60 Hz equipment from 100
receptacle.
Hz
11
15 V 9 A 100 Hz AC Recep
tacle RC4
Receptacle supplies single-phase
power at weld speed only. Total
available is 1 kV
output
2 Circuit Breaker CB3
CB3 protects receptacle from
overload.
does
If CB3 opens, receptacle
not work.
A/kW.
-
4-2. AC Auxiliary Power Curve
Ref. ST-168 046
SB-115 571
TM-428 Page 10
Miller Legend
Page 15
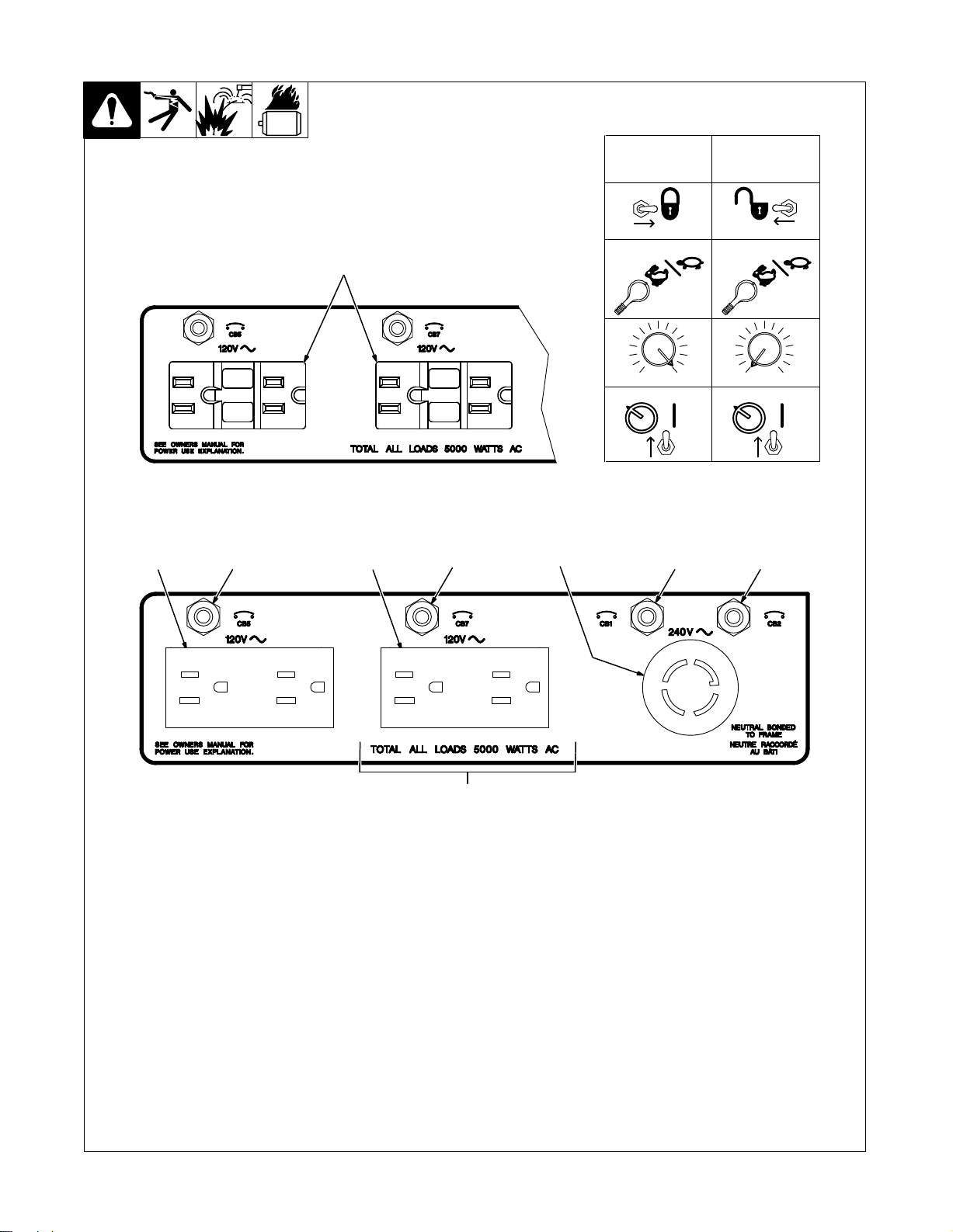
4-3. 60 Hz Auxiliary Power Receptacles And Circuit Breakers
4
5 7812
6
3
For 60 Hz
Auxiliary Power
While W
elding
LOCK UNLOCK
RUN/IDLE RUN/IDLE
0 100
PANEL
ON
For 60 Hz
Auxiliary
Power Only
0 100
PANEL
ON
YIf unit does not have GFCI recep-
tacles, use GFCI-protected exten-
cord.
sion
1 120
V 15 A AC
2
120 V 15 A AC Duplex Receptacle RC2
3 240
V 30 A T
Duplex Receptacle RC1
wistlock Receptacle RC3
Receptacles supply 60 Hz single-phase
power at power/idle speed only. Maximum
from each duplex receptacle
output
kVA/kW
. Maximum output from twistlock re
ceptacle is 5 kVA/kW. For 60 Hz auxiliary
set controls as shown in table.
power,
4
120 V 15 A AC Duplex GFCI Recep
tacles GFCI1 And GFCI2 (Optional)
If a ground fault is detected, the GFCI recep
Miller Legend
is is 2.5
-
9
tacle Reset button pops out and the circuit
opens to disconnect the faulty equipment.
for damaged tools, cords, plugs, etc.
Check
connected
reset
.
to the receptacle. Press button to
receptacle and resume operation.
At least once a month, run engine at
power/idle
speed and press T
to verify GFCI is working properly.
5 Circuit Breaker CB5
-
6 Circuit Breaker CB7
CB5 protects RC1 and CB7 protects RC2
overload. If CB5 or CB7 opens, the re
from
ceptacle does not work. Press button to re-
breaker
set
-
7 Circuit Breaker CB1
.
est
button
Ref. ST-168 046
8 Circuit Breaker CB2
CB1 and CB2 protect all the 60 Hz recep-
tacles from overload. If CB1 or CB2 opens,
the 240 volt receptacle and one of the 120
volt receptacles does not work. 120 volts
may still be present at the 240 volt recep-
Press button to reset breaker
tacle.
otal Auxiliary Power Output
9T
Combined output of receptacles limited to
A/kW output of the generator:
the 5 kV
EXAMPLE:
plex
240
(120
If 10 A is drawn from a 120 V du
receptacle, only 16 A is available at the
V receptacle:
V x 10 A) + (240 V x 16 A) = 5.0 kV
TM-428 Page 1
.
-
A/kW
1
Page 16
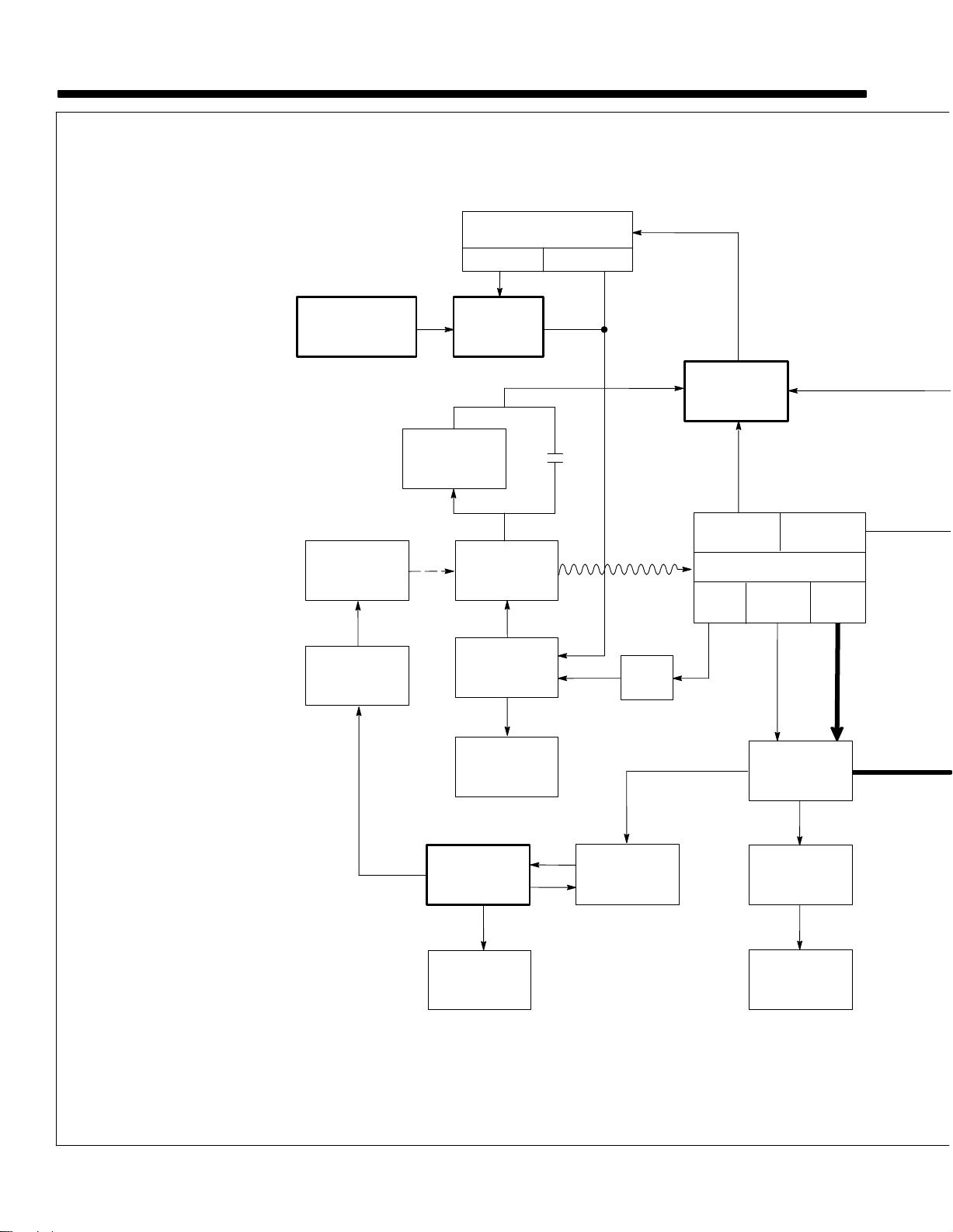
SECTION 5 – THEORY OF OPERATION
1 Engine
Supplies force to turn revolving
fields.
2 Revolving
Turn
at 1860 rpm maximum for pow
er/idle and 3000 rpm maximum for
weld.
The speed and excitation cur
rent of the field coils determine volt
ages in stator windings.
3
Stator Windings
Supply power to exciter, auxiliary
power,
4
Fuse F1
Protects exciter excitation winding
overload.
from
5
Integrated Rectifier SR2
Changes ac output of stator windings
to dc to supply excitation current
to
the exciter revolving field.
6
Control Relay CR5
Energizes
exciter stator to disconnect field
flashing circuit.
Idle Module PC1 And Idle Lock
7
Switch S1
PC1 and S1 control engine speed.
Without
ers engine speed to power/idle rpm.
8 Throttle
Increases
when
energized.
9
Current T
Senses output from either weld or
100 Hz auxiliary power windings,
and signals PC1 to increase to or
maintain
10 Control Relays CR2, CR3, CR4
CR2
energizes at weld rpm to supply
power
CR3 energizes at power/idle rpm to
bypass
CR4 energizes at power/idle rpm to
provide 50/60 Hz auxiliary power
output.
11 Voltage
And T
PC2 monitors 50/60 Hz auxiliary
power
tains
proper output by adjusting
current.
12 Capacitor
14 Receptacle RC1, Remote
Control Board PC3
PC5
protects unit from high frequen
cy.
RC1
and contactor control to unit through
control
Fields (Rotor)
and weld circuits.
when voltage is present in
a signal from CT1, PC1 low
Solenoid TS1
engine speed to weld rpm
ransformer CT1
weld rpm.
to throttle solenoid TS1.
fine amperage control R1.
Regulator Board PC2
ransformer T1
voltage through T1, and main
field
Board PC5, Remote
connects remote amperage
board PC3.
-
-
-
♦
12
Capacitor Board
PC5
And Remote 14
Receptacle RC1
18
Amperage
Control R1
1
-
-
-
8
Engine
Throttle
Solenoid
TS1
7
10
♦
13
Remote Control
Remote 14
♦
12
Remote
Control Board
PC3
Fine
2
Revolving
Fields (Rotor)
5
Integrated
Rectifier SR2
♦
6
Control
Relay
CR5
Idle Module
PC1
Control Relays
CR2, CR3, CR4
Switch S4
Panel
CR3
7
4
Fuse
F1
Idle Lock
Switch S1
11
3
Exciter
Voltage
Regulator
Board PC2
Voltage
Regulator
Stator Windings
9
16
17
60 Hz Auxiliary
Power
100 Hz
Auxiliary
Power
Current
Transformer
Breaker
100 Hz
Auxiliary Power
Receptacle RC4
Weld
CT1
Circuit
CB3
TM-428 Page 12
Miller Legend
Page 17
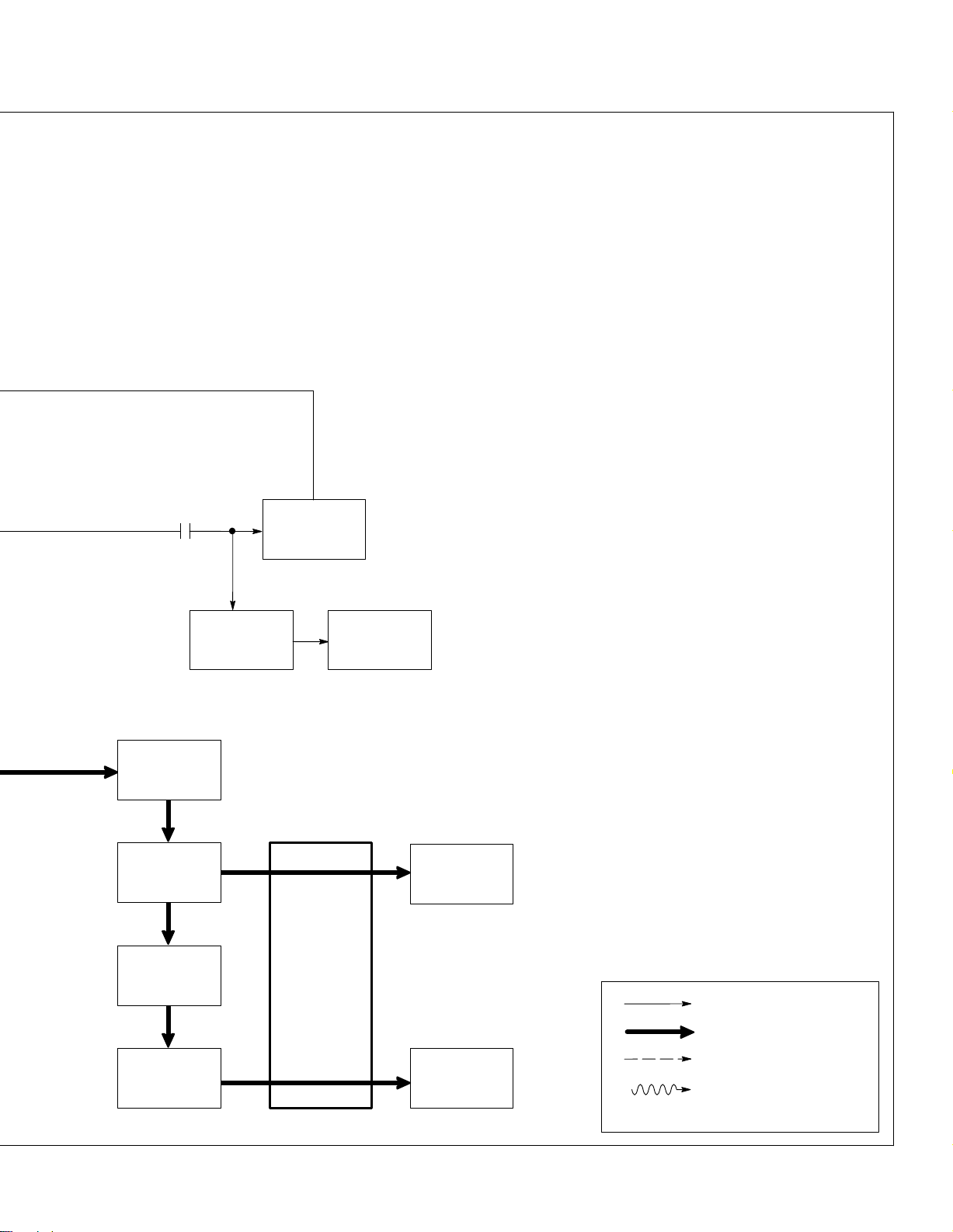
19
20
CR4
14 15
Circuit
Breakers
CB1, CB2,
CB5, CB7
Ampere
Ranges
Switch S5
Reactor
AC-Z
11
Transformer
23
T1
Auxiliary Power
Receptacles
RC1, RC2, RC3
50/60 Hz
25
Electrode
Work AC Weld
Output
T erminals
And
13
Remote Control Switch S4
Selects
Panel or remote
control.
14 Circuit Breakers CB1, CB2,
CB5, And CB7
Protect 50/60 Hz auxiliary power
receptacles RC1, RC2, and RC3
from
overload.
15
50/60 Hz Auxiliary Power Re
ceptacles RC1, RC2, And
RC3
Provide connection points and
for auxiliary equipment.
power
16 Circuit Breaker CB3
Protects
100 Hz auxiliary power
ceptacle
RC4 from overload.
17 100 Hz Auxiliary Power Re-
ceptacle RC4
Provides connection point and
power for auxiliary equipment
while
welding.
18
Fine Amperage Control R1
Adjusts
amperage
lected by Ampere Ranges switch
S5.
19 Ampere
Selects coarse range of weld out-
put
from weld stator
20 Reactor AC-Z
Tapped reactor limits weld output
and
21
Changes ac output from weld
windings
22
Smooths out current to dc weld
output
23
Protects unit from high frequency
24
Provide dc weld output.
25
Provide ac weld output.
Ranges Switch S5
provides coarse ranges.
Main Rectifier SR1
to dc.
Stabilizer DC-Z
terminals.
HF Filter Board PC4
Positive (+) And Negative (–)
DC W
eld Output T
Electrode And W
Output T
erminals
amperage
re
within range se
.
erminals
ork AC Weld
-
-
-
.
21
22
Stabilizer
Miller Legend
Main
Rectifier
SR1
DC-Z
HF Filter
Board
PC4
24
Positive (+)
Negative (–) DC
eld Output
W
Terminals
And
AC Or DC Control Circuits
W
eld Current Circuit
Mechanical Coupling
Magnetic Coupling
♦ Optional
TM-428 Page 13
Page 18

NOTES
TM-428 Page 14
Miller Legend
Page 19

SECTION 6 – TROUBLESHOOTING
6-1. Troubleshooting Tables
A. Welding
Trouble Remedy
.
See Sections 6-2 and 6-3 for test
points and values and Section 10
parts location.
for
No weld output.
No or erratic weld output.
Check fuse F1, and replace if necessary (see Section 8-6).
Check integrated rectifier SR2, and replace if necessary
Check diode D4, and replace if necessary
Clean slip rings, and install new brushes if necessary (see Section 6-15).
Disconnect leads 21, 23, and 33 from brushes, and check continuity across slip rings. Replace rotor
if necessary.
Check resistance and connections of resistors R2 and R4; R2 and R4 are each 12 ohms
place resistor(s) if necessary
Check
resistance and connections of Fine Amperage Control
R1
if necessary (see Section 3-1).
Disconnect
22
and 29. Replace exciter stator if necessary
For
nections. Replace C5 if necessary.
Check voltage regulator board PC2 and connections, and replace if necessary (see Section 6-9).
Clean and tighten weld connections both inside and outside unit.
Check engine speed, and adjust if necessary (see Section 8-5).
Check
replace if necessary.
Check
connections. Replace AC-Z if necessary.
leads 22 and 29 from SCR/integrated rectifier SR2, and check for continuity between leads
units with optional remote control, check capacitor C5 for a short or open, and check for proper con
to make sure Ampere Ranges switch S5 is not between positions. Check continuity of S5, and
reactor AC-Z for signs of winding failure. Check continuity across windings, and check for proper
. Adjust R2 and R4 according to Section 6-16.
.
.
.
R1; R1 is 0 to 30 ohms ±10%. Replace
±10%.
Re
-
-
No or erratic DC weld output only
Low or high weld output.
Miller Legend
Check
resistance and connections of Fine Amperage control R1; R1 is 0 to 30 ohms ± 10%. Replace
R1 if necessary.
Disconnect leads 21, 23, and 33 from brushes, and check continuity across slip rings. Replace rotor
if necessary.
.
Check modular main rectifier SR1, and replace if necessary
Check stabilizer DC-Z for signs of winding failure. Check continuity across windings, and check for
proper connections. Replace DC-Z if necessary.
Check engine speed, and adjust if necessary (see Section 8-5).
Adjust resistor R4 slider until 128 to 132 volts ac is obtained at 100 Hz receptacle RC4 (see Section
6-16).
Adjust
resistor R2 slider until proper open-circuit-voltage is obtained at
tion
6-16).
Check
resistance
10%.
Replace R3, VR1 module if necessary
Check
reactor AC-Z for signs of winding failure. Check continuity across windings, and check for proper
connections. Replace AC-Z if necessary.
and connections of resistor R3 on suppressor R3, VR1 module; R3 is 1000 ohms
.
.
weld output terminals (see Sec
-
±
TM-428 Page 15
Page 20
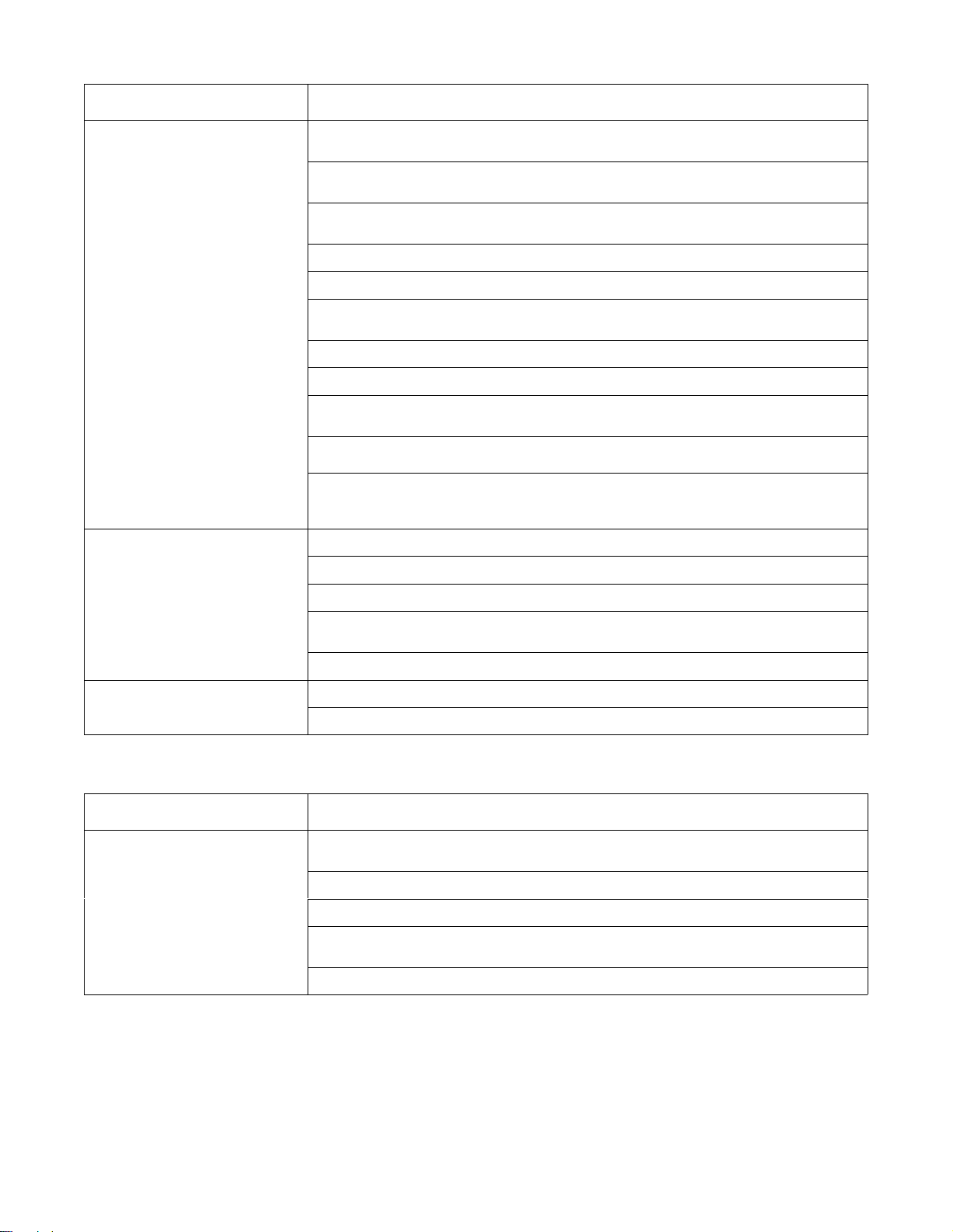
B. 50 Or 60 Hz Auxiliary Power
Trouble Remedy
No auxiliary power output at receptacles RC1, RC2, or RC3.
Low auxiliary power output.
Run engine at power/idle speed.
Reset circuit breakers CB1 and CB2. Effective with Serial No. KE629034, also reset circuit breakers
CB5
and CB7 (see Section 4-3).
Check
receptacles RC1, RC2, RC3 for continuity and proper connections. Replace receptacle(s) if nec
essary.
Check
connections to terminal strip 1T
Clean slip rings, and install new brushes if necessary (see Section 6-15).
Check
coil voltage and connections of control relay CR4. Check continuity of coil and condition of
tacts. Replace CR4 if necessary.
Check diode D4, and replace if necessary
Check idle board/module PC1 and connections (see Section 6-5).
Check
control transformer T1 for signs of winding failure. Check continuity across windings, and check
for
proper connections. Check primary and secondary voltages. Replace T1 if necessary
Disconnect leads 21, 23, and 33 from brushes, and check continuity across slip rings. Replace rotor
if necessary.
Disconnect
and
and 52 and 53. Replace stator if necessary
Check connections to terminal strip 1T
Clean slip rings, and install new brushes if necessary (see Section 6-15).
leads 48 and 49
49. Disconnect leads 50, 51, 52, and 53 from stator
from voltage regulator board PC2, and check continuity between leads 48
.
con
.
.
. Check continuity between leads 50 and 51,
.
.
-
-
High auxiliary power output.
C. 100 Hz Auxiliary Power
Trouble Remedy
No
auxiliary power output at receptacle
RC4.
Check integrated rectifier SR2, and replace if necessary
Check
coil voltage and connections of control relay CR3. Check continuity of coil and condition of
tacts. Replace CR3 if necessary.
Check voltage regulator board PC2 and connections, and replace if necessary
Check engine speed, and adjust if necessary
Check voltage regulator board PC2 and connections, and replace if necessary (see Section 6-9).
Run
engine at weld speed.
Reset circuit breaker CB3 (see Section 4-1).
Check receptacle RC4 for continuity and proper connections. Replace receptacle if necessary
Disconnect
93. Replace stator if necessary.
Check diode D4, and replace if necessary
leads 90, 91, 92, and 93 from stator
.
. Check continuity between leads 90 and 91, and 92 and
.
.
.
.
con
-
TM-428 Page 16
Miller Legend
Page 21

D. Engine
Trouble Remedy
Engine will not start.
Engine starts but
gine Control switch S2 returns to Run
position.
Engine stopped during normal operation.
Battery discharges between uses.
stops as soon as En
Check fuel level (see Section 2-4).
Check battery and engine charging system according to engine manual.
Check continuity of Engine Control switch S2, and replace if necessary
See engine manual.
-
Check
oil
for
Check
manual).
Check
Check
for
Check continuity of Engine Control switch S2, and replace if necessary
Make
3-1).
Prior
Clean battery, terminals and posts with baking soda solution; rinse with clear water
Periodically recharge battery (approximately every 3 months).
Check voltage regulator according to engine manual.
level (see Section 2-4). Check low oil pressure shutdown switch S3 (see engine parts manual
location). S3 should close when engine is running.
and refill crankcase with proper
continuity of Engine Control switch S2, and replace if necessary
oil
level (see Section 2-4). Check low oil pressure shutdown switch S3 (see engine parts manual
location). S3 should close when engine is running.
sure Engine Control switch
to Serial No. KA780044, check fuse F2 and replace if necessary
viscosity oil for operating temperature, if necessary (see engine
S2 is placed in the Of
f position when engine is not in use (see Section
.
.
.
.
.
Engine idles, but does not come up to
weld
speed.
Engine does not return to idle speed.
Unstable or sluggish engine speeds.
Replace battery
W
ait 10 seconds for throttle solenoid circuit breaker CB4 to reset (see Section 8-6).
Place Idle Lock switch S1 in Unlock position (see Section 3-1).
Check continuity and connections of current transformer CT1, and replace if necessary
Check continuity of Engine Control switch S2, and replace if necessary
Check
coil voltage and connections of control relay CR2. Check continuity of coil and condition of
tacts. Replace CR2 if necessary.
Check diode D6 in throttle solenoid TS1 circuit, and replace if necessary
Check resistance at throttle solenoid TS1 terminals. With plunger out, resistance is less than 1 ohm.
With plunger bottomed, resistance is 17 ohms
Check throttle linkage for smooth, non-binding operation.
Check idle board/module PC1 and connections, and replace if necessary (see Section 6-5).
Remove weld load.
Check continuity of Engine Control switch S2, and replace if necessary
Check throttle linkage for smooth, non-binding operation.
Readjust throttle linkage if necessary
T
une-up engine according to engine manual.
.
.
.
con
.
±10%.
.
.
-
Miller Legend
TM-428 Page 17
Page 22

6-2. Troubleshooting Circuit Diagram For Welding Generator
Resistance Values
a) Tolerance –
b) Condition – 70
±10% unless specified
°F (21°C); cold machine
(no warm-up)
c) Wiring Diagram – see Section 9
d) Stop engine before checking resistance
R1 29
R2
R3
R4
R5
R6 thru R17
R18
ohms
34 ohms
35 ohms
2 ohms
2 ohms
Less than 1 ohm
Pull: Less than 1 ohm Hold: 16.5 ohms
Test
Equipment Needed:
V14/R17
See Section
6-16 for R2 and
R4 adjustment
V18
V19
R18
V15
See Section 6-5
for PC1 data
V16/
R16 R15
V17/
V11,
V12,
V13/R12
I2
I1
R1 R2
R14
Field current
control relay CR3
and auxiliary power
control relay CR4
energized at
power/idle rpm
R13
Throttle
control relay
CR2 energized
at weld rpm
TM-428 Page 18
Miller Legend
Page 23

Amperage Readings
a) Tolerance –
±5% unless specified
b) Condition – 70
(no warm-up); no load
I1 3
I2
amps dc
1.8 amps dc (R1 at min.)
3.1 amps dc (R1 at max.)
°F (21°C); cold machine
Voltage Readings
a) Tolerance –
b) Condition – 70
±10% unless specified
°F (21°C); cold
machine (no warm-up); no load
c) Reference – to circuit common
(lead 33) unless noted
d) Wiring Diagram – see Section 9
R6
R7
V10/R8
V2/C/D V1/A/B
R11
V6/R3
V7/
R4
V9/R9
See Section 5 for
PC4 information
See Section 6-4 for
waveforms A thru D
V8/
R5
R10
V3
V5
V4
See Sections 6-7
thru 6-9 for PC2 data
V1 DC/CC
V2 AC/CC OCV
V3
V4
V5
V6
V7
V8
V9
V10
V11
V12
V13 Idle Lock switch S1 in Lock:
V14
V15
V16
V17
V18
V19
OCV at weld rpm:
58 volts dc (R1 at min.)
70 volts dc (R1 at max.)
(Do not exceed 72 volts dc)
65 volts ac (R1 at min.)
80 volts ac (R1 at max.)
(Do not exceed 80 volts ac)
At RC3 at power/idle rpm:
244 volts ac ±5% (50 or 60 Hz)
At RC2 at power/idle rpm:
122 volts ac ±5% (50 or 60 Hz)
At RC1 at power/idle rpm:
122 volts ac ±5% (50 or 60 Hz)
AC input to transformer T1: 122 volts ac
(power/idle rpm), 0 volts ac (weld rpm)
AC output to PC2: 21 volts ac
AC output to PC2: 21 volts ac
AC output from Regulator Power
Winding (power/idle rpm)
158 volts ac
AC output from W
weld rpm: 65 volts ac (R1 at min.), 80
volts ac (R1 at max.) (Do not exceed 80
volts ac)
At rated DC weld load: At least
1 volts ac
At weld rpm and 100 watt light bulb load
applied: 3 volts ac or greater
0 volts ac at all times
AC output from Exciter Winding
80 volts ac (power/idle rpm)
145 volts ac (weld rpm)
At RC4 at weld speed: at least 120
volts ac (Do not exceed 132 volts ac)
Auxiliary power winding at weld rpm:
at least 120 volts ac (Do not exceed
132 volts ac)
Auxiliary power winding at weld rpm:
at least 120 volts ac (Do not exceed
132 volts ac)
Battery output whenever engine is
running: 14 volts dc.
AC Alternator output:
17 volts ac (power/idle rpm)
39 volts ac (weld rpm)
, at weld rpm:
±5%
eld Winding at
±5%
±5%
Miller Legend
SC-168 053-A
TM-428 Page 19
Page 24

6-3. Troubleshooting
Circuit Diagram For W
Resistance Values
a) Tolerance
– ±10% unless specified
b) Condition – 70°F (21°C); cold
machine (no warm-up)
c) Wiring Diagram – see Section 9
d) Stop engine before checking
resistance
R1 29
R2
R3
R4
R5
R6 thru R17
ohms
34 ohms
35 ohms
2 ohms
2 ohms
Less than 1 ohm
elding Generator W
See Section 6-13
for PC5 data
Test
Equipment Needed:
ith Optional Remote Control
See Section
6-11
for PC3 data
V18
Field flashing
disconnect relay CR5
V15
V14/R17
V16/ V17/
R16 R15
I1
R1 R2
R14
CR2 energized
See Section
6-16 for R2 and
R4 adjustment
I2
R13
V1
1, V12,
V13/R12
Throttle
control relay
at weld rpm
TM-428 Page 20
V19
See Section 6-5
for PC1 data
Field current
control relay CR3
and auxiliary power
control relay CR4
energized at
power/idle rpm
Miller Legend
Page 25

Amperage Readings
a) Tolerance –
±5% unless specified
b) Condition – 70
(no warm-up); no load
I1 3
I2
amps dc
1.8 amps dc (R1 at min.)
3.1 amps dc (R1 at max.)
°F (21°C); cold machine
Voltage Readings
a) Tolerance –
b) Condition – 70
±10% unless specified
°F (21°C); cold
machine (no warm-up); no load
c) Reference – to circuit common
(lead 33) unless noted
d) Wiring Diagram – see Section 9
R6
R7
V10/R8
V2/C/D V1/A/B
R11
See Section 5 for
See Section 6-4 for
waveforms A thru D
V6/R3
V7/
R4
V9/R9
PC4 information
V8/
R5
R10
V3
See Sections 6-7
thru 6-9 for PC2 data
V4
V5
V1 DC/CC
V2 AC/CC OCV
V3
V4
V5
V6
V7
V8
V9
V10
V11
V12
V13 Idle Lock switch S1 in Lock:
V14
V15
V16
V17
V18
V19
OCV at weld rpm:
58 volts dc (R1 at min.)
70 volts dc (R1 at max.)
(Do not exceed 72 volts dc)
65 volts ac (R1 at min.)
80 volts ac (R1 at max.)
(Do not exceed 80 volts ac)
At RC3 at power/idle rpm:
244 volts ac ±5% (50 or 60 Hz)
At RC2 at power/idle rpm:
122 volts ac ±5% (50 or 60 Hz)
At RC1 at power/idle rpm:
122 volts ac ±5% (50 or 60 Hz)
AC input to transformer T1: 122 volts ac
(power/idle rpm), 0 volts ac (weld rpm)
AC output to PC2: 21 volts ac
AC output to PC2: 21 volts ac
AC output from Regulator Power
Winding (power/idle rpm)
158 volts ac
AC output from W
weld rpm: 65 volts ac (R1 at min.), 80
volts ac (R1 at max.) (Do not exceed 80
volts ac)
At rated DC weld load: At least
1 volts ac
At weld rpm and 100 watt light bulb load
applied: 3 volts ac or greater
0 volts ac at all times
AC output from Exciter Winding
80 volts ac (power/idle rpm)
145 volts ac (weld rpm)
At RC4 at weld speed: at least 120
volts ac (Do not exceed 132 volts ac)
Auxiliary power winding at weld rpm:
at least 120 volts ac (Do not exceed
132 volts ac)
Auxiliary power winding at weld rpm:
at least 120 volts ac (Do not exceed
132 volts ac)
Battery output whenever engine is
running: 14 volts dc.
AC Alternator output:
17 volts ac (power/idle rpm)
39 volts ac (weld rpm)
, at weld rpm:
±5%
eld Winding at
±5%
±5%
Miller Legend
SC-168 054-A
TM-428 Page 21
Page 26

6-4. Waveforms For Sections 6-2 And 6-3
A. DC Open-Circuit
V
Switch S5 In Max Position
2 ms 50 V
oltage, Ampere Ranges
5 ms 50 V
2 ms 10 V
gndgnd
B. DC Weld Output, 25 Volts DC, 100 Am-
peres,
Ampere Range Switch S5 In
70-105
Position (Resistive Load)
5 ms 20 V
C. AC Open-Circuit Voltage, Ampere Ranges
Switch S5 In Max Position
W
aveforms shown are for 60 Hertz models;
waveforms for 50 Hertz models are similar
.
gndgnd
D. AC Weld Output, 25 Volts AC, 100 Amperes,
Ampere Range
Switch S5 In 70-105 Position
(Resistive Load)
Test
Equipment Needed:
TM-428 Page 22
Miller Legend
Page 27

6-5. Idle Control Board/Module PC1 Testing Information
OR
Be sure plugs are secure before
See Section 6-6 for specif
testing.
values during testing.
ic
1
Idle Control Board PC1 (Prior
T
o Serial No. JH300534)
2
Idle Module PC1 (Ef
With Serial No. JH300534)
1
fective
-
T
est Equipment Needed:
2
Miller Legend
Ref. ST-800 698-A / SC-113 702-A
TM-428 Page 23
Page 28

6-6. Troubleshooting Flowcharts For Idle Control Board/Module PC1
Engine does not go to power/idle rpm
with no weld load applied.
Connect meter (AC) between
terminal G and terminal E.
Start
engine. Place Engine Control
switch S2 in Run/Idle position.
0 (zero) volts ac present?
YES
Connect meter (DC) between
terminal D (+) and E (–).
0 (zero) volts dc present?
YES
Connect meter (DC) between
terminal C (+) and terminal E (–).
Check for internal
NO
shorted diode in
main rectifier SR1.
NO
Check connections
to Engine Control
load such as
switch S2.
Engine does not go to weld rpm with
load applied.
Connect meter (DC) between
terminal B (+) and terminal E (–).
Start engine. Place Engine Control
switch S2 in Run/Idle position; Idle
Lock switch S1 in Unlock position.
+12 volts dc present?
YES
Connect meter (AC) between
terminal G and terminal E.
Start engine. Place Engine
Control switch in Run/Idle position.
Connect a 100 watt light bulb to
100 Hz ac receptacle.
Check connections
to Engine Control
NO
switch S2 and
ground connection
(lead 33).
0 (zero) volts dc
present after 12 to 18 seconds?
YES
Check throttle solenoid TS1
linkage.
Reinstall cover.
NO
Replace idle
board/module
PC1
Minimum of 1 volt ac present?
YES
Connect meter (DC) between
terminal C (+) and terminal E (–).
+12 volts dc present?
YES
Check circuit breaker CB4, throttle
solenoid TS1 connections and
linkage, and control relay CR2.
Disconnect 100 watt light bulb
and meter leads.
Reinstall cover.
NO
Check connections
transformer CT1.
NO
board/module
to current
Replace idle
PC1
TM-428 Page 24
Miller Legend
Page 29

Engine does not go to weld rpm with
Engine Control switch S2 in Run position.
Control Relays CR3 and CR4 do not
energize at idle rpm (See Section 5 for
CR3 and CR4 information)
Connect meter (DC) between
terminals D (+) and E (–).
Start
engine. Place Engine
Control switch S2 in Run position.
Prior to Serial No. JH300534,
move W
eld/Power switch S1 to
W
eld position.
+12 volts dc present?
YES
Connect meter (DC) between
terminals C (+) and E (–).
+12 volts dc present?
YES
Check connections
to Engine Control
NO
NO
switch S2 and
ground connection
board/module
(lead 33).
Replace idle
PC1
Connect
terminal A (+) and F (–) prior to
Serial No. JH300534, or B (+) and
Control switch in Run position.
Place Engine Control switch S2
meter (DC) between
F (–) ef
fective with Serial No.
JH300534.
Start engine. Place Engine
0 (zero) volts dc present?
YES
in Run/Idle position.
+12 volts dc present?
YES
Check control relays
CR3 andCR4.
NO
NO
Replace idle
board/module
PC1
Replace idle
board/module
PC1
Check circuit breaker CB4, throttle
solenoid TS1 connections and
linkage, and control relay CR2.
Reinstall cover.
Reinstall cover.
Miller Legend
TM-428 Page 25
Page 30

6-7. Voltage Regulator Board PC2 Testing Information Prior To Serial No. KE604176
Be sure plugs are secure before
See Section 6-8 for specif
2
1
testing.
values during testing.
ic
1V
oltage Regulator Board PC2
2T
erminals A Thru G
-
T
est Equipment Needed:
Ref. ST-800 698-A / SA-099 497-B
6-8. Voltage Regulator Board PC2 Test Point Values Prior To Serial No. KE604176
±10% unless
– to circuit com
Miller Legend
PC2 Voltage Readings
Receptacle Value
A Circuit
B
C
D
E
F
G
TM-428 Page 26
common
18 volts ac input with respect to pin A
18 volts ac input with respect to pin A
Circuit common
130 volts ac input with respect to terminal G at power/idle rpm
55 volts dc output with respect to terminal D at power/idle rpm
130 volts ac input with respect to terminal E at power/idle rpm
a) Tolerance –
specified
b) Reference
mon
(lead 33) unless noted
-
Page 31

6-9. Voltage Regulator Board PC2 Testing Information Effective With Serial No.
KE604176
1 2
Be sure plugs are secure before
testing. See Section 6-10 for spe-
values during testing.
cific
1V
oltage Regulator Board PC2
2 Receptacle RC1
T
est Equipment Needed:
Ref. ST-800 698-A / SA-160 889-A
6-10. Voltage Regulator Board PC2 Test Point Values Effective With Serial No. KE604176
±10% unless
– to circuit com
TM-428 Page 27
-
PC2 Voltage Readings
Receptacle Pin Value
RC1 1 18
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Miller Legend
volts ac input with respect to pin 5
Not used
18 volts ac input with respect to pin 5
Circuit common
Circuit common
130 volts ac input with respect to pin 8 at power/idle rpm
Not used
130 volts ac input with respect to pin 6 at power/idle rpm
55 volts dc output with respect to pin 4 at power/idle rpm
a) Tolerance –
specified
b) Reference
mon
(lead 33) unless noted
Page 32

6-11. Optional Remote Control Board PC3 Testing Information
1
2
Be sure plugs are secure before
testing. See Section 6-12 for spe-
values during testing.
cific
1
Remote Control Board PC3
2 Receptacle RC1
est Equipment Needed:
T
6-12. Optional Remote Control Board PC3 Test Point Values
PC3 Voltage Readings
Receptacle Pin* Value
RC1 1 (A)
2 (B)
3 (C)
4 (D)
5 (E)
6 (F)
7 (G)
8 (H)
9 (J)
10 (K)
Circuit common
Circuit common
+50 volts dc input at power/idle rpm; 100 volts dc input at weld rpm
+12 volts dc input with respect to pin 5 at power/idle or weld rpm
Chassis ground (lead 33)
59 to 6.8 volts dc output with respect to pin 1 from min to max of remote control with remote contac
tor control switch closed, 130 volts dc output with remote contactor control switch open
Circuit common
Command reference output, +4.5 volts dc output with respect to pin 7
0 volts dc output with remote contactor control switch closed, +15 volts dc output with remote con
tactor control switch open
0 to +4.5 volts dc input from min to max of Fine Amperage control R1 at power/idle rpm
Ref. ST-800 698-A / ST-115 941-L / SA-138 247
a) Tolerance –
±10% unless
specified
b) Reference
mon
– to circuit com
(lead 33) unless noted
-
-
-
*Letter(s) in parenthesis ( ) is pin letter prior to Serial No. KA840710.
TM-428 Page 28
Miller Legend
Page 33

6-13.
Optional Remote Capacitor Board PC5 T
KD346698
43
T
est Equipment Needed:
esting Information Effective W
2
1
ith Serial No.
Be sure plugs are secure before
testing. See Section 6-14 for spe-
values during testing.
cific
1
Capacitor Board PC5
2
Remote 14 Receptacle RC1
3 Receptacle RC2
erminal K
4T
Ref. ST-800 698-A / SA-156 026-C
6-14. Optional Remote Capacitor Board PC5 Test Point Values Effective With Serial No.
KD346698
±10% unless
– to circuit com
TM-428 Page 29
-
PC5 Voltage Readings
Receptacle Pin Value
RC1 A Contact
B
C
D
E
K
RC2 1
2
3
4
5
6
Terminal K
Miller Legend
closure to pin B completes the dc contactor control circuit
+15 volts dc output
Command reference, +4.5 volts dc output
Remote control circuit command
Input command signal from potentiometer wiper
Chassis ground (lead 33)
Remote control circuit common
Command reference, +4.5 volts dc input
+15 volts dc input
Command signal from potentiometer wiper
Not used
Contact closure to pin 3 completes contactor control circuit
Chassis ground (lead 33)
, 0 to +4.5 volts dc output
a) Tolerance –
specified
b) Reference
mon
, 0 to +4.5 volts dc input
(lead 33) unless noted
Page 34

6-15. Replacing Brushes And Cleaning Slip Rings
A. Checking Brushes And Cleaning Slip Rings
Stop
engine and allow to cool.
1
Brush Holder Retaining Bar
2 Brush Holder Bracket
Remove brush holder bracket.
hardware for reinstallation.
Keep
3
Brush Holder
4
Brush With Spring
5
Brush Holder Cap
Mark and disconnect leads at
caps, and remove brushes from
bracket.
Replace brushes if damaged, or if
brush
is
at or near minimum length.
6 Slip Rings
Inspect slip rings. Under normal
use,
rings turn dark brown.
If
slip rings are corroded or surface
is uneven, insulate brush leads,
start
engine,
commutator stone. Remove as
little
gine.
Install brushes, bracket, and remaining generator parts. Adjust
brushes
Reinstall both side panels and top
cover.
and clean rings with a
material as possible. Stop en
as shown in Section B.
-
Tools
Needed:
1/2 in
2
5
3
4
1
5/16 in. (8 mm)
Minimum Length
9/16 in. (14.3 mm)
New Length
Replace
Damaged Brushes
TM-428 Page 30
ST-800 698-A / Ref. ST-115 942-F / S-0233-A
Miller Legend
Page 35

B. Adjusting Brush Position
3/32 in
(2.4 mm)
Side V
iew
Stop
engine.
After installing brushes, adjust
position as follows:
brush
1
Brush Holder
2 Brass Sleeve
3 Brush
4
Slip Ring
Loosen brush holder bracket
mounting
until brass sleeves are positioned
as
Reinstall side panels and cover
If
qualified machine shop turn and
polish
hardware. Move bracket
shown. T
operation is still not okay
ighten hardware.
slip rings.
.
, have a
T
ools Needed:
3/8, 1/2 in
Center
brushes on slip
rings.
3
4
Correct Brush Position
Correct
Brush Position
2
1
Incorrect Brush Position
T
op V
iew
1234
Incorrect
Brush Position
Miller Legend
Ref. ST-800 698-A / Ref. ST-800 677-B
TM-428 Page 31
Page 36

6-16. Checking Unit Output After Servicing
1
4
2
3
Check engine speeds, and adjust
if necessary (see Section 8-5).
11
15 V
AC 100 Hz Receptacle
RC4
With no load applied and engine
running at weld rpm, there should
be 128 to 132 volts ac present at
RC4.
2 Slider
3 Resistor
Y Stop engine before adjust-
If necessary, adjust slider on R4
until
at RC4. Do not exceed 132 volts
ac.
4DC
Turn
max.
gine running at weld rpm, there
should
at
2
5
dc weld terminals.
5 Resistor R2
Y Stop engine before adjust-
If
correct voltage is not present, ad
just slider on R2 until correct voltage is obtained at dc weld terminals.
Stop engine. Allow engine to
and
then complete pre-operational
checks
Reinstall cover and side panels.
R4
R4
ing
128 to
132 volts ac is obtained
W
eld Output T
Fine Amperage control R1 to
With no load applied and en
be 70
to 72 volts dc present
R2
ing
Do not exceed 72 volts dc.
in table.
erminals
cool,
-
-
Pre-Operational Checks
Wipe engine surfaces clean.
Check labels; replace labels that are unreadable or damaged.
Check fuel and oil (see Section 2-4).
Check and correct any fluid leaks.
Clean weld output and battery terminals. Tighten connections.
Clean outside of entire unit.
T
ools Needed:
Ref. ST-800 698-A / ST-800 249
TM-428 Page 32
Miller Legend
Page 37

SECTION 7 – DISASSEMBLY AND REASSEMBLY
7-1. Disassembly Of Unit
Use Section 6-1 to determine if
is
in rotor
, stator
trouble
a combination of these components.
Remove sheet metal panels from
unit. Disconnect negative (–) battery cable from battery. Remove
spark plugs. Mark and disconnect
stator leads.
all
Y Do not damage rotor or sta-
during this procedure.
tor
Use hoist and lifting strap to remove the engine/generator assembly.
, engine or
T
ools Needed:
3/8, 7/16, 1/2, 9/16 in
Miller Legend
ST-800 710-A
TM-428 Page 33
Page 38

7-2. Disassembly Of Generator
Hardware may differ from that shown.
Torques:
Prior T
o Serial No. KD523655
A
15 ft lb (20 N.m) A
B
30 ft lb (41 N.m) B
C
25 ft lb (34 N.m) C
D
15 ft lb (20 N.m) D
E
15 ft lb (20 N.m) E
Ef
fective With Serial No. KD523655
15 ft lb (20 N.m)
20 ft lb (27 N.m)
25 ft lb (34 N.m)
20 ft lb (27 N.m)
15 ft lb (20 N.m)
5
A
B
4
3
2
1
E
Y Do
not
damage stator or rotor wind
during this procedure.
ings
Disassembly
With
engine properly supported with blocks,
remove
hardware securing stator to engine.
Remove
generator parts as needed:
1
Fan Guard
2 O-Ring
3 Endbell
4 Stator Assembly
5
Engine Adapter
16
15
6
Fan Rotor Adapter
-
7
Rotor Fan
8 Rotor
Ball Bearing
9
10
Retaining Ring
11
Integrated Rectifier SR2
12 Brush Holder Bracket
Brush Holder Retaining Bar
13
14
Brush Holder Cap
15 Brush
C
6
D
7
8
9
10
11
12
1314
ST-115 942-F
16
Brush Holder
Reassembly
Reinstall engine and generator parts as
(see torque table).
needed
Reconnect
ground
and tray
Use cable ties to secure leads in existing
wiring
hot
Reconnect negative (–) battery cable.
fuel line, choke cable, and base
cable. Reinstall spark plugs, battery
, panels, and cover
harnesses
parts.
and away from moving or
.
TM-428 Page 34
Miller Legend
Page 39

SECTION 8 – MAINTENANCE
8-1. Routine Maintenance
Recycle
8 Hours
engine
fluids.
Y
Stop engine before maintaining.
.
See also Engine Manual and mainte-
label. Service engine more
nance
during
severe conditions.
often
Wipe
Up
Spills
Change
Oil. See
Section 8-4 And
Maintenance
Label
20 Hours
Check
Clean Spark
Arrestor Screen
25 Hours
50 Hours
100 Hours
And
Clean
And
Check Air
Cleaner
Clean
T
ighten W
Terminals
And
eld
OIL
Full
Check Fluid
Levels.
See Section 2-4
Change Oil Filter
Section 8-4 And
Maintenance Label
. See
Miller Legend
Check
Valve
Clearance
Clean Cooling
System,
See Engine
Manual
Repair Or Replace
Cracked Cables
OR
200 Hours
Replace
Filter
Fuel
See Section
8-4.
500 Hours
1000 Hours
Blow Out Or V
During Heavy Service,
.
acuum Inside.
Clean Monthly
Clean And
Tighten
Battery
Connections
Replace
Unreadable
Labels
Check
Spark
Plugs
TM-428 Page 35
Page 40

8-2. Maintenance Label
Recommended Oil
Oil & Filter
Oil
Filter
Oil Capacity
ONAN P218 GAS ENGINE
See
Engine Manual for complete engine care. Give engine
Specification and Serial Number when ordering parts.
°C
Check
daily.
. .
Change .
. . . . . . . . .
dirty conditions
normal conditions
.
. . . . . . . . . . .
.
. . . . . . .
T
o Drain Oil:
Push And
Turn CCW
1/2 in. ID Hose
Pull
API Service Classification.
SF, SG, SF/CC, SG/CE
25 hours or less.
. .
100
hours
.
MILLER 065 251, Onan 122-0645
1.5 qt (1.4 L) or 1.75 qt (1.6 L) with filter change
+30
+20
+10
-10
-20
-30
°F
+100
+40
0
30
10W
0
5W-30
Gasoline
+
Optional
Fuel Grade
Fuel
Air
Filter Service 100 hours or less – see Owner’s Manual
Air
Filter Element
Air
Filter W
12 V
Cranking
Engine
Power
.
. . . . . . . .
Filter
.
. . . . . . . . .
rapper
olt Battery
Performance at 0°F (-18
RPM – No Load
1650 (50 Hz)
.
. .
1860 (60 Hz)
. . . .
Weld 3000.
Spark
Plug Gap
Spark
Plug
.
. . . . . . . .
Regular or Unleaded
MILLER 066 1
Fram
G10E1
.
. . .
MILLER 064 617, Onan 140-2522
.
. . .
MILLER 065 653, Onan 140-1496
.
. . .
.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
13, Onan 149-2206-01,
°C)
.
. . .
Valve
In.
.
. .
Ex. 0.013
.
.
0.025 in. (0.6 mm)
.
. . . .
Champion RS17YX Preferred or
BCI Group 58
430 Amps min.
Clearance – Cold
0.005 in (0.13 mm)
in (0.33 mm)
RS14YC
Use
only resistor spark plugs and wires.
Spark
Arrestor Inspection And Service
20 operating hours -
.
see Owner’
s Manual
S-176 891
TM-428 Page 36
Miller Legend
Page 41

8-3. Servicing Air Cleaner
Y Do not run engine without
air cleaner or with dirty ele-
1
2
ment.
engine.
Stop
1 Precleaner
Wash precleaner with soap and
solution.
water
air
dry completely
Spread 1 tablespoon SAE 30 oil
evenly into precleaner. Squeeze
out excess oil.
2 Element
Replace element if dirty or oily
Allow precleaner to
.
.
oil
aircleaner3 1/96 – ST-156 852 / S-0759
Miller Legend
TM-428 Page 37
Page 42

8-4. Changing Engine Oil, Oil Filter, And Fuel Filter
Full
Stop
engine and allow to cool.
1
Oil Drain V
2
1/2 ID x 12 in Hose
3
Oil Filter
Change engine oil and filter according
Y Close valve and valve cap
before adding oil and running
Fill crankcase with new oil to full
on dipstick
mark
4 Fuel
5
Fuel Line
Replace line if cracked or worn.
Install new filter. Wipe up any
spilled
Start engine, and check for fuel
leaks.
Stop engine, tighten connections
as necessary
alve
to engine owner’s manual.
engine.
(see Section 8-2).
Filter
fuel.
, and wipe up fuel.
3
T
ools Needed:
4
5
2
1
TM-428 Page 38
ST-140 091-E / ST-144 840-C Ref. ST-168 046 / ST-800 395 / S-0842
Miller Legend
Page 43

8-5. Adjusting Engine Speed
2
Rear V
iew
1
59
1860 rpm
(Power/Idle)
3000 rpm
(Weld)
After tuning engine, check engine
speeds with a tachometer. See
table for proper no load speeds. If
necessary, adjust speeds as follows:
Start engine, and place Engine
switch
Control
Turn Fine Amperage control to
100.
1 Carburetor
2 Throttle
Power/Idle Speed Adjustment
3
Power/Idle Speed Rod
4 Lock Nut
5
Adjustment Nut
Loosen
ment nut until engine runs at pow
er/idle speed. T
W
Place
Engine Control
position.
6 Lock
Loosen nut.
7 Hex Swivel
Turn swivel until engine runs at
speed. T
weld
8W
9
Power/Idle Speed Governor
Spring
If a spring becomes loose or dis-
connected,
in Run/Idle position.
Solenoid
lock nut and rotate adjust
ighten lock nut.
eld Speed Adjustment
switch in Run
Nut
ighten lock nut.
eld Speed Governor Spring
reattach as shown.
-
-
Tools
Miller Legend
4
Needed:
3/8 in,
8, 1
1 mm
3
2
8
T
op V
67
iew
ST-116 049-C
TM-428 Page 39
Page 44

8-6. Overload Protection
Stop
engine.
1
Circuit Breaker CB4 (Internal
– Not Shown)
CB4 protects the unit from over-
load due to an obstructed throttle
solenoid. If CB4 opens, engine
speed drops to power/idle rpm for
10 seconds before
about
resetting.
cally
If CB4 continues to open, check
throttle solenoid TS1 and throttle
linkage.
2 Fuse
F1 protects the exciter excitation
winding
2
Replace open fuse and reinstall
panel
If
grated
F1 (See Parts List For
Rating)
from overload.
before operating unit.
F1 continues to
rectifier SR2 and rotor
automati
open, check inte
.
-
-
ools Needed:
T
3/8 in
8-7. Inspecting And Cleaning Optional Spark Arrestor
1
ST-152 264-A
Stop
engine and allow to cool.
1 Spark Arrestor Screen
Clean and inspect screen. Re-
spark arrestor if screen wires
place
are
broken or missing.
Tools
TM-428 Page 40
Needed:
1/4 in
ST-140 091-E / ST-801 206 / Ref. ST-168 046
Miller Legend
Page 45

SECTION 9 – ELECTRICAL DIAGRAMS
.
The
circuits in this manual can be used for troubleshooting, but there
machine
case or contact factory for actual circuit, if needed.
The following is a list of all diagrams for models covered by this manual. T
1
Know unit Model and Serial or Style Number
2
Use this list to find diagram number
Include your F
3
4 FAX T
AX number or mailing address with your request.
echnical Publications Department at 414-735-401
.
.
1 or call 414-735-4356.
might be minor circuit differences from your machine. Use circuit inside
o order a copy, proceed as follows:
Model Serial Or Style Number
Miller
Legend Without Re
mote Control
Miller Legend With Re
mote Control
-
JH2421
14 thru JH300533
JH300534 thru JJ420470
JJ420471 thru JK713331 C-123 087-B
JK713332 thru KA780043
KA780044 thru KA870083
KA870084 thru KD346697
KD346698 thru KD438828
KD438829 thru KD548029
KD548030 thru KE604175
KE604176 thru KE629033
KE629034 and following
-
JH2421
14 thru JH300533
JH300534 thru JJ420470
Circuit
Diagram
SC-1
14 477-A
C-1
17 626-B
SC-130 929
C-135 624
C-137 000-A
C-157 770
C-162 148
C-166 823
C-167 423
SC-168 053-A SD-168 051-B
SC-1
C-1
18 207-A
♦♦
♦♦
♦♦
♦♦
♦♦
♦♦
♦♦
♦♦
♦♦
15 947-A
♦♦
Wiring
Diagram
D-1
17 651
♦♦
D-123 101
D-130 651-A
D-130 651-A
D-135 628
D-136 855-D
D-157 767-A
D-162 146
D-166 822
D-167 422
♦♦
♦♦
♦♦
♦♦
♦♦
♦♦
♦♦
♦♦
♦♦
Main Reason
For Change
Changed PC1 and S1, add
ed D5
Added D6
Removed S1
Removed F2
Added S1
Added PC4, PC5
Added stator lead 33
Hourmeter standard
Changed PC2
Added CB5, CB7, D8, GFCI
Changed PC1 and S1, add
ed D5
-
-
Circuit Board PC1
Circuit Board PC2
Circuit Board PC3
Circuit Board PC4
Circuit Board PC5
♦ Optional
♦♦ Not
JJ420471 thru JK713331 C-123 088-B
JK713332 thru KA780043 C-130 928
KA780044 thru KA870083
KA870084 thru KD346697
KD346698 thru KD438828
KD438829 thru KE604175
KE604176 thru KE629033
KE629034 and following
JH2421
JH2421
KE604176 and following
♦ JH2421
KA840710 and following
KD346698 and following
♦
KD346698 and following
included in this manual
14 thru JH300533
14 thru KE604175
14 thru KA840709
♦♦
C-135 801
C-137 003-B
C-157 764
C-162 147
C-167 402
SC-168 054-A
SB-1
B-049 506-C
SB-160 891
B-1
SB-136 249
SA-148 024-A
SB-156 027
♦♦
♦♦
♦♦
♦♦
13 710
15 891-A
♦♦
♦♦
♦♦
♦♦
Added D6
Removed S1
Removed F2
Added S1
Added PC4, PC5
Added stator lead 33
Hourmeter standard,
changed PC2
Added CB5, CB7, D8, GFCI
Miller Legend
TM-428 Page 41
Page 46

TM-428 Page 42
SC-114 477-A
Figure 9-1. Circuit Diagram For Miller Legend Without Remote Control
Effective With Serial No. JH242114 Thru JH300533
Miller Legend
Page 47

Miller Legend
SC-168 053-A
Figure 9-2. Circuit Diagram For Miller Legend Without Remote Control
Effective With Serial No. KE629034 And Following
TM-428 Page 43
Page 48

Coat
terminals with dielectric grade, nonconductive,
electric grease (MILLER Part No. 146 557) or equivalent.
Figure 9-3. Wiring Diagram For Miller Legend Without Remote Control
Effective With Serial No. KE629034 And Following
TM-428 Page 44
Miller Legend
Page 49

SD-168 051-B
Miller Legend
TM-428 Page 45
Page 50

TM-428 Page 46
SC-115 947-A
Figure 9-4. Circuit Diagram For Miller Legend With Remote Control
Effective With Serial No. JH242114 Thru JH300533
Miller Legend
Page 51

Miller Legend
SC-168 054-A
Figure 9-5. Circuit Diagram For Miller Legend With Remote Control
Effective With Serial No. KE629034 And Following
TM-428 Page 47
Page 52

Figure 9-6. Circuit Diagram For Idle Control Board PC1
Effective With Serial No. JH242114 Thru JH300533
SB-113 710
TM-428 Page 48
SB-160 891
Figure 9-7. Circuit Diagram For Voltage Regulator Board PC2
Effective With Serial No. KE604176 And Following
Miller Legend
Page 53

OUTPUT
POSITIVE
SUPPLY+
Figure 9-8. Circuit Diagram For Optional Remote Control Board PC3
Effective With Serial No. KA840710 And Following
SB-136 249
Miller Legend
SB-148 024-A
Figure 9-9. Circuit Diagram For HF Filter Board PC4
Effective With Serial No. KD346698 And Following
TM-428 Page 49
Page 54

Figure 9-10. Circuit Diagram For Optional Capacitor Board PC5
Effective With Serial No. KD346698 And Following
SB-156 027
TM-428 Page 50
Miller Legend
Page 55

February 1996 Form: TM-428
Effective With Serial No. JH242114
SECTION 10 – PARTS LIST
Miller Legend
Miller Legend
(Formerly The Legend AEAD-200LE)
CC AC/DC Welding Generator For SMAW, GMAW, GTAW Welding
TM-428 Page 51
Page 56

19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
18
17
16
15
14
27
28
29
34
30
33
Figure 10-2
31
32
35
13
12
46
45
43
10
11
50
49
48
42
41
51
40
39
7
9
8
6
5
3
2
Figure 10-5
Figure 10-6
4
47
1
44
Figure 10-3
36
Figure 10-1. Main Assembly
37
38
TM-428 Page 52
Miller Legend
Page 57

Item
No.
Dia.
Mkgs.
Part
No.
Description Quantity
Figure 10-1. Main Assembly
1 ++042 132 REMOTE CONTROL, (Figure 10-6) (Prior to JK713332) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1 ++042 383 REMOTE CONTROL, (Figure 10-6) (Eff w/JK713332) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2 Figure 10-5 CONTROL PANEL, w/components 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3 113 302 UPRIGHT, base (Prior to KA780148) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3 129 384 UPRIGHT, base (Eff w/KA780148 thru KA892304) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3 136 057 UPRIGHT, base (Eff w/KA892305 and on) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4 107 342
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5 113 303 P
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6 +113 304 COVER, top (Prior to JJ365634) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6 +114 557 COVER, top (Eff w/JJ365634 thru KF812088) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6 +173 209 COVER, top (Eff w/KF812089) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
7 108 487 LABEL, warning falling equipment etc 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
8 113 439 PANEL, rear lower (Prior to KA780148) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
8 128 789 PANEL, rear lower (Eff w/KA780148 thru KA892304) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
8 136 059 PANEL, rear lower (Eff w/KA892305 and on) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
9 095 970 STRIP, nprn wsl eng firewall 18 in 2.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
10 088 731 BUSHING, snap-in nyl .375 ID 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
11 PLG5 HOUSING, (part of engine wiring harness).
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
12 147 601 CAP, tank screw-on w/vent 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
13 130 123 TANK, fuel 7.5gal (Eff w/KA780148 thru KG037343) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
13 177 606 TANK, fuel 7.5gal (Eff w/KG037344 and on) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
14 145 976 HOSE, nprn SAE .250 ID 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
15 084 173 CLAMP, hose .460–.545clp dia 2.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
16 066 113 FILTER, fuel inline .250 (included w/engine) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
17 CLAMP, hose .460–.545clp dia (included w/engine) 2.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
18 HOSE, nprn SAE .250 ID (included w/engine) (order by ft) 1ft.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
19 135 627 ENGINE, gas elect start (Prior to KG037344) (consisting of) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
19 178 479 ENGINE, gas elect start (Eff w/KG037344) (consisting of) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
20 165 271 VALVE, oil drain (Eff w/KF933389) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
21 107 297 MUFFLER, exhaust engine (Prior to KF926822) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
21 164 353 MUFFLER, exhaust (Eff w/KF926822) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
22 106 977
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
23 113 563 BRACKET, mtg solenoid (Prior to JK595850) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
23 128 534 BRACKET, mtg solenoid(Eff w/JK595850) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
24 128 869
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
24 128 431 SWIVEL, in-line .250-28 (Eff w/JJ404117) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
25 128 533 LINK, throttle (Eff w/JJ404117) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
26 064 646 SPRING, high speed 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Miller Legend
120 304 BLANK, snap-in nyl .250mtg hole (Eff w/JJ365634 thru KB133271) 2.
143 397 BLANK, snap-in nyl .312mtg hole (Eff w/KB133272 thru KF812088) 2.
113 248 TANK, fuel (Prior to KA780148) (consisting of) 1.
015 603 CAP, tank fuel 1.
107 345 NECK, tank fuel 1.
113 685 TUBE, pick up fuel 1.
010 863 CLAMP, hose 2 1/16-3 clamp dia (Prior to KA780148) 2.
107 346 HOSE, fuel tank (Prior to KA780148) 1.
107 324 BRACKET, support pipe filler (Prior to KA780148) 1.
107 343 GROMMET, rubber neck filler fuel (Prior to KA780148) 1.
113 486 COVER, fuel tank (Prior to KA780148) 1.
113 392 HOLD DOWN, fuel tank (Prior to KA780148) 1.
113 294 SUPPORT, center mtg engine (Prior to KA780148) 1.
113 251 FITTING, pipe brs cap .375NPT (Prior to KF933389) 1.
113 250 FITTING, pipe galv nipple L .375NPT (Prior to KF933389) 1.
137 046 TUNE-UP & FILTER KIT, (consisting of) 1.
064 617 ELEMENT, air cleaner 1.
065 251 OIL FILTER 1.
121 652 FILTER/CLAMPS, fuel 1.
065 709 SP
SEAL, lift eye
ANEL, side
. . . . . . . .
. . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SOLENOID, 12VDC 20A
LINKAGE KIT
, (Prior to JJ404117) 1.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
ARK PLUG
1.
2.
1.
2.
TM-428 Page 53
Page 58

Item
No.
Dia.
Mkgs.
Part
No.
Description Quantity
Figure 10-1. Main Assembly (Continued)
27 107 308 HOLD DOWN, bat (Prior to KB113874) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
27 146 697 HOLD DOWN, bat (Ef
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
27 165 631 HOLD DOWN, bat (Eff w/KF959177 and on) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
28 165 630 BOLT, J stl .250–20 x 6.125 (Eff w/KF959177) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
29 168 385 LABEL, warning battery explosion 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
30 107 270 DOOR, access battery (Prior to KF959177) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
30 175 887 DOOR, access battery (Eff w/KF959177) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
31 088 577 CABLE, bat pos (Prior to KF959177) (consisting of) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
31 167 731 CABLE, bat pos (Eff w/KF959177) (included w/engine) (consisting of) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
32 BAT 071 678 BATTERY, stor 12V (Prior to KF959177) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
32 BAT 168 037 BATTERY, stor 12V (Eff w/KF959177) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
33 107 753 CABLE, bat neg (Prior to KA780148) (consisting of) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
33 023 641 CABLE, bat neg (Eff w/KA780148 thru KE668694) (consisting of) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
33 167 730 CABLE, bat neg (Eff w/KE668695) (consisting of) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
34 Figure 10-2 GENERATOR 1
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
35 113 298 BASE, (Prior to KA780148) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
35 132 195
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
35 146 710
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
36 134 792 LABEL, warning general precautionary engine etc 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
37 057 360 BLANK, snap-in nyl 1.375mtg hole 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
38 DC-Z 113 450 STABILIZER 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
39 AC-Z 113 451 REACTOR 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
40 SR1 142 503 RECTIFIER, si 1ph 300A 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
41 113 562 BRACKET, mtg resistor (Prior to JK559100) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
41 126 072 BRACKET, mtg-resistor (Eff w/JK559100) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
42 114 544 PANEL, front lower 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
43 Figure 10-3 PANEL, front w/components 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
44 CT1 105 370 TRANSFORMER, current 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
45 012 571 HOLDER, fuse mintr 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
46 *083 596 FUSE, mintr cer 12A 250V 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
47 R2,4 008 951 RESISTOR, WW adj 180W 12 ohm 2.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
48 R3,VR1 046 819 SUPPRESSOR 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
49 RC5 116 045 HOUSING PLUG & PINS, (consisting of) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
50 109 994 LABEL, warning engine fuel can cause fire 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
51 013 367 LABEL, warning moving parts can cause serious injury 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
010 493 BUSHING, snap-in nyl .625 ID x .875mtg hole (Prior to KA780148) 2.
115 511 BRACKET, support cover (Prior to KF812089) 2.
071 970 COVER, cable bat post red 1.
114 923 BOOT, insulator term post red (Prior to KA780148) 1.
135 571 BOOT, insulator term post red ( Eff w/KA780148 thru KC220663) 1.
108 081 TERMINAL PROTECTOR, battery post mtg 2.
020 279 CLAMP, stl cushion .750 dia x .281mtg hole (Eff w/KA780148) 2.
071 971 COVER, cable bat post blk 1.
113 633 CONNECTOR, rect univ 084 pin 20-14ga 6.
135 475 KIT, label (Prior to KF959177) 1.
176 908 KIT, label (Eff w/KF959177) 1.
. . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
BASE, (Ef
BASE, (Ef
f w/KA780148 thru KB113873) 1.
f w/KB1
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
13874 and on) 1.
f w/KB1
13874 thru KF959176) 1.
+When ordering a component originally displaying a precautionary label, the label should also be ordered.
*Recommended Spare Parts.
++Optional Parts
BE SURE T
TM-428 Page 54
O PROVIDE MODEL AND SERIAL NUMBER WHEN ORDERING REPLACEMENT P
ARTS.
Miller Legend
Page 59

Item
No.
Dia.
Mkgs.
Part
No.
Description Quantity
Figure 10-2. Generator (Figure 10-1 Item 34)
1 013 367 LABEL, warning fan 2.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2 115 500 LABEL, engine maintenance Onan (Prior to KA780148) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2 134 092 LABEL, engine maintenance Onan P218 (Eff w/KA780148 thru KF959176) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2 176 891 LABEL, engine maintenance Onan P218 (Eff w/KF959177 and on) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3 +113 410 GUARD, fan gen 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4 153 297 ENDBELL, gen (consisting of) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5 143 220 O-RING, 2.859 ID x .139CS 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6 165 756 STATOR, gen 60Hz (Prior to KD438829) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6 162 138 STATOR, gen 60Hz (Eff w/KD438829) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6 165 755 STATOR, gen 50Hz (Prior to KD438829) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6 162 141 STATOR, gen 50Hz (Eff w/KD438829) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
7 017 702
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
8 021 934 ADAPTER, fan rotor (Prior to KA780148) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
8 134 981 ADAPTER, fan rotor (Eff w/KA780148) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
9 008 917 WASHER, flat stl .343 ID x 2 (part of engine) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
10 049 286 ROT
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
11 017 624 FAN, rotor gen 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
12 053 390 BEARING, ball rdl sgl row 1.37 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
13 024 617 RING, retaining ext 1.272 shaft 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
14 SR2 035 704 RECTIFIER, integ 40A 800V 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
15 007 250 BRACKET, mtg brushholder 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
16 047 878 BAR, retaining brushholder 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
17 161 306 CAP, brushholder 3.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
18 *126 984
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
19 005 614 HOLDER, brush 3.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
003 455 KEY, woodruff .250 x .750 SAE No. 91 (part of engine) (Prior to KA780148) 1.
602 348 KEY, stl .250 x .250 x .750 1.
ADAPTER, engine
. . .
OR ASSEMBL
Y, gen (consisting of) 1.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
BRUSH w/SPRING
1.
3.
7
8
9
12 354
11
6
19
18
17
12
13
14
15
16
10
Figure 10-2. Generator
+When ordering a component originally displaying a precautionary label, the label should also be ordered.
*Recommended Spare Parts.
BE SURE T
Miller Legend
O PROVIDE MODEL AND SERIAL NUMBER WHEN ORDERING REPLACEMENT P
ARTS.
TM-428 Page 55
ST-115 942-F
Page 60

Item
No.
Dia.
Mkgs.
Part
No.
Description Quantity
Figure 10-3. Panel, Front w/Components (Figure 10-1 Item 43)
1 RC1,2 604 176 RECEPTACLE, str dx grd 2P3W 15A 125V (Prior to KE629034) 2.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1 RC1,2 167 657 RECEPTACLE, str dx grd 2P3W 15A 125V (Eff w/KE629034) 2.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2 CB1,2 115 427 CIRCUIT BREAKER, man reset 1P 25A 250VAC (Prior to KE629034) 2.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . .
2 CB5,7 168 057 CIRCUIT BREAKER, man reset 1P 20A 250V
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3 113 315 PANEL, front (Prior to JK713332) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3 130 352 PANEL, front (Eff w/JK713332 thru KB133271) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3 143 383 PANEL, front (Eff w/KB133272 thru KF790319) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3 170 554 PANEL, front (Eff w/KF790320 and on) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4 S5 005 563 SWITCH, selector (Figure 10-4) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5 R1 081 712 RHEOSTAT, WW 100W 30 ohm 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6 S4 ++011 609 SWITCH, tgl SPDT 15A 125VAC (Prior to JK713332) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6 S4 ++011 611 SWITCH, tgl DPDT 15A 125V (Eff w/JK713332) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
7 RC7 035 523 CONNECTOR, circ MS/MET 5skt sz 16S rect MS-3102A-16S-8S.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . .
073 690 PLUG, str grd armd 2P3W 15A 125V P&S 5266 DF.
. . .
Amphenol (Prior to JK713332) 1.
Figure 10-4
4
AC (Ef
f w/KE629034) 2.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
28
27
2
1
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
3
5 6 7
8
18
12
13
9
11
17
14 15
10
16
26
25
24
21
TM-428 Page 56
23
20
21
19
22
ST-115 943-J
Figure 10-3. Panel, Front w/Components
Miller Legend
Page 61

Item
No.
Dia.
Mkgs.
Part
No.
Description Quantity
Figure 10-3. Panel, Front w/Components (Figure 10-1 Item 43)
(Continued)
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
7 RC7 ++086 022 CONNECTOR, circ MS/MET 14skt sz 20 MS-3102A-20-27S.
. .
. . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
039 273 CONNECTOR, circ MS/MET 5 pin sz 16S MS-3106A-16S-8P Amphenol.
039 685 CONNECTOR, circ MS/MET clamp str rlf sz 16-16S AN-3057-8 Amphenol.
109 766 CONNECTOR, circ 14 pin MS sz 20 Amphenol 97-4106A-20-27P.
109 770 CONNECTOR, circ MS pin push-in 16-22ga.
039 734 CONNECTOR, circ MS/MET clamp str rlf sz 20-22S.
. . .
. . .
(Eff w/JK713332 thru KD344393) 1.
. . .
. . .
. . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Amphenol AN-3057-12
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
7 PC5 156 025 CIRCUIT CARD, connector/receptacle (Eff w/KD344394) 1.
. . . . . . . . .
8 S1 011 622 SWITCH, tgl 3PDT 15A 125VAC (Prior to JK713332) 1.
. .
8 S1 011 611 SWITCH, tgl DPDT 15A 125V (Eff w/JK713332) 1.
. .
9 S2 172 070 SWITCH, ignition 1.
. .
10 CB3 083 432 CIRCUIT BREAKER, man reset 1P 10A 250V 1.
. .
11 601 836 NUT, brs hex jam hvy .250-20 3.
. .
12 010 915 WASHER, flat brs .250 ID x .625 OD 2.
. .
13 083 030 STUD, brs grd .250-20 x 1.750 1.
. .
14 ♦042 130 METER KIT, (Prior to KD548030) (consisting of) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . .
14 145 247 METER, hour 12-24VDC (Eff w/KD548030) 1.
. .
15 CB1,2 144 474 CIRCUIT BREAKER, man reset 1P 25A 250V
. .
16 RC3 604 103 RECEPTACLE, str dx grd 2P3W 15A 250V (Prior to JH300534) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
16 RC3 129 067 RECEPTACLE, twlk grd 3P4W 30A 125/250V (Eff w/JH300534) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
17 RC4 034 952 RECEPTACLE, str 3P3W 15A 125V 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
18 NAMEPLATE, (order by model & serial number) 1.
. .
19 POS 039 047 TERMINAL, pwr output red (consisting of) 1.
. .
20 NEG 039 046 TERMINAL, pwr output black (consisting of) 1.
. .
21 099 255 TERMINAL, pwr output neutral (consisting of) 2.
. .
22 601 976 SCREW, cap stl hex hd .500-13 x 1.500 1.
. .
23 039 049 TERMINAL BOARD, red 1.
. .
23 039 045 TERMINAL BOARD, black 1.
. .
23 039 040 TERMINAL BOARD, neutral 1.
. .
24 601 880 NUT, stl hex jam .500-13 1.
. .
25 039 044 BUS BAR, term bd 1.
. .
26 601 879 NUT, stl hex full fnsh .500-13 1.
. .
27 073 756 STAND-OFF, No. 6-32 x .625 lg x .250 hex (Eff w/KD344394) 2.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
28 C6 115 109 CAPACITOR, (Prior to KD344394) 1.
. .
28 PC4 148 021 CIRCUIT CARD, filter HF (Eff w/KD344394) 1.
. .
29 111 584 CONTROL, push-pull (Prior to JH283238) 1.
. .
29 116 813 CONTROL, push-pull (Eff w/JH283238) 1.
. .
30 119 014
. .
31 ++108 864 CAP, dust connector 9760-16 (Prior to JK713332) 1.
. .
31 ++109 993 CAP, dust connector 9760-20 (Eff w/JK713332) 1.
. .
32 097 924 KNOB, pointer 1.
. .
33 010 647 PIN, spring cs .156 x 1.250 1.
. .
34 ++021 385 BOOT, tgl switch lever 1.
. .
35 115 493 HANDLE, switch range 1.
. .
C7-11 ++097 749 CAPACITOR, (Eff w/JK713332 thru KD344393) 5.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
HM 032 936 METER, hour 1.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
AC (Ef
. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
f w/KE629034) 2.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
025 234 PLUG, str grd 2P3W 15A 250V Leviton 5443.
. . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
088 898 PLUG, twlk grd 3P4W 30A 125/250V.
. . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
073 690 PLUG, str grd armd 2P3W 15A 125V P&S 5266 DF.
. . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
153 501
147 995 CONNECTOR, rect univ 039skt 22-18 6.
HOUSING PLUG & SOCKETS, (Ef
. . . . . . . . .
f w/KD344394) (consisting of) 1.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
LEVER, switch
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.
++Part of Remote Control Option
♦Effective w/KD548030 Optional Meter Kit became Standard Equipment.
BE SURE T
Miller Legend
O PROVIDE MODEL AND SERIAL NUMBER WHEN ORDERING REPLACEMENT P
ARTS.
TM-428 Page 57
Page 62

Item
No.
Part
No.
Description Quantity
005 563
1 005 562 BRACKET, mtg-switch 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2 005 561 SHAFT, rotor 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3 005 564 INSULATOR, screw switch 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4 605 276 SCREW, cap stl hex hd .250-20 x 1.250 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5 005 559 CONTACT BOARD, movable switch 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6 005 560 CONTACT, switch movable 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
7 008 485 SPACER, contact switch 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
8 005 566 CONTACT BOARD, stationary switch 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
9 011 644 CONTACT, stationary switch 7.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
10 052 405 SPRING, pressure contact switch 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
11 052 404 CONTACT, movable switch 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
12 005 557 BUS BAR, switch range 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
13 005 558 SPRING, selector switch 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 10-4. Switch, Selector (Figure 10-3 Item 4)
10
9
8
7
6
11
1
BE SURE T
5
4
3
2
13
Figure 10-4. Switch, Selector
O PROVIDE MODEL AND SERIAL NUMBER WHEN ORDERING REPLACEMENT P
12
ST-097 264-A
ARTS.
TM-428 Page 58
Miller Legend
Page 63

Item
No.
Dia.
Mkgs.
Part
No.
Description Quantity
Figure 10-5. Control Panel, w/Components (Figure 10-1 Item 2)
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1 1T 038 601 BLOCK, term 30A 9P (Prior to JK713332) 1.
1 1T 130 648 BLOCK, term 30A 10P (Eff w/JK713332) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2 113 682 BRACKET, mtg components (Prior to JK713332) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2 130 649 BRACKET, mtg components (Eff w/JK713332) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3 083 147 GROMMET, scr No.8/10 4.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4 PC2 049 404 CIRCUIT CARD, regulator 115V (Prior to KE604176) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4 PC2 160 888 CIRCUIT CARD, voltage regulator (Eff w/KE604176) (Figure 10-7) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5 CR4 113 247 RELAY, encl 12VDC DPDT 1.
. .
6 CR3 044 588 RELAY, encl 12VDC 3PDT 1.
. .
7 CR2 173 069 RELAY, encl 12VDC SPDT 1.
. .
8 CB4 045 061 CIRCUIT BREAKER, auto reset 24VDC 7A 1.
. .
9 PC1 113 492 CIRCUIT CARD, weld/idle (Prior to JH300534) 1.
. .
9 PC1 142 725 MODULE, pull to weld/power delay (Eff w/JH300534) 1.
. .
10 D4 059 389 DIODE, rect 3A 1000V SP (Prior to JH300534) 1.
. .
10 D4,5 059 389 DIODE, rect 3A 1000V SP (Eff w/JH300534) 2.
. .
11 T1 116 083 TRANSFORMER, control (Prior to KE604176) 1.
. .
11 T1 167 404 TRANSFORMER, control (Eff w/KE604176) 1.
. .
12 038 620 LINK, jumper term blk 30A 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . .
PLG1 168 071 CONNECT
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
114 066 CONNECTOR, rect skt 20-14ga 9.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
D6 117 566 DIODE, rect 6A 600V 1.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1
OR & SOCKETS, (Ef
f w/KE604176) (consisting of) 1.
12
2
3
Figure 10-7
4
11
10
BE SURE T
Miller Legend
7
9
8
6
5
Figure 10-5. Control Panel, w/Components
O PROVIDE MODEL AND SERIAL NUMBER WHEN ORDERING REPLACEMENT P
ST-114 309-B
ARTS.
TM-428 Page 59
Page 64

Item
No.
Dia.
Mkgs.
Part
No.
Description Quantity
+042 132
+042 383
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1 PC3 136 246
2 110 375 STAND-OFF SUPPORT, PC card 4.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3 116 086 BRACKET, mtg remote control (Prior to JK563388) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3 125 873 BRACKET, mtg remote control (Eff w/JK563388) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4 CR5 052 603 RELAY, encl 110VDC DPDT 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5 007 532 CLAMP, capacitor 1.000dia 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6 C5 059 887 CAPACITOR, polyp met film 10uf 220V 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
7 2T 116 005 BLOCK, term 10A 7P 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
8 108 023 LINK, jumper term blk 10A 4.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
9 PLG6 115 091 HOUSING PLUG & SOCKETS, (consisting of) 1.
. .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
113 746 TERMINAL, female 1skt 18-24W 10.
1
Figure 10-6. Remote Control, Option (Figure 10-1 Item 1)
CIRCUIT CARD ASSEMBL
Y, remote control 1.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3
2
9
8
7
Figure 10-6. Remote Control, Option
+See Figure 10-3 for additional parts not listed
BE SURE T
O PROVIDE MODEL AND SERIAL NUMBER WHEN ORDERING REPLACEMENT P
56
4
SB-116 028
ARTS.
TM-428 Page 60
Miller Legend
Page 65

Dia.
Mkgs.
Part
No.
Description Quantity
PC2 160 888
. . . . .
. . . . . .
. . . . .
. . . . .
. . . . .
. . . . .
. . . . .
. . . . .
. . . . .
. . . . .
. . . . .
. . . . .
. . . .
. . . .
. . . . .
. . . . .
. . . .
. . . .
. . . . .
. . . . .
. . . . .
R53,54,65 072 559 RESISTOR, MF .25W 22.1K ohm 3.
. .
. . . . .
. . . .
. . . .
. . . .
. . . . .
. . . . .
. . . . .
. . . . .
. . . . .
. . . . .
. . . . .
. . . . .
. . . . .
. . . . .
. . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
A50 165 411 IC, linear 2904 1.
C1 003 530 CAPACITOR, cer mono 1uf 50VDC 1.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
C50 119 199 CAPACITOR, polye met film 1uf 50V 1.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
C51 053 992 CAPACITOR, cer disc .001uf 1000VDC 1.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
C52 000 348 CAPACITOR, tantlm .47uf 35V 1.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
C53 005 023 CAPACITOR, tantlm 2.2uf 20V 1.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
C54 072 935 CAPACITOR, elctlt 33uf 35VDC 1.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
C55 137 463 CAPACITOR, polye met film .22uf 100VDC 1.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
C56 072 113 CAPACITOR, tantlm 4.7uf 35VDC 1.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
C57 028 292 CAPACITOR, cer disc .005uf 1000VDC 1.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
D50 028 351 DIODE, sig 200mA 75V SP 1.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
D51 049 641 DIODE, zener 27V 1W 1.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
D52-54 026 202 DIODE, rect 1A 400V SP 3.
D55-58 070 250 DIODE, rect 3A 600V 4.
D59 030 529 DIODE, rect 22A 600V RP 1.
Q50 039 355 TRANSISTOR, ujt 15mA 40V 1.
Q51,52 037 200 TRANSISTOR, NPN 200mA 40V 2.
Q53,54 049 642 THYRIST
R50 094 447 RESISTOR, MF .25W 681K ohm 1.
R51 044 789 RESISTOR, MF .25W 100K ohm 1.
R52 035 829 RESISTOR, MF .25W 1.5K ohm 1.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
R55 115 530 RESISTOR, MF .25W 2.67K ohm 1.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
R56,64 000 885 RESISTOR, MF .25W 10K ohm 2.
R57,62 028 285 RESISTOR, C .5W 100 ohm 2.
R58,63 035 823 RESISTOR, MF .25W 100 ohm 2.
R59 072 559 RESISTOR, MF .25W 22.1K ohm 1.
R60 074 026 RESISTOR, C .25W 150 ohm 1.
R61 138 301 POTENTIOMETER, cermet trmr 1/T .5W 25K ohm 1.
R66 093 030 RESISTOR, MF .25W 15K ohm 1.
R67 093 032 RESISTOR, MF .25W 26.7K ohm 1.
R68 108 437 RESISTOR, MF .25W 4.75K ohm 1.
R69 049 439 RESISTOR, C 2W 47K ohm 1.
R70 074 099 RESISTOR, C 1W 150 ohm 1.
R71 030 707 RESISTOR, C 1W 47 ohm 1.
RC1 160 892 CONNECTOR, rect 9 pin 3 row rcpt 1.
VR50 083 772 IC, rgltr 7815 1.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 10-7. Circuit Card, Voltage Regulator (Figure 10-5 Item 4)
OR, SCR 8A 600V
2.
BE SURE T
Miller Legend
Figure 10-7. Circuit Card, Voltage Regulator PC2
O PROVIDE MODEL AND SERIAL NUMBER WHEN ORDERING REPLACEMENT P
SA-160 889
ARTS.
TM-428 Page 61
Page 66

Notes
Page 67

Notes
Page 68

 Loading...
Loading...