Miller Electric AEAD-200-LE User Manual
February 1996 |
Form: TM-428 |
Effective With Serial No. JH242114
TECHNICAL MANUAL
Service And Parts
Miller Legend
(Formerly The Legend AEAD-200LE)
CC AC/DC Welding Generator For SMAW, GMAW, GTAW Welding
Welding |
Weld |
Rated |
Maximum |
Auxiliary Power |
|
|
|
Output |
Welding |
Open-Circu |
Fuel Capacity |
Engine |
|||
Mode |
Rating |
||||||
Range |
Output |
it Voltage |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
225 A, 25 V, |
|
Single-Phase, |
|
|
|
CC/AC |
35 ± 225 A |
100% Duty |
80 |
5 kVA/kW, 42/21 A, |
|
Onan P218 Air-Cooled, |
|
|
|
Cycle |
|
120/240 V AC, 60 Hz |
|
||
|
|
|
|
And |
7.5 gal (28 L) Tank |
Two-Cylinder, Four-Cycle, |
|
|
|
200 A, 25 V, |
|
Single-Phase, |
|
Gasoline Engine |
|
CC/DC |
25 ± 200 A |
100% Duty |
72 |
1 kVA/kW, 9 A, |
|
|
|
|
|
Cycle |
|
115 V AC, 100 Hz |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
cover_tm 4/95 ± ST-140 091-E |
|
1996 |
MILLER Electric Mfg. Co. |
|
PRINTED IN USA |
||

TABLE OF CONTENTS
SECTION 1 ± SAFETY PRECAUTIONS FOR SERVICING . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
1 |
|
1-1. |
Symbol Usage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
1 |
1-2. |
Servicing Hazards . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
1 |
1-3. |
EMF Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
2 |
SECTION 2 ± INSTALLATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
3 |
|
2-1. |
Installing Welding Generator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
3 |
2-2. |
Dimensions, Weights, And Operating Angles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
3 |
2-3. |
Fuel Consumption . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
4 |
2-4. |
Engine Prestart Checks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
4 |
2-5. |
Connecting The Battery . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
5 |
2-6. |
Connecting To Weld Output Terminals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
5 |
2-7. |
Selecting Weld Cable Sizes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
6 |
2-8. |
Remote 14 Receptacle RC1 Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
6 |
SECTION 3 ± OPERATING WELDING GENERATOR . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
7 |
|
3-1. |
Front Panel Controls . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
7 |
3-2. |
Remote Control (Optional) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
8 |
3-3. |
Duty Cycle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
8 |
3-4. |
Volt-Ampere Curves . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
9 |
SECTION 4 ± OPERATING AUXILIARY EQUIPMENT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
10 |
|
4-1. |
100 Hz Auxiliary Power Receptacle And Circuit Breaker . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
10 |
4-2. |
AC Auxiliary Power Curve . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
10 |
4-3. |
60 Hz Auxiliary Power Receptacles And Circuit Breakers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
11 |
SECTION 5 ± THEORY OF OPERATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
12 |
|
SECTION 6 ± TROUBLESHOOTING . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
15 |
|
6-1. |
Troubleshooting Tables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
15 |
6-2. |
Troubleshooting Circuit Diagram For Welding Generator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
18 |
6-3. |
Troubleshooting Circuit Diagram For Welding Generator With Optional Remote Control . . |
20 |
6-4. |
Waveforms For Sections 6-2 And 6-3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
22 |
6-5. |
Idle Control Board/Module PC1 Testing Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
23 |
6-6. |
Troubleshooting Flowcharts For Idle Control Board/Module PC1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
24 |
6-7. |
Voltage Regulator Board PC2 Testing Information Prior To Serial No. KE604176 . . . . . . . . |
26 |
6-8. |
Voltage Regulator Board PC2 Test Point Values Prior To Serial No. KE604176 . . . . . . . . . |
26 |
6-9. |
Voltage Regulator Board PC2 Testing Information Effective With Serial No. KE604176 . . . |
27 |
6-10. |
Voltage Regulator Board PC2 Test Point Values Effective With Serial No. KE604176 . . . . |
27 |
6-11. |
Optional Remote Control Board PC3 Testing Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
28 |
6-12. |
Optional Remote Control Board PC3 Test Point Values . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
28 |
6-13. |
Optional Remote Capacitor Board PC5 Testing Information Effective With |
|
|
Serial No. KD346698 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
29 |
6-14. |
Optional Remote Capacitor Board PC5 Test Point Values Effective With |
|
|
Serial No. KD346698 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
29 |
6-15. |
Replacing Brushes And Cleaning Slip Rings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
30 |
6-16. |
Checking Unit Output After Servicing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
32 |
WHO DO I CONTACT FOR HELP?
|
|
|
|
H CALL: |
|
|
|
H FAX: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
H WRITE: |
|
|
|
|
|
Miller Customer Service |
|
|
|
800-637-2348 (in USA), |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Miller Electric Mfg. Co. |
|
|
|
|
|
Department at |
|
|
|
|
or |
|
|
|
|
|
|
P.O. Box 1079 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
414-735-4505 |
|
|
|
|
414-735-4136 (outside USA) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Appleton, WI 54912 USA |
||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Always provide Model Name and Serial or Style Number
OM-428N 1/96 ± SPM-428C 6/94
SECTION 7 ± DISASSEMBLY AND REASSEMBLY . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
33 |
|
7-1. |
Disassembly Of Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
33 |
7-2. |
Disassembly Of Generator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
34 |
SECTION 8 ± MAINTENANCE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
35 |
|
8-1. |
Routine Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
35 |
8-2. |
Maintenance Label . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
36 |
8-3. |
Servicing Air Cleaner . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
37 |
8-4. Changing Engine Oil, Oil Filter, And Fuel Filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
38 |
|
8-5. |
Adjusting Engine Speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
39 |
8-6. |
Overload Protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
40 |
8-7. Inspecting And Cleaning Optional Spark Arrestor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
40 |
|
SECTION 9 ± ELECTRICAL DIAGRAMS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
41 |
|
SECTION 10 ± PARTS LIST . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
51 |
|

SECTION 1 ± SAFETY PRECAUTIONS FOR SERVICING
safety_rtm1 4/95
1-1. Symbol Usage
Means Warning! Watch Out! There are possible hazards with this procedure! The possible hazards are shown in the adjoining symbols.
Y Marks a special safety message.
. Means NOTE; not safety related.
This group of symbols means Warning! Watch Out! possible ELECTRIC SHOCK, MOVING PARTS, and HOT PARTS hazards. Consult symbols and related instructions below for necessary actions to avoid the hazards.
1-2. Servicing Hazards
WARNING |
The symbols shown below are used throughout this manual to call attention to and identify possible hazards. When you see the symbol, watch out, and follow the related instructions to avoid the hazard.
Only qualified persons should service, test, maintain, and repair this unit.
During servicing, keep everybody, especially children, away.
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill.
1.Do not touch live electrical parts.
2.Stop engine before testing or repairing unit unless the procedure specifically requires an energized unit.
3.Insulate yourself from ground by standing or working on dry insulating mats big enough to prevent contact with the ground.
4.Do not leave live unit unattended.
5.When testing live unit, use the one-hand method.
Do not put both hand inside unit. Keep one hand free.
MOVING PARTS can cause injury.
1.Keep away from moving parts such as fans, belts, and rotors.
2.Have only qualified people remove guards or covers for maintenance and troubleshooting as necessary.
3.Keep hands, hair, loose clothing, and tools away from moving parts.
4.Before working on generator, remove spark plugs or injectors to keep engine from kicking back or starting.
5.Block flywheel so that it will not turn while working on generator components.
6.Reinstall panels or guards and close doors when servicing is finished and before starting engine.
FLYING PIECES OF METAL or DIRT can cause injury.
1.Always wear safety glasses with side shields or face shield during servicing.
2.Be careful not to short metal tools, parts, or wires together during testing and servicing.
STATIC ELECTRICITY can damage parts on circuit boards.
1.Put on grounded wrist strap BEFORE handling boards or parts.
2.Use proper static-proof bags to store, move, or ship PC boards.
ENGINE EXHAUST GASES can kill.
1.Do not breathe exhaust fumes.
2.Use in open, well-ventilated areas, or vent exhaust outside and away from any building air intakes.
ENGINE FUEL can cause fire or explosion.
1.Stop engine before fueling.
2.Do not fuel while smoking or near sparks or flames.
3.Do not overfill tank; clean up any spilled fuel.
BATTERY EXPLOSION can BLIND and INJURE.
1.Always wear a face shield when working on a battery.
2.Stop engine before disconnecting or connecting battery cables.
3.Do not allow tools to cause sparks when working on a battery.
4.Do not use welder to charge batteries or jump start vehicles.
5.Observe correct polarity (+ and ±) on batteries.
BATTERY ACID can BURN SKIN.
1.Do not tip.
2.Replace damaged battery.
3.Flush eyes and skin immediately with water.
STEAM AND PRESSURIZED HOT COOLANT can burn face, eyes, and skin.
1.Check coolant level when engine is cold to avoid scalding.
2.If the engine is warm and checking is needed, follow steps 3 and 4.
3.Wear safety glasses and gloves and put a rag over cap.
4.Turn cap slightly and let pressure escape slowly before completely removing cap.
FALLING EQUIPMENT can cause serious personal injury and equipment damage.
1.Use equipment of adequate capacity to lift components.
2.Use a lifting eye to lift unit only, NOT running gear, gas cylinders, or any other accessories.
3.Securely attach components to lifting equipment.
Miller Legend |
TM-428 Page 1 |
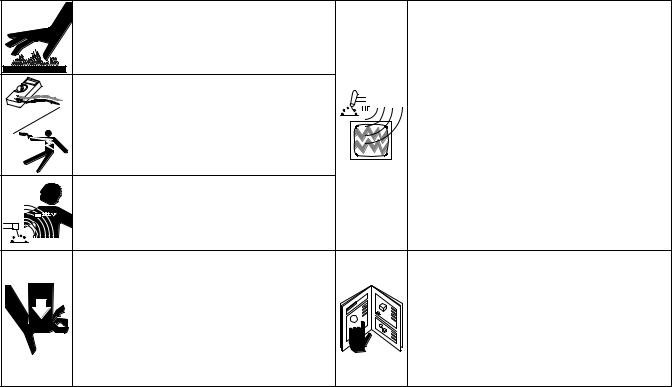
HOT PARTS can cause severe burns. |
HIGH-FREQUENCY RADIATION can |
||||||||
1. |
Allow cooling period before servicing. |
|
interfere with radio navigation, safety |
||||||
2. |
Wear protective gloves and clothing when working |
services, |
computers, |
and |
|||||
|
on a hot engine. |
|
|
communications equipment. |
|
||||
ELECTRIC |
SHOCK |
HAZARD |
from |
1. |
Have only qualified persons familiar with |
||||
|
electronic equipment perform this installation. |
||||||||
incorrect use of test equipment. |
|
2. |
The user is responsible for having a qualified |
||||||
1. |
Stop engine before making or changing meter |
|
electrician promptly correct any interference |
||||||
|
lead connections. |
|
|
|
problem resulting from the installation. |
|
|||
2. |
At least one meter lead should be a self-retaining |
3. |
If notified by the FCC about interference, stop |
||||||
|
spring clip such as an alligator clamp. |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
using the equipment at once. |
|
|||||
3. |
Read instructions for test equipment. |
|
|
|
|||||
|
4. |
Have the installation regularly checked and |
|||||||
MAGNETIC |
FIELDS |
FROM |
HIGH |
||||||
|
maintained. |
|
|
||||||
CURRENTS |
can affect pacemaker |
5. |
Keep high-frequency source doors and panels |
||||||
operation. |
|
|
|
|
tightly shut, keep spark gaps at correct setting, |
||||
1. |
Pacemaker wearers keep away from servicing |
|
and use grounding and shielding to minimize the |
||||||
|
areas until consulting your doctor. |
|
|
possibility of interference. |
|
||||
UNCONTROLLED TILTING OR TIPPING |
READ INSTRUCTIONS. |
|
|||||||
OF UNIT can result in personal injury |
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||
and equipment damage. |
|
1. |
Use MILLER Testing Booklet (Part No. 150 853) |
||||||
1. |
Do not put any body part under unit while lifting. |
|
when servicing this unit. |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
||||||
2. |
Use adequate blocks to support components as |
2. |
Consult the Owner's Manual for welding safety |
||||||
|
needed during job. |
|
|
|
precautions. |
|
|
||
PINCH POINTS can injure. |
|
3. |
Use only genuine MILLER replacement parts. |
||||||
1. |
Be careful when working on stator and rotor |
4. |
Reinstall injectors and bleed air from fuel system |
||||||
|
assemblies. |
|
|
|
|
according to engine manual. |
|
||
1-3. EMF Information
Considerations About Welding And The Effects Of Low Frequency |
To reduce magnetic fields in the workplace, use the following |
||
Electric And Magnetic Fields |
procedures: |
||
The following is a quotation from the General Conclusions Section |
1. |
Keep cables close together by twisting or taping them. |
|
of the U.S. Congress, Office of Technology Assessment, Biological |
|||
|
|
||
Effects of Power Frequency Electric & Magnetic Fields ± |
2. |
Arrange cables to one side and away from the operator. |
|
Background Paper, OTA-BP-E-53 (Washington, DC: U.S. |
|
|
|
Government Printing Office, May 1989): ª. . . there is now a very |
3. |
Do not coil or drape cables around the body. |
|
large volume of scientific findings based on experiments at the |
4. |
Keep welding power source and cables as far away as |
|
cellular level and from studies with animals and people which clearly |
|||
establish that low frequency magnetic fields can interact with, and |
|
practical. |
|
produce changes in, biological systems. While most of this work is of |
5. |
Connect work clamp to workpiece as close to the weld as |
|
very high quality, the results are complex. Current scientific |
|||
understanding does not yet allow us to interpret the evidence in a |
|
possible. |
|
single coherent framework. Even more frustrating, it does not yet |
About Pacemakers: |
||
allow us to draw definite conclusions about questions of possible |
|||
|
|
||
risk or to offer clear science-based advice on strategies to minimize |
The above procedures are also recommended for pacemaker |
||
or avoid potential risks.º |
wearers. Consult your doctor for complete information. |
||
|
|
|
|
TM-428 Page 2 |
Miller Legend |
SECTION 2 ± INSTALLATION
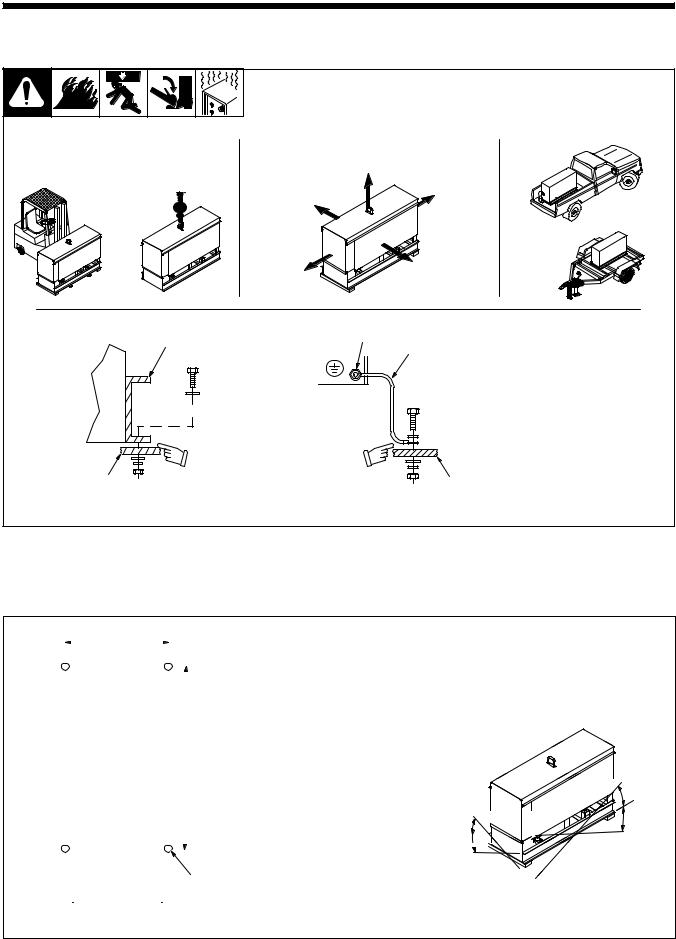
2-1. Installing Welding Generator
Movement |
Airflow |
Location |
Y Do Not Lift Unit From End |
|
18 in |
|
|
(460 mm) |
|
|
18 in |
|
18 in |
(460 mm) |
|
|
|
|
(460 mm) |
OR |
|
|
|
OR |
|
|
|
18 in |
18 in |
|
(460 mm) |
|
|
(460 mm) |
|
|
|
Grounding
1 |
3 |
|
4 |
||
|
||
|
GND/PE |
|
|
OR |
|
Electrically bond generator frame to |
|
2 |
vehicle frame |
by metal-to-metal |
contact. |
2 |
|
1Generator Base
2Metal Vehicle Frame
3Equipment Grounding Terminal
4Grounding Cable
Use #10 AWG or larger insulated copper wire.
YIf unit does not have GFCI receptacles, use GFCI-pro- tected extension cord.
install1 10/95 ± Ref. ST-800 652 / Ref. ST-800 477-A / ST-158 936-A / S-0854
2-2. Dimensions, Weights, And Operating Angles
|
|
|
A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dimensions |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Height |
31-5/8 in (803 mm) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Width |
18 in (457 mm) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Depth |
45 in (1143 mm) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
B |
|
|
A |
16-1/2 in (419 mm) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
B |
32-3/4 in (832 mm) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C |
13/16 in (21 mm) Dia. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weight |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net |
559 lb (254 kg) |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Engine End |
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
Ship |
600 lb (272 kg) |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
YDo not exceed operating angles while running or engine damage will occur.
YDo not move or operate unit where it could tip.
25°
25° |
25° |
|
25°


Miller Legend |
TM-428 Page 3 |
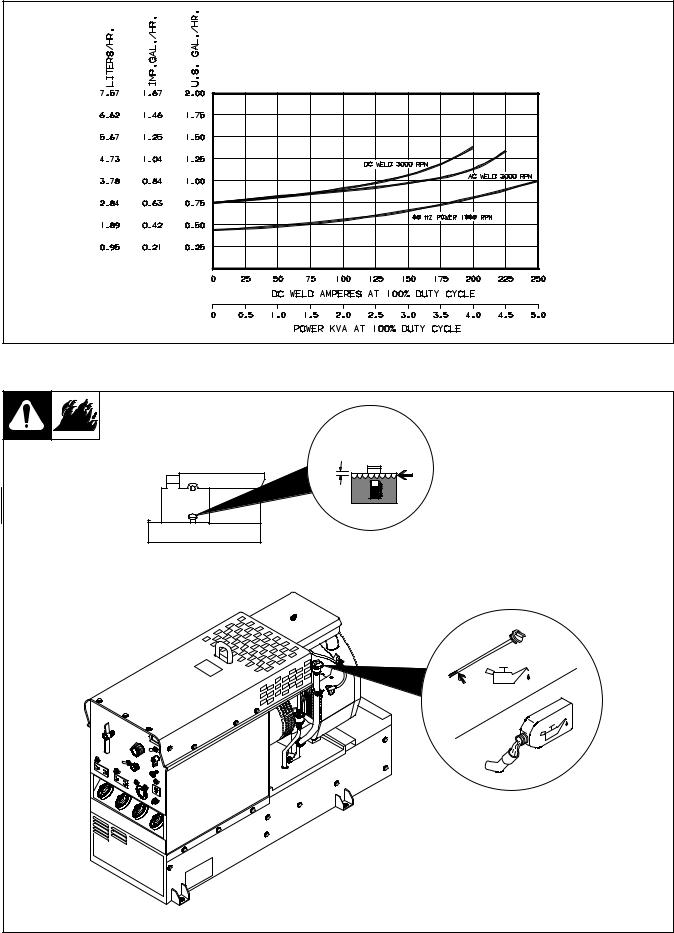
2-3. Fuel Consumption
|
|
SB-115 572 |
2-4. Engine Prestart Checks |
|
|
|
|
Check all fluids daily. Engine must |
|
|
be cold and on a level surface. |
|
1/2 in |
Engine stops if oil pressure gets |
|
too low. |
|
|
(13 mm) |
|
|
Full |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Full |
|
|
ST-140 091-E / Ref. ST-151 983 |
TM-428 Page 4 |
|
Miller Legend |
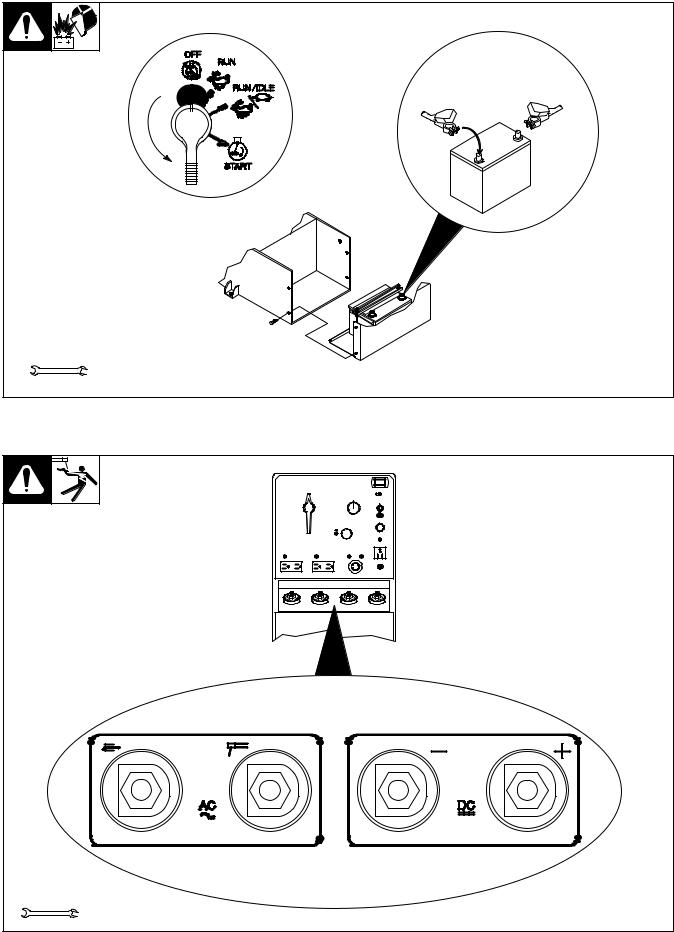
2-5. Connecting The Battery
Y Connect (±) cable last.
+ ±
Tools Needed:
3/8, 1/2 in
Ref. ST-144 839-F / Ref. ST-168 046 / Ref. S-0756-D
2-6. Connecting To Weld Output Terminals
Y Use ONLY one set of terminals at a time. Disconnect weld cables from set of weld output terminals not in use.
Tools Needed:
3/4 in
ST-140 092-B / Ref. ST-168 046
Miller Legend |
TM-428 Page 5 |
2-7. Selecting Weld Cable Sizes
|
|
Total Cable (Copper) Length In Weld Circuit Not Exceeding |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
100 ft (30 m) Or Less |
150 ft |
200 ft |
250 ft |
300 ft |
|
350 ft |
400 ft |
|
|
(45 m) |
(60 m) |
(70 m) |
(90 m) |
|
(105 m) |
(120 m) |
||
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Welding |
10 ± 60% |
60 ± 100% |
|
|
10 ± 100% Duty Cycle |
|
|
||
Amperes |
Duty Cycle |
Duty Cycle |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
100 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
|
1/0 |
1/0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
150 |
3 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
1/0 |
2/0 |
|
3/0 |
3/0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
200 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
1/0 |
2/0 |
3/0 |
|
4/0 |
4/0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
250 |
2 |
1 |
1/0 |
2/0 |
3/0 |
4/0 |
|
2-2/0 |
2-2/0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
300 |
1 |
1/0 |
2/0 |
3/0 |
4/0 |
2-2/0 |
|
2-3/0 |
2-3/0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
350 |
1/0 |
2/0 |
3/0 |
4/0 |
2-2/0 |
2-3/0 |
|
2-3/0 |
2-4/0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weld cable size (AWG) is based on either a 4 volts or less drop or a current density of at least 300 circular mils per ampere. |
S-0007-D |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
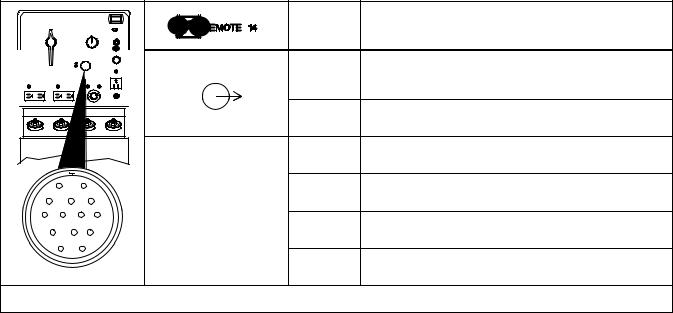
2-8. Remote 14 Receptacle RC1 Information
|
|
|
|
Socket* |
Socket Information |
|
|
|
|
A |
Contact closure to B completes 15 volts dc contactor control |
|
|
|
|
|
circuit. |
|
|
|
|
B |
15 volts dc. |
|
|
|
|
C |
+4.5 volts dc output to remote control. |
A |
K |
J |
A |
D |
Remote control circuit common. |
B |
I |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
C L |
N |
H |
E |
0 to +4.5 volts dc input command signal from remote control. |
|
D |
M |
G |
|||
|
E |
F |
|
K |
Chassis common. |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
ST-140 092-B |
|
|
|
*The remaining sockets are not used.
TM-428 Page 6 |
Miller Legend |
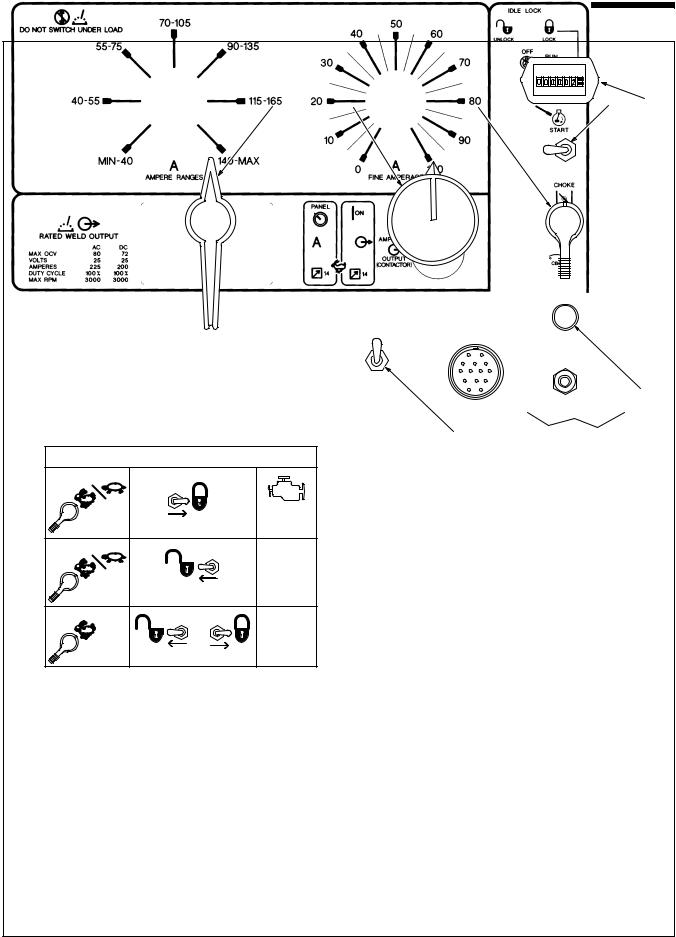
SECTION 3 ± OPERATING WELDING GENERATOR
3-1. Front Panel Controls
5 |
6 |
1 |
2 |
7 |
3
4
Using Idle Lock Switch
RUN/IDLE |
|
LOCK |
1860 rpm |
(Power/Idle) |
|
RUN/IDLE |
No Load: |
|
1860 rpm |
|
(Power/Idle) |
UNLOCK |
Load: |
3000 rpm |
|
|
(Weld) |
RUN |
|
OR |
3000 rpm |
|
(Weld) |
UNLOCK |
LOCK |
Ref. ST-168 046
1 Engine Control Switch S2
Use switch to start engine, select speed, and stop engine. In Run/Idle position, engine runs at power/idle rpm at no load, and weld/power rpm under weld or 100 Hz auxiliary power receptacle load. In Run position, engine runs at weld rpm.
2 Idle Lock Switch S1
Use switch to lock engine at power/idle speed (see Table). In Unlock position, Engine Control switch and optional Remote Control switch determine engine speed.
3 Engine Choke Control
Use control to change engine air-fuel mix.
To Start: pull out choke and turn Engine
Control switch to Start position. Release switch and slowly push choke in when engine starts. Do not crank engine while flywheel is turning.
To Stop: turn Engine Control switch to Off position.
4 Remote Control Switch S4
Use switch to select front panel or remote amperage control (see Section 3-2).
5 Ampere Ranges Switch S5
Use switch to select weld amperage range.
.For best arc starts, use lowest amperage range possible.
6 Fine Amperage Control R1
Use control to select weld amperage within the range selected by the Ampere Ranges switch. Control may be adjusted while welding. Scale is for reference only. Weld output would be 88 A DC with control settings as shown (50% of 70 to 105 A).
7 Engine Hour Meter HM
Miller Legend |
TM-428 Page 7 |
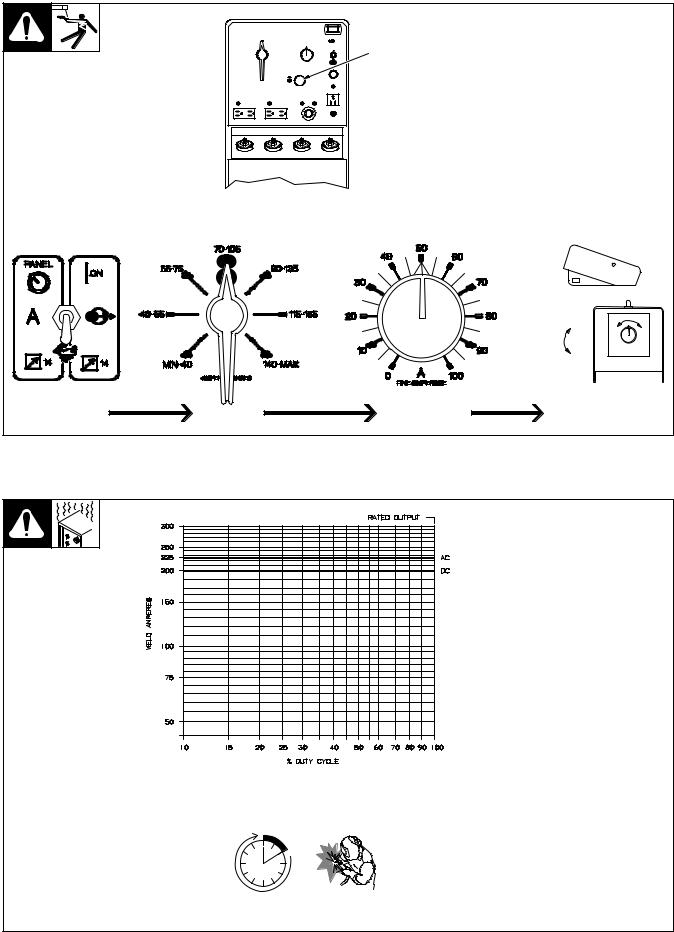
3-2. Remote Control (Optional) |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
Y Weld output terminals are |
||
|
|
|
|
energized |
when |
Remote |
|
|
|
1 |
Control switch S4 is in Pan- |
||
|
|
|
el/On position and engine is |
|||
|
|
|
|
running. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 Remote 14 Receptacle RC1 |
||
|
|
|
|
Connect optional remote control to |
||
|
|
|
|
RC1 (see Section 2-8). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
In Example: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Min = 70 A DC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Percentage Of Range = 50% |
||
|
|
|
|
Max = 88 A DC (50% of 70 to 105) |
||
|
|
|
|
Max (88 A DC) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Min (70 A DC) |
|
|
|
Set Switch |
Set Range |
Set Percentage |
Adjust Remote Control |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
ST-140 092-B |
3-3. |
Duty Cycle |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Duty cycle is the percentage of 10 |
||
|
|
|
|
minutes that unit can weld at rated |
||
|
|
|
|
load without overheating. |
||
|
|
|
|
Y Exceeding |
duty cycle can |
|
|
|
|
|
damage unit and void war- |
||
|
|
|
|
ranty. |
|
|
100% Duty Cycle at 225 Amperes AC
Continuous Welding
SB-115 570
TM-428 Page 8 |
Miller Legend |
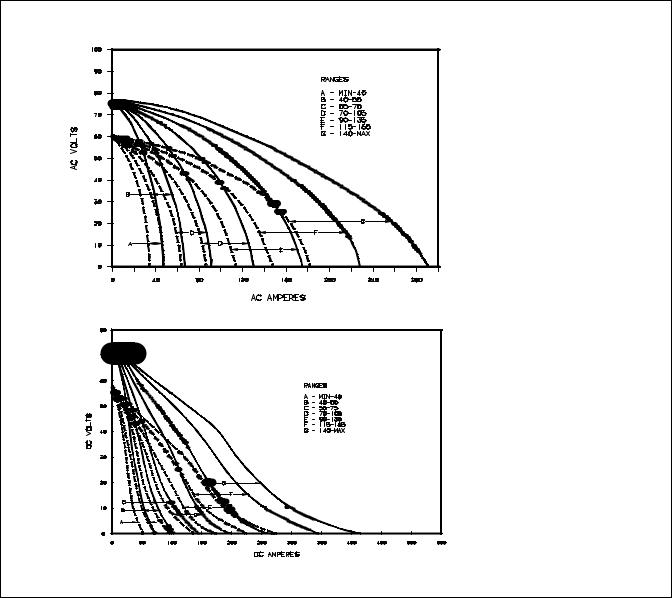
3-4. Volt-Ampere Curves
The volt-ampere curves show the minimum and maximum voltage and amperage output capabilities of the welding generator. Curves of other settings fall between the curves shown.
SB-115 529-A / SB-115 528-A
Miller Legend |
TM-428 Page 9 |
SECTION 4 ± OPERATING AUXILIARY EQUIPMENT
4-1. 100 Hz Auxiliary Power Receptacle And Circuit Breaker
|
Y Do not operate 50/60 Hz or |
|
|
60 Hz equipment from 100 |
|
|
Hz receptacle. |
|
|
1 115 V 9 A 100 Hz AC Recep- |
|
|
tacle RC4 |
|
|
Receptacle supplies single-phase |
|
|
power at weld speed only. Total |
|
|
output available is 1 kVA/kW. |
|
|
2 Circuit Breaker CB3 |
|
|
CB3 protects receptacle from |
|
2 |
overload. If CB3 opens, receptacle |
|
does not work. |
||
|
1
Ref. ST-168 046
4-2. AC Auxiliary Power Curve
SB-115 571
TM-428 Page 10 |
Miller Legend |
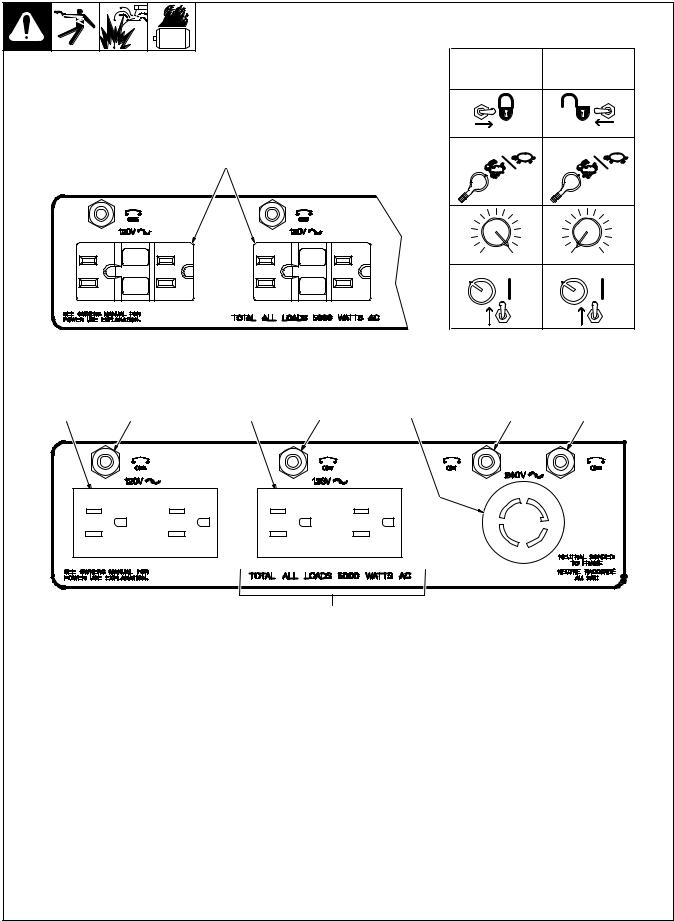
4-3. 60 Hz Auxiliary Power Receptacles And Circuit Breakers
For 60 Hz |
For 60 Hz |
||
Auxiliary Power |
Auxiliary |
||
While Welding |
Power Only |
||
|
LOCK |
UNLOCK |
|
|
RUN/IDLE |
RUN/IDLE |
|
4 |
|
|
|
0 |
100 |
0 |
100 |
PANEL |
PANEL |
|
|
|
ON |
|
ON |
1 |
5 |
2 |
6 |
3 |
7 |
8 |
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
9 |
|
Ref. ST-168 046 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
YIf unit does not have GFCI receptacles, use GFCI-protected extension cord.
1120 V 15 A AC Duplex Receptacle RC1
2120 V 15 A AC Duplex Receptacle RC2
3240 V 30 A Twistlock Receptacle RC3
Receptacles supply 60 Hz single-phase power at power/idle speed only. Maximum output from each duplex receptacle is is 2.5 kVA/kW. Maximum output from twistlock receptacle is 5 kVA/kW. For 60 Hz auxiliary power, set controls as shown in table.
4120 V 15 A AC Duplex GFCI Receptacles GFCI1 And GFCI2 (Optional)
If a ground fault is detected, the GFCI recep-
tacle Reset button pops out and the circuit opens to disconnect the faulty equipment. Check for damaged tools, cords, plugs, etc. connected to the receptacle. Press button to reset receptacle and resume operation.
.At least once a month, run engine at power/idle speed and press Test button to verify GFCI is working properly.
5Circuit Breaker CB5
6Circuit Breaker CB7
CB5 protects RC1 and CB7 protects RC2 from overload. If CB5 or CB7 opens, the receptacle does not work. Press button to reset breaker.
7 Circuit Breaker CB1
8 Circuit Breaker CB2
CB1 and CB2 protect all the 60 Hz receptacles from overload. If CB1 or CB2 opens, the 240 volt receptacle and one of the 120 volt receptacles does not work. 120 volts may still be present at the 240 volt receptacle. Press button to reset breaker.
9 Total Auxiliary Power Output
Combined output of receptacles limited to the 5 kVA/kW output of the generator:
EXAMPLE: If 10 A is drawn from a 120 V duplex receptacle, only 16 A is available at the 240 V receptacle:
(120 V x 10 A) + (240 V x 16 A) = 5.0 kVA/kW
Miller Legend |
TM-428 Page 11 |
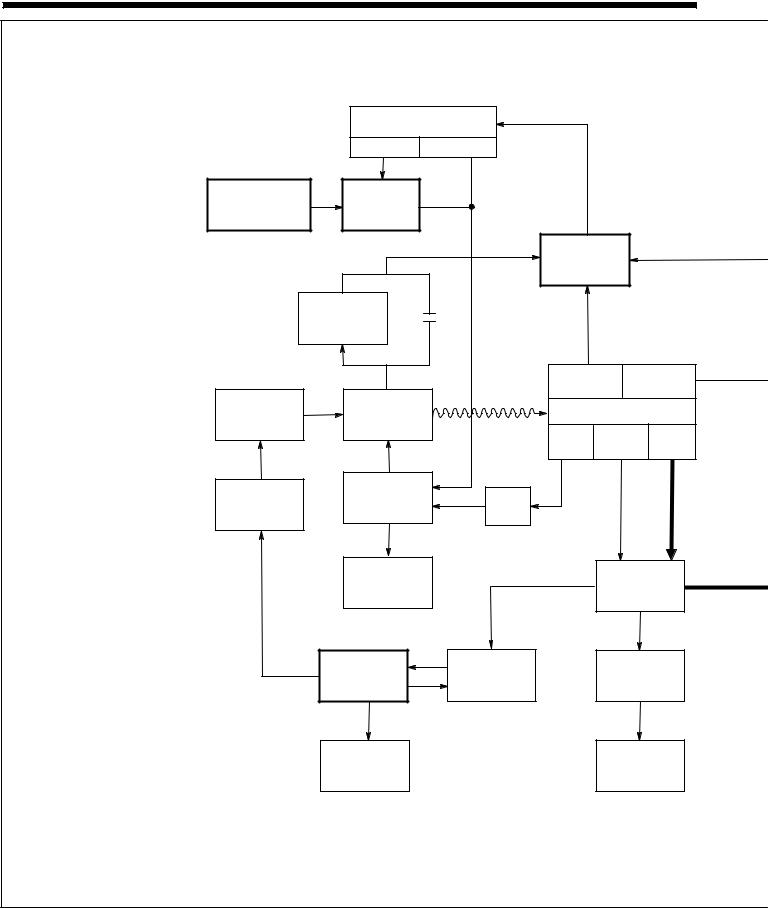
SECTION 5 ± THEORY OF OPERATION
1 Engine
Supplies force to turn revolving fields.
2 Revolving Fields (Rotor)
Turn at 1860 rpm maximum for power/idle and 3000 rpm maximum for weld. The speed and excitation current of the field coils determine voltages in stator windings.
3 Stator Windings
Supply power to exciter, auxiliary power, and weld circuits.
4 Fuse F1
Protects exciter excitation winding from overload.
5 Integrated Rectifier SR2
Changes ac output of stator windings to dc to supply excitation current to the exciter revolving field.
6 Control Relay CR5
Energizes when voltage is present in exciter stator to disconnect field flashing circuit.
7Idle Module PC1 And Idle Lock
Switch S1
PC1 and S1 control engine speed. Without a signal from CT1, PC1 lowers engine speed to power/idle rpm.
8 Throttle Solenoid TS1
Increases engine speed to weld rpm when energized.
9 Current Transformer CT1
Senses output from either weld or 100 Hz auxiliary power windings, and signals PC1 to increase to or maintain weld rpm.
10 Control Relays CR2, CR3, CR4
CR2 energizes at weld rpm to supply power to throttle solenoid TS1.
CR3 energizes at power/idle rpm to bypass fine amperage control R1.
CR4 energizes at power/idle rpm to provide 50/60 Hz auxiliary power output.
11Voltage Regulator Board PC2
And Transformer T1
PC2 monitors 50/60 Hz auxiliary power voltage through T1, and maintains proper output by adjusting field current.
12Capacitor Board PC5, Remote 14 Receptacle RC1, Remote Control Board PC3
PC5 protects unit from high frequency. RC1 connects remote amperage and contactor control to unit through control board PC3.
|
13♦ |
|
|
|
|
|
Remote Control |
|
|
|
|
|
Switch S4 |
|
|
|
|
|
Remote 14 |
Panel |
|
|
|
12♦ |
12♦ |
|
|
|
|
Capacitor Board |
Remote |
|
|
|
|
PC5 And Remote 14 |
Control Board |
|
|
|
|
Receptacle RC1 |
PC3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
11 |
|
|
|
|
|
Voltage |
|
|
|
|
|
Regulator |
|
|
|
|
|
Board PC2 |
|
|
|
18 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fine |
CR3 |
|
|
|
|
Amperage |
|
|
|
|
|
Control R1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
1 |
2 |
Voltage |
60 Hz Auxiliary |
||
Regulator |
Power |
||||
Engine |
Revolving |
Stator Windings |
|
||
Fields (Rotor) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
100 Hz |
|
||
|
|
Exciter |
Weld |
||
|
|
Auxiliary |
|||
|
5 |
|
Power |
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
Integrated |
|
|
|
|
Throttle |
Fuse |
|
|
|
|
Solenoid |
Rectifier SR2 |
|
|
|
|
F1 |
|
|
|
||
TS1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6♦ |
|
9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Control |
|
|
Current |
|
|
Relay |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Transformer |
||
|
CR5 |
|
|
CT1 |
|
|
7 |
7 |
16 |
|
|
|
Idle Module |
Idle Lock |
|
Circuit |
|
|
PC1 |
Switch S1 |
|
Breaker |
|
|
|
|
|
CB3 |
|
|
10 |
|
17 |
|
|
|
Control Relays |
|
|
100 Hz |
|
|
CR2, CR3, CR4 |
|
Auxiliary Power |
||
|
|
|
Receptacle RC4 |
||
TM-428 Page 12 |
Miller Legend |

11
CR4
Transformer
T1
14 |
15 |
||
|
Circuit |
|
50/60 Hz |
|
Breakers |
|
Auxiliary Power |
|
CB1, CB2, |
|
Receptacles |
|
CB5, CB7 |
|
RC1, RC2, RC3 |
|
|
|
|
19
Ampere
Ranges
Switch S5
|
20 |
|
|
|
23 |
|
25 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
Reactor |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Electrode And |
||
|
AC-Z |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Work AC Weld |
||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Output Terminals |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
21 |
|
|
|
|
HF Filter |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Main |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
Board |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Rectifier |
|
|
PC4 |
|
|
|
|
||
|
SR1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
22 |
|
|
|
|
|
24 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Positive (+) And |
|
Stabilizer |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Negative (±) DC |
||
|
DC-Z |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weld Output |
||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Terminals |
13 Remote Control Switch S4
Selects Panel or remote amperage control.
14Circuit Breakers CB1, CB2, CB5, And CB7
Protect 50/60 Hz auxiliary power receptacles RC1, RC2, and RC3 from overload.
1550/60 Hz Auxiliary Power Receptacles RC1, RC2, And RC3
Provide connection points and power for auxiliary equipment.
16 Circuit Breaker CB3
Protects 100 Hz auxiliary power receptacle RC4 from overload.
17100 Hz Auxiliary Power Receptacle RC4
Provides connection point and power for auxiliary equipment while welding.
18 Fine Amperage Control R1
Adjusts amperage within range selected by Ampere Ranges switch
S5.
19 Ampere Ranges Switch S5
Selects coarse range of weld output from weld stator.
20 Reactor AC-Z
Tapped reactor limits weld output and provides coarse ranges.
21 Main Rectifier SR1
Changes ac output from weld windings to dc.
22 Stabilizer DC-Z
Smooths out current to dc weld output terminals.
23HF Filter Board PC4 Protects unit from high frequency.
24Positive (+) And Negative (±)
DC Weld Output Terminals
Provide dc weld output.
25Electrode And Work AC Weld Output Terminals
Provide ac weld output.
AC Or DC Control Circuits
Weld Current Circuit
Mechanical Coupling
Magnetic Coupling
♦Optional
Miller Legend |
TM-428 Page 13 |

NOTES
TM-428 Page 14 |
Miller Legend |
SECTION 6 ± TROUBLESHOOTING
6-1. Troubleshooting Tables
A. Welding
. |
See Sections 6-2 and 6-3 for test points and values and Section 10 for parts location.
Trouble |
Remedy |
|
|
No weld output. |
Check fuse F1, and replace if necessary (see Section 8-6). |
|
|
|
Check integrated rectifier SR2, and replace if necessary. |
|
|
|
Check diode D4, and replace if necessary. |
|
|
|
Clean slip rings, and install new brushes if necessary (see Section 6-15). |
|
|
|
Disconnect leads 21, 23, and 33 from brushes, and check continuity across slip rings. Replace rotor |
|
if necessary. |
|
|
|
Check resistance and connections of resistors R2 and R4; R2 and R4 are each 12 ohms ±10%. Re- |
|
place resistor(s) if necessary. Adjust R2 and R4 according to Section 6-16. |
|
|
|
Check resistance and connections of Fine Amperage Control R1; R1 is 0 to 30 ohms ±10%. Replace |
|
R1 if necessary (see Section 3-1). |
|
|
|
Disconnect leads 22 and 29 from SCR/integrated rectifier SR2, and check for continuity between leads |
|
22 and 29. Replace exciter stator if necessary. |
|
|
|
For units with optional remote control, check capacitor C5 for a short or open, and check for proper con- |
|
nections. Replace C5 if necessary. |
|
|
|
Check voltage regulator board PC2 and connections, and replace if necessary (see Section 6-9). |
|
|
No or erratic weld output. |
Clean and tighten weld connections both inside and outside unit. |
|
|
|
Check engine speed, and adjust if necessary (see Section 8-5). |
|
|
|
Check to make sure Ampere Ranges switch S5 is not between positions. Check continuity of S5, and |
|
replace if necessary. |
|
|
|
Check reactor AC-Z for signs of winding failure. Check continuity across windings, and check for proper |
|
connections. Replace AC-Z if necessary. |
|
|
|
Check resistance and connections of Fine Amperage control R1; R1 is 0 to 30 ohms ± 10%. Replace |
|
R1 if necessary. |
|
|
|
Disconnect leads 21, 23, and 33 from brushes, and check continuity across slip rings. Replace rotor |
|
if necessary. |
|
|
No or erratic DC weld output only. |
Check modular main rectifier SR1, and replace if necessary. |
|
|
|
Check stabilizer DC-Z for signs of winding failure. Check continuity across windings, and check for |
|
proper connections. Replace DC-Z if necessary. |
|
|
Low or high weld output. |
Check engine speed, and adjust if necessary (see Section 8-5). |
|
|
|
Adjust resistor R4 slider until 128 to 132 volts ac is obtained at 100 Hz receptacle RC4 (see Section |
|
6-16). |
|
|
|
Adjust resistor R2 slider until proper open-circuit-voltage is obtained at weld output terminals (see Sec- |
|
tion 6-16). |
|
|
|
Check resistance and connections of resistor R3 on suppressor R3, VR1 module; R3 is 1000 ohms ± |
|
10%. Replace R3, VR1 module if necessary. |
|
|
|
Check reactor AC-Z for signs of winding failure. Check continuity across windings, and check for proper |
|
connections. Replace AC-Z if necessary. |
|
|
Miller Legend |
TM-428 Page 15 |
B. 50 Or 60 Hz Auxiliary Power
Trouble |
Remedy |
|
|
No auxiliary power output at recep- |
Run engine at power/idle speed. |
tacles RC1, RC2, or RC3. |
|
|
|
|
Reset circuit breakers CB1 and CB2. Effective with Serial No. KE629034, also reset circuit breakers |
|
CB5 and CB7 (see Section 4-3). |
|
|
|
Check receptacles RC1, RC2, RC3 for continuity and proper connections. Replace receptacle(s) if nec- |
|
essary. |
|
|
|
Check connections to terminal strip 1T. |
|
|
|
Clean slip rings, and install new brushes if necessary (see Section 6-15). |
|
|
|
Check coil voltage and connections of control relay CR4. Check continuity of coil and condition of con- |
|
tacts. Replace CR4 if necessary. |
|
|
|
Check diode D4, and replace if necessary. |
|
|
|
Check idle board/module PC1 and connections (see Section 6-5). |
|
|
|
Check control transformer T1 for signs of winding failure. Check continuity across windings, and check |
|
for proper connections. Check primary and secondary voltages. Replace T1 if necessary. |
|
|
|
Disconnect leads 21, 23, and 33 from brushes, and check continuity across slip rings. Replace rotor |
|
if necessary. |
|
|
|
Disconnect leads 48 and 49 from voltage regulator board PC2, and check continuity between leads 48 |
|
and 49. Disconnect leads 50, 51, 52, and 53 from stator. Check continuity between leads 50 and 51, |
|
and 52 and 53. Replace stator if necessary. |
|
|
Low auxiliary power output. |
Check connections to terminal strip 1T. |
|
|
|
Clean slip rings, and install new brushes if necessary (see Section 6-15). |
|
|
|
Check integrated rectifier SR2, and replace if necessary. |
|
|
|
Check coil voltage and connections of control relay CR3. Check continuity of coil and condition of con- |
|
tacts. Replace CR3 if necessary. |
|
|
|
Check voltage regulator board PC2 and connections, and replace if necessary. |
|
|
High auxiliary power output. |
Check engine speed, and adjust if necessary. |
|
|
|
Check voltage regulator board PC2 and connections, and replace if necessary (see Section 6-9). |
|
|
C. 100 Hz Auxiliary Power
Trouble |
Remedy |
|
|
No auxiliary power output at receptacle |
Run engine at weld speed. |
RC4. |
|
|
|
|
Reset circuit breaker CB3 (see Section 4-1). |
|
|
|
Check receptacle RC4 for continuity and proper connections. Replace receptacle if necessary. |
|
|
|
Disconnect leads 90, 91, 92, and 93 from stator. Check continuity between leads 90 and 91, and 92 and |
|
93. Replace stator if necessary. |
|
|
|
Check diode D4, and replace if necessary. |
|
|
TM-428 Page 16 |
Miller Legend |
D. Engine
Trouble |
Remedy |
|
|
Engine will not start. |
Check fuel level (see Section 2-4). |
|
|
|
Check battery and engine charging system according to engine manual. |
|
|
|
Check continuity of Engine Control switch S2, and replace if necessary. |
|
|
|
See engine manual. |
|
|
Engine starts but stops as soon as En- |
Check oil level (see Section 2-4). Check low oil pressure shutdown switch S3 (see engine parts manual |
gine Control switch S2 returns to Run |
for location). S3 should close when engine is running. |
position. |
|
|
|
|
Check and refill crankcase with proper viscosity oil for operating temperature, if necessary (see engine |
|
manual). |
|
|
|
Check continuity of Engine Control switch S2, and replace if necessary. |
|
|
Engine stopped during normal opera- |
Check oil level (see Section 2-4). Check low oil pressure shutdown switch S3 (see engine parts manual |
tion. |
for location). S3 should close when engine is running. |
|
|
|
Check continuity of Engine Control switch S2, and replace if necessary. |
|
|
Battery discharges between uses. |
Make sure Engine Control switch S2 is placed in the Off position when engine is not in use (see Section |
|
3-1). |
|
|
|
Prior to Serial No. KA780044, check fuse F2 and replace if necessary. |
|
|
|
Clean battery, terminals and posts with baking soda solution; rinse with clear water. |
|
|
|
Periodically recharge battery (approximately every 3 months). |
|
|
|
Check voltage regulator according to engine manual. |
|
|
|
Replace battery. |
|
|
Engine idles, but does not come up to |
Wait 10 seconds for throttle solenoid circuit breaker CB4 to reset (see Section 8-6). |
weld speed. |
|
|
|
|
Place Idle Lock switch S1 in Unlock position (see Section 3-1). |
|
|
|
Check continuity and connections of current transformer CT1, and replace if necessary. |
|
|
|
Check continuity of Engine Control switch S2, and replace if necessary. |
|
|
|
Check coil voltage and connections of control relay CR2. Check continuity of coil and condition of con- |
|
tacts. Replace CR2 if necessary. |
|
|
|
Check diode D6 in throttle solenoid TS1 circuit, and replace if necessary. |
|
|
|
Check resistance at throttle solenoid TS1 terminals. With plunger out, resistance is less than 1 ohm. |
|
With plunger bottomed, resistance is 17 ohms ±10%. |
|
|
|
Check throttle linkage for smooth, non-binding operation. |
|
|
|
Check idle board/module PC1 and connections, and replace if necessary (see Section 6-5). |
|
|
Engine does not return to idle speed. |
Remove weld load. |
|
|
|
Check continuity of Engine Control switch S2, and replace if necessary. |
|
|
|
Check throttle linkage for smooth, non-binding operation. |
|
|
Unstable or sluggish engine speeds. |
Readjust throttle linkage if necessary. |
|
|
|
Tune-up engine according to engine manual. |
|
|
Miller Legend |
TM-428 Page 17 |
 Loading...
Loading...