
MFJ-835 Balanced Line RF Ammeter Instruction Manual
IMPORTANT:
Please read entire manual before attempting to operate this equipment. This
unit does not provide a dc or low frequency earth ground. A separate wire
from the station ground bus to an electric ground. Do
MFJ-835 RF Ammeter
Introduction
Congratulations on purchasing the MFJ-835 Balanced Line RF Ammeter. The MFJ-835
is designed for measuring balanced RF feedline current on 1.8-30 MHz while having low
interaction on the primary lines. Connect the Balanced Line RF Ammeter between your
antenna and tuner/ transmitter/amplifier and feedline currents are simultaneously
displayed on separate calibrated scales in three calibrated ranges: 0.3 Amperes, 1
Ampere, and 3 Amperes. Balance is clearly revealed on MFJ's exclusive BalancedBar.
When currents are balanced, the dual needles cross in the center. If the needles cross
within the vertical BalancedBar, the balance is within 10%.
Uses
Equal currents in the feeder wires minimize feedline radiation and reduce pattern
distortion, RFI, TVI and wasted power. You could lose up to 10% of your power.
Imbalance is due to feedline not being perpendicular to antenna, if one side runs close to
metal or is shorter or closer to ground. The MFJ-836 helps you solve all your unbalanced
problems.
• Use it for tuning your antenna tuner/transmitter/amplifier for maximum radiated
power, for determining antenna feedpoint impedance, for comparing antennas and
tuners, for troubleshooting and for checking for changes.
• Minimum SWR does not always mean maximum radiated power. Your tuner or
lossy coax may be dissipating power and you may not get peak output power even
if your tuner or amplifier is properly tuned.
• Use the MFJ-835 Balanced Line RF Ammeter to determine best antenna tuner
settings and to compare various tuners. Calculate your antenna feedpoint
impedance by dividing your applied power by the square of the feedpoint current.
• Your antenna can change when you apply power. Insulators break down, traps
heat up, capacitors leak and your feedpoint impedance may be drastically
different from your SWR Analyzer measurements.
should be connected
not place any non-coaxial feed wires near metallic or RF sensitive devices.
1
MFJ-835 Balanced Line RF Ammeter Instruction Manual
Range
Installation
1. Connect your transmitter to the Heavy-duty 5-way binding posts on the back of
the unit labeled TRANSMITTER and your antenna to the Heavy-duty 5-way
binding posts labeled ANTENNA. It is important that you use good quality
feedline and properly installed connectors.
2. An internal lamp backlights the RF Ammeter scale. The lamp circuit requires 12
VDC. The rear panel accepts a 2.1 mm coaxial plug with the center conductor
positive (+) and the sleeve negative (-). The negative lead is grounded inside the
meter.
3. To measure the power output capability of a transmitter/amplifier you should
connect a quality 50-ohm dummy load to the ANTENNA connector of the MFJ-
835.
Operation
1. The Balanced Line RF Ammeter measures RF current in three calibrated ranges:
0.3 Amperes, 1 Ampere, and 3 Amperes. Simply turn the Current Range knob to
the desired range.
2. The meter is scaled from 0 to 100. On the 100-mA range, readout is direct (100 =
100 mA). On the 1-A range, move the decimal point 2 places to the left (100 =
1.00 A). To convert meter readings made on the 30 mA, 300 mA, and 3-A
ranges, multiply accordingly. For example, a reading of 85 on the 300-mA range
equals 300 x .85, or 255 mA. See Table 1 below to estimate readings quickly.
3. The BalancedBar easily displays when currents are balanced by using the dual
needles. When the needles cross within the vertical BalancedBar, the balance is
within 10%.
4. To prevent meter pegging, begin checks on a high range and work down. To
estimate unknown current levels, use the formula below (I = Unknown Current in
Amps, P = Applied Power in Watts, and R = Load Resistance in Ohms).
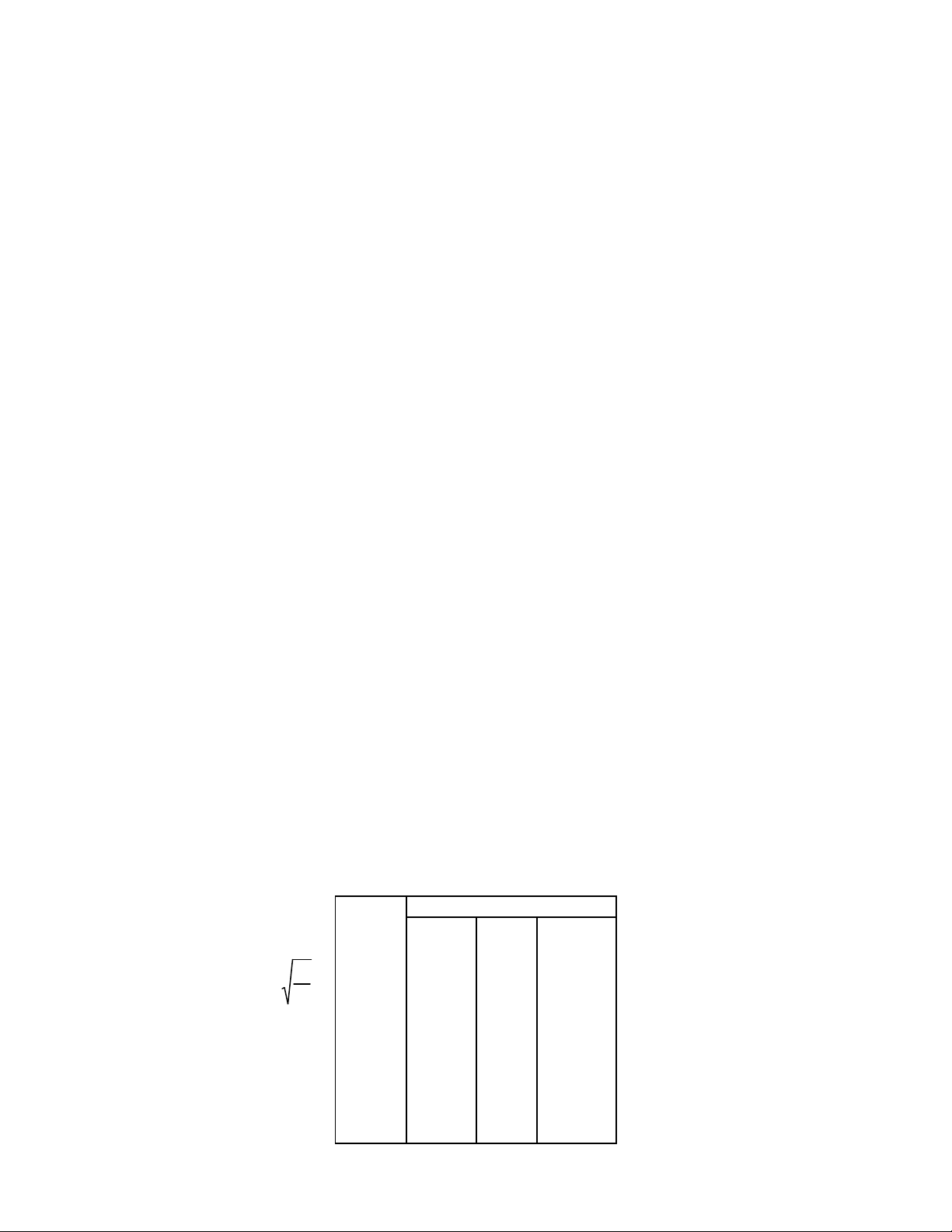
I
Table 1: Actual
Current Value
=
Meter 300 mA 1 A 3 A
10 30 0.1 0.3
P
R
20 60 0.2 0.6
30 90 0.3 0.9
40 120 0.4 1.2
50 150 0.5 1.5
60 180 0.6 1.8
70 210 0.7 2.1
80 240 0.8 2.4
90 270 0.9 2.7
100 300 1.0 3.0
2
 Loading...
Loading...