Page 1

www.metabo.com
de Originalbetriebsanleitung 4
en Original instructions 10
fr Notice d'utilisation originale 15
nl Oorspronkelijke gebruiksaanwijzing 21
es Manual original 26
no Originalbruksanvisning 32
pl Instrukcja oryginalna 37
hu Eredeti használati utasítás 43
ru ȣəɑɌɑɖɉɔɥɖɗɎ əɜɓɗɋɗɍɚɛɋɗ ɘɗ
ɦɓɚɘɔɜɉɛɉɟɑɑ 48
cs Originální návod k použití 54
DG 25 Set
Page 2

2
1 62 3 4 5 7 10 11 128 9
Page 3
3
DG 25 Set
V
1
l/min 300
p
max.
bar 6,2
n
0
../min 25000
d
S
mm (in)
3 ; 6 (
1
/
8 ;
1
/
4
)
D
max
mm (in) 50 (2)
d
i
mm (in)
10 (
3
/
8
)
C “
1
/
4
A mm
160 x 39 x 67
(6
5
/
16
x 1
17
/
32
x 2
5
/
8
)
m kg (lbs) 0,5 (1.1)
ah/K
h
m/s
2
0,1 / 1,5
LpA/K
pA
dB(A)
75 / 3
LWA/K
WA
dB(A)
87 / 3
11.
EN 11148
2006/42/EG,2011/65/EU
Director Product Engineering & Quality
Responsible Person for Documentation
Metabowerke GmbH, 72622 Nuertingen, Germany
2012-08-15
Volker Siegle
Page 4

DEUTSCHde
4
Originalbetriebsanleitung
Wir erklären in alleiniger Verantwortlichkeit, dass
diese Stabschleifer mit den auf Seite 3
angegebenen Normen und Richtlinien
übereinstimmen.
Dieses Druckluftwerkzeug ist bestimmt...
- ... für Feinschleifarbeiten mit Schleifstiften,
- ...zum Arbeiten mit Formpolierkörpern,
- ...zum Arbeiten mit Filzpolierkörpern,
- ...zum Arbeiten mit Lamellen-Schleifrädern ,
im professionellen Bereich.
Dieses Werkzeug darf nur mit einer Druckluftversorgung angetrieben werden. Der auf dem
Druckluftwerkzeug angegebene maximal zulässige
Arbeitsdruck darf nicht überschritten werden.
Dieses Druckluftwerkzeug darf nicht mit
explosiven, brennbaren oder
gesundheitsgefährdenden Gasen betrieben
werden. Nicht verwenden als Hebel, Brech- oder
Schlagwerkzeug.
Jede andere Verwendung ist bestimmungswidrig.
Durch bestimmungswidrige Verwendung,
Veränderungen am Druckluftwerkzeug oder durch
den Gebrauch von Teilen, die nicht vom Hersteller
geprüft und freigegeben sind, können
unvorhersehbare Schäden entstehen!
Für Schäden durch nicht bestimmungsgemäßen
Gebrauch haftet allein der Benutzer.
Allgemein anerkannte Unfallverhütungsvorschriften
und beigelegte Sicherheitshinweise müssen
beachtet werden.
Beachten Sie die mit diesem Symbol
gekennzeichneten Textstellen zu Ihrem
eigenen Schutz und zum Schutz Ihres
Druckluftwerkzeugs!
WARNUNG – Zur Verringerung eines
Verletzungsrisikos Betriebsanleitung lesen.
WARNUNG Lesen Sie alle Sicherheitshinweise und Anweisungen. Versäumnisse
bei der Einhaltung der Sicherheitshinweise und
Anweisungen können elektrischen Schlag, Brand
und/oder schwere Verletzungen verursachen.
Bewahren Sie alle Sicherheitshinweise und
Anweisungen für die Zukunft auf.
Geben Sie Ihr Druckluftwerkzeug nur zusammen
mit diesen Dokumenten weiter.
- Der Benutzer oder der Arbeitgeber des Benutzers
muss die spezifischen Risiken bewerten, die
aufgrund jeder Verwendung auftreten können.
- Die Sicherheitshinweise sind vor dem Einrichten,
dem Betrieb, der Reparatur, der Wartung und
dem Austausch von Zubehörteilen sowie vor der
Arbeit in der Nähe des Druckluftwerkzeugs zu
lesen und müssen verstanden werden. Ist dies
nicht der Fall, so kann dies zu schweren
körperlichen Verletzungen führen.
- Das Druckluftwerkzeug sollte ausschließlich von
qualifizierten und geschulten Bedienern
eingerichtet, eingestellt oder verwendet werden.
- Das Druckluftwerkzeug darf nicht verändert
werden. Veränderungen können die Wirksamkeit
der Sicherheitsmaßnahmen verringern und die
Risiken für den Bediener erhöhen.
- Benutzen Sie niemals beschädigte
Druckluftwerkzeuge. Pflegen Sie
Druckluftwerkzeuge mit Sorgfalt. Kontrollieren Sie
regelmäßig, ob bewegliche Teile einwandfrei
funktionieren und nicht klemmen, ob Teile
gebrochen oder so beschädigt sind, dass die
Funktion des Druckluftwerkzeugs beeinträchtigt
ist. Prüfen sie Schilder und Aufschriften auf
Vollständigkeit und Lesbarkeit. Lassen Sie
beschädigte Teile vor dem Einsatz des Gerätes
reparieren oder erneuern. Viele Unfälle haben ihre
Ursache in schlecht gewarteten
Druckluftwerkzeugen.
4.1 Gefährdungen durch
herausgeschleuderte Teile
- Bei einem Bruch des Werkstücks, von
Zubehörteilen oder des Druckluftwerkzeugs,
können Teile mit hoher Geschwindigkeit
herausgeschleudert werden.
- Beim Betrieb, beim Austausch von Zubehörteilen
sowie bei Reparatur- oder Wartungsarbeiten am
Druckluftwerkzeug ist immer ein schlagfester
Augenschutz zu tragen. Der Grad des
erforderlichen Schutzes sollte für jeden einzelnen
Einsatz gesondert bewertet werden.
- Stellen Sie sicher, dass das Werkstück sicher
befestigt ist.
- Es muss regelmäßig überprüft werden, ob die
Drehzahl des Druckluftwerkzeugs nicht höher ist
als die auf dem Druckluftwerkzeug angebrachte
Drehzahlangabe. Diese Drehzahlüberprüfungen
müssen ohne angebrachtes Einsatzwerkzeug
erfolgen. Der Metabo-Kundendienst kann solche
Überprüfungen vornehmen.
- Stellen Sie sicher, dass beim Arbeiten
entstehende Funken und Bruchstücke keine
Gefährdung darstellen.
- Trennen Sie das Druckluftwerkzeug von der
Druckluftversorgung, bevor Sie das
Einsatzwerkzeug oder Zubehörteile austauschen
oder eine Einstellung oder Wartung oder
Reinigung vorgenommen wird.
- Stellen sie sicher, dass auch für andere Personen
keine Gefahren entstehen.
1. Konformitätserklärung
2. Bestimmungsgemäße
Verwendung
3. Allgemeine
Sicherheitshinweise
4. Spezielle Sicherheitshinweise
Page 5

DEUTSCH de
5
4.2 Gefährdungen durch Erfassen/
Aufwickeln
- Tragen Sie geeignete Kleidung. Tragen Sie keine
weite Kleidung oder Schmuck. Halten Sie Haare,
Kleidung und Handschuhe fern vom
Druckluftwerkzeug und von sich bewegenden
Teilen. Lockere Kleidung, Schmuck oder lange
Haare können von sich bewegenden Teilen
erfasst werden. Es besteht Verletzungsgefahr.
4.3 Gefährdungen im Betrieb
- Vermeiden Sie den Kontakt mit dem rotierenden
Schaft und dem Einsatzwerkzeug, um Schnitte an
Händen und anderen Körperteilen zu verhindern.
- Beim Einsatz des Druckluftwerkzeugs können die
Hände des Bedieners Gefährdungen wie z. B.
Schnitten, Abschürfungen und Wärme ausgesetzt
sein. Tragen Sie geeignete Handschuhe zum
Schutz der Hände.
- Der Bediener und das Wartungspersonal müssen
physisch in der Lage sein, die Größe, das Gewicht
und die Leistung des Druckluftwerkzeugs zu
beherrschen.
- Halten Sie das Druckluftwerkzeug richtig: Seien
Sie bereit, den üblichen oder plötzlichen
Bewegungen entgegenzuwirken – halten Sie
beide Hände bereit.
- Sorgen Sie für einen sicheren Stand und halten
Sie jederzeit das Gleichgewicht.
- Vermeiden Sie eine unbeabsichtigte
Inbetriebnahme. Bei einer Unterbrechung der
Luftversorgung, das Druckluftwerkzeug am Ein-/
Ausschalter ausschalten.
- Verwenden Sie nur die vom Hersteller
empfohlenen Schmiermittel.
- Tragen Sie persönliche Schutzausrüstung und
immer eine Schutzbrille. Das Tragen persönlicher
Schutzausrüstung, wie Schutzhandschuhe,
Schutzkleidung, Staubmaske, rutschfeste
Sicherheitsschuhe, Schutzhelm oder
Gehörschutz, je nach Art und Einsatz des
Gerätes, verringert das Risiko von Verletzungen
und wird empfohlen.
- Die zulässige Drehzahl des Einsatzwerkzeugs
muss mindestens so hoch sein wie die auf dem
Druckluftwerkzeug angegebene Höchstdrehzahl.
Zubehör, das sich schneller als zulässig dreht,
kann zerbrechen und umherfliegen.
- Bei Arbeiten über Kopf ist ein Schutzhelm zu
tragen.
- Das Werkzeug läuft nach, nachdem das
Druckluftwerkzeug ausgeschaltet wurde.
- Sorgen Sie dafür, dass beim Gebrauch
entstehende Funken keine Gefahr hervorrufen.
Beim beabeiten von Werkstoffen können
explosionsgefährliche oder berennbare Stäube
entstehen. Es besteht das Risiko der Explosion
oder eines Feuers.
4.4 Gefährdungen durch wiederholte
Bewegungen
- Beim Arbeiten mit dem Druckluftwerkzeug
können unangenehme Empfindungen in den
Händen, Armen, Schultern, im Halsbereich oder
an anderen Körperteilen auftreten.
- Nehmen Sie für die Arbeit mit dem
Druckluftwerkzeug eine bequeme Stellung ein,
achten Sie auf sicheren Halt und vermeiden Sie
ungünstige Positionen oder solche, bei denen es
schwierig ist, das Gleichgewicht zu halten. Der
Bediener sollte während lang dauernder Arbeiten
die Körperhaltung verändern, was helfen kann,
Unannehmlichkeiten und Ermüdung zu
vermeiden.
- Falls beim Bediener Symptome wie z. B.
andauerndes Unwohlsein, Beschwerden,
Pochen, Schmerz, Kribbeln, Taubheit, Brennen
oder Steifheit auftreten, sollten diese warnenden
Anzeichen nicht ignoriert werden. Der Bediener
sollte diese seinem Arbeitgeber mitteilen und
einen qualifizierten Arzt konsultieren.
4.5 Gefährdungen durch Zubehörteile
- Trennen Sie das Druckluftwerkzeug von der
Luftversorgung, bevor das Einsatzwerkzeug oder
Zubehörteil befestigt oder gewechselt wird.
- Verwenden Sie nur Zubehör, das für dieses Gerät
bestimmt ist und die in dieser Betriebsanleitung
angegebenen Anforderungen und Kenndaten
erfüllt.
- Vermeiden Sie direkten Kontakt mit dem
Einsatzwerkzeug während und nach der
Benutzung, weil es heiß oder scharfkantig sein
kann.
- Die zulässige Drehzahl des Einsatzwerkzeugs
muss mindestens so hoch sein wie die auf dem
Druckluftwerkzeug angegebene Höchstdrehzahl.
Zubehör, das sich schneller als zulässig dreht,
kann zerbrechen und umherfliegen.
- Niemals eine Schleifscheibe, Trennscheibe oder
Fräser montieren. Eine berstende Schleifscheibe
kann sehr ernste Verletzungen oder den Tod
verursachen.
- Verwenden Sie keine Scheiben, die
angeschlagen, angerissen sind oder die
heruntergefallen sein könnten.
- Es dürfen nur zugelassene Einsatzwerkzeuge mit
dem passenden Schaftdurchmesser verwendet
werden.
- Beachten Sie die Empfehlungen des Herstellers
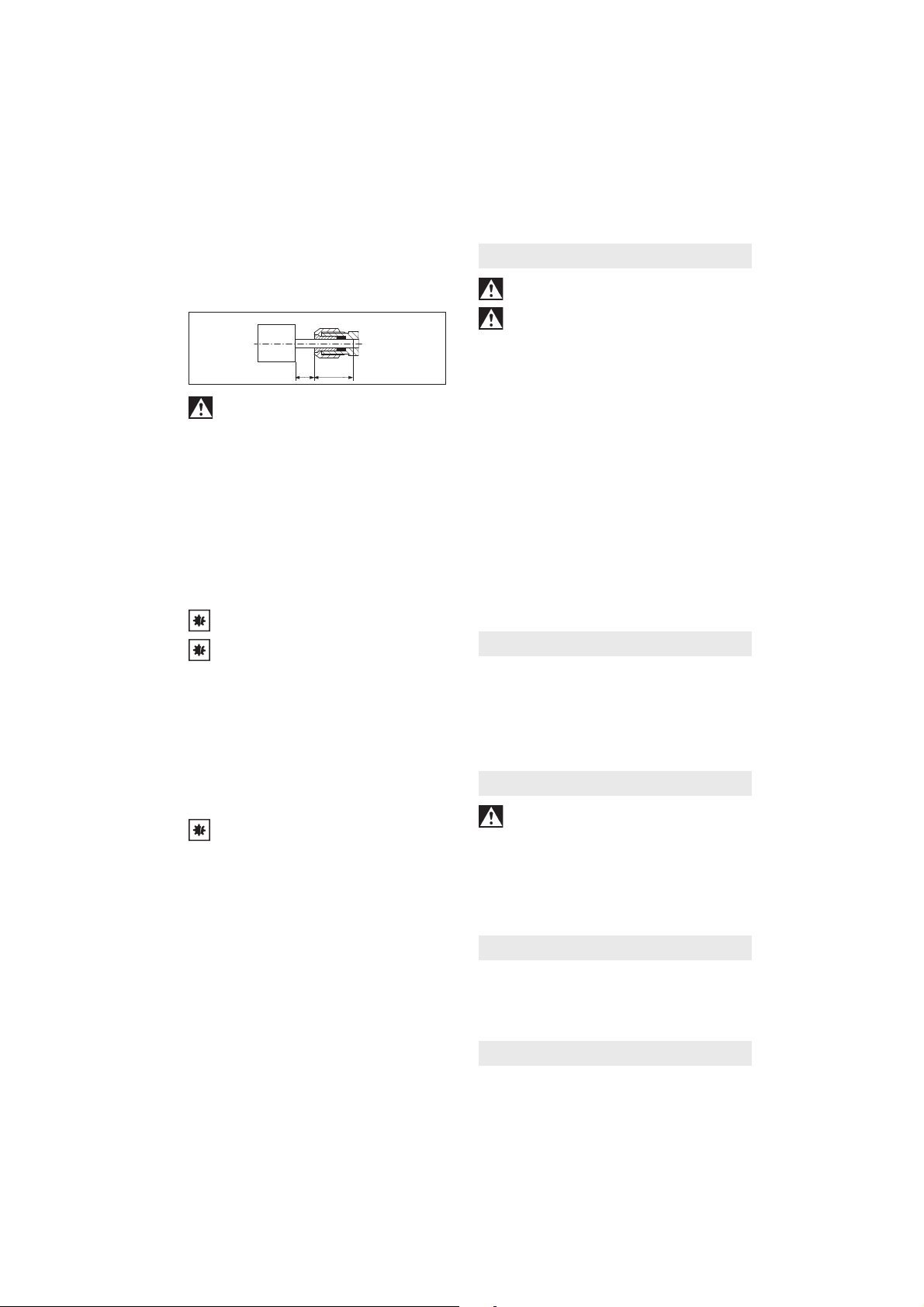
von Kleinschleifkörpern. Bei Kleinschleifkörpern
darf der vom Hersteller angegebene maximal
zulässige Überhang (L
0
=Länge des Schaftes
zwischen dem Spannzangenende und dem
Kleinschleifkörper) nicht überschritten werden!
Bei einer Erhöhung des Überhangs (L0) muss die
zulässige Drehzahl herabgesetzt werden. Das
Einsatzwerkzeug möglichst mit der ganzen Länge
des Schaftes in die Spannzange einsetzen.
Stellen sie sicher, dass die Einspannlänge (Lg)
mindestens 10 mm beträgt.
- Der Schaftdurchmesser des Einsatzwerkzeugs
muss genau der Spannbohrung der Spannzange
entsprechen!
LoL
g
Page 6

DEUTSCHde
6
4.6 Gefährdungen am Arbeitsplatz
- Ausrutschen, Stolpern und Stürzen sind
Hauptgründe für Verletzungen am Arbeitsplatz.
Achten Sie auf Oberflächen, die durch den
Gebrauch des Druckluftwerkzeugs rutschig
geworden sein können, und auf durch den
Luftschlauch bedingte Gefährdungen durch
Stolpern.
- Gehen Sie in unbekannten Umgebungen mit
Vorsicht vor. Es können versteckte Gefährdungen
durch Stromkabel oder sonstige
Versorgungsleitungen gegeben sein.
- Das Druckluftwerkzeug ist nicht zum Einsatz in
explosionsgefährdeten Atmosphären bestimmt
und nicht gegen den Kontakt mit elektrischen
Stromquellen isoliert.
- Überzeugen Sie sich, dass sich an der Stelle, die
bearbeitet werden soll, keine Strom-, Wasseroder Gasleitungen befinden (z.B. mit Hilfe eines
Metallsuchgerätes).
4.7 Gefährdungen durch Staub und Dämpfe
- Die beim Einsatz des Druckluftwerkzeugs
entstehenden Stäube und Dämpfe können
gesundheitliche Schäden (wie z. B. Krebs,
Geburtsfehler, Asthma und/oder Dermatitis)
verursachen; es ist unerlässlich, eine
Risikobewertung in Bezug auf diese
Gefährdungen durchzuführen und geeignete
Regelungsmechanismen umzusetzen.
- In die Risikobewertung sollten der bei der
Verwendung des Druckluftwerkzeugs
entstehende Staub und der dabei möglicherweise
aufwirbelnde vorhandene Staub einbezogen
werden.
- Das Druckluftwerkzeug ist nach den in dieser
Anleitung enthaltenen Empfehlungen zu
betreiben und zu warten, um die Freisetzung von
Staub und Dämpfen auf ein Mindestmaß zu
reduzieren.
- Die Abluft ist so abzuführen, dass die
Aufwirbelung von Staub in einer staubgefüllten
Umgebung auf ein Mindestmaß reduziert wird.
- Falls Staub oder Dämpfe entstehen, muss die
Hauptaufgabe sein, diese am Ort ihrer
Freisetzung zu kontrollieren.
- Alle zum Auffangen, Absaugen oder zur
Unterdrückung von Flugstaub oder Dämpfen
vorgesehenen Einbau- oder Zubehörteile des
Druckluftwerkzeugs sollten den Anweisungen des
Herstellers entsprechend ordnungsgemäß
eingesetzt und gewartet werden.
- Die Verbrauchsmaterialien und das
Einsatzwerkzeug sind den Empfehlungen dieser
Anleitung entsprechend auszuwählen, zu warten
und zu ersetzen, um eine unnötige Intensivierung
der Staub- oder Dampfentwicklung zu vermeiden.
- Verwenden Sie Atemschutzausrüstungen nach
den Anweisungen Ihres Arbeitgebers oder wie
nach den Arbeits- und
Gesundheitsschutzvorschriften gefordert.
- Arbeiten mit bestimmten Materialien führen zu
Emissionen von Staub und Dampf, die eine
potentielle explosive Umwelt hervorrufen.
4.8 Gefährdungen durch Lärm
- Die Einwirkung hoher Lärmpegel kann bei
ungenügendem Gehörschutz zu dauerhaften
Gehörschäden, Gehörverlust und anderen
Problemen, wie z. B. Tinnitus (Klingeln, Sausen,
Pfeifen oder Summen im Ohr), führen.
- Es ist unerlässlich, eine Risikobewertung in Bezug
auf diese Gefährdungen durchzuführen und
geeignete Regelungsmechanismen umzusetzen.
- Zu den für die Risikominderung geeigneten
Regelungsmechanismen gehören Maßnahmen
wie die Verwendung von Dämmstoffen, um an
den Werkstücken auftretende Klingelgeräusche
zu vermeiden.
- Verwenden Sie Gehörschutzausrüstungen nach
den Anweisungen Ihres Arbeitgebers und wie
nach den Arbeits- und
Gesundheitsschutzvorschriften gefordert.
- Das Druckluftwerkzeug ist nach den in dieser
Anleitung enthaltenen Empfehlungen zu
betreiben und zu warten, um eine unnötige
Erhöhung der Lärmpegel zu vermeiden.
- Die Verbrauchsmaterialien und das
Einsatzwerkzeug sind den Empfehlungen dieser
Anleitung entsprechend auszuwählen, zu warten
und zu ersetzen, um eine unnötige Erhöhung des
Lärmpegels zu vermeiden.
- Der integrierte Schalldämpfer darf nicht entfernt
werden und muss sich in einem guten
Arbeitszustand befinden.
4.9 Gefährdungen durch Schwingungen
- Die Einwirkung von Schwingungen kann
Schädigungen an den Nerven und Störungen der
Blutzirkulation in Händen und Armen
verursachen.
- Tragen Sie bei Arbeiten in kalter Umgebung
warme Kleidung und halten Sie Ihre Hände warm
und trocken.
- Falls Sie feststellen, dass die Haut an Ihren
Fingern oder Händen taub wird, kribbelt, schmerzt
oder sich weiß verfärbt, stellen Sie die Arbeit mit
dem Druckluftwerkzeug ein, benachrichtigen Sie
Ihren Arbeitgeber und konsultieren Sie einen Arzt.
- Das Druckluftwerkzeug ist nach den in dieser
Anleitung enthaltenen Empfehlungen zu
betreiben und zu warten, um eine unnötige
Verstärkung der Schwingungen zu vermeiden.
- Die Verbrauchsmaterialien und das
Einsatzwerkzeug sind den Empfehlungen dieser
Anleitung entsprechend auszuwählen, zu warten
und zu ersetzen, um eine unnötige Verstärkung
der Schwingungen zu vermeiden.
- Nutzen Sie zum Halten des Gewichts des
Druckluftwerkzeugs, wann immer möglich, einen
Ständer, einen Spanner oder eine
Ausgleichseinrichtung.
- Halten Sie das Druckluftwerkzeug mit nicht allzu
festem, aber sicherem Griff unter Einhaltung der
erforderlichen Hand-Reaktionskräfte, denn das
Schwingungsrisiko wird in der Regel mit
zunehmender Griffkraft größer.
- Ein ungenügend montiertes oder beschädigtes
Einsatzwerkzeug kann zu überhöhten
Schwingungen führen.
Page 7

DEUTSCH de
7
4.10 Zusätzliche Sicherheitsanweisungen
- Druckluft kann ernsthafte Verletzungen
verursachen.
- Wenn das Druckluftwerkzeug nicht in Gebrauch
ist, vor dem Austausch von Zubehörteilen oder bei
der Ausführung von Reparaturarbeiten ist stets
die Luftzufuhr abzusperren, der Luftschlauch
drucklos zu machen und das Druckluftwerkzeug
von der Druckluftzufuhr zu trennen.
- Richten Sie den Luftstrom niemals auf sich selbst
oder gegen andere Personen.
- Umherschlagende Schläuche können ernsthafte
Verletzungen verursachen. Überprüfen Sie daher
immer, ob die Schläuche und ihre
Befestigungsmittel unbeschädigt sind und sich
nicht gelöst haben.
- Falls Universal-Drehkupplungen
(Klauenkupplungen) verwendet werden, müssen
Arretierstifte eingesetzt werden und verwenden
Sie Whipcheck-Schlauchsicherungen, um Schutz
für den Fall eines Versagens der Verbindung des
Schlauchs mit dem Druckluftwerkzeug oder von
Schläuchen untereinander zu bieten.
- Sorgen Sie dafür, dass der auf dem
Druckluftwerkzeug angegebene Höchstdruck
nicht überschritten wird.
- Tragen Sie Druckluftwerkzeuge niemals am
Schlauch.
- Wird das Druckluftwerkzeug in einem Halter
betrieben: das Druckluftwerkzeug sicher
befestigen. Der Verlust der Kontrolle kann zu
Verletzungen führen.
4.11 Weitere Sicherheitshinweise
- Beachten Sie gegebenenfalls spezielle
Arbeitsschutz- oder UnfallverhütungsVorschriften für den Umgang mit Kompressoren
und Druckluftwerkzeugen.
- Stellen Sie sicher, dass der in den Technischen
Daten angegebene maximal zulässige
Arbeitsdruck nicht überschritten wird.
- Überlasten Sie dieses Werkzeug nicht – benutzen
Sie dieses Werkzeug nur im Leistungsbereich,
der in den Technischen Daten angegeben ist.
- Verwenden Sie unbedenkliche Schmierstoffe.
Sorgen sie für ausreichende Belüftung des
Arbeitsplatzes. Bei erhöhtem Austrag:
Druckluftwerkzeug prüfen und ggf. reparieren
lassen.
- Benutzen Sie dieses Werkzeug nicht, wenn Sie
unkonzentriert sind. Seien Sie aufmerksam,
achten Sie darauf, was Sie tun, und gehen Sie mit
Vernunft an die Arbeit mit einem
Druckluftwerkzeug. Benutzen Sie kein Werkzeug,
wenn Sie müde sind oder unter dem Einfluss von
Drogen, Alkohol oder Medikamenten stehen. Ein
Moment der Unachtsamkeit beim Gebrauch des
Werkzeuges kann zu ernsthaften Verletzungen
führen.
- Halten Sie Ihren Arbeitsbereich sauber und gut
beleuchtet. Unordnung oder unbeleuchtete
Arbeitsbereiche können zu Unfällen führen.
- Druckluftwerkzeuge vor Kindern sichern.
- Werkzeug nicht ungeschützt im Freien oder in
feuchter Umgebung aufbewahren.
- Schützen Sie das Druckluftwerkzeug,
insbesondere den Druckluftanschluss und die
Bedienelemente vor Staub und Schmutz.
Die Informationen in dieser Betriebsanleitung sind
wie folgt gekennzeichnet:
Gefahr! Warnung vor Personenschäden
oder Umweltschäden.
Achtung. Warnung vor Sachschäden.
4.12 Symbole auf dem Druckluftwerkzeug
Vor der Inbetriebnahme die
Bedienungsanleitung lesen.
Augenschutz tragen
Gehörschutz tragen
Drehrichtung
Siehe Seite 2.
1 Gabelschlüssel
2 Spannzangenmutter
3 Spannzange
4 Spannzangenhalter
5 Spindel
6 Gabelschlüssel
7 Schalter (Ein-/Aussschalten)
8 Einschaltsperre
9 Regulierschraube zum Einstellen der Drehzahl
10 Luftaustritt
11 Druckluftanschluss mit Filter
12 Stecknippel 1/4"
6.1 Vor dem ersten Betrieb
Stecknippel (12) einschrauben.
6.2 Spannzange einsetzen
Der Schaftdurchmesser des Werkzeugs muss
genau der Spannbohrung der Spannzange (3)
entsprechen!
Es stehen Spannzangen für verschiedene
Schaftdurchmesser zur Verfügung. Die
Spannzange (3) in den Spannzangenhalter (4)
einsetzen und dann die Spannzangenmutter (2)
von Hand aufschrauben.
Wenn kein Werkzeug in die Spannzange
eingesetzt ist, die Spannzange nicht mit dem
Gabelschlüssel festziehen, sondern nur von Hand
aufschrauben!
6.3 Einsatzwerkzeug anbringen
Bei Kleinschleifkörpern darf der vom
Hersteller angegebene maximal zulässige
5. Überblick
6. Betrieb
Page 8
DEUTSCHde
8
Überhang (L0) nicht überschritten werden! Das
Einsatzwerkzeug möglichst mit der ganzen Länge
seines Schaftes in die Spannzange (3) einsetzen.
Stellen sie sicher, dass die Einspannlänge (Lg)
mindestens 10 mm beträgt.
Der Schaftdurchmesser des
Einsatzwerkzeugs muss genau der
Spannbohrung der Spannzange (3) entsprechen!
- Die Spindel (5) mit dem Gabelschlüssel (6)
anhalten.
- Die Spannzangenmutter (2) mit dem
Gabelschlüssel (1) festziehen.
- Auf sicheren Sitz des Einsatzwerkzeugs achten.
6.4 Druckluftwerkzeug benutzen
Um die volle Leistung Ihres Druckluftwerkzeuges zu
erzielen, verwenden Sie bitte stets
Druckluftschläuche mit einem Innendurchmesser
von mindestens 9 mm. Ein zu geringer
Innendurchmesser kann die Leistung deutlich
mindern.
Achtung. Die Druckluftleitung darf kein
Kondenswasser enthalten.
Achtung. Damit dieses Werkzeug lange
einsatzbereit bleibt, muss es ausreichend mit
Pneumatiköl versorgt werden. Dies kann wie folgt
geschehen:
– Geölte Druckluft verwenden durch Anbau eines
Nebelölers.
– Ohne Nebelöler: Täglich von Hand über den
Druckluftanschluss ölen. Ca. 3-5 Tropfen
Pneumatiköl je 15 Betriebsminuten bei
Dauereinsatz.
War das Werkzeug mehrere Tage außer Betrieb,
etwa 5 Tropfen Pneumatiköl von Hand in den
Druckluftanschluss geben.
Achtung. Werkzeug nur kurze Zeit im
Leerlauf laufen lassen.
1. Geeignete Spannzange (3) auswählen (siehe
Kapitel 6.2).
2. Passendes Einsatzwerkzeug anbringen (siehe
Kapitel 6.3).
3. Die Drehzahl kann an der Regulierschraube (9)
verändert werden.
4. Arbeitsdruck einstellen (gemessen am
Lufteintritt bei eingeschaltetem
Druckluftwerkzeug). Maximal zulässiger
Arbeitsdruck siehe Kapitel „Technische Daten“.
5. Druckluftwerkzeug an die Druckluftversorgung
anschließen.
6. Einschalten: Einschaltsperre (8) in Pfeilrichtung
schieben (siehe Abb., Seite 2) und Schalter (7)
drücken.
Ausschalten: Schalter (7) loslassen
.
Gefahr! Vor allen Arbeiten am Werkzeug
Druckluftanschluss trennen.
Gefahr! Weitergehende Wartungs- oder
Reparaturarbeiten, als die in diesem Kapitel
beschriebenen, dürfen nur Fachkräfte
durchführen.
- Stellen Sie durch regelmäßige Wartung die
Sicherheit des Druckluftwerkzeugs sicher.
- Verschraubungen auf festen Sitz prüfen, ggf.
festziehen.
- Filter im Druckluftanschluss mindestens
wöchentlich reinigen.
- Es wird empfohlen, dem Druckluftwerkzeug einen
Druckminderer mit Wasserabscheider und einen
Öler vorzuschalten.
- Bei erhöhtem Öl- oder Luftaustritt das
Druckluftwerkzeug prüfen und ggf. instand setzen
lassen. (Siehe Kapitel 9.)
- Überprüfen Sie regelmäßig und nach jedem
Einsatz die Drehzahl und führen Sie eine einfache
Überprüfung des Schwingungspegels durch.
- Vermeiden sie den Kontakt mit gefährlichen
Substanzen, die sich auf dem Werkzeug
abgelagert haben. Tragen sie geeignete
persönliche Schutzausrüstung und beseitigen Sie
gefährlichen Substanzen mit geeigneten
Maßnahmen vor der Wartung.
f
Verwenden Sie nur original Metabo Zubehör.
Verwenden Sie nur Zubehör, das für dieses
Druckluftwerkzeug bestimmt ist und die in dieser
Betriebsanleitung angegebenen Anforderungen
und Kenndaten erfüllt.
Zubehör-Komplettprogramm siehe
www.metabo.com oder Katalog.
Gefahr! Reparaturen an Druckluftwerkzeugen dürfen nur Fachkräfte mit original
Metabo-Ersatzteilen ausführen!
Mit reparaturbedürftigen Metabo
Druckluftwerkzeugen wenden Sie sich bitte an Ihre
Metabo-Vertretung. Adressen siehe
www.metabo.com.
Ersatzteillisten können Sie unter www.metabo.com
herunterladen.
Befolgen Sie nationale Vorschriften zu umweltgerechter Entsorgung und zum Recycling
ausgedienter Druckluftwerkzeuge, Verpackungen
und Zubehör. Es dürfen keine Gefährdungen für
Personen und Umwelt entstehen.
Erläuterungen zu den Angaben auf Seite 3.
LoL
g
7. Wartung und Pflege
8. Zubehör
9. Reparatur
10. Umweltschutz
11. Technische Daten
Page 9

DEUTSCH de
9
Änderungen im Sinne des technischen Fortschritts
vorbehalten.
V1= Luftbedarf
p
max.
= maximal zulässiger Arbeitsdruck
n0= Drehzahl
dS= Spannbohrung der Spannzange
D
max
= maximaler Durchmesser des
Kleinschleifkörpers
di= Schlauchdurchmesser (innen)
C = Anschlussgewinde
A = Abmessungen:
Länge x Breite x Höhe
m = Gewicht
Die angegebenen technischen Daten sind
toleranzbehaftet (entsprechend den jeweils
gültigen Standards).
Emissionswerte
Diese Werte ermöglichen die Abschätzung
der Emissionen des Werkzeugs und den Vergleich
verschiedener Werkzeuge. Je nach
Einsatzbedingung, Zustand des Werkzeuges oder
der Einsatzwerkzeuge kann die tatsächliche
Belastung höher oder geringer ausfallen.
Berücksichtigen Sie zur Abschätzung
Arbeitspausen und Phasen geringerer Belastung.
Legen Sie aufgrund entsprechend angepasster
Schätzwerte Schutzmaßnahmen für den Anwender
fest, z.B. organisatorische Maßnahmen.
Vibration
(gewichteter Effektivwert der
Beschleunigung; EN 28927) :
a
h
=Schwingungsemissionswert
K
h
=Messunsicherheit (Schwingung)
Schallpegel (EN ISO 15744):
L
pA
=Schalldruckpegel
L
WA
=Schallleistungspegel
KpA, KWA= Messunsicherheit
Gehörschutz tragen!
Page 10

ENGLISHen
10
Original instructions
We, being solely responsible, hereby declare that
these bar grinders conform to the standards and
directives specified on page 3.
This compressed air tool is designed for...
- ... for fine grinding work with abrasive points
- ...for working with polishing bobs
- ...for working with felt polishing tools
- ...for working with lamellar grinding wheels
by professionals.
The tool must only ever be operated with a compressed air supply. The maximum supply pressure
specified on the air tool must never be exceeded.
The air tool must not be operated using explosive,
inflammable or hazardous gases. It must not be
used as a lever, crushing tool or striking tool.
Any other use does not comply with the intended
purpose. Unspecified use, modification of the air
tool or use of parts that have not been tested and
approved by the manufacturer can cause unforeseeable damage.
The user bears sole responsibility for any damage
caused by improper use.
Generally accepted accident prevention regulations and the enclosed safety information must be
observed.
For your own protection and for the
protection of your pneumatic tool, pay
attention to all parts of the text that are
marked with this symbol!
WARNING – Reading the operating instructions will reduce the risk of injury.
WARNING Read all safety warnings and
instructions. Failure to follow all safety warn-
ings and instructions may result in electric shock,
fire and/or serious injury.
Keep all safety instructions and information for
future reference.
Pass on your pneumatic tool only together with
these documents.
- The user or the user's employer must evaluate the
specific risks associated with each application of
the tool.
- The Safety Instructions must be read and understood before installing, operating, repairing or
maintaining the tool, and also before replace any
accessory parts or carrying out any work in the
vicinity of the pneumatic tool. Failure to read and
follow the instructions may lead to serious injury.
- Only qualified, trained operators are authorised to
install, adjust or use the pneumatic tool.
- The pneumatic tool must not be modified. Any
modifications may reduce the efficiency of the
safety measures and increase risks for the operator.
- Never use pneumatic tools that have been
damaged. Look after your pneumatic tools carefully. Regularly check that all moving parts are
functioning correctly without jamming, ensure that
no parts are broken or damaged to an extent that
they affect the operation of the pneumatic tool.
Check that all signs and labels are legible and
intelligible. Have damaged parts repaired or
replaced before using the tool. Many accidents
are caused by poorly maintained pneumatic tools.
4.1 Risks associated with ejected parts
- If either the workpiece, accessory parts or the
pneumatic tool breaks, parts may be ejected at
high speed.
- While operating, maintaining or repairing the
pneumatic tool, or replacing accessory parts, you
must always wear impact-resistant safety
goggles. The degree of protection required for
each individual task must be evaluated separately
in each case.
- Ensure that the workpiece is secure.
- Regular checks must be carried out to verify that
the rotational speed of the pneumatic tool does
not exceed the speed specified on the pneumatic
tool. These speed checks must be conducted
when no accessory is fitted. Metabo's Service
Centre can perform these checks for you.
- Ensure that any sparks or fragments emitted
during operation do not pose a risk.
- Disconnect the pneumatic tool from the
compressed air supply before replacing the
accessory or accessory parts, and also before
carrying out maintenance, settings or cleaning.
- Also ensure that no other people are placed at
risk.
4.2 Risks associated with items catching/
getting entwined
- Wear suitable clothing. Do not wear loose clothing
or jewellery. Keep hair, clothing and gloves at a
safe distance from the pneumatic tool and moving
parts. Loose clothing, jewellery or long hair could
catch in moving parts. There is a risk of injury in
this case.
4.3 Risks during operation
- Avoid any contact with the rotating shaft and the
accessory to prevent cuts to your hands and other
body parts.
- When using the pneumatic tool, the operator's
hands may be exposed to potential risk of cuts,
abrasions and heat damage. To protect your
hands, wear suitable gloves.
- The operator and maintenance staff must be
physically capable of handling the size, weight
and power output of the pneumatic tool.
1. Declaration of Conformity
2. Specified Use
3. General safety instructions
4. Special Safety Instructions
Page 11
ENGLISH en
11
- Make sure you hold the pneumatic tool correctly:
Be prepared to counter any standard or unexpected movements, so keep both hands ready.
- Ensure you stand in a safe position and keep your
balance at all times.
- Avoid accidental operation. If the air supply is
interrupted, switch off the pneumatic tool using the
On/Off switch.
- Only use lubricants that have been recommended
by the manufacturer.
- Wear personal protective equipment and always
wear safety glasses. By wearing personal protective equipment such as gloves, protective
clothing, a dust mask, non-skid safety shoes, a
safety helmet or ear protectors, to suit the type of
machine and its use, you reduce the risk of injury.
Wearing this equipment is recommended.
- The rated speed of the accessory must be at least
equal to the maximum speed marked on the pneumatic tool. Accessories running faster than their
rated speed can break and fly apart.
- Wear a safety helmet if carrying out work above
your head.
- The tool continues running after the pneumatic
tool has been switched off.
- Ensure the sparks emitted during use do not pose
any risk. Explosive or flammable dust may be
generated while you work on workpieces. There is
therefore a risk of explosion or fire.
4.4 Risks associated with recurring move-
ments
- When working with the pneumatic tool, you may
experience an uncomfortable sensation in your
hands, arms, shoulders, neck or in other body
parts.
- Make sure you are in a comfortable position to
carry out work with the pneumatic tool, check that
the tool is held securely, and avoid any awkward
positions that make it difficult, for example, to keep
your balance. If carrying out work over an
extended period, the operator should change
position occasionally. This should help to avoid
fatigue and any unpleasant sensation.
- If the operator experiences persistent symptoms
such as feeling unwell, aches, pains or throbbing,
a prickling or burning sensation, loss of hearing, or
joint stiffening, these warning signs must not be
ignored. The operator should advise the employer
of these symptoms and consult a qualified doctor.
4.5 Risks associated with accessory parts
- Disconnect the pneumatic tool from the air supply
before the accessory or accessory part is secured
or replaced.
- Only use accessories that are designed for this
machine and that fulfil the requirements and the
specifications listed in these operating instructions.
- Avoid any direct contact with the accessory both
during and after use because it may be hot or have
sharp edges.
- The rated speed of the accessory must be at least
equal to the maximum speed marked on the pneumatic tool. Accessories running faster than their
rated speed can break and fly apart.
- Never fit a grinding wheel, cut-off wheel or milling
cutter. If a grinding wheel burst, it can cause
serious or even fatal injury.
- Do not use wheels that are chipped, ripped or that
may have fallen.
- Only the permissible accessories with the appropriate shank diameter must be used.
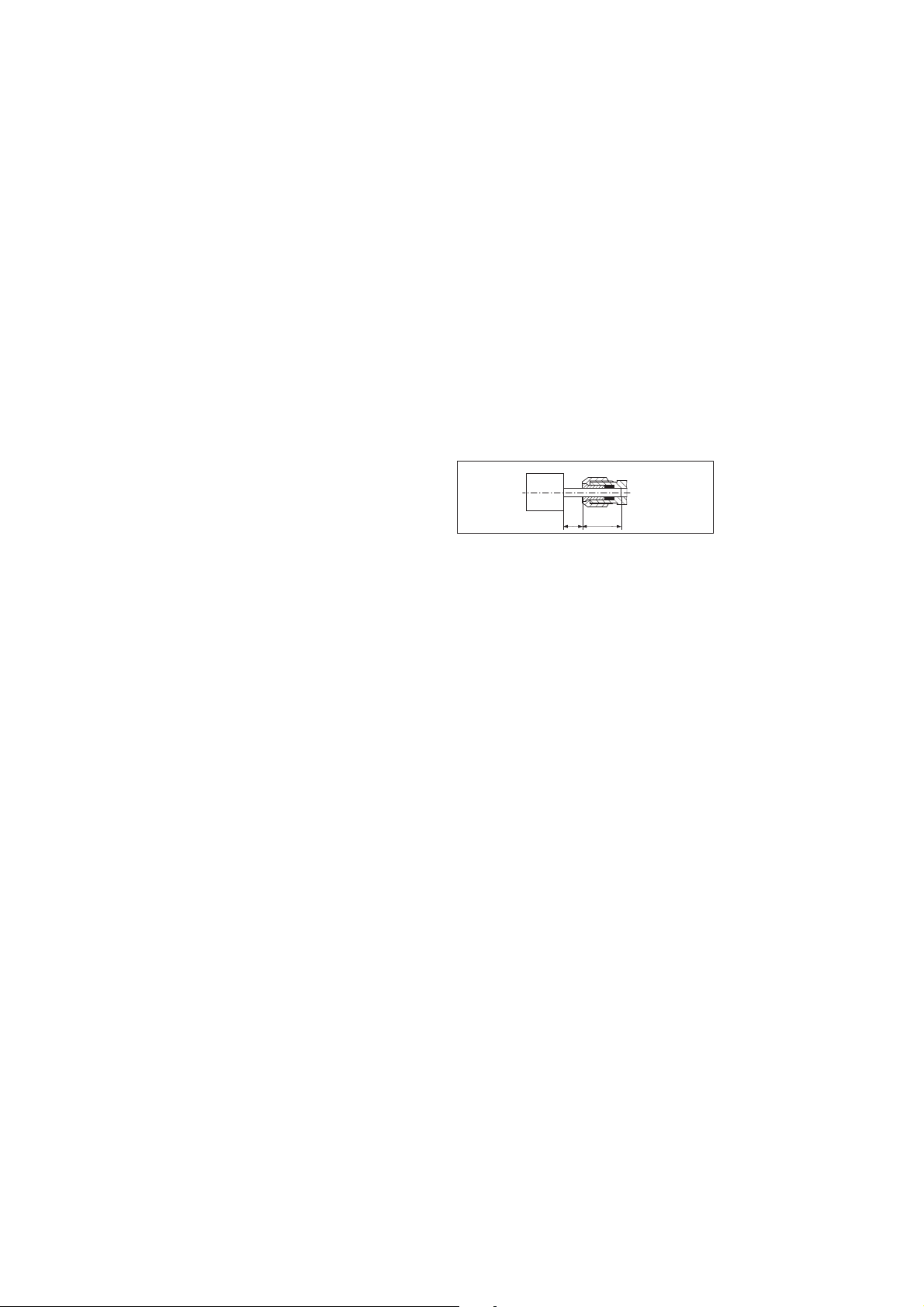
- Observe the manufacturer's recommendations for
small grinding tools. For small grinding tools, the
maximum permissible projection allowed by the
manufacturer (L
0
=length of shank between the
end of the collet chuck and the small grinding tool)
must not be exceeded! If the projection is
increased (L0), the permissible speed must be
lowered. Insert the accessory with the full length of
the shank if possible into the collet chuck. Ensure
that the clamping length (Lg) is at least 10mm.
- The accessory's shank diameter must correspond
exactly to the collet bore of the collet chuck!
4.6 Risks in the workplace
- Slipping, tripping and falling are the main reasons
for accidents in the workplace. Pay attention to
surfaces that may have become slippy as a result
of using the pneumatic tool, and also watch that
the air hose does not cause someone to trip.
- Proceed carefully when working in unfamiliar environments. Power cables and other supply lines
may represent a hidden risk.
- The pneumatic tool is not designed for use in
explosive environments and is not insulated
against contact with sources of electric power.
- Ensure that the spot where you wish to work is free
of power cables, gas lines or water pipes (e.g.
using a metal detector).
4.7 Risks associated with dust and vapours
- The dust and vapours generated when the pneumatic tool is used may carry health risks (e.g.
cancer, birth defects, asthma and/or dermatitis); it
is therefore imperative that a risk assessment is
carried out in relation to these risks and that suitable controls are then implemented.
- The risk assessment should take into account
both the dust generated while the pneumatic tool
is used and any existing dust that may be raised
during operation.
- The pneumatic tool must be operated in accordance with the recommendations set forth in these
instructions and must be maintained in order to
minimise the release of dust and vapours.
- The extracted air must be discharged in such a
way that the minimum of dust is raised in a dustfilled environment.
- If dust or vapours are generated, the main priority
is to control these at the location where they are
released.
- All built-in or accessory parts on the pneumatic
tool that are designed to collect, extract or prevent
LoL
g
Page 12

ENGLISHen
12
air-borne dust or vapours must be used and maintained in accordance with the manufacturer's
instructions.
- To avoid increasing the amount of dust or vapours
generated unnecessarily, it must ensured that
consumables and the accessory are selected,
maintained and replaced in accordance with
these instructions.
- Use protective breathing apparatus in accordance
with your employer instructions or in accordance
with health and safety regulations.
- Working with certain materials causes emissions
of dust and vapours that can give rise to potentially
explosive conditions.
4.8 Risks associated with noise
- Failure to use adequate ear protectors when the
noise level is high can result in lasting damage to
hearing, hearing loss and other problems, such as
tinnitus (ringing, whistling or buzzing in the ear).
- It is vital to carry out a risk assessment in relation
to these risks and to implement appropriate
control measures that take the risks into account.
- Appropriate risk control measures may include,
for example, the use of sound-insulating materials
to prevent the knocking sounds that occur on the
workpieces.
- Use ear protection in accordance with your
employer instructions or in accordance with health
and safety regulations.
- The pneumatic tool must be operated in accordance with the recommendations provided in these
instructions and must be maintained in order to
avoid unnecessarily raising the noise level.
- To avoid increasing the noise level unnecessarily,
consumables and the accessory must be
selected, maintained and replaced in accordance
with these instructions.
- The integrated sound absorber must not be
removed. You must ensure it is in good working
order.
4.9 Risks associated with vibration
- The effects of vibrations can damage nerves and
impair blood circulation in the hands and arms.
- When working in cold environments, you must
wear warm clothing and keep your hands warm
and dry.
- If you notice that the skin on your fingers or hands
is numb, prickling or turning white, stop working
with the pneumatic tool immediately, notify your
employer and consult a doctor.
- The pneumatic tool must be operated in accordance with the recommendations provided in these
instructions and must be maintained in order to
avoid unnecessarily raising the level of vibration.
- To avoid increasing the level of vibration unnecessarily, consumables and the accessory must be
selected, maintained and replaced in accordance
with these instructions.
- To support the weight of the pneumatic tool, use a
stand, a clamp or an equaliser whenever possible.
- Hold the pneumatic tool firmly but not too tightly
using the required manual torque reaction: the risk
of vibration is increased when the grip force is
higher.
- An accessory that is either damaged or incorrectly
mounted can cause excessive vibration.
4.10 Additional safety instructions
- Compressed air can cause serious injury.
- When the pneumatic tool is not in use, before
replacing accessory parts or when carrying out
repairs, you must ensure that air supply is shut off,
that the air hose is depressurised and that the
pneumatic tool is disconnected from the
compressed air supply.
- Never direct the air jet at yourself or other people.
- Hoses that whip about can cause serious injury.
Therefore always check that the hoses and their
fixtures are in good condition and that they have
not become loose.
- If universal swivel couplings (claw couplings) are
being used, locking pins must also be used. You
should also use whip check hose restraints in
case there is a problem with the connection
between the hose and pneumatic tool or between
the hoses themselves.
- Ensure that the maximum pressure specified on
the pneumatic tool is not exceeded.
- Never carry pneumatic tools by the hose.
- Secure the pneumatic tool if it is operated in a
holder. Loss of control can cause personal injury.
4.11 Additional Safety Instructions
- If applicable, observe any particular health and
safety or accident prevention regulations
governing the use of compressors and
compressed pneumatic tools.
- Ensure that the maximum supply pressure specified in the Technical Specifications is not
exceeded.
- Do not overload the tool – use it only within the
performance range for which it was designed (see
“Technical Specifications”).
- Use non-hazardous lubricants. Ensure the workplace is adequately ventilated. If there is a large
amount of discharge: Check the pneumatic tool
and have it repaired if necessary.
- Do not operate the tool unless you are completely
focused. You must be alert, pay attention to what
you are doing and proceed cautiously when
working with a pneumatic tool. Never use a tool
when you are tired or under the influence of drugs,
alcohol or medication. Just one moment's carelessness when using the tool can cause serious
injury.
- Make sure your workplace is clean and well lit.
Untidy or poorly lit workplaces can cause accidents.
- Keep pneumatic tools away from children.
- Do not store the tool outdoors or in damp conditions without protection.
- Protect the pneumatic tool, especially the
compressed air connection and the control
elements from dust and dirt.
Information in these operating instructions is categorised as shown below:
Danger! Risk of personal injury or environmental damage.
Caution. Risk of material damage
Page 13
ENGLISH en
13
4.12 Symbols on the pneumatic tool
Read the Operating Instructions before
starting to use the machine.
Wear safety goggles.
Wear ear protectors.
Direction of rotation
See page 2.
1 Open-ended spanner
2 Collet chuck nut
3 Collet chuck
4 Collet chuck holder
5 Spindle
6 Open-ended spanner
7 Switch (on/off)
8 Switch-on lock
9 Adjusting screw for setting the speed
10 Air outlet
11 Compressed air connection with filter
12 Plug-in nipple 1/4"
6.1 Before using the tool for the first time
Insert plug-in nipple (12).
6.2 Inserting the collet chuck
The tool's shank diameter must correspond
exactly to the collet bore of the collet chuck (3)!
Various collet chucks are available for different
shank diameters. Insert the collet chuck (3) into the
collet chuck holder (4) and manually tighten the
collet chuck nut (2).
If there is no tool inserted in the collet chuck,
you can tighten the collet chuck manually
rather than with the open-end spanner.
6.3 Attaching the accessory
For small grinding tools, the maximum permissible projection allowed by the manufacturer
(L
0
) must not be exceeded! Insert the accessory
with the full length of the shank if possible into the
collet chuck (3). Ensure that the clamping length
(Lg) is at least 10mm.
The accessory's shank diameter must correspond exactly to the collet bore of the collet
chuck (3).
- Bring the spindle (5) to a standstill using the openend spanner (6).
- Tighten the collet chuck nut (2) using the openend spanner (1).
- Ensure that the accessory is fitted securely.
6.4 Using the pneumatic tool
To benefit from the pneumatic tool's full performance, always use compressed air hoses with an
inner diameter of at least 9 mm. Tool performance
can be significantly impaired if the inner diameter is
too small.
Caution. The compressed air line must not
contain any water condensation.
Caution. To preserve and extend the service
life of this tool, you must ensure that it is regularly maintained with pneumatic oil lubricator. You
can do this as follows:
– Use oiled compressed air by fitting an oil-fog lu-
bricator.
– Without an oil-fog lubricator: Manually apply oil
every day via the compressed air connection.
Use approx. 3-5 drops of pneumatic oil lubricator
for each 15 minutes of continuous operation.
If the tool has not been in use for several days, you
should manually apply about 5 drops of pneumatic
oil lubricator into the compressed air connection.
Caution. Only allow the tool to run at idle
speed for a brief period.
1. Select a suitable collet chuck (3) (see Chapter
6.2).
2. Fit an appropriate accessory (see Chapter 6.3).
3. You can adjust the speed on the adjusting
screw (9).
4. Adjust the supply pressure (this is measured at
the air outlet while the pneumatic tool is
switched on). For details of the maximum permissible supply pressure, see the Chapter on
"Technical Specifications".
5. Connect the pneumatic tool to the compressed
air supply.
6. To switch on: Push the switch-on lock (8) in the
direction of the arrow (see Fig., Page 2) and
press switch (7).
To switch off: Release switch (7)
.
Danger! Disconnect the compressed air con-
nection before carrying out any work.
Danger! Repair and maintenance work other
than described in this section should only be
carried out by qualified specialists.
- Carry out regular maintenance to ensure the
safety of the pneumatic tool.
- Check that all screw fittings are seated securely,
and tighten if necessary.
5. Overview
6. Operation
LoL
g
7. Care And Maintenance
Page 14

ENGLISHen
14
- Clean the filter in the compressed air connection
at least once a week.
- It is recommended that you install a pressure
reducer with an air-water separator and lubricator
upstream of the pneumatic tool.
- If a large amount of air or oil is escaping, check the
pneumatic tool and have it maintained if necessary. (see Section 9.)
- Check the rotational speed regularly and after
every use. Also carry out a simple check on vibration emission.
- Avoid contact with dangerous substances that
have collected on the tool. Wear suitable personal
protective equipment and take appropriate measures to remove any dangerous substances before
maintenance.
f
Use only genuine Metabo accessories.
Only use accessories that are designed for this
pneumatic tool and that fulfil the requirements and
the specifications listed in these operating instructions.
For a complete range of accessories, see
www.metabo.com or the catalogue.
Danger! Repairs to pneumatic tools must only
be carried out by qualified specialists, using
original Metabo spare parts!
If you have Metabo pneumatic tools that require
repairs, please contact your Metabo service centre.
For addresses see www.metabo.com.
You can download spare parts lists from
www.metabo.com.
Observe national regulations on environmentally
compatible disposal and on the recycling of disused
pneumatic tools, packaging and accessories. You
must not cause risks to people or the environment.
Explanatory notes on the specifications on page 3.
Changes due to technological progress reserved.
V1= Air requirement
p
max.
= maximum permissible supply pressure
n0= Rotational speed
dS= Collet bore of the collet chuck
D
max
= maximum diameter of the small grinding
tool
di= Hose diameter (inner)
C = Connecting thread
A = Dimensions:
Length x Width x Height
m = Weight
The technical specifications quoted are subject to
tolerances (in compliance with the relevant valid
standards).
Emission values
Using these values, you can estimate the
emissions from this tool and compare these with the
values emitted by other tools. The actual values
may be higher or lower, depending on the particular
application and the condition of the tool or accessory. In estimating the values, you should also
include work breaks and periods of low use. Based
on the estimated emission values, specify protective measures for the user - for example, any organisational steps that must be put in place.
Vibration
(acceleration value, frequency-weighted
according to EN 28927):
a
h
=Vibration emission level
K
h
=Measurement uncertainty (vibration)
Sound level (EN ISO 15744):
L
pA
=Sound pressure level
L
WA
=Acoustic power level
KpA, KWA= Measurement uncertainty
Wear ear protectors!
8. Accessories
9. Repairs
10. Environmental Protection
11. Technical specifications
Page 15

FRANÇAIS fr
15
Notice d'utilisation originale
Nous déclarons, sous notre propre responsabilité,
que cette meuleuse à tige est conforme aux normes
et directives indiquées à la page 3.
Cet outil pneumatique a été spécialement conçu...
- ... pour les travaux de ponçage fin avec meule sur
tige,
- ... pour les travaux avec corps de polissage de
forme,
- ... pour les travaux avec corps de polissage à
feutre,
- ... pour les travaux avec meules à lamelles
dans un cadre professionnel.
Cet outil ne peut fonctionner que s’il est raccordé à
une alimentation en air comprimé. La pression de
service maximale admissible indiquée pour cet outil pneumatique ne doit surtout pas être dépassée.
Il est interdit d’utiliser des gaz explosifs, inflammables ou nocifs pour actionner cet outil pneumatique. Cet outil ne doit pas servir de levier, d’outil
de démolition ou de percussion.
Toute autre utilisation est considérée comme
contraire aux prescriptions. Une utilisation
contraire aux prescriptions, des modifications apportées à l’outil pneumatique ou l’emploi de pièces
qui n’ont été ni testées, ni homologuées par le fabricant peuvent entraîner des dommages
imprévisibles !
L'utilisateur est entièrement responsable de tous
dommages résultant d'une utilisation non conforme
aux prescriptions.
Il est impératif de respecter les directives de
prévention des accidents reconnues et les
consignes de sécurité ci-jointes.
Pour des raisons de sécurité et afin de
protéger l’outil pneumatique, il faut se
conformer aux passages de texte
repérés par ce symbole !
AVERTISSEMENT – Lire la notice d'utilisation afin d'éviter tout risque de blessures.
AVERTISSEMENT Lire toutes les
consignes de sécurité et instructions. Le
non-respect des consignes de sécurité et des
instructions peut être à l'origine d'un choc électrique, d'un incendie et/ou de blessures graves.
Conserver toutes les consignes de sécurité et
instructions.
En cas de transmission de l’outil pneumatique,
remettre également tous les documents qui
l’accompagnent.
- L’utilisateur ou son employeur est dans l’obligation d’évaluer les risques spécifiques qui sont
susceptibles de se produire en fonction des
modalités d’utilisation.
- Il est indispensable de lire et de bien comprendre
les consignes de sécurité avant d’assembler,
d’utiliser, de réparer, d’effectuer la maintenance
de l’outil, de remplacer des accessoires, ou même
de travailler à proximité de l’outil pneumatique.
Dans le cas contraire, il peut y avoir des blessures
graves.
- Cet outil pneumatique ne doit être assemblé,
réglé et utilisé que par des personnes dûment
qualifiées et formées.
- Il est interdit d’apporter des modifications à cet
outil pneumatique. Toute modification risque
d’altérer l’efficacité des dispositifs de sécurité et,
par conséquent, d’aggraver les risques encourus
par l’utilisateur.
- Ne jamais utiliser des outils pneumatiques
endommagés. Manipuler les outils pneumatiques
avec soin. Vérifier régulièrement que les pièces
mobiles fonctionnent bien et qu’elles ne sont pas
bloquées, mais aussi qu’il n’y a pas de pièces
cassées ou endommagées susceptibles d’altérer
le fonctionnement de l’outil pneumatique. Vérifier
que les plaques et les marquages sont complets
et bien lisibles. Faire réparer ou remplacer les
pièces endommagées avant d’utiliser l’appareil.
De nombreux accidents proviennent d’un
mauvais entretien des outils pneumatiques.
4.1 Risques inhérents à la projection d’élé-
ments
- En cas de rupture du matériau, d’accessoires ou
de l’outil pneumatique lui-même, des éléments
risquent d’être projetés à une grande vitesse.
- Porter systématiquement des lunettes de protection à l’épreuve des chocs pour utiliser l’outil pneumatique, pour changer les accessoires ou encore
effectuer des opérations de réparation ou de
maintenance de l’outil. Le degré de protection
nécessaire doit être déterminé au cas par cas.
- Vérifier que le matériau est correctement fixé.
- Il est indispensable de contrôler régulièrement
que la vitesse de rotation de l’outil pneumatique
n’est pas supérieure à la vitesse qui figure sur
l’outil lui-même. Ces contrôles de vitesse de rotation doivent être effectués sans embout. Le
service après-vente Metabo est en mesure
d’effectuer ce type de contrôles.
- Vérifier que les étincelles et les éclats qui se
produisent lors des travaux ne présentent pas de
danger.
- Débrancher l’outil pneumatique de l’alimentation
en air comprimé avant de changer l’embout ou les
accessoires, d’effectuer un réglage, la maintenance ou un nettoyage.
- Veiller à ce que les autres personnes éventuellement présentes ne soient pas exposées à des
risques.
1. Déclaration de conformité
2. Utilisation conforme aux
prescriptions
3. Consignes de sécurité
générales
4. Consignes de sécurité
particulières
Page 16

FRANÇAISfr
16
4.2 Risques en cas de happement/enroulement
- Porter des vêtements adaptés. Proscrire les vête-
ments amples et les bijoux. Faire en sorte que les
cheveux, les vêtements et les gants soient à une
distance suffisante de l’outil pneumatique et des
pièces mobiles. Les vêtements amples, les bijoux
ou les cheveux longs risquent d’être happés par
les pièces mobiles. Cela peut provoquer des blessures.
4.3 Risques en cours de fonctionnement
- Éviter tout contact avec l’axe tournant et l’embout,
afin d’éviter des blessures au niveau des mains ou
d’autres parties du corps.
- Les mains de l’utilisateur sont exposées à des
risques de coupures, d’écorchures et de brûlures
au cours de l’utilisation de l’outil pneumatique.
Porter des gants adaptés pour protéger ses
mains.
- L’utilisateur et le personnel de maintenance
doivent être physiquement en mesure de
maîtriser la taille, le poids et la puissance de l’outil
pneumatique.
- Tenir l’outil pneumatique correctement : l’utilisa-
teur doit être en mesure de contenir tout mouvement brutal ou usuel de l’appareil. Il doit donc
pouvoir utiliser ses deux mains.
- Veiller à un bon équilibre et toujours se tenir en
équilibre.
- Eviter toute mise en marche intempestive. En cas
de coupure de l’alimentation en air comprimé,
éteindre l’outil pneumatique en agissant sur l’interrupteur marche/arrêt.
- Utiliser exclusivement le lubrifiant préconisé par le
fabricant.
- Porter systématiquement des accessoires et des
lunettes de protection. Le port d’accessoires de
protection tels que gants de protection, vêtements
de protection, masque, chaussures de sécurité
antidérapantes, casque de protection ou protection auditive réduit les risques de blessures et est
par conséquent recommandé, suivant le type et
les modalités d’utilisation de l’appareil.
- La vitesse admissible de l’embout doit être au
moins égale à la vitesse maximale indiquée sur
l’outil pneumatique. Les accessoires tournant plus
vite que leur vitesse admissible peuvent se
rompre et être projetés.
- Porter un casque de protection pour travailler en
hauteur avec les bras levés.
- L’outil continue de tourner après que l’interrupteur
a été mis en position d’arrêt.
- Faire en sorte que les étincelles provoquées par
l’utilisation de l’outil ne présentent pas de danger.
Certains matériaux sont susceptibles de former
des poussières inflammables ou explosives. Il y a
alors un risque d’explosion ou d’inflammation.
4.4 Risques inhérents à des mouvements
répétitifs
- L’utilisation d’un outil pneumatique peut s’accom-
pagner de sensations désagréables au niveau
des mains, des bras, des épaules, du cou ou
d’autres parties du corps.
- Faire en sorte d’adopter une position confortable
et d’avoir de bons appuis pour utiliser l’outil pneu-
matique. Éviter les positions inconfortables ou les
postures qui permettent difficilement de garder
l’équilibre. Il est conseillé de changer de posture
lors des travaux prolongés, puisque ceci
contribue à éviter les sensations désagréables et
la fatigue.
- Si l’utilisateur ressent des symptômes comme un
malaise persistant, des troubles, des palpitations,
des douleurs, des fourmillements, des engourdissements, des sensations de brûlure ou des ankyloses, il ne doit surtout pas ignorer les signaux
d’alerte que cela représente. L’utilisateur doit
alors en faire part à son employeur et consulter un
médecin qualifié.
4.5 Risques inhérents aux accessoires
- Isoler l’outil pneumatique de l’alimentation en air
comprimé avant de fixer ou de changer d’embout
ou d’accessoire.
- Utiliser uniquement des accessoires spécialement conçus pour cet appareil et qui sont
conformes aux exigences et aux données caractéristiques indiquées dans les présentes instructions d’utilisation.
- Éviter de toucher l’embout en cours d’utilisation ou
juste après l’utilisation, alors qu’il est encore
chaud ou coupant.
- La vitesse admissible de l’embout doit être au
moins égale à la vitesse maximale indiquée sur
l’outil pneumatique. Les accessoires tournant plus
vite que leur vitesse admissible peuvent se
rompre et être projetés.
- Ne jamais monter de disque abrasif, de meule ou
de fraise sur l’outil. L’éclatement d’un disque
abrasif peut provoquer des blessures très graves,
voire même la mort.
- Ne pas utiliser de disque ayant subi des chocs,
comportant des fissures ou susceptible d’être
tombé à terre.
- Utiliser uniquement des embouts homologués,
qui présentent un diamètre de tige adapté.
- Se conformer aux recommandations du fabricant
des petites meules sur tige. Les petites meules
sur tige ne doivent pas dépasser le porte-à-faux
maximal spécifié par le fabricant (L0 = longueur de
tige entre l’extrémité de la pince de serrage et la
meule) ! En cas d’augmentation du porte-à-faux
(L0), la vitesse de rotation doit être réduite en
conséquence. Insérez l’embout sur toute la
longueur de la tige dans la pince de serrage.
Veiller à ce que la longueur de serrage (Lg) soit au
moins de 10 mm.
- Le diamètre de tige de l’embout doit correspondre
exactement à l’orifice de serrage de la pince de
serrage !
4.6 Risques inhérents au poste de travail
- Les glissades, pertes d’équilibre et les chutes
constituent les principales causes de blessures
LoL
g
Page 17

FRANÇAIS fr
17
sur le lieu de travail. Faire très attention en cas
d’évolution sur des surfaces rendues glissantes
par l’utilisation de l’outil pneumatique et veiller à
ne pas trébucher en se prenant les pieds dans le
flexible pneumatique.
- Agir avec circonspection dans les environnements qui ne sont pas familiers. Les câbles électriques et autres câbles d’alimentation sont autant
de sources de danger qui peuvent passer inaperçues.
- L’outil pneumatique n’a pas été conçu pour être
utilisé dans des atmosphères explosives et il ne
bénéficie pas d’une isolation spécifique en cas de
contact avec des sources électriques.
- Vérifier que l'endroit prévu pour l'intervention ne
comporte aucune conduite électrique, d'eau ou de
gaz (p. ex. à l'aide d'un détecteur de métaux).
4.7 Risques inhérents à la poussière et aux
vapeurs
- La poussière et les vapeurs produites par le fonctionnement de l’outil pneumatique peuvent être
néfastes pour la santé (et provoquer notamment
des cancers, des fausses couches, de l’asthme
et/ou des dermatites). Il est donc indispensable
de procéder à une analyse des risques liés à ces
facteurs et de mettre en place des mécanismes
de régulation adaptés.
- L’analyse des risques doit notamment tenir
compte de la poussière produite lors de l’utilisation de l’outil pneumatique et des risques de tourbillonnement de poussière afférents.
- L’outil pneumatique doit être utilisé et entretenu
conformément aux recommandations des
présentes instructions d’utilisation, afin de réduire
au minimum la production de poussière et de
vapeurs.
- L’air vicié doit être évacué de façon à réduire au
minimum les risques de tourbillonnement de particules dans les environnements poussiéreux.
- Si la formation de poussière ou de vapeurs est
inévitable, tout l’enjeu est alors de les maîtriser au
niveau du point d’émanation.
- Tous les éléments et accessoires de l’outil pneumatique conçus pour recueillir, aspirer ou éliminer
les poussières et les vapeurs volatiles doivent être
utilisés et entretenus correctement, dans le
respect des consignes du fabricant.
- Les accessoires consommables et les embouts
doivent être sélectionnés, entretenus et
remplacés conformément aux recommandations
des présentes instructions, afin d’éviter
d’augmenter inutilement la quantité de poussière
ou de vapeurs produite.
- Utiliser des équipements de protection des voies
respiratoires conformes aux consignes de
l’employeur ou aux directives en matière de santé
et de sécurité au travail.
- Certains matériaux produisent de la poussière et
des vapeurs. Celles-ci peuvent créer un environnement potentiellement explosif.
4.8 Risques inhérents au bruit
- En cas de protection auditive insuffisante, l’exposition à un niveau de bruit élevé risque d’endommager durablement l’audition, d’entraîner une
perte d’audition et d’autres problèmes, comme les
acouphènes (tintement, chuintement, sifflement
ou bourdonnement dans les oreilles).
- Il est indispensable de procéder à une analyse
des risques eu égard à ces facteurs et de mettre
en œuvre des mécanismes de régulation appropriés.
- Les mécanismes de régulation susceptibles
d’être mis en œuvre pour réduire les risques
incluent notamment l’utilisation de matériaux
isolants pour éviter les tintements qui se
produisent au niveau des matériaux.
- Utiliser des équipements de protection de l’audition conformes aux consignes de l’employeur et
aux directives en matière de santé et de sécurité
au travail.
- L’outil pneumatique doit être utilisé et entretenu
conformément aux recommandations des
présentes instructions pour éviter toute élévation
inutile du niveau sonore.
- Les accessoires consommables et les embouts
doivent être sélectionnés, entretenus et
remplacés conformément aux recommandations
des présentes instructions, afin d’éviter toute
augmentation inutile du niveau sonore.
- Il est interdit de retirer le silencieux intégré. Par
ailleurs, ce silencieux doit être en bon état de
fonctionnement.
4.9 Risques inhérents aux vibrations
- Les vibrations peuvent provoquer des troubles
nerveux, mais aussi perturber la circulation
sanguine au niveau des mains et des bras.
- Si la température est basse, porter des vêtements
chauds et faire en sorte de garder les mains au
chaud et au sec.
- Si la peau des doigts ou des mains s’engourdit,
qu’elle picote, qu’elle fait mal ou qu’elle devient
blanche, cesser d’utiliser l’outil pneumatique,
avertir l’employeur et consulter un médecin.
- L’outil pneumatique doit être utilisé et entretenu
conformément aux recommandations des
présentes instructions pour éviter tout renforcement inutile des vibrations.
- Les accessoires consommables et les embouts
doivent être sélectionnés, entretenus et
remplacés conformément aux recommandations
des présentes instructions, afin d’éviter tout
renforcement inutile des vibrations.
- Utiliser un support, un dispositif tendeur ou un
dispositif d’équilibrage chaque fois que cela est
possible pour supporter le poids de l’outil pneumatique.
- Exercer une force suffisante sur l’outil pneumatique pour maîtriser les forces de réaction au
niveau des mains, sans pour autant exercer une
pression excessive, puisque les risques de vibrations augmentent avec la force de préhension
exercée sur l’outil.
- Un embout qui n’est pas correctement monté ou
qui est endommagé peut entraîner des vibrations
accrues.
4.10 Consignes de sécurité supplémentaires
- L’air comprimé risque de provoquer de graves
blessures.
- Lorsque l’outil pneumatique n’est pas utilisé,
avant de changer des accessoires ou d’effectuer
Page 18
FRANÇAISfr
18
des réparations, il faut systématiquement couper
l’alimentation pneumatique, dépressuriser le
flexible pneumatique et débrancher l’outil pneumatique de l’alimentation en air comprimé.
- Ne jamais orienter le flux d’air vers soi ou vers
d’autres personnes.
- Les flexibles qui serpentent sous l’effet de l’air
comprimé qu’ils contiennent peuvent provoquer
de graves blessures. Il faut donc systématiquement s’assurer que les flexibles et les dispositifs
de fixation ne sont pas endommagés ou
desserrés.
- En cas d’utilisation de raccords tournants universels (accouplement à griffes), il est indispensable
de mettre en place des goupilles d’arrêt et
d’utiliser des câbles de sécurité pour les flexibles,
afin de se protéger en cas de défaillance de la
liaison entre le flexible et l’outil pneumatique ou
entre deux flexibles.
- Faire en sorte que la pression maximale indiquée
pour l’outil pneumatique ne soit pas dépassée.
- Ne jamais utiliser le flexible pour transporter l’outil
pneumatique.
- En cas de placement de l’outil pneumatique dans
un support, veiller à bien fixer l’outil. En cas de
perte de contrôle, il y a risque de blessures.
4.11 Autres consignes de sécurité
- Respecter, le cas échéant, les instructions spécifiques de prévention des accidents et de sécurité
au travail relatives à la manipulation de compresseurs et d’outils pneumatiques.
- Veiller à ce que la pression de service maximale
admissible qui figure dans les caractéristiques
techniques soit bien respectée.
- Ne pas surcharger l’outil ; n’utiliser cet outil que
dans la plage de puissance indiquée dans les
caractéristiques techniques.
- Utiliser des lubrifiants non nocifs. Veiller à ce que
le poste de travail soit suffisamment ventilé. En
cas d’usure prononcée, faire contrôler et réparer
l’outil pneumatique le cas échéant.
- Ne pas utiliser cet outil si l’on n’est pas concentré.
Il faut être vigilant, être attentif à ce que l’on fait et
prendre toutes les précautions qui s’imposent
pour utiliser un outil pneumatique. Ne pas utiliser
d’outil sous l’influence de la fatigue, de drogues,
d’alcool ou de médicaments. Il suffit d’un moment
d’inattention lors de l’utilisation de cet outil pour
encourir de graves blessures.
- Veiller à ce que la zone de travail soit propre et
bien éclairée. Les zones de travail encombrées et
mal éclairées peuvent provoquer des accidents.
- Conserver les outils pneumatiques hors de portée
des enfants.
- Ne pas mettre l’outil à l’extérieur sans protection,
ni dans un environnement humide.
- Protéger l’outil pneumatique de la poussière et
des salissures, et tout spécialement le raccord
pneumatique et les éléments de commande.
Les informations qui figurent dans les présentes
instructions d'utilisation sont signalées comme suit
:
Danger ! Risques de dommages corporels
ou de dégâts causés à l'environnement.
Attention. Risque de dommages matériels.
4.12 Symboles sur l’outil pneumatique
Lire les instructions d’utilisation avant la
mise en service.
Porter des lunettes de protection
Porter un casque antibruit
Sens de rotation
Voir page 2.
1 Clé à fourche
2 Ecrou de la pince de serrage
3 Pince de serrage
4 Support de pince de serrage
5 Broche
6 Clé à fourche
7 Interrupteur (marche/arrêt)
8 Sécurité antidémarrage
9 Vis de réglage de la vitesse
10 Sortie d’air
11 Raccord pneumatique avec filtre
12 Raccord enfichable 1/4"
6.1 Avant la mise en service
Visser le raccord enfichable (12).
6.2 Mise en place de la pince de serrage
Le diamètre de la tige de l'outil doit exactement correspondre à l'orifice de serrage de la
pince de serrage (3) !
Des pinces de serrage pour différents diamètres de
tige sont disponibles. Placer la pince de serrage (3)
dans le support de pince de serrage (4) et visser
l’écrou de la pince de serrage (2) à la main.
Si aucun outil n’est inséré dans la pince de
serrage, ne pas serrer la pince de serrage
avec la clé, mais uniquement à la main !
6.3 Pose de l'accessoire
Les meules sur tige ne doivent pas dépasser
le porte-à-faux maximal spécifié par le fabricant (L0) ! Insérer l’embout sur toute la longueur de
la tige dans la pince de serrage (3). Veiller à ce que
la longueur de serrage (Lg) soit au moins de 10 mm.
5. Vue d'ensemble
6. Fonctionnement
LoL
g
Page 19

FRANÇAIS fr
19
Le diamètre de tige de l’embout doit correspondre exactement à l’orifice de serrage de la
pince de serrage (3) !
- Maintenir la broche (5) avec la clé (6).
- Serrer l’écrou de la pince de serrage (2) à fond
avec la clé (1).
- Veiller à ce que l’embout soit bien fixé.
6.4 Utilisation de l’outil pneumatique
Pour profiter de toute la puissance de cet outil pneumatique, utiliser systématiquement des flexibles
pneumatiques avec un diamètre intérieur d’au
moins 9 mm. Un diamètre intérieur insuffisant
risque d’altérer considérablement la puissance.
Attention. Le tuyau d’air comprimé doit être
dépourvu de condensation.
Attention. Pour que cet outil reste opération-
nel longtemps, il doit être suffisamment lubrifié en utilisant de l’huile pneumatique. La marche à
suivre est la suivante :
– Utiliser de l’air comprimé lubrifié en montant un
système de lubrification par brouillard d’huile.
– Sans lubrificateur par brouillard d’huile : lubrifier
quotidiennement l’outil par le biais du raccord
pneumatique. Verser 3 à 5 gouttes d’huile pneumatique pour 15 minutes de fonctionnement
continu.
Si l’outil n’a pas été utilisé pendant plusieurs jours,
verser manuellement environ 5 gouttes d’huile
pneumatique dans le raccord d’air comprimé.
Attention. Ne jamais faire tourner les outils à
vide de façon prolongée.
1. Sélectionner une pince de serrage (3) adaptée
(voir chapitre 6.2).
2. Insérer un embout adapté (voir chapitre 6.3).
3. Agir sur la vis de réglage (9) pour ajuster la vi-
tesse.
4. Régler la pression de service (mesurée au ni-
veau de la sortie de l’air avec l’outil pneumatique en marche). Pour la pression de service
maximale admissible, voir le chapitre
« Caractéristiques techniques ».
5. Raccorder l’outil pneumatique à l’alimentation
en air comprimé.
6. Mise en marche : pousser la sécurité antidé-
marrage (8) dans le sens de la flèche (voir fig.,
page 2) et appuyer sur l’interrupteur (7).
Arrêt : relâcher l’interrupteur (7).
.
Danger ! Avant toute intervention sur l’outil
pneumatique, couper le raccordement pneumatique.
Danger ! Les travaux de maintenance et de
réparation autres que ceux décrits dans ce
chapitre ne doivent être exécutés que par une per-
sonne qualifiée et compétente.
- Entretenir régulièrement l’outil pneumatique pour
garantir sa sécurité de fonctionnement.
- Vérifier que les raccords sont bien fixés et les
resserrer si nécessaire.
- Nettoyer le filtre du raccord pneumatique au
moins une fois par semaine.
- Il est préconisé de placer un réducteur de pression avec séparateur d’eau et dispositif de lubrification en amont de l’outil pneumatique.
- En cas de fuite d’huile ou d’air prononcée, vérifier
l’outil pneumatique et le faire réparer si nécessaire. (voir chapitre 9.)
- Vérifier la vitesse de rotation régulièrement, et
plus précisément après chaque utilisation, et
effectuer un contrôle du niveau des vibrations.
- Éviter tout contact avec les substances nocives
qui se sont déposées sur l’outil. Porter des équipements de protection adaptés et retirer les substances nocives avec des moyens appropriés
avant de procéder à la maintenance.
f
Utiliser uniquement des accessoires Metabo.
Utiliser uniquement des accessoires spécialement
conçus pour cet outil pneumatique et qui sont
conformes aux exigences et aux données caractéristiques des présentes instructions d’utilisation.
Gamme d'accessoires complète, voir
www.metabo.com ou catalogue.
Danger ! Seuls des techniciens compétents
sont habilités à réparer les outils pneumatiques, à condition d’utiliser des pièces de rechange
Metabo d’origine !
Pour toute réparation d’un outil pneumatique
Metabo, contacter l’agence Metabo. Voir les
adresses sur www.metabo.com.
Les listes des pièces de rechange peuvent être
téléchargées sur le site Internet www.metabo.com.
Se conformer aux réglementations nationales
concernant la mise au rebut dans le respect de
l’environnement et le recyclage des outils pneumatiques, emballages et accessoires. Il est interdit de
mettre en danger des personnes ou de nuire à
l’environnement.
Explications concernant les indications de la page
3.
Sous réserve de modifications allant dans le sens
du progrès technique.
V1= besoins en air
p
max.
= pression de service maximale admissible
n0= vitesse de rotation
dS= orifice de fixation de la pince de serrage
D
max
= diamètre maximal de meule sur tige
di= diamètre (intérieur) de flexible
C = filetage de raccordement
7. Maintenance et entretien
8. Accessoires
9. Réparation
10. Protection de l'environnement
11. Caractéristiques techniques
Page 20

FRANÇAISfr
20
A = dimensions :
longueur x largeur x hauteur
m = poids
Les caractéristiques techniques indiquées sont
soumises à tolérance (selon les normes en vigueur
correspondantes).
Valeurs d'émission
Ces valeurs permettent l’estimation des émissions de l’outil et la comparaison entre différents
outils. Selon les conditions d’utilisation, l’état de
l’outil ou les embouts utilisés, la charge réelle peut
plus ou moins varier. Pour l'estimation, tenir compte
des pauses de travail et des phases de sollicitation
moindre. Définir des mesures de protection pour
l'utilisateur sur la base des valeurs estimatives
adaptées en conséquence, p. ex. mesures organisationnelles.
Vibrations
(valeur efficace d’accélération
pondérée ; EN 28927) :
a
h
=Valeur d’émission de vibrations
K
h
=incertitude de mesure (vibrations)
Niveau sonore (EN ISO 15744) :
L
pA
=niveau de pression acoustique
L
WA
=niveau de puissance acoustique
KpA, KWA= incertitude de mesure
Porter un casque antibruit !
Page 21

NEDERLANDS nl
21
Oorspronkelijke gebruiksaanwijzing
Wij verklaren op eigen en uitsluitende verantwoording, dat deze staafslijpers voldoen aan de op
pagina 3 genoemde normen en richtlijnen.
Dit persluchtgereedschap is bestemd...
- ... voor het fijnslijpen met slijpstiften,
- ...voor het werken met elastische polijstschijven,
- ...voor het werken met viltpolijstschijven,
- ...voor het werken met lamellen-schuurwielen,
op professioneel terrein.
Dit gereedschap mag uitsluitend met persluchtaanvoer worden aangedreven. De op het persluchtgereedschap aangegeven maximaal toelaatbare werkdruk mag niet worden overschreden. Dit
persluchtgereedschap mag niet worden aangedreven met explosieve, brandbare of gezondheidsbedreigende gassen. Niet gebruiken als hefboom,
breek- of slagwerktuig.
Iedere andere toepassing is niet volgens de voorschriften. Door onreglementair gebruik, veranderingen aan het persluchtgereedschap of door gebruik van onderdelen die niet door de fabrikant
gekeurd en vrijgegeven zijn, kunnen niet te voorziene beschadigingen ontstaan!
Voor schade door oneigenlijk gebruik is alleen de
gebruiker aansprakelijk.
De algemeen erkende veiligheidsvoorschriften en
de bijgevoegde veiligheidsvoorschriften dienen te
worden nageleefd.
Let ter bescherming van uzelf en het
persluchtgereedschap op de met dit
symbool aangegeven passages!
WAARSCHUWING – Lees de gebruiksaanwijzing om het risico van letsel te verminderen.
WAARSCHUWING Lees alle veiligheidsvoorschriften en aanwijzingen. Worden de
veiligheidsinstructies en aanwijzingen niet in acht
genomen, dan kan dit een elektrische schok, brand
en/of ernstig letsel tot gevolg hebben.
Bewaar alle veiligheidsvoorschriften en
aanwijzingen goed met het oog op toekomstig
gebruik.
Geef het persluchtgereedschap alleen met deze
documenten aan anderen door.
- De gebruiker of werkgever van de gebruiker moet
de specifieke risico's inschatten die door het
gebruik kunnen optreden.
- Vóór installatie, bediening, reparatie, onderhoud
en vervanging van toebehoren en voordat in de
buurt van het persluchtgereedschap wordt
gewerkt, dienen de veiligheidsvoorschriften te
worden gelezen en begrepen. Gebeurt dit niet,
dan kan dit leiden tot ernstig lichamelijk letsel.
- Het persluchtgereedschap mag uitsluitend door
gekwalificeerd en geschoold personeel worden
geïnstalleerd of gebruikt.
- Aan het persluchtgereedschap mogen geen wijzigingen worden aangebracht. Wijzigingen kunnen
de effectiviteit van de veiligheidsmaatregelen
verminderen en de risico's voor de bediener
verhogen.
- Gebruik nooit beschadigd persluchtgereedschap.
Onderhoud het persluchtgereedschap zorgvuldig.
Controleer regelmatig of beweeglijke onderdelen
correct functioneren en niet klemmen, of er onderdelen gebroken of dermate beschadigd zijn dat de
werking van het persluchtgereedschap hieronder
lijdt. Controleer borden en opschriften op volledigheid en leesbaarheid. Laat beschadigde delen
repareren of vernieuwen voordat u het apparaat
gebruikt. Veel ongevallen hebben hun oorzaak in
slecht onderhouden persluchtgereedschap.
4.1 Gevaar door wegslingerende onderdelen
- Wanneer een werkstuk, toebehoren of persluchtgereedschap breekt, kunnen onderdelen met
hoge snelheid worden weggeslingerd.
- Bij de bediening, het vervangen van toebehoren
en bij reparatie- en onderhoudswerkzaamheden
aan het persluchtgereedschap moet altijd een
slagvaste oogbescherming worden gedragen.
Het niveau van de vereiste bescherming dient
voor elk geval apart te worden beoordeeld.
- Controleer of het werkstuk stevig is bevestigd.
- Er moet regelmatig worden gecontroleerd of het
toerental van het persluchtgereedschap niet
hoger is dan het op het persluchtgereedschap
aangegeven toerental. Deze toerentalcontroles
dienen zonder ingebracht inzetgereedschap
plaats te vinden. De Metabo-klantenservice kan
zulke controles uitvoeren.
- Zorg ervoor dat vonken en brokstukken die bij het
werk ontstaan, geen gevaar vormen.
- Maak het persluchtgereedschap los van de persluchtvoorziening, voordat u het inzetgereedschap
of toebehoren vervangt of instel-, onderhouds- of
reinigingswerkzaamheden uitvoert.
- Zorg ervoor dat er voor andere personen geen
gevaar ontstaat.
4.2 Gevaar te worden meegetrokken/verwik-
keld
- Draag geschikte kleding. Draag geen loshangende kleding of sieraden. Houd haren, kleding
en handschoenen uit de buurt van het persluchtgereedschap. Loshangende kleding, sieraden en
lange haren kunnen door bewegende delen
worden meegenomen. Er bestaat letselgevaar.
1. Conformiteitsverklaring
2. Gebruik volgens de
voorschriften
3. Algemene
veiligheidsvoorschriften
4. Speciale
veiligheidsvoorschriften
Page 22

NEDERLANDSnl
22
4.3 Gevaren tijdens bedrijf
- Vermijd het contact met de draaiende schacht en
het inzetgereedschap om te voorkomen dat u uw
handen of andere lichaamsdelen snijdt.
- Bij gebruik van het persluchtgereedschap kunnen
de handen van de bediener blootgesteld worden
aan gevaren, zoals snij-, schaaf- en verbrandingsletsel. Draag ter bescherming van uw
handen geschikte handschoenen.
- Het bedienings- en onderhoudspersoneel dient
fysiek in staat te zijn de grootte, het gewicht en het
vermogen van de machine te hanteren.
- Houd het persluchtgereedschap correct vast:
Wees erop voorbereid de normale of plotselinge
bewegingen op te vangen – houd beide handen
gereed.
- Zorg ervoor dat u stevig staat en steeds in evenwicht blijft.
- Voorkom dat het apparaat onbedoeld wordt ingeschakeld. Wordt de luchtvoorziening onderbroken, het persluchtgereedschap bij de in-/
uitschakelaar uitzetten.
- Gebruik uitsluitend de door de fabrikant aanbevolen smeermiddelen.
- Draag persoonlijke beschermende uitrusting en
altijd een veiligheidsbril. Het dragen van een
persoonlijke beschermende uitrusting, zoals
veiligheidshandschoenen, beschermende
kleding, stofmasker, slipvrije werkschoenen,
veiligheidshelm of gehoorbescherming, afhankelijk van soort en gebruik van het apparaat, vermindert het risico op letsel en wordt aanbevolen.
- Het toelaatbare toerental van het inzetgereedschap dient minstens zo hoog te zijn als het maximale toerental dat op het persluchtgereedschap
staat aangegeven. Accessoires die sneller
draaien dan toelaatbaar kunnen breken en
wegvliegen.
- Draag bij bovenhandse werkzaamheden een
veiligheidshelm.
- Nadat het persluchtgereedschap is uitgeschakeld, loopt het gereedschap na.
- Zorg ervoor dat vonken die bij het gebruik
ontstaan, geen gevaar veroorzaken. Bij het
bewerken van materialen kunnen explosieve of
brandbare stoffen ontstaan. Er bestaat het risico
van explosie of vuur.
4.4 Gevaar door herhalende bewegingen
- Bij het werken met het persluchtgereedschap
kunnen onaangename gevoelens in handen,
armen, schouders, de halsstreek of andere
lichaamsdelen optreden.
- Neem bij het werk met het persluchtgereedschap
een gemakkelijke positie in, let op een goede
steun en voorkom een stand die ongunstig is of
waarbij het moeilijk is het evenwicht te behouden.
Bij langdurige werkzaamheden moet de bediener
zijn lichaamshouding af en toe veranderen, om
onaangenaamheden en vermoeidheid te voorkomen.
- Indien bij een bediener symptomen zoals aanhoudende onpasselijkheid, klachten, kloppen, pijn,
kriebels, doofheid, branden of stijfheid optreden,
mogen deze waarschuwingsindicatoren niet
worden genegeerd. De bediener dient zijn werk-
gever te informeren en een gekwalificeerde arts te
raadplegen.
4.5 Gevaar door toebehoren
- Maak het persluchtgereedschap los van de persluchtvoorziening, voordat inzetgereedschap of
toebehoren worden bevestigd of vervangen.
- Gebruik alleen toebehoren die voor dit apparaat
bestemd zijn en voldoen aan de in deze gebruiksaanwijzing genoemde eisen en kenmerken.
- Voorkom tijdens en na gebruik direct contact met
het inzetgereedschap, omdat het heet of scherp
kan zijn.
- Het toelaatbare toerental van het inzetgereedschap dient minstens zo hoog te zijn als het maximale toerental dat op het persluchtgereedschap
staat aangegeven. Accessoires die sneller
draaien dan toelaatbaar kunnen breken en
wegvliegen.
- Monteer nooit een slijpschijf, doorslijpschijf of
frees. Een uit elkaar springende slijpschijf kan
zeer ernstige verwondingen of de dood veroorzaken.
- Gebruik geen schijven die mogelijk beschadigd,
ingescheurd of gevallen zijn.
- Er mag alleen toegelaten inzetgereedschap met
een geschikte schachtdiameter worden gebruikt.
- Neem de aanbevelingen in acht van de fabrikant
van kleine slijplichamen. Bij kleine slijplichamen
mag de door de fabrikant aangegeven maximaal
toelaatbare oversteek (L0=lengte van de schacht
tussen het uiteinde van de spantang en het kleine
slijplichaam) niet worden overschreden! Is de
oversteek (L0) groter, dan moet het toelaatbare
toerental worden verlaagd. Het gereedschap zo
mogelijk met de gehele lengte van de schacht in
de spantang inbrengen. Zorg ervoor dat de
inspanlengte (Lg) minstens 10 mm bedraagt.
- De schachtdiameter van het inzetgereedschap
moet exact overeenkomen met het spanboorgat
van de spantang!
4.6 Gevaar op de werkplek
- Het meeste letsel op de werkplek wordt veroorzaakt door uitglijden, struikelen of vallen. Let op
oppervlakken die door het gebruik van het persluchtgereedschap glad geworden kunnen zijn en
op het mogelijke gevaar van struikelen door de
luchtslang.
- Ga in een onbekende omgeving voorzichtig te
werk. Er kan sprake zijn van verborgen gevaar
door stroomkabels of andere voedingsleidingen.
- Het persluchtgereedschap is niet bestemd voor
gebruik in een explosieve omgeving en niet geïsoleerd tegen contact met elektrische stroombronnen.
- Controleer (bijv. met behulp van een metaaldetector) of er op de plaats die bewerkt moet
worden, geen stroom-, water- of gasleidingen
aanwezig zijn.
LoL
g
Page 23

NEDERLANDS nl
23
4.7 Gevaar door stof en dampen
- De stoffen en dampen die bij het gebruik van het
persluchtgereedschap ontstaan kunnen schadelijke gevolgen hebben voor de gezondheid (bijv.
kanker, geboorteafwijkingen, astma en/of dermatitis); het is beslist noodzakelijk een risicoanalyse
van deze gevaren te maken en deze om te zetten
in passende regelingsmechanismes.
- In de risicoanalyse moet rekening worden
gehouden met het stof dat bij het gebruik van het
persluchtgereedschap ontstaat en het reeds
aanwezige stof dat hierbij mogelijk opstuift.
- Het persluchtgereedschap dient te worden
bediend en onderhouden volgens de aanbevelingen in deze gebruiksaanwijzing, om het vrijkomen van stof en dampen tot een minimum te
beperken.
- De afzuiglucht moet zo worden afgevoerd, dat in
een stoffige omgeving zo min mogelijk stof
opstuift.
- Indien stof en dampen ontstaan, moeten alle
inspanningen erop zijn gericht deze te controleren
op de plaats waar ze vrijkomen.
- Alle inbouwelementen- en toebehoren van het
persluchtgereedschap, die voor het opvangen,
afzuigen of onderdrukken van zwevend stof of
dampen zijn aangebracht, dienen volgens de
aanwijzingen van de fabricant volgens voorschrift
te worden geplaatst en onderhouden.
- Het verbruiksmateriaal en het inzetgereedschap
moet volgens de aanbevelingen van deze
gebruikshandleiding worden gekozen, onderhouden en vervangen om onnodige intensivering
van de stof- en dampontwikkeling te voorkomen.
- Gebruik beschermende ademhalingsvoorzieningen volgens de aanwijzingen van uw werkgever of zoals vereist in de voorschriften voor de
veiligheid op het werk en ter bescherming van de
gezondheid.
- Het werken met bepaalde materialen leidt tot
emissies van stof en damp die een potentieel
explosieve omgeving veroorzaken.
4.8 Gevaar door geluid
- De invloed van hoge geluidsniveaus kan bij onvoldoende gehoorbescherming leiden tot permanente gehoorschade, gehoorverlies en andere
problemen, zoals tinnitus (bellen, suizen, fluiten of
zoemen in het oor).
- Het is beslist noodzakelijk een risicoanalyse van
deze gevaren te maken en deze om te zetten in
passende regelingsmechanismes.
- Tot de passende regelingsmechanismes ter
vermindering van het risico behoren maatregelen
zoals het gebruik van isolatiemateriaal ter voorkoming van het geluid dat bij de werkstukken
optreedt.
- Gebruik gehoorbeschermende voorzieningen
volgens de aanwijzingen van uw werkgever of
zoals vereist in de voorschriften voor de veiligheid
op het werk en ter bescherming van de gezondheid.
- Het persluchtgereedschap dient te worden
bediend en onderhouden volgens de aanbevelingen in deze gebruiksaanwijzing, om een onnodige verhoging van het geluidsniveau te voorkomen.
- Het verbruiksmateriaal en het inzetgereedschap
moet volgens de aanbevelingen van deze
gebruikshandleiding worden gekozen, onderhouden en vervangen om een onnodige verhoging van het geluidsniveau te voorkomen.
- De geïntegreerde geluidsdemper mag niet
worden verwijderd en moet zich in een goede
werktoestand bevinden.
4.9 Gevaar door trillingen
- De invloed van trillingen kan beschadiging van de
zenuwen en storingen in de bloedcirculatie in
handen en armen veroorzaken.
- Draag bij het werken in een koude omgeving
warme kleding en houd de handen warm en
droog.
- Indien u merkt dat de huid van uw vingers of
handen gevoelloos wordt, jeukt, pijn doet of wit
verkleurt, moet u stoppen met het persluchtgereedschap, uw werkgever informeren en een arts
raadplegen.
- Het persluchtgereedschap dient te worden
bediend en onderhouden volgens de aanbevelingen in deze gebruiksaanwijzing om een onnodige versterking van de trillingen te voorkomen.
- Het verbruiksmateriaal en het inzetgereedschap
moet volgens de aanbevelingen van deze
gebruikshandleiding worden gekozen, onderhouden en vervangen om een onnodige versterking van de trillingen te voorkomen.
- Maak, om het gewicht van het persluchtgereedschap te houden, zo mogelijk gebruik van een
standaard, een spanner of egalisatie-inrichting.
- Houd het persluchtgereedschap vast met een niet
al te vaste, maar zekere greep en neem de
vereiste hand-reactiekrachten in acht, want het
trillingsrisico wordt normaal gesproken met een
toenemende grijpkracht groter.
- Een niet goed gemonteerd of beschadigd inzetgereedschap kan verhoogde trillingen veroorzaken.
4.10 Extra veiligheidsvoorschriften
- Perslucht kan tot ernstig letsel leiden.
- Wanneer het persluchtgereedschap niet in
gebruik is, is het altijd vereist om de luchttoevoer
af te sluiten, de luchtslang drukloos te maken en
het persluchtgereedschap van de persluchttoevoer te scheiden, voordat toebehoren worden
vervangen of reparaties worden uitgevoerd.
- Richt de luchtstroom nooit op uzelf of andere
personen.
- Rondslaande slangen kunnen tot ernstig letsel
leiden. Controleer daarom altijd of de slangen en
het bevestigingsmateriaal beschadigd of losgeraakt zijn.
- Bij universele draaikoppelingen (klauwkoppelingen) dient u gebruik te maken van arrêteerpennen en Whipcheck-slangbeveiligingen om
bescherming te bieden voor het geval dat een
verbinding van de slang met het persluchtgereedschap of tussen slangen defect raakt.
- Zorg ervoor dat de op het persluchtgereedschap
aangegeven maximale druk niet wordt overschreden.
- Draag persluchtgereedschap nooit bij de slang.
- Wordt het persluchtgereedschap in een houder
gebruikt: het persluchtgereedschap goed bevestigen. Verlies van controle kan tot letsel leiden.
Page 24

NEDERLANDSnl
24
4.11 Overige veiligheidsvoorschriften
- Neem eventueel de speciale werkbeschermingsof ongevalpreventievoorschriften voor de omgang
met compressoren en persluchtgereedschap in
acht.
- Zorg ervoor dat de in de Technische gegevens
aangegeven maximaal toelaatbare werkdruk niet
wordt overschreden.
- Zorg dat u het gereedschap niet overbelast –
gebruik dit toestel gereedschap alleen binnen het
vermogensbereik dat in de Technische gegevens
vermeld wordt.
- Gebruik geen twijfelachtige smeermiddelen. Zorg
voor een voldoende ventilatie van de werkplek. Bij
verhoogde uittreding: persluchtgereedschap
controleren en eventueel laten repareren.
- Gebruik dit gereedschap niet, wanneer u niet
geconcentreerd bent. Wees alert, let goed op wat
u doet en ga met verstand te werk bij het gebruik
van het persluchtgereedschap. Gebruik geen
gereedschap wanneer u moe bent of onder
invloed staat van drugs, alcohol of medicijnen.
Een moment van onoplettendheid bij het gebruik
van gereedschap kan tot ernstig letsel leiden.
- Houd uw werkomgeving schoon en goed verlicht.
Een rommelige of onverlichte werkomgeving kan
tot ongevallen leiden.
- Persluchtgereedschap voor kinderen beveiligen.
- Het gereedschap mag niet in de open of in een
vochtige ruimte opgeborgen worden.
- Bescherm het persluchtgereedschap, met name
de persluchtaansluiting en bedieningselementen,
tegen stof en vuil.
De informatie in deze handleiding is als volgt gekenmerkt:
Gevaar! Waarschuwing voor lichamelijk letsel of milieuschade.
Let opWaarschuwing voor materiële schade.
4.12 Symbolen op het persluchtgereedschap
Voor inbedrijfstelling de gebruiksaanwijzing
lezen.
Draag oogbescherming
Draag gehoorbescherming
Draairichting
Zie bladzijde 2.
1 Steeksleutel
2 Spantangmoer
3 Spantang
4 Spantanghouder
5 Spindel
6 Steeksleutel
7 Schakelaar (In-/Uitschakelen)
8 Inschakelblokkering
9 Regelschroef voor het instellen van het
toerental
10 Luchtuitlaat
11 Persluchtaansluiting met filter
12 Steeknippel 1/4"
6.1 Voor het eerste bedrijf
Steeknippel (12) inschroeven.
6.2 Spantang inbrengen
De schachtdiameter van het gereedschap
moet exact overeenkomen met het span-
boorgat van de spantang (3)!
Er bestaan spantangen voor verschillende schacht-
diameters. De spantang (3) in de spantanghouder
(4) plaatsen en vervolgens de spantangmoer (2)
met de hand vastschroeven.
Wanneer er geen gereedschap in de span-
tang is geplaatst, deze niet met een steeksleutel aantrekken maar met de hand vastschroeven!
6.3 Inzetgereedschap aanbrengen
Bij kleine slijplichamen mag de door de fabri-
kant aangegeven maximaal toelaatbare oversteek (L
0
) niet worden overschreden! Het gereedschap zo mogelijk met de gehele lengte van de
schacht in de spantang (3) inbrengen. Zorg ervoor
dat de inspanlengte (Lg) minstens 10 mm bedraagt.
De schachtdiameter van het inzetgereedschap moet exact overeenkomen met het
spanboorgat van de spantang (3)!
- De spindel (5) met de steeksleutel (6) vast-
houden.
- De spantangmoer (2) met de steeksleutel (1)
aantrekken.
- Let op een veilige passing van het inzetgereed-
schap.
6.4 Persluchtgereedschap gebruiken
Gebruik altijd persluchtslangen met een binnendiameter van minstens 9 mm om het volledige
vermogen van uw persluchtgereedschap te
bereiken. Een te geringe binnendiameter kan het
vermogen aanmerkelijk verminderen.
Let opDe persluchtleiding mag geen condenswater bevatten.
Let opDit gereedschap dient van voldoende
pneumatische olie voorzien te worden om
lang gebruiksklaar te blijven. Dit kan als volgt gebeuren:
– Geoliede perslucht gebruiken door aanbouw van
een olievernevelaar.
– Zonder olievernevelaar: Dagelijks met de hand
via de persluchtaansluiting oliën. Ca. 3-5 drup-
5. Overzicht
6. Bediening
LoL
g
Page 25

NEDERLANDS nl
25
pels pneumatische olie bij 15 minuten continugebruik.
Is het gereedschap meerdere dagen buiten gebruik geweest, de persluchtaansluiting handmatig
vullen met ca. 5 druppels pneumatische olie.
Let opHet gereedschap slechts kort onbelast
laten lopen.
1. Geschikte spantang (3) kiezen (zie hoofdstuk
6.2).
2. Passend inzetgereedschap plaatsen (zie
hoofdstuk 6.3).
3. Het toerental kan met de regelschroef (9) worden gewijzigd.
4. Werkdruk instellen (gemeten bij de luchtinlaat
bij ingeschakeld persluchtgereedschap). Maximaal toelaatbare werkdruk zie hoofdstuk „Technische gegevens“.
5. Persluchtgereedschap op de persluchtvoorziening aansluiten.
6. Inschakelen: inschakelblokkering (8) in de richting van de pijl schuiven (zie afb., pagina 2) en
schakelaar (7) indrukken.
Uitschakelen: schakelaar (7) loslaten.
.
Gevaar! Alvorens u met werkzaamheden
aan het gereedschap begint, persluchtaan-
sluiting losmaken.
Gevaar! Andere dan de in dit hoofdstuk beschreven onderhouds- of reparatiewerkzaam-
heden mogen uitsluitend door geschoold per-
soneel worden uitgevoerd.
- Verzeker u door regelmatig onderhoud van de
veiligheid van het persluchtgereedschap.
- Schroefverbindingen op goede zitting controleren
resp. aantrekken.
- Filter in de persluchtaansluiting tenminste weke-
lijks reinigen.
- Aanbevolen wordt om bij het persluchtgereed-
schap een drukregelaar met waterafscheider en
een smeerbus voor te schakelen.
- Bij verhoogde olie- of luchtuittreding het pers-
luchtgereedschap controleren en eventueel laten
repareren. (Zie hoofdstuk 9.)
- Controleer regelmatig en na elk gebruik het
toerental en voer een eenvoudige controle uit op
het trillingsniveau.
- Vermijd het contact met gevaarlijke substanties
die zich op het werkstuk hebben afgezet. Draag
een geschikte persoonlijke veiligheidsuitrusting
en verwijder vóór het onderhoud gevaarlijke
substanties met passende maatregelen.
f
Gebruik uitsluitend originele Metabo toebehoren.
Gebruik alleen toebehoren die voor dit persluchtge-
reedschap bestemd zijn en voldoen aan de in deze
gebruiksaanwijzing genoemde eisen en
kenmerken.
Compleet toebehorenprogramma, zie
www.metabo.com of de catalogus.
Gevaar! Reparaties aan persluchtgereed-
schap mogen alleen door geschoold personeel en met originele Metabo-onderdelen worden
uitgevoerd!
Neem voor persluchtgereedschap van Metabo dat
gerepareerd dient te worden contact op met uw
Metabo-vertegenwoordiging. Zie voor adressen
www.metabo.com.
Onderdeellijsten kunt u downloaden via
www.metabo.com.
Neem de nationale voorschriften in acht voor een
milieuvriendelijke verwijdering en voor de recycling
van afgedankt persluchtgereedschap, verpakkingen en toebehoren. Personen en leefmilieu
mogen niet in gevaar worden gebracht.
Toelichting bij de gegevens van pagina 3.
Wijzigingen en technische verbeteringen voorbe-
houden.
V
1
= luchtverbruik
p
max.
= maximaal toelaatbare werkdruk
n0= toerental
dS= spanboorgat van de spantang
D
max
= maximale diameter van het kleine slijpli-
chaam
di= slangdiameter (binnen)
C = aansluitdraad
A = afmetingen: lengte x breedte x hoogte
m = gewicht
De vermelde technische gegevens zijn
tolerantiewaarden (overeenkomstig de
toepasselijke norm).
Emissiewaarden
Deze waarden maken een beoordeling van de
emissie van het gereedschap en een vergelijking
van de verschillende gereedschappen mogelijk.
Afhankelijk van het gebruik, de toestand van het
gereedschap of het inzetgereedschap kan de daadwerkelijke belasting hoger of lager uitvallen. Houd
bij de beoordeling rekening met pauzes en fases
met een lagere belasting. Bepaal op basis van de
overeenkomstig aangepaste taxatiewaarden de
maatregelen ter bescherming van de gebruiker,
bijv. organisatorische maatregelen.
Trilling
(gewogen effectieve waarde van de
versnelling; EN 28927):
a
h
=trillingsemissiewaarde
K
h
=meetonzekerheid (trilling)
Geluidsniveau (EN ISO 15744):
L
pA
=geluidsdrukniveau
L
WA
=geluidsvermogensniveau
KpA, KWA= meetonzekerheid
Draag gehoorbescherming!
7. Service en onderhoud
8. Toebehoren
9. Reparatie
10. Milieubescherming
11. Technische gegevens
Page 26

ESPAÑOLes
26
Manual original
Declaramos, bajo nuestra exclusiva responsabilidad, que esta amoladora de barra cumple con las
normas y las directivas mencionadas en la
página 3.
Esta herramienta neumática ha sido desarrollada...
- ... para el amolado de precisión con barritas de
abrasivo,
- ...para trabajar con cuerpos de pulido de forma
- ...para trabajar con cuerpos de pulido fieltro
- ...para trabajar con rueda de afilar para laminillas
en el ámbito profesional.
Esta herramienta sólo debe activarse con una alimentación neumática. No está permitido exceder
la presión máxima de trabajo indicada en la herramienta. Esta herramienta neumática no debe usarse con gases explosivos, inflamables o nocivos
para la salud. No lo use como palanca ni como herramienta de ruptura o de golpe.
Cualquier otro uso está en desacuerdo a su finalidad. Mediante un uso contrario a su finalidad, modificaciones en la herramienta neumática o al usar
piezas que no hayan sido controladas ni habilitadas por el productor se pueden producir daños
imprevisibles.
Los posibles daños derivados de un uso inadecuado son responsabilidad exclusiva del usuario.
Deben observarse las normas sobre prevención de
accidentes aceptados de forma general y la información sobre seguridad incluida.
Para su propia protección y la de su
herramienta neumática, observe las
partes marcadas con este símbolo.
ADVERTENCIA: Lea el manual de instrucciones para reducir el riesgo de accidentes.
AVISO Lea íntegramente las indicaciones
de seguridad y las instrucciones. La no
observancia de las instrucciones de seguridad
siguientes puede dar lugar a descargas eléctricas,
incendios y/o lesiones graves.
Guarde estas instrucciones de seguridad en
un lugar seguro.
Si entrega su herramienta neumática a otra
persona, es imprescindible acompañarla de este
documento.
- El usuario o el empleador del usuario debe
evaluar los riesgos específicos que puedan darse
a partir de cada uso de la herramienta.
- Previo a la configuración, el uso, la reparación, el
mantenimiento y el recambio de accesorios así
como antes de realizar trabajos cerca de la herramienta neumática, es necesario haber leído y
entendido las indicaciones de seguridad. En caso
contrario, se puede sufrir lesiones corporales
mayores.
- La herramienta neumática debe ser ajustada,
configurada o usada únicamente por usuarios
calificados y capacitados.
- No está permitido modificar la herramienta. Modificaciones pueden reducir el efecto de medidas
de seguridad y aumentar los riesgos para el
usuario.
- Jamás utilice herramientas neumáticas que estén
dañadas. Cuide las herramientas neumáticas con
cuidado. Controle con regularidad, si funcionan
correctamente, sin atascarse, las partes móviles
de la herramienta neumática y si existen piezas
rotas o deterioradas que pudieran afectar su
funcionamiento. Controle si los letreros y los
textos están completos y legibles. Si la herramienta eléctrica estuviese defectuosa, hágala
reparar o recambiar antes de volver a utilizarla.
Muchos de los accidentes se deben a herramientas neumáticas con un mantenimiento deficiente.
4.1 Peligros por piezas que salen despedi-
das
- En caso de que una pieza, un accesorio o la
misma herramienta neumática se rompa, estas
piezas pueden salir despedidas a alta velocidad.
- Use siempre gafas protectoras a prueba de
golpes al usar la máquina, cambiar accesorios o
realizar trabajos de reparación o de mantenimiento en la herramienta neumática. El grado de
la protección necesaria debe ser evaluado individualmente antes de cada aplicación de la herramienta.
- Asegúrese de que la pieza a trabajar esté fijamente sujeta.
- Hay que controlar con regularidad que las revoluciones de la herramienta neumática no sean
mayores a las que han sido indicadas en ésta.
Estos controles de revoluciones deben realizarse
con herramienta de inserción desmontada. El
servicio técnico de Metabo puede realizar tales
controles.
- Asegúrese de que chispas y fragmentos que se
producen a partir de los trabajos no representen
ningún peligro.
- Separe la herramienta neumática de la alimentación neumática antes de realizar un ajuste, un
mantenimiento, una limpieza o cambiar la herramienta de inserción o accesorios.
- Asegúrese de que no se produzcan peligros para
otras personas.
4.2 Peligros de arrastre/embobinado
- Lleve puesta una vestimenta de trabajo
adecuada. No utilice vestimenta amplia ni joyas.
1. Declaración de conformidad
2. Uso según su finalidad
3. Instrucciones generales de
seguridad
4. Instrucciones especiales de
seguridad
Page 27

ESPAÑOL es
27
Mantenga su pelo, vestimenta y guantes alejados
de la herramienta neumática y de sus piezas
móviles. La vestimenta suelta, las joyas y el pelo
largo se pueden enganchar con las piezas en
movimiento. Usted corre peligro de lesionarse.
4.3 Peligros durante la marcha
- Evite el contacto con el manguito rotatorio y la
herramienta de inserción a fin de evitar cortes en
las manos y en otras partes del cuerpo.
- Al usar la herramienta neumática, las manos del
operador pueden estar expuestas a peligros
como p. ej. cortes, excoriaciones y calor. Utilice
guantes adecuados como protección de las
manos.
- El operador y el personal de mantenimiento
deben estar en la disposición física para poder
controlar el tamaño, el peso y la potencia de la
herramienta neumática.
- Agarre correctamente la herramienta neumática:
Esté dispuesto a contrarrestar los movimientos
normales y repentinos, sujetando la máquina con
ambas manos.
- Trabaje sobre una base firme y mantenga el equilibrio en todo momento.
- Evite una puesta en marcha fortuita del aparato.
En caso de haber una interrupción de la alimentación neumática, desconecte la herramienta
neumática con el interruptor principal.
- Utilice únicamente los lubricantes recomendados
por el productor.
- Utilice un equipo de protección y en todo caso
unas gafas de protección. Usando un equipo de
protección como lo son guantes o ropa de protección, mascarilla, zapatos de seguridad antideslizantes, casco protector o protección auricular,
dependiendo del modo y el uso del aparato, se
reduce el riesgo de sufrir lesiones por lo que se
recomienda hacerlo.
- El número de revoluciones autorizado de la herramienta de inserción debe ser al menos tan alto
como el número de revoluciones máximo indicado en la herramienta neumática. Si los accesorios giran a una velocidad mayor que la permitida
pueden romperse y salir despedidos.
- Utilice siempre un casco protector al realizar
trabajo sobre su cabeza.
- La herramienta sigue funcionando, aun después
de haber desconectado la herramienta neumática.
- Cuide que las chispas generadas al utilizar la
pistola no provoquen ningún peligro. Al trabajar
piezas pueden generarse polvos inflamables o
explosivos. Se corre el riesgo de una explosión o
de una ignición.
4.4 Peligro por movimientos repetitivos
- Al trabajar con la herramienta neumática pueden
producirse sensaciones incómodas en las
manos, los brazos, los hombros, en el cuello o en
otras partes del cuerpo.
- Posiciónese cómodamente al trabajar con la
herramienta neumática, asegúrese de tener una
posición fija y evite posiciones inadecuadas o
aquellas en las que es difícil mantener el equilibrio. Al realizar trabajos más largos, se recomienda que el operador cambie su posición, lo
cual puede ayudar a evitar incomodidades y el
cansancio.
- En caso de que el operador sienta síntomas
como, por ejemplo, malestar constante, molestias, dolor, comezón, entumecimiento, quemazón
o rigidez, no debe ignorarse estas señales de
aviso. El operador debe informar la situación al
empleador y consultar a un médico calificado.
4.5 Peligros por accesorios
- Separe la herramienta neumática de la alimentación neumática antes de fijar o cambiar la herramienta de inserción o un accesorio.
- Utilice únicamente accesorios que hayan sido
desarrollados para este aparato y que cumple con
los requerimientos y los datos indicados en este
manual de uso.
- Evite tener contacto directo con la herramienta de
inserción durante o después del uso porque
puede estar caliente o afilada.
- El número de revoluciones autorizado de la herramienta de inserción debe ser al menos tan alto
como el número de revoluciones máximo indicado en la herramienta neumática. Si los accesorios giran a una velocidad mayor que la permitida
pueden romperse y salir despedidos.
- Jamás monte un disco para amolar, un disco para
tronzar o una fresa. Un disco para amolar que se
dañe puede causar lesiones muy serias o aun la
muerte.
- No utilice discos que presenten un golpe, que
estén rotas o que se hayan caído al suelo.
- Sólo debe usarse herramientas de inserción
homologadas que presenten el diámetro correcto
del manguito.
- Observe las recomendaciones del fabricante de
cuerpos pequeños de amolado. En el caso de
usar cuerpos pequeños de amolado no está
permitido exceder el máximo exceso permitido
por el fabricante (L
0
=longitud del manguito entre
el final de la pinza de tensión y el cuerpo de
amolado). En caso de aumentar el exceso (L0)
será necesario reducir las revoluciones permitidas. De ser posible, coloque la herramienta con
el manguito completo en la pinza de tensión.
asegúrese de que la longitud de tensión (Lg) sea
mínimo de 10 mm.
- El diámetro del manguito de la herramienta de
inserción debe coincidir exactamente con la
perforación de tensión de las pinzas de tensión.
4.6 Peligros en el puesto laboral
- Los principales motivos para sufrir lesiones en el
puesto laboral es al resbalarse, tropezarse o
caerse. Tenga cuidado con superficies que
puedan haber quedado resbalosas después de
usar la herramienta neumática así como posibles
peligros de tropiezo generados por la manguera
neumática.
LoL
g
Page 28

ESPAÑOLes
28
- Proceda cuidadosamente al encontrarse en un
entorno desconocido. Puede haber peligros
escondidos por cables de corriente o cualquier
otro tipo de líneas de alimentación.
- La herramienta neumática no ha sido desarrollada para usarse en un entorno explosivo y no
está aislado contra el contacto con fuentes de
corriente eléctrica.
- Asegúrese de que en el lugar de trabajo no
existan cables, tuberías de agua o gas (por
ejemplo, con ayuda de un detector de metales).
4.7 Peligros por polvos y vapores
- Los polvos y vapores producidos al trabajar con la
herramienta neumática pueden generar daños a
la salud (como p. ej. cáncer, defectos congénitos,
asma y/o dermatitis); es imprescindible realizar
una evaluación de riesgo en relación a estos peligros y aplicar mecanismo de regulación
adecuados.
- En la evaluación de riesgos deben incluirse el
polvo generado por el uso de la herramienta
neumática así como el polvo que puede arremolinarse por ello.
- Es importante usar y mantener la herramienta
neumática según las recomendaciones presentadas en este manual a fin de reducir la liberación
de polvo y de vapores a un mínimo.
- El aire de salida debe salir de tal manera que las
polvaredas se reduzcan a un mínimo en un
entorno polvoriento.
- En caso de generarse polvos y vapores, es muy
importante controlarlos en el lugar donde se
generan.
- Todos los accesorios previstos para la recolección, aspiración o supresión de polvo volátil o de
vapores en la herramienta neumática deben
usarse y mantenerse correctamente según lo
indique el fabricante.
- Es importante elegir, mantener y recambiar los
materiales de consumo y la herramienta de inserción conforme a las recomendaciones presentadas en este manual a fin de evitar una intensificación de polvo o de vapores.
- Utilice las mascarillas protectoras según las indicaciones del empleador o como se lo indique en
las normas de protección laboral y de la salud.
- Trabajos con cierto materiales conllevan a
emisiones de polvo y de vapor que pueden
generar un entorno potencialmente explosivo.
4.8 Peligros por ruido
- El efecto de altos niveles de ruido puede producir
daños constantes de oído, la pérdida del oído u
otros problemas como, por ejemplo, el tínito
(silbido, sonidos en el oído).
- Es imprescindible realizar una evaluación de
riesgo en relación a estos peligros y aplicar mecanismo de regulación adecuados.
- Parte de los mecanismos adecuados de regulación para reducir el riesgo son medidas como el
uso de materiales aislantes a fin de evitar ruidos
que se generen en las piezas a trabajar.
- Utilice los equipos de protección auricular según
las indicaciones del empleador o como se lo
indique en las normas de protección laboral y de
la salud.
- Debe usarse y mantenerse la herramienta
neumática según las recomendaciones hechas
en este manual a fin de evitar un incremento innecesario del nivel de ruido.
- Es importante elegir, mantener y recambiar los
materiales de consumo y la herramienta de inserción conforme a las recomendaciones presentadas en este manual a fin de evitar un incremento
del nivel de ruido.
- No está permitido retirar el silenciador integrado
en la herramienta y éste siempre debe estar en
perfecto estado de funcionamiento.
4.9 Peligro por vibraciones
- El efecto de vibraciones puede producir daños en
los nervios y problemas en la circulación
sanguínea en manos y brazos.
- Use ropa caliente al trabajar en un entorno frío y
mantenga sus manos calientes y secas.
- En caso de observar que la piel en los dedos o
manos quede insensible, sienta cosquilleos,
dolores o que la piel quede en blanco, interrumpa
el trabajo con la herramienta neumática e informe
a su empleador y consulte a un médico.
- Debe usarse y mantenerse la herramienta
neumática según las recomendaciones hechas
en este manual a fin de evitar un incremento innecesario de las vibraciones.
- Es importante elegir, mantener y recambiar los
materiales de consumo y la herramienta de inserción conforme a las recomendaciones presentadas en este manual a fin de evitar un incremento
de las vibraciones.
- A fin de poder sostener el peso de la herramienta
neumática, utilice siempre que sea posible, un
soporte, pinzas tensoras o un dispositivo
compensador.
- No agarre la herramienta neumática demasiado
fuerte pero lo suficientemente segura, observando las fuerzas necesarias para contrarrestar el
par de giro de la máquina porque el riesgo de
vibraciones suele incrementarse mientras mayor
es la fuerza que utiliza al agarrar la máquina.
- Una herramienta de inserción insuficientemente
montada o dañada puede causar vibraciones
mayores.
4.10 Indicaciones adicionales de seguridad
- Aire comprimido puede causar lesiones serias.
- Si la herramienta neumática no está en uso,
previo al cambio de accesorios o al realizar
trabajos de reparación, siempre es recomendable
desconectar la alimentación de aire, despresurizar la manguera neumática y separar la herramienta neumática de la alimentación neumática.
- Jamás dirija el caudal de aire a sí mismo o contra
otras personas.
- Mangueras sueltas pueden causar lesiones
serias. Por lo tanto, controle siempre si las
mangueras y los elementos de soporte estén en
buen estado y que no se hayan soltado.
- En caso de utilizar acoplamientos giratorios
universales, debe colocarse pernos fijadores y
utilizar seguros de manguera Whipcheck a fin de
proteger la unión de la manguera con la herramienta neumática o con otras mangueras en caso
de que se dañe la unión de la manguera.
Page 29

ESPAÑOL es
29
- Asegúrese de que no se exceda la presión
máxima indicada en la herramienta neumática.
- Jamás agarre las herramientas neumáticas de la
manguera.
- En caso de usar la herramienta neumática en un
soporte, fijela correctamente. El usuario puede
resultar herido por la pérdida del control de la
herramienta.
4.11 Otras indicaciones de seguridad
- En caso de ser necesario, observe las normas de
protección laboral y de prevención de accidentes
al trabajar con compresores y herramientas
neumáticas.
- Asegúrese de no exceder la máxima presión
laboral permitida indicada en los datos técnicos.
- No sobrecargue el aparato. Utilice este equipo
solamente dentro de los márgenes de potencia
indicados en las Especificaciones técnicas.
- Utilice lubricantes inofensivos. Ventile adecuadamente su lugar de trabajo. En caso de haber un
desgaste mayor: controle la herramienta neumática y hágala reparar.
- No utilice esta herramienta si no puede concentrarse. Esté atento a lo que hace y emplee la
herramienta eléctrica con prudencia. No utilice la
herramienta si está cansado, ni tampoco después
de haber consumido alcohol, drogas o medicamentos. El no estar atento durante el uso de la
herramienta puede provocarle serias lesiones.
- Mantenga limpio y bien iluminado su puesto de
trabajo. El desorden y una iluminación deficiente
en las áreas de trabajo pueden provocar accidentes.
- Asegure las herramientas neumáticas contra
niños.
- No guarde nunca la máquina a la intemperie sin
protección ni en un ambiente húmedo.
- Proteja la herramienta neumática, sobre todo la
conexión neumática así como los elementos de
mando, contra polvo y suciedad.
La información de este manual de uso se indica
según sigue:
¡Peligro! Advertencia de daños personales o
medioambientales.
¡Atención! Advertencia de daños materiales.
4.12 Símbolos en la herramienta neumática
Lea el manual de uso antes de la puesta en
marcha.
Use protección ocular
Use auriculares protectores
Sentido de giro
Véase la página 2.
1 Llave de boca
2 Tuerca de pinzas de tensión
3 Pinzas de tensión
4 Soporte de pinzas de tensión
5 Husillo
6 Llave de boca
7 Interruptor (conectar y desconectar)
8 Bloqueo de conexión
9 Tornillo regulador para ajustar las revoluciones
10 Salida de aire
11 Conexión neumática con filtro
12 Racor de conexión 1/4"
6.1 Previo a la primera puesta en marcha
Montar los racores de conexión (12).
6.2 Colocar la pinza de tensión
El diámetro del manguito de la herramienta
debe coincidir exactamente con la perforación
de tensión de las pinzas de tensión (3).
Están a la disposición pinzas de tensión para dife-
rentes diámetros del manguito. Coloque la pinza de
tensión (3) en el soporte de la pinza de tensión (4) y
atornille a continuación la tuerca de la pinza de
tensión (2) con la mano.
Si no se usa herramienta alguna para las
pinzas de tensión, ésta no debe sujetarse con
una llave de pinza sino tan sólo con la mano.
6.3 Montar herramienta de inserción
En caso de los cuerpos pequeños de amolado
no está permitido exceder el máximo exceso
(L
0
) indicado por el fabricante. De ser posible,
coloque la herramienta con el manguito completo
en la pinza de tensión (3). Asegúrese de que la
longitud de tensión (Lg) sea mínimo de 10 mm.
El diámetro del manguito de la herramienta de
inserción debe coincidir exactamente con la
perforación de tensión de las pinzas de tensión (3).
- Detener el husillo (5) con la llave para la pinza de
tensión (6).
- Ajuste la tuerca de la pinza de tensión (2) con la
llave para la pinza de tensión (1).
- Asegúrese de que la herramienta de inserción
esté fijamente montada.
6.4 Usar la herramienta neumática
A fin de desarrollar la potencia completa de su
herramienta neumática, utilice siempre mangueras
neumáticas con un diámetro interior de por lo
menos 9 mm. Un diámetro demasiado pequeño
puede reducir claramente la potencia de la herramienta.
5. Descripción general
6. Funcionamiento
LoL
g
Page 30
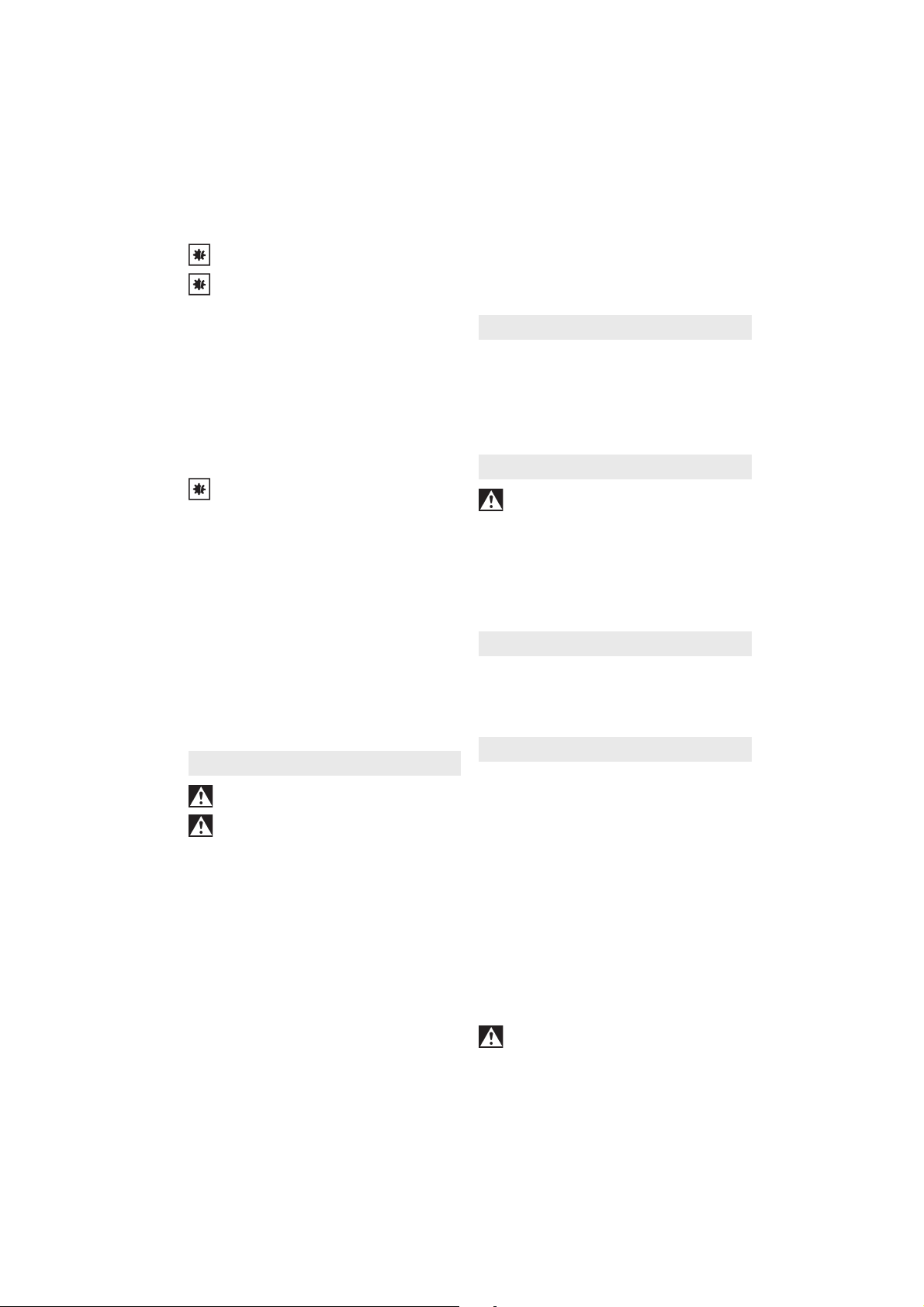
ESPAÑOLes
30
¡Atención! La línea neumática no debe contener agua condensada.
¡Atención! A fin de que la herramienta tenga
una larga vida útil, debe alimentarsela lo suficiente con aceite neumático. Esto puede suceder
de la siguiente manera:
– Use aire a presión con aceite, montando un vola-
tilizador de aceite.
– Sin volatilizador de aceite: lubricar diariamente a
mano en la conexión de aire a presión. Aprox. 35 gotas de aceite neumático para cada 15 minutos de marcha en caso de una aplicación constante.
En caso de que la herramienta estuvo sin usar durante varios días, aplicar manualmente unas 5 gotas de aceite neumático en el racor de conexión de
aire a presión.
¡Atención! Dejar la máquina en ralentí sólo
durante poco tiempo.
1. Elija la pinza de tensión (3) adecuada (véase el
capítulo 6.2).
2. Monte la herramienta de inserción adecuada
(véase el capítulo 6.3).
3. Con el tornillo regulador (9) se puede modificar
las revoluciones.
4. Ajustar presión de trabajo (a medir en la entra-
da de aire con herramienta neumática conectada). Máxima presión de trabajo permitida, véase capítulo "Datos técnicos".
5. Conecte la herramienta neumática a la alimen-
tación neumática.
6. Conectar: desplace el bloqueo de conexión (8)
en dirección de la flecha (véase imagen, página 2) y pulse el interruptor (7).
Desconectar la herramienta: suelte el interruptor (7)
.
¡Peligro! Previo a cualquier trabajo en la má-
quina desconecte la conexión neumática.
¡Peligro! Cualquier trabajo de reparación o
de mantenimiento que exceda el descrito en
este capítulo debe ser efectuado exclusivamente
por especialistas.
- Asegure la seguridad de la herramienta neumá-
tica mediante un mantenimiento constante de
ésta.
- Controle la posición fija de los atornillamientos y,
en caso de ser necesario, ajústelos.
- Limpie el filtro en la conexión neumática por lo
menos una vez a la semana.
- Se recomienda montar un reductor de presión con
separador de agua y volatilizador de aceite a la
herramienta neumática.
- En caso de un consumo mayor de aceite o de aire,
controle la herramienta neumática y, en caso de
ser necesario, hágala reparar. (véase el capítulo
9.)
- Controle con regularidad y después de cada uso
las revoluciones y realice un control sencillo del
nivel de vibraciones.
- Evite el contacto con sustancias peligrosas que
pueden haberse ubicado sobre la herramienta.
Use siempre un equipo de protección y elimine
sustancias peligrosas mediante medidas
adecuadas, antes de realizar el mantenimiento.
f
Use únicamente accesorios Metabo originales.
Utilice únicamente accesorios que hayan sido
desarrollados para esta herramienta neumática y
que cumple con los requerimientos y los datos indicados en este manual de uso.
Programa completo de accesorios véase
www.metabo.com o catálogo.
¡Peligro! Reparaciones en herramientas
neumáticas sólo deben realizarlas especialistas y usar para ello repuestos originales de
Metabo.
Si su herramienta neumática Metabo necesita ser
reparada sírvase dirigir a su representante de
Metabo. En la página www.metabo.com encontrará
las direcciones necesarias.
En la página web www.metabo.com puede
descargar listas de repuestos.
Cumpla lo estipulado por las normativas nacionales
relativas a la gestión ecológica de los residuos y al
reciclaje de herramientas neumáticas, embalaje y
accesorios usados. No deben producirse peligros
para personas ni para el medio ambiente.
Notas explicativas sobre la información de la
página 3.
Nos reservamos el derecho a efectuar modificaciones conforme al avance técnico.
V1= Requerimiento de aire
p
max.
= Máxima presión de trabajo permitida
n0= Revoluciones
dS= Perforación de tensión de las pinzas de
tensión
D
max
= máximo diámetro del cuerpo pequeño de
amolado
di= Diámetro interior de la manguera
C = Rosca de conexión
A = Medidas:
Largo x ancho x alto
m = Peso
Las especificaciones técnicas aquí indicadas se
entienden dentro de determinadas tolerancias
(conformes a las normas que rigen actualmente).
Valores de emisión
Estos valores permiten evaluar las emisiones
de la herramienta y compararla con otras herramientas. Dependiendo de la condición de uso,
7. Mantenimiento y conservación
8. Accesorios
9. Reparación
10. Protección ecológica
11. Especificaciones técnicas
Page 31

ESPAÑOL es
31
estado de la herramienta o de las herramientas de
uso, la carga real puede ser mayor o menor. Considere para la valoración las pausas de trabajo y las
fases de trabajo reducido. Determine a partir de los
valores estimados las medidas de seguridad para
el operador, p. ej. medidas de organización.
Vibración (Valor efectivo de la aceleración;
EN 28927) :
a
h
=Valor de emisión de vibraciones
K
h
=Inseguridad de medición (vibración)
Nivel de ruido (EN ISO 15744):
L
pA
=Nivel de intensidad acústica
L
WA
=Nivel de potencia acústica
KpA, KWA= Inseguridad de medición
¡Use auriculares protectores!
Page 32

NORSKno
32
Originalbruksanvisning
Vi erklærer under eget ansvar at denne stavsliperen
er i overensstemmelse med standardene og direktivene på side 3.
Dette trykkluftverktøyet er beregnet ...
- ... til finsliping med slipestifter,
- ...til arbeider med formpolering,
- ...til arbeider med filtpolering,
- ..arbeider med lamellslipehjul,
for profesjonelle.
Dette verktøyet skal bare drives med trykkluftforsyning. Maksimalt tillatt arbeidstrykk angitt på trykkluftverktøyet må ikke overskrides. Dette trykkluftverktøyet må ikke drives med eksplosive,
brennbare eller farlige gasser. Ikke bruk det som
brekkstang, knuse- eller slagverktøy.
All annen bruk er ikke tiltenkt bruk. Ved endringer
av trykkluftverktøyet i strid med tiltenkt bruk, eller
ved bruk av deler som ikke er kontrollert og godkjent av produsenten, kan det oppstå uforutsigelige skader
Brukeren er alene ansvarlig for skader som oppstår
pga. ikke-forskriftsmessig bruk.
Gjeldende arbeidsmiljøforskrifter og vedlagt sikkerhetsinformasjon må overholdes.
For din egen sikkerhet og for å beskytte
verktøyet må du ta hensyn til tekst som er
merket med dette symbolet.
ADVARSEL – Les bruksanvisningen for å
minimere skaderisikoen.
ADVARSEL Les gjennom all sikkerhetsinformasjon og alle anvisninger. Dersom
sikkerhetsinformasjonen og anvisningene ikke
overholdes, kan det medføre elektrisk støt, brann
og/eller alvorlige skader.
Oppbevar all sikkerhetsinformasjon og alle
anvisninger for fremtidig bruk.
Lån bare ut trykkluftverktøyet ditt sammen med
disse dokumentene.
- Brukeren eller brukerens arbeidsgiver må vurdere
de spesifikke risikoene som kan oppstå på grunn
av enhver bruk.
- Sikkerhetsanvisningene skal leses og forstås før
konfigurasjon, drift, reparasjon, vedlikehold og
utskifting av tilbehør, samt før arbeid i nærheten av
trykkluftverktøyet. I motsatt fall kan dette resultere
i alvorlig personskade.
- Trykkluftverktøyet skal utelukkende konfigureres,
justeres eller brukes av kvalifiserte og operatører
med riktig opplæring.
- Trykkluftverktøyet skal ikke modifiseres. Modifikasjoner kan redusere effekten av sikkerhetstiltakene og øke risikoen for operatøren.
- Bruk aldri ødelagte trykkluftverktøy. Stell godt
med trykkluftverktøyet. Kontroller regelmessig at
bevegelige maskindeler fungerer feilfritt og ikke
hindres, og om det er deler som er brukket eller
skadet og har negativ innvirkning på trykkluftverktøyets funksjon. Kontroller at skilt og merking er
fullstendige og lesbare. Se til at defekte deler blir
reparert eller skiftet før apparatet tas i bruk. Dårlig
vedlikeholdte trykkluftverktøy er årsaken til mange
uhell.
4.1 Fare på grunn av deler som slynges ut
- Ved brudd på arbeidsemnet, tilbehør eller trykkluftverktøy, kan deler slynges ut i høy hastighet.
- Når du bytter tilbehør under drift samt ved reparasjon eller vedlikeholdsarbeid på trykkluftverktøy
må du alltid bruke støtsikre vernebriller. Graden av
beskyttelse som kreves må vurderes separat for
hvert enkelt bruksområde.
- Kontroller at arbeidsemnet er sikkert festet.
- Det må kontrolleres regelmessig at turtallet på
trykkluftverktøyet ikke er høyere enn turtallangivelsen angitt på trykkluftverktøyet . Kontroll av
turtall må foretas uten påmontert innsatsverktøy.
Metabos kundeservice kan foreta slik kontroll.
- Sørg for at gnister og bruddstykker som oppstår
fra arbeidet, ikke utgjør noen fare.
- Koble trykkluftverktøyet fra trykklufttilførselen før
du bytter innsatsverktøy eller tilbehør eller foretar
justering, vedlikehold eller rengjøring.
- Kontroller at det ikke kan oppstå fare for andre
personer.
4.2 Fare på grunn av klær/kroppsdeler gri-
pes fast / vikles opp
- Bruk egnede klær. Ikke bruk vide klær eller
smykker. Hold hår, tøy og hansker unna trykkluftverktøyet og deler som beveger seg. Løstsittende
tøy, smykker eller langt hår kan komme inn i deler
som beveger seg. Det er fare for personskade.
4.3 Farer under drift
- Unngå kontakt med den roterende tangen og
innsatsverktøyet for å hindre kutt i hendene eller
andre kroppsdeler.
- Når du bruker trykkluftverktøyet, kan operatørens
hender bli utsatt for farer som kutt, skrubbsår og
varme. Bruk egnede hansker for å beskytte
hendene.
- Operatøren og vedlikeholdspersonell må fysisk
være i stand til å kontrollere størrelsen, vekten og
effekten av trykkluftverktøyet.
- Holde trykkluftverktøyet riktig: Vær forberedt på å
stå imot vanlige eller plutselige bevegelser – hold
begge hendene klare.
- Sørg for å stå stødig og i balanse.
1. Samsvarserklæring
2. Hensiktsmessig bruk
3. Generell
sikkerhetsinformasjon
4. Spesiell
sikkerhetsinformasjon
Page 33

NORSK no
33
- Unngå utilsiktet bruk. Ved brudd i lufttilførselen,
slå trykkluftverktøyet av med på/av-bryteren.
- Bruk bare smøremidler anbefalt av produsenten.
- Bruk personlig verneutstyr og husk alltid å bruke
vernebriller. Bruk av personlig verneutstyr som
hansker, verneklær, støvmaske, sklisikre
vernesko, hjelm eller hørselsvern – avhengig av
type og bruk av apparatet – reduserer risikoen for
skader og anbefales.
- Tillatt turtall på innsatsverktøyet må være minst
like høyt som det maksimale turtallet som er angitt
på trykkluftverktøyet. Tilbehør som dreier raskere
enn tillatt, kan gå i stykker og kastes rundt
omkring.
- Bruk hjelm ved arbeid over hodehøyde.
- Trykkluftverktøyet fortsetter å gå etter at maskinen
er slått av.
- Sørg for at gnister som oppstår under bruk ikke
forårsaker noen fare. Ved bearbeiding av materialer kan det oppstå eksplosjonsfarlig eller brennbart støv. Det er risiko for eksplosjon eller brann.
4.4 Fare ved gjentatte bevegelser
- Når du arbeider med trykkluftverktøy, kan det forekomme ubehag i hendene, armene, skuldrene,
nakken eller andre kroppsdeler.
- Innta en komfortabel posisjon for arbeid med
trykkluftverktøy, sørg for å ha et sikkert grep og
unngå ugunstige stillinger eller stillinger som gjør
det vanskelig å holde balansen. Operatøren bør
endre arbeidsstilling ved langvarig arbeid, noe
som kan bidra til å unngå ubehag og tretthet.
- Hvis brukeren opplever symptomer som vedvarende kvalme, smerter, bankende, smerte, prikking, nummenhet, svie eller stivhet, bør disse
varslene ikke ignoreres. Operatøren må si fra om
dette til sin arbeidsgiver og kontakte en kvalifisert
lege.
4.5 Fare på grunn av tilbehørsdeler
- Koble trykkluftverktøyet fra trykklufttilførselen før
du bytter eller fester innsatsverktøy eller tilbehør.
- Bruk kun tilbehør som er beregnet for dette apparatet og som oppfyller kravene og spesifikasjonene som er nevnt i denne bruksanvisningen.
- Unngå direkte kontakt med innsatsverktøyet
under og etter bruk, da de kan være varme eller
skarpe.
- Tillatt turtall på innsatsverktøyet må være minst
like høyt som det maksimale turtallet som er angitt
på trykkluftverktøyet. Tilbehør som dreier raskere
enn tillatt, kan gå i stykker og kastes rundt
omkring.
- Monter aldri slipeskive, kappeskive eller fres. En
bristende slipeskive kan forårsake alvorlige
skader eller død.
- Ikke bruk skiver som har slagmerker, riper eller
som kan falle av.
- Det må bare brukes tillatte innsatsverktøy med
passende tangediameter.
- Følg anbefalingene fra produsenten av slipelegemer. For små slipelegemer må det tillatte
maksimale overhenget (L
0
=lengden på tangen
mellom spenntangeende og slipelegemet) angitt
av produsenten ikke overskrides! Ved økning av
overhenget (L0) må det tillatte turtallet reduseres.
Sett innsatsverktøyet med hele skaftlengden inn i
spenntangen. Kontroller at innspenningslengden
(Lg) er på minst 10 mm.
- Innsatsverktøyets tangediameter må passe
nøyaktig til spenntangens boring!
4.6 Farer på arbeidsplassen
- Skliing, snubling og fall er hovedårsakene til
skader på arbeidsplassen. Vær forsiktig med
overflater som kan ha blitt glatte på grunn av bruk
av trykkluftverktøy, og med luftslangen på grunn
av snublefare.
- Gå forsiktig inn i ukjente omgivelser. Det kan
finnes skjulte farer i form av strømkabler eller
andre forsyningsledninger.
- Trykkluftverktøyet er ikke beregnet for bruk i
eksplosjonsfarlige atmosfærer og er ikke isolert
mot kontakt med elektriske strømkilder.
- Kontroller at det ikke finnes strøm-, vann- eller
gassledninger på stedet der du skal arbeide (for
eksempel ved hjelp av en metalldetektor).
4.7 Farer på grunn av støv og damp
- Støv og røyk som resulterer fra bruk av trykkverktøyet, kan føre til helseproblemer (for eksempel
kreft, fødselsdefekter, astma og/eller dermatitt).
Det er viktig å foreta en risikovurdering med
hensyn til disse farene og iverksette egnede
kontrollmekanismer.
- I risikovurderingen må det tas i betraktning støv
som oppstår ved bruk av trykkluftverktøyet og
eventuelt også eksisterende støv som virvles opp.
- Trykkluftverktøyet skal drives og vedlikeholdes i
samsvar med anbefalingene i denne bruksanvisningen for å redusere utslipp av støv og røyk til et
minimum.
- Utblåsingsluften skal føres slik at oppvirvling av
støv i et støvfylt miljø minimaliseres.
- Hvis det oppstår støv eller gasser, må den
viktigste oppgaven være å kontrollere disse der
de oppstår.
- Alle monterings- eller tilbehørsdeler til trykkluftverktøyet som brukes til innsamling, avsug eller
demping av flyvestøv eller røyk skal brukes i
henhold til produsentens instruksjoner og vedlikeholdes riktig.
- Forbruksmateriell og innsatsverktøy skal velges
ut, vedlikeholdes og byttes i samsvar med anbefalingene i denne veiledningen, for å unngå unødvendig intensivering av støv- eller damputvikling.
- Bruk egnet pustemaske i henhold til instruksene
fra din arbeidsgiver eller kravene i HMS-forskriftene.
- Arbeid med bestemte materialer fører til utslipp av
støv og damp, som kan skape en potensiell
eksplosiv atmosfære.
4.8 Fare på grunn av støy
- Påvirkning av høye støynivåer kan ved manglende
hørselsvern føre til permanent hørselsskade,
LoL
g
Page 34

NORSKno
34
hørselstap og andre problemer som tinnitus
(øresus, susing, piping eller brumming i øret).
- Det er viktig å foreta en risikovurdering med
hensyn til disse farene og iverksette egnede
kontrollmekanismer.
- Kontrollmekanismer som er egnet som risikoreduserende tiltak, inkluderer bruk av isolerende materialer for å unngå ringestøy fra arbeidsemnet.
- Bruk egnet hørselsvern i henhold til instruksene
fra din arbeidsgiver og kravene i HMS-forskriftene.
- Trykkluftverktøyet skal drives og vedlikeholdes i
samsvar med anbefalingene i denne bruksanvisningen for å unngå unødvendig økning av støynivået.
- Forbruksmateriell og innsatsverktøy skal velges
ut, vedlikeholdes og byttes i samsvar med anbefalingene i denne veiledningen, for å unngå unødvendig høyning av støynivået.
- Den integrerte lyddemperen må ikke fjernes og
må være i god stand.
4.9 Fare på grunn av vibrasjoner
- Virkningene av vibrasjon kan føre til skade på
nerver og forstyrrelser i blodsirkulasjonen i hender
og armer.
- Bruk varme klær når du arbeider i kalde omgivelser og hold hendene varme og tørre.
- Hvis du oppdager at huden på fingrene eller
hendene er nummen, kribler, verker eller blir
misfarget hvit, må du avbryte arbeidet med trykkluftverktøyet, varsle arbeidsgiver umiddelbart og
oppsøke lege.
- Trykkluftverktøyet skal drives og vedlikeholdes i
samsvar med anbefalingene i denne bruksanvisningen for å unngå unødvendig forsterkning av
vibrasjoner.
- Forbruksmateriell og innsatsverktøy skal velges
ut, vedlikeholdes og byttes i samsvar med anbefalingene i denne veiledningen, for å unngå unødvendig økning av vibrasjoner.
- Bruk stativ, fastspenningsanordning eller utbalanseringsanordning hvis mulig for å holde oppe
vekten av trykkluftverktøyet.
- Hold trykkluftverktøyet med et ikke altfor fast, men
sikkert grep samtidig som du opprettholder
nødvendig håndreaksjonskraft, for vibrasjonsrisikoen blir generelt større med økende grepskraft.
- Et utilstrekkelig montert eller skadet innsatsverktøy kan føre til kraftige vibrasjoner.
4.10 Ekstra sikkerhetsanvisninger
- Trykkluft kan forårsake alvorlige personskader.
- Når trykkluftverktøyet ikke er i bruk, før du skifter
tilbehør eller når du utfører reparasjoner, må lufttilførselen alltid slås av, luftslangen gjøres trykkløs
og trykkluftverktøyet kobles fra trykklufttilførselen.
- Rett aldri luftstrømmen mot deg selv eller andre
mennesker.
- Slanger som fyker omkring, kan forårsake alvorlige skader. Derfor må du alltid kontrollere at slangene og festene er intakte og ikke har løsnet.
- Hvis det benyttes universal-rotasjonskoblinger
(klokoblinger) benyttes, må det brukes låsetapper, og bruk Whipcheck-slangesikringer som
beskyttelse i tilfelle svikt i forbindelsen mellom
slangen og lufttrykkverktøyet eller mellom slangene.
- Sørg for at det angitte maksimaltrykket for trykkluftverktøyet ikke overskrides.
- Bær aldri trykkluftverktøy etter slangen.
- Hvis trykkluftverktøyet brukes i en holder: trykkluftverktøyet må festes forsvarlig. Tap av kontroll
kan føre til skader.
4.11 Flere sikkerhetsanvisninger
- Følg eventuelt HMS-forskrifter eller ulykkesforebyggende forskrifter for bruk av kompressorer og
trykkluftverktøy.
- Sørg for at maksimalt arbeidstrykk angitt i de
tekniske spesifikasjonene ikke overskrides.
- Verktøyet må ikke overbelastes – bruk verktøyet
kun i det ytelsesområdet som er oppgitt i de
tekniske data.
- Bruk bare trygge smøremidler. Sørg for at det er
tilstrekkelig ventilasjon på arbeidsplassen. Ved
økt utstrømming: Kontroller trykkluftverktøyet og
reparer ved behov.
- Ikke bruk dette verktøyet når du er ukonsentrert.
Vær oppmerksom, pass på hva du gjør, gå
fornuftig frem når du arbeider med et trykkluftverktøy. Ikke bruk verktøyet når du er trett eller er
påvirket av narkotika, alkohol eller medikamenter.
Et øyeblikks uoppmerksomhet ved bruk av verktøyet kan føre til alvorlige skader.
- Hold arbeidsplassen ren og ha tilstrekkelig belysning. Rotete arbeidsområder og arbeidsområder
uten lys kan føre til ulykker.
- Sikre trykkluftverktøy mot barn.
- Ikke oppbevar verktøyet ubeskyttet utendørs eller
i fuktige omgivelser.
- Beskytt trykkluftverktøy, spesielt trykkluftforsyningen og betjeningselementer, mot støv og
smuss.
Informasjoner i denne bruksanvisningen er merket
som følger:
Fare! Advarsel mot personskader eller miljøskader.
OBS! Advarsel mot materielle skader.
4.12 Symboler på trykkluftverktøyet
Les bruksanvisningen før verktøyet tas i
bruk.
Bruk hørselsvern!
Bruk hørselsvern!
Rotasjonsretning
Se side 2.
1 Fastnøkkel
2 Spenntangmutter
3 Spenntang
5. Oversikt
Page 35

NORSK no
35
4 Spenntangmutter
5 Spindel
6 Fastnøkkel
7 Bryter (på/av)
8 Innkoblingssperre
9 Reguleringsskrue for turtall
10 Luftutløp
11 Trykklufttilkobling med filter
12 Innstikksnippel 1/4"
6.1 Før første gangs bruk
Skru inn innstikksnippelen (12).
6.2 Sette inn spenntang
Verktøyets tangediameter må passe nøyaktig
til spenntangens (3) boring!
Det finnes spenntenger er til forskjellig tangdiameter. Sett inn spenntangen (3) i spenntangholderen (4) og skru deretter på spenntangmutteren
(2) for hånd.
Dersom det ikke er satt inn noe verktøy i
spenntangen, skru opp spenntangen for hånd
og ikke med fastnøkkelen!
6.3 Montering av innsatsverktøy
For små slipelegemer må det tillatte maksimale overhenget (L
0
=lengden på tangen
mellom spenntangeende og slipelegemet) angitt av
produsenten ikke overskrides! Sett innsatsverktøyet med hele skaftlengden inn i spenntangen (3).
Kontroller at innspenningslengden (Lg) er på minst
10 mm.
Innsatsverktøyets tangediameter må passe
nøyaktig til spenntangens (3) boring!
- Hold spindelen (5) fast med fastnøkkelen (6).
- Trekk til spenntangmutteren (2) med fastnøkkelen
(1).
- Kontroller at innsatsverktøyet sitter forsvarlig fast.
6.4 Bruke trykkluftverktøyet
For å oppnå full effekt med trykkluftverktøyet, skal
du alltid bruke en trykkluftslange med en innvendig
diameter på minst 9 mm. For liten innvendig
diameter kan redusere ytelsen betraktelig.
OBS! Trykkluftledningen må ikke inneholde
kondens.
OBS! For at dette verktøyet skal få en lang levetid, må det være tilført pneumatisk olje i til-
strekkelig grad. Dette kan gjøres som følger:
– Bruk smurt trykkluft uten påmontering av tå-
kesmøreapparat.
– Uten tåkesmøreapparat: Tilsett daglig olje via
trykklufttilkoblingen. Ca. 3–5 dråper pneumatikkolje per 15 driftsminutter ved kontinuerlig bruk.
Hvis verktøyet ikke har vært i bruk på flere dager,
må det tilsettes ca. 5 dråper pneumatikkolje for
hånd i trykklufttilkoblingen.
OBS! Verktøyet må bare gå kort tid på
tomgang.
1. Velg en egnet spenntang (3) (se kapittel6.2).
2. Montert et passende innsatsverktøy (se
kapittel6.3).
3. Turtallet kan endres med reguleringsskruen (9).
4. Still inn arbeidstrykket (målt ved luftinngangen
når trykkluftverktøyet er i gang). Maksimalt tillatt
arbeidstrykk, se kapittelet "Tekniske spesifikasjoner".
5. Koble trykkluftverktøyet til trykklufttilførselen.
6. Slå på: Skyv innkoblingssperren (8) i pilens retning (se figur side 2) og trykk inn bryteren (7).
Slå av: Slipp opp bryteren (7)
.
Fare! Koble fra trykklufttilkoblingen før ethvert arbeid på verktøyet.
Fare! Vedlikeholds- eller reparasjonsarbeider
utover det som er beskrevet i dette kapittelet,
må kun utføres av fagfolk.
- Sørg for at trykkluftverktøyet er sikkert ved å foreta
regelmessig vedlikehold.
- Kontroller at skruefester sitter fast, trekk til ved
behov.
- Rengjør filteret i trykklufttilkoblingen minst en
gang i uken.
- Det anbefales å koble en trykkreduksjonsenhet
med vannutskiller og smøreapparat før trykkluftverktøyet.
- Ved økt utstrømming av olje elle luft må trykkluft-
verktøyet kontrolleres og ev. utbedres. (Se kapittel
9.)
- Kontroller turtallet regelmessig, og etter hver
gangs bruk, foreta en enkel kontroll av vibrasjonsnivået.
- Unngå kontakt med farlige stoffer som kan ha
samlet seg på verktøyet. Bruk egnet personlig
verneutstyr og bortskaff farlige stoffer med
egnede tiltak før vedlikehold.
f
Bruk kun originalt Metabo-tilbehør.
Bruk kun tilbehør som er beregnet for dette trykkluft-
verktøyet og som oppfyller kravene og spesifikasjonene som er nevnt i denne bruksanvisningen.
Det komplette tilbehørsprogrammet finner du på
www.metabo.com eller i katalogen.
Fare! Reparasjoner av trykkluftverktøy skal
bare utføres av fagfolk med originale Metabo-
reservedeler!
6. Bruk
LoL
g
7. Vedlikehold og stell
8. Tilbehør
9. Reparasjon
Page 36

NORSKno
36
Ta kontakt med din Metabo-forhandler dersom du
har Metabo trykkluftverktøy som må repareres.
Adresser på www.metabo.com.
Du kan laste ned reservedelslister fra
www.metabo.com.
Følg nasjonale forskrifter for miljøvennlig kassering
og resirkulering av gamle trykkluftverktøy, emballasjer og tilbehør. Det må ikke oppstå fare fore
personer og miljø.
Forklaringer til opplysningene på side 3.
Med forbehold om endringer som følge av tekniske
forbedringer.
V1= Luftbehov
p
max.
= Maksimalt tillatt arbeidstrykk
n0= Turtall
d s = spenntangens boring
D
maks
= Maksimal diameter på lite slipelegeme
di= Slangediameter (innvendig)
C = Tilkoblingsgjenge
A = Mål:
Lengde x bredde x høyde
m = vekt
Angitte tekniske data kan variere i henhold til de til
enhver tid gjeldende normer.
Emisjonsverdier
Disse verdiene gjør det mulig å beregne utslippene til verktøyet og sammenligne det med andre
verktøy. Den faktiske belastningen kan variere
avhengig av bruksforhold og verktøyets tilstand. Ta
hensyn til arbeidspauser og perioder med mindre
belastning i beregningen. Sett opp vernetiltak for
brukeren i henhold til de beregnede verdiene, f.eks.
organisatoriske tiltak.
Vibrasjon
(vektet effektiv akselerasjonsverdi; EN
28927):
a
h
=Vibrasjonsemisjonsverdi
K
h
=Måleusikkerhet (svingning)
Lydnivå (EN ISO 15744):
L
pA
=lydtrykknivå
L
WA
=lydeffektnivå
KpA, KWA= Måleusikkerhet
Bruk hørselsvern!
10. Miljøvern
11. Tekniske data
Page 37

POLSKI pl
37
Instrukcja oryginalna
Oľwiadczamy z peĝnå odpowiedzialnoľciå, ũe
opisywane szlifierki proste speĝniajå normy i dyrektywy wymienione na stronie 3.
To narzādzie pneumatyczne przeznaczone jest
do...
- ... szlifowania precyzyjnego za pomocå ľciernic
trzpieniowych,
... do prac z uũyciem trzpieniowych ľciernic polerskich,
... do prac z uũyciem ľciernic polerskich filcowych,
... do prac z uũyciem tarcz ľciernych paskowych,
w profesjonalnych zastosowaniach.
Narzādzie to moũe byê zasilane wyĝåcznie sprāũo-
nym powietrzem. Nie wolno przekraczaê podanego na narzādziu, maksymalnego ciľnienia roboczego. To narzādzie pneumatyczne nie moũe byê
wykorzystywane z uũyciem wybuchowych, ĝatwopalnych ani szkodliwych dla zdrowia gazów. Nie
uũywaê w charakterze dŧwigni, narzādzia do kruszenia ani jako mĝota.
Kaũde inne zastosowanie uznawane jest za niezgodne z przeznaczeniem. Uũytkowanie wbrew
przeznaczeniu, modyfikacje narzādzia pneumatycznego lub uũywanie cz
āľci, które nie zostaĝy
sprawdzone i dopuszczone przez producenta,
mogå spowodowaê nieprzewidywalne szkody!
Za szkody powstaĝe w wyniku uũytkowania
niezgodnego z przeznaczeniem odpowiada
wyĝåcznie uũytkownik.
Naleũy przestrzegaê ogólnie obowiåzujåcych przepisów zapobiegania wypadkom oraz zaĝåczonych
wskazówek bezpieczeĞstwa.
Dla wĝasnego bezpieczeĞstwa oraz w
celu ochrony uũytkowanego urzådzenia
pneumatycznego naleũy zwracaê uwagā
na miejsca w tekľcie oznaczone tym
symbolem!
OSTRZE²ENIE – W celu zminimalizowania
ryzyka odniesienia obraũeĞ naleũy zapoznaê siā z instrukcjå obsĝugi.
OSTRZE²ENIE Naleũy przeczytaê
wszystkie wskazówki bezpieczeĞstwa i
instrukcje. Nieprzestrzeganie wskazówek bezpie-
czeĞstwa i instrukcji moũe spowodowaê poraũenie
prå
dem, poũar i/lub ciāũkie obraũenia ciaĝa.
Wskazówki bezpieczeĞstwa i instrukcje naleũy
zachowaê na przyszĝoľê.
Narzādzie pneumatyczne przekazywaê innym
osobom wyĝåcznie z doĝåczonå dokumentacjå.
- Uũytkownik lub pracodawca uũytkownika musi
dokonaê oceny szczególnych zagroũeĞ, które
mogå wyståpiê ze wzglādu na wszelkie zastosowania.
- Naleũy przeczytaê wskazówki bezpieczeĞstwa
przed przyståpieniem do ustawiania, eksploatacji,
napraw, konserwacji i wymiany wyposaũenia oraz
przed przyståpieniem do pracy w pobliũu narzādzia pneumatycznego. Te wskazówki muszå
zostaê zrozumiane. Jeľli tak nie jest, moũe to
prowadziê to powaũnych obraũeĞ cielesnych.
- Narzādzie pneumatyczne powinno byê przygotowywane, ustawiane i wykorzystywane wyĝåcznie
przez wykwalifikowany i przeszkolony personel.
- Nie wolno przeprowadzaê zmian w narzādziu
pneumatycznym. Zmiany mogå zmniejszyê
skutecznoľê ľrodków bezpieczeĞstwa i zwiākszyê ryzyko dla uũytkownika.
- Nigdy nie uũywaê uszkodzonych narzādzi pneumatycznych. Starannie pielāgnowaê narzādzia
pneumatyczne. Naleũy regularnie sprawdzaê, czy
ruchome czāľci dziaĝajå prawidĝowo i nie zakleszczajå siā, czy nie så pākniāte lub uszkodzone w
sposób negatywnie wpĝywajåcy na funkcjonowanie narzādzia pneumatycznego. Kontrolowaê,
czy etykiety i napisy så kompletne i czytelne.
Przed uũyciem urzådzenia uszkodzone czāľci
naleũy oddaê do naprawy lub wymieniê. Wiele
wypadków spowodowanych jest przez niewĝaľciwå konserwacjā narzādzi pneumatycznych.
4.1 Zagroũenia przez czāľci katapultowane
w powietrze
- W razie pākniācia obrabianego przedmiotu,
elementów wyposaũenia lub narzādzia pneumatycznego, w powietrze katapultowane mogå
zostaê róũne czāľci z duũå prādkoľciå.
- Podczas pracy, przy wymianie wyposaũenia oraz
podczas prac konserwacyjnych i naprawczych
przy narzādziach pneumatycznych naleũy
zawsze nosiê okulary ochronne odporne na
uderzenia. StopieĞ wymaganej ochrony powinien
byê oceniany dla kaũdego zastosowania
oddzielnie.
- Naleũy upewniê siā, czy obrabiany przedmiot jest
bezpiecznie zamocowany.
- Naleũy regularnie kontrolowaê, czy prādkoľê
obrotowa narzādzia pneumatycznego nie jest
wyũsza niũ prādkoľê obrotowa podana na narzādziu pneumatycznym. Takie kontrole prādkoľci
obrotowej powinny odbywaê siā
bez zaĝoũonego
narzādzia roboczego. Takie kontrole moũe przeprowadziê serwis Metabo.
- Naleũy zadbaê o to, aby iskry i odĝamki powstajåce w trakcie pracy nie stanowiĝy zagroũenia.
- Naleũy odĝåczyê narzādzie pneumatyczne od
zasilania sprāũonym powietrzem, zanim wymieniane bādå narzādzia robocze albo elementy
wyposaũenia lub wykonywane bādå ustawienia
lub czynnoľci konserwacyjne albo czyszczenie.
1. Deklaracja zgodnoľci
2. Uũytkowanie zgodne z
przeznaczeniem
3. Ogólne wskazówki
bezpieczeĞstwa
4. Specjalne wskazówki
bezpieczeĞstwa
Page 38

POLSKIpl
38
- Naleũy upewniê siā, czy nie stwarza siā zagroũenia równieũ dla innych osób.
4.2 Zagroũenia na skutek pochwycenia/nawi-
niācia
- Naleũy nosiê odpowiedniå odzieũ. Nie naleũy
nosiê luŧnego ubrania lub biũuterii. Wĝosy, odzieũ
i rākawice naleũy trzymaê w odpowiedniej odlegĝoľci od narzādzia pneumatycznego i ruchomych czāľci. Luŧne ubranie, biũuteria lub dĝugie
wĝosy mogå zostaê ujāte przez poruszajåce siā
czāľci. Istnieje niebezpieczeĞstwo odniesienia
obraũeĞ.
4.3 Zagroũenia w trakcie uũytkowania
- Naleũy unikaê kontaktu z obracajåcym siā trzpieniem i narzādziem roboczym, aby uniknåê ran
ciātych na dĝoniach i innych czāľciach ciaĝa.
- Podczas uũytkowania narzādzia pneumatycznego dĝonie uũytkownika mogå byê naraũone na
niebezpieczeĞstwa jak np. rany ciāte, otarcia i
wysoka temperatura. W celu ochrony dĝoni naleũy
nosiê odpowiednie rākawice.
- Uũytkownik i personel konserwacyjny muszå byê
w stanie, opanowaê fizycznie wielkoľê, masā i
moc narzādzia pneumatycznego.
- Naleũy prawidĝowo trzymaê narzādzie pneumatyczne: trzeba byê gotowym, na przeciwdziaĝanie
zwykĝym lub nagĝym ruchom – trzymaê obie
dĝonie w pogotowiu.
- Naleũy dbaê o bezpiecznå postawā przy pracy i
zawsze utrzymywaê równowagā.
- Naleũy unikaê niezamierzonego uruchomienia
narzādzia. W razie przerwania zasilania sprāũonym powietrzem naleũy wyĝåczyê narzādzie
pneumatyczne za pomocå wĝåcznika/wyĝåcznika.
- Naleũy stosowaê wyĝåcznie ľrodki smarne zalecane przez producenta.
- Naleũy nosiê osobiste wyposaũenie ochronne i
zawsze zakĝadaê okulary ochronne. Noszenie
osobistego wyposaũenia ochronnego, jak rākawic
ochronnych, odzieũy ochronnej, maski przeciwpyĝowej, antypoľlizgowego obuwia roboczego,
kasku lub ochraniaczy sĝuchu, w zaleũnoľci od
typu i zastosowania urzådzenia, zmniejsza ryzyko
obraũeĞ i jest zalecane.
- Dopuszczalna prādkoľê obrotowa dla narzādzia
roboczego musi byê co najmniej tak duũa, jak
najwiāksza prādkoľê obrotowa, podana na narzādziu pneumatycznym. Element wyposaũenia,
który obraca si
ā szybciej niũ jest to dopuszczalne,
moũe pāknåê i rozpaľê siā na wszystkie strony.
- Podczas prac ponad gĝowå naleũy nosiê heĝm
ochronny.
- Po wyĝåczeniu urzådzenia narzādzie zatrzymuje
siā z opóŧnieniem.
- Naleũy zadbaê o to, aby iskry powstajåce w
trakcie pracy nie wywoĝywaĝy zagroũeĞ. Podczas
obróbki przedmiotów mogå powstawaê wybuchowe i ĝatwopalne pyĝy. Istnieje ryzyko wybuchu
i poũaru.
4.4 Zagroũenie ze wzglādu na powtarzajåce
siā ruchy
- Podczas prac z zuũyciem narzādzia pneumatycznego moũe pojawiê siā nieprzyjemne odczucie w
dĝoniach, rākach, ramionach, w okolicy szyi lub
innych czāľciach ciaĝa .
- Podczas pracy z u
ũyciem tego narzādzia pneumatycznego naleũy przyjåê wygodnå postawā,
zwróciê uwagā na pewne trzymanie narzādzia i
unikaê niewygodnych pozycji lub takich, przy
których trudno jest zachowaê równowagā.
Podczas dĝugotrwaĝej pracy uũytkownik powinien
zmieniaê postawā, gdyũ moũe to pomóc w unikniāciu nieprzyjemnych odczuê i zmāczenia.
- Jeľli uũytkownik zacznie odczuwaê symptomy
takie, jak np. dĝuũsza niedyspozycja, dolegliwoľci,
uczucie pulsowania, ból, mrowienie, ogĝuszenie,
pieczenie czy sztywnoľê, wówczas nie wolno
ignorowaê tych objawów ostrzegawczych. Uũytkownik powinien zgĝosiê je swojemu pracodawcy i
skonsultowaê siā z wykwalifikowanym lekarzem.
4.5 Zagroũenia ze strony elementów wypo-
saũenia
- Naleũy odĝåczyê narzādzie pneumatyczne od
zasilania sprāũonym powietrzem, zanim naståpi
mocowanie lub wymiana narzādzi roboczych lub
elementów wyposaũenia.
- Wolno stosowaê wyĝåcznie wyposaũenie, które
jest przeznaczone dla tego urzådzenia i speĝnia
wymogi i parametry opisane w niniejszej instrukcji
obsĝugi.
- Naleũy unikaê bezpoľredniego kontaktu z narzādziem roboczym podczas pracy i po jej zakoĞczeniu, poniewaũ moũe byê ono goråce lub mieê
ostre krawādzie.
- Dopuszczalna prādkoľê obrotowa dla narzādzia
roboczego musi byê co najmniej tak duũa, jak
podana na narzādziu pneumatycznym najwiāksza
prādkoľê obrotowa. Element wyposaũenia, który
obraca siā szybciej niũ jest to dopuszczalne,
moũe pāknåê i rozpaľê siā na wszystkie strony.
- Nigdy nie montowaê tarczy szlifierskiej, ľciernicy
tnåcej ani frezów. Pākajåca tarcza szlifierska
moũe spowodowaê bardzo powaũne obraũenia
lub ľmierê.
- Nie stosowaê tarcz, które zostaĝy uderzone, så
nadpākniāte lub upadĝy.
- Wolno stosowaê wyĝåcznie dopuszczone narzādzia robocze o odpowiedniej ľrednicy trzonka.
- Przestrzegaê zalecenia producenta maĝych
narzādzi szlifierskich. W przypadku maĝych
narzādzi szlifierskich nie wolno przekraczaê
podanego przez producenta maksymalnego
dozwolonego wysiāgu (L0= dĝugoľê trzonka
pomiādzy koĞcem tulei zaciskowej a narzādziem
szlifierskim)! W razie zwiākszenia wysiāgu (L0)
naleũy zmniejszyê dopuszczalnå prādkoľê obrotowå. Wĝoũyê narzādzie robocze w miarā moũliwoľci caĝå dĝugoľciå chwytu w tulejā zaciskowå.
Upewniê siā, ũe dĝugoľê zamocowania (Lg)
wynosi przynajmniej 10 mm.
- rednica wrzeciona narzādzia roboczego musi
odpowiadaê dokĝadnie otworowi tulei zaciskowej!
LoL
g
Page 39

POLSKI pl
39
4.6 Zagroũenia na stanowisku pracy
- Poľliŧniācie siā, potkniācie i przewrócenie så
gĝównymi przyczynami obraũeĞ na stanowisku
pracy. Naleũy uwaũaê na powierzchnie, które ze
wzglādu na uũytkowanie narzādzia pneumatycznego mogå staê siā ľliskie oraz na zagroũenia ze
strony wāũa pneumatycznego, który moũe byê
przyczynå potkniāê.
- W nieznanym otoczeniu naleũy postāpowaê
ostroũnie. Mogå wystāpowaê ukryte zagroũenia
np. ze wzglādu na obecnoľê przewodów elektrycznych czy innych przewodów zasilajåcych.
- Narzādzie pneumatyczne nie jest przeznaczone
do uũytku w strefach zagroũonych wybuchem i nie
jest izolowane na wypadek stycznoľci ze ŧródĝami
prådu elektrycznego.
- Naleũy sprawdziê, czy w miejscu, które ma byê
obrabiane, nie znajdujå siā ũadne przewody elektryczne, wodociågowe lub gazowe (np. za
pomocå wyszukiwacza metali).
4.7 Zagroũenia przez pyĝy i opary
- Pyĝy i opary powstajåce przy uũytkowaniu narzādzia pneumatycznego mogå spowodowaê szkody
zdrowotne (jak np. rak, uszkodzenia pĝodu, astmā
i/lub zapalenia skóry); nieodzowne jest przeprowadzenie oceny ryzyka w odniesieniu do tych
zagroũeĞ i wprowadzenie odpowiednich mechanizmów zapobiegawczych.
- W ocenie ryzyka uwzglādnione powinny byê pyĝy,
powstajåce w trakcie uũytkowania narzādzia
pneumatycznego oraz pyĝy obecne na miejscu,
wzbijajåce siā przy tym w powietrze.
- Narzādzie pneumatyczne naleũy uũytkowaê i
konserwowaê wedĝug zaleceĞ zawartych w niniejszej instrukcji, aby zredukowaê uwalnianie pyĝów i
oparów do minimum.
- Powietrze powrotne powinno by
ê odprowadzane
w taki sposób, aby zredukowaê wzbijanie siā
pyĝów w zapylonym otoczeniu do minimum.
- Jeľli dochodzi do uwalniania pyĝów lub oparów, to
gĝównym zadaniem musi byê kontrolowanie ich w
miejscu ich powstawania.
- Wszystkie elementy podstawowe lub wyposaũenie dodatkowe narzādzia pneumatycznego do
wyĝapywania, odsysania lub redukcji powstawania lotnych pyĝów i oparów powinny byê
prawidĝowo stosowane i konserwowane zgodnie z
zaleceniami producenta.
- Materiaĝy podlegajåce zuũyciu oraz narzādzia
robocze naleũy dobieraê, konserwowaê i wymieniaê zgodnie z zaleceniami niniejszej instrukcji,
aby uniknåê niepotrzebnego nasilenia powstawania pyĝów lub oparów.
- Naleũy stosowaê ľrodki ochrony dróg oddechowych wedĝug zaleceĞ swojego pracodawcy lub
wedĝug wymogów BHP.
- Prace z okreľlonymi materiaĝami powodujå emisjā
pyĝów i oparów, które mogå wywoĝaê potencjalnie
wybuchowå atmosferā
.
4.8 Zagroũenia przez haĝas
- W razie niedostatecznej ochrony sĝuchu dziaĝanie
silnego haĝasu moũe prowadziê do trwaĝego
uszkodzenia sĝuchu, utraty sĝuchu i innych problemów, jak np. szumy uszne (dzwonienie, szum,
ľwist lub brzāczenie w uszach).
- Nieodzowne jest przeprowadzenie oceny ryzyka
w odniesieniu do tych zagroũeĞ i wprowadzenie
odpowiednich mechanizmów zapobiegawczych.
- Do mechanizmów zapobiegawczych pozwalajåcych na zmniejszenie zagroũeĞ naleũå takie dziaĝania jak zastosowanie materiaĝów izolacyjnych,
aby uniknåê dŧwiāków dzwonienia wystāpujåcych
na obrabianych przedmiotach.
- Naleũy stosowaê ľrodki ochrony sĝuchu wedĝug
zaleceĞ swojego pracodawcy lub wedĝug
wymogów BHP.
- Narzādzie pneumatyczne naleũy uũytkowaê i
konserwowaê zgodnie z zaleceniami niniejszej
instrukcji, aby uniknåê niepotrzebnego zwiākszenia natāũenia haĝ
asu.
- Materiaĝy podlegajåce zuũyciu oraz narzādzia
robocze naleũy dobieraê, konserwowaê i wymieniaê zgodnie z zaleceniami niniejszej instrukcji,
aby uniknåê niepotrzebnego zwiākszenia natāũenia haĝasu.
- Zintegrowany tĝumik nie moũe byê usuwany i
powinien znajdowaê siā w dobrym stanie roboczym.
4.9 Zagroũenia ze wzglādu na drgania
- Oddziaĝywanie drgaĞ moũe powodowaê uszkodzenia nerwów i zakĝócenia w cyrkulacji krwi w
dĝoniach i ramionach.
- Podczas prac w zimnym otoczeniu naleũy nosiê
ciepĝå odzieũ i zadbaê o to, aby dĝonie byĝy ciepĝe
i suche.
- Jeľli pojawi siā wraũenie, ũe skóra palców lub
dĝoni staĝa siā nieczuĝa, mrowi, boli lub zabarwi
ĝa
siā na biaĝo, to naleũy przerwaê pracā z uũyciem
narzādzia pneumatycznego, powiadomiê
swojego przeĝoũonego i skonsultowaê siā z lekarzem.
- Narzādzie pneumatyczne naleũy uũytkowaê i
konserwowaê zgodnie z zaleceniami niniejszej
instrukcji, aby uniknåê niepotrzebnego nasilenia
siā drgaĞ.
- Materiaĝy podlegajåce zuũyciu oraz narzādzia
robocze naleũy dobieraê, konserwowaê i wymieniaê zgodnie z zaleceniami niniejszej instrukcji,
aby uniknåê niepotrzebnego nasilenia siā drgaĞ.
- Do przytrzymywania masy narzādzia pneumatycznego, tam gdzie to moũliwe, naleũy stosowaê
stojak, urzådzenie mocujåce lub kompensacyjne.
- Narzādzie pneumatyczne naleũy trzymaê nie za
mocnym, ale pewnym chwytem z zachowaniem
wymaganych rācznych si
ĝ reakcyjnych, gdyũ wraz
ze wzrostem siĝy chwytu ryzyko drgaĞ z reguĝy
zwiāksza siā.
- Niedostatecznie zamontowane lub uszkodzone
narzādzie robocze moũe spowodowaê nadmierne
drgania.
4.10 Dodatkowe wskazówki z zakresu bezpie-
czeĞstwa
- Sprāũone powietrze moũe powodowaê powaũne
obraũenia.
- Jeľli narzādzie pneumatyczne nie jest uũywane,
przed przyståpieniem do wymiany elementów
wyposaũenia lub wykonywania prac naprawczych
naleũy zawsze odciåê dopĝyw sprāũonego powietrza, spuľciê ciľnienie z wāũa powietrza i odĝå-
Page 40

POLSKIpl
40
czyê narzādzie pneumatyczne od dopĝywu sprāũonego powietrza.
- Nigdy nie wolno kierowaê strumienia powietrza na
siebie ani inne osoby.
- Uderzajåce dookoĝa wāũe mogå spowodowaê
powaũne obraũenia. Dlatego naleũy zawsze
sprawdzaê, czy wāũe i ich elementy mocujåce nie
så uszkodzone i czy nie poluzowaĝy siā.
- Jeľli stosowane så uniwersalne zĝåcza obrotowe
(zĝåcza pazurowe), to naleũy uũyê koĝków blokujåcych zabezpieczeĞ wāũy Whipcheck, aby
zapewniê ochronā na wypadek, gdyby poĝåczenie
wāũa z narzādziem pneumatycznym lub poszczególnych wāũy z sobå zawiodĝo.
- Naleũy zadbaê o to, aby podane dla narzādzia
pneumatycznego ciľnienie maksymalne nie byĝo
przekraczane.
- Nigdy nie przenosiê narzādzia pneumatycznego
za wåũ.
- Jeľli narzādzie pneumatyczne uũytkowane jest w
uchwycie, to naleũy je bezpiecznie zamocowaê.
Utrata kontroli nad urzådzeniem moũe spowodowaê obraũenia ciaĝa.
4.11 Dalsze wskazówki bezpieczeĞstwa
- Naleũy przestrzegaê ewentualnych specjalnych
przepisów BHP i przepisów o zapobieganiu
wypadkom dot. obchodzenia siā z kompresorami
i narzādziami pneumatycznymi.
- Naleũy upewniê siā, ũe podane w danych technicznych maksymalne dozwolone ciľnienie
robocze nie zostanie przekroczone.
- Nie wolno przeciåũaê tego narzādzia – wykorzystywaê narzādzie wyĝåcznie w zakresie wydajnoľci, podanym w danych technicznych.
- Stosowaê ľrodki smarne nie budzåce zastrzeũeĞ.
Naleũy zadbaê o dostatecznå wentylacjā w
miejscu pracy. W razie zwi
ākszonej emisji do
otoczenia: skontrolowaê narzādzie pneumatyczne i w razie potrzeby zleciê jego naprawā.
- Nie naleũy korzystaê z tego narzādzia bez naleũytej koncentracji. Naleũy byê uwaũnym, zwaũaê
na to co siā robi i pracā narzādziem pneumatycznym rozpoczynaê z rozsådkiem. Narzādzia
nie naleũy uũywaê w przypadku zmāczenia ani
pod wpĝywem narkotyków, alkoholu lub leków.
Moment nieuwagi przy uũyciu tego narzādzia
moũe doprowadziê do powaũnych obraũeĞ ciaĝa.
- Miejsce pracy naleũy utrzymywaê w czystoľci i
dobrze oľwietlone. Nieporzådek i brak oľwietlenia miejsc pracy mogå doprowadziê do
wypadków.
- Narzādzia pneumatyczne powinny byê przechowywane w miejscu niedostāpnym dla dzieci.
- Nie przechowywaê narzādzia bez odpowiedniego
zabezpieczenia na ľwieũym powietrzu ani w
wilgotnym otoczeniu.
- Naleũy chroniê narzādzie pneumatyczne, szczególnie przyĝåcze sprāũonego powietrza i elementy
sterownicze, przed pyĝem i brudem.
Informacje w niniejszej instrukcji obsĝugi oznaczone zostaĝy w nastāpujåcy sposób:
NiebezpieczeĞstwo! Ostrzeũenie przed
szkodami osobowymi lub szkodliwoľciå dla
ľrodowiska.
Uwaga. Ostrzeũenie przed szkodami mate-
rialnymi.
4.12 Symbole na narzādziu pneumatycznym
Przed uruchomieniem przeczytaê instrukcjā
obsĝugi.
Nosiê okulary ochronne
Nosiê ochraniacze sĝuchu
Kierunek obrotów
Patrz strona 2.
1 Klucz pĝaski
2 Nakrātka tulei zaciskowej
3 Tuleja zaciskowa
4 Uchwyt tulei zaciskowej
5 Wrzeciono
6 Klucz pĝaski
7 Przeĝåcznik (wĝåcznik/wyĝåcznik)
8 Blokada wĝåczenia
9 ruba regulacyjna do ustawiania prā
dkoľci
obrotowej
10 Wylot powietrza
11 Przyĝåcze sprāũonego powietrza z filtrem
12 Zĝåczka wtykowa 1/4"
6.1 Przed pierwszym uruchomieniem
Wkrāciê zĝåczkā wtykowå (12).
6.2 Wkĝadanie tulei zaciskowej
rednica wrzeciona musi odpowiadaê
dokĝadnie otworowi tulei zaciskowej (3)!
Dostāpne så tuleje zaciskowe do róũnych ľrednic
wrzeciona. Wĝoũyê tulejā zaciskowå (3) w uchwyt
tulei zaciskowej (4) i przykrāciê rācznie nakrātkā
tulei zaciskowej (2) .
Jeľli do tulei zaciskowej nie jest wĝoũone
ũadne narzādzie, to tulei zaciskowej nie
naleũy dokrācaê kluczem pĝaskim, a jedynie
rācznie!
6.3 Zakĝadanie narzādzia roboczego
W przypadku maĝych narzādzi szlifierskich nie
wolno przekraczaê
podanego przez producenta maksymalnego dozwolonego wysiāgu (L0)!
Wĝoũyê narzādzie robocze w miarā moũliwoľci caĝå
dĝugoľciå chwytu w tulejā zaciskowå (3). Upewniê
siā, ũe dĝugoľê zamocowania (Lg) wynosi przynajmniej 10 mm.
5. Przeglåd
6. Eksploatacja
Page 41

POLSKI pl
41
rednica wrzeciona narzādzia roboczego
musi odpowiadaê dokĝadnie otworowi tulei
zaciskowej (3)!
- Przytrzymaê wrzeciono (5) za pomocå klucza
pĝaskiego (6).
- Dociågnåê nakrātkā tulei zaciskowej (2) za
pomocå klucza pĝaskiego (1).
- Zwróciê uwagā na pewne zamocowanie narzādzia roboczego.
6.4 Uũytkowanie narzādzia pneumatycznego
Aby uzyskaê peĝnå moc swojego narzādzia pneumatycznego, naleũy zawsze stosowaê wāũe pneumatyczne o ľrednicy wewnātrznej minimum 9 mm.
Zbyt maĝa ľrednica wāũa moũe znacznie zmniejszyê moc.
Uwaga. Przewód pneumatyczny nie moũe
zawieraê skroplin.
Uwaga. Aby narzādzi to pozostaĝo sprawne
przez dĝugi czas, musi byê w dostatecznym
stopniu zasilane olejem do pneumatyki. Moũe siā
to odbywaê w nastāpujåcy sposób:
– Zastosowanie oliwionego sprāũonego powietrza
poprzez zamontowanie olejarki mgĝawicowej.
– Bez olejarki mgĝawicowej: oliwiê codziennie rācz-
nie przez przyĝåcze sprāũonego powietrza. Ok.
3-5 kropli oleju do pneumatyki co 15 minut roboczych przy ciågĝym uũytkowaniu.
Jeľli narzādzie nie byĝo uũywane przez kilka dnia,
wkropliê rācznie ok. 5 kropli oleju do pneumatyki
do przyĝåcza sprāũonego powietrza.
Uwaga. Narzādzie uruchamiaê w trybie
jaĝowym jedynie na krótki czas.
1. Dobraê odpowiedniå tulejā zaciskowå (3) (patrz
rozdziaĝ 6.2).
2. Zaĝoũyê pasujåce narzādzie robocze (patrz roz-
dziaĝ 6.3).
3. Prādkoľê obrotowå moũna zmieniaê za pomo-
c
å ľruby regulacyjnej (9).
4. Ustawiê ciľnienie robocze (mierzone na wlocie
powietrza przy wĝåczonym narzādziu pneumatycznym). Maksymalne dopuszczalne ciľnienie
robocze patrz rozdziaĝ „Dane techniczne“.
5. Podĝåczyê narzādzie pneumatyczne do zasila-
nia sprāũonym powietrzem.
6. Wĝåczanie: przesunåê blokadā wĝåczania (8) w
kierunku strzaĝki (patrz rys., strona 2) i wcisnåê
przeĝåcznik (7).
Wyĝåczanie: puľciê przeĝåcznik (7)
.
NiebezpieczeĞstwo! Przed przyståpieniem
do jakichkolwiek prac odĝåczyê sprāũone powietrze.
NiebezpieczeĞstwo! Inne prace konserwacyjne lub naprawcze, niũ opisane w niniej-
szym rozdziale, mogå byê przeprowadzane wy-
ĝåcznie przez wykwalifikowanych
pracowników.
- Naleũy zadbaê o bezpieczeĞstwo narzādzia
pneumatycznego poprzez jego regularnå konserwacjā.
- Kontrolowaê prawidĝowe dociågniācie zĝåcz gwintowych, w razie potrzeby dociågnåê.
- Filtry w przyĝåczu sprāũonego powietrza czyľciê
przynajmniej raz na tydzieĞ.
- Zaleca siā, podĝåczenie przed narzādziem pneumatycznym reduktora ciľnienia z separatorem
wody i olejarkå.
- W przypadku zwiākszonego wycieku oleju lub
powietrza skontrolowaê narzādzie pneumatyczne
i w razie potrzeby oddaê do naprawy. (Patrz
rozdziaĝ 9.)
- Regularnie i po kaũdym uũyciu naleũy sprawdzaê
prādkoľê obrotowå oraz przeprowadzaê prostå
kontrolā poziomu drgaĞ.
- Unikaê stycznoľci z niebezpiecznymi substancjami, które odkĝadajå siā na narzādziu. Naleũy
nosiê osobiste wyposaũenie ochronne i usuwaê
niebezpieczne substancje za pomocå odpowiednich ľrodków przed przyståpieniem do prac
konserwacyjnych.
f
Naleũy stosowaê wyĝåcznie oryginalne akcesoria
Metabo.
Wolno stosowaê wyĝåcznie wyposaũenie, które jest
przeznaczone dla tego narzādzia pneumatycznego
i speĝnia wymogi i parametry opisane w niniejszej
instrukcji obsĝugi.
Peĝny zestaw akcesoriów, patrz na stronie
www.metabo.com lub w katalogu.
NiebezpieczeĞstwo! Naprawy narzādzia
pneumatycznego mogå przeprowadzaê
wyĝåcznie wykwalifikowani pracownicy z uũyciem
oryginalnych czāľci zamiennych Metabo!
W sprawie naprawy narzādzi pneumatycznych
naleũy siā zwróciê do przedstawicielstwa Metabo.
Adresy så podane na stronie www.metabo.com.
Listā czāľci zamiennych moũna pobraê pod
adresem www.metabo.com.
Naleũy przestrzegaê krajowych przepisów dotyczåcych usuwania i recyklingu zuũytych narzādzi pneumatycznych, opakowaĞ i akcesoriów. Nie wolno
stwarzaê zagroũeĞ dla ludzi i ľrodowiska.
Wyjaľnienia do informacji podanych na stronie 3.
7. Konserwacja i pielāgnacja
LoL
g
8. Akcesoria
9. Naprawa
10. Ochrona ľrodowiska
11. Dane techniczne
Page 42

POLSKIpl
42
Zastrzegamy sobie prawo do zmian konstrukcyjnych.
V1= zapotrzebowanie powietrza
p
max.
= maksymalne dopuszczalne ciľnienie
robocze
n0= prādkoľê obrotowa
dS= otwór tulei zaciskowej
D
max
= maksymalna ľrednica narzādzia szlifier-
skiego
di= ľrednica wāũa (wewnātrzna)
C = gwint przyĝåcza
A = wymiary:
dĝugoľê x szerokoľê x wysokoľê
m = ciāũar
Podane dane techniczne okreľlone så w granicach
tolerancji (odpowiednio do obowiåzujåcych
standardów).
Wartoľci emisji
Wartoľci te umoũliwiajå oszacowanie emisji
narzādzia i porównanie róũnych narzādzi. W zaleũnoľci od warunków uũytkowania, stanu narzādzia
lub narzādzi roboczych rzeczywiste obciåũenie
moũe byê wiāksze lub mniejsze. Wartoľci te naleũy
uwzglādniê dla oszacowania przerw w pracy i faz
mniejszego obciåũenia. Ustaliê na podstawie odpowiednio dopasowanych wartoľci szacunkowych
ľrodki ochronne dla uũytkownika, np. ľrodki organi-
zacyjne.
Wibracja
(waũona wartoľê efektywna
przyspieszenia; EN 28927) :
a
h
=Wartoľê emisji drgaĞ
K
h
=niepewnoľê pomiarowa (wibracja)
Poziom haĝasu (EN ISO 15744):
L
pA
=poziom ciľnienia akustycznego
L
WA
=poziom mocy akustycznej
KpA, KWA= niepewnoľê pomiarowa
Nosiê ochraniacze sĝuchu!
Page 43

MAGYAR hu
43
Eredeti használati utasítás
Kizárólagos felelįsségünk tudatában igazoljuk,
hogy ez a lyukcsiszológép mindenben megfelel a 3.
oldalon felsorolt szabványoknak és irányelveknek.
Ennek a sŒrített levegįs szerszámnak a rendeltetése...
- ... finom csiszolási munkák végzése csiszolócsapokkal,
- ...formapolírozó idomokkal való munkavégzés,
- ...filc polírozóidomokkal való munkavégzés,
- ...lamellás csiszolókorongokkal való munkavégzés
professzionális szinten.
A szerszámot csak sŒrítettlevegį-tápellátással
szabad üzemeltetni. A sŒrített levegįs szerszámon
megadott maximális megengedett munkanyomást
nem szabad túllépni. A sŒrített levegįs szerszámot
nem szabad robbanásveszélyes, éghetį vagy az
egészségre ártalmas gázokkal üzemeltetni. Nem
alkalmazható emelį-, törį vagy ütįszerszámként.
Bármely más felhasználás ellentétes a szerszám
rendeltetésével. A nem rendeltetésszerŒ használat, a sŒrített levegįs szerszámon végrehajtott módosítások, illetve a gyártó által nem ellenįrzött és
nem engedélyezett módosítások miatt beláthatatlan károk keletkezhetnek!
A nem rendeltetésszerŒ használatból eredį
mindennemŒ kárért a felelįsség kizárólag a
felhasználót terheli.
Feltétlenül tartsa be az általánosan elfogadott
balesetvédelmi szabályokat, valamint a mellékelt
biztonsági tudnivalókat.
Saját testi épsége és a sŒrített levegįs
szerszám védelme érdekében tartsa be
az ezzel a szimbólummal jelölt szövegrészekben foglaltakat!
FIGYELMEZTETÉS – A sérülésveszély
csökkentése érdekében olvassa át a használati utasítást.
FIGYELMEZTETÉS Olvassa át az összes
biztonsági tudnivalót és utasítást. A bizton-
sági tudnivalók és utasítások betartásának elmulasztása elektromos áramütést, tüzet és/vagy
súlyos személyi sérüléseket okozhat.
Gondosan įrizze meg valamennyi biztonsági
tudnivalót és elįírást.
Csak ezekkel a dokumentumokkal együtt adja
tovább másnak a sŒrített levegį
s szerszámot.
- A felhasználónak vagy a felhasználó munkaadójának fel kell becsülnie azokat a speciális kockázatokat, amelyek az egyes alkalmazások során
felléphetnek.
- A biztonsági tudnivalókat a beüzemelés, az
üzemeltetés, a javítások, karbantartások végzése
és a tartozékalkatrészek cseréje elįtt, valamint a
sŒrített levegįs szerszám közelében végzendį
munka elįtt el kell olvasni és meg kell érteni.
Ennek elmulasztása súlyos testi sérülésekhez
vezethet.
- A sŒrített levegįs szerszámot kizárólag képesített
és kiképzett kezelįszemélyzet üzemelheti be,
állíthatja be és használhatja.
- A sŒrített levegįs szerszámon nem szabad módosításokat végrehajtani. A módosítások a biztonsági óvintézkedések hatékonyságát csökkenthetik, és a kezelį veszélyeztetettségét növelhetik.
- Soha ne használjon sérült sŒrített levegįs szerszámot. Ügyeljen a sŒrített levegįs szerszámok
gondozására. Ellenįrizze rendszeresen a mozgó
alkatrészek kifogástalan mŒködését és szorulásmentességét, továbbá azt, hogy vannak-e törött
vagy olyan mértékben sérült alkatrészek, hogy
azok már a sŒrített levegįs szerszám mŒködését
akadályozzák. Ellenįrizze a táblák (címkék) és a
feliratok hiánytalanságát és olvashatóságát. A
sérült részeket a készülék használata elįtt javíttassa meg vagy újíttassa fel. Sok olyan baleset
történik, amelyet a sŒrített levegįs szerszám nem
kielégítį karbantartására lehet visszavezetni.
4.1 A kirepülį alkatrészek veszélyei
- A munkadarab, a tartozékok vagy a sŒrített
levegįs szerszám törése esetén nagy sebességgel alkatrészek repülhetnek ki.
- Üzemeltetéskor, tartozékalkatrészek cseréjekor,
valamint a sŒrített levegį
s szerszámon végzett
javítási és karbantartási munkák alkalmával
mindig ütésálló szemvédį eszközt kell viselni. A
védelem szükséges fokozatát minden használat
elįtt külön kell megítélni.
- Gyįzįdjön meg a munkadarab szilárd rögzítésérįl.
- Rendszeresen ellenįrizni kell, hogy a sŒrített
levegįs szerszám fordulatszáma nem haladja-e
meg a sŒrített levegįs szerszámon feltüntetett
fordulatszám-adatot. Ezeket a fordulatszámellenįrzéseket betétszerszám nélkül kell végrehajtani. Ezeket az ellenįrzéseket elvégezheti a
Metabo ügyfélszolgálata.
- Ügyeljen arra, hogy a munka közben keletkezį
szikrák és letörį részecskék ne képezzenek
veszélyforrást.
- Betétszerszám- vagy tartozékcsere, illetve beállítás vagy karbantartás, tisztítás végzése elįtt
válassza le a sŒrített levegįs szerszámot a sŒrített
levegį tápellátásáról.
- Ügyeljen arra, hogy más személyeket fenyegetį
veszélyek se lépjenek fel.
4.2 Behúzás és rácsavarodás veszélye
- Viseljen megfelelį ruházatot. Ne viseljen bį ruhát
vagy ékszereket. Tartsa távol a haját, a ruháját és
a kesztyŒjét a sŒrített levegįs szerszámtól és a
1. Megfelelįségi nyilatkozat
2. RendeltetésszerŒ használat
3. Általános biztonsági
tudnivalók
4. Különleges biztonsági
tudnivalók
Page 44

MAGYARhu
44
mozgó részektįl. A bį ruhát, az ékszereket és a
hosszú hajat a mozgó alkatrészek magukkal ránthatják. Fennáll a sérülés veszélye.
4.3 Az üzemelés közben fennálló veszélyek
- Kerülje a kapcsolatba kerülést a forgó tengellyel
és a betétszerszámmal, hogy ne keletkezzenek
vágási sérülések a kezein és egyéb testrészein.
- A sŒrített levegįs szerszám használatakor a
kezelį kezei olyan veszélyeknek lehetnek kitéve,
mint pl. vágások, horzsolódások és hįhatás.
Viseljen megfelelį, a kezeit védį kesztyŒt.
- A sŒrített levegįs szerszám mérete, súlya és teljesítménye miatt a kezelįnek és a karbantartó
személyzetnek fizikailag alkalmasnak kell lennie a
szerszám biztos használatára.
- Tartsa helyesen a sŒrített levegįs szerszámot:
álljon készen arra, hogy ellenhatást fejtsen ki a
normál vagy hirtelen mozgásokkal szemben –
legyen mindkét keze készenlétben.
- Ügyeljen arra, hogy mindig biztosan álljon és az
egyensúlyát megtartsa.
- Kerülje el a véletlenszerŒ bekapcsolást. A táplevegį-ellátás kimaradása esetén kapcsolja ki a Ki/
Be kapcsolóval a sŒrített levegįs szerszámot.
- Csak a gyártó által ajánlott kenįanyagokat használja.
- Viseljen személyi védįfelszerelést és mindig
viseljen védįszemüveget. A személyi védįfelszerelések, mint a védįkesztyŒ, a védįöltözék, a
porvédį álarc, a csúszásbiztos védįcipį, a védįsisak vagy a hallásvédį viselése a készülék fajtájának és alkalmazásának megfelelįen csökkenti a
sérülések kockázatát, és ajánlott az ilyen
eszközök viselése.
- A betétszerszám megengedett fordulatszámának
legalább a sŒrített leveg
įs szerszámon megadott
maximális fordulatszám értékét el kell érnie. A
megengedettnél gyorsabban forgó tartozék
eltörhet és darabjai szerteszét repülhetnek.
- A fejmagasság felett végzett munkák alkalmával
viseljen védįsisakot.
- A szerszám a sŒrített levegįs szerszám kikapcsolása után még mozog.
- Ügyeljen arra, hogy a használat közben keletkezį
szikrák ne okozzanak veszélyt. Az anyagok
megmunkálása során robbanásveszélyes vagy
éghetį porok keletkezhetnek. Fennáll a robbanás
vagy tŒz keletkezésének a veszélye.
4.4 Az ismétlįdį mozgások veszélyei
- A sŒrített levegįs szerszámmal végzett munka
során kellemetlen érzet támadhat a kezekben, a
karokban, a vállakban, a nyaki zónában vagy
egyéb testrészekben.
- A sŒrített levegįs szerszámmal végzett
munkához vegyen fel kényelmes testtartást,
ügyeljen a biztonságos tartásra, és kerülje a
kedvezįtlen testhelyzeteket, illetve azon testhelyzeteket, amelyekben nehéz az egyensúly megtartása. A kezelįnek hosszú ideig tartó munka
közben változtatnia kell a testtartását, ez segíthet
a kellemetlen következmények és a kifáradás
elkerülésében.
- Ha a felhasználó olyan tünetek fellépését érzékeli,
mint pl. tartós rossz közérzet, panaszok, zakatolás, fájdalom, bizsergés, süketség, égetį érzés
vagy merevség, akkor ne hagyja figyelmen kívül
ezeket a figyelmeztetį jeleket. A kezelį tájékoztassa ezekrįl a munkaadóját, és konzultáljon
képesített orvossal.
4.5 A tartozékok veszélyei
- Betétszerszám vagy tartozék rögzítése vagy
cseréje elįtt válassza le a sŒrített levegįs szerszámot a táplevegį-ellátásról.
- Csak olyan tartozékot használjon, amely ehhez a
készülékhez készült, és megfelel az ebben a
használati utasításban megadott követelményeknek és adatoknak.
- Kerülje a közvetlen kapcsolatot a betétszerszámmal használat közben és után, mert az forró
és éles lehet.
- A betétszerszám megengedett fordulatszámának
legalább a sŒrített levegįs szerszámon megadott
maximális fordulatszám értékét el kell érnie. A
megengedettnél gyorsabban forgó tartozék
eltörhet és darabjai szerteszét repülhetnek.
- Soha ne szereljen fel csiszolótárcsát, darabolótárcsát vagy marót. A darabokra tör
į csiszolótárcsa
komoly sérüléseket vagy halált okozhat.
- Ne használjon törött, repedezett vagy esetleg leejtett tárcsákat.
- Csak engedélyezett, megfelelį tengelyátmérįjŒ
betétszerszámokat használjon.
- Tartsa be a kis csiszolótestek gyártójának az ajánlásait. A kis csiszolótestekre vonatkozóan a
gyártó által megadott maximálisan megengedett
túlnyúlást (L0=a rögzítįfogó végzįdése és a kis
csiszolótest közötti tengelyhossz) nem szabad
túllépni! A túlnyúlás (L0) növelése esetén csökkenteni kell a megengedett fordulatszámot.
Helyezze be a betétszerszámot lehetįleg a szár
teljes hosszával a rögzítįfogóba. Ügyeljen arra,
hogy a befogási hossz (Lg) legalább 10 mm
legyen.
- A betétszerszám szárátmérįje pontosan feleljen
meg a rögzítįfogó rögzítįfuratának!
4.6 A veszélyek a munkahelyen
- A munkahelyi sérülések fį okai a megcsúszás,
megbotlás és az elesés. Ügyeljen az olyan felületekre, amelyek a sŒrített levegįs szerszám használata folytán csúszóssá válhatnak, ügyeljen
továbbá a levegįtömlį miatt fennálló megbotlási
veszélyre.
- Ismeretlen környezetben viselkedjék óvatosan.
Rejtett veszélyforrást képezhetnek az áramkábelek vagy egyéb tápvezetékek.
- A sŒrített levegįs szerszámot nem robbanásveszélyes légtérben való használatra tervezték, és
nem rendelkezik az elektromos áramforrásokkal
való érintkezés elleni szigeteléssel.
- Gyįzįdjön meg róla (pl. fémdetektor segítségével), hogy a megmunkálandó felületben,
nincsen áram-, víz- vagy gázvezeték.
LoL
g
Page 45

MAGYAR hu
45
4.7 A por és a gįzök miatt fellépį veszélyek
- A sŒrített levegįs szerszám használatakor keletkezį porok és gįzök egészségkárosodást (pl.
rák, szülési rendellenesség, asztma és/vagy
bįrbetegség) okozhatnak; ezen veszélyek vonatkozásában elengedhetetlen a kockázatok felmérésének lefolytatása és a megfelelį szabályozási
mechanizmusok életbe léptetése.
- A kockázatfelmérésbe be kell vonni a sŒrített
levegįs szerszám használatakor keletkezį port
és figyelembe kell venni az ekkor esetlegesen
felkavarodó egyéb jelen levį port is.
- A sŒrített levegįs szerszámot a jelen útmutatóban
szereplį ajánlások szerint kell üzemeltetni és
karban tartani, hogy a felszabaduló porok és
gįzök mennyisége a minimális mértékre korlátozódjon.
- A távozó levegįt úgy kell elvezetni, hogy poros
környezetben a por felkavarodása a minimális
mértékre korlátozódjon.
- Ha por vagy gįzök keletkeznek, a fį feladat
azoknak ellenįrzés alatt tartása a felszabadulásuk helyén.
- Minden, a szálló por vagy a gįzök felfogására,
elszívására vagy elnyomására szolgáló beépített
alkatrészt vagy tartozékot a gyártó utasításainak
megfelelįen, szabályszerŒen kell használni és
karbantartani.
- A fogyó anyagokat és a betétszerszámot a jelen
útmutató ajánlásainak megfelelįen kell kiválasztani, karbantartani és cserélni a por- vagy gįzképzįdés szükségtelen fokozódásának elkerülése
céljából.
- Használja a munkaadója utasításainak megfelelį,
vagy a munka- és egészségvédelmi elįírásokban
megkövetelt légzésvédelmi berendezéseket.
- Bizonyos anyagokkal végzett munka por és gįz
kibocsátását eredményezi, ez potenciálisan
robbanékony környezetet hozhat létre.
4.8 A zaj által okozott veszélyek
- A magas zajszint hatására elégtelen hallásvédelem esetén tartós halláskárosodás, a hallás
elvesztése és egyéb problémák léphetnek fel, pl.
tinnitus (csengés, zúgás, fütty, zengés a fülben).
- Elengedhetetlen a kockázatfelmérés végzése
ezen veszélyek vonatkozásában, és a megfelelį
szabályozási mechanizmusok életbe léptetése.
- A kockázat csökkentésére alkalmas szabályozási
mechanizmusok közé tartoznak az olyan intézkedések, mint a hangcsillapító anyagok alkalmazása, amelyekkel megakadályozható a csengį
zajok fellépése a munkadarabokon.
- Használja a munkaadója utasításai szerinti, vagy
a munka- és egészségvédelmi elįírásokban
megkövetelt hallásvédelmi berendezéseket.
- A sŒrített levegįs szerszámot a jelen útmutatóban
szereplį ajánlások szerint kell üzemeltetni és
karbantartani a zajszint felesleges növekedésének elkerülése végett.
- A fogyó anyagokat és a betétszerszámot a jelen
útmutató ajánlásainak megfelelįen kell kiválasztani, karbantartani és cserélni a zajszint szükségtelen fokozódásának elkerülése végett.
- Az integrált hangcsillapítót nem szabad eltávolítani, és annak jó állapotban kell lennie.
4.9 A rezgések által okozott veszélyek
- A rezgések az idegrendszer károsodását okozhatják, illetve a kezekben és a karokban vérkeringési zavarokat idézhetnek elį.
- Hideg környezetben végzett munka esetén
viseljen meleg ruházatot, tartsa a kezeit melegen
és szárazon.
- Ha azt észleli, hogy a bįr az ujjain vagy a kezein
zsibbad, bizsereg, fáj vagy fehéren elszínezįdik,
hagyja abba a munkát a sŒrített levegįs szerszámmal, tájékoztassa munkaadóját, és forduljon
orvoshoz.
- A sŒrített levegįs szerszámot a jelen útmutatóban
szereplį ajánlások szerint kell üzemeltetni és
karbantartani a rezgések felesleges felerįsödésének elkerülése végett.
- A fogyó anyagokat és a betétszerszámot a jelen
útmutató ajánlásainak megfelelįen kell kiválasztani, karbantartani és cserélni a rezgések szükségtelen felerįsödésének elkerülése végett.
- A sŒrített levegįs szerszám súlyának tartásához
lehetįség szerint használjon állványt, feszítįeszközt vagy kiegyenlítį szerelvényt.
- A sŒrített levegį
s szerszámot nem túl erįsen, de
azért mégis biztonságosan megfogva és a szükséges kézi reakcióerįk biztosításával tartsa, mert
a rezgés kockázata a megfogási erį növekedésével rendszerint nagyobbá válik.
- A nem megfelelįen felszerelt vagy sérült betétszerszám miatt túl nagy rezgések jöhetnek létre.
4.10 Egyéb biztonsági utasítások
- A sŒrített levegį komoly sérüléseket okozhat.
- Ha a sŒrített levegįs szerszám nincs használatban, tartozékok cseréje vagy javítási munkák
végzése elįtt mindig el kell zárni a levegįbevezetést, a levegįtömlįt nyomásmentessé kell tenni,
és a sŒrített levegįs szerszámot le kell választani
a sŒrített levegį bevezetésérįl.
- Soha ne irányítsa a levegį áramlását önmagára
vagy más személyekre.
- Az ide-oda vágódó tömlįk komoly sérüléseket
okozhatnak. Ezért mindig ellenįrizze a tömlįk és
rögzítįeszközeik sérülésmentes állapotát, és azt,
hogy nem oldódtak-e ki.
- Univerzális forgókuplungok (körmös kuplungok)
használata esetén arretáló csapokat kell alkalmazni és azokat Whipcheck-tömlįrögzítésekként
kell használni védelemként a tömlį és a sŒrített
levegįs szerszám kapcsolatának, illetve a tömlįk
egymás közötti kapcsolatának megszakadása
esetére.
- Gondoskodjék arról, hogy ne történhessen meg a
sŒrített levegįs szerszámon megadott maximális
nyomásérték a túllépése.
- A sŒrített levegįs szerszámokat soha ne tartsa a
tömlįnél fogva.
- Ha a sŒrített levegįs szerszám tartóban üzemel:
rögzítse biztonságosan a s
Œrített levegįs szerszámot. A gép fölötti uralom elvesztése sérüléshez vezethet.
4.11 További biztonsági tudnivalók
- Tartsa be a kompresszorok és a sŒrített levegįs
szerszámok használatára vonatkozó speciális
munkavédelmi és balesetmegelįzési
elįírásokat.
Page 46

MAGYARhu
46
- Ügyeljen arra, hogy ne kerüljön sor a mŒszaki
adatokban megadott maximálisan megengedhetį
munkanyomás túllépésére.
- Ne terhelje túl a szerszámot – csak a mŒszaki
adatokban megadott teljesítménytartományban
üzemeltesse.
- Aggálymentesen használható kenįanyagokat
alkalmazzon. Gondoskodjon a munkahely kielégítį szellįzésérįl. Megnövekedett kihozatal
(hozam) esetén: vizsgálja meg a sŒrített levegįs
szerszámot, szükség esetén javíttassa meg.
- Ne dolgozzon a szerszámmal olyankor, amikor
nem tud koncentrálni. Munka közben figyeljen
oda, ügyeljen arra, amit csinál, és meggondoltan
dolgozzon a sŒrített levegįs szerszámmal. Ne
használja a szerszámot, ha fáradt, ha kábítószerek, alkohol vagy gyógyszerek hatása alatt
van. A szerszámmal végzett munka közben már
egy pillanatnyi figyelmetlenség is komoly sérülésekhez vezethet.
- Tartsa tisztán és jól megvilágítva a munkaterületét. Rendetlen és megvilágítatlan munkaterületek balesetekhez vezethetnek.
- Biztosítsa, hogy a sŒrített levegįs szerszámokhoz
ne férhessenek hozzá gyermekek.
- A szabad ég alatt vagy nedves levegįn csak
megfelelį védelemmel ellátva szabad tárolni a
szerszámot.
- Gondoskodjék a sŒrített levegįs szerszám védettségérįl, kiváltképpen a sŒrített levegį csatlakozójának és a kezelįszerveknek a por és szennyezés
elleni védettségérįl.
Az adott üzemeltetési útmutatóban az egyes elįírásokat az alábbi jelöléssel láttuk el:
Veszély! Veszélyben forog a kezelį testi ép-
sége, vagy környezeti kár keletkezhet.
Figyelem. Figyelmeztetés anyagi károk fellépésének a lehetįségérįl.
4.12 Szimbólumok sŒrített levegįs szerszá-
mon
Üzembevétel elįtt olvassa el a kezelési
útmutatót.
Viseljen szemvédį
eszközt
Viseljen hallásvédį eszközt
Forgásirány
Lásd a 2. oldalt.
1 Villáskulcs
2 Rögzítįfogó anya
3 Rögzítįfogó
4 Rögzítįfogó-tartó
5 Tengely
6 Villáskulcs
7 Kapcsoló (ki- és bekapcsolás)
8 Bekapcsolásgátló
9 Szabályozócsavar a fordulatszám beállítására
10 Levegįelvezetés
11 SŒrített levegį csatlakozó szŒrįvel
12 1/4" méretŒ karmantyú
6.1 Az elsį üzemeltetés elįtt
Csavarozza be a karmantyút (12).
6.2 A rögzítįfogó behelyezése
A szerszám szárátmérįje pontosan feleljen
meg a rögzítįfogó (3) rögzítįfuratának!
Különbözį szárátmérįkhöz való rögzítįfogók
állnak rendelkezésre. Helyezze be a rögzítįfogót
(3) a rögzítįfogó-tartóba (4), és utána kézzel csavarozza fel a rögzítįfogó-anyát (2).
Ha nincs szerszám a rögzítįfogóban, akkor
villás kulccsal meghúzni nem szabad, csak
kézzel kell megszorítani!
6.3 A betétszerszám felszerelése
A kis csiszolótesteknél nem szabad túllépni a
gyártó által megadott maximálisan megenge-
dett túlnyúlást (L
0
)! Helyezze be a betétszerszámot
lehetįleg a szár teljes hosszával a rögzítįfogóba
(3). Ügyeljen arra, hogy a befogási hossz (Lg)
legalább 10 mm legyen.
A betétszerszám szárátmérįje pontosan
feleljen meg a rögzítįfogó (3) rögzítįfura-
tának!
- Rögzítse az orsót (5) a villás kulccsal (6).
- Húzza meg feszesre a rögzítįfogó-anyát (2) a
villás kulccsal (1).
- Ügyeljen a betétszerszám biztonságos illeszke-
désére.
6.4 Vegye használatba a sŒrített levegįs
szerszámot
A sŒrített levegįs szerszám teljesítményének a
teljes kihasználásához mindig legalább 9 mm belsį
átmérįjŒ sŒrítettlevegį-tömlįket használjon. Túl kis
belsį átmérį esetén lényegesen csökkenhet a
teljesítmény.
Figyelem. A sŒrítettlevegį-vezeték nem tar-
talmazhat kondenzvizet.
Figyelem. Ahhoz, hogy a szerszám hosszú
idįn át használható maradjon, elegendįen el
kell látni pneumatikaolajjal. Ez a következį módon
történhet:
– Olajozott sŒrített levegį alkalmazása ködolajozó
rászerelésével.
– Ködolajozó nélkül: kézi olajozás naponta a sŒrí-
tett levegį csatlakoztatásán át. Kb. 3-5 csepp
pneumatikaolaj az üzemelés minden 15. percében tartós használat esetén.
5. Áttekintés
6. Üzemeltetés
LoL
g
Page 47

MAGYAR hu
47
Ha a szerszám több napon át üzemen kívül volt,
kb. 5 csepp pneumatikaolajat kell kézileg bejuttatni
a sŒrített levegį csatlakozójába.
Figyelem. A szerszámot csak rövid ideig
szabad üresjáratban üzemeltetni.
1. Az alkalmas rögzítįfogó (3) kiválasztása (lásd
6.2 fejezet).
2. Az odaillį betétszerszám felszerelése (lásd 6.3
fejezet).
3. A fordulatszámot a szabályozócsavaron (9) lehet módosítani.
4. Állítsa be a munkanyomást (a levegį belépésénél mérve a sŒrített levegįs szerszám bekapcsolt állapotában). A megengedett maximális
munkanyomást lásd a „MŒszaki adatok“ fejezetben.
5. Csatlakoztassa a sŒrített levegįs szerszámot a
sŒrítettlevegį-tápellátásra.
6. Bekapcsolás: tolja a bekapcsolásgátlót (8) a
nyíl irányába (lásd az ábrát, 2. oldal) és nyomja
meg a kapcsolót (7).
Kikapcsolás: engedje el a kapcsolót (7)
.
Veszély! A szerszámon végzendį minden
munka elįtt válassza le a sŒrített levegį csat-
lakozását.
Veszély! A jelen fejezetben leírtakon túlmenį
javítási vagy karbantartási munkákat csak
szakember végezheti.
- A sŒrített levegįs szerszám biztonságáról
gondoskodjon rendszeres karbantartással.
- Ellenįrizze a csavarkötések szoros illeszkedését,
szükség esetén húzza azokat meg szorosra.
- A sŒrített levegį csatlakozójában levį szŒrįt
legalább hetente tisztítani kell.
- Ajánlott a sŒrített levegįs szerszám elé nyomás-
csökkentįt beiktatni vízleválasztóval és
olajozóval.
- Ha megnövekszik a kilépį olaj és levegį mennyi-
sége, ellenįrizze a sŒrített levegįs szerszámot,
és szükség esetén újíttassa fel. (Lásd a 9. fejezetet)
- Ellenįrizze rendszeresen, valamint minden hasz-
nálat után a fordulatszámot, és végezze el a
rezgés szintjének egyszerŒ ellenįrzését.
- Kerülje a kapcsolatba kerülést a szerszámon lera-
kódott veszélyes anyagokkal. Viseljen alkalmas
személyi védįfelszerelést, és a karbantartás elįtt
távolítsa el megfelelį intézkedések révén a
veszélyes anyagokat.
f
Csak eredeti Metabo tartozékokat használjon.
Csak olyan tartozékot használjon, amely ehhez a
sŒrített levegįs szerszámhoz készült, és megfelel
az ebben a használati utasításban megadott követelményeknek és adatoknak.
A teljes tartozékprogram a www.metabo.com
honlapon vagy a katalógusban található.
Veszély! A sŒrített levegįs szerszámokon
csak szakemberek végezhetnek javításokat
eredeti Metabo pótalkatrészekkel!
A javításra szoruló Metabo sŒrített levegįs szerszá-
mokkal forduljon Metabo szakkereskedįjéhez. A
címeket a www.metabo.com oldalon találja.
A pótalkatrészek listája letölthetį a
www.metabo.com oldalról.
A régi sŒrített levegįs szerszámok, csomagolásaik
és tartozékaik környezetbarát ártalmatlanításával
és újrahasznosításával kapcsolatban tartsa be a
helyi elįírásokat. Tilos személyek és a környezet
épségének veszélyeztetése.
Az adatok értelmezését lásd a 3. oldalon.
A változtatás jogát a mŒszaki fejlesztés érdekében
fenntartjuk.
V
1
= Levegįigény
p
max.
= maximálisan megengedett munkanyomás
n0= Fordulatszám
dS= A rögzítįfogó rögzítįfurata
D
max
= a kis csiszolótest maximális átmérįje
di= Tömlįátmérį (belsį)
C = Csatlakozómenet
A = Méretek: hossz x szélesség x magasság
m = súly
A fenti adatoknak tŒrése van (a mindenkor
érvényben levį szabványoknak megfelelįen).
Kibocsátási értékek
Ezek az értékek lehetįvé teszik a szerszám
kibocsátási jellemzįinek becslését, illetve különbözį szerszámok összehasonlítását. Az alkalmazási feltételektįl, a szerszám állapotától vagy a
használt betétszerszámoktól függįen a tényleges
környezeti terhelés nagyobb vagy kisebb is lehet. A
becsléshez vegye figyelembe a munkaszüneteket
és az alacsonyabb környezeti terheléssel járó fázisokat is. A megfelelįen alkalmazott becsült értékek
alapján írjon elį védįintézkedéseket a felhasználó
számára, illetve hozzon szervezési intézkedéseket.
Vibráció
(a gyorsulás súlyozott effektív értéke;
EN 28927):
a
h
= rezgéskibocsátási érték
K
h
=mérési bizonytalanság (rezgés)
Hangszint (EN ISO 15744):
L
pA
=hangnyomásszint
L
WA
=hangteljesítményszint
KpA, KWA= mérési bizonytalanság
Viseljen hallásvédį eszközt!
7. Karbantartás és ápolás
8. Tartozékok
9. Javítás
10. Környezetvédelem
11. MŒszaki adatok
Page 48

ȥȨȦȦȟȝȞru
48
ȣəɑɌɑɖɉɔɥɖɗɎ əɜɓɗɋɗɍɚɛɋɗ ɘɗ ɦɓɚɘɔɜɉɛɉɟɑɑ
ȡɤ ɚ ɘɗɔɖɗɒ ɗɛɋɎɛɚɛɋɎɖɖɗɚɛɥɧ ɐɉɨɋɔɨɎɕ, ɠɛɗ
ɦɛɑ ɘəɨɕɤɎ ɡɔɑɝɗɋɉɛɎɔɑ ɚɗɗɛɋɎɛɚɛɋɜɎɛ
ɖɗəɕɉɕ ɑ ɍɑəɎɓɛɑɋɉɕ, ɜɓɉɐɉɖɖɤɕ ɖɉ ɚ. 3.
Ȳɛɗɛ ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛ ɘəɎɍɖɉɐɖɉɠɎɖ:
- ...ɍɔɨ ɛɗɖɓɗɒ ɡɔɑɝɗɋɓɑ ɚ ɡɉəɗɡɓɉɕɑ;
- ...ɍɔɨ əɉɊɗɛɤ ɚ ɘəɗɝɑɔɥɖɤɕɑ ɘɗɔɑəɗɋɉɔɥɖɤɕɑ
ɖɉɚɉɍɓɉɕɑ;
- ...ɍɔɨ əɉɊɗɛɤ ɚ ɝɎɛəɗɋɤɕɑ ɘɗɔɑəɗɋɉɔɥɖɤɕɑ
ɖɉɚɉɍɓɉɕɑ;
- ...ɍɔɨ əɉɊɗɛɤ ɚ ɟɑɔɑɖɍəɑɠɎɚɓɑɕɑ ɢɫɛɓɉɕɑ ɚ
ɋɗɒɔɗɠɖɤɕɑ ɘɔɉɚɛɑɖɉɕɑ
ɑ ɨɋɔɨɎɛɚɨ ɘəɗɝɎɚɚɑɗɖɉɔɥɖɤɕ.
Ȳɓɚɘɔɜɉɛɉɟɑɨ ɦɛɗɌɗ
ɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɉ ɍɗɘɜɚɓɉɎɛɚɨ
ɛɗɔɥɓɗ ɚ ɘɗɍɉɠɎɒ ɚɏɉɛɗɌɗ ɋɗɐɍɜɞɉ. ȜɉɘəɎɢɉɎɛɚɨ ɘəɎɋɤɡɉɛɥ ɜɓɉɐɉɖɖɗɎ ɖɉ ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɎ ɕɉɓɚɑɕɉɔɥɖɗ ɍɗɘɜɚɛɑɕɗɎ əɉɊɗɠɎɎ ɍɉɋɔɎɖɑɎ.
ȜɉɘəɎɢɉɎɛɚɨ ɦɓɚɘɔɜɉɛɉɟɑɨ ɦɛɗɌɗ ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɉ ɚɗ ɋɐəɤɋɗɗɘɉɚɖɤɕɑ, Ɍɗəɧɠɑɕɑ ɑɔɑ
ɗɘɉɚɖɤɕɑ ɍɔɨ ɐɍɗəɗɋɥɨ Ɍɉɐɉɕɑ. ȢɎ ɑɚɘɗɔɥɐɗɋɉɛɥ ɋ ɓɉɠɎɚɛɋɎ əɤɠɉɌɉ, ɜɍɉəɖɗɌɗ ɑɔɑ ɍəɗɊɑɔɥɖɗɌɗ ɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɉ.
ȠɧɊɗɎ ɍəɜɌɗɎ ɑɚɘɗɔɥɐɗɋɉɖɑɎ ɨɋɔɨɎɛɚɨ ɖɎɍɗɘɜɚɛɑɕɤɕ. ȝɚɘɗɔɥɐɗɋɉɖɑɎ ɖɎ ɘɗ ɖɉɐɖɉɠɎɖɑɧ, ɑɐɕɎɖɎɖɑɨ ɓɗɖɚɛəɜɓɟɑɑ ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɉ ɑɔɑ
ɑɚɘɗɔɥɐɗɋɉɖɑɎ ɍɎɛɉɔɎɒ, ɓɗɛɗəɤɎ ɖɎ Ɋɤɔɑ ɘəɗɋɎəɎɖɤ ɑɔɑ ɍɗɘɜɢɎɖɤ ɘəɗɑɐɋɗɍɑɛɎɔɎɕ, ɕɗɌɜɛ
ɘɗɋɔɎɠɥ ɐɉ ɚɗɊɗɒ ɖɎɘəɎɍɋɑɍɎɖɖɤɒ ɕɉɛɎəɑɉɔɥɖɤɒ ɜɢɎəɊ!
Ȝɉ ɜɢɎəɊ, ɋɗɐɖɑɓɡɑɒ ɋ əɎɐɜɔɥɛɉɛɎ ɑɚɘɗɔɥɐɗɋɉɖɑɨ ɖɎ ɘɗ ɖɉɐɖɉɠɎɖɑɧ, ɗɛɋɎɛɚɛɋɎɖɖɗɚɛɥ ɖɎɚɫɛ
ɛɗɔɥɓɗ ɘɗɔɥɐɗɋɉɛɎɔɥ.
ȢɎɗɊɞɗɍɑɕɗ ɚɗɊɔɧɍɉɛɥ ɗɊɢɎɘəɑɖɨɛɤɎ ɘəɉɋɑɔɉ
ɛɎɞɖɑɓɑ ɊɎɐɗɘɉɚɖɗɚɛɑ, ɉ ɛɉɓɏɎ ɜɓɉɐɉɖɑɨ,
ɘəɑɔɉɌɉɎɕɤɎ ɓ ɍɉɖɖɗɕɜ
əɜɓɗɋɗɍɚɛɋɜ.
șɔɨ ɋɉɡɎɒ ɚɗɊɚɛɋɎɖɖɗɒ ɊɎɐɗɘɉɚɖɗɚɛɑ
ɑ ɐɉɢɑɛɤ ɋɉɡɎɌɗ ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɉ
ɗɛ ɘɗɋəɎɏɍɎɖɑɒ ɚɗɊɔɧɍɉɒɛɎ
ɜɓɉɐɉɖɑɨ, ɗɛɕɎɠɎɖɖɤɎ ɍɉɖɖɤɕ
ɚɑɕɋɗɔɗɕ.
ȤȥȚșȨȤȥȚțșȚȢȝȚ! șɔɨ ɚɖɑɏɎɖɑɨ
əɑɚɓɉ ɛəɉɋɕɑəɗɋɉɖɑɨ ɘəɗɠɛɑɛɎ əɜɓɗɋɗɍɚɛɋɗ ɘɗ ɦɓɚɘɔɜɉɛɉɟɑɑ.
ȤȥȚșȨȤȥȚțșȚȢȝȚ! ȤəɗɠɛɑɛɎ ɋɚɎ
ɑɖɚɛəɜɓɟɑɑ ɑ ɜɓɉɐɉɖɑɨ ɘɗ ɛɎɞɖɑɓɎ
ɊɎɐɗɘɉɚɖɗɚɛɑ. ȢɎɋɤɘɗɔɖɎɖɑɎ ɑɖɚɛəɜɓɟɑɒ ɑ
ɜɓɉɐɉɖɑɒ ɘɗ ɛɎɞɖɑɓɎ ɊɎɐɗɘɉɚɖɗɚɛɑ ɕɗɏɎɛ
ɘəɑɋɎɚɛɑ ɓ ɘɗəɉɏɎɖɑɧ ɦɔɎɓɛəɑɠɎɚɓɑɕ ɛɗɓɗɕ,
ɋɗɐɌɗəɉɖɑɧ ɑ/ɑɔɑ ɓ ɘɗɔɜɠɎɖɑɧ ɛɨɏɎɔɤɞ ɛəɉɋɕ.
ȦɗɞəɉɖɑɛɎ ɋɚɎ ɑɖɚɛəɜɓɟɑɑ ɑ ɜɓɉɐɉɖɑɨ ɘɗ
ɛɎɞɖɑɓɎ ɊɎɐɗɘɉɚɖɗɚɛɑ.
ȤɎəɎɍɉɋɉɒɛɎ ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛ ɚɔɎɍɜɧɢɎɕɜ
ɋɔɉɍɎɔɥɟɜ ɛɗɔɥɓɗ ɋɕɎɚɛɎ ɚ ɦɛɑɕɑ ɍɗɓɜɕɎɖɛɉɕɑ.
- ȤɗɔɥɐɗɋɉɛɎɔɥ ɑɔɑ əɉɊɗɛɗɍɉɛɎɔɥ ɍɗɔɏɖɤ
ɗɟɎɖɑɛɥ ɋɚɎ ɘɗɛɎɖɟɑɉɔɥɖɤɎ ɗɘɉɚɖɗɚɛɑ,
ɓɗɛɗəɤɎ ɕɗɌɜɛ ɋɗɐɖɑɓɉɛɥ ɘəɑ ɓɉɏɍɗɕ ɑɚɘɗɔɥɐɗɋɉɖɑɑ ɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɉ.
- ȤɎəɎɍ ɖɉɔɉɍɓɗɒ, ɦɓɚɘɔɜɉɛɉɟɑɎɒ, əɎɕɗɖɛɗɕ,
ɛɎɞɖɑɠɎɚɓɑɕ ɗɊɚɔɜɏɑɋɉɖɑɎɕ ɑ ɐɉɕɎɖɗɒ
ɘəɑɖɉɍɔɎɏɖɗɚɛɎɒ, ɉ ɛɉɓɏɎ ɘɎəɎɍ ɖɉɠɉɔɗɕ
əɉɊɗɛ ɋɊɔɑɐɑ ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɉ ɚɔɎɍɜɎɛ
ɗɐɖɉɓɗɕɑɛɥɚɨ ɚ ɜɓɉɐɉɖɑɨɕɑ ɘɗ ɛɎɞɖɑɓɎ
ɊɎɐɗɘɉɚɖɗɚɛɑ. ȗ ɘəɗɛɑɋɖɗɕ ɚɔɜɠɉɎ ɋɗɐɕɗɏɖɗ
ɘɗɔɜɠɎɖɑɎ ɚɎəɥɫɐɖɤɞ ɛɎɔɎɚɖɤɞ ɘɗɋəɎɏɍɎɖɑɒ.
- ȟ ɖɉɔɉɍɓɎ, əɎɌɜɔɑəɗɋɓɎ ɑɔɑ ɑɚɘɗɔɥɐɗɋɉɖɑɧ
ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɉ ɍɗɘɜɚɓɉɎɛɚɨ ɛɗɔɥɓɗ
ɓɋɉɔɑɝɑɟɑəɗɋɉɖɖɤɒ ɑ ɗɊɜɠɎɖɖɤɒ ɘɎəɚɗɖɉɔ.
- ȝɐɕɎɖɎɖɑɨ ɓɗɖɚɛəɜɓɟɑɑ/ɕɗɍɑɝɑɓɉɟɑɑ ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɉ ɖɎ ɍɗɘɜɚɓɉɧɛɚɨ. ȝɐɕɎɖɎɖɑɨ
ɓɗɖɚɛəɜɓɟɑɑ ɕɗɌɜɛ ɚɖɑɐɑɛɥ ɦɝɝɎɓɛɑɋɖɗɚɛɥ
ɕɎə ɘɗ ɐɉɢɑɛɎ ɑ ɘɗɋɤɚɑɛɥ ɚɛɎɘɎɖɥ ɜɌəɗɐɤ ɍɔɨ
ɘɗɔɥɐɗɋɉɛɎɔɨ.
- ȟɉɛɎɌɗəɑɠɎɚɓɑ ɐɉɘəɎɢɉɎɛɚɨ ɑɚɘɗɔɥɐɗɋɉɛɥ
ɘɗɋəɎɏɍɫɖɖɤɎ ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɤ. ȗɖɑɕɉɛɎɔɥɖɗ ɚɔɎɍɑɛɎ ɐɉ ɚɗɚɛɗɨɖɑɎɕ ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɗɋ. ȥɎɌɜɔɨəɖɗ ɘəɗɋɎəɨɒɛɎ ɑɚɘəɉɋɖɗɚɛɥ
ɝɜɖɓɟɑɗɖɑəɗɋɉɖɑɨ ɘɗɍɋɑɏɖɤɞ ɦɔɎɕɎɖɛɗɋ,
ɔɫɌɓɗɚɛɥ ɑɞ ɞɗɍɉ, ɟɎɔɗɚɛɖɗɚɛɥ ɋɚɎɞ ɍɎɛɉɔɎɒ ɑ
ɗɛɚɜɛɚɛɋɑɎ ɘɗɋəɎɏɍɎɖɑɒ, ɓɗɛɗəɤɎ ɕɗɌɔɑ Ɋɤ
ɗɛəɑɟɉɛɎɔɥɖɗ ɚɓɉɐɉɛɥɚɨ ɖɉ əɉɊɗɛɎ ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɉ. ȤəɗɋɎəɨɒɛɎ ɖɉɔɑɠɑɎ ɑ əɉɐɊɗəɠɑɋɗɚɛɥ ɛɉɊɔɑɠɎɓ ɑ ɖɉɍɘɑɚɎɒ. ȦɍɉɋɉɒɛɎ ɑɔɑ
ɐɉɕɎɖɨɒɛɎ ɘɗɋəɎɏɍɫɖɖɤɎ ɠɉɚɛɑ ɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɉ
ɋ əɎɕɗɖɛ ɍɗ ɎɌɗ ɑɚɘɗɔɥɐɗɋɉɖɑɨ. Ȥəɑɠɑɖɗɒ
Ɋɗɔɥɡɑɖɚɛɋɉ ɖɎɚɠɉɚɛɖɤɞ ɚɔɜɠɉɎɋ ɨɋɔɨɎɛɚɨ
ɖɎɚɗɊɔɧɍɎɖɑɎ ɘəɉɋɑɔ ɛɎɞɖɑɠɎɚɓɗɌɗ ɗɊɚɔɜɏɑɋɉɖɑɨ ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɗɋ.
4.1 ȣɘɉɚɖɗɚɛɑ ɋɚɔɎɍɚɛɋɑɎ ɗɛɔɎɛɉɖɑɨ
ɍɎɛɉɔɎɒ
- ȗ ɚɔɜɠɉɎ ɘɗɔɗɕɓɑ ɐɉɌɗɛɗɋɓɑ, ɘəɑɖɉɍɔɎɏɖɗɚɛɎɒ ɑɔɑ ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɉ ɍɎɛɉɔɑ ɕɗɌɜɛ
ɗɛɔɎɛɉɛɥ ɋ əɉɐɖɤɎ ɚɛɗəɗɖɤ ɚ ɋɤɚɗɓɗɒ ɚɓɗəɗɚɛɥɧ.
- Ȥəɑ ɦɓɚɘɔɜɉɛɉɟɑɑ, ɐɉɕɎɖɎ ɘəɑɖɉɍɔɎɏɖɗɚɛɎɒ,
ɉ ɛɉɓɏɎ ɋ ɞɗɍɎ
əɎɕɗɖɛɉ ɑɔɑ ɛɎɞɖɑɠɎɚɓɗɌɗ
ɗɊɚɔɜɏɑɋɉɖɑɨ ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɉ ɚɔɎɍɜɎɛ
ɋɚɎɌɍɉ ɖɉɍɎɋɉɛɥ ɜɍɉəɗɘəɗɠɖɤɎ ɐɉɢɑɛɖɤɎ
ɗɠɓɑ. ȦɛɎɘɎɖɥ ɛəɎɊɜɎɕɗɒ ɐɉɢɑɛɤ ɚɔɎɍɜɎɛ
ɗɟɎɖɑɋɉɛɥ ɍɔɨ ɓɉɏɍɗɌɗ ɚɔɜɠɉɨ ɗɛɍɎɔɥɖɗ.
- ȨɊɎɍɑɛɎɚɥ ɋ ɛɗɕ, ɠɛɗ ɐɉɌɗɛɗɋɓɉ ɖɉɍɫɏɖɗ
ɐɉɓəɎɘɔɎɖɉ.
- ȦɔɎɍɜɎɛ əɎɌɜɔɨəɖɗ ɘəɗɋɎəɨɛɥ, ɖɎ ɘəɎɋɤɡɉɎɛ
ɔɑ ɠɉɚɛɗɛɉ ɋəɉɢɎɖɑɨ ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɉ
ɐɖɉɠɎɖɑɎ ɠɉɚɛɗɛɤ ɋəɉɢɎɖɑɨ, ɜɓɉɐɉɖɖɗɎ ɖɉ
ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɎ. ȤəɗɋɎəɓɜ ɠɉɚɛɗɛɤ
ɋəɉɢɎɖɑɨ ɚɔɎɍɜɎɛ ɋɤɘɗɔɖɨɛɥ ɘəɑ ɚɖɨɛɗɕ
ɚɕɎɖɖɗɕ ɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɎ. ȤɗɍɗɊɖɤɎ ɘəɗɋɎəɓɑ
ɕɗɏɎɛ ɋɤɘɗɔɖɨɛɥ ɚɎəɋɑɚɖɉɨ ɚɔɜɏɊɉ Metabo.
1. șɎɓɔɉəɉɟɑɨ ɚɗɗɛɋɎɛɚɛɋɑɨ
2. ȝɚɘɗɔɥɐɗɋɉɖɑɎ ɘɗ
ɖɉɐɖɉɠɎɖɑɧ
3. ȣɊɢɑɎ ɜɓɉɐɉɖɑɨ ɘɗ ɛɎɞɖɑɓɎ
ɊɎɐɗɘɉɚɖɗɚɛɑ
4. ȦɘɎɟɑɉɔɥɖɤɎ ɜɓɉɐɉɖɑɨ ɘɗ
ɛɎɞɖɑɓɎ ɊɎɐɗɘɉɚɖɗɚɛɑ
Page 49

ȥȨȦȦȟȝȞ ru
49
- ȨɊɎɍɑɛɎɚɥ ɋ ɛɗɕ, ɠɛɗ ɋɗɐɖɑɓɉɧɢɑɎ ɘəɑ ɋɤɘɗɔ-
ɖɎɖɑɑ əɉɊɗɛ ɑɚɓəɤ ɑ ɗɚɓɗɔɓɑ ɖɎ ɘəɎɍɚɛɉɋɔɨɧɛ
ɗɘɉɚɖɗɚɛɑ.
- ȣɛɚɗɎɍɑɖɨɒɛɎ ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛ ɗɛ ɚɑɚɛɎɕɤ
ɘɗɍɉɠɑ ɚɏɉɛɗɌɗ ɋɗɐɍɜɞɉ ɘɎəɎɍ ɐɉɕɎɖɗɒ əɉɊɗɠɎɌɗ (ɚɕɎɖɖɗɌɗ) ɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɉ/ɘəɑɖɉɍɔɎɏɖɗɚɛɎɒ, əɎɌɜɔɑəɗɋɓɗɒ, ɛɎɞɖɑɠɎɚɓɑɕ ɗɊɚɔɜɏɑɋɉɖɑɎɕ ɑɔɑ ɗɠɑɚɛɓɗɒ.
- ȨɊɎɍɑɛɎɚɥ ɋ ɗɛɚɜɛɚɛɋɑɑ ɗɘɉɚɖɗɚɛɎɒ ɍɔɨ
ɍəɜɌɑɞ ɔɑɟ.
4.2 ȣɘɉɚɖɗɚɛɑ ɋɚɔɎɍɚɛɋɑɎ ɐɉɞɋɉɛɉ/ɖɉɕɉ-
ɛɤɋɉɖɑɨ
- ȥɉɊɗɛɉɒɛɎ
ɋ ɘɗɍɞɗɍɨɢɎɒ (ɚɘɎɟɑɉɔɥɖɗɒ)
ɗɍɎɏɍɎ. ȢɎ ɖɉɍɎɋɉɒɛɎ ɘəɗɚɛɗəɖɜɧ ɗɍɎɏɍɜ
ɑɔɑ ɜɓəɉɡɎɖɑɨ. ȣɊɎəɎɌɉɒɛɎ ɋɗɔɗɚɤ, ɗɍɎɏɍɜ ɑ
ɘɎəɠɉɛɓɑ ɘɗɍɉɔɥɡɎ ɗɛ ɋəɉɢɉɧɢɑɞɚɨ ɜɐɔɗɋ
ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɉ. ȦɋɗɊɗɍɖɉɨ ɗɍɎɏɍɉ,
ɜɓəɉɡɎɖɑɨ ɑɔɑ ɍɔɑɖɖɤɎ ɋɗɔɗɚɤ ɕɗɌɜɛ Ɋɤɛɥ
ɐɉɞɋɉɠɎɖɤ ɑɕɑ. ȣɘɉɚɖɗɚɛɥ ɛəɉɋɕɑəɗɋɉɖɑɨ!
4.3 ȣɘɉɚɖɗɚɛɑ ɋ ɞɗɍɎ ɦɓɚɘɔɜɉɛɉɟɑɑ
- ȝɐɊɎɌɉɒɛɎ ɓɗɖɛɉɓɛɉ ɚ ɋəɉɢɉɧɢɑɕɚɨ ɞɋɗɚɛɗɋɑɓɗɕ ɑ ɚɕɎɖɖɤɕ ɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɗɕ, ɠɛɗɊɤ ɖɎ
ɍɗɘɜɚɛɑɛɥ ɘɗəɎɐɗɋ ɓɑɚɛɎɒ əɜɓ ɑ ɍəɜɌɑɞ ɠɉɚɛɎɒ
ɛɎɔɉ.
- Ȥəɑ əɉɊɗɛɎ ɚ ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɗɕ ɓɑɚɛɑ əɜɓ
ɘɗɔɥɐɗɋɉɛɎɔɨ ɘɗɍɋɎəɌɉɧɛɚɨ əɉɐɔɑɠɖɤɕ
ɗɘɉɚɖɗɚɛɨɕ, ɖɉɘəɑɕɎə ɘɗəɎɐɉɕ, ɚɚɉɍɑɖɉɕ ɑ
ɖɉɌəɎɋɜ. șɔɨ ɐɉɢɑɛɤ əɜɓ ɖɉɍɎɋɉɒɛɎ ɘɗɍɞɗɍɨɢɑɎ ɘɎəɠɉɛɓɑ.
- ȤɗɔɥɐɗɋɉɛɎɔɥ ɑ ɗɊɚɔɜɏɑɋɉɧɢɑɒ ɘɎəɚɗɖɉɔ
ɍɗɔɏɖɤ Ɋɤɛɥ ɋ ɚɗɚɛɗɨɖɑɑ ɗɊəɉɢɉɛɥɚɨ ɚ ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɗɕ ɚ ɜɠɫɛɗɕ ɎɌɗ əɉɐɕɎəɗɋ, ɋɎɚɉ
ɑ ɕɗɢɖɗɚɛɑ.
- Ȥəɉɋɑɔɥɖɗ ɍɎəɏɑɛɎ ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛ:
ɊɜɍɥɛɎ Ɍɗɛɗɋɤ ɚəɎɉɌɑəɗɋɉɛɥ ɖɉ ɗɏɑɍɉɎɕɤɎ ɑ
ɖɎɗɏɑɍɉɖɖɤɎ ɍɋɑɏɎɖɑɨ — ɍɎəɏɑɛɎ ɗɊɎ əɜɓɑ
ɖɉɌɗɛɗɋɎ!
- ȤəɑɕɑɛɎ ɜɚɛɗɒɠɑɋɗɎ ɘɗɔɗɏɎɖɑɎ ɑ ɗɊɎɚɘɎɠɥɛɎ
ɖɉɍɫɏɖɤɒ ɞɋɉɛ ɦɔɎɓɛəɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɉ ɍɔɨ
ɚɗɞəɉɖɎɖɑɨ əɉɋɖɗɋɎɚɑɨ ɋ ɔɧɊɗɒ əɉɊɗɠɎɒ ɚɑɛɜɉɟɑɑ.
- ȝɐɊɎɌɉɒɛɎ ɖɎɘəɎɍɖɉɕɎəɎɖɖɗɌɗ ɋɓɔɧɠɎɖɑɨ
ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɉ. ȗ ɚɔɜɠɉɎ ɘəɎəɤɋɉɖɑɨ
ɘɗɍɉɠɑ ɋɗɐɍɜɞɉ ɋɤɓɔɧɠɑɛɎ ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛ
ɚ ɘɗɕɗɢɥɧ ɋɤɓɔɧɠɉɛɎɔɨ.
- ȝɚɘɗɔɥɐɜɒɛɎ ɛɗɔɥɓɗ əɎɓɗɕɎɖɍɗɋɉɖɖɤɎ ɑɐɌɗɛɗɋɑɛɎɔɎɕ Ȧȣț.
- ȤɗɔɥɐɜɒɛɎɚɥ ɚəɎɍɚɛɋɉɕɑ ɑɖɍɑɋɑɍɜɉɔɥɖɗɒ
ɐɉɢɑɛɤ ɑ ɋɚɎɌɍɉ ɖɉɍɎɋɉɒɛɎ ɐɉɢɑɛɖɤɎ ɗɠɓɑ.
ȝɚɘɗɔɥɐɗɋɉɖɑɎ ɚəɎɍɚɛɋ ɑɖɍɑɋɑɍɜɉɔɥɖɗɒ
ɐɉɢɑɛɤ, ɖɉɘəɑɕɎə ɐɉɢɑɛɖɤɞ ɘɎəɠɉɛɗɓ,
ɐɉɢɑɛɖɗɒ ɗɍɎɏɍɤ, əɎɚɘɑəɉɛɗəɉ, ɖɎɚɓɗɔɥɐɨɢɎɒ ɐɉɢɑɛɖɗɒ ɗɊɜɋɑ, ɐɉɢɑɛɖɗɌɗ ɡɔɎɕɉ ɑɔɑ
ɐɉɢɑɛɖɤɞ ɖɉɜɡɖɑɓɗɋ, ɋ ɐɉɋɑɚɑɕɗɚɛɑ ɗɛ ɋɑɍɉ ɑ
ɗɊɔɉɚɛɑ ɘəɑɕɎɖɎɖɑɨ ɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɉ ɚɖɑɏɉɎɛ
əɑɚɓ ɛəɉɋɕɑəɗɋɉɖɑɨ ɑ ɘɗɦɛɗɕɜ ɖɉɚɛɗɨɛɎɔɥɖɗ
əɎɓɗɕɎɖɍɜɎɛɚɨ.
- șɗɘɜɚɛɑɕɉɨ ɠɉɚɛɗɛɉ ɋəɉɢɎɖɑɨ əɉɊɗɠɎɌɗ
ɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɉ ɍɗɔɏɖɉ Ɋɤɛɥ ɖɎ ɖɑɏɎ ɕɉɓɚɑɕɉɔɥɖɗɒ ɠɉɚɛɗɛɤ ɋəɉɢɎɖɑɨ, ɜɓɉɐɉɖɖɗɒ ɖɉ
ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɎ. ȤəɑɖɉɍɔɎɏɖɗɚɛɑ,
ɋəɉɢɉɧɢɑɎɚɨ ɚ ɘəɎɋɤɡɎɖɑɎɕ ɍɗɘɜɚɛɑɕɗɒ
ɚɓɗəɗɚɛɑ, ɕɗɌɜɛ əɉɐəɜɡɑɛɥɚɨ.
- Ȥəɑ ɋɤɘɗɔɖɎɖɑɑ əɉɊɗɛ ɖɉɍ Ɍɗɔɗɋɗɒ ɖɉɍɎɋɉɒɛɎ
ɐɉɢɑɛɖɤɒ ɡɔɎɕ.
- ȤɗɚɔɎ ɋɤɓɔɧɠɎɖɑɨ ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɉ
əɉɊɗɠɑɒ ɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛ Ɏɢɫ ɖɎɓɗɛɗəɗɎ ɋəɎɕɨ
əɉɊɗɛɉɎɛ ɘɗ ɑɖɎəɟɑɑ.
- ȤɗɐɉɊɗɛɥɛɎɚɥ ɗ ɛɗɕ, ɠɛɗɊɤ ɋɗɐɖɑɓɉɧɢɑɎ ɘəɑ
ɋɤɘɗɔɖɎɖɑɑ əɉɊɗɛ ɑɚɓəɤ ɖɎ ɘəɎɍɚɛɉɋɔɨɔɑ
ɗɘɉɚɖɗɚɛɑ. Ȥəɑ ɗɊəɉɊɗɛɓɎ ɓɗɖɚɛəɜɓɟɑɗɖɖɤɞ
ɕɉɛɎəɑɉɔɗɋ ɋɗɐɕɗɏɖɗ ɘɗɨɋɔɎɖɑɎ ɋɐəɤɋɗɗɘɉɚɖɗɒ ɑɔɑ ɌɗəɧɠɎɒ ɘɤɔɑ. ȗ əɎɐɜɔɥɛɉɛɎ ɦɛɗɌɗ
ɚɜɢɎɚɛɋɜɎɛ əɑɚɓ ɋɐəɤɋɉ ɑɔɑ ɋɗɐɌɗəɉɖɑɨ.
4.4 ȣɘɉɚɖɗɚɛɑ ɋɚɔɎɍɚɛɋɑɎ ɘɗɋɛɗəɨɧ-
ɢɑɞɚɨ ɍɎɒɚɛɋɑɒ
- Ȥəɑ ɋɤɘɗɔɖɎɖɑɑ əɉɊɗɛ ɚ ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɗɕ
ɋɗɐɕɗɏɖɗ ɘɗɨɋɔɎɖɑɨ ɖɎɘəɑɨɛɖɤɞ ɗɢɜɢɎɖɑɒ ɋ
ɓɑɚɛɨɞ əɜɓ, ɘəɎɍɘɔɎɠɥɨɞ, ɘɔɎɠɉɞ, ɋ ɗɊɔɉɚɛɑ
ɡɎɑ ɑɔɑ ɍəɜɌɑɞ ɠɉɚɛɨɞ ɛɎɔɉ.
- ȤəɑɖɑɕɉɒɛɎ ɘəɉɋɑɔɥɖɗɎ ɘɗɔɗɏɎɖɑɎ ɍɔɨ
əɉɊɗɛɤ ɚ ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɗɕ, ɗɊəɉɢɉɒɛɎ
ɋɖɑɕɉɖɑɎ ɖɉ ɊɎɐɗɘɉɚɖɗɚɛɥ ɑ ɑɐɊɎɌɉɒɛɎ
əɉɊɗɛɤ ɋ ɛɉɓɑɞ ɘɗɔɗɏɎɖɑɨɞ, ɋ ɓɗɛɗəɤɞ ɋɉɕ
ɚɔɗɏɖɗ ɚɗɞəɉɖɑɛɥ əɉɋɖɗɋɎɚɑɎ ɑ ɓɗɛɗəɤɎ
ɍɗɚɛɉɋɔɨɧɛ ɋɉɕ ɍɑɚɓɗɕɝɗəɛ. ȗ ɞɗɍɎ ɖɎɘəɎəɤɋɖɗɒ əɉɊɗɛɤ ɘɗɔɥɐɗɋɉɛɎɔɥ ɍɗɔɏɎɖ ɕɎɖɨɛɥ
ɘɗɔɗɏɎɖɑɎ ɛɎɔɉ ɋɗ ɑɐɊɎɏɉɖɑɎ ɘɗɨɋɔɎɖɑɨ
ɜɚɛɉɔɗɚɛɑ ɑ ɍɑɚɓɗɕɝɗəɛɉ.
- ȢɎɔɥɐɨ ɑɌɖɗəɑəɗɋɉɛɥ ɛɉɓɑɎ ɚɑɕɘɛɗɕɤ ɓɉɓ
ɘəɗɍɗɔɏɑɛɎɔɥɖɗɎ ɖɎɍɗɕɗɌɉɖɑɎ, ɖɉəɜɡɎɖɑɎ
ɚɎəɍɟɎɊɑɎɖɑɨ, ɘɗɨɋɔɎɖɑɎ ɊɗɔɎɒ, «ɕɜəɉɡɎɓ»,
ɗɖɎɕɎɖɑɨ. ȤɗɔɥɐɗɋɉɛɎɔɥ ɍɗɔɏɎɖ ɜɋɎɍɗɕɑɛɥ
ɗɊ ɦɛɗɕ ɚɋɗɎɌɗ əɉɊɗɛɗɍɉɛɎɔɨ ɑ ɘəɗɓɗɖɚɜɔɥɛɑəɗɋɉɛɥɚɨ ɚ ɋəɉɠɗɕ-ɚɘɎɟɑɉɔɑɚɛɗɕ.
4.5 ȣɘɉɚɖɗɚɛɑ ɗɛ ɑɚɘɗɔɥɐɜɎɕɗɒ ɗɚɖɉɚɛɓɑ
(ɘəɑɖɉɍɔɎɏɖɗɚɛɎɒ)
- ȣɛɚɗɎɍɑɖɨɒɛɎ ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛ ɗɛ ɚɑɚɛɎɕɤ
ɘɗɍɉɠɑ ɚɏɉɛɗɌɗ ɋɗɐɍɜɞɉ ɘɎəɎɍ ɜɚɛɉɖɗɋɓɗɒ ɑɔɑ
ɐɉɕɎɖɗɒ ɚɕɎɖɖɗɌɗ ɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɉ/ɘəɑɖɉɍɔɎɏɖɗɚɛɎɒ.
- ȝɚɘɗɔɥɐɜɒɛɎ ɛɗɔɥɓɗ ɛɎ ɘəɑɖɉɍɔɎɏɖɗɚɛɑ,
ɓɗɛɗəɤɎ ɚɘɎɟɑɉɔɥɖɗ ɘəɎɍɖɉɐɖɉɠɎɖɤ ɍɔɨ ɦɛɗɌɗ
ɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɉ ɑ ɗɛɋɎɠɉɧɛ ɛəɎɊɗɋɉɖɑɨɕ ɑ
ɞɉəɉɓɛɎəɑɚɛɑɓɉɕ, ɘəɑɋɗɍɑɕɤɕ ɋ ɖɉɚɛɗɨɢɎɕ əɜɓɗɋɗɍɚɛɋɎ ɘɗ ɦɓɚɘɔɜɉɛɉɟɑɑ.
- ȝɐɊɎɌɉɒɛɎ ɘəɨɕɗɌɗ ɓɗɖɛɉɓɛɉ ɚ əɉɊɗɠɑɕ
ɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɗɕ ɋɗ ɋəɎɕɨ əɉɊɗɛɤ ɑ ɚəɉɐɜ ɘɗɚɔɎ
ɖɎɫ, ɛɉɓ ɓɉɓ ɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛ ɕɗɏɎɛ Ɋɤɛɥ Ɍɗəɨɠɑɕ
ɑɔɑ ɑɕɎɛɥ ɗɚɛəɤɎ ɓəɗɕɓɑ.
- șɗɘɜɚɛɑɕɉɨ ɠɉɚɛɗɛɉ ɋəɉɢɎɖɑɨ əɉɊɗɠɎɌɗ
ɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɉ ɍɗɔɏɖɉ Ɋɤɛɥ ɖɎ ɖɑɏɎ ɕɉɓɚɑɕɉɔɥɖɗɒ ɠɉɚɛɗɛɤ ɋəɉɢɎɖɑɨ, ɜɓɉɐɉɖɖɗɒ ɖɉ
ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɎ. ȤəɑɖɉɍɔɎɏɖɗɚɛɑ,
ɋəɉɢɉɧɢɑɎɚɨ ɚ ɘəɎɋɤɡɎɖɑɎɕ ɍɗɘɜɚɛɑɕɗɒ
ɚɓɗəɗɚɛɑ, ɕɗɌɜɛ əɉɐəɜɡɑɛɥɚɨ.
- ȟɉɛɎɌɗəɑɠɎɚɓɑ ɐɉɘəɎɢɉɎɛɚɨ ɜɚɛɉɖɉɋɔɑɋɉɛɥ
ɉɊəɉɐɑɋɖɤɎ/ɗɛəɎɐɖɤɎ ɓəɜɌɑ ɑɔɑ ɝəɎɐɤ. Ƞɗɕɉɧɢɑɒɚɨ ɉɊəɉɐɑɋɖɤɒ ɓəɜɌ ɕɗɏɎɛ ɚɛɉɛɥ
ɘəɑɠɑɖɗɒ ɗɠɎɖɥ ɛɨɏɫɔɤɞ ɑ ɍɉɏɎ ɚɕɎəɛɎɔɥɖɤɞ
ɛəɉɋɕ.
- ȢɎ ɑɚɘɗɔɥɐɜɒɛɎ ɓəɜɌɑ, ɓɗɛɗəɤɎ ɕɗɌɜɛ ɖɎəɉɋɖɗɕɎəɖɗ ɋəɉɢɉɛɥɚɨ, əɉɚɛəɎɚɓɉɛɥɚɨ ɑɔɑ ɚɗɚɓɗɠɑɛɥ ɋɖɑɐ.
- ȥɉɐəɎɡɉɎɛɚɨ ɑɚɘɗɔɥɐɗɋɉɛɥ ɛɗɔɥɓɗ ɍɗɘɜɢɎɖɖɤɎ ɚɕɎɖɖɤɎ ɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɤ ɚ ɞɋɗɚɛɗɋɑɓɗɕ
ɘɗɍɞɗɍɨɢɎɌɗ ɍɑɉɕɎɛəɉ.
- ȦɔɎɍɜɒɛɎ ɜɓɉɐɉɖɑɨɕ ɘəɗɑɐɋɗɍɑɛɎɔɨ ɉɊəɉɐɑɋɖɤɞ Ɍɗɔɗɋɗɓ. ȗ ɚɔɜɠɉɎ ɑɚɘɗɔɥɐɗɋɉɖɑɨ
ɉɊəɉɐɑɋɖɤɞ Ɍɗɔɗɋɗɓ ɐɉɘəɎɢɉɎɛɚɨ ɘəɎɋɤɡɉɛɥ
Page 50

ȥȨȦȦȟȝȞru
50
ɜɓɉɐɉɖɖɤɒ ɘəɗɑɐɋɗɍɑɛɎɔɎɕ ɕɉɓɚɑɕɉɔɥɖɗ
ɍɗɘɜɚɛɑɕɤɒ ɋɤɔɎɛ (L0=ɍɔɑɖɉ ɞɋɗɚɛɗɋɑɓɉ
ɕɎɏɍɜ ɓɗɖɟɗɕ ɟɉɖɌɗɋɗɌɗ ɐɉɏɑɕɉ ɑ ɉɊəɉɐɑɋɖɗɒ Ɍɗɔɗɋɓɗɒ)! ȗ ɚɔɜɠɉɎ ɘəɎɋɤɡɎɖɑɨ
ɋɤɔɎɛɉ (L0) ɖɎɗɊɞɗɍɑɕɗ ɚɖɑɐɑɛɥ ɍɗɘɜɚɛɑɕɜɧ
ɠɉɚɛɗɛɜ ɋəɉɢɎɖɑɨ. ȗɚɛɉɋɔɨɒɛɎ əɉɊɗɠɑɒ
ɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛ ɋ ɟɉɖɌɗɋɤɒ ɐɉɏɑɕ ɘɗ ɋɗɐɕɗɏɖɗɚɛɑ ɖɉ ɋɚɧ ɍɔɑɖɜ ɞɋɗɚɛɗɋɑɓɉ. ȨɊɎɍɑɛɎɚɥ ɋ
ɛɗɕ, ɠɛɗ ɍɔɑɖɉ ɐɉɏɑɕɉɎɕɗɒ ɠɉɚɛɑ (Lg) ɚɗɚɛɉɋɔɨɎɛ ɖɎ ɕɎɖɎɎ 10 ɕɕ.
- șɑɉɕɎɛə ɞɋɗɚɛɗɋɑɓɉ əɉɊɗɠɎɌɗ ɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɉ
ɍɗɔɏɎɖ ɛɗɠɖɗ ɚɗɗɛɋɎɛɚɛɋɗɋɉɛɥ ɍɑɉɕɎɛəɜ
ɗɛɋɎəɚɛɑɨ ɟɉɖɌɗɋɗɌɗ ɐɉɏɑɕɉ!
4.6 ȣɘɉɚɖɗɚɛɑ ɖɉ əɉɊɗɠɎɕ ɕɎɚɛɎ
- ȤɗɚɓɉɔɥɐɤɋɉɖɑɎ, ɚɘɗɛɤɓɉɖɑɎ ɑ ɘɉɍɎɖɑɎ ɨɋɔɨɧɛɚɨ ɗɚɖɗɋɖɤɕɑ ɘəɑɠɑɖɉɕɑ ɛəɉɋɕɑəɗɋɉɖɑɨ
ɖɉ əɉɊɗɠɎɕ ɕɎɚɛɎ. ȣɊəɉɢɉɒɛɎ ɋɖɑɕɉɖɑɎ ɖɉ
ɘɗɋɎəɞɖɗɚɛɑ, ɓɗɛɗəɤɎ ɋ əɎɐɜɔɥɛɉɛɎ ɑɚɘɗɔɥɐɗɋɉɖɑɨ ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɉ ɕɗɌɜɛ ɚɛɉɛɥ ɚɓɗɔɥɐɓɑɕɑ, ɉ ɛɉɓɏɎ ɖɉ
ɗɘɉɚɖɗɚɛɥ ɚɘɗɛɓɖɜɛɥɚɨ ɗ
ɋɗɐɍɜɡɖɤɒ ɡɔɉɖɌ.
- Ȥəɑ ɋɤɘɗɔɖɎɖɑɑ əɉɊɗɛ ɋ ɖɎɐɖɉɓɗɕɤɞ ɜɚɔɗɋɑɨɞ ɚɗɊɔɧɍɉɒɛɎ ɗɚɛɗəɗɏɖɗɚɛɥ: ɋɗɐɕɗɏɖɗ
ɖɉɔɑɠɑɎ ɚɓəɤɛɗɒ ɘəɗɋɗɍɓɑ ɘɗɍ ɦɔɎɓɛəɑɠɎɚɓɑɕ ɖɉɘəɨɏɎɖɑɎɕ.
- ȤɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛ ɖɎ ɘəɎɍɖɉɐɖɉɠɎɖ ɍɔɨ
ɑɚɘɗɔɥɐɗɋɉɖɑɨ ɋɗ ɋɐəɤɋɗɗɘɉɚɖɗɒ ɋɗɐɍɜɡɖɗɒ
ɚəɎɍɎ ɑ ɖɎ ɑɐɗɔɑəɗɋɉɖ ɗɛ ɓɗɖɛɉɓɛɉ ɚ ɑɚɛɗɠɖɑɓɉɕɑ ɦɔɎɓɛəɑɠɎɚɓɗɌɗ ɛɗɓɉ.
- ȨɊɎɍɑɛɎɚɥ, ɠɛɗ ɋ ɛɗɕ ɕɎɚɛɎ, ɌɍɎ Ɋɜɍɜɛ ɘəɗɑɐɋɗɍɑɛɥɚɨ əɉɊɗɛɤ, ɖɎ ɘəɗɞɗɍɨɛ ɔɑɖɑɑ ɦɔɎɓɛəɗ-,
ɋɗɍɗ- ɑ ɌɉɐɗɚɖɉɊɏɎɖɑɨ, (ɖɉɘəɑɕɎə, ɚ ɘɗɕɗɢɥɧ
ɕɎɛɉɔɔɗɑɚɓɉɛɎɔɨ).
4.7 ȣɘɉɚɖɗɚɛɥ ɋɚɔɎɍɚɛɋɑɎ ɘɤɔɑ ɑ ɘɉəɗɋ
- ȗɗɐɖɑɓɉɧɢɑɎ ɋ ɞɗɍɎ əɉɊɗɛɤ ɚ ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɗɕ ɘɤɔɥ ɑ ɘɉəɤ ɕɗɌɜɛ ɘəɑɠɑɖɑɛɥ ɋəɎɍ
ɋɉɡɎɕɜ ɐɍɗəɗɋɥɧ (ɖɉɘəɑɕɎə ɚɘɗɚɗɊɚɛɋɗɋɉɛɥ
əɉɐɋɑɛɑɧ əɉɓɉ, ɘəɑəɗɍɖɤɞ ɖɎɍɗɚɛɉɛɓɗɋ,
ɉɚɛɕɤ ɑ/ɑɔɑ ɘɗɨɋɔɎɖɑɧ ɓɗɏɖɤɞ ɋɗɚɘɉɔɎɖɑɒ);
ɋ ɗɊɨɐɉɛɎɔɥɖɗ ɘɗəɨɍɓɎ ɗɟɎɖɑɛɎ ɋɗɐɕɗɏɖɤɎ
əɑɚɓɑ ɚ ɜɠɫɛɗɕ ɦɛɑɞ ɗɘɉɚɖɗɚɛɎɒ ɑ ɘəɑɕɑɛɎ
ɚɗɗɛɋɎɛɚɛɋɜɧɢɑɎ ɕɎəɤ ɘəɎɍɗɚɛɗəɗɏɖɗɚɛɑ.
- Ȥəɑ ɗɟɎɖɓɎ əɑɚɓɗɋ, ɚɋɨɐɉɖɖɤɞ ɚ ɋɗɐɖɑɓɖɗɋɎɖɑɎɕ ɘɤɔɑ ɋ ɞɗɍɎ ɋɤɘɗɔɖɎɖɑɨ əɉɊɗɛ ɚ ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɗɕ, ɚɔɎɍɜɎɛ ɛɉɓɏɎ ɜɠɑɛɤɋɉɛɥ ɑ ɛɜ
ɘɤɔɥ, ɓɗɛɗəɉɨ ɜɏɎ ɋɗɐɕɗɏɖɗ ɑɕɎɔɉɚɥ ɋ ɕɎɚɛɎ
ɘəɗɋɎɍɎɖɑɨ əɉɊɗɛ ɑ Ɋɤɔɉ ɘɗɍɖɨɛɉ ɋ ɋɗɐɍɜɞ
əɉɊɗɛɉɧɢɑɕ ɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɗɕ.
- ȤɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛ ɚɔɎɍɜɎɛ ɦɓɚɘɔɜɉɛɑəɗɋɉɛɥ
ɑ ɗɊɚɔɜɏɑɋɉɛɥ ɋ ɚɗɗɛɋɎɛɚɛɋɑɑ ɚ əɎɓɗɕɎɖɍɉɟɑɨɕɑ, ɜɓɉɐɉɖɖɤɕɑ ɋ ɖɉɚɛɗɨɢɎɕ əɜɓɗɋɗɍɚɛɋɎ,
ɍɔɨ ɚɋɎɍɎɖɑɨ ɓ ɕɑɖɑɕɜɕɜ ɋɤɚɋɗɊɗɏɍɎɖɑɨ
ɗɘɉɚɖɤɞ ɍɔɨ ɐɍɗəɗɋɥɨ ɘɤɔɑ ɑ ɘɉəɗɋ.
- ȣɛəɉɊɗɛɉɖɖɤɒ ɋɗɐɍɜɞ ɚɔɎɍɜɎɛ ɗɛɋɗɍɑɛɥ ɛɉɓɑɕ
ɗɊəɉɐɗɕ, ɠɛɗɊɤ ɚɋɎɚɛɑ ɓ ɕɑɖɑɕɜɕɜ ɐɉɋɑɞəɎɖɑɎ ɘɤɔɑ ɋ ɜɚɔɗɋɑɨɞ ɚɑɔɥɖɗɒ ɐɉɘɤɔɫɖɖɗɚɛɑ
ɋ ɕɎɚɛɎ ɘəɗɋɎɍɎɖɑɨ əɉɊɗɛ.
- Ȥəɑ ɋɗɐɖɑɓɖɗɋɎɖɑɑ ɘɤɔɑ ɑɔɑ ɘɉəɗɋ ɗɚɖɗɋɖɗɒ
ɐɉɍɉɠɎɒ ɨɋɔɨɎɛɚɨ ɓɗɖɛəɗɔɥ ɑɞ ɋɤɚɋɗɊɗɏɍɎɖɑɨ.
- ȢɎɗɊɞɗɍɑɕɗ ɘəɉɋɑɔɥɖɗ ɑɚɘɗɔɥɐɗɋɉɛɥ ɑ ɗɊɚɔɜɏɑɋɉɛɥ ɋɚɧ ɖɎɗɊɞɗɍɑɕɜɧ ɍɔɨ ɚɊɗəɉ, ɋɚɉɚɤɋɉɖɑɨ ɑɔɑ ɜɍɉɔɎɖɑɨ ɔɎɛɜɠɎɒ ɘɤɔɑ ɑɔɑ ɘɉəɗɋ
ɗɚɖɉɚɛɓɜ ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɉ ɚɗɌɔɉɚɖɗ ɜɓɉɐɉɖɑɨɕ ɑɐɌɗɛɗɋɑɛɎɔɨ.
- ȥɉɚɞɗɍɖɤɎ ɕɉɛɎəɑɉɔɤ ɑ əɉɊɗɠɑɒ ɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛ
ɚɔɎɍɜɎɛ ɋɤɊɑəɉɛɥ, ɗɊɚɔɜɏɑɋɉɛɥ ɑ ɐɉɕɎɖɨɛɥ
ɚɗɌɔɉɚɖɗ ɜɓɉɐɉɖɑɨɕ ɑɐ ɖɉɚɛɗɨɢɎɌɗ əɜɓɗɋɗɍɚɛɋɉ ɋɗ ɑɐɊɎɏɉɖɑɎ ɖɎɖɜɏɖɗɌɗ ɜɋɎɔɑɠɎɖɑɨ
ɘɤɔɎ- ɑɔɑ ɘɉəɗɗɊəɉɐɗɋɉɖɑɨ.
- ȝɚɘɗɔɥɐɜɒɛɎ ɐɉɢɑɛɖɤɎ əɎɚɘɑəɉɛɗəɤ
ɚɗɌɔɉɚɖɗ ɘəɗɑɐɋɗɍɚɛɋɎɖɖɤɕ ɑɖɚɛəɜɓɟɑɨɕ ɑɔɑ
ɋ ɚɗɗɛɋɎɛɚɛɋɑɑ ɚ ɛəɎɊɗɋɉɖɑɨɕɑ ɘɗ ɗɞəɉɖɎ
ɛəɜɍɉ ɑ ɛɎɞɖɑɓɎ ɊɎɐɗɘɉɚɖɗɚɛɑ.
- ȣɊəɉɊɗɛɓɉ ɗɘəɎɍɎɔɫɖɖɤɞ ɕɉɛɎəɑɉɔɗɋ ɚɗɘəɨɏɎɖɉ ɚ ɋɤɍɎɔɎɖɑɎɕ ɘɤɔɑ ɑ ɘɉəɉ, ɓɗɛɗəɤɎ
ɕɗɌɜɛ ɚɗɐɍɉɛɥ ɘɗɛɎɖɟɑɉɔɥɖɗ ɋɐəɤɋɗɗɘɉɚɖɜɧ
ɋɗɐɍɜɡɖɜɧ ɚəɎɍɜ.
4.8 ȣɘɉɚɖɗɚɛɥ ɋɚɔɎɍɚɛɋɑɎ ɡɜɕɉ
- ȗɤɚɗɓɑɒ ɜəɗɋɎɖɥ ɡɜɕɗɋɤɞ ɖɉɌəɜɐɗɓ ɘəɑ
ɗɛɚɜɛɚɛɋɑɑ ɍɗɔɏɖɗɒ ɐɉɢɑɛɤ ɚɔɜɞɉ ɕɗɏɎɛ
ɘəɑɋɎɚɛɑ ɓ ɘəɗɍɗɔɏɑɛɎɔɥɖɤɕ ɖɉəɜɡɎɖɑɨɕ
ɚɔɜɞɉ, ɘɗɛɎəɎ ɚɔɜɞɉ ɑ ɑɖɤɕ ɘəɗɊɔɎɕɉɕ,
ɖɉɘəɑɕɎə ɜɡɖɗɕɜ (ɐɋɎɖɨɢɎɕɜ, ɚɋɑɚɛɨɢɎɕɜ
ɑɔɑ ɏɜɏɏɉɢɎɕɜ) ɡɜɕɜ.
- ȦɔɎɍɜɎɛ ɖɎɘəɎɕɎɖɖɗ ɗɟɎɖɑɛɥ ɋɗɐɕɗɏɖɤɎ
əɑɚɓɑ ɚ ɜɠɫɛɗɕ ɦɛɑɞ ɗɘɉɚɖɗɚɛɎɒ ɑ ɘəɑɖɨɛɥ
ɚɗɗɛɋɎɛɚɛɋɜɧɢɑɎ ɕɎəɤ ɘəɎɍɗɚɛɗəɗɏɖɗɚɛɑ.
- ȗ ɓɉɠɎɚɛɋɎ ɛɉɓɑɞ ɕɎə ɘəɎɍɗɚɛɗəɗɏɖɗɚɛɑ
ɕɗɏɎɛ ɋɤɚɛɜɘɉɛɥ, ɖɉɘəɑɕɎə, ɘəɑɕɎɖɎɖɑɎ
ɑɐɗɔɨɟɑɗɖɖɤɞ ɕɉɛɎəɑɉɔɗɋ ɋ ɟɎɔɨɞ ɜɚɛəɉɖɎɖɑɨ ɐɋɎɖɨɢɑɞ ɡɜɕɗɋ, ɋɗɐɖɑɓɉɧɢɑɞ ɖɉ ɐɉɌɗɛɗɋɓɎ.
- ȝɚɘɗɔɥɐɜɒɛɎ ɐɉɢɑɛɖɤɎ ɖɉɜɡɖɑɓɑ ɚɗɌɔɉɚɖɗ
ɘəɗɑɐɋɗɍɚɛɋɎɖɖɤɕ ɑɖɚɛəɜɓɟɑɨɕ ɑɔɑ ɋ ɚɗɗɛɋɎɛɚɛɋɑɑ ɚ ɛəɎɊɗɋɉɖɑɨɕɑ ɘɗ ɗɞəɉɖɎ ɛəɜɍɉ ɑ
ɛɎɞɖɑɓɎ ɊɎɐɗɘɉɚɖɗɚɛɑ.
- ȤɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛ ɚɔɎɍɜɎɛ ɦɓɚɘɔɜɉɛɑəɗɋɉɛɥ
ɑ ɗɊɚɔɜɏɑɋɉɛɥ ɋ ɚɗɗɛɋɎɛɚɛɋɑɑ ɚ ɘəɑɋɗɍɑɕɤɕɑ
ɋ ɖɉɚɛɗɨɢɎɕ əɜɓɗɋɗɍɚɛɋɎ ɜɓɉɐɉɖɑɨɕɑ ɋɗ
ɑɐɊɎɏɉɖɑɎ ɖɎɖɜɏɖɗɌɗ ɘɗɋɤɡɎɖɑɨ ɜəɗɋɖɨ
ɡɜɕɉ.
- ȥɉɚɞɗɍɖɤɎ ɕɉɛɎəɑɉɔɤ ɑ əɉɊɗɠɑɒ ɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛ
ɚɔɎɍɜɎɛ ɋɤɊɑəɉɛɥ, ɗɊɚɔɜɏɑɋɉɛɥ ɑ ɐɉɕɎɖɨɛɥ
ɚɗɌɔɉɚɖɗ ɜɓɉɐɉɖɑɨɕ ɑɐ ɖɉɚɛɗɨɢɎɌɗ əɜɓɗɋɗɍɚɛɋɉ ɋɗ ɑɐɊɎɏɉɖɑɎ ɖɎɖɜɏɖɗɌɗ ɘɗɋɤɡɎɖɑɨ
ɜəɗɋɖɨ ɡɜɕɉ.
- ȜɉɘəɎɢɉɎɛɚɨ ɜɍɉɔɨɛɥ ɋɚɛəɗɎɖɖɤɒ ɌɔɜɡɑɛɎɔɥ.
ȣɖ ɍɗɔɏɎɖ ɖɉɞɗɍɑɛɥɚɨ ɋ ɛɎɞɖɑɠɎɚɓɑ
ɑɚɘəɉɋɖɗɕ ɚɗɚɛɗɨɖɑɑ.
4.9 ȣɘɉɚɖɗɚɛɑ ɋɚɔɎɍɚɛɋɑɎ ɋɑɊəɉɟɑɒ
- șɔɑɛɎɔɥɖɗɎ ɋɗɐɍɎɒɚɛɋɑɎ ɋɑɊəɉɟɑɒ ɕɗɏɎɛ
ɚɛɉɛɥ ɘəɑɠɑɖɗɒ ɖɎəɋɖɤɞ əɉɚɚɛəɗɒɚɛɋ ɑ ɖɉəɜɡɎɖɑɒ ɋ ɟɑəɓɜɔɨɟɑɑ ɓəɗɋɑ ɋ ɓɑɚɛɨɞ ɑ ɘəɎɍɘɔɎɠɥɨɞ əɜɓ.
- Ȥəɑ ɋɤɘɗɔɖɎɖɑɑ
əɉɊɗɛ ɋ ɜɚɔɗɋɑɨɞ ɖɑɐɓɗɒ
ɛɎɕɘɎəɉɛɜəɤ ɖɗɚɑɛɎ ɛɫɘɔɜɧ ɗɍɎɏɍɜ ɑ
ɍɎəɏɑɛɎ əɜɓɑ ɋ ɛɎɘɔɎ ɑ ɚɜɞɑɕɑ.
- Țɚɔɑ ɋɤ ɘɗɠɜɋɚɛɋɜɎɛɎ/ɜɋɑɍɑɛɎ, ɠɛɗ ɓɗɏɉ ɖɉ
ɘɉɔɥɟɉɞ ɑɔɑ ɓɑɚɛɨɞ əɜɓ ɚɛɉɔɉ ɖɎɠɜɋɚɛɋɑɛɎɔɥɖɗɒ, ɘɗɨɋɑɔɑɚɥ «ɕɜəɉɡɓɑ», ɗɖɉ Ɋɗɔɑɛ ɑɔɑ
ɘɗɊɎɔɎɔɉ, ɘəɎɓəɉɛɑɛɎ əɉɊɗɛɜ ɚ ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜ-
LoL
g
Page 51

ȥȨȦȦȟȝȞ ru
51
ɕɎɖɛɗɕ, ɜɋɎɍɗɕɑɛɎ ɗɊ ɦɛɗɕ ɚɋɗɎɌɗ əɉɊɗɛɗɍɉɛɎɔɨ ɑ ɘəɗɓɗɖɚɜɔɥɛɑəɜɒɛɎɚɥ ɚ ɋəɉɠɗɕ.
- ȤɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛ ɚɔɎɍɜɎɛ ɦɓɚɘɔɜɉɛɑəɗɋɉɛɥ
ɑ ɗɊɚɔɜɏɑɋɉɛɥ ɋ ɚɗɗɛɋɎɛɚɛɋɑɑ ɚ ɘəɑɋɗɍɑɕɤɕɑ
ɋ ɖɉɚɛɗɨɢɎɕ əɜɓɗɋɗɍɚɛɋɎ ɜɓɉɐɉɖɑɨɕɑ ɋɗ
ɑɐɊɎɏɉɖɑɎ ɖɎɖɜɏɖɗɌɗ ɘɗɋɤɡɎɖɑɨ ɜəɗɋɖɨ
ɋɑɊəɉɟɑɒ.
- ȥɉɚɞɗɍɖɤɎ ɕɉɛɎəɑɉɔɤ ɑ əɉɊɗɠɑɒ ɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛ
ɚɔɎɍɜɎɛ ɋɤɊɑəɉɛɥ, ɗɊɚɔɜɏɑɋɉɛɥ ɑ ɐɉɕɎɖɨɛɥ
ɚɗɌɔɉɚɖɗ ɜɓɉɐɉɖɑɨɕ ɑɐ ɖɉɚɛɗɨɢɎɌɗ əɜɓɗɋɗɍɚɛɋɉ ɋɗ ɑɐɊɎɏɉɖɑɎ ɖɎɖɜɏɖɗɌɗ ɘɗɋɤɡɎɖɑɨ
ɜəɗɋɖɨ ɋɑɊəɉɟɑɒ.
- șɔɨ ɜɍɎəɏɉɖɑɨ ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɉ, ɓɗɌɍɉ ɦɛɗ
ɋɗɐɕɗɏɖɗ, ɑɚɘɗɔɥɐɜɒɛɎ ɚɛɗɒɓɜ, ɖɉɛɨɏɖɗɎ
ɘəɑɚɘɗɚɗɊɔɎɖɑɎ ɑɔɑ ɊɉɔɉɖɚɑəɗɋɗɠɖɗɎ
ɜɚɛəɗɒɚɛɋɗ.
- ȟəɎɘɓɗ ɍɎəɏɑɛɎ ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛ ɚ ɜɠɫɛɗɕ
ɖɎɗɊɞɗɍɑɕɤɞ ɜɚɑɔɑɒ əɎɉɓɟɑɑ, ɖɗ ɖɎ ɐɉɊɤɋɉɒɛɎ ɘəɑ ɦɛɗɕ ɗ ɛɗɕ, ɠɛɗ əɑɚɓ ɋɑɊəɉɟɑɒ, ɓɉɓ
ɘəɉɋɑɔɗ, ɋɗɐəɉɚɛɉɎɛ ɘəɑ ɜɋɎɔɑɠɎɖɑɑ ɜɚɑɔɑɨ
ɞɋɉɛɉ.
- ȢɎɘəɉɋɑɔɥɖɗ ɚɕɗɖɛɑəɗɋɉɖɖɤɒ ɑɔɑ ɘɗɋəɎɏɍɫɖɖɤɒ ɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛ ɕɗɏɎɛ ɘəɑɋɎɚɛɑ ɓ ɘɗɋɤɡɎɖɖɤɕ ɋɑɊəɉɟɑɨɕ.
4.10 șɗɘɗɔɖɑɛɎɔɥɖɤɎ ɜɓɉɐɉɖɑɨ ɘɗ ɛɎɞɖɑɓɎ
ɊɎɐɗɘɉɚɖɗɚɛɑ
- Ȧɏɉɛɤɒ ɋɗɐɍɜɞ ɕɗɏɎɛ ɚɛɉɛɥ ɘəɑɠɑɖɗɒ ɚɎəɥɫɐɖɗɌɗ ɛəɉɋɕɑəɗɋɉɖɑɨ.
- Țɚɔɑ ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛ ɖɎ ɑɚɘɗɔɥɐɜɎɛɚɨ, ɉ
ɛɉɓɏɎ ɘɎəɎɍ ɐɉɕɎɖɗɒ ɘəɑɖɉɍɔɎɏɖɗɚɛɎɒ ɑɔɑ
ɘəɑ ɋɤɘɗɔɖɎɖɑɑ əɎɕɗɖɛɖɤɞ əɉɊɗɛ ɋɚɎɌɍɉ
ɊɔɗɓɑəɜɒɛɎ ɘɗɍɉɠɜ ɋɗɐɍɜɞɉ, əɉɐɌəɜɏɉɒɛɎ ɗɛ
ɍɉɋɔɎɖɑɨ ɋɗɐɍɜɡɖɤɒ ɡɔɉɖɌ ɑ ɗɛɚɗɎɍɑɖɨɒɛɎ
ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛ ɗɛ ɚɑɚɛɎɕɤ (ɑɚɛɗɠɖɑɓɉ)
ɘɗɍɉɠɑ ɚɏɉɛɗɌɗ ɋɗɐɍɜɞɉ.
- ȢɑɓɗɌɍɉ ɖɎ ɖɉɘəɉɋɔɨɒɛɎ ɋɗɐɍɜɡɖɤɒ ɘɗɛɗɓ ɖɉ
ɚɎɊɨ ɑɔɑ ɍəɜɌɑɞ ɔɑɟ.
- ȣɛɔɎɛɉɧɢɑɎ ɋ ɚɛɗəɗɖɜ ɡɔɉɖɌɑ ɕɗɌɜɛ ɚɛɉɛɥ
ɘəɑɠɑɖɗɒ ɚɎəɥɫɐɖɗɌɗ ɛəɉɋɕɑəɗɋɉɖɑɨ. ȗ ɚɋɨɐɑ
ɚ ɦɛɑɕ ɋɚɎɌɍɉ ɘəɗɋɎəɨɒɛɎ, ɖɎ ɘɗɋəɎɏɍɎɖɤ ɔɑ
ɡɔɉɖɌɑ ɑ ɖɎ ɘɗɋəɎɏɍɎɖɤ/əɉɚɝɑɓɚɑəɗɋɉɖɤ ɔɑ
ɑɞ ɓəɎɘɫɏɖɤɎ ɦɔɎɕɎɖɛɤ.
- Ȥəɑ ɑɚɘɗɔɥɐɗɋɉɖɑɑ ɜɖɑɋɎəɚɉɔɥɖɤɞ ɘɗɋɗəɗɛɖɤɞ (ɓɜɔɉɠɓɗɋɤɞ) ɕɜɝɛ ɖɎɗɊɞɗɍɑɕɗ
ɑɚɘɗɔɥɐɗɋɉɛɥ ɚɛɗɘɗəɖɤɎ ɡɛɑɝɛɤ ɑ ɞɗɕɜɛɤ
Whipcheck ɍɔɨ ɐɉɢɑɛɤ ɡɔɉɖɌɗɋ ɗɛ ɋɗɔɗɠɎɖɑɨ
(ɐɉɞɔɫɚɛɤɋɉɖɑɨ) ɋ ɟɎɔɨɞ ɗɊɎɚɘɎɠɎɖɑɨ ɊɎɐɗɘɉ-
ɚɖɗɚɛɑ ɖɉ ɚɔɜɠɉɒ əɉɐɣɎɍɑɖɎɖɑɨ ɡɔɉɖɌɗɋɤɞ
ɚɗɎɍɑɖɎɖɑɒ.
- ȤɗɐɉɊɗɛɥɛɎɚɥ ɗ ɛɗɕ, ɠɛɗɊɤ ɖɎ ɍɗɘɜɚɛɑɛɥ
ɘəɎɋɤɡɎɖɑɨ ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɗɕ ɜɓɉɐɉɖɖɗɌɗ
ɕɉɓɚɑɕɉɔɥɖɗɌɗ ɍɉɋɔɎɖɑɨ.
- ȟɉɛɎɌɗəɑɠɎɚɓɑ ɐɉɘəɎɢɉɎɛɚɨ ɘɎəɎɖɗɚɑɛɥ
ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛ ɐɉ ɡɔɉɖɌ.
- Ȥəɑ ɦɓɚɘɔɜɉɛɉɟɑɑ ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɉ,
ɐɉɝɑɓɚɑəɗɋɉɖɖɗɕ ɋ ɍɎəɏɉɛɎɔɎ: ɖɉɍɫɏɖɗ
ɐɉɓəɎɘɑɛɎ ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛ. ȤɗɛɎəɨ
ɓɗɖɛəɗɔɨ ɖɉɍ ɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɗɕ ɕɗɏɎɛ ɘəɑɋɎɚɛɑ ɓ
ɛəɉɋɕɑəɗɋɉɖɑɧ.
4.11 șɗɘɗɔɖɑɛɎɔɥɖɤɎ ɜɓɉɐɉɖɑɨ ɘɗ ɛɎɞɖɑɓɎ
ɊɎɐɗɘɉɚɖɗɚɛɑ:
- Ȥəɑ ɖɎɗɊɞɗɍɑɕɗɚɛɑ ɚɗɊɔɧɍɉɒɛɎ ɗɚɗɊɤɎ ɘəɎɍɘɑɚɉɖɑɨ ɘɗ ɊɎɐɗɘɉɚɖɗɚɛɑ ɛəɜɍɉ ɑɔɑ ɘəɎɍɜɘəɎɏɍɎɖɑɧ ɘəɗɑɐɋɗɍɚɛɋɎɖɖɗɌɗ ɛəɉɋɕɉɛɑɐɕɉ ɘəɑ
ɗɊəɉɢɎɖɑɑ ɚ ɓɗɕɘəɎɚɚɗəɉɕɑ ɑ
ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɉɕɑ.
- ȨɊɎɍɑɛɎɚɥ ɋ ɛɗɕ, ɠɛɗ ɖɎ ɘəɎɋɤɡɉɎɛɚɨ
ɜɓɉɐɉɖɖɗɎ ɋ ɛɎɞɖɑɠɎɚɓɑɞ ɞɉəɉɓɛɎəɑɚɛɑɓɉɞ
ɕɉɓɚ. ɍɗɘɜɚɛɑɕɗɎ əɉɊɗɠɎɎ ɍɉɋɔɎɖɑɎ.
- ȢɎ ɘɎəɎɌəɜɏɉɒɛɎ ɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛ, ɑɚɘɗɔɥɐɜɒɛɎ
ɎɌɗ ɛɗɔɥɓɗ ɋ
ɛɗɕ ɍɑɉɘɉɐɗɖɎ ɕɗɢɖɗɚɛɑ,
ɓɗɛɗəɤɒ ɜɓɉɐɉɖ ɋ ɛɎɞɖɑɠɎɚɓɑɞ ɞɉəɉɓɛɎəɑɚɛɑɓɉɞ.
- ȝɚɘɗɔɥɐɜɒɛɎ ɍɗɘɜɢɎɖɖɤɎ ɚɕɉɐɗɠɖɤɎ ɕɉɛɎəɑɉɔɤ/Ȧȣț. ȤɗɐɉɊɗɛɥɛɎɚɥ ɗ ɍɗɚɛɉɛɗɠɖɗɒ
ɋɎɖɛɑɔɨɟɑɑ əɉɊɗɠɎɒ ɐɗɖɤ. Ȥəɑ ɘɗɋɤɡɎɖɖɗɕ
əɉɚɞɗɍɎ ɚɏɉɛɗɌɗ ɋɗɐɍɜɞɉ: ɘəɗɋɎəɥɛɎ ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛ, ɘəɑ ɖɎɗɊɞɗɍɑɕɗɚɛɑ ɗɛəɎɕɗɖɛɑəɜɒɛɎ.
- ȤəɎɓəɉɛɑɛɎ əɉɊɗɛɜ ɚ ɦɛɑɕ ɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɗɕ, Ɏɚɔɑ
ɋɉɚ ɠɛɗ-ɔɑɊɗ ɗɛɋɔɎɓɉɎɛ! ȖɜɍɥɛɎ ɋɖɑɕɉɛɎɔɥɖɤ,
ɚɔɎɍɑɛɎ ɐɉ ɚɋɗɑɕɑ ɍɎɒɚɛɋɑɨɕɑ ɑ ɚɎəɥɫɐɖɗ
ɗɛɖɗɚɑɛɎɚɥ ɓ əɉɊɗɛɎ ɚ ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɗɕ.
ȢɎ ɘɗɔɥɐɜɒɛɎɚɥ ɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɗɕ, Ɏɚɔɑ ɋɤ
ɜɚɛɉɔɑ, ɖɉɞɗɍɑɛɎɚɥ ɘɗɍ ɍɎɒɚɛɋɑɎɕ ɖɉəɓɗɛɑɓɗɋ, ɉɔɓɗɌɗɔɨ ɑɔɑ ɔɎɓɉəɚɛɋ. ȢɎɋɖɑɕɉɛɎɔɥɖɗɚɛɥ ɘəɑ əɉɊɗɛɎ ɚ ɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɗɕ ɕɗɏɎɛ
ɘəɑɋɎɚɛɑ ɓ ɚɎəɥɎɐɖɤɕ ɛəɉɋɕɉɕ.
- ȦɔɎɍɑɛɎ ɐɉ ɠɑɚɛɗɛɗɒ ɑ ɘɗəɨɍɓɗɕ ɖɉ ɚɋɗɫɕ
əɉɊɗɠɎɕ ɕɎɚɛɎ. ȖɎɚɘɗəɨɍɗɓ ɖɉ əɉɊɗɠɎɕ ɕɎɚɛɎ
ɑ ɘɔɗɞɗɎ ɗɚɋɎɢɎɖɑɎ ɕɗɌɜɛ ɘəɑɋɎɚɛɑ ɓ
ɖɎɚɠɉɚɛɖɤɕ ɚɔɜɠɉɨɕ.
- șɎəɏɑɛɎ ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛ ɋ ɖɎɍɗɚɛɜɘɖɗɕ
ɍɔɨ ɍɎɛɎɒ ɕɎɚɛɎ.
- ȜɉɘəɎɢɉɎɛɚɨ ɞəɉɖɎɖɑɎ ɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɉ ɋɖɎ
ɘɗɕɎɢɎɖɑɒ ɑɔɑ ɋɗ ɋɔɉɏɖɤɞ ɘɗɕɎɢɎɖɑɨɞ ɊɎɐ
ɚɗɗɛɋɎɛɚɛɋɜɧɢɎɒ ɐɉɢɑɛɤ.
- ȜɉɢɑɢɉɒɛɎ ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛ, ɗɚɗɊɎɖɖɗ
ɡɛɜɟɎə ɘɗɍɉɠɑ ɚɏɉɛɗɌɗ ɋɗɐɍɜɞɉ ɑ ɗəɌɉɖɤ
ɜɘəɉɋɔɎɖɑɨ ɗɛ ɘɗɘɉɍɉɖɑɨ ɘɤɔɑ ɑ Ɍəɨɐɑ.
ȝɖɝɗəɕɉɟɑɨ ɗɊɗɐɖɉɠɎɖɉ ɋ ɍɉɖɖɗɕ əɜɓɗɋɗɍɚɛɋɎ ɘɗ ɦɓɚɘɔɜɉɛɉɟɑɑ ɚɔɎɍɜɧɢɑɕ ɗɊəɉɐɗɕ:
ȣɘɉɚɖɗɚɛɥ! ȤəɎɍɜɘəɎɏɍɎɖɑɎ
ɗɊ ɗɘɉɚɖɗ-
ɚɛɑ ɛəɉɋɕɑəɗɋɉɖɑɨ ɑɔɑ ɋəɎɍɎ ɍɔɨ ɗɓəɜɏɉ-
ɧɢɎɒ ɚəɎɍɤ.
ȗɖɑɕɉɖɑɎ! ȤəɎɍɜɘəɎɏɍɎɖɑɎ ɗ ɋɗɐɕɗɏ-
ɖɗɕ ɕɉɛɎəɑɉɔɥɖɗɕ ɜɢɎəɊɎ.
4.12 Ȧɑɕɋɗɔɤ ɖɉ ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɎ
ȤɎəɎɍ ɋɋɗɍɗɕ ɋ ɦɓɚɘɔɜɉɛɉɟɑɧ ɘəɗɠɛɑɛɎ
əɜɓɗɋɗɍɚɛɋɗ ɘɗ ɦɓɚɘɔɜɉɛɉɟɑɑ.
ȝɚɘɗɔɥɐɜɒɛɎ ɐɉɢɑɛɖɤɎ ɗɠɓɑ
ȢɉɍɎɋɉɒɛɎ ɐɉɢɑɛɖɤɎ ɖɉɜɡɖɑɓɑ
ȢɉɘəɉɋɔɎɖɑɎ ɋəɉɢɎɖɑɨ
Ȧɕ. ɚ. 2.
1 ȘɉɎɠɖɤɒ ɓɔɧɠ
2 Șɉɒɓɉ ɟɉɖɌɗɋɗɌɗ ɐɉɏɑɕɉ
3 ȫɉɖɌɗɋɤɒ ɐɉɏɑɕ
4 șɎəɏɉɛɎɔɥ ɟɉɖɌɗɋɗɌɗ ɐɉɏɑɕɉ
5. ȣɊɐɗə
Page 52

ȥȨȦȦȟȝȞru
52
5 ȭɘɑɖɍɎɔɥ
6 ȘɉɎɠɖɤɒ ɓɔɧɠ
7 ȗɤɓɔɧɠɉɛɎɔɥ (ȗɓɔ/ȗɤɓɔ)
8 Ȗɔɗɓɑəɉɛɗə ɋɓɔɧɠɎɖɑɨ
9 ȗɑɖɛ əɎɌɜɔɑəɗɋɓɑ ɠɉɚɛɗɛɤ ɋəɉɢɎɖɑɨ
10 ȗɤɞɗɍ ɋɗɐɍɜɞɉ
11 ȭɛɜɟɎə ɘɗɍɉɠɑ ɚɏɉɛɗɌɗ ɋɗɐɍɜɞɉ ɚ ɝɑɔɥɛəɗɕ
12 Ȧɣɫɕɖɤɒ ɖɑɘɘɎɔɥ 1/4"
6.1 ȤɎəɎɍ ɘɎəɋɤɕ ɑɚɘɗɔɥɐɗɋɉɖɑɎɕ
ȗɋɎəɖɑɛɎ ɚɣɫɕɖɤɒ ɖɑɘɘɎɔɥ (12).
6.2 Ȩɚɛɉɖɗɋɓɉ ɟɉɖɌɗɋɗɌɗ ɐɉɏɑɕɉ
șɑɉɕɎɛə ɞɋɗɚɛɗɋɑɓɉ əɉɊɗɠɎɌɗ ɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɉ ɍɗɔɏɎɖ ɛɗɠɖɗ ɚɗɗɛɋɎɛɚɛɋɗɋɉɛɥ
ɍɑɉɕɎɛəɜ ɗɛɋɎəɚɛɑɨ ɟɉɖɌɗɋɗɌɗ ɐɉɏɑɕɉ (3)!
ȝɕɎɧɛɚɨ ɟɉɖɌɗɋɤɎ ɐɉɏɑɕɤ ɍɔɨ ɞɋɗɚɛɗɋɑɓɗɋ
əɉɐɔɑɠɖɗɌɗ
ɍɑɉɕɎɛəɉ. ȨɚɛɉɖɗɋɑɛɎ ɟɉɖɌɗɋɤɒ
ɐɉɏɑɕ (3) ɋ ɍɎəɏɉɛɎɔɥ (4) ɑ ɐɉɛɎɕ ɖɉɋɎəɖɑɛɎ
Ɍɉɒɓɜ (2) ɗɛ əɜɓɑ.
Țɚɔɑ ɋ ɟɉɖɌɗɋɗɕ ɐɉɏɑɕɎ ɖɎ ɜɚɛɉɖɗɋɔɎɖ
əɉɊɗɠɑɒ ɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛ, ɖɎ ɐɉɛɨɌɑɋɉɒɛɎ
ɐɉɏɑɕ ɓɔɧɠɗɕ, ɉ ɐɉɋɎəɖɑɛɎ Ɍɉɒɓɜ ɋəɜɠɖɜɧ!
6.3 Ȩɚɛɉɖɗɋɓɉ əɉɊɗɠɎɌɗ ɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɉ
ȗ ɚɔɜɠɉɎ ɑɚɘɗɔɥɐɗɋɉɖɑɨ ɉɊəɉɐɑɋɖɤɞ
Ɍɗɔɗɋɗɓ ɐɉɘəɎɢɉɎɛɚɨ ɘəɎɋɤɡɉɛɥ
ɜɓɉɐɉɖɖɤɒ ɘəɗɑɐɋɗɍɑɛɎɔɎɕ ɕɉɓɚɑɕɉɔɥɖɗ ɍɗɘɜɚɛɑɕɤɒ ɋɤɔɎɛ (L
0
)! ȗɚɛɉɋɔɨɒɛɎ əɉɊɗɠɑɒ ɑɖɚɛəɜ-
ɕɎɖɛ ɋ ɟɉɖɌɗɋɤɒ ɐɉɏɑɕ (3) ɘɗ ɋɗɐɕɗɏɖɗɚɛɑ ɖɉ
ɋɚɧ ɍɔɑɖɜ ɞɋɗɚɛɗɋɑɓɉ. ȨɊɎɍɑɛɎɚɥ ɋ ɛɗɕ, ɠɛɗ
ɍɔɑɖɉ ɐɉɏɑɕɉɎɕɗɒ ɠɉɚɛɑ (Lg) ɚɗɚɛɉɋɔɨɎɛ ɖɎ
ɕɎɖɎɎ 10 ɕɕ.
șɑɉɕɎɛə ɞɋɗɚɛɗɋɑɓɉ əɉɊɗɠɎɌɗ ɑɖɚɛəɜ-
ɕɎɖɛɉ ɍɗɔɏɎɖ ɛɗɠɖɗ ɚɗɗɛɋɎɛɚɛɋɗɋɉɛɥ
ɍɑɉɕɎɛəɜ ɗɛɋɎəɚɛɑɨ ɟɉɖɌɗɋɗɌɗ ɐɉɏɑɕɉ (3)!
- ȤəɑɍɎəɏɑɋɉɒɛɎ ɡɘɑɖɍɎɔɥ (5) ɌɉɎɠɖɤɕ
ɓɔɧɠɗɕ (6).
- ȜɉɛɨɖɑɛɎ Ɍɉɒɓɜ (2) ɟɉɖɌɗɋɗɌɗ ɐɉɏɑɕɉ ɌɉɎɠɖɤɕ
ɓɔɧɠɗɕ (1).
- ȣɊɎɚɘɎɠɥɛɎ ɖɉɍɎɏɖɜɧ ɝɑɓɚɉɟɑɧ əɉɊɗɠɎɌɗ
ɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɉ.
6.4 ȝɚɘɗɔɥɐɗɋɉɖɑɎ ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɉ
șɔɨ ɗɊɎɚɘɎɠɎɖɑɨ ɘɗɔɖɗɒ ɕɗɢɖɗɚɛɑ ɚɋɗɎɌɗ
ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɉ ɋɚɎɌɍɉ ɑɚɘɗɔɥɐɜɒɛɎ ɘɖɎɋɕɗɡɔɉɖɌɑ ɚ ɋɖɜɛəɎɖɖɑɕ ɍɑɉɕɎɛəɗɕ ɕɑɖ. 9 ɕɕ.
ȢɎɍɗɚɛɉɛɗɠɖɤɒ
ɋɖɜɛəɎɖɖɑɒ ɍɑɉɕɎɛə ɕɗɏɎɛ
ɐɉɕɎɛɖɗ ɚɖɑɐɑɛɥ ɘəɗɑɐɋɗɍɑɛɎɔɥɖɗɚɛɥ ɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɉ.
ȗɖɑɕɉɖɑɎ! ȗ ɡɔɉɖɌɎ ɘɗɍɉɠɑ ɋɗɐɍɜɞɉ ɖɎ
ɍɗɔɏɖɗ Ɋɤɛɥ ɓɗɖɍɎɖɚɉɛɉ.
ȗɖɑɕɉɖɑɎ! ȬɛɗɊɤ ɦɛɗɛ ɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛ ɗɚɛɉ-
ɋɉɔɚɨ ɝɜɖɓɟɑɗɖɉɔɥɖɤɕ ɋ ɛɎɠɎɖɑɎ ɍɗɔɌɗɌɗ
ɋəɎɕɎɖɑ, ɎɌɗ ɖɎɗɊɞɗɍɑɕɗ ɚɕɉɐɤɋɉɛɥ ɍɗɚɛɉɛɗɠɖɤɕ ɓɗɔɑɠɎɚɛɋɗɕ ɚɕɉɐɓɑ. ȗɉəɑɉɖɛɤ ɚɕɉɐɓɑ:
– ȨɚɛɉɖɗɋɑɛɎ ɕɉɚɔɗəɉɚɘɤɔɑɛɎɔɥ ɍɔɨ ɘɗɍɉɠɑ
ɘəɗɕɉɚɔɎɖɖɗɌɗ ɚɏɉɛɗɌɗ ɋɗɐɍɜɞɉ.
– ȖɎɐ ɕɉɚɔɗəɉɚɘɤɔɑɛɎɔɨ: ɎɏɎɍɖɎɋɖɗ ɚɕɉɐɤ-
ɋɉɒɛɎ ɋəɜɠɖɜɧ ɡɛɜɟɎə ɘɗɍɉɠɑ ɚɏɉɛɗɌɗ ɋɗɐɍɜɞɉ. Ȥəɑɕ. 3–5 ɓɉɘɎɔɥ ɕɉɚɔɉ ɍɔɨ ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɗɋ ɠɎəɎɐ ɓɉɏɍɤɎ 15 ɕɑɖɜɛ əɉɊɗɛɤ ɋ
ɖɎɘəɎəɤɋɖɗɕ əɎɏɑɕɎ.
Țɚɔɑ ɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛ ɖɎ ɑɚɘɗɔɥɐɗɋɉɔɚɨ ɋ ɛɎɠɎɖɑɎ
ɖɎɚɓɗɔɥɓɑɞ ɍɖɎɒ, ɍɗɊɉɋɥɛɎ ɋəɜɠɖɜɧ ɋ ɡɛɜɟɎə
ɘɗɍɉɠɑ ɚɏɉɛɗɌɗ ɋɗɐɍɜɞɉ ɘəɑɕ. 5 ɓɉɘɎɔɥ ɕɉɚɔɉ
ɍɔɨ ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɉ.
ȗɖɑɕɉɖɑɎ! șɉɒɛɎ ɘɗəɉɊɗɛɉɛɥ ɑɖɚɛəɜ-
ɕɎɖɛɜ ɋ ɛɎɠɎɖɑɎ ɓɗəɗɛɓɗɌɗ ɋəɎɕɎɖɑ ɖɉ
ɞɗɔɗɚɛɗɕ ɞɗɍɜ.
1. ȗɤɊɎəɑɛɎ ɘɗɍɞɗɍɨɢɑɒ ɟɉɖɌɗɋɤɒ ɐɉɏɑɕ (3)
(ɚɕ. Ɍɔɉɋɜ 6.2).
2. ȨɚɛɉɖɗɋɑɛɎ ɘɗɍɞɗɍɨɢɑɒ ɚɕɎɖɖɤɒ ɑɖɚɛəɜ-
ɕɎɖɛ (ɚɕ. Ɍɔɉɋɜ 6.3).
3. Ȭɉɚɛɗɛɜ ɋəɉɢɎɖɑɨ ɕɗɏɖɗ ɑɐɕɎɖɨɛɥ ɚ ɘɗɕɗ-
ɢɥɧ əɎɌɜɔɑəɗɋɗɠɖɗɌɗ ɋɑɖɛɉ (9).
4. ȣɛəɎɌɜɔɑəɜɒɛɎ əɉɊɗɠɎɎ ɍɉɋɔɎɖɑɎ (ɑɐɕɎəɎɖ-
ɖɗɎ ɖɉ ɋɞɗɍɎ ɋɗɐɍɜɞɉ ɘəɑ ɋɓɔɧɠɫɖɖɗɕ ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɎ). ȡɉɓɚ. ɍɗɘɜɚɛɑɕɗɎ əɉɊɗɠɎɎ
ɍɉɋɔɎɖɑɎ — ɚɕ. Ɍɔɉɋɜ «ȧɎɞɖɑɠɎɚɓɑɎ ɞɉəɉɓɛɎəɑɚɛɑɓɑ».
5. ȤɗɍɓɔɧɠɑɛɎ ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛ ɓ ɚɑɚɛɎɕɎ
ɘɗɍɉɠɑ ɚɏɉɛɗɌɗ ɋɗɐɍɜɞɉ.
6. ȗɓɔɧɠɎɖɑɎ: ɚɍɋɑɖɥɛɎ Ɋɔɗɓɑəɉɛɗə ɋɓɔɧɠɎ-
ɖɑɨ (8) ɋ ɖɉɘəɉɋɔɎɖɑɑ ɚɛəɎɔɓɑ (ɚɕ. əɑɚ., ɚ.
2) ɑ ɖɉɏɕɑɛɎ ɋɤɓɔɧɠɉɛɎɔɥ (7).
ȗɤɓɔɧɠɎɖɑɎ: ɗɛɘɜɚɛɑɛɎ ɋɤɓɔɧɠɉɛɎɔɥ (7)
.
ȣɘɉɚɖɗɚɛɥ! ȤɎəɎɍ ɔɧɊɤɕɑ əɉɊɗɛɉɕɑ ɖɉ
ɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɎ ɗɛɚɗɎɍɑɖɨɒɛɎ ɡɛɜɟɎə ɘɗɍɉɠɑ
ɚɏɉɛɗɌɗ ɋɗɐɍɜɞɉ.
ȣɘɉɚɖɗɚɛɥ! ȣɘɑɚɉɖɖɤɎ ɋ ɖɉɚɛɗɨɢɎɕ əɉɐ-
ɍɎɔɎ əɉɊɗɛɤ ɘɗ ɛɎɞɗɊɚɔɜɏɑɋɉɖɑɧ ɑ əɎɕɗɖɛɜ ɍɗɔɏɖɤ ɋɤɘɗɔɖɨɛɥɚɨ ɛɗɔɥɓɗ ɚɘɎɟɑɉɔɑ-
ɚɛɉɕɑ.
- Ȥɜɛɫɕ əɎɌɜɔɨəɖɗɌɗ ɛɎɞɖɑɠɎɚɓɗɌɗ ɗɊɚɔɜɏɑ-
ɋɉɖɑɨ ɗɊɎɚɘɎɠɥɛɎ ɊɎɐɗɘɉɚɖɗɚɛɥ ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɉ.
- ȤəɗɋɎəɨɒɛɎ ɖɉɍɫɏɖɗɚɛɥ əɎɐɥɊɗɋɤɞ ɚɗɎɍɑ-
ɖɎɖɑɒ, ɘəɑ ɖɎɗɊɞɗɍɑɕɗɚɛɑ ɐɉɛɨɌɑɋɉɒɛɎ ɑɞ.
- Ȥɗ ɓəɉɒɖɎɒ ɕɎəɎ əɉɐ ɋ ɖɎɍɎɔɧ ɗɠɑɢɉɒɛɎ
ɝɑɔɥɛə ɋ ɡɛɜɟɎəɎ ɘɗɍɉɠɑ ɚɏɉɛɗɌɗ ɋɗɐɍɜɞɉ.
- Ȣɉ ɋɞɗɍɎ ɚɏɉɛɗɌɗ ɋɗɐɍɜɞɉ ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜ-
ɕɎɖɛɉ əɎɓɗɕɎɖɍɜɎɛɚɨ ɜɚɛɉɖɗɋɑɛɥ əɎɍɜɓɟɑɗɖɖɤɒ ɓɔɉɘɉɖ ɚ ɋɔɉɌɗɗɛɍɎɔɑɛɎɔɎɕ ɑ ɕɉɚɔɫɖɓɜ.
- Ȥəɑ ɑɐɊɤɛɗɠɖɗɕ ɋɤɞɗɍɎ ɕɉɚɔɉ ɑɔɑ ɋɗɐɍɜɞɉ
ɚɔɎɍɜɎɛ ɘəɗɋɎəɑɛɥ ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛ ɑ ɘəɑ
ɖɎɗɊɞɗɍɑɕɗɚɛɑ ɗɛəɎɕɗɖɛɑəɗɋɉɛɥ. (ɚɕ. Ɍɔɉɋɜ
9.)
6. Ȳɓɚɘɔɜɉɛɉɟɑɨ
LoL
g
7. ȧɎɞɖɑɠɎɚɓɗɎ ɗɊɚɔɜɏɑɋɉɖɑɎ
ɑ ɜɞɗɍ
Page 53

ȥȨȦȦȟȝȞ ru
53
- ȥɎɌɜɔɨəɖɗ ɑ ɘɗɚɔɎ ɓɉɏɍɗɌɗ ɑɚɘɗɔɥɐɗɋɉɖɑɨ
ɘəɗɋɎəɨɒɛɎ ɠɉɚɛɗɛɜ ɋəɉɢɎɖɑɨ ɑ ɜəɗɋɎɖɥ
ɋɑɊəɉɟɑɑ.
- ȢɎ ɍɗɘɜɚɓɉɒɛɎ ɓɗɖɛɉɓɛɉ ɚ ɗɘɉɚɖɤɕɑ ɋɎɢɎɚɛɋɉɕɑ, ɓɗɛɗəɤɎ ɕɗɌɔɑ ɗɛɔɗɏɑɛɥɚɨ ɖɉ ɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɎ. ȝɚɘɗɔɥɐɜɒɛɎ ɘɗɍɞɗɍɨɢɑɎ ɚəɎɍɚɛɋɉ
ɑɖɍɑɋɑɍɜɉɔɥɖɗɒ ɐɉɢɑɛɤ ɑ ɜɚɛəɉɖɑɛɎ ɗɘɉɚɖɤɎ
ɋɎɢɎɚɛɋɉ ɘɜɛɎɕ ɘəɑɖɨɛɑɨ ɘɗɍɞɗɍɨɢɑɞ ɕɎə
ɘɎəɎɍ ɛɎɞɖɑɠɎɚɓɑɕ ɗɊɚɔɜɏɑɋɉɖɑɎɕ.
f
ȝɚɘɗɔɥɐɜɒɛɎ ɛɗɔɥɓɗ ɗəɑɌɑɖɉɔɥɖɤɎ ɘəɑɖɉɍɔɎɏɖɗɚɛɑ Metabo.
ȝɚɘɗɔɥɐɜɒɛɎ ɛɗɔɥɓɗ ɛɎ ɘəɑɖɉɍɔɎɏɖɗɚɛɑ,
ɓɗɛɗəɤɎ ɘəɎɍɖɉɐɖɉɠɎɖɤ ɍɔɨ ɦɛɗɌɗ ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɉ ɑ ɚɗɗɛɋɎɛɚɛɋɜɧɛ ɛəɎɊɗɋɉɖɑɨɕ ɑ
ɘɉəɉɕɎɛəɉɕ, ɘəɑɋɗɍɑɕɤɕ ɋ ɖɉɚɛɗɨɢɎɕ əɜɓɗɋɗɍɚɛɋɎ ɘɗ ɦɓɚɘɔɜɉɛɉɟɑɑ.
Ȥɗɔɖɤɒ ɉɚɚɗəɛɑɕɎɖɛ ɘəɑɖɉɍɔɎɏɖɗɚɛɎɒ ɚɕ. ɖɉ
ɚɉɒɛɎ www.metabo.com ɑɔɑ ɋ ɓɉɛɉɔɗɌɎ.
ȣɘɉɚɖɗɚɛɥ! ȥɎɕɗɖɛ ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɗɋ
ɍɗɔɏɖɤ ɘəɗɋɗɍɑɛɥ ɛɗɔɥɓɗ ɓɋɉɔɑɝɑɟɑəɗɋɉɖɖɤɎ ɚɘɎɟɑɉɔɑɚɛɤ ɚ ɑɚɘɗɔɥɐɗɋɉɖɑɎɕ ɗəɑɌɑɖɉɔɥɖɤɞ ɐɉɘɠɉɚɛɎɒ Metabo!
șɔɨ əɎɕɗɖɛɉ ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɗɋ ɘəɗɑɐɋɗɍɚɛɋɉ Metabo ɗɊəɉɢɉɒɛɎɚɥ ɋ ɊɔɑɏɉɒɡɎɎ ɘəɎɍɚɛɉɋɑɛɎɔɥɚɛɋɗ Metabo. ȕɍəɎɚɉ ɚɕ. ɖɉ ɚɉɒɛɎ
www.metabo.com.
Ȧɘɑɚɓɑ ɐɉɘɉɚɖɤɞ ɠɉɚɛɎɒ ɕɗɏɖɗ ɚɓɉɠɉɛɥ ɖɉ
ɚɉɒɛɎ www.metabo.com.
ȗɤɘɗɔɖɨɒɛɎ ɖɉɟɑɗɖɉɔɥɖɤɎ ɘəɉɋɑɔɉ ɜɛɑɔɑɐɉɟɑɑ ɑ ɘɎəɎəɉɊɗɛɓɑ ɗɛɚɔɜɏɑɋɡɎɌɗ ɘɖɎɋɕɗɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɉ, ɜɘɉɓɗɋɓɑ ɑ ɘəɑɖɉɍɔɎɏɖɗɚɛɎɒ. ȗ
ɞɗɍɎ ɜɛɑɔɑɐɉɟɑɑ ɖɎ ɍɗɔɏɖɗ ɋɗɐɖɑɓɉɛɥ ɖɑɓɉɓɑɞ
ɜɌəɗɐ ɍɔɨ ɔɧɍɎɒ ɑ ɗɓəɜɏɉɧɢɎɒ ɚəɎɍɤ.
ȤɗɨɚɖɎɖɑɨ ɓ ɍɉɖɖɤɕ, ɜɓɉɐɉɖɖɤɕ ɖɉ ɚ. 3.
ȣɚɛɉɋɔɨɎɕ ɐɉ ɚɗɊɗɒ ɘəɉɋɗ ɖɉ ɛɎɞɖɑɠɎɚɓɑɎ
ɑɐɕɎɖɎɖɑɨ.
V1= əɉɚɞɗɍ ɋɗɐɍɜɞɉ
p
ɕɉɓɚ.
= ɕɉɓɚ. ɍɗɘɜɚɛɑɕɗɎ əɉɊɗɠɎɎ ɍɉɋɔɎɖɑɎ
n0= ɠɉɚɛɗɛɉ ɋəɉɢɎɖɑɨ
dS= ɍɑɉɕɎɛə ɗɛɋɎəɚɛɑɨ ɟɉɖɌɗɋɗɌɗ ɐɉɏɑɕɉ
D
ɕɉɓɚ.
= ɕɉɓɚ. ɍɑɉɕɎɛə ɉɊəɉɐɑɋɖɗɒ Ɍɗɔɗɋɓɑ
di= ɍɑɉɕɎɛə ɡɔɉɖɌɉ (ɋɖɜɛəɎɖɖɑɒ)
C = ɘəɑɚɗɎɍɑɖɑɛɎɔɥɖɉɨ əɎɐɥɊɉ
A = əɉɐɕɎəɤ:
ɍɔɑɖɉ x ɡɑəɑɖɉ x ɋɤɚɗɛɉ
m = ɕɉɚɚɉ
Ȣɉ ɜɓɉɐɉɖɖɤɎ ɛɎɞɖɑɠɎɚɓɑɎ ɞɉəɉɓɛɎəɑɚɛɑɓɑ
əɉɚɘəɗɚɛəɉɖɨɧɛɚɨ ɍɗɘɜɚɓɑ, ɘəɎɍɜɚɕɗɛəɎɖɖɤɎ
ɍɎɒɚɛɋɜɧɢɑɕɑ ɚɛɉɖɍɉəɛɉɕɑ.
ȜɖɉɠɎɖɑɨ ɡɜɕɉ ɑ ɋɑɊəɉɟɑɑ
Ȳɛɑ ɐɖɉɠɎɖɑɨ ɘɗɐɋɗɔɨɧɛ ɗɟɎɖɑɋɉɛɥ ɑ ɚəɉɋɖɑɋɉɛɥ ɡɜɕ ɑ ɋɑɊəɉɟɑɧ, ɚɗɐɍɉɋɉɎɕɤɎ ɘəɑ
əɉɊɗɛɎ əɉɐɔɑɠɖɤɞ (ɘɖɎɋɕɗ)ɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɗɋ. ȗ
ɐɉɋɑɚɑɕɗɚɛɑ ɗɛ ɜɚɔɗɋɑɒ ɦɓɚɘɔɜɉɛɉɟɑɑ, ɚɗɚɛɗɨɖɑɨ (ɘɖɎɋɕɗ)ɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɉ ɑɔɑ əɉɊɗɠɑɞ
(
ɚɕɎɖɖɤɞ) ɑɖɚɛəɜɕɎɖɛɗɋ ɝɉɓɛɑɠɎɚɓɉɨ ɖɉɌəɜɐɓɉ
ɕɗɏɎɛ Ɋɤɛɥ ɋɤɡɎ ɑɔɑ ɖɑɏɎ. Ȥəɑ ɗɘəɎɍɎɔɎɖɑɑ
ɘəɑɕɎəɖɗɌɗ ɜəɗɋɖɨ ɡɜɕɉ ɑ ɋɑɊəɉɟɑɑ ɜɠɑɛɤɋɉɒɛɎ ɘɎəɎəɤɋɤ ɋ əɉɊɗɛɎ ɑ ɝɉɐɤ əɉɊɗɛɤ ɚ ɘɗɖɑɏɎɖɖɗɒ (ɡɜɕɗɋɗɒ) ɖɉɌəɜɐɓɗɒ. ȣɘəɎɍɎɔɑɛɎ
ɘɎəɎɠɎɖɥ ɗəɌɉɖɑɐɉɟɑɗɖɖɤɞ ɕɎə ɘɗ ɐɉɢɑɛɎ
ɘɗɔɥɐɗɋɉɛɎɔɨ ɚ ɜɠɎɛɗɕ ɛɎɞ ɑɔɑ ɑɖɤɞ ɐɖɉɠɎɖɑɒ
ɡɜɕɉ ɑ ɋɑɊəɉɟɑɑ.
ȗɑɊəɉɟɑɨ
(ɜɚəɎɍɖɫɖɖɗɎ ɦɝɝɎɓɛɑɋɖɗɎ ɐɖɉɠɎɖɑɎ
ɜɚɓɗəɎɖɑɨ; EN 28927):
a
h
=ɐɖɉɠɎɖɑɎ ɋɑɊəɉɟɑɑ
K
h
=ɓɗɦɝɝɑɟɑɎɖɛ ɘɗɌəɎɡɖɗɚɛɑ (ɋɑɊəɉɟɑɨ)
ȨəɗɋɎɖɥ ɡɜɕɉ (EN ISO 15744):
L
pA
=ɜəɗɋɎɖɥ ɐɋɜɓɗɋɗɌɗ ɍɉɋɔɎɖɑɨ
L
WA
=ɜəɗɋɎɖɥ ɐɋɜɓɗɋɗɒ ɕɗɢɖɗɚɛɑ
KpA, KWA= ɓɗɦɝɝɑɟɑɎɖɛ ɘɗɌəɎɡɖɗɚɛɑ
ȢɉɍɎɋɉɒɛɎ ɐɉɢɑɛɖɤɎ ɖɉɜɡɖɑɓɑ!
8. ȤəɑɖɉɍɔɎɏɖɗɚɛɑ
9. ȥɎɕɗɖɛ
10. Ȝɉɢɑɛɉ ɗɓəɜɏɉɧɢɎɒ ɚəɎɍɤ
11. ȧɎɞɖɑɠɎɚɓɑɎ
ɞɉəɉɓɛɎəɑɚɛɑɓɑ
Page 54

9ESKYcs
54
Originální návod k použití
Prohlašujeme s výhradní odpovúdností, že tato
pļímá bruska je v souladu s normami a smúrnicemi
uvedenými na stranú 3.
Toto pneumatické náļadí je urìeno:
- pro jemné broušení s brusnými túlísky,
- pro práci s leštícími túlísky na formy,
- pro práci s plstúnými leštícími túlísky,
- pro práci s lamelovými kotouìi,
v profesionální oblasti.
Náļadí smí být pohánúno pouze pļipojením stlaìeného vzduchu. Maximální pļípustný pracovní tlak
uvedený na pneumatickém náļadí nesmí být pļekroìen. Toto náļadí se nesmí provozovat
s výbušnými, hoļlavými nebo zdraví škodlivými plyny. Nepoužívejte jako páìicí, vylamovací nebo pļíklepové náļadí.
Jakékoliv jiné použití je v rozporu s urìením. Použitím v rozporu s urìením, úpravami na pneumatickém náļadí nebo použitím dílő, které nejsou pļezkoušeny a schváleny výrobcem, mohou vzniknout
nepļedvídatelné škody!
Za škody zpősobené použitím, které je v rozporu
s urìeným úìelem, pļebírá zodpovúdnost pouze
uživatel.
Je nutné dodržovat všeobecnú uznávané pļedpisy
pro ochranu pļ
ed úrazem a pļiložené bezpeìnostní
pokyny.
Pozor na místa v textu oznaìená tímto
symbolem, slouží k vaší bezpeìnosti
a k ochranú vašeho pneumatického
náļadí!
VÝSTRAHA – Za úìelem minimalizace
nebezpeìí poranúní si pļeìtúte návod
k použití.
VÝSTRAHA Pļeìtúte si všechny bezpeìnostní pokyny a instrukce. Nedodržení
bezpeìnostních pokynő a instrukcí mőže mít za
následek úraz elektrickým proudem, požár a/nebo
túžká poranúní.
Všechny bezpeìnostní pokyny a instrukce
uschovejte pro pozdújší použití.
Pļedávejte Vaše pneumatické náļadí jen spoleìnú
s túmito dokumenty.
- Uživatel nebo zamústnavatel uživatele musí
posoudit zvláštní rizika spojená s používáním
náļadí.
- Pļed seļizováním, používáním, opravou, údržbou
nebo výmúnou dílő pļíslušenství, jakož i pļed
prací v blízkosti pneumatického náļadí, si pļeìtúte
bezpeìnostní pokyny, kterým musíte porozumút.
Pokud tomu tak není, mőže to vést k túžkým
zranúním.
- Pneumatické náļadí by múla seļizovat, nastavovat nebo používat výhradnú kvalifikovaná
a vyškolená obsluha.
- Na pneumatickém náļadí se nesmí provádút
žádné úpravy. Zmúny mohou snížit úìinnost
bezpeìnostních opatļení a zvýšit rizika pro
obsluhu.
- Nikdy nepoužívejte poškozené pneumatické
náļadí. Pneumatické náļadí peìlivú ošetļujte.
Pravidelnú kontrolujte, zda pohyblivé díly
bezvadnú fungují a nevzpļiìují se, zda díly nejsou
zlomené nebo poškozené tak, že je omezena
funkce pneumatického náļadí. Zkontrolujte
úplnost a ìitelnost štítkő a nápiső. Poškozené díly
nechte pļed použitím náļadí opravit nebo vymúnit.
Mnoho úraző má pļíìinu ve špatnú udržovaném
pneumatickém náļadí.
4.1 Ohrožení vymrštúnými díly
- Pļi prasknutí obrobku, poškození dílő pļíslušenství nebo pneumatického náļadí mohou být
vysokou rychlostí vymrštúny díly.
- Pļi provozu, výmúnú dílő pļíslušenství, pļi provádúní oprav nebo údržby pneumatického náļadí
noste vždy ochranu oìí odolnou proti nárazu.
Stupeğ nezbytné ochrany by se múl posuzovat
samostatnú pro každé použití.
- Zajistúte, aby byl obrobek bezpeìnú upevnún.
- Pravidelnú se musí kontrolovat, zda otáìky pneumatického náļadí nejsou vyšší než otáìky
uvedené na pneumatickém náļadí. Tyto kontroly
otáìek se musí provádút bez nasazeného používaného nástroje. Tyto kontroly mőže provádút
zákaznický servis Metabo.
- Zajistúte, aby jiskry a úlomky vznikající pļi práci
nepļedstavovaly žádné nebezpeìí.
- Pļed výmúnou používaného nástroje nebo dílő
pļíslušenství, pļed provádúním nastavení, údržby
nebo ì
ištúní odpojte pneumatické náļadí od záso-
bování stlaìeným vzduchem.
- Zajistúte, aby také ostatním osobám nehrozilo
nebezpeìí.
4.2 Ohrožení zachycením/navinutím
- Noste vhodný odúv. Nenoste žádný volný odúv
nebo šperky. Vlasy, odúv a rukavice udržujte
daleko od pneumatického náļadí a pohybujících
se dílő. Volný odúv, šperky nebo dlouhé vlasy
mohou být zachyceny pohybujícími se díly. Hrozí
nebezpeìí zranúní.
4.3 Ohrožení za provozu
- Zabrağte kontaktu s otáìející se stopkou
a používaným nástrojem, aby nedošlo k poļezání
rukou a dalších ìástí túla.
- Pļi používání pneumatického náļadí mohou být
ruce obsluhy vystaveny nebezpeìí, napļ. ļezným
1. Prohlášení o shodú
2. Použití v souladu s urìeným
úìelem
3. Všeobecné bezpeìnostní
pokyny
4. Speciální bezpeìnostní
pokyny
Page 55

9ESKY cs
55
poranúním, odļeninám a pősobení tepla.
K ochranú rukou noste vhodné rukavice.
- Obsluha a pracovníci údržby musí být fyzicky
schopni zvládat velikost, hmotnost a výkon pneumatického náļadí.
- Držte správnú pneumatické náļadí: Buïte pļipraveni reagovat na obvyklé nebo náhlé pohyby –
mújte pļipravené obú ruce.
- Zajistúte si bezpeìný postoj a vždy udržujte
rovnováhu.
- Zabrağte neúmyslnému uvedení náļadí do
provozu. Pļi pļerušení zásobování stlaìeným
vzduchem vypnúte pneumatické náļadí vypínaìem.
- Používejte pouze maziva doporuìená výrobcem.
- Noste osobní ochranné pomőcky a vždy
ochranné brýle. Nošení osobních ochranných
pomőcek, jako jsou ochranné rukavice, ochranný
odúv, maska proti prachu, bezpeìnostní obuv
s protiskluzovou podrážkou, ochranná pļilba nebo
ochrana sluchu, podle druhu nasazení náļadí
snižuje riziko poranúní a doporuìuje se.
- Pļípustné otáìky používaného nástroje musí být
minimálnú tak vysoké jako maximální otáìky
uvedené na pneumatickém náļadí. Pļíslušenství,
které se otáìí rychleji, než je p
ļípustné, se mőže
rozlomit a rozletút do okolí.
- Pļi práci nad úrovní hlavy noste ochrannou pļilbu.
- Pneumatické náļadí po vypnutí dobíhá.
- Dbejte o to, aby jiskry vznikající pļi používání
nepļedstavovaly nebezpeìí. Pļi obrábúní núkterých materiálő mőže vznikat výbušný nebo
hoļlavý prach. Hrozí nebezpeìí výbuchu nebo
požáru.
4.4 Ohrožení opakovanými pohyby
- Pļi práci s pneumatickým náļadím mőžete vnímat
nepļíjemné pocity v rukou, pažích, ramenech,
v oblasti krku nebo v jiných ìástech túla.
- Pro práci s pneumatickým náļadím zaujmúte
pohodlný postoj, dbejte na dobrou stabilitu
a vyvarujte se nevhodných pozic pļi držení túla
a takových pozic, u kterých je obtížené udržovat
rovnováhu. Pracovník obsluhy by múl búhem
prací, které trvají dlouho dobu, múnit držení túla,
což mőže pomoci zabránit únavú a nepļíjemným
pocitőm.
- Pokud se u pracovníka obsluhy objeví symptomy
jako trvalá nevolnost, obtíže, bušení srdce, bolest,
mravenìení, hluchota, pálení nebo ztuhlost,
nemúl by tyto varující signály ignorovat. Múl by
tuto skuteì
nost sdúlit zamústnavateli
a konzultovat s odborným lékaļem.
4.5 Ohrožení díly pļíslušenství
- Pļed upevğováním nebo výmúnou používaného
nástroje nebo dílu pļíslušenství odpojte pneumatické náļadí od zásobování stlaìeným vzduchem.
- Používejte pouze pļíslušenství urìené pro toto
náļadí, které splğuje požadavky a parametry
uvedené v tomto návodu k obsluze.
- Búhem používání a po núm se vyvarujte pļímého
kontaktu s používaným nástrojem, protože mőže
být horký nebo mít ostré hrany.
- Pļípustné otáìky používaného nástroje musí být
minimálnú tak vysoké jako maximální otáìky
uvedené na pneumatickém náļadí. Pļíslušenství,
které se otáìí rychleji, než je pļípustné, se mőže
rozlomit a rozletút do okolí.
- Nikdy nemontujte brusný kotouì, ļezací kotouì
nebo frézu. Prasklý brusný kotouì mőže zpősobit
velmi vážná poranúní nebo smrt.
- Nepoužívejte kotouìe, které jsou naražené nebo
natržené, nebo které mohly spadnout.
- Smí se používat jen schválené nástroje
s vhodným prőmúrem stopky.
- Dodržujte doporu
ìení výrobce malých brusných
túlísek. U malých brusných túlísek se nesmí
pļekroìit výrobcem uvádúný maximální pļesah
(L0=délka stopky mezi koncem kleštiny a malým
brusným túlískem)! Pļi zvýšení pļesahu (L0) se
musí snížit pļípustné otáìky. Vložte používaný
nástroj pokud možno celou délkou stopky do kleštiny. Zajistúte, aby délka upnutí (Lg) byla minimálnú 10 mm.
- Prőmúr stopky používaného nástroje musí pļesnú
odpovídat upínacímu otvoru kleštiny!
4.6 Ohrožení na pracovišti
- Uklouznutí, zakopnutí nebo pád jsou hlavní pļíìiny
zranúní na pracovišti. Všímejte si povrchő, které
mohou být používáním pneumatického náļadí
kluzké, nezapomeğte, že mőžete zakopnout
o vzduchovou hadici.
- V neznámém prostļedí postupujte opatrnú.
Mohou zde hrozit skrytá nebezpeìí elektrickým
kabelem nebo jinými zásobovacími vedeními.
- Pneumatické náļadí není urìeno pro použití ve
výbušných atmosférách a není izolované proti
kontaktu se zdroji elektrické energie.
- Zkontrolujte, zda se na místú, kde chcete vrtat
nebo šroubovat, nenachází žádné elektrické,
vodovodní nebo plynové vedení (napļ. pomocí
detektoru kovő).
4.7 Ohrožení prachem a párami
- Prach a páry vznikající pļi používání pneumatického náļadí mohou poškodit zdraví (napļ. rakovina, vrozené vady, astma a/nebo dermatitida); je
nezbytné provést posouzení rizika s ohledem na
tato ohrožení a realizovat vhodná opatļení.
- Posouzení rizika by múlo zahrnovat prach vznikající pļi používání pneumatického náļadí
a pļípadný prach v prostļedí zvíļený používání
tohoto náļadí.
- Pneumatické náļadí se musí provozovat a jeho
údržba provádút podle doporuìení uvedených
v tomto návodu, aby se uvolğování prachu a par
snížilo na minimální možnou úroveğ.
- Odpadní vzduch se musí odvádút tak, aby se
zvíļení prachu v prašném prostļedí snížilo na minimální možnou úroveğ.
- Vznikají-li prach nebo páry, je hlavním úkolem
jejich uvolğování v místú kontrolovat.
- Namontované díly nebo díly pļíslušenství pneumatického náļadí urìené k zachycení, odsávání
LoL
g
Page 56

9ESKYcs
56
nebo potlaìení vzniku polétavého prachu nebo
par by se múly ļádnú používat a udržovat podle
pokynő výrobce.
- Spotļební materiál a používaný nástroj je tļeba
volit, udržovat a múnit podle doporuìení tohoto
návodu. Tím zabráníte zvýšenému vytváļení
prachu a par.
- Používejte ochranné pracovní pomőcky k ochranú
dýchacích cest podle pokynő zamústnavatele
nebo tak, jak to vyžadují pļedpisy ochrany zdraví.
- Práce s urìitými materiály vedou k emisím prachu
a páry, které mohou vytváļet prostļedí
s nebezpeìím výbuchu.
4.8 Ohrožení hlukem
- Vysoká hluìnost mőže pļi nedostateìné ochranú
sluchu zpősobit trvalá poškození sluchu, ztrátu
sluchu a jiné problémy, jako tinnitus (zvonúní,
huìení, pískání nebo bzuìení v uchu).
- Je nezbytné provést posouzení rizika s ohledem
na tato ohrožení a realizovat vhodná opatļení.
- Mezi vhodná opatļení ke snížení rizika patļí používání izolace, jež zabrağuje vzniku zvonivého hluku
u obrobkő.
- Používejte ochranné pracovní pomőcky k ochranu
sluchu podle pokynő zamústnavatele a tak, jak to
vyžadují pļedpisy ochrany zdraví.
- Pneumatické ná
ļadí používejte a jeho údržbu
provádújte podle doporuìení uvedených v tomto
návodu. Tím zabráníte zbyteìnému zvýšení hluìnosti.
- Spotļební materiál a používaný nástroj je tļeba
volit, udržovat a múnit podle doporuìení tohoto
návodu. Tím zabráníte zbyteìnému zvýšení hluìnosti.
- Integrovaný tlumiì hluku se nesmí demontovat
a musí být v dobrém stavu.
4.9 Ohrožení vibracemi
- Pősobení vibrací mőže zpősobit poškození nervő
a poruchy krevního obúhu v rukách a pažích.
- Pļi práci v chladném prostļedí noste teplé obleìení, vaše ruce musí být teplé a suché.
- Pokud zjistíte, že pokožka na prstech nebo rukách
znecitlivúla, brní, bolí nebo zbledla, pļestağte
s pneumatickým náļadím pracovat, informujte
svého zamústnavatele a konzultujte s lékaļem.
- Pneumatické náļadí používejte a jeho údržbu
provádújte podle doporuìení uvedených v tomto
návodu. Tím zabráníte zbyteìnému zesílení
vibrací.
- Spotļební materiál a používaný nástroj je tļeba
volit, udržovat a múnit podle doporuìení tohoto
návodu. Tím zabráníte zbyteìnému zesílení
vibrací.
- K držení hmotnosti pneumatického náļadí vždy
používejte, je-li to možné, stojan, držák nebo
vyrovnávací za
ļízení.
- Nedržte náļadí pļíliš pevnú, ale jistú. Pļitom musí
zőstat zachovány potļebné reakìní síly ruky,
neboņ riziko vibrací zpravidla roste se zvyšující se
silou vynaloženou na držení náļadí.
- Nedostateìnú namontovaný nebo poškozený
používaný nástroj mőže vést ke zvýšeným
vibracím.
4.10 Dodateìné bezpeìností pokyny
- Stlaìený vzduch mőže zpősobit vážná zranúní.
- Pokud pneumatické náļadí nepoužíváte, pļed
výmúnou dílő pļíslušenství nebo pļi provádúní
oprav vždy uzavļete pļívod vzduchu, odtlakujte
vzduchovou hadici a odpojte pneumatické náļadí
od pļívodu stlaìeného vzduchu.
- Proud vzduchu nikdy nesmúļujte na sebe nebo
jiné osoby.
- Uvolnúné hadice šlehající okolo mohou zpősobit
vážná zranúní. Vždy proto zkontrolujte, zda
nejsou hadice a jejich upevğovací prvky poškozené a zda se neuvolnily.
- Používají-li se univerzální otoìné spojky (zubové
spojky), musí se nasadit aretaì
ní kolíky
a doporuìuje se používat hadicové spojky
Whipcheck, abyste zajistili ochranu v pļípadú
selhání propojení hadice s pneumatickým
náļadím nebo vzájemného propojení hadic.
- Zajistúte, aby nebyl pļekroìen max. tlak uvedený
na pneumatickém náļadí.
- Nikdy nenoste pneumatické náļadí za hadici.
- Provozujete-li pneumatické náļadí v držáku:
náļadí bezpeìnú upevnúte. Ztráta kontroly nad
náļadím mőže zpősobit poranúní.
4.11 Další bezpeìnostní pokyny
- Dodržujte speciální pļedpisy bezpeìnosti práce
a prevence úraző pļi zacházení s kompresory
a pneumatickým náļadím.
- Zajistúte, aby nebyl pļekroìen maximální
pļípustný pracovní tlak uvedený v Technických
údajích.
- Nepļetúžujte toto náļadí – používejte jej pouze
v rozsahu výkonu, který je uveden v Technických
údajích.
- Používejte nezávadná maziva. Zajistúte dostateìné vútrání pracovištú. Pļi zvýšeném úbúru:
nechte pneumatické náļadí zkontrolovat a pļ
íp.
opravit.
- Nepoužívejte tento nástroj, když nejste soustļedúni. Buïte pozorní, dávejte pozor na to, co
dúláte a pļistupujte k práci s pneumatickým
náļadím rozumnú. Náļadí nepoužívejte, pokud
jste unavení nebo pod vlivem drog, alkoholu nebo
lékő. Moment nepozornosti pļi použití náļadí
mőže vést k vážným poranúním.
- Udržujte své pracovní místo ìisté a dobļe osvútlené. Nepoļádek nebo neosvútlené pracovní
oblasti mohou vést k úrazőm.
- Zajistúte pneumatické náļadí pļed dútmi.
- Neuchovávejte náļadí nechránúné venku nebo ve
vlhkém prostļedí.
- Chrağte pneumatické náļadí, pļedevším pļípojku
stlaìeného vzduchu a ovládací prvky, pļed
prachem a neìistotou.
Informace v tomto návodu k obsluze jsou oznaìeny následovnú:
Nebezpeìí! Varování pļed nebezpeìím úra-
zu nebo poškození životního prostļedí.
Pozor. Varování pļed vúcnými škodami.
Page 57

9ESKY cs
57
4.12 Symboly na pneumatickém náļadí
Pļed zprovoznúním si pļeìtúte návod
k obsluze.
Noste ochranu oìí
Noste ochranu sluchu
Smúr otáìení
Viz strana 2.
1 Stranový klíì
2 Matice kleštiny
3 Kleština
4 Držák kleštiny
5 Vļeteno
6 Stranový klíì
7 Spínaì (vypínaì)
8 Pojistka proti zapnutí
9 Regulaìní šroub k nastavení otáìek
10 Výstup vzduchu
11 Pļípojka stlaìeného vzduchu s filtrem
12 Spojka 1/4"
6.1 Pļed prvním uvedením do provozu
Našroubujte spojku k nasazení hadice (12).
6.2 Nasaïte kleštinu
Prőmúr stopky nástroje musí pļesnú odpovídat upínacímu otvoru kleštiny (3)!
K dispozici jsou kleštiny pro rőzné prőmúry stopky.
Vložte kleštinu (3) do držáku kleštiny (4), a poté
našroubujte rukou matici kleštiny (2).
Není-li v kleštinú vložen nástroj, neutahujte
kleštinu stranovým klíìem, ale našroubujte ji
pouze rukou!
6.3 Upnutí používaného nástroje
U malých brusných túlísek se nesmí pļekroìit
výrobcem uvádúný maximální pļesah (L
0
)!
Vložte používaný nástroj pokud možno celou
délkou jeho stopky do kleštiny (3). Zajistúte, aby
délka upnutí (Lg) byla minimálnú 10 mm.
Prőmúr stopky používaného nástroje musí
pļesnú odpovídat upínacímu otvoru kleštiny
(3)!
- Pļidržujte vļeteno (5) stranovým klíìem (6).
- Dotáhnúte matici kleštiny (2) stranovým klíìem
(1).
- Dbejte na to, aby používaný nástroj byl spolehlivú
upevnún.
6.4 Používání pneumatického náļadí
Chcete-li dosáhnout max. výkonu pneumatického
náļadí, používejte vždy pneumatické hadice
s vnitļním prőmúrem minimálnú 9 mm. Pļíliš malý
vnitļní prőmúr mőže výraznú snížit výkon.
Pozor. Vedení stlaìeného vzduchu nesmí
obsahovat kondenzovanou vodu.
Pozor. S cílem, aby zőstalo toto náļadí dlou-
ho provozuschopné, musí být zásobováno
dostateìným množstvím pneumatického oleje. To
se mőže provádút následovnú:
– Používejte stlaìený vzduch obohacený olejovou
mlhou, k tomu namontujte mlhovou maznici.
– Bez mlhové maznice: Mažte ruìnú olejem každý
den pļes pļípojku stlaìeného vzduchu. Cca 3-5
kapek pneumatického oleje na každých 15 minut
pļi trvalém provozu.
Pokud bylo náļadí núkolik dnő mimo provoz, ruìnú
aplikujte 5 kapek pneumatického oleje do pļípojky
stlaìeného vzduchu.
Pozor. Náļadí smí búžet naprázdno jen krát-
kodobú.
1. Zvolte vhodnou kleštinu (3) (viz kapitola 6.2).
2. Upnúte vhodný používaný nástroj (viz kapitola
6.3).
3. Otáìky je možné múnit regulaìním šroubem
(9).
4. Nastavte pracovní tlak (múļeno na pļívodu
vzduchu pļi zapnutém pneumatickém náļadí).
Maximální pļípustný pracovní tlak viz kapitola
„Technické údaje“.
5. Pļipojte pneumatické náļadí k zásobování stla-
ìeným vzduchem.
6. Zapnutí: Posuğte pojistku proti zapnutí (8) ve
smúru šipky (viz obr., strana 2) a stisknúte spínaì (7).
Vypnutí: Uvolnúte spínaì (7).
.
Nebezpeìí! Pļed provádúním všech prací na
náļadí odpojte pļípojku stlaìeného vzduchu.
Nebezpeìí! Údržbu a opravy, které nároì-
ností pļekraìují úkony popsané v této kapitole, smí provádút jen odborníci.
- Pravidelnou údržbou zajistúte bezpeìnost
a spolehlivost pneumatického náļadí.
- Zkontrolujte dotažení šroubových spojő a v
pļípadú potļeby je dotáhnúte.
- Minimálnú týdnú ìistúte filtr v pļípojce stlaìeného
vzduchu.
- Doporuìujeme zapojit pļed pneumatické náļadí
redukìní ventil s odluìovaìem vody a mlhovou
maznicí.
5. Pļehled
6. Provoz
LoL
g
7. Údržba a ošetļování
Page 58

9ESKYcs
58
- Pļi zvýšeném úniku oleje a vzduchu nechte pneumatické náļadí zkontrolovat a pļíp. opravit. (viz
kapitola 9.)
- Pravidelnú a po každém použití zkontrolujte
otáìky a proveïte jednoduchou kontrolu hladiny
vibrací.
- Vyvarujte se kontaktu s nebezpeìnými látkami
usazenými na náļadí. Noste vhodné osobní
ochranné pomőcky a vhodnými opatļeními
odstrağte nebezpeìné látky pļed provádúním
údržby.
f
Používejte pouze originální pļíslušenství Metabo.
Používejte pouze pļíslušenství urìené pro toto
pneumatické náļadí, které splğuje požadavky
a parametry uvedené v tomto návodu k obsluze.
Kompletní nabídku pļíslušenství najdete na
www.metabo.com nebo v katalogu.
Nebezpeìí! Opravy pneumatického náļadí
smí provádút pouze odborníci s použitím origi-
nálních náhradních dílő Metabo!
S pneumatickým náļadím Metabo vyžadujícím
opravu se prosím obraņte na Vaše zastoupení
Metabo. Adresy viz www.metabo.com.
Seznamy náhradních dílő se mőžete stáhnout na
adrese www.metabo.com.
iïte se národními pļedpisy k ekologické likvidaci
a recyklaci vysloužilého pneumatického náļadí,
obalő a pļíslušenství. Nesmí být ohroženy osoby
a životní prostļedí.
Vysvútlivky k údajőm na stranú 3.
Zmúny na základú technického pokroku vyhrazeny.
V
1
= spotļeba vzduchu
p
max.
= maximální pļípustný pracovní tlak
n0= otáìky
dS= upínací otvor kleštiny
D
max
= maximální prőmúr malého brusného
túlíska
di= prőmúr hadice (vnitļní)
C = pļipojovací závit
A = rozmúry:
délka x šíļka x výška
m = hmotnost
U uvedených technických údajő je nutno poìítat
s odpovídajícími tolerancemi (dle pļíslušných
platných norem).
Emisní hodnoty
Tyto hodnoty umožğují odhadnout emise
náļadí a porovnat rőzná náļadí. V závislosti na
podmínkách použití, stavu náļadí nebo použitých
nástrojích mőže být skuteìné zatížení vyšší nebo
nižší. Pļi odhadování zohlednúte pļestávky v práci
a fáze nižšího zatížení. Na základú náležitú pļizpősobených odhadnutých hodnot stanovte ochranná
opatļení pro uživatele, napļ. organizaìní opatļení.
Vibrace
(vážená efekt. hodnota zrychlení;
EN 28927):
a
h
=emisní hodnota vibrací
K
h
=nejistota múļení (vibrace)
Hladina akustického tlaku (EN ISO 15744):
L
pA
=hladina akustického tlaku
L
WA
=hladina akustického výkonu
KpA, KWA= nejistota múļení
Noste ochranu sluchu!
8. Pļíslušenství
9. Opravy
10. Ochrana životního prostļedí
11. Technické údaje
Page 59

Page 60

Metabowerke GmbH,
72622 Nürtingen, Germany
www.metabo.com
170 27 1520 - 1012
 Loading...
Loading...