Page 1

4Gb: x16, x32 GDDR5 SGRAM
Features
GDDR5 SGRAM
EDW4032BABG – 8 Meg x 32 I/O x 16 banks, 16 Meg x 16 I/O x 16 banks
Features
• VDD = V
• Data rate: 6.0 Gb/s, 7.0 Gb/s, 8.0 Gb/s
• 16 internal banks
• Four bank groups for tCCDL = 3 tCK
• 8n-bit prefetch architecture: 256-bit per array read
or write access for x32; 128-bit for x16
• Burst length (BL): 8 only
• Programmable CAS latency: 7–25
• Programmable WRITE latency: 4–7
• Programmable CRC READ latency: 2–3
• Programmable CRC WRITE latency: 8–14
• Programmable EDC hold pattern for CDR
• Precharge: Auto option for each burst access
• Auto refresh and self refresh modes
• Refresh cycles: 16,384 cycles/32ms
• Interface: Pseudo open drain (POD-15) compatible
outputs: 40Ω pull-down, 60Ω pull-up
• On-die termination (ODT): 60Ω or 120Ω (NOM)
• ODT and output driver strength auto calibration
with external resistor ZQ pin: 120Ω
• Programmable termination and driver strength offsets
• Selectable external or internal V
programmable offsets for internal V
• Separate external V
inputs
• TC = 0°C to +95°C
• x32/x16 mode configuration set at power-up with
EDC pin
• Single-ended interface for data, address, and
command
• Quarter data rate differential clock inputs CK_t,
CK_c for address and commands
• Two half data rate differential clock inputs, WCK_t
and WCK_c, each associated with two data bytes
(DQ, DBI_n, EDC)
• DDR data (WCK) and addressing (CK)
• SDR command (CK)
• Write data mask function via address bus (single/
double byte mask)
• Data bus inversion (DBI) and address bus inversion
(ABI)
• Input/output PLL on/off mode
• Duty cycle corrector (DCC) for data clock (WCK)
• Digital RAS lockout
= 1.6V/1.55V/1.5V ±3% and 1.35V ±3%
DDQ
for data inputs;
REF
REF
for address/command
REF
• Address training: Address input monitoring via DQ
pins
• WCK2CK clock training: Phase information via EDC
pins
• Data read and write training via read FIFO (FIFO
depth = 6)
• Read FIFO pattern preloaded by LDFF command
• Direct write data load to read FIFO by WRTR command
• Consecutive read of read FIFO by RDTR command
• Read/write data transmission integrity secured by
cyclic redundancy check (CRC-8)
• Read/write EDC on/off mode
• Low power modes
• RDQS mode on EDC pin
• On-die temperature sensor with readout
• Automatic temperature sensor controlled self
refresh rate
• Vendor ID, FIFO depth and density info fields for
identification
• Mirror function with MF pin
• Boundary scan function with SEN pin
Options
1
Marking
• Organization
– Density 40
– 128 Meg x 32 (words x bits) 32
• FBGA package
– 170-ball (12mm x 14mm) BG
• Package environment code
– Lead- and halogen-free
-F
(RoHS-compliant)
• Package media
– Dry pack (tray) -D
– Reel -R
• Timing – maximum data rate
– 6.0 Gb/s, 5.0 Gb/s -60
– 7.0 Gb/s, 6.0 Gb/s -70
– 8.0 Gb/s, 6.0 Gb/s -80
• Operating temperature
– Commercial (0°C ≤ TC ≤ +95°C) None
• Revision A
Note:
1. Not all options listed can be combined to
define an offered product. Use the part
catalog search on http://www.micron.com
for available offerings.
09005aef858b7e92
4gb_gddr5_sgram_brief.pdf - Rev. E 6/17 EN
Products and specifications discussed herein are subject to change by Micron without notice.
1
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2014 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 2
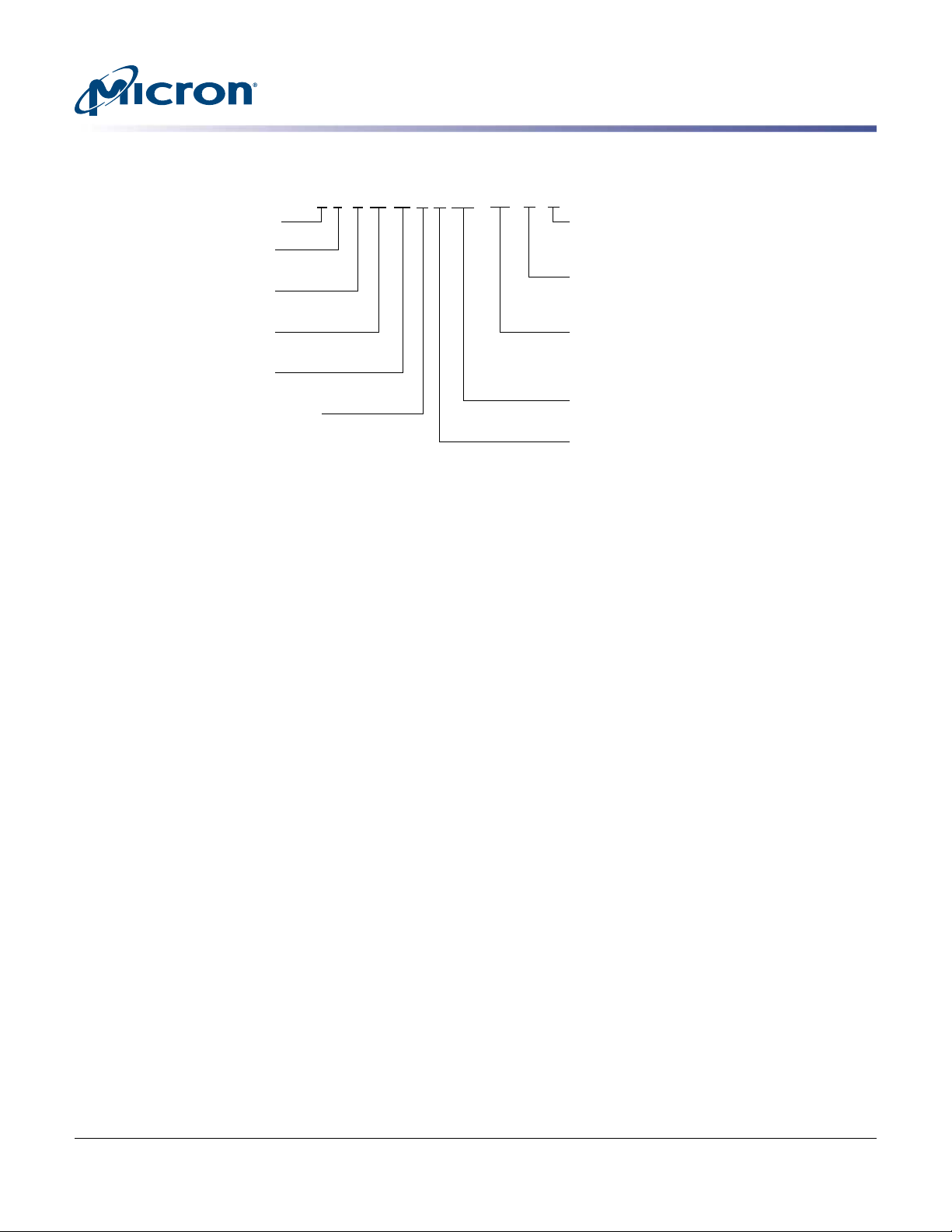
Figure 1: Part Numbering
Micron Memory
Type
D = Packaged device
Product Family
W = GDDR5 SGRAM
Density/Bank
40 = 4Gb/16-bank
Organization
32 = x32
Power Supply, Interface
B = VDD = 1.6V/1.55V/1.5V
E D W 40 32 B A BG - 70 - -F D
Packing Media
D = Dry pack (tray)
R = Reel
Environment Code
F = Lead-free (RoHS-compliant)
and halogen-free
Speed
-60 = 6.0 Gb/s
-70 = 7.0 Gb/s
-80 = 8.0 Gb/s
Package
BG = 170-ball FBGA, 12mm x 14mm
Revision
4Gb: x16, x32 GDDR5 SGRAM
Features
Note:
1. This Micron GDDR5 SGRAM is available in different speed bins. The operating range and AC timings of a
faster speed bin are a superset of all slower speed bins. Therefore it is safe to use a faster bin device as a
drop-in replacement of a slower bin device when operated within the supply voltage and frequency range
of the slower bin device.
FBGA Part Marking Decoder
Due to space limitations, FBGA-packaged components have an abbreviated part marking that is different from the
part number. For a quick conversion of an FBGA code, see the FBGA Part Marking Decoder on Micron’s web site:
http://www.micron.com.
09005aef858b7e92
4gb_gddr5_sgram_brief.pdf - Rev. E 6/17 EN
2
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2014 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 3
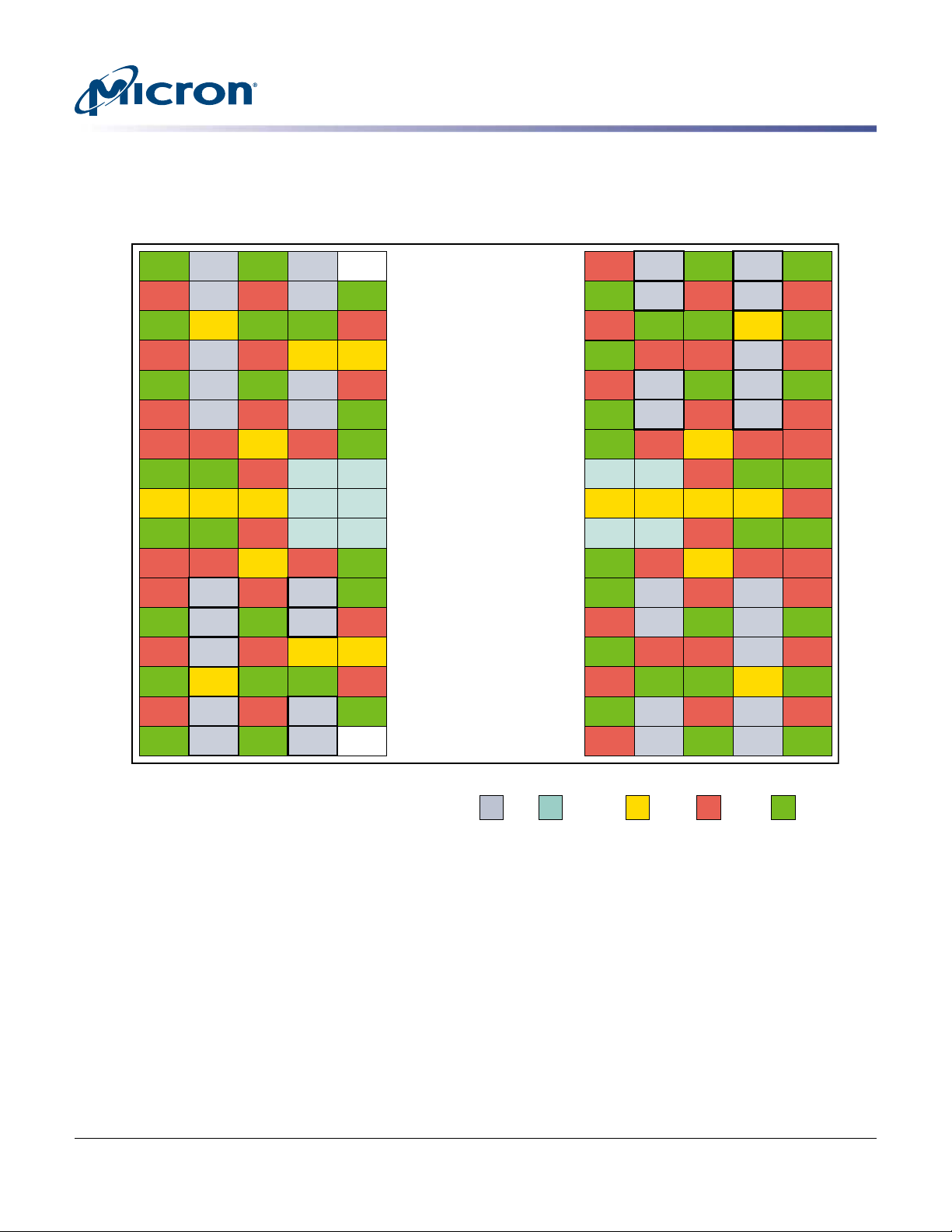
Ball Assignments and Descriptions
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
M
N
P
R
T
U
(Top view)
GroundSupplyGDDR5AddressesData
1
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
V
DD
V
SS
MF
V
SS
V
DD
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
2
DQ1
DQ3
EDC0
DBI0_n
DQ5
DQ7
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
RESET_n
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
DQ31
DQ29
DBI3_n
EDC3
DQ27
DQ25
3
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
RAS_n
V
DDQ
CKE_n
V
DDQ
CAS_n
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
4
DQ0
DQ2
V
SSQ
WCK01_t
DQ4
DQ6
V
DD
A10, A0
ABI_n
A8, A7
V
DD
DQ30
DQ28
WCK23_t
V
SSQ
DQ26
DQ24
6 7 8 9 10
V
REFD
V
SS
V
DD
V
SS
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
V
SS
BA3, A3
SEN
BA1, A5
V
SS
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
V
SS
V
DD
V
SS
V
REFD
11
DQ8
DQ10
V
SSQ
V
DD
DQ12
DQ14
V
DD
BA0, A2
CK_c
BA2, A4
V
DD
DQ22
DQ20
V
DD
V
SSQ
DQ18
DQ16
12
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
CS_n
V
DDQ
CK_t
V
DDQ
WE_n
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
13
DQ9
DQ11
EDC1
DBI1_n
DQ13
DQ15
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
ZQ
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
DQ23
DQ21
DBI2_n
EDC2
DQ19
DQ17
14
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
V
DD
V
SS
V
REFC
V
SS
V
DD
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
5
NC
V
SS
V
DD
WCK01_c
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
V
SS
A9, A1
A12, A13
A11, A6
V
SS
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
WCK23_c
V
DD
V
SS
NC
Figure 2: 170-Ball FBGA – MF = 0 (Top View)
4Gb: x16, x32 GDDR5 SGRAM
Ball Assignments and Descriptions
09005aef858b7e92
4gb_gddr5_sgram_brief.pdf - Rev. E 6/17 EN
Note:
1. Balls shown with a heavy, solid outline are off in x16 mode.
3
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2014 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 4

Figure 3: 170-Ball FBGA – MF = 1 (Top View)
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
M
N
P
R
T
U
(Top view)
GroundSupplyGDDR5AddressesData
1
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
V
DD
V
SS
MF
V
SS
V
DD
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
2
DQ25
DQ27
EDC3
DBI3_n
DQ29
DQ31
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
RESET_n
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
DQ7
DQ5
DBI0_n
EDC0
DQ3
DQ1
3
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
CAS_n
V
DDQ
CKE_n
V
DDQ
RAS_n
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
4
DQ24
DQ26
V
SSQ
WCK23_t
DQ28
DQ30
V
DD
A8, A7
ABI_n
A10, A0
V
DD
DQ6
DQ4
WCK01_t
V
SSQ
DQ2
DQ0
6 7 8 9 10
V
REFD
V
SS
V
DD
V
SS
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
V
SS
BA1, A5
SEN
BA3, A3
V
SS
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
V
SS
V
DD
V
SS
V
REFD
11
DQ16
DQ18
V
SSQ
V
DD
DQ20
DQ22
V
DD
BA2, A4
CK_c
BA0, A2
V
DD
DQ14
DQ12
V
DD
V
SSQ
DQ10
DQ8
12
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
WE_n
V
DDQ
CK_t
V
DDQ
CS_n
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
13
DQ17
DQ19
EDC2
DBI2_n
DQ21
DQ23
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
ZQ
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
DQ15
DQ13
DBI1_n
EDC1
DQ11
DQ9
14
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
V
DD
V
SS
V
REFC
V
SS
V
DD
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
5
NC
V
SS
V
DD
WCK23_c
V
DDQ
V
SSQ
V
SS
A11, A6
A12, A13
A9, A1
V
SS
V
SSQ
V
DDQ
WCK01_c
V
DD
V
SS
NC
4Gb: x16, x32 GDDR5 SGRAM
Ball Assignments and Descriptions
Note:
1. Balls shown with a heavy, solid outline are off in x16 mode.
09005aef858b7e92
4gb_gddr5_sgram_brief.pdf - Rev. E 6/17 EN
4
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2014 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 5

4Gb: x16, x32 GDDR5 SGRAM
Ball Assignments and Descriptions
Table 1: 170-Ball FBGA Ball Descriptions
Symbol Type Description
A[13:0] Input Address inputs: Provide the row address for ACTIVE commands. A[5:0] (A6) provide
the column address and A8 defines the auto precharge bit for READ/WRITE commands, to select one location out of the memory array in the respective bank. A8
sampled during a PRECHARGE command determines whether the PRECHARGE applies to one bank (A8 LOW, bank selected by BA[3:0]) or all banks (A8 HIGH). The address inputs also provide the op-code during a MODE REGISTER SET command and
the data bits during LDFF commands. A[12:8] are sampled with the rising edge of
CK_t and A[7:0], A13 are sampled with the rising edge of CK_c.
ABI_n Input Address bus inversion: Reduces the power requirements on address pins by limit-
ing the number of address lines driving LOW to 5. ABI_n is enabled by the corresponding ABI mode register bit.
BA[3:0] Input Bank address inputs: Define the bank to which an ACTIVE, READ, WRITE, or PRE-
CHARGE command is being applied. BA[3:0] define which mode register is loaded
during the MODE REGISTER SET command. BA[3:0] are sampled with the rising edge
of CK_t.
CK_t, CK_c Input Clock: CK_t and CK_c are differential clock inputs. Command inputs are latched on
the rising edge of CK_t. Address inputs are latched on the rising edge of CK_t and
the rising edge of CK_c. All latencies are referenced to CK_t. CK_t and CK_c are externally terminated.
WCK01_t, WCK01_c/
WCK23_t, WCK23_c
CKE_n Input Clock enable: CKE_n enables (registered LOW) and disables (registered HIGH) inter-
CS_n Input Chip select: CS_n enables (registered LOW) and disables (registered HIGH) the
MF Input Mirror function: V
RAS_n, CAS_n, WE_n Input Command inputs: RAS_n, CAS_n, and WE_n (along with CS_n) define the com-
RESET_n Input Reset: RESET_n is an active LOW CMOS input referenced to VSS. A full chip reset may
SEN Input Scan enable: V
Input Data Clocks: WCK_t and WCK_c are differential clocks used for write data capture
and read data output. WCK01_t and WCK01_c are associated with DQ[15:0], DBI0_n,
DBI1_n, EDC0, and EDC1. WCK23_t and WCK23_c are associated with DQ[31:16],
DBI2_n, DBI3_n, EDC2, and EDC3. WCK clocks operate at nominally twice the CK
clock frequency.
nal circuitry and clocks on the device. The specific circuitry that is enabled/disabled is
dependent upon the device configuration and operating mode. Taking CKE_n HIGH
provides PRECHARGE POWER-DOWN and SELF REFRESH operations (all banks idle),
or active power-down (row active in any bank). CKE_n is synchronous for powerdown entry and exit and for self refresh entry. CKE_n must be maintained LOW
throughout read and write accesses. Input buffers (excluding CKE_n) are disabled
during SELF REFRESH operation. The value of CKE_n latched at power-up with RESET_n going HIGH determines the termination value of the address and command
inputs.
command decoder. All commands are masked when CS_n is registered HIGH, but internal command execution continues. CS_n is considered part of the command code.
CMOS input. Must be tied to V
DDQ
DDQ
or VSS.
mand being entered.
be performed at any time by pulling RESET_n LOW. With RESET_n LOW all ODTs are
disabled.
CMOS input. Must be tied to VSS when not in use.
DDQ
09005aef858b7e92
4gb_gddr5_sgram_brief.pdf - Rev. E 6/17 EN
5
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2014 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 6

4Gb: x16, x32 GDDR5 SGRAM
Ball Assignments and Descriptions
Table 1: 170-Ball FBGA Ball Descriptions (Continued)
Symbol Type Description
DQ[31:0] I/O Data input/output: Bidirectional 32-bit data bus.
DBI[3:0]_n I/O Data bus inversion: Reduces the DC power consumption and supply noise induced
jitter on data pins. DBI0_n is associated with DQ[7:0], DBI1_n with DQ[15:8], DBI2_n
with DQ[23:16], and DBI3_n with DQ[31:24].
EDC[3:0] Output Error detection code: The calculated CRC data is transmitted on these pins. In ad-
dition, these pins drive a hold pattern when idle and can be used as an RDQS function. EDC0 is associated with DQ[7:0], EDC1 with DQ[15:8], EDC2 with DQ[23:16], and
EDC3 with DQ[31:24].
V
DD
V
DDQ
V
REFC
V
REFD
V
SS
V
SSQ
ZQ Reference External reference ball for impedance calibration: This ball is tied to an
NC – No connect: These balls should be left unconnected (the ball has no connection to
Supply Power supply: 1.6V/1.55V/1.5V ±3% and 1.35V ±3%.
Supply DQ power supply: 1.6V/1.55V/1.5V ±3% and 1.35V ±3%. Isolated on the device for
improved noise immunity.
Supply Reference voltage for control and address: V
must be maintained at all
REFC
times (including self refresh) for proper device operation.
Supply Reference voltage for data: V
must be maintained at all times (including self
REFD
refresh) for proper device operation.
Supply Ground.
Supply DQ ground: Isolated on the device for improved noise immunity.
external 120Ω resistor (ZQ), which is tied to V
SSQ
.
the device or to other balls).
09005aef858b7e92
4gb_gddr5_sgram_brief.pdf - Rev. E 6/17 EN
6
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2014 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 7

Package Dimensions
0.15
Seating plane
0.1 A
Ball A1 ID
Ball A1 ID
0.35 ±0.05
1.1 ±0.1
10.4 CTR
12 ±0.1
0.8 TYP
12.8 CTR
14 ±0.1
170X Ø0.47
Dimensions apply
to solder balls postreflow on Ø0.42 SMD
ball pads.
0.8 TYP
123101112
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
M
N
P
R
T
U
451314
A
2.2 CTR
nonconductive
overmold
Figure 4: 170-Ball FBGA (BG)
4Gb: x16, x32 GDDR5 SGRAM
Package Dimensions
Although considered final, these specifications are subject to change, as further product development and data characterization some-
Notes:
1. All dimensions are in millimeters.
2. Solder ball material: SAC302 (96.8% Sn, 3% Ag, 0.2% Cu).
8000 S. Federal Way, P.O. Box 6, Boise, ID 83707-0006, Tel: 208-368-4000
www.micron.com/products/support Sales inquiries: 800-932-4992
Micron and the Micron logo are trademarks of Micron Technology, Inc.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
This data sheet contains minimum and maximum limits specified over the power supply and temperature range set forth herein.
times occur.
09005aef858b7e92
4gb_gddr5_sgram_brief.pdf - Rev. E 6/17 EN
7
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2014 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Loading...
Loading...